diff --git a/published/20170309 How To Record Everything You Do In Terminal.md b/published/20170309 How To Record Everything You Do In Terminal.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..a73022764e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20170309 How To Record Everything You Do In Terminal.md
@@ -0,0 +1,99 @@
+如何记录你在终端中执行的所有操作
+======
+
+
+
+几天前,我们发布了一个解释如何[保存终端中的命令并按需使用][1]的指南。对于那些不想记忆冗长的 Linux 命令的人来说,这非常有用。今天,在本指南中,我们将看到如何使用 `script` 命令记录你在终端中执行的所有操作。你可能已经在终端中运行了一个命令,或创建了一个目录,或者安装了一个程序。`script` 命令会保存你在终端中执行的任何操作。如果你想知道你几小时或几天前做了什么,那么你可以查看它们。我知道我知道,我们可以使用上/下箭头或 `history` 命令查看以前运行的命令。但是,你无法查看这些命令的输出。而 `script` 命令记录并显示完整的终端会话活动。
+
+`script` 命令会在终端中创建你所做的所有事件的记录。无论你是安装程序,创建目录/文件还是删除文件夹,一切都会被记录下来,包括命令和相应的输出。这个命令对那些想要一份交互式会话拷贝作为作业证明的人有用。无论是学生还是导师,你都可以将所有在终端中执行的操作和所有输出复制一份。
+
+### 在 Linux 中使用 script 命令记录终端中的所有内容
+
+`script` 命令预先安装在大多数现代 Linux 操作系统上。所以,我们不用担心安装。
+
+让我们继续看看如何实时使用它。
+
+运行以下命令启动终端会话记录。
+
+```
+$ script -a my_terminal_activities
+```
+
+其中,`-a` 标志用于将输出追加到文件(记录)中,并保留以前的内容。上述命令会记录你在终端中执行的所有操作,并将输出追加到名为 `my_terminal_activities` 的文件中,并将其保存在当前工作目录中。
+
+示例输出:
+
+```
+Script started, file is my_terminal_activities
+```
+
+现在,在终端中运行一些随机的 Linux 命令。
+
+```
+$ mkdir ostechnix
+$ cd ostechnix/
+$ touch hello_world.txt
+$ cd ..
+$ uname -r
+```
+
+运行所有命令后,使用以下命令结束 `script` 命令的会话:
+
+```
+$ exit
+```
+
+示例输出:
+
+```
+exit
+Script done, file is my_terminal_activities
+```
+
+如你所见,终端活动已存储在名为 `my_terminal_activities` 的文件中,并将其保存在当前工作目录中。
+
+要查看你的终端活动,只需在任何编辑器中打开此文件,或者使用 `cat` 命令直接显示它。
+
+```
+$ cat my_terminal_activities
+```
+
+示例输出:
+
+```
+Script started on Thu 09 Mar 2017 03:33:44 PM IST
+[sk@sk]: ~>$ mkdir ostechnix
+[sk@sk]: ~>$ cd ostechnix/
+[sk@sk]: ~/ostechnix>$ touch hello_world.txt
+[sk@sk]: ~/ostechnix>$ cd ..
+[sk@sk]: ~>$ uname -r
+4.9.11-1-ARCH
+[sk@sk]: ~>$ exit
+exit
+
+Script done on Thu 09 Mar 2017 03:37:49 PM IST
+```
+
+正如你在上面的输出中看到的,`script` 命令记录了我所有的终端活动,包括 `script` 命令的开始和结束时间。真棒,不是吗?使用 `script` 命令的原因不仅仅是记录命令,还有命令的输出。简单地说,脚本命令将记录你在终端上执行的所有操作。
+
+### 结论
+
+就像我说的那样,脚本命令对于想要保留其终端活动记录的学生,教师和 Linux 用户非常有用。尽管有很多 CLI 和 GUI 可用来执行此操作,但 `script` 命令是记录终端会话活动的最简单快捷的方式。
+
+就是这些。希望这有帮助。如果你发现本指南有用,请在你的社交,专业网络上分享,并支持我们。
+
+干杯!
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://www.ostechnix.com/record-everything-terminal/
+
+作者:[SK][a]
+选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
+译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:https://www.ostechnix.com/author/sk/
+[1]:https://www.ostechnix.com/save-commands-terminal-use-demand/
diff --git a/published/20171228 Container Basics- Terms You Need to Know.md b/published/20171228 Container Basics- Terms You Need to Know.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..fe266d0cb6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20171228 Container Basics- Terms You Need to Know.md
@@ -0,0 +1,48 @@
+容器基础知识:你需要知道的术语
+======
+
+
+
+[在前一篇文章中][1],我们谈到了容器是什么以及它是如何培育创新并助力企业快速发展的。在以后的文章中,我们将讨论如何使用容器。然而,在深入探讨这个话题之前,我们需要了解关于容器的一些术语和命令。掌握了这些术语,才不至于产生混淆。
+
+让我们来探讨 [Docker][2] 容器世界中使用的一些基本术语吧。
+
+容器:到底什么是容器呢?它是一个 Docker 镜像的运行实例。它包含一个 Docker 镜像、执行环境和说明。它与系统完全隔离,所以可以在系统上运行多个容器,并且完全无视对方的存在。你可以从同一镜像中复制出多个容器,并在需求较高时扩展服务,在需求低时对这些容器进行缩减。
+
+Docker 镜像:这与你下载的 Linux 发行版的镜像别无二致。它是一个安装包,包含了用于创建、部署和执行容器的一系列依赖关系和信息。你可以在几秒钟内创建任意数量的完全相同的容器。镜像是分层叠加的。一旦镜像被创建出来,是不能更改的。如果你想对容器进行更改,则只需创建一个新的镜像并从该镜像部署新的容器即可。
+
+仓库(repo):Linux 的用户对于仓库这个术语一定不陌生吧。它是一个软件库,存储了可下载并安装在系统中的软件包。在 Docker 容器中,唯一的区别是它管理的是通过标签分类的 Docker 镜像。你可以找到同一个应用程序的不同版本或不同变体,他们都有适当的标记。
+
+镜像管理服务:可以将其想象成 GitHub。这是一个在线服务,管理并提供了对 Docker 镜像仓库的访问,例如默认的公共镜像仓库——DockerHub。供应商可以将他们的镜像库上传到 DockerHub 上,以便他们的客户下载和使用官方镜像。一些公司为他们的镜像提供自己的服务。镜像管理服务不必由第三方机构来运行和管理。组织机构可以使用预置的服务来管理内部范围的镜像库访问。
+
+标签:当你创建 Docker 镜像时,可以给它添加一个合适的标签,以便轻松识别不同的变体或版本。这与你在任何软件包中看到的并无区别。Docker 镜像在添加到镜像仓库时被标记。
+
+现在你已经掌握了基本知识,下一个阶段是理解实际使用 Docker 容器时用到的术语。
+
+**Dockerfile** :这是一个文本文件,包含为了为构建 Docker 镜像需手动执行的命令。Docker 使用这些指令自动构建镜像。
+
+构建:这是从 Dockerfile 创建成镜像的过程。
+
+推送:一旦镜像创建完成,“push” 是将镜像发布到仓库的过程。该术语也是我们下一篇文章要学习的命令之一。
+
+拉取:用户可以通过 “pull” 过程从仓库检索该镜像。
+
+编组:复杂的应用程序会包含多个容器。docker-compose 是一个用于运行多容器应用程序的命令行工具。它允许你用单条命令运行一个多容器的应用程序,简化了多容器带来的问题。
+
+### 总结
+
+容器术语的范围很广泛,这里是经常遇到的一些基本术语。下一次当你看到这些术语时,你会确切地知道它们的含义。在下一篇文章中,我们将开始使用 Docker 容器。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://www.linux.com/blog/intro-to-linux/2017/12/container-basics-terms-you-need-know
+
+作者:[Swapnil Bhartiya][a]
+译者:[jessie-pang](https://github.com/jessie-pang)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:https://www.linux.com/users/arnieswap
+[1]:https://linux.cn/article-9468-1.html
+[2]:https://www.docker.com/
diff --git a/translated/tech/20180411 Make your first contribution to an open source project.md b/published/20180411 Make your first contribution to an open source project.md
similarity index 61%
rename from translated/tech/20180411 Make your first contribution to an open source project.md
rename to published/20180411 Make your first contribution to an open source project.md
index 2fb8e735a0..a9734cc9a5 100644
--- a/translated/tech/20180411 Make your first contribution to an open source project.md
+++ b/published/20180411 Make your first contribution to an open source project.md
@@ -4,11 +4,12 @@
> 这是许多事情的第一步

+
图片提供 : [WOCinTech Chat][16]. 图片修改 : Opensource.com. [CC BY-SA 4.0][17]
有一个普遍的误解,那就是对开源做出贡献是一件很难的事。你可能会想,“有时我甚至不能理解我自己的代码;那我怎么可能理解别人的?”
-放轻松。直到去年,我都以为是这样。阅读和理解他人的代码,然后把你自己的写在顶上,这是一件令人气馁的任务;但如果有合适的资源,这不像你想象的那么糟。
+放轻松。直到去年,我都以为是这样。阅读和理解他人的代码,然后在他们的基础上写上你自己的代码,这是一件令人气馁的任务;但如果有合适的资源,这不像你想象的那么糟。
第一步要做的是选择一个项目。这个决定是可能是一个菜鸟转变成一个老练的开源贡献者的关键一步。
@@ -16,7 +17,7 @@
### 理解产品
-在开始贡献之前,你需要理解项目是怎么工作的。为了理解这一点,你需要自己来尝试。如果你发现这个产品很有趣并且游泳,它就值得你来做贡献。
+在开始贡献之前,你需要理解项目是怎么工作的。为了理解这一点,你需要自己来尝试。如果你发现这个产品很有趣并且有用,它就值得你来做贡献。
初学者常常选择参与贡献那些他们没有使用过的软件。他们会失望,并且最终放弃贡献。如果你没有用过这个软件,你不会理解它是怎么工作的。如果你不理解它是怎么工作的,你怎么能解决 bug 或添加新特性呢?
@@ -31,77 +32,59 @@
这里介绍了怎么确认一个项目是否还是活跃的:
* **贡献者数量:** 一个增加的贡献者数量表明开发者社区乐于接受新的贡献者。
-
-* **提交频率:** 查看最近的提交时间。如果是一周之内,甚至是一两个月内,这个项目应该是定期维护的。
-
-* **维护者数量:** 维护者的数量越多,你越可能得到指导。
-
-* **聊天室活动等级:** 一个繁忙的聊天室意味着你的问题可以更快得到回复。
+* **提交频率:** 查看最近的提交时间。如果是一周之内,甚至是一两个月内,这个项目应该是定期维护的。
+* **维护者数量:** 维护者的数量越多,你越可能得到指导。
+* **聊天室或 IRC 活跃度:** 一个繁忙的聊天室意味着你的问题可以更快得到回复。
### 新手资源
Coala 是一个开源项目的例子。它有自己的教程和文档,让你可以使用它(每一个类和方法)的 API。这个网站还设计了一个有吸引力的界面,让你有阅读的兴趣。
-**文档:** 所有水平的开发者都需要可靠的,被很好地维护的文档,来理解项目的细节。找找在 [GitHub][19](或者承载的任何位置)上,或者在单独的类似于 [阅读文档][20] 的页面上提供完善文档的项目,这样可以帮助你深入了解代码。
-
-### [Coala 新手指南.png][2]
+**文档:** 不管哪种水平的开发者都需要可靠的、被很好地维护的文档,来理解项目的细节。找找在 [GitHub][19](或者放在其它位置)或者类似于 [Read the Docs][20] 之类的独立站点上提供了完善文档的项目,这样可以帮助你深入了解代码。

-**教程:** 教程会给新手解释如何在项目里添加特性 (然而,你可以在任何项目里找到它)。例如,Coala 提供了 [tutorials for writing _bears_][21] (执行代码分析的格式化代码工具的Python 包装器).
-
-### [Coala 界面.png][3]
+**教程:** 教程会给新手解释如何在项目里添加特性 (然而,你不是在每个项目中都能找到它)。例如,Coala 提供了 [小熊编写指南][21] (进行代码分析的代码格式化工具的 Python 包装器)。

-**添加标签的讨论点:** 对刚刚想明白如何选择第一个项目的初学者来说,选择一个讨论点是一个更加困难的任务。标签被设为“难度/低”,“难度/新手”,“利于初学者”,以及“low-hanging fruit”都表明是对新手友好的。F
-
-### [Coala 讨论点标签.png][4]
+**分类的讨论点:** 对刚刚想明白如何选择第一个项目的初学者来说,选择一个讨论点是一个更加困难的任务。标签被设为“难度/低”、“难度/新手”、“利于初学者”,以及“触手可及”都表明是对新手友好的。

### 其他因素
-### [ci_历史纪录.png][5]
-

-* **维护者对新的贡献者的态度:** 从我的经验来看,大部分开源贡献者都很乐于帮助他们项目里的新手。然而,当你问问题时,你也有可能遇到一些不太友好的人(甚至可能有点粗鲁)。不要因为这些人失去信心。他们只是因为在比他们经验更丰富的人那儿得不到发泄的机会。还有很多其他人愿意提供帮助。
-
-* **审阅过程/结构:** 你的拉取请求将被你的同事和有经验的开发者查看和更改很多次——这就是你学习软件开发最主要的方式。一个具有严格审阅过程的项目使您能够通过编写生产级代码来作为开发人员成长。
-
-* **一个稳健的持续整合管道:** 开源项目会向新手们介绍持续整合和部署服务。一个稳健的 CI 管道将帮助你学习阅读和理解 CI 日志。它也将带给你处理失败的测试案例和代码覆盖率问题的经验。
-
-* **参加编程项目 (例如 [Google Summer Of Code][1]):** 参加组织证明了你乐于对一个项目的长期发展做贡献。他们也会给新手提供一个机会来获得现实世界中的开发经验,从而获得报酬。大多数参加这些项目的组织都欢迎新人加入。
+* **维护者对新的贡献者的态度:** 从我的经验来看,大部分开源贡献者都很乐于帮助他们项目里的新手。然而,当你问问题时,你也有可能遇到一些不太友好的人(甚至可能有点粗鲁)。不要因为这些人失去信心。他们只是因为在比他们经验更丰富的人那儿得不到发泄的机会而已。还有很多其他人愿意提供帮助。
+* **审阅过程/机制:** 你的拉取请求将经历几遍你的同伴和有经验的开发者的查看和更改——这就是你学习软件开发最主要的方式。一个具有严格审阅过程的项目使您在编写生产级代码的过程中成长。
+* **一个稳健的持续集成管道:** 开源项目会向新手们介绍持续集成和部署服务。一个稳健的 CI 管道将帮助你学习阅读和理解 CI 日志。它也将带给你处理失败的测试用例和代码覆盖率问题的经验。
+* **参加编程项目(例如 [Google Summer Of Code][1]):** 参加组织证明了你乐于对一个项目的长期发展做贡献。他们也会给新手提供一个机会来获得现实世界中的开发经验,从而获得报酬。大多数参加这些项目的组织都欢迎新人加入。
### 7 对新手友好的组织
* [coala (Python)][7]
-
* [oppia (Python, Django)][8]
-
* [DuckDuckGo (Perl, JavaScript)][9]
-
* [OpenGenus (JavaScript)][10]
-
* [Kinto (Python, JavaScript)][11]
-
* [FOSSASIA (Python, JavaScript)][12]
-
* [Kubernetes (Go)][13]
### 关于作者
- [][22] Palash Nigam - 我是一个印度计算机科学专业本科生,十分乐于参与开源软件的开发,我在 GitHub 上花费了大部分的时间。我现在的兴趣包括 web 后端开发,区块链,和 All things python.[更多关于我][14]
+ [][22]
+
+Palash Nigam - 我是一个印度计算机科学专业本科生,十分乐于参与开源软件的开发,我在 GitHub 上花费了大部分的时间。我现在的兴趣包括 web 后端开发,区块链,和 All things python。[更多关于我][14]
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
via: https://opensource.com/article/18/4/get-started-open-source-project
-作者:[ Palash Nigam ][a]
+作者:[Palash Nigam][a]
译者:[lonaparte](https://github.com/lonaparte)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/published/20180418 The Linux Filesystem Explained.md b/published/20180418 The Linux Filesystem Explained.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..589c7e9672
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20180418 The Linux Filesystem Explained.md
@@ -0,0 +1,208 @@
+Linux 文件系统详解
+=====================
+
+> 这篇教程将帮你快速了解 Linux 文件系统。
+
+
+
+早在 1996 年,在真正理解文件系统的结构之前,我就学会了如何在我崭新的 Linux 上安装软件。这是一个问题,但对程序来说不是大问题,因为即使我不知道实际的可执行文件在哪里,它们也会神奇地工作。问题在于文档。
+
+你知道,那时候,Linux 不是像今天这样直观、用户友好的系统。你必须读很多东西。你必须知道你的 CRT 显示器的扫描频率以及拨号调制解调器的噪音来龙去脉,以及其他数以百计的事情。 我很快就意识到我需要花一些时间来掌握目录的组织方式以及 `/etc`(不是用于“其它”文件),`/usr`(不是用于“用户”文件)和 `/bin` (不是“垃圾桶”)的意思。
+
+本教程将帮助你比我当时更快地了解这些。
+
+### 结构
+
+从终端窗口探索 Linux 文件系统是有道理的,这并不是因为作者是一个脾气暴躁的老人,并且对新孩子和他们漂亮的图形工具不以为然(尽管某些事实如此),而是因为终端,尽管只是文本界面,才是更好地显示 Linux 目录树结构的工具。
+
+事实上,帮助你了解这一切的、应该首先安装的第一个工具的名为:`tree`。如果你正在使用 Ubuntu 或 Debian ,你可以:
+
+```
+sudo apt install tree
+```
+
+在 Red Hat 或 Fedora :
+
+```
+sudo dnf install tree
+```
+
+对于 SUSE/openSUSE 可以使用 `zypper`:
+
+```
+sudo zypper install tree
+```
+
+对于使用 Arch (Manjaro,Antergos,等等)使用:
+
+```
+sudo pacman -S tree
+```
+
+……等等。
+
+一旦安装好,在终端窗口运行 `tree` 命令:
+
+```
+tree /
+```
+
+上述指令中的 `/` 指的是根目录。系统中的其他目录都是从根目录分支而出,当你运行 `tree` 命令,并且告诉它从根目录开始,那么你就可以看到整个目录树,系统中的所有目录及其子目录,还有它们的文件。
+
+如果你已经使用你的系统有一段时间了,这可能需要一段时间,因为即使你自己还没有生成很多文件,Linux 系统及其应用程序总是在记录、缓存和存储各种临时文件。文件系统中的条目数量会快速增长。
+
+不过,不要感到不知所措。 相反,试试这个:
+
+```
+tree -L 1 /
+```
+
+你应该看到如图 1 所示。
+
+
+
+上面的指令可以翻译为“只显示以 `/`(根目录) 开头的目录树的第一级”。 `-L` 选项告诉树你想看到多少层目录。
+
+大多数 Linux 发行版都会向你显示与你在上图中看到的相同或非常类似的结构。 这意味着,即使你现在感到困惑,掌握这一点,你将掌握大部分(如果不是全部的话)全世界的 Linux 文件系统。
+
+为了让你开始走上掌控之路,让我们看看每个目录的用途。 当我们查看每一个目录的时候,你可以使用 `ls` 来查看他们的内容。
+
+### 目录
+
+从上到下,你所看到的目录如下
+
+#### /bin
+
+`/bin` 目录是包含一些二进制文件的目录,即可以运行的一些应用程序。 你会在这个目录中找到上面提到的 `ls` 程序,以及用于新建和删除文件和目录、移动它们基本工具。还有其它一些程序,等等。文件系统树的其他部分有更多的 *bin* 目录,但我们将在一会儿讨论这些目录。
+
+#### /boot
+
+`/boot` 目录包含启动系统所需的文件。我必须要说吗? 好吧,我会说:**不要动它**! 如果你在这里弄乱了其中一个文件,你可能无法运行你的 Linux,修复被破坏的系统是非常痛苦的一件事。 另一方面,不要太担心无意中破坏系统:你必须拥有超级用户权限才能执行此操作。
+
+#### /dev
+
+`/dev 目录包含设备文件。 其中许多是在启动时或甚至在运行时生成的。 例如,如果你将新的网络摄像头或 USB 随身碟连接到你的机器中,则会自动弹出一个新的设备条目。
+
+#### /etc
+
+`/etc` 的目录名称会让人变得非常的困惑。`/etc` 得名于最早的 Unix 系统们,它的字面意思是 “etcetera”(诸如此类) ,因为它是系统文件管理员不确定在哪里放置的文件的垃圾场。
+
+现在,说 `/etc` 是“要配置的所有内容”更为恰当,因为它包含大部分(如果不是全部的话)的系统配置文件。 例如,包含系统名称、用户及其密码、网络上计算机名称以及硬盘上分区的安装位置和时间的文件都在这里。 再说一遍,如果你是 Linux 的新手,最好是不要在这里接触太多,直到你对系统的工作有更好的理解。
+
+#### /home
+
+`/home` 是你可以找到用户个人目录的地方。在我的情况下,`/home` 下有两个目录:`/home/paul`,其中包含我所有的东西;另外一个目录是 `/home/guest` 目录,以防有客人需要使用我的电脑。
+
+#### /lib
+
+`/lib` 是库文件所在的地方。库是包含应用程序可以使用的代码文件。它们包含应用程序用于在桌面上绘制窗口、控制外围设备或将文件发送到硬盘的代码片段。
+
+在文件系统周围散布着更多的 `lib` 目录,但是这个直接挂载在 `/` 的 `/lib` 目录是特殊的,除此之外,它包含了所有重要的内核模块。 内核模块是使你的显卡、声卡、WiFi、打印机等工作的驱动程序。
+
+#### /media
+
+在 `/media` 目录中,当你插入外部存储器试图访问它时,将自动挂载它。与此列表中的大多数其他项目不同,`/media` 并不追溯到 1970 年代,主要是因为当计算机正在运行而动态地插入和检测存储(U 盘、USB 硬盘、SD 卡、外部 SSD 等),这是近些年才发生的事。
+
+#### /mnt
+
+然而,`/mnt` 目录是一些过去的残余。这是你手动挂载存储设备或分区的地方。现在不常用了。
+
+#### /opt
+
+`/opt` 目录通常是你编译软件(即,你从源代码构建,并不是从你的系统的软件库中安装软件)的地方。应用程序最终会出现在 `/opt/bin` 目录,库会在 `/opt/lib` 目录中出现。
+
+稍微的题外话:应用程序和库的另一个地方是 `/usr/local`,在这里安装软件时,也会有 `/usr/local/bin` 和 `/usr/local/lib` 目录。开发人员如何配置文件来控制编译和安装过程,这就决定了软件安装到哪个地方。
+
+#### /proc
+
+`/proc`,就像 `/dev` 是一个虚拟目录。它包含有关你的计算机的信息,例如关于你的 CPU 和你的 Linux 系统正在运行的内核的信息。与 `/dev` 一样,文件和目录是在计算机启动或运行时生成的,因为你的系统正在运行且会发生变化。
+
+#### /root
+
+`/root` 是系统的超级用户(也称为“管理员”)的主目录。 它与其他用户的主目录是分开的,**因为你不应该动它**。 所以把自己的东西放在你自己的目录中,伙计们。
+
+#### /run
+
+`/run` 是另一个新出现的目录。系统进程出于自己不可告人的原因使用它来存储临时数据。这是另一个**不要动它**的文件夹。
+
+#### /sbin
+
+`/sbin` 与 `/bin` 类似,但它包含的应用程序只有超级用户(即首字母的 `s` )才需要。你可以使用 `sudo` 命令使用这些应用程序,该命令暂时允许你在许多 Linux 发行版上拥有超级用户权限。`/sbin` 目录通常包含可以安装、删除和格式化各种东西的工具。你可以想象,如果你使用不当,这些指令中有一些是致命的,所以要小心处理。
+
+#### /usr
+
+`/usr` 目录是在 UNIX 早期用户的主目录所处的地方。然而,正如我们上面看到的,现在 `/home` 是用户保存他们的东西的地方。如今,`/usr` 包含了大量目录,而这些目录又包含了应用程序、库、文档、壁纸、图标和许多其他需要应用程序和服务共享的内容。
+
+你还可以在 `/usr` 目录下找到 `bin`,`sbin`,`lib` 目录,它们与挂载到根目录下的那些有什么区别呢?现在的区别不是很大。在早期,`/bin` 目录(挂载在根目录下的)只会包含一些基本的命令,例如 `ls`、`mv` 和 `rm` ;这是一些在安装系统的时候就会预装的一些命令,用于维护系统的一个基本的命令。 而 `/usr/bin` 目录则包含了用户自己安装和用于工作的软件,例如文字处理器,浏览器和一些其他的软件。
+
+但是许多现代的 Linux 发行版只是把所有的东西都放到 `/usr/bin` 中,并让 `/bin` 指向 `/usr/bin`,以防彻底删除它会破坏某些东西。因此,Debian、Ubuntu 和 Mint 仍然保持 `/bin` 和 `/usr/bin` (和 `/sbin` 和 `/usr/sbin` )分离;其他的,比如 Arch 和它衍生版,只是有一个“真实”存储二进制程序的目录,`/usr/bin`,其余的任何 `bin` 目录是指向 `/usr/`bin` 的“假”目录。
+
+#### /srv
+
+`/srv` 目录包含服务器的数据。如果你正在 Linux 机器上运行 Web 服务器,你网站的 HTML文件将放到 `/srv/http`(或 `/srv/www`)。 如果你正在运行 FTP 服务器,则你的文件将放到 `/srv/ftp`。
+
+#### /sys
+
+`/sys` 是另一个类似 `/proc` 和 `/dev` 的虚拟目录,它还包含连接到计算机的设备的信息。
+
+在某些情况下,你还可以操纵这些设备。 例如,我可以通过修改存储在 `/sys/devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:02.0/drm/card1/card1-eDP-1/intel_backlight/brightness` 中的值来更改笔记本电脑屏幕的亮度(在你的机器上你可能会有不同的文件)。但要做到这一点,你必须成为超级用户。原因是,与许多其它虚拟目录一样,在 `/sys` 中打乱内容和文件可能是危险的,你可能会破坏系统。直到你确信你知道你在做什么。否则不要动它。
+
+#### /tmp
+
+`/tmp` 包含临时文件,通常由正在运行的应用程序放置。文件和目录通常(并非总是)包含应用程序现在不需要但以后可能需要的数据。
+
+你还可以使用 `/tmp` 来存储你自己的临时文件 —— `/tmp` 是少数挂载到根目录下而你可以在不成为超级用户的情况下与它进行实际交互的目录之一。
+
+#### /var
+
+`/var` 最初被如此命名是因为它的内容被认为是可变的,因为它经常变化。今天,它有点用词不当,因为还有许多其他目录也包含频繁更改的数据,特别是我们上面看到的虚拟目录。
+
+不管怎样,`/var` 目录包含了放在 `/var/log` 子目录的日志文件之类。日志是记录系统中发生的事件的文件。如果内核中出现了什么问题,它将被记录到 `/var/log` 下的文件中;如果有人试图从外部侵入你的计算机,你的防火墙也将记录尝试。它还包含用于任务的假脱机程序。这些“任务”可以是你发送给共享打印机必须等待执行的任务,因为另一个用户正在打印一个长文档,或者是等待递交给系统上的用户的邮件。
+
+你的系统可能还有一些我们上面没有提到的目录。例如,在屏幕截图中,有一个 `/snap` 目录。这是因为这张截图是在 Ubuntu 系统上截取的。Ubuntu 最近将 [snap][1] 包作为一种分发软件的方式。`/snap` 目录包含所有文件和从 snaps 安装的软件。
+
+### 更深入的研究
+
+这里仅仅谈了根目录,但是许多子目录都指向它们自己的一组文件和子目录。图 2 给出了基本文件系统的总体概念(图片是在 Paul Gardner 的 CC BY-SA 许可下提供的),[Wikipedia 对每个目录的用途进行了总结][2]。
+
+
+![filesystem][4]
+
+*图 2:标准 Unix 文件系统 [许可][5] Paul Gardner*
+
+要自行探索文件系统,请使用 `cd` 命令:`cd`将带你到你所选择的目录( `cd` 代表更改目录)。
+
+如果你不知道你在哪儿,`pwd`会告诉你,你到底在哪里,( `pwd` 代表打印工作目录 ),同时 `cd`命令在没有任何选项或者参数的时候,将会直接带你到你自己的主目录,这是一个安全舒适的地方。
+
+最后,`cd ..`将会带你到上一层目录,会使你更加接近根目录,如果你在 `/usr/share/wallpapers` 目录,然后你执行 `cd ..` 命令,你将会跳转到 `/usr/share` 目录
+
+要查看目录里有什么内容,使用 `ls` 或这简单的使用 `l` 列出你所在目录的内容。
+
+当然,你总是可以使用 `tree` 来获得目录中内容的概述。在 `/usr/share` 上试试——里面有很多有趣的东西。
+
+### 总结
+
+尽管 Linux 发行版之间存在细微差别,但它们的文件系统的布局非常相似。 你可以这么说:一旦你了解一个,你就会都了解了。 了解文件系统的最好方法就是探索它。 因此,伴随 `tree` ,`ls` 和 `cd` 进入未知的领域吧。
+
+你不会只是因为查看文件系统就破坏了文件系统,因此请从一个目录移动到另一个目录并进行浏览。 很快你就会发现 Linux 文件系统及其布局的确很有意义,并且你会直观地知道在哪里可以找到应用程序,文档和其他资源。
+
+通过 Linux 基金会和 edX 免费的 “[Linux入门][6]” 课程了解更多有关 Linux 的信息。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://www.linux.com/blog/learn/intro-to-linux/2018/4/linux-filesystem-explained
+
+作者:[PAUL BROWN][a]
+选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
+译者:[amwps290](https://github.com/amwps290)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:https://www.linux.com/users/bro66
+[1]:https://www.ubuntu.com/desktop/snappy
+[2]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Unix_filesystem#Conventional_directory_layout
+[3]:https://www.linux.com/files/images/standard-unix-filesystem-hierarchypng
+[4]:https://www.linux.com/sites/lcom/files/styles/rendered_file/public/standard-unix-filesystem-hierarchy.png?itok=CVqmyk6P "filesystem"
+[5]:https://www.linux.com/licenses/category/used-permission
+[6]:https://training.linuxfoundation.org/linux-courses/system-administration-training/introduction-to-linux
diff --git a/published/20180519 Python Debugging Tips.md b/published/20180519 Python Debugging Tips.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..4689377da4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20180519 Python Debugging Tips.md
@@ -0,0 +1,69 @@
+Python 调试技巧
+======
+
+当进行调试时,你有很多选择,但是很难给出一直有效的通用建议(除了“你试过关闭再打开么?”以外)。
+
+这里有一些我最喜欢的 Python 调试技巧。
+
+### 建立一个分支
+
+请相信我。即使你从来没有打算将修改提交回上游,你也会很乐意将你的实验被包含在它们自己的分支中。
+
+不说别的,它会使清理更容易!
+
+### 安装 pdb++
+
+认真地说,如果你使用命令行,它会让你的生活更轻松。
+
+pdb++ 所做的一切就是用更好的模块替换标准的 pdb 模块。以下是你在 `pip install pdbpp` 会看到的:
+
+ * 彩色提示!
+ * 制表符补全!(非常适合探索!)
+ * 支持切分!
+
+好的,也许最后一个是有点多余……但是非常认真地说,安装 pdb++ 非常值得。
+
+### 探索
+
+有时候最好的办法就是胡乱试试,然后看看会发生什么。在“明显”的位置放置一个断点并确保它被命中。在代码中加入 `print()` 和/或 `logging.debug()` 语句,并查看代码执行的位置。
+
+检查传递给你的函数的参数,检查库的版本(如果你已经非常绝望了)。
+
+### 一次只能改变一件事
+
+在你在探索了一下后,你将会对你可以做的事情有所了解。但在你开始摆弄代码之前,先退一步,考虑一下你可以改变什么,然后只改变一件事。
+
+做出改变后,然后测试一下,看看你是否接近解决问题。如果没有,请将它改回来,然后尝试其他方法。
+
+只更改一件事就可以让你知道什可以工作,哪些不工作。另外,一旦可以工作后,你的新提交将会小得多(因为将有更少的变化)。
+
+这几乎是科学过程中所做的事情:一次只更改一个变量。通过让自己看到并衡量一次更改的结果,你可以节省你的理智,并更快地找到解决方案。
+
+### 不要假设,提出问题
+
+偶尔一个开发人员(当然不是你咯!)会匆忙提交一些有问题的代码。当你去调试这段代码时,你需要停下来,并确保你明白它想要完成什么。
+
+不要做任何假设。仅仅因为代码在 `model.py` 文件中并不意味着它不会尝试渲染一些 HTML。
+
+同样,在做任何破坏性的事情之前,仔细检查你的所有外部关联。要删除一些配置数据?**请确保你没有连接到你的生产系统。**
+
+### 聪明,但不要聪明过头
+
+有时候我们编写的代码神奇般地奏效,不知道它是如何做的。
+
+当我们发布代码时,我们可能会觉得自己很聪明,但当代码崩溃时,我们往往会感到愚蠢,我们必须记住它是如何工作的,以便弄清楚它为什么不起作用。
+
+留意任何看起来过于复杂、冗长或极短的代码段。这些可能是隐藏复杂并导致错误的地方。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://pythondebugging.com/articles/python-debugging-tips
+
+作者:[PythonDebugging.com][a]
+选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
+译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:https://pythondebugging.com
diff --git a/published/20140110 Caffeinated 6.828- Lab 1- Booting a PC.md b/published/201806/20140110 Caffeinated 6.828- Lab 1- Booting a PC.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20140110 Caffeinated 6.828- Lab 1- Booting a PC.md
rename to published/201806/20140110 Caffeinated 6.828- Lab 1- Booting a PC.md
diff --git a/published/201806/20140119 10 Killer Tips To Speed Up Ubuntu Linux.md b/published/201806/20140119 10 Killer Tips To Speed Up Ubuntu Linux.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..d38be53dcb
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201806/20140119 10 Killer Tips To Speed Up Ubuntu Linux.md
@@ -0,0 +1,184 @@
+10 条加速 Ubuntu Linux 的杀手级技巧
+======
+
+> 一些实用的**加速 Ubuntu Linux 的技巧**。 这里的技巧对于大多数版本的 Ubuntu 是有效的,也可以应用于 Linux Mint 以及其他的基于 Ubuntu 的发行版。
+
+也许你经历过使用 Ubuntu 一段时间后系统开始运行缓慢的情况。 在这篇文章里,我们将看到几项调整以及使 Ubuntu 运行更快的窍门。
+
+在我们了解如何提升 Ubuntu 的总体系统表现之前,首先让我们思考为什么系统逐渐变慢。这个问题可能有很多原因。也许你有一台只有基础配置的简陋的电脑;也许你安装了一些在启动时即耗尽资源的应用。事实上原因无穷无尽。
+
+这里我列出一些能够帮助你稍微加速 Ubuntu 的小调整。也有一些你能够采用以获取一个更流畅、有所提升的系统表现的经验。你可以选择遵循全部或部分的建议。将各项调整一点一点的结合就能给你一个更流畅、更迅捷快速的 Ubuntu。
+
+### 使 Ubuntu 更快的技巧
+
+![Tips to speed up Ubuntu][1]
+
+我在一个较老版本的 Ubuntu 上使用了这些调整,但是我相信其他的 Ubuntu 版本以及其他的例如 Linux Mint、 Elementary OS Luna 等基 Ubuntu 的 Linux 版本也是同样适用的。
+
+#### 1、 减少默认的 grub 载入时间
+
+Grub 给你 10 秒的时间以让你在多系统启动项或恢复模式之间改变。对我而言,它是多余的。它也意味着你将不得不坐在电脑旁,敲下回车键以尽可能快的启动进入 Ubuntu。这花了一点时间,不是吗? 第一个技巧便是改变这个启动时间。如果你使用图形工具更舒适,阅读这篇文章来[使用 Grub 定制器改变 grub 时间以及启动顺序][2]。
+
+如果更倾向于命令行,你可以简单地使用以下的命令来打开 grub 配置:
+
+```
+sudo gedit /etc/default/grub &
+```
+
+并且将 `GRUB_TIMEOUT=10` 改为 `GRUB_TIMEOUT=2`。这将改变启动时间为 2 秒。最好不要将这里改为 0,因为这样你将会失去在操作系统及恢复选项之间切换的机会。一旦你更改了 grub 配置,使用以下命令来使更改生效:
+
+```
+sudo update-grub
+```
+
+#### 2、 管理开机启动的应用
+
+渐渐地你开始安装各种应用。 如果你是我们的老读者, 你也许从 [App of the week][3] 系列安装了许多应用。
+
+这些应用中的一些在每次开机时都会启动,当然资源运行这些应用也会陷入繁忙。结果:一台电脑因为每次启动时的持续时间而变得缓慢。进入 Unity Dash 寻找 “Startup Applications”:
+
+
+
+在这里,看看哪些应用在开机时被载入。现在考虑在你每次启动 Ubuntu 时是否有不需要启动的应用。尽管移除它们:
+
+
+
+但是要是你不想从启动里移除它们怎么办?举个例子,如果你安装了 [Ubuntu 最好的指示器程序][4]之一, 你将想要它们在每次开机时自动地启动。
+
+这里你所能做的就是延迟一些程序的启动时间。这样你将能够释放开机启动时的资源,并且一段时间后你的应用将被自动启动。在上一张图片里点击 Edit 并使用 sleep 选项来更改运行命令。
+
+例如,如果你想要延迟 Dropbox 指示器的运行,我们指定时间 20 秒,你只需要在已有的命令里像这样**加入一个命令**:
+
+```
+sleep 20;
+```
+
+所以,命令 `dropbox start -i` 变为 `sleep 20; drobox start -i` 。这意味着现在 Dropbox 将延迟 20 秒启动。你可以通过相似的方法来改变另一个开机启动应用的启动时间。
+
+
+
+#### 3、 安装 preload 来加速应用载入时间:
+
+Preload 是一个后台运行的守护进程,它分析用户行为和频繁运行的应用。打开终端,使用如下的命令来安装 preload:
+
+```
+sudo apt-get install preload
+```
+
+安装后,重启你的电脑就不用管它了。它将在后台工作。[阅读更多关于preload][5]
+
+#### 4、 选择最好的软件更新镜像
+
+验证你更新软件是否正在使用最好的镜像是很好的做法。Ubuntu 的软件仓库镜像跨过全球,使用离你最近的一个是相当明智的。随着从服务器获取包的时间减少,这将形成更快的系统更新。
+
+在 “Software & Updates->Ubuntu Software tab->Download From” 里选择 “Other” 紧接着点击 “Select Best Server”:
+
+
+
+它将运行测试来告知你那个是最好的镜像。正常地,最好的镜像已经被设置,但是我说过,验证它没什么坏处。并且,如果仓库缓存的最近的镜像没有频繁更新的话,这将引起获取更新时的一些延迟。这对于网速相对慢的人们是有用的。你可以使用这些技巧来[加速 Ubuntu 的 wifi][6]。
+
+#### 5、 为了更快的更新,使用 apt-fast 而不是 apt-get
+
+`apt-fast` 是 `apt-get` 的一个 shell 脚本包装器,通过从多连接同时下载包来提升更新及包下载速度。 如果你经常使用终端以及 `apt-get` 来安装和更新包,你也许会想要试一试 `apt-fast`。使用下面的命令来通过官方 PPA 安装 `apt-fast`:
+
+```
+sudo add-apt-repository ppa:apt-fast/stable
+sudo apt-get update
+sudo apt-get install apt-fast
+```
+
+#### 6、 从 apt-get 更新移除语言相关的 ign
+
+你曾经注意过 `sudo apt-get` 更新的输出吗?其中有三种行,`hit`、`ign` 和 `get`。 你可以在[这里][7]阅读它们的意义。如果你看到 IGN 行,你会发现它们中的大多数都与语言翻译有关。如果你使用所有的英文应用及包,你将完全不需要英文向英文的包数据库的翻译。
+
+如果你从 `apt-get` 制止语言相关的更新,它将略微地增加 `apt-get` 的更新速度。为了那样,打开如下的文件:
+
+```
+sudo gedit /etc/apt/apt.conf.d/00aptitude
+```
+
+然后在文件末尾添加如下行:
+
+```
+Acquire::Languages "none";
+```
+
+[![speed up apt get update in Ubuntu][8]][9]
+
+#### 7、 减少过热
+
+现在过热是电脑普遍的问题。一台过热的电脑运行相当缓慢。当你的 CPU 风扇转得像 [尤塞恩·博尔特][10] 一样快,打开一个程序将花费很长的时间。有两个工具你可以用来减少过热,使 Ubuntu 获得更好的系统表现,即 TLP 和 CPUFREQ。
+
+在终端里使用以下命令来安装 TLP:
+
+```
+sudo add-apt-repository ppa:linrunner/tlp
+sudo apt-get update
+sudo apt-get install tlp tlp-rdw
+sudo tlp start
+```
+
+安装完 TLP 后你不需要做任何事。它在后台工作。
+
+使用如下命令来安装 CPUFREQ 指示器:
+
+```
+sudo apt-get install indicator-cpufreq
+```
+
+重启你的电脑并使用 Powersave 模式:
+
+
+
+#### 8、 调整 LibreOffice 来使它更快
+
+如果你是频繁使用 office 产品的用户,那么你会想要稍微调整默认的 LibreOffice 使它更快。这里你将调整内存选项。打开 Open LibreOffice,进入 “Tools->Options”。在那里,从左边的侧栏选择“Memory”并启用 “Systray Quickstarter” 以及增加内存分配。
+
+
+
+你可以阅读更多关于[如何提速 LibreOffice][11] 的细节。
+
+#### 9、 使用轻量级的桌面环境 (如果你可以)
+
+如果你选择安装默认的 Unity of GNOME 桌面环境, 你也许会选择一个轻量级的桌面环境像 [Xfce][12] 或 [LXDE][13]。
+
+这些桌面环境使用更少的内存,消耗更少的 CPU。它们也自带轻量应用集来更深入地帮助更快地使用 Ubuntu。你可以参考这篇详细指南来学习[如何在 Ubuntu 上安装 Xfce][14]。
+
+当然,桌面也许没有 Unity 或 GNOME 看起来现代化。那是你必须做出的妥协。
+
+#### 10、 使用不同应用的更轻量可选
+
+这不仅仅是建议和喜好。一些默认的或者流行的应用是耗资源的且可能不适合低端的电脑。你能做的就是使用这些应用的一些替代品。例如,使用 [AppGrid][15] 而不是 Ubuntu 软件中心。使用 [Gdebi][16] 来安装包。使用 AbiWord 而不是 LibreOffice Writer 等。
+
+可以断定这些技巧的汇总使 Ubuntu 14.04,16.04 以及其他版本更快。我确定这些技巧会提供一个总体上更好的系统表现。
+
+对于加速 Ubuntu 你也有妙计吗?这些技巧也帮到你了吗?分享你的观点。 问题,建议总是受欢迎的。请在评论区里提出来。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://itsfoss.com/speed-up-ubuntu-1310/
+
+作者:[Abhishek Prakash][a]
+选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
+译者:[darsh8](https://github.com/darsh8)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]: https://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/
+[1]:https://itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/speed-up-ubuntu-featured-800x450.jpeg
+[2]:https://itsfoss.com/windows-default-os-dual-boot-ubuntu-1304-easy/ (Make Windows Default OS In Dual Boot With Ubuntu 13.04: The Easy Way)
+[3]:https://itsfoss.com/tag/app-of-the-week/
+[4]:https://itsfoss.com/best-indicator-applets-ubuntu/ (7 Best Indicator Applets For Ubuntu 13.10)
+[5]:https://itsfoss.com/improve-application-startup-speed-with-preload-in-ubuntu/ (Improve Application Startup Speed With Preload in Ubuntu)
+[6]:https://itsfoss.com/speed-up-slow-wifi-connection-ubuntu/ (Speed Up Slow WiFi Connection In Ubuntu 13.04)
+[7]:http://ubuntuforums.org/showthread.php?t=231300
+[8]:https://itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/01/ign_language-apt_get_update-e1510129903529.jpeg
+[9]:https://itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/01/ign_language-apt_get_update.jpeg
+[10]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Usain_Bolt
+[11]:https://itsfoss.com/speed-libre-office-simple-trick/ (Speed Up LibreOffice With This Simple Trick)
+[12]:https://xfce.org/
+[13]:https://lxde.org/
+[14]:https://itsfoss.com/install-xfce-desktop-xubuntu/
+[15]:https://itsfoss.com/app-grid-lighter-alternative-ubuntu-software-center/ (App Grid: Lighter Alternative Of Ubuntu Software Center)
+[16]:https://itsfoss.com/install-deb-files-easily-and-quickly-in-ubuntu-12-10-quick-tip/ (Install .deb Files Easily And Quickly In Ubuntu 12.10 [Quick Tip])
diff --git a/published/20140519 Epilogues Canaries and Buffer Overflows.md b/published/201806/20140519 Epilogues Canaries and Buffer Overflows.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20140519 Epilogues Canaries and Buffer Overflows.md
rename to published/201806/20140519 Epilogues Canaries and Buffer Overflows.md
diff --git a/published/20140523 Tail Calls Optimization and ES6.md b/published/201806/20140523 Tail Calls Optimization and ES6.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20140523 Tail Calls Optimization and ES6.md
rename to published/201806/20140523 Tail Calls Optimization and ES6.md
diff --git a/published/20141027 Closures Objects and the Fauna of the Heap.md b/published/201806/20141027 Closures Objects and the Fauna of the Heap.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20141027 Closures Objects and the Fauna of the Heap.md
rename to published/201806/20141027 Closures Objects and the Fauna of the Heap.md
diff --git a/published/20141217 The Best Linux Tools for Teachers and Students.md b/published/201806/20141217 The Best Linux Tools for Teachers and Students.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20141217 The Best Linux Tools for Teachers and Students.md
rename to published/201806/20141217 The Best Linux Tools for Teachers and Students.md
diff --git a/published/20160330 How to turn any syscall into an event Introducing eBPF Kernel probes.md b/published/201806/20160330 How to turn any syscall into an event Introducing eBPF Kernel probes.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20160330 How to turn any syscall into an event Introducing eBPF Kernel probes.md
rename to published/201806/20160330 How to turn any syscall into an event Introducing eBPF Kernel probes.md
diff --git a/published/20160526 How To Downgrade A Package In Arch Linux.md b/published/201806/20160526 How To Downgrade A Package In Arch Linux.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20160526 How To Downgrade A Package In Arch Linux.md
rename to published/201806/20160526 How To Downgrade A Package In Arch Linux.md
diff --git a/published/20171002 High Dynamic Range Imaging using OpenCV Cpp python.md b/published/201806/20171002 High Dynamic Range Imaging using OpenCV Cpp python.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20171002 High Dynamic Range Imaging using OpenCV Cpp python.md
rename to published/201806/20171002 High Dynamic Range Imaging using OpenCV Cpp python.md
diff --git a/published/20171006 How To Convert DEB Packages Into Arch Linux Packages.md b/published/201806/20171006 How To Convert DEB Packages Into Arch Linux Packages.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20171006 How To Convert DEB Packages Into Arch Linux Packages.md
rename to published/201806/20171006 How To Convert DEB Packages Into Arch Linux Packages.md
diff --git a/published/20171007 A Large-Scale Study of Programming Languages and Code Quality in GitHub.md b/published/201806/20171007 A Large-Scale Study of Programming Languages and Code Quality in GitHub.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20171007 A Large-Scale Study of Programming Languages and Code Quality in GitHub.md
rename to published/201806/20171007 A Large-Scale Study of Programming Languages and Code Quality in GitHub.md
diff --git a/published/20171011 LEAST PRIVILEGE CONTAINER ORCHESTRATION.md b/published/201806/20171011 LEAST PRIVILEGE CONTAINER ORCHESTRATION.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20171011 LEAST PRIVILEGE CONTAINER ORCHESTRATION.md
rename to published/201806/20171011 LEAST PRIVILEGE CONTAINER ORCHESTRATION.md
diff --git a/published/20171103 3 ways robotics affects the CIO role.md b/published/201806/20171103 3 ways robotics affects the CIO role.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20171103 3 ways robotics affects the CIO role.md
rename to published/201806/20171103 3 ways robotics affects the CIO role.md
diff --git a/published/20171208 Overcoming challenges when building great global communities.md b/published/201806/20171208 Overcoming challenges when building great global communities.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20171208 Overcoming challenges when building great global communities.md
rename to published/201806/20171208 Overcoming challenges when building great global communities.md
diff --git a/published/20171212 Asynchronous decision-making- Helping remote teams succeed.md b/published/201806/20171212 Asynchronous decision-making- Helping remote teams succeed.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20171212 Asynchronous decision-making- Helping remote teams succeed.md
rename to published/201806/20171212 Asynchronous decision-making- Helping remote teams succeed.md
diff --git a/published/20180103 5 ways open source can strengthen your job search.md b/published/201806/20180103 5 ways open source can strengthen your job search.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20180103 5 ways open source can strengthen your job search.md
rename to published/201806/20180103 5 ways open source can strengthen your job search.md
diff --git a/published/20180108 How to Install Docker CE on Your Desktop.md b/published/201806/20180108 How to Install Docker CE on Your Desktop.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20180108 How to Install Docker CE on Your Desktop.md
rename to published/201806/20180108 How to Install Docker CE on Your Desktop.md
diff --git a/published/20180131 A history of low-level Linux container runtimes.md b/published/201806/20180131 A history of low-level Linux container runtimes.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20180131 A history of low-level Linux container runtimes.md
rename to published/201806/20180131 A history of low-level Linux container runtimes.md
diff --git a/published/20180201 IT automation- How to make the case.md b/published/201806/20180201 IT automation- How to make the case.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20180201 IT automation- How to make the case.md
rename to published/201806/20180201 IT automation- How to make the case.md
diff --git a/published/20180206 Why Linux is better than Windows or macOS for security.md b/published/201806/20180206 Why Linux is better than Windows or macOS for security.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20180206 Why Linux is better than Windows or macOS for security.md
rename to published/201806/20180206 Why Linux is better than Windows or macOS for security.md
diff --git a/published/20180207 How DevOps helps deliver cool apps to users.md b/published/201806/20180207 How DevOps helps deliver cool apps to users.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20180207 How DevOps helps deliver cool apps to users.md
rename to published/201806/20180207 How DevOps helps deliver cool apps to users.md
diff --git a/published/20180208 Token ERC Comparison for Fungible Tokens - Blockchainers.md b/published/201806/20180208 Token ERC Comparison for Fungible Tokens - Blockchainers.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20180208 Token ERC Comparison for Fungible Tokens - Blockchainers.md
rename to published/201806/20180208 Token ERC Comparison for Fungible Tokens - Blockchainers.md
diff --git a/published/20180219 Learn to code with Thonny - a Python IDE for beginners.md b/published/201806/20180219 Learn to code with Thonny - a Python IDE for beginners.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20180219 Learn to code with Thonny - a Python IDE for beginners.md
rename to published/201806/20180219 Learn to code with Thonny - a Python IDE for beginners.md
diff --git a/published/20180220 How to enable repository using subscription-manager in RHEL.md b/published/201806/20180220 How to enable repository using subscription-manager in RHEL.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20180220 How to enable repository using subscription-manager in RHEL.md
rename to published/201806/20180220 How to enable repository using subscription-manager in RHEL.md
diff --git a/published/201806/20180224 How To Run A Command For A Specific Time In Linux.md b/published/201806/20180224 How To Run A Command For A Specific Time In Linux.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..bb25482902
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201806/20180224 How To Run A Command For A Specific Time In Linux.md
@@ -0,0 +1,113 @@
+如何在 Linux 中的特定时间运行命令
+======
+
+
+
+有一天,我使用 `rsync` 将大文件传输到局域网上的另一个系统。由于它是非常大的文件,大约需要 20 分钟才能完成。我不想再等了,我也不想按 `CTRL+C` 来终止这个过程。我只是想知道在类 Unix 操作系统中是否有简单的方法可以在特定的时间运行一个命令,并且一旦超时就自动杀死它 —— 因此有了这篇文章。请继续阅读。
+
+### 在 Linux 中在特定时间运行命令
+
+我们可以用两种方法做到这一点。
+
+#### 方法 1 - 使用 timeout 命令
+
+最常用的方法是使用 `timeout` 命令。对于那些不知道的人来说,`timeout` 命令会有效地限制一个进程的绝对执行时间。`timeout` 命令是 GNU coreutils 包的一部分,因此它预装在所有 GNU/Linux 系统中。
+
+假设你只想运行一个命令 5 秒钟,然后杀死它。为此,我们使用:
+
+```
+$ timeout
+```
+
+例如,以下命令将在 10 秒后终止。
+
+```
+$ timeout 10s tail -f /var/log/pacman.log
+```
+
+![][2]
+
+你也可以不用在秒数后加后缀 `s`。以下命令与上面的相同。
+
+```
+$ timeout 10 tail -f /var/log/pacman.log
+```
+
+其他可用的后缀有:
+
+ * `m` 代表分钟。
+ * `h` 代表小时。
+ * `d` 代表天。
+
+
+如果你运行这个 `tail -f /var/log/pacman.log` 命令,它将继续运行,直到你按 `CTRL+C` 手动结束它。但是,如果你使用 `timeout` 命令运行它,它将在给定的时间间隔后自动终止。如果该命令在超时后仍在运行,则可以发送 `kill` 信号,如下所示。
+
+```
+$ timeout -k 20 10 tail -f /var/log/pacman.log
+```
+
+在这种情况下,如果 `tail` 命令在 10 秒后仍然运行,`timeout` 命令将在 20 秒后发送一个 kill 信号并结束。
+
+有关更多详细信息,请查看手册页。
+
+```
+$ man timeout
+```
+
+有时,某个特定程序可能需要很长时间才能完成并最终冻结你的系统。在这种情况下,你可以使用此技巧在特定时间后自动结束该进程。
+
+另外,可以考虑使用 `cpulimit`,一个简单的限制进程的 CPU 使用率的程序。有关更多详细信息,请查看下面的链接。
+
+- [如何在 Linux 中限制一个进程的使用的 CPU][8]
+
+#### 方法 2 - 使用 timelimit 程序
+
+`timelimit` 使用提供的参数执行给定的命令,并在给定的时间后使用给定的信号终止进程。首先,它会发送警告信号,然后在超时后发送 kill 信号。
+
+与 `timeout` 不同,`timelimit` 有更多选项。你可以传递参数数量,如 `killsig`、`warnsig`、`killtime`、`warntime` 等。它存在于基于 Debian 的系统的默认仓库中。所以,你可以使用命令来安装它:
+
+```
+$ sudo apt-get install timelimit
+```
+
+对于基于 Arch 的系统,它在 AUR 中存在。因此,你可以使用任何 AUR 助手进行安装,例如 [Pacaur][3]、[Packer][4]、[Yay][5]、[Yaourt][6] 等。
+
+对于其他发行版,请[在这里][7]下载源码并手动安装。安装 `timelimit` 后,运行下面的命令执行一段特定的时间,例如 10 秒钟:
+
+```
+$ timelimit -t10 tail -f /var/log/pacman.log
+```
+
+如果不带任何参数运行 `timelimit`,它将使用默认值:`warntime=3600` 秒、`warnsig=15` 秒、`killtime=120` 秒、`killsig=9`。有关更多详细信息,请参阅本指南最后给出的手册页和项目网站。
+
+```
+$ man timelimit
+```
+
+今天就是这些。我希望对你有用。还有更好的东西。敬请关注!
