mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-02-28 01:01:09 +08:00
translated
This commit is contained in:
parent
192021c5bf
commit
3793a4a646
@ -1,179 +0,0 @@
|
||||
translating---geekpi
|
||||
|
||||
How to Install or Upgrade to Latest Kernel Version in CentOS 7
|
||||
============================================================
|
||||
|
||||
by [Gabriel Cánepa][14] | Published: March 1, 2017 | Last Updated: March 6, 2017
|
||||
|
||||
Download Your Free eBooks NOW - [10 Free Linux eBooks for Administrators][15] | [4 Free Shell Scripting eBooks][16]
|
||||
|
||||
Although some people use the word Linux to represent the operating system as a whole, it is important to note that, strictly speaking, Linux is only the kernel. On the other hand, a distribution is a fully-functional system built on top of the kernel with a wide variety of application tools and libraries.
|
||||
|
||||
During normal operations, the kernel is responsible for performing two important tasks:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Acting as an interface between the hardware and the software running on the system.
|
||||
2. Managing system resources as efficiently as possible.
|
||||
|
||||
To do this, the kernel communicates with the hardware through the drivers that are built into it or those that can be later installed as a module.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, when an application running on your machine wants to connect to a wireless network, it submits that request to the kernel, which in turns uses the right driver to connect to the network.
|
||||
|
||||
**Suggested Read:** [How to Upgrade Kernel in Ubuntu][1]
|
||||
|
||||
With new devices and technology coming out periodically, it is important to keep our kernel up to date if we want to make the most of out them. Additionally, updating our kernel will help us to leverage new kernel functions and to protect ourselves from vulnerabilities that have been discovered in previous versions.
|
||||
|
||||
Ready to update your kernel on CentOS 7 or one of their derivatives such as RHEL 7 and Fedora? If so, keep reading!
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 1: Checking Installed Kernel Version
|
||||
|
||||
When we install a distribution it includes a certain version of the Linux kernel. To show the current version installed on our system we can do:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# uname -sr
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
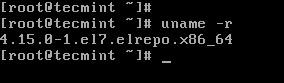
The following image shows the output of the above command in a CentOS 7 server:
|
||||
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||
][2]
|
||||
|
||||
Check Kernel Version in CentOS 7
|
||||
|
||||
If we now go to [https://www.kernel.org/][3], we will see that the latest kernel version is 4.10.1 at the time of this writing (other versions are available from the same site).
|
||||
|
||||
One important thing to consider is the life cycle of a kernel version – if the version you are currently using is approaching its end of life, no more bug fixes will be provided after that date. For more info, refer to the [kernel Releases][4] page.
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 2: Upgrading Kernel in CentOS 7
|
||||
|
||||
Most modern distributions provide a way to upgrade the kernel using a [package management system such as yum][5] and an officially-supported repository.
|
||||
|
||||
However, this will only perform the upgrade to the most recent version available from the distribution’s repositories – not the latest one available in the [https://www.kernel.org/][6]. Unfortunately, Red Hat only allows to upgrade the kernel using the former option.
|
||||
|
||||
As opposed to Red Hat, CentOS allows the use of ELRepo, a third-party repository that makes the upgrade to a recent version a kernel.
