mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2024-12-26 21:30:55 +08:00
Merge branch 'master' of git@github.com:LCTT/TranslateProject.git
This commit is contained in:
commit
43503b9e43
@ -0,0 +1,157 @@
|
||||
Mhddfs:将多个小分区合并成一个大的虚拟存储
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
让我们假定你有30GB的电影,并且你有3个驱动器,每个的大小为20GB。那么,你会怎么来存放东西呢?
|
||||
|
||||
很明显,你可以将你的视频分割成2个或者3个不同的卷,并将它们手工存储到驱动器上。这当然不是一个好主意,它成了一项费力的工作,它需要你手工干预,而且花费你大量时间。
|
||||
|
||||
另外一个解决方案是创建一个 [RAID磁盘阵列][1]。然而,RAID在存储可靠性,磁盘空间可用性差等方面声名狼藉。另外一个解决方案,就是mhddfs。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*Mhddfs——在Linux中合并多个分区*
|
||||
|
||||
mhddfs是一个用于Linux的设备驱动,它可以将多个挂载点合并到一个虚拟磁盘中。它是一个基于FUSE的驱动,提供了一个用于大数据存储的简单解决方案。它可以将所有小文件系统合并,创建一个单一的大虚拟文件系统,该文件系统包含其成员文件系统的所有内容,包括文件和空闲空间。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 你为什么需要Mhddfs? ####
|
||||
|
||||
你的所有存储设备会创建为一个单一的虚拟池,它可以在启动时被挂载。这个小工具可以智能地照看并处理哪个存储满了,哪个存储空着,以及将数据写到哪个存储中。当你成功创建虚拟驱动器后,你可以使用[SAMBA][2]来共享你的虚拟文件系统。你的客户端将在任何时候都看到一个巨大的驱动器和大量的空闲空间。
|
||||
|
||||
#### Mhddfs特性 ####
|
||||
|
||||
- 获取文件系统属性和系统信息。
|
||||
- 设置文件系统属性。
|
||||
- 创建、读取、移除和写入目录和文件。
|
||||
- 在单一设备上支持文件锁和硬链接。
|
||||
|
||||
|mhddfs的优点|mhddfs的缺点|
|
||||
|-----------|-----------|
|
||||
|适合家庭用户|mhddfs驱动没有内建在Linux内核中 |
|
||||
|运行简单|运行时需要大量处理能力|
|
||||
|没有明显的数据丢失|没有冗余解决方案|
|
||||
|不需要分割文件|不支持移动硬链接|
|
||||
|可以添加新文件到组成的虚拟文件系统||
|
||||
|可以管理文件保存的位置||
|
||||
|支持扩展文件属性||
|
||||
|
||||
### Linux中安装Mhddfs ###
|
||||
|
||||
在Debian及其类似的移植系统中,你可以使用下面的命令来安装mhddfs包。
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get update && apt-get install mhddfs
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*安装Mhddfs到基于Debian的系统中*
|
||||
|
||||
在RHEL/CentOS Linux系统中,你需要开启[epel仓库][3],然后执行下面的命令来安装mhddfs包。
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install mhddfs
|
||||
|
||||
在Fedora 22及以上系统中,你可以通过dnf包管理来获得它,就像下面这样。
|
||||
|
||||
# dnf install mhddfs
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*安装Mhddfs到Fedora*
|
||||
|
||||
如果万一mhddfs包不能从epel仓库获取到,那么你需要解决下面的依赖,然后像下面这样来编译源码并安装。
|
||||
|
||||
- FUSE头文件
|
||||
- GCC
|
||||
- libc6头文件
|
||||
- uthash头文件
|
||||
- libattr1头文件(可选)
|
||||
|
||||
接下来,只需从下面建议的地址下载最新的源码包,然后编译。
|
||||
|
||||
# wget http://mhddfs.uvw.ru/downloads/mhddfs_0.1.39.tar.gz
|
||||
# tar -zxvf mhddfs*.tar.gz
|
||||
# cd mhddfs-0.1.39/
|
||||
# make
|
||||
|
||||
你应该可以在当前目录中看到mhddfs的二进制文件,以root身份将它移动到/usr/bin/和/usr/local/bin/中。
|
||||
|
||||
# cp mhddfs /usr/bin/
|
||||
# cp mhddfs /usr/local/bin/
|
||||
|
||||
一切搞定,mhddfs已经可以用了。
|
||||
|
||||
### 我怎么使用Mhddfs? ###
|
||||
|
||||
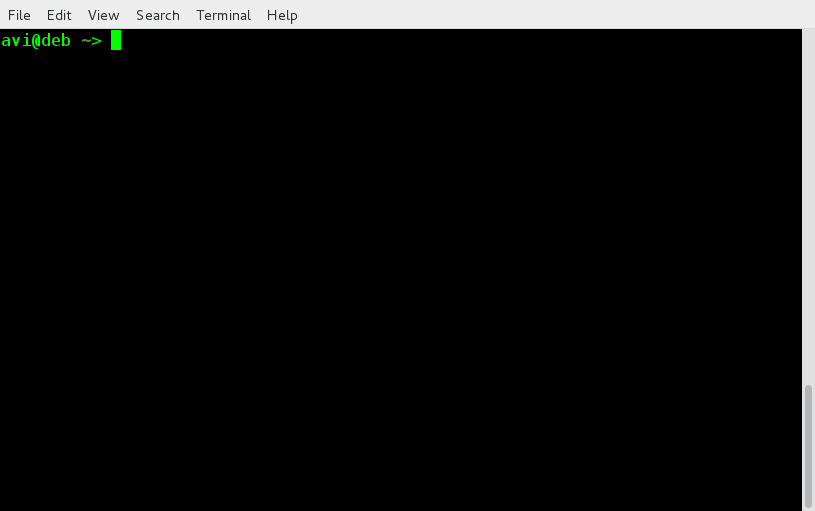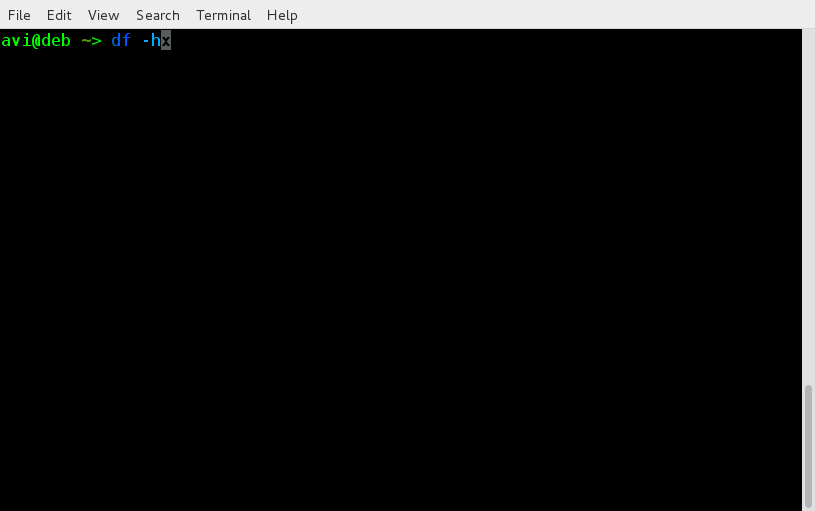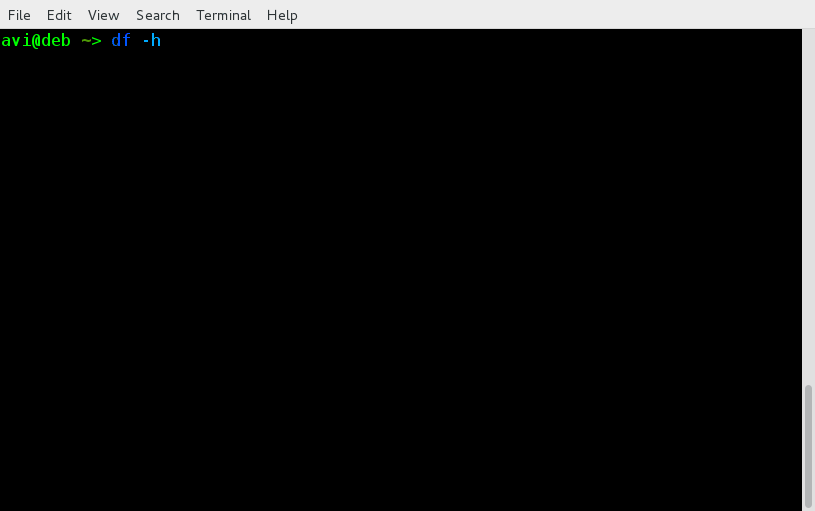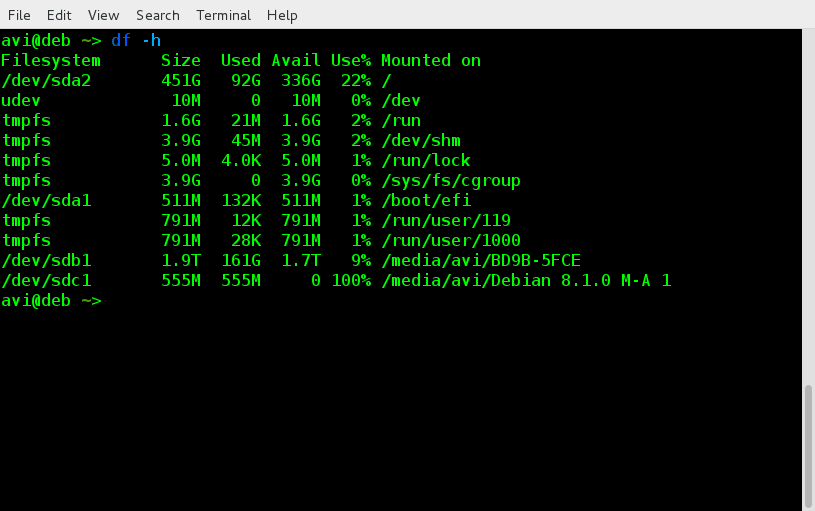
1、 让我们看看当前所有挂载到我们系统中的硬盘。
|
||||
|
||||
$ df -h
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**样例输出**
