mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-03-12 01:40:10 +08:00
commit
418d24a5aa
@ -1,15 +1,15 @@
|
||||
给linux用户的11个高级MySQL数据库面试问题和答案
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
我们已经发表了两篇MySQL的文章,非常感谢Tecmint社区的大力支持.这是MySQL面试系列的第三篇文章,并且在面试专栏中排第16.
|
||||
我们已经发表了两篇MySQL的文章,非常感谢Tecmint社区的大力支持。这是MySQL面试系列的第三篇文章,并且在面试专栏中排第16。
|
||||
- [15个基本的MySQL面试问题][1]
|
||||
- [给中级人员的10个MySQL面试问题][1]
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
感谢你们这一路上对我们的支持.这篇文章主要针对MySQL的实用性,讲面试方面的问题.
|
||||
因为有大家的支持,我们才能做到现在,感谢你们这一路上对我们的支持.在这篇文章中,我们将主要针对MySQL的实用技巧,讲讲面试中相关的问题.
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. 如何使用SELECT语句找到你正在运行的服务器的版本并打印出当前数据库的名称? ###
|
||||
**Ans**:下面的语句的结果会显示服务器的版本和当前的数据库名称
|
||||
**答**:下面的语句的结果会显示服务器的版本和当前的数据库名称
|
||||
|
||||
mysql> SELECT VERSION(), DATABASE();
|
||||
|
||||
@ -20,7 +20,7 @@
|
||||
+-------------------------+------------+
|
||||
1 row in set (0.06 sec)
|
||||
|
||||
在Database一栏中显示**NULL**是因为我们当前没有选择任何数据库.因此,使用下面的语句先选择一个数据库,就能看到相应的结果.
|
||||
在Database一列中显示**NULL**是因为我们当前没有选择任何数据库。因此,使用下面的语句先选择一个数据库,就能看到相应的结果。
|
||||
|
||||
mysql> use Tecmint;
|
||||
|
||||
@ -40,9 +40,9 @@
|
||||
+-------------------------+------------+
|
||||
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. 使用非运算符(!)从表"Tecmint"中列出除了user等于"SAM"的所有记录
|
||||
### 2. 使用非运算符(!)从表"Tecmint"中列出除了"SAM"以外的所有user记录
|
||||
|
||||
**Ans**:使用下面的语句
|
||||
**答**:使用下面的语句
|
||||
|
||||
mysql> SELECT * FROM Tecmint WHERE user !=SAM;
|
||||
|
||||
@ -53,13 +53,13 @@
|
||||
| 2001-05-15 08:50:57 | TIM | venus | phil | venus | 978 |
|
||||
+---------------------+---------+---------+---------+---------+-------+
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. 是否能够使用非运算符(!)来实现'AND'运算
|
||||
### 3. ‘AND’运算符有可能带着非运算符(!)一起用吗?
|
||||
|
||||
**Ans**: 我们使用’=’号和OR运算符或者'!='和AND运算符,下面是'='和AND运算符的例子
|
||||
**答**:当我们使用‘=’号时用‘AND’连接,用‘!=’时用‘OR’连接,下面是‘=’和AND运算符一起用的例子
|
||||
|
||||
mysql> SELECT * FROM mail WHERE user = SAM AND root = phil
|
||||
|
||||
'!='和OR运算符的例子
|
||||
‘!=’和OR运算符的例子
|
||||
|
||||
mysql> SELECT * FROM mail WHERE user != SAM OR root != phil
|
||||
|
||||
@ -71,13 +71,13 @@
|
||||
|
||||
- = : 等于
|
||||
- != : 不等于
|
||||
- ! : 非运算符
|
||||
- ! : 代表“非”的运算符
|
||||
|
||||
AND和OR在MySQL中被看作加入运算符
|
||||
AND和OR在MySQL中被看作连接运算符
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. IFNULL()语句在MySQL中有什么作用? ###
|
||||
### 4. IFNULL()当打在MySQL中有什么作用? ###
|
||||
|
||||
**Ans**: **IFNULL**语句的使用使得MySQL中的查询更加精确。IFNULL()语句先测试它的的一个参数,若不为空就返回该参数的值,否则返回第二个参数的值
|
||||
**答**:使用**IFNULL()**方法能使MySQL中的查询更加精确。IFNULL()方法将会测试它的第一个参数,若不为NULL则返回该参数的值,否则返回第二个参数的值
|
||||
|
||||
mysql> SELECT name, IFNULL(id,'Unknown') AS 'id' FROM taxpayer;
|
||||
|
||||
@ -90,9 +90,9 @@ AND和OR在MySQL中被看作加入运算符
|
||||
| bill | 475-83 |
|
||||
+---------+---------+
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. 如果你只想知道从一个结果集的开头或者结尾开始的特定条数的行记录改如何实现?
|
||||
### 5. 如果你只想知道从一个结果集的开头或者结尾开始的特定几条记录,该如何实现?
|
||||
|
||||
**Ans**: 我们可以用**LIMIT**和**ORDER BY**从句。
|
||||
**答**:我们需要把**LIMIT**语句接在**ORDER BY**语句后使用,以达到上述效果。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 显示一行记录 ####
|
||||
|
||||
@ -128,20 +128,20 @@ AND和OR在MySQL中被看作加入运算符
|
||||
| 9 | Dick | 1952-08-20 | green | lutefisk,fadge | 0 |
|
||||
+----+------+------------+-------+----------------+------+
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. Oracle 和 MySQL该如何选择? ###
|
||||
### 6. Oracle 和 MySQL该如何选择,为什么? ###
|
||||
|
||||
**Ans**: 它们都有各自的优点和缺点。
|
||||
**答**:它们都有各自的优点和缺点。考虑到时间因素,我倾向于MySQL。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 选择MySQL而不选orcale的原因 ####
|
||||
|
||||
- 开源
|
||||
- 轻便快捷
|
||||
- 有命令行和图形界面
|
||||
- 能通过查询器进行数据库的管理
|
||||
- MySQL开源
|
||||
- MySQL轻便快捷
|
||||
- MySQL对命令行和图形界面的支持都很好
|
||||
- MySQL支持通过Query Browser进行管理
|
||||
|
||||
### 7. MySQL中如何得到当前日期? ###
|
||||
|
||||
**Ans**: 使用CURRENT_DATE()函数
|
||||
**答**:在MySQL中获取当前日期就是如下的SELECT语句这么简单。
|
||||
|
||||
mysql> SELECT CURRENT_DATE();
|
||||
|
||||
@ -153,23 +153,23 @@ AND和OR在MySQL中被看作加入运算符
|
||||
|
||||
### 8. MySQL中如何将表导出为XML文件? ###
|
||||
|
||||
**Ans**: 使用'-e'(export)参数来把MySQL表或整个数据库导出到XML文件。当处理大型表的时候或许我们需要手动导出,但是只是导出小文件的话可以直接使用想phpMyAdmin这样的工具。
|
||||
**答**:我们可以使用'-e'(export)选项来把MySQL表或整个数据库导出到XML文件。当处理大型表的时候我们可能需要手动导出,不过对于小表的话可以直接使用想phpMyAdmin等这样的工具。
|
||||
|
||||
mysql -u USER_NAME –xml -e 'SELECT * FROM table_name' > table_name.xml
|
||||
mysql -u USER_NAME -xml -e 'SELECT * FROM table_name' > table_name.xml
|
||||
|
||||
上面的例子中USER_NAME是数据库的用户名,table_name是待导出为xml文件的表名,table_name.xml是存放数据的xml文件
|
||||
|
||||
### 9. MySQL_pconnect是什么? 它和MySQL_connect有什么区别? ###
|
||||
|
||||
**Ans**: MySQL_pconnect()打开一个永久的数据库连接,这意味着数据库不是在每次页面加载的时候被打开,因此我们不能使用MySQL_close()来关闭一个永久的连接
|
||||
**答**:MySQL_pconnect()打开一个持久的数据库连接,这意味着数据库不是在每次页面加载的时候被打开一个新连接,因此我们不能使用MySQL_close()来关闭一个持久的连接
|
||||
|
||||
MySQL_pconnect和MySQL_connect有一定的差别
|
||||
MySQL_pconnect和MySQL_connect最简要的区别是:
|
||||
|
||||
和MySQL_pconnect不同,MySQL_connect在每次页面被加载的时候打开,并且可以使用MySQL_close()语句来关闭连接
|
||||
与MySQL_pconnect不同,MySQL_connect在每次页面被加载的时候打开连接,这个连接可以使用MySQL_close()语句来关闭
|
||||
|
||||
### 10. 如何查看一个名为'mysql'的数据库中'user'表中的所有索引? ###
|
||||
### 10. 当你需要查看一个名为'mysql'的数据库中'user'表中的所有索引时,你会如何做? ###
|
||||
|
||||
**Ans**: 可以使用下面的语句
|
||||
**答**:下面的命令将会显示出‘user’表中所有的索引
|
||||
|
||||
mysql> show index from user;
|
||||
+-------+------------+----------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
|
||||
@ -182,17 +182,17 @@ MySQL_pconnect和MySQL_connect有一定的差别
|
||||
|
||||
### 11. 什么是CSV表? ###
|
||||
|
||||
**Ans**: CSV是逗号分隔值的缩写,也称为字符分隔值。CSV表中存放纯文本和表格数据。
|
||||
**答**:CSV是逗号分隔值(Comma-Separated Values)或也被称为字符分隔值(Character-Separated Values)的缩写。CSV表以纯文本和表格形式来存储数据。
|
||||
|
||||
每一条记录使用具体的分隔符隔开(如逗号,分号,...),CSV表广泛的用来存放易于导入和导出的电话联系人,能够用来存放任何数量的纯文本。
|
||||
每一条记录都使用特定的分隔符隔开(如逗号,分号,...),并且每条记录都有着顺序相同的列。CSV表最广泛地被用来存储用于导入和导出的电话联系人,并能够用来存储任何类型的纯文本数据。
|
||||
|
||||
以上就是这次要将的内容。我还会带来其他的有趣的文章,向往你们喜欢。连接到Tecmint继续关注我们,不要忘了在评论栏中留下你们的宝贵意见。
|
||||
以上就是这次要讲的全部内容。我还会带来其他你们应该会喜欢的有趣的文章。到那时敬请关注并访问Tecmint,不要忘了在下方的评论栏中留下你们的宝贵意见。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/mysql-advance-interview-questions/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux) 校对:[ReiNoir](https://github.com/reinoir)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,97 @@
