diff --git a/published/20200317 Create Stunning Pixel Art With Free and Open Source Editor Pixelorama.md b/published/20200317 Create Stunning Pixel Art With Free and Open Source Editor Pixelorama.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..7a267a672e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20200317 Create Stunning Pixel Art With Free and Open Source Editor Pixelorama.md
@@ -0,0 +1,105 @@
+[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
+[#]: translator: (geekpi)
+[#]: reviewer: (wxy)
+[#]: publisher: (wxy)
+[#]: url: (https://linux.cn/article-12173-1.html)
+[#]: subject: (Create Stunning Pixel Art With Free and Open Source Editor Pixelorama)
+[#]: via: (https://itsfoss.com/pixelorama/)
+[#]: author: (Abhishek Prakash https://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/)
+
+使用 Pixelorama 创建令人惊叹的像素艺术
+======
+
+> Pixelorama 是一个跨平台、自由开源的 2D 精灵编辑器。它在一个整洁的用户界面中提供了创建像素艺术所有必要工具。
+
+### Pixelorama:开源 Sprite 编辑器
+
+[Pixelorama][1] 是 [Orama 互动][2]公司的年轻游戏开发人员创建的一个工具。他们已经开发了一些 2D 游戏,其中一些使用了像素艺术。
+
+虽然 Orama 主要从事于游戏开发,但开发人员也创建实用工具,帮助他们(和其他人)创建这些游戏。
+
+自由开源的精灵编辑器 Pixelorama 就是这样一个实用工具。它构建在 [Godot 引擎][3]之上,非常适合创作像素艺术。
+
+![Pixelorama screenshot][4]
+
+你看到上面截图中的像素艺术了吗?它是使用 Pixelorama 创建的。这段视频展示了制作上述图片的时间推移视频。
+
+### Pixelorama 的功能
+
+以下是 Pixelorama 提供的主要功能:
+
+ * 多种工具,如铅笔、橡皮擦、填充桶、取色器等
+ * 多层系统,你可以根据需要添加、删除、上下移动、克隆和合并多个层
+ * 支持 Spritesheets
+ * 导入图像并在 Pixelorama 中编辑它们
+ * 带有 [Onion Skinning][5] 的动画时间线
+ * 自定义画笔
+ * 以 Pixelorama 的自定义文件格式 .pxo 保存并打开你的项目
+ * 水平和垂直镜像绘图
+ * 用于创建图样的磁贴模式
+ * 拆分屏幕模式和迷你画布预览
+ * 使用鼠标滚轮缩放
+ * 无限次撤消和重做
+ * 缩放、裁剪、翻转、旋转、颜色反转和去饱和图像
+ * 键盘快捷键
+ * 提供多种语言
+ * 支持 Linux、Windows 和 macOS
+
+### 在 Linux 上安装 Pixelorama
+
+Pixelorama 提供 Snap 应用,如果你使用的是 Ubuntu,那么可以在软件中心找到它。
+
+![Pixelorama is available in Ubuntu Software Center][6]
+
+或者,如果你在 [Linux 发行版上启用了 Snap 支持][7],那么可以使用此命令安装它:
+
+```
+sudo snap install pixelorama
+```
+
+如果你不想使用 Snap,不用担心。你可以从[他们的 GitHub 仓库][8]下载最新版本的 Pixelorama,[解压 zip 文件][9],你会看到一个可执行文件。授予此文件执行权限,并双击它运行应用。
+
+- [下载 Pixelorama][10]
+
+### 总结
+
+![Pixelorama Welcome Screen][11]
+
+在 Pixeloaram 的功能中,它说你可以导入图像并对其进行编辑。我想,这只是对某些类型的文件,因为当我尝试导入 PNG 或 JPEG 文件,程序崩溃了。
+
+然而,我可以像一个 3 岁的孩子那样随意涂鸦并制作像素艺术。我对艺术不是很感兴趣,但我认为这[对 Linux 上的数字艺术家是个有用的工具][12]。
+
+我喜欢这样的想法:尽管是游戏开发人员,但他们创建的工具,可以帮助其他游戏开发人员和艺术家。这就是开源的精神。
+
+如果你喜欢这个项目,并且会使用它,请考虑通过捐赠来支持他们。[It’s FOSS 捐赠了][13] 25 美元,以感谢他们的努力。
+
+- [向 Pixelorama 捐赠(主要开发者的个人 Paypal 账户)][14]
+
+你喜欢 Pixelorama 吗?你是否使用其他开源精灵编辑器?请随时在评论栏分享你的观点。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+via: https://itsfoss.com/pixelorama/
+
+作者:[Abhishek Prakash][a]
+选题:[lujun9972][b]
+译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]: https://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/
+[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
+[1]: https://www.orama-interactive.com/pixelorama
+[2]: https://www.orama-interactive.com/
+[3]: https://godotengine.org/
+[4]: https://i1.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/03/pixelorama-v6.jpg?ssl=1
+[5]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Onion_skinning
+[6]: https://i0.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/03/pixelorama-ubuntu-software-center.jpg?ssl=1
+[7]: https://itsfoss.com/install-snap-linux/
+[8]: https://github.com/Orama-Interactive/Pixelorama
+[9]: https://itsfoss.com/unzip-linux/
+[10]: https://github.com/Orama-Interactive/Pixelorama/releases
+[11]: https://i1.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/03/pixelorama.jpg?ssl=1
+[12]: https://itsfoss.com/best-linux-graphic-design-software/
+[13]: https://itsfoss.com/donations-foss/
+[14]: https://www.paypal.me/erevos
diff --git a/translated/tech/20200331 Rambox is an All-in-one Messenger for Linux.md b/published/20200331 Rambox is an All-in-one Messenger for Linux.md
similarity index 76%
rename from translated/tech/20200331 Rambox is an All-in-one Messenger for Linux.md
rename to published/20200331 Rambox is an All-in-one Messenger for Linux.md
index 28a57f2842..93a73f4a54 100644
--- a/translated/tech/20200331 Rambox is an All-in-one Messenger for Linux.md
+++ b/published/20200331 Rambox is an All-in-one Messenger for Linux.md
@@ -1,16 +1,16 @@
[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
[#]: translator: (geekpi)
-[#]: reviewer: ( )
-[#]: publisher: ( )
-[#]: url: ( )
+[#]: reviewer: (wxy)
+[#]: publisher: (wxy)
+[#]: url: (https://linux.cn/article-12171-1.html)
[#]: subject: (Rambox is an All-in-one Messenger for Linux)
[#]: via: (https://itsfoss.com/rambox/)
[#]: author: (Ankush Das https://itsfoss.com/author/ankush/)
-Rambox 是 Linux 中多合一的消息收发工具
+Rambox:Linux 中多合一的消息收发工具
======
-_**简介:Rambox 是一个多合一消息收发工具,允许你将多种服务(如 Discord、Slack、Facebook Messenger)和数百个此类服务结合在一起。**_
+> Rambox 是一个多合一消息收发工具,允许你将多种服务(如 Discord、Slack、Facebook Messenger)和数百个此类服务结合在一起。
### Rambox:在单个应用中添加多个消息服务
@@ -18,7 +18,7 @@ _**简介:Rambox 是一个多合一消息收发工具,允许你将多种服
Rambox 是通过安装单个应用管理多个通信服务的最佳方式之一。你可以在一个界面使用[多个消息服务][2],如 Facebook Messenger、Gmail chats、AOL、Discord、Google Duo、[Viber][3] 等。
-这样,你就不需要安装单独的应用或者在浏览器中保持打开。你可以使用主密码锁定 Rambox 应用。你还可以使用"请勿打扰"功能。
+这样,你就不需要安装单独的应用或者在浏览器中一直打开着。你可以使用主密码锁定 Rambox 应用。你还可以使用“请勿打扰”功能。
Rambox 提供可免费使用的[开源社区版][4]。付费专业版允许你访问 600 多个应用,而社区版则包含 99 多个应用。专业版本具有额外的功能,如主题、休眠、ad-block、拼写检查和高级支持。
@@ -44,24 +44,22 @@ Rambox 提供可免费使用的[开源社区版][4]。付费专业版允许你
* Ad-block (**专业版**)
* 休眠支持 (**专业版**)
* 主题支持(**专业版**)
- * 移动视图 (**专业版**)
+ * 移动设备视图 (**专业版**)
* 拼写检查 (**专业版**)
- * 工作时间 - 计划传入通知时间 (**专业版**)
- * 代理支持 (**专业版**)
-
-
+ * 工作时间 - 计划传入通知的时间 (**专业版**)
+ * 支持代理 (**专业版**)
除了我在这里列出的内容外,你还可以在 Rambox Pro 版本中找到更多功能。要了解有关它的更多信息,你可以参考[正式功能列表][6]。
-还值得注意的是,你不能有超过 3 个活跃并发设备连接。
+还值得注意的是,你不能超过 3 个活跃并发设备的连接。
### 在 Linux 上安装 Rambox
-你可以在[官方下载页][4]获取 **.AppImage** 文件来运行 Rambox。如果你好奇,你可以参考我们的指南,了解如何[在 Linux 上使用 AppImage 文件][7]。
+你可以在[官方下载页][4]获取 .AppImage 文件来运行 Rambox。如果你不清楚,你可以参考我们的指南,了解如何[在 Linux 上使用 AppImage 文件][7]。
-另外,你也可以从 [Snap 商店][8]获取它。此外,请查看其 [GitHub release][9] 部分的 **.deb / .rpm** 或其他包。
+另外,你也可以从 [Snap 商店][8]获取它。此外,请查看其 [GitHub release][9] 部分的 .deb / .rpm 或其他包。
-[Download Rambox Community Edition][4]
+- [下载 Rambox 社区版][4]
### 总结
@@ -69,7 +67,7 @@ Rambox 提供可免费使用的[开源社区版][4]。付费专业版允许你
还有一个类似的应用称为 [Franz][10],它也像 Rambox 部分开源、部分高级版。
-尽管像 Rambox 或 Franz 这样的解决方案非常有用,但它们并不总是资源友好,特别是如果你同时使用数十个服务。因此,请留意系统资源(如果你注意到对性能的影响)。
+尽管像 Rambox 或 Franz 这样的解决方案非常有用,但它们并不总是节约资源,特别是如果你同时使用数十个服务。因此,请留意系统资源(如果你注意到对性能的影响)。
除此之外,这是一个令人印象深刻的应用。你有试过了么?欢迎随时让我知道你的想法!
@@ -80,7 +78,7 @@ via: https://itsfoss.com/rambox/
作者:[Ankush Das][a]
选题:[lujun9972][b]
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/published/20190107 Different Ways To Update Linux Kernel For Ubuntu.md b/published/202004/20190107 Different Ways To Update Linux Kernel For Ubuntu.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20190107 Different Ways To Update Linux Kernel For Ubuntu.md
rename to published/202004/20190107 Different Ways To Update Linux Kernel For Ubuntu.md
diff --git a/published/20190116 Best Audio Editors For Linux.md b/published/202004/20190116 Best Audio Editors For Linux.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20190116 Best Audio Editors For Linux.md
rename to published/202004/20190116 Best Audio Editors For Linux.md
diff --git a/published/20190205 Installing Kali Linux on VirtualBox- Quickest - Safest Way.md b/published/202004/20190205 Installing Kali Linux on VirtualBox- Quickest - Safest Way.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20190205 Installing Kali Linux on VirtualBox- Quickest - Safest Way.md
rename to published/202004/20190205 Installing Kali Linux on VirtualBox- Quickest - Safest Way.md
diff --git a/published/20190429 10 moments that shaped Linux history.md b/published/202004/20190429 10 moments that shaped Linux history.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20190429 10 moments that shaped Linux history.md
rename to published/202004/20190429 10 moments that shaped Linux history.md
diff --git a/published/20190523 Run your blog on GitHub Pages with Python.md b/published/202004/20190523 Run your blog on GitHub Pages with Python.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20190523 Run your blog on GitHub Pages with Python.md
rename to published/202004/20190523 Run your blog on GitHub Pages with Python.md
diff --git a/published/20190605 What is GraphQL.md b/published/202004/20190605 What is GraphQL.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20190605 What is GraphQL.md
rename to published/202004/20190605 What is GraphQL.md
diff --git a/published/20190612 How to write a loop in Bash.md b/published/202004/20190612 How to write a loop in Bash.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20190612 How to write a loop in Bash.md
rename to published/202004/20190612 How to write a loop in Bash.md
diff --git a/published/20190612 Why use GraphQL.md b/published/202004/20190612 Why use GraphQL.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20190612 Why use GraphQL.md
rename to published/202004/20190612 Why use GraphQL.md
diff --git a/published/20190712 What is Silverblue.md b/published/202004/20190712 What is Silverblue.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20190712 What is Silverblue.md
rename to published/202004/20190712 What is Silverblue.md
diff --git a/published/20190814 9 open source cloud native projects to consider.md b/published/202004/20190814 9 open source cloud native projects to consider.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20190814 9 open source cloud native projects to consider.md
rename to published/202004/20190814 9 open source cloud native projects to consider.md
diff --git a/published/20190822 How the Linux desktop has grown.md b/published/202004/20190822 How the Linux desktop has grown.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20190822 How the Linux desktop has grown.md
rename to published/202004/20190822 How the Linux desktop has grown.md
diff --git a/published/20191014 How to make a Halloween lantern with Inkscape.md b/published/202004/20191014 How to make a Halloween lantern with Inkscape.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20191014 How to make a Halloween lantern with Inkscape.md
rename to published/202004/20191014 How to make a Halloween lantern with Inkscape.md
diff --git a/published/20191209 Use the Fluxbox Linux desktop as your window manager.md b/published/202004/20191209 Use the Fluxbox Linux desktop as your window manager.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20191209 Use the Fluxbox Linux desktop as your window manager.md
rename to published/202004/20191209 Use the Fluxbox Linux desktop as your window manager.md
diff --git a/published/20191216 Relive Linux history with the ROX desktop.md b/published/202004/20191216 Relive Linux history with the ROX desktop.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20191216 Relive Linux history with the ROX desktop.md
rename to published/202004/20191216 Relive Linux history with the ROX desktop.md
diff --git a/translated/tech/20191220 The Difference Between DNF and YUM, Why is Yum Replaced by DNF.md b/published/202004/20191220 The Difference Between DNF and YUM, Why is Yum Replaced by DNF.md
similarity index 84%
rename from translated/tech/20191220 The Difference Between DNF and YUM, Why is Yum Replaced by DNF.md
rename to published/202004/20191220 The Difference Between DNF and YUM, Why is Yum Replaced by DNF.md
index f73a3e180b..8521ab4291 100644
--- a/translated/tech/20191220 The Difference Between DNF and YUM, Why is Yum Replaced by DNF.md
+++ b/published/202004/20191220 The Difference Between DNF and YUM, Why is Yum Replaced by DNF.md
@@ -1,20 +1,22 @@
[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
[#]: translator: (wxy)
-[#]: reviewer: ( )
-[#]: publisher: ( )
-[#]: url: ( )
+[#]: reviewer: (wxy)
+[#]: publisher: (wxy)
+[#]: url: (https://linux.cn/article-12161-1.html)
[#]: subject: (The Difference Between DNF and YUM, Why is Yum Replaced by DNF?)
[#]: via: (https://www.2daygeek.com/comparison-difference-between-dnf-vs-yum/)
[#]: author: (Magesh Maruthamuthu https://www.2daygeek.com/author/magesh/)
-DNF 和 YUM 的区别,为什么 YUM 会被 DNF 取代?
+DNF 和 Yum 的区别,为什么 Yum 会被 DNF 取代?
======
由于 Yum 中许多长期存在的问题仍未得到解决,因此 [Yum 包管理器][1]已被 [DNF 包管理器][2]取代。这些问题包括性能差、内存占用过多、依赖解析速度变慢等。
-DNF 使用 `libsolv` 进行依赖解析,由 SUSE 开发和维护,旨在提高性能。DNF 主要是用 Python 编写的,它有自己的应对依赖解析的方法。
+DNF 使用 `libsolv` 进行依赖解析,由 SUSE 开发和维护,旨在提高性能。
-Yum 是 RPM 的前端工具,它管理依赖关系和资源库,然后使用 RPM 来安装、下载和删除包。它的 API 没有完整的文档,它的扩展系统只允许 Python 插件。
+Yum 主要是用 Python 编写的,它有自己的应对依赖解析的方法。它的 API 没有完整的文档,它的扩展系统只允许 Python 插件。
+
+Yum 是 RPM 的前端工具,它管理依赖关系和资源库,然后使用 RPM 来安装、下载和删除包。
为什么他们要建立一个新的工具,而不是修复现有的问题呢?
@@ -33,17 +35,17 @@ Ales Kozamblak 解释说,这个修复在技术上是不可行的,而且 Yum
2 | API 有完整的文档 | API 没有完整的文档
3 | 由 C、C++、Python 编写的 | 只用 Python 编写
4 | DNF 目前在 Fedora、RHEL 8、CentOS 8、OEL 8 和 Mageia 6/7 中使用 | YUM 目前在 RHEL 6/7、CentOS 6/7、OEL 6/7 中使用
-5 | DNf 支持各种扩展 | Yum 只支持基于 Python 的扩展
+5 | DNF 支持各种扩展 | Yum 只支持基于 Python 的扩展
6 | API 有良好的文档,因此很容易创建新的功能 | 因为 API 没有正确的文档化,所以创建新功能非常困难
7 | DNF 在同步存储库的元数据时,使用的内存较少 | 在同步存储库的元数据时,YUM 使用了过多的内存
8 | DNF 使用满足性算法来解决依赖关系解析(它是用字典的方法来存储和检索包和依赖信息)| 由于使用公开 API 的原因,Yum 依赖性解析变得迟钝
9 | 从内存使用量和版本库元数据的依赖性解析来看,性能都不错 | 总的来说,在很多因素的影响下,表现不佳
10 | DNF 更新:在 DNF 更新过程中,如果包中包含不相关的依赖,则不会更新 | YUM 将在没有验证的情况下更新软件包
-11 | 如果启用的存储库没有响应,DNF 将跳过它,并继续使用可用的存储库出来事务 | 如果有存储库不可用,YUM 会立即停止
+11 | 如果启用的存储库没有响应,DNF 将跳过它,并继续使用可用的存储库处理事务 | 如果有存储库不可用,YUM 会立即停止
12 | `dnf update` 和 `dnf upgrade` 是等价的 | 在 Yum 中则不同
13 | 安装包的依赖关系不更新 | Yum 为这种行为提供了一个选项
14 | 清理删除的包:当删除一个包时,DNF 会自动删除任何没有被用户明确安装的依赖包 | Yum 不会这样做
-15 | 存储库缓存更新计划:默认情况下,系统启动后 10 分钟后,DNF 每小时检查一次对配置的存储库的更新。这个动作由系统定时器单元 `/usr/lib/systemd/system/system/dnf-makecache.timer` 控制 | Yum 也会这样做
+15 | 存储库缓存更新计划:默认情况下,系统启动后 10 分钟后,DNF 每小时会对配置的存储库检查一次更新。这个动作由系统定时器单元 `dnf-makecache.timer` 控制 | Yum 也会这样做
16 | 内核包不受 DNF 保护。不像 Yum,你可以删除所有的内核包,包括运行中的内核包 | Yum 不允许你删除运行中的内核
17 | libsolv:用于解包和读取资源库。hawkey: 为 libsolv 提供简化的 C 和 Python API 库。librepo: 提供 C 和 Python(类似 libcURL)API 的库,用于下载 Linux 存储库元数据和软件包。libcomps: 是 yum.comps 库的替代品。它是用纯 C 语言编写的库,有 Python 2 和 Python 3 的绑定。| Yum 不使用单独的库来执行这些功能
18 | DNF 包含 29000 行代码 | Yum 包含 56000 行代码
@@ -56,7 +58,7 @@ via: https://www.2daygeek.com/comparison-difference-between-dnf-vs-yum/
作者:[Magesh Maruthamuthu][a]
选题:[lujun9972][b]
译者:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/published/20191224 Why your Python code should be flat and sparse.md b/published/202004/20191224 Why your Python code should be flat and sparse.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20191224 Why your Python code should be flat and sparse.md
rename to published/202004/20191224 Why your Python code should be flat and sparse.md
diff --git a/published/20200211 Navigating man pages in Linux.md b/published/202004/20200211 Navigating man pages in Linux.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20200211 Navigating man pages in Linux.md
rename to published/202004/20200211 Navigating man pages in Linux.md
diff --git a/published/20200213 Manage complex Git workspaces with Great Teeming Workspaces.md b/published/202004/20200213 Manage complex Git workspaces with Great Teeming Workspaces.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20200213 Manage complex Git workspaces with Great Teeming Workspaces.md
rename to published/202004/20200213 Manage complex Git workspaces with Great Teeming Workspaces.md
diff --git a/published/20200228 Getting started with Linux firewalls.md b/published/202004/20200228 Getting started with Linux firewalls.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20200228 Getting started with Linux firewalls.md
rename to published/202004/20200228 Getting started with Linux firewalls.md
diff --git a/published/20200309 Fish - A Friendly Interactive Shell.md b/published/202004/20200309 Fish - A Friendly Interactive Shell.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20200309 Fish - A Friendly Interactive Shell.md
rename to published/202004/20200309 Fish - A Friendly Interactive Shell.md
diff --git a/published/20200311 Directing Kubernetes traffic with Traefik.md b/published/202004/20200311 Directing Kubernetes traffic with Traefik.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20200311 Directing Kubernetes traffic with Traefik.md
rename to published/202004/20200311 Directing Kubernetes traffic with Traefik.md
diff --git a/published/20200311 What you need to know about variables in Emacs.md b/published/202004/20200311 What you need to know about variables in Emacs.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20200311 What you need to know about variables in Emacs.md
rename to published/202004/20200311 What you need to know about variables in Emacs.md
diff --git a/published/20200312 Make SSL certs easy with k3s.md b/published/202004/20200312 Make SSL certs easy with k3s.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20200312 Make SSL certs easy with k3s.md
rename to published/202004/20200312 Make SSL certs easy with k3s.md
diff --git a/published/20200313 What is the internet backbone and how it works.md b/published/202004/20200313 What is the internet backbone and how it works.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20200313 What is the internet backbone and how it works.md
rename to published/202004/20200313 What is the internet backbone and how it works.md
diff --git a/published/20200320 Build a private social network with a Raspberry Pi.md b/published/202004/20200320 Build a private social network with a Raspberry Pi.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20200320 Build a private social network with a Raspberry Pi.md
rename to published/202004/20200320 Build a private social network with a Raspberry Pi.md
diff --git a/published/20200320 Control the firewall at the command line.md b/published/202004/20200320 Control the firewall at the command line.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20200320 Control the firewall at the command line.md
rename to published/202004/20200320 Control the firewall at the command line.md
diff --git a/published/20200320 How to Check Password Expiration Date for All Users on Linux.md b/published/202004/20200320 How to Check Password Expiration Date for All Users on Linux.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20200320 How to Check Password Expiration Date for All Users on Linux.md
rename to published/202004/20200320 How to Check Password Expiration Date for All Users on Linux.md
diff --git a/published/20200323 Don-t love diff- Use Meld instead.md b/published/202004/20200323 Don-t love diff- Use Meld instead.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20200323 Don-t love diff- Use Meld instead.md
rename to published/202004/20200323 Don-t love diff- Use Meld instead.md
diff --git a/published/20200325 Linux firewall basics with ufw.md b/published/202004/20200325 Linux firewall basics with ufw.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20200325 Linux firewall basics with ufw.md
rename to published/202004/20200325 Linux firewall basics with ufw.md
diff --git a/published/20200326 3 open source tools for sticking to a budget.md b/published/202004/20200326 3 open source tools for sticking to a budget.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20200326 3 open source tools for sticking to a budget.md
rename to published/202004/20200326 3 open source tools for sticking to a budget.md
diff --git a/published/20200327 Build a private chat server with a Raspberry Pi and Rocket.Chat.md b/published/202004/20200327 Build a private chat server with a Raspberry Pi and Rocket.Chat.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20200327 Build a private chat server with a Raspberry Pi and Rocket.Chat.md
rename to published/202004/20200327 Build a private chat server with a Raspberry Pi and Rocket.Chat.md
diff --git a/published/20200329 How to install Microsoft TrueType Fonts on Ubuntu-based Distributions.md b/published/202004/20200329 How to install Microsoft TrueType Fonts on Ubuntu-based Distributions.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20200329 How to install Microsoft TrueType Fonts on Ubuntu-based Distributions.md
rename to published/202004/20200329 How to install Microsoft TrueType Fonts on Ubuntu-based Distributions.md
diff --git a/published/20200329 Oracle Announces Java 14- How to Install it on Ubuntu Linux.md b/published/202004/20200329 Oracle Announces Java 14- How to Install it on Ubuntu Linux.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20200329 Oracle Announces Java 14- How to Install it on Ubuntu Linux.md
rename to published/202004/20200329 Oracle Announces Java 14- How to Install it on Ubuntu Linux.md
diff --git a/published/20200329 The Keyring Concept in Ubuntu- What is It and How to Use it.md b/published/202004/20200329 The Keyring Concept in Ubuntu- What is It and How to Use it.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20200329 The Keyring Concept in Ubuntu- What is It and How to Use it.md