|
||||
|
||||
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
|
||||
|
||||
/dev/sda1 511M 132K 511M 1% /boot/efi
|
||||
/dev/sda2 451G 92G 336G 22% /
|
||||
/dev/sdb1 1.9T 161G 1.7T 9% /media/avi/BD9B-5FCE
|
||||
/dev/sdc1 555M 555M 0 100% /media/avi/Debian 8.1.0 M-A 1
|
||||
|
||||
注意这里的‘挂载点’名称,我们后面会使用到它们。
|
||||
|
||||
2、 创建目录‘/mnt/virtual_hdd’,所有这些文件系统将会在这里组织到一起。
|
||||
|
||||
# mkdir /mnt/virtual_hdd
|
||||
|
||||
3、 然后,挂载所有文件系统。你可以通过root或者FUSE组中的某个用户来完成。
|
||||
|
||||
# mhddfs /boot/efi, /, /media/avi/BD9B-5FCE/, /media/avi/Debian\ 8.1.0\ M-A\ 1/ /mnt/virtual_hdd -o allow_other
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*在Linux中挂载所有文件系统*
|
||||
|
||||
**注意**:这里我们使用了所有硬盘的挂载点名称,很明显,你的挂载点名称会有所不同。也请注意“-o allow_other”选项可以让这个虚拟文件系统让其它所有人可见,而不仅仅是创建它的人。
|
||||
|
||||
4、 现在,运行“df -h”来看看所有文件系统。它应该包含了你刚才创建的那个。
|
||||
|
||||
$ df -h
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*验证虚拟文件系统挂载*
|
||||
|
||||
你可以像对已挂在的驱动器那样给虚拟文件系统应用所有的选项。
|
||||
|
||||
5、 要在每次系统启动创建这个虚拟文件系统,你应该以root身份添加下面的这行代码(在你那里会有点不同,取决于你的挂载点)到/etc/fstab文件的末尾。
|
||||
|
||||
mhddfs# /boot/efi, /, /media/avi/BD9B-5FCE/, /media/avi/Debian\ 8.1.0\ M-A\ 1/ /mnt/virtual_hdd fuse defaults,allow_other 0 0
|
||||
|
||||
6、 如果在任何时候你想要添加/移除一个新的驱动器到/从虚拟硬盘,你可以挂载一个新的驱动器,拷贝/mnt/vritual_hdd的内容,卸载卷,弹出你要移除的的驱动器并/或挂载你要包含的新驱动器。使用mhddfs命令挂载全部文件系统到Virtual_hdd下,这样就全部搞定了。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 我怎么卸载Virtual_hdd? ####
|
||||
|
||||
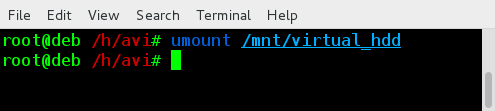
卸载virtual_hdd相当简单,就像下面这样
|
||||
|
||||
# umount /mnt/virtual_hdd
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
*卸载虚拟文件系统*
|
||||
|
||||
注意,是umount,而不是unmount,很多用户都输错了。
|
||||
|
||||
到现在为止全部结束了。我正在写另外一篇文章,你们一定喜欢读的。到那时,请保持连线。请在下面的评论中给我们提供有用的反馈吧。请为我们点赞并分享,帮助我们扩散。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/combine-partitions-into-one-in-linux-using-mhddfs/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Avishek Kumar][a]
|
||||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/avishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/understanding-raid-setup-in-linux/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/mount-filesystem-in-linux/
|
||||
[3]:https://linux.cn/article-2324-1.html
|
||||
126
published/20150901 How to Defragment Linux Systems.md
Normal file
126
published/20150901 How to Defragment Linux Systems.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,126 @@
|
||||
如何在 Linux 中整理磁盘碎片
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
有一神话是 linux 的磁盘从来不需要整理碎片。在大多数情况下这是真的,大多数因为是使用的是优秀的日志系统(ext2、3、4等等)来处理文件系统。然而,在一些特殊情况下,碎片仍旧会产生。如果正巧发生在你身上,解决方法很简单。
|
||||
|
||||
### 什么是磁盘碎片 ###
|
||||
|
||||
文件系统会按块更新文件,如果这些块没有连成一整块而是分布在磁盘的各个角落中时,就会形成磁盘碎片。这对于 FAT 和 FAT32 文件系统而言是这样的。在 NTFS 中这种情况有所减轻,但在 Linux(extX)中却几乎不会发生。下面是原因:
