mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-03-27 02:30:10 +08:00
translated
This commit is contained in:
parent
6f27330d6c
commit
337e69c37d
@ -1,123 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Translating---geekpi
|
||||
|
||||
Linux FAQs with Answers--How to install and access CentOS remote desktop on VPS
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **Question**: I want to install CentOS desktop on VPS, and be able to access the desktop GUI remotely from home. What is a recommended way to set up and access CentOS-based remote desktop on VPS?
|
||||
|
||||
Nowadays teleworking or remote working with flexible hours is increasingly popular in tech industry. One of the enabling technologies behind this trend is remote desktop. Your desktop environment is in the cloud, and you can access the remote desktop anywhere you go, either from home or at your workplace.
|
||||
|
||||
This tutorial describes how you can set up CentOS based remote desktop on VPS. Here we are going to demonstrate CentOS 7 based environment.
|
||||
|
||||
We assume that you already created a CentOS 7 VPS instance somewhere (e.g., using [DigitalOcean][1] or Amazon EC2). Make sure that the VPS instance has at least 1GB memory. Otherwise, CentOS desktop will crash when you try to access remote desktop.
|
||||
|
||||
### Step One: Install CentOS Desktop ###
|
||||
|
||||
If an available CentOS image is a minimal version of CentOS without desktop, you will need to install desktop (e.g., GNOME) on your CentOS VPS before proceeding. For example, DigitalOcean's CentOS image is such a minimal version, which requires [desktop GUI installation][2] as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
# yum groupinstall "GNOME Desktop"
|
||||
|
||||
Reboot a VPS after finishing installation.
|
||||
|
||||
### Step Two: Install and Configure VNC Server ###
|
||||
|
||||
The next step is to install and configure VNC server. We are going to use TigerVNC, an open-source VNC server implementation.
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install tigervnc-server
|
||||
|
||||
Now create a user account (e.g., xmodulo) which will be used to access remote desktop.
|
||||
|
||||
# useradd xmodulo
|
||||
# passwd xmodulo
|
||||
|
||||
When a user tries to access remote desktop using VNC, a dedicated VNC server daemon will be launched to handle its requests. This means that you will need to create a separate VNC server configuration for each user.
|
||||
|
||||
CentOS 7 relies on systemd to manage and configure system services. So we are going to configure VNC server for xmodulo user using systemd.
|
||||
|
||||
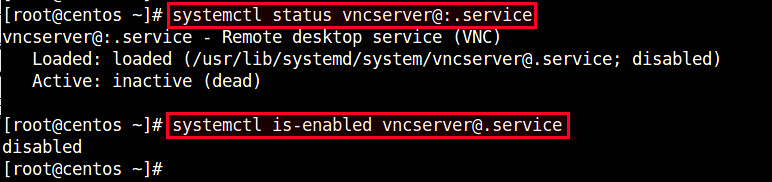
Let's first check the status of VNC server by running either command below:
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl status vncserver@:.service
|
||||
# systemctl is-enabled vncserver@.service
|
||||
|
||||
By default, freshly installed VNC service is not active (disabled).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Now create a VNC service configuration for xmodulo user by copying a generic VNC service unit file as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
# cp /lib/systemd/system/vncserver@.service /etc/systemd/system/vncserver@:1.service
|
||||
|
||||
Open the configuration file with a text editor, and replace <USER> with an actual user name (e.g., xmodulo) under [Service] section. Also, append "-geometry <resolution>" parameter in ExecStart. In the end, the following two lines with bold font will be modified.
|
||||
|
||||
# vi /etc/systemd/system/vncserver@:1.service
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
[Service]
|
||||
Type=forking
|
||||
# Clean any existing files in /tmp/.X11-unix environment
|
||||
ExecStartPre=/bin/sh -c '/usr/bin/vncserver -kill %i > /dev/null 2>&1 || :'
|
||||
ExecStart=/sbin/runuser -l xmodulo -c "/usr/bin/vncserver %i -geometry 1024x768"
|
||||
PIDFile=/home/xmodulo/.vnc/%H%i.pid
|
||||
ExecStop=/bin/sh -c '/usr/bin/vncserver -kill %i > /dev/null 2>&1 || :'
|
||||
|
||||
Now set up (optional) VNC password for xmodulo user for security. For this, switch to the user, and run vncserver command.
|
||||
|
||||
# su - xmodulo
|
||||
# vncserver
|
||||
|
||||
You will be prompted to enter a VNC password for the user. Once the password is set, you will need to use this password to gain access to remote desktop.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Finally, reload services to activate the new VNC configuration:
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl daemon-reload
|
||||
|
||||
and enable VNC service to make it start automatically upon boot:
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl enable vncserver@:1.service
|
||||
|
||||
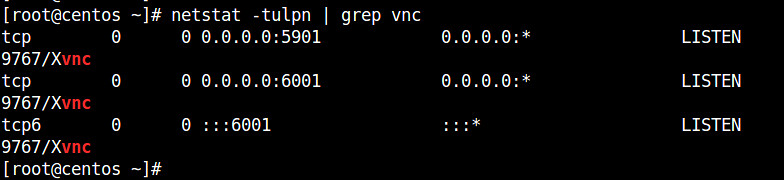
Check the port number that a VNC server is listening on by running:
|
||||
|
||||
# netstat -tulpn | grep vnc
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Port 5901 is the default port number for VNC client to connect to a VNC server.