+
+干杯!
+
+### 资源
+
+- [timelimit 网站][9]
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://www.ostechnix.com/run-command-specific-time-linux/
+
+作者:[SK][a]
+译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:https://www.ostechnix.com/author/sk/
+[2]:http://www.ostechnix.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/02/Timeout.gif
+[3]:https://www.ostechnix.com/install-pacaur-arch-linux/
+[4]:https://www.ostechnix.com/install-packer-arch-linux-2/
+[5]:https://www.ostechnix.com/yay-found-yet-another-reliable-aur-helper/
+[6]:https://www.ostechnix.com/install-yaourt-arch-linux/
+[7]:http://devel.ringlet.net/sysutils/timelimit/#download
+[8]:https://www.ostechnix.com/how-to-limit-cpu-usage-of-a-process-in-linux/
+[9]:http://devel.ringlet.net/sysutils/timelimit/
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/published/20180301 Best Websites For Programmers.md b/published/201806/20180301 Best Websites For Programmers.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20180301 Best Websites For Programmers.md
rename to published/201806/20180301 Best Websites For Programmers.md
diff --git a/published/20180308 Dynamic Linux Routing with Quagga.md b/published/201806/20180308 Dynamic Linux Routing with Quagga.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20180308 Dynamic Linux Routing with Quagga.md
rename to published/201806/20180308 Dynamic Linux Routing with Quagga.md
diff --git a/published/20180322 Simple Load Balancing with DNS on Linux.md b/published/201806/20180322 Simple Load Balancing with DNS on Linux.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20180322 Simple Load Balancing with DNS on Linux.md
rename to published/201806/20180322 Simple Load Balancing with DNS on Linux.md
diff --git a/published/20180323 Top Linux tools for writers.md b/published/201806/20180323 Top Linux tools for writers.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20180323 Top Linux tools for writers.md
rename to published/201806/20180323 Top Linux tools for writers.md
diff --git a/published/20180326 How To Archive Files And Directories In Linux.md b/published/201806/20180326 How To Archive Files And Directories In Linux.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20180326 How To Archive Files And Directories In Linux.md
rename to published/201806/20180326 How To Archive Files And Directories In Linux.md
diff --git a/published/20180327 How to build a digital pinhole camera with a Raspberry Pi.md b/published/201806/20180327 How to build a digital pinhole camera with a Raspberry Pi.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20180327 How to build a digital pinhole camera with a Raspberry Pi.md
rename to published/201806/20180327 How to build a digital pinhole camera with a Raspberry Pi.md
diff --git a/published/20180328 College student reflects on getting started in open source.md b/published/201806/20180328 College student reflects on getting started in open source.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20180328 College student reflects on getting started in open source.md
rename to published/201806/20180328 College student reflects on getting started in open source.md
diff --git a/published/20180331 How to build a plotter with Arduino.md b/published/201806/20180331 How to build a plotter with Arduino.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20180331 How to build a plotter with Arduino.md
rename to published/201806/20180331 How to build a plotter with Arduino.md
diff --git a/published/20180404 Containerization, Atomic Distributions, and the Future of Linux.md b/published/201806/20180404 Containerization, Atomic Distributions, and the Future of Linux.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20180404 Containerization, Atomic Distributions, and the Future of Linux.md
rename to published/201806/20180404 Containerization, Atomic Distributions, and the Future of Linux.md
diff --git a/published/20180406 How To Register The Oracle Linux System With The Unbreakable Linux Network (ULN).md b/published/201806/20180406 How To Register The Oracle Linux System With The Unbreakable Linux Network (ULN).md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20180406 How To Register The Oracle Linux System With The Unbreakable Linux Network (ULN).md
rename to published/201806/20180406 How To Register The Oracle Linux System With The Unbreakable Linux Network (ULN).md
diff --git a/published/20180410 Top 9 open source ERP systems to consider - Opensource.com.md b/published/201806/20180410 Top 9 open source ERP systems to consider - Opensource.com.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20180410 Top 9 open source ERP systems to consider - Opensource.com.md
rename to published/201806/20180410 Top 9 open source ERP systems to consider - Opensource.com.md
diff --git a/published/20180415 Some Common Concurrent Programming Mistakes.md b/published/201806/20180415 Some Common Concurrent Programming Mistakes.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20180415 Some Common Concurrent Programming Mistakes.md
rename to published/201806/20180415 Some Common Concurrent Programming Mistakes.md
diff --git a/published/20180416 Running Jenkins builds in containers.md b/published/201806/20180416 Running Jenkins builds in containers.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20180416 Running Jenkins builds in containers.md
rename to published/201806/20180416 Running Jenkins builds in containers.md
diff --git a/published/20180418 Getting started with Anaconda Python for data science.md b/published/201806/20180418 Getting started with Anaconda Python for data science.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20180418 Getting started with Anaconda Python for data science.md
rename to published/201806/20180418 Getting started with Anaconda Python for data science.md
diff --git a/published/20180418 Passwordless Auth Server.md b/published/201806/20180418 Passwordless Auth Server.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20180418 Passwordless Auth Server.md
rename to published/201806/20180418 Passwordless Auth Server.md
diff --git a/published/20180424 How to share files between Linux and Windows.md b/published/201806/20180424 How to share files between Linux and Windows.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20180424 How to share files between Linux and Windows.md
rename to published/201806/20180424 How to share files between Linux and Windows.md
diff --git a/published/20180425 Configuring local storage in Linux with Stratis.md b/published/201806/20180425 Configuring local storage in Linux with Stratis.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20180425 Configuring local storage in Linux with Stratis.md
rename to published/201806/20180425 Configuring local storage in Linux with Stratis.md
diff --git a/published/20180425 How will the GDPR impact open source communities.md b/published/201806/20180425 How will the GDPR impact open source communities.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20180425 How will the GDPR impact open source communities.md
rename to published/201806/20180425 How will the GDPR impact open source communities.md
diff --git a/published/20180425 Using machine learning to color cartoons.md b/published/201806/20180425 Using machine learning to color cartoons.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20180425 Using machine learning to color cartoons.md
rename to published/201806/20180425 Using machine learning to color cartoons.md
diff --git a/published/20180426 Continuous Profiling of Go programs.md b/published/201806/20180426 Continuous Profiling of Go programs.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20180426 Continuous Profiling of Go programs.md
rename to published/201806/20180426 Continuous Profiling of Go programs.md
diff --git a/published/20180426 Get started with Pidgin- An open source replacement for Skype for Business.md b/published/201806/20180426 Get started with Pidgin- An open source replacement for Skype for Business.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20180426 Get started with Pidgin- An open source replacement for Skype for Business.md
rename to published/201806/20180426 Get started with Pidgin- An open source replacement for Skype for Business.md
diff --git a/published/20180426 What Stratis learned from ZFS, Btrfs, and Linux Volume Manager - Opensource.com.md b/published/201806/20180426 What Stratis learned from ZFS, Btrfs, and Linux Volume Manager - Opensource.com.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20180426 What Stratis learned from ZFS, Btrfs, and Linux Volume Manager - Opensource.com.md
rename to published/201806/20180426 What Stratis learned from ZFS, Btrfs, and Linux Volume Manager - Opensource.com.md
diff --git a/published/20180427 3 Python template libraries compared.md b/published/201806/20180427 3 Python template libraries compared.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20180427 3 Python template libraries compared.md
rename to published/201806/20180427 3 Python template libraries compared.md
diff --git a/published/20180502 Writing Systemd Services for Fun and Profit.md b/published/201806/20180502 Writing Systemd Services for Fun and Profit.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20180502 Writing Systemd Services for Fun and Profit.md
rename to published/201806/20180502 Writing Systemd Services for Fun and Profit.md
diff --git a/published/20180507 A reading list for Linux and open source fans.md b/published/201806/20180507 A reading list for Linux and open source fans.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20180507 A reading list for Linux and open source fans.md
rename to published/201806/20180507 A reading list for Linux and open source fans.md
diff --git a/published/20180507 Systemd Services- Beyond Starting and Stopping.md b/published/201806/20180507 Systemd Services- Beyond Starting and Stopping.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20180507 Systemd Services- Beyond Starting and Stopping.md
rename to published/201806/20180507 Systemd Services- Beyond Starting and Stopping.md
diff --git a/published/20180508 Orbital Apps - A New Generation Of Linux applications.md b/published/201806/20180508 Orbital Apps - A New Generation Of Linux applications.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20180508 Orbital Apps - A New Generation Of Linux applications.md
rename to published/201806/20180508 Orbital Apps - A New Generation Of Linux applications.md
diff --git a/published/20180509 How to kill a process or stop a program in Linux.md b/published/201806/20180509 How to kill a process or stop a program in Linux.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20180509 How to kill a process or stop a program in Linux.md
rename to published/201806/20180509 How to kill a process or stop a program in Linux.md
diff --git a/published/20180510 Analyzing Ansible runs using ARA.md b/published/201806/20180510 Analyzing Ansible runs using ARA.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20180510 Analyzing Ansible runs using ARA.md
rename to published/201806/20180510 Analyzing Ansible runs using ARA.md
diff --git a/published/20180510 Creating small containers with Buildah.md b/published/201806/20180510 Creating small containers with Buildah.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20180510 Creating small containers with Buildah.md
rename to published/201806/20180510 Creating small containers with Buildah.md
diff --git a/published/20180510 Get more done at the Linux command line with GNU Parallel.md b/published/201806/20180510 Get more done at the Linux command line with GNU Parallel.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20180510 Get more done at the Linux command line with GNU Parallel.md
rename to published/201806/20180510 Get more done at the Linux command line with GNU Parallel.md
diff --git a/published/20180511 3 useful things you can do with the IP tool in Linux.md b/published/201806/20180511 3 useful things you can do with the IP tool in Linux.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20180511 3 useful things you can do with the IP tool in Linux.md
rename to published/201806/20180511 3 useful things you can do with the IP tool in Linux.md
diff --git a/published/20180514 A CLI Game To Learn Vim Commands.md b/published/201806/20180514 A CLI Game To Learn Vim Commands.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20180514 A CLI Game To Learn Vim Commands.md
rename to published/201806/20180514 A CLI Game To Learn Vim Commands.md
diff --git a/published/20180515 Protect your Fedora system against this DHCP flaw.md b/published/201806/20180515 Protect your Fedora system against this DHCP flaw.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20180515 Protect your Fedora system against this DHCP flaw.md
rename to published/201806/20180515 Protect your Fedora system against this DHCP flaw.md
diff --git a/published/20180516 A guide to Git branching.md b/published/201806/20180516 A guide to Git branching.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20180516 A guide to Git branching.md
rename to published/201806/20180516 A guide to Git branching.md
diff --git a/translated/tech/20180521 An introduction to cryptography and public key infrastructure.md b/published/201806/20180521 An introduction to cryptography and public key infrastructure.md
similarity index 81%
rename from translated/tech/20180521 An introduction to cryptography and public key infrastructure.md
rename to published/201806/20180521 An introduction to cryptography and public key infrastructure.md
index ede14e282e..b15e629991 100644
--- a/translated/tech/20180521 An introduction to cryptography and public key infrastructure.md
+++ b/published/201806/20180521 An introduction to cryptography and public key infrastructure.md
@@ -1,16 +1,19 @@
密码学及公钥基础设施入门
======
+
+> 学习密码学背后的基本概念,主要是保密性、完整性和身份认证。
+

-安全通信正快速成为当今互联网的规范。从 2018 年 7 月起,Google Chrome 将对**全部**使用 HTTP 传输(而不是 HTTPS 传输)的站点[开始显示“不安全”警告][1]。虽然密码学已经逐渐变广为人知,但其本身并没有变得更容易理解。[Let's Encrypt][3] 设计并实现了一套令人惊叹的解决方案,可以提供免费安全证书和周期性续签;但如果不了解底层概念和缺陷,你也不过是加入了类似”[船货崇拜][4]“的技术崇拜的程序员大军。
+安全通信正快速成为当今互联网的规范。从 2018 年 7 月起,Google Chrome 将对**全部**使用 HTTP 传输(而不是 HTTPS 传输)的站点[开始显示“不安全”警告][1]。虽然密码学已经逐渐变广为人知,但其本身并没有变得更容易理解。[Let's Encrypt][3] 设计并实现了一套令人惊叹的解决方案,可以提供免费安全证书和周期性续签;但如果不了解底层概念和缺陷,你也不过是加入了类似“[货物崇拜][4]”的技术崇拜的程序员大军。
### 安全通信的特性
密码学最直观明显的目标是保密性:消息传输过程中不会被窥探内容。为了保密性,我们对消息进行加密:对于给定消息,我们结合一个密钥生成一个无意义的乱码,只有通过相同的密钥逆转加密过程(即解密过程)才能将其转换为可读的消息。假设我们有两个朋友 [Alice 和 Bob][5],以及他们的八卦邻居 Eve。Alice 加密类似 "Eve 很讨厌" 的消息,将其发送给 Bob,期间不用担心 Eve 会窥探到这条消息的内容。
-对于真正的安全通信,保密性是不够的。假如 Eve 收集了足够多 Alice 和 Bob 之间的消息,发现单词 "Eve" 被加密为 "Xyzzy"。除此之外,Eve 还知道 Alice 和 Bob 正在准备一个派对,Alice 会将访客名单发送给 Bob。如果 Eve 拦截了消息并将 "Xyzzy" 加到访客列表的末尾,那么她已经成功的破坏了这个派对。因此,Alice 和 Bob 需要他们之间的通信可以提供完整性:消息应该不会被篡改。
+对于真正的安全通信,保密性是不够的。假如 Eve 收集了足够多 Alice 和 Bob 之间的消息,发现单词 “Eve” 被加密为 "Xyzzy"。除此之外,Eve 还知道 Alice 和 Bob 正在准备一个派对,Alice 会将访客名单发送给 Bob。如果 Eve 拦截了消息并将 “Xyzzy” 加到访客列表的末尾,那么她已经成功的破坏了这个派对。因此,Alice 和 Bob 需要他们之间的通信可以提供完整性:消息应该不会被篡改。
-而且我们还有一个问题有待解决。假如 Eve 观察到 Bob 打开了标记为”来自 Alice“的信封,信封中包含一条来自 Alice 的消息”再买一加仑冰淇淋“。Eve 看到 Bob 外出,回家时带着冰淇淋,这样虽然 Eve 并不知道消息的完整内容,但她对消息有了大致的了解。Bob 将上述消息丢弃,但 Eve 找出了它并在下一周中的每一天都向 Bob 的邮箱中投递一封标记为”来自 Alice“的信封,内容拷贝自之前 Bob 丢弃的那封信。这样到了派对的时候,冰淇淋严重超量;派对当晚结束后,Bob 分发剩余的冰淇淋,Eve 带着免费的冰淇淋回到家。消息是加密的,完整性也没问题,但 Bob 被误导了,没有认出发信人的真实身份。身份认证这个特性用于保证你正在通信的人的确是其声称的那样。
+而且我们还有一个问题有待解决。假如 Eve 观察到 Bob 打开了标记为“来自 Alice”的信封,信封中包含一条来自 Alice 的消息“再买一加仑冰淇淋”。Eve 看到 Bob 外出,回家时带着冰淇淋,这样虽然 Eve 并不知道消息的完整内容,但她对消息有了大致的了解。Bob 将上述消息丢弃,但 Eve 找出了它并在下一周中的每一天都向 Bob 的邮箱中投递一封标记为“来自 Alice”的信封,内容拷贝自之前 Bob 丢弃的那封信。这样到了派对的时候,冰淇淋严重超量;派对当晚结束后,Bob 分发剩余的冰淇淋,Eve 带着免费的冰淇淋回到家。消息是加密的,完整性也没问题,但 Bob 被误导了,没有认出发信人的真实身份。身份认证这个特性用于保证你正在通信的人的确是其声称的那样。
信息安全还有[其它特性][6],但保密性、完整性和身份验证是你必须了解的三大特性。
@@ -20,17 +23,17 @@
(LCTT 译注:cipher 一般被翻译为密码,但其具体表达的意思是加密算法,这里采用加密算法的翻译)
-加密算法使用密钥加密明文。考虑到希望能够解密密文,我们用到的加密算法也必须是可逆的。作为简单示例,我们可以使用 [XOR][7]。该算子可逆,而且逆算子就是本身(P ^ K = C; C ^ K = P),故可同时用于加密和解密。该算子的平凡应用可以是一次性密码本,但一般而言并不[可行][9]。但可以将 XOR 与一个基于单个密钥生成任意随机数据流的函数结合起来。现代加密算法 AES 和 Chacha20 就是这么设计的。
+加密算法使用密钥加密明文。考虑到希望能够解密密文,我们用到的加密算法也必须是可逆的。作为简单示例,我们可以使用 [XOR][7]。该算子可逆,而且逆算子就是本身(`P ^ K = C; C ^ K = P`),故可同时用于加密和解密。该算子的平凡应用可以是一次性密码本,不过一般而言并不[可行][9]。但可以将 XOR 与一个基于单个密钥生成任意随机数据流的函数结合起来。现代加密算法 AES 和 Chacha20 就是这么设计的。
-我们把加密和解密使用同一个密钥的加密算法称为对称加密算法。对称加密算法分为流加密算法和分组加密算法两类。流加密算法依次对明文中的每个比特或字节进行加密。例如,我们上面提到的 XOR 加密算法就是一个流加密算法。流加密算法适用于明文长度未知的情形,例如数据从管道或 socket 传入。[RC4][10] 是最为人知的流加密算法,但在多种不同的攻击面前比较脆弱,以至于最新版本 (1.3)的 TLS ("HTTPS" 中的 "S")已经不再支持该加密算法。[Efforts][11] 正着手创建新的加密算法,候选算法 [ChaCha20][12] 已经被 TLS 支持。
+我们把加密和解密使用同一个密钥的加密算法称为对称加密算法。对称加密算法分为流加密算法和分组加密算法两类。流加密算法依次对明文中的每个比特或字节进行加密。例如,我们上面提到的 XOR 加密算法就是一个流加密算法。流加密算法适用于明文长度未知的情形,例如数据从管道或 socket 传入。[RC4][10] 是最为人知的流加密算法,但在多种不同的攻击面前比较脆弱,以至于最新版本 (1.3)的 TLS (“HTTPS” 中的 “S”)已经不再支持该加密算法。[Efforts][11] 正着手创建新的加密算法,候选算法 [ChaCha20][12] 已经被 TLS 支持。
-分组加密算法对固定长度的分组,使用固定长度的密钥加密。在分组加密算法领域,排行第一的是 [先进加密标准][13],使用的分组长度为 128 比特。分组包含的数据并不多,因而分组加密算法包含一个[工作模式][14],用于描述如何对任意长度的明文执行分组加密。最简单的工作模式是 [电子密码本][15],将明文按分组大小划分成多个分组(在必要情况下,填充最后一个分组),使用密钥独立的加密各个分组。
+分组加密算法对固定长度的分组,使用固定长度的密钥加密。在分组加密算法领域,排行第一的是 [先进加密标准][13](AES),使用的分组长度为 128 比特。分组包含的数据并不多,因而分组加密算法包含一个[工作模式][14],用于描述如何对任意长度的明文执行分组加密。最简单的工作模式是 [电子密码本][15](ECB),将明文按分组大小划分成多个分组(在必要情况下,填充最后一个分组),使用密钥独立的加密各个分组。

-这里我们留意到一个问题:如果相同的分组在明文中出现多次(例如互联网流量中的 "GET / HTTP/1.1" 词组),由于我们使用相同的密钥加密分组,我们会得到相同的加密结果。我们的安全通信中会出现一种模式规律,容易受到攻击。
+这里我们留意到一个问题:如果相同的分组在明文中出现多次(例如互联网流量中的 `GET / HTTP/1.1` 词组),由于我们使用相同的密钥加密分组,我们会得到相同的加密结果。我们的安全通信中会出现一种模式规律,容易受到攻击。
-因此还有很多高级的工作模式,例如 [密码分组链接][16],其中每个分组的明文在加密前会与前一个分组的密文进行 XOR 操作,而第一个分组的明文与一个随机数构成的初始化向量进行 XOR 操作。还有其它一些工作模式,在安全性和执行速度方面各有优缺点。甚至还有 Counter (CTR) 这种工作模式,可以将分组加密算法转换为流加密算法。
+因此还有很多高级的工作模式,例如 [密码分组链接][16](CBC),其中每个分组的明文在加密前会与前一个分组的密文进行 XOR 操作,而第一个分组的明文与一个随机数构成的初始化向量进行 XOR 操作。还有其它一些工作模式,在安全性和执行速度方面各有优缺点。甚至还有 Counter (CTR) 这种工作模式,可以将分组加密算法转换为流加密算法。
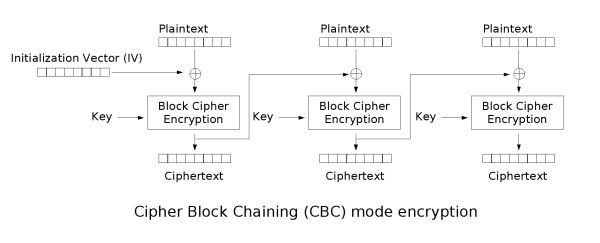
@@ -54,7 +57,7 @@
如果我们同时发送消息及其摘要,接收者可以使用相同的哈希函数独立计算摘要。如果两个摘要相同,可以认为消息没有被篡改。考虑到 [SHA-1][25] 已经变得[有些过时][26],目前最流行的密码散列函数是 [SHA-256][24]。
-散列函数看起来不错,但如果有人可以同时篡改消息及其摘要,那么消息发送仍然是不安全的。我们需要将哈希与加密算法结合起来。在对称加密算法领域,我们有消息认证码技术。MACs 有多种形式,但哈希消息认证码 这类是基于哈希的。[HMAC][27] 使用哈希函数 H 处理密钥 K、消息 M,公式为 H(K + H(K + M)),其中 "+" 代表连接。公式的独特之处并不在本文讨论范围内,大致来说与保护 HMAC 自身的完整性有关。发送加密消息的同时也发送 MAC。Eve 可以任意篡改消息,但一旦 Bob 独立计算 MAC 并与接收到的 MAC 做比较,就会发现消息已经被篡改。
+散列函数看起来不错,但如果有人可以同时篡改消息及其摘要,那么消息发送仍然是不安全的。我们需要将哈希与加密算法结合起来。在对称加密算法领域,我们有消息认证码(MAC)技术。MAC 有多种形式,但哈希消息认证码(HMAC) 这类是基于哈希的。[HMAC][27] 使用哈希函数 H 处理密钥 K、消息 M,公式为 `H(K + H(K + M))`,其中 `+` 代表连接。公式的独特之处并不在本文讨论范围内,大致来说与保护 HMAC 自身的完整性有关。发送加密消息的同时也发送 MAC。Eve 可以任意篡改消息,但一旦 Bob 独立计算 MAC 并与接收到的 MAC 做比较,就会发现消息已经被篡改。
在非对称加密算法领域,我们有数字签名技术。如果使用 RSA,使用公钥加密的内容只能通过私钥解密,反过来也是如此;这种机制可用于创建一种签名。如果只有我持有私钥并用其加密文档,那么只有我的公钥可以用于解密,那么大家潜在的承认文档是我写的:这是一种身份验证。事实上,我们无需加密整个文档。如果生成文档的摘要,只要对这个指纹加密即可。对摘要签名比对整个文档签名要快得多,而且可以解决非对称加密存在的消息长度限制问题。接收者解密出摘要信息,独立计算消息的摘要并进行比对,可以确保消息的完整性。对于不同的非对称加密算法,数字签名的方法也各不相同;但核心都是使用公钥来检验已有签名。
@@ -64,7 +67,7 @@
密码学的世界博大精深,我希望这篇文章能让你对密码学的核心目标及其组件有一个大致的了解。这些概念为你打下坚实的基础,让你可以继续深入学习。
-感谢 Hubert Kario,Florian Weimer 和 Mike Bursell 在本文写作过程中提供的帮助。
+感谢 Hubert Kario、Florian Weimer 和 Mike Bursell 在本文写作过程中提供的帮助。
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
@@ -73,7 +76,7 @@ via: https://opensource.com/article/18/5/cryptography-pki
作者:[Alex Wood][a]
选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
译者:[pinewall](https://github.com/pinewall)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/published/20180521 Audacity quick tip- quickly remove background noise.md b/published/201806/20180521 Audacity quick tip- quickly remove background noise.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20180521 Audacity quick tip- quickly remove background noise.md
rename to published/201806/20180521 Audacity quick tip- quickly remove background noise.md
diff --git a/published/20180521 How to Install and Configure KVM on Ubuntu 18.04 LTS Server.md b/published/201806/20180521 How to Install and Configure KVM on Ubuntu 18.04 LTS Server.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20180521 How to Install and Configure KVM on Ubuntu 18.04 LTS Server.md
rename to published/201806/20180521 How to Install and Configure KVM on Ubuntu 18.04 LTS Server.md
diff --git a/published/20180521 Linux vs. Unix- What-s the difference.md b/published/201806/20180521 Linux vs. Unix- What-s the difference.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20180521 Linux vs. Unix- What-s the difference.md
rename to published/201806/20180521 Linux vs. Unix- What-s the difference.md
diff --git a/published/20180522 Using Stratis to manage Linux storage from the command line.md b/published/201806/20180522 Using Stratis to manage Linux storage from the command line.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20180522 Using Stratis to manage Linux storage from the command line.md
rename to published/201806/20180522 Using Stratis to manage Linux storage from the command line.md
diff --git a/published/20180523 Set up zsh on your Fedora system.md b/published/201806/20180523 Set up zsh on your Fedora system.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20180523 Set up zsh on your Fedora system.md
rename to published/201806/20180523 Set up zsh on your Fedora system.md
diff --git a/published/20180524 4 Markdown-powered slide generators.md b/published/201806/20180524 4 Markdown-powered slide generators.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20180524 4 Markdown-powered slide generators.md
rename to published/201806/20180524 4 Markdown-powered slide generators.md
diff --git a/published/20180525 15 books for kids who (you want to) love Linux and open source.md b/published/201806/20180525 15 books for kids who (you want to) love Linux and open source.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20180525 15 books for kids who (you want to) love Linux and open source.md
rename to published/201806/20180525 15 books for kids who (you want to) love Linux and open source.md
diff --git a/published/20180525 A Bittorrent Filesystem Based On FUSE.md b/published/201806/20180525 A Bittorrent Filesystem Based On FUSE.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20180525 A Bittorrent Filesystem Based On FUSE.md
rename to published/201806/20180525 A Bittorrent Filesystem Based On FUSE.md
diff --git a/translated/tech/20180525 How insecure is your router.md b/published/201806/20180525 How insecure is your router.md
similarity index 57%
rename from translated/tech/20180525 How insecure is your router.md
rename to published/201806/20180525 How insecure is your router.md
index a08ba41b2e..9d8622d290 100644
--- a/translated/tech/20180525 How insecure is your router.md
+++ b/published/201806/20180525 How insecure is your router.md
@@ -1,64 +1,63 @@
你的路由器有多不安全?
======
+
+> 你的路由器是你与互联网之间的第一个联系点。它给你带来了多少风险?
+

-我一直对写在 T 恤上的“127.0.0.1 这个地方是独一无二的” 这句话持有异议。我知道你可能会认为应该将它读作是“家”,但是对于我来说,我认为应该是“本地主机是独一无二的地方”,就像世界上没有完全相同的二个戒指一样。在本文中,我想去讨论一些宽泛的问题:家庭网络的入口,对大多数人来说它是线缆或宽带路由器。英国和美国政府刚公布了“俄罗斯”攻击路由器的通告。我估计这次的攻击主要针对的是机构,而不是家庭,(看我以前的文章 "[国家行为者是什么,我们应该注意些什么?][1]"),但这对我们所有人都是一个警示。
+我一直对写在 T 恤上的“127.0.0.1 是独一无二的地方” 这句话持有异议。我知道你可能会认为应该将它看作是“家”,但是对于我来说,我认为应该是“本地主机是独一无二的地方”,就像世界上没有完全相同的二个戒指一样。在本文中,我想去讨论一些宽泛的问题:家庭网络的入口,对大多数人来说它是线缆或宽带路由器。^1 英国和美国政府刚公布了“俄罗斯” ^2 攻击路由器的通告。我估计这次的攻击主要针对的是机构,而不是家庭,(看我以前的文章 “[国家行为者是什么,我们应该注意些什么?][1]”),但这对我们所有人都是一个警示。
### 路由器有什么用?
-路由器很重要。它用于将一个网络(在本文中,是我们的家庭网络)与另外一个网络(在本文中,是指因特网,通过我们的因特网服务提供商的网络)连接。事实上,对于大多数人来说,我们所谓的”路由器“这个小盒子能够做的事情远比我们想到的要多。"routing" 比特就像它的发音一样;它让网络中的计算机能够找到一条向外部网络中计算机发送数据的路径 —— 当你接收数据时,正好是相反的方式。
+路由器很重要。它用于将一个网络(在本文中,是我们的家庭网络)与另外一个网络(在本文中,是指互联网,通过我们的互联网服务提供商的网络)连接。事实上,对于大多数人来说,我们所谓的“路由器” ^3 这个小盒子能够做的事情远比我们想到的要多。“路由” 一个比特就就如其听起来的意思一样:它让网络中的计算机能够找到一条向外部网络中计算机发送数据的路径 —— 当你接收数据时,反之。
-在路由器的其它功能中,大多数时候也作为一台调制解调器来使用。在英国大部分到因特网的连接是通过电话线来实现的 —— 无论是电缆还是标准电话线 —— 尽管现在的最新趋势是通过移动互联网连接到家庭中。当你通过电话线连接时,我们所使用的因特网信号必须转换成其它的一些东西,(从另一端来的)返回信号也是如此。对于那些还记得过去的”拨号上网“时代的人来说,它就是你的电脑边上那个用于上网的发出刺耳声音的小盒子。
+在路由器的其它功能中,大多数时候也作为一台调制解调器来使用。我们中的大部分人 ^4 到互联网的连接是通过电话线来实现的 —— 无论是电缆还是标准电话线 —— 尽管现在的最新趋势是通过移动互联网连接到家庭中。当你通过电话线连接时,我们所使用的互联网信号必须转换成其它的一些东西,(从另一端来的)返回信号也是如此。对于那些还记得过去的“拨号上网”时代的人来说,它就是你的电脑边上那个用于上网的发出刺耳声音的小盒子。
但是路由器能做的事情很多,有时候很多的事情,包括流量记录、作为一个无线接入点、提供 VPN 功能以便于从外部访问你的内网、儿童上网控制、防火墙等等。
-现在的家用路由器越来越复杂;虽然国家行为者并不想参与其中,但是其它人可以。
+现在的家用路由器越来越复杂;虽然国家行为者也行不会想着攻破它,但是其它人也许会。
你会问,这很重要吗?如果其它人可以进入你的系统,他们可以很容易地攻击你的笔记本电脑、电话、网络设备等等。他们可以访问和删除未被保护的个人数据。他们可以假装是你。他们使用你的网络去寄存非法数据或者用于攻击其它人。基本上所有的坏事都可以做。
-幸运的是,现在的路由器趋向于因特网提供商来做设置,言外之意是你可以忘了它的存在,他们将保证它是运行良好和安全的。
+幸运的是,现在的路由器趋向于由互联网提供商来做设置,言外之意是你可以忘了它的存在,他们将保证它是运行良好和安全的。
### 因此,我们是安全的吗?
不幸的是,事实并非如此。
-第一个问题是,因特网提供商是在有限的预算范围内做这些事情,而使用便宜的设备来做这些事可以让他们的利益最大化。因特网提供商的路由器质量越来越差。它是恶意攻击者的首选目标:如果他们知道特定型号的路由器被安装在几百万个家庭使用,那么很容易找到攻击的动机,因为攻击那个型号的路由器对他们来说是非常有价值的。
+第一个问题是,互联网提供商是在有限的预算范围内做这些事情,而使用便宜的设备来做这些事可以让他们的利益最大化。互联网提供商的路由器质量越来越差。它是恶意攻击者的首选目标:如果他们知道特定型号的路由器被安装在几百万个家庭使用,那么很容易找到攻击的动机,因为攻击那个型号的路由器对他们来说是非常有价值的。
产生的其它问题还包括:
- * 修复 bug 或者漏洞的过程很缓慢。升级固件可能会让因特网提供商产生较高的成本,因此,修复过程可能非常缓慢(如果他们打算修复的话)。
+ * 修复 bug 或者漏洞的过程很缓慢。升级固件可能会让互联网提供商产生较高的成本,因此,修复过程可能非常缓慢(如果他们打算修复的话)。
* 非常容易获得或者默认的管理员密码,这意味着攻击者甚至都不需要去找到真实的漏洞 —— 他们就可以登入到路由器中。
-
-
### 对策
-对于进入因特网第一跳的路由器,如何才能提升它的安全性,这里给你提供一个快速应对的清单。我是按从简单到复杂的顺序来列出它们的。在你对路由器做任何改变之前,需要先保存配置数据,以便于你需要的时候回滚它们。
-
- 1. **密码:** 一定,一定,一定要改变你的路由器的管理员密码。你可能很少会用到它,所以你一定要把密码记录在某个地方。它用的次数很少,你可以考虑将密码粘贴到路由器上,因为路由器一般都放置在仅授权的人(你和你的家人)才可以接触到的地方。
- 2. **仅允许管理员从内部进行访问:** 除非你有足够好的理由和你知道如何去做,否则不要允许任何机器从外部的因特网上管理你的路由器。在你的路由器上有一个这样的设置。
- 3. **WiFi 密码:** 一旦你做到了第 2 点,也要确保在你的网络上的那个 WiFi 密码 —— 无论是设置为你的路由器管理密码还是别的 —— 一定要是强密码。为了简单,为连接你的网络的访客设置一个”友好的“简单密码,但是,如果附近一个恶意的人猜到了密码,他做的第一件事情就是查找网络中的路由器。由于他在内部网络,他是可以访问路由器的(因此,第 1 点很重要)。
- 4. **仅打开你知道的并且是你需要的功能:** 正如我在上面所提到的,现代的路由器有各种很酷的选项。不要使用它们。除非你真的需要它们,并且你真正理解了它们是做什么的,并且打开它们后有什么危险。否则,将增加你的路由器被攻击的风险。
- 5. **购买你自己的路由器:** 用一个更好的路由器替换掉因特网提供商给你的路由器。去到你本地的电脑商店,让他们给你一些建议。你可能会花很多钱,但是也可能会遇到一些非常便宜的设备,而且比你现在拥有的更好、性能更强、更安全。你也可以只买一个调制解调器。一般设置调制解调器和路由器都很简单,并且,你可以从你的因特网提供商给你的设备中复制配置,它一般就能”正常工作“。
- 6. **更新固件:** 我喜欢使用最新的功能,但是通常这并不容易。有时,你的路由器上会出现固件更新的提示。大多数的路由器会自动检查并且提示你在下次登入的时候去更新它。问题是如果更新失败则会产生灾难性后果或者丢失配置数据,那就需要你重新输入。但是你真的需要考虑去持续关注修复安全问题的固件更新,并更新它们。
- 7. **转向开源:** 有一些非常好的开源路由器项目,可以让你用在现有的路由器上,用开源的软件去替换它的固件/软件。你可以在 [Wikipedia][2] 上找到许多这样的项目,以及在 [Opensource.com 上搜索 "router"][3],你将看到很多非常好的东西。对于谨慎的人来说要小心,这将会让你的路由器失去保修,但是如果你想真正控制你的路由器,开源永远是最好的选择。
-
+对于进入互联网第一跳的路由器,如何才能提升它的安全性,这里给你提供一个快速应对的清单。我是按从简单到复杂的顺序来列出它们的。在你对路由器做任何改变之前,需要先保存配置数据,以便于你需要的时候回滚它们。
+ 1. **密码:** 一定,一定,一定要改变你的路由器的管理员密码。你可能很少会用到它,所以你一定要把密码记录在某个地方。它用的次数很少,你可以考虑将密码粘贴到路由器上,因为路由器一般都放置在仅供授权的人(你和你的家人 ^5 )才可以接触到的地方。
+ 2. **仅允许管理员从内部进行访问:** 除非你有足够好的理由和你知道如何去做,否则不要允许任何机器从外部的互联网上管理你的路由器。在你的路由器上有一个这样的设置。
+ 3. **WiFi 密码:** 一旦你做到了第 2 点,也要确保在你的网络上的那个 WiFi 密码 —— 无论是设置为你的路由器管理密码还是别的 —— 一定要是强密码。为了简单,为连接你的网络的访客设置一个“友好的”简单密码,但是,如果附近一个恶意的人猜到了密码,他做的第一件事情就是查找网络中的路由器。由于他在内部网络,他是可以访问路由器的(因此,第 1 点很重要)。
+ 4. **仅打开你知道的并且是你需要的功能:** 正如我在上面所提到的,现代的路由器有各种很酷的选项。不要使用它们。除非你真的需要它们,并且你真正理解了它们是做什么的,以及打开它们后有什么危险。否则,将增加你的路由器被攻击的风险。
+ 5. **购买你自己的路由器:** 用一个更好的路由器替换掉互联网提供商给你的路由器。去到你本地的电脑商店,让他们给你一些建议。你可能会花很多钱,但是也可能会遇到一些非常便宜的设备,而且比你现在拥有的更好、性能更强、更安全。你也可以只买一个调制解调器。一般设置调制解调器和路由器都很简单,并且,你可以从你的互联网提供商给你的设备中复制配置,它一般就能“正常工作”。
+ 6. **更新固件:** 我喜欢使用最新的功能,但是通常这并不容易。有时,你的路由器上会出现固件更新的提示。大多数的路由器会自动检查并且提示你在下次登入的时候去更新它。问题是如果更新失败则会产生灾难性后果 ^6 或者丢失配置数据,那就需要你重新输入。但是你真的需要考虑去持续关注修复安全问题的固件更新,并更新它们。
+ 7. **转向开源:** 有一些非常好的开源路由器项目,可以让你用在现有的路由器上,用开源的软件去替换它的固件/软件。你可以在 [Wikipedia][2] 上找到许多这样的项目,以及在 [Opensource.com 上搜索 “router”][3],你将看到很多非常好的东西。对于谨慎的人来说要小心,这将会让你的路由器失去保修,但是如果你想真正控制你的路由器,开源永远是最好的选择。
### 其它问题
-一旦你提升了你的路由器的安全性,你的家庭网络将变的很好,这是假像,事实并不是如此。你家里的物联网设备(Alexa、Nest、门铃、智能灯泡、等等)安全性如何?连接到其它网络的 VPN 安全性如何?通过 WiFi 的恶意主机、你的孩子手机上的恶意应用程序 …?
