mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-01-13 22:30:37 +08:00
Merge branch 'master' of https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject
This commit is contained in:
commit
417e584276
@ -1,10 +1,10 @@
|
|||||||
Flow 'N Play视频播放器有着独具风格的界面[在Ubuntu上安装]
|
在Ubuntu上安装Flow 'N Play—界面独具风格的视频播放器
|
||||||
================================================================================
|
================================================================================
|
||||||
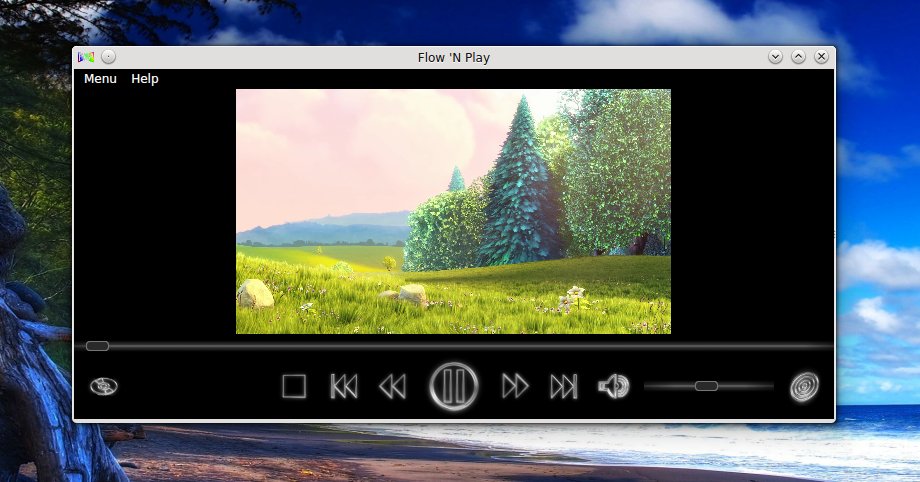
**Flow ‘N Play**是个用Qt编写的新视频播放器。它有着漂亮又简洁的界面,只提供基本播放功能。
|
**Flow ‘N Play**是个用Qt编写的新视频播放器。它有着漂亮又简洁的界面,只提供基本播放功能。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
[Flow ‘N Play][1]是个比较新的视频播放器,它有着漂亮的界面和简单的操作(今年三月份第一次发行)。其中一个功能就是能通过拖动鼠标滑动视频列表。播放器带有基本功能,一个搜索功能,支持彩色主题。
|
[Flow ‘N Play][1]是个比较新的视频播放器,它有着漂亮的界面和简单的操作(2014年3月份第一次发行)。其中一个功能就是能通过拖动鼠标滑动视频列表。播放器带有基本功能,一个搜索功能,支持彩色主题。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
打开一个新的视频——你还可以在同一个对话框下自定义一个封面:
|
打开一个新的视频——你还可以在同一个对话框下自定义一个封面:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
|||||||
|
Translating By H-mudcup
|
||||||
CD Audio Grabbers - Graphical Based
|
CD Audio Grabbers - Graphical Based
|
||||||
================================================================================
|
================================================================================
|
||||||
CD audio grabbers are designed to extract ("rip") the raw digital audio (in a format commonly called CDDA) from a compact disc to a file or other output. This type of software enables a user to encode the digital audio into a variety of formats, and download and upload disc info from freedb, an internet compact disc database.
|
CD audio grabbers are designed to extract ("rip") the raw digital audio (in a format commonly called CDDA) from a compact disc to a file or other output. This type of software enables a user to encode the digital audio into a variety of formats, and download and upload disc info from freedb, an internet compact disc database.
|
||||||
@ -125,4 +126,4 @@ via: http://www.linuxlinks.com/article/20150125043738417/AudioGrabbersGraphical.
|
|||||||
[1]:http://www.freac.org/
|
[1]:http://www.freac.org/
|
||||||
[2]:http://kde.maniatek.com/audex/
|
[2]:http://kde.maniatek.com/audex/
|
||||||
[3]:http://burtonini.com/blog/computers/sound-juicer
|
[3]:http://burtonini.com/blog/computers/sound-juicer
|
||||||
[4]:http://sourceforge.net/projects/ripperx/
|
[4]:http://sourceforge.net/projects/ripperx/
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@ -1,41 +0,0 @@
|
|||||||
Ubuntu 15.04 Finally Lets You Set Menus To ‘Always Show’
|
|
||||||
================================================================================
|
|
||||||
**If you hate the way that Unity’s global menus fade out of view after you mouse away, Ubuntu 15.04 has a little extra to win you around.**
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||

|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The latest build of Unity for Ubuntu 15.04, currently sitting in the ‘proposed’ channel, offers an option to **make app menus visible in Ubuntu**.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
No fading, no timeout, no missing menus.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The drawback for now is that it can currently only be enabled through a dconf switch and not a regular user-facing option.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
I’d hope (if not expect) that an option to set the feature is added to the Ubuntu System Settings > Appearance section as development continues.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Right now, if you’re on Ubuntu 15.04 and have the “Proposed” update channel enabled, you should find this switch waiting in **com > canonical > unity >** ‘always show menus’.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### Better Late Than Never? ###
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Developers plan to backport the option to Ubuntu 14.04 LTS in the next SRU (assuming nothing unexpected crops up during testing).
