mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-03-24 02:20:09 +08:00
Merge pull request #3200 from strugglingyouth/master
翻译完成 20150816 How to migrate MySQL to MariaDB on Linux.md
This commit is contained in:
commit
2912307b24
@ -1,187 +0,0 @@
|
||||
translation by strugglingyouth
|
||||
How to migrate MySQL to MariaDB on Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Since the Oracle's acquisition of MySQL, a lot of MySQL developers and users moved away from MySQL due to Oracle's more closed-door stance on MySQL development and maintenance. The community-driven outcome of such movement is a fork of MySQL, called MariaDB. Led by original MySQL developers, the development of MariaDB follows the open-source philosophy and makes sure of [its binary compatibility with MySQL][1]. The Linux distributions such as Red Hat families (Fedora, CentOS, RHEL), Ubuntu and Mint, openSUSE and Debian already started to use and support MariaDB as a drop-in replacement of MySQL.
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to migrate your database from MySQL to MariaDB, this article is what you are looking for. Fortunately, due to their binary compatibility, MySQL-to-MariaDB migration process is pretty much straightforward. If you follow the steps below, the migration from MySQL to MariaDB will most likely be painless.
|
||||
|
||||
### Prepare a MySQL Database and a Table ###
|
||||
|
||||
For demonstration purpose, let's create a test MySQL database and one table in the database before doing the migration. Skip this step if you already have existing MySQL database(s) to migrate to MariaDB. Otherwise proceed as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
Log in into MySQL from a terminal by typing your MySQL root user password.
|
||||
|
||||
$ mysql -u root -p
|
||||
|
||||
Create a database and a table.
|
||||
|
||||
mysql> create database test01;
|
||||
mysql> use test01;
|
||||
mysql> create table pet(name varchar(30), owner varchar(30), species varchar(20), sex char(1));
|
||||
|
||||
Add some records to the table.
|
||||
|
||||
mysql> insert into pet values('brandon','Jack','puddle','m'),('dixie','Danny','chihuahua','f');
|
||||
|
||||
Then quit the MySQL database.
|
||||
|
||||
### Backup the MySQL Database ###
|
||||
|
||||
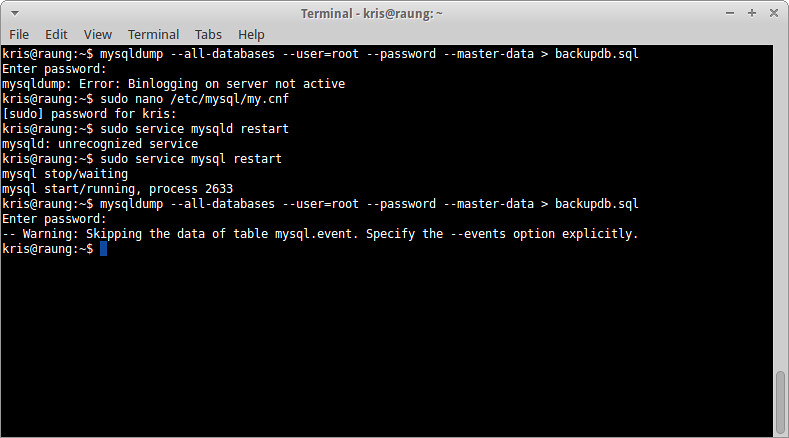
The next step is to back up existing MySQL database(s). Use the following mysqldump command to export all existing databases to a file. Before running this command, make sure that binary logging is enabled in your MySQL server. If you don't know how to enable binary logging, see the instructions toward the end of the tutorial.
|
||||
|
||||
$ mysqldump --all-databases --user=root --password --master-data > backupdb.sql
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Now create a backup of my.cnf file somewhere in your system before uninstalling MySQL. This step is optional.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo cp /etc/mysql/my.cnf /opt/my.cnf.bak
|
||||
|
||||
### Uninstall MySQL Package ###
|
||||
|
||||
First, you need to stop the MySQL service.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo service mysql stop
|
||||
|
||||
or:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo systemctl stop mysql
|
||||
|
||||
or:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo /etc/init.d/mysql stop
|
||||
|
||||
Then go ahead and remove MySQL packages and configurations as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
On RPM based system (e.g., CentOS, Fedora or RHEL):
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum remove mysql* mysql-server mysql-devel mysql-libs
|
||||
$ sudo rm -rf /var/lib/mysql
|
||||
|
||||
On Debian based system (e.g., Debian, Ubuntu or Mint):
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get remove mysql-server mysql-client mysql-common
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get autoremove
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get autoclean
|
||||
$ sudo deluser mysql
|
||||
$ sudo rm -rf /var/lib/mysql
|
||||
|
||||
### Install MariaDB Package ###
|
||||
|
||||
The latest CentOS/RHEL 7 and Ubuntu (14.04 or later) contain MariaDB packages in their official repositories. In Fedora, MariaDB has become a replacement of MySQL since version 19. If you are using an old version or LTS type like Ubuntu 13.10 or earlier, you still can install MariaDB by adding its official repository.