rename to published/202004/20200329 The Keyring Concept in Ubuntu- What is It and How to Use it.md
diff --git a/published/20200329 Turn Your Regular TV into a Smart TV With KDE Plasma Bigscreen.md b/published/202004/20200329 Turn Your Regular TV into a Smart TV With KDE Plasma Bigscreen.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20200329 Turn Your Regular TV into a Smart TV With KDE Plasma Bigscreen.md
rename to published/202004/20200329 Turn Your Regular TV into a Smart TV With KDE Plasma Bigscreen.md
diff --git a/published/20200330 Using data from spreadsheets in Fedora with Python.md b/published/202004/20200330 Using data from spreadsheets in Fedora with Python.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20200330 Using data from spreadsheets in Fedora with Python.md
rename to published/202004/20200330 Using data from spreadsheets in Fedora with Python.md
diff --git a/published/20200331 5 ways to level up your Vim skills.md b/published/202004/20200331 5 ways to level up your Vim skills.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20200331 5 ways to level up your Vim skills.md
rename to published/202004/20200331 5 ways to level up your Vim skills.md
diff --git a/published/20200401 How to Find Which Graphics Card do You Have in Linux.md b/published/202004/20200401 How to Find Which Graphics Card do You Have in Linux.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20200401 How to Find Which Graphics Card do You Have in Linux.md
rename to published/202004/20200401 How to Find Which Graphics Card do You Have in Linux.md
diff --git a/published/20200401 IEEE Standards Association Launches an Open Source Collaboration Platform.md b/published/202004/20200401 IEEE Standards Association Launches an Open Source Collaboration Platform.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20200401 IEEE Standards Association Launches an Open Source Collaboration Platform.md
rename to published/202004/20200401 IEEE Standards Association Launches an Open Source Collaboration Platform.md
diff --git a/published/20200402 How to Upgrade to Ubuntu 20.04 Beta from 18.04 - 19.10.md b/published/202004/20200402 How to Upgrade to Ubuntu 20.04 Beta from 18.04 - 19.10.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20200402 How to Upgrade to Ubuntu 20.04 Beta from 18.04 - 19.10.md
rename to published/202004/20200402 How to Upgrade to Ubuntu 20.04 Beta from 18.04 - 19.10.md
diff --git a/published/20200403 Scheduling tasks on Linux using the at command.md b/published/202004/20200403 Scheduling tasks on Linux using the at command.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20200403 Scheduling tasks on Linux using the at command.md
rename to published/202004/20200403 Scheduling tasks on Linux using the at command.md
diff --git a/published/20200403 Take back your dotfiles with Chezmoi.md b/published/202004/20200403 Take back your dotfiles with Chezmoi.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20200403 Take back your dotfiles with Chezmoi.md
rename to published/202004/20200403 Take back your dotfiles with Chezmoi.md
diff --git a/published/20200404 Bodhi Linux 5.1 Review- Slightly Different Lightweight Linux.md b/published/202004/20200404 Bodhi Linux 5.1 Review- Slightly Different Lightweight Linux.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20200404 Bodhi Linux 5.1 Review- Slightly Different Lightweight Linux.md
rename to published/202004/20200404 Bodhi Linux 5.1 Review- Slightly Different Lightweight Linux.md
diff --git a/published/20200404 What is Arch User Repository (AUR)- How to Use AUR on Arch and Manjaro Linux.md b/published/202004/20200404 What is Arch User Repository (AUR)- How to Use AUR on Arch and Manjaro Linux.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20200404 What is Arch User Repository (AUR)- How to Use AUR on Arch and Manjaro Linux.md
rename to published/202004/20200404 What is Arch User Repository (AUR)- How to Use AUR on Arch and Manjaro Linux.md
diff --git a/published/20200407 15 years of Git- How to get started or learn something new.md b/published/202004/20200407 15 years of Git- How to get started or learn something new.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20200407 15 years of Git- How to get started or learn something new.md
rename to published/202004/20200407 15 years of Git- How to get started or learn something new.md
diff --git a/published/20200407 Bitwarden- A Free - Open Source Password Manager.md b/published/202004/20200407 Bitwarden- A Free - Open Source Password Manager.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20200407 Bitwarden- A Free - Open Source Password Manager.md
rename to published/202004/20200407 Bitwarden- A Free - Open Source Password Manager.md
diff --git a/published/20200407 New Linux Distribution UbuntuDDE Brings The Beautiful Deepin Desktop to Ubuntu.md b/published/202004/20200407 New Linux Distribution UbuntuDDE Brings The Beautiful Deepin Desktop to Ubuntu.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20200407 New Linux Distribution UbuntuDDE Brings The Beautiful Deepin Desktop to Ubuntu.md
rename to published/202004/20200407 New Linux Distribution UbuntuDDE Brings The Beautiful Deepin Desktop to Ubuntu.md
diff --git a/published/20200408 Create web tutorials with Reveal.js and Git.md b/published/202004/20200408 Create web tutorials with Reveal.js and Git.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20200408 Create web tutorials with Reveal.js and Git.md
rename to published/202004/20200408 Create web tutorials with Reveal.js and Git.md
diff --git a/published/20200408 How to Create Templates in LibreOffice to Save Time and Increase Productivity.md b/published/202004/20200408 How to Create Templates in LibreOffice to Save Time and Increase Productivity.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20200408 How to Create Templates in LibreOffice to Save Time and Increase Productivity.md
rename to published/202004/20200408 How to Create Templates in LibreOffice to Save Time and Increase Productivity.md
diff --git a/published/20200409 Here-s How to Find Out Which Desktop Environment You are Using.md b/published/202004/20200409 Here-s How to Find Out Which Desktop Environment You are Using.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20200409 Here-s How to Find Out Which Desktop Environment You are Using.md
rename to published/202004/20200409 Here-s How to Find Out Which Desktop Environment You are Using.md
diff --git a/published/20200410 How I-m using AI to translate -wash your hands- in 500 languages.md b/published/202004/20200410 How I-m using AI to translate -wash your hands- in 500 languages.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20200410 How I-m using AI to translate -wash your hands- in 500 languages.md
rename to published/202004/20200410 How I-m using AI to translate -wash your hands- in 500 languages.md
diff --git a/published/20200410 How to Go Full Dark Mode in Ubuntu 20.04.md b/published/202004/20200410 How to Go Full Dark Mode in Ubuntu 20.04.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20200410 How to Go Full Dark Mode in Ubuntu 20.04.md
rename to published/202004/20200410 How to Go Full Dark Mode in Ubuntu 20.04.md
diff --git a/published/20200413 A handy utility for creating Raspberry Pi SD card images.md b/published/202004/20200413 A handy utility for creating Raspberry Pi SD card images.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20200413 A handy utility for creating Raspberry Pi SD card images.md
rename to published/202004/20200413 A handy utility for creating Raspberry Pi SD card images.md
diff --git a/published/20200413 How to Add Multiple Time Zones in Ubuntu.md b/published/202004/20200413 How to Add Multiple Time Zones in Ubuntu.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20200413 How to Add Multiple Time Zones in Ubuntu.md
rename to published/202004/20200413 How to Add Multiple Time Zones in Ubuntu.md
diff --git a/published/20200413 How to install Python on Linux.md b/published/202004/20200413 How to install Python on Linux.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20200413 How to install Python on Linux.md
rename to published/202004/20200413 How to install Python on Linux.md
diff --git a/published/20200415 How to Open Files and Folders as Administrator in Nautilus File Manager in Linux.md b/published/202004/20200415 How to Open Files and Folders as Administrator in Nautilus File Manager in Linux.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20200415 How to Open Files and Folders as Administrator in Nautilus File Manager in Linux.md
rename to published/202004/20200415 How to Open Files and Folders as Administrator in Nautilus File Manager in Linux.md
diff --git a/published/20200416 How to package Python applications for Linux.md b/published/202004/20200416 How to package Python applications for Linux.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20200416 How to package Python applications for Linux.md
rename to published/202004/20200416 How to package Python applications for Linux.md
diff --git a/published/20200417 12 Linux Commands to Have Some Fun in the Terminal.md b/published/202004/20200417 12 Linux Commands to Have Some Fun in the Terminal.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20200417 12 Linux Commands to Have Some Fun in the Terminal.md
rename to published/202004/20200417 12 Linux Commands to Have Some Fun in the Terminal.md
diff --git a/published/20200418 Ethernet consortium announces completion of 800GbE spec.md b/published/202004/20200418 Ethernet consortium announces completion of 800GbE spec.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20200418 Ethernet consortium announces completion of 800GbE spec.md
rename to published/202004/20200418 Ethernet consortium announces completion of 800GbE spec.md
diff --git a/published/20200421 MystiQ- A Free and Open Source Audio-Video Converter.md b/published/202004/20200421 MystiQ- A Free and Open Source Audio-Video Converter.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20200421 MystiQ- A Free and Open Source Audio-Video Converter.md
rename to published/202004/20200421 MystiQ- A Free and Open Source Audio-Video Converter.md
diff --git a/translated/tech/20200422 How to Check the Available Network Interfaces, Associated IP Addresses, MAC Addresses, and Interface Speed on Linux.md b/published/202004/20200422 How to Check the Available Network Interfaces, Associated IP Addresses, MAC Addresses, and Interface Speed on Linux.md
similarity index 60%
rename from translated/tech/20200422 How to Check the Available Network Interfaces, Associated IP Addresses, MAC Addresses, and Interface Speed on Linux.md
rename to published/202004/20200422 How to Check the Available Network Interfaces, Associated IP Addresses, MAC Addresses, and Interface Speed on Linux.md
index e586660e0c..8464da643e 100644
--- a/translated/tech/20200422 How to Check the Available Network Interfaces, Associated IP Addresses, MAC Addresses, and Interface Speed on Linux.md
+++ b/published/202004/20200422 How to Check the Available Network Interfaces, Associated IP Addresses, MAC Addresses, and Interface Speed on Linux.md
@@ -1,34 +1,30 @@
[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
[#]: translator: (geekpi)
-[#]: reviewer: ( )
-[#]: publisher: ( )
-[#]: url: ( )
+[#]: reviewer: (wxy)
+[#]: publisher: (wxy)
+[#]: url: (https://linux.cn/article-12165-1.html)
[#]: subject: (How to Check the Available Network Interfaces, Associated IP Addresses, MAC Addresses, and Interface Speed on Linux)
[#]: via: (https://www.2daygeek.com/linux-unix-check-network-interfaces-names-nic-speed-ip-mac-address/)
[#]: author: (Magesh Maruthamuthu https://www.2daygeek.com/author/magesh/)
-如何在 Linux 上检查可用的网络接口、关联的 IP 地址、MAC 地址和接口速度
+如何在 Linux 上检查网卡信息
======
-默认在设置服务器时,你将配置主网络接口。
+
-这是每个人所做的构建工作的一部分。
+默认情况下,在设置服务器时你会配置主网络接口。这是每个人所做的构建工作的一部分。有时出于各种原因,你可能需要配置额外的网络接口。
-有时出于各种原因,你可能需要配置额外的网络接口。
+这可以是通过网络绑定/协作来提供高可用性,也可以是用于应用需求或备份的单独接口。
-这可以是网络绑定/团队合作或高可用性,也可以是用于应用需求或备份的单独接口。
+为此,你需要知道计算机有多少接口以及它们的速度来配置它们。
-为此,你需要知道计算机有多少接口以及它们的配置速度。
-
-有许多命令可检查可用的网络接口,但是我们仅使用 IP 命令。
-
-稍后,我们将使用所有这些工具编写单独的文章。
+有许多命令可检查可用的网络接口,但是我们仅使用 `ip` 命令。以后,我们会另外写一篇文章来全部介绍这些工具。
在本教程中,我们将向你显示可用网络网卡(NIC)信息,例如接口名称、关联的 IP 地址、MAC 地址和接口速度。
-### 什么是 IP 命令
+### 什么是 ip 命令
-**[IP 命令][1]**类似于 ifconfig, 用于分配静态 IP 地址、路由和默认网关等。
+[ip 命令][1] 类似于 `ifconfig`, 用于分配静态 IP 地址、路由和默认网关等。
```
# ip a
@@ -47,15 +43,15 @@
### 什么是 ethtool 命令
-ethtool 用于查询或控制网络驱动或硬件设置。
+`ethtool` 用于查询或控制网络驱动或硬件设置。
```
# ethtool eth0
```
-### 1)如何在 Linux 上使用 IP 命令检查可用的网络接口
+### 1)如何在 Linux 上使用 ip 命令检查可用的网络接口
-在不带任何参数的情况下运行 IP 命令时,它会提供大量信息,但是,如果仅需要可用的网络接口,请使用以下定制的 IP 命令。
+在不带任何参数的情况下运行 `ip` 命令时,它会提供大量信息,但是,如果仅需要可用的网络接口,请使用以下定制的 `ip` 命令。
```
# ip a |awk '/state UP/{print $2}'
@@ -64,13 +60,13 @@ eth0:
eth1:
```
-### 2)如何在 Linux 上使用 IP 命令检查网络接口的 IP 地址
+### 2)如何在 Linux 上使用 ip 命令检查网络接口的 IP 地址
-如果只想查看 IP 地址分配给了哪个接口,请使用以下定制的 IP 命令。
+如果只想查看 IP 地址分配给了哪个接口,请使用以下定制的 `ip` 命令。
```
# ip -o a show | cut -d ' ' -f 2,7
-or
+或
ip a |grep -i inet | awk '{print $7, $2}'
lo 127.0.0.1/8
@@ -78,18 +74,18 @@ lo 127.0.0.1/8
192.168.1.102/24
```
-### 3)如何在 Linux 上使用 IP 命令检查网卡的 MAC 地址
+### 3)如何在 Linux 上使用 ip 命令检查网卡的 MAC 地址
如果只想查看网络接口名称和相应的 MAC 地址,请使用以下格式。
-检查特定的网络接口的 MAC 地址。
+检查特定的网络接口的 MAC 地址:
```
# ip link show dev eth0 |awk '/link/{print $2}'
00:00:00:55:43:5c
```
-检查所有网络接口的 MAC 地址。
+检查所有网络接口的 MAC 地址,创建该脚本:
```
# vi /opt/scripts/mac-addresses.sh
@@ -97,12 +93,12 @@ lo 127.0.0.1/8
#!/bin/sh
ip a |awk '/state UP/{print $2}' | sed 's/://' | while read output;
do
-echo $output:
-ethtool -P $output
+ echo $output:
+ ethtool -P $output
done
```
-运行下面的 shell 脚本获取多个网络接口的 MAC 地址。
+运行该脚本获取多个网络接口的 MAC 地址:
```
# sh /opt/scripts/mac-addresses.sh
@@ -115,9 +111,9 @@ Permanent address: 00:00:00:55:43:5d
### 4)如何在 Linux 上使用 ethtool 命令检查网络接口速度
-如果要在 Linux 上检查网络接口速度,请使用 ethtool 命令。
+如果要在 Linux 上检查网络接口速度,请使用 `ethtool` 命令。
-检查特定网络接口的速度。
+检查特定网络接口的速度:
```
# ethtool eth0 |grep "Speed:"
@@ -125,7 +121,7 @@ Permanent address: 00:00:00:55:43:5d
Speed: 10000Mb/s
```
-检查所有网络接口速度。
+检查所有网络接口速度,创建该脚本:
```
# vi /opt/scripts/port-speed.sh
@@ -133,12 +129,12 @@ Speed: 10000Mb/s
#!/bin/sh
ip a |awk '/state UP/{print $2}' | sed 's/://' | while read output;
do
-echo $output:
-ethtool $output |grep "Speed:"
+ echo $output:
+ ethtool $output |grep "Speed:"
done
```
-运行以下 shell 脚本获取多个网络接口速度。
+运行该脚本获取多个网络接口速度:
```
# sh /opt/scripts/port-speed.sh
@@ -151,7 +147,7 @@ Speed: 10000Mb/s
### 5)验证网卡信息的 Shell 脚本
-通过此 **[shell 脚本][2]**,你可以收集上述所有信息,例如网络接口名称、网络接口的 IP 地址,网络接口的 MAC 地址以及网络接口的速度。
+通过此 shell 脚本你可以收集上述所有信息,例如网络接口名称、网络接口的 IP 地址,网络接口的 MAC 地址以及网络接口的速度。创建该脚本:
```
# vi /opt/scripts/nic-info.sh
@@ -161,14 +157,14 @@ hostname
echo "-------------"
for iname in $(ip a |awk '/state UP/{print $2}')
do
-echo "$iname"
-ip a | grep -A2 $iname | awk '/inet/{print $2}'
-ip a | grep -A2 $iname | awk '/link/{print $2}'
-ethtool $iname |grep "Speed:"
+ echo "$iname"
+ ip a | grep -A2 $iname | awk '/inet/{print $2}'
+ ip a | grep -A2 $iname | awk '/link/{print $2}'
+ ethtool $iname |grep "Speed:"
done
```
-运行以下 shell 脚本检查网卡信息。
+运行该脚本检查网卡信息:
```
# sh /opt/scripts/nic-info.sh
@@ -192,7 +188,7 @@ via: https://www.2daygeek.com/linux-unix-check-network-interfaces-names-nic-spee
作者:[Magesh Maruthamuthu][a]
选题:[lujun9972][b]
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/published/20200422 Things You Should Know About Ubuntu 20.04.md b/published/202004/20200422 Things You Should Know About Ubuntu 20.04.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20200422 Things You Should Know About Ubuntu 20.04.md
rename to published/202004/20200422 Things You Should Know About Ubuntu 20.04.md
diff --git a/published/20200424 Ubuntu 20.04 LTS Released. Download Now.md b/published/202004/20200424 Ubuntu 20.04 LTS Released. Download Now.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20200424 Ubuntu 20.04 LTS Released. Download Now.md
rename to published/202004/20200424 Ubuntu 20.04 LTS Released. Download Now.md
diff --git a/published/20200424 What you need to know about open source ad blockers.md b/published/202004/20200424 What you need to know about open source ad blockers.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20200424 What you need to know about open source ad blockers.md
rename to published/202004/20200424 What you need to know about open source ad blockers.md
diff --git a/translated/tech/20200425 What Happened to IPv5- Why there is IPv4, IPv6 but no IPv5.md b/published/202004/20200425 What Happened to IPv5- Why there is IPv4, IPv6 but no IPv5.md
similarity index 60%
rename from translated/tech/20200425 What Happened to IPv5- Why there is IPv4, IPv6 but no IPv5.md
rename to published/202004/20200425 What Happened to IPv5- Why there is IPv4, IPv6 but no IPv5.md
index 71bfe2137a..3a8ab6b8bd 100644
--- a/translated/tech/20200425 What Happened to IPv5- Why there is IPv4, IPv6 but no IPv5.md
+++ b/published/202004/20200425 What Happened to IPv5- Why there is IPv4, IPv6 but no IPv5.md
@@ -1,8 +1,8 @@
[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
[#]: translator: (geekpi)
-[#]: reviewer: ( )
-[#]: publisher: ( )
-[#]: url: ( )
+[#]: reviewer: (wxy)
+[#]: publisher: (wxy)
+[#]: url: (https://linux.cn/article-12168-1.html)
[#]: subject: (What Happened to IPv5? Why there is IPv4, IPv6 but no IPv5?)
[#]: via: (https://itsfoss.com/what-happened-to-ipv5/)
[#]: author: (John Paul https://itsfoss.com/author/john/)
@@ -20,19 +20,19 @@ IPv5 发生了什么?为什么有 IPv4、IPv6 但没有 IPv5?
![ARPA Logical Map in 1977 | Image courtesy: Wikipedia][1]
-在 1960 年代后期,美国国防部的[高级研究计划局][2] (ARPA) 发起了一个[项目][3]来连接全国的计算机。最初的目标是创建一个由全国 ARPA 资助的所有计算机组成的网络系统。
+在 1960 年代后期,美国国防部的[高级研究计划局][2](DARPA)发起了一个[项目][3]来连接全国的计算机。最初的目标是创建一个由全国 ARPA 资助的所有计算机组成的网络系统。
-由于这是第一次将如此规模的网络整合在一起,因此他们也在不断发展自己的技术和硬件。他们的第一件工作是名为[传输控制协议][4] (TCP) 的互联网协议 (IP)。该协议“可靠、有序、并会对通过 IP 网络传输的八进制(字节)流错误检测”。基本上,它确保数据安全到达。
+由于这是第一次将如此规模的网络整合在一起,因此他们也在不断发展自己的技术和硬件。他们首先做的工作之一就是开发名为[传输控制协议][4](TCP)的互联网协议(IP)。该协议“可靠、有序,并会对运行于通过 IP 网络传输的主机上的应用的八进制(字节)流通讯进行错误检测”。简单来说,它可以确保数据安全到达。
-最初,TCP 被设计为[“主机级别的端到端协议以及打包和路由协议”][5]。但是,他们意识到他们需要拆分协议以使其更易于管理。于是决定由 IP 处理打包和路由。
+最初,TCP 被设计为[“主机级别的端到端协议以及封装和路由协议”][5]。但是,他们意识到他们需要拆分协议以使其更易于管理。于是决定由 IP 协议处理封装和路由。
那时,TCP 已经经历了三个版本,因此新协议被称为 IPv4。
### IPv5 的诞生
-IPv5 以不同的名称开始使用:互联网流协议(或 ST)。它是[由 Apple、NeXT 和 Sun Microsystems][6] 创建用于实验流式传输语音和视频。
+IPv5 开始时有个不同的名字:互联网流协议(ST)。它是[由 Apple、NeXT 和 Sun Microsystems][6] 为试验流式语音和视频而创建的。
-该新协议能够“在保持通信的同时在特定频率上传输数据包”。
+该新协议能够“在保持通信的同时,以特定频率传输数据包”。
### 那么 IPv5 发生了什么?
@@ -40,15 +40,15 @@ IPv5 以不同的名称开始使用:互联网流协议(或 ST)。它是[
IPv5 从未被接受为正式的互联网协议。这主要是由于 32 位限制。
-IPV5 使用与 IPv4 相同的寻址系统。每个地址由 0 到 255 之间的四组数字组成。这将可能的地址数量限制为 [43 亿][6]。
+IPV5 使用与 IPv4 相同的寻址系统。每个地址由 0 到 255 之间的四组数字组成。这将可能的地址数量限制为 [43 亿][6]个。
-在 1970 年代初,这似乎比全世界所需要的还要多。但是,互联网的爆炸性增长证明了这一想法是错误的。2011年,世界正式耗尽了 IPv4 地址。
+在 1970 年代初,这似乎比全世界所需要的还要多。但是,互联网的爆炸性增长证明了这一想法是错误的。2011 年,世界上的IPv4地址正式用完了。
-在 1990 年代,一个新项目开始致力于下一代互联网协议 (IPng)。这导致了 128 位的 IPv6。IPv6 地址包含 [“8 组 4 字符的十六进制数字”][6],它可以包含从 0 到 9 的数字和从 A 到 F 的字母。与 IPv4 不同,IPv6 拥有数万亿个可能的地址,因此我们应该能安全一阵子。
+在 1990 年代,一个新项目开始致力于研究下一代互联网协议(IPng)。这形成了 128 位的 IPv6。IPv6 地址包含 [“8 组 4 字符的十六进制数字”][6],它可以包含从 0 到 9 的数字和从 A 到 F 的字母。与 IPv4 不同,IPv6 拥有数万亿个可能的地址,因此我们应该能安全一阵子。
-同时,IPv5 奠定了 VoIP 的基础,而该技术已被我们用于当今世界范围内的通信。**因此,我想往小了说,你可以说 IPv5 仍然可以保留到了今天**。
+同时,IPv5 奠定了 VoIP 的基础,而该技术已被我们用于当今世界范围内的通信。**因此,我想在某种程度上,你可以说 IPv5 仍然可以保留到了今天**。
-希望你喜欢有关互联网历史的轶事。你可以阅读其他[关于 Linux 和技术的琐事文章] [8]。
+希望你喜欢有关互联网历史的轶事。你可以阅读其他[关于 Linux 和技术的琐事文章][8]。
如果你觉得这篇文章有趣,请花一点时间在社交媒体、Hacker News 或 [Reddit][9] 上分享它。
@@ -59,7 +59,7 @@ via: https://itsfoss.com/what-happened-to-ipv5/
作者:[John Paul][a]
选题:[lujun9972][b]
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/published/202004/20200428 Fedora 32 is officially here.md b/published/202004/20200428 Fedora 32 is officially here.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..acad6862f5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/202004/20200428 Fedora 32 is officially here.md
@@ -0,0 +1,77 @@
+[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
+[#]: translator: (wxy)
+[#]: reviewer: (wxy)
+[#]: publisher: (wxy)
+[#]: url: (https://linux.cn/article-12164-1.html)
+[#]: subject: (Fedora 32 is officially here!)
+[#]: via: (https://fedoramagazine.org/announcing-fedora-32/)
+[#]: author: (Matthew Miller https://fedoramagazine.org/author/mattdm/)
+
+Fedora 32 正式发布!
+======
+
+![][1]
+
+它来了! 我们很荣幸地宣布 Fedora 32 的发布。感谢成千上万的 Fedora 社区成员和贡献者的辛勤工作,我们又一次准时发布了。
+
+如果你只想马上就能拿到它,请马上访问 。更多详情,请继续阅读本文。
+
+### Fedora 的全部变种
+
+Fedora Editions 是针对特定的“展示”用途输出的。
+
+Fedora Workstation 专注于桌面系统。特别是,它面向的是那些希望获得“可以工作的” Linux 操作系统体验的软件开发者。这个版本采用了 [GNOME 3.36][2],一如既往地有很多很棒的改进。我最喜欢的是新的锁屏!