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Locally Integrated Menus (LIM) debuted in Ubuntu 14.04 LTS to much appreciation, being widely seen as the best compromise between those who liked the simplicity of the “hidden” approach and those who disliked the mouse and trackpad aerobics using it required.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
While locally integrated menus brought us half way to silencing the criticisms levelled at this aspect of Unity, the default “fade in/fade out” behaviour left an itch unscratched.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The past few releases of Ubuntu has seen proactive addressing of concerns and issues experienced by its earlier UX decisions. After several years on the ‘to do’ list [we finally got Locally Integrated Menus last year][1], as well as an unsupported [option to minimise and restore apps to the Unity Launcher][2] by clicking on their icon.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
A year on from that we finally get an option to make application menus always show, no matter where our mouse is. Better late than never, right?
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2015/01/ubuntu-15-04-always-show-menu-bar-option
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
作者:[Joey-Elijah Sneddon][a]
|
|
||||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
|
||||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
[a]:https://plus.google.com/117485690627814051450/?rel=author
|
|
||||||
[1]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/02/locally-integrated-menus-ubuntu-14-04
|
|
||||||
[2]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/03/minimize-click-launcher-option-ubuntu-14-04
|
|
||||||
@ -1,87 +0,0 @@
|
|||||||
translating by martin.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
How to Setup Passwordless SSH Logon to Ubuntu 14.04
|
|
||||||
================================================================================
|
|
||||||
Hi all, today we'll gonna learn how we can setup Passwordless SSH Logon to Ubuntu 14.04 "Trusty". Only the workstations having the correct matching key pair (private and public) will be allowed to logon to the SSH server, without the key paring, access will not be allowed.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Usually, we need to enter username and password combination to connect to an SSH console. If the combination is correct to that of the system's then, we get access to the server else we are denied from the access. But, there is something more secure than Password logon, we have passwordless SSH logon using the encrypted keys.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