+一旦你提升了你的路由器的安全性,你的家庭网络将变的很好——这是假像,事实并不是如此。你家里的物联网设备(Alexa、Nest、门铃、智能灯泡、等等)安全性如何?连接到其它网络的 VPN 安全性如何?通过 WiFi 的恶意主机、你的孩子手机上的恶意应用程序 …?
-不,你永远不会有绝对的安全。但是正如我们前面讨论的,虽然没有绝对的”安全“这种事情,但是并不意味着我们不需要去提升安全标准,以让坏人干坏事更困难。
+不,你永远不会有绝对的安全。但是正如我们前面讨论的,虽然没有绝对的“安全”这种事情,但是并不意味着我们不需要去提升安全标准,以让坏人干坏事更困难。
+
+### 脚注
1. 我写的很简单 — 但请继续读下去,我们将达到目的。
- 2. "俄罗斯政府赞助的信息技术国家行为者"
- 3. 或者,以我父母的例子来说,我不相信 ”这个路由器“。
+ 2. “俄罗斯政府赞助的信息技术国家行为者”
+ 3. 或者,以我父母的例子来说,我猜叫做 “互联网盒子”。
4. 这里还有一种这样的情况,我不希望在评论区告诉我,你是直接以 1TB/s 的带宽连接到本地骨干网络的。非常感谢!
- 5. 或许并没有包含全部的家庭。
- 6. 你的路由器现在是一块”砖“,并且你不想访问因特网。
-
-
+ 5. 或许并没有包含整个家庭。
+ 6. 你的路由器现在是一块“砖”,并且你不能访问互联网了。
这篇文章最初发表在 [Alice, Eve, 和 Bob – 安全博客][4] 并授权重发布。
@@ -69,7 +68,7 @@ via: https://opensource.com/article/18/5/how-insecure-your-router
作者:[Mike Bursell][a]
选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
译者:[qhwdw](https://github.com/qhwdw)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/published/20180525 How to clean up your data in the command line.md b/published/201806/20180525 How to clean up your data in the command line.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20180525 How to clean up your data in the command line.md
rename to published/201806/20180525 How to clean up your data in the command line.md
diff --git a/published/20180528 What is a Linux server and why does your business need one.md b/published/201806/20180528 What is a Linux server and why does your business need one.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20180528 What is a Linux server and why does your business need one.md
rename to published/201806/20180528 What is a Linux server and why does your business need one.md
diff --git a/published/20180529 Copying and renaming files on Linux.md b/published/201806/20180529 Copying and renaming files on Linux.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20180529 Copying and renaming files on Linux.md
rename to published/201806/20180529 Copying and renaming files on Linux.md
diff --git a/published/20180529 The Source Code Line Counter And Analyzer.md b/published/201806/20180529 The Source Code Line Counter And Analyzer.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20180529 The Source Code Line Counter And Analyzer.md
rename to published/201806/20180529 The Source Code Line Counter And Analyzer.md
diff --git a/published/20180530 How to load or unload a Linux kernel module.md b/published/201806/20180530 How to load or unload a Linux kernel module.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20180530 How to load or unload a Linux kernel module.md
rename to published/201806/20180530 How to load or unload a Linux kernel module.md
diff --git a/published/20180531 How To Disable Built-in Webcam In Linux.md b/published/201806/20180531 How To Disable Built-in Webcam In Linux.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20180531 How To Disable Built-in Webcam In Linux.md
rename to published/201806/20180531 How To Disable Built-in Webcam In Linux.md
diff --git a/published/20180601 8 basic Docker container management commands.md b/published/201806/20180601 8 basic Docker container management commands.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20180601 8 basic Docker container management commands.md
rename to published/201806/20180601 8 basic Docker container management commands.md
diff --git a/published/20180601 Vim-plug - A Minimalist Vim Plugin Manager.md b/published/201806/20180601 Vim-plug - A Minimalist Vim Plugin Manager.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20180601 Vim-plug - A Minimalist Vim Plugin Manager.md
rename to published/201806/20180601 Vim-plug - A Minimalist Vim Plugin Manager.md
diff --git a/published/201806/20180603 Let-s migrate away from GitHub.md b/published/201806/20180603 Let-s migrate away from GitHub.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..d878deb0f4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201806/20180603 Let-s migrate away from GitHub.md
@@ -0,0 +1,48 @@
+让我们从 GitHub 中迁移出来
+======
+
+正如你们之前听到的那样,[微软收购了 GitHub][1]。这对 GitHub 的未来意味着什么尚不清楚,但 [Gitlab 的人][2]认为微软的最终目标是将 GitHub 整合到他们的 Azure 帝国。对我来说,这很有道理。
+
+尽管我仍然不情愿地将 GitHub 用于某些项目,但我前一段时间将所有个人仓库迁移到了 Gitlab 中。现在是时候让你做同样的事情,并抛弃 GitHub。
+
+![Microsft loven't Linux][3]
+
+有些人可能认为微软的收购没有问题,但对我来说,这是压垮骆驼的最后一根稻草。几年来,微软一直在开展一场关于他们如何热爱 Linux 的大型营销活动,并突然决定用所有它的形式拥抱自由软件。更像 MS BS 给我的。
+
+让我们花点时间提醒自己:
+
+* Windows 仍然是一个巨大的专有怪物,数十亿人每天都丧失了他们的隐私和权利中。
+* 微软公司(曾经)以传播自由软件的“危害”闻名,以防止政府和学校放弃 Windows,转而支持 FOSS。
+* 为了确保他们的垄断地位,微软通过向全世界的小学颁发“免费”许可证来吸引孩子使用 Windows。毒品经销商使用相同的策略并提供免费样品来获取新客户。
+* 微软的 Azure 平台 - 即使它可以运行 Linux 虚拟机 - 它仍然是一个巨大的专有管理程序。
+
+我知道移动 git 仓库看起来像是一件痛苦的事情,但是 Gitlab 的员工正在乘着人们离开 GitHub 的浪潮,并通过[提供 GitHub 导入器][4]使迁移变得容易。
+
+如果你不想使用 Gitlab 的主实例([gitlab.org][5]),下面是另外两个你可以用于自由软件项目的备选实例:
+
+* [Debian Gitlab 实例][6]适用于每个 FOSS 项目,它不仅适用于与 Debian 相关的项目。只要项目符合 [Debian 自由软件指南][7],你就可以使用该实例及其 CI。
+* Riseup 为名为 [0xacab][8] 的激进项目维护了一个 Gitlab 实例。如果你的[理念与 Riseup 的一致][9],他们很乐意在那里托管你的项目。
+
+朋友不要再让人使用 Github 了。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://veronneau.org/lets-migrate-away-from-github.html
+
+作者:[Louis-Philippe Véronneau][a]
+选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
+译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:https://veronneau.org/
+[1]:https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2018-06-03/microsoft-is-said-to-have-agreed-to-acquire-coding-site-github
+[2]:https://about.gitlab.com/2018/06/03/microsoft-acquires-github/
+[3]:https://veronneau.org/media/blog/2018-06-03/ms-lovent-linux.png (Microsoft loven't Linux)
+[4]:https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/user/project/import/github.html
+[5]:https://gitlab.org
+[6]:https://salsa.debian.org
+[7]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Debian_Free_Software_Guidelines
+[8]:https://0xacab.org
+[9]:https://riseup.net/en/about-us/politics
diff --git a/published/20180604 How to use the history command in Linux.md b/published/201806/20180604 How to use the history command in Linux.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20180604 How to use the history command in Linux.md
rename to published/201806/20180604 How to use the history command in Linux.md
diff --git a/published/20180605 How To Test A Package Without Installing It In Linux.md b/published/201806/20180605 How To Test A Package Without Installing It In Linux.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20180605 How To Test A Package Without Installing It In Linux.md
rename to published/201806/20180605 How To Test A Package Without Installing It In Linux.md
diff --git a/published/20180605 MySQL without the MySQL- An introduction to the MySQL Document Store.md b/published/201806/20180605 MySQL without the MySQL- An introduction to the MySQL Document Store.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20180605 MySQL without the MySQL- An introduction to the MySQL Document Store.md
rename to published/201806/20180605 MySQL without the MySQL- An introduction to the MySQL Document Store.md
diff --git a/published/20180606 A friendly alternative to the find tool in Linux.md b/published/201806/20180606 A friendly alternative to the find tool in Linux.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20180606 A friendly alternative to the find tool in Linux.md
rename to published/201806/20180606 A friendly alternative to the find tool in Linux.md
diff --git a/published/20180611 How to partition a disk in Linux.md b/published/201806/20180611 How to partition a disk in Linux.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20180611 How to partition a disk in Linux.md
rename to published/201806/20180611 How to partition a disk in Linux.md
diff --git a/published/20180612 What version of Linux am I running.md b/published/201806/20180612 What version of Linux am I running.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20180612 What version of Linux am I running.md
rename to published/201806/20180612 What version of Linux am I running.md
diff --git a/published/20180615 How to Mount and Use an exFAT Drive on Ubuntu Linux.md b/published/201806/20180615 How to Mount and Use an exFAT Drive on Ubuntu Linux.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20180615 How to Mount and Use an exFAT Drive on Ubuntu Linux.md
rename to published/201806/20180615 How to Mount and Use an exFAT Drive on Ubuntu Linux.md
diff --git a/translated/tech/20180619 How to disable iptables firewall temporarily.md b/published/201806/20180619 How to disable iptables firewall temporarily.md
similarity index 91%
rename from translated/tech/20180619 How to disable iptables firewall temporarily.md
rename to published/201806/20180619 How to disable iptables firewall temporarily.md
index 38f2fe7d43..be95cc7011 100644
--- a/translated/tech/20180619 How to disable iptables firewall temporarily.md
+++ b/published/201806/20180619 How to disable iptables firewall temporarily.md
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
如何暂时禁用 iptables 防火墙
======
-了解如何在 Linux 中暂时禁用 iptables 防火墙来进行故障排除。还要学习如何保存策略以及如何在启用防火墙时恢复它们。
+> 了解如何在 Linux 中暂时禁用 iptables 防火墙来进行故障排除。还要学习如何保存策略以及如何在启用防火墙时恢复它们。
![How to disable iptables firewall temporarily][1]
@@ -32,6 +32,7 @@ root@kerneltalks # iptables-save > /root/firewall_rules.backup
对于较老的 Linux 内核,你可以选择使用 `service iptables stop` 停止 iptables 服务,但是如果你在用新内核,则只需清除所有策略并允许所有流量通过防火墙。这和你停止防火墙效果一样。
使用下面的命令列表来做到这一点。
+
```
root@kerneltalks # iptables -F
root@kerneltalks # iptables -X
@@ -42,11 +43,9 @@ root@kerneltalks # iptables -P FORWARD ACCEPT
这里 –
- * -F:删除所有策略链
- * -X:删除用户定义的链
- * -P INPUT/OUTPUT/FORWARD :接受指定的流量
-
-
+ * `-F`:删除所有策略链
+ * `-X`:删除用户定义的链
+ * `-P INPUT/OUTPUT/FORWARD` :接受指定的流量
完成后,检查当前的防火墙策略。它应该看起来像下面这样接受所有流量(和禁用/停止防火墙一样)
@@ -69,6 +68,7 @@ target prot opt source destination
```
root@kerneltalks # iptables-restore Vimwiki 和 GitLab 是记录笔记的强大组合。
+
+![1][]
+
+用 vi 来管理 wiki 来记录你的笔记,这听起来不像是一个符合常规的主意,但当你的日常工作都会用到 vi , 那它是有意义的。
+
+作为一个软件开发人员,使用同编码一样的工具来写笔记会更加简单。我想将我的笔记变成一种编辑器命令,无论我在哪里,都能够用管理我代码的方法来管理我的笔记。这便是我创建一个基于 vi 的环境来搭建我自己的知识库的原因。简单概括起来,我在笔记本电脑上用 vi 插件 [Viwiki][2] 来本地管理我的 wiki。用 Git 来进行版本控制(以保留一个中心化的更新版本),并用 GitLab 来进行在线修改(例如在我的手机上)。
+
+### 为什么用 wiki 来进行笔记保存是有意义
+
+我尝试过许多不同的工具来持续的记录我的笔记,笔记里保存着我的灵感以及需要记住的任务安排。这包括线下的笔记本 (没错,纸质的)、特殊的记录笔记的软件,以及思维导图软件。
+
+但每种方案都有不好一面,没有一个能够满足我所有的需求。例如[思维导图][6],能够很好的形象化你的想法(因而得名),但是这种工具的搜索功能很差(和纸质笔记本一样)。此外,当一段时间过去,思维导图会变得很难阅读,所以思维导图不适合长时间保存的笔记。
+
+我为一个合作项目配置了 [DokuWiki][2],我发现这个 wiki 模型符合了我大多数的需求。在 wiki 上,你能够创建一个笔记(和你在文本编辑器中所作的一样),并在笔记间创建链接。如果一个链接指向一个不存在的页面(你想让本页面添加一条还没有创建的信息), wiki 会为你建立这个页面。这个特性使得 wiki 很好的适应了那些需要快速写下心中所想的人的需求,而仍将你的笔记保持在能够容易浏览和搜索关键字的页面结构中。
+
+这看起来很有希望,并且配置 DokuWiki 也很容易,但我发现只是为了记个笔记而配置整个 wiki 需要花费太多工作。在一番搜索后,我发现了 Vimwiki,这是一个我想要的 vi 插件。因为我每天使用 vi,记录笔记就行编辑代码一样。甚至在 vimwiki 创建一个页面比 Dokuwiki 更简单。你只需要对光标下的单词按下回车键就行。如果没有文件是这个名字,vimwiki 会为你创建一个。
+
+为了更一步的实现用每天都会使用的工具来做笔记的计划,我不仅用这个我最爱的 IDE 来写笔记,而且用 Git 和 GitLab —— 我最爱的代码管理工具 —— 在我的各个机器间分发我的笔记,以便我可以在线访问它们。我也是在 Gitlab 的在线 markdown 工具上用 markdown 语法来写的这篇文章。
+
+### 配置 vimwiki
+
+用你已有的插件管理工具来安装 vimwiki 很简单,只需要添加 vimwiki/vimwiki 到你的插件。对于我的喜爱的插件管理器 Vundle 来说,你只需要在 `/.vimrc` 中添加 `plugin vimwiki/vimwiki` 这一行,然后执行 `:source ~/.vimrc | PluginInstall` 就行。
+
+下面是我的文件 `.vimrc` 的一部分,展示了一些 vimwiki 配置。你能在 [vimwiki][2] 页面学到更多的配置和使用的的信息。
+
+```
+let wiki_1 = {}
+let wiki_1.path = '~/vimwiki_work_md/'
+let wiki_1.syntax = 'markdown'
+let wiki_1.ext = '.md'
+
+let wiki_2 = {}
+let wiki_2.path = '~/vimwiki_personal_md/'
+let wiki_2.syntax = 'markdown'
+let wiki_2.ext = '.md'
+
+let g:vimwiki_list = [wiki_1, wiki_2]
+let g:vimwiki_ext2syntax = {'.md': 'markdown', '.markdown': 'markdown', '.mdown': 'markdown'}
+```
+
+如你在上述配置中所见,我的配置还有一个优点。你能简单的区分个人和工作相关的笔记,而不用切换笔记软件。我想让我的个人笔记可以随时随地访问,而不想我的工作笔记同步到我私人的 GitLab 和计算机中。在 vimwiki 这样配置要比我试过的其他软件都要简单。
+
+这个配置告诉 vimwiki 有两个不同 Wiki,都使用 markdown 语法(再一次,因为我的日常工作中天天都在用 markdown 语法)。我也告诉 Vimwiki 在哪个文件夹存储 wiki 页面。
+
+如果你进入存储 wiki 页面的文件夹,你会找到你的 wiki 的普通的 markdown 页面文件,而没有其他特殊的 Vimwiki 相关内容,这使得很容易的初始化 Git 仓库和同步你的 wiki 到中心仓库。
+
+### 同步你的 wiki 到 GitLab
+
+这一步检出一个 GitLab 项目到本地的 VimWiki 文件夹,这步操作和你操作任何 GitHub 的仓库相同,只不过因为我更喜欢保存我的笔记到我的私人 GitLab 仓库,所以我运行了一个 GitLab 实例用于我个人的项目。
+
+GitLab 的 wiki 功能可以用来为你的项目创建 wiki 页面。这些 wiki 就是 Git 仓库本身。它们使用 markdown 语法,你懂得。
+
+只需要初始化你需要的 wiki ,让它与你为笔记而创建的项目的 wiki 同步即可。
+
+```
+cd ~/vimwiki_personal_md/
+git init
+git remote add origin git@your.gitlab.com:your_user/vimwiki_personal_md.wiki
+git add .
+git commit -m "Initial commit"
+git push -u origin master
+```
+
+在 GitLab 创建一个新的项目后,你就可以从页面上复制这些步骤的代码。唯一的改变是仓库地址结尾是 .wiki(而不是 .git)。 这会告诉 Git 克隆 wiki 仓库而不是项目本身。
+
+就是这样!现在你能够通过 Git 来管理你的笔记,通过 GitLab wiki 用户界面来修改笔记。
+
+你可能(像我一样)不想手动的为每个添加到笔记本的笔记创建一个提交。为了解决这个问题,我使用了 Vim 插件 [chazy/dirsetting][4]。我添加一个 `.vimaddr` 文件,已经下面的内容:
+
+```
+:cd %:p:h
+silent! !git pull > /dev/null
+:e!
+autocmd! BufWritePost * silent! !git add .;git commit -m "vim autocommit" > /dev/null; git push > /dev/null&
+```
+
+每当我打开 Wiki 文件按下 `:w` 发布我的修改时,它就会更新到最新的版本。这样做会使你的本地文件与中心仓库保持同步。如果你有合并冲突,通常你需要解决它们。
+
+目前,这就是以我的知识来互动的方法,我很喜欢这方法;请告诉我你对于这个方法的想法,可以在评论区分享你如何追踪笔记的方法。
+
+-----------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://opensource.com/article/18/6/vimwiki-gitlab-notes
+
+作者:[Manuel Dewald][a]
+选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
+译者:[octopus](https://github.com/singledo)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:https://opensource.com/users/ntlx
+[1]:https://camo.githubusercontent.com/9901c750dce2008ea7a459201121077c355fc257/68747470733a2f2f6f70656e736f757263652e636f6d2f73697465732f64656661756c742f66696c65732f7374796c65732f696d6167652d66756c6c2d73697a652f7075626c69632f6c6561642d696d616765732f636865636b6c6973745f68616e64735f7465616d5f636f6c6c61626f726174696f6e2e706e673f69746f6b3d753832516570506b
+[2]:https://vimwiki.github.io/
+[3]:https://www.dokuwiki.org/dokuwiki
+[4]:https://github.com/chazy/dirsettings
+[6]:https://opensource.com/article/17/8/mind-maps-creative-dashboard
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/published/20180627 Historical inventory of collaborative editors.md b/published/20180627 Historical inventory of collaborative editors.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..8ac45e5803
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20180627 Historical inventory of collaborative editors.md
@@ -0,0 +1,86 @@
+协同编辑器的历史性清单
+======
+
+按时间顺序快速列出主要协同编辑器的演变。
+
+正如任何这样的清单一样,它必定会在一开始便提到被誉为“[所有演示之母][25]”,在这个演示里[道格·恩格尔巴特][26]早在 1968 年就描述了几乎所有软件的详尽清单。这不仅包括协同编辑器,还包括图形、编程和数学编辑器。
+
+一切都始于那个演示,只不过软件的实现跟不上硬件的发展罢了。
+
+> 软件发展的速度比硬件提升的速度慢。——沃斯定律
+
+闲话少说,这里是我找到的可圈可点的协同编辑器的清单。我说“可圈可点”的意思是它们具有可圈可点的特征或实现细节。
+
+| 项目 | 日期 | 平台 | 说明 |
+| --- | --- | --- | --- |
+| [SubEthaEdit][1] | 2003-2015? | 仅 Mac|我能找到的首个协同的、实时的、多光标的编辑器, [有个在 Emacs 上的逆向工程的尝试][2]却没有什么结果。 |
+| [DocSynch][3] | 2004-2007 | ? | 建立于 IRC 之上! |
+| [Gobby][4] | 2005 至今 | C,多平台 | 首个开源、稳固可靠的实现。 仍然存在!众所周知 [libinfinoted][5] 协议很难移植到其他编辑器中(例如: [Rudel][6] 不能在 Emacs 上实现此协议)。 2017 年 1 月发行的 0.7 版本添加了也许可以改善这种状况的 Python 绑定。 值得注意的插件: 自动保存到磁盘。|
+| [Ethercalc][27] | 2005 至今 | Web,JavaScript | 首个电子表格,随同 [Google Docs][28]。 |
+| [moonedit][7] | 2005-2008? | ? | 原网站已关闭。其他用户的光标可见并且会模仿击键的声音。 包括一个计算器和音乐定序器。 |
+| [synchroedit][8] | 2006-2007 | ? | 首个 Web 应用。|
+| [Inkscape][29] | 2007-2011 | C++ | 首个具备协同功能的图形编辑器,其背后的“whiteboard” 插件构建于 Jabber 之上,现已停摆。|
+| [Abiword][30] | 2008 至今|C++| 首个文字处理器。|
+| [Etherpad][9] | 2008 至今 | Web |首款稳定的 Web 应用。 最初在 2008 年被开发时是一款大型 Java 应用,在 2009 年被谷歌收购并开源,然后在 2011 年被用 Node.JS 重写。使用广泛。|
+| [Wave][31]|2009-2010|Web, Java| 在大一统协议的尝试上失败。|
+| [CRDT][10] | 2011 | 特定平台| 在不同电脑间可靠地复制一个文件的数据结构的标准。 |
+| [Operational transform][11] | 2013 | 特定平台| 与 CRDT 类似,然而确切地说,两者是不同的。 |
+| [Floobits][12] | 2013 至今 | ? | 商业软件,但有对各种编辑器的开源插件。 |
+| [LibreOffice Online][32]| 2015至今| Web| 免费的 Google docs 替代品,现已集成到 [Nextcloud][33] |
+| [HackMD][13] | 2015 至今| ? | 商业软件,[开源][14]。灵感来自于(已被 Dropbox 收购的) hackpad。 |
+| [Cryptpad][15] | 2016 至今 | Web ? | Xwiki 的副产品。服务器端的加密的、“零知识” 产品。|
+| [Prosemirror][16] | 2016 至今 | Web, Node.JS | “试图架起消除 Markdown 文本编辑和传统的所见即所得编辑器之间隔阂的桥梁。”不是完全意义上的编辑器,而是一种可以用来构建编辑器的工具。 |
+| [Qill][17] | 2013 至今 | Web, Node.JS | 富文本编辑器,同时也是 JavaScript 编辑器。不确定是否是协同式的。 |
+| [Teletype][19] | 2017 至今 | WebRTC, Node.JS | 为 GitHub 的 [Atom 编辑器][20] 引入了“门户”的思路 ,使得访客可以夸多个文档跟踪主人的操作。访问介绍服务器后使用实时通讯的点对点技术(P2P),基于 CRDT。 |
+| [Tandem][21] | 2018 至今 | Node.JS? | Atom、 Vim、Neovim、 Sublime 等的插件。 使用中继来设置基于 CRDT 的 P2P 连接。多亏 Debian 开发者的参与,[可疑证书问题][22]已被解决,这使它成为很有希望在未来被遵循的标准。 |
+
+### 其他清单
+
+* [Emacs 维基][23]
+* [维基百科][24]
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://anarc.at/blog/2018-06-26-collaborative-editors-history/
+
+作者:[Anacr][a]
+选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
+译者:[ZenMoore](https://github.com/ZenMoore)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:https://anarc.at
+[1]:https://www.codingmonkeys.de/subethaedit/
+[2]:https://www.emacswiki.org/emacs/SubEthaEmacs
+[3]:http://docsynch.sourceforge.net/
+[4]:https://gobby.github.io/
+[5]:http://infinote.0x539.de/libinfinity/API/libinfinity/
+[6]:https://www.emacswiki.org/emacs/Rudel
+[7]:https://web.archive.org/web/20060423192346/http://www.moonedit.com:80/
+[8]:http://www.synchroedit.com/
+[9]:http://etherpad.org/
+[10]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conflict-free_replicated_data_type
+[11]:http://operational-transformation.github.io/
+[12]:https://floobits.com/
+[13]:https://hackmd.io/
+[14]:https://github.com/hackmdio/hackmd
+[15]:https://cryptpad.fr/
+[16]:https://prosemirror.net/
+[17]:https://quilljs.com/
+[18]:https://nextcloud.com/collaboraonline/
+[19]:https://teletype.atom.io/
+[20]:https://atom.io
+[21]:http://typeintandem.com/
+[22]:https://github.com/typeintandem/tandem/issues/131
+[23]:https://www.emacswiki.org/emacs/CollaborativeEditing
+[24]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Collaborative_real-time_editor
+[25]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/The_Mother_of_All_Demos
+[26]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Douglas_Engelbart
+[27]:https://ethercalc.net/
+[28]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Google_docs
+[29]:http://wiki.inkscape.org/wiki/index.php/WhiteBoard
+[30]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/AbiWord
+[31]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Apache_Wave
+[32]:https://wiki.documentfoundation.org/Development/LibreOffice_Online
+[33]:https://nextcloud.com/collaboraonline/
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/talk/20180320 Can we build a social network that serves users rather than advertisers.md b/sources/talk/20180320 Can we build a social network that serves users rather than advertisers.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 9ea639c4e5..0000000000
--- a/sources/talk/20180320 Can we build a social network that serves users rather than advertisers.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,70 +0,0 @@
-Can we build a social network that serves users rather than advertisers?
-======
-
-
-
-Today, open source software is far-reaching and has played a key role driving innovation in our digital economy. The world is undergoing radical change at a rapid pace. People in all parts of the world need a purpose-built, neutral, and transparent online platform to meet the challenges of our time.
-
-And open principles might just be the way to get us there. What would happen if we married digital innovation with social innovation using open-focused thinking?
-
-This question is at the heart of our work at [Human Connection][1], a forward-thinking, Germany-based knowledge and action network with a mission to create a truly social network that serves the world. We're guided by the notion that human beings are inherently generous and sympathetic, and that they thrive on benevolent actions. But we haven't seen a social network that has fully supported our natural tendency towards helpfulness and cooperation to promote the common good. Human Connection aspires to be the platform that allows everyone to become an active changemaker.
-
-In order to achieve the dream of a solution-oriented platform that enables people to take action around social causes by engaging with charities, community groups, and social change activists, Human Connection embraces open values as a vehicle for social innovation.
-
-Here's how.
-
-### Transparency first
-
-Transparency is one of Human Connection's guiding principles. Human Connection invites programmers around the world to jointly work on the platform's source code (JavaScript, Vue, nuxt) by [making their source code available on Github][2] and support the idea of a truly social network by contributing to the code or programming additional functions.
-
-But our commitment to transparency extends beyond our development practices. In fact—when it comes to building a new kind of social network that promotes true connection and interaction between people who are passionate about changing the world for the better—making the source code available is just one step towards being transparent.
-
-To facilitate open dialogue, the Human Connection team holds [regular public meetings online][3]. Here we answer questions, encourage suggestions, and respond to potential concerns. Our Meet The Team events are also recorded and made available to the public afterwards. By being fully transparent with our process, our source code, and our finances, we can protect ourselves against critics or other potential backlashes.
-
-The commitment to transparency also means that all user contributions that shared publicly on Human Connection will be released under a Creative Commons license and can eventually be downloaded as a data pack. By making crowd knowledge available, especially in a decentralized way, we create the opportunity for social pluralism.
-
-Guiding all of our organizational decisions is one question: "Does it serve the people and the greater good?" And we use the [UN Charter][4] and the Universal Declaration of Human Rights as a foundation for our value system. As we'll grow bigger, especially with our upcoming open beta launch, it's important for us to stay accountable to that mission. I'm even open to the idea of inviting the Chaos Computer Club or other hacker clubs to verify the integrity of our code and our actions by randomly checking into our platform.
-
-When it comes to building a new kind of social network that promotes true connection and interaction between people who are passionate about changing the world for the better, making the source code available is just one step towards being transparent.
-
-### A collaborative community
-
-A [collaborative, community-centered approach][5] to programming the Human Connection platform is the foundation for an idea that extends beyond the practical applications of a social network. Our team is driven by finding an answer to the question: "What makes a social network truly social?"
-
-A network that abandons the idea of a profit-driven algorithm serving advertisers instead of end-users can only thrive by turning to the process of peer production and collaboration. Organizations like [Code Alliance][6] and [Code for America][7], for example, have demonstrated how technology can be created in an open source environment to benefit humanity and disrupt the status quo. Community-driven projects like the map-based reporting platform [FixMyStreet][8] or the [Tasking Manager][9] built for the Humanitarian OpenStreetMap initiative have embraced crowdsourcing as a way to move their mission forward.
-
-Our approach to building Human Connection has been collaborative from the start. To gather initial data on the necessary functions and the purpose of a truly social network, we collaborated with the National Institute for Oriental Languages and Civilizations (INALCO) at the University Sorbonne in Paris and the Stuttgart Media University in Germany. Research findings from both projects were incorporated into the early development of Human Connection. Thanks to that research, [users will have a whole new set of functions available][10] that put them in control of what content they see and how they engage with others. As early supporters are [invited to the network's alpha version][10], they can experience the first available noteworthy functions. Here are just a few:
-
- * Linking information to action was one key theme emerging from our research sessions. Current social networks leave users in the information stage. Student groups at both universities saw a need for an action-oriented component that serves our human instinct of working together to solve problems. So we built a ["Can Do" function][11] into our platform. It's one of the ways individuals can take action after reading about a certain topic. "Can Do's" are user-suggested activities in the "Take Action" area that everyone can implement.
- * The "Versus" function is another defining result. Where traditional social networks are limited to a comment function, our student groups saw the need for a more structured and useful way to engage in discussions and arguments. A "Versus" is a counter-argument to a public post that is displayed separately and provides an opportunity to highlight different opinions around an issue.
- * Today's social networks don't provide a lot of options to filter content. Research has shown that a filtering option by emotions can help us navigate the social space in accordance with our daily mood and potentially protect our emotional wellbeing by not displaying sad or upsetting posts on a day where we want to see uplifting content only.
-
-
-
-Human Connection invites changemakers to collaborate on the development of a network with the potential to mobilize individuals and groups around the world to turn negative news into "Can Do's"—and participate in social innovation projects in conjunction with charities and non-profit organizations.
-
-[Subscribe to our weekly newsletter][12] to learn more about open organizations.
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: https://opensource.com/open-organization/18/3/open-social-human-connection
-
-作者:[Dennis Hack][a]
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:https://opensource.com/users/dhack
-[1]:https://human-connection.org/en/
-[2]:https://github.com/human-connection/
-[3]:https://youtu.be/tPcYRQcepYE
-[4]:http://www.un.org/en/charter-united-nations/index.html
-[5]:https://youtu.be/BQHBno-efRI
-[6]:http://codealliance.org/
-[7]:https://www.codeforamerica.org/
-[8]:http://fixmystreet.org/
-[9]:https://tasks.hotosm.org/
-[10]:https://youtu.be/AwSx06DK2oU
-[11]:https://youtu.be/g2gYLNx686I
-[12]:https://opensource.com/open-organization/resources/newsletter
diff --git a/sources/talk/20180603 Let-s migrate away from GitHub.md b/sources/talk/20180603 Let-s migrate away from GitHub.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 0b41dfa37b..0000000000
--- a/sources/talk/20180603 Let-s migrate away from GitHub.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,53 +0,0 @@
-translating---geekpi
-
-Let's migrate away from GitHub
-======
-As many of you heard today, [Microsoft is acquiring GitHub][1]. What this means for the future of GitHub is not yet clear, but [the folks at Gitlab][2] think Microsoft's end goal is to integrate GitHub in their Azure empire. To me, this makes a lot of sense.
-
-Even though I still reluctantly use GitHub for some projects, I migrated all my personal repositories to Gitlab instances a while ago. Now is time for you to do the same and ditch GitHub.
-
-![Microsft loven't Linux][3]
-
-Some people might be fine with Microsoft's takeover, but to me it's the straw that breaks the camel's back. For a few years now, MS has been running a large marketing campaign on how they love Linux and suddenly decided to embrace Free Software in all of its forms. More like MS BS to me.
-
-Let us take a moment to remind ourselves that:
-
- * Windows is still a huge proprietary monster that rips billions of people from their privacy and rights every day.
- * Microsoft is known for spreading FUD about "the dangers" of Free Software in order to keep governments and schools from dropping Windows in favor of FOSS.
- * To secure their monopoly, Microsoft hooks up kids on Windows by giving out "free" licences to primary schools around the world. Drug dealers use the same tactics and give out free samples to secure new clients.
- * Microsoft's Azure platform - even though it can run Linux VMs - is still a giant proprietary hypervisor.
-
-
-
-I know moving git repositories around can seem like a pain in the ass, but the folks at Gitlab are riding the wave of people leaving GitHub and made the the migration easy [by providing a GitHub importer][4].
-
-If you don't want to use Gitlab's main instance ([gitlab.org][5]), here are two other alternative instances you can use for Free Software projects:
-
- * The [Debian Gitlab instance][6] is available for every FOSS project and not only for Debian-related ones. As long as the project respects the [Debian Free Software Guidelines][7], you can use the instance and its CI runners.
- * Riseup maintains a Gitlab instance for radical projects named [0xacab][8]. If your [ethos aligns with Riseup's][9], chances are they'll be happy to host your projects there.
-
-
-
-Friends don't let friends use GitHub anymore.
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: https://veronneau.org/lets-migrate-away-from-github.html
-
-作者:[Louis-Philippe Véronneau][a]
-选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:https://veronneau.org/
-[1]:https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2018-06-03/microsoft-is-said-to-have-agreed-to-acquire-coding-site-github
-[2]:https://about.gitlab.com/2018/06/03/microsoft-acquires-github/
-[3]:https://veronneau.org/media/blog/2018-06-03/ms-lovent-linux.png (Microsoft loven't Linux)
-[4]:https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/user/project/import/github.html
-[5]:https://gitlab.org
-[6]:https://salsa.debian.org
-[7]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Debian_Free_Software_Guidelines
-[8]:https://0xacab.org
-[9]:https://riseup.net/en/about-us/politics
diff --git a/sources/tech/20170309 How To Record Everything You Do In Terminal.md b/sources/tech/20170309 How To Record Everything You Do In Terminal.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 6748f911e1..0000000000
--- a/sources/tech/20170309 How To Record Everything You Do In Terminal.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,92 +0,0 @@
-translating---geekpi
-
-How To Record Everything You Do In Terminal
-======
-
-
-A few days ago, we published a guide that explained how to [**save commands in terminal itself and use them on demand**][1]. It is very useful for those who don’t want to memorize a lengthy Linux command. Today, in this guide, we are going to see how to record everything you do in Terminal using **‘script’** command. You might have run a command, or created a directory, or installed an application in Terminal. Script command simply saves whatever you do in the Terminal. You can then view them if you want to know what you did few hours or few days ago. I know I know, we can use UP/DOWN arrow keys or history command to view previously running commands. However, you can’t view the output of those commands. But, Script command records and displays complete terminal session activities.
-
-The script command creates a typescript of everything you do in the Terminal. It doesn’t matter whether you install an application, create a directory/file, remove a folder. Everything will be recorded, including the commands and the respective outputs. This command will be helpful who wants a hard-copy record of an interactive session as proof of an assignment. Whether you’re a student or a tutor, you can make a copy of everything you do in the Terminal along with all outputs.
-
-### Record Everything You Do In Terminal using script command in Linux
-
-The script command comes pre-installed on most modern Linux operating systems. So, let us not bother about the installation.
-
-Let us go ahead and see how to use it in real time.
-
-Run the following command to start the Terminal session recording.
-```
-$ script -a my_terminal_activities
-
-```
-
-Where, **-a** flag is used to append the output to file or to typescript, retaining the prior contents. The above command records everything you do in the Terminal and append the output to a file called **‘my_terminal_activities’** and save it in your current working directory.
-
-Sample output would be:
-```
-Script started, file is my_terminal_activities
-
-```
-
-Now, run some random Linux commands in your Terminal.
-```
-$ mkdir ostechnix
-
-$ cd ostechnix/
-
-$ touch hello_world.txt
-
-$ cd ..
-
-$ uname -r
-
-```
-
-After running all commands, end the ‘script’ command’s session using command:
-```
-$ exit
-
-```
-
-**Sample output:**
-```
-exit
-Script done, file is my_terminal_activities
-
-```
-
-As you see, the Terminal activities have been stored in a file called **‘my_terminal_activities’** and saves it in the current working directory.
-
-To view your Terminal activities, just open this file in any editor or simply display it using the ‘cat’ command.
-```
-$ cat my_terminal_activities
-
-```
-
-**Sample output:**
-
-As you see in the above output, script command has recorded all my Terminal activities, including the start and end time of the script command. Awesome, isn’t it? The reason to use script command is it’s not just records the commands, but also the commands’ output as well. To put this simply, Script command will record everything you do on the Terminal.
-
-### Conclusion
-
-Like I said, script command would be useful for students, teachers and any Linux users who wants to keep the record of their Terminal activities. Even though there are many CLI and GUI to do this, script command is an easiest and quickest way to record the Terminal session activities.
-
-And, that’s all. Hope this helps. If you find this guide useful, please share it on your social, professional networks and **support OSTechNix**.
-
-Cheers!
-
-
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: https://www.ostechnix.com/record-everything-terminal/
-
-作者:[SK][a]
-选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:https://www.ostechnix.com/author/sk/
-[1]:https://www.ostechnix.com/save-commands-terminal-use-demand/
diff --git a/sources/tech/20171010 Operating a Kubernetes network.md b/sources/tech/20171010 Operating a Kubernetes network.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 1598e98508..0000000000
--- a/sources/tech/20171010 Operating a Kubernetes network.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,217 +0,0 @@
-Translating by qhwdw
-Operating a Kubernetes network
-============================================================
-
-I’ve been working on Kubernetes networking a lot recently. One thing I’ve noticed is, while there’s a reasonable amount written about how to **set up** your Kubernetes network, I haven’t seen much about how to **operate** your network and be confident that it won’t create a lot of production incidents for you down the line.
-
-In this post I’m going to try to convince you of three things: (all I think pretty reasonable :))
-
-* Avoiding networking outages in production is important
-
-* Operating networking software is hard
-
-* It’s worth thinking critically about major changes to your networking infrastructure and the impact that will have on your reliability, even if very fancy Googlers say “this is what we do at Google”. (google engineers are doing great work on Kubernetes!! But I think it’s important to still look at the architecture and make sure it makes sense for your organization.)
-
-I’m definitely not a Kubernetes networking expert by any means, but I have run into a few issues while setting things up and definitely know a LOT more about Kubernetes networking than I used to.
-
-### Operating networking software is hard
-
-Here I’m not talking about operating physical networks (I don’t know anything about that), but instead about keeping software like DNS servers & load balancers & proxies working correctly.
-
-I have been working on a team that’s responsible for a lot of networking infrastructure for a year, and I have learned a few things about operating networking infrastructure! (though I still have a lot to learn obviously). 3 overall thoughts before we start:
-
-* Networking software often relies very heavily on the Linux kernel. So in addition to configuring the software correctly you also need to make sure that a bunch of different sysctls are set correctly, and a misconfigured sysctl can easily be the difference between “everything is 100% fine” and “everything is on fire”.
-
-* Networking requirements change over time (for example maybe you’re doing 5x more DNS lookups than you were last year! Maybe your DNS server suddenly started returning TCP DNS responses instead of UDP which is a totally different kernel workload!). This means software that was working fine before can suddenly start having issues.
-
-* To fix a production networking issues you often need a lot of expertise. (for example see this [great post by Sophie Haskins on debugging a kube-dns issue][1]) I’m a lot better at debugging networking issues than I was, but that’s only after spending a huge amount of time investing in my knowledge of Linux networking.