|
||||
|
||||
[MariaDB website][2] provide an online tool to help you add MariaDB's official repository according to your Linux distribution. This tool provides steps to add the MariaDB repository for openSUSE, Arch Linux, Mageia, Fedora, CentOS, RedHat, Mint, Ubuntu, and Debian.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
As an example, let's use the Ubuntu 14.04 distribution and CentOS 7 to configure the MariaDB repository.
|
||||
|
||||
**Ubuntu 14.04**
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install software-properties-common
|
||||
$ sudo apt-key adv --recv-keys --keyserver hkp://keyserver.ubuntu.com:80 0xcbcb082a1bb943db
|
||||
$ sudo add-apt-repository 'deb http://mirror.mephi.ru/mariadb/repo/5.5/ubuntu trusty main'
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get update
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install mariadb-server
|
||||
|
||||
**CentOS 7**
|
||||
|
||||
Create a custom yum repository file for MariaDB as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo vi /etc/yum.repos.d/MariaDB.repo
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
[mariadb]
|
||||
name = MariaDB
|
||||
baseurl = http://yum.mariadb.org/5.5/centos7-amd64
|
||||
gpgkey=https://yum.mariadb.org/RPM-GPG-KEY-MariaDB
|
||||
gpgcheck=1
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install MariaDB-server MariaDB-client
|
||||
|
||||
After all necessary packages are installed, you may be asked to type a new password for root user account. After setting the root password, don't forget to recover my.cnf backup file.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo cp /opt/my.cnf /etc/mysql/
|
||||
|
||||
Now start MariaDB service as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo service mariadb start
|
||||
|
||||
or:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo systemctl start mariadb
|
||||
|
||||
or:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo /etc/init.d/mariadb start
|
||||
|
||||
### Importing MySQL Database(s) ###
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, we have to import the previously exported database(s) back to MariaDB server as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
$ mysql -u root -p < backupdb.sql
|
||||
|
||||
Enter your MariaDB's root password, and the database import process will start. When the import process is finished, it will return to a command prompt.
|
||||
|
||||
To check whether or not the import process is completed successfully, log in into MariaDB server and perform some sample queries.
|
||||
|
||||
$ mysql -u root -p
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
MariaDB [(none)]> show databases;
|
||||
MariaDB [(none)]> use test01;
|
||||
MariaDB [test01]> select * from pet;
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
As you can see in this tutorial, MySQL-to-MariaDB migration is not difficult. MariaDB has a lot of new features than MySQL, that you should know about. As far as configuration is concerned, in my test case, I simply used my old MySQL configuration file (my.cnf) as a MariaDB configuration file, and the import process was completed fine without any issue. My suggestion for the configuration is that you read the documentation on MariaDB configuration options carefully before the migration, especially if you are using specific MySQL configurations.
|
||||
|
||||
If you are running more complex setup with tons of tables and databases including clustering or master-slave replication, take a look at the [more detailed guide][3] by the Mozilla IT and Operations team, or the [official MariaDB documentation][4].
|
||||
|
||||
### Troubleshooting ###
|
||||
|
||||
1. While running mysqldump command to back up databases, you are getting the following error.
|
||||
|
||||
$ mysqldump --all-databases --user=root --password --master-data > backupdb.sql
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
mysqldump: Error: Binlogging on server not active
|
||||
|
||||
By using "--master-data", you are trying to include binary log information in the exported output, which is useful for database replication and recovery. However, binary logging is not enabled in MySQL server. To fix this error, modify your my.cnf file, and add the following option under [mysqld] section.