If you want to enable this secured option, we can simply disable password-logon and only allow logon using an encryption key. When using encryption keys option, the client computer generates a private and public key pair. The client then must upload the public key to the SSH server authorized_key file. Before access is granted, the server and client computer validate the key pair. If the public key on the server matches the private key submitted via the client then access will be granted else will be denied.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
This is a very secure way authenticating to a SSH server and it’s a recommended method if you wish to implement secure logon with single user SSH logon. Here's a quick step-wise process on how to enable Passwordless SSH logon.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### 1. Installing Openssh Server ###
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
First off all, we'll need to update our local repository index. To do so, we'll first need to run apt-get update as shown below.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
$ sudo apt-get update
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||

|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Now, we can install openssh-server by running following command.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
$ sudo apt-get install openssh-server
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||

|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### 2. Enabling Openssh Server ###
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Now, we'll want to enable OpenSSH server after we successfully installed it on our Ubuntu 14.04 Operating System. The command to enable/start the server is given as follows.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
$ sudo service ssh start
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
OR
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
$ sudo /etc/init.d/ssh start
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### 3. Configuring Key Pair ###
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
After we have installed our OpenSSH Server and enabled it. We'll now finally wanna go for generating our Public and Private Key Pair. To do that, run the following command in a terminal or console.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
$ ssh-keygen -t rsa