+
+Fedora Server 以一种易于部署的方式为系统管理员带来了新锐的开源服务器软件。对于边缘计算用例,[Fedora IoT][3] 为 IoT 生态系统提供了坚实的基础。
+
+Fedora CoreOS 是一个新兴的 Fedora Edition。它是一个自动更新的、最小化的操作系统,用于安全地大规模运行容器化工作负载。它提供了几个[更新流][4],遵循大约每两周一次的自动更新。目前,next 流是基于 Fedora 32,后续还有 testing 流和 stable 流。你可以从[下载页面][5]中找到关于按 next 流发布的工件的信息,并在 [Fedora CoreOS 文档][6]中找到关于如何使用这些工件的信息。
+
+当然,我们制作的不仅仅是 Editions。[Fedora Spins][7] 和[实验室][8]针对的是不同的受众和用例,包括[Fedora 天文学实验室][9],它为业余和专业的天文学家带来了完整的开源工具链,还有像 [KDE Plasma][10] 和 [Xfce][11] 这样的桌面环境。Fedora 32 中新增的 [计算神经科学实验室][12] 是由我们的神经科学特别兴趣小组开发的,它可以实现计算神经科学。
+
+还有,别忘了我们的备用架构,[ARM AArch64、Power 和 S390x][13]。特别值得一提的是,我们改进了对 Rockchip 系统级芯片的支持,包括 Rock960、RockPro64 和 Rock64。
+
+### 一般性的改进
+
+无论你使用 Fedora 的哪个变体,你都能获得最新的开源世界。遵循我们的“[First][14]”理念,我们更新了关键的编程语言和系统库包,包括 GCC 10、Ruby 2.7 和 Python 3.8。当然,随着 Python 2 已经过了报废期,我们已经从 Fedora 中删除了大部分 Python 2 包,但我们为仍然需要它的开发者和用户提供了一个遗留的 python27 包。在 Fedora Workstation 中,我们默认启用了 EarlyOOM 服务,以改善低内存情况下的用户体验。
+
+我们非常期待你能尝试一下新版本的使用体验! 现在就去 下载它。或者如果你已经在运行 Fedora 操作系统,请按照简单的[升级说明][15]进行升级。
+
+### 万一出现问题……
+
+如果你遇到问题,请查看[Fedora 32 常见错误][16]页面,如果有问题,请访问我们的 [Askedora][17] 用户支持平台。
+
+### 谢谢大家
+
+感谢在这个发布周期中为 Fedora 项目做出贡献的成千上万的人,特别是感谢那些在大流行期间为又一次准时发布而付出额外努力的人。Fedora 是一个社区,很高兴看到我们彼此之间的支持。我邀请大家参加 4 月28-29 日的[红帽峰会虚拟体验][18],了解更多关于 Fedora 和其他社区的信息。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://fedoramagazine.org/announcing-fedora-32/
+
+作者:[Matthew Miller][a]
+选题:[lujun9972][b]
+译者:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]: https://fedoramagazine.org/author/mattdm/
+[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
+[1]: https://fedoramagazine.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/f32-final-816x345.png
+[2]: https://www.gnome.org/news/2020/03/gnome-3-36-released/
+[3]: https://iot.fedoraproject.org/
+[4]: https://docs.fedoraproject.org/en-US/fedora-coreos/update-streams/
+[5]: https://getfedora.org/en/coreos/download?stream=next
+[6]: https://docs.fedoraproject.org/en-US/fedora-coreos/getting-started/
+[7]: https://spins.fedoraproject.org/
+[8]: https://labs.fedoraproject.org/
+[9]: https://labs.fedoraproject.org/en/astronomy/
+[10]: https://spins.fedoraproject.org/en/kde/
+[11]: https://spins.fedoraproject.org/en/xfce/
+[12]: https://labs.fedoraproject.org/en/comp-neuro
+[13]: https://alt.fedoraproject.org/alt/
+[14]: https://docs.fedoraproject.org/en-US/project/#_first
+[15]: https://docs.fedoraproject.org/en-US/quick-docs/upgrading/
+[16]: https://fedoraproject.org/wiki/Common_F32_bugs
+[17]: http://ask.fedoraproject.org
+[18]: https://www.redhat.com/en/summit
diff --git a/published/202004/20200429 Manjaro 20 Lysia Arrives with ZFS and Snap Support.md b/published/202004/20200429 Manjaro 20 Lysia Arrives with ZFS and Snap Support.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..2ed94dd0a8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/202004/20200429 Manjaro 20 Lysia Arrives with ZFS and Snap Support.md
@@ -0,0 +1,110 @@
+[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
+[#]: translator: (wxy)
+[#]: reviewer: (wxy)
+[#]: publisher: (wxy)
+[#]: url: (https://linux.cn/article-12166-1.html)
+[#]: subject: (Manjaro 20 Lysia Arrives with ZFS and Snap Support)
+[#]: via: (https://itsfoss.com/manjaro-20-release/)
+[#]: author: (Abhishek Prakash https://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/)
+
+Manjaro 20 Lysia 到来,支持 ZFS 和 Snap
+======
+
+
+
+> Manjaro Linux 刷新了其 Manjaro 20 “Lysia” 的 ISO。现在在 Pamac 中支持了 Snap 和 Flatpak 软件包。在 Manjaro Architect 安装程序中增加了 ZFS 选项,并使用最新的内核 5.6 作为基础。
+
+最近新的发行版的发布像下雨一样。在上周发布了 [Ubuntu 20.04 LTS](https://linux.cn/article-12142-1.html) ,紧接着 [Fedora 32](https://linux.cn/article-12164-1.html) 也刚刚发布,而现在 [Manjaro 发布了版本 20][1],代号为 Lysia。
+
+### Manjaro 20 Lysia 有什么新东西?
+
+其实有很多。让我给大家介绍一下 Manjaro 20 中的一些主要新功能。
+
+#### 新的抹茶主题
+
+Manjaro 20 有一个新的默认主题,名为 Matcha(抹茶)。它让桌面看起来更有质感。
+
+![][2]
+
+#### 对 Snap 和 Flatpak 的支持
+
+Snap 和 Flatpak 软件包的支持得到了改进。如果你愿意,你可以在命令行中使用它们。
+
+你还可以在 Pamac 图形界面包管理器中启用 Snap 和 Flatpak 支持。
+
+![Enable Snap support in Pamac Manjaro][3]
+
+启用后,你可以在 Pamac 软件管理器中找到并安装 Snap/Flatpak 应用程序。
+
+![Snap applications in Pamac][4]
+
+#### Pamac 提供了基于搜索安装新软件的方式(在 GNOME 中)
+
+在 GNOME 变种中,如果你搜索某个东西,Pamac 软件管理器会提供安装符合查询的软件。在其他使用 GNOME 桌面的发行版中,GNOME 软件中心也会这样做。
+
+#### ZFS 支持登陆了 Manjaro Architect
+
+现在,你可以在 Manjaro Linux 中轻松地使用 ZFS 作为根文件系统。在 [Manjaro Architect][6] 中提供了对 [ZFS 文件系统][5]的支持。
+
+请注意,我说的是 Manjaro Architect,即基于终端的安装程序。它和普通的图形化的 [Calamares 安装程序][7]不一样。
+
+![][8]
+
+#### Linux kernel 5.6
+
+最新的稳定版 [Linux 内核 5.6][9] 带来了更多的硬件支持,如 thunderbolt、Nvidia 和 USB4。你也可以使用 [WireGuard VPN][10]。
+
+![][11]
+
+#### 其他杂项变化
+
+ * 新的桌面环境版本:Xfce 4.14、GNOME 3.36 和 KDE Plasma 5.18。
+ * 新的默认 shell 是 zsh。
+ * Display-Profiles 允许你存储一个或多个配置文件,用于你的首选显示配置。
+ * 改进后的 Gnome-Layout-Switcher。
+ * 最新的驱动程序。
+ * 改进和完善了 Manjaro 工具。
+
+### 如何取得 Manjaro 20 Lysia?
+
+如果你已经在使用 Manjaro,只需更新你的 Manjaro Linux 系统,你就应该已经在使用 Lysia 了。
+
+Manjaro 采用了滚动发布模式,这意味着你不必手动从一个版本升级到另一个版本。只要有新的版本发布,不需要重新安装就可以使用了。
+
+既然 Manjaro 是滚动发布的,为什么每隔一段时间就会发布一个新版本呢?这是因为他们要刷新 ISO,这样下载 Manjaro 的新用户就不用再安装过去几年的更新了。这就是为什么 Arch Linux 也会每个月刷新一次 ISO 的原因。
+
+Manjaro 的“ISO 刷新”是有代号和版本的,因为它可以帮助开发者清楚地标明每个开发阶段的发展方向。
+
+所以,如果你已经在使用它,只需使用 Pamac 或命令行[更新你的 Manjaro Linux 系统][12]即可。
+
+如果你想尝试 Manjaro 或者想使用 ZFS,那么你可以通过从它的网站上[下载 ISO][14] 来[安装 Manjaro][13]。
+
+愿你喜欢新的 Manjaro Linux 发布。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://itsfoss.com/manjaro-20-release/
+
+作者:[Abhishek Prakash][a]
+选题:[lujun9972][b]
+译者:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]: https://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/
+[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
+[1]: https://forum.manjaro.org/t/manjaro-20-0-lysia-released/138633
+[2]: https://i2.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/manjaro-20-lysia.jpeg?resize=800%2C440&ssl=1
+[3]: https://i2.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/enable-snap-in-pamac-manjaro.jpg?resize=800%2C490&ssl=1
+[4]: https://i1.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/snap-app-pacman.jpg?resize=800%2C489&ssl=1
+[5]: https://itsfoss.com/what-is-zfs/
+[6]: https://itsfoss.com/manjaro-architect-review/
+[7]: https://calamares.io/
+[8]: https://i2.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/pacman-prompts-install-apps.jpg?resize=800%2C331&ssl=1
+[9]: https://itsfoss.com/linux-kernel-5-6/
+[10]: https://itsfoss.com/wireguard/
+[11]: https://i2.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/manjaro-20-neofetch-screen.jpg?resize=800%2C495&ssl=1
+[12]: https://itsfoss.com/update-arch-linux/
+[13]: https://itsfoss.com/install-manjaro-linux/
+[14]: https://manjaro.org/download/
diff --git a/translated/tech/20200420 4 Git scripts I can-t live without.md b/published/20200420 4 Git scripts I can-t live without.md
similarity index 81%
rename from translated/tech/20200420 4 Git scripts I can-t live without.md
rename to published/20200420 4 Git scripts I can-t live without.md
index 089c81e20f..43102c69e6 100644
--- a/translated/tech/20200420 4 Git scripts I can-t live without.md
+++ b/published/20200420 4 Git scripts I can-t live without.md
@@ -1,8 +1,8 @@
[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
[#]: translator: (wxy)
-[#]: reviewer: ( )
-[#]: publisher: ( )
-[#]: url: ( )
+[#]: reviewer: (wxy)
+[#]: publisher: (wxy)
+[#]: url: (https://linux.cn/article-12180-1.html)
[#]: subject: (4 Git scripts I can't live without)
[#]: via: (https://opensource.com/article/20/4/git-extras)
[#]: author: (Vince Power https://opensource.com/users/vincepower)
@@ -12,11 +12,11 @@
> Git Extras 版本库包含了 60 多个脚本,它们是 Git 基本功能的补充。以下是如何安装、使用和贡献的方法。
-![Person using a laptop][1]
+
-2005 年,[Linus Torvalds][2] 创建了 [Git][3],以取代他之前用于维护 Linux 内核的专有的分布式源码控制管理解决方案。从那时起,Git 已经成为开源和云原生开发团队的主流版本控制解决方案。
+2005 年,[Linus Torvalds][2] 创建了 [Git][3],以取代他之前用于维护 Linux 内核的分布式源码控制管理的专有解决方案。从那时起,Git 已经成为开源和云原生开发团队的主流版本控制解决方案。
-但即使是像 Git 这样功能丰富的应用程序,也没有人们想要或需要的每个功能,所以人们会花大力气去创建这些功能。就 Git 而言,这个人就是 [TJ Holowaychuk][4]。他的 [Git Extras][5] 项目承载了 60 多个“附加功能”,这些功能扩展了 Git 的基本功能。
+但即使是像 Git 这样功能丰富的应用程序,也没有人们想要或需要的每个功能,所以会有人花大力气去创建这些缺少的功能。就 Git 而言,这个人就是 [TJ Holowaychuk][4]。他的 [Git Extras][5] 项目承载了 60 多个“附加功能”,这些功能扩展了 Git 的基本功能。
### 使用 Git 附加功能
@@ -24,9 +24,9 @@
#### git-ignore
-`git ignore` 是一个方便的附加功能,它可以让你手动添加文件类型和注释到 `.git-ignore` 文件中,而不需要打开文本编辑器。它可以操作你的个人用户帐户的全局忽略文件和单独用于你正在工作的版本库的忽略文件。
+`git ignore` 是一个方便的附加功能,它可以让你手动添加文件类型和注释到 `.git-ignore` 文件中,而不需要打开文本编辑器。它可以操作你的个人用户帐户的全局忽略文件和单独用于你正在工作的版本库中的忽略文件。
-在没有参数的情况下执行 `git ignore` 会先列出全局忽略文件,然后是本地的忽略文件。
+在不提供参数的情况下执行 `git ignore` 会先列出全局忽略文件,然后是本地的忽略文件。
```
$ git ignore
@@ -105,7 +105,7 @@ branch.master.merge=refs/heads/master
* `git mr` 检出来自 GitLab 的合并请求。
* `git pr` 检出来自 GitHub 的拉取请求。
-无论是哪种情况,你只需要合并请求号、拉取请求号或完整的 URL,它就会抓取远程引用,检出分支,并调整配置,这样 Git 就知道要替换哪个分支了。
+无论是哪种情况,你只需要合并请求号/拉取请求号或完整的 URL,它就会抓取远程引用,检出分支,并调整配置,这样 Git 就知道要替换哪个分支了。
```
$ git mr 51
@@ -142,7 +142,7 @@ $ git extras --help
$ brew install git-extras
```
-在 Linux 上,每个平台的原生包管理器中都有 Git Extras。有时,你需要启用一个额外的仓库,比如在 CentOS 上的 [EPEL][10],然后运行一条命令。
+在 Linux 上,每个平台原生的包管理器中都包含有 Git Extras。有时,你需要启用额外的仓库,比如在 CentOS 上的 [EPEL][10],然后运行一条命令。
```
$ sudo yum install git-extras
@@ -152,9 +152,9 @@ $ sudo yum install git-extras
### 贡献
-你是否你认为 Git 中有缺少的功能,并且已经构建了一个脚本来处理它?为什么不把它作为 Git Extras 发布版的一部分,与全世界分享呢?
+你是否认为 Git 中有缺少的功能,并且已经构建了一个脚本来处理它?为什么不把它作为 Git Extras 发布版的一部分,与全世界分享呢?
-要做到这一点,请将该功能贡献到 Git Extras 仓库中。更多具体细节请参见仓库中的 [CONTRIBUTING.md][12] 文件,但基本的操作方法很简单。
+要做到这一点,请将该功能贡献到 Git Extras 仓库中。更多具体细节请参见仓库中的 [CONTRIBUTING.md][12] 文件,但基本的操作方法很简单:
1. 创建一个处理该功能的 Bash 脚本。
2. 创建一个基本的 man 文件,让大家知道如何使用它。
@@ -171,7 +171,7 @@ via: https://opensource.com/article/20/4/git-extras
作者:[Vince Power][a]
选题:[lujun9972][b]
译者:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/translated/tech/20200421 Using Python to visualize COVID-19 projections.md b/published/20200421 Using Python to visualize COVID-19 projections.md
similarity index 84%
rename from translated/tech/20200421 Using Python to visualize COVID-19 projections.md
rename to published/20200421 Using Python to visualize COVID-19 projections.md
index 3768686e8c..aaf5fc72d0 100644
--- a/translated/tech/20200421 Using Python to visualize COVID-19 projections.md
+++ b/published/20200421 Using Python to visualize COVID-19 projections.md
@@ -1,8 +1,8 @@
[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
[#]: translator: (wxy)
-[#]: reviewer: ( )
-[#]: publisher: ( )
-[#]: url: ( )
+[#]: reviewer: (wxy)
+[#]: publisher: (wxy)
+[#]: url: (https://linux.cn/article-12172-1.html)
[#]: subject: (Using Python to visualize COVID-19 projections)
[#]: via: (https://opensource.com/article/20/4/python-data-covid-19)
[#]: author: (AnuragGupta https://opensource.com/users/999anuraggupta)
@@ -10,11 +10,11 @@
使用 Python 来可视化 COVID-19 预测
======
-> 我将演示如何使用开源库利用提供的全球病毒传播的开放数据来创建两个可视效果。
+> 我将演示如何利用提供的全球病毒传播的开放数据,使用开源库来创建两个可视效果。
-![Colorful sound wave graph][1]
+
-使用 [Python][2] 和一些图形库,你可以预测出 COVID-19 确诊病例的总数,也可以显示一个国家(本文以印度为例)在给定日期的死亡总数。人们有时需要帮助解释和处理数据的意义,所以本文还演示了如何为五个国家创建一个动画横条形图,以显示按日期显示病例的变化。
+使用 [Python][2] 和一些图形库,你可以预测 COVID-19 确诊病例总数,也可以显示一个国家(本文以印度为例)在给定日期的死亡总数。人们有时需要帮助解释和处理数据的意义,所以本文还演示了如何为五个国家创建一个动画横条形图,以显示按日期显示病例的变化。
### 印度的确诊病例和死亡人数预测
@@ -28,7 +28,6 @@
直接将数据加载到 Pandas `DataFrame` 中。Pandas 提供了一个函数 `read_csv()`,它可以获取一个 URL 并返回一个 `DataFrame` 对象,如下所示。
-
```
import pycountry
import plotly.express as px
@@ -87,8 +86,8 @@ print(df_india.head(3))
在这里,我们创建一个条形图。我们将把日期放在 X 轴上,把确诊的病例数和死亡人数放在 Y 轴上。这一部分的脚本有以下几个值得注意的地方。
- * `plt.rcParams["_figure.figure.figsize"_]=20,20` 这一行代码只适用于 Jupyter。所以如果你使用其他 IDE,请删除它。
- * 注意这行代码:`ax1 = plt.gca()`。为了确保两个图,即确诊病例和死亡病例的图都被绘制在同一个图上,我们需要给第二个图的 `ax` 对象。所以我们使用 `gca()` 来完成这个任务。(顺便说一下,`gca` 代表“get current axis”)
+ * `plt.rcParams["figure.figsize"]=20,20` 这一行代码只适用于 Jupyter。所以如果你使用其他 IDE,请删除它。
+ * 注意这行代码:`ax1 = plt.gca()`。为了确保两个图,即确诊病例和死亡病例的图都被绘制在同一个图上,我们需要给第二个图的 `ax` 对象。所以我们使用 `gca()` 来完成这个任务。(顺便说一下,`gca` 代表 “获取当前坐标轴”)
完整的脚本如下所示。
@@ -120,9 +119,9 @@ plt.show()
整个脚本[可在 GitHub 上找到][4]。
-#### 为五个国家创建一个动画水平条形图
+### 为五个国家创建一个动画水平条形图
-关于 Jupyter 的注意事项:要在 Jupyter 中以动态动画的形式运行,而不是静态 png 的形式,你需要在单元格的开头添加一个神奇的命令,即: `%matplotlib notebook`。这将使图形保持动态,而不是显示静态的 png 文件,因此也可以显示动画。如果你在其他 IDE 上,请删除这一行。
+关于 Jupyter 的注意事项:要在 Jupyter 中以动态动画的形式运行,而不是静态 png 的形式,你需要在单元格的开头添加一个神奇的命令,即: `%matplotlib notebook`。这将使图形保持动态,而不是显示为静态的 png 文件,因此也可以显示动画。如果你在其他 IDE 上,请删除这一行。
#### 1、下载数据
@@ -130,11 +129,11 @@ plt.show()
#### 2、创建一个所有日期的列表
-如果你检查你下载的数据,你会发现它有一列 `Date`。现在,这一列对每个国家都有一个日期值。因此,同一个日期会出现多次。我们需要创建一个只具有唯一值的日期列表。这会用在我们条形图的 X 轴上。我们有一行代码,如 `list_dates = df[_'Date'_].unique()`。`unique()` 方法将只提取每个日期的唯一值。
+如果你检查你下载的数据,你会发现它有一列 `Date`。现在,这一列对每个国家都有一个日期值。因此,同一个日期会出现多次。我们需要创建一个只具有唯一值的日期列表。这会用在我们条形图的 X 轴上。我们有一行代码,如 `list_dates = df[‘Date’].unique()`。`unique()` 方法将只提取每个日期的唯一值。
#### 3、挑选五个国家并创建一个 `ax` 对象。
-做一个五个国家的名单。(你可以选择你喜欢的国家,甚至可以增加或减少国家的数量。)我也做了一个五个颜色的列表,每个国家的条形图的颜色对应一种。(如果你喜欢的话,也可以改一下。)这里有一行重要的代码是:`fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(15, 8))`。这是创建一个 `ax` 对象所需要的。
+做一个五个国家的名单。(你可以选择你喜欢的国家,也可以增加或减少国家的数量。)我也做了一个五个颜色的列表,每个国家的条形图的颜色对应一种。(如果你喜欢的话,也可以改一下。)这里有一行重要的代码是:`fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(15, 8))`。这是创建一个 `ax` 对象所需要的。
#### 4、编写回调函数
@@ -148,7 +147,7 @@ plt.show()
```
my_anim = animation.FuncAnimation(fig = fig, func = plot_bar,
- frames= list_dates, blit=True,
+ frames = list_dates, blit = True,
interval=20)
```
@@ -226,7 +225,7 @@ via: https://opensource.com/article/20/4/python-data-covid-19
作者:[AnuragGupta][a]
选题:[lujun9972][b]
译者:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/translated/tech/20200423 Difference Between YUM and RPM Package Manager.md b/published/20200423 Difference Between YUM and RPM Package Manager.md
similarity index 92%
rename from translated/tech/20200423 Difference Between YUM and RPM Package Manager.md
rename to published/20200423 Difference Between YUM and RPM Package Manager.md
index c0bf8b7352..bf916108e1 100644
--- a/translated/tech/20200423 Difference Between YUM and RPM Package Manager.md
+++ b/published/20200423 Difference Between YUM and RPM Package Manager.md
@@ -1,8 +1,8 @@
[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
[#]: translator: (wxy)
-[#]: reviewer: ( )
-[#]: publisher: ( )
-[#]: url: ( )
+[#]: reviewer: (wxy)
+[#]: publisher: (wxy)
+[#]: url: (https://linux.cn/article-12170-1.html)
[#]: subject: (Difference Between YUM and RPM Package Manager)
[#]: via: (https://www.2daygeek.com/comparison-difference-between-yum-vs-rpm/)
[#]: author: (Magesh Maruthamuthu https://www.2daygeek.com/author/magesh/)
@@ -10,6 +10,8 @@
YUM 和 RPM 包管理器的不同之处
======
+
+
软件包管理器在 Linux 系统中扮演着重要的角色。它允许你安装、更新、查看、搜索和删除软件包,以满足你的需求。
每个发行版都有自己的一套包管理器,依据你的 Linux 发行版来分别使用它们。
@@ -18,7 +20,7 @@ RPM 是最古老的传统软件包管理器之一,它是为基于 Red Hat 的
> 如果你想知道 [YUM 和 DNF 包管理器的区别][1]请参考该文章。