|
||||
|
||||
在像 FAT 和 FAT32 这类文件系统中,文件紧挨着写入到磁盘中。文件之间没有空间来用于增长或者更新:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
NTFS 中在文件之间保留了一些空间,因此有空间进行增长。但因块之间的空间是有限的,碎片也会随着时间出现。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Linux 的日志型文件系统采用了一个不同的方案。与文件相互挨着不同,每个文件分布在磁盘的各处,每个文件之间留下了大量的剩余空间。这就给文件更新和增长留下了很大的空间,碎片很少会发生。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
此外,碎片一旦出现了,大多数 Linux 文件系统会尝试将文件和块重新连续起来。
|
||||
|
||||
### Linux 中的磁盘整理 ###
|
||||
|
||||
除非你用的是一个很小的硬盘或者空间不够了,不然 Linux 很少会需要磁盘整理。一些可能需要磁盘整理的情况包括:
|
||||
|
||||
- 如果你编辑的是大型视频文件或者 RAW 照片,但磁盘空间有限
|
||||
- 如果你使用一个老式硬件,如旧笔记本,你的硬盘会很小
|
||||
- 如果你的磁盘开始满了(大约使用了85%)
|
||||
- 如果你的家目录中有许多小分区
|
||||
|
||||
最好的解决方案是购买一个大硬盘。如果不可能,磁盘碎片整理就很有用了。
|
||||
|
||||
### 如何检查碎片 ###
|
||||
|
||||
`fsck` 命令会为你做这个,换句话说,如果你可以在 LiveCD 中运行它,那么就可以用于**所有卸载的分区**。
|
||||
|
||||
这一点很重要:**在已经挂载的分区中运行 fsck 将会严重危害到你的数据和磁盘**。
|
||||
|
||||
你已经被警告过了。开始之前,先做一个完整的备份。
|
||||
|
||||
**免责声明**: 本文的作者与本站将不会对您的文件、数据、系统或者其他损害负责。你需要自己承担风险。如果你继续,你需要接受并了解这点。
|
||||
|
||||
你应该启动到一个 live 会话中(如使用安装磁盘,系统救援CD等)并在你**卸载**的分区上运行 `fsck` 。要检查是否有任何问题,请在使用 root 权限运行下面的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
fsck -fn [/path/to/your/partition]
|
||||
|
||||
您可以运行以下命令找到分区的路径
|
||||
|
||||
sudo fdisk -l
|
||||
|
||||
有一个在已挂载的分区中运行 `fsck`(相对)安全的方法是使用`-n`开关。这会对分区进行只读文件系统检查,而不会写入任何东西。当然,这并不能保证十分安全,你应该在创建备份之后进行。在 ext2 中,运行
|
||||
|
||||
sudo fsck.ext2 -fn /path/to/your/partition
|
||||
|
||||
这会产生大量的输出,大多数错误信息的原因是分区已经挂载了。最后会给出一个碎片相关的信息。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
如果碎片率大于 20% 了,那么你应该开始整理你的磁盘碎片了。
|
||||
|
||||
### 如何简单地在 Linux 中整理碎片 ###
|
||||
|
||||
你要做的是备份你**所有**的文件和数据到另外一块硬盘中(手动**复制**他们),格式化分区,然后重新复制回去(不要使用备份软件)。日志型文件系统会把它们作为新的文件,并将它们整齐地放置到磁盘中而不产生碎片。
|
||||
|
||||
要备份你的文件,运行
|
||||
|
||||
cp -afv [/path/to/source/partition]/* [/path/to/destination/folder]
|
||||
|
||||
记住星号(*)是很重要的。
|
||||
|
||||
注意:通常认为复制大文件或者大量文件,使用 `dd` 或许是最好的。这是一个非常底层的操作,它会复制一切,包含空闲的空间甚至是留下的垃圾。这不是我们想要的,因此这里最好使用 `cp`。
|
||||
|
||||
现在你只需要删除源文件。
|
||||
|
||||
sudo rm -rf [/path/to/source/partition]/*
|
||||
|
||||
**可选**:你可以使用如下命令将空闲空间用零填充。也可以用格式化来达到这点,但是如果你并没有复制整个分区而仅仅是复制大文件(它通常会形成碎片)的话,就不应该使用格式化的方法了。
|
||||
|
||||
sudo dd if=/dev/zero of=[/path/to/source/partition]/temp-zero.txt
|
||||
|
||||
等待它结束。你可以用 `pv` 来监测进度。
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install pv
|
||||
sudo pv -tpreb | of=[/path/to/source/partition]/temp-zero.txt
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
这就完成了,只要删除这个用于填充的临时文件就行。
|
||||
|
||||
sudo rm [/path/to/source/partition]/temp-zero.txt
|
||||
|
||||
待你清零了空闲空间(或者跳过了这步)。重新复制回文件,将第一个`cp`命令翻转一下:
|
||||
|
||||
cp -afv [/path/to/original/destination/folder]/* [/path/to/original/source/partition]
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用 e4defrag ###