|
||||
|
||||
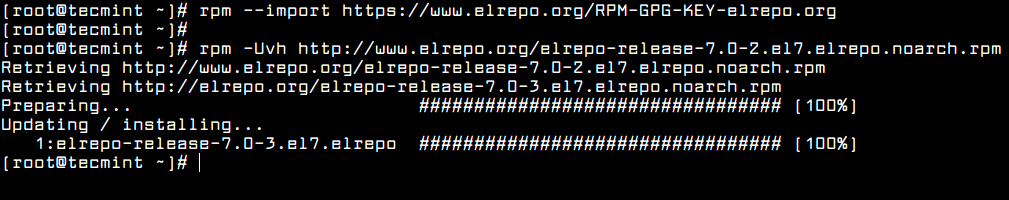
To enable the ELRepo repository on CentOS 7, do:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# rpm --import https://www.elrepo.org/RPM-GPG-KEY-elrepo.org
|
||||
# rpm -Uvh http://www.elrepo.org/elrepo-release-7.0-2.el7.elrepo.noarch.rpm
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||
][7]
|
||||
|
||||
Enable ELRepo in CentOS 7
|
||||
|
||||
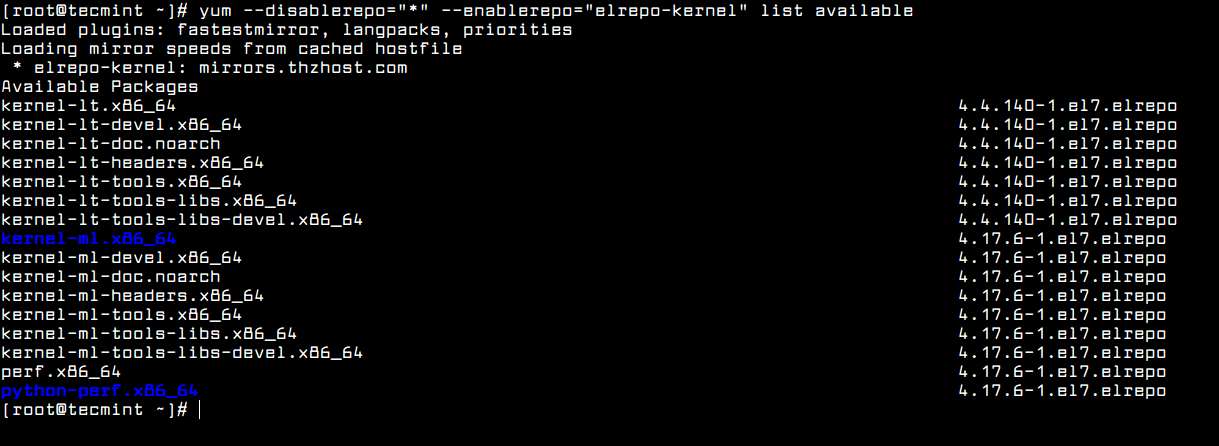
Once the repository has been enabled, you can use the following command to list the available kernel.related packages:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# yum --disablerepo="*" --enablerepo="elrepo-kernel" list available
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||
][8]
|
||||
|
||||
Yum – Find Available Kernel Versions
|
||||
|
||||
Next, install the latest mainline stable kernel:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# yum --enablerepo=elrepo-kernel install kernel-ml
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][9]
|
||||
|
||||
Install Latest Kernel Version in CentOS 7
|
||||
|
||||
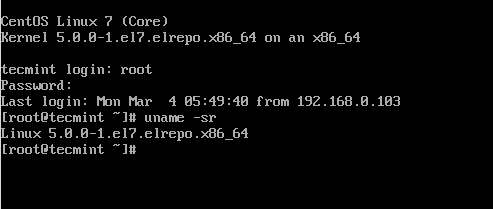
Finally, reboot your machine to apply the latest kernel, and then run following command to check the kernel version:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
uname -sr
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||
][10]
|
||||
|
||||
Verify Kernel Version
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 3: Set Default Kernel Version in GRUB
|
||||
|
||||
To make the newly-installed version the default boot option, you will have to modify the GRUB configuration as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
Open and edit the file /etc/default/grub and set `GRUB_DEFAULT=0`. This means that the first kernel in the GRUB initial screen will be used as default.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
GRUB_TIMEOUT=5
|
||||
GRUB_DEFAULT=0
|
||||
GRUB_DISABLE_SUBMENU=true
|
||||
GRUB_TERMINAL_OUTPUT="console"
|
||||
GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX="rd.lvm.lv=centos/root rd.lvm.lv=centos/swap crashkernel=auto rhgb quiet"
|
||||
GRUB_DISABLE_RECOVERY="true"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
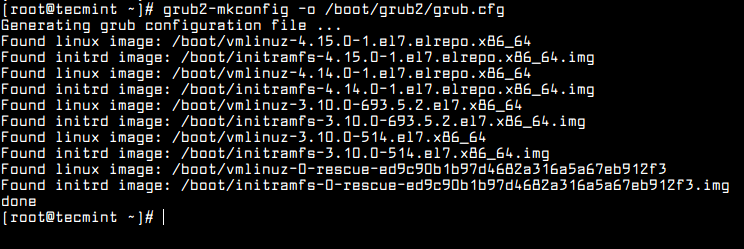
Next, run the following command to recreate the kernel configuration.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# grub2-mkconfig -o /boot/grub2/grub.cfg
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||
][11]
|
||||
|
||||
Set Kernel in GRUB
|
||||
|
||||
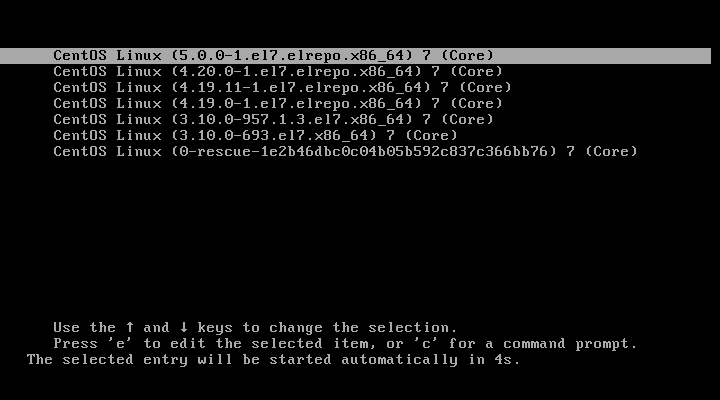
Reboot and verify that the latest kernel is now being used by default.
|
||||
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||
][12]
|
||||
|
||||
Booting Default Kernel Version in CentOS 7
|