-这意味着 yum 可以自动下载并安装所有需要的依赖项,但 rpm 会告诉你安装一个依赖项列表,然后你必须手动安装。
+这意味着 `yum` 可以自动下载并安装所有需要的依赖项,但 `rpm` 会告诉你安装一个依赖项列表,然后你必须手动安装。
当你想用 [rpm 命令][2] 安装一组包时,这实际上是不可能的,而且很费时间。
@@ -76,13 +78,13 @@ via: https://www.2daygeek.com/comparison-difference-between-yum-vs-rpm/
作者:[Magesh Maruthamuthu][a]
选题:[lujun9972][b]
译者:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
[a]: https://www.2daygeek.com/author/magesh/
[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
-[1]: https://www.2daygeek.com/comparison-difference-between-dnf-vs-yum/
+[1]: https://linux.cn/article-12161-1.html
[2]: https://www.2daygeek.com/linux-rpm-command-examples-manage-packages-fedora-centos-rhel-systems/
[3]: https://www.2daygeek.com/linux-yum-command-examples-manage-packages-rhel-centos-systems/
[4]: https://www.2daygeek.com/list-of-command-line-package-manager-for-linux/
diff --git a/published/20200424 16 Things to do After Installing Ubuntu 20.04.md b/published/20200424 16 Things to do After Installing Ubuntu 20.04.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..ded221ab6c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20200424 16 Things to do After Installing Ubuntu 20.04.md
@@ -0,0 +1,283 @@
+[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
+[#]: translator: (qfzy1233)
+[#]: reviewer: (wxy)
+[#]: publisher: (wxy)
+[#]: url: (https://linux.cn/article-12183-1.html)
+[#]: subject: (16 Things to do After Installing Ubuntu 20.04)
+[#]: via: (https://itsfoss.com/things-to-do-after-installing-ubuntu-20-04/)
+[#]: author: (Abhishek Prakash https://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/)
+
+安装完 Ubuntu 20.04 后要做的 16 件事
+======
+
+> 以下是安装 Ubuntu 20.04 之后需要做的一些调整和事项,它将使你获得更流畅、更好的桌面 Linux 体验。
+
+[Ubuntu 20.04 LTS(长期支持版)带来了许多新的特性][1]和观感上的变化。如果你要安装 Ubuntu 20.04,让我向你展示一些推荐步骤便于你的使用。
+
+### 安装完 Ubuntu 20.04 LTS “Focal Fossa” 后要做的 16 件事
+
+![][2]
+
+我在这里提到的步骤仅是我的建议。如果一些定制或调整不适合你的需要和兴趣,你可以忽略它们。
+
+同样的,有些步骤看起来很简单,但是对于一个 Ubuntu 新手来说是必要的。
+
+这里的一些建议适用于启用 GNOME 作为默认桌面 Ubuntu 20.04,所以请检查 [Ubuntu 版本][3]和[桌面环境][4]。
+
+以下列表便是安装了代号为 Focal Fossa 的 Ubuntu 20.04 LTS 之后要做的事。
+
+#### 1、通过更新和启用额外的软件仓库来准备你的系统
+
+安装 Ubuntu 或任何其他 Linux 发行版之后,你应该做的第一件事就是更新它。Linux 的运作是建立在本地的可用软件包数据库上,而这个缓存需要同步以便你能够安装软件。
+
+升级 Ubuntu 非常简单。你可以运行软件更新从菜单(按 `Super` 键并搜索 “software updater”):
+
+![Ubuntu 20.04 的软件升级器][5]
+
+你也可以在终端使用以下命令更新你的系统:
+
+```
+sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade
+```
+
+接下来,你应该确保启用了 [universe(宇宙)和 multiverse(多元宇宙)软件仓库][6]。使用这些软件仓库,你可以访问更多的软件。我还推荐阅读关于 [Ubuntu 软件仓库][6]的文章,以了解它背后的基本概念。
+
+在菜单中搜索 “Software & Updates”:
+
+![软件及更新设置项][7]
+
+请务必选中软件仓库前面的勾选框:
+
+![启用额外的软件仓库][8]
+
+#### 2、安装媒体解码器来播放 MP3、MPEG4 和其他格式媒体文件
+
+如果你想播放媒体文件,如 MP3、MPEG4、AVI 等,你需要安装媒体解码器。由于各个国家的版权问题, Ubuntu 在默认情况下不会安装它。
+
+作为个人,你可以[使用 Ubuntu Restricted Extra 安装包][9]很轻松地安装这些媒体编解码器。这将[在你的 Ubuntu 系统安装][10]媒体编解码器、Adobe Flash 播放器和微软 True Type 字体等。
+
+你可以通过[点击这个链接][11]来安装它(它会要求在软件中心打开它),或者使用以下命令:
+
+```
+sudo apt install ubuntu-restricted-extras
+```
+
+如果遇到 EULA 或许可证界面,请记住使用 `tab` 键在选项之间进行选择,然后按回车键确认你的选择。
+
+![按 tab 键选择 OK 并按回车键][12]
+
+#### 3、从软件中心或网络上安装软件
+
+现在已经设置好了软件仓库并更新了软件包缓存,应该开始安装所需的软件了。
+
+在 Ubuntu 中安装应用程序有几种方法,最简单和正式的方法是使用软件中心。
+
+![Ubuntu 软件中心][14]
+
+如果你想要一些关于软件的建议,请参考这个[丰富的各种用途的 Ubuntu 应用程序列表][15]。
+
+一些软件供应商提供了 .deb 文件来方便地安装他们的应用程序。你可以从他们的网站获得 .deb 文件。例如,要[在 Ubuntu 上安装谷歌 Chrome][16],你可以从它的网站上获得 .deb 文件,双击它开始安装。
+
+#### 4、享受 Steam Proton 和 GameModeEnjoy 上的游戏
+
+[在 Linux 上进行游戏][17]已经有了长足的发展。你不再受限于自带的少数游戏。你可以[在 Ubuntu 上安装 Steam][18]并享受许多游戏。
+
+[Steam 新的 Proton 项目][19]可以让你在 Linux 上玩许多只适用于 Windows 的游戏。除此之外,Ubuntu 20.04 还默认安装了 [Feral Interactive 的 GameMode][20]。
+
+GameMode 会自动调整 Linux 系统的性能,使游戏具有比其他后台进程更高的优先级。
+
+这意味着一些支持 GameMode 的游戏(如[古墓丽影·崛起][21])在 Ubuntu 上的性能应该有所提高。
+
+#### 5、管理自动更新(适用于进阶用户和专家)
+
+最近,Ubuntu 已经开始自动下载并安装对你的系统至关重要的安全更新。这是一个安全功能,作为一个普通用户,你应该让它保持默认开启。
+
+但是,如果你喜欢自己进行配置更新,而这个自动更新经常导致你[“无法锁定管理目录”错误][22],也许你可以改变自动更新行为。
+
+你可以选择“立即显示”,这样一有安全更新就会立即通知你,而不是自动安装。
+
+![管理自动更新设置][23]
+
+#### 6、控制电脑的自动挂起和屏幕锁定
+
+如果你在笔记本电脑上使用 Ubuntu 20.04,那么你可能需要注意一些电源和屏幕锁定设置。
+
+如果你的笔记本电脑处于电池模式,Ubuntu 会在 20 分钟不活动后休眠系统。这样做是为了节省电池电量。就我个人而言,我不喜欢它,因此我禁用了它。
+
+类似地,如果你离开系统几分钟,它会自动锁定屏幕。我也不喜欢这种行为,所以我宁愿禁用它。
+
+![Ubuntu 20.04 的电源设置][24]
+
+#### 7、享受夜间模式
+
+[Ubuntu 20.04 中最受关注的特性][25]之一是夜间模式。你可以通过进入设置并在外观部分中选择它来启用夜间模式。
+
+![开启夜间主题 Ubuntu][26]
+
+你可能需要做一些[额外的调整来获得完整的 Ubuntu 20.04 夜间模式][27]。
+
+#### 8、控制桌面图标和启动程序
+
+如果你想要一个最简的桌面,你可以禁用桌面上的图标。你还可以从左侧禁用启动程序,并在顶部面板中禁用软件状态栏。
+
+所有这些都可以通过默认的新 GNOME 扩展来控制,该程序默认情况下已经可用。
+
+![禁用 Ubuntu 20 04 的 Dock][28]
+
+顺便说一下,你也可以通过“设置”->“外观”来将启动栏的位置改变到底部或者右边。
+
+#### 9、使用表情符和特殊字符,或从搜索中禁用它
+
+Ubuntu 提供了一个使用表情符号的简单方法。在默认情况下,有一个专用的应用程序叫做“字符”。它基本上可以为你提供表情符号的 [Unicode][29]。
+
+不仅是表情符号,你还可以使用它来获得法语、德语、俄语和拉丁语字符的 unicode。单击符号你可以复制 unicode,当你粘贴该代码时,你所选择的符号便被插入。
+
+![Ubuntu 表情符][30]
+
+你也能在桌面搜索中找到这些特殊的字符和表情符号。也可以从搜索结果中复制它们。
+
+![表情符出现在桌面搜索中][31]
+
+如果你不想在搜索结果中看到它们,你应该禁用搜索功能对它们的访问。下一节将讨论如何做到这一点。
+
+#### 10、掌握桌面搜索
+
+GNOME 桌面拥有强大的搜索功能,大多数人使用它来搜索已安装的应用程序,但它不仅限于此。
+
+按 `Super` 键并搜索一些东西,它将显示与搜索词匹配的任何应用程序,然后是系统设置和软件中心提供的匹配应用程序。
+
+![桌面搜索][32]
+
+不仅如此,搜索还可以找到文件中的文本。如果你正在使用日历,它也可以找到你的会议和提醒。你甚至可以在搜索中进行快速计算并复制其结果。
+
+![Ubuntu搜索的快速计算][33]
+
+你可以进入“设置”中来控制可以搜索的内容和顺序。
+
+![][34]
+
+#### 11、使用夜灯功能,减少夜间眼睛疲劳
+
+如果你在晚上使用电脑或智能手机,你应该使用夜灯功能来减少眼睛疲劳。我觉得这很有帮助。
+
+夜灯的特点是在屏幕上增加了一种黄色的色调,比白光少了一些挤压感。
+
+你可以在“设置”->“显示”切换到夜灯选项卡来开启夜光功能。你可以根据自己的喜好设置“黄度”。
+
+![夜灯功能][35]
+
+#### 12、使用 2K/4K 显示器?使用分辨率缩放得到更大的图标和字体
+
+如果你觉得图标、字体、文件夹在你的高分辨率屏幕上看起来都太小了,你可以利用分辨率缩放。
+
+启用分辨率缩放可以让你有更多的选项来从 100% 增加到 200%。你可以选择适合自己喜好的缩放尺寸。
+
+![在设置->显示中启用高分缩放][36]
+
+#### 13、探索 GNOME 扩展功能以扩展 GNOME 桌面可用性
+
+GNOME 桌面有称为“扩展”的小插件或附加组件。你应该[学会使用 GNOME 扩展][37]来扩展系统的可用性。
+
+如下图所示,天气扩展顶部面板中显示了天气信息。不起眼但十分有用。你也可以在这里查看一些[最佳 GNOME 扩展][38]。不需要全部安装,只使用那些对你有用的。
+
+![天气扩展][39]
+
+#### 14、启用“勿扰”模式,专注于工作
+
+如果你想专注于工作,禁用桌面通知会很方便。你可以轻松地启用“勿扰”模式,并静音所有通知。
+
+![启用“请勿打扰”清除桌面通知][40]
+
+这些通知仍然会在消息栏中,以便你以后可以阅读它们,但是它们不会在桌面上弹出。
+
+#### 15、清理你的系统
+
+这是你安装 Ubuntu 后不需要马上做的事情。但是记住它会对你有帮助。
+
+随着时间的推移,你的系统将有大量不再需要的包。你可以用这个命令一次性删除它们:
+
+```
+sudo apt autoremove
+```
+
+还有其他[清理 Ubuntu 以释放磁盘空间的方法][41],但这是最简单和最安全的。
+
+#### 16、根据你的喜好调整和定制 GNOME 桌面
+
+我强烈推荐[安装 GNOME 设置工具][42]。这将让你可以通过额外的设置来进行定制。
+
+![Gnome 设置工具][43]
+
+比如,你可以[以百分比形式显示电池容量][44]、[修正在触摸板右键问题][45]、改变 Shell 主题、改变鼠标指针速度、显示日期和星期数、改变应用程序窗口行为等。
+
+定制是没有尽头的,我可能仅使用了它的一小部分功能。这就是为什么我推荐[阅读这些][42]关于[自定义 GNOME 桌面][46]的文章。
+
+你也可以[在 Ubuntu 中安装新主题][47],不过就我个人而言,我喜欢这个版本的默认主题。这是我第一次在 Ubuntu 发行版中使用默认的图标和主题。
+
+#### 安装 Ubuntu 之后你会做什么?
+
+如果你是 Ubuntu 的初学者,我建议你[阅读这一系列 Ubuntu 教程][48]开始学习。
+
+这就是我的建议。安装 Ubuntu 之后你要做什么?分享你最喜欢的东西,我可能根据你的建议来更新这篇文章。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://itsfoss.com/things-to-do-after-installing-ubuntu-20-04/
+
+作者:[Abhishek Prakash][a]
+选题:[lujun9972][b]
+译者:[qfzy1233](https://github.com/qfzy1233)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]: https://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/
+[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
+[1]: https://linux.cn/article-12146-1.html
+[2]: https://i2.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/things-to-do-after-installing-ubuntu-20-04.jpg?ssl=1
+[3]: https://linux.cn/article-9872-1.html
+[4]: https://linux.cn/article-12124-1.html
+[5]: https://i0.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/software-updater-ubuntu-20-04.jpg?ssl=1
+[6]: https://itsfoss.com/ubuntu-repositories/
+[7]: https://i0.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/software-updates-settings-ubuntu-20-04.jpg?ssl=1
+[8]: https://i1.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/extra-repositories-ubuntu-20.jpg?ssl=1
+[9]: https://linux.cn/article-11906-1.html
+[10]: https://linux.cn/article-12074-1.html
+[11]: //ubuntu-restricted-extras/
+[12]: https://i2.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/02/installing_ubuntu_restricted_extras.jpg?ssl=1
+[13]: https://itsfoss.com/remove-install-software-ubuntu/
+[14]: https://i0.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/software-center-ubuntu-20.png?resize=800%2C509&ssl=1
+[15]: https://itsfoss.com/best-ubuntu-apps/
+[16]: https://itsfoss.com/install-chrome-ubuntu/
+[17]: https://linux.cn/article-7316-1.html
+[18]: https://itsfoss.com/install-steam-ubuntu-linux/
+[19]: https://linux.cn/article-10054-1.html
+[20]: https://github.com/FeralInteractive/gamemode
+[21]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rise_of_the_Tomb_Raider
+[22]: https://itsfoss.com/could-not-get-lock-error/
+[23]: https://i0.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/auto-updates-ubuntu.png?resize=800%2C361&ssl=1
+[24]: https://i0.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/power-settings-ubuntu-20-04.png?fit=800%2C591&ssl=1
+[25]: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lpq8pm_xkSE
+[26]: https://i1.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/enable-dark-theme-ubuntu.png?ssl=1
+[27]: https://linux.cn/article-12098-1.html
+[28]: https://i0.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/disable-dock-ubuntu-20-04.png?ssl=1
+[29]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_Unicode_characters
+[30]: https://i2.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/emoji-ubuntu.jpg?ssl=1
+[31]: https://i2.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/emojis-desktop-search-ubuntu.jpg?ssl=1
+[32]: https://i1.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/ubuntu-desktop-search-1.jpg?ssl=1
+[33]: https://i2.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/quick-calculations-ubuntu-search.jpg?ssl=1
+[34]: https://i1.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/search-settings-control-ubuntu.png?resize=800%2C534&ssl=1
+[35]: https://i2.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/nightlight-ubuntu-20-04.png?ssl=1
+[36]: https://i1.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/fractional-scaling-ubuntu.jpg?ssl=1
+[37]: https://itsfoss.com/gnome-shell-extensions/
+[38]: https://itsfoss.com/best-gnome-extensions/
+[39]: https://i2.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/weather-extension-ubuntu.jpg?ssl=1
+[40]: https://i1.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/03/do-not-distrub-option-ubuntu-20-04.png?ssl=1
+[41]: https://itsfoss.com/free-up-space-ubuntu-linux/
+[42]: https://itsfoss.com/gnome-tweak-tool/
+[43]: https://i1.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/gnome-tweaks-tool-ubuntu-20-04.png?fit=800%2C551&ssl=1
+[44]: https://itsfoss.com/display-battery-ubuntu/
+[45]: https://itsfoss.com/fix-right-click-touchpad-ubuntu/
+[46]: https://itsfoss.com/gnome-tricks-ubuntu/
+[47]: https://itsfoss.com/install-themes-ubuntu/
+[48]: https://itsfoss.com/getting-started-with-ubuntu/
diff --git a/translated/tech/20200425 Inlining optimisations in Go.md b/published/20200425 Inlining optimisations in Go.md
similarity index 57%
rename from translated/tech/20200425 Inlining optimisations in Go.md
rename to published/20200425 Inlining optimisations in Go.md
index dc13968c1d..12f1cb67b7 100644
--- a/translated/tech/20200425 Inlining optimisations in Go.md
+++ b/published/20200425 Inlining optimisations in Go.md
@@ -1,8 +1,8 @@
[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
[#]: translator: (lxbwolf)
-[#]: reviewer: ( )
-[#]: publisher: ( )
-[#]: url: ( )
+[#]: reviewer: (wxy)
+[#]: publisher: (wxy)
+[#]: url: (https://linux.cn/article-12176-1.html)
[#]: subject: (Inlining optimisations in Go)
[#]: via: (https://dave.cheney.net/2020/04/25/inlining-optimisations-in-go)
[#]: author: (Dave Cheney https://dave.cheney.net/author/davecheney)
@@ -10,33 +10,35 @@
Go 中的内联优化
======
-本文讨论 Go 编译器是如何实现内联的以及这种优化方法如何影响你的 Go 代码。
+> 本文讨论 Go 编译器是如何实现内联的,以及这种优化方法如何影响你的 Go 代码。
-*请注意:*本文重点讨论 *gc*,实际上是 [golang.org](https://github.com/golang/go) 的 Go 编译器。讨论到的概念可以广泛用于其他 Go 编译器,如 gccgo 和 llgo,但它们在实现方式和功能上可能有所差异。
+
+
+*请注意:*本文重点讨论 *gc*,这是来自 [golang.org](https://github.com/golang/go) 的事实标准的 Go 编译器。讨论到的概念可以广泛适用于其它 Go 编译器,如 gccgo 和 llgo,但它们在实现方式和功效上可能有所差异。
### 内联是什么?
-内联就是把简短的函数在调用它的地方展开。在计算机发展历程的早期,这个优化是由程序员手动实现的。现在,内联已经成为编译过程中自动实现的基本优化过程的其中一步。
+内联就是把简短的函数在调用它的地方展开。在计算机发展历程的早期,这个优化是由程序员手动实现的。现在,内联已经成为编译过程中自动实现的基本优化过程的其中一步。
### 为什么内联很重要?
-有两个原因。第一个是它消除了函数调用本身的虚耗。第二个是它使得编译器能更高效地执行其他的优化策略。
+有两个原因。第一个是它消除了函数调用本身的开销。第二个是它使得编译器能更高效地执行其他的优化策略。
-#### 函数调用的虚耗
+#### 函数调用的开销
-在任何语言中,调用一个函数 [1][2] 都会有消耗。把参数编组进寄存器或放入栈中(取决于 ABI),在返回结果时倒序取出时会有虚耗。引入一次函数调用会导致程序计数器从指令流的一点跳到另一点,这可能导致管道阻塞。函数内部通常有前置处理,需要为函数执行准备新的栈帧,还有与前置相似的后续处理,需要在返回给调用方之前释放栈帧空间。
+在任何语言中,调用一个函数 [^1] 都会有消耗。把参数编组进寄存器或放入栈中(取决于 ABI),在返回结果时的逆反过程都会有开销。引入一次函数调用会导致程序计数器从指令流的一点跳到另一点,这可能导致管道滞后。函数内部通常有前置处理,需要为函数执行准备新的栈帧,还有与前置相似的后续处理,需要在返回给调用方之前释放栈帧空间。
-在 Go 中函数调用会消耗额外的资源来支持栈的动态增长。在进入函数时,goroutine 可用的栈空间与函数需要的空间大小相等。如果可用空间不同,前置处理就会跳到把数据复制到一块新的、更大的空间的运行时逻辑,而这会导致栈空间变大。当这个复制完成后,运行时跳回到原来的函数入口,再执行栈空间检查,函数调用继续执行。这种方式下,goroutine 开始时可以申请很小的栈空间,在有需要时再申请更大的空间。[2][3]
+在 Go 中函数调用会消耗额外的资源来支持栈的动态增长。在进入函数时,goroutine 可用的栈空间与函数需要的空间大小进行比较。如果可用空间不同,前置处理就会跳到运行时的逻辑中,通过把数据复制到一块新的、更大的空间的来增长栈空间。当这个复制完成后,运行时就会跳回到原来的函数入口,再执行栈空间检查,现在通过了检查,函数调用继续执行。这种方式下,goroutine 开始时可以申请很小的栈空间,在有需要时再申请更大的空间。[^2]
-这个检查消耗很小 — 只有几个指令 — 而且由于 goroutine 是成几何级数增长的,因此这个检查很少失败。这样,现代处理器的分支预测单元会通过假定检查肯定会成功来隐藏栈空间检查的消耗。当处理器预测错了栈空间检查,必须要抛弃它推测性执行的操作时,与为了增加 goroutine 的栈空间运行时所需的操作消耗的资源相比,管道阻塞的代价更小。
+这个检查消耗很小,只有几个指令,而且由于 goroutine 的栈是成几何级数增长的,因此这个检查很少失败。这样,现代处理器的分支预测单元可以通过假定检查肯定会成功来隐藏栈空间检查的消耗。当处理器预测错了栈空间检查,不得不放弃它在推测性执行所做的操作时,与为了增加 goroutine 的栈空间运行时所需的操作消耗的资源相比,管道滞后的代价更小。
-虽然现代处理器可以用预测性执行技术优化每次函数调用中的泛型和 Go 特定的元素的虚耗,但那些虚耗不能被完全消除,因此在每次函数调用执行必要的工作过程中都会有性能消耗。一次函数调用本身的虚耗是固定的,与更大的函数相比,调用小函数的代价更大,因为在每次调用过程中它们做的有用的工作更少。
+虽然现代处理器可以用预测性执行技术优化每次函数调用中的泛型和 Go 特定的元素的开销,但那些开销不能被完全消除,因此在每次函数调用执行必要的工作过程中都会有性能消耗。一次函数调用本身的开销是固定的,与更大的函数相比,调用小函数的代价更大,因为在每次调用过程中它们做的有用的工作更少。
-消除这些虚耗的方法必须是要消除函数调用本身,Go 的编译器就是这么做的,在某些条件下通过用函数的内容来替换函数调用来实现。这个过程被称为*内联*,因为它在函数调用处把函数体展开了。
+因此,消除这些开销的方法必须是要消除函数调用本身,Go 的编译器就是这么做的,在某些条件下通过用函数的内容来替换函数调用来实现。这个过程被称为*内联*,因为它在函数调用处把函数体展开了。
#### 改进的优化机会
-Cliff Click 博士把内联描述为现代编译器做的优化措施,像常量传播(译注:此处作者笔误,原文为 constant proportion,修正为 constant propagation)和死码消除一样,都是编译器的基本优化方法。实际上,内联可以让编译器看得更深,使编译器可以观察调用的特定函数的上下文内容,可以看到能继续简化或彻底消除的逻辑。由于可以递归地执行内联,因此不仅可以在每个独立的函数上下文处进行这种优化,也可以在整个函数调用链中进行。
+Cliff Click 博士把内联描述为现代编译器做的优化措施,像常量传播(LCTT 译注:此处作者笔误,原文为 constant proportion,修正为 constant propagation)和死代码消除一样,都是编译器的基本优化方法。实际上,内联可以让编译器看得更深,使编译器可以观察调用的特定函数的上下文内容,可以看到能继续简化或彻底消除的逻辑。由于可以递归地执行内联,因此不仅可以在每个独立的函数上下文处进行这种优化决策,也可以在整个函数调用链中进行。
### 实践中的内联
@@ -66,14 +68,14 @@ func BenchmarkMax(b *testing.B) {
}
```
-运行这个基准,会得到如下结果:[3][4]
+运行这个基准,会得到如下结果:[^3]
```bash
% go test -bench=.
BenchmarkMax-4 530687617 2.24 ns/op
```
-在我的 2015 MacBook Air 上 `max(-1, i)` 的耗时约为 2.24 纳秒。现在去掉 `//go:noinline` 编译指令,再看下结果:
+在我的 2015 MacBook Air 上 `max(-1, i)` 的耗时约为 2.24 纳秒。现在去掉 `//go:noinline` 编译指令,再看下结果:
```bash
% go test -bench=.
@@ -90,7 +92,7 @@ Max-4 2.21ns ± 1% 0.49ns ± 6% -77.96% (p=0.000 n=18+19)
这个提升是从哪儿来的呢?