|
||||
教你如何在Fedora,CentOS,RHEL中检查RPM包的依赖性
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
我们都知道,在基于红帽的Linux系统中,一个RPM包,需要把先将它依赖的其他包安装好才能正常的工作。对于终端用户,RPM的安装、更新、删除中存在的依赖关系已经被工具透明化了(如 yum或 DNF等)。但如果你是系统管理员或者RPM包的管理员,你需要谙熟RPM包的依赖关系,以便及时更新、删除适当的包来保证系统的正常运行。
|
||||
|
||||
在本教程中,我将教大家**如何检查RPM包的依赖关系**。无论这个包是否已经安装进操作系统中,我们都有一些办法来检查它们的依赖性。
|
||||
|
||||
### 方法一 ###
|
||||
|
||||
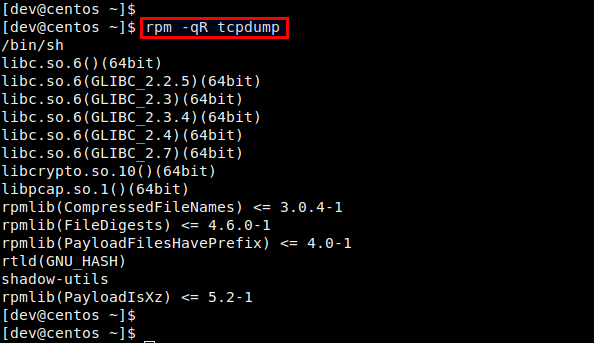
使用RPM命令可以列出目标包所依赖的所有包,如下:
|
||||
$ rpm -qR <package-name>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
注意,这种方法只适用于**已安装**的包。如果你需要检查一个**未安装**包的依赖关系,你首先需要把这个包先下载到本地来(不需要安装)。
|
||||
|
||||
要下载一个 RPM 包而不安装,可以使用叫做'yumdownloader'的工具,下面我们先安装yumdownloader:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install yum-utils
|
||||
|
||||
现在我们来检查一个未安装的RPM包的依赖关系(本例使用 tcpdump)。首先,我们使用yumdownloader把tcpdump的RPM包下载下来
|
||||
|
||||
$ yumdownloader --destdir=. tcpdump
|
||||
|
||||
然后再使用 "-qpR"参数显示该包的依赖关系。
|
||||
|
||||
# rpm -qpR tcpdump-4.4.0-2.fc19.i686.rpm
|
||||
|
||||
### 方法二 ###
|
||||
|
||||
你可以使用repoquery工具来罗列包的依赖关系,它与包是否安装无关,这个工具包含在yum-utils中。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install yum-utils
|
||||
|
||||
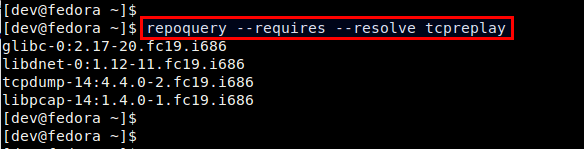
显示目标包所依赖的包:
|
||||
|
||||
$ repoquery --requires --resolve <package-name>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
为让repoquery正常的工作,需要保持网络的畅通,应为repoquery需要在Yum库中查找信息。
|
||||
|
||||
### 方法三 ###
|
||||
|
||||
第三个方法是使用rpmreaper工具。这个工具本来是用作清理系统中无用以及它们所依赖的包,rpmreaper有很直观的ncurses界面来展示已安装的包和它们依赖关系的树形图。
|
||||
|
||||
安装rpmrepater,在CentOS中,你需要先[设置好EPEL库][1]
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install rpmreaper
|
||||
|
||||
只需运行rpmreaper就可以看到RPM包的依赖关系:
|
||||
|
||||
$ rpmreaper
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
rpmrepater会向用户显示已安装包的列表,你可以使用上/下箭头来滚动屏幕。
|
||||
|
||||
你可以在指定包上使用"r"键来显示其依赖关系,循环在指定包上按下"r"键可以展示出余下的信息。
|
||||
|
||||
"L"标志的意思是说这个包是一片“孤叶”,意思说说没有任何包依赖它。
|
||||
|
||||
"o"标志是说这个包是整个依赖链的中间部分。
|
||||
|
||||
按下"b"键会显示其他依赖于该包的其他包。
|
||||
|
||||
### 方法四 ###
|
||||
|
||||
还有一个办法是使用rpmdep工具,rpmdep是一个命令行工具,可以显示已安装包的完整包依赖关系图。该工具会分析RPM包的依赖性,从完整的排完序的拓扑图中摘取部分包的信息,形成列表展示给用户。该工具的输出结果可以直接使用到Dotty(可视化展示工具)中去。
|
||||
|
||||
在Fedora中安装rpmdep和dotty:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install rpmorphan graphviz
|
||||
|
||||
在CentOs中安装:
|
||||
$ wget http://downloads.sourceforge.net/project/rpmorphan/rpmorphan/1.14/rpmorphan-1.14-1.noarch.rpm
|
||||
$ sudo rpm -ivh rpmorphan-1.14-1.noarch.rpm
|
||||
$ sudo yum install graphviz
|
||||
|
||||
生成包依赖的拓扑关系图(例如 gzip):
|
||||
|
||||
$ rpmdep.pl -dot gzip.dot gzip
|
||||
$ dot -Tpng -o output.png gzip.dot
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
教程到这个地方,我们用到了几种办法来检查包的依赖关系。如果您想知道如何在居于Debian的系统中检查.deb的包依赖关系,请阅读另外一篇[文档][2]
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/07/check-rpm-package-dependencies-fedora-centos-rhel.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[nd0104](https://github.com/nd0104) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://xmodulo.com/2013/03/how-to-set-up-epel-repository-on-centos.html
|
||||
[2]:http://xmodulo.com/2013/07/how-to-check-package-dependencies-on-ubuntu-or-debian.html
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,52 @@
|
||||
红帽旨在标准化Linux的64位ARM服务器
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> 红帽希望通过 Linux for ARM 服务器来避免困扰在Unix身上的几十年的分裂的发生 。
|
||||
|
||||
IDG通讯社 - 红帽公司已经开发出一个服务器版本的Linux操作系统,可以用来测试基于ARMv8-A 64-bit架构的芯片及其周边硬件,志在统一服务器市场。
|
||||
|
||||
该发行版基于该公司的红帽企业Linux(RHEL),是红帽在周三为潜在的[ARM硬件厂商][2]推出的的[合作伙伴计划][1]的一部分。
|
||||
|
||||
“我们并不称其为RHEL,但它作为一种功能性,不提供技术支持,可以用在合作伙伴的开发中使用的操作系统”,红帽平台产品营销高级主管Mark Coggin说。
|
||||
|
||||
红帽的设计方案符合硬件厂商的ARMv8-A规格实施标准。 ARM本身并不生产自己的处理器,而是将其设计产权授权于芯片制造商。
|
||||
|
||||
标准的解决方案将意味着用户可以从任何制造商购买ARMv8-A的服务器,他们知道自己的ARM 64位操作系统和软件将能完美地工作在不管是谁生产的芯片上,Coggin说。红帽希望Linux的ARM能避免像AT&T的Unix操作系统,分裂成许多不同不兼容的版本的命运。
|
||||
|
||||
“我们看到了早期进入市场的重要性,并且确信我们不会陷入到这样的碎片化:如果你想运行一个AMD的ARM解决方案;你需要一个相应的Linux版本,如果你想运行博通的ARM解决方案,你就需要另外一个版本”Coggin说。
|
||||
|
||||
今年早些时候开始,一些ARM的服务器的标准化工作已经制定完成,这是由一个被称为服务器系统基础架构(SBSA)规范的行业协会以及Linaro企业集团完成的。 Red Hat尚未命名的ARM Linux发行版使用着来自这两个组织的规范。
|
||||
|
||||
红帽不仅希望能影响到芯片生产商同时也包括硬件供应商、OEM 和 ODM。
|
||||
|
||||
迄今为止,像Advanced Micro Devices公司,American Megatrends,AppliedMicro,博通,Cavium公司,戴尔和惠普这样的制造商都承诺将支持Red Hat的标准化工作。
|
||||
|
||||
“如果ARM在服务器领域终将成为一个有力的的竞争者的话,[硬件提供商]将达成一种共识,即这种架构的服务器也是可行的。当前,客户及其需求都处于x86世界, “Yan Fisher,红帽技术产品营销经理说。
|
||||
|
||||
通过这种方式,红帽将了解到更多有关制造商对企业版 64位 ARM Linux 发行版的需求,Coggin说。可能有一天基础操作系统会成为RHEL的ARM版本。
|
||||
|
||||
“我们正在试图从技术层面了解其平台的需求,”Coggin说。 “我们不知道它是否或何时会成为一个产品,但是我们有自我定位的方式,在某些时候,我们相信可以我们进入市场。”
|
||||
|
||||
尽管Red Hat的Fedora项目过去和现在一直在提供ARM架构的发行版,但是基于Fedora的工作,可以支持更多的 ARM 服务器使用。
|
||||
|
||||
尽管ARM处理器在大多数移动设备使用广泛,但是直到最近才出现了在同行业中使用它们作为数据中心的迹象,它们的低功耗设计可以大大降低能源消耗。
|
||||
|
||||
目前只有极少数的ARMv8-A处理器和相关的硬件是可用的,大部分是一些早期的开发者预览版的或预装的专有系统。
|
||||
|
||||
AMD皓龙A1100系列ARM处理器,专为服务器设计,周三将会释放给开发者。 AMD还提供了专为SOC(注:system-on-a-chip 片上系统)架构设计的Cortex-A57 ARMv8。
|
||||
|
||||
AppliedMicro提供已经产品级的ARM服务器,在X-Gene的品牌之下,惠普正在准备推出其准备试水的ARM服务器产品线。主板制造商美国Megatrends提供了一个BIOS芯片用来启动ARM处理器。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.computerworld.com/s/article/9250061/Red_Hat_aims_to_standardize_Linux_for_64_bit_ARM_servers?taxonomyId=122
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Joab Jackson
|
||||
译者:[owen-carter](https://github.com/owen-carter)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://connect.redhat.com/early-access-programs/red-hat-and-64-bit-arm-ecosystem
|
||||
[2]:https://engage.redhat.com/arm-s-201407291033
|
||||
[3]:http://infocenter.arm.com/help/index.jsp?topic=/com.arm.doc.den0029/index.html
|
||||
[4]:http://www.networkworld.com/article/2171235/servers/arm-servers-with-64-bit-calxeda-chips-to-ship-next-year.html
|
||||
@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
|
||||
Linux常见问题及答案——如何在Linux Mint Cinnamon桌面启用并配置桌面共享
|
||||
Linux有问必答:如何在Linux Mint Cinnamon启用桌面共享
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
>**问题**:我试着在Linux Mint 17 Cinnamon桌面上通过Vino VNC服务器(vino-server)启用桌面共享。但是,我发现用来配置vino-server(如,共享选项,安全,通知开/关)的vino首选项工具已经不复存在了。同时,我也的Cinnamon桌面上也找不到共享菜单。我怎样才能在最新的Linux Mint 17 Cinnamon桌面上通过vino-server配置桌面共享?