||||
|
||||
Congratulations! You have upgraded your kernel in CentOS 7!
|
||||
|
||||
##### Summary
|
||||
|
||||
In this article we have explained how to easily upgrade the Linux kernel on your system. There is yet another method which we haven’t covered as it involves compiling the kernel from source, which would deserve an entire book and is not recommended on production systems.
|
||||
|
||||
Although it represents one of the best learning experiences and allows for a fine-grained configuration of the kernel, you may render your system unusable and may have to reinstall it from scratch.
|
||||
|
||||
If you are still interested in building the kernel as a learning experience, you will find instructions on how to do it at the [Kernel Newbies][13] page.
|
||||
|
||||
As always, feel free to use the form below if you have any questions or comments about this article.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
作者简介:
|
||||
|
||||
I'am a computer addicted guy, a fan of open source and linux based system software, have about 4 years experience with Linux distributions desktop, servers and bash scripting.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/install-upgrade-kernel-version-in-centos-7/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Matei Cezar][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/cezarmatei/
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/upgrade-kernel-in-ubuntu/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/Check-Kernel-Version-in-CentOS-7.png
|
||||
[3]:https://www.kernel.org/
|
||||
[4]:https://www.kernel.org/category/releases.html
|
||||
[5]:http://www.tecmint.com/20-linux-yum-yellowdog-updater-modified-commands-for-package-mangement/
|
||||
[6]:https://www.kernel.org/
|
||||
[7]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/Enable-ELRepo-in-CentOS-7.png
|
||||
[8]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/Yum-Find-Available-Kernel-Versions.png
|
||||
[9]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/Install-Latest-Kernel-Version-in-CentOS-7.png
|
||||
[10]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/Verify-Kernel-Version.png
|
||||
[11]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/Set-Kernel-in-GRUB.png
|
||||
[12]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/Booting-Default-Kernel-Version.png
|
||||
[13]:https://kernelnewbies.org/KernelBuild
|
||||
[14]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/gacanepa/
|
||||
[15]:http://www.tecmint.com/10-useful-free-linux-ebooks-for-newbies-and-administrators/
|
||||
[16]:http://www.tecmint.com/free-linux-shell-scripting-books/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,177 @@
|
||||
如何在 CentOS 7 中安装或升级最新的内核
|
||||
============================================================