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想要简单的方法,安装 `e2fsprogs`,
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install e2fsprogs
|
||||
|
||||
用 root 权限在分区中运行 `e4defrag`。如果你不想或不能卸载该分区,你可以使用它的挂载点而不是路径。要整理整个系统的碎片,运行:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo e4defrag /
|
||||
|
||||
在挂载的情况下不保证成功(你也应该在它运行时不要使用你的系统),但是它比复制全部文件再重新复制回来简单多了。
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结 ###
|
||||
|
||||
linux 系统中由于它的日志型文件系统有效的数据处理很少会出现碎片。如果你因任何原因产生了碎片,简单的方法是重新分配你的磁盘,如复制出去所有文件并复制回来,或者使用`e4defrag`。然而重要的是保证你数据的安全,因此在进行任何可能影响你全部或者大多数文件的操作之前,确保你的文件已经被备份到了另外一个安全的地方去了。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://www.maketecheasier.com/defragment-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Attila Orosz][a]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/author/attilaorosz/
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,5 @@
|
||||
mikecoder translating...
|
||||
|
||||
Xenlism WildFire: Minimal Icon Theme For Linux Desktop
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,120 @@
|
||||
struggling 翻译中
|
||||
|
||||
HTTP/2 Now Fully Supported in NGINX Plus
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Earlier this week we released [NGINX Plus R7][1] with support for HTTP/2. As the latest standard for the HTTP protocol, HTTP/2 is designed to bring increased performance and security to modern web applications.
|
||||
|
||||
The HTTP/2 implementation in NGINX Plus works seamlessly with existing sites and applications. Minimal changes are required, as NGINX Plus delivers HTTP/1.x and HTTP/2 traffic in parallel for the best experience, no matter what browser your users choose.
|
||||
|
||||
HTTP/2 support is available in the optional **nginx‑plus‑http2** package only. The **nginx‑plus** and **nginx‑plus‑extras** packages provide SPDY support and are currently recommended for production sites because of wider browser support and code maturity.
|
||||
|
||||
### Why Move to HTTP/2? ###
|
||||
|
||||
HTTP/2 makes data transfer more efficient and more secure for your applications. HTTP/2 adds five key features that improve performance when compared to HTTP/1.x:
|
||||
|
||||
- **True multiplexing** – HTTP/1.1 enforces strict in-order completion of requests that come in over a keepalive connection. A request must be satisfied before processing on the next one can begin. HTTP/2 eliminates this requirement and allows requests to be satisfied in parallel and out of order.
|
||||
- **Single, persistent connection** – As HTTP/2 allows for true multiplexing of requests, all objects on a web page can now be downloaded in parallel over a single connection. WIth HTTP/1.x, multiple connections are used to download resources in parallel, leading to inefficient use of the underlying TCP protocol.