-首先,移除掉函数调用以及与之关联的前置处理 [4][5] 是主要因素。把 `max` 函数的函数体在调用处展开,减少了处理器执行的指令数量并且消除了一些分支。
+首先,移除掉函数调用以及与之关联的前置处理 [^4] 是主要因素。把 `max` 函数的函数体在调用处展开,减少了处理器执行的指令数量并且消除了一些分支。
现在由于编译器优化了 `BenchmarkMax`,因此它可以看到 `max` 函数的内容,进而可以做更多的提升。当 `max` 被内联后,`BenchmarkMax` 呈现给编译器的样子,看起来是这样的:
@@ -116,7 +118,7 @@ name old time/op new time/op delta
Max-4 2.21ns ± 1% 0.48ns ± 3% -78.14% (p=0.000 n=18+18)
```
-现在编译器能看到在 `BenchmarkMax` 里内联 `max` 的结果,可以执行以前不能执行的优化措施。例如,编译器注意到 `i` 初始值为 `0`,仅做自增操作,因此所有与 `i` 的比较都可以假定 `i` 不是负值。这样条件表达式 `-1 > i` 永远不是 true。[5][6]
+现在编译器能看到在 `BenchmarkMax` 里内联 `max` 的结果,可以执行以前不能执行的优化措施。例如,编译器注意到 `i` 初始值为 `0`,仅做自增操作,因此所有与 `i` 的比较都可以假定 `i` 不是负值。这样条件表达式 `-1 > i` 永远不是 `true`。[^5]
证明了 `-1 > i` 永远不为 true 后,编译器可以把代码简化为:
@@ -150,7 +152,7 @@ func BenchmarkMax(b *testing.B) {
### 内联的限制
-本文中我论述的内联称作*叶子*内联;把函数调用栈中最底层的函数在调用它的函数处展开的行为。内联是个递归的过程,当把函数内联到调用它的函数 A 处后,编译器会把内联后的结果代码再内联到 A 的调用方,这样持续内联下去。例如,下面的代码:
+本文中我论述的内联称作叶子内联:把函数调用栈中最底层的函数在调用它的函数处展开的行为。内联是个递归的过程,当把函数内联到调用它的函数 A 处后,编译器会把内联后的结果代码再内联到 A 的调用方,这样持续内联下去。例如,下面的代码:
```go
func BenchmarkMaxMaxMax(b *testing.B) {
@@ -166,11 +168,11 @@ func BenchmarkMaxMaxMax(b *testing.B) {
下一篇文章中,我会论述当 Go 编译器想要内联函数调用栈中间的某个函数时选用的另一种内联策略。最后我会论述编译器为了内联代码准备好要达到的极限,这个极限 Go 现在的能力还达不到。
-1. 在 Go 中,一个方法就是一个有预先定义的形参和接受者的函数。假设这个方法不是通过接口调用的,调用一个无消耗的函数所消耗的代价与引入一个方法是相同的。[][7]
-2. 在 Go 1.14 以前,栈检查的前置处理也被 gc 用于 STW,通过把所有活跃的 goroutine 栈空间设为 0,来强制它们切换为下一次函数调用时的运行时状态。这个机制[最近被替换][8]为一种新机制,新机制下运行时可以不用等 goroutine 进行函数调用就可以暂停 goroutine。[][9]
-3. 我用 `//go:noinline` 编译指令来阻止编译器内联 `max`。这是因为我想把内联 `max` 的影响与其他影响隔离开,而不是用 `-gcflags='-l -N'` 选项在全局范围内禁止优化。关于 `//go:` 注释在[这篇文章][10]中详细论述。[][11]
-4. 你可以自己通过比较 `go test -bench=. -gcflags=-S`有无 `//go:noinline` 注释时的不同结果来验证一下。[][12]
-5. 你可以用 `-gcflags=-d=ssa/prove/debug=on` 选项来自己验证一下。[][13]
+[^1]: 在 Go 中,一个方法就是一个有预先定义的形参和接受者的函数。假设这个方法不是通过接口调用的,调用一个无消耗的函数所消耗的代价与引入一个方法是相同的。
+[^2]: 在 Go 1.14 以前,栈检查的前置处理也被垃圾回收器用于 STW,通过把所有活跃的 goroutine 栈空间设为 0,来强制它们切换为下一次函数调用时的运行时状态。这个机制[最近被替换][8]为一种新机制,新机制下运行时可以不用等 goroutine 进行函数调用就可以暂停 goroutine。
+[^3]: 我用 `//go:noinline` 编译指令来阻止编译器内联 `max`。这是因为我想把内联 `max` 的影响与其他影响隔离开,而不是用 `-gcflags='-l -N'` 选项在全局范围内禁止优化。关于 `//go:` 注释在[这篇文章][10]中详细论述。
+[^4]: 你可以自己通过比较 `go test -bench=. -gcflags=-S` 有无 `//go:noinline` 注释时的不同结果来验证一下。
+[^5]: 你可以用 `-gcflags=-d=ssa/prove/debug=on` 选项来自己验证一下。
#### 相关文章:
@@ -186,7 +188,7 @@ via: https://dave.cheney.net/2020/04/25/inlining-optimisations-in-go
作者:[Dave Cheney][a]
选题:[lujun9972][b]
译者:[lxbwolf](https://github.com/lxbwolf)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/published/20200430 Three Methods Boot CentOS-RHEL 7-8 Systems in Single User Mode.md b/published/20200430 Three Methods Boot CentOS-RHEL 7-8 Systems in Single User Mode.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..4b7edb67e9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20200430 Three Methods Boot CentOS-RHEL 7-8 Systems in Single User Mode.md
@@ -0,0 +1,165 @@
+[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
+[#]: translator: (lxbwolf)
+[#]: reviewer: (wxy)
+[#]: publisher: (wxy)
+[#]: url: (https://linux.cn/article-12181-1.html)
+[#]: subject: (Three Methods Boot CentOS/RHEL 7/8 Systems in Single User Mode)
+[#]: via: (https://www.2daygeek.com/boot-centos-7-8-rhel-7-8-single-user-mode/)
+[#]: author: (Magesh Maruthamuthu https://www.2daygeek.com/author/magesh/)
+
+以单用户模式启动 CentOS/RHEL 7/8 的三种方法
+======
+
+
+
+单用户模式,也被称为维护模式,超级用户可以在此模式下恢复/修复系统问题。
+
+通常情况下,这类问题在多用户环境中修复不了。系统可以启动但功能不能正常运行或者你登录不了系统。
+
+在基于 [Red Hat][1](RHEL)7/8 的系统中,使用 `runlevel1.target` 或 `rescue.target` 来实现。
+
+在此模式下,系统会挂载所有的本地文件系统,但不开启网络接口。
+
+系统仅启动特定的几个服务和修复系统必要的尽可能少的功能。
+
+当你想运行文件系统一致性检查来修复损坏的文件系统,或忘记 root 密码后重置密码,或要修复系统上的一个挂载点问题时,这个方法会很有用。
+
+你可以用下面三种方法以单用户模式启动 [CentOS][2]/[RHEL][3] 7/8 系统。
+
+ * 方法 1:通过向内核添加 `rd.break` 参数来以单用户模式启动 CentOS/RHEL 7/8 系统
+ * 方法 2:通过用 `init=/bin/bash` 或 `init=/bin/sh` 替换内核中的 `rhgb quiet` 语句来以单用户模式启动 CentOS/RHEL 7/8 系统
+ * 方法 3:通过用 `rw init=/sysroot/bin/sh` 参数替换内核中的 `ro` 语句以单用户模式启动 CentOS/RHEL 7/8 系统
+
+### 方法 1
+
+通过向内核添加 `rd.break` 参数来以单用户模式启动 CentOS/RHEL 7/8 系统。
+
+重启你的系统,在 GRUB2 启动界面,按下 `e` 键来编辑选中的内核。你需要选中第一行,第一个是最新的内核,然而如果你想用旧的内核启动系统你也可以选择其他的行。
+
+
+
+根据你的 RHEL/CentOS 版本,找到 `linux16` 或 `linux` 语句,按下键盘上的 `End` 键,跳到行末,像下面截图中展示的那样添加关键词 `rd.break`,按下 `Ctrl+x` 或 `F10` 来进入单用户模式。
+
+如果你的系统是 RHEL/CentOS 7,你需要找 `linux16`,如果你的系统是 RHEL/CentOS 8,那么你需要找 `linux`。
+
+
+
+这个修改会让你的 root 文件系统以 “只读(`ro`)” 模式挂载。你可以用下面的命令来验证下。下面的输出也明确地告诉你当前是在 “紧急模式”。
+
+```
+# mount | grep root
+```
+
+
+
+为了修改 `sysroot` 文件系统,你需要用读写模式(`rw`)重新挂载它。
+
+```
+# mount -o remount,rw /sysroot
+```
+
+运行下面的命令修改环境,这就是大家熟知的 “监禁目录” 或 “chroot 监狱”。
+
+```
+# chroot /sysroot
+```
+
+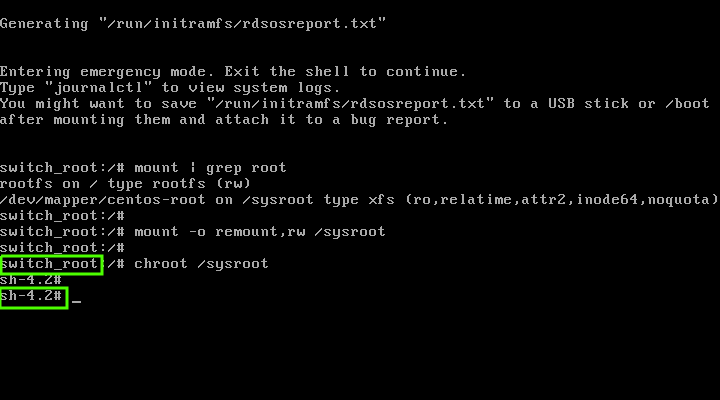
+
+现在,单用户模式已经完全准备好了。当你修复了你的问题要退出单用户模式时,执行下面的步骤。
+
+CentOS/RHEL 7/8 默认使用 SELinux,因此创建下面的隐藏文件,这个文件会在下一次启动时重新标记所有文件。
+
+```
+# touch /.autorelabel
+```
+
+最后,用下面的命令重启系统。你也可以输入两次 `exit` 命令来重启你的系统。
+
+```
+# reboot -f
+```
+
+### 方法 2
+
+通过用 `init=/bin/bash` 或 `init=/bin/sh` 替换内核中的 `rhgb quiet` 语句来以单用户模式启动 CentOS/RHEL 7/8 系统。
+
+重启你的系统,在 GRUB2 启动界面,按下 `e` 键来编辑选中的内核。
+
+
+
+找到语句 `rhgb quiet`,用 `init=/bin/bash` 或 `init=/bin/sh` 替换它,然后按下 `Ctrl+x` 或 `F10` 来进入单用户模式。
+
+`init=/bin/bash` 的截图。
+
+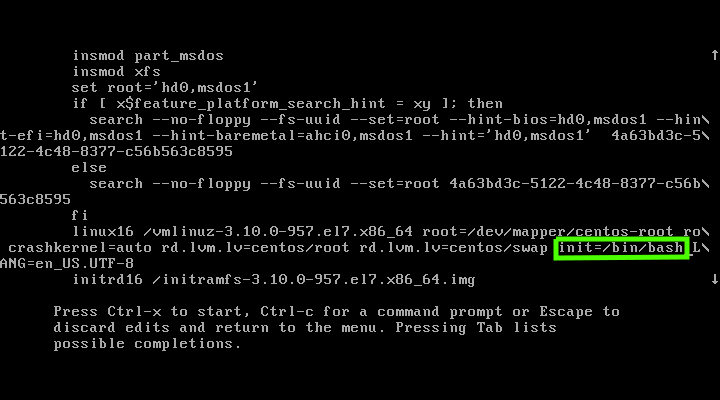
+
+`init=/bin/sh` 的截图。
+
+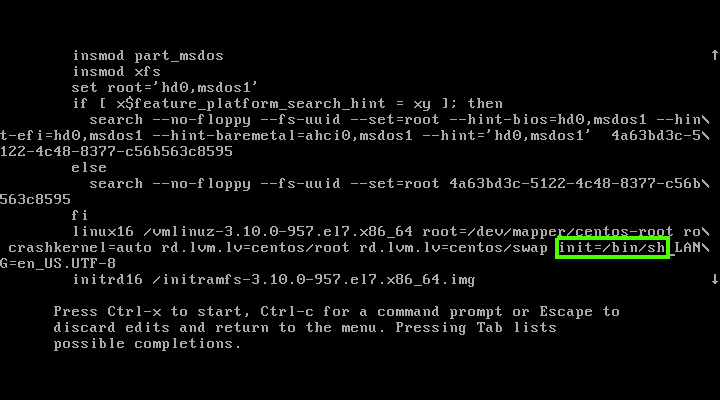
+
+默认情况下,上面的操作会以只读(`ro`)模式挂载你的 `/` 分区,因此你需要以读写(`rw`)模式重新挂载 `/` 文件系统,这样才能修改它。
+
+```
+# mount -o remount,rw /
+```
+
+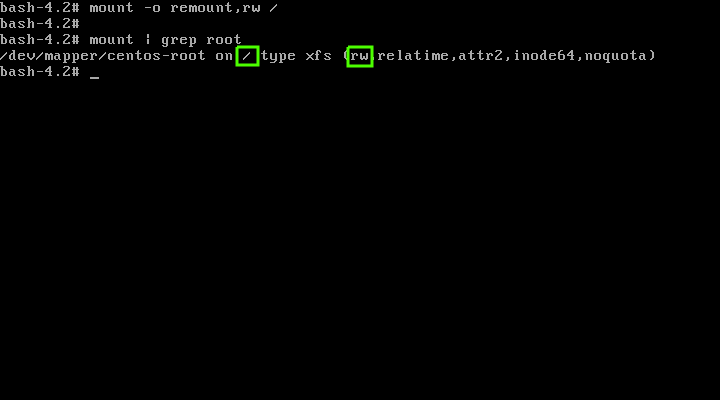
+
+现在你可以执行你的任务了。当结束时,执行下面的命令来开启重启时的 SELinux 重新标记。
+
+```
+# touch /.autorelabel
+```
+
+最后,重启系统。
+
+```
+# exec /sbin/init 6
+```
+
+### 方法 3
+
+通过用 `rw init=/sysroot/bin/sh` 参数替换内核中的 `ro` 单词,以单用户模式启动 CentOS/RHEL 7/8 系统。
+
+为了中断自动启动的过程,重启你的系统并在 GRUB2 启动界面按下任意键。
+
+现在会展示你系统上所有可用的内核,选择最新的内核,按下 `e` 键来编辑选中的内核参数。
+
+找到以 `linux` 或 `linux16` 开头的语句,用 `rw init=/sysroot/bin/sh` 替换 `ro`。替换完后按下 `Ctrl+x` 或 `F10` 来进入单用户模式。
+
+运行下面的命令把环境切换为 “chroot 监狱”。
+
+```
+# chroot /sysroot
+```
+
+如果需要,做出必要的修改。修改完后,执行下面的命令来开启重启时的 SELinux 重新标记。
+
+```
+# touch /.autorelabel
+```
+
+最后,重启系统。
+
+```
+# reboot -f
+```
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://www.2daygeek.com/boot-centos-7-8-rhel-7-8-single-user-mode/
+
+作者:[Magesh Maruthamuthu][a]
+选题:[lujun9972][b]
+译者:[lxbwolf](https://github.com/lxbwolf)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]: https://www.2daygeek.com/author/magesh/
+[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
+[1]: https://www.2daygeek.com/category/red-hat/
+[2]: https://www.2daygeek.com/category/centos/
+[3]: https://www.2daygeek.com/category/rhel/
+[4]: data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7
diff --git a/published/20200502 Mid-stack inlining in Go.md b/published/20200502 Mid-stack inlining in Go.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..588286626a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20200502 Mid-stack inlining in Go.md
@@ -0,0 +1,208 @@
+[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
+[#]: translator: (lxbwolf)
+[#]: reviewer: (wxy)
+[#]: publisher: (wxy)
+[#]: url: (https://linux.cn/article-12184-1.html)
+[#]: subject: (Mid-stack inlining in Go)
+[#]: via: (https://dave.cheney.net/2020/05/02/mid-stack-inlining-in-go)
+[#]: author: (Dave Cheney https://dave.cheney.net/author/davecheney)
+
+Go 中对栈中函数进行内联
+======
+
+
+
+[上一篇文章][1]中我论述了叶子内联是怎样让 Go 编译器减少函数调用的开销的,以及延伸出了跨函数边界的优化的机会。本文中,我要论述内联的限制以及叶子内联与栈中内联的对比。
+
+### 内联的限制
+
+把函数内联到它的调用处消除了调用的开销,为编译器进行其他的优化提供了更好的机会,那么问题来了,既然内联这么好,内联得越多开销就越少,*为什么不尽可能多地内联呢?*
+
+内联可能会以增加程序大小换来更快的执行时间。限制内联的最主要原因是,创建许多函数的内联副本会增加编译时间,并导致生成更大的二进制文件的边际效应。即使把内联带来的进一步的优化机会考虑在内,太激进的内联也可能会增加生成的二进制文件的大小和编译时间。
+
+内联收益最大的是[小函数][2],相对于调用它们的开销来说,这些函数做很少的工作。随着函数大小的增长,函数内部做的工作与函数调用的开销相比省下的时间越来越少。函数越大通常越复杂,因此优化其内联形式相对于原地优化的好处会减少。
+
+### 内联预算
+
+在编译过程中,每个函数的内联能力是用*内联预算*计算的 [^1]。开销的计算过程可以巧妙地内化,像一元和二元等简单操作,在抽象语法数(AST)中通常是每个节点一个单位,更复杂的操作如 `make` 可能单位更多。考虑下面的例子:
+
+```go
+package main
+
+func small() string {
+ s := "hello, " + "world!"
+ return s
+}
+
+func large() string {
+ s := "a"
+ s += "b"
+ s += "c"
+ s += "d"
+ s += "e"
+ s += "f"
+ s += "g"
+ s += "h"
+ s += "i"
+ s += "j"
+ s += "k"
+ s += "l"
+ s += "m"
+ s += "n"
+ s += "o"
+ s += "p"
+ s += "q"
+ s += "r"
+ s += "s"
+ s += "t"
+ s += "u"
+ s += "v"
+ s += "w"
+ s += "x"
+ s += "y"
+ s += "z"
+ return s
+}
+
+func main() {
+ small()
+ large()
+}
+```
+
+使用 `-gcflags=-m=2` 参数编译这个函数能让我们看到编译器分配给每个函数的开销:
+
+```bash
+% go build -gcflags=-m=2 inl.go
+# command-line-arguments
+./inl.go:3:6: can inline small with cost 7 as: func() string { s := "hello, world!"; return s }
+./inl.go:8:6: cannot inline large: function too complex: cost 82 exceeds budget 80
+./inl.go:38:6: can inline main with cost 68 as: func() { small(); large() }
+./inl.go:39:7: inlining call to small func() string { s := "hello, world!"; return s }
+```
+
+编译器根据函数 `func small()` 的开销(7)决定可以对它内联,而 `func large()` 的开销太大,编译器决定不进行内联。`func main()` 被标记为适合内联的,分配了 68 的开销;其中 `small` 占用 7,调用 `small` 函数占用 57,剩余的(4)是它自己的开销。
+
+可以用 `-gcflag=-l` 参数控制内联预算的等级。下面是可使用的值:
+
+ * `-gcflags=-l=0` 默认的内联等级。
+ * `-gcflags=-l`(或 `-gcflags=-l=1`)取消内联。
+ * `-gcflags=-l=2` 和 `-gcflags=-l=3` 现在已经不使用了。和 `-gcflags=-l=0` 相比没有区别。
+ * `-gcflags=-l=4` 减少非叶子函数和通过接口调用的函数的开销。[^2]
+
+#### 不确定语句的优化
+
+一些函数虽然内联的开销很小,但由于太复杂它们仍不适合进行内联。这就是函数的不确定性,因为一些操作的语义在内联后很难去推导,如 `recover`、`break`。其他的操作,如 `select` 和 `go` 涉及运行时的协调,因此内联后引入的额外的开销不能抵消内联带来的收益。
+
+不确定的语句也包括 `for` 和 `range`,这些语句不一定开销很大,但目前为止还没有对它们进行优化。
+
+### 栈中函数优化
+
+在过去,Go 编译器只对叶子函数进行内联 —— 只有那些不调用其他函数的函数才有资格。在上一段不确定的语句的探讨内容中,一次函数调用就会让这个函数失去内联的资格。
+
+进入栈中进行内联,就像它的名字一样,能内联在函数调用栈中间的函数,不需要先让它下面的所有的函数都被标记为有资格内联的。栈中内联是 David Lazar 在 Go 1.9 中引入的,并在随后的版本中做了改进。[这篇文稿][5]深入探究了保留栈追踪行为和被深度内联后的代码路径里的 `runtime.Callers` 的难点。
+
+在前面的例子中我们看到了栈中函数内联。内联后,`func main()` 包含了 `func small()` 的函数体和对 `func large()` 的一次调用,因此它被判定为非叶子函数。在过去,这会阻止它被继续内联,虽然它的联合开销小于内联预算。
+
+栈中内联的最主要的应用案例就是减少贯穿函数调用栈的开销。考虑下面的例子:
+
+```go
+package main
+
+import (
+ "fmt"
+ "strconv"
+)
+
+type Rectangle struct {}
+
+//go:noinline
+func (r *Rectangle) Height() int {
+ h, _ := strconv.ParseInt("7", 10, 0)
+ return int(h)
+}
+
+func (r *Rectangle) Width() int {
+ return 6
+}
+
+func (r *Rectangle) Area() int { return r.Height() * r.Width() }
+
+func main() {
+ var r Rectangle
+ fmt.Println(r.Area())
+}
+```
+
+在这个例子中, `r.Area()` 是个简单的函数,调用了两个函数。`r.Width()` 可以被内联,`r.Height()` 这里用 `//go:noinline` 指令标注了,不能被内联。[^3]
+
+```bash
+% go build -gcflags='-m=2' square.go
+# command-line-arguments
+./square.go:12:6: cannot inline (*Rectangle).Height: marked go:noinline
+./square.go:17:6: can inline (*Rectangle).Width with cost 2 as: method(*Rectangle) func() int { return 6 }
+./square.go:21:6: can inline (*Rectangle).Area with cost 67 as: method(*Rectangle) func() int { return r.Height() * r.Width() }
+./square.go:21:61: inlining call to (*Rectangle).Width method(*Rectangle) func() int { return 6 }
+./square.go:23:6: cannot inline main: function too complex: cost 150 exceeds budget 80
+./square.go:25:20: inlining call to (*Rectangle).Area method(*Rectangle) func() int { return r.Height() * r.Width() }
+./square.go:25:20: inlining call to (*Rectangle).Width method(*Rectangle) func() int { return 6 }
+```
+
+由于 `r.Area()` 中的乘法与调用它的开销相比并不大,因此内联它的表达式是纯收益,即使它的调用的下游 `r.Height()` 仍是没有内联资格的。
+
+#### 快速路径内联
+
+关于栈中内联的效果最令人吃惊的例子是 2019 年 [Carlo Alberto Ferraris][7] 通过允许把 `sync.Mutex.Lock()` 的快速路径(非竞争的情况)内联到它的调用方来[提升它的性能][7]。在这个修改之前,`sync.Mutex.Lock()` 是个很大的函数,包含很多难以理解的条件,使得它没有资格被内联。即使锁可用时,调用者也要付出调用 `sync.Mutex.Lock()` 的代价。
+
+Carlo 把 `sync.Mutex.Lock()` 分成了两个函数(他自己称为外联)。外部的 `sync.Mutex.Lock()` 方法现在调用 `sync/atomic.CompareAndSwapInt32()` 且如果 CAS(比较并交换)成功了之后立即返回给调用者。如果 CAS 失败,函数会走到 `sync.Mutex.lockSlow()` 慢速路径,需要对锁进行注册,暂停 goroutine。[^4]
+
+```bash
+% go build -gcflags='-m=2 -l=0' sync 2>&1 | grep '(*Mutex).Lock'
+../go/src/sync/mutex.go:72:6: can inline (*Mutex).Lock with cost 69 as: method(*Mutex) func() { if "sync/atomic".CompareAndSwapInt32(&m.state, 0, mutexLocked) { if race.Enabled { }; return }; m.lockSlow() }
+```
+
+通过把函数分割成一个简单的不能再被分割的外部函数,和(如果没走到外部函数就走到的)一个处理慢速路径的复杂的内部函数,Carlo 组合了栈中函数内联和[编译器对基础操作的支持][9],减少了非竞争锁 14% 的开销。之后他在 `sync.RWMutex.Unlock()` 重复这个技巧,节省了另外 9% 的开销。
+
+[^1]: 不同发布版本中,在考虑该函数是否适合内联时,Go 编译器对同一函数的预算是不同的。
+[^2]: 时刻记着编译器的作者警告过[“更高的内联等级(比 -l 更高)可能导致错误或不被支持”][11]。 Caveat emptor。
+[^3]: 编译器有足够的能力来内联像 `strconv.ParseInt` 的复杂函数。作为一个实验,你可以尝试去掉 `//go:noinline` 注释,使用 `-gcflags=-m=2` 编译后观察。
+[^4]: `race.Enable` 表达式是通过传递给 `go` 工具的 `-race` 参数控制的一个常量。对于普通编译,它的值是 `false`,此时编译器可以完全省略代码路径。
+
+### 相关文章:
+
+ 1. [Go 中的内联优化][15]
+ 2. [goroutine 的栈为什么会无限增长?][16]
+ 3. [栈追踪和 errors 包][17]
+ 4. [零值是什么,为什么它很有用?][18]
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://dave.cheney.net/2020/05/02/mid-stack-inlining-in-go
+
+作者:[Dave Cheney][a]
+选题:[lujun9972][b]
+译者:[lxbwolf](https://github.com/lxbwolf)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]: https://dave.cheney.net/author/davecheney
+[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
+[1]: https://linux.cn/article-12176-1.html
+[2]: https://medium.com/@joshsaintjacque/small-functions-considered-awesome-c95b3fd1812f
+[3]: tmp.FyRthF1bbF#easy-footnote-bottom-1-4076 (The budget the Go compiler applies to each function when considering if it is eligible for inlining changes release to release.)
+[4]: tmp.FyRthF1bbF#easy-footnote-bottom-2-4076 (Keep in mind that the compiler authors warn that “Additional levels of inlining (beyond -l) may be buggy and are not supported”. Caveat emptor.)
+[5]: https://docs.google.com/presentation/d/1Wcblp3jpfeKwA0Y4FOmj63PW52M_qmNqlQkNaLj0P5o/edit#slide=id.p
+[6]: tmp.FyRthF1bbF#easy-footnote-bottom-3-4076 (The compiler is powerful enough that it can inline complex functions like strconv.ParseInt. As a experiment, try removing the //go:noinline annotation and observe the result with -gcflags=-m=2.)
+[7]: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/148959
+[8]: tmp.FyRthF1bbF#easy-footnote-bottom-4-4076 (The expression race.Enable is a constant controlled by the -race flag passed to the go tool. It is false for normal builds which allows the compiler to elide those code paths entirely.)
+[9]: https://dave.cheney.net/2019/08/20/go-compiler-intrinsics
+[10]: tmp.FyRthF1bbF#easy-footnote-1-4076
+[11]: https://github.com/golang/go/blob/be08e10b3bc07f3a4e7b27f44d53d582e15fd6c7/src/cmd/compile/internal/gc/inl.go#L11
+[12]: tmp.FyRthF1bbF#easy-footnote-2-4076
+[13]: tmp.FyRthF1bbF#easy-footnote-3-4076
+[14]: tmp.FyRthF1bbF#easy-footnote-4-4076
+[15]: https://dave.cheney.net/2020/04/25/inlining-optimisations-in-go (Inlining optimisations in Go)
+[16]: https://dave.cheney.net/2013/06/02/why-is-a-goroutines-stack-infinite (Why is a Goroutine’s stack infinite ?)
+[17]: https://dave.cheney.net/2016/06/12/stack-traces-and-the-errors-package (Stack traces and the errors package)
+[18]: https://dave.cheney.net/2013/01/19/what-is-the-zero-value-and-why-is-it-useful (What is the zero value, and why is it useful?)
diff --git a/published/20200502 Pop OS 20.04 Review- Best Ubuntu-based Distribution Just Got Better.md b/published/20200502 Pop OS 20.04 Review- Best Ubuntu-based Distribution Just Got Better.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..731c14fa0b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20200502 Pop OS 20.04 Review- Best Ubuntu-based Distribution Just Got Better.md
@@ -0,0 +1,228 @@
+[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
+[#]: translator: (wxy)
+[#]: reviewer: (wxy)
+[#]: publisher: (wxy)
+[#]: url: (https://linux.cn/article-12175-1.html)
+[#]: subject: (Pop OS 20.04 Review: Best Ubuntu-based Distribution Just Got Better)
+[#]: via: (https://itsfoss.com/pop-os-20-04-review/)
+[#]: author: (Ankush Das https://itsfoss.com/author/ankush/)
+
+Pop!_OS 20.04 点评:最好的基于 Ubuntu 的发行版越来越好了
+======
+
+> Pop!_OS 20.04 是一款令人印象深刻的基于 Ubuntu 的 Linux 发行版。我在这篇评论中回顾了其主要的新功能,并分享了我对最新版本的体验。
+
+现在,Ubuntu 20.04 LTS 及其官方变体版本已经发布了 - 是时候看看 [System76][1] 的 Pop!_OS 20.04 了,这是基于 Ubuntu 的最好的发行版之一。
+
+老实说,Pop!_OS 是我最喜欢的 Linux 发行版,主要用于我做的所有事情。
+
+现在,Pop!_OS 20.04 终于来了。是时候来看看它提供了哪些功能,以及你是否应该升级?
+
+### Pop!_OS 20.04 LTS 中有什么新东西?