|
||||
@ -20,7 +20,7 @@ Linux常见问题及答案——如何在Linux Mint Cinnamon桌面启用并配
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
最重要的是,点击“enabled”来激活桌面远程访问。除此之外,你还可以自定义其它选项。
|
||||
For example, you can enable VNC password authentication by changing the following fields:
|
||||
|
||||
例如,你可以通过修改以下字段来启用VNC密码验证:
|
||||
|
||||
- **authentication-methods**: 设置为 ['vnc']
|
||||
@ -49,6 +49,6 @@ For example, you can enable VNC password authentication by changing the followin
|
||||
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/enable-configure-desktop-sharing-linux-mint-cinnamon-desktop.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -1,46 +0,0 @@
|
||||
OpenMorrowind 0.31.0 RPG Remake Is Already Looking Great
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**OpenMW, an open source implementation of The Elder Scrolls 3: Morrowind game engine and functionality, is now at version 0.31.0 and packs lots of new features.**
|
||||
|
||||
OpenMW, or OpenMorrowind, is a project that aims to bring one of best role-playing games ever created into the open source world, but not by simple porting. The makers of this title have been working non-stop in the last months and it seems that the game is really starting to take shape.
|
||||
|
||||
Half a year ago, players couldn't do much in OpenMW, but now a lot of features have been integrated, and it's almost playable if you don't expect too much. Even with all the changes in place, the version number indicates that the development is moving rather slowly and numerous problems still remain. It will take a long time until the game reaches a stable version, but when it gets there, it's going to be an awesome RPG.
|
||||
|
||||
“The OpenMW team is proud to announce the release of version 0.31.0! This release includes implementation of many smaller features that have been sorely missing, as well fixes for a ridiculous amount of bugs. Many thanks to our developers for their relentless attention to detail. Some optimization has made it into this release, let us know if you see any increased performance,” reads the announcement on the official website.
|
||||
|
||||
A number of important changes have been made and lots of new stuff has been added. For example, a periodic cleanup/refill has been added, precipitation and weather particles are now ready in the engine, the dialog has been merged, saving missing creature state is now working properly, the murder crime has been implemented, a number of sneak skill enhancements have been added, and animated main menu support has been implemented.
|
||||
|
||||
Also, the clouds and weather have been modified to better match vanilla Morrowind, the background tracks are no longer repeating, the dead body collision behavior has been improved, and lots of other fixes have been implemented.
|
||||
|
||||
A complete list of changes and new features can be found in the official [announcement][1]. Users must legally own and install the game before they can use OpenMW – as it is intended – to play Morrowind.
|
||||
|
||||
Download OpenMW 0.31.0:
|
||||
|
||||
- [tar.gz][2][sources] [3.20 MB]
|
||||
- [tar.gz (64-bit)][3][binary] [33.40 MB]
|
||||
- [tar.gz (32-bit)][4][binary] [33.10 MB]
|
||||
- [Ubuntu PPA Repository][5][ubuntu_deb] [0 KB]
|
||||
- [Arch Linux Package][6][binary] [0 KB]
|
||||
- [Debian PPA Repository][7][debian_deb] [0 KB]
|
||||
|
||||
OpenMW aims to be a full-featured reimplementation of the Morrowind engine capable to work natively on all supported platforms and to support all existing content, including Tribunal, Bloodmoon, and all user-created mods.
|
||||
|
||||
Keep in mind that this is not a stable version and bugs might still appear.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/OpenMorrowind-0-31-0-RPG-Remake-Is-Already-Looking-Great-451120.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:https://openmw.org/2014/openmw-0-31-0/
|
||||
[2]:https://github.com/OpenMW/openmw/archive/openmw-0.31.0.tar.gz
|
||||
[3]:https://github.com/OpenMW/openmw/releases/download/openmw-0.31.0/openmw-0.31.0-Linux-64Bit.tar.gz
|
||||
[4]:https://github.com/OpenMW/openmw/releases/download/openmw-0.31.0/openmw-0.31.0-Linux.tar.gz
|
||||
[5]:https://launchpad.net/~openmw/+archive/openmw
|
||||
[6]:https://aur.archlinux.org/packages/?O=0&K=openmw
|
||||
[7]:http://forum.openmw.org/viewtopic.php?f=20&t=1298
|
||||
@ -1,53 +0,0 @@
|
||||
owen-carter translating
|
||||
Red Hat aims to standardize Linux for 64-bit ARM servers
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> Red Hat wants Linux for ARM servers to avoid the fragmentation that plagued Unix in decades past
|
||||
|
||||
DG News Service - Red Hat has developed a version of the Linux operating system that can be used to test chips and associated hardware based on the ARMv8-A 64-bit architecture for servers with the aim of standardizing that market.
|
||||
|
||||
Based on the company's Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL), the Linux distribution is part of a [partner program][1] that Red Hat launched Wednesday for potential [ARM hardware vendors][2].
|
||||
|
||||
"We don't call it RHEL, but it is a functional, unsupported, operating system for partners to use in their development activities," said Mark Coggin, Red Hat senior director of platform product marketing.
|
||||
|
||||
Red Hat designed the program to get the hardware manufacturers to settle on a standard implementation of the ARMv8-A specification. ARM does not manufacture its own processors, licensing its designs to chip manufacturers instead.
|
||||
|
||||
A standard implementation would mean that customers could purchase ARMv8-A servers from any manufacturer, knowing that their ARM 64-bit operating systems and software will work no matter who created the chip, Coggin said. Red Hat would like Linux ARM to avoid the fate of AT&T's Unix operating system, which fragmented into a number of different and incompatible versions.
|
||||
|
||||
"We see the importance of stepping in early and ensure that we don't end up with a fragmented approach, where if you wanted to run an AMD implementation of ARM, you'd need one version of Linux, and if you wanted to run a Broadcom implementation of ARM, you'd need another version," Coggin said.
|
||||
|
||||
Some of the work of standardizing ARM for servers has been done through an industry consortium started earlier this year, called the [Server Base System Architecture][3] (SBSA) specification, as well as through ongoing work from the Linaro Enterprise Group. Red Hat's unnamed ARM Linux distribution uses specifications from both groups.
|
||||
|
||||
Red Hat hopes to influence not only the companies that make the chips but also hardware vendors, original equipment manufacturers and original design manufacturers.
|
||||
|
||||
Thus far, manufacturers such as Advanced Micro Devices, American Megatrends, AppliedMicro, Broadcom, Cavium, Dell and Hewlett-Packard have all pledged support to Red Hat's standardization efforts.
|
||||
|
||||
"If ARM is to be a viable competitor in the server space, [hardware providers] have to comply to the common understanding of what is possible to run on this type of server. Customers and users demand that from manufacturers today in the x86 world," said Yan Fisher, Red Hat technical product marketing manager.
|
||||
|
||||
Through the program, Red Hat will learn more about what the manufacturers need from an enterprise Linux distribution for 64-bit ARM, Coggin said. The operating system may one day become the basis for an ARM version of RHEL.
|
||||
|
||||
"We're trying to understand the platform dependencies from a technology requirements perspective," Coggin said. "We don't know if or when this will ever become a product, but we are positioning ourselves in a way that at some point we could enter the market."
|
||||
|
||||
Red Hat's Fedora project has offered an ARM distribution for the past several years and this release, though based on the Fedora work, is configured more toward ARM server use.