|
||||
- **Binary encoding** – Header information is sent in compact, binary format, rather than plain text, saving bytes on the wire.
|
||||
- **Header compression** – Headers are compressed using a purpose-built algorithm, HPACK compression, which further reduces the amount of data crossing the network.
|
||||
- **SSL/TLS encryption** – With HTTP/2, SSL/TLS encryption is mandatory. This is not enforced in the [RFC][2], which allows for plain-text HTTP/2, but rather by all web browsers that currently implement HTTP/2. SSL/TLS makes your site more secure, and with all the performance improvements in HTTP/2, the performance penalty from encryption and decryption is mitigated.
|
||||
|
||||
To learn more about HTTP/2:
|
||||
|
||||
- Please read our [white paper][3], which covers everything you need to know about HTTP/2.
|
||||
- Download our [special edition of the High Performance Browser Networking ebook][4] by Ilya Grigorik of Google.
|
||||
|
||||
### How NGINX Plus Implements HTTP/2 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Our implementation of HTTP/2 is based on our support for SPDY, which is widely deployed (nearly 75% of websites that use SPDY use NGINX or NGINX Plus). With NGINX Plus, you can deploy HTTP/2 with very little change to your application infrastructure. This section discusses how NGINX Plus implements support for HTTP/2.
|
||||
|
||||
#### An HTTP/2 Gateway ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
NGINX Plus acts an HTTP/2 gateway. It talks HTTP/2 to client web browsers that support it, but translates HTTP/2 requests back to HTTP/1.x (or FastCGI, SCGI, uWSGI, etc. – whatever protocol you are currently using) for communication with back-end servers.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Backward Compatibility ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
For the foreseeable future you’ll need to support HTTP/2 and HTTP/1.x side by side. As of this writing, over 50% of users already run a web browser that [supports HTTP/2][5], but this also means almost 50% don’t.
|
||||
|
||||
To support both HTTP/1.x and HTTP/2 side by side, NGINX Plus implements the Next Protocol Negotiation (NPN) extension to TLS. When a web browser connects to a server, it sends a list of supported protocols to the server. If the browser includes h2 – that is, HTTP/2 – in the list of supported protocols, NGINX Plus uses HTTP/2 for connections to that browser. If the browser doesn’t implement NPN, or doesn’t send h2 in its list of supported protocols, NGINX Plus falls back to HTTP/1.x.
|
||||
|
||||
### Moving to HTTP/2 ###
|
||||
|
||||
NGINX, Inc. aims to make the transition to HTTP/2 as seamless as possible. This section goes through the changes that need to be made to enable HTTP/2 for your applications, which include just a few changes to the configuration of NGINX Plus.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Prerequisites ####
|
||||
|
||||
Upgrade to the NGINX Plus R7 **nginx‑plus‑http2** package. Note that an HTTP/2-enabled version of the **nginx‑plus‑extras** package is not available at this time.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Redirecting All Traffic to SSL/TLS ####
|
||||
|
||||
If your app is not already encrypted with SSL/TLS, now would be a good time to make that move. Encrypting your app protects you from spying as well as from man-in-the-middle attacks. Some search engines even reward encrypted sites with [improved rankings][6] in search results. The following configuration block redirects all plain HTTP requests to the encrypted version of the site.
|
||||
|
||||
server {
|
||||
listen 80;
|
||||
location / {
|
||||
return 301 https://$host$request_uri;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#### Enabling HTTP/2 ####
|
||||
|
||||
To enable HTTP/2 support, simply add the http2 parameter to all [listen][7] directives. Also include the ssl parameter, required because browsers do not support HTTP/2 without encryption.
|
||||
|
||||
server {
|
||||
listen 443 ssl http2 default_server;
|
||||
|
||||
ssl_certificate server.crt;
|
||||
ssl_certificate_key server.key;
|
||||
…
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
If necessary, restart NGINX Plus, for example by running the nginx -s reload command. To verify that HTTP/2 translation is working, you can use the “HTTP/2 and SPDY indicator” plug-in available for [Google Chrome][8] and [Firefox][9].
|
||||
|
||||
### Caveats ###
|
||||
|
||||
- Before installing the **nginx‑plus‑http2** package, you must remove the spdy parameter on all listen directives in your configuration (replace it with the http2 and ssl parameters to enable support for HTTP/2). With this package, NGINX Plus fails to start if any listen directives have the spdy parameter.
|
||||
- If you are using a web application firewall (WAF) that is sitting in front of NGINX Plus, ensure that it is capable of parsing HTTP/2, or move it behind NGINX Plus.
|
||||
- The “Server Push” feature defined in the HTTP/2 RFC is not supported in this release. Future releases of NGINX Plus might include it.
|
||||
- NGINX Plus R7 supports both SPDY and HTTP/2. In a future release we will deprecate support for SPDY. Google is [deprecating SPDY][10] in early 2016, making it unnecessary to support both protocols at that point.