|
||||
|
||||
log-bin=mysql-bin
|
||||
|
||||
Save my.cnf file, and restart the MySQL service:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo service mysql restart
|
||||
|
||||
or:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo systemctl restart mysql
|
||||
|
||||
or:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo /etc/init.d/mysql restart
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/migrate-mysql-to-mariadb-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Kristophorus Hadiono][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/kristophorus
|
||||
[1]:https://mariadb.com/kb/en/mariadb/mariadb-vs-mysql-compatibility/
|
||||
[2]:https://downloads.mariadb.org/mariadb/repositories/#mirror=aasaam
|
||||
[3]:https://blog.mozilla.org/it/2013/12/16/upgrading-from-mysql-5-1-to-mariadb-5-5/
|
||||
[4]:https://mariadb.com/kb/en/mariadb/documentation/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,188 @@
|
||||
|
||||
在 Linux 中怎样将 MySQL 迁移到 MariaDB 上
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
自从甲骨文收购 MySQL 后,很多 MySQL 的开发者和用户放弃了 MySQL 由于甲骨文对 MySQL 的开发和维护更多倾向于闭门的立场。在社区驱动下,促使更多人移到 MySQL 的另一个分支中,叫 MariaDB。在原有 MySQL 开发人员的带领下,MariaDB 的开发遵循开源的理念,并确保 [它的二进制格式与 MySQL 兼容][1]。Linux 发行版如 Red Hat 家族(Fedora,CentOS,RHEL),Ubuntu 和Mint,openSUSE 和 Debian 已经开始使用,并支持 MariaDB 作为 MySQL 的简易替换品。
|
||||
|
||||
如果想要将 MySQL 中的数据库迁移到 MariaDB 中,这篇文章就是你所期待的。幸运的是,由于他们的二进制兼容性,MySQL-to-MariaDB 迁移过程是非常简单的。如果你按照下面的步骤,将 MySQL 迁移到 MariaDB 会是无痛的。
|
||||
|
||||
### 准备 MySQL 数据库和表 ###
|
||||
|
||||
出于演示的目的,我们在做迁移之前在数据库中创建一个测试的 MySQL 数据库和表。如果你在 MySQL 中已经有了要迁移到 MariaDB 的数据库,跳过此步骤。否则,按以下步骤操作。
|
||||
|
||||
在终端输入 root 密码登录到 MySQL 。
|
||||
|
||||
$ mysql -u root -p
|
||||
|
||||
创建一个数据库和表。
|
||||
|
||||
mysql> create database test01;
|
||||
mysql> use test01;
|
||||
mysql> create table pet(name varchar(30), owner varchar(30), species varchar(20), sex char(1));
|
||||
|
||||
在表中添加一些数据。
|
||||
|
||||
mysql> insert into pet values('brandon','Jack','puddle','m'),('dixie','Danny','chihuahua','f');
|
||||
|
||||
退出 MySQL 数据库.
|
||||
|
||||
### 备份 MySQL 数据库 ###
|
||||
|
||||
下一步是备份现有的 MySQL 数据库。使用下面的 mysqldump 命令导出现有的数据库到文件中。运行此命令之前,请确保你的 MySQL 服务器上启用了二进制日志。如果你不知道如何启用二进制日志,请参阅结尾的教程说明。
|
||||
|
||||
$ mysqldump --all-databases --user=root --password --master-data > backupdb.sql
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
现在,在卸载 MySQL 之前先在系统上备份 my.cnf 文件。此步是可选的。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo cp /etc/mysql/my.cnf /opt/my.cnf.bak
|
||||
|
||||
### 卸载 MySQL ###
|
||||
|
||||
首先,停止 MySQL 服务。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo service mysql stop
|
||||
|
||||
或者:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo systemctl stop mysql
|
||||
|
||||
或:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo /etc/init.d/mysql stop
|
||||
|
||||
然后继续下一步,使用以下命令移除 MySQL 和配置文件。
|
||||
|
||||
在基于 RPM 的系统上 (例如, CentOS, Fedora 或 RHEL):
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum remove mysql* mysql-server mysql-devel mysql-libs
|
||||
$ sudo rm -rf /var/lib/mysql
|
||||
|
||||
在基于 Debian 的系统上(例如, Debian, Ubuntu 或 Mint):
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get remove mysql-server mysql-client mysql-common
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get autoremove
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get autoclean
|
||||
$ sudo deluser mysql
|
||||
$ sudo rm -rf /var/lib/mysql
|
||||
|
||||
### 安装 MariaDB ###
|
||||
|
||||
在 CentOS/RHEL 7和Ubuntu(14.04或更高版本)上,最新的 MariaDB 包含在其官方源。在 Fedora 上,自19版本后 MariaDB 已经替代了 MySQL。如果你使用的是旧版本或 LTS 类型如 Ubuntu 13.10 或更早的,你仍然可以通过添加其官方仓库来安装 MariaDB。
|
||||
|
||||
[MariaDB 网站][2] 提供了一个在线工具帮助你依据你的 Linux 发行版中来添加 MariaDB 的官方仓库。此工具为 openSUSE, Arch Linux, Mageia, Fedora, CentOS, RedHat, Mint, Ubuntu, 和 Debian 提供了 MariaDB 的官方仓库.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