|
||||
|
||||
Although ARM processors are used in most mobile devices, only recently [has there been a movement in the industry][4] to use them in data-center servers as well, where their low-power design could cut energy costs.
|
||||
|
||||
Only a handful of ARMv8-A processors and associated hardware are currently available, mostly as early previews for developers or packaged in proprietary systems.
|
||||
|
||||
AMD Opteron A1100-Series ARM processors, designed specifically for servers, were released Wednesday to developers. AMD also offers the ARM Cortex-A57 ARMv8 which was designed for system-on-a-chip architectures.
|
||||
|
||||
AppliedMicro offers production-ready ARM servers, under the X-Gene brand and Hewlett-Packard is prepping its Moonshot line of ARM servers. Motherboard manufacturer American Megatrends offers a BIOS chip to boot ARM processors.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.computerworld.com/s/article/9250061/Red_Hat_aims_to_standardize_Linux_for_64_bit_ARM_servers?taxonomyId=122
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Joab Jackson
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://connect.redhat.com/early-access-programs/red-hat-and-64-bit-arm-ecosystem
|
||||
[2]:https://engage.redhat.com/arm-s-201407291033
|
||||
[3]:http://infocenter.arm.com/help/index.jsp?topic=/com.arm.doc.den0029/index.html
|
||||
[4]:http://www.networkworld.com/article/2171235/servers/arm-servers-with-64-bit-calxeda-chips-to-ship-next-year.html
|
||||
@ -1,35 +0,0 @@
|
||||
乌龙茶 占坑
|
||||
Valve SteamOS: A Linux-based Gaming Operating System Announced
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The year of Linux on the desktop or living room is here. Today Valve software announced SteamOS, a free Linux-based gaming operating system designed for the TV, DIY enthusiast and the living room. From the announcement page:
|
||||
|
||||
> As we've been working on bringing Steam to the living room, we’ve come to the conclusion that the environment best suited to delivering value to customers is an operating system built around Steam itself. SteamOS combines the **rock-solid architecture of Linux with a gaming experience** built for the big screen. It will be available soon as a free stand-alone operating system for living room machines.
|
||||
|
||||
### More about SteamOS ###
|
||||
|
||||
- Hundreds of great games are already running natively on SteamOS. More AAA titles coming natively to SteamOS in 2014.
|
||||
- You can stream games from your desktop and stream those games over your home network to your TV via a SteamOS machine.
|
||||
- You can play all your Windows and Mac games on your SteamOS machine, too.
|
||||
- Stream music and video with the SteamOS media services.
|
||||
- In SteamOS, Valve have achieved significant performance increases in graphics processing, and Valve working on audio performance and reductions in input latency at the operating system level. Game developers are already taking advantage of these gains as they target SteamOS for their new releases.
|
||||
- You can modify or replace any part of the software or hardware you want. No more lock-ins.
|
||||
- Valve are working on improving Linux kernel, drivers and debugging tools. This is a great news for both developers and users.
|
||||
- Standard parental controls for games and streaming services.
|
||||
|
||||
### Input lag over a network... a horrible experience? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Streaming games over the internet adds the the network latency. However, SteamOS machine and TV will be in a local network. This will keep delay to minimum including encoding and decoding video between the two systems. This is just a guess and I will wait for the reviews.
|
||||
|
||||
I think Valve is following Android model. User will get consistent environment for all your devices or you can build your own device. SteamOS will be available soon as a free download for users and as a freely licensable operating system for manufacturers. For more information see [SteamOS][1] announcement page.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.cyberciti.biz/linux-games/valve-announces-linux-based-steamos/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://store.steampowered.com/livingroom/SteamOS/
|
||||
@ -1,4 +1,3 @@
|
||||
Translating by Alisa-annie
|
||||
The People Who Support Linux: Hacking on Linux Since Age 16
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,52 +0,0 @@
|
||||
[translated by blueabysm]
|
||||
|
||||
Linux System Administration Skills are Changing
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
When was the last time you compiled a kernel? For many of the latest generation of Linux admins, the answer is really simple: never. I am one of those, provided we don't count a few times I tried it just for fun, then couldn't see why I would need a custom kernel and went back to my out-of-the-box kernel.
|
||||
|
||||
For many of the longer-time Linux admins and engineers this may seem laughable, but it is a reality: As Linux adoption grows in the enterprise, a new generation of Linux admins is created that has extremely good technical skills, but lacks these 'simple' low level skills seen by many as fundamental to being a good Linux admin. We can build a high performance, highly available web infrastructure that uses the latest of the latest techniques, but don't ask us to fix a non-booting Linux machine: our advice will be to ditch it and set up a new vm.
|
||||
|
||||
Over the past decade or so, we have seen some interesting trends. Linux became a commodity in the enterprise, and as that happened the various distributions became powerful yet flexible enough to remove the need for the average admin to ever have to do low level things like compiling a kernel.
|
||||
|
||||
Next, we welcomed virtual machine technology as a commodity, which added another layer of abstraction. Users of clouds like amazon or VPS providers will possibly never have to deal with deploying Linux on bare metal. As hybrid and private clouds are becoming common as well, many enterprise admins will also not have to deal with this kind of thing anymore, they will just log into a web interface and spin up 5 more apache vm's.
|
||||
|
||||
The newest two trends add even more abstraction: configuration management and the seemingly brand new (yet not new at all) containerization with tools like docker. Whenever a client asks us at [OlinData][1] to configure a Linux machine, our first action will be to set up [Puppet][2]. With our trusted library of well-functioning Puppet modules, that is very easy and will cost me less time then doing this manually.
|
||||
|
||||
For example with Puppet, I can install Apache on a new machine as simple as this:
|
||||
|
||||
node 'web01.olindata.com' {
|
||||
include apache
|
||||
apache::vhost{ 'www.olindata.com':
|
||||
docroot => '/var/www/olindata'
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Depending on the environment, I don't even have to log into the machine anymore. Deploying this code through Continuous Deployment tools like [Jenkins][3] will allow me to deploy my infrastructure code automatically as it passes the tests I set up.
|
||||
|
||||
### SysAdmin skills move up the stack ###
|
||||
|
||||
Even as we move toward higher levels of abstraction, ongoing Linux training is still highly valuable and desirable for admins today and will be well into the future. Knowing the fundamentals is key but as abstraction removes some of the old tasks, this requires sysadmins to move up further in the stack and enhance their skills in the higher level tools and practices. It is critical for a sysadmin to become familiar with the tools that enable these higher levels of abstraction. It pushes them to become more skilled in things like coding so that they can do more with these "new" tools.
|
||||
|
||||
Will the need for low(er) level linux skills ever go away completely? Of course not. We still have many other uses for Linux then just the commodity server deployments. Also, people will still benefit hugely from knowing how to do lower level operations in their everyday work. On top of that, with demonstrable Linux skills on your resume, I (and many other employers with me) will always prefer you over candidates that don't have them. You never know when you need those low-level skills!
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Walter Heck is CEO and Founder of OlinData, an authorized Linux Foundation training partner. Here's a list of [scheduled official Linux Foundation courses by OlinData][4].
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linux.com/news/enterprise/systems-management/780956-linux-system-administration-skills-are-changing
|
||||
|
||||
原文作者:[Walter Heck][a]
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.linux.com/community/forums/person/59207
|
||||
[1]:http://olindata.com/
|
||||
[2]:http://puppetlabs.com/
|
||||
[3]:http://jenkins.org/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.olindata.com/training/upcoming?technology=295
|
||||
@ -1,38 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Lime Text: An Open Source Alternative Of Sublime Text
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[Sublime Text][1] is one of the best (if not best) text editor for programmers. Packed with numerous feature and great looking interface, Sublime is available for all three major desktop OS i.e. Windows, Mac and Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
But it is not that Sublime Text is perfect. There are bugs, crashes and almost no support. If you have been following Sublime Text development, you know that the beta version of Sublime Text has been out for more than a year now and there is no clear communication to users about its release date. And above all, Sublime Text is neither free nor [Open Source][2].
|
||||
|
||||
All these issues also frustrated [Fredrik Ehnbom][3] and hence he started an Open Source project, [Lime Text][4], on [Github][5] to make a new text editor which looks and works exactly the same way as Sublime Text. On the question of why he decided to “clone” an existing text editor, Frederic mentions:
|
||||
|
||||
> As none of the other text editors I’ve tried come close to the love I had for Sublime Text, I decided I had to create my own.
|
||||
|
||||
Lime Text is built in Go for backend while the frontend is in ermbox, Qt (QML) and HTML/JavaScript. The development is in progress with clear [goals][6] in sight. You can contribute to the project on its [Github page][7].
