mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-03-27 02:30:10 +08:00
Update 20170114 Set Date and Time for Each Command You Execute in Bash History.md
This commit is contained in:
parent
aea6d3f21e
commit
355ada6986
@ -1,10 +1,10 @@
|
||||
Translating by Hymantin
|
||||
Set Date and Time for Each Command You Execute in Bash History
|
||||
设置
|
||||
为你在 Bash 历史中执行过的每一项指令设置时间和日期
|
||||
============================================================
|
||||
|
||||
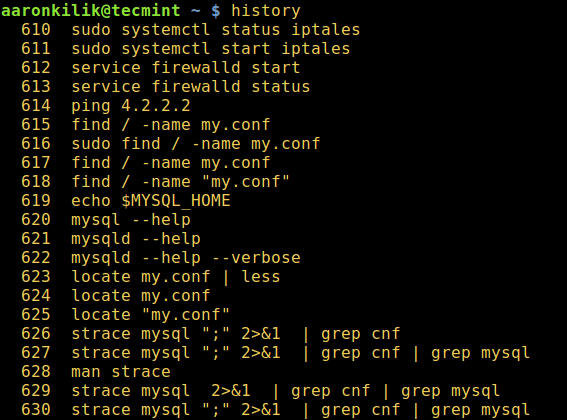
By default, all commands executed by Bash on the command line are stored in history buffer or recorded in a file called ~/.bash_history. This means that a system administrator can view a list of commands executed by users on the system or a user can view his/her command history using the [history command][1] like so.
|
||||
|
||||
在默认情况下,所有通过 Bash 在指令行中执行过的指令都被存储在历史缓存区或者一个叫做 ~/.bash_history 的文件里。这意味着系统管理员可以看到系统上用户执行过的指令清单或者用户可以通过像[历史指令][1]这样的选项来看他/她的指令历史。
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ history
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -12,18 +12,18 @@ $ history
|
||||
|
||||
][2]
|
||||
|
||||
Linux History Command
|
||||
Linux 历史指令
|
||||
|
||||
From the output of the [history command][3] above, the date and time when a command was executed is not shown. This is the default setting on most if not all Linux distributions.
|
||||
|
||||
从上面[历史指令][3]的输出可知,一个指令被执行的日期和时间并没有显示出来。这对大部分但非所有的 Linux 发行版是默认设置。
|
||||
In this article, we will explain how you can configure time stamp information when each command in the Bash history was executed to be displayed.
|
||||
|
||||
在这篇文章里,我们将解释当每一项在 Bash 历史中被执行并展示的时候,你如何配置时间戳信息。
|
||||
The date and time associated with each history entry can be written to the history file, marked with the history comment character by setting the HISTTIMEFORMAT variable.
|
||||
|
||||
每一次历史登入的日期和时间通过设置 HISTTIMEFORMAT 变量标记与历史注释字符都被写进了历史文件。
|
||||
There are two possible ways of doing this: one does it temporarily while the other makes it permanent.
|
||||
|
||||
这里有两种可行的方式来达到目的:一种是暂时的效果,一种是永久的效果。
|
||||
To set HISTTIMEFORMAT variable temporarily, export it as below on the command line:
|
||||
|
||||
为了设置 HISTTIMEFORMAT 为已读变量,输入以下指令:
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ export HISTTIMEFORMAT='%F %T'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user