-
-I am still far from an expert at networking operations but I think it seems important to:
-
-1. Very rarely make major changes to the production networking infrastructure (because it’s super disruptive)
-
-2. When you _are_ making major changes, think really carefully about what the failure modes are for the new network architecture are
-
-3. Have multiple people who are able to understand your networking setup
-
-Switching to Kubernetes is obviously a pretty major networking change! So let’s talk about what some of the things that can go wrong are!
-
-### Kubernetes networking components
-
-The Kubernetes networking components we’re going to talk about in this post are:
-
-* Your overlay network backend (like flannel/calico/weave net/romana)
-
-* `kube-dns`
-
-* `kube-proxy`
-
-* Ingress controllers / load balancers
-
-* The `kubelet`
-
-If you’re going to set up HTTP services you probably need all of these. I’m not using most of these components yet but I’m trying to understand them, so that’s what this post is about.
-
-### The simplest way: Use host networking for all your containers
-
-Let’s start with the simplest possible thing you can do. This won’t let you run HTTP services in Kubernetes. I think it’s pretty safe because there are less moving parts.
-
-If you use host networking for all your containers I think all you need to do is:
-
-1. Configure the kubelet to configure DNS correctly inside your containers
-
-2. That’s it
-
-If you use host networking for literally every pod you don’t need kube-dns or kube-proxy. You don’t even need a working overlay network.
-
-In this setup your pods can connect to the outside world (the same way any process on your hosts would talk to the outside world) but the outside world can’t connect to your pods.
-
-This isn’t super important (I think most people want to run HTTP services inside Kubernetes and actually communicate with those services) but I do think it’s interesting to realize that at some level all of this networking complexity isn’t strictly required and sometimes you can get away without using it. Avoiding networking complexity seems like a good idea to me if you can.
-
-### Operating an overlay network
-
-The first networking component we’re going to talk about is your overlay network. Kubernetes assumes that every pod has an IP address and that you can communicate with services inside that pod by using that IP address. When I say “overlay network” this is what I mean (“the system that lets you refer to a pod by its IP address”).
-
-All other Kubernetes networking stuff relies on the overlay networking working correctly. You can read more about the [kubernetes networking model here][10].
-
-The way Kelsey Hightower describes in [kubernetes the hard way][11] seems pretty good but it’s not really viable on AWS for clusters more than 50 nodes or so, so I’m not going to talk about that.
-
-There are a lot of overlay network backends (calico, flannel, weaveworks, romana) and the landscape is pretty confusing. But as far as I’m concerned an overlay network has 2 responsibilities:
-
-1. Make sure your pods can send network requests outside your cluster
-
-2. Keep a stable mapping of nodes to subnets and keep every node in your cluster updated with that mapping. Do the right thing when nodes are added & removed.
-
-Okay! So! What can go wrong with your overlay network?
-
-* The overlay network is responsible for setting up iptables rules (basically `iptables -A -t nat POSTROUTING -s $SUBNET -j MASQUERADE`) to ensure that containers can make network requests outside Kubernetes. If something goes wrong with this rule then your containers can’t connect to the external network. This isn’t that hard (it’s just a few iptables rules) but it is important. I made a [pull request][2] because I wanted to make sure this was resilient
-
-* Something can go wrong with adding or deleting nodes. We’re using the flannel hostgw backend and at the time we started using it, node deletion [did not work][3].
-
-* Your overlay network is probably dependent on a distributed database (etcd). If that database has an incident, this can cause issues. For example [https://github.com/coreos/flannel/issues/610][4] says that if you have data loss in your flannel etcd cluster it can result in containers losing network connectivity. (this has now been fixed)
-
-* You upgrade Docker and everything breaks
-
-* Probably more things!
-
-I’m mostly talking about past issues in Flannel here but I promise I’m not picking on Flannel – I actually really **like** Flannel because I feel like it’s relatively simple (for instance the [vxlan backend part of it][12] is like 500 lines of code) and I feel like it’s possible for me to reason through any issues with it. And it’s obviously continuously improving. They’ve been great about reviewing pull requests.
-
-My approach to operating an overlay network so far has been:
-
-* Learn how it works in detail and how to debug it (for example the hostgw network backend for Flannel works by creating routes, so you mostly just need to do `sudo ip route list` to see whether it’s doing the correct thing)
-
-* Maintain an internal build so it’s easy to patch it if needed
-
-* When there are issues, contribute patches upstream
-
-I think it’s actually really useful to go through the list of merged PRs and see bugs that have been fixed in the past – it’s a bit time consuming but is a great way to get a concrete list of kinds of issues other people have run into.
-
-It’s possible that for other people their overlay networks just work but that hasn’t been my experience and I’ve heard other folks report similar issues. If you have an overlay network setup that is a) on AWS and b) works on a cluster more than 50-100 nodes where you feel more confident about operating it I would like to know.
-
-### Operating kube-proxy and kube-dns?
-
-Now that we have some thoughts about operating overlay networks, let’s talk about
-
-There’s a question mark next to this one because I haven’t done this. Here I have more questions than answers.
-
-Here’s how Kubernetes services work! A service is a collection of pods, which each have their own IP address (like 10.1.0.3, 10.2.3.5, 10.3.5.6)
-
-1. Every Kubernetes service gets an IP address (like 10.23.1.2)
-
-2. `kube-dns` resolves Kubernetes service DNS names to IP addresses (so my-svc.my-namespace.svc.cluster.local might map to 10.23.1.2)
-
-3. `kube-proxy` sets up iptables rules in order to do random load balancing between them. Kube-proxy also has a userspace round-robin load balancer but my impression is that they don’t recommend using it.
-
-So when you make a request to `my-svc.my-namespace.svc.cluster.local`, it resolves to 10.23.1.2, and then iptables rules on your local host (generated by kube-proxy) redirect it to one of 10.1.0.3 or 10.2.3.5 or 10.3.5.6 at random.
-
-Some things that I can imagine going wrong with this:
-
-* `kube-dns` is misconfigured
-
-* `kube-proxy` dies and your iptables rules don’t get updated
-
-* Some issue related to maintaining a large number of iptables rules
-
-Let’s talk about the iptables rules a bit, since doing load balancing by creating a bajillion iptables rules is something I had never heard of before!
-
-kube-proxy creates one iptables rule per target host like this: (these rules are from [this github issue][13])
-
-```
--A KUBE-SVC-LI77LBOOMGYET5US -m comment --comment "default/showreadiness:showreadiness" -m statistic --mode random --probability 0.20000000019 -j KUBE-SEP-E4QKA7SLJRFZZ2DD[b][c]
--A KUBE-SVC-LI77LBOOMGYET5US -m comment --comment "default/showreadiness:showreadiness" -m statistic --mode random --probability 0.25000000000 -j KUBE-SEP-LZ7EGMG4DRXMY26H
--A KUBE-SVC-LI77LBOOMGYET5US -m comment --comment "default/showreadiness:showreadiness" -m statistic --mode random --probability 0.33332999982 -j KUBE-SEP-RKIFTWKKG3OHTTMI
--A KUBE-SVC-LI77LBOOMGYET5US -m comment --comment "default/showreadiness:showreadiness" -m statistic --mode random --probability 0.50000000000 -j KUBE-SEP-CGDKBCNM24SZWCMS
--A KUBE-SVC-LI77LBOOMGYET5US -m comment --comment "default/showreadiness:showreadiness" -j KUBE-SEP-RI4SRNQQXWSTGE2Y
-
-```
-
-So kube-proxy creates a **lot** of iptables rules. What does that mean? What are the implications of that in for my network? There’s a great talk from Huawei called [Scale Kubernetes to Support 50,000 services][14] that says if you have 5,000 services in your kubernetes cluster, it takes **11 minutes** to add a new rule. If that happened to your real cluster I think it would be very bad.
-
-I definitely don’t have 5,000 services in my cluster, but 5,000 isn’t SUCH a bit number. The proposal they give to solve this problem is to replace this iptables backend for kube-proxy with IPVS which is a load balancer that lives in the Linux kernel.
-
-It seems like kube-proxy is going in the direction of various Linux kernel based load balancers. I think this is partly because they support UDP load balancing, and other load balancers (like HAProxy) don’t support UDP load balancing.
-
-But I feel comfortable with HAProxy! Is it possible to replace kube-proxy with HAProxy! I googled this and I found this [thread on kubernetes-sig-network][15] saying:
-
-> kube-proxy is so awesome, we have used in production for almost a year, it works well most of time, but as we have more and more services in our cluster, we found it was getting hard to debug and maintain. There is no iptables expert in our team, we do have HAProxy&LVS experts, as we have used these for several years, so we decided to replace this distributed proxy with a centralized HAProxy. I think this maybe useful for some other people who are considering using HAProxy with kubernetes, so we just update this project and make it open source: [https://github.com/AdoHe/kube2haproxy][5]. If you found it’s useful , please take a look and give a try.
-
-So that’s an interesting option! I definitely don’t have answers here, but, some thoughts:
-
-* Load balancers are complicated
-
-* DNS is also complicated
-
-* If you already have a lot of experience operating one kind of load balancer (like HAProxy), it might make sense to do some extra work to use that instead of starting to use an entirely new kind of load balancer (like kube-proxy)
-
-* I’ve been thinking about where we want to be using kube-proxy or kube-dns at all – I think instead it might be better to just invest in Envoy and rely entirely on Envoy for all load balancing & service discovery. So then you just need to be good at operating Envoy.
-
-As you can see my thoughts on how to operate your Kubernetes internal proxies are still pretty confused and I’m still not super experienced with them. It’s totally possible that kube-proxy and kube-dns are fine and that they will just work fine but I still find it helpful to think through what some of the implications of using them are (for example “you can’t have 5,000 Kubernetes services”).
-
-### Ingress
-
-If you’re running a Kubernetes cluster, it’s pretty likely that you actually need HTTP requests to get into your cluster so far. This blog post is already too long and I don’t know much about ingress yet so we’re not going to talk about that.
-
-### Useful links
-
-A couple of useful links, to summarize:
-
-* [The Kubernetes networking model][6]
-
-* How GKE networking works: [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=y2bhV81MfKQ][7]
-
-* The aforementioned talk on `kube-proxy` performance: [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4-pawkiazEg][8]
-
-### I think networking operations is important
-
-My sense of all this Kubernetes networking software is that it’s all still quite new and I’m not sure we (as a community) really know how to operate all of it well. This makes me worried as an operator because I really want my network to keep working! :) Also I feel like as an organization running your own Kubernetes cluster you need to make a pretty large investment into making sure you understand all the pieces so that you can fix things when they break. Which isn’t a bad thing, it’s just a thing.
-
-My plan right now is just to keep learning about how things work and reduce the number of moving parts I need to worry about as much as possible.
-
-As usual I hope this was helpful and I would very much like to know what I got wrong in this post!
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: https://jvns.ca/blog/2017/10/10/operating-a-kubernetes-network/
-
-作者:[Julia Evans ][a]
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:https://jvns.ca/about
-[1]:http://blog.sophaskins.net/blog/misadventures-with-kube-dns/
-[2]:https://github.com/coreos/flannel/pull/808
-[3]:https://github.com/coreos/flannel/pull/803
-[4]:https://github.com/coreos/flannel/issues/610
-[5]:https://github.com/AdoHe/kube2haproxy
-[6]:https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/cluster-administration/networking/#kubernetes-model
-[7]:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=y2bhV81MfKQ
-[8]:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4-pawkiazEg
-[9]:https://jvns.ca/categories/kubernetes
-[10]:https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/cluster-administration/networking/#kubernetes-model
-[11]:https://github.com/kelseyhightower/kubernetes-the-hard-way/blob/master/docs/11-pod-network-routes.md
-[12]:https://github.com/coreos/flannel/tree/master/backend/vxlan
-[13]:https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/issues/37932
-[14]:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4-pawkiazEg
-[15]:https://groups.google.com/forum/#!topic/kubernetes-sig-network/3NlBVbTUUU0
diff --git a/sources/tech/20171228 Container Basics- Terms You Need to Know.md b/sources/tech/20171228 Container Basics- Terms You Need to Know.md
deleted file mode 100644
index a68e33a5d9..0000000000
--- a/sources/tech/20171228 Container Basics- Terms You Need to Know.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,48 +0,0 @@
-Container Basics: Terms You Need to Know
-======
-
-
-
-[In the previous article][1], we talked about what containers are and how they breed innovation and help companies move faster. And, in the following articles in this series, we will discuss how to use them. Before we dive more deeply into the topic, however, we need to understand some of the terms and commands used in the container world. Without a confident grasp of this terminology, things could get confusing.
-
-Let's explore some of the basic terms used in the [Docker][2] container world.
-
-**Container** **:** What exactly is container? It 's a runtime instance of a Docker image. It contains a Docker image, an execution environment, and instructions. It's totally isolated from the system so multiple containers can run on the system, completely oblivious of each other. You can replicate multiple containers from the same image and scale the service when the demand is high and nuke those containers when demand is low.
-
-**Docker Image** **:** This is no different from the image of a Linux distribution that you download. It's a package of dependencies and information for creating, deploying, and executing a container. You can spin up as many containers as you want in a matter of seconds. Each behaves exactly the same. Images are built on top of one another in layers. Once an image is created, it doesn't change. If you want to make changes to your container, you simply create a new image and deploy new containers from that image.
-
-**Repository (repo)** **:** Linux users will already be familiar with the term repository; it's a reservoir where packages are stored that can be downloaded and installed on a system. In the context of Docker containers, the only difference is that it hosts Docker images which are categorized via labels. You can have different variants of the same applications or different versions, all tagged appropriately.
-
-**Registry** **:** Think of this as like GitHub. It 's an online service that hosts and provides access to repositories of docker images. DockerHub, for example is the default registry for public images. Vendors can upload their repositories on DockerHub so that their customers can download and use official images. Some companies offer their own registries for their images. Registries don't have to be run and managed by third party vendors. Organizations can have on-prem registries to manage organization-wide access to repositories.
-
-**Tag** **:** When you create a Docker image, you can tag it appropriately so that different variants or versions can be easily identified. It's no different from what you see in any software package. Docker images are tagged when you add them to the repository.
-
-Now that you have an understanding of the basics, the next phase is understanding the terminology used when working with actual Docker containers.
-
-**Dockerfile** **:** This is a text file that comprises the commands that are executed manually in order to build a Docker image. These instructions are used by Docker to automatically build images.
-
-**Build** **:** This is the process that creates an image from Dockerfile.
-
-**Push** **:** Once the image is created, "push" is the process to publish that image to the repository. The term is also used as part of a command that we will learn in the next articles.
-
-**Pull** **:** A user can retrieve that image from repository through the "pull" process.
-
-**Compose** **:** Most complex applications comprise more than one container. Compose is a command-line tool that 's used to run a multi-container application. It allows you to run a multi-container application with one command. It eases the headache of running multiple containers needed for that application.
-
-### Conclusion
-
-The scope of container terminology is massive, but these are some basic terms that you will frequently encounter. The next time you see these terms, you will know exactly what they mean. In the next article, we will get started working with Docker containers.
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: https://www.linux.com/blog/intro-to-linux/2017/12/container-basics-terms-you-need-know
-
-作者:[Swapnil Bhartiya][a]
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:https://www.linux.com/users/arnieswap
-[1]:https://www.linux.com/blog/intro-to-linux/2017/12/what-are-containers-and-why-should-you-care
-[2]:https://www.docker.com/
diff --git a/sources/tech/20180228 Why Python devs should use Pipenv.md b/sources/tech/20180228 Why Python devs should use Pipenv.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 1b2efeebb7..0000000000
--- a/sources/tech/20180228 Why Python devs should use Pipenv.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,136 +0,0 @@
-Translating by MjSeven
-
-
-Why Python devs should use Pipenv
-======
-
-
-
-This article was co-written with [Jeff Triplett][1].
-
-Pipenv, the "Python Development Workflow for Humans" created by Kenneth Reitz a little more than a year ago, has become the [official Python-recommended resource][2] for managing package dependencies. But there is still confusion about what problems it solves and how it's more useful than the standard workflow using `pip` and a `requirements.txt` file. In this month's Python column, we'll fill in the gaps.
-
-### A brief history of Python package installation
-
-To understand the problems that Pipenv solves, it's useful to show how Python package management has evolved.
-
-Take yourself back to the first Python iteration. We had Python, but there was no clean way to install packages.
-
-Then came [Easy Install][3], a package that installs other Python packages with relative ease. But it came with a catch: it wasn't easy to uninstall packages that were no longer needed.
-
-Enter [pip][4], which most Python users are familiar with. `pip` lets us install and uninstall packages. We could specify versions, run `pip freeze > requirements.txt` to output a list of installed packages to a text file, and use that same text file to install everything an app needed with `pip install -r requirements.txt`.
-
-But `pip` didn't include a way to isolate packages from each other. We might work on apps that use different versions of the same libraries, so we needed a way to enable that. Along came [virtual environments][5], which enabled us to create small, isolated environments for each app we worked on. We've seen many tools for managing virtual environments: [virtualenv][6], [venv][7], [virtualenvwrapper][8], [pyenv][9], [pyenv-virtualenv][10], [pyenv-virtualenvwrapper][11], and even more. They all play well with `pip` and `requirements.txt` files.
-
-### The new kid: Pipenv
-
-Pipenv aims to solve several problems.
-
-`pip` library for package installation, plus a library for creating a virtual environment, plus a library for managing virtual environments, plus all the commands associated with those libraries. That's a lot to manage. Pipenv ships with package management and virtual environment support, so you can use one tool to install, uninstall, track, and document your dependencies and to create, use, and organize your virtual environments. When you start a project with it, Pipenv will automatically create a virtual environment for that project if you aren't already using one.
-
-First, the problem of needing thelibrary for package installation, plus a library for creating a virtual environment, plus a library for managing virtual environments, plus all the commands associated with those libraries. That's a lot to manage. Pipenv ships with package management and virtual environment support, so you can use one tool to install, uninstall, track, and document your dependencies and to create, use, and organize your virtual environments. When you start a project with it, Pipenv will automatically create a virtual environment for that project if you aren't already using one.
-
-Pipenv accomplishes this dependency management by abandoning the `requirements.txt` norm and trading it for a new document called a [Pipfile][12]. When you install a library with Pipenv, a `Pipfile` for your project is automatically updated with the details of that installation, including version information and possibly the Git repository location, file path, and other information.
-
-Second, Pipenv wants to make it easier to manage complex interdependencies. Your app might depend on a specific version of a library, and that library might depend on a specific version of another library, and it's just dependencies and turtles all the way down. When two libraries your app uses have conflicting dependencies, your life can become hard. Pipenv wants to ease that pain by keeping track of a tree of your app's interdependencies in a file called `Pipfile.lock`. `Pipfile.lock` also verifies that the right versions of dependencies are used in production.
-
-Also, Pipenv is handy when multiple developers are working on a project. With a `pip` workflow, Casey might install a library and spend two days implementing a new feature using that library. When Casey commits the changes, they might forget to run `pip freeze` to update the requirements file. The next day, Jamie pulls down Casey's changes, and suddenly tests are failing. It takes time to realize that the problem is libraries missing from the requirements file that Jamie doesn't have installed in the virtual environment.
-
-Because Pipenv auto-documents dependencies as you install them, if Jamie and Casey had been using Pipenv, the `Pipfile` would have been automatically updated and included in Casey's commit. Jamie and Casey would have saved time and shipped their product faster.
-
-Finally, using Pipenv signals to other people who work on your project that it ships with a standardized way to install project dependencies and development and testing requirements. Using a workflow with `pip` and requirements files means that you may have one single `requirements.txt` file, or several requirements files for different environments. It might not be clear to your colleagues whether they should run `dev.txt` or `local.txt` when they're running the project on their laptops, for example. It can also create confusion when two similar requirements files get wildly out of sync with each other: Is `local.txt` out of date, or is it really supposed to be that different from `dev.txt`? Multiple requirements files require more context and documentation to enable others to install the dependencies properly and as expected. This workflow has the potential to confuse colleagues and increase your maintenance burden.
-
-Using Pipenv, which gives you `Pipfile`, lets you avoid these problems by managing dependencies for different environments for you. This command will install the main project dependencies:
-```
-pipenv install
-
-```
-
-Adding the `--dev` tag will install the dev/testing requirements:
-```
-pipenv install --dev
-
-```
-
-There are other benefits to using Pipenv: It has better security features, graphs your dependencies in an easier-to-understand format, seamlessly handles `.env` files, and can automatically handle differing dependencies for development versus production environments in one file. You can read more in the [documentation][13].
-
-### Pipenv in action
-
-The basics of using Pipenv are detailed in the [Managing Application Dependencies][14] section of the official Python packaging tutorial. To install Pipenv, use `pip`:
-```
-pip install pipenv
-
-```
-
-To install packages to use in your project, change into the directory for your project. Then to install a package (we'll use Django as an example), run:
-```
-pipenv install django
-
-```
-
-You will see some output that indicates that Pipenv is creating a `Pipfile` for your project.
-
-If you aren't already using a virtual environment, you will also see some output from Pipenv saying it is creating a virtual environment for you.
-
-Then, you will see the output you are used to seeing when you install packages.
-
-To generate a `Pipfile.lock` file, run:
-```
-pipenv lock
-
-```
-
-You can also run Python scripts with Pipenv. To run a top-level Python script called `hello.py`, run:
-```
-pipenv run python hello.py
-
-```
-
-And you will see your expected result in the console.
-
-To start a shell, run:
-```
-pipenv shell
-
-```
-
-If you would like to convert a project that currently uses a `requirements.txt` file to use Pipenv, install Pipenv and run:
-```
-pipenv install requirements.txt
-
-```
-
-This will create a Pipfile and install the specified requirements. Consider your project upgraded!
-
-### Learn more
-
-Check out the Pipenv documentation, particularly [Basic Usage of Pipenv][15], to take you further. Pipenv creator Kenneth Reitz gave a talk on Pipenv, "[The Future of Python Dependency Management][16]," at a recent PyTennessee event. The talk wasn't recorded, but his [slides][17] are helpful in understanding what Pipenv does and the problems it solves.
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: https://opensource.com/article/18/2/why-python-devs-should-use-pipenv
-
-作者:[Lacey Williams Henschel][a]
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:https://opensource.com/users/laceynwilliams
-[1]:https://opensource.com/users/jefftriplett
-[2]:https://packaging.python.org/tutorials/managing-dependencies/#managing-dependencies
-[3]:http://peak.telecommunity.com/DevCenter/EasyInstall
-[4]:https://packaging.python.org/tutorials/installing-packages/#use-pip-for-installing
-[5]:https://packaging.python.org/tutorials/installing-packages/#creating-virtual-environments
-[6]:https://virtualenv.pypa.io/en/stable/
-[7]:https://docs.python.org/3/library/venv.html
-[8]:https://virtualenvwrapper.readthedocs.io/en/latest/
-[9]:https://github.com/pyenv/pyenv
-[10]:https://github.com/pyenv/pyenv-virtualenv
-[11]:https://github.com/pyenv/pyenv-virtualenvwrapper
-[12]:https://github.com/pypa/pipfile
-[13]:https://docs.pipenv.org/
-[14]:https://packaging.python.org/tutorials/managing-dependencies/
-[15]:https://docs.pipenv.org/basics/
-[16]:https://www.pytennessee.org/schedule/presentation/158/
-[17]:https://speakerdeck.com/kennethreitz/the-future-of-python-dependency-management
diff --git a/sources/tech/20180313 Migrating to Linux- Using Sudo.md b/sources/tech/20180313 Migrating to Linux- Using Sudo.md
index a97dc4d289..7ad9426ab8 100644
--- a/sources/tech/20180313 Migrating to Linux- Using Sudo.md
+++ b/sources/tech/20180313 Migrating to Linux- Using Sudo.md
@@ -1,3 +1,5 @@
+translating---geekpi
+
Migrating to Linux: Using Sudo
======
diff --git a/sources/tech/20180529 5 trending open source machine learning JavaScript frameworks.md b/sources/tech/20180529 5 trending open source machine learning JavaScript frameworks.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 76a05c9155..0000000000
--- a/sources/tech/20180529 5 trending open source machine learning JavaScript frameworks.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,67 +0,0 @@
-translated by hopefully2333
-
-5 trending open source machine learning JavaScript frameworks
-======
-
-
-The tremendous growth of the machine learning field has been driven by the availability of open source tools that allow developers to build applications easily. (For example, [AndreyBu][1], who is from Germany and has more than five years of experience in machine learning, has been utilizing various open source frameworks to build captivating machine learning projects.)
-
-Although the Python programming language powers most of the machine learning frameworks, JavaScript hasn’t been left behind. JavaScript developers have been using various frameworks for training and deploying machine learning models in the browser.
-
-Here are the five trending open source machine learning frameworks in JavaScript.
-
-### 1\. TensorFlow.js
-
-[TensorFlow.js][2] is an open source library that allows you to run machine learning programs completely in the browser. It is the successor of Deeplearn.js, which is no longer supported. TensorFlow.js improves on the functionalities of Deeplearn.js and empowers you to make the most of the browser for a deeper machine learning experience.
-
-With the library, you can use versatile and intuitive APIs to define, train, and deploy models from scratch right in the browser. Furthermore, it automatically offers support for WebGL and Node.js.
-
-If you have pre-existing trained models you want to import to the browser, TensorFlow.js will allow you do that. You can also retrain existing models without leaving the browser.
-
-The [machine learning tools][3] library is a compilation of resourceful open source tools for supporting widespread machine learning functionalities in the browser. The tools provide support for several machine learning algorithms, including unsupervised learning, supervised learning, data processing, artificial neural networks (ANN), math, and regression.
-
-If you are coming from a Python background and looking for something similar to Scikit-learn for JavaScript in-browser machine learning, this suite of tools could have you covered.
-
-### 3\. Keras.js
-
-[Keras.js][4] is another trending open source framework that allows you to run machine learning models in the browser. It offers GPU mode support using WebGL. If you have models in Node.js, you’ll run them only in CPU mode. Keras.js also offers support for models trained using any backend framework, such as the Microsoft Cognitive Toolkit (CNTK).
-
-Some of the Keras models that can be deployed on the client-side browser include Inception v3 (trained on ImageNet), 50-layer Residual Network (trained on ImageNet), and Convolutional variational auto-encoder (trained on MNIST).
-
-### 4\. Brain.js
-
-Machine learning concepts are very math-heavy, which may discourage people from starting. The technicalities and jargons in this field may make beginners freak out. This is where [Brain.js][5] becomes important. It is an open source, JavaScript-powered framework that simplifies the process of defining, training, and running neural networks.
-
-If you are a JavaScript developer who is completely new to machine learning, Brain.js could reduce your learning curve. It can be used with Node.js or in the client-side browser for training machine learning models. Some of the networks that Brain.js supports include feed-forward networks, Ellman networks, and Gated Recurrent Units networks.
-
-### 5\. STDLib
-
-[STDLib][6] is an open source library for powering JavaScript and Node.js applications. If you are looking for a library that emphasizes in-browser support for scientific and numerical web-based machine learning applications, STDLib could suit your needs.
-
-The library comes with comprehensive and advanced mathematical and statistical functions to assist you in building high-performing machine learning models. You can also use its expansive utilities for building applications and other libraries. Furthermore, if you want a framework for data visualization and exploratory data analysis, you’ll find STDLib worthwhile.
-
-### Conclusion
-
-If you are a JavaScript developer who intends to delve into the exciting world of [machine learning][7] or a machine learning expert who intends to start using JavaScript, the above open source frameworks will intrigue you.
-
-Do you know of another open source library that offers in-browser machine learning capabilities? Please let us know in the comment section below.
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: https://opensource.com/article/18/5/machine-learning-javascript-frameworks
-
-作者:[Dr.Michael J.Garbade][a]
-选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:https://opensource.com/users/drmjg
-[1]:https://www.liveedu.tv/andreybu/REaxr-machine-learning-model-python-sklearn-kera/
-[2]:https://js.tensorflow.org/
-[3]:https://github.com/mljs/ml
-[4]:https://transcranial.github.io/keras-js/#/
-[5]:https://github.com/BrainJS/brain.js
-[6]:https://stdlib.io/
-[7]:https://www.liveedu.tv/guides/artificial-intelligence/machine-learning/
diff --git a/sources/tech/20180530 3 Python command-line tools.md b/sources/tech/20180530 3 Python command-line tools.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 6aad040b71..0000000000
--- a/sources/tech/20180530 3 Python command-line tools.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,270 +0,0 @@
-3 Python command-line tools
-======
-
-
-
-This article was co-written with [Lacey Williams Henschel][1].
-
-Sometimes the right tool for the job is a command-line application. A command-line application is a program that you interact with and run from something like your shell or Terminal. [Git][2] and [Curl][3] are examples of command-line applications that you might already be familiar with.
-
-Command-line apps are useful when you have a bit of code you want to run several times in a row or on a regular basis. Django developers run commands like `./manage.py runserver` to start their web servers; Docker developers run `docker-compose up` to spin up their containers. The reasons you might want to write a command-line app are as varied as the reasons you might want to write code in the first place.
-
-For this month's Python column, we have three libraries to recommend to Pythonistas looking to write their own command-line tools.
-
-### Click
-
-[Click][4] is our favorite Python package for command-line applications. It:
-
- * Has great documentation filled with examples
-
- * Includes instructions on packaging your app as a Python application so it's easier to run
-
- * Automatically generates useful help text
-
- * Lets you stack optional and required arguments and even [several commands][5]
-
- * Has a Django version ([][6]
-
-`django-click`
-
-) for writing management commands
-
-
-
-
-Click uses its `@click.command()` to declare a function as a command and specify required or optional arguments.
-```
-# hello.py
-
-import click
-
-
-
-@click.command()
-
-@click.option('--name', default='', help='Your name')
-
-def say_hello(name):
-
- click.echo("Hello {}!".format(name))
-
-
-
-if __name__ == '__main__':
-
- hello()
-
-```
-
-The `@click.option()` decorator declares an [optional argument][7], and the `@click.argument()` decorator declares a [required argument][8]. You can combine optional and required arguments by stacking the decorators. The `echo()` method prints results to the console.
-```
-$ python hello.py --name='Lacey'
-
-Hello Lacey!
-
-```
-
-### Docopt
-
-[Docopt][9] is a command-line application parser, sort of like Markdown for your command-line apps. If you like writing the documentation for your apps as you go, Docopt has by far the best-formatted help text of the options in this article. It isn't our favorite command-line app library because its documentation throws you into the deep end right away, which makes it a little more difficult to get started. Still, it's a lightweight library that is very popular, especially if exceptionally nice documentation is important to you.
-
-`help` and `version` flags.
-
-Docopt is very particular about how you format the required docstring at the top of your file. The top element in your docstring after the name of your tool must be "Usage," and it should list the ways you expect your command to be called (e.g., by itself, with arguments, etc.). Usage should includeandflags.
-
-The second element in your docstring should be "Options," and it should provide more information about the options and arguments you identified in "Usage." The content of your docstring becomes the content of your help text.
-```
-"""HELLO CLI
-
-
-
-Usage:
-
- hello.py
-
- hello.py
-
- hello.py -h|--help
-
- hello.py -v|--version
-
-
-
-Options:
-
- Optional name argument.
-
- -h --help Show this screen.
-
- -v --version Show version.
-
-"""
-
-
-
-from docopt import docopt
-
-
-
-def say_hello(name):
-
- return("Hello {}!".format(name))
-
-
-
-
-
-if __name__ == '__main__':
-
- arguments = docopt(__doc__, version='DEMO 1.0')
-
- if arguments['']:
-
- print(say_hello(arguments['']))
-
- else:
-
- print(arguments)
-
-```
-
-At its most basic level, Docopt is designed to return your arguments to the console as key-value pairs. If I call the above command without specifying a name, I get a dictionary back:
-```
-$ python hello.py
-
-{'--help': False,
-
- '--version': False,
-
- '': None}
-
-```
-
-This shows me I did not input the `help` or `version` flags, and the `name` argument is `None`.
-
-But if I call it with a name, the `say_hello` function will execute.
-```
-$ python hello.py Jeff
-
-Hello Jeff!
-
-```
-
-Docopt allows both required and optional arguments and has different syntax conventions for each. Required arguments should be represented in `ALLCAPS` or in ``, and options should be represented with double or single dashes, like `--name`. Read more about Docopt's [patterns][10] in the docs.
-
-### Fire
-
-[Fire][11] is a Google library for writing command-line apps. We especially like it when your command needs to take more complicated arguments or deal with Python objects, as it tries to handle parsing your argument types intelligently.
-
-Fire's [docs][12] include a ton of examples, but I wish the docs were a bit better organized. Fire can handle [multiple commands in one file][13], commands as methods on [objects][14], and [grouping][15] commands.
-
-Its weakness is the documentation it makes available to the console. Docstrings on your commands don't appear in the help text, and the help text doesn't necessarily identify arguments.
-```
-import fire
-
-
-
-
-
-def say_hello(name=''):
-
- return 'Hello {}!'.format(name)
-
-
-
-
-
-if __name__ == '__main__':
-
- fire.Fire()
-
-```
-
-Arguments are made required or optional depending on whether you specify a default value for them in your function or method definition. To call this command, you must specify the filename and the function name, more like Click's syntax:
-```
-$ python hello.py say_hello Rikki
-
-Hello Rikki!
-
-```
-
-You can also pass arguments as flags, like `--name=Rikki`.
-
-### Bonus: Packaging!
-
-Click includes instructions (and highly recommends you follow them) for [packaging][16] your commands using `setuptools`.
-
-To package our first example, add this content to your `setup.py` file:
-```
-from setuptools import setup
-
-
-
-setup(
-
- name='hello',
-
- version='0.1',
-
- py_modules=['hello'],
-
- install_requires=[
-
- 'Click',
-
- ],
-
- entry_points='''
-
- [console_scripts]
-
- hello=hello:say_hello
-
- ''',
-
-)
-
-```
-
-Everywhere you see `hello`, substitute the name of your module but omit the `.py` extension. Where you see `say_hello`, substitute the name of your function.
-
-Then, run `pip install --editable` to make your command available to the command line.
-
-You can now call your command like this:
-```
-$ hello --name='Jeff'
-
-Hello Jeff!
-
-```
-
-By packaging your command, you omit the extra step in the console of having to type `python hello.py --name='Jeff'` and save yourself several keystrokes. These instructions will probably also work for the other libraries we mentioned.
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: https://opensource.com/article/18/5/3-python-command-line-tools
-
-作者:[Jeff Triplett][a]
-选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:https://opensource.com/users/laceynwilliams
-[1]:https://opensource.com/users/laceynwilliams
-[2]:https://git-scm.com/
-[3]:https://curl.haxx.se/
-[4]:http://click.pocoo.org/5/
-[5]:http://click.pocoo.org/5/commands/
-[6]:https://github.com/GaretJax/django-click
-[7]:http://click.pocoo.org/5/options/
-[8]:http://click.pocoo.org/5/arguments/
-[9]:http://docopt.org/
-[10]:https://github.com/docopt/docopt#usage-pattern-format
-[11]:https://github.com/google/python-fire
-[12]:https://github.com/google/python-fire/blob/master/docs/guide.md
-[13]:https://github.com/google/python-fire/blob/master/docs/guide.md#exposing-multiple-commands
-[14]:https://github.com/google/python-fire/blob/master/docs/guide.md#version-3-firefireobject
-[15]:https://github.com/google/python-fire/blob/master/docs/guide.md#grouping-commands
-[16]:http://click.pocoo.org/5/setuptools/
diff --git a/sources/tech/20180620 Stop merging your pull requests manually.md b/sources/tech/20180620 Stop merging your pull requests manually.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 06de0ea7f3..0000000000
--- a/sources/tech/20180620 Stop merging your pull requests manually.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,87 +0,0 @@
-translating---geekpi
-
-Stop merging your pull requests manually
-======
-
-
-
-If there's something that I hate, it's doing things manually when I know I could automate them. Am I alone in this situation? I doubt so.
-
-Nevertheless, every day, they are thousands of developers using [GitHub][1] that are doing the same thing over and over again: they click on this button:
-
-![Screen-Shot-2018-06-19-at-18.12.39][2]
-
-This does not make any sense.
-
-Don't get me wrong. It makes sense to merge pull requests. It just does not make sense that someone has to push this damn button every time.
-
-It does not make any sense because every development team in the world has a known list of pre-requisite before they merge a pull request. Those requirements are almost always the same, and it's something along those lines:
-
- * Is the test suite passing?
- * Is the documentation up to date?
- * Does this follow our code style guideline?
- * Have N developers reviewed this?
-
-
-
-As this list gets longer, the merging process becomes more error-prone. "Oops, John just clicked on the merge button while there were not enough developer that reviewed the patch." Rings a bell?
-
-In my team, we're like every team out there. We know what our criteria to merge some code into our repository are. That's why we set up a continuous integration system that runs our test suite each time somebody creates a pull request. We also require the code to be reviewed by 2 members of the team before it's approbated.
-
-When those conditions are all set, I want the code to be merged.
-
-Without clicking a single button.
-
-That's exactly how [Mergify][3] started.
-
-![github-branching-1][4]
-
-[Mergify][3] is a service that pushes that merge button for you. You define rules in the `.mergify.yml` file of your repository, and when the rules are satisfied, Mergify merges the pull request.
-
-No need to press any button.
-
-Take a random pull request, like this one:
-
-![Screen-Shot-2018-06-20-at-17.12.11][5]
-
-This comes from a small project that does not have a lot of continuous integration services set up, just Travis. In this pull request, everything's green: one of the owners reviewed the code, and the tests are passing. Therefore, the code should be already merged: but it's there, hanging, chilling, waiting for someone to push that merge button. Someday.
-
-With [Mergify][3] enabled, you'd just have to put this `.mergify.yml` a the root of the repository:
-```
-rules:
- default:
- protection:
- required_status_checks:
- contexts:
- - continuous-integration/travis-ci
- required_pull_request_reviews:
- required_approving_review_count: 1
-
-```
-
-With such a configuration, [Mergify][3] enables the desired restrictions, i.e., Travis passes, and at least one project member reviewed the code. As soon as those conditions are positive, the pull request is automatically merged.
-
-We built [Mergify][3] as a **free service for open-source projects**. The [engine powering the service][6] is also open-source.
-
-Now go [check it out][3] and stop letting those pull requests hang out one second more. Merge them!
-
-If you have any question, feel free to ask us or write a comment below! And stay tuned — as Mergify offers a few other features that I can't wait to talk about!
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: https://julien.danjou.info/stop-merging-your-pull-request-manually/
-
-作者:[Julien Danjou][a]
-选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:https://julien.danjou.info/author/jd/
-[1]:https://github.com
-[2]:https://julien.danjou.info/content/images/2018/06/Screen-Shot-2018-06-19-at-18.12.39.png
-[3]:https://mergify.io
-[4]:https://julien.danjou.info/content/images/2018/06/github-branching-1.png
-[5]:https://julien.danjou.info/content/images/2018/06/Screen-Shot-2018-06-20-at-17.12.11.png
-[6]:https://github.com/mergifyio/mergify-engine
diff --git a/sources/tech/20180622 Automatically Change Wallpapers in Linux with Little Simple Wallpaper Changer.md b/sources/tech/20180622 Automatically Change Wallpapers in Linux with Little Simple Wallpaper Changer.md
index 3c4d220a6a..d3d3c00937 100644
--- a/sources/tech/20180622 Automatically Change Wallpapers in Linux with Little Simple Wallpaper Changer.md
+++ b/sources/tech/20180622 Automatically Change Wallpapers in Linux with Little Simple Wallpaper Changer.md
@@ -1,3 +1,5 @@
+translating----geekpi
+
Automatically Change Wallpapers in Linux with Little Simple Wallpaper Changer
======
diff --git a/sources/tech/20180628 Blockchain evolution- A quick guide and why open source is at the heart of it.md b/sources/tech/20180628 Blockchain evolution- A quick guide and why open source is at the heart of it.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..585a7203d1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/tech/20180628 Blockchain evolution- A quick guide and why open source is at the heart of it.md
@@ -0,0 +1,97 @@
+Blockchain evolution: A quick guide and why open source is at the heart of it
+======
+
+
+
+It isn't uncommon, when working on a new version of an open source project, to suffix it with "-ng", for "next generation." Fortunately, in their rapid evolution blockchains have so far avoided this naming pitfall. But in this evolutionary open source ecosystem, changes have been abundant, and good ideas have been picked up, remixed, and evolved between many different projects in a typical open source fashion.
+
+In this article, I will look at the different generations of blockchains and what ideas have emerged to address the problems the ecosystem has encountered. Of course, any attempt at classifying an ecosystem will have limits—and objectors—but it should provide a rough guide to the jungle of blockchain projects.
+
+### The beginning: Bitcoin
+
+The first generation of blockchains stems from the [Bitcoin][1] blockchain, the ledger underpinning the decentralized, peer-to-peer cryptocurrency that has gone from [Slashdot][2] miscellanea to a mainstream topic.
+
+This blockchain is a distributed ledger that keeps track of all users' transactions to prevent them from double-spending their coins (a task historically entrusted to third parties: banks). To prevent attackers from gaming the system, the ledger is replicated to every computer participating in the Bitcoin network and can be updated by only one computer in the network at a time. To decide which computer earns the right to update the ledger, the system organizes every 10 minutes a race between the computers, which costs them (a lot of) energy to enter. The winner wins the right to commit the last 10 minutes of transactions to the ledger (the "block" in blockchain) and some Bitcoin as a reward for their efforts. This setup is called a _proof of work_ consensus mechanism.
+
+The goal of using a blockchain is to raise the level of trust participants have in the network.
+
+This is where it gets interesting. Bitcoin was released as an [open source project][3] in January 2009. In 2010, realizing that quite a few of these elements can be tweaked, the community that had aggregated around Bitcoin, often on the [bitcointalk forums][4], started experimenting with them.
+
+First, seeing that the Bitcoin blockchain is a form of a distributed database, the [Namecoin][5] project emerged, suggesting to store arbitrary data in its transaction database. If the blockchain can record the transfer of money, it could also record the transfer of other assets, such as domain names. This is exactly Namecoin's main use case, which went live in April 2011, two years after Bitcoin's introduction.
+
+Where Namecoin tweaked the content of the blockchain, [Litecoin][6] tweaked two technical aspects: reducing the time between two blocks from 10 to 2.5 minutes and changing how the race is run (replacing the SHA-256 secure hashing algorithm with [scrypt][7]). This was possible because Bitcoin was released as open source software and Litecoin is essentially identical to Bitcoin in all other places. Litecoin was the first fork to modify the consensus mechanism, paving the way for many more.
+
+Along the way, many more variations of the Bitcoin codebase have appeared. Some started as proposed extensions to Bitcoin, such as the [Zerocash][8] protocol, which aimed to provide transaction anonymity and fungibility but was eventually spun off into its own currency, [Zcash][9].
+
+While Zcash has brought its own innovations, using recent cryptographic advances known as zero-knowledge proofs, it maintains compatibility with the vast majority of the Bitcoin code base, meaning it too can benefit from upstream Bitcoin innovations.
+
+Another project, [CryptoNote][10], didn't use the same code base but sprouted from the same community, building on (and against) Bitcoin and again, on older ideas. Published in December 2012, it led to the creation of several cryptocurrencies, of which [Monero][11] (2014) is the best-known. Monero takes a different approach to Zcash but aims to solve the same issues: privacy and fungibility.
+
+As is often the case in the open source world, there is more than one tool for the job.
+
+### The next generations: "Blockchain-ng"
+
+So far, however, all these variations have only really been about refining cryptocurrencies or extending them to support another type of transaction. This brings us to the second generation of blockchains.
+
+Once the community started modifying what a blockchain could be used for and tweaking technical aspects, it didn't take long for some people to expand and rethink them further. A longtime follower of Bitcoin, [Vitalik Buterin][12] suggested in late 2013 that a blockchain's transactions could represent the change of states of a state machine, conceiving the blockchain as a distributed computer capable of running applications ("smart contracts"). The project, [Ethereum][13], went live in July 2015. It has seen fair success in running distributed apps, and the popularity of some of its better-known distributed apps ([CryptoKitties][14]) have even caused the Ethereum blockchain to slow down.
+
+This demonstrates one of the big limitations of current blockchains: speed and capacity. (Speed is often measured in transactions per second, or TPS.) Several approaches have been suggested to solve this, from sharding to sidechains and so-called "second-layer" solutions. The need for more innovation here is strong.
+
+With the words "smart contract" in the air and a proved—if still slow—technology to run them, another idea came to fruition: permissioned blockchains. So far, all the blockchain networks we've described have had two unsaid characteristics: They are public (anyone can see them function), and they are without permission (anyone can join them). These two aspects are both desirable and necessary to run a distributed, non-third-party-based currency.
+
+As blockchains were being considered more and more separately from cryptocurrencies, it started to make sense to consider them in some private, permissioned settings. A consortium-type group of actors that have business relationships but don't necessarily trust each other fully can benefit from these types of blockchains—for example, actors along a logistics chain, financial or insurance institutions that regularly do bilateral settlements or use a clearinghouse, idem for healthcare institutions.