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
If you want to try the beta version, you can build Lime Text by following the instructions on the [wiki][8]. Meanwhile, if you are looking for other powerful text editors, give [SciTE][9] a go.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/lime-text-open-source-alternative/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[bhishek][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://itsfoss.com/author/Abhishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.sublimetext.com/
|
||||
[2]:http://itsfoss.com/category/open-source-software/
|
||||
[3]:https://github.com/quarnster
|
||||
[4]:http://limetext.org/
|
||||
[5]:https://github.com/
|
||||
[6]:https://github.com/limetext/lime/wiki/Goals
|
||||
[7]:https://github.com/limetext/lime/issues
|
||||
[8]:https://github.com/limetext/lime/wiki/Building
|
||||
[9]:http://itsfoss.com/scite-the-notepad-for-linux/
|
||||
@ -1,126 +0,0 @@
|
||||
10 More Tweaks To Make Ubuntu Feel Like Home
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Not too long ago [we gave you 12 tips on how to tweak your Ubuntu installation][1]. However, it’s been a little while since then, and we’ve come up with another 10 things you can do to make Ubuntu feel even more like home.
|
||||
|
||||
These 10 tips are quick and simple to do, so let’s get started!
|
||||
|
||||
### Install TLP ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[We covered TLP a while back][2], which is a piece of software that can optimize your power settings so that you can enjoy a longer battery life. We talked about TLP in depth before, and it’s a good item to mention in this list as well. To install it, run the following command in a terminal:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository -y ppa:linrunner/tlp && sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install -y tlp tlp-rdw tp-smapi-dkms acpi-call-tools && sudo tlp start
|
||||
|
||||
This will add the necessary repository, update the package lists so that it includes the new packages provided by the new repository, installs TLP, and starts the service.
|
||||
|
||||
### System Load Indicator ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Adding a system load indicator to your Ubuntu desktop can give you an idea of how much of your system’s resources are being used at a quick glance. You don’t have to add this if you’d rather not have technical graphs on your desktop, but it’s a good addition for those who are interested in something like this. You can install it by running the terminal command:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install indicator-multiload
|
||||
|
||||
Then, find it in the Dash and launch it.
|
||||
|
||||
### Weather Indicator ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu used to offer a built-in weather indicator, but since it switched to Gnome 3 as the backbone, this hasn’t been included by default. Instead, you’ll need to install a separate indicator. You can install it by running the command:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository -y ppa:atareao/atareao && sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install -y my-weather-indicator
|
||||
|
||||
This will add another repository, update the package lists, and install the indicator. Then, find it in the Dash and launch it.
|
||||
|
||||
### Install Dropbox or Other Cloud Storage Solution ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
One of the things that I have to install on all my Linux systems is Dropbox. Without it, it just really doesn’t feel like home, mainly because all of my most-used files are stored on Dropbox. Installing Dropbox is pretty straightforward, but it takes a bit more than just a simple command. Before you even start, you need to run this command to be able to see the Dropbox icon in the icon tray:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install libappindicator1
|
||||
|
||||
Then you need to head to Dropbox’s download page and install the .deb file that you download. You should now have Dropbox going.
|
||||
|
||||
If you’re a bit tired of Dropbox, you can also try using Copy [or even OneDrive][3]. Both services offer more storage for free, which is a big reason to consider using them. I recommend Copy more than OneDrive because Copy can work on all Linux distros.
|
||||
|
||||
### Install Pidgin and Skype ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
It’s great to stay connected with friends, and if you use instant messaging, you’re in luck. Pidgin and Skype are both pretty good on Linux, and they are able to connect to all the major networks. Installing Pidgin is as easy as running the command
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install pidgin
|
||||
|
||||
Installing Skype is also easy — you just need to head to Skype’s download page and get the .deb file under Ubuntu 12.04 multiarch.
|
||||
|
||||
### Remove Keyboard Indicator ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Having the keyboard indicator appear on the desktop can be annoying for some. For English speakers, it just shows “EN”, and it’s potentially annoying because a lot of people don’t have a need to change keyboard layouts or be reminded that they are speaking English. To remove the indicator, choose System Settings, then Text Entry, and then uncheck “Show current input source in the menu bar”.
|
||||
|
||||
### Bring Back Classic Menu ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Before Ubuntu made the switch to Unity, it had used Gnome 2 as the default desktop environment. This included a simple menu for accessing your installed applications, which had categories such as Games, Office, Internet, and more. You can get this “classic menu” back with another simple package. To install, run the command:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository -y ppa:diesch/testing && sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install -y classicmenu-indicator
|
||||
|
||||
### Install Flash and Java ###
|
||||
|
||||
While in the previous tips article I mentioned installing codecs and Silverlight, I should have probably included Flash and Java as they are also major plugins that people need, although sometimes they can be forgotten about. To install both of them, run the command:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository -y ppa:webupd8team/java && sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install oracle-java7-installer flashplugin-installer
|
||||
|
||||
The additional repository is needed for installing Java because Ubuntu no longer includes the proprietary version (which most people recommend for best functionality), but rather just the open source OpenJDK implementation.
|
||||
|
||||
### Install VLC ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The default media player, Totem, is pretty good but it relies on separately-installed codecs to work properly. I’d personally recommend you install the VLC media player, as it includes all codecs and supports virtually every media format under the sun. To install it, just run the command
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install vlc
|
||||
|
||||
### Install PuTTY (Or Not) ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Lastly, if you’ve used PuTTY for all of your SSH needs, you have two options: install PuTTY for Linux, or just use the terminal directly. Installing PuTTY can be done with the command
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install putty
|
||||
|
||||
if you want to install it using the terminal. However, there’s no direct need to install it, because you can connect to any remote host with the command
|
||||
|
||||
ssh username@this.domain.here
|
||||
|
||||
where you replace “username” with the username you’d like to connect as, and replace “this.domain.here” with the host’s actual domain name or IP address — both work.
|
||||
|
||||
### What Are Your Recommended Tweaks? ###
|
||||
|
||||
With these additional 10 tweaks, you should feel right at home in your Ubuntu installation, which can easily make or break your Linux experience. There are so many different ways to customize your experience to make it suit your needs; you just have to look around for yourself to see what you want.
|
||||
|
||||
**What other tweaks and recommendations can you share with readers?** Let us know in the comments!
|
||||
|
||||
*Image Credits: Home doormat Via Shutterstock*
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.makeuseof.com/tag/10-tweaks-make-ubuntu-feel-like-home/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Danny Stieben][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.makeuseof.com/tag/author/danny/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.makeuseof.com/tag/11-tweaks-perform-ubuntu-installation/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.makeuseof.com/tag/easily-increase-battery-life-tlp-linux/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.makeuseof.com/tag/synchronize-files-ubuntu-onedrive/
|
||||
@ -1,67 +0,0 @@
|
||||
[sailing]
|
||||
How to Achieve Better Security With Proper Management of Open Source
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
Bill Ledingham is the Chief Technology Officer (CTO) and Executive Vice President of Engineering at Black Duck Software.
|
||||
|
||||
Companies increasingly understand that the key to developing innovative software faster and better than the competition is through the use of open source software (OSS). It’s nearly impossible to use only commercially sourced code and get your software to market with the speed and cost constraints required by today’s product life cycles. Without the ability to choose and integrate best-of-breed OSS, some of the greatest product ideas might never see the light of day.
|
||||
|
||||
With the use of open source, however, comes a different set of challenges. While your teams can gain speed and agility, it’s often more difficult to ascertain the code’s true origin and assure that it is secure.
|
||||
|
||||
As the OpenSSL Heartbleed vulnerability proved, not knowing what code is in your application or finished product can potentially create critical security threats that require time-consuming remediation efforts. Conversely, having an accurate inventory of what OSS components and versions are used and where can prove invaluable for quickly responding to and remediating vulnerabilities.
|
||||
|
||||
### It’s What’s Inside That Counts ###
|
||||
|
||||
The Heartbleed bug reminded developers and companies just how important security is. While there has been widespread debate over whether proprietary or open source software is more secure, the issue is largely moot. The reality is that code defects exist in most pieces of software, regardless of origin, and some affect security.
|
||||
|
||||
Security challenges can become even more complex when open source is integrated with internal, proprietary code. In addition to the obvious risk of not properly managing license compliance, tracking code origins and use throughout an organization can become very difficult, very quickly.
|
||||
|
||||
To have a truly accurate understanding of your potential vulnerabilities, you need to understand three things:
|
||||
|
||||
1. What code is in your current products and applications?
|
||||
1. What code is being used in the front end of the development process and where are developers acquiring these components?
|
||||
1. What components are being used at the back end of the process and where does code need to be validated before it is deployed?
|
||||
|
||||
### Assessing the Situation ###
|
||||
|
||||
All companies should check their code against common vulnerability databases, such as the United States National Institute of Standards and Technology’s [National Vulnerability Database][1] (NVD). Resources like the NVD track security vulnerabilities and provide severity rankings to help companies keep their code secure and up to date.
|
||||
|
||||
If you’ve never reviewed your code against a vulnerability database, it may seem like a daunting task. Fortunately, there are [tools][2] that leverage these databases to regularly and automatically identify all open source security vulnerabilities, alerting and tracking where affected components are in use and in need of remediation.
|
||||
|
||||
Continuously monitoring your codebase helps guarantee that unknown code is identified, code origin is understood, license information is up to date and future security vulnerabilities are quickly flagged for resolution. If your company has an accurate code inventory in place, you can easily find vulnerable code and remediate it to ensure your business – and your customers – remain secure.
|
||||
|
||||
### Preventing Future Problems ###
|
||||
|
||||
Most developers are attracted to OSS because it’s easy to access and free to acquire, usually allowing them to forgo a formal procurement process. Yet, while many development organizations have policies or guidelines for open source use, they are not always enforced and often not properly tracked. It’s important to track what code is coming into your organization, whether it’s been approved for use and where it’s used throughout your organization.
|
||||
|
||||
Once you know what you have, you need to establish governance. By implementing a management framework throughout the development process, you can ensure accurate descriptions of the code are captured and eliminate questions as to what code is where and whether it’s up to date. Manually managing this process is nearly impossible, which is why best-in-class companies actively manage their use of open source through automated code management and audit solutions.
|
||||
|
||||
Although every company and development team is different, the following processes have been proven to help organizations of all sizes manage and secure their use of OSS:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Automate Approvals and Cataloging** – Capture and track all relevant attributes of OSS components, assess license compliance and review possible security vulnerabilities through automated scanning, approval and inventory processes.
|
||||
-
|
||||
- **Maintain Updated Code Versions** – Assess code quality and make sure your product is built using the most updated versions of the code.
|
||||
-
|
||||
- **Verify Code** – Evaluate all OSS in use; audit code for security, license, or export risk and remediate any issues.