+
+![][2]
+
+从视觉上看,Pop!\_OS 20.04 LTS 与 Pop!\_OS 19.10 并没有太大的区别。然而,你可以发现几个新功能和改进。
+
+但是,如果你之前使用的是 Pop!_OS 18.04 LTS,则可以发现有很多东西可以尝试。
+
+随着 [GNOME 3.36][3] 的到来,及其带来的一些新功能,Pop!_OS 20.04 成为了一个令人激动的版本。
+
+总的来说,以下是一些主要的亮点。
+
+ * 自动窗口平铺
+ * 新的应用程序切换器和启动器
+ * 在 Pop!_Shop 中增加了对 Flatpack 的支持。
+ * GNOME 3.36
+ * Linux 内核 5.4
+ * 改进的混合图形支持
+
+虽然听起来很有趣,但我们还是来了解一下详细的变化,以及到目前为止 Pop!_OS 20.04 的体验如何。
+
+#### Pop!_OS 20.04 中的用户体验提升
+
+毫无疑问,很多 Linux 发行版都提供了开箱即用的用户体验。同样的,[Ubuntu 20.04 LTS 也有一流的改进和功能][4]。
+
+而对于 System76 的 Pop!_OS,他们总是试图更进一步。并且,大多数新功能旨在通过提供有用的功能来改善用户体验。
+
+在这里,我将介绍一些改进,其中包括 [GNOME 3.36][3] 和 Pop!_OS 特有的一些功能。
+
+#### 支持系统托盘图标
+
+总算是有了!这可能不是什么大的改变 —— 但 Pop!_OS 以前没有支持系统托盘图标(或小程序图标)。
+
+![][5]
+
+随着 20.04 LTS 的发布,默认情况就有了系统托盘,不需要任何扩展。
+
+依靠系统托盘图标的程序可能并不多 —— 但它仍然是重要的东西。
+
+就我而言,我以前无法在 Pop!_OS 19.10 上使用 [ActivityWatch][6] —— 但现在可以了。
+
+#### 自动窗口平铺
+
+![][7]
+
+自动窗口平铺是我一直想尝试的东西 —— 但从来没花时间使用过 [i3][9] 这样的[平铺窗口管理器][8]来设置它,更别说是 [Regolith 桌面][10]了。
+
+在 Pop!_OS 20.04 中,你就不需要这样做了。自动窗口平铺功能已经内置,无需设置。
+
+它还提供了“显示活动提示”的选项,也就是说,它将高亮显示活动窗口以避免混淆。而且,你还可以调整窗口之间的间隙。
+
+![][11]
+
+你可以在他们的官方视频中看到它是如何工作的:
+
+- [System76 Pop!_OS 20.04 - Auto Tiling](https://youtu.be/-fltwBKsMY0)
+
+而且,我得说,这是 Pop!_OS 20.04 上最大的新增功能之一,有可能帮助你更有效地进行多任务处理。
+
+即使每次使用该功能都很方便,但为了最大程度地利用它,最好是使用一个大于 21 英寸的显示屏(至少)! 而且,因为这个原因 —— 我真的很想把我的显示器也升级一下!
+
+#### 新的扩展应用
+
+![][13]
+
+Pop!_OS 内置了一些独特的 GNOME 扩展。但是,你不需要用 GNOME Tweaks 来管理扩展。
+
+新增加的 “Extensions” 应用可以让你在 Pop!_OS 20.04 上配置和管理扩展程序。
+
+#### 改进的通知中心
+
+![][14]
+
+在新的 GNOME 3.36 中,通知中心的外观经过了改进。这里,我启用了黑暗模式。
+
+#### 新的应用程序切换器 & 启动器
+
+![][15]
+
+你仍然可以用 `ALT+TAB` 或 `Super+TAB` 来浏览正在运行的应用程序。
+
+但是,当你有很多事情要做的时候,这很耗时。所以,在 Pop!_OS 20.04上,你可以使用 `Super+ /` 激活应用程序切换器和启动器。
+
+一旦你习惯了这个快捷键,它将是非常方便的东西。
+
+除此以外,你可能会发现 Pop!_OS 20.04 上的图标/窗口在视觉上有许多其它细微的改进。
+
+#### 新的登录界面
+
+嗯,这是 GNOME 3.36 带来的一个明显的变化。但是,它看起来确实很不错!
+
+![][16]
+
+#### Pop!_Shop 支持 Flatpak
+
+通常,Pop!_Shop 已经是一个非常有用的东西了,包括它自有的在内,它带有一个巨大的软件仓库。
+
+现在,在 Pop!\_OS 20.04 中,你可以用 Pop!_Shop 安装任何可用软件的 Debian 包或 Flatpak(通过 Flathub) —— 当然,前提是某个软件有 Flatpak 软件包。
+
+如果你没有使用 Pop!_OS 20.04,你可能要看看[如何在 Linux 上使用 Flatpak][18]。
+
+![][19]
+
+就我个人而言,我并不是 Flatpak 的粉丝,但有些应用如 GIMP 需要你安装 Flatpak 包才能获得最新版本。所以,在 Pop!_Shop 上直接支持了 Flatpak 绝对是一件好事。
+
+#### 键盘快捷键更改
+
+如果你习惯了 Pop!_OS 19.10 或更早的版本上现有的键盘快捷键,这可能会让你很烦。
+
+不管是哪种情况,有几个重要的键盘快捷键变化可能会改善你的体验,如下:
+
+ * 锁定屏幕:`Super + L` 改为 `Super + Escape`。
+ * 移动工作区:`Super + 上/下箭头键` 改为 `Super + CTRL + 上/下箭头键`。
+ * 关闭窗口:`Super + W` 变更为 `Super + Q`。
+ * 切换最大化:`Super +向上箭头` 改为 `Super + M`。
+
+#### Linux 内核 5.4
+
+与其他大多数最新的 Linux 发行版相似,Pop!_OS 20.04 搭载了 [Linux 内核 5.4][20]。
+
+所以,很明显,你可以期望获得对 [exFAT 支持][21]、改进的 AMD 图形兼容性以及它附带所有其他功能。
+
+#### 性能提升
+
+尽管 Pop!_OS 并不称自己是轻量级的 Linux 发行版,但它仍然是一个资源节约型的发行版。而且,有了 GNOME 3.36 的支持,它的速度应该足够快了。
+
+考虑到我已经将 Pop!\_OS 作为主要发行版使用已经一年多了,我从来没有遇到过性能问题。这就是你安装了 Pop!_OS 20.04 之后的资源使用情况(取决于你的系统配置)。
+
+![][22]
+
+给你一个作为参考,我的台式机配置包括 i5-7400 处理器、16GB 内存(2400MHz)、NVIDIA GTX 1050ti 显卡和 SSD。
+
+我不是一个系统基准测试的忠实拥护者,因为除非你去尝试,否则它并不能让你知道特定的应用或游戏的性能。
+
+你可以试试 [Phoronix 测试套件][23]来分析你的系统表现。但是,Pop!_OS 20.04 LTS 应该是一个很爽快的体验!
+
+#### 软件包更新 & 其他改进
+
+尽管每个基于Ubuntu的发行版都受益于Ubuntu 20.04 LTS的改进,但也有一些 Pop!_OS 特有的错误修复和改进。
+
+除此之外,一些主要的应用程序/包(如 Firefox 75.0)也已经更新到了最新版本。
+
+到现在为止,应该没有任何严重的错误,至少对我来说没有。
+
+你可以在 [GitHub 上查看他们的开发进度][24],以了解他们在测试期间已经修复的问题和发布后即将修复的问题。
+
+### 下载 & 支持 Pop!_OS 20.04
+
+![][25]
+
+在这个版本中,System76 终于增加了一个可选的订阅模式来支持 Pop!_OS 的开发。
+
+你可以免费下载 Pop!_OS 20.04 —— 但如果你想支持他们,我建议你只需要 \$1/月就可以订阅。
+
+- [Pop!_OS 20.04][26]
+
+### 我对 Pop OS 20.04 的看法
+
+我必须提到的是,我正在为最新的 20.04 版本提供全新的墙纸。但是,这没什么大不了的。
+
+有了窗口平铺功能、支持 flatpak,以及众多其他改进,到目前为止,我对 Pop!_OS 20.04 的体验是一流的。另外,很高兴看到他们在一些流行软件的开箱即用支持上突出了他们对创意专业人士的关注。
+
+![][27]
+
+Ubuntu 20.04 的所有优点,再加上 System76 的一些额外的加料,让我印象深刻!
+
+你试过 Pop!_OS 20.04 吗?请在下面的评论中告诉我你的想法。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://itsfoss.com/pop-os-20-04-review/
+
+作者:[Ankush Das][a]
+选题:[lujun9972][b]
+译者:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]: https://itsfoss.com/author/ankush/
+[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
+[1]: https://system76.com
+[2]: https://i0.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/05/pop_os_20_04_review.jpg?ssl=1
+[3]: https://itsfoss.com/gnome-3-36-release/
+[4]: https://itsfoss.com/ubuntu-20-04-release-features/
+[5]: https://i1.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/system-tray-icons-pop-os.jpg?ssl=1
+[6]: https://activitywatch.net/
+[7]: https://i1.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/pop-os-automatic-screen-tiling.png?ssl=1
+[8]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tiling_window_manager
+[9]: https://i3wm.org/
+[10]: https://itsfoss.com/regolith-linux-desktop/
+[11]: https://i2.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/tile-feature-options-popos.jpg?ssl=1
+[12]: https://www.youtube.com/c/itsfoss?sub_confirmation=1
+[13]: https://i2.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/pop-os-extensions.jpg?ssl=1
+[14]: https://i2.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/notification-center-pop-os.jpg?ssl=1
+[15]: https://i2.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/pop-os-application-launcher.jpg?ssl=1
+[16]: https://i1.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/pop-os-20-04-lock-screen.jpg?ssl=1
+[17]: https://launchpad.net/~system76/+archive/ubuntu/pop
+[18]: https://itsfoss.com/flatpak-guide/
+[19]: https://i2.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/pop-os-flatpak-deb.jpg?ssl=1
+[20]: https://itsfoss.com/linux-kernel-5-4/
+[21]: https://itsfoss.com/mount-exfat/
+[22]: https://i2.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/pop-os-20-04-performance.jpg?ssl=1
+[23]: https://www.phoronix-test-suite.com/
+[24]: https://github.com/orgs/pop-os/projects/13
+[25]: https://i1.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/05/support-pop-os.jpg?ssl=1
+[26]: https://pop.system76.com/
+[27]: https://i0.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/05/pop-os-stem-focus.jpg?ssl=1
diff --git a/sources/news/20200429 Java security, mainframes having a moment, and more industry trends.md b/sources/news/20200429 Java security, mainframes having a moment, and more industry trends.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..beeac5df9d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/news/20200429 Java security, mainframes having a moment, and more industry trends.md
@@ -0,0 +1,71 @@
+[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
+[#]: translator: ( )
+[#]: reviewer: ( )
+[#]: publisher: ( )
+[#]: url: ( )
+[#]: subject: (Java security, mainframes having a moment, and more industry trends)
+[#]: via: (https://opensource.com/article/20/4/java-mainframes-dev-skills-more-industry-trends)
+[#]: author: (Tim Hildred https://opensource.com/users/thildred)
+
+Java security, mainframes having a moment, and more industry trends
+======
+A weekly look at open source community and industry trends.
+![Person standing in front of a giant computer screen with numbers, data][1]
+
+As part of my role as a senior product marketing manager at an enterprise software company with an open source development model, I publish a regular update about open source community, market, and industry trends for product marketers, managers, and other influencers. Here are five of my and their favorite articles from that update.
+
+## [How secure is Java compared to other languages?][2]
+
+> In this article, we'll look at how the most commonly used programming languages rank in terms of security. I'll explain some factors that make one language less secure than another, and why identified vulnerabilities have increased so much in the past few years. Finally, I'll suggest a few ways Java developers can reduce vulnerabilities in code.
+
+**The impact**: If software is eating the world, then hackers are... I guess the thrush thriving in the gullet? Hyperbole aside, the more stuff made of software, the more incentive clever people have to try and figure out how to do things they probably shouldn't be able to. This applies to Java too.
+
+## [Mainframes are having a moment][3]
+
+> In addition to being abundant, mainframe jobs pay well, and so far, appear not to be as affected by the pandemic as other areas of tech employment. Salaries for entry-level enterprise computing jobs [average US $70,100 a year][4] [PDF], according to a 2019 report from tech analyst [Forrester Research][5] commissioned by IBM. As recently as this week, jobs boards such as [Indeed][6] and [Dice.com][7] listed hundreds or in some cases thousands of openings for mainframe positions at all levels. Advertised pay ranges from $30 to $35 an hour for a junior mainframe developer to well over $150,000 a year for a mainframe database administration manager.
+
+**The impact**: That is much, much better than a poke in the eye.
+
+## [The developer skills on the rise, and in decline][8]
+
+> Indeed.com analysed job postings using a list of 500 key technology skill terms to see which ones employers are looking for more these days and which are falling out of favour. Such research has helped identify cutting-edge skills over the past five years, with some previous years’ risers now well establish, thanks to explosive growth.
+
+**The impact**: The "on the rise" skills outnumber the "in decline" skills. Bad news for browser developers...
+
+## [The IT Pro Podcast: Building cloud-native apps][9]
+
+> The cloud is eating enterprise IT, and while on-premise applications are going to be around for a long time to come, the importance of being able to successfully take advantage of cloud technologies should not be understated. However, it’s one thing to simply port an existing application to the cloud, but developing software to be run in cloud environments is a different matter altogether.
+
+**The impact**: What is technology if not manifested mindset?
+
+## [Communication is key to culture change][10]
+
+> The outcome is staggering. Business teams feel invested in the development of the solution, they feel a sense of excitement and ownership. So much so, they go out into the corridors of the organisation to evangelise and promote the solution. Conversely, this improves the status of the developers within the business. It allows them to integrate with other stakeholders, contribute to new processes and help to achieve common goals.
+
+**The impact**: As a communications person, I couldn't agree more. Communication is the difference between an organization and a movement.
+
+_I hope you enjoyed this list and come back next week for more open source community, market, and industry trends._
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://opensource.com/article/20/4/java-mainframes-dev-skills-more-industry-trends
+
+作者:[Tim Hildred][a]
+选题:[lujun9972][b]
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]: https://opensource.com/users/thildred
+[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
+[1]: https://opensource.com/sites/default/files/styles/image-full-size/public/lead-images/data_metrics_analytics_desktop_laptop.png?itok=9QXd7AUr (Person standing in front of a giant computer screen with numbers, data)
+[2]: https://www.javaworld.com/article/3537561/how-secure-is-java-compared-to-other-languages.html
+[3]: https://spectrum.ieee.org/tech-talk/computing/software/mainframes-programming-language-cobol-news-coronavirus
+[4]: https://www.ibm.com/downloads/cas/1EPYAP5D
+[5]: https://go.forrester.com/
+[6]: https://www.indeed.com/q-Mainframe-jobs.html
+[7]: https://www.dice.com/jobs/q-Mainframe-jobs
+[8]: https://www.techcentral.ie/10-developer-skills-on-the-rise-and-five-on-the-decline/
+[9]: https://www.itpro.co.uk/cloud/355348/the-it-pro-podcast-building-cloud-native-apps
+[10]: https://www.verdict.co.uk/culture-service-digital-enterprise/
diff --git a/sources/talk/20200401 The ins and outs of high-performance computing as a service.md b/sources/talk/20200401 The ins and outs of high-performance computing as a service.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 0b0a1ac39b..0000000000
--- a/sources/talk/20200401 The ins and outs of high-performance computing as a service.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,104 +0,0 @@
-[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
-[#]: translator: (messon007)
-[#]: reviewer: ( )
-[#]: publisher: ( )
-[#]: url: ( )
-[#]: subject: (The ins and outs of high-performance computing as a service)
-[#]: via: (https://www.networkworld.com/article/3534725/the-ins-and-outs-of-high-performance-computing-as-a-service.html)
-[#]: author: (Josh Fruhlinger https://www.networkworld.com/author/Josh-Fruhlinger/)
-
-The ins and outs of high-performance computing as a service
-======
-HPC services can be a way to meet expanding supercomputing needs, but depending on the use case, they’re not necessarily better than on-premises supercomputers.
-Dell EMC
-
-Electronics on missiles and military helicopters need to survive extreme conditions. Before any of that physical hardware can be deployed, defense contractor McCormick Stevenson Corp. simulates the real-world conditions it will endure, relying on finite element analysis software like Ansys, which requires significant computing power.
-
-Then one day a few years ago, it unexpectedly ran up against its computing limits.
-
-[10 of the world's fastest supercomputers][1]
-
-"We had some jobs that would have overwhelmed the computers that we had in office," says Mike Krawczyk, principal engineer at McCormick Stevenson. "It did not make economic or schedule sense to buy a machine and install software." Instead, the company contracted with Rescale, which could sell them cycles on a supercomputer-class system for a tiny fraction of what they would've spent on new hardware.
-
-McCormick Stevenson had become an early adopter in a market known as supercomputing as a service or high-performance computing (HPC) as a service – two terms that are closely related. HPC is the application of supercomputers to computationally complex problems, while supercomputers are those computers at the cutting edge of processing capacity, according to the National Institute for Computational Sciences.
-
-Whatever it's called, these services are upending the traditional supercomputing market and bringing HPC power to customers who could never afford it before. But it's no panacea, and it's definitely not plug-and-play – at least not yet.
-
-### HPC services in practice
-
-From the end user's perspective, HPC as a service resembles the batch-processing model that dates back to the early mainframe era. "We create an Ansys batch file and send that up, and after it runs, we pull down the result files and import them locally here," Krawczyk says.
-
-Behind the scenes, cloud providers are running the supercomputing infrastructure in their own data centers – though that doesn't necessarily imply the sort of cutting-edge hardware you might be visualizing when you hear "supercomputer." As Dave Turek, Vice President of Technical Computing at IBM OpenPOWER, explains it, HPC services at their core are "a collection of servers that are strung together with an interconnect. You have the ability to invoke this virtual computing infrastructure that allows you to bring a lot of different servers to work together in a parallel construct to solve the problem when you present it."
-
-[][2]
-
-Sounds simple in theory. But making it viable in practice required some chipping away at technical problems, according to Theo Lynn, Professor of Digital Business at Dublin City University. What differentiates ordinary computing from HPC is those interconnects – high-speed, low-latency, and expensive – so those needed to be brought to the world of cloud infrastructure. Storage performance and data transport also needed to be brought up to a level at least in the same ballpark as on-prem HPC before HPC services could be viable.
-
-But Lynn says that some of the innovations that have helped HPC services take off have been more institutional than technological. In particular, "we are now seeing more and more traditional HPC applications adopting cloud-friendly licensing models – a barrier to adoption in the past."
-
-And the economics have also shifted the potential customer base, he says. "Cloud service providers have opened up the market more by targeting low-end HPC buyers who couldn’t afford the capex associated with traditional HPC and opening up the market to new users. As the markets open up, the hyperscale economic model becomes more and more feasible, costs start coming down."
-
-Avoid on-premises CAPEX**
-**
-
-HPC services are attractive to private-sector customers in the same fields where traditional supercomputing has long held sway. These include sectors that rely heavily on complex mathematical modeling, including defense contractors like McCormick Stevenson, along with oil and gas companies, financial services firms, and biotech companies. Dublin City University's Lynn adds that loosely coupled workloads are a particularly good use case, which meant that many early adopters used it for 3D image rendering and related applications.
-
-But when does it make sense to consider HPC services over on-premises HPC? For hhpberlin, a German company that simulates smoke propagation in and fire damage to structural components of buildings, the move came as it outgrew its current resources.
-
-"For several years, we had run our own small cluster with up to 80 processor cores," says Susanne Kilian, hhpberlin's scientific head of numerical simulation. "With the rise in application complexity, however, this constellation has increasingly proven to be inadequate; the available capacity was not always sufficient to handle projects promptly."
-
-But just spending money on a new cluster wasn't an ideal solution, she says: "In view of the size and administrative environment of our company, the necessity of constant maintenance of this cluster (regular software and hardware upgrades) turned out to be impractical. Plus, the number of required simulation projects is subject to significant fluctuations, such that the utilization of the cluster was not really predictable. Typically, phases with very intensive use alternate with phases with little to no use." By moving to an HPC service model, hhpberlin shed that excess capacity and the need to pay up front for upgrades.
-
-IBM's Turek explains the calculus that different companies go through while assessing their needs. For a biosciences startup with 30 people, "you need computing, but you really can't afford to have 15% of your staff dedicated to it. It's just like you might also say you don't want to have on-staff legal representation, so you'll get that as a service as well." For a bigger company, though, it comes down to weighing the operational expense of an HPC service against the capacity expense of buying an in-house supercomputer or HPC cluster.
-
-So far, those are the same sorts of arguments you'd have over adopting any cloud service. But the opex vs. capex dilemma can be weighted towards the former by some of the specifics of the HPC market. Supercomputers aren't commodity hardware like storage or x86 servers; they're very expensive, and technological advances can swiftly render them obsolete. As McCormick Stevenson's Krawczyk puts it, "It's like buying a car: as soon as you drive off the lot it starts to depreciate." And for many companies –especially larger and less nimble ones – the process of buying a supercomputer can get hopelessly bogged down. "You're caught up in planning issues, building issues, construction issues, training issues, and then you have to execute an RFP," says IBM's Turek. "You have to work through the CIO. You have to work with your internal customers to make sure there's continuity of service. It's a very, very complex process and not something that a lot of institutions are really excellent at executing."
-
-Once you choose to go down the services route for HPC, you'll find you get many of the advantages you expect from cloud services, particularly the ability to pay only for HPC power when you need it, which results in an efficient use of resources. Chirag Dekate, Senior Director and Analyst at Gartner, says bursty workloads, when you have short-term needs for high-performance computing, are a key use case driving adoption of HPC services.
-
-"In the manufacturing industry, you tend to have a high peak of HPC activity around the product design stage," he says. "But once the product is designed, HPC resources are less utilized during the rest of the product-development cycle." In contrast, he says, "when you have large, long-running jobs, the economics of the cloud wear down."
-
-With clever system design, you can integrate those HPC-services bursts of activity with your own in-house conventional computing. Teresa Tung, managing director in Accenture Labs, gives an example: "Accessing HPC via APIs makes it seamless to mix with traditional computing. A traditional AI pipeline might have its training done on a high-end supercomputer at the stage when the model is being developed, but then the resulting trained model that runs predictions over and over would be deployed on other services in the cloud or even devices at the edge."
-
-### It's not for all use cases**
-
-**
-
-Use of HPC services lends itself to batch-processing and loosely-coupled use cases. That ties into a common HPC downside: data transfer issues. High-performance computing by its very nature often involves huge data sets, and sending all that information over the internet to a cloud service provider is no simple thing. "We have clients I talk to in the biotech industry who spend $10 million a month on just the data charges," says IBM's Turek.
-
-And money isn't the only potential problem. Building a workflow that makes use of your data can challenge you to work around the long times required for data transfer. "When we had our own HPC cluster, local access to the simulation results already produced – and thus an interactive interim evaluation — was of course possible at any time," says hhpberlin's Kilian. "We're currently working on being able to access and evaluate the data produced in the cloud even more efficiently and interactively at any desired time of the simulation without the need to download large amounts of simulation data."
-
-Mike Krawczyk cites another stumbling block: compliance issues. Any service a defense contractor uses needs to be complaint with the International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR), and McCormick Stevenson went with Rescale in part because it was the only vendor they found that checked that box. While more do today, any company looking to use cloud services should be aware of the legal and data-protection issues involved in living on someone else's infrastructure, and the sensitive nature of many of HPC's use cases makes this doubly true for HPC as a service.
-
-In addition, the IT governance that HPC services require goes beyond regulatory needs. For instance, you'll need to keep track of whether your software licenses permit cloud use – especially with specialized software packages written to run on an on-premises HPC cluster. And in general, you need to keep track of how you use HPC services, which can be a tempting resource, especially if you've transitioned from in-house systems where staff was used to having idle HPC capabilities available. For instance, Ron Gilpin, senior director and Azure Platform Services global lead at Avanade, suggests dialing back how many processing cores you use for tasks that aren't time sensitive. "If a job only needs to be completed in an hour instead of ten minutes," he says, "that might use 165 processors instead of 1,000, a savings of thousands of dollars."
-
-### A premium on HPC skills**
-
-**
-
-One of the biggest barriers to HPC adoption has always been the unique in-house skills it requires, and HPC services don't magically make that barrier vanish. "Many CIOs have migrated a lot of their workloads into the cloud and they have seen cost savings and increased agility and efficiency, and believe that they can achieve similar results in HPC ecosystems," says Gartner's Dekate. "And a common misperception is that they can somehow optimize human resource cost by essentially moving away from system admins and hiring new cloud experts who can solve their HPC workloads."
-
-"But HPC is not one of the main enterprise environments," he says. "You're dealing with high-end compute nodes interconnected with high-bandwidth, low-latency networking stacks, along with incredibly complicated application and middleware stacks. Even the filesystem layers in many cases are unique to HPC environments. Not having the right skills can be destabilizing."
-
-But supercomputing skills are in shortening supply, something Dekate refers to as the workforce "greying," in the wake of a generation of developers going to splashy startups rather than academia or the more staid firms where HPC is in use. As a result, vendors of HPC services are doing what they can to bridge the gap. IBM's Turek says that many HPC vets will always want to roll their own exquisitely fine-tuned code and will need specialized debuggers and other tools to help them do that for the cloud. But even HPC newbies can make calls to code libraries built by vendors to exploit supercomputing's parallel processing. And third-party software providers sell turnkey software packages that abstract away much of HPC's complication.
-
-Accenture's Tung says the sector needs to lean further into this in order to truly prosper. "HPCaaS has created dramatically impactful new capability, but what needs to happen is making this easy to apply for the data scientist, the enterprise architect, or the software developer," she says. "This includes easy to use APIs, documentation, and sample code. It includes user support to answer questions. It’s not enough to provide an API; that API needs to be fit-for-purpose. For a data scientist this should likely be in Python and easily change out for the frameworks she is already using. The value comes from enabling these users who ultimately will have their jobs improved through new efficiencies and performance, if only they can access the new capabilities." If vendors can pull that off, HPC services might truly bring supercomputing to the masses.
-
-Join the Network World communities on [Facebook][3] and [LinkedIn][4] to comment on topics that are top of mind.
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: https://www.networkworld.com/article/3534725/the-ins-and-outs-of-high-performance-computing-as-a-service.html
-
-作者:[Josh Fruhlinger][a]
-选题:[lujun9972][b]
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]: https://www.networkworld.com/author/Josh-Fruhlinger/
-[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
-[1]: https://www.networkworld.com/article/3236875/embargo-10-of-the-worlds-fastest-supercomputers.html
-[2]: https://www.networkworld.com/blog/itaas-and-the-corporate-storage-technology/?utm_source=IDG&utm_medium=promotions&utm_campaign=HPE22140&utm_content=sidebar (ITAAS and Corporate Storage Strategy)
-[3]: https://www.facebook.com/NetworkWorld/
-[4]: https://www.linkedin.com/company/network-world
diff --git a/sources/talk/20200428 How I empower and reach millions through open source.md b/sources/talk/20200428 How I empower and reach millions through open source.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..a3c23dd073
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/talk/20200428 How I empower and reach millions through open source.md
@@ -0,0 +1,78 @@
+[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
+[#]: translator: ( )
+[#]: reviewer: ( )
+[#]: publisher: ( )
+[#]: url: ( )
+[#]: subject: (How I empower and reach millions through open source)
+[#]: via: (https://opensource.com/article/20/4/interview-Netha-Hussain)
+[#]: author: (Jay Barber https://opensource.com/users/jaybarber)
+
+How I empower and reach millions through open source
+======
+Learn how Netha Hussain, winner of the 2020 Women in Open Source
+Academic Award, shares knowledge and inspires people.