|
||||
- If [ssl_prefer_server_ciphers][11] is set to on and/or a list of [ssl_ciphers][12] that are defined in [Appendix A: TLS 1.2 Ciper Suite Black List][13] is used, the browser will experience handshake-errors and not work. Please refer to [section 9.2.2 of the HTTP/2 RFC][14] for more details.-
|
||||
|
||||
### Special Thanks ###
|
||||
|
||||
NGINX, Inc. would like to thank [Dropbox][15] and [Automattic][16], who are heavy users of our software and graciously cosponsored the development of our HTTP/2 implementation. Their contributions have helped accelerate our ability to bring this software to you, and we hope you are able to support them in turn.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[O'REILLY'S BOOK ABOUT HTTP/2 & PERFORMANCE TUNING][17]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://www.nginx.com/blog/http2-r7/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Faisal Memon][a]
|
||||
译者:[struggling](https://github.com/struggling)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://www.nginx.com/blog/author/fmemon/
|
||||
[1]:https://www.nginx.com/blog/nginx-plus-r7-released/
|
||||
[2]:https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7540
|
||||
[3]:https://www.nginx.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/09/NGINX_HTTP2_White_Paper_v4.pdf
|
||||
[4]:https://www.nginx.com/http2-ebook/
|
||||
[5]:http://caniuse.com/#feat=http2
|
||||
[6]:http://googlewebmastercentral.blogspot.co.uk/2014/08/https-as-ranking-signal.html
|
||||
[7]:http://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_core_module.html#listen
|
||||
[8]:https://chrome.google.com/webstore/detail/http2-and-spdy-indicator/mpbpobfflnpcgagjijhmgnchggcjblin?hl=en
|
||||
[9]:https://addons.mozilla.org/en-us/firefox/addon/spdy-indicator/
|
||||
[10]:http://blog.chromium.org/2015/02/hello-http2-goodbye-spdy-http-is_9.html
|
||||
[11]:http://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_ssl_module.html#ssl_prefer_server_ciphers
|
||||
[12]:http://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_ssl_module.html#ssl_ciphers
|
||||
[13]:https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7540#appendix-A
|
||||
[14]:https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7540#section-9.2.2
|
||||
[15]:http://dropbox.com/
|
||||
[16]:http://automattic.com/
|
||||
[17]:https://www.nginx.com/http2-ebook/
|
||||
@ -1,183 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Mhddfs——将多个小分区合并成一个大的虚拟存储
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
让我们假定你有30GB的电影,并且你有3个驱动器,每个的大小为20GB。那么,你会怎么来存放东西呢?
|
||||
|
||||
很明显,你可以将你的视频分割成2个或者3个不同的卷,并将它们手工存储到驱动器上。这当然不是一个好主意,它成了一项费力的工作,它需要你手工干预,而且花费你大量时间。
|
||||
|
||||
另外一个解决方案是创建一个[RAID磁盘阵列][1]。然而,RAID在缺乏存储可靠性,磁盘空间可用性差等方面声名狼藉。另外一个解决方案,就是mhddfs。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Mhddfs——在Linux中合并多个分区
|
||||
|
||||
mhddfs是一个用于Linux的驱动,它可以将多个挂载点合并到一个虚拟磁盘中。它是一个基于FUSE的驱动,提供了一个用于大数据存储的简单解决方案。它将所有小文件系统合并,以创建一个单一的大虚拟文件系统,该文件系统包含其成员文件系统的所有颗粒,包括文件和空闲空间。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 你为什么需要Mhddfs? ####
|
||||
|
||||
你所有存储设备创建了一个单一的虚拟池,它可以在启动时被挂载。这个小工具可以智能地照看并处理哪个驱动器满了,哪个驱动器空着,将数据写到哪个驱动器中。当你成功创建虚拟驱动器后,你可以使用[SAMBA][2]来共享你的虚拟文件系统。你的客户端将在任何时候都看到一个巨大的驱动器和大量的空闲空间。
|
||||
|
||||
#### Mhddfs特性 ####
|
||||
|
||||
- 获取文件系统属性和系统信息。
|
||||
- 设置文件系统属性。
|
||||
- 创建、读取、移除和写入目录和文件。
|
||||
- 支持文件锁和单一设备上的硬链接。
|
||||
|
||||
注:表格
|
||||
<table cellspacing="0" border="0">
|
||||
<colgroup width="472"></colgroup>
|
||||
<colgroup width="491"></colgroup>
|
||||
<tbody>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td height="29" align="center" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><b><span style="color: black; font-size: large;">mhddfs的优点</span></b></td>
|
||||
<td align="center" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><b><span style="color: black; font-size: large;">mhddfs的缺点</span></b></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td height="25" align="left" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="color: black; font-size: medium;"> 适合家庭用户</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="left" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="color: black; font-size: medium;">mhddfs驱动没有内建在Linux内核中 </span></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td height="25" align="left" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="color: black; font-size: medium;"> 运行简单</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="left" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="color: black; font-size: medium;"> 运行时需要大量处理能力</span></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td