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
After running the above command, we'll be prompted to complete a series of tasks. The first will be where to save the keys, press Enter to choose the default location which is in a hidden .ssh folder in the home directory. The next prompt will be to enter the Paraphrase. I personally leave this blank (just press enter) to continue. It will then create the key pair and we’re done.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||

|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
After generation of the key pair, we will need to **copy the client’s public key to the SSH server** or host inorder to create trusted relationship with it. We'll need to run the commands below to copy the client public key to the server.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
$ ssh-copy-id user@ip_address
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
After the public key is copied to the server, we can now go and disable password logon via SSH. To do that, we'll need to open **/etc/ssh/ssh_config** via a text editor by run the commands below.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
$ sudo nano /etc/ssh/sshd_config
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Now, we'll need to uncomment the lines and set the values as shown below.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||

|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### 4. Restarting the SSH Server ###
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Finally, after we are done configuring SSH Server, we'll want to restart our SSH Server so that all the changes will take affect. To restart one can run the following command in a terminal or the console.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
$ sudo service ssh restart
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
OR
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
$ sudo /etc/init.d/ssh restart
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||

|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Finally, we can now ssh in to the server without a password and only from the client having the same key pair not the password.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### Conclusion ###
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Hurray! We have successfully enabled Passwordless SSH logon. It is a lot secure to enable Encrypted Key Pair SSH logon . This is a very secure way authenticating to a SSH server and it’s a recommended method if you wish to implement secure logon with single user SSH logon. So, if you have any questions, suggestions, feedback please write them in the comment box below. Thank you ! Enjoy Encrypted Secure SSH Login :-)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