+
+Once you change the setting from "anyone can join" to "invitation-only," further changes and tweaks to the blockchain building blocks become possible, yielding interesting results for some.
+
+For a start, proof of work, designed to protect the network from malicious and spammy actors, can be replaced by something simpler and less resource-hungry, such as a [Raft][15]-based consensus protocol. A tradeoff appears between a high level of security or faster speed, embodied by the option of simpler consensus algorithms. This is highly desirable to many groups, as they can trade some cryptography-based assurance for assurance based on other means—legal relationships, for instance—and avoid the energy-hungry arms race that proof of work often leads to. This is another area where innovation is ongoing, with [Proof of Stake][16] a notable contender for the public network consensus mechanism of choice. It would likely also find its way to permissioned networks too.
+
+Several projects make it simple to create permissioned blockchains, including [Quorum][17] (a fork of Ethereum) and [Hyperledger][18]'s [Fabric][19] and [Sawtooth][20], two open source projects based on new code.
+
+Permissioned blockchains can avoid certain complexities that public, non-permissioned ones can't, but they still have their own set of issues. Proper management of participants is one: Who can join? How do they identify? How can they be removed from the network? Does one entity on the network manage a central public key infrastructure (PKI)?
+
+The open nature of blockchains is seen as a form of governance.
+
+### Open nature of blockchains
+
+In all of the cases so far, one thing is clear: The goal of using a blockchain is to raise the level of trust participants have in the network and the data it produces—ideally, enough to be able to use it as is, without further work.
+
+Reaching this level of trust is possible only if the software that powers the network is free and open source. Even a correctly distributed proprietary blockchain is essentially a collection of independent agents running the same third party's code. By nature, it's necessary—but not sufficient—for a blockchain's source code to be open source. This has both been a minimum guarantee and the source of further innovation as the ecosystem keeps growing.
+
+Finally, it is worth mentioning that while the open nature of blockchains has been a source of innovation and variation, it has also been seen as a form of governance: governance by code, where users are expected to run whichever specific version of the code contains a function or approach they think the whole network should embrace. In this respect, one can say the open nature of some blockchains has also become a cop-out regarding governance. But this is being addressed.
+
+### Third and fourth generations: governance
+
+Next, I will look at what I am currently considering the third and fourth generations of blockchains: blockchains with built-in governance tools and projects to solve the tricky question of interconnecting the multitude of different blockchain projects to let them exchange information and value with each other.
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://opensource.com/article/18/6/blockchain-guide-next-generation
+
+作者:[Axel Simon][a]
+选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:https://opensource.com/users/axel
+[1]:https://bitcoin.org
+[2]:https://slashdot.org/
+[3]:https://github.com/bitcoin/bitcoin
+[4]:https://bitcointalk.org/
+[5]:https://www.namecoin.org/
+[6]:https://litecoin.org/
+[7]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Scrypt
+[8]:http://zerocash-project.org/index
+[9]:https://z.cash
+[10]:https://cryptonote.org/
+[11]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Monero_(cryptocurrency)
+[12]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vitalik_Buterin
+[13]:https://ethereum.org
+[14]:http://cryptokitties.co/
+[15]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Raft_(computer_science)
+[16]:https://www.investopedia.com/terms/p/proof-stake-pos.asp
+[17]:https://www.jpmorgan.com/global/Quorum
+[18]:https://hyperledger.org/
+[19]:https://www.hyperledger.org/projects/fabric
+[20]:https://www.hyperledger.org/projects/sawtooth
diff --git a/sources/tech/20180628 Sosreport - A Tool To Collect System Logs And Diagnostic Information.md b/sources/tech/20180628 Sosreport - A Tool To Collect System Logs And Diagnostic Information.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..a476c5e0cd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/tech/20180628 Sosreport - A Tool To Collect System Logs And Diagnostic Information.md
@@ -0,0 +1,142 @@
+translating---geekpi
+
+
+Sosreport – A Tool To Collect System Logs And Diagnostic Information
+======
+
+
+
+If you’re working as RHEL administrator, you might definitely heard about **Sosreport** – an extensible, portable and support data collection tool. It is a tool to collect system configuration details and diagnostic information from a Unix-like operating system. When the user raise a support ticket, he/she has to run this tool and send the resulting report generated by Sosreport tool to the Red Hat support executive. The executive will then perform an initial analysis based on the report and try to find what’s the problem in the system. Not just on RHEL system, you can use it on any Unix-like operating systems for collecting system logs and other debug information.
+
+### Installing Sosreport
+
+Sosreport is available on Red Hat official systems, so you can install it using Yum Or DNF package managers as shown below.
+```
+$ sudo yum install sos
+
+```
+
+Or,
+```
+$ sudo dnf install sos
+
+```
+
+On Debian, Ubuntu and Linux Mint, run:
+```
+$ sudo apt install sosreport
+
+```
+
+### Usage
+
+Once installed, run the following command to collect your system configuration details and other diagnostic information.
+```
+$ sudo sosreport
+
+```
+
+You will be asked to enter some details of your system, such as system name, case id etc. Type the details accordingly, and press ENTER key to generate the report. If you don’t want to change anything and want to use the default values, simply press ENTER.
+
+Sample output from my CentOS 7 server:
+```
+sosreport (version 3.5)
+
+This command will collect diagnostic and configuration information from
+this CentOS Linux system and installed applications.
+
+An archive containing the collected information will be generated in
+/var/tmp/sos.DiJXi7 and may be provided to a CentOS support
+representative.
+
+Any information provided to CentOS will be treated in accordance with
+the published support policies at:
+
+https://wiki.centos.org/
+
+The generated archive may contain data considered sensitive and its
+content should be reviewed by the originating organization before being
+passed to any third party.
+
+No changes will be made to system configuration.
+
+Press ENTER to continue, or CTRL-C to quit.
+
+Please enter your first initial and last name [server.ostechnix.local]:
+Please enter the case id that you are generating this report for []:
+
+Setting up archive ...
+Setting up plugins ...
+Running plugins. Please wait ...
+
+Running 73/73: yum...
+Creating compressed archive...
+
+Your sosreport has been generated and saved in:
+/var/tmp/sosreport-server.ostechnix.local-20180628171844.tar.xz
+
+The checksum is: 8f08f99a1702184ec13a497eff5ce334
+
+Please send this file to your support representative.
+
+```
+
+If you don’t want to be prompted for entering such details, simply use batch mode like below.
+```
+$ sudo sosreport --batch
+
+```
+
+As you can see in the above output, an archived report is generated and saved in **/var/tmp/sos.DiJXi7** file. In RHEL 6/CentOS 6, the report will be generated in **/tmp** location. You can now send this report to your support executive, so that he can do initial analysis and find what’s the problem.
+
+You might be concerned or wanted to know what’s in the report. If so, you can view it by running the following command:
+```
+$ sudo tar -tf /var/tmp/sosreport-server.ostechnix.local-20180628171844.tar.xz
+
+```
+
+Or,
+```
+$ sudo vim /var/tmp/sosreport-server.ostechnix.local-20180628171844.tar.xz
+
+```
+
+Please note that above commands will not extract the archive, but only display the list of files and folders in the archive. If you want to view the actual contents of the files in the archive, first extract the archive using command:
+```
+$ sudo tar -xf /var/tmp/sosreport-server.ostechnix.local-20180628171844.tar.xz
+
+```
+
+All the contents of the archive will be extracted in a directory named “sosreport-server.ostechnix.local-20180628171844/” in the current working directory. Go to the directory and view the contents of any file using cat command or any other text viewer:
+```
+$ cd sosreport-server.ostechnix.local-20180628171844/
+
+$ cat uptime
+17:19:02 up 1:03, 2 users, load average: 0.50, 0.17, 0.10
+
+```
+
+For more details about Sosreport, refer man pages.
+```
+$ man sosreport
+
+```
+
+And, that’s all for now. Hope this was useful. More good stuffs to come. Stay tuned!
+
+Cheers!
+
+
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://www.ostechnix.com/sosreport-a-tool-to-collect-system-logs-and-diagnostic-information/
+
+作者:[SK][a]
+选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:https://www.ostechnix.com/author/sk/
diff --git a/sources/tech/20180629 100 Best Ubuntu Apps.md b/sources/tech/20180629 100 Best Ubuntu Apps.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..581d22b527
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/tech/20180629 100 Best Ubuntu Apps.md
@@ -0,0 +1,1184 @@
+100 Best Ubuntu Apps
+======
+
+Earlier this year we have published the list of [20 Best Ubuntu Applications for 2018][1] which can be very useful to many users. Now we are almost in the second half of 2018, so today we are going to have a look at 100 best applications for Ubuntu which you will find very useful.
+
+![100 Best Ubuntu Apps][2]
+
+Many users who have recently switched to Ubuntu from Microsoft Windows or any other operating system face the dilemma of finding best alternative to application software they have been using for years on their previous OS. Ubuntu has thousands of free to use and open-source application software’s that perform way better than many paid software’s on Windows and other OS.
+
+Following list features many application software in various categories, so that you can find best application which best matched to your requirements.
+
+### **1\. Google Chrome Browser**
+
+Almost all the Linux distributions feature Mozilla Firefox web browser by default and it is a tough competitor to Google Chrome. But Chrome has its own advantages over Firefox like Chrome gives you direct access to your Google account from where you can sync bookmarks, browser history, extensions, etc. from Chrome browser on other operating systems and mobile phones.
+
+![Chrome][3]
+
+Google Chrome features up-to-date Flash player for Linux which is not the case with other web browsers on Linux including Mozilla Firefox and Opera web browser. If you continuously use Chrome on Windows then it is best choice to use it on Linux too.
+
+### 2\. **Steam**
+
+Gaming on Linux is a real deal now, which was a distant dream few years ago. In 2013, Valve announced Steam gaming client for Linux and everything has changed since then. Earlier users were hesitant to switch to Linux from Windows just because they would not be able to play their favourite games on Ubuntu but that is not the case now.
+
+![Steam][4]
+
+Some users might find installing Steam on Linux tricky but it worth all your efforts as thousands of Steam games are available for Linux. Some popular high-end games like Counter Strike: Global Offensive, Hitman, Dota 2 are available for Linux, you just need to make sure you have minimum hardware required to play these games.
+
+```
+$ sudo add-apt-repository multiverse
+
+$ sudo apt-get update
+
+$ sudo apt-get install steam
+```
+
+### **3\. WordPress Desktop Client**
+
+Yes you read it correct, WordPress has its dedicated desktop client for Ubuntu from where you can manage your WordPress sites. You can also write and design separately on desktop client without need for switching browser tabs.
+
+![][5]
+
+If you have websites backed by WordPress then this desktop client is must have application for you as you can also keep track of all the WordPress notifications in one single window. You can also check stats for performance of posts on website. Desktop client is available in Ubuntu Software Centre from where you can download and install it.
+
+### **4\. VLC Media Player**
+
+VLC is a very popular cross-platform and open-source media player which is also available for Ubuntu. What makes VLC a best media player is that it can play videos in all the Audio and Video formats available on planet without any issue.
+
+![][6]
+
+VLC has a slick user interface which is very easy to use and apart from that it offers lot of features such as online video streaming, audio and video customization, etc.
+
+```
+$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:videolan/master-daily
+$ sudo apt update
+$ sudo apt-get install vlc qtwayland5
+```
+
+### **5\. Atom Text Editor**
+
+Having developed by Github, Atom is a free and open-source text editor which can also be used as Integrated Development Environment (IDE) for coding and editing in major programming languages. Atom developers claim it to be a completely hackable text editor for 21st Century.
+
+![][7]
+
+Atom Text Editor has one of the best user interfaces and it is a feature rich text editor with offerings like auto-completion, syntax highlighting and support of extensions and plug-ins.
+
+```
+$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:webupd8team/atom
+$ sudo apt-get update
+$ sudo apt-get install atom
+```
+
+### **6\. GIMP Photo Editor**
+
+GIMP (GNU Image Manipulation Programme) is free and open-source photo editor for Ubuntu. It is arguably a best alternative to Adobe Photoshop on Windows. If you have been continuously using Adobe Photoshop and finding it difficult to get used to GIMP, then you can customize GIMP to look very similar to Photoshop.
+
+![][8]
+
+GIMP is a feature rich Photo editor and you can always use additional features by installing extensions and plug-ins anytime.
+
+```
+$ sudo apt-get install gimp
+```
+
+### **7\. Google Play Music Desktop Player**
+
+Google Play Music Desktop Player is an open-source music player which is replica of Google Play Music or you can say it’s better than that. Google always lacked a desktop music client but this third-party app fills the void perfectly.
+
+![][9]
+
+Like you can see in above screenshot, its interface is second to none in terms of look and feel. You just need to sign in into Google account and then it will import all your music and favorites into this desktop client. You can download installation files from its official [website][10] and install it using Software Center.
+
+### **8\. Franz**
+
+Franz is an instant messaging client that combines chat and messaging services into one application. It is one of the modern instant messaging platforms and it supports Facebook Messenger, WhatsApp, Telegram, HipChat, WeChat, Google Hangouts, Skype integration under one single application.
+
+![][11]
+
+Franz is complete messaging platform which you can use for business as well to manage mass customer service. To install Franz you need to download installation package from its [website][12] and open it using Software Center.
+
+### **9\. Synaptic Package Manager**
+
+Synaptic Package Manager is one of the must have tools on Ubuntu because it works for graphical interface for ‘apt-get’ command which we usually use to install apps on Ubuntu using Terminal. It gives tough competition to default app stores on various Linux distros.
+
+![][13]
+
+Synaptic comes with very simple user interface which is very fast and easy to use as compared to other app stores. On left-hand side you can browse various apps in different categories from where you can easily install and uninstall apps.
+
+```
+$ sudo apt-get install synaptic
+```
+
+### **10\. Skype**
+
+Skype is a very popular cross-platform video calling application which is now also available for Linux as a Snap app. Skype is an instant messaging application which offers features like voice and video calls, desktop screen sharing, etc.
+
+![][14]
+
+Skype has an excellent user interface which very similar to desktop client on Windows and it is very easy to use. It could be very useful app for many switchers from Windows.
+
+```
+$ sudo snap install skype
+```
+
+### **13\. VirtualBox**
+
+VirtualBox is a cross-platform virtualization software application developed by Oracle Corporation. If you love trying out new operating systems then VirtualBox is the must have Ubuntu application for you. You can tryout Linux, Mac inside Windows Operating System or Windows and Mac inside Linux.
+
+![][15]
+
+What VB actually does is it lets you run guest operating system on host operating system virtually. It creates virtual hard drive and installs guest OS on it. You can download and install VB directly from Ubuntu Software Center.
+
+### **12\. Unity Tweak Tool**
+
+Unity Tweak Tool (Gnome Tweak Tool) is must have tool for every Linux user because it gives user ability to customize desktop according to your need. You can try new GTK themes, set up desktop hot corners, customize icon set, tweak unity launcher, etc.
+
+![][16]
+
+Unity Tweak Tool can be very useful to user as it has everything covered right from the basic to advanced configurations.
+
+```
+$ sudo apt-get install unity-tweak-tool
+```
+
+### **13\. Ubuntu Cleaner**
+
+Ubuntu Cleaner is a system maintenance tool especially designed to remove packages that are no longer useful, remove unnecessary apps and clean-up browser caches. Ubuntu Cleaner has very simple user interface which is very easy to use.
+
+![][17]
+
+Ubuntu Cleaner is one of the best alternatives to BleachBit which is also a decent cleaning tool available for Linux distros.
+
+```
+$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:gerardpuig/ppa
+$ sudo apt-get update
+$ sudo apt-get install ubuntu-cleaner
+```
+
+### 14\. Visual Studio Code
+
+Visual Studio Code is code editor which you will find very similar to Atom Text Editor and Sublime Text if you have already used them. Visual Studio Code proves to be very good educational tool as it explains everything from HTML tags to syntax in programming.
+
+![][18]
+
+Visual Studio comes with Git integration out of the box and it has excellent user interface which you will find very similar to likes of Atom Text Editor and Sublime Text. You can download and install it from Ubuntu Software Center.
+
+### **15\. Corebird**
+
+If you are looking for desktop client where you can use your Twitter then Corebird Twitter Client is the app you are looking for. It is arguably best Twitter client available for Linux distros and it offers features very similar to Twitter app on your mobile phone.
+
+![][19]
+
+Corebird Twitter Client also gives notifications whenever someone likes and retweets your tweet or messages you. You can also add multiple Twitter accounts on this client.
+
+```
+$ sudo snap install corebird
+```
+
+### **16\. Pixbuf**
+
+Pixbuf is a desktop client from Pixbuf photo community hub which lets you upload, share and sale your photos. It supports photo sharing to social media networks like Facebook, Pinterest, Instagram, Twitter, etc. and photography services including Flickr, 500px and Youpic.
+
+![][20]
+
+Pixbuf offers features like analytics which gives you stats about clicks, retweets, repins on your photo, scheduled posts, dedicated iOS extension. It also has mobile app, so that you can always be connected with your Pixbuf account from anywhere. Pixbuf is available for download in Ubuntu Software Center as a snap package.
+
+### **17\. Clementine Music Player**
+
+Clementine is a cross-platform music player and a good competitor to Rhythmbox which is default music player on Ubuntu. It is fast and easy to use music player thanks to its user friendly interface. It supports audio playback in all the major audio file formats.
+
+![][21]
+
+Apart from playing music from local library you can also listen to online radio from Spotify, SKY.fm, Soundcloud, etc. It also offers other features like smart and dynamic playlists, syncing music from cloud storages like Dropbox, Google Drive, etc.
+
+```
+$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:me-davidsansome/clementine
+$ sudo apt-get update
+$ sudo apt-get install clementine
+```
+
+### **18\. Blender**
+
+Blender is free and open-source 3D creation application software which you can use to create 3D printed models, animated films, video games, etc. It comes with integrated game engine out of the box which you can use to develop and test video games.
+
+![blender][22]
+
+Blender has catchy user interface which is easy to use and it includes features like built-in render engine, digital sculpturing, simulation tool, animation tools and many more. It is one of the best applications you will ever find for Ubuntu considering it’s free and features it offers.
+
+### **19\. Audacity**
+
+Audacity is an open-source audio editing application which you can use to record, edit audio files. You can record audio from various inputs like microphone, electric guitar, etc. It also gives ability to edit and trim audio clips according to your need.
+
+![][23]
+
+Recently Audacity released with new features for Ubuntu which includes theme improvements, zoom toggle command, etc. Apart from these it offers features like various audio effects including noise reduction and many more.
+
+```
+$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:ubuntuhandbook1/audacity
+$ sudo apt-get update
+$ sudo apt-get install audacity
+```
+
+### **20\. Vim**
+
+Vim is an Integrated Development Environment which you can use as standalone application or command line interface for programming in various major programming languages like Python.
+
+![][24]
+
+Most of the programmers prefer coding in Vim because it is fast and highly customizable IDE. Initially you might find it difficult to use but you will quickly get used to it.
+
+```
+$ sudo apt-get install vim
+```
+
+### **21\. Inkscape**
+
+Inkscape is an open-source and cross-platform vector graphics editor which you will find very much similar to Corel Draw and Adobe Illustrator. Using it you can create and edit vector graphics such as charts, logos, diagrams, illustrations, etc.
+
+![][25]
+
+Inkscape uses Scalable Vector Graphics (SVG) and an open XML-based W3C standard as a primary format. It supports various formats including JPEG, PNG, GIF, PDF, AI (Adobe Illustrator Format), VSD, etc.
+
+```
+$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:inkscape.dev/stable
+$ sudo apt-get update
+$ sudo apt-get install inkscape
+```
+
+### **22\. Shotcut**
+
+Shotcut is a free, open-source and cross-platform video editing application developed by Meltytech, LLC on the MLT Multimedia Framework. It is one of the most powerful video editors you will ever find for Linux distros as it supports all the major audio, video and image formats.
+
+![][26]
+
+It gives ability to edit multiple tracks with various file formats using non-linear video editing. It also comes with support for 4K video resolutions and features like various audio and video filters, tone generator, audio mixing and many others.
+
+```
+snap install shotcut -- classic
+```
+
+### **23\. SimpleScreenRecorder**
+
+SimpleScreenRecorder is a free and lightweight screen video recorder for Ubuntu. This screen recorder can be very useful tool for you if you are a YouTube creator or application developer.
+
+![][27]
+
+It can capture a video/audio record of desktop screen or record video games directly. You can set video resolution, frame rate, etc. before starting the screen recording. It has simple user interface which you will find very easy to use.
+
+```
+$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:marten-baert/simplescreenrecorder
+$ sudo apt-get update
+$ sudo apt-get install simplescreenrecorder
+```
+
+### **24\. Telegram**
+
+Telegram is a cloud-based instant messaging and VoIP platform which has got lot of popularity in recent years. It is an open-source and cross-platform messenger where user can send messages, share videos, photos, audio and other files.
+
+![][28]
+
+Some of the notable features in Telegram are secrete chats, voice messages, bots, telescope for video messages, live locations and social login. Privacy and security is at highest priority in Telegram, so all messages you send and receive are end-to-end encrypted.
+
+```
+```
+$ sudo snap install telegram-desktop
+
+### **25\. ClamTk**
+
+As we know viruses meant to harm Windows PC cannot do any harm to Ubuntu but it is always prone to get infected by some mails from Windows PC containing harmful files. So it is safe to have some antivirus applications on Linux too.
+
+![][29]
+
+ClamTk is a lightweight malware scanner which scans files and folders on your system and cleans if any harmful files are found. ClamTk is available as a Snap package and can be downloaded from Ubuntu Software Center.
+
+### **26\. MailSpring**
+
+MailSpring earlier known as Nylas Mail or Nylas N1 is an open-source email client. It saves all the mails locally on computer so that you can access them anytime you need. It features advanced search which uses AND and OR operations so that you can search for mails based on different parameters.
+
+![][30]
+
+MailSpring comes with excellent user interface which you will find only on handful of other mail clients. Privacy and security, scheduler, contact manager, calendar are some of the features MailSpring offers.
+
+### **27\. PyCharm**
+
+PyCharm is one of my favorite Python IDEs after Vim because it has slick user interface with lot of extensions and plug-in support. Basically it comes in two editions, one is community edition which is free and open-source and other is professional edition which is paid one.
+
+![][31]
+
+PyCharm is highly customizable IDE and sports features such as error highlighting, code analysis, integrated unit testing and Python debugger, etc. PyCharm is the preferred IDE by most of the Python programmers and developers.
+
+### **28\. Caffeine**
+
+Imagine you are watching something on YouTube or reading a news article and suddenly Ubuntu locks your screen, I know that is very annoying. It happens with many of us, so Caffeine is the tool that will help you block the Ubuntu lock screen or screensaver.
+
+![][32]
+
+Caffeine Inhibitor is lightweight tool, it adds icon on notification bar from where you can activate or deactivate it easily. No additional setting needs to be done in order to use this tool.
+
+```
+$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:eugenesan/ppa
+$ sudo apt-get update
+$ sudo apt-get install caffeine -y
+```
+
+### **29\. Etcher USB Image Writer**
+
+Etcher is an open-source USB Image Writer developed by resin.io. It is a cross-platform application which helps you burn image files like ZIP, ISO, IMG to USB storage. If you always try out new OS then Etcher is the must have tool for you as it is easy to use and reliable.
+
+![][33]
+
+Etcher has clean user interface that guides you through process of burning image file to USB drive or SD card in three easy steps. Steps involve selecting Image file, selecting USB drive and finally flash (writes files to USB drive). You can download and install Etcher from its [website][34].
+
+### **30\. Neofetch**
+
+Neofetch is a cool system information tool that gives you all the information about your system by running “neofetch” command in Terminal. It is cool tool to have because it gives you information about desktop environment, kernel version, bash version and GTK theme you are running.
+
+![][35]
+
+As compared to other system information tools Nefetch is highly customizable tool. You can perform various customizations using command line.
+
+```
+$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:dawidd0811/neofetch
+$ sudo apt-get update
+$ sudo apt-get update install neofetch
+```
+
+### 31\. Liferea
+
+Liferea (Linux Feed Reader) is a free and open-source news aggregator for online news feeds. It is a fast and easy to use new aggregator that supports various formats such as RSS/RDF, Atom, etc.
+
+![][36]
+Liferea comes with sync support with TinyTinyRSS out of the box and it gives you an ability to read feeds in offline mode. It is one of the best feed readers you will find for Linux in terms of reliability and flexibility.
+
+```
+$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:ubuntuhandbook1/apps
+$ sudo apt-get update
+$ sudo apt-get install liferea
+```
+
+### 32\. Shutter
+
+It is easy to take screenshots in Ubuntu but when it comes to edit screenshots Shutter is the must have application for you. It helps you capture, edit and share screenshots easily. Using Shutter’s selector tool you can select particular part of your screen to take screenshot.
+
+![][37]
+
+Shutter is a feature-rich screenshot tool which offers features like adding effects to screenshot, draw lines, etc. It also gives you option to upload your screenshot to various image hosting sites. You can directly download and install Shutter from Software Center.
+
+### 33\. Weather
+
+Weather is a small application which gives you real-time weather information for your city or any other location in the world. It is simple and lightweight tool which gives you detailed forecast of up to 7 days and hourly details for current and next day.
+
+![][38]
+
+It integrates with GNOME shell to give you information about current weather conditions at recently searched locations. It has minimalist user interface which works smoothly on minimum hardware requirement.
+
+### 34\. Ramme
+
+Ramme is cool unofficial Instagram desktop client which gives you feel of Instagram mobile phone app. It is an Electron-based client so it replicates Instagram app and offers features like theme customization, etc.
+
+![][39]
+
+But due to Instagram’s API restrictions you can’t upload image using Ramme client but you can always go through Instagram feed, like and comment on posts, message friends. You can download Ramme installation files from[Github.][40]
+
+### **35\. Thunderbird**
+
+Thunderbird is an open-source email client which is also a default email client in most of the Linux distributions. Despite parting ways with Mozilla in 2017, Thunderbird is still very popular and best email client on Linux platform. It comes with features like spam filtering, IMAP and POP email syncing, calendar support, address book integration and many other features out of the box.
+
+![][41]
+
+It is a cross-platform email client with full community support across all supported platforms. You can always change its look and feel thanks to its highly customizable nature.
+
+### **36\. Pidgin**
+
+Pidgin is an instant messaging client where you can login into different instant messaging networks under single window. You can login to instant messaging networks like Google Talk, XMPP, AIM, Bonjour, etc.
+
+![][42]
+
+Pidgin has all the features you can expect in an instant messenger and you can always enhance its performance by installing additional plug-ins.
+
+```
+```
+$ sudo apt-get install pidgin
+
+### **37\. Krita**
+
+Krita is a free and open-source digital painting, editing and animation application developed by KDE. It has excellent user interface with everything placed perfectly so that you can easily find the tool you need.
+
+![][43]
+
+It uses OpenGL canvas which boosts Krita’s performance and it offers many features like different painting tools, animation tools, vector tools, layers and masks and many more. Krita is available in Ubuntu Software Center, you can easily download it from there.
+
+### **38\. Dropbox**
+
+Dropbox is stand-out player in cloud storage and its Linux clients works really well on Ubuntu once installed properly. While Google Drive comes out of the box on Ubuntu 16.04 LTS and later, Dropbox is still a preferred cloud storage tool on Linux in terms of features it offers.
+
+![][44]
+It always works in background and back up new files from your system to cloud storage, syncs files continuously between your computer and its cloud storage.
+
+```
+$ sudo apt-get install nautilus-dropbox
+```
+
+### 39\. Kodi
+
+Kodi formerly known as Xbox Media Center (XBMC) is an open-source media player. You can play music, videos, podcasts and video games both in online and offline mode. This software was first developed for first generation of Xbox gaming console and then slowly ported to personal computers.
+
+![][45]
+
+Kodi has very impressive video interface which is fast and powerful. It is highly customizable media player and by installing additional plug-ins you can access online streaming services like Pandora, Spotify, Amazon Prime Video, Netflix and YouTube.
+
+### **40\. Spotify**
+
+Spotify is one of the best online media streaming sites. It provides music, podcast and video streaming services both on free and paid subscription basis. Earlier Spotify was not supported on Linux but now it has its own fully functional desktop client for Ubuntu.
+
+![][46]
+
+Alongside Google Play Music Desktop Player, Spotify is must have media player for you. You just need to login to your Spotify account to access your favorite online content from anywhere.
+
+### 41\. Brackets
+
+Brackets is an open-source text editor developed by Adobe. It can be used for web development and design in web technologies such as HTML, CSS and JavaScript. It sports live preview mode which is great feature to have as it can get real-time view of whatever the changes you make in script.
+
+![][47]
+
+It is one of the modern text editors on Ubuntu and has slick user interface which takes web development task to new level. It also offers features like inline editor and supports for popular extensions like Emmet, Beautify, Git, File Icons, etc.
+
+### 42\. Bitwarden
+
+Account safety is serious concern now as we can see rise in security breaches in which users passwords are stolen and important data being compromised. So Bitwarden is recommended tool for you which stores all your account logins and passwords safe and secure at one place.
+
+![][48]
+
+Bitwarden uses AES-256 bit encryption technique to store all the login details and only user has access to his data. It also helps you to create strong passwords which are less likely to be hacked.
+
+### 43\. Terminator
+
+Terminator is an open-source terminal emulator programmed and developed in Java. It is a cross-platform emulator which lets you have privilege of multiple terminals in one single window which is not the case in Linux default terminal emulator.
+
+![][49]
+
+Other stand-out feature in Terminator includes automatic logging, drag and drop, intelligent vertical and horizontal scrolling, etc.
+
+```
+$ sudo apt-get install terminator
+```
+
+### 44\. Yak Yak
+
+Yak Yak is an open-source unofficial desktop client for Google Hangouts messenger. It could be good alternative to Microsoft’s Skype as it comes with bunch of some amazing features out of the box. You can enable desktop notifications, language preferences, and works on minimal memory and power requirements.
+
+![][50]
+
+Yak Yak comes with all the features you would expect in any instant messaging app such as typing indicator, drag and drop media files, and audio/video calling.
+
+### 45\. **Thonny**
+
+Thonny is a simple and lightweight IDE especially designed for beginners in programming. If you are new to programming then this is the must have IDE for you because it lets you learn while programming in Python.
+
+![][51]
+
+Thonny is also great tool for debugging as it supports live variables during debugging, apart from this it offers features like separate windows for executing function call, simple user interface, etc.
+
+```
+$ sudo apt-get install thonny
+```
+
+### **46\. Font Manager**
+
+Font Manager is a lightweight tool for managing, adding or removing fonts on your Ubuntu system. It is specially built for Gnome desktop environment, users don’t having idea about managing fonts using command line will find this tool very useful.
+
+![][52]
+
+Gtk+ Font Manager is not meant to be for professional users, it has simple user interface which you will find very easy to navigate. You just need to download font files from internet and add them using Font Manager.
+
+$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:font-manager/staging
+$ sudo apt-get update
+$ sudo apt-get install font-manager
+
+### **47\. Atril Document Viewer**
+
+Atril is a simple document viewer which supports file formats like Portable Document Format (PDF), PostScript (PS), Encapsulated PostScript (EPS), DJVU and DVI. Atril comes bundled with MATE desktop environment and it is identical to Evince which is default document on the most of the Linux distros.
+
+![][53]
+
+Atril has simple and lightweight user interface which is highly customizable and offers features like search, bookmarks and UI includes thumbnails on the left-hand side.
+
+```
+$ sudo apt-get install atril
+```
+
+### **48\. Notepadqq**
+
+If you have ever used Notepad++ on Windows and looking for similar program on Linux then don’t worry developers have ported it to Linux as Notepadqq. It is a simple yet powerful text editor which you can use for daily tasks or programming in various languages.
+
+![][54]
+
+Despite being a simple text editor it has some amazing features like you can set theme between dark and light color scheme, multiple selection, regular expression search and real-time highlighting.
+
+```
+$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:notpadqq-team/notepadqq
+$ sudo apt-get update
+$ sudo apt-get install notepadqq
+```
+
+### **49\. Amarok**
+
+Amarok is an open-source music player developed under KDE projetct. It has an intuitive interface which makes you feel home so you can discover your favorite music easily. Besides Clementine, Amarok is very good choice to have when you are looking for perfect music player for Ubuntu.
+
+![][55]
+
+Some of the top features in Amarok include intelligent playlist support, integration support for online services like MP3tunes, Last.fm, Magnatune, etc.
+
+### **50\. Cheese**
+
+Cheese is a Linux default webcam application which can be useful to you in some video chat or instant messaging applications. Apart from that you can also use this app to take photos and videos with fancy effects.
+
+![][56]
+
+It also sports burst mode which lets you take multiple snaps in quick succession and option to share your photos with friends and family. Cheese come pre-installed with most of the Linux distros but you can also download and install it from Software Center.
+
+### **51\. MyPaint**
+
+MyPaint is a free and open-source raster graphics editor which focuses on digital painting rather than image manipulation and post processing. It is cross-platform application and more or less similar to Corel Painter.
+
+![][57]
+
+MyPaint could be good alternative to those who use Microsoft Paint application on Windows. It has simple user interface which is fast and powerful. MyPaint is available is Software Center for download.
+
+### **52\. PlayOnLinux**
+
+PlayOnLinux is a front-end for WINE emulator which allows you to run Windows applications on Linux. You just need to install Windows applications and game on WINE then you can easily launch applications and games using PlayOnLinux.
+
+![][58]
+
+### **53\. Akregator**
+
+Akregator is a default RSS reader for KDE Plasma Environment developed under KDE project. It has simple user interface and comes with KDE’s Konqueror browser so that you don’t need to switch between apps while reading news feeds.
+
+![][59]
+
+Akregator also offers features like desktop notifications, automatic feeds, etc. It is one of the best feed readers you will find for across most of the Linux distros.
+
+### **54\. Brave**
+
+Brave is an open-source web browser which blocks ads and trackers so that you can browse your content fast and safely. What it actually does is that it pays to websites and YouTubers on behalf of you. If you prefer contributing to websites and YouTubers rather than seeing advertisements then this browser is for you.
+
+![][60]
+
+This is a new concept and could be good browser for those who prefer safe browsing without compromising important data on internet.
+
+### **55\. Bitcoin Core**
+
+Bitcoin Core is an official Bitcoin client which is highly secure and reliable. It keeps track of all your transactions and makes sure all transactions are valid. It restricts Bitcoin miners and banks from taking full control of your Bitcoin wallet.
+
+![][61]
+
+Bitcoin Core also offers other important features like, private keys backup, cold storage, security notifications.
+
+```
+$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:bitcoin/bitcoin
+$ sudo apt-get update
+$ sudo apt-get install bitcoin-qt
+```
+
+### **56\. Speedy Duplicate Finder**
+
+Speedy Duplicate Finder is a cross-platform file finder which helps you find duplicate files on your system and free-up disk space. It is a smart tool which searches for duplicate files on entire hard disk and also features smart filter which helps you find file by file type, extension or size.
+
+![][62]
+
+It has a simple and clean user interface which is very easy to handle. As soon as you download it from Software Center you are good to go with disk space clean-up.
+
+### **57\. Zulip**
+
+Zulip is a free and open-source group chat application which was acquired by Dropbox. It is written in Python and uses PostgreSQL database. It was designed and developed to be a good alternative to other chat applications like Slack and HipChat.
+
+![][63]
+
+Zulip is a feature-rich application with features such as drag and drop files, group chats, private messaging, image previews and many more. It also supports integration with likes of Github, JIRA, Sentry, and hundreds of other services.
+
+### **58\. Okular**
+
+Okular is a cross-platform document viewer developed by KDE for KDE desktop environment. It is a simple document viewer and supports file formats like Portable Document Format (PDF), PostScript, DjVu, Microsoft Compiled HTML help, and many other major file formats.
+
+![][64]
+
+Okular is one of the best document viewers you should try on Ubuntu as it offers features like commenting on PDF documents, drawing lines, highlighting and much more. You can also extract text from PDF document to text file.
+
+### **59\. FocusWriter**
+
+FocusWriter is a distraction-free word processor which hides your desktop screen so that you can only focus on writing. Like you can see in the screenshot below whole Ubuntu screen is hidden, it’s just you and your word processor. But you can always access Ubuntu screen whenever you need it by just moving your mouse cursor to the edges of the screen.
+
+![][65]
+
+It is a lightweight word processor with support for file formats like TXT, RTF and ODT files. It also offers fully customizable user interface and features like timers and alarms, daily goals, sound effects and support for translation into 20 languages.
+
+### **60\. Guake**
+
+Guake is a cool drop-down terminal for GNOME Desktop Environment. Guake comes in a flash whenever you need it and disappears as soon as your task is completed. You just need to click F12 button to launch or exit it so launching Guake is way faster than launching new Terminal window.
+
+![][66]
+
+Guake is a feature-rich terminal with features like support for multiple tabs, ability to save your terminal content to file in few clicks, and fully customizable user interface.
+
+```
+$ sudo apt-get install guake
+```
+
+### **61\. KDE Connect**
+
+KDE Connect is an awesome application on Ubuntu and I would have loved to list this application much higher in this marathon article but competition is intense. Anyways KDE Connect helps you get your Android smartphone notifications directly on Ubuntu desktop.
+
+![][67]
+
+With KDE Connect you can do whole lot of other things like check your phones battery level, exchange files between computer and Android phone, clipboard sync, send SMS, and you can also use your phone as wireless mouse or keyboard.
+
+```
+$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:webupd8team/indicator-kedeconnect
+$ sudo apt-get update
+$ sudo apt-get install kdeconnect indicator-kdeconnect
+```
+
+### **62\. CopyQ**
+
+CopyQ is a simple but very useful clipboard manager which stores content of the system clipboard whenever any changes you make so that you can search and restore it back whenever you need. It is a great tool to have as it supports text, images, HTML and other formats.
+
+![][68]
+
+CopyQ comes pre-loaded with features like drag and drop, copy/paste, edit, remove, sort, create, etc. It also supports integration with text editors like Vim, so it could be very useful tool if you are a programmer.
+
+```
+$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:hluk/copyq
+$ sudo apt-get update
+$ sudo apt-get install copyq
+```
+
+### **63\. Tilix**
+
+Tilix is feature-rich advanced GTK3 tiling terminal emulator. If you uses GNOME desktop environment then you’re going to love Tilix as it follows GNOME Human Interface Guidelines. What Tilix emulator offers different than default terminal emulators on most of the Linux distros is it gives you ability to split terminal window into multiple terminal panes.
+
+![][69]
+
+Tilix offers features like custom links, image support, multiple panes, drag and drop, persistent layout and many more. It also has support for keyboard shortcuts and you can customize shortcuts from the Preferences settings according to your need.
+
+```
+$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:webupd8team/terminix
+$ sudo apt-get update
+$ sudo apt-get install tilix
+```
+
+### **64\. Anbox**
+
+Anbox is an Android emulator which lets you install and run Android apps on your Linux system. It is free and open-source Android emulator that executes Android runtime environment by using Linux Containers. It uses latest Linux technologies and Android releases so that you can run any Android app like any other native application.
+
+![][70]
+
+Anbox is one of the modern and feature-rich emulators and offers features like no limit for application use, powerful user interface, and seamless integration with host operating system.
+
+First you need to install kernel modules.
+
+```
+$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:morphis/anbox-support
+$ sudo apt-get update
+$ sudo apt install anbox-modules-dkms Now install Anbox using snap
+$ snap install --devmode -- beta anbox
+```
+
+### **65\. OpenShot**
+
+OpenShot is the best open-source video editor you will find for Linux distros. It is a cross-platform video editor which is very easy to use without any compromise with its performance. It supports all the major audio, video and image formats.
+
+![][71]
+
+OpenShot has clean user interface and offers features like drag and drop, clip resizing, scaling, trimming, snapping, real-time previews, audio mixing and editing and many other features.
+
+```
+$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:openshot.developers/ppa
+$ sudo apt-get update
+$ sudo apt-get install openshot -qt
+```
+
+### **66\. Plank**
+
+If you are looking for cool and simple dock for your Ubuntu desktop then Plank should be #1 choice for you. It is perfect dock and you don’t need to make any tweaks after installation but if you want to, then it has built-in preferences panel where you can customize themes, dock size and position.
+
+![][72]
+
+Despite being a simple dock, Plank offers features like item rearrangement by simple drag and drop, pinned and running apps icon, transparent theme support.
+
+```
+$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:ricotz/docky
+$ sudo apt-get update
+$ sudo apt-get install plank
+```
+
+### **67\. Filezilla**
+
+Filezilla is a free and cross-platform FTP application which sports FileZilla client and server. It lets you transfer files using FTP and encrypted FTP like FTPS and SFTP and supports IPv6 internet protocol.
+
+![][73]
+
+It is simple file transfer application with features like drag and drop, support for various languages used worldwide, powerful user interface for multitasking, control and configures transfer speed and many other features.
+
+### **68\. Stacer**
+
+Stacer is an open-source system diagnostic tool and optimizer developed using Electron development framework. It has an excellent user interface and you can clean cache memory, start-up applications, uninstall apps that are no longer needed, monitor background system processes.
+
+![][74]
+
+It also lets you check disk, memory and CPU usage and also gives real-time stats of downloads and uploads. It looks like a tough competitor to Ubuntu cleaner but both have unique features that separate them apart.
+
+```
+$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:oguzhaninan/stacer
+$ sudo apt-get update
+$ sudo apt-get install stacer
+```
+
+### **69\. 4K Video Downloader**
+
+4K Video Downloader is simple video downloading tool which you can use to download videos, playlists, channels from Vimeo, Facebook, YouTube and other online video streaming sites. It supports downloading YouTube playlists and channels in MP4, MKV, M4A, 3GP and many other video/audio file formats.
+
+![][75]
+
+4K Video Downloader is not as simple as you would think, apart from normal video downloads it supports 3D and 360 degree video downloading. It also offers features like in-app proxy setup and direct transfer to iTunes. You can download it from [here][76].
+
+### 70\. **Qalculate**
+
+Qalculate is multi-purpose, cross-platform desktop calculator which is simple but very powerful calculator. It can be used for solving complicated maths problems and equations, currency conversions, and many other daily calculations.
+
+![][77]
+
+It has an excellent user interface and offers features such as customizable functions, unit calculations, symbolic calculations, arithmetic, plotting and many other functions you will find in any scientific calculator.
+
+### **71\. Hiri**
+
+Hiri is a cross-platform email client developed in Python programming language. It has slick user interface and it can be a good alternative to Microsoft Outlook in terms of features and services offered. This is great email client that can be used for sending and receiving emails, managing contacts, calendars and tasks.
+
+![][78]
+
+It is a feature-rich email client that offers features like integrated task manager, email synchronization, email rating, email filtering and many more.
+
+```
+$ sudo snap install hiri
+```
+
+### **72\. Sublime Text**
+
+Sublime Text is a cross-platform source code editor programmed in C++ and Python. It has Python Application Programming Interface (API) and supports all the major programming and markup languages. It is simple and lightweight text editor which can be used as IDE with features like auto-completion, syntax highlighting, split editing, etc.
+
+![][79]
+
+Some additional features in this text editor include Goto anything, Goto definition, multiple selections, command palette and fully customizable user interface.
+
+```
+$ sudo apt-get install sublime-text
+```
+
+### **73\. TeXstudio**
+
+TeXstudio is an integrated writing environment for creating and editing LaTex documents. It is an open-source editor which offers features like syntax highlighting, integrated viewer, interactive spelling checker, code folding, drag and drop, etc.
+
+![][80]
+
+It is a cross-platform editor and has very simple, lightweight user interface which is easy to use. It ships in with integration for BibTex and BibLatex bibliographies managers and also integrated PDF viewer. You can download TeXstudio installation package from its [website][81] or Ubuntu Software Center.
+
+### **74\. QtQR**
+
+QtQR is a Qt based application that lets you create and read QR codes in Ubuntu. It is developed in Python and Qt and has simple and lightweight user interface. You can encode website URL, email, text, SMS, etc. and you can also decode barcode using webcam camera.
+
+![][82]
+
+QtQR could prove to be useful tool to have if you generally deal with product sales and services because I don’t think we have any other similar tool to QtQR which requires minimal hardware to function smoothly.
+
+```
+$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa: qr-tools-developers/qr-tools-stable
+$ sudo apt-get update
+$ sudo apt-get install qtqr
+```
+
+### **75\. Kontact**
+
+Kontact is an integrated personal information manager (PIM) developed by KDE for KDE desktop environment. It is all-in-one software suite that integrates KMail, KOrganizer and KAddressBook into a single user interface from where you can manage all your mails, contacts, schedules, etc.
+
+![][83]
+
+It could be very good alternative to Microsoft Outlook as it is fast and highly configurable information manager. It has very good user interface which you will find very easy to use.