|
||||
-
|
||||
- **Ensure Compliance** – Create and implement an open source policy, establish an automated compliance process to ensure open source policies, regulations, legal obligations, etc., are followed across the organization.
|
||||
|
||||
### Active Management is Key ###
|
||||
|
||||
As the use of software across industries proliferates, open source will continue to play a crucial role in developing the newest innovations. To prevent security vulnerabilities in this increasingly complex environment, companies must actively manage the flow of open source throughout their organization and establish processes to regularly check their code against vulnerability databases for fast and easy remediation.
|
||||
|
||||
*Bill Ledingham is the Chief Technology Officer (CTO) and Executive Vice President of Engineering at Black Duck Software. Previously, Bill was CTO of Verdasys, a leader in information and cyber security, where he worked closely with leading Global 2000 companies and government organizations to safeguard their most sensitive information. Bill has been on the founding team of four companies, is active in the Boston start-up community, and has been a partner/investor with CommonAngels for the past 6 years.*
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linux.com/news/software/applications/782953-how-to-achieve-better-security-by-proper-management-of-open-source
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Bill Ledingham][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.linux.com/community/forums/person/59656
|
||||
[1]:http://nvd.nist.gov/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.blackducksoftware.com/oss-logistics/secure
|
||||
@ -1,4 +1,3 @@
|
||||
[translating by KayGuoWhu]
|
||||
Linux FAQs with Answers--How to check the last time system was rebooted on Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **Question**: Is there a way to quickly check how long a Linux system has been running? That is, how can I find out the last time a Linux system was rebooted?
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,78 @@
|
||||
How to manage a WiFi connection from the command line
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Whenever you install a new Linux distribution on a computer, it is in general recommended that you connect to the internet via a wired connection. There are two main reasons for this: one, your wireless adapter may not have the right driver loaded; second, if you are installing from the command line, managing WiFi is scary. I always tried to avoid dealing with WiFi over the command line. But in the Linux world, there is no place for fear. If you do not know how to do something, that is the only reason you need to go ahead and learn it. So I forced myself to learn how to manage a WiFi connection from the command line on Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
There are of course multiple ways to connect to a WiFi from the command line. But for the sake of this post, and as an advice, I will try to use the most basic way: the one that uses programs and utilities included in the "default packages" of any distribution. Or at least I will try. An obvious reason for this choice is that the process can potentially be reproduced on any Linux computer. The downside is its relative complexity.
|
||||
|
||||
First, I will assume that you have the correct drivers loaded for your wireless LAN card. There is no way to start anything without that. And if you don't, you should take a look at the Wiki and documentation for your distribution.
|
||||
|
||||
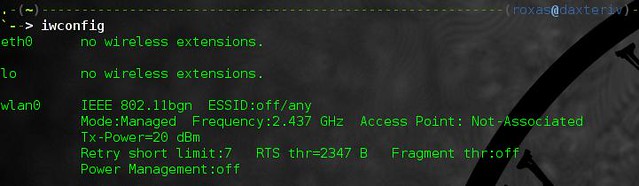
Then you can check which interface supports wireless connections with the command
|
||||
|
||||
$ iwconfig
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
In general, the wireless interface is called wlan0. There are of course exceptions, but for the rest of this tutorial, I will call it that way.
|
||||
|
||||
Just in case, you should make sure that the interface is up with:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo ip link set wlan0 up
|
||||
|
||||
Once you know that your interface is operational, you should scan for nearby wireless networks with:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo iw dev wlan0 scan | less
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
From the output, you can extract the name of the network (its SSID), its signal power, and which type of security it uses (e.g., WEP, WPA/WPA2). From there, the road splits into two: the nice and easy, and the slightly more complicated case.
|
||||
|
||||
If the network you want to connect to is not encrypted, you can connect straight to it with:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo iw dev wlan0 connect [network SSID]
|
||||
|
||||
If the network uses WEP encryption, it is also quite easy:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo iw dev wlan0 connect [network SSID] key 0:[WEP key]
|
||||
|
||||
But everything gets worse if the network uses WPA or WPA2 protocols. In this case, you have to use the utility called wpa_supplicant, which is not always included by default. You then have to modify the file at /etc/wpa_supplicant/wpa_supplicant.conf to add the lines:
|
||||
|
||||
network={
|
||||
ssid="[network ssid]"
|
||||
psk="[the passphrase]"
|
||||
priority=1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
I recommend that you append it at the end of the file, and make sure that the other configurations are commented out. Be careful that both the ssid and the passphrase are case sensitive. You can also technically put the name of the access point as the ssid, and wpa_supplicant will replace it with the proper ssid.
|
||||
|
||||
Once the configuration file is completed, launch this command in the background:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo wpa_supplicant -i wlan0 -c /etc/wpa_supplicant/wpa_supplicant.conf
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, whether you connected to an open or a secure network, you have to get an IP address. Simply use:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo dhcpcd wlan0
|
||||
|
||||
If everything goes well, you should get a brand new local IP via DHCP, and the process will fork in the background. If you want to be sure that you are connected, you can always check again with:
|
||||
|
||||
$ iwconfig
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
To conclude, I think that getting over the first step is completely worth it. You never know when your GUI will be down, or when you cannot access a wired connection, so getting ready now seems very important. Also, as mentioned before, there are a lot of ways (e.g., NetworkManager, [wicd][1], [netcfg][2], [wifi][3]) to manage a wireless connection. If I try to stick to the most basic way, I know that in some cases, the utilities that I used may not even be available to you, and that you would have to download them prior to that. On the other side of the balance, there are some more advanced programs, which are definitely not included in the "default packages," which will greatly simplify the whole process. But as a general advice, it is good to stick to the basics at first.
|
||||
|
||||
What other ways would you recommend to connect via WiFi from the command line? Please let us know in the comments.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/08/manage-wifi-connection-command-line.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Adrien Brochard][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/adrien
|
||||
[1]:http://wicd.sourceforge.net/
|
||||
[2]:https://www.archlinux.org/netcfg/
|
||||
[3]:https://github.com/rockymeza/wifi
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,38 @@
|
||||
Lime Text: 一款可以替代 Sublime Text 的开源项目
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[Sublime Text][1] 可能是为程序员准备的一个最好的(尽管不是最最好的)文本编辑器。Sublime 囊括了众多特色并且拥有很棒的界面外观,能够运行在所有的三大主流桌面操作系统,亦即 Windows, Mac 还有 Linux 之上。
|
||||
|
||||
但这并不表示 Sublime Text 是完美的。时常会出现 bug,崩溃但却几乎没有任何技术支持。如果你注意到 Sublime Text 的开发过程,你就会发现此时 Sublime Text beta 版已经公开超过一年了,却没有告知用户任何关于它的发行日期的确切信息。最重要的是,Sublime Text 既不免费也不[开源][2]。
|
||||
|
||||
这一系列问题也使 [Fredrik Ehnbom][3] 感到沮丧,因此他在 [Github][5] 上发起了一个开源项目 [Lime Text][4],希望能开发出一款新的文本编辑器,其外观和工作方式完全与 Sublime Text 一致。在关于为什么他决定去“克隆”一款现有的文本编辑器这个问题上,Frederic 说道:
|
||||
|
||||
> 因为没有一款我试过的其他文本编辑器能达到我对 Sublime Text 的喜爱程度,我决定了我不得不开发出我自己的文本编辑器。
|
||||
|
||||
Lime Text 后台用 Go 写成,前端则使用了 ermbox,Qt (QML) 及 HTML/JavaScript。开发过程正在进行中,同时完全公布确切[目标][6]。你可以在它的 [Github 页面][7]为项目做贡献。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
如果你想要尝试 beta 版本,你可以通过 [wiki][8] 的介绍搭建 Lime Text。同时,如果你想找寻其他强大的文本编辑器的话,试一试 [SciTE][9] 吧。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/lime-text-open-source-alternative/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[bhishek][a]
|
||||
译者:[SteveArcher](https://github.com/SteveArcher)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://itsfoss.com/author/Abhishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.sublimetext.com/
|
||||
[2]:http://itsfoss.com/category/open-source-software/
|
||||
[3]:https://github.com/quarnster
|
||||
[4]:http://limetext.org/
|
||||
[5]:https://github.com/
|
||||
[6]:https://github.com/limetext/lime/wiki/Goals
|
||||
[7]:https://github.com/limetext/lime/issues
|
||||
[8]:https://github.com/limetext/lime/wiki/Building
|
||||
[9]:http://itsfoss.com/scite-the-notepad-for-linux/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,126 @@
|
||||
10个调整让Ubuntu找到家的感觉
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
不久以前我提供给大家[12个调整Ubuntu的小建议][1]。 然而,从那以后多了一段时间了, 我们又提出了另外10个建议,能够使你的Ubuntu找到家的感觉。
|
||||
|
||||
这10个建议执行起来十分简单方便,那就让我们开始吧!