via: http://linoxide.com/ubuntu-how-to/setup-passwordless-ssh-logon-ubuntu-14-04/
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
作者:[Arun Pyasi][a]
|
|
||||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
|
||||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arunp/
|
|
||||||
@ -1,63 +0,0 @@
|
|||||||
How To Fix “Not Enough Free Disk Space On /boot” In Ubuntu
|
|
||||||
================================================================================
|
|
||||||
### Question: How To Fix “Not Enough Free Disk Space On /boot” In Ubuntu? ###
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Today, I got the following error, but a simple one, when try to update my Lubuntu 14.04 desktop.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
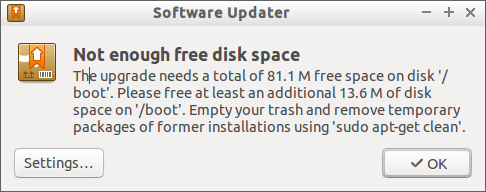
> “Not Enough Free Disk Space On /boot”
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
This is because my /boot partition has caught up with unwanted old kernels, packages etc.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### Answer: ###
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
I heard about **Computer Janitor** feature which will remove unwanted old junk files in Ubuntu Tweak tool. Using the Computer Janitor, you can clean up your system like a freshly installed system. Janitor will remove;
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- Apps cache(Firefox/Chrome cache, Software center cache);
|
|
||||||
- Thumbnail cache;
|
|
||||||
- Apt cache;
|
|
||||||
- Old kernels;
|
|
||||||
- Package configs;
|
|
||||||
- And unneeded packages.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
If you haven’t install this tool, look at the following link.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- **[How To Install And Use Ubuntu Tweak On Ubuntu][1]**
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
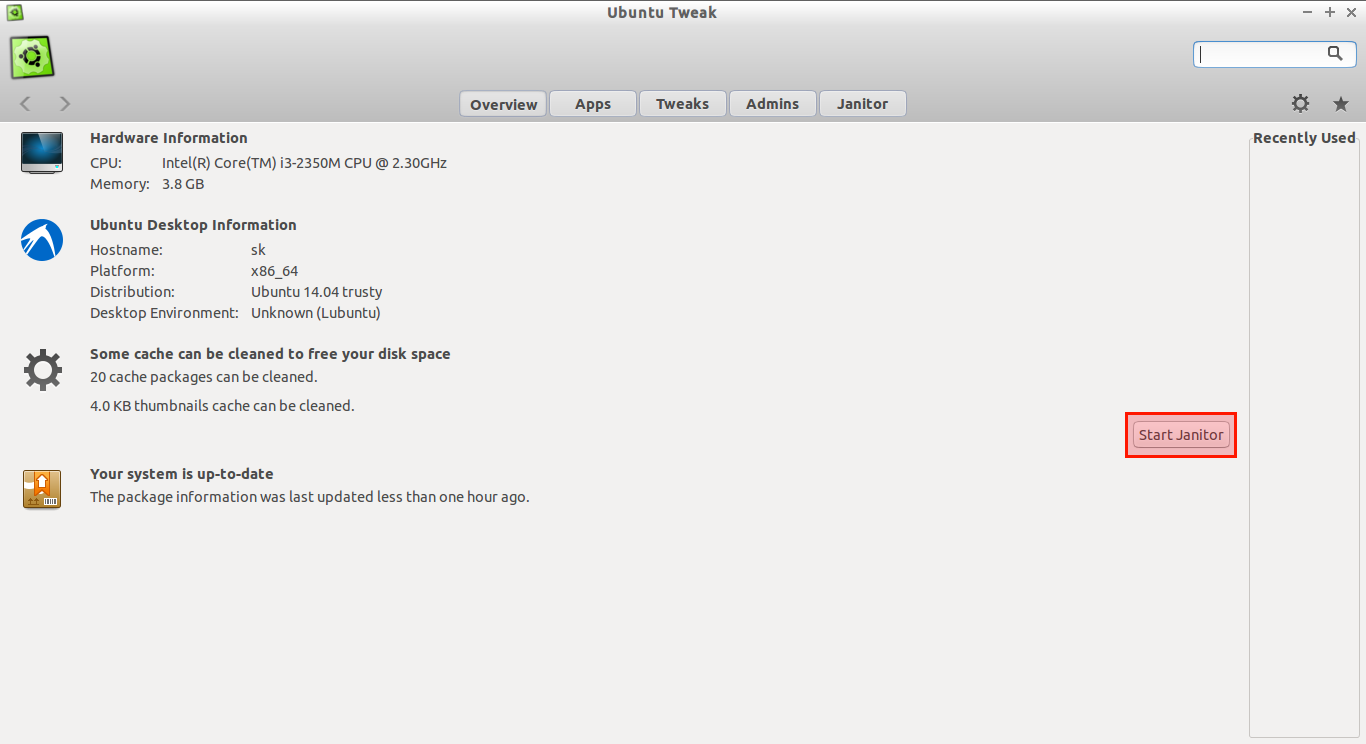
To remove unwanted junk files, open Ubuntu Tweak, and click on the **Janitor** option.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
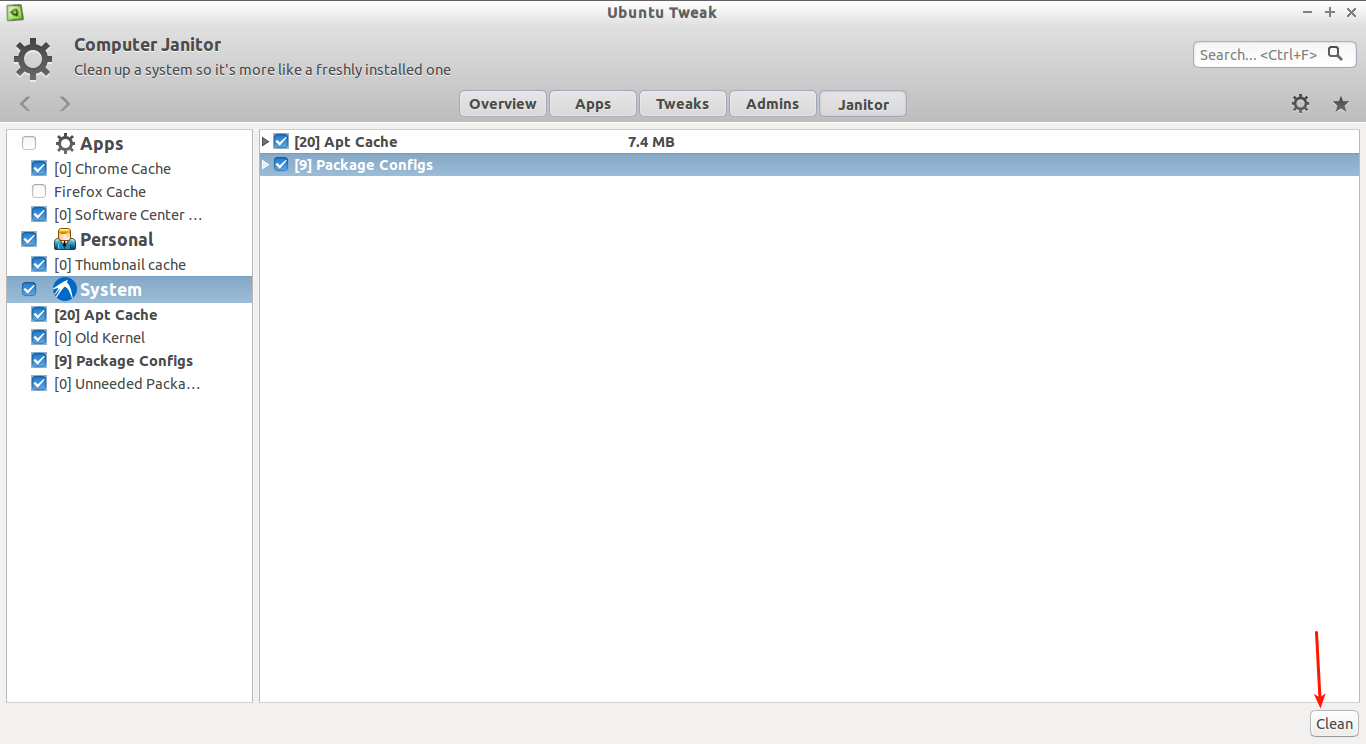
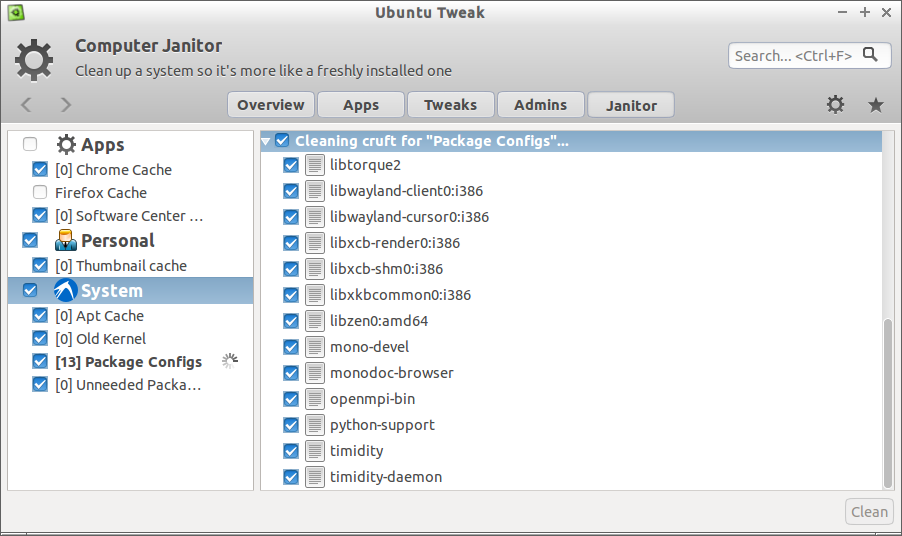
Select the check the boxes to remove unwanted junk from your system, and click **Clean** button.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Janitor will now start to clean up your system