|
||||
|
||||
### Step Three: Connect to Remote Desktop over SSH ###
|
||||
|
||||
By design, Remote Frame Buffer (RFB) protocol used by VNC is not a secure protocol. Thus it is not a good idea to directly connect to a remote VNC server running on VPS using a VNC client. Any sensitive information such as password could easily be leaked from VNC traffic. So instead, I strongly recommend that you [tunnel VNC traffic][3] over a secure SSH tunnel, as described here.
|
||||
|
||||
On a local host where you want to run VNC client, create an SSH tunnel to a remote VPS using the following command. When prompted for SSH password, type the password of the user.
|
||||
|
||||
$ ssh xmodulo@<VPS-IP-address> -L 5901:127.0.0.1:5901
|
||||
|
||||
Replace "xmodulo" with your own VNC user, and fill in the IP address of your VPS instance.
|
||||
|
||||
Once an SSH tunnel is established, remote VNC traffic will be routed over the SSH tunnel, and be sent to 127.0.0.1:5901.
|
||||
|
||||
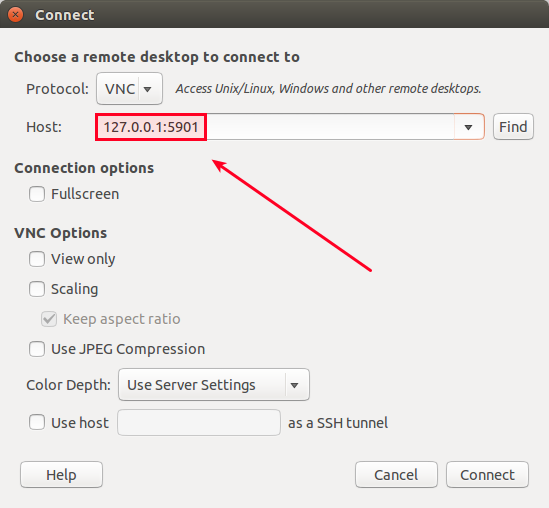
Now go ahead and launch your favorite VNC client (e.g., vinagre), and connect to 127.0.0.1:5901.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
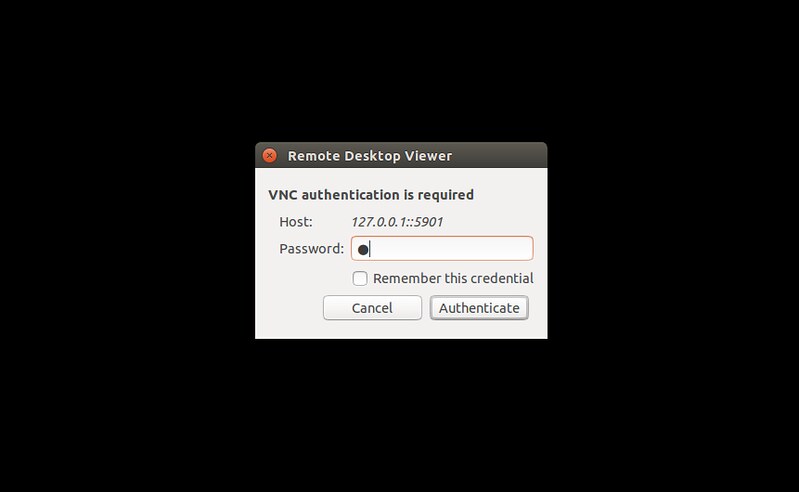
You will be asked to enter a VNC password. When you type a correct VNC password, you will finally be able to CentOS remote desktop on VPS securely.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/centos-remote-desktop-vps.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/author/nanni
|
||||
[1]:http://xmodulo.com/go/digitalocean
|
||||
[2]:http://xmodulo.com/how-to-install-gnome-desktop-on-centos.html
|
||||
[3]:http://xmodulo.com/how-to-set-up-vnc-over-ssh.html
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,121 @@
|
||||
Linux有问必答-- 如何在VPS上安装和访问CentOS远程桌面
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **提问**: 我想在VPS中安装CentOS桌面,并可以直接从我家远程访问GUI桌面。有什么建议可以在VPS上设置和访问CentOS远程桌面?