height="25" align="left" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="color: black; font-size: medium;"> 没有明显的数据丢失</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="left" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="color: black; font-size: medium;"> 没有冗余解决方案</span></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td height="25" align="left" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="color: black; font-size: medium;"> 不分割文件</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="left" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="color: black; font-size: medium;"> 不支持移动硬链接</span></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td height="25" align="left" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="color: black; font-size: medium;"> 添加新文件到合并的虚拟文件系统</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="left" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-size: medium;"> </span></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td height="25" align="left" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="color: black; font-size: medium;"> 管理文件保存的位置</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="left" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-size: medium;"> </span></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td height="25" align="left" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="color: black; font-size: medium;"> 扩展文件属性</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="left" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-size: medium;"> </span></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</tbody>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
|
||||
### Linux中安装Mhddfs ###
|
||||
|
||||
在Debian及其类似的移植系统中,你可以使用下面的命令来安装mhddfs包。
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get update && apt-get install mhddfs
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
安装Mhddfs到基于Debian的系统中
|
||||
|
||||
在RHEL/CentOS Linux系统中,你需要开启[epel仓库][3],然后执行下面的命令来安装mhddfs包。
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install mhddfs
|
||||
|
||||
在Fedora 22及以上系统中,你可以通过dnf包管理来获得它,就像下面这样。
|
||||
|
||||
# dnf install mhddfs
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
安装Mhddfs到Fedora
|
||||
|
||||
如果万一mhddfs包不能从epel仓库获取到,那么你需要解决下面的依赖,然后像下面这样来编译源码并安装。
|
||||
|
||||
- FUSE头文件
|
||||
- GCC
|
||||
- libc6头文件
|
||||
- uthash头文件
|
||||
- libattr1头文件(可选)
|
||||
|
||||
接下来,只需从下面建议的地址下载最新的源码包,然后编译。
|
||||
|
||||
# wget http://mhddfs.uvw.ru/downloads/mhddfs_0.1.39.tar.gz
|
||||
# tar -zxvf mhddfs*.tar.gz
|
||||
# cd mhddfs-0.1.39/
|
||||
# make
|
||||
|
||||
你应该可以在当前目录中看到mhddfs的二进制文件,以root身份将它移动到/usr/bin/和/usr/local/bin/中。
|
||||
|
||||
# cp mhddfs /usr/bin/
|
||||
# cp mhddfs /usr/local/bin/
|
||||
|
||||
一切搞定,mhddfs已经可以用了。
|
||||
|
||||
### 我怎么使用Mhddfs? ###
|
||||
|
||||
1.让我们看看当前所有挂载到我们系统中的硬盘。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
$ df -h
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
**样例输出**
|
||||
|
||||
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
|
||||
|
||||
/dev/sda1 511M 132K 511M 1% /boot/efi
|
||||
/dev/sda2 451G 92G 336G 22% /
|
||||
/dev/sdb1 1.9T 161G 1.7T 9% /media/avi/BD9B-5FCE
|
||||
/dev/sdc1 555M 555M 0 100% /media/avi/Debian 8.1.0 M-A 1
|
||||
|
||||
注意这里的‘挂载点’名称,我们后面会使用到它们。
|
||||
|
||||
2.创建目录‘/mnt/virtual_hdd’,在这里,所有这些文件系统将被组成组。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# mkdir /mnt/virtual_hdd
|
||||
|
||||
3.然后,挂载所有文件系统。你可以通过root或者FUSE组中的某个成员来完成。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# mhddfs /boot/efi, /, /media/avi/BD9B-5FCE/, /media/avi/Debian\ 8.1.0\ M-A\ 1/ /mnt/virtual_hdd -o allow_other
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
在Linux中挂载所有文件系统
|
||||
|
||||
**注意**:这里我们使用了所有硬盘的挂载点名称,很明显,你的挂载点名称会有所不同。也请注意“-o allow_other”选项可以让这个虚拟文件系统让其它所有人可见,而不仅仅是创建它的人。
|
||||
|
||||
4.现在,运行“df -h”来看看所有文件系统。它应该包含了你刚才创建的那个。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
$ df -h
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
验证虚拟文件系统挂载
|
||||
|
||||
你可以像对已挂在的驱动器那样给虚拟文件系统部署所有的选项。
|
||||
|
||||
5.要在每次系统启动创建这个虚拟文件系统,你应该以root身份添加下面的这行代码(在你那里会有点不同,取决于你的挂载点)到/etc/fstab文件的末尾。
|
||||
|
||||
mhddfs# /boot/efi, /, /media/avi/BD9B-5FCE/, /media/avi/Debian\ 8.1.0\ M-A\ 1/ /mnt/virtual_hdd fuse defaults,allow_other 0 0
|
||||
|
||||
6.如果在任何时候你想要添加/移除一个新的驱动器到/从虚拟硬盘,你可以挂载一个新的驱动器,拷贝/mnt/vritual_hdd的内容,卸载卷,弹出你要移除的的驱动器并/或挂载你要包含的新驱动器。使用mhddfs命令挂载全部文件系统到Virtual_hdd下,这样就全部搞定了。
|
||||
#### 我怎么卸载Virtual_hdd? ####
|
||||
|
||||
卸载virtual_hdd相当简单,就像下面这样
|
||||
|
||||
# umount /mnt/virtual_hdd
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
卸载虚拟文件系统
|
||||