|
||||
|
||||
### 安装 TLP ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[We covered TLP a while back][2], 这是一款优化电源设置的软件,为了让你能享受到一个更长的电池寿命。之前我们深入的探讨过TLP, 并且我们也在列表中提到这真是一个好东西。要安装它,在终端运行以下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository -y ppa:linrunner/tlp && sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install -y tlp tlp-rdw tp-smapi-dkms acpi-call-tools && sudo tlp start
|
||||
|
||||
上面的命令将添加必要的仓库,更新包的列表以便它能包含被新仓库提供的包,安装TLP并且开启这个服务。
|
||||
|
||||
### 系统负载指示器 ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
给你的Ubuntu桌面添加一个系统负载指示器能让你了解到你的系统资源被占用了多少。 如果你宁愿不在桌面上添加这个技术图表,那么可以不要添加它, 但是对于那些对这个感兴趣的人来说,这真是一个好的扩展。 你可以运行这个命令去安装它:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install indicator-multiload
|
||||
|
||||
然后在Dash里面找到它并且打开。
|
||||
|
||||
### 天气指示器 ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu过去提供内置的天气指示器, 但是自从它切换到Gnome 3以后,就不在默认提供了。代替地,你需要安装一个独立的指示器。 你可以通过以下命令安装它:
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository -y ppa:atareao/atareao && sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install -y my-weather-indicator
|
||||
|
||||
这将添加另外一个仓库,更新包的列表,并且安装这个指示器。然后在Dash里面找到并开启它。
|
||||
|
||||
### 安装 Dropbox 或其他云存储解决方案 ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
我在我所有的Linux系统里面都安装过的一个东西就是Dropbox。没有它,真的就找不到一个家的感觉,主要是因为我所有经常使用的文件都储存在Dropbox中。安装Dropbox非常直截了当,但是要花点时间执行一个简单的命令。 在开始之前,你需要运行这个命令为了你能在系统托盘里看到Dropbox的图标:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install libappindicator1
|
||||
|
||||
然后你需要去Dropbox的下载页面,接着安装你已下载的.deb文件。现在你的Dropbox应该已经运行了。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你有点讨厌Dropbox, 你也可以尝试使用Copy [或者OneDrive][3]。两者提供更多免费存储空间,这是考虑使用他们的很大一个原因。比起OneDrive我更推荐使用Copy因为Copy能工作在所有的Linux发行版上。
|
||||
|
||||
### 安装Pidgin和Skype ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
和朋友们保持联系特别好,并且如果你使用即时通讯,那么你很幸运。 Pidgin和Skype在Linux都十分出色,它们都能连接所有主要网络。安装Pidgin就像运行这个命令一样简单:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install pidgin
|
||||
|
||||
安装Skype也很简单 — 你仅仅需要去Skype的下载页面并且下载你Ubuntu12.04对应架构的.deb文件就可以了。
|
||||
|
||||
###移除键盘指示器 ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在桌面上显示键盘指示器可能让一些人很苦恼。对于讲英语的人来说,它仅仅显示一个“EN”,这可能是恼人的,因为很多人不需要改变键盘布局或者被提醒他们正则使用英语。要移除这个指示器,选择系统设置,然后文本输入,接着去掉“在菜单栏显示当前输入源”的勾。
|
||||
>[译注]:国人可能并不适合这个建议。
|
||||
|
||||
### 回归传统菜单###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在Ubuntu切换到Unity之前,它使用Gnome 2 作为默认的桌面环境。 这包含一个简单的菜单去访问已安装的应用,菜单包含的很多分类,比如: 游戏,办公, 互联网,等等。 你可以用另外一个简单的包找回这个“传统菜单” 。要安装它,运行这个命令:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository -y ppa:diesch/testing && sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install -y classicmenu-indicator
|
||||
|
||||
### 安装Flash和Java ###
|
||||
|
||||
在之前的文章中我提到了安装解码器和Silverlight,我应该也提到了Flash和Java是他们所需要的主要插件,虽然他们有时可能忘了它们。要安装它们只需运行这个命令:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository -y ppa:webupd8team/java && sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install oracle-java7-installer flashplugin-installer
|
||||
|
||||
安装Java需要新增仓库,因为Ubuntu不再包含它的专利版本(大多数人为了最好的性能推荐使用这个版本),而是使用开源的OpenJDK。
|
||||
|
||||
### 安装VLC ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
默认的媒体播放器, Totem,十分优秀但是它依赖很多独立安装的解码器才能很好的工作。我个人推荐你安装VLC媒体播放器, 因为它包含所有解码器并且实际上它支持世界上每一种媒体格式。要安装它,仅仅需要运行如下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install vlc
|
||||
|
||||
### 安装PuTTY (或者不) ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
最近,如果你出于SSH的需要而使用PuTTY,你有两个选择:为Linux安装PuTTY,或者直接使用终端。如果你想使用终端安装PuTTY,需要用到这个命令:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install putty
|
||||
|
||||
然而,并不需要直接安装它,因为你可以使用这个命令来连接任何远程主机。
|
||||
|
||||
ssh username@this.domain.here
|
||||
|
||||
用你想要连接的用户名来替换掉“username”,然后用主机的直接域名或者IP地址替换掉“this.domain.here” 都可以。
|
||||
|
||||
### 你推荐如何调整? ###
|
||||
|
||||
补充了这10个调整,你应该感觉你的Ubuntu真的找到了家的感觉,这很容易重建或击溃你的Linux体验。有许多不同的方式去定制你自己的体验去让它更适合你的需要;你只需要环顾自己并且找到你想要的东西
|
||||
|
||||
**你有什么调整和建议想和读者分享?**在评论中让我们知道吧!
|
||||
|
||||
*图片致谢: Home doormat Via Shutterstock*
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.makeuseof.com/tag/10-tweaks-make-ubuntu-feel-like-home/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Danny Stieben][a]
|
||||
译者:[guodongxiaren](https://github.com/guodongxiaren)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.makeuseof.com/tag/author/danny/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.makeuseof.com/tag/11-tweaks-perform-ubuntu-installation/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.makeuseof.com/tag/easily-increase-battery-life-tlp-linux/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.makeuseof.com/tag/synchronize-files-ubuntu-onedrive/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,67 @@
|
||||
恰当地管理开源,让软件更加安全
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Bill Ledingham 是 Black Duck Software 公司的首席技术官(CTO)兼工程执行副总裁。
|
||||
|
||||
越来越多的公司意识到,要想比对手率先开发出高质量具有创造性的软件,关键在于积极使用开源项目。软件版本更迭要求市场推广速度足够快,成本足够低,而仅仅使用商业源代码已经无法满足这些需求了。如果不能选择最合适的开源软件集成到自己的项目里,一些令人称道的点子怕是永无出头之日了。
|
||||
|
||||
然而,使用开源软件也要面对新的挑战。一方面,你的团队从开源软件中汲取力量变得更快更灵活,另一方面,开源代码在传播过程中是否经历了不可控修改、安全性该如何保障的问题也日益凸显了出来。
|
||||
|
||||
OpenSSL Heartbleed 漏洞已经证实。如果你不了解你的应用程序或者已发布的产品中到底运行着什么代码,那你就可能面临需要大量时间才能解决的潜在安全威胁。相反,如果对项目里什么地方使用了什么版本的开源组件都了如指掌,一旦遇到漏洞,响应速度和解决速度都会是千金不换的。
|
||||
|
||||
### 安全性藏在代码内部 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Heartbleed bug 让开发人员和企业知道了软件安全性有多重要。专利软件和开源软件哪个更安全?这场广泛受到关注的讨论并没有一个简单的结论。现实情况是,不论是专利软件还是开源软件,它们绝大部分都有缺陷,其中一些缺陷还威胁到软件的安全性。
|
||||
|
||||
如果开源软件被内部代码、专利代码引用了,那开发人员将不得不面对更复杂的安全性挑战。要是管理授权许可的手段再不恰当,那想追溯一段代码的来源和引用就得把相关人员全都牵连进来,难度必然急剧增加。
|
||||
|
||||
要想切实了解你软件的潜在漏洞,首先你得理解以下三件事儿:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 你的产品和应用程序里现在跑着什么代码?
|
||||
2. 那些开发前期使用的代码,开发人员是从哪儿弄来的?
|
||||
3. 开发后期使用了哪些组件,这些组件有哪些地方要在部署之前充分测试?
|
||||
|
||||
### 现状怎么样 ###
|
||||
|
||||
所有企业都应该对比常见漏洞数据库——比如美国国家标准与技术学会的[国家漏洞数据库][1](NVD)——来检查他们的代码。NVD 等组织追踪并收集了各种安全漏洞的信息以及排名,这些数据可以协助企业确保代码及时更新,规避安全风险。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你从没对照漏洞数据库检查过你的代码,那你可有的忙了。好在我们有个可以利用这些数据库定期自动识别开源安全漏洞的[工具][2],这个工具还可以警示和追踪项目中使用的受影响的开源组件并提供必要的解决方案。
|
||||
|
||||
持续监控你的代码库能保证及时发现未知代码、了解代码来源、授权信息不会过时、安全漏洞一旦出现就能第一时间掌握并寻求解决方案。如果你的公司有详细的代码清单,你就能轻而易举地找到漏洞所在并及时修复,确保你的业务和客户不会面临危险。
|
||||
|
||||
### 预防未来的问题 ###
|
||||
|
||||
相当多开发人员青睐开源软件是因为开源软件易于获得且免费,他们不用为此再走采购流程。目前来看,尽管很多开源组织都有自己的使用策略或使用指引,他们却并没有强制使用者遵守,也没有追查使用者是否遵守。知道你的组织将会使用哪些开源代码、这些代码是否有授权、你的组织中什么地方引用了它们是非常重要的。
|
||||
|
||||
你知道你用了什么代码之后,就该好好整理它们了。你可以实现一个贯穿整个开发流程的管理框架,这样你可以掌握每段代码的详细信息,不用再在诸如代码更新了没有、什么时候更新的以及在哪儿更新的这类问题上浪费时间。手工管理这些信息不大可能,所以一流公司都使用自动化代码管理和审查工具。
|
||||
|
||||
虽然每个公司、每个开发团队都面临各不相同的问题,但实践证明下面几条安全管理经验对使用开源软件的任何规模的组织都有意义:
|
||||
|
||||
- **自动认证并分类** - 捕捉并追踪开源组件的相关属性,评估授权许可,自动扫描可能出现的安全漏洞,自动认证并归档。
|
||||
-
|
||||
- **维护最新代码的版本** - 评估代码质量,确保你的产品使用的是最新版本的代码。
|
||||
-
|
||||
- **评估代码** - 评估所有在使用的开源代码;审查代码安全性、授权许可、列出风险并予以解决。
|
||||
-
|
||||
- **确保代码合法** - 创建并实现开源政策,建立自动化合规检查流程确保开源政策、法规、法律责任等符合开源组织的要求。
|
||||
|
||||
### 关键是,要让管理流程运作起来 ###
|
||||
|
||||
随着软件飞速渗入各行各业,开放源代码将在创新发展的道路上扮演越来越重要的角色。为了规避安全问题给日益复杂的环境带来的风险,企业必须运行起一套管理其组织中开源代码使用情况的流程,构筑一个定期对照漏洞数据库检查代码并快速消除风险的流程。
|
||||
|
||||
*作者 Bill Ledingham 是 Black Duck Software 公司的首席技术官(CTO)兼工程执行副总裁。在这之前,Bill 是 Verdasys 的首席技术官,领导信息和网络安全团队为全球顶尖的 2000 家公司和政府机构提供敏感信息的安全保障。 Bill 曾经与人合伙创办过四家公司,现在活跃于波士顿创业社区,作为 CommonAngels 的合作伙伴和投资人迄今已有 6 年历史。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linux.com/news/software/applications/782953-how-to-achieve-better-security-by-proper-management-of-open-source
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Bill Ledingham][a]
|
||||
译者:[sailing](https://github.com/sailing)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.linux.com/community/forums/person/59656
|
||||
[1]:http://nvd.nist.gov/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.blackducksoftware.com/oss-logistics/secure
|
||||
@ -1,111 +0,0 @@
|
||||
How to check RPM package dependencies on Fedora, CentOS or RHEL
|
||||
教你如何在Fedora,CentOS,RHEL中检查RPM包的依赖性
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
A typical RPM package on Red Hat-based systems requires all its dependent packages be installed to function properly.