|
||||
|
||||
如何远程办公或者远程弹性化工作制在技术领域正变得越来越流行。这个趋势背后的一个技术就是远程桌面。你的桌面环境在云中,你可以在任何你去的地方,或者在家或者工作场所访问你的远程桌面。
|
||||
|
||||
这个教程介绍如何VPS中设置基于CentOS的远程桌面。现在,我们会先展示CentOS的基础环境。
|
||||
|
||||
我们假设你已经创建了CentOS 7的VPS实例(比如,使用[DigitalOcean][1] 或者 Amazon EC2)。请确保你的VPS实例有至少1GB的内存。不然,CentOS将会在你访问远程桌面的时候回崩溃。
|
||||
|
||||
### 第一步: 安装CentOS桌面 ###
|
||||
|
||||
如果现在的CentOS版本是没有桌面的最小版本,你需要先在VPS上安装桌面(比如GNOME)。比如,DigitalOcean的镜像就是最小版本,它需要如下安装[桌面GUI][2]
|
||||
|
||||
# yum groupinstall "GNOME Desktop"
|
||||
|
||||
在安装完成之后重启VPS。
|
||||
|
||||
### 第二步:安装和配置VNC服务器 ###
|
||||
|
||||
接下来就是安装和配置VNC服务器。我们使用的是TigerVNC,一个开源的VNC服务实现。
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install tigervnc-server
|
||||
|
||||
现在创建一个用户账户(比如:xmodulo)用来访问远程桌面。
|
||||
|
||||
# useradd xmodulo
|
||||
# passwd xmodulo
|
||||
|
||||
当一个用户尝试使用VNC访问远程桌面时,VNC守护进程就会启动来处理这个请求。这意味着你需要为每个用户创建一个独立的VNC配置文件。
|
||||
|
||||
CentOS依靠systemd来管理和配置系统服务。所以我们将使用systemd来为用户xmodulo配置VNC服务器。
|
||||
|
||||
首先让我们使用下面任意一条命令来检查VNC服务器的状态。
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl status vncserver@:.service
|
||||
# systemctl is-enabled vncserver@.service
|
||||
|
||||
默认上,刚安装的VNC服务并没有激活(禁用)。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
现在服务一份通用的VNC服务文件来位用户xmodulo创建一个VNC服务配置。
|
||||
|
||||
# cp /lib/systemd/system/vncserver@.service /etc/systemd/system/vncserver@:1.service
|
||||
|
||||
用本文编辑器来打开配置文件,用实际的用户名(比如:xmodulo)来替换[Service]下面的<USER>。同样。在ExecStart后面追加 "-geometry <resolution>" 参数。最后,要修改下面两行加粗字体的两行。
|
||||
|
||||
# vi /etc/systemd/system/vncserver@:1.service
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
[Service]
|
||||
Type=forking
|
||||
# Clean any existing files in /tmp/.X11-unix environment
|
||||
ExecStartPre=/bin/sh -c '/usr/bin/vncserver -kill %i > /dev/null 2>&1 || :'
|
||||
ExecStart=/sbin/runuser -l xmodulo -c "/usr/bin/vncserver %i -geometry 1024x768"
|
||||
PIDFile=/home/xmodulo/.vnc/%H%i.pid
|
||||
ExecStop=/bin/sh -c '/usr/bin/vncserver -kill %i > /dev/null 2>&1 || :'
|
||||
|
||||
现在为用户xmodulo设置密码(可选)。首先切换到该用户,并运行vncserver命令。
|
||||
|
||||
# su - xmodulo
|
||||
# vncserver
|
||||
|
||||
你会被提示输入用户的VNC密码。密码设置完成后,你下次需要用这个密码来访问你的远程桌面。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
最后,重新加载服务来使新的VNC配置生效:
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl daemon-reload
|
||||
|
||||
在启动时自动启动VNC服务:
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl enable vncserver@:1.service
|
||||
|
||||
检查vnc服务正在监听的端口:
|
||||
|
||||
# netstat -tulpn | grep vnc
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
端口5901是VNC默认的客户端连接到VNC服务器使用的端口。
|
||||
|
||||
### 第三步:通过SSH连接到远程桌面 ###
|
||||
|
||||
设计上,VNC使用的远程帧缓存(RFB)并不是一种安全的协议。那么在VNC客户端上直接连接到VNC服务器上并不是一个好主意。任何敏感信息比如密码都可以在VNC流量中被轻易地泄露。因此,我强烈建议使用SSH隧道来[加密你的VNC流量][3]。
|
||||
|
||||
在你要运行VNC客户端的本机上,使用下面的命令来创建一个连接到远程VPS的SSH通道。当被要输入SSH密码时,输入用户的密码。
|
||||
|
||||
$ ssh xmodulo@<VPS-IP-address> -L 5901:127.0.0.1:5901
|
||||
|
||||
用你自己的VNC用户名来替换“xmodulo”,并填上你自己的VPS IP地址。
|
||||
|
||||
一旦SSH通道建立之后,远程VNC流量就会通过ssh通道路由并发送到127.0.0.1:5901。
|
||||
|
||||
现在启动你最爱的VNC客户端(比如:vinagre),来连接到127.0.0.1:5901。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
你将被要求输入VNC密码。当你输入VNC密码时,你就可以安全地连接到CentOS的远程桌面了.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/centos-remote-desktop-vps.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/author/nanni
|
||||
[1]:http://xmodulo.com/go/digitalocean
|
||||
[2]:http://xmodulo.com/how-to-install-gnome-desktop-on-centos.html
|
||||
[3]:http://xmodulo.com/how-to-set-up-vnc-over-ssh.html
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user