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
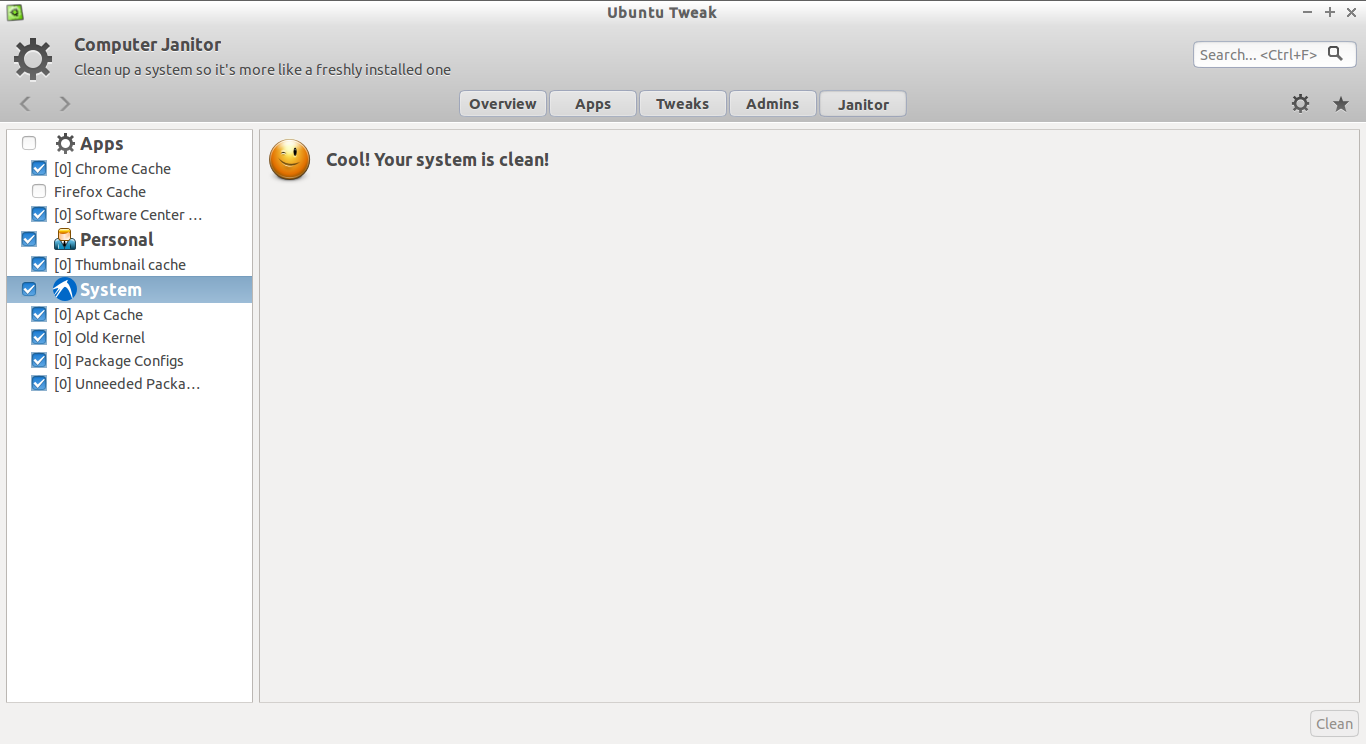
Cool! The system is clean now.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
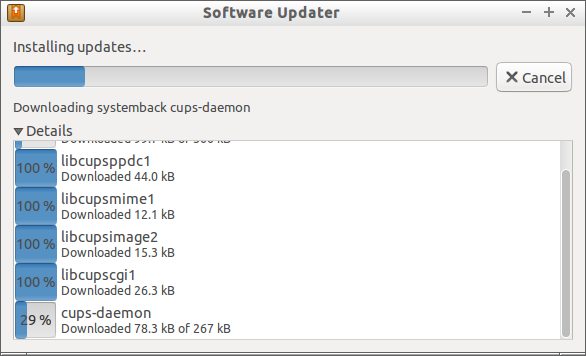
Again I re-launched the software updater. This time it went smoothly without any issues.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
That’s all. Enjoy. There are others ways also available to clean up the system. But, this seems very easy to follow. We can do system clean up in few mouse clicks.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Cheers!
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
via: https://www.unixmen.com/how-to-fix-not-enough-free-disk-space-on-boot-in-ubuntu/
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
作者:[SK][a]
|
|
||||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
|
||||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
[a]:https://www.unixmen.com/author/sk/
|
|
||||||
[1]:http://www.unixmen.com/after-a-fresh-install-of-ubuntu-1010-maverick-meerkat-configuration-made-easy-with-ubuntu-tweak/
|
|
||||||
@ -0,0 +1,42 @@
|
|||||||
|
Ubuntu 15.04 最终实现你可以设置你的菜单 ‘始终可见’
|
||||||
|
================================================================================
|
||||||
|
**如果你不喜欢 Unity 的全局菜单在你的鼠标离开后就淡出你的视野, Ubuntu 15.04 有一些额外附加去实现这点.**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
最新的Ubuntu 15.04的Unity界面通过在提议通道提供了一个选项**使应用程序菜单在Ubuntu中可见**.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
不时尚, 不过时, 没有丢失的菜单.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
最大的缺点是它目前只能通过dconf来控制,而不是常规的面向用户的选项设置。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
我希望(如果不是期望)能有一个设置这个特性的选项被加入到Ubuntu的【系统设置】>【外观】部分的开发仍在继续。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
现在,如果你使用的是Ubuntu15.04,并启用“建议”的更新通道后,你会发现这个开关存在于在COM>规范>Unity>“始终显示菜单”。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 迟到总比没有要好? ###
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
开发者计划在Ubuntu14.04 LTS的下一个SRU中反向移植这个选项(假设在测试阶段没有任何意外发生)。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
本地集成菜单(LIM)在Ubuntu 14.04 LTS 首次获得了欣赏,被广泛认为在那些喜欢隐藏方式的和那些不喜欢必须使用鼠标和触摸板的人之间的最佳的折衷方法
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
虽然本地集成菜单给我们带来了半路上沉默的批评在统一方面,默认的“淡入/淡出”行为给我们留下了令人发痒的伤痕
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
在Ubuntu 过去的几个版本中已经能够看到积极的去解决早期UX的经历过的关切的问题。在经过几年“打算去做”的列表[我们去年终于得到了本地集成菜单][1],以及不支持的通过点击图标实现[减少和恢复Unity启动程序中不支持的应用程序的选项]。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
一年以来我们终于得到一个选项以使应用程序菜单始终显示,无论我们的鼠标在哪里。迟来总比没有好,对不对?