+
+```
+$ sudo apt-get install kontact
+```
+
+### **76\. NitroShare**
+
+NitroShare is a cross-platform, open-source network file sharing application. It lets you easily share files between multiple operating systems local network. It is a simple yet powerful application and it automatically detects other devices running NitroShare on local network.
+
+![][84]
+
+File transfer speed is what makes NitroShare a stand-out file sharing application as it achieves gigabit speed on capable hardware. There is no need for additional configuration required, you can start file transfer as soon as you install it.
+
+```
+$ sudo apt-add-repository ppa:george-edison55/nitroshare
+$ sudo apt-get update
+$ sudo apt-get install nitroshare
+```
+
+### **77\. Konversation**
+
+Konversation is an open-source Internet Relay Chat (IRC) client developed for KDE desktop environment. It gives speedy access to Freenode network’s channels where you can find support for most distributions.
+
+![][85]
+
+It is simple chat client with features like support for IPv6 connection, SSL server support, bookmarks, on-screen notifications, UTF-8 detection, and additional themes. It has easy to use GUI which is highly configurable.
+
+```
+$ sudo apt-get install konversation
+```
+
+### **78\. Discord**
+
+If you’re hardcore gamer and play online games frequently then I have a great application for you. Discord which is free Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) application especially designed for online gamers around the world. It is a cross-platform application and can be used for text and audio chats.
+
+![][86]
+
+Discord is very popular VoIP application gaming community and as it is completely free application, it is very good competitor to likes of Skype, Ventrilo and Teamspeak. It also offers features like crystal clear voice quality, modern text chat where you can share images, videos and links.
+
+### **79\. QuiteRSS**
+
+QuiteRSS is an open-source news aggregator for RSS and Atom news feeds. It is cross-platform feed reader written in Qt and C++. It has simple user interface which you can tweak in either classic or newspaper mode. It comes integrated with webkit browser out of the box so that you can perform all the tasks under single window.
+
+![][87]
+
+QuiteRSS comes with features such as content blocking, automatic scheduled feeds, import/export OPML, system tray integration and many other features you could expect in any feed reader.
+
+```
+$ sudo apt-get install quiterss
+```
+
+### **80\. MPV Media Player**
+
+MPV is a free and open-source media player based on MPlayer and MPlayer 2. It has simple user interface where user just needs to drag and drop audio/video files to play them as there is no option to add media files on GUI.
+
+![][88]
+
+One of the things about MPV is that it can play 4K videos effortlessly which is not the case with other media players on Linux distros. It also gives user ability to play videos from online video streaming sites including YouTube and Dailymotion.
+
+```
+$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:mc3man/mpv-tests
+$ sudo apt-get update
+$ sudo apt-get install -y mpv
+```
+
+### **81\. Plume Creator**
+
+If you’re a writer then Plume Creator is must have application for you because you will not find other app for Ubuntu with privileges like Plume Creator. Writing and editing stories, chapters is tedious task and Plume Creator will ease this task for you with the help of some amazing tools it has to offer.
+
+![][89]
+
+It is an open-source application with minimal user interface which you could find confusing in the beginning but you will get used to it in some time. It offers features like edit notes, synopses, export in HTML and ODT formats support, and rich text editing.
+
+```
+$ sudo apt-get install plume-creator
+```
+
+### **82\. Chromium Web Browser**
+
+Chromium is an open-source web browser developed and distributed by Google. Chromium is very identical to Google Chrome web browser in terms of appearance and features. It is a lightweight and fast web browser with minimalist user interface.
+
+![][90]
+
+If you use Google Chrome regularly on Windows and looking for similar browser for Linux then Chromium is the best browser for you as you can login into your Google account to access all your Google services including Gmail.
+
+### **83\. Simple Weather Indicator**
+
+Simple Weather Indicator is an open-source weather indicator app developed in Python. It automatically detects your location and shows you weather information like temperature, possibility of rain, humidity, wind speed and visibility.
+
+![][91]
+
+Weather indicator comes with configurable options such as location detection, temperature SI unit, location visibility on/off, etc. It is cool app to have which adjusts with your desktop comfortably.
+
+### **84\. SpeedCrunch**
+
+SpeedCrunch is a fast and high-precision scientific calculator. It comes preloaded with math functions, user-defined functions, complex numbers and unit conversions support. It has simple user interface which is easy to use.
+
+![][92]
+
+This scientific calculator has some amazing features like result preview, syntax highlighting and auto-completion. It is a cross-platform calculator with multi-language support.
+
+### **85\. Scribus**
+
+Scribus is a free and open-source desktop publishing application that lets you create posters, magazines and books. It is a cross-platform application based on Qt toolkit and released under GNU general public license. It is a professional application with features like CMYK and ICC color management, Python based scripting engine, and PDF creation.
+
+![][93]
+
+Scribus comes with decent user interface which is easy to use and works effortlessly on systems with low hardware. It could be downloaded and installed from Software Center on all the latest Linux distros.
+
+### **86.** **Cura**
+
+Cura is an open-source 3D printing application developed by David Braam. Ultimaker Cura is the most popular software in 3D printing world and used by millions of users worldwide. It follows 3 step 3D printing model: Design, Prepare and Print.
+
+![][94]
+
+It is a feature-rich 3D printing application with seamless integration support for CAD plug-ins and add-ons. It is very simple and easy to use tool, novice artists can start right away. It supports major file formats like STL, 3MF and OBJ file formats.
+
+### **87\. Nomacs**
+
+Nomacs is an open-source, cross-platform image viewer which is supports all the major image formats including RAW and psd images. It has ability to browse images in zip or Microsoft Office files and extract them to a directory.
+
+![][95]
+
+Nomacs has very simple user interface with image thumbnails at the top and it offers some basic image manipulation features like crop, resize, rotate, color correction, etc.
+
+```
+$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:nomacs/stable
+$ sudo apt-get update
+$ sudo apt-get install nomacs
+```
+
+### **88\. BitTicker**
+
+BitTicker is a live bitcoin-USDT Ticker for Ubuntu. It is a simple tool that connects to bittrex.com market and retrieves the latest price for BTC-USDT and display Ubuntu clock on system tray.
+
+![][96]
+
+It is simple but very useful too if you invest in Bitcoin regularly and have to study price fluctuations regulary.
+
+### **89\. Organize My Files**
+
+Organize My Files is cross-platform one click file organizer and it is available in Ubuntu as a snap package. It is a simple but powerful tool that will help you find unorganized files in a simple click and take them under control.
+
+![][97]
+
+It has intuitive user interface which is powerful and fast. It offers features such as auto organizing, recursive organizing, smart filters and multi folders organizing.
+
+### **90\. GnuCash**
+
+GnuCash is financial accounting software licensed under GNU general public license for free usage. It is an ideal software for personal and small business accounting. It has simple user interface which allows you to keep track of bank accounts, stocks, income and expenses.
+
+![][98]
+
+GnuCash implements double-entry bookkeeping system and based on professional accounting principle to ensure balanced books and accurate reports.
+
+### **91\. Calibre**
+
+Calibre is a cross-platform, open-source solution to all your e-book needs. It is a simple e-book organizer that offers features like displaying, creating, editing e-books, organizing existing e-books into virtual libraries, syncing and many more.
+
+![][99]
+
+Calibre also helps you convert e-books into whichever format you need and send them to your e-book reading device. Calibre is a very good tool to have if you regularly read and manage e-books.
+
+### **92\. MATE Dictionary**
+
+MATE Dictionary is a simple dictionary basically developed for MATE desktop environment. You just need to type the word and then this dictionary will display the meaning and references for it.
+
+![][100]
+
+It is simple and lightweight online dictionary with minimalist user interface.
+
+### **93\. Converseen**
+
+Converseen is a free cross-platform batch image processing application that lets you convert, edit, resize, rotate and flip large number of images with a single mouse click. It offers features like renaming bunch of images using prefix/suffix, extract image from a Windows icon file, etc.
+
+![][101]
+
+It has very good user interface which is easy to use even if you are a novice user. It can also convert entire PDF file into collection of images.
+
+### **94\. Tiled Map Editor**
+
+Tiled is a free software level map editor which you can use to edit the maps in various projections such as orthogonal, isometric and hexagonal. This tool can be very useful for game developers during game engine development cycle.
+
+![][102]
+
+Tiled is a versatile map editor which lets you create power boost positions, map layouts, collision areas, and enemy positions. It saves all the data in tmx format.
+
+### **95.** **Qmmp**
+
+Qmmp is a free and open-source audio player developed in Qt and C++. It is a cross-platform audio player with user interface very similar to Winamp. It has simple and intuitive user interface, Winamp skins can be used instead of default UI.
+
+![][103]
+
+It offers features such as automatic album cover fetching, multiple artists support, additional plug-ins and add-ons support and other features similar to Winamp.
+
+```
+$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:forkotov02/ppa
+$ sudo apt-get update
+$ sudo apt-get install qmmp qmmp-q4 qmmp-plugin-pack-qt4
+```
+
+### **96\. Arora**
+
+Arora is free and open-source web browser which offers features like dedicated download manager, bookmarks, privacy mode and tabbed browsing.
+
+![][104]
+
+Arora web browser is developed by Benjamin C. Meyer and it is popular among Linux users for its lightweight nature and flexibility.
+
+### **97\. XnSketch**
+
+XnSketch is a cool application for Ubuntu that will help you transform your photos into cartoon or sketch images in few clicks. It sports 18 different effects such as black strokes, white strokes, pencil sketch and others.
+
+![][105]
+
+It has an excellent user interface which you will find easy to use. Some additional features in XnSketch include opacity and edge strength adjustment, contrast, brightness and saturation adjustment.
+
+### **98\. Geany**
+
+Geany is a simple and lightweight text editor which works like an Integrated Development Environment (IDE). It is a cross-platform text editor and supports all the major programming languages including Python, C++, LaTex, Pascal, C#, etc.
+
+![][106]
+
+Geany has simple user interface which resembles to programming editors like Notepad++. It offers IDE like features such as code navigation, auto-completion, syntax highlighting, and extensions support.
+
+```
+$ sudo apt-get install geany
+```
+
+### **99\. Mumble**
+
+Mumble is another Voice over Internet Protocol application very similar to Discord. Mumble is also basically designed for online gamers and uses client-server architecture for end-to-end chat. Voice quality is very good on Mumble and it offers end-to-end encryption to ensure privacy.
+
+![][107]
+
+Mumble is an open-source application and features very simple user interface which is easy to use. Mumble is available for download in Ubuntu Software Center.
+
+```
+$ sudo apt-get install mumble-server
+```
+
+### **100\. Deluge**
+
+Deluge is a cross-platform and lightweight BitTorrent client that can be used for downloading files on Ubuntu. BitTorrent client come bundled with many Linux distros but Deluge is the best BitTorrent client which has simple user interface which is easy to use.
+
+![][108]
+
+Deluge comes with all the features you will find in BitTorrent clients but one feature that stands out is it gives user ability to access the client from other devices as well so that you can download files to your computer even if you are not at home.
+
+```
+$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:deluge-team/ppa
+$ sudo apt-get update
+$ sudo apt-get install deluge
+```
+
+So these are my picks for best 100 applications for Ubuntu in 2018 which you should try. All the applications listed here are tested on Ubuntu 18.04 and will definitely work on older versions too. Feel free to share your view about the article at [@LinuxHint][109] and [@SwapTirthakar][110].
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://linuxhint.com/100_best_ubuntu_apps/
+
+作者:[Swapnil Tirthakar][a]
+选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:https://linuxhint.com/author/swapnil/
+[1]:https://linuxhint.com/applications-2018-ubuntu/
+[2]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/100-Best-Ubuntu-Apps.png
+[3]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Chrome.png
+[4]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Steam.png
+[5]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Wordpress.png
+[6]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/VLC.png
+[7]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Atom-Text-Editor.png
+[8]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/GIMP.png
+[9]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Google-Play.png
+[10]:https://www.googleplaymusicdesktopplayer.com/
+[11]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Franz.png
+[12]:https://meetfranz.com/#download
+[13]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Synaptic.png
+[14]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Skype.png
+[15]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/VirtualBox.png
+[16]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Unity-Tweak-Tool.png
+[17]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Ubuntu-Cleaner.png
+[18]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Visual-Studio-Code.png
+[19]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Corebird.png
+[20]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Pixbuf.png
+[21]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Clementine.png
+[22]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/06/blender.jpg
+[23]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Audacity.png
+[24]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Vim.png
+[25]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Inkscape-1.png
+[26]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/ShotCut.png
+[27]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Simple-Screen-Recorder.png
+[28]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Telegram.png
+[29]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/ClamTk.png
+[30]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Mailspring.png
+[31]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/PyCharm.png
+[32]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Caffeine.png
+[33]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Etcher.png
+[34]:https://etcher.io/
+[35]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Neofetch.png
+[36]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Liferea.png
+[37]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Shutter.png
+[38]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Weather.png
+[39]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Ramme.png
+[40]:https://github.com/terkelg/ramme/releases
+[41]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Thunderbird.png
+[42]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Pidgin.png
+[43]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Krita.png
+[44]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Dropbox.png
+[45]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/kodi.png
+[46]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Spotify.png
+[47]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Brackets.png
+[48]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Bitwarden.png
+[49]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Terminator.png
+[50]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Yak-Yak.png
+[51]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Thonny.png
+[52]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Font-Manager.png
+[53]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Atril.png
+[54]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Notepadqq.png
+[55]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Amarok.png
+[56]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Cheese.png
+[57]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/MyPaint.png
+[58]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/PlayOnLinux.png
+[59]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Akregator.png
+[60]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Brave.png
+[61]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Bitcoin-Core.png
+[62]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Speedy-Duplicate-Finder.png
+[63]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Zulip.png
+[64]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Okular.png
+[65]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Focus-Writer.png
+[66]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Guake.png
+[67]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/KDE-Connect.png
+[68]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/CopyQ.png
+[69]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Tilix.png
+[70]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Anbox.png
+[71]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/OpenShot.png
+[72]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Plank.png
+[73]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/FileZilla.png
+[74]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Stacer.png
+[75]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/4K-Video-Downloader.png
+[76]:https://www.4kdownload.com/download
+[77]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Qalculate.png
+[78]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Hiri.png
+[79]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Sublime-text.png
+[80]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/TeXstudio.png
+[81]:https://www.texstudio.org/
+[82]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/QtQR.png
+[83]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Kontact.png
+[84]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Nitro-Share.png
+[85]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Konversation.png
+[86]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Discord.png
+[87]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/QuiteRSS.png
+[88]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/MPU-Media-Player.png
+[89]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Plume-Creator.png
+[90]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Chromium.png
+[91]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Simple-Weather-Indicator.png
+[92]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/SpeedCrunch.png
+[93]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Scribus.png
+[94]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Cura.png
+[95]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Nomacs.png
+[96]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Bit-Ticker-1.png
+[97]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Organize-My-Files.png
+[98]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/GNU-Cash.png
+[99]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Calibre.png
+[100]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/MATE-Dictionary.png
+[101]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Converseen.png
+[102]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Tiled-Map-Editor.png
+[103]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Qmmp.png
+[104]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Arora.png
+[105]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/XnSketch.png
+[106]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Geany.png
+[107]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Mumble.png
+[108]:https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Deluge.png
+[109]:https://twitter.com/linuxhint
+[110]:https://twitter.com/SwapTirthakar
diff --git a/sources/tech/20180629 Discover hidden gems in LibreOffice.md b/sources/tech/20180629 Discover hidden gems in LibreOffice.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..fdb7f288e3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/tech/20180629 Discover hidden gems in LibreOffice.md
@@ -0,0 +1,97 @@
+Discover hidden gems in LibreOffice
+======
+
+
+
+LibreOffice is the most popular free and open source office suite. It’s included by default in many Linux distributions, such as [Fedora Workstation][1]. Chances are that you use it fairly often, but how many of its features have you really explored? What hidden gems are there in LibreOffice that not so many people know about?
+
+This article explores some lesser-known features in the suite, and shows you how to make the most of them. Then it wraps up with a quick look at the LibreOffice community, and how you can help to make the software even better.
+
+### Notebookbar
+
+Recent versions of LibreOffice have seen gradual improvements to the user interface, such as reorganized menus and additional toolbar buttons. However, the general layout hasn’t changed drastically since the software was born back in 2010. But now, a completely new (and optional!) user interface called the [Notebookbar][2] is under development, and it looks like this:
+
+![LibreOffice's \(experimental\) Notebookbar][3]
+
+Yes, it’s substantially different to the current “traditional” design, and there are a few variants. Because LibreOffice’s design team is still working on the Notebookbar, it’s not available by default in current versions of the suite. Instead, it’s an experimental option.
+
+To try it, make sure you’re running a recent release of LibreOffice, such as 5.4 or 6.0. (LibreOffice 6.x is already available in Fedora 28.) Then go to Tools > Options in the menu. In the dialog box that appears, go to Advanced on the left-hand side. Tick the Enable experimental features box, click OK, and then you’ll be prompted to restart LibreOffice. Go ahead and do that.
+
+Now, in Writer, Calc and Impress, go to View > Toolbar Layout in the menu, and choose Notebookbar. You’ll see the new interface straight away. Remember that this is still experimental, though, and not ready for production use, so don’t be surprised if you see some bugs or glitches in places!
+
+The default Notebookbar layout is called “tabbed”, and you can see tabs along the top of the window to display different sets of buttons. But if you go to View > Notebookbar in the menu, you’ll see other variants of the design as well. Try them out! If you need to access the familiar menu bar, you’ll find an icon for it in the top-right of the window. And to revert back to the regular interface, just go to View > Toolbar Layout > Default.
+
+### Command line tips and tricks
+
+Yes, you can even use LibreOffice from the Bash prompt. This is most useful if you want to perform batch operations on large numbers of files. For instance, let’s say you have 20 .odt (OpenDocument Text) files in a directory, and want to make PDFs of them. Via LibreOffice’s graphical user interface, you’d have to do a lot of clicking to achieve this. But at the command line, it’s simple:
+```
+libreoffice --convert-to pdf *.odt
+
+```
+
+Or take another example: you have a set of Microsoft Office documents, and you want to convert them all to ODT:
+```
+libreoffice --convert-to odt *.docx
+
+```
+
+Another useful batch operation is printing. If you have a bunch of documents and want to print them all in one fell swoop, without manually opening them and clicking on the printer icon, do this:
+```
+libreoffice -p *.odt
+
+```
+
+It’s also worth noting some of the other command line flags that LibreOffice uses. For instance, if you want to create a launcher in your program menu that starts Calc directly, instead of showing the opening screen, use:
+```
+libreoffice --calc
+
+```
+
+It’s also possible to launch Impress and jump straight into the first slide of a presentation, without showing the LibreOffice user interface:
+```
+libreoffice --show presentation.odp
+
+```
+
+### Extra goodies in Draw
+
+Writer, Calc and Impress are the most popular components of LibreOffice. But Draw is a capable tool as well for creating diagrams, leaflets and other materials. When you’re working with multiple objects, there are various tricks you can do to speed up your work.
+
+For example, you probably know you can select multiple objects by clicking and dragging a selection area around them. But you can also select and deselect objects in the group by holding down the Shift key while clicking.
+
+When moving individual shapes or groups of shapes, you can use keyboard modifiers to change the movement speed. Try it out: select a bunch of objects, then use the cursor keys to move them around. Now try holding Shift to move them in greater increments, or Alt for fine-tuning. (The Ctrl key comes in useful here too, for panning around inside a document without moving the shapes.)
+
+[LibreOffice 5.1][4] added a useful feature to equalize the widths and heights of multiple shapes. Select them with the mouse, right-click on the selection, and then go to the Shapes part of the context menu. There you’ll see the Equalize options. This is good for making objects more consistent, and it works in Impress too!
+
+![Equalizing shape sizes in Draw][5]
+
+Lastly, here’s a shortcut for duplicating objects: the Ctrl key. Try clicking and dragging on an object, with Ctrl held down, and you’ll see that a copy of the object is made immediately. This is quicker and more elegant than using the Duplicate dialog box.
+
+### Over to you!
+
+So those are some features and tricks in LibreOffice you can now use in your work. But there’s always room for improvement, and the LibreOffice community is working hard on the next release, [LibreOffice 6.1][6], which is due in early August. Give them a hand! You can help to test the beta releases, trying out new features and reporting bugs. Or [get involved in other areas][7] such as design, marketing, documentation, translations and more.
+
+Photo by [William Iven][8] on [Unsplash][9].
+
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://fedoramagazine.org/discover-hidden-gems-libreoffice/
+
+作者:[Mike Saunders][a]
+选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:https://fedoramagazine.org/author/mikesaunders/
+[1]:https://getfedora.org/workstation
+[2]:https://wiki.documentfoundation.org/Development/NotebookBar
+[3]:https://fedoramagazine.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/libreoffice_gems_notebookbar-300x109.png
+[4]:https://wiki.documentfoundation.org/ReleaseNotes/5.1
+[5]:https://fedoramagazine.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/libreoffice_gems_draw-300x178.png
+[6]:https://wiki.documentfoundation.org/ReleaseNotes/6.1
+[7]:https://www.libreoffice.org/community/get-involved/
+[8]:https://unsplash.com/photos/jrh5lAq-mIs?utm_source=unsplash&utm_medium=referral&utm_content=creditCopyText
+[9]:https://unsplash.com/search/photos/documents?utm_source=unsplash&utm_medium=referral&utm_content=creditCopyText
diff --git a/sources/tech/20180629 Reflecting on the GPLv3 license for its 11th anniversary.md b/sources/tech/20180629 Reflecting on the GPLv3 license for its 11th anniversary.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..af352aefe1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/tech/20180629 Reflecting on the GPLv3 license for its 11th anniversary.md
@@ -0,0 +1,65 @@
+Reflecting on the GPLv3 license for its 11th anniversary
+======
+
+
+
+Last year, I missed the opportunity to write about the 10th anniversary of [GPLv3][1], the third version of the GNU General Public License. GPLv3 was officially released by the Free Software Foundation (FSF) on June 29, 2007—better known in technology history as the date Apple launched the iPhone. Now, one year later, I feel some retrospection on GPLv3 is due. For me, much of what is interesting about GPLv3 goes back somewhat further than 11 years, to the public drafting process in which I was an active participant.
+
+In 2005, following nearly a decade of enthusiastic self-immersion in free software, yet having had little open source legal experience to speak of, I was hired by Eben Moglen to join the Software Freedom Law Center as counsel. SFLC was then outside counsel to the FSF, and my role was conceived as focusing on the incipient public phase of the GPLv3 drafting process. This opportunity rescued me from a previous career turn that I had found rather dissatisfying. Free and open source software (FOSS) legal matters would come to be my new specialty, one that I found fascinating, gratifying, and intellectually rewarding. My work at SFLC, and particularly the trial by fire that was my work on GPLv3, served as my on-the-job training.
+
+GPLv3 must be understood as the product of an earlier era of FOSS, the contours of which may be difficult for some to imagine today. By the beginning of the public drafting process in 2006, Linux and open source were no longer practically synonymous, as they might have been for casual observers several years earlier, but the connection was much closer than it is now.
+
+Reflecting the profound impact that Linux was already having on the technology industry, everyone assumed GPL version 2 was the dominant open source licensing model. We were seeing the final shakeout of a Cambrian explosion of open source (and pseudo-open source) business models. A frothy business-fueled hype surrounded open source (for me most memorably typified by the Open Source Business Conference) that bears little resemblance to the present-day embrace of open source development by the software engineering profession. Microsoft, with its expanding patent portfolio and its competitive opposition to Linux, was commonly seen in the FOSS community as an existential threat, and the [SCO litigation][2] had created a cloud of legal risk around Linux and the GPL that had not quite dissipated.
+
+That environment necessarily made the drafting of GPLv3 a high-stakes affair, unprecedented in free software history. Lawyers at major technology companies and top law firms scrambled for influence over the license, convinced that GPLv3 was bound to take over and thoroughly reshape open source and all its massive associated business investment.
+
+A similar mindset existed within the technical community; it can be detected in the fears expressed in the final paragraph of the Linux kernel developers' momentous September 2006 [denunciation][3] of GPLv3. Those of us close to the FSF knew a little better, but I think we assumed the new license would be either an overwhelming success or a resounding failure—where "success" meant something approximating an upgrade of the existing GPLv2 project ecosystem to GPLv3, though perhaps without the kernel. The actual outcome was something in the middle.
+
+I have no confidence in attempts to measure open source license adoption, which have in recent years typically been used to demonstrate a loss of competitive advantage for copyleft licensing. My own experience, which is admittedly distorted by proximity to Linux and my work at Red Hat, suggests that GPLv3 has enjoyed moderate popularity as a license choice for projects launched since 2007, though most GPLv2 projects that existed before 2007, along with their post-2007 offshoots, remained on the old license. (GPLv3's sibling licenses LGPLv3 and AGPLv3 never gained comparable popularity.) Most of the existing GPLv2 projects (with a few notable exceptions like the kernel and Busybox) were licensed as "GPLv2 or any later version." The technical community decided early on that "GPLv2 or later" was a politically neutral license choice that embraced both GPLv2 and GPLv3; this goes some way to explain why adoption of GPLv3 was somewhat gradual and limited, especially within the Linux community.
+
+During the GPLv3 drafting process, some expressed concerns about a "balkanized" Linux ecosystem, whether because of the overhead of users having to understand two different, strong copyleft licenses or because of GPLv2/GPLv3 incompatibility. These fears turned out to be entirely unfounded. Within mainstream server and workstation Linux stacks, the two licenses have peacefully coexisted for a decade now. This is partly because such stacks are made up of separate units of strong copyleft scope (see my discussion of [related issues in the container setting][4]). As for incompatibility inside units of strong copyleft scope, here, too, the prevalence of "GPLv2 or later" was seen by the technical community as neatly resolving the theoretical problem, despite the fact that nominal license upgrading of GPLv2-or-later to GPLv3 hardly ever occurred.
+
+I have alluded to the handwringing that some of us FOSS license geeks have brought to the topic of supposed copyleft decline. GPLv3 has taken its share of abuse from critics as far back as the beginning of the public drafting process, and some, predictably, have drawn a link between GPLv3 in particular and GPL or copyleft disfavor in general.
+
+I have viewed it somewhat differently: Largely because of its complexity and baroqueness, GPLv3 was a lost opportunity to create a strong copyleft license that would appeal very broadly to modern individual software authors and corporate licensors. I believe individual developers today tend to prefer short, simple, easy to understand, minimalist licenses, the most obvious example of which is the [MIT License][5].
+
+Some corporate decisionmakers around open source license selection may naturally share that view, while others may associate some parts of GPLv3, such as the patent provisions or the anti-lockdown requirements, as too risky or incompatible with their business models. The great irony is that the characteristics of GPLv3 that fail to attract these groups are there in part because of conscious attempts to make the license appeal to these same sorts of interests.
+
+How did GPLv3 come to be so baroque? As I have said, GPLv3 was the product of an earlier time, in which FOSS licenses were viewed as the primary instruments of project governance. (Today, we tend to associate governance with other kinds of legal or quasi-legal tools, such as structuring of nonprofit organizations, rules around project decision making, codes of conduct, and contributor agreements.)
+
+GPLv3, in its drafting, was the high point of an optimistic view of FOSS licenses as ambitious means of private regulation. This was already true of GPLv2, but GPLv3 took things further by addressing in detail a number of new policy problems—software patents, anti-circumvention laws, device lockdown. That was bound to make the license longer and more complex than GPLv2, as the FSF and SFLC noted apologetically in the first GPLv3 [rationale document][6].
+
+But a number of other factors at play in the drafting of GPLv3 unintentionally caused the complexity of the license to grow. Lawyers representing vendors' and commercial users' interests provided useful suggestions for improvements from a legal and commercial perspective, but these often took the form of making simply worded provisions more verbose, arguably without net increases in clarity. Responses to feedback from the technical community, typically identifying loopholes in license provisions, had a similar effect.
+
+The GPLv3 drafters also famously got entangled in a short-term political crisis—the controversial [Microsoft/Novell deal][7] of 2006—resulting in the permanent addition of new and unusual conditions in the patent section of the license, which arguably served little purpose after 2007 other than to make license compliance harder for conscientious patent-holding vendors. Of course, some of the complexity in GPLv3 was simply the product of well-intended attempts to make compliance easier, especially for community project developers, or to codify FSF interpretive practice. Finally, one can take issue with the style of language used in GPLv3, much of which had a quality of playful parody or mockery of conventional software license legalese; a simpler, straightforward form of phrasing would in many cases have been an improvement.
+
+The complexity of GPLv3 and the movement towards preferring brevity and simplicity in license drafting and unambitious license policy objectives meant that the substantive text of GPLv3 would have little direct influence on later FOSS legal drafting. But, as I noted with surprise and [delight][8] back in 2012, MPL 2.0 adapted two parts of GPLv3: the 30-day cure and 60-day repose language from the GPLv3 termination provision, and the assurance that downstream upgrading to a later license version adds no new obligations on upstream licensors.
+
+The GPLv3 cure language has come to have a major impact, particularly over the past year. Following the Software Freedom Conservancy's promulgation, with the FSF's support, of the [Principles of Community-Oriented GPL Enforcement][9], which calls for extending GPLv3 cure opportunities to GPLv2 violations, the Linux Foundation Technical Advisory Board published a [statement][10], endorsed by over a hundred Linux kernel developers, which incorporates verbatim the cure language of GPLv3. This in turn was followed by a Red Hat-led series of [corporate commitments][11] to extend the GPLv3 cure provisions to GPLv2 and LGPLv2.x noncompliance, a campaign to get individual open source developers to extend the same commitment, and an announcement by Red Hat that henceforth GPLv2 and LGPLv2.x projects it leads will use the commitment language directly in project repositories. I discussed these developments in a recent [blog post][12].
+
+One lasting contribution of GPLv3 concerns changed expectations for how revisions of widely-used FOSS licenses are done. It is no longer acceptable for such licenses to be revised entirely in private, without opportunity for comment from the community and without efforts to consult key stakeholders. The drafting of MPL 2.0 and, more recently, EPL 2.0 reflects this new norm.
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://opensource.com/article/18/6/gplv3-anniversary
+
+作者:[Richard Fontana][a]
+选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:https://opensource.com/users/fontana
+[1]:https://www.gnu.org/licenses/gpl-3.0.en.html
+[2]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/SCO%E2%80%93Linux_disputes
+[3]:https://lwn.net/Articles/200422/
+[4]:https://opensource.com/article/18/1/containers-gpl-and-copyleft
+[5]:https://opensource.org/licenses/MIT
+[6]:http://gplv3.fsf.org/gpl-rationale-2006-01-16.html
+[7]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Novell#Agreement_with_Microsoft
+[8]:https://opensource.com/law/12/1/the-new-mpl
+[9]:https://sfconservancy.org/copyleft-compliance/principles.html
+[10]:https://www.kernel.org/doc/html/v4.16/process/kernel-enforcement-statement.html
+[11]:https://www.redhat.com/en/about/press-releases/technology-industry-leaders-join-forces-increase-predictability-open-source-licensing
+[12]:https://www.redhat.com/en/blog/gpl-cooperation-commitment-and-red-hat-projects?source=author&term=26851
diff --git a/sources/tech/20180629 SoCLI - Easy Way To Search And Browse Stack Overflow From The Terminal.md b/sources/tech/20180629 SoCLI - Easy Way To Search And Browse Stack Overflow From The Terminal.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..acf05c6872
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/tech/20180629 SoCLI - Easy Way To Search And Browse Stack Overflow From The Terminal.md
@@ -0,0 +1,188 @@
+SoCLI – Easy Way To Search And Browse Stack Overflow From The Terminal
+======
+Stack Overflow is the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their programming knowledge, and build their careers. It’s world’s largest developer community and allows users to ask and answer questions. It’s open alternative to earlier question and answer sites such as Experts-Exchange.
+
+It’s my preferred website, i have learned many program stuffs also i found many Linux related stuffs as well. Even i asked many questions and answered few questions too when i have time.
+
+Today i have stumbled upon good CLI utility called SoCLI & how2 both are used to browse stackoverflow website from the terminal easily and it’s very helpful when you doesn’t have GUI. Today we are going to discuss about SoCLI and will discuss about how2 in upcoming article.
+
+**Suggested Read :**
+**(#)** [How To Search The Arch Wiki Website Right From Terminal][1]
+**(#)** [Googler – Google Search from the command line on Linux][2]
+**(#)** [Buku – A Powerful Command-line Bookmark Manager for Linux][3]
+
+This might have very useful for NIX guys, whoever spending most of the time in CLI.
+
+[SoCLI][4] is a Stack overflow command line interface written in python. It’s allows you to search and browse stack overflow from the terminal.
+
+### SoCLI Featues:
+
+ * Verity of search is available like Quick Search, Manual Search & interactive Search
+ * Coloured interface
+ * Question stats view
+ * Topic Based Search using tag
+ * Can view user profiles
+ * Can create a new question via the web browser
+ * Can open the page in a browser
+
+
+
+### How to Install Python
+
+Make sure your system should have python-pip package in order to install SoCLI. pip is a python module bundled with setuptools, it’s one of the recommended tool for installing Python packages in Linux.
+
+For **`Debian/Ubuntu`** , use [apt-get command][5] or [apt command][6] to install pip.
+```
+$ sudo apt install python-pip
+
+```
+
+For **`RHEL/CentOS`** , use [YUM command][7] to install pip.
+```
+$ sudo yum install python-pip python-devel
+
+```
+
+For **`Fedora`** , use [dnf command][8] to install pip.
+```
+$ sudo dnf install python-pip
+
+```
+
+For **`Arch Linux`** , use [pacman command][9] to install pip.
+```
+$ sudo pacman -S python-pip
+
+```
+
+For **`openSUSE`** , use [Zypper Command][10] to install pip.
+```
+$ sudo pacman -S python-pip
+
+```
+
+### How to Install SoCLI
+
+Simple use pip command to install socli.
+```
+$ sudo pip install socli
+
+```
+
+### How to Update SoCLI
+
+Run the following command to update your existing version of socli to the newest version to avail latest features.
+```
+$ sudo pip install --upgrade socli
+
+```
+
+### How to Use SoCLI
+
+Simple fire the socli command on terminal to start explorer stackoverflow from the Linux command line. It’s offering varies arguments which will speedup your search even more faster.
+
+Common syntax for **`SoCLI`**
+```
+socli [Arguments] [Search Query]
+
+```
+
+### Quick Search
+
+The following command will search for the given query `command to check apache active connections` and displays the first most voted question in Stack Overflow with its most voted answer.
+```
+$ socli command to check apache active connections
+
+```
+
+![][12]
+
+### Interactive Search
+
+To enable interactive search, use `-iq` arguments followed by your search query.
+
+The following command will search for the given query `delete matching string` and print a list of questions from Stack Overflow.
+```
+$ socli -iq delete matching string
+
+```
+
+![][13]
+
+It will allows users to choose any of the questions interactively by hitting questing number in end of the results. In my case i have choose a question `2` then it will display the complete description of the chosen question with its most voted answer.
+![][14]
+
+Use `UP` and `DOWN` arrow keys to navigate to other answers. Press `LEFT` arrow key to go back to the list of questions.
+
+### Manual Search
+
+SoCLI allows you to display mentioned question number for given query. The following command will search for the given query `netstat command examples` in Stack Overflow and displays the second question full information for given query alike quick search.
+```
+$ socli -r 2 -q netstat command examples
+
+```
+
+![][15]
+
+### Topic Based Search
+
+SoCLI allows topic based search by using specific tags. Just mention the specific tags using `-t` arguments and followed by search query `command to increase jvm heap memory`.
+```
+$ socli -t linux -q command to increase jvm heap memory
+
+```
+
+![][16]
+
+For multiple tags, Just separate them with a comma.
+```
+$ socli -t linux,unix -q grep
+
+```
+
+### Post a New Question
+
+If you can’t find an answer for your question in Stack Overflow? don’t worry, post a new question by running following command.
+```
+$ socli -n
+
+```
+
+It will open the new question page of Stack Overflow in the web browser for you to create a new question.
+
+### Man Page
+
+To know more options & arguments about SoCLI, navigate to help section.
+```
+$ socli -h
+
+```
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://www.2daygeek.com/socli-search-and-browse-stack-overflow-from-linux-terminal/
+
+作者:[Magesh Maruthamuthu][a]
+选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:https://www.2daygeek.com/author/magesh/
+[1]:https://www.2daygeek.com/search-arch-wiki-website-command-line-terminal/
+[2]:https://www.2daygeek.com/googler-google-search-from-the-command-line-on-linux/
+[3]:https://www.2daygeek.com/buku-command-line-bookmark-manager-linux/
+[4]:https://github.com/gautamkrishnar/socli
+[5]:https://www.2daygeek.com/apt-get-apt-cache-command-examples-manage-packages-debian-ubuntu-systems/
+[6]:https://www.2daygeek.com/apt-command-examples-manage-packages-debian-ubuntu-systems/
+[7]:https://www.2daygeek.com/yum-command-examples-manage-packages-rhel-centos-systems/
+[8]:https://www.2daygeek.com/dnf-command-examples-manage-packages-fedora-system/
+[9]:https://www.2daygeek.com/pacman-command-examples-manage-packages-arch-linux-system/
+[10]:https://www.2daygeek.com/zypper-command-examples-manage-packages-opensuse-system/
+[11]:data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7
+[12]:https://www.2daygeek.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/08/socli-search-and-browse-stack-overflow-from-command-line-1.png
+[13]:https://www.2daygeek.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/08/socli-search-and-browse-stack-overflow-from-command-line-2.png
+[14]:https://www.2daygeek.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/08/socli-search-and-browse-stack-overflow-from-command-line-2a.png
+[15]:https://www.2daygeek.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/08/socli-search-and-browse-stack-overflow-from-command-line-3.png
+[16]:https://www.2daygeek.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/08/socli-search-and-browse-stack-overflow-from-command-line-4.png
diff --git a/translated/talk/20180320 Can we build a social network that serves users rather than advertisers.md b/translated/talk/20180320 Can we build a social network that serves users rather than advertisers.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..bd279216ca
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/talk/20180320 Can we build a social network that serves users rather than advertisers.md
@@ -0,0 +1,70 @@
+我们能否建立一个服务于用户而非广告商的社交网络?
+=====
+
+
+
+如今,开源软件具有深远的意义,在推动数字经济创新方面发挥着关键作用。世界正在快速彻底地改变。世界各地的人们需要一个专门的,中立的,透明的在线平台来迎接我们这个时代的挑战。
+
+开放的原则可能会成为让我们到达那里的方法(to 校正者:这句上下文没有理解)。如果我们用开放的思维方式将数字创新与社会创新结合在一起,会发生什么?
+
+这个问题是我们在 [Human Connection][1] 工作的核心,这是一个具有前瞻性的,以德国为基础的知识和行动网络,其使命是创建一个服务于全球的真正的社交网络。我们受到这样一种观念为指引,即人类天生慷慨而富有同情心,并且他们在慈善行为上茁壮成长。但我们还没有看到一个完全支持我们自然倾向,于乐于助人和合作以促进共同利益的社交网络。Human Connection 渴望成为让每个人都成为积极变革者的平台。
+
+为了实现一个以解决方案为导向的平台的梦想,让人们通过与慈善机构、社区团体和社会变革活动人士的接触,围绕社会公益事业采取行动,Human Connection 将开放的价值观作为社会创新的载体。
+
+以下是有关它如何工作的。
+
+### 首先是透明
+
+透明是 Human Connection 的指导原则之一。Human Connection 邀请世界各地的程序员通过[在 Github 上提交他们的源代码][2]共同开发平台的源代码(JavaScript, Vue, nuxt),并通过贡献代码或编程附加功能来支持真正的社交网络。
+
+但我们对透明的承诺超出了我们的发展实践。事实上,当涉及到建立一种新的社交网络,促进那些对让世界变得更好的人之间的真正联系和互动,分享源代码只是迈向透明的一步。
+
+为促进公开对话,Human Connection 团队举行[定期在线公开会议][3]。我们在这里回答问题,鼓励建议并对潜在的问题作出回应。我们的 Meet The Team (to 校正者:这里如果可以,请翻译得稍微优雅,我想不出来一个词)活动也会记录下来,并在事后向公众开放。通过对我们的流程,源代码和财务状况完全透明,我们可以保护自己免受批评或其他潜在的不利影响。
+
+对透明的承诺意味着,所有在 Human Connection 上公开分享的用户贡献者将在 Creative Commons 许可下发布,最终作为数据包下载。通过让大众知识变得可用,特别是以一种分散的方式,我们创造了一个多元化社会的机会。
+
+一个问题指导我们所有的组织决策:“它是否服务于人民和更大的利益?”我们用[联合国宪章(UN Charter)][4]和“世界人权宣言(Universal Declaration of Human Rights)”作为我们价值体系的基础。随着我们的规模越来越大,尤其是即将推出的公测版,我们必须对此任务负责。我甚至愿意邀请 Chaos Computer Club (译者注:这是欧洲最大的黑客联盟)或其他黑客俱乐部通过随机检查我们的平台来验证我们的代码和行为的完整性。
+
+### 一个合作的社会
+
+以一种[以社区为中心的协作方法][5]来编写 Human Connection 平台是超越社交网络实际应用理念的基础。我们的团队是通过找到问题的答案来驱动:“是什么让一个社交网络真正地社会化?”
+
+一个抛弃了以利润为导向的算法,为广告商而不是最终用户服务的网络,只能通过转向对等生产和协作的过程而繁荣起来。例如,像 [Code Alliance][6] 和 [Code for America][7] 这样的组织已经证明了如何在一个开源环境中创造技术,造福人类并破坏(to 校正:这里译为改变较好)现状。社区驱动的项目,如基于地图的报告平台 [FixMyStreet][8],或者为 Humanitarian OpenStreetMap 而建立的 [Tasking Manager][9],已经将众包作为推动其使用的一种方式。
+
+我们建立 Human Connection 的方法从一开始就是合作。为了收集关于必要功能和真正社交网络的目的的初步数据,我们与巴黎索邦大学(University Sorbonne)的国家东方语言与文明研究所(National Institute for Oriental Languages and Civilizations (INALCO) )和德国斯图加特媒体大学(Stuttgart Media University )合作。这两个项目的研究结果都被纳入了 Human Connection 的早期开发。多亏了这项研究,[用户将拥有一套全新的功能][10],让他们可以控制自己看到的内容以及他们如何与他人的互动。由于早期的支持者[被邀请到网络的 alpha 版本][10],他们可以体验到第一个可用的值得注意的功能。这里有一些:
+
+ * 将信息与行动联系起来是我们研究会议的一个重要主题。当前的社交网络让用户处于信息阶段。这两所大学的学生团体都认为,需要一个以行动为导向的组件,以满足人类共同解决问题的本能。所以我们在平台上构建了一个[“Can Do”功能][11]。这是一个人在阅读了某个话题后可以采取行动的一种方式。“Can Do” 是用户建议的活动,在“采取行动(Take Action)”领域,每个人都可以实现。
+
+ * “Versus” 功能是另一个定义结果的方式(to 校正者:这句话稍微注意一下)。在传统社交网络仅限于评论功能的地方,我们的学生团体认为需要采用更加结构化且有用的方式进行讨论和争论。“Versus” 是对公共帖子的反驳,它是单独显示的,并提供了一个机会来突出围绕某个问题的不同意见。
+
+ * 今天的社交网络并没有提供很多过滤内容的选项。研究表明,情绪过滤选项可以帮助我们根据日常情绪驾驭社交空间,并可能通过在我们希望仅看到令人振奋的内容的那一天时,不显示悲伤或难过的帖子来潜在地保护我们的情绪健康。
+
+
+Human Connection 邀请改革者合作开发一个网络,有可能动员世界各地的个人和团体将负面新闻变成 “Can Do”,并与慈善机构和非营利组织一起参与社会创新项目。
+
+[订阅我们的每周时事通讯][12]以了解有关开放组织的更多信息。
+
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://opensource.com/open-organization/18/3/open-social-human-connection
+
+作者:[Dennis Hack][a]
+译者:[MjSeven](https://github.com/MjSeven)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:https://opensource.com/users/dhack
+[1]:https://human-connection.org/en/
+[2]:https://github.com/human-connection/
+[3]:https://youtu.be/tPcYRQcepYE
+[4]:http://www.un.org/en/charter-united-nations/index.html
+[5]:https://youtu.be/BQHBno-efRI
+[6]:http://codealliance.org/
+[7]:https://www.codeforamerica.org/
+[8]:http://fixmystreet.org/
+[9]:https://tasks.hotosm.org/
+[10]:https://youtu.be/AwSx06DK2oU
+[11]:https://youtu.be/g2gYLNx686I
+[12]:https://opensource.com/open-organization/resources/newsletter
diff --git a/translated/tech/20140119 10 Killer Tips To Speed Up Ubuntu Linux.md b/translated/tech/20140119 10 Killer Tips To Speed Up Ubuntu Linux.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 05778a99d7..0000000000
--- a/translated/tech/20140119 10 Killer Tips To Speed Up Ubuntu Linux.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,173 +0,0 @@
-"翻译完成"
-10条加速Ubuntu Linux的杀手级贴士
-======
-**摘要** : 一些实际的**加速Ubuntu Linux的贴士**。 这里的贴士对于大多数版本的Ubuntu是有效的,也可以应用于Linux Mint以及其他的基于Ubuntu的发行版。
-
-也许你经历过使用Ubuntu一段时间后系统开始运行缓慢的情况。 在这篇文章里,我们将看到几项调整以及**使Ubuntu运行更快的窍门**。
-
-在我们了解如何提升Ubuntu的总体系统表现之前,首先让我们思考为什么系统逐渐变慢。这个问题可能有很多原因。也许你有一台只有基础配置的简陋的电脑;也许你安装了一些在启动时即耗尽资源的应用。事实上原因无穷无尽。
-
-这里我列出一些能够帮助你稍微加速Ubuntu的小调整。也有一些你能够采用过来以获取一个更流畅、有所提升的系统表现的最好的尝试。你可以选择遵循全部或部分的建议。将各项调整一点一点的结合就能给你一个更流畅、更迅捷快速的Ubuntu。
-
-### 使Ubuntu更快的贴士:
-
-![Tips to speed up Ubuntu][1]
-我在一个较老版本的Ubuntu上使用了这些调整,但是我相信其他的Ubuntu版本以及其他的例如Linux Mint, Elementary OS Luna等基于Ubuntu的Linux版本也是同样适用的。
-
-#### 1\. 减少默认的grub载入时间:
-
-Grub给你10秒的时间以让你在多系统启动项或恢复模式之间改变。对我而言,它是多余的。它也意味着你将不得不坐在电脑旁,敲着Enter键以尽可能快的启动进入Ubuntu。这花了一点时间,不是吗? 第一个技巧便是改变这个启动时间。如果你使用图形工具更舒适,阅读这篇文章来[使用Grub定制器改变grub时间以及启动顺序][2].