下面例子中,我们使用 Ubuntu 14.04 发行版和 CentOS 7 配置 MariaDB 库。
|
||||
|
||||
**Ubuntu 14.04**
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install software-properties-common
|
||||
$ sudo apt-key adv --recv-keys --keyserver hkp://keyserver.ubuntu.com:80 0xcbcb082a1bb943db
|
||||
$ sudo add-apt-repository 'deb http://mirror.mephi.ru/mariadb/repo/5.5/ubuntu trusty main'
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get update
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install mariadb-server
|
||||
|
||||
**CentOS 7**
|
||||
|
||||
以下为 MariaDB 创建一个自定义的 yum 仓库文件。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo vi /etc/yum.repos.d/MariaDB.repo
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
[mariadb]
|
||||
name = MariaDB
|
||||
baseurl = http://yum.mariadb.org/5.5/centos7-amd64
|
||||
gpgkey=https://yum.mariadb.org/RPM-GPG-KEY-MariaDB
|
||||
gpgcheck=1
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install MariaDB-server MariaDB-client
|
||||
|
||||
安装了所有必要的软件包后,你可能会被要求为 root 用户创建一个新密码。设置 root 的密码后,别忘了恢复备份的 my.cnf 文件。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo cp /opt/my.cnf /etc/mysql/
|
||||
|
||||
现在启动 MariaDB 服务。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo service mariadb start
|
||||
|
||||
或者:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo systemctl start mariadb
|
||||
|
||||
或:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo /etc/init.d/mariadb start
|
||||
|
||||
### 导入 MySQL 的数据库 ###
|
||||
|
||||
最后,我们将以前导出的数据库导入到 MariaDB 服务器中。
|
||||
|
||||
$ mysql -u root -p < backupdb.sql
|
||||
|
||||
输入你 MariaDB 的 root 密码,数据库导入过程将开始。导入过程完成后,将返回到命令提示符下。
|
||||
|
||||
要检查导入过程是否完全成功,请登录到 MariaDB 服务器,并查看一些样本来检查。
|
||||
|
||||
$ mysql -u root -p
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
MariaDB [(none)]> show databases;
|
||||
MariaDB [(none)]> use test01;
|
||||
MariaDB [test01]> select * from pet;
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 结论 ###
|
||||
|
||||
如你在本教程中看到的,MySQL-to-MariaDB 的迁移并不难。MariaDB 相比 MySQL 有很多新的功能,你应该知道的。至于配置方面,在我的测试情况下,我只是将我旧的 MySQL 配置文件(my.cnf)作为 MariaDB 的配置文件,导入过程完全没有出现任何问题。对于配置文件,我建议你在迁移之前请仔细阅读MariaDB 配置选项的文件,特别是如果你正在使用 MySQL 的特殊配置。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你正在运行更复杂的配置有海量的数据库和表,包括群集或主从复制,看一看 Mozilla IT 和 Operations 团队的 [更详细的指南][3] ,或者 [官方的 MariaDB 文档][4]。
|
||||
|
||||
### 故障排除 ###
|
||||
|
||||
1.在运行 mysqldump 命令备份数据库时出现以下错误。
|
||||
|
||||
$ mysqldump --all-databases --user=root --password --master-data > backupdb.sql
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
mysqldump: Error: Binlogging on server not active
|
||||
|
||||
通过使用 "--master-data",你要在导出的输出中包含二进制日志信息,这对于数据库的复制和恢复是有用的。但是,二进制日志未在 MySQL 服务器启用。要解决这个错误,修改 my.cnf 文件,并在 [mysqld] 部分添加下面的选项。
|
||||
|
||||
log-bin=mysql-bin
|
||||
|
||||
保存 my.cnf 文件,并重新启动 MySQL 服务:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo service mysql restart
|
||||
|
||||
或者:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo systemctl restart mysql
|
||||
|
||||
或:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo /etc/init.d/mysql restart
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/migrate-mysql-to-mariadb-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Kristophorus Hadiono][a]
|
||||
译者:[strugglingyouth](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[strugglingyouth](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/kristophorus
|
||||
[1]:https://mariadb.com/kb/en/mariadb/mariadb-vs-mysql-compatibility/
|
||||
[2]:https://downloads.mariadb.org/mariadb/repositories/#mirror=aasaam
|
||||
[3]:https://blog.mozilla.org/it/2013/12/16/upgrading-from-mysql-5-1-to-mariadb-5-5/
|
||||
[4]:https://mariadb.com/kb/en/mariadb/documentation/
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user