|
||||
|
||||
by [Gabriel Cánepa][14] | Published: March 1, 2017 | Last Updated: March 6, 2017
|
||||
|
||||
现在下载你的免费电子书 - [10 本免费的 Linux 电子书][15] | [4 本免费的 shell 脚本电子书][16]
|
||||
|
||||
虽然有些人使用 Linux 来表示整个操作系统,但要注意的是,严格地来说,Linux 只是个内核。另一方面,发行版是一个完整功能的系统,它建立在内核之上,具有各种各样的应用程序工具和库。
|
||||
|
||||
在正常操作期间,内核负责执行两个重要任务:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 作为硬件和系统上运行的软件之间的接口。
|
||||
2. 尽可能高效地管理系统资源。
|
||||
|
||||
为此,内核通过内置的驱动程序或以后可作为模块安装的驱动程序与硬件通信。
|
||||
|
||||
例如,当你计算机上运行的程序想要连接到无线网络时,它会将该请求提交给内核,后者又会使用正确的驱动程序连接到网络。
|
||||
|
||||
**建议阅读:** [如何在 Ubuntu 中升级内核][1]
|
||||
|
||||
随着新的设备和技术定期出来,如果我们想充分利用它们,保持最新的内核就很重要。此外,更新内核将帮助我们利用新的内核函数,并保护自己免受先前版本中发现的漏洞的攻击。
|
||||
|
||||
准备好了在 CentOS 7 或其衍生产品(如 RHEL 7和 Fedora)上更新内核了么?如果是这样,请继续阅读!
|
||||
|
||||
### 步骤 1:检查已安装的内核版本
|
||||
|
||||
让我们安装了一个发行版,它包含了一个特定版本的内核。为了展示当前系统中已安装的版本,我们可以:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# uname -sr
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
下面的图片展示了在一台 CentOS 7 服务器上的输出信息:
|
||||
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][2]
|
||||
|
||||
在 CentOS 7 上检查内核版本
|
||||
|
||||
如果我们现在进入 [https://www.kernel.org/][3],在撰写本文时,我们看到最新的内核版本是4.10.1(其他版本可以从同一网站获得)。
|
||||
|
||||
还要考虑的一个重要的事情是内核版本的生命周期 - 如果你当前使用的版本接近它的生命周期,那么在该日期后将不会提供更多的 bug 修复。关于更多信息,请参阅[内核发布][4]页。
|
||||
|
||||
### 步骤 2:在 CentOS 7 中升级内核
|
||||
|
||||
大多数现代发行版提供了一种使用[ yum 等包管理系统][5]和官方支持的仓库升级内核的方法。
|
||||
|
||||
但是,这只会升级内核到仓库中可用的最新版本 - 而不是在 [https://www.kernel.org/][6] 中可用的最新版本。不幸的是,Red Hat 只允许使用前者升级内核。
|
||||
|
||||
与 Red Hat 不同,CentOS 允许使用 ELRepo,这是一个第三方仓库,可以将内核升级到最新版本。
|
||||
|
||||
要在 CentOS 7 上启用 ELRepo 仓库,请运行:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# rpm --import https://www.elrepo.org/RPM-GPG-KEY-elrepo.org
|
||||
# rpm -Uvh http://www.elrepo.org/elrepo-release-7.0-2.el7.elrepo.noarch.rpm
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][7]
|
||||
|
||||
在 CentOS 7 启用 ELRepo
|
||||
|
||||
仓库启用后,你可以使用下面的命令列出可用的内核相关包:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# yum --disablerepo="*" --enablerepo="elrepo-kernel" list available
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][8]
|
||||
|
||||
yum - 找出可用的内核版本
|
||||
|
||||
接下来,安装最新的主线稳定内核:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# yum --enablerepo=elrepo-kernel install kernel-ml
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][9]
|
||||
|
||||
在 CentOS 7 中安装最新的内核版本
|
||||
|
||||
最后,重启机器并应用最新内核,接着运行下面的命令检查最新内核版本:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
uname -sr
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][10]
|
||||
|
||||
验证内核版本
|
||||
|
||||
### 步骤 3:设置 GRUB 默认的内核版本
|
||||
|
||||
为了让新安装的内核成为默认启动选项,你需要如下修改 GRUB 配置:
|
||||
|
||||
打开并编辑 /etc/default/grub 并设置 `GRUB_DEFAULT=0`。意思是 GRUB 初始化页面的第一个内核将作为默认内核。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