|
||||
For end users, the complexity of such RPM dependency is hidden by package managers (e.g., yum or DNF) during package install/upgrade/removal process. However, if you are a sysadmin or a RPM maintainer, you need to be well-versed in RPM dependencies to maintain run-time environment for the system or roll out up-to-date RPM specs.
|
||||
我们都知道,在基于红帽的Linux系统中,一个RPM包,需要把先将它依赖的其他包安装好才能正常的工作。对于终端用户,RPM的安装、更新、删除中存在的依赖关系已经被工具透明化了(如 yum或 DNF等)。但如果你是系统管理员或者RPM包的管理员,你需要对RPM包中存在的依赖关系以及时更新、删除适当的包来保证系统的正常运行。
|
||||
In this tutorial, I am going to show **how to check RPM package dependencies**. Depending on whether a package is installed or not, there are several ways to identify its RPM dependencies.
|
||||
在本教程中,我将教大家**如何检查RPM包的依赖关系**无论这个包是否已经安装进操作系统中,我们都有一些办法来检查它们的依赖性。
|
||||
### Method One ###
|
||||
### 方法一 ###
|
||||
One way to find out RPM dependencies for a particular package is to use rpm command. The following command lists all dependent packages for a target package.
|
||||
使用RPM命令可以列出目标包所依赖的所有包,如下:
|
||||
$ rpm -qR <package-name>
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Note that this command will work only if the target package is already **installed**. If you want to check package dependencies for any **uninstalled** package, you first need to download the RPM package locally (no need to install it).
|
||||
注意,这种方法只适用于**已安装**的包。如果你需要检查一个**未安装**包的依赖关系,你需要把这个包先下载到本地来。
|
||||
To download a RPM package without installing it, use a command-line utility called `yumdownloader`. Install yumdownloader as follows.
|
||||
对于已在本地但未安装的包,可以使用叫做'yumdownloader'的工具,下面我们先安装yumdownloader:
|
||||
$ sudo yum install yum-utils
|
||||
|
||||
Now let's check RPM depenencies of a uninstalled package (e.g., tcpdump). First download the package in the current folder with yumdownloader:
|
||||
现在我们来检查一个未安装的RPM包的依赖关系(本列使用 tcpdump)。首先,我们使用yumdownloader把tcpdump的RPM包下载下来
|
||||
$ yumdownloader --destdir=. tcpdump
|
||||
|
||||
Then use rpm command with "-qpR" options to list dependencies of the downloaded package.
|
||||
然后再使用 "-qpR"参数显示该包的依赖关系。
|
||||
# rpm -qpR tcpdump-4.4.0-2.fc19.i686.rpm
|
||||
|
||||
### Method Two ###
|
||||
### 方法二 ###
|
||||
You can also get a list of dependencies for a RPM package using repoquery tool. repoquery works whether or not a target package is installed. This tool is included in yum-utils package.
|
||||
你可以使用repoquery工具来罗列包的依赖关系,这个工具包含在yum-utils中。
|
||||
$ sudo yum install yum-utils
|
||||
|
||||
To show all required packages for a particular package:
|
||||
显示目标包所依赖的包:
|
||||
$ repoquery --requires --resolve <package-name>
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
For repoquery to work, your computer needs network connectivity since repoquery pulls information from Yum repositories.
|
||||
为让repoquery正常的工作,需要保持网络的畅通,应为repoquery需要在Yum库中查找信息。
|
||||
### Method Three ###
|
||||
### 方法三 ###
|
||||
The third method to show RPM package dependencies is to use rpmreaper tool.
|
||||
Originally this tool is developed to clean up unnecessary packages and their dependencies on RPM-based systems.
|
||||
rpmreaper has an ncurses-based intuitive interface for browsing installed packages and their dependency trees.
|
||||
第三个方法是使用rpmreaper工具。这个工具本来是用作清理系统中无用以及它们所依赖的包,rpmreaper有很直观的界面来展示已安装的包和它们依赖关系的树形图。
|
||||
To install rpmrepater, use yum command. On CentOS, you need to [set up EPEL repo][1] first.
|
||||
安装rpmrepater,在CentOS中,你需要先[设置好EPEL库][1]
|
||||
$ sudo yum install rpmreaper
|
||||
|
||||
To browser RPM dependency trees, simply run:
|
||||
只需运行rpmreaper就可以看到RPM包的依赖关系:
|
||||
$ rpmreaper
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The rpmrepater interface will show you a list of all installed packages. You can navigate the list using up/down arrow keys.
|
||||
Press "r" on a highlighted package to show its dependencies.
|
||||
You can expand the whole dependency tree by recursively pressing "r" keys on individual dependent packages.
|
||||
The "L" flag indicates that a given package is a "leaf", meaning that no other package depends on this package.
|
||||
The "o" flag implies that a given package is in the middle of dependency chain.
|
||||
Pressing "b" on such a package will show you what other packages require the highlighted package.
|
||||
rpmrepater会向用户显示已安装包的列表,你可以使用上/下箭头来滚动屏幕。
|
||||
你可以在指定包上使用"r"键来显示其依赖关系,循环在指定包上按下"r"键可以展示出余下的信息。
|
||||
"L"标志的意思是说这个包是一片“孤叶”,意思说说没有任何包依赖它。
|
||||
"o"标志是说这个包是整个依赖链的中间部分。
|
||||
按下"b"键会显示其他依赖于该包的其他包。
|
||||
### Method Four ###
|
||||
### 方法四 ###
|
||||
Another way to show package dependencies on RPM-based systems
|
||||
is to use rpmdep which is a command-line tool for generating a full package dependency graph of
|
||||
any installed RPM package. The tool analyzes RPM dependencies, and produce partially ordered package lists from
|
||||
topological sorting. The output of this tool can be fed into dotty graph visualization tool
|
||||
to generate a dependency graph image.
|
||||
还有一个办法是使用rpmdep工具,rpmdep是一个命令行工具,可以显示已安装包的完整包依赖关系图。该工具会分析RPM包的依赖性,从完整的排完序
|
||||
的拓扑图中摘取部分包的信息,形成列表展示给用户。该工具的输出结果可以直接使用到Dotty(可视化展示工具)中去。
|
||||
To install rpmdep and dotty on Fedora:
|
||||
在Fedora中安装rpmdep和dotty:
|
||||
$ sudo yum install rpmorphan graphviz
|
||||
|
||||
To install the same tools on CentOS:
|
||||
在CentOs中安装:
|
||||
$ wget http://downloads.sourceforge.net/project/rpmorphan/rpmorphan/1.14/rpmorphan-1.14-1.noarch.rpm
|
||||
$ sudo rpm -ivh rpmorphan-1.14-1.noarch.rpm
|
||||
$ sudo yum install graphviz
|
||||
|
||||
To generate and plot a dependency graph of a particular installed package (e.g., gzip):
|
||||
生成包依赖的拓扑关系图:
|
||||
$ rpmdep.pl -dot gzip.dot gzip
|
||||
$ dot -Tpng -o output.png gzip.dot
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
So far in this tutorial, I demonstrate several ways to check what other packages a given RPM package relies on.
|
||||
If you want to know more about .deb package dependencies for Debian-based systems,
|
||||
you can refer to [this guide][2] instead.
|
||||
教程到这个地方,我们用到了几种办法来检查包的依赖关系。如果您想知道如何在居于Debian的系统中检查.deb的包依赖关系,请阅读另外一篇[文档][2]
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/07/check-rpm-package-dependencies-fedora-centos-rhel.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[nd0104](https://github.com/nd0104) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://xmodulo.com/2013/03/how-to-set-up-epel-repository-on-centos.html
|
||||
[2]:http://xmodulo.com/2013/07/how-to-check-package-dependencies-on-ubuntu-or-debian.html
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user