+![Lightbulb][1]
+
+"I wanted to link to a particular Wikipedia article on my blog, but I found there wasn't one on that topic, so I wrote it myself," says Netha Hussain, 2020 [Women in Open Source Academic Award][2] winner. "That's the beauty of open source; anyone can contribute."
+
+![Photo by Lvova Anastasiya \(Львова Анастасия, Lvova\), CC BY-SA][3]
+
+Practicality drove Netha's entry into open source culture, and it has continued to be at the center of her work in the ten years since.
+
+She received her first computer in high school, but it did not immediately spark her passion. She says she mostly used it for games and other diversions, as many teenagers do. It wasn't until she entered medical school and realized that technology could be a powerful tool to help her achieve her goals that Netha truly found her path. Taking stock of her many contributions to [Wikimedia][4], [Mozilla][5], and [TED][6], it's fair to say that once she engaged with open source culture, she never looked back.
+
+### Finding ways to help
+
+Growing up in India, Netha was initially drawn to mathematics but soon found herself pulled in other directions. "At the time, I would have expected to continue down that path, mathematics or maybe writing, but the thing that I've always most wanted to do is help people," Netha says. "Medicine seemed to be the most direct path to providing real, tangible assistance to those around me, so I became a doctor."
+
+That drive to help continues to guide her now as she prepares to defend her doctoral thesis in clinical neuroscience at the University of Gothenburg in Sweden.
+
+"At a certain point, I decided that rather than limiting myself to what I could do through treating patients, I could also contribute in a research capacity, working to discover new, better ways to help others. I came to all of this via an unexpected route, but I love the idea of exploring and finding my own ways to help. I'm so satisfied and fulfilled by the work I'm doing now. It has been a wonderful journey."
+
+As she nears the completion of her degree, Netha reflects upon what she's looking forward to next. An infectious smile appears as she remarks, "I'm really excited to have more time to contribute to projects in the open source community."
+
+Why is she so enamored with open source? It comes back to utility. "In open source practices, I found a philosophy that closely matched my own ideals and a way of doing things that allowed me to help more people. Open source is fueled by collaboration. I've seen the things that can be accomplished by people working together, and it makes me very excited to think where it will take us in the future."
+
+### Reaching millions, one edit at a time
+
+Her first article, written to help an international audience understand her blog post, was only the first of many. Netha has now written 300 articles (200 in English and 100 in Malayalam), contributed 13,000 edits for [Wikipedia][7], added 9,000 images to [Wikimedia Commons][8], and provided 120,000 edits to [Wikidata][9]. Her commitment to bringing useful information to others can also be seen in her five years spent volunteering to translate Mozilla projects and TED talks into the Malayalam language.
+
+Such prolific output was born out of a simple realization. "I had shared so much on my blog but was only reaching a select audience. On Wikipedia and elsewhere, I had access to a potential audience of millions. There's a lot of power in that."
+
+Many of the articles Netha has written center on issues relevant to women, and that is very much by design. "I find myself writing on topics that are important to women because I feel they are an underserved community, and it is important to me that Wikipedia, as such a vital repository of information, be reflective of all users, all voices. I care deeply about the visibility of women on Wikipedia."
+
+Netha's commitment to women's issues led her to organize edit-a-thon initiatives and other activities with women's groups. She was also able to leverage similar strategies to assist the LGBTQ+ community in India during the campaign to legalize gay marriage.
+
+"In India, there are a lot of taboos around homosexuality, and I saw an opportunity to utilize my experience to help another segment of the population. Together, we were able to generate a lot of awareness, whether through raising up biographical articles on famous members of the LGBTQ+ community or shining a spotlight on anti-LGBTQ+ laws. I'm very proud of the opportunities I've had to support such efforts."
+
+### A path to the future
+
+It's clear that Netha believes strongly in empowering people, especially other women who may wish to explore open source methodologies as she has. Her advice is simple, but powerful. "Believe in yourself, and know that you have the skills and talent to do whatever you'd like to do," she finds the words easily, as if she's been waiting to be asked the question. "Follow your passion, and do what you want. There will be times of uncertainty but always move forward. Keep studying. Keep learning new things. That's how you grow, both in your field and as a person."
+
+Having achieved so much already, it's no surprise that Netha is enthusiastic about new challenges on the horizon. "I've put in a lot of effort to get here, but as you learn new strategies and new ways of collaborating, the work gets easier. Now, I don't consider it work at all. It's mostly fun to me."
+
+_Also read Jay Barber's [interview with Megan Byrd-Sanicki][10], who won the 2020 Women in Open Source Community Award._
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://opensource.com/article/20/4/interview-Netha-Hussain
+
+作者:[Jay Barber][a]
+选题:[lujun9972][b]
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]: https://opensource.com/users/jaybarber
+[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
+[1]: https://opensource.com/sites/default/files/styles/image-full-size/public/lead-images/lightbulb-idea-think-yearbook-lead.png?itok=5ZpCm0Jh (Lightbulb)
+[2]: https://www.redhat.com/en/about/women-in-open-source
+[3]: https://opensource.com/sites/default/files/uploads/netha_headshot.png (Photo by Lvova Anastasiya (Львова Анастасия, Lvova), CC BY-SA)
+[4]: https://www.wikimedia.org/
+[5]: https://www.mozilla.org/en-US/
+[6]: https://www.ted.com/
+[7]: https://www.wikipedia.org/
+[8]: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Main_Page
+[9]: https://www.wikidata.org/wiki/Wikidata:Main_Page
+[10]: https://opensource.com/article/20/4/interview-Megan-Byrd-Sanicki
diff --git a/sources/talk/20200430 Industrial robots could -eat metal- to power themselves.md b/sources/talk/20200430 Industrial robots could -eat metal- to power themselves.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..45995a9660
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/talk/20200430 Industrial robots could -eat metal- to power themselves.md
@@ -0,0 +1,67 @@
+[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
+[#]: translator: ( )
+[#]: reviewer: ( )
+[#]: publisher: ( )
+[#]: url: ( )
+[#]: subject: (Industrial robots could 'eat metal' to power themselves)
+[#]: via: (https://www.networkworld.com/article/3540194/industrial-robots-could-eat-metal-to-power-themselves.html)
+[#]: author: (Patrick Nelson https://www.networkworld.com/author/Patrick-Nelson/)
+
+Industrial robots could 'eat metal' to power themselves
+======
+Scavenging energy by foraging for metal could power Internet of Things electronics and robots, suggest researchers at University of Pennsylvania.
+Jiraroj Praditcharoenkul / Getty Images
+
+A fundamental manufacturing shift is on the horizon, some say. It's where robots run all elements of our future factories. The machines will operate using brain-copying artificial intelligence and handle not only manufacturing processes, but also supply-chain logistics, planning, and other roles formerly performed by humans.
+
+This vision of the future anticipates an industrial workplace where Internet-connected machines will mimic humans, yet do the jobs more precisely, faster and cheaper than humans.
+
+And the human-copying element may not end there. Researchers at the University of Pennsylvania are suggesting that robots could end up eating like humans, too.
+
+Robots will "eat metal for energy," according to a [news article][1] published in Medium. The researchers' vision for a "metal-air scavenger" could solve one of the quandaries of future IoT-enabled factories. That quandary is how to power a device that moves without adding mass and weight, as one does by adding bulky batteries.
+
+The answer, according to the University of Pennsylvania researchers, is to try to electromechanically forage for energy from the metal surfaces that a robot or IoT device traverses, thus converting material garnered, using a chemical reaction, into power.
+
+"Robots and electronics [would] extract energy from large volumes of energy dense material without having to carry the material on-board," the researchers say in a paper they've published in [ACS Energy Letters][2].
+
+It would be like "eating metal, breaking down its chemical bonds for energy like humans do with food." Batteries work by repeatedly breaking and creating chemical bonds.
+
+The research references the dichotomy between computing and power storage. Computing is well suited to miniaturization, and processers have been progressively reduced in size while performance has increased, but battery storage hasn't. You need a bigger battery for more energy.
+
+Even if swarming, industrial robots became the size of insects (I've [written about][3] the possibility), there's an issue powering the nano devices – the required size of the power source would defeat the object of the miniaturization. The battery alone could crush the device, and even if it didn't, the machine would need excessive amounts of energy to move, because of the battery mass. This conundrum is one of the reasons there's an emphasis in IoT development to find ways to harvest energy ambiently.
+
+However, with ambient power – such as is found in [solar or potentially magnetism][4], for example – power density comes into play. That's where the harvesting technology can't pull enough energy out of the environment, or it does it so slowly that it's not as power-effective as traditional batteries.
+
+Enter the metal-eating robot. The University of Pennsylvania researchers' form of harvesting efficiently replicates a power-dense battery. Metal is more dense than the battery chemistry.
+
+The group performs their foraging energy production with a hydrogel electrolyte sponge towed by the robot. It uses a cathode, dragged over the surface, to extract amperages from the metal fuel source, such as steel or aluminum.
+
+"Our [metal-air scavenger] has a power density that's ten times better than the best harvesters, to the point that we can compete against batteries," said James Pikul, an assistant professor in the University of Pennsylvania's Department of Mechanical Engineering and Applied Mechanics and one of the paper authors, in the Medium post. "It's using battery chemistry, but doesn't have the associated weight, because it's taking those chemicals from the environment."
+
+This method is also potentially better than existing lithium-ion battery chemistry, according to Pikul.
+
+"One day, a robot that needs to recharge its batteries will just need to find some aluminum to 'eat,'" Pikul said.
+
+The robot, although ultimately likely to be a better worker than the human, is a messy eater. As it oxidizes the metal it passes over, it leaves a "microscopic layer of rust in its wake," according to the article.
+
+Join the Network World communities on [Facebook][5] and [LinkedIn][6] to comment on topics that are top of mind.
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://www.networkworld.com/article/3540194/industrial-robots-could-eat-metal-to-power-themselves.html
+
+作者:[Patrick Nelson][a]
+选题:[lujun9972][b]
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]: https://www.networkworld.com/author/Patrick-Nelson/
+[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
+[1]: https://medium.com/penn-engineering/penn-engineerings-new-scavenger-technology-allows-robots-to-eat-metal-for-energy-bd12f3b83893
+[2]: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsenergylett.9b02661
+[3]: https://www.networkworld.com/article/3429200/self-organizing-micro-robots-may-soon-swarm-the-industrial-iot.html
+[4]: https://www.networkworld.com/article/3536697/harvesting-ambient-energy-will-power-iot-scientists-say.html
+[5]: https://www.facebook.com/NetworkWorld/
+[6]: https://www.linkedin.com/company/network-world
diff --git a/sources/talk/20200501 Red Hat Summit 2020 virtual experience.md b/sources/talk/20200501 Red Hat Summit 2020 virtual experience.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..334c52c1f9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/talk/20200501 Red Hat Summit 2020 virtual experience.md
@@ -0,0 +1,64 @@
+[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
+[#]: translator: ( )
+[#]: reviewer: ( )
+[#]: publisher: ( )
+[#]: url: ( )
+[#]: subject: (Red Hat Summit 2020 virtual experience)
+[#]: via: (https://www.networkworld.com/article/3541289/red-hat-summit-2020-virtual-experience.html)
+[#]: author: (Sandra Henry-Stocker https://www.networkworld.com/author/Sandra-Henry_Stocker/)
+
+Red Hat Summit 2020 virtual experience
+======
+
+[Virginiambe][1] [(CC BY-SA 3.0)][2]
+
+In the last couple days, Red Hat was able to demonstrate that an online technical conference can succeed. The Summit, normally held in Boston or San Francisco, was held online thanks to the Covid-19 pandemic still gripping the world.
+
+The fact that 80,000 people attended the online event warrants a huge applause. By comparison, last year’s in-person conference broke the record with only 8,900 attendees.
+
+[[Get regularly scheduled insights by signing up for Network World newsletters.]][3]
+
+### **Being “there”**
+
+The experience of attending the conference was in many ways what you would expect when attending a large conference in person. There were keynotes, general sessions and breakout sessions. There were many opportunities to ask questions. And it was often difficult but necessary to choose between parallel sessions. I attended both days and was very impressed.
+
+I also enjoyed some nostalgia about how we’ve all arrived at the places we are today with respect to Linux. It was clear that many attendees were overwhelmed by the progress that has been made just since last year. Linux, and [RHEL][4] in particular, is becoming more innovative, more clever in the ways that it can detect and respond to problems and yet in some important ways easier to manage because of the way the tools have evolved.
+
+Announcements at the conference included Red Hat OpenShift 4.4, OpenShift virtualization and Red Hat Advanced Container Management for Kubernetes.
+
+What was novel about attending a technical conference online was that we didn’t have to leave our home or office and that we could review sessions that we missed by selecting them later from the session layout pages. In fact, the sessions are still online and may well be for the coming year. If you didn’t participate in Red Hat Summit 2020, you can still sign up and you can still watch the sessions at your convenience. Just go to the [summit site][5]. And, did I mention, that it's free?
+
+### Catching up
+
+Once you’re signed up, you can click on the Watch and Learn at the top of the page and choose General Sessions or Sessions and Labs. The presentations will now all be labeled On Demand though they once displayed upcoming time slots. The individuals presenting information are excellent and the material is exciting. Even if you’re not working with Red Hat Enterprise Linux, you will learn a lot about Linux in general and how open source has evolved over the decades and is still evolving in important and critical ways.
+
+Topics covered at the conference include OpenShift, open hybrid cloud, future technologies, robotics and automation, advances on the edge and the power of open source. Red Hat Summit also includes joint sessions with both Red Hat and technology collaborators such as Ford, Verizon, Intel, Microsoft and Credit Suisse.
+
+### What’s next?
+
+Watching the conference online at a time when I can't leave my home was informative, but also encouraging and comforting. Linux has been an important part of my life for decades. It felt good to be connected to the larger community and to sense the currents of progress through my desktop system.
+
+While there’s no way to know at this point whether future Red Hat Summits or other Linux conferences will be held or made available online, the fact that Red Hat Summit 2020 was available online when so many of us are still huddled up at home wondering when our world will reopen was a testament not just to great technology but to the deep-seated conviction that it is critical that we work together and that open source can make that happen in ways that nothing else can.
+
+Join the Network World communities on [Facebook][6] and [LinkedIn][7] to comment on topics that are top of mind.
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://www.networkworld.com/article/3541289/red-hat-summit-2020-virtual-experience.html
+
+作者:[Sandra Henry-Stocker][a]
+选题:[lujun9972][b]
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]: https://www.networkworld.com/author/Sandra-Henry_Stocker/
+[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
+[1]: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Red_hat_with_bow2.JPG
+[2]: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/legalcode
+[3]: https://www.networkworld.com/newsletters/signup.html
+[4]: https://www.networkworld.com/article/3540189/red-hat-enterprise-linux-82-hits-the-stage.html
+[5]: https://www.redhat.com/summit
+[6]: https://www.facebook.com/NetworkWorld/
+[7]: https://www.linkedin.com/company/network-world
diff --git a/sources/talk/20200502 The real impact of canceling PyCon due to COVID-19.md b/sources/talk/20200502 The real impact of canceling PyCon due to COVID-19.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..aebbbf28c4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/talk/20200502 The real impact of canceling PyCon due to COVID-19.md
@@ -0,0 +1,129 @@
+[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
+[#]: translator: ( )
+[#]: reviewer: ( )
+[#]: publisher: ( )
+[#]: url: ( )
+[#]: subject: (The real impact of canceling PyCon due to COVID-19)
+[#]: via: (https://opensource.com/article/20/5/pycon-covid-19)
+[#]: author: (Matthew Broberg https://opensource.com/users/mbbroberg)
+
+The real impact of canceling PyCon due to COVID-19
+======
+An interview with Ewa Jodlowska on how the Python Software Foundation is
+responding to the cancelation of in-person events.
+![A dollar sign in a network][1]
+
+The Python Software Foundation (PSF) had to [cancel its popular PyCon US][2] event in response to COVID-19. I interviewed [Ewa Jodlowska][3], Executive Director of the PSF, to talk about the experience and see what we all can learn, and how we can be supportive of the non-profit that supports one of my favorite programming languages.
+
+### The impact on PSF employees
+
+I asked Jodlowska "how have you had to adjust your work in light of COVID-19?"
+
+In her response, the day-to-day didn't sound like much of a change. PSF staff "have always worked remotely." The organization practices a [fully remote work][4] culture and doesn’t have an office. The small staff of seven employees is well versed in collaborating outside of an office.
+
+Familiarity aside, the emotional impact of needing to cancel an event they put a year’s worth of planning into hurt.
+
+> **"We all believe in what we do. Which is particularly why we’re such a great small team. So it really impacted us emotionally and mentally. And it continues to."**
+
+We spoke about how the team is reliving what the days would have looked like if PyCon wasn't interrupted by COVID-19–keynotes would start _now_, the sponsor booths would be in full motion right _now_–and just how emotionally taxing it all was. Throughout the discussion, Jodlowska always came back to recognizing the staff for their resiliency and energy to pivot the event online.
+
+### The cascading impact of event cancellation
+
+Jodlowska has been incredibly transparent about the experience. In her March 31st [article on the financial outcome][5], she outlines it clearly: the Python Software Foundation would take a hit from the event cancelation.
+
+Jodlowska notes that part of the challenge is that PyCon accounts for too much of the organization’s financial health. About 63% of the 2020 revenue was projected to come from the show. While that number is down from the [2017 estimate of 80%][6], it’s still a concern when in-person events will remain limited to keep attendees safe during the COVID-19 outbreak.
+
+> **"We don’t want to rely on one event**–**or events in general**–**to operate and provide community support."**
+
+The PSF board of directors is hard at work to look into the diversification of funding. In the meantime, PyCon remains essential to sustainability running the organization.
+
+### Community support makes all the difference
+
+It's at this point that Jodlowska again recognizes the incredible work of the PSF staff. They quickly pivoted the vision of the event, and the community of attendees, sponsors, and speakers were all supportive of the move.
+
+> **"[We] have been brought to tears many times by the generosity of our sponsors and our individual donors."**
+
+Jodlowska noted that the generosity of so many resulted in reducing the financial impact on the PSF. An incredible amount of Individual attendees are donating their registration costs to the PSF. They are also showing up across social media sites to participate in their own distributed virtual experience of PyCon.
+
+Another important part of the community, the corporate sponsors of the show, are also showing up to support the non-profit. Many sponsors had already canceled physical presence at the show before the event was officially moved online. Some of them were kind enough, as Jodlowska noted, to donate the cost of sponsorship to the PSF. In a huge turn of events, the list of sponsors **grew** as the online event came together.
+
+> **[M]any sponsors have opted into participating in PyCon 2020 online. Because of this we have decreased the amount needed from our reserve by 77%! The PSF will now only need $141,713 from its financial reserve to get through 2020.**
+
+For more on the data side, see Jodlowska’s article _[Thank you to donors & sponsors][7]_.
+
+Support in all its forms led to the conference feeling like it is well on its way. Some sponsors are even moving to a virtual booth experience.
+
+> Since our sponsors can’t be with you in person, we’ve created a place to provide their content online - . [#PyCon2020][8] Gold Sponsor Weekly Python Exercise shared this video to introduce you to their offerings: .
+>
+> — PyCon US (@pycon) [April 18, 2020][9]
+
+Maybe most impressively, many speakers and tutorial instructors made the effort of recording their sessions. That’s helped PyCon to [gradually unfold online][10] with incredible educational content. The audience is still able to interact as well: YouTube comments are open for moderation so speakers can interact with their audience.
+
+Lastly, there remains an army of volunteers who shifted their in-person plans online and continue to help in any way possible.
+
+### Some of the surprising positives from this difficult change
+
+While it is without a doubt a challenging time for the organization, Jodlowska noted a number of positives that are unfolding due to this move to virtual.
+
+To start, the staff of the PSF “have never been closer,” as they bond over the experience and spend more time getting to know each other through weekly video calls and baking competitions.
+
+Jodlowska was inspired to get involved in another open source effort, [FOSS responders][11], who are helping organizations respond to the cancelation of events due to COVID-19. (If you’ve been affected as well, they are there to help.)
+
+The generosity mentioned above is a silver lining to the experience and encouraging to the hardworking team that uplifts the popular Python programming language.
+
+There is also a broader impact on participation in PyCon. While the final numbers are not in yet, an international audience has access to all of PyCon as it unfolds, which gives the entire world a chance to be part of an excellent event [I got to attend][12] last year. On the development side, Jodlowska mentioned that the [core-dev team][13] that maintains Python, who would normally meet in person, shifted to a virtual meeting. As a result of that shift, some participants got to attend that otherwise would not have had the opportunity to join in person.
+
+### How you can help the Python Software Foundation
+
+I reached out to Jodlowska because I am impressed with and supportive of their mission to support the Python community. If you want to support them as well, you have options:
+
+ * Become a [free or supporting member][14] of the PSF to get involved in our future.
+ * [Sign up for the PSF’s free newsletter][15] to stay up to date.
+ * [Donate][16] directly to the PSF (and thank you to those that already have).
+ * Ask your employer to [sponsor the PSF][17].
+ * Ask your employer if they match donations to 501(c)(3) non-profits, and ask for your donations to the PSF to be matched.
+
+
+
+Last but not least, participate in PyCon over the next few weeks. You can learn from all kinds of smart people on a range of topics like [Matt Harrison][18]’s [Hands-on Python for Programmers][19] that guides attendees through analyzing COVID-19 data to [Katie McLaughlin][20]’s thoughtful talk on [What is deployment, anyway?][21]
+
+Be sure to [review the full][10] list and engage with the amazing lineup of speakers.
+
+* * *
+
+_Are you part of a non-profit looking to connect with your open source community at this time of social distancing? Let me know at matt @ opensource.com._
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://opensource.com/article/20/5/pycon-covid-19
+
+作者:[Matthew Broberg][a]
+选题:[lujun9972][b]
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]: https://opensource.com/users/mbbroberg
+[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
+[1]: https://opensource.com/sites/default/files/styles/image-full-size/public/lead-images/osdc_whitehurst_money.png?itok=ls-SOzM0 (A dollar sign in a network)
+[2]: https://pycon.blogspot.com/2020/03/pycon-us-2020-in-pittsburgh.html
+[3]: https://www.python.org/psf/records/staff/
+[4]: https://opensource.com/tags/wfh
+[5]: http://pyfound.blogspot.com/2020/03/psfs-projected-2020-financial-outcome.html
+[6]: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=79AIzbjLzdk
+[7]: http://pyfound.blogspot.com/2020/04/thank-you-to-donors-sponsors.html
+[8]: https://twitter.com/hashtag/PyCon2020?src=hash&ref_src=twsrc%5Etfw
+[9]: https://twitter.com/pycon/status/1251563142641000455?ref_src=twsrc%5Etfw
+[10]: https://us.pycon.org/2020/online/
+[11]: https://fossresponders.com/
+[12]: https://opensource.com/article/19/5/jupyterlab-python-developers-magic
+[13]: https://devguide.python.org/coredev/
+[14]: https://www.python.org/psf/membership/
+[15]: https://www.python.org/psf/newsletter/
+[16]: https://www.python.org/psf/donations/
+[17]: https://www.python.org/psf/sponsorship/
+[18]: https://us.pycon.org/2020/speaker/profile/454/
+[19]: https://youtu.be/fuJcSNUMrW0
+[20]: https://opensource.com/users/glasnt
+[21]: https://youtu.be/8vstov3Y7uE
diff --git a/sources/tech/20180612 Systemd Services- Reacting to Change.md b/sources/tech/20180612 Systemd Services- Reacting to Change.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 125b871602..0000000000
--- a/sources/tech/20180612 Systemd Services- Reacting to Change.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,276 +0,0 @@
-//messon007 translating
-Systemd Services: Reacting to Change
-======
-
-
-
-[I have one of these Compute Sticks][1] (Figure 1) and use it as an all-purpose server. It is inconspicuous and silent and, as it is built around an x86 architecture, I don't have problems getting it to work with drivers for my printer, and that’s what it does most days: it interfaces with the shared printer and scanner in my living room.
-
-![ComputeStick][3]
-
-An Intel ComputeStick. Euro coin for size.
-
-[Used with permission][4]
-
-Most of the time it is idle, especially when we are out, so I thought it would be good idea to use it as a surveillance system. The device doesn't come with its own camera, and it wouldn't need to be spying all the time. I also didn't want to have to start the image capturing by hand because this would mean having to log into the Stick using SSH and fire up the process by writing commands in the shell before rushing out the door.
-
-So I thought that the thing to do would be to grab a USB webcam and have the surveillance system fire up automatically just by plugging it in. Bonus points if the surveillance system fired up also after the Stick rebooted, and it found that the camera was connected.
-
-In prior installments, we saw that [systemd services can be started or stopped by hand][5] or [when certain conditions are met][6]. Those conditions are not limited to when the OS reaches a certain state in the boot up or powerdown sequence but can also be when you plug in new hardware or when things change in the filesystem. You do that by combining a Udev rule with a systemd service.
-
-### Hotplugging with Udev
-
-Udev rules live in the _/etc/udev/rules_ directory and are usually a single line containing _conditions_ and _assignments_ that lead to an _action_.
-
-That was a bit cryptic. Let's try again:
-
-Typically, in a Udev rule, you tell systemd what to look for when a device is connected. For example, you may want to check if the make and model of a device you just plugged in correspond to the make and model of the device you are telling Udev to wait for. Those are the _conditions_ mentioned earlier.
-
-Then you may want to change some stuff so you can use the device easily later. An example of that would be to change the read and write permissions to a device: if you plug in a USB printer, you're going to want users to be able to read information from the printer (the user's printing app would want to know the model, make, and whether it is ready to receive print jobs or not) and write to it, that is, send stuff to print. Changing the read and write permissions for a device is done using one of the _assignments_ you read about earlier.