GRUB_TIMEOUT=5
|
||||
GRUB_DEFAULT=0
|
||||
GRUB_DISABLE_SUBMENU=true
|
||||
GRUB_TERMINAL_OUTPUT="console"
|
||||
GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX="rd.lvm.lv=centos/root rd.lvm.lv=centos/swap crashkernel=auto rhgb quiet"
|
||||
GRUB_DISABLE_RECOVERY="true"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
接下来运行下面的命令来重新创建内核配置。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# grub2-mkconfig -o /boot/grub2/grub.cfg
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][11]
|
||||
|
||||
在 GRUB 中设置内核
|
||||
|
||||
重启并验证最新的内核已作为默认内核。
|
||||
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][12]
|
||||
|
||||
在 CentOS 7 中启动默认内核版本
|
||||
|
||||
恭喜你!你已经在 CentOS 7 中升级内核了!
|
||||
|
||||
##### 总结
|
||||
|
||||
在本文中,我们解释了如何轻松升级系统上的 Linux 内核。我们还没讲到另外一个方法,因为它涉及从源代码编译内核,这可以写成一本书,并且不推荐在生产系统上这么做。
|
||||
|
||||
虽然它是最好的学习体验之一,并且允许细粒度配置内核,但是你可能会让你的系统不可用,并且可能必须从头重新安装它。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你仍然有兴趣构建内核作为学习经验,你可以在 [Kernel Newbies][13]页面中获得指导。
|
||||
|
||||
一如既往,如果你对本文有任何问题或意见,请随时使用下面的评论栏。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
作者简介:
|
||||
|
||||
我是一个计算机上瘾的家伙,并且是开源和 linux 系统软件的粉丝,有大约 4 年的 Linux 发行版桌面、服务器和 bash 脚本的经验。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/install-upgrade-kernel-version-in-centos-7/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Matei Cezar][a]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/cezarmatei/
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/upgrade-kernel-in-ubuntu/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/Check-Kernel-Version-in-CentOS-7.png
|
||||
[3]:https://www.kernel.org/
|
||||
[4]:https://www.kernel.org/category/releases.html
|
||||
[5]:http://www.tecmint.com/20-linux-yum-yellowdog-updater-modified-commands-for-package-mangement/
|
||||
[6]:https://www.kernel.org/
|
||||
[7]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/Enable-ELRepo-in-CentOS-7.png
|
||||
[8]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/Yum-Find-Available-Kernel-Versions.png
|
||||
[9]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/Install-Latest-Kernel-Version-in-CentOS-7.png
|
||||
[10]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/Verify-Kernel-Version.png
|
||||
[11]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/Set-Kernel-in-GRUB.png
|
||||
[12]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/Booting-Default-Kernel-Version.png
|
||||
[13]:https://kernelnewbies.org/KernelBuild
|
||||
[14]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/gacanepa/
|
||||
[15]:http://www.tecmint.com/10-useful-free-linux-ebooks-for-newbies-and-administrators/
|
||||
[16]:http://www.tecmint.com/free-linux-shell-scripting-books/
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user