-
-如果更倾向于命令行,你可以简单地使用以下的命令来打开grub配置:
-```
-sudo gedit /etc/default/grub &
-
-```
-
-并且将**GRUB_TIMEOUT=10**改为**GRUB_TIMEOUT=2**.这将改变启动时间为2秒。最好不要将这里改为0,因为这样你将会失去在操作系统及恢复选项之间切换的机会。一旦你更改了grub配置,使用以下命令来使更改生效:
-```
-sudo update-grub
-
-```
-
-#### 2\. 管理开机启动的应用:
-渐渐地你倾向于开始安装应用。 如果你是日常的“It’s FOSS”读者, 你也许从[App of the week][3]系列安装了许多apps.
-
-这些apps的其中一些在每次开机时都会启动,当然资源运行这些应用也会陷入繁忙。结果:一台电脑因为每次启动时的持续时间而变得缓慢。进入Unity Dash寻找**Startup Applications** :
-
-
-在这里,看看哪些应用在开机时被载入。现在考虑在你每次启动Ubuntu时是否有不需要启动的应用。尽管移除它们:
-
-
-但是要是你不想从启动里移除它们怎么办?举个例子,如果你安装了[Ubuntu最好的指示器程序][4]之一, 你将想要它们在每次开机时自动地启动。
-
-这里你所能做的就是延迟一些程序的启动时间。这样你将能够释放开机启动时的资源,并且一段时间后你的应用将被自动启动。在上一张图片里点击Edit并使用sleep选项来更改运行命令。
-例如,如果你想要延迟Dropbox指示器的运行,我们指定时间20秒,你只需要在已有的命令里像这样**加入一个命令**:
-```
-sleep 20;
-
-```
-
-所以,命令‘ **dropbox start -i** ‘变为‘ **sleep 20; drobox start -i** ‘。这意味着现在Dropbox将延迟20秒启动。你可以通过相似的方法来改变另一个开机启动应用的启动时间。
-
-
-#### 3\. 安装preload来加速应用载入时间:
-
-Preload是一个后台运行的守护进程,分析用户行为,频繁地运行应用。打开终端,使用如下的命令来安装preload:
-```
-sudo apt-get install preload
-
-```
-
-安装后,重启你的电脑就不用管它了。它将在后台工作。[阅读更多关于preload][5]
-
-#### 4\. 选择最好的软件更新镜像:
-验证你正在使用最好的更新软件的镜像是很好的做法。Ubuntu的软件仓库镜像跨过全球, 使用离你最近的一个是相当明智的。随着从服务器获取包的时间减少,这将形成更快的系统更新。
-在**Software & Updates->Ubuntu Software tab->Download From**里选择**Other**紧接着点击**Select Best Server**:
-
-
-它将运行测试来告知你那个是最好的镜像。正常地,最好的镜像已经被设置,但是我说过,验证它没什么坏处。并且,如果仓库缓存的最近的镜像没有频繁更新的话,这将引起获取更新时的一些延迟。这对于网速相对慢的人们是有用的。你可以使用这些贴士来[加速Ubuntu的wifi][6].
-
-#### 5\. 为了更快的更新,使用apt-fast而不是apt-get:
-
-apt-fast是“apt-get”的一个shell脚本包装器,通过从多连接同时下载包来提升更新及包下载速度。 如果你经常使用终端以及apt-get来安装和更新包,你也许会想要试一试apt-fast。使用下面的命令来通过官方PPA安装apt-fast:
-```
-sudo add-apt-repository ppa:apt-fast/stable
-sudo apt-get update
-sudo apt-get install apt-fast
-
-```
-
-#### 6\. 从apt-get更新移除语言相关的ign:
-
-你曾经注意过sudo apt-get更新的输出吗?其中有三种行,**hit**,**ign**和**get**. 你可以在[这里][7]阅读它们的意义。如果你看到IGN行,你会发现它们中的大多数都与语言翻译有关。如果你使用所有的英文应用及包,你将完全不需要英文向英文的包数据库的翻译。
-
-如果你从apt-get制止语言相关的更新,它将略微地增加apt-get的更新速度。为了那样,打开如下的文件:
-```
-sudo gedit /etc/apt/apt.conf.d/00aptitude
-
-```
-
-然后在文件末尾添加如下行:
-```
-Acquire::Languages "none";
-
-```
-[![speed up apt get update in Ubuntu][8]][9]
-
-#### 7\. 减少过热:
-
-现在过热是电脑普遍的问题。一台过热的电脑运行相当缓慢。当你的CPU风扇转得像[Usain Bolt][10],打开一个程序将花费很长的时间。有两个工具你可以用来极少过热,使Ubuntu获得更好的系统表现,即TLP和CPUFREQ。
-
-在终端里使用以下命令来安装TLP:
-```
-sudo add-apt-repository ppa:linrunner/tlp
-sudo apt-get update
-sudo apt-get install tlp tlp-rdw
-sudo tlp start
-
-```
-
-安装完TLP后你不需要做任何事。它在后台工作。
-
-使用如下命令来安装CPUFREQ indicator:
-```
-sudo apt-get install indicator-cpufreq
-
-```
-
-重启你的电脑并使用**Powersave**模式:
-
-
-
-#### 8\. 调整LibreOffice来使它更快:
-
-如果你是office产品频繁使用的用户, 那么你会想要稍微调整默认的LibreOffice使它更快。这里你将调整内存选项。打开Open LibreOffice,进入**Tools- >Options**。在那里,从左边的侧栏选择**Memory**并启用 **Systray Quickstarter** 以及增加内存分配。
-
-
-你可以阅读更多关于[如何提速LibreOffice][11]的细节。
-
-#### 9\. 使用轻量级的桌面环境 (如果你可以):
-
-如果你选择安装默认的Unity of GNOME桌面环境, 你也许会选择一个轻量级的桌面环境像[Xfce][12]或[LXDE][13]。
-
-这些桌面环境使用更少的内存,消耗更少的CPU。它们也自带轻量应用集来更深入地帮助更快地使用Ubuntu。你可以参考这篇详细指南来学习[如何在Ubuntu上安装Ubuntu][14]。
-
-当然,桌面也许没有Unity或GNOME看起来现代化。那是你必须做出的妥协。
-
-#### 10\. 使用不同应用的更轻量可选:
-
-这不仅仅是建议和喜好。一些默认的或者流行的应用是耗资源的且可能不适合低端的电脑。你能做的就是使用这些应用的一些替代品。例如,使用[AppGrid][15]而不是Ubuntu软件中心。使用[Gdebi][16]来安装包。使用 AbiWord而不是LibreOffice Writer等。
-
-可以断定这些贴士的汇总使Ubuntu 14.04,16.04以及其他版本更快。我确定这些贴士会提供一个总体上更好的系统表现。
-
-对于**加速Ubuntu**你也有妙计吗?这些贴士也帮到你了吗?分享你的观点。 问题,建议总是受欢迎的。请在评论区里提出来。
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: https://itsfoss.com/speed-up-ubuntu-1310/
-
-作者:[Abhishek Prakash][a]
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/darsh8)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]: https://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/
-[1]:https://itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/speed-up-ubuntu-featured-800x450.jpeg
-[2]:https://itsfoss.com/windows-default-os-dual-boot-ubuntu-1304-easy/ (Make Windows Default OS In Dual Boot With Ubuntu 13.04: The Easy Way)
-[3]:https://itsfoss.com/tag/app-of-the-week/
-[4]:https://itsfoss.com/best-indicator-applets-ubuntu/ (7 Best Indicator Applets For Ubuntu 13.10)
-[5]:https://itsfoss.com/improve-application-startup-speed-with-preload-in-ubuntu/ (Improve Application Startup Speed With Preload in Ubuntu)
-[6]:https://itsfoss.com/speed-up-slow-wifi-connection-ubuntu/ (Speed Up Slow WiFi Connection In Ubuntu 13.04)
-[7]:http://ubuntuforums.org/showthread.php?t=231300
-[8]:https://itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/01/ign_language-apt_get_update-e1510129903529.jpeg
-[9]:https://itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/01/ign_language-apt_get_update.jpeg
-[10]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Usain_Bolt
-[11]:https://itsfoss.com/speed-libre-office-simple-trick/ (Speed Up LibreOffice With This Simple Trick)
-[12]:https://xfce.org/
-[13]:https://lxde.org/
-[14]:https://itsfoss.com/install-xfce-desktop-xubuntu/
-[15]:https://itsfoss.com/app-grid-lighter-alternative-ubuntu-software-center/ (App Grid: Lighter Alternative Of Ubuntu Software Center)
-[16]:https://itsfoss.com/install-deb-files-easily-and-quickly-in-ubuntu-12-10-quick-tip/ (Install .deb Files Easily And Quickly In Ubuntu 12.10 [Quick Tip])
diff --git a/translated/tech/20171010 Operating a Kubernetes network.md b/translated/tech/20171010 Operating a Kubernetes network.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..ef7bb6b888
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20171010 Operating a Kubernetes network.md
@@ -0,0 +1,216 @@
+运营一个 Kubernetes 网络
+============================================================
+
+最近我一直在研究 Kubernetes 网络。我注意到一件事情就是,虽然关于如何设置 Kubernetes 网络的文章很多,也写得很不错,但是却没有看到关于如何去运营 Kubernetes 网络的文章、以及如何完全确保它不会给你造成生产事故。
+
+在本文中,我将尽力让你相信三件事情(我觉得这些都很合理 :)):
+
+* 避免生产系统网络中断非常重要
+
+* 运营联网软件是很难的
+
+* 有关你的网络基础设施的重要变化值得深思熟虑,以及这种变化对可靠性的影响。虽然非常“牛x”的谷歌人常说“这是我们在谷歌正在用的”(谷歌工程师在 Kubernetes 上正做着很重大的工作!但是我认为重要的仍然是研究架构,并确保它对你的组织有意义)。
+
+我肯定不是 Kubernetes 网络方面的专家,但是我在配置 Kubernetes 网络时遇到了一些问题,并且比以前更加了解 Kubernetes 网络了。
+
+### 运营联网软件是很难的
+
+在这里,我并不讨论有关运营物理网络的话题(对于它我不懂),而是讨论关于如何让像 DNS 服务、负载均衡以及代理这样的软件正常工作方面的内容。
+
+我在一个负责很多网络基础设施的团队工作过一年时间,并且因此学到了一些运营网络基础设施的知识!(显然我还有很多的知识需要继续学习)在我们开始之前有三个整体看法:
+
+* 联网软件经常重度依赖 Linux 内核。因此除了正确配置软件之外,你还需要确保许多不同的系统控制(sysctl)配置正确,而一个错误配置的系统控制就很容易让你处于“一切都很好”和“到处都出问题”的差别中。
+
+* 联网需求会随时间而发生变化(比如,你的 DNS 查询或许比上一年多了五倍!或者你的 DNS 服务器突然开始返回 TCP 协议的 DNS 响应而不是 UDP 的,它们是完全不同的内核负载!)。这意味着之前正常工作的软件突然开始出现问题。
+
+* 修复一个生产网络的问题,你必须有足够的经验。(例如,看这篇 [由 Sophie Haskins 写的关于 kube-dns 问题调试的文章][1])我在网络调试方面比以前进步多了,但那也是我花费了大量时间研究 Linux 网络知识之后的事了。
+
+我距离成为一名网络运营专家还差得很远,但是我认为以下几点很重要:
+
+1. 对生产网络的基础设施做重要的更改是很难得的(因为它会产生巨大的混乱)
+
+2. 当你对网络基础设施做重大更改时,真的应该仔细考虑如果新网络基础设施失败该如何处理
+
+3. 是否有很多人都能理解你的网络配置
+
+切换到 Kubernetes 显然是个非常大的更改!因此,我们来讨论一下可能会导致错误的地方!
+
+### Kubernetes 网络组件
+
+在本文中我们将要讨论的 Kubernetes 网络组件有:
+
+* 网络覆盖后端(像 flannel/calico/weave 网络/romana)
+
+* `kube-dns`
+
+* `kube-proxy`
+
+* 入站控制器 / 负载均衡器
+
+* `kubelet`
+
+如果你打算配置 HTTP 服务,或许这些你都会用到。这些组件中的大部分我都不会用到,但是我尽可能去理解它们,因此,本文将涉及它们有关的内容。
+
+### 最简化的方式:为所有容器使用宿主机网络
+
+我们从你能做到的最简单的东西开始。这并不能让你在 Kubernetes 中运行 HTTP 服务。我认为它是非常安全的,因为在这里面可以让你动的东西很少。
+
+如果你为所有容器使用宿主机网络,我认为需要你去做的全部事情仅有:
+
+1. 配置 kubelet,以便于容器内部正确配置 DNS
+
+2. 没了,就这些!
+
+如果你为每个 Pod 直接使用宿主机网络,那就不需要 kube-dns 或者 kube-proxy 了。你都不需要一个作为基础的覆盖网络。
+
+这种配置方式中,你的 pod 们都可以连接到外部网络(同样的方式,你的宿主机上的任何进程都可以与外部网络对话),但外部网络不能连接到你的 pod 们。
+
+这并不是最重要的(我认为大多数人想在 Kubernetes 中运行 HTTP 服务并与这些服务进行真实的通讯),但我认为有趣的是,从某种程度上来说,网络的复杂性并不是绝对需要的,并且有时候你不用这么复杂的网络就可以实现你的需要。如果可以的话,尽可能地避免让网络过于复杂。
+
+### 运营一个覆盖网络
+
+我们将要讨论的第一个网络组件是有关覆盖网络的。Kubernetes 假设每个 pod 都有一个 IP 地址,这样你就可以与那个 pod 中的服务进行通讯了。我在说到“覆盖网络”这个词时,指的就是这个意思(“让你通过它的 IP 地址指向到 pod 的系统)。
+
+所有其它的 Kubernetes 网络的东西都依赖正确工作的覆盖网络。更多关于它的内容,你可以读 [这里的 kubernetes 网络模型][10]。
+
+Kelsey Hightower 在 [kubernetes the hard way][11] 中描述的方式看起来似乎很好,但是,事实上它的作法在超过 50 个节点的 AWS 上是行不通的,因此,我不打算讨论它了。
+
+有许多覆盖网络后端(calico、flannel、weaveworks、romana)并且规划非常混乱。就我的观点来看,我认为一个覆盖网络有 2 个职责:
+
+1. 确保你的 pod 能够发送网络请求到外部的集群
+
+2. 保持一个到子网络的稳定的节点映射,并且保持集群中每个节点都可以使用那个映射得以更新。当添加和删除节点时,能够做出正确的反应。
+
+Okay! 因此!你的覆盖网络可能会出现的问题是什么呢?
+
+* 覆盖网络负责设置 iptables 规则(最基本的是 `iptables -A -t nat POSTROUTING -s $SUBNET -j MASQUERADE`),以确保那个容器能够向 Kubernetes 之外发出网络请求。如果在这个规则上有错误,你的容器就不能连接到外部网络。这并不很难(它只是几条 iptables 规则而已),但是它非常重要。我发起了一个 [pull request][2],因为我想确保它有很好的弹性。
+
+* 添加或者删除节点时可能会有错误。我们使用 `flannel hostgw` 后端,我们开始使用它的时候,节点删除 [尚未开始工作][3]。
+
+* 你的覆盖网络或许依赖一个分布式数据库(etcd)。如果那个数据库发生什么问题,这将导致覆盖网络发生问题。例如,[https://github.com/coreos/flannel/issues/610][4] 上说,如果在你的 `flannel etcd` 集群上丢失了数据,最后的结果将是在容器中网络连接会丢失。(现在这个问题已经被修复了)
+
+* 你升级 Docker 以及其它东西导致的崩溃
+
+* 还有更多的其它的可能性!
+
+我在这里主要讨论的是过去发生在 Flannel 中的问题,但是我并不是要承诺不去使用 Flannel —— 事实上我很喜欢 Flannel,因为我觉得它很简单(比如,类似 [vxlan 在后端这一块的部分][12] 只有 500 行代码),并且我觉得对我来说,通过代码来找出问题的根源成为了可能。并且很显然,它在不断地改进。他们在审查 `pull requests` 方面做的很好。
+
+到目前为止,我运营覆盖网络的方法是:
+
+* 学习它的工作原理的详细内容以及如何去调试它(比如,Flannel 用于创建路由的 hostgw 网络后端,因此,你只需要使用 `sudo ip route list` 命令去查看它是否正确即可)
+
+* 如果需要的话,维护一个内部构建版本,这样打补丁比较容易
+
+* 有问题时,向上游贡献补丁
+
+我认为去遍历所有已合并的 PR 以及过去已修复的 bug 清单真的是非常有帮助的 —— 这需要花费一些时间,但这是得到一个其它人遇到的各种问题的清单的好方法。
+
+对其他人来说,他们的覆盖网络可能工作的很好,但是我并不能从中得到任何经验,并且我也曾听说过其他人报告类似的问题。如果你有一个类似配置的覆盖网络:a) 在 AWS 上并且 b) 在多于 50-100 节点上运行,我想知道你运营这样的一个网络有多大的把握。
+
+### 运营 kube-proxy 和 kube-dns?
+
+现在,我有一些关于运营覆盖网络的想法,我们来讨论一下。
+
+这个标题的最后面有一个问号,那是因为我并没有真的去运营过。在这里我还有更多的问题要问答。
+
+这里的 Kubernetes 服务是如何工作的!一个服务是一群 pod 们,它们中的每个都有自己的 IP 地址(像 10.1.0.3、10.2.3.5、10.3.5.6 这样)
+
+1. 每个 Kubernetes 服务有一个 IP 地址(像 10.23.1.2 这样)
+
+2. `kube-dns` 去解析 Kubernetes 服务 DNS 名字为 IP 地址(因此,my-svc.my-namespace.svc.cluster.local 可能映射到 10.23.1.2 上)
+
+3. `kube-proxy` 配置 `iptables` 规则是为了在它们之间随机进行均衡负载。Kube-proxy 也有一个用户空间的轮询负载均衡器,但是在我的印象中,他们并不推荐使用它。
+
+因此,当你发出一个请求到 `my-svc.my-namespace.svc.cluster.local` 时,它将解析为 10.23.1.2,然后,在你本地主机上的 `iptables` 规则(由 kube-proxy 生成)将随机重定向到 10.1.0.3 或者 10.2.3.5 或者 10.3.5.6 中的一个上。
+
+在这个过程中我能想像出的可能出问题的地方:
+
+* `kube-dns` 配置错误
+
+* `kube-proxy` 挂了,以致于你的 `iptables` 规则没有得以更新
+
+* 维护大量的 `iptables` 规则相关的一些问题
+
+我们来讨论一下 `iptables` 规则,因为创建大量的 `iptables` 规则是我以前从没有听过的事情!
+
+kube-proxy 像如下这样为每个目标主机创建一个 `iptables` 规则:这些规则来自 [这里][13])
+
+```
+-A KUBE-SVC-LI77LBOOMGYET5US -m comment --comment "default/showreadiness:showreadiness" -m statistic --mode random --probability 0.20000000019 -j KUBE-SEP-E4QKA7SLJRFZZ2DD[b][c]
+-A KUBE-SVC-LI77LBOOMGYET5US -m comment --comment "default/showreadiness:showreadiness" -m statistic --mode random --probability 0.25000000000 -j KUBE-SEP-LZ7EGMG4DRXMY26H
+-A KUBE-SVC-LI77LBOOMGYET5US -m comment --comment "default/showreadiness:showreadiness" -m statistic --mode random --probability 0.33332999982 -j KUBE-SEP-RKIFTWKKG3OHTTMI
+-A KUBE-SVC-LI77LBOOMGYET5US -m comment --comment "default/showreadiness:showreadiness" -m statistic --mode random --probability 0.50000000000 -j KUBE-SEP-CGDKBCNM24SZWCMS
+-A KUBE-SVC-LI77LBOOMGYET5US -m comment --comment "default/showreadiness:showreadiness" -j KUBE-SEP-RI4SRNQQXWSTGE2Y
+
+```
+
+因此,kube-proxy 创建了许多 `iptables` 规则。它们都是什么意思?它对我的网络有什么样的影响?这里有一个来自华为的非常好的演讲,它叫做 [支持 50,000 个服务的可伸缩 Kubernetes][14],它说如果在你的 Kubernetes 集群中有 5,000 服务,增加一个新规则,将需要 **11 分钟**。如果这种事情发生在真实的集群中,我认为这将是一件非常糟糕的事情。
+
+在我的集群中肯定不会有 5,000 个服务,但是 5,000 并不是那么大的一个数字。为解决这个问题,他们给出的解决方案是 kube-proxy 用 IPVS 来替换这个 `iptables` 后端,IPVS 是存在于 Linux 内核中的一个负载均衡器。
+
+看起来,像 kube-proxy 正趋向于使用各种基于 Linux 内核的负载均衡器。我认为这只是一定程度上是这样,因为他们支持 UDP 负载均衡,而其它类型的负载均衡器(像 HAProxy)并不支持 UDP 负载均衡。
+
+但是,我觉得使用 HAProxy 更舒服!它能够用于去替换 kube-proxy!我用谷歌搜索了一下,然后发现了这个 [thread on kubernetes-sig-network][15],它说:
+
+> kube-proxy 是很难用的,我们在生产系统中使用它近一年了,它在大部分的时间都表现的很好,但是,随着我们集群中的服务越来越多,我们发现它的排错和维护工作越来越难。在我们的团队中没有 iptables 方面的专家,我们只有 HAProxy&LVS 方面的专家,由于我们已经使用它们好几年了,因此我们决定使用一个中心化的 HAProxy 去替换分布式的代理。我觉得这可能会对在 Kubernetes 中使用 HAProxy 的其他人有用,因此,我们更新了这个项目,并将它开源:[https://github.com/AdoHe/kube2haproxy][5]。如果你发现它有用,你可以去看一看、试一试。
+
+因此,那是一个有趣的选择!我在这里确实没有答案,但是,有一些想法:
+
+* 负载均衡器是很复杂的
+
+* DNS 也很复杂
+
+* 如果你有运营某种类型的负载均衡器(比如 HAProxy)的经验,与其使用一个全新的负载均衡器(比如 kube-proxy),还不如做一些额外的工作去使用你熟悉的那个来替换,或许更有意义。
+
+* 我一直在考虑,我们希望在什么地方能够完全使用 kube-proxy 或者 kube-dns —— 我认为,最好是只在 Envoy 上投入,并且在负载均衡&服务发现上完全依赖 Envoy 来做。因此,你只需要将 Envoy 运营好就可以了。
+
+正如你所看到的,我在关于如何运营 Kubernetes 中的内部代理方面的思路还是很混乱的,并且我也没有使用它们的太多经验。总体上来说,kube-proxy 和 kube-dns 还是很好的,也能够很好地工作,但是我仍然认为应该去考虑使用它们可能产生的一些问题(例如,”你不能有超出 5000 的 Kubernetes 服务“)。
+
+### 入口
+
+如果你正在运行着一个 Kubernetes 集群,那么到目前为止,很有可能的是,你事实上需要 HTTP 请求去进入到你的集群中。这篇博客已经太长了,并且关于入口我知道的也不多,因此,我们将不讨论关于入口的内容。
+
+### 有用的链接
+
+几个有用的链接,总结如下:
+
+* [Kubernetes 网络模型][6]
+
+* GKE 网络是如何工作的:[https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=y2bhV81MfKQ][7]
+
+* 上述的有关 `kube-proxy` 上性能的讨论:[https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4-pawkiazEg][8]
+
+### 我认为网络运营很重要
+
+我对 Kubernetes 的所有这些联网软件的感觉是,它们都仍然是非常新的,并且我并不能确定我们(作为一个社区)真的知道如何去把它们运营好。这让我作为一个操作者感到很焦虑,因为我真的想让我的网络运行的很好!:) 而且我觉得作为一个组织,运行你自己的 Kubernetes 集群需要相当大的投入,以确保你理解所有的代码片段,这样当它们出现问题时你可以去修复它们。这不是一件坏事,它只是一个事而已。
+
+我现在的计划是,继续不断地学习关于它们都是如何工作的,以尽可能多地减少对我动过的那些部分的担忧。
+
+一如继往,我希望这篇文章对你有帮助,并且如果我在这篇文章中有任何的错误,我非常喜欢你告诉我。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://jvns.ca/blog/2017/10/10/operating-a-kubernetes-network/
+
+作者:[Julia Evans ][a]
+译者:[qhwdw](https://github.com/qhwdw)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:https://jvns.ca/about
+[1]:http://blog.sophaskins.net/blog/misadventures-with-kube-dns/
+[2]:https://github.com/coreos/flannel/pull/808
+[3]:https://github.com/coreos/flannel/pull/803
+[4]:https://github.com/coreos/flannel/issues/610
+[5]:https://github.com/AdoHe/kube2haproxy
+[6]:https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/cluster-administration/networking/#kubernetes-model
+[7]:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=y2bhV81MfKQ
+[8]:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4-pawkiazEg
+[9]:https://jvns.ca/categories/kubernetes
+[10]:https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/cluster-administration/networking/#kubernetes-model
+[11]:https://github.com/kelseyhightower/kubernetes-the-hard-way/blob/master/docs/11-pod-network-routes.md
+[12]:https://github.com/coreos/flannel/tree/master/backend/vxlan
+[13]:https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/issues/37932
+[14]:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4-pawkiazEg
+[15]:https://groups.google.com/forum/#!topic/kubernetes-sig-network/3NlBVbTUUU0
diff --git a/translated/tech/20180224 How To Run A Command For A Specific Time In Linux.md b/translated/tech/20180224 How To Run A Command For A Specific Time In Linux.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 7fe8281934..0000000000
--- a/translated/tech/20180224 How To Run A Command For A Specific Time In Linux.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,107 +0,0 @@
-如何在 Linux 中的特定时间运行命令
-======
-
-
-有一天,我使用 rsync 将大文件传输到局域网上的另一个系统。由于它是非常大的文件,大约需要 20 分钟才能完成。我不想再等了,我也不想按 CTRL+C 来终止这个过程。我只是想知道在类 Unix 操作系统中是否有简单的方法可以在特定的时间运行一个命令,并且一旦超时就自动杀死它 - 因此有了这篇文章。请继续阅读。
-
-### 在 Linux 中在特定时间运行命令
-
-我们可以用两种方法做到这一点。
-
-#### 方法 1 - 使用 “timeout” 命令
-
-最常用的方法是使用 **timeout** 命令。对于那些不知道的人来说,timeout 命令会有效地限制一个进程的绝对执行时间。timeout 命令是 GNU coreutils 包的一部分,因此它预装在所有 GNU/Linux 系统中。
-
-假设你只想运行一个命令 5 秒钟,然后杀死它。为此,我们使用:
-```
-$ timeout
-
-```
-
-例如,以下命令将在 10 秒后终止。
-```
-$ timeout 10s tail -f /var/log/pacman.log
-
-```
-
-![][2]
-
-你也可以不用在秒数后加后缀 “s”。以下命令与上面的相同。
-```
-$ timeout 10 tail -f /var/log/pacman.log
-
-```
-
-其他可用的后缀有:
-
- * ‘m‘ 代表分钟。
- * ’h‘ 代表小时。
- * ’d‘ 代表天。
-
-
-
-如果你运行这个 **tail -f /var/log/pacman.log** 命令,它将继续运行,直到你按 CTRL+C 手动结束它。但是,如果你使用 **timeout** 命令运行它,它将在给定的时间间隔后自动终止。如果该命令在超时后仍在运行,则可以发送 **kill** 信号,如下所示。
-```
-$ timeout -k 20 10 tail -f /var/log/pacman.log
-
-```
-
-在这种情况下,如果 tail 命令在 10 秒后仍然运行,timeout 命令将在 20 秒后发送一个 kill 信号并结束。
-
-有关更多详细信息,请查看手册页。
-```
-$ man timeout
-
-```
-
-有时,某个特定程序可能需要很长时间才能完成并最终冻结你的系统。在这种情况下,你可以使用此技巧在特定时间后自动结束该进程。
-
-另外,可以考虑使用 **cpulimit**,一个简单的限制进程的 CPU 使用率的程序。有关更多详细信息,请查看下面的链接。
-
-#### 方法 2 - 使用 “Timelimit” 程序
-
-Timelimit 使用提供的参数执行给定的命令,并在给定的时间后使用给定的信号终止进程。首先,它会发送警告信号,然后在超时后发送 **kill** 信号。
-
-与 timeout 不同,Timelimit 有更多选项。你可以传递参数数量,如 killsig、warnsig、killtime、warntime 等。它存在于基于 Debian 的系统的默认仓库中。所以,你可以使用命令来安装它:
-```
-$ sudo apt-get install timelimit
-
-```
-
-对于基于 Arch 的系统,它在 AUR 中存在。因此,你可以使用任何 AUR 助手进行安装,例如 [**Pacaur**][3]、[**Packer**][4]、[**Yay**][5]、[**Yaourt**][6] 等。
-
-对于其他发行版,请[**在这里**][7]下载源码并手动安装。安装 Timelimit 后,运行下面的命令一段特定的时间,例如 10 秒钟:
-```
-$ timelimit -t10 tail -f /var/log/pacman.log
-
-```
-
-如果不带任何参数运行 timelimit,它将使用默认值:warntime=3600 秒、warnsig=15、killtime=120、killsig=9。有关更多详细信息,请参阅本指南最后给出的手册页和项目网站。
-```
-$ man timelimit
-
-```
-
-今天就是这些。我希望对你有用。还有更好的东西。敬请关注!
-
-干杯!
-
-
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: https://www.ostechnix.com/run-command-specific-time-linux/
-
-作者:[SK][a]
-译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:https://www.ostechnix.com/author/sk/
-[2]:http://www.ostechnix.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/02/Timeout.gif
-[3]:https://www.ostechnix.com/install-pacaur-arch-linux/
-[4]:https://www.ostechnix.com/install-packer-arch-linux-2/
-[5]:https://www.ostechnix.com/yay-found-yet-another-reliable-aur-helper/
-[6]:https://www.ostechnix.com/install-yaourt-arch-linux/
-[7]:http://devel.ringlet.net/sysutils/timelimit/#download
diff --git a/translated/tech/20180228 Why Python devs should use Pipenv.md b/translated/tech/20180228 Why Python devs should use Pipenv.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..1e5d3dcd79
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20180228 Why Python devs should use Pipenv.md
@@ -0,0 +1,132 @@
+为什么 Python 开发人员应该使用 Pipenv
+=====
+
+
+
+这篇文章是与 [Jeff Triplett][1] 共同撰写的。
+
+Pipenv 是由 Kenneth Reitz 在一年多前创建的“面向人类(to校正者:这里为人类感觉翻译为为开发者更好一点)而生的 Python 开发工作流”,它已经成为管理软件包依赖关系的[ Python 官方推荐资源][2]。但是对于它解决了什么问题,以及它如何比使用 `pip` 和 `requirements.txt` 文件的标准工作流更有用处,这两点仍然存在困惑。在本月的 Python 专栏中,我们将填补这些空白。
+
+### Python 包安装简史
+
+为了理解 Pipenv 所解决的问题,看一看 Python 包管理如何发展十分有用的。
+
+让我们回到第一个 Python 版本,我们有 Python,但是没有干净的方法来安装软件包。
+
+然后有了 [Easy Install][3],这是一个可以相对容易地安装其他 Python 包的软件包,但它也带来了一个问题:卸载不需要的包并不容易。
+
+[pip][4] 登场,绝大多数 Python 用户都熟悉它。`pip` 可以让我们安装和卸载包。我们可以指定版本,运行 `pip freeze > requirements.txt` 来输出一个已安装包列表到一个文本文件,还可以用相同的文本文件配合 `pip install -r requirements.txt` 来安装一个应用程序需要的所有包。
+
+但是 `pip` 并没有包含将包彼此隔离的方法。我们可能会开发使用相同库的不同版本的应用程序,因此我们需要一种方法来实现这一点。随之而来的是[虚拟环境][5],它使我们能够为我们开发的每个应用程序创建一个小型的,隔离的环境。我们已经看到了许多管理虚拟环境的工具:[virtualenv][6], [venv][7], [virtualenvwrapper][8], [pyenv][9], [pyenv-virtualenv][10], [pyenv-virtualenvwrapper][11] 等等。它们都可以很好地使用 `pip` 和 `requirements.txt` 文件。
+
+### 新方法:Pipenv
+
+Pipenv 旨在解决几个问题:
+
+首先,问题是需要 `pip` 库来安装包,外加一个用于创建虚拟环境的库,以及用于管理虚拟环境的库,以及与这些库相关的所有命令。这些都需要管理。Pipenv 附带包管理和虚拟环境支持,因此你可以使用一个工具来安装、卸载、跟踪和记录依赖性,并创建、使用和组织你的虚拟环境。当你使用它启动一个项目时,如果你还没有使用它的话,Pipenv 将自动为该项目创建一个虚拟环境。
+
+Pipenv 通过放弃 `requirements.txt` 规范转而将其移动到一个名为 [Pipfile][12] 的新文档中来完成这种依赖管理。当你使用 Pipenv 安装一个库时,项目的 `Pipfile` 会自动更新安装细节,包括版本信息,还有可能的 Git 仓库位置,文件路径和其他信息。
+
+其次,Pipenv 希望能更容易地管理复杂的相互依赖关系。你的应用程序可能依赖于某个特定版本的库,而那个库可能依赖于另一个特定版本的库,而它只是依赖关系(to 校正者:这句话不太理解)。当你的应用程序使用的两个库有冲突的依赖关系时,你的情况会变得很艰难。Pipenv 希望通过在一个名为 `Pipfile.lock` 的文件中跟踪应用程序相互依赖关系树来减轻这种痛苦。`Pipfile.lock` 还会验证生产中是否使用了正确版本的依赖关系。
+
+另外,当多个开发人员在开发一个项目时,Pipenv 很方便。通过 `pip` 工作流,Casey 可能会安装一个库,并花两天时间使用该库实现一个新功能。当 Casey 提交更改时,他可能会忘记运行 `pip freeze` 来更新 requirements 文件。第二天,Jamie 拉取 Casey 的变化,突然测试失败。这样会花费好一会儿才能意识到问题是在 requirements 文件中缺少相关库,而 Jamie 尚未在虚拟环境中安装这些文件。
+
+因为 Pipenv 会在安装时自动记录依赖性,如果 Jamie 和 Casey 使用了 Pipenv,`Pipfile` 会自动更新并包含在 Casey 的提交中。这样 Jamie 和 Casey 就可以节省时间并更快地运送他们的产品。
+
+最后,将 Pipenv 推荐给在你项目上工作的其他人,因为它使用标准化的方式来安装项目依赖项,开发和测试需求。使用 `pip` 工作流和 requirements 文件意味着你可能只有一个 `requirements.txt` 文件,或针对不同环境的多个 requirements 文件。例如,你的同事可能不清楚他们是否应该在他们的笔记本电脑上运行项目时运行 `dev.txt` 还是 `local.txt`。当两个相似的 requirements 文件彼此不同步时它也会造成混淆:`local.txt` 是否过时了,还是真的应该与 `dev.txt` 不同?多个 requirements 文件需要更多的上下文和文档,以使其他人能够按照预期正确安装依赖关系。这个工作流程有可能会混淆同时并增加你的维护负担。
+
+使用 Pipenv,它会生成 `Pipfile`,通过为你管理对不同环境的依赖关系,可以避免这些问题。该命令将安装主项目依赖项:
+```
+pipenv install
+
+```
+
+添加 `--dev` 标志将安装 dev/testing requirements:
+```
+pipenv install --dev
+
+```
+
+使用 Pipenv 还有其他好处:它具有更好的安全特性,以易于理解的格式绘制你的依赖关系,无缝处理 `.env` 文件,并且可以在一个文件中自动处理开发与生产环境的不同依赖关系。你可以在[文档][13]中阅读更多内容。
+
+### Pipenv 行动
+
+使用 Pipenv 的基础知识在官方 Python 包管理教程[管理应用程序依赖关系][14]部分中详细介绍。要安装 Pipenv,使用 `pip`:
+```
+pip install pipenv
+
+```
+
+要安装在项目中使用的包,请更改为项目的目录。然后安装一个包(我们将使用 Django 作为例子),运行:
+```
+pipenv install django
+
+```
+
+你会看到一些输出,表明 Pipenv 正在为你的项目创建一个 `Pipfile`。
+
+如果你还没有使用虚拟环境,你还会看到 Pipenv 的一些输出,说明它正在为你创建一个虚拟环境。
+
+然后,你将看到你在安装包时习惯看到的输出。
+
+为了生成 `Pipfile.lock` 文件,运行:
+```
+pipenv lock
+
+```
+
+你也可以使用 Pipenv 运行 Python 脚本。运行名为 `hello.py` 的(to 校正者:这里 top-level该怎么翻译)Python 脚本:
+```
+pipenv run python hello.py
+
+```
+
+你将在控制台中看到预期结果。
+
+启动一个 shell,运行:
+```
+pipenv shell
+
+```
+
+如果你想将当前使用 `requirements.txt` 文件的项目转换为使用 Pipenv,请安装 Pipenv 并运行:
+```
+pipenv install requirements.txt
+
+```
+
+这将创建一个 Pipfile 并安装指定的 requirements。考虑一下升级你的项目!