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2015/01/ubuntu-15-04-always-show-menu-bar-option
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
作者:[Joey-Elijah Sneddon][a]
|
||||||
|
译者:[JeffDing](https://github.com/JeffDing)
|
||||||
|
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
[a]:https://plus.google.com/117485690627814051450/?rel=author
|
||||||
|
[1]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/02/locally-integrated-menus-ubuntu-14-04
|
||||||
|
[2]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/03/minimize-click-launcher-option-ubuntu-14-04
|
||||||
@ -6,7 +6,7 @@ Linux有问必答:如何在Debian或Ubuntu上安装完整的内核源码
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
只有在你需要生成一个定制的内核,而且内核源码中的一些内核默认设置要被你调整了的情况下,你才需要完整的内核源码树。
|
只有在你需要生成一个定制的内核,而且内核源码中的一些内核默认设置要被你调整了的情况下,你才需要完整的内核源码树。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
这里将会解答如何**在Debian或Ubuntu的库中下载并安装完整树结构的内核源码**。虽然你可以在这个网站[https://www.kernel.org/pub/linux/kernel/][2]下载官方的内核源码,但是发行版软件仓库可以允许你下载包含补丁的内核源码。
|
这里将会解答如何**在Debian或Ubuntu的库中下载并安装完整树结构的内核源码**。你可以在[https://www.kernel.org/pub/linux/kernel/][2]下载官方的内核源码,不过使用发行版软件仓库可以允许你下载包含补丁的内核源码。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### 在Debian上安装完整的内核源码 ###
|
### 在Debian上安装完整的内核源码 ###
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@ -20,7 +20,7 @@ Linux有问必答:如何在Debian或Ubuntu上安装完整的内核源码
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
伴随着完整内核源码(linux_X.X.XX.orig.tar.xz)的还有一些可用的内核补丁(linux_X.X.X+XXX.debian.tar.xz)和源码控制文件(linux_XXXX.dsc),这些都将被下载并存储到当前目录。在.dsc文件中会指出如何给内核源码打补丁。
|
伴随着完整内核源码(linux_X.X.XX.orig.tar.xz)的还有一些可用的内核补丁(linux_X.X.X+XXX.debian.tar.xz)和源码控制文件(linux_XXXX.dsc),这些都将被下载并存储到当前目录。在.dsc文件中会指出如何给内核源码打补丁。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
当下载完成,以上的命令将会自动调用工具dpkg-source将下载的内核源码解压到当前的目录中,与此同时更具.dsc文件来下补丁。
|
当下载完成,以上的命令将会自动调用工具dpkg-source将下载的内核源码解压到当前的目录中,与此同时根据.dsc文件来下补丁。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
最终完整的内核源码树将会以"linux-X.X.XX"的形式呈现在当前目录中。
|
最终完整的内核源码树将会以"linux-X.X.XX"的形式呈现在当前目录中。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@ -35,7 +35,7 @@ Linux有问必答:如何在Debian或Ubuntu上安装完整的内核源码
|
|||||||
$ sudo apt-get install git
|
$ sudo apt-get install git
|
||||||
$ git clone git://kernel.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/ubuntu-$(lsb_release --codename | cut -f2).git
|
$ git clone git://kernel.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/ubuntu-$(lsb_release --codename | cut -f2).git
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
举个例子,如果你使用的是Ubuntu14.04,以上的命令将会查看Git的"ubuntu-trusty"仓库中的代码。
|
举个例子,如果你使用的是Ubuntu 14.04,以上的命令将会查看Git的"ubuntu-trusty"仓库中的代码。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||

|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@ -49,7 +49,7 @@ via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/install-full-kernel-source-debian-ubuntu.html
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
|
作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
|
||||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@ -0,0 +1,85 @@
|
|||||||
|
设置Ubuntu14.04无密码登录SSH
|
||||||
|
================================================================================
|
||||||
|
大家好,今天我来向大家介绍如何在可信的Ubuntu12.04上设置无密码登录SSH功能。仅在工作站有正确的(公私)密钥以供匹配时SSH服务端才会允许你登录,反之访问将不会被允许。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
正常情况下,我们需要连上SSH的控制台输入用户名和密码,两者结合使用。如果两者全部正确,我们就可以访问,反之访问被服务端拒绝。不过相比而言还有一种比用密码更安全的登录方式,我们用的不是密码在登录SSH我们用的是密钥。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
如果你想使用这个安全的方式,我们只需简单的禁用密码登录并只允许密钥即可。使用这种方式时,客户端计算机上会产生公私一对密钥。接着客户端得把公钥上传到SSH服务端的密要验证文件中去。在访问被授予前,服务器及客户端电脑互验密钥对。如果服务器上的公钥与客服端提交的私钥匹配访问开始,否则访问被拒绝。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
这是获取SSH服务器认证中非常安全的一种做法,如果你想为SSH用户登录实施安全的认证,这也是备受推崇的方式。这里快速的过一遍允许无密码登录SSH的配置过程。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 1.安装Openssh服务端 ###
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
首先,我们需要更新我们的本地库索引。所以如下所见,我们需要先输入“apt-get update”
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
$ sudo apt-get update
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
现在我们可以通过以下命令安装openssh-server:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
$ sudo apt-get install openssh-server
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 2. 开启openssh服务 ###
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
在OpenSSH已经成功安装在Ubuntu14.04操作系统上了之后,我们要启动OpenSSH的服务。以下命令让你启动/开启服务。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
