mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-02-25 00:50:15 +08:00
翻译初稿
This commit is contained in:
parent
1c79afaf9d
commit
2f5ce6e3d5
82
translated/tech/20170211 Who Is Root Why Does Root Exist.md
Normal file
82
translated/tech/20170211 Who Is Root Why Does Root Exist.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,82 @@
|
||||
Root 是谁?为什么会有 Root 账户?
|
||||
============================================================
|
||||
|
||||
在 Linux 中为什么会有一个名为 `root` 的特定账户?`root` 账户的最佳实践是什么?它在哪些场景下必须使用,那些场景下不能使用?对于以上几个问题,如果你感兴趣的话,那么请继续阅读。
|
||||
|
||||
本文中,我们提供了一些关于 `root` 账户的参考资料,方便您收藏。
|
||||
|
||||
### root 是什么?
|
||||
|
||||
首先,记住这一点,在 `Unix-like` 操作系统中,目录的层级结构被设计为树状结构。起始目录是一个特殊目录,使用斜杠 `(/)` 表示,而其他目录都是从起始目录开始分支。由于这种结构很像现实中的树,所以 `/` 也被称为根目录。
|
||||
|
||||
下图,我们可以看到以下命令的输出:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ tree -d / | less
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
该命令主要是演示一下 `/` 根目录和树`根`的比喻。
|
||||
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][1]
|
||||
|
||||
Linux 中的目录层级
|
||||
|
||||
虽然 `root` 账户命名的原因还不是很清楚,可能是因为 `root` 账户是唯一一个在根目录 `/` 中有写权限的账号吧。
|
||||
|
||||
此外,由于 `root` 账户可以访问 `Unix-like` 操作系统中的所有文件和命令,因此,它也常被称为超级用户。
|
||||
|
||||
另外,根目录 `(/)` 和 `/root` 目录不能混淆了,`/root` 目录是 `root` 账户的家目录。实际上,`/root` 目录是根目录 `/` 的子目录。
|
||||
|
||||
### 获取 root 权限
|
||||
|
||||
当我们讨论有关 `root`(或者超级用户)权限的时候,我们会引用这样一种账户的权限,其在系统上的权限包含(但不限于)修改系统并授权其他用户对系统资源的访问权限。
|
||||
|
||||
胡乱使用 `root` 账户,轻则系统崩溃重则系统完全故障。这就是为什么会说,以下准则是使用 `root` 账户的最佳实践:
|
||||
|
||||
首先,使用 `root` 账户运行 `visudo` 命令编辑 `/etc/sudoers` 文件,给指定账户(如:`supervisor`)授予最低超级用户权限。
|
||||
|
||||
当然,最低超级用户权限还可以包括,例如:[添加用户 (adduser)][2]、[修改用户 (usermod)][3]等权限。
|
||||
|
||||
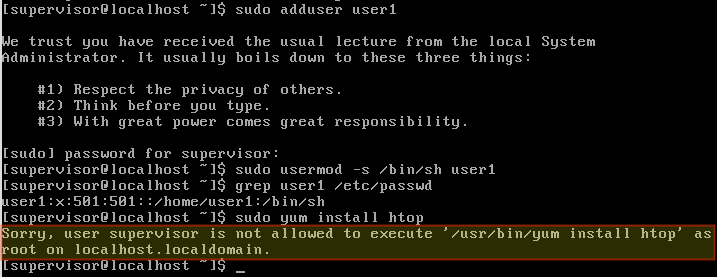
接着,使用 `supervisor` 账户登录并[使用 `sudo` 执行用户管理任务][4]。此时,你可能会发现,当你执行需要超级用户权限(例如:删除软件包)的其他任务时,会失败。
|
||||
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||
][5]
|
||||
|
||||
不使用超级用户权限运行命令
|
||||
|
||||
在需要使用超级用户权限时,重复执行以上两个步骤,一旦执行完成,则立即使用 `exit` 命令退回到无权限的账户。
|
||||
|
||||
此时,你需要确定一下其他周期性的任务是否需要超级用户权限?如果需要,那么在 `/etc/sudoers` 中,给指定的账户或组授予必要的权限,尽量避免直接使用 `root` 账户操作。
|
||||
|
||||
##### 摘要
|
||||
|
||||
本文可以作为在 `Unix-like` 操作系统中正确使用 `root` 账户的简单参考。收藏一下,你就可以随时翻阅!
|
||||
|
||||
还是一样,如果您对本文有什么疑问或建议,请使用以下的评论表单给我们评论留言,期待您的回音!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
作者简介:
|
||||
|
||||
Gabriel Cánepa 来自 Villa Mercedes, San Luis, Argentina。他是一名 GNU/Linux 系统管理员和 Web 开发员,现在一家全球领先的消费品公司就职。他很喜欢使用 FOSS 工具来提高自己的工作效率。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/who-is-root-why-does-root-exist-in-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Gabriel Cánepa][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/zhb127)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/gacanepa/
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/Linux-root-Directory-Tree.png
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/add-users-in-linux/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/usermod-command-examples/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.tecmint.com/sudoers-configurations-for-setting-sudo-in-linux/
|
||||
[5]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/Run-Commands-Without-sudo.png
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user