+
+### 了解更多
+
+查看 Pipenv 文档,特别是 [Pipenv 的基本用法][15],以帮助你进一步学习。Pipenv 的创建者 Kenneth Reitz 为 Pipenv 在最近的 PyTennessee 发表了一篇演讲:“[Python 依赖管理的未来][16]”。这次演讲没有被记录下来,但他的[幻灯片][17]有助于理解 Pipenv 所做的以及解决的问题。
+
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://opensource.com/article/18/2/why-python-devs-should-use-pipenv
+
+作者:[Lacey Williams Henschel][a]
+译者:[MjSeven](https://github.com/MjSeven)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:https://opensource.com/users/laceynwilliams
+[1]:https://opensource.com/users/jefftriplett
+[2]:https://packaging.python.org/tutorials/managing-dependencies/#managing-dependencies
+[3]:http://peak.telecommunity.com/DevCenter/EasyInstall
+[4]:https://packaging.python.org/tutorials/installing-packages/#use-pip-for-installing
+[5]:https://packaging.python.org/tutorials/installing-packages/#creating-virtual-environments
+[6]:https://virtualenv.pypa.io/en/stable/
+[7]:https://docs.python.org/3/library/venv.html
+[8]:https://virtualenvwrapper.readthedocs.io/en/latest/
+[9]:https://github.com/pyenv/pyenv
+[10]:https://github.com/pyenv/pyenv-virtualenv
+[11]:https://github.com/pyenv/pyenv-virtualenvwrapper
+[12]:https://github.com/pypa/pipfile
+[13]:https://docs.pipenv.org/
+[14]:https://packaging.python.org/tutorials/managing-dependencies/
+[15]:https://docs.pipenv.org/basics/
+[16]:https://www.pytennessee.org/schedule/presentation/158/
+[17]:https://speakerdeck.com/kennethreitz/the-future-of-python-dependency-management
diff --git a/translated/tech/20180418 The Linux Filesystem Explained.md b/translated/tech/20180418 The Linux Filesystem Explained.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 9f7e4fd90e..0000000000
--- a/translated/tech/20180418 The Linux Filesystem Explained.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,257 +0,0 @@
-# Linux文件系统详解
-
-
-
-早在1996年,在真正理解文件系统的结构之前,我就学会了如何在我崭新的 Linux 上安装软件。这是一个问题,但不是程序的问题,因为即使我不知道实际的可执行文件在哪里,它们也会神奇地工作。问题在于文档。
-
-你看,那时候,Linux 不是像今天这样直观,用户友好的系统。 你必须读很多东西。 你必须知道你的 CRT 显示器的频率以及拨号调制解调器的噪音来龙去脉,以及其他数以百计的事情。 我很快就意识到我需要花一些时间来掌握目录的组织方式以及 /etc(不用于其他文件),/usr(不是用于用户文件)和 /*bin *( 不是垃圾桶)的意思。
-
-本教程将帮助您加快速度,比我做得更快。
-
-### 结构
-
-从终端窗口探索 Linux 文件系统是有道理的,这并不是因为作者是一个脾气暴躁的老人,并且对新孩子和他们漂亮的图形工具不以为然——尽管有一些事实——但是因为终端,尽管是文本——只有更好的工具才能显示 Linux 目录树的结构。
-
-事实上,这是您将安装的第一个工具的名称:*tree*。如果你正在使用 Ubuntu 或 Debian ,你可以:
-
-```
-sudo apt install tree
-
-```
-
-在 Red Hat 或 Fedora :
-
-```
-sudo dnf install tree
-
-```
-
-对于 SUSE/openSUSE 可以使用 `zypper`:
-
-```
-sudo zypper install tree
-
-```
-
-对于使用 Arch (Manjaro,Antergos,等等)使用:
-
-```
-sudo pacman -S tree
-
-```
-
-...等等。
-
-一旦安装好,在终端窗口运行 *tree* 命令:
-
-```
-tree /
-
-```
-
-上述指令中的 `/` 指的是根目录。系统中的其他目录都是从根目录分支而出,当你运行 `tree` 命令,并且告诉它从根目录开始,那么你就可以看到整个目录树,系统中的所有目录及其子目录,还有他们的文件。
-
-如果您已经使用您的系统有一段时间了,这可能需要一段时间,因为即使您自己还没有生成很多文件,Linux系统及其应用程序总是记录、缓存和存储临时文件。文件系统中的条目数量可以快速增长。
-
-不过,不要感到不知所措。 相反,试试这个:
-
-```
-tree -L 1 /
-
-```
-
-您应该看到如图 1 所示。
-
-
-
-上面的指令可以翻译为“只显示以 /(根目录) 开头的目录树的第一级”。 `-L` 选项告诉树你想看到多少层目录。
-
-大多数 Linux 发行版都会向您显示与您在上图中看到的相同或非常类似的结构。 这意味着,即使你现在感到困惑,掌握这一点,你将掌握大部分(如果不是全部的话)整个世界的 Linux 文件系统。
-
-为了让您开始走上掌握之路,让我们看看每个目录的用途。 当我们查看每一个目录的时候,你可以使用 *ls* 来查看他们的内容。
-
-### 目录
-
-从上到下,你所看到的目录如下
-
-#### _/bin_
-
-*/bin* 目录是包含一些二进制文件的目录,即可以运行的一些应用程序。 你会在这个目录中找到上面提到的 *ls* 程序,以及用于新建和删除文件和目录,移动它们基本工具。还有其他一些程序,等等, 文件系统树的其他部分有更多的 *bin* 目录,但我们将在一分钟内讨论这些目录。
-
-#### _/boot_
-
-*/boot* 目录包含启动系统所需的文件。 我必须要说吗? 好吧,我会说:**不要动它**! 如果你在这里弄乱了其中一个文件,你可能无法运行你的 Linux,修复破坏的系统是非常痛苦的一件事。 另一方面,不要太担心无意中破坏系统:您必须拥有超级用户权限才能执行此操作。
-
-#### _/dev_
-
-*/dev* 目录包含设备文件。 其中许多是在启动时或甚至在运行时生成的。 例如,如果您将新的网络摄像头或 USB 随身碟连接到您的机器中,则会自动弹出一个新的设备条目。
-
-#### _/etc_
-
-*/etc* 的目录名称会让人变得非常的困惑。*/etc* 从最早的 Unixes 系统中得到它的名称,它的字面意思是 “et cetera” ,因为它是系统文件管理员不确定在哪里放置文件的垃圾场。
-
-现在,说 */etc* 是“要配置的所有内容”更为恰当,因为它包含大部分(如果不是全部的话)系统配置文件。 例如,包含系统名称,用户及其密码,网络上计算机名称以及硬盘上分区的安装位置和时间的文件都在这里。 再说一遍,如果你是 Linux 的新手,最好是不要在这里接触太多,直到你对系统的工作有更好的理解。
-
-#### _/home_
-
-*/home* 是您可以找到用户个人目录的地方。 在我的情况下,*/home* 下有两个目录:*/home/paul*,其中包含我所有的东西;另外一个目录是 */home/guest* 目录,以防有人需要使用我的电脑。
-
-#### _/lib_
-
-*/lib* 是库文件所在的地方。 库是包含应用程序可以使用的代码文件。 它们包含应用程序用于在桌面上绘制窗口,控制外围设备或将文件发送到硬盘的代码片段。
-
-在文件系统周围散布着更多的 *lib* 目录,但是这个直接挂载在 / 的 */lib* 目录是特殊的,除此之外,它包含了所有重要的内核模块。 内核模块是使您的视频卡,声卡,WiFi,打印机等工作的驱动程序。
-
-#### _/media_
-
-在 */media* 目录中,当您插入外部存储并试图访问它时,将自动挂载它。与此列表中的大多数其他项目不同,*/media* 并不追溯到 1970 年代,主要是因为当计算机正在运行而动态地插入和检测存储( U 盘, USB 硬盘,SD卡,外部 SSD 等),这是最近才发生的事。
-
-#### _/mnt_
-
-然而,*/mnt* 目录是一些过去的残余。这是您手动挂载存储设备或分区的地方。现在不常用了。
-
-#### _/opt_
-
-*/opt* 目录通常是您编译软件(即,您从源代码构建,并不是从您的系统的软件库中安装软件)的地方。应用程序最终会出现在 */opt/bin* 目录,库会在 */opt/lib* 目录中出现。
-
-稍微的题外话:应用程序和库的另一个地方是 */usr/local*,在这里安装软件时,也会有 */usr/local/bin* 和 */usr/local/lib* 目录。开发人员如何配置文件来控制编译和安装过程,这就决定了软件安装到哪个地方。
-
-#### _/proc_
-
-*/proc*,就像 */dev* 是一个虚拟目录。它包含有关您的计算机的信息,例如关于您的 CPU 和您的 Linux 系统正在运行的内核的信息。与 */dev* 一样,文件和目录是在计算机启动或运行时生成的,因为您的系统正在运行且会发生变化。
-
-#### _/root_
-
-*/root* 是系统的超级用户(也称为“管理员”)的主目录。 它与其他用户的主目录是分开的,因为您打算去动它。 所以把自己的东西放在你自己的目录中,伙计们。
-
-#### _/run_
-
-*/run* 是另一个新目录。系统进程出于自己的邪恶原因使用它来存储临时数据。这是另一个不要动它的文件夹例子。
-
-#### _/sbin_
-
-*/sbin* 与 */bin* 类似,但它包含的应用程序只有超级用户(即首字母的 s )才需要。您可以使用 `sudo` 命令使用这些应用程序,该命令暂时允许您在许多发行版上拥有超级用户权限。*/sbin* 目录通常包含可以安装、删除和格式化内容的工具。你可以想象,如果你使用不当,这些指令中有一些是致命的,所以要小心处理。
-
-#### _/usr_
-
-*/usr* 目录是在 UNIX 早期用户的主目录被保留的地方。然而,正如我们上面看到的,现在 */home* 是用户保存他们的东西的地方。如今,*/usr* 包含了大量目录,而这些目录又包含了应用程序、库、文档、壁纸、图标和许多其他需要应用程序和服务共享的内容。
-
-您还可以在 */usr* 目录下找到 */bin*,*/sbin*,*/lib* 目录,他们与挂载到根目录下的那些有什么区别呢?现在的区别不是很大。在早期,/bin 目录(挂载在根目录下的)只会包含一些基本的命令,例如 *ls*,*mv* 和 *rm* ;这是一些在安装系统的时候就会预装的一些命令,用于维护系统的一个基本的命令。 而 */usr/bin* 目录则包含了用户自己安装和用于工作的软件,例如文字处理器,浏览器和一些其他的软件。
-
-但是许多现代的 Linux 发行版只是把所有的东西都放到 */usr/bin* 中,并让 */bin* 指向 */usr/bin*,以防彻底删除它会破坏某些东西。因此,Debian、Ubuntu 和 Mint 仍然保持 */bin* 和 */usr/bin* (和 */sbin* 和 */usr/sbin* )分离;其他的,比如 Arch 和它衍生版,只是有一个二进制的“真实”目录,*/usr/bin*,其余的或 *bin 是指向 */usr/ bin* 的“假”目录。
-
-#### _/srv_
-
-*/srv* 目录包含服务器的数据。 如果您正在 Linux 机器上运行 Web 服务器,您网站的 HTML文件将放到 */srv/http*(或 */srv/www*)。 如果您正在运行 FTP 服务器,则您的文件将放到 */srv/ftp*。
-
-#### _/sys_
-
-*/sys* 是另一个类似 */proc* 和 */dev* 的虚拟目录,它还包含连接到计算机的设备的信息。
-
-在某些情况下,您还可以操纵这些设备。 例如,我可以通过修改存储在 /sys/devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:02.0/drm/card1/card1-eDP-1/intel_backlight/brightness 中的值来更改笔记本电脑屏幕的亮度(在你的机器上你可能会有不同的文件)。但要做到这一点,你必须成为超级用户。原因是,与许多其他虚拟目录一样,在 */sys* 中打乱内容和文件可能是危险的,您可能会破坏系统。直到你确信你知道你在做什么。否则不要动它。
-
-#### _/tmp_
-
-*/tmp* 包含临时文件,通常由正在运行的应用程序放置。文件和目录通常(并非总是)包含应用程序现在不需要但以后可能需要的数据。为了释放内存,它被存储在这里。
-
-您还可以使用 */tmp* 来存储您自己的临时文件—— /tmp 是挂载到根目录下您可以在不成为超级用户的情况下与它进行实际交互少数目录之一。问题是,应用程序有时不会回来检索和删除文件和目录,而且 */tmp* 常常会耗尽硬盘上的空间,使其塞满垃圾。在本系列的后面,我们将看到如何清理它。
-
-#### _/var_
-
-*/var* 最初被命名是因为它的内容被认为是可变的,因为它经常变化。今天,它有点用词不当,因为还有许多其他目录也包含频繁更改的数据,特别是我们上面看到的虚拟目录。
-
-不管怎样,*/var* 目录包含了类似 */var/log* 子目录的日志文件。日志是记录系统中发生的事件的文件。如果内核中出现了什么问题,它将被记录到 */var/log* 文件中;如果有人试图从外部侵入您的计算机,您的防火墙也将记录尝试。它还包含用于任务的假脱机程序。这些“任务”可以是您在不得不等待时发送给共享打印机的任务,因为另一个用户正在打印一个长文档,或者是等待发送给系统上的用户的邮件。
-
-您的系统可能还有一些我们上面没有提到的目录。例如,在屏幕截图中,有一个 */snap* 目录。这是因为这张截图是在Ubuntu系统上截取的。Ubuntu 最近将 [snap][1] 包作为一种分发软件的方式。*/snap* 目录包含所有文件和从 snaps 安装的软件。
-
-### 更深入的研究
-
-这里仅仅谈了根目录,但是许多子目录都指向它们自己的一组文件和子目录。图 2 给出了基本文件系统的总体概念(图片是在 Paul Gardner 的 CC BY-SA 许可下提供的),[Wikipedia 对每个目录的用途进行了总结][2]。
-
-
-![filesystem][4]
-
-图 2:标准 Unix 文件系统
-
-[许可][5]
-
-Paul Gardner
-
-要自行探索文件系统,请使用 `cd` 命令:
-
-```
-cd
-
-```
-
-将带您到您所选择的目录( *cd* 代表更改目录)。
-
-如果你不知道你在哪儿,
-
-```
-pwd
-
-```
-
-*pwd* 会告诉你,你到底在哪里,( *pwd* 代表打印工作目录 ),同时
-
-```
-cd
-
-```
-
-*cd* 命令在没有任何选项或者参数的时候,将会直接带你到你自己的主目录,这是一个安全舒适的地方。
-
-最后,
-
-```
-cd ..
-
-```
-
-*cd ..* 将会带你到上一层目录,会使你更加接近根目录,如果你在 */usr/share/wallpapers* 目录,然后你执行 `cd ..` 命令,你将会跳转到 `/usr/share` 目录
-
-要查看目录里有什么内容,使用
-
-```
-ls
-
-```
-
-或这简单的使用
-
-```
-l
-
-```
-
-列出你所在目录的内容。
-
-当然,您总是可以使用 `tree` 来获得目录中内容的概述。在 */usr/share* 上试试——里面有很多有趣的东西。
-
-### 总结
-
-尽管 Linux 发行版之间存在细微差别,但它们的文件系统的布局非常相似。 你可以这么说:一旦你认识一个,你就会知道他们。 知道文件系统的最好方法就是探索它。 因此,伴随 `tree` ,`ls` 和 `cd` 进入未知的领域吧。
-
-您不能仅仅通过查看文件系统就破坏文件系统,因此请从一个目录移动到另一个目录并进行浏览。 很快你就会发现 Linux 文件系统及其布局的确很有意义,并且你会直观地知道在哪里可以找到应用程序,文档和其他资源。
-
-通过 Linux 基金会和 edX 免费的 “[Linux入门][6]” 课程了解更多有关 Linux 的信息。
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: https://www.linux.com/blog/learn/intro-to-linux/2018/4/linux-filesystem-explained
-
-作者:[PAUL BROWN][a]
-选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
-译者:[amwps290](https://github.com/amwps290)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:https://www.linux.com/users/bro66
-[1]:https://www.ubuntu.com/desktop/snappy
-[2]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Unix_filesystem#Conventional_directory_layout
-[3]:https://www.linux.com/files/images/standard-unix-filesystem-hierarchypng
-[4]:https://www.linux.com/sites/lcom/files/styles/rendered_file/public/standard-unix-filesystem-hierarchy.png?itok=CVqmyk6P "filesystem"
-[5]:https://www.linux.com/licenses/category/used-permission
-[6]:https://training.linuxfoundation.org/linux-courses/system-administration-training/introduction-to-linux
diff --git a/translated/tech/20180519 Python Debugging Tips.md b/translated/tech/20180519 Python Debugging Tips.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 9d7c62a98b..0000000000
--- a/translated/tech/20180519 Python Debugging Tips.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,70 +0,0 @@
-Python 调试技巧
-======
-当涉及到调试时,你可以做出很多选择。很难提供总是有效的通用建议(除了“你试过关闭再打开么?”)。
-
-这里有一些我最喜欢的 Python 调试技巧。
-
-### 建立一个分支
-
-请相信我。即使你从来没有打算将修改提交回上游,你也会乐意你的实验被包含在它们自己的分支中。
-
-如果没有其他的东西,它会使清理更容易!
-
-### 安装 pdb++
-
-认真地说,如果你使用命令行,它会让你的生活更轻松。
-
-pdb++ 所做的一切就是用更好的模块替换标准的 pdb 模块。以下是你在 `pip install pdbpp` 会看到的:
-
- * 彩色提示!
- * tab补全!(非常适合探索!)
- * 支持切分!
-
-
-
-好的,也许最后一个是有点多余......但是非常认真地说,安装 pdb++ 非常值得。
-
-### 探索
-
-有时候最好的办法就是搞乱,然后看看会发生什么。在“明显”的位置放置一个断点并确保它被击中。在代码中加入 `print()` 和/或 `logging.debug()` 语句,并查看代码执行的位置。
-
-检查传递给你的函数的参数。检查库的版本(如果事情变得非常绝望)。
-
-### 一次只能改变一件事
-
-在你在探索一下后,你将会对你可以做的事情有所了解。但在你开始使用代码之前,先退一步,考虑一下你可以改变什么,然后只改变一件事。
-
-做出改变后,然后测试一下,看看你是否接近解决问题。如果没有,请将它改回来,然后尝试其他方法。
-
-只更改一件事就可以让你知道什么工作,哪些不工作。另外,一旦工作后,你的新提交将会小得多(因为将有更少的变化)。
-
-这几乎是科学过程中所做的事情:一次只更改一个变量。通过让自己看到并衡量一次更改的结果,你可以节省你的理智,并更快地找到解决方案。
-
-### 不要假设,提出问题
-
-偶尔一个开发人员(当然不是你!)会匆忙提交一些有问题的代码。当你去调试这段代码时,你需要停下来,并确保你明白它想要完成什么。
-
-不要做任何假设。仅仅因为代码在 `model.py` 中并不意味着它不会尝试渲染一些 HTML。
-
-同样,在做任何破坏性的事情之前,仔细检查你的所有外部连接。要删除一些配置数据?请确保你没有连接到你的生产系统。
-
-### 聪明,但不太聪明
-
-有时候我们编写的代码非常棒,不知道它是如何做的。
-
-当我们发布代码时,我们可能会觉得很聪明,但当代码崩溃时,我们往往会感到愚蠢,我们必须记住它是如何工作的,以便弄清楚它为什么不起作用。
-
-留意任何看起来过于复杂,冗长或极短的代码段。这些可能是隐藏复杂并导致错误的地方。
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: https://pythondebugging.com/articles/python-debugging-tips
-
-作者:[PythonDebugging.com][a]
-选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
-译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:https://pythondebugging.com
diff --git a/translated/tech/20180529 5 trending open source machine learning JavaScript frameworks.md b/translated/tech/20180529 5 trending open source machine learning JavaScript frameworks.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..4c59c540df
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20180529 5 trending open source machine learning JavaScript frameworks.md
@@ -0,0 +1,70 @@
+
+五个最热门的开源机器学习 JavaScript 框架
+======
+
+
+开源工具的可用性使得开发者能够更加轻松地开发应用,这一点使机器学习领域本身获得了巨大的极高。(例如,AndreyBu,他来自德国,在机器学习领域拥有五年以上的经验,他一直在使用各种各样的开源框架来创造富有魅力的机器学习项目。
+
+虽然 python 支持绝大多数的机器学习框架,但是 JavaScript 也并没有被抛弃。JavaScript 开发者可以在浏览器中使用各种框架来训练和部署机器学习模型。
+
+下面是 JavaScript 中最热门五个机器学习框架
+
+### 1\. TensorFlow.js
+
+[TensorFlow.js][2] 是一个开源库,它使你能在浏览器中完整地运行机器学习程序,它是 Deeplearn.js 的继承者,Deeplearn.js 不再被提供更新。TensorFlow.js 在 Deeplearn.js 功能的基础上进行了改善,使你能够充分利用浏览器,得到更加深入的机器学习经验。
+
+通过这个开源库,你可以在浏览器中使用有各种功能的、直观的 API 来定义、训练和部署模型。除此之外,它能够自动为 WebGL 和 Node.js 提供支持。
+
+如果您有了一个已经训练过的模型,你想要导入到浏览器中。TensorFlow.js 可以让你做到这一点,你也可以在不离开浏览器的情况下重新训练已有的模型。
+
+现在有很多在浏览器中提供广泛的机器学习功能的资源型开源工具,这个机器学习工具库就是这些开源工具的集合。这个工具库为好几种机器学习算法提供支持,包括非监督式学习、监督式学习、数据处理、人工神经网络(ANN)、数学和回归。
+
+如果你以前使用 python,现在想找类似于 Scikit-learn 的,能在浏览器中使用 JavaScript 进行机器学习的工具,这套工具会满足你的要求。
+
+### 3\. Keras.js
+
+[Keras.js][4] 是另外一个热门的开源框架,它使你能够在浏览器中运行机器学习模型,它使用 WebGL 来提供 GPU 模式的支持。如果你有使用 Node.js 的模型,你就只能在 GPU 模式下运行它。Keras.js 还为使用任意后端框架的模型训练提供支持,例如 Microsoft Cognitive Toolkit (CNTK) 。
+
+一些 Keras 模型可以部署在客户端浏览器上,包括 Inception v3 (训练在 ImageNet 上),50 层冗余网络(训练在 ImageNet 上),和卷积变化自动编码器(训练在 MNIST 上)。
+
+### 4\. Brain.js
+
+机器学习里的概念非常重要,它可能会使刚开始进入这个领域的人们气馁,这个领域里的学术用语和专业词汇可能会使初学者感到崩溃,而解决以上问题的能力就是 Brain.js 的优势所在。它是开源的,基于 JavaScript 的框架,简化了定义、训练和运行神经网络的流程。
+
+如果你是一个 JavaScript 开发者,并且在机器学习领域是完全的新手,Brain.js 能减低你学习的难度曲线。它可以和 Node.js 一起使用,或者运行在客户端浏览器里来训练机器学习模型。Brain.js 支持部分类型的神经网络,包括前馈式网络、Ellman 网络,和门循环单元网络。
+
+### 5\. STDLib
+
+[STDLib][6] 是一个基于 JavaScript 和 Node.js 应用的开源库,如果您正在寻找一种在浏览器中运行,支持科学和数字化的基于 web 的机器学习应用,STDLib 能满足你的需要。
+
+
+这个库能提供全面而先进的数学和统计学上的功能,来帮助你构建高性能的机器学习模型。你同样也可以使用它扩展的公用程序来构建应用程序和其他的库。除此之外,如果你想要一个数据可视化和探索性数据分析的框架。
+
+STDLib,你,值得拥有。
+
+
+### Conclusion
+
+如果你是一个 JavaScript 开发者,并且打算深入研究令人兴奋的机器学习世界,或者说,你是一个机器学习方面的专家,打算开始尝试使用 JavaScript ,那么上述的开源框架会激起您的兴趣。
+
+你有知道其他的,提供在浏览器里运行机器学习功能的开源库吗?请在下面的评论区里告诉我们。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://opensource.com/article/18/5/machine-learning-javascript-frameworks
+
+作者:[Dr.Michael J.Garbade][a]
+选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
+译者:[hopefully2333](https://github.com/hopefully2333)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:https://opensource.com/users/drmjg
+[1]:https://www.liveedu.tv/andreybu/REaxr-machine-learning-model-python-sklearn-kera/
+[2]:https://js.tensorflow.org/
+[3]:https://github.com/mljs/ml
+[4]:https://transcranial.github.io/keras-js/#/
+[5]:https://github.com/BrainJS/brain.js
+[6]:https://stdlib.io/
+[7]:https://www.liveedu.tv/guides/artificial-intelligence/machine-learning/
diff --git a/translated/tech/20180530 3 Python command-line tools.md b/translated/tech/20180530 3 Python command-line tools.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..0233fe7268
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20180530 3 Python command-line tools.md
@@ -0,0 +1,196 @@
+3个 Python 命令行工具
+======
+
+
+
+这篇文章是与 [Lacey Williams Hensche][1] 共同撰写的。
+
+有时对于某项工作来说一个命令行工具就足以胜任。命令行工具是一个交互程序,类似你的 shell 或者终端。[Git][2] 和 [Curl][3] 就是两个你也许已经很熟悉的命令行工具。
+
+当你有一小段代码需要在一行中执行多次或者经常性地被执行,命令行工具会很实用。Django 开发者执行 `./manage.py runserver` 命令来启动他们的网络服务器;Docker 开发者执行 `docker-compose up` 来启动他们的容器。你想要写一个命令行工具的原因可能和你一开始想写代码的原因有很大不同。
+
+对于这个月的 Python 专栏,我们有 3 个库想介绍给希望为自己编写命令行工具的 Python 使用者。
+
+### Click
+
+[Click][4] 是我们最爱的用来开发命令行工具的 Python 包。其:
+
+ * 有一个富含例子的出色文档
+ * 包含说明如何将命令行工具打包成一个更加易于执行的 Python 应用程序
+ * 自动生成实用的帮助文本
+ * 使你能够叠加使用可选和必要参数,甚至是 [多个命令][5]
+ * 有一个 Django 版本( [`django-click`][6] )来编写管理命令
+
+Click 使用 `@click.command()` 去声明一个函数作为命令,同时可以指定必要和可选参数。
+
+```
+# hello.py
+import click
+
+@click.command()
+@click.option('--name', default='', help='Your name')
+def say_hello(name):
+ click.echo("Hello {}!".format(name))
+
+if __name__ == '__main__':
+ hello()
+```
+
+`@click.option()` 修饰器声明了一个 [可选参数][7] 并且 `@click.argument()` 修饰器声明了一个 [必要参数][8]。你可以通过叠加修饰器来组合可选和必要参数。`echo()` 方法将结果打印到控制台。
+
+```
+$ python hello.py --name='Lacey'
+Hello Lacey!
+```
+
+### Docopt
+
+[Docopt][9] 是一个命令行工具解析器,类似于命令行工具的 Markdown。如果你喜欢流畅地编写应用文档,在本文推荐的库中 Docopt 有着最好的格式化帮助文本。它不是我们最爱的命令行工具开发包的原因是它的文档犹如把人扔进深渊,使你开始使用时会有一些小困难。然而,它仍是一个轻量级广受欢迎的库,特别是当一个漂亮的说明文档对你来说很重要的时候。
+
+Docopt 对于如何格式化文章开头的 docstring 是很特别的。在工具名称后面的 docsring 中,顶部元素必须是“Usage:”并且需要列出你希望命令被调用的方式(比如:自身调用,使用参数等等)。Usage 需要包含 **help** 和 **version** 标记。
+
+docstring 中的第二个元素是“Options:”,对于在“Usages:”中提及的可选项和参数,它应当提供更多的信息。你的 docstring 的内容变成了你帮助文本的内容。
+
+```
+"""HELLO CLI
+
+Usage:
+ hello.py
+ hello.py
+ hello.py -h|--help
+ hello.py -v|--version
+
+Options:
+ Optional name argument.
+ -h --help Show this screen.
+ -v --version Show version.
+"""
+
+from docopt import docopt
+
+def say_hello(name):
+ return("Hello {}!".format(name))
+
+
+if __name__ == '__main__':
+ arguments = docopt(__doc__, version='DEMO 1.0')
+ if arguments['']:
+ print(say_hello(arguments['']))
+ else:
+ print(arguments)
+```
+
+在最基本的层面,Docopt 被设计用来返回你的参数键值对。如果我不指定名字调用上面的命令,我会得到一个字典的返回:
+
+```
+$ python hello.py
+{'--help': False,
+ '--version': False,
+ '': None}
+```
+
+这里可看到我没有输入 `help` 和 `version` 标记并且 `name` 参数是 `None`。
+
+但是如果我带着一个 name 参数调用,`say_hello` 函数就会执行了。
+
+```
+$ python hello.py Jeff
+Hello Jeff!
+```
+
+Docopt 允许同时制定必要和可选参数,且各自有着不同的语法约定。必要参数需要在 `ALLCAPS` 和 `` 中展示,而可选参数需要单双横杠显示,就像‘--like’。更多内容可以阅读 Docopt 有关 [patterns][10] 的文档。
+
+### Fire
+
+[Fire][11] 是谷歌的一个命令行工具开发库。尤其令人喜欢的是当你的命令需要更多复杂参数或者处理 Python 对象时,它会聪明地尝试解析你的参数类型。
+
+Fire 的 [文档][12] 包括了海量的样例,但是我希望这些文档能被更好地组织。Fire 能够处理 [同一个文件中的多条命令][13]、使用 [对象][14] 的方法作为命令和 [组][15] 命令。
+
+它的弱点在于输出到控制台的文档。命令行中的 docstring 不会出现在帮助文本中,并且帮助文本也不一定标识出参数。
+
+```
+import fire
+
+
+def say_hello(name=''):
+ return 'Hello {}!'.format(name)
+
+
+if __name__ == '__main__':
+ fire.Fire()
+```
+
+参数是必要还是可选取决于你是否在函数或者方法定义中为其指定了一个默认值。要调用命令,你必须指定文件名和函数名,比较类似 Click 的语法:
+
+```
+$ python hello.py say_hello Rikki
+Hello Rikki!
+```
+
+你还可以像标记一样传参,比如 `--name=Rikki`。
+
+### 额外奖赏:打包!
+
+Click 包含了使用 `setuptools` [打包][16] 命令行工具的使用说明(强烈推荐按照说明操作)。
+
+要打包我们第一个例子中的命令行工具,将以下内容加到你的 `setup.py` 文件里:
+
+```
+from setuptools import setup
+
+setup(
+ name='hello',
+ version='0.1',
+ py_modules=['hello'],
+ install_requires=[
+ 'Click',
+ ],
+ entry_points='''
+ [console_scripts]
+ hello=hello:say_hello
+ ''',
+)
+```
+
+任何你看见 `hello` 的地方,使用你自己的模块名称替换掉,但是要记得忽略`.py` 后缀名。将 `say_hello` 替换成你的函数名称。
+
+然后,执行 `pip install --editable` 来使你的命令在命令行中可用。
+
+现在你可以调用你的命令,就像这样:
+
+```
+$ hello --name='Jeff'
+Hello Jeff!
+```
+
+通过打包你的命令,你可以省掉在控制台键入 `python hello.py --name='Jeff'` 这种额外的步骤以减少键盘敲击。这些指令也很可能可在我们提到的其他库中使用。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://opensource.com/article/18/5/3-python-command-line-tools
+
+作者:[Jeff Triplett][a]
+选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
+译者:[hoppipolla-](https://github.com/hoppipolla-)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:https://opensource.com/users/laceynwilliams
+[1]:https://opensource.com/users/laceynwilliams
+[2]:https://git-scm.com/
+[3]:https://curl.haxx.se/
+[4]:http://click.pocoo.org/5/
+[5]:http://click.pocoo.org/5/commands/
+[6]:https://github.com/GaretJax/django-click
+[7]:http://click.pocoo.org/5/options/
+[8]:http://click.pocoo.org/5/arguments/
+[9]:http://docopt.org/
+[10]:https://github.com/docopt/docopt#usage-pattern-format
+[11]:https://github.com/google/python-fire
+[12]:https://github.com/google/python-fire/blob/master/docs/guide.md
+[13]:https://github.com/google/python-fire/blob/master/docs/guide.md#exposing-multiple-commands
+[14]:https://github.com/google/python-fire/blob/master/docs/guide.md#version-3-firefireobject
+[15]:https://github.com/google/python-fire/blob/master/docs/guide.md#grouping-commands
+[16]:http://click.pocoo.org/5/setuptools/
+
diff --git a/translated/tech/20180619 Use this vi setup to keep and organize your notes.md b/translated/tech/20180619 Use this vi setup to keep and organize your notes.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 29f3837ea9..0000000000
--- a/translated/tech/20180619 Use this vi setup to keep and organize your notes.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,94 +0,0 @@
-# 用这样的 VI 配置来保存和组织你的笔记
-
-![1][]
-
-用 vi 来管理 wiki 笔记 , 这听起来不像是一个符合常规的主意 ; 但当你的日常工作都会用到 vi , 那它是有意义的 ;
-
-作为一个软件开发人员 , 用编码工具来写笔记会更加简单 ; 我想将我的笔记变成一种编辑器命令 , 无论我在哪 , 都能够用管理我代码的方法来管理我的笔记 , 这便是我在我知识基础上建立这个 vi 配置的原因 ; 简单概括起来 ,在笔记本上我用 vi 插件 [Viwiki][2] 来管理我的本地百科 ; 用 GIT 来进行版本控制 ( 保持中心节点和更新版本 ) ; 用 Gitlab 来进行在线修改 ( 例如在我的手机上 ) .
-
-## 为什么用百科来进行笔记保存是有意义
-
-我尝试过许多不同的工具来持续的追踪我的笔记 , 笔记里保存着我的灵感以及不应该被忘记的任务模型 . 这包括离线笔记本 ( 是的 , 包含纸质笔记本 ) , 特殊的笔记软件 , 以及思维导图软件 .
-
-但每种方案都有不好一面 , 没有一个能够满足我所有的需求 . 例如思维导图 , 能够很好的形象化你的想法 ( 因此得名 ) . 我尝试提供一些简单的搜索方法 ( 和纸质笔记一样 ) ; 但当一段时间过去 , 思维导图会变得很难阅读 , 所以思维导图不适合长时间保存的笔记 .
-
-我为一个合作项目配置 [DokuWiki][2] , 我发现这个 wiki 模型符合了我大多数的需求 . 在百科上 , 你能够创建一个文件 ( 和你在文本编辑器中所作的一样 ) , 创建一个笔记的链接 . 如果一个链接指向一个不存在的页面 ( 你想让本页面添加一条还没有创建的信息 ) , wiki 会为你建立这个页面 . 这个特性使得 wiki 很好的适应了那些需要快速写下心中所想的人的需求 . 然而笔记页面仍保持在能够容易浏览和搜索关键字的界面 .
-
-这看起来很有希望 , 并且配置 DokuWiki 也很容易 , 但我发现配置整个 wiki 太复杂 , 而仅仅只是为了追踪笔记 . 在一番搜索后 , 我发现了 Vimwiki , 我想要的 vi 插件 . 自从我每天使用 vi , 做笔记和修改代码一样简单 . 创建一个界面 , vimwiki 比 Dokuwiki 简单 . 你只需要在光标下的单词按下 Enter 键 , 如果本地没有文件是这个名字 , vimwiki 会为你创建一个 . 为了更一步的实现用每天都会使用的工具来做笔记的计划 , 我不仅用我最爱的 IDE 来写笔记 , 而且用 GIT - 我最爱的代码管理工具 , Gilab - 发布我的笔记并且在线访问 . 我也在 Gitlab markdown 在线工具上用 markdown 语法来写这篇文章 .
-
-## 配置 vimwiki
-
-用存在的插件管理工具来安装 vimwiki 很简单 , 只需要添加 vimwiki/vimwiki 到你的插件 . 对于我的喜爱的插件管理器 , Vundle , 你只需要在 /.vimrc 中添加 "plugin vimwiki/vimwiki " 这一行 . 然后执行 :source ~/.vimrc | PluginInstall .
-
-下面是我的文件 .vimrc 的一部分 , 展示一些 vimwiki 配置 . 你能在 [vimwiki][2] 页面学到更多的配置和使用的的信息 .
-
-```code
- let wiki_1 = {}
- let wiki_1.path = '~/vimwiki_work_md/'
- let wiki_1.syntax = 'markdown'
- let wiki_1.ext = '.md'
-
- let wiki_2 = {}
- let wiki_2.path = '~/vimwiki_personal_md/'
- let wiki_2.syntax = 'markdown'
- let wiki_2.ext = '.md'
-
- let g:vimwiki_list = [wiki_1, wiki_2]
- let g:vimwiki_ext2syntax = {'.md': 'markdown', '.markdown': 'markdown', '.mdown': 'markdown'}
-
-```
-
-我的配置有一个优点 , 你能简单的区分个人和工作相关的文件 , 而不用切换笔记软件 . 我想能随时随地访问我的个人笔记 , 而不想我的工作笔记同步到我私人的 GitLab 和 电脑 . 这样配置对于 vimwiki 要比其他软件简单 . 这个配置告诉 vimwiki 有两个不同 Wiki , 两个 wiki 都使用 markdown 语法 ( 我用 markdown 语法在每天的工作 ) . 同样的告诉 Vimwiki wiki 页面存储到那个文件夹 .
-
-如果你操作 wiki 页面存储的文件夹 , 你会你的单一的 wiki 的 markdown 页面文件而没有其他特殊的 Vimwiki 内容 , 这使得很容易的初始化 GIT 仓库和同步你的 wiki 到中心仓库 .
-
-## 同步你的 wiki 到 GitLab
-
-这一步检查 GitLab 工程到本地的 VimWiki 文件夹 , 这步操作和你操作任何 GitHub 的仓库相同 . 只是我更喜欢保存我的笔记到我的私人 GitLab 仓库 , 所以我为我个人的工程保持运行 GitLab .
-
-你可以使用 GitLab 的 wiki 功能来为你的工程创建 wiki 页面 . 这些 wiki 是 GIT 仓库本身 , 用 markdown 语法 , 你到主要的地址 .
-
-只需要初始化你想要的笔记 , 那些你为你的笔记所创建的 wiki 工程 :
-
-```codecd ~/vimwiki_personal_md/
- git init
- git remote add origin git@your.gitlab.com:your_user/vimwiki_personal_md.wiki
- git add .
- git commit -m "Initial commit"
- git push -u origin master
-```
-
-能够在 GitLab 创建一个新的工程后 , 这些步骤能复制到你导入的界面到新的工程 . 唯一的改变是仓库地址结尾是 .wiki ( 而不是 .git ) . 告诉 git 拷贝 wiki 仓库而不是工程本身 .
-
-就是这样 ! 现在你能够通过 git 来管理你的笔记 , 通过 GitLab wiki 用户接口来修改笔记 .
-
-你可能不想手动的为每个添加到笔记本的笔记创建提交 , 为了解决这个问题 , 我使用 Vim 插件 [chazy/dirsetting][4] , 我添加一个 .vimaddr 文件 , 通过下面的内容 :
-
-```code
- :cd %:p:h
- silent! !git pull > /dev/null
- :e!
- autocmd! BufWritePost * silent! !git add .;git commit -m "vim autocommit" > /dev/null; git push > /dev/null&
-```
-
-当我打开 Wiki 文件时会更新到最新的版本 , 没一次的写入命令 ( :w ) 都会提交 ; 这样做会同步你的本地文件到中心仓库 . 如果你有合并冲突 ,通常你需要解决它们 .
-
-目前 , 这就是以我的知识基础来互动的方法 , 我很喜欢这方法 ; 请告诉我你对于这个方法的想法 , 可以在评论区分享你最爱的方法 , 对于如何追踪笔记 .
-
------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: https://opensource.com/article/18/6/vimwiki-gitlab-notes
-
-作者:[Manuel Dewald][a]
-选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
-译者:[octopus][5]
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-
-[1]:https://camo.githubusercontent.com/9901c750dce2008ea7a459201121077c355fc257/68747470733a2f2f6f70656e736f757263652e636f6d2f73697465732f64656661756c742f66696c65732f7374796c65732f696d6167652d66756c6c2d73697a652f7075626c69632f6c6561642d696d616765732f636865636b6c6973745f68616e64735f7465616d5f636f6c6c61626f726174696f6e2e706e673f69746f6b3d753832516570506b
-[2]:https://vimwiki.github.io/
-[3]:https://www.dokuwiki.org/dokuwiki
-[4]:https://github.com/chazy/dirsettings
-[5]:https://github.com/singledo
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/translated/tech/20180620 Stop merging your pull requests manually.md b/translated/tech/20180620 Stop merging your pull requests manually.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..1a9fbe29ae
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20180620 Stop merging your pull requests manually.md
@@ -0,0 +1,85 @@
+停止手动合并你的 pull 请求
+======
+
+
+
+如果有什么我讨厌的东西,那就是当我知道我可以自动化它们时,但我手动进行了操作。只有我有这种情况么?我很怀疑。
+
+尽管如此,他们每天都有数千名使用 [GitHub][1] 的开发人员一遍又一遍地做同样的事情:他们点击这个按钮:
+
+![Screen-Shot-2018-06-19-at-18.12.39][2]
+
+这没有任何意义。
+
+不要误解我的意思。合并 pull 请求是有意义的。只是每次点击这个该死的按钮是没有意义的。
+
+这样做没有意义因为世界上的每个开发团队在合并 pull 请求之前都有一个已知的先决条件列表。这些要求几乎总是相同的,而且这些要求也是如此:
+
+ * 是否通过测试?
+ * 文档是否更新了?
+ * 这是否遵循我们的代码风格指南?
+ * 是否有 N 位开发人员对此进行审查?
+
+
+
+随着此列表变长,合并过程变得更容易出错。 “糟糕,John 点了合并按钮,但没有足够的开发人员审查补丁。” 要发出警报么?
+
+在我的团队中,我们就像外面的每一支队伍。我们知道我们将一些代码合并到我们仓库的标准是什么。这就是为什么我们建立一个持续集成系统,每次有人创建一个 pull 请求时运行我们的测试。我们还要求代码在获得批准之前由团队的 2 名成员进行审查。
+
+当这些条件全部设定好时,我希望代码被合并。
+
+而不用点击一个按钮。
+
+这正是启动 [Mergify][3] 的原因。
+
+![github-branching-1][4]
+
+[Mergify][3] 是一个为你按下合并按钮的服务。你可以在仓库的 .mergify.yml 中定义规则,当规则满足时,Mergify 将合并该请求。
+
+无需按任何按钮。
+
+随机抽取一个请求,就像这样:
+
+![Screen-Shot-2018-06-20-at-17.12.11][5]
+
+这来自一个小型项目,没有很多持续集成服务,只有 Travis。在这个 pull 请求中,一切都是绿色的:其中一个所有者审查了代码,并且测试通过。因此,该代码应该被合并:但是它还在那里挂起这,等待某人有一天按下合并按钮。
+
+使用 [Mergify][3] 后,你只需将 `.mergify.yml` 放在仓库的根目录即可:
+```
+rules:
+ default:
+ protection:
+ required_status_checks:
+ contexts:
+ - continuous-integration/travis-ci
+ required_pull_request_reviews:
+ required_approving_review_count: 1
+
+```
+
+通过这样的配置,[Mergify][3] 可以实现所需的限制,即 Travis 通过,并且至少有一个项目成员审阅了代码。只要这些条件是肯定的,pull 请求就会自动合并。
+
+我们为将 [Mergify][3] **在开源项目中作为一个免费服务**。[提供服务的引擎][6]也是开源的。
+
+现在去[尝试它][3],并停止让这些 pull 请求挂起一秒钟。合并它们!
+
+如果你有任何问题,请随时在下面向我们提问或写下评论!并且敬请期待 - 因为 Mergify 还提供了其他一些我迫不及待想要介绍的功能!
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://julien.danjou.info/stop-merging-your-pull-request-manually/
+
+作者:[Julien Danjou][a]
+选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
+译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:https://julien.danjou.info/author/jd/
+[1]:https://github.com
+[2]:https://julien.danjou.info/content/images/2018/06/Screen-Shot-2018-06-19-at-18.12.39.png
+[3]:https://mergify.io
+[4]:https://julien.danjou.info/content/images/2018/06/github-branching-1.png
+[5]:https://julien.danjou.info/content/images/2018/06/Screen-Shot-2018-06-20-at-17.12.11.png
+[6]:https://github.com/mergifyio/mergify-engine
diff --git a/translated/tech/20180627 Historical inventory of collaborative editors.md b/translated/tech/20180627 Historical inventory of collaborative editors.md
deleted file mode 100644
index abecef8e2b..0000000000
--- a/translated/tech/20180627 Historical inventory of collaborative editors.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,76 +0,0 @@
-协同编辑器的历史性发明
-======
-不妨按时间顺序快速列出在主要协同编辑器上付出的努力。
-
-正如任何如此的清单一样,它必定会在一开始便提到受人尊敬的所有编辑器的先祖,道格·恩格尔巴特描述了在那期间什么基本是 1968 年来所写的所有可能软件的详尽清单。这不仅包括协同编辑器,还包括图形、编程和数学编辑器。
-
-那个示范之后的所有编辑器仅仅是为了弥补硬件发展的加速度的更缓慢的实现。
-
-> 软件加快的速度比硬件加快的速度慢。——沃斯定律
-
-因此没有进一步的麻烦的话,这里是我找到的可圈可点的协同编辑器的清单。我说“可圈可点”的意思是他们具有可圈可点的特征或者实现细节。
-
-| 项目 | 日期 | 平台 | 说明 |
-| --- | --- | --- | --- |
-| [SubEthaEdit][1] | 2003-2015? | 仅 Mac|首次协同, 实时的, 我能找到的多指针编辑器, [在 Emacs 上的逆向工程的尝试。][2] |
-| [DocSynch][3] | 2004-2007 | ? | 在互联网交互式聊天程序之上构造! [(!)](https://anarc.at/smileys/idea.png)|
-| [Gobby][4] | 2005 至今 | C, 多平台 | 首次开放,实现稳固可靠。 仍然存在!众所周知 ("[libinfinoted][5]") 协议很难移植到其他编辑器中 (例如: [Rudel][6] 不能在 Emacs 上实现此协议。 2017 年 1 月发行的 0.7 版本添加了也许可以改善这种状况的 Python 捆绑。 有趣的插件: 自动保存到磁盘。|
-| [moonedit][7] | 2005-2008? | ? | 原网站已关闭。其他用户的光标可见并且会模仿击键的声音。 计算器和音乐定序器。 |
-| [synchroedit][8] | 2006-2007 | ? |首款网络应用。|
-| [Etherpad][9] | 2008 至今 | 网络 |首款稳定的网络应用。 最初在 2008 年被开发为一款大型 Java 应用,在 2009 年被谷歌获取并开源,然后在 2011 年被用 Node.JS 重写。广泛使用。|
-| [CRDT][10] | 2011 | 特定平台| 对在不同电脑间可靠地复制一个文件的数据结构是标准的。 |
-| [Operational transform][11] | 2013 | 特定平台| 与 CRDT 类似, 然而, 确切地说, 两者是不同的。 |
-| [Floobits][12] | 2013 至今 | ? | 对不同编辑器是商业的但开源的插件。 |
-| [HackMD][13] | 2015 至今| ? | 商业的但是[开源][14]。受 hackpad 的启发( hackpad 已被 Dropbox 收购)。 |
-| [Cryptpad][15] | 2016 至今 | 网络? |Xwiki 的副产品。加密的, 在服务器"零知识"。|
-| [Prosemirror][16] | 2016 至今 | 网络, Node.JS | "试图架起 Markdown 文本编辑和 传统 WYSIWYG 编辑器之间隔阂的桥梁。"不是完全意义上的编辑器,但是一种可以用来构建编辑器的工具。 |
-| [Qill][17] | 2013 至今 | 网络, Node.JS | 富文本编辑器,同时支持 JavaScript.不确定是否是协同式的。 |
-| [Nextcloud][18] | 2017 至今 | Web |一种类似谷歌文档的文档。 |
-| [Teletype][19] | 2017 至今 | WebRTC, Node.JS | 为 GitHub 的[ Atom 编辑器][20] 引入了 "可移植"的想法,这种想法使访客可以跟踪主人在对多个文档做什么.访问介绍服务器后使用实时通讯的点对点技术( P2P ),基于 CRDT. |
-| [Tandem][21] | 2018 至今 | Node.JS? | Atom, Vim, Neovim, Sublime 等的插件。 使用中继安装基于 CRDT 的 P2P 连接。多亏 Debian 开发者的参与,[可疑证书问题][22]已被解决,这使它成为很有希望在未来被遵循的标准。 |
-
-### 其他清单
-
-* Emacs 维基
-* 维基百科
-
-
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: https://anarc.at/blog/2018-06-26-collaborative-editors-history/
-
-作者:[Anacr][a]
-选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
-译者:[ZenMoore](https://github.com/ZenMoore)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:https://anarc.at
-[1]:https://www.codingmonkeys.de/subethaedit/
-[2]:https://www.emacswiki.org/emacs/SubEthaEmacs
-[3]:http://docsynch.sourceforge.net/
-[4]:https://gobby.github.io/
-[5]:http://infinote.0x539.de/libinfinity/API/libinfinity/
-[6]:https://www.emacswiki.org/emacs/Rudel
-[7]:https://web.archive.org/web/20060423192346/http://www.moonedit.com:80/
-[8]:http://www.synchroedit.com/
-[9]:http://etherpad.org/
-[10]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conflict-free_replicated_data_type
-[11]:http://operational-transformation.github.io/
-[12]:https://floobits.com/
-[13]:https://hackmd.io/
-[14]:https://github.com/hackmdio/hackmd
-[15]:https://cryptpad.fr/
-[16]:https://prosemirror.net/
-[17]:https://quilljs.com/
-[18]:https://nextcloud.com/collaboraonline/
-[19]:https://teletype.atom.io/
-[20]:https://atom.io
-[21]:http://typeintandem.com/
-[22]:https://github.com/typeintandem/tandem/issues/131
-[23]:https://www.emacswiki.org/emacs/CollaborativeEditing
-[24]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Collaborative_real-time_editor
-[25]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/The_Mother_of_All_Demos
-[26]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Douglas_Engelbart