|
||||
注意,是umount,而不是unmount,很多用户都输错了。
|
||||
|
||||
到现在为止全部结束了。我正在写另外一篇文章,你们一定喜欢读的。到那时,请保持连线到Tecmint。请在下面的评论中给我们提供有用的反馈吧。请为我们点赞并分享,帮助我们扩散。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/combine-partitions-into-one-in-linux-using-mhddfs/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Avishek Kumar][a]
|
||||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/avishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/understanding-raid-setup-in-linux/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/mount-filesystem-in-linux/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/how-to-enable-epel-repository-for-rhel-centos-6-5/
|
||||
@ -1,125 +0,0 @@
|
||||
如何在Linux中整理磁盘碎片
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
有一神话是linux的磁盘从来不需要整理碎片。在大多数情况下这是真的,大多数因为是使用的是优秀的日志系统(ext2、3、4等等)来处理文件系统。然而,在一些特殊情况下,碎片仍旧会产生。如果正巧发生在你身上,解决方法很简单。
|
||||
|
||||
### 什么是磁盘碎片 ###
|
||||
|
||||
碎片发生在不同的小块中更新文件时,但是这些快没有形成连续完整的文件而是分布在磁盘的各个角落中。这对于FAT和FAT32文件系统而言是这样的。这在NTFS中有所减轻,在Linux(extX)中几乎不会发生。下面是原因。
|
||||
|
||||
在像FAT和FAT32这类文件系统中,文件紧挨着写入到磁盘中。文件之间没有空间来用于增长或者更新:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
NTFS中在文件之间保留了一些空间,因此有空间进行增长。因为块之间的空间是有限的,碎片也会随着时间出现。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Linux的日志文件系统采用了一个不同的方案。与文件之间挨着不同,每个文件分布在磁盘的各处,每个文件之间留下了大量的剩余空间。这里有很大的空间用于更新和增长,并且碎片很少会发生。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
此外,碎片一旦出现了,大多数Linux文件系统会尝试将文件和块重新连续起来。
|
||||
|
||||
### Linux中的磁盘整理 ###
|
||||
|
||||
除非你用的是一个很小的硬盘或者空间不够了,不然Linux很少会需要磁盘整理。一些可能需要磁盘整理的情况包括:
|
||||
|
||||
- 如果你编辑的是大型视频文件或者原生照片,但磁盘空间有限
|
||||
- if you use older hardware like an old laptop, and you have a small hard drive
|
||||
- 如果你的磁盘开始满了(大约使用了85%)
|
||||
- 如果你的家目录中有许多小分区
|
||||
|
||||
最好的解决方案是购买一个大硬盘。如果不可能,磁盘碎片整理就很有用了。
|
||||
|
||||
### 如何检查碎片 ###
|
||||
|
||||
`fsck`命令会为你做这个 -也就是说如果你可以在liveCD中运行它,那么就可以**卸载所有的分区**。
|
||||
|
||||
这一点很重要:**在已经挂载的分区中运行fsck将会严重危害到你的数据和磁盘**。
|
||||
|
||||
你已经被警告过了。开始之前,先做一个完整的备份。
|
||||
|
||||
**免责声明**: 本文的作者与Make Tech Easier将不会对您的文件、数据、系统或者其他损害负责。你需要自己承担风险。如果你继续,你需要接收并了解这点。
|
||||
|
||||
你应该启动到一个live会话中(如安装磁盘,系统救援CD等)并运行`fsck`卸载分区。要检查是否有任何问题,请在运行root权限下面的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
fsck -fn [/path/to/your/partition]
|
||||
|
||||
您可以检查一下运行中的分区的路径
|
||||
|
||||
sudo fdisk -l
|
||||
|
||||
有一个(相对)安全地在已挂载的分区中运行`fsck`的方法是使用‘-n’开关。这会让分区处在只读模式而不能创建任何文件。当然,这里并不能保证安全,你应该在创建备份之后进行。在ext2中,运行
|
||||
|
||||
sudo fsck.ext2 -fn /path/to/your/partition
|
||||
|
||||
会产生大量的输出-- 大多数错误信息的原因是分区已经挂载了。最后会给出一个碎片相关的信息。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
如果碎片大于20%了,那么你应该开始整理你的磁盘碎片了。
|
||||
|
||||
### 如何简单地在Linux中整理碎片 ###
|
||||
|
||||
你要做的是备份你**所有**的文件和数据到另外一块硬盘中(手动**复制**他们)。格式化分区然后重新复制回去(不要使用备份软件)。日志系统会把它们作为新的文件,并将它们整齐地放置到磁盘中而不产生碎片。
|
||||
|
||||
要备份你的文件,运行
|
||||
|
||||
cp -afv [/path/to/source/partition]/* [/path/to/destination/folder]
|
||||
|
||||
记住星号(*)是很重要的。
|
||||
|
||||
注意:通常认为复制大文件或者大量文件,使用dd或许是最好的。这是一个非常底层的操作,它会复制一切,包含空闲的空间甚至是留下的垃圾。这不是我们想要的,因此这里最好使用`cp`。
|
||||
|
||||
现在你只需要删除源文件。
|
||||
|
||||
sudo rm -rf [/path/to/source/partition]/*
|
||||
|
||||
**可选**:你可以将空闲空间置零。你也可以用格式化来达到这点,但是例子中你并没有复制整个分区而仅仅是大文件(这很可能会造成碎片)。这恐怕不能成为一个选项。
|
||||
|
||||
sudo dd if=/dev/zero of=[/path/to/source/partition]/temp-zero.txt
|
||||
|
||||
等待它结束。你可以用`pv`来监测进程。
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install pv
|
||||
sudo pv -tpreb | of=[/path/to/source/partition]/temp-zero.txt
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
这就完成了,只要删除临时文件就行。
|
||||
|
||||
sudo rm [/path/to/source/partition]/temp-zero.txt
|
||||
|
||||
待你清零了空闲空间(或者跳过了这步)。重新复制回文件,将第一个cp命令翻转一下:
|
||||
|
||||
cp -afv [/path/to/original/destination/folder]/* [/path/to/original/source/partition]
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用 e4defrag ###
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想要简单的方法,安装`e2fsprogs`,
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install e2fsprogs
|
||||
|
||||
用root权限在分区中运行 `e4defrag`。如果你不想卸载分区,你可以使用它的挂载点而不是路径。要整理整个系统的碎片,运行:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo e4defrag /
|
||||
|
||||
在挂载的情况下不保证成功(你也应该保证在它运行时停止使用你的系统),但是它比服务全部文件再重新复制回来简单多了。
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结 ###
|
||||
|
||||
linux系统中很少会出现碎片因为它的文件系统有效的数据处理。如果你因任何原因产生了碎片,简单的方法是重新分配你的磁盘如复制所有文件并复制回来,或者使用`e4defrag`。然而重要的是保证你数据的安全,因此在进行任何可能影响你全部或者大多数文件的操作之前,确保你的文件已经被备份到了另外一个安全的地方去了。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://www.maketecheasier.com/defragment-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Attila Orosz][a]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/author/attilaorosz/
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user