$ sudo service ssh start
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
OR
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
$ sudo /etc/init.d/ssh start
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 3. 配置密钥对 ###
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
在我们安装并启动了OpenSSH服务以后。现在终于到了要我们搞定公私钥对的时候了,在终端中运行以下命令:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
$ ssh-keygen -t rsa
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
在运行完以上命令了以后,我们完成一系列的提示的任务。首先选择保存密钥路径,按回车将会选择默认路径即家目录的一个隐藏的.ssh文件夹。下一个提示是请输入提醒。我个人将此留白(回车过)。之后密钥对就会创建,大功告成。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
在密钥对生成以后,我们需要将**客户端的上的公钥复制到SSH服务端**或者宿主来创建对客户端的信任关系。运行以下命令复制客户端的公钥到服务端。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
$ ssh-copy-id user@ip_address
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
在公钥上传之后,我们现在可以不用通过密码登陆SSH了。为此,我们需要通过以下命令用文本编辑器打开**etc/ssh/ssh_config**。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
$ sudo nano /etc/ssh/sshd_config
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
现在,我们需要按照下图所示去到几行注释并进行一些赋值。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 4. 重启SSH服务 ###
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
最后,在我们配置完SSH服务端后,为了使改动生效我们需要重启SSH服务。在终端或控制台运行以下命令重启。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
$ sudo service ssh restart
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
OR
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
$ sudo /etc/init.d/ssh restart
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
现在,我们可以试试不用密码仅用密钥配对的方式登录ssh服务端了。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 总结 ###
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
太好了!我们成功的配置了无密码登录SSH。这是获取SSH服务器认证中非常安全的一种做法,如果你想为SSH但用户登录实施安全的认证这也是备受推崇的方式。所以,如果你还有什么问题或建议,请在意见框中向我们反馈。很欣慰你能读完,祝你SSH登录愉快 :-)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
via: http://linoxide.com/ubuntu-how-to/setup-passwordless-ssh-logon-ubuntu-14-04/
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
作者:[Arun Pyasi][a]
|
||||||
|
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||||
|
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arunp/
|
||||||
@ -0,0 +1,64 @@
|
|||||||
|
如何在Ubuntu上修复“Not Enough Free Disk Space On /boot”
|
||||||
|
================================================================================
|
||||||
|
### 提问:如何在Ubuntu上修复“Not Enough Free Disk Space On /boot”错误?###
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
今天,当我在升级Lubuntu 14.04的时候遇到了下面这个错误,但是很简单。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
> “Not Enough Free Disk Space On /boot”
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
这是因为我的启动分区超出了不再要的旧内核与包等。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 回答: ###
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
我听说**Computer Janitor**这个特性可以在Ubuntu Tweak中删除不想要的垃圾文件。使用Computer Janitor,你可以将你的系统清理成像新安装的那样。Janitor会删除:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- 程序缓存(Firefox/Chrome 缓存、软件中心缓存);
|
||||||
|
- 略缩图缓存;
|
||||||
|
- apt缓存;
|
||||||
|
- 旧内核;
|
||||||
|
- 包的配置;
|
||||||
|
- 不再需要的包。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
If you haven’t install this tool, look at the following link.
|
||||||
|
如果你还没有安装这个工具,参考下面的链接
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- **[如何安装和使用Ubuntu Tweak][1]**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
要删除不需要的垃圾文件,打开Ubuntu Tweak,点击 **Janitor** 选项。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
选择你想要删除的文件的选框,并点击 **Clean** 按钮。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Janitor现在就开始清理你的系统了。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
真酷!系统清理完成了。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
我重启启动了软件更新。这个没再遇到问题了。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
就是这样。当然也有其他的方法可以清理系统。但是,这个方法很容易学。我们可以只点击几次鼠标就可以清理系统。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
干杯!
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
via: https://www.unixmen.com/how-to-fix-not-enough-free-disk-space-on-boot-in-ubuntu/
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
作者:[SK][a]
|
||||||
|
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||||
|
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
[a]:https://www.unixmen.com/author/sk/
|
||||||
|
[1]:http://www.unixmen.com/after-a-fresh-install-of-ubuntu-1010-maverick-meerkat-configuration-made-easy-with-ubuntu-tweak/
|
||||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user