-
-Finally, you will probably want the system to do something when the conditions mentioned above are met, like start a backup application to copy important files when a certain external hard disk drive is plugged in. That is an example of an _action_ mentioned above.
-
-With that in mind, ponder this:
-
-```
-ACTION=="add", SUBSYSTEM=="video4linux", ATTRS{idVendor}=="03f0", ATTRS{idProduct}=="e207",
-SYMLINK+="mywebcam", TAG+="systemd", MODE="0666", ENV{SYSTEMD_WANTS}="webcam.service"
-```
-
-The first part of the rule,
-
-```
-ACTION=="add", SUBSYSTEM=="video4linux", ATTRS{idVendor}=="03f0",
-ATTRS{idProduct}=="e207" [etc... ]
-```
-
-shows the conditions that the device has to meet before doing any of the other stuff you want the system to do. The device has to be added (`ACTION=="add"`) to the machine, it has to be integrated into the `video4linux` subsystem. To make sure the rule is applied only when the correct device is plugged in, you have to make sure Udev correctly identifies the manufacturer (`ATTRS{idVendor}=="03f0"`) and a model (`ATTRS{idProduct}=="e207"`) of the device.
-
-In this case, we're talking about this device (Figure 2):
-
-![webcam][8]
-
-The HP webcam used in this experiment.
-
-[Used with permission][4]
-
-Notice how you use `==` to indicate that these are a logical operation. You would read the above snippet of the rule like this:
-
-```
-if the device is added and the device controlled by the video4linux subsystem
-and the manufacturer of the device is 03f0 and the model is e207, then...
-```
-
-But where do you get all this information? Where do you find the action that triggers the event, the manufacturer, model, and so on? You will probably have to use several sources. The `IdVendor` and `idProduct` you can get by plugging the webcam into your machine and running `lsusb`:
-
-```
-lsusb
-Bus 002 Device 002: ID 8087:0024 Intel Corp. Integrated Rate Matching Hub
-Bus 002 Device 001: ID 1d6b:0002 Linux Foundation 2.0 root hub
-Bus 004 Device 001: ID 1d6b:0003 Linux Foundation 3.0 root hub
-Bus 003 Device 003: ID 03f0:e207 Hewlett-Packard
-Bus 003 Device 001: ID 1d6b:0002 Linux Foundation 2.0 root hub
-Bus 001 Device 003: ID 04f2:b1bb Chicony Electronics Co., Ltd
-Bus 001 Device 002: ID 8087:0024 Intel Corp. Integrated Rate Matching Hub
-Bus 001 Device 001: ID 1d6b:0002 Linux Foundation 2.0 root hub
-```
-
-The webcam I’m using is made by HP, and you can only see one HP device in the list above. The `ID` gives you the manufacturer and the model numbers separated by a colon (`:`). If you have more than one device by the same manufacturer and not sure which is which, unplug the webcam, run `lsusb` again and check what's missing.
-
-OR...
-
-Unplug the webcam, wait a few seconds, run the command `udevadmin monitor --environment` and then plug the webcam back in again. When you do that with the HP webcam, you get:
-
-```
-udevadmin monitor --environment
-UDEV [35776.495221] add /devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:1c.3/0000:04:00.0
- /usb3/3-1/3-1:1.0/input/input21/event11 (input)
-.MM_USBIFNUM=00
-ACTION=add
-BACKSPACE=guess
-DEVLINKS=/dev/input/by-path/pci-0000:04:00.0-usb-0:1:1.0-event
- /dev/input/by-id/usb-Hewlett_Packard_HP_Webcam_HD_2300-event-if00
-DEVNAME=/dev/input/event11
-DEVPATH=/devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:1c.3/0000:04:00.0/
- usb3/3-1/3-1:1.0/input/input21/event11
-ID_BUS=usb
-ID_INPUT=1
-ID_INPUT_KEY=1
-ID_MODEL=HP_Webcam_HD_2300
-ID_MODEL_ENC=HP\x20Webcam\x20HD\x202300
-ID_MODEL_ID=e207
-ID_PATH=pci-0000:04:00.0-usb-0:1:1.0
-ID_PATH_TAG=pci-0000_04_00_0-usb-0_1_1_0
-ID_REVISION=1020
-ID_SERIAL=Hewlett_Packard_HP_Webcam_HD_2300
-ID_TYPE=video
-ID_USB_DRIVER=uvcvideo
-ID_USB_INTERFACES=:0e0100:0e0200:010100:010200:030000:
-ID_USB_INTERFACE_NUM=00
-ID_VENDOR=Hewlett_Packard
-ID_VENDOR_ENC=Hewlett\x20Packard
-ID_VENDOR_ID=03f0
-LIBINPUT_DEVICE_GROUP=3/3f0/e207:usb-0000:04:00.0-1/button
-MAJOR=13
-MINOR=75
-SEQNUM=3162
-SUBSYSTEM=input
-USEC_INITIALIZED=35776495065
-XKBLAYOUT=es
-XKBMODEL=pc105
-XKBOPTIONS=
-XKBVARIANT=
-```
-
-That may look like a lot to process, but, check this out: the `ACTION` field early in the list tells you what event just happened, i.e., that a device got added to the system. You can also see the name of the device spelled out on several of the lines, so you can be pretty sure that it is the device you are looking for. The output also shows the manufacturer's ID number (`ID_VENDOR_ID=03f0`) and the model number (`ID_VENDOR_ID=03f0`).
-
-This gives you three of the four values the condition part of the rule needs. You may be tempted to think that it a gives you the fourth, too, because there is also a line that says:
-
-```
-SUBSYSTEM=input
-```
-
-Be careful! Although it is true that a USB webcam is a device that provides input (as does a keyboard and a mouse), it is also belongs to the _usb_ subsystem, and several others. This means that your webcam gets added to several subsystems and looks like several devices. If you pick the wrong subsystem, your rule may not work as you want it to, or, indeed, at all.
-
-So, the third thing you have to check is all the subsystems the webcam has got added to and pick the correct one. To do that, unplug your webcam again and run:
-
-```
-ls /dev/video*
-```
-
-This will show you all the video devices connected to the machine. If you are using a laptop, most come with a built-in webcam and it will probably show up as `/dev/video0`. Plug your webcam back in and run `ls /dev/video*` again.
-
-Now you should see one more video device (probably `/dev/video1`).
-
-Now you can find out all the subsystems it belongs to by running `udevadm info -a /dev/video1`:
-
-```
-udevadm info -a /dev/video1
-
-Udevadm info starts with the device specified by the devpath and then
-walks up the chain of parent devices. It prints for every device
-found, all possible attributes in the udev rules key format.
-A rule to match, can be composed by the attributes of the device
-and the attributes from one single parent device.
-
- looking at device '/devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:1c.3/0000:04:00.0
- /usb3/3-1/3-1:1.0/video4linux/video1':
- KERNEL=="video1"
- SUBSYSTEM=="video4linux"
- DRIVER==""
- ATTR{dev_debug}=="0"
- ATTR{index}=="0"
- ATTR{name}=="HP Webcam HD 2300: HP Webcam HD"
-
-[etc...]
-```
-
-The output goes on for quite a while, but what you're interested is right at the beginning: `SUBSYSTEM=="video4linux"`. This is a line you can literally copy and paste right into your rule. The rest of the output (not shown for brevity) gives you a couple more nuggets, like the manufacturer and mode IDs, again in a format you can copy and paste into your rule.
-
-Now you have a way of identifying the device and what event should trigger the action univocally, it is time to tinker with the device.
-
-The next section in the rule, `SYMLINK+="mywebcam", TAG+="systemd", MODE="0666"` tells Udev to do three things: First, you want to create symbolic link from the device to (e.g. _/dev/video1_ ) to _/dev/mywebcam_. This is because you cannot predict what the system is going to call the device by default. When you have an in-built webcam and you hotplug a new one, the in-built webcam will usually be _/dev/video0_ while the external one will become _/dev/video1_. However, if you boot your computer with the external USB webcam plugged in, that could be reversed and the internal webcam can become _/dev/video1_ and the external one _/dev/video0_. What this is telling you is that, although your image-capturing script (which you will see later on) always needs to point to the external webcam device, you can't rely on it being _/dev/video0_ or _/dev/video1_. To solve this problem, you tell Udev to create a symbolic link which will never change in the moment the device is added to the _video4linux_ subsystem and you will make your script point to that.
-
-The second thing you do is add `"systemd"` to the list of Udev tags associated with this rule. This tells Udev that the action that the rule will trigger will be managed by systemd, that is, it will be some sort of systemd service.
-
-Notice how in both cases you use `+=` operator. This adds the value to a list, which means you can add more than one value to `SYMLINK` and `TAG`.
-
-The `MODE` values, on the other hand, can only contain one value (hence you use the simple `=` assignment operator). What `MODE` does is tell Udev who can read from or write to the device. If you are familiar with `chmod` (and, if you are reading this, you should be), you will also be familiar of [how you can express permissions using numbers][9]. That is what this is: `0666` means " _give read and write privileges to the device to everybody_ ".
-
-At last, `ENV{SYSTEMD_WANTS}="webcam.service"` tells Udev what systemd service to run.
-
-Save this rule into file called _90-webcam.rules_ (or something like that) in _/etc/udev/rules.d_ and you can load it either by rebooting your machine, or by running:
-
-```
-sudo udevadm control --reload-rules && udevadm trigger
-```
-
-## Service at Last
-
-The service the Udev rule triggers is ridiculously simple:
-
-```
-# webcam.service
-
-[Service]
-Type=simple
-ExecStart=/home/[user name]/bin/checkimage.sh
-```
-
-Basically, it just runs the _checkimage.sh_ script stored in your personal _bin/_ and pushes it the background. [This is something you saw how to do in prior installments][5]. It may seem something little, but just because it is called by a Udev rule, you have just created a special kind of systemd unit called a _device_ unit. Congratulations.
-
-As for the _checkimage.sh_ script _webcam.service_ calls, there are several ways of grabbing an image from a webcam and comparing it to a prior one to check for changes (which is what _checkimage.sh_ does), but this is how I did it:
-
-```
-#!/bin/bash
-# This is the checkimage.sh script
-
-mplayer -vo png -frames 1 tv:// -tv driver=v4l2:width=640:height=480:device=
- /dev/mywebcam &>/dev/null
-mv 00000001.png /home/[user name]/monitor/monitor.png
-
-while true
-do
- mplayer -vo png -frames 1 tv:// -tv driver=v4l2:width=640:height=480:device=/dev/mywebcam &>/dev/null
- mv 00000001.png /home/[user name]/monitor/temp.png
-
- imagediff=`compare -metric mae /home/[user name]/monitor/monitor.png /home/[user name]
- /monitor/temp.png /home/[user name]/monitor/diff.png 2>&1 > /dev/null | cut -f 1 -d " "`
- if [ `echo "$imagediff > 700.0" | bc` -eq 1 ]
- then
- mv /home/[user name]/monitor/temp.png /home/[user name]/monitor/monitor.png
- fi
-
- sleep 0.5
-done
-```
-
-Start by using [MPlayer][10] to grab a frame ( _00000001.png_ ) from the webcam. Notice how we point `mplayer` to the `mywebcam` symbolic link we created in our Udev rule, instead of to `video0` or `video1`. Then you transfer the image to the _monitor/_ directory in your home directory. Then run an infinite loop that does the same thing again and again, but also uses [Image Magick's _compare_ tool][11] to see if there any differences between the last image captured and the one that is already in the _monitor/_ directory.
-
-If the images are different, it means something has moved within the webcam's frame. The script overwrites the original image with the new image and continues comparing waiting for some more movement.
-
-### Plugged
-
-With all the bits and pieces in place, when you plug your webcam in, your Udev rule will be triggered and will start the _webcam.service_. The _webcam.service_ will execute _checkimage.sh_ in the background, and _checkimage.sh_ will start taking pictures every half a second. You will know because your webcam's LED will start flashing indicating every time it takes a snap.
-
-As always, if something goes wrong, run
-
-```
-systemctl status webcam.service
-```
-
-to check what your service and script are up to.
-
-### Coming up
-
-You may be wondering: Why overwrite the original image? Surely you would want to see what's going on if the system detects any movement, right? You would be right, but as you will see in the next installment, leaving things as they are and processing the images using yet another type of systemd unit makes things nice, clean and easy.
-
-Just wait and see.
-
-Learn more about Linux through the free ["Introduction to Linux" ][12]course from The Linux Foundation and edX.
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: https://www.linux.com/blog/intro-to-linux/2018/6/systemd-services-reacting-change
-
-作者:[Paul Brown][a]
-选题:[lujun9972][b]
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]: https://www.linux.com/users/bro66
-[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
-[1]: https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/products/boards-kits/compute-stick/stk1a32sc.html
-[2]: https://www.linux.com/files/images/fig01png
-[3]: https://www.linux.com/sites/lcom/files/styles/floated_images/public/fig01.png?itok=cfEHN5f1 (ComputeStick)
-[4]: https://www.linux.com/licenses/category/used-permission
-[5]: https://www.linux.com/blog/learn/intro-to-linux/2018/5/writing-systemd-services-fun-and-profit
-[6]: https://www.linux.com/blog/learn/2018/5/systemd-services-beyond-starting-and-stopping
-[7]: https://www.linux.com/files/images/fig02png
-[8]: https://www.linux.com/sites/lcom/files/styles/floated_images/public/fig02.png?itok=esFv4BdM (webcam)
-[9]: https://chmod-calculator.com/
-[10]: https://mplayerhq.hu/design7/news.html
-[11]: https://www.imagemagick.org/script/compare.php
-[12]: https://training.linuxfoundation.org/linux-courses/system-administration-training/introduction-to-linux
diff --git a/sources/tech/20190915 How to Configure SFTP Server with Chroot in Debian 10.md b/sources/tech/20190915 How to Configure SFTP Server with Chroot in Debian 10.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 9d57192270..0000000000
--- a/sources/tech/20190915 How to Configure SFTP Server with Chroot in Debian 10.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,197 +0,0 @@
-[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
-[#]: translator: (robsean)
-[#]: reviewer: ( )
-[#]: publisher: ( )
-[#]: url: ( )
-[#]: subject: (How to Configure SFTP Server with Chroot in Debian 10)
-[#]: via: (https://www.linuxtechi.com/configure-sftp-chroot-debian10/)
-[#]: author: (Pradeep Kumar https://www.linuxtechi.com/author/pradeep/)
-
-How to Configure SFTP Server with Chroot in Debian 10
-======
-
-**SFTP** stands for Secure File Transfer Protocol / SSH File Transfer Protocol, it is one of the most common method which is used to transfer files securely over ssh from our local system to remote server and vice-versa. The main advantage of sftp is that we don’t need to install any additional package except ‘**openssh-server**’, in most of the Linux distributions ‘openssh-server’ package is the part of default installation. Other benefit of sftp is that we can allow user to use sftp only not ssh.
-
-[![Configure-sftp-debian10][1]][2]
-
-Recently Debian 10, Code name ‘Buster’ has been released, in this article we will demonstrate how to configure sftp with Chroot ‘Jail’ like environment in Debian 10 System. Here Chroot Jail like environment means that user’s cannot go beyond from their respective home directories or users cannot change directories from their home directories. Following are the lab details:
-
- * OS = Debian 10
- * IP Address = 192.168.56.151
-
-
-
-Let’s jump into SFTP Configuration Steps,
-
-### Step:1) Create a Group for sftp using groupadd command
-
-Open the terminal, create a group with a name “**sftp_users**” using below groupadd command,
-
-```
-root@linuxtechi:~# groupadd sftp_users
-```
-
-### Step:2) Add Users to Group ‘sftp_users’ and set permissions
-
-In case you want to create new user and want to add that user to ‘sftp_users’ group, then run the following command,
-
-**Syntax:** # useradd -m -G sftp_users <user_name>
-
-Let’s suppose user name is ’Jonathan’
-
-```
-root@linuxtechi:~# useradd -m -G sftp_users jonathan
-```
-
-set the password using following chpasswd command,
-
-```
-root@linuxtechi:~# echo "jonathan:" | chpasswd
-```
-
-In case you want to add existing users to ‘sftp_users’ group then run beneath usermod command, let’s suppose already existing user name is ‘chris’
-
-```
-root@linuxtechi:~# usermod -G sftp_users chris
-```
-
-Now set the required permissions on Users,
-
-```
-root@linuxtechi:~# chown root /home/jonathan /home/chris/
-```
-
-Create an upload folder in both the user’s home directory and set the correct ownership,
-
-```
-root@linuxtechi:~# mkdir /home/jonathan/upload
-root@linuxtechi:~# mkdir /home/chris/upload
-root@linuxtechi:~# chown jonathan /home/jonathan/upload
-root@linuxtechi:~# chown chris /home/chris/upload
-```
-
-**Note:** User like Jonathan and Chris can upload files and directories to upload folder from their local systems.
-
-### Step:3) Edit sftp configuration file (/etc/ssh/sshd_config)
-
-As we have already stated that sftp operations are done over the ssh, so it’s configuration file is “**/etc/ssh/sshd_config**“, Before making any changes I would suggest first take the backup and then edit this file and add the following content,
-
-```
-root@linuxtechi:~# cp /etc/ssh/sshd_config /etc/ssh/sshd_config-org
-root@linuxtechi:~# vim /etc/ssh/sshd_config
-………
-#Subsystem sftp /usr/lib/openssh/sftp-server
-Subsystem sftp internal-sftp
-
-Match Group sftp_users
- X11Forwarding no
- AllowTcpForwarding no
- ChrootDirectory %h
- ForceCommand internal-sftp
-…………
-```
-
-Save & exit the file.
-
-To make above changes into the affect, restart ssh service using following systemctl command
-
-```
-root@linuxtechi:~# systemctl restart sshd
-```
-
-In above ‘sshd_config’ file we have commented out the line which starts with “Subsystem” and added new entry “Subsystem sftp internal-sftp” and new lines like,
-
-“**Match Group sftp_users”** –> It means if a user is a part of ‘sftp_users’ group then apply rules which are mentioned below to this entry.
-
-“**ChrootDierctory %h**” –> It means users can only change directories within their respective home directories, they cannot go beyond their home directories, or in other words we can say users are not permitted to change directories, they will get jai like environment within their directories and can’t access any other user’s and system’s directories.
-
-“**ForceCommand internal-sftp**” –> It means users are limited to sftp command only.
-
-### Step:4) Test and Verify sftp
-
-Login to any other Linux system which is on the same network of your sftp server and then try to ssh sftp server via the users that we have mapped in ‘sftp_users’ group.
-
-```
-[root@linuxtechi ~]# ssh root@linuxtechi
-root@linuxtechi's password:
-Write failed: Broken pipe
-[root@linuxtechi ~]# ssh root@linuxtechi
-root@linuxtechi's password:
-Write failed: Broken pipe
-[root@linuxtechi ~]#
-```
-
-Above confirms that users are not allowed to SSH , now try sftp using following commands,
-
-```
-[root@linuxtechi ~]# sftp root@linuxtechi
-root@linuxtechi's password:
-Connected to 192.168.56.151.
-sftp> ls -l
-drwxr-xr-x 2 root 1001 4096 Sep 14 07:52 debian10-pkgs
--rw-r--r-- 1 root 1001 155 Sep 14 07:52 devops-actions.txt
-drwxr-xr-x 2 1001 1002 4096 Sep 14 08:29 upload
-```
-
-Let’s try to download a file using sftp ‘**get**‘ command
-
-```
-sftp> get devops-actions.txt
-Fetching /devops-actions.txt to devops-actions.txt
-/devops-actions.txt 100% 155 0.2KB/s 00:00
-sftp>
-sftp> cd /etc
-Couldn't stat remote file: No such file or directory
-sftp> cd /root
-Couldn't stat remote file: No such file or directory
-sftp>
-```
-
-Above output confirms that we are able to download file from our sftp server to local machine and apart from this we have also tested that users cannot change directories.
-
-Let’s try to upload a file under “**upload**” folder,
-
-```
-sftp> cd upload/
-sftp> put metricbeat-7.3.1-amd64.deb
-Uploading metricbeat-7.3.1-amd64.deb to /upload/metricbeat-7.3.1-amd64.deb
-metricbeat-7.3.1-amd64.deb 100% 38MB 38.4MB/s 00:01
-sftp> ls -l
--rw-r--r-- 1 1001 1002 40275654 Sep 14 09:18 metricbeat-7.3.1-amd64.deb
-sftp>
-```
-
-This confirms that we have successfully uploaded a file from our local system to sftp server.
-
-Now test the SFTP server with winscp tool, enter the sftp server ip address along user’s credentials,
-
-[![Winscp-sftp-debian10][1]][3]
-
-Click on Login and then try to download and upload files
-
-[![Download-file-winscp-debian10-sftp][1]][4]
-
-Now try to upload files in upload folder,
-
-[![Upload-File-using-winscp-Debian10-sftp][1]][5]
-
-Above window confirms that uploading is also working fine, that’s all from this article. If these steps help you to configure SFTP server with chroot environment in Debian 10 then please do share your feedback and comments.
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: https://www.linuxtechi.com/configure-sftp-chroot-debian10/
-
-作者:[Pradeep Kumar][a]
-选题:[lujun9972][b]
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]: https://www.linuxtechi.com/author/pradeep/
-[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
-[1]: data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7
-[2]: https://www.linuxtechi.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/09/Configure-sftp-debian10.jpg
-[3]: https://www.linuxtechi.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/09/Winscp-sftp-debian10.jpg
-[4]: https://www.linuxtechi.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/09/Download-file-winscp-debian10-sftp.jpg
-[5]: https://www.linuxtechi.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/09/Upload-File-using-winscp-Debian10-sftp.jpg
diff --git a/sources/tech/20200317 Create Stunning Pixel Art With Free and Open Source Editor Pixelorama.md b/sources/tech/20200317 Create Stunning Pixel Art With Free and Open Source Editor Pixelorama.md
deleted file mode 100644
index b4b0949dab..0000000000
--- a/sources/tech/20200317 Create Stunning Pixel Art With Free and Open Source Editor Pixelorama.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,108 +0,0 @@
-[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
-[#]: translator: (geekpi)
-[#]: reviewer: ( )
-[#]: publisher: ( )
-[#]: url: ( )
-[#]: subject: (Create Stunning Pixel Art With Free and Open Source Editor Pixelorama)
-[#]: via: (https://itsfoss.com/pixelorama/)
-[#]: author: (Abhishek Prakash https://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/)
-
-Create Stunning Pixel Art With Free and Open Source Editor Pixelorama
-======
-
-_**Brief: Pixelorama is a cross-platform, free and open source 2D sprite editor. It provides all the necessary tools to create pixel art in a neat user interface.**_
-
-### Pixelorama: open source sprite editor
-
-[Pixelorama][1] is a tool created by young game developers at [Orama Interactive][2]. They have developed a few 2D games and a couple of them use pixel art.
-
-While Orama is primarily into game development, the developers are also creating utility tools that help them (and others) create those games.
-
-The free and open source sprite editor, Pixelorama is such a utility tool. It’s built on top of [Godot Engine][3] and is perfect for creating pixel art.
-
-![Pixelorama screenshot][4]
-
-You see the pixel art in the screenshot above? It’s been created using Pixelorama. This video shows a timelapse video of creating the above image.
-
-### Features of Pixelorama
-
-Here are the main features Pixelorama provides:
-
- * Multiple tools like penicl, erase, fill bucket color picker etc
- * Multiple layer system that allows you to add, remove, move up and down, clone and merge as many layers as you like
- * Support for spritesheets
- * Import images and edit them inside Pixelorama
- * Animation timeline with [Onion Skinning][5]
- * Custom brushes
- * Save and open your projects in Pixelorama’s custom file format, .pxo
- * Horizontal & vertical mirrored drawing
- * Tile Mode for pattern creation
- * Split screen mode and mini canvas preview
- * Zoom with mouse scroll wheel
- * Unlimited undo and redo
- * Scale, crop, flip, rotate, color invert and desaturate your images
- * Keyboard shortcuts
- * Available in several languages
- * Supports Linux, Windows and macOS
-
-
-
-### Installing Pixelorama on Linux
-
-Pixelorama is available as a Snap application and if you are using Ubuntu, you can find it in the software center itself.
-
-![Pixelorama is available in Ubuntu Software Center][6]
-
-Alternatively, if you have [Snap support enabled on your Linux distribution][7], you can install it using this command:
-
-```
-sudo snap install pixelorama
-```
-
-If you don’t want to use Snap, no worries. You can download the latest release of Pixelorama from [their GitHub repository][8], [extract the zip file][9] and you’ll see an executable file. Give this file execute permission and double click on it to run the application.
-
-[Download Pixelorama][10]
-
-**Conclusion**
-
-![Pixelorama Welcome Screen][11]
-
-In the Pixeloaram features, it says that you can import images and edit them. I guess that’s only true for certain kind of files because when I tried to import PNG or JPEG files, the application crashed.
-
-However, I could easily doodle like a 3 year old and make random pixel art. I am not that into arts but I think this is a [useful tool for digital artists on Linux][12].
-
-I liked the idea that despite being game developers, they are creating tools that could help other game developers and artists. That’s the spirit of open source.
-
-If you like the project and will be using it, consider supporting them by a donation. [It’s FOSS has made a humble donation][13] of $25 to thank their effort.
-
-[Donate to Pixelorama (personal Paypal account of the lead developer)][14]
-
-Do you like Pixelorama? Do you use some other open source sprite editor? Feel free to share your views in the comment section.
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: https://itsfoss.com/pixelorama/
-
-作者:[Abhishek Prakash][a]
-选题:[lujun9972][b]
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]: https://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/
-[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
-[1]: https://www.orama-interactive.com/pixelorama
-[2]: https://www.orama-interactive.com/
-[3]: https://godotengine.org/
-[4]: https://i1.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/03/pixelorama-v6.jpg?ssl=1
-[5]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Onion_skinning
-[6]: https://i0.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/03/pixelorama-ubuntu-software-center.jpg?ssl=1
-[7]: https://itsfoss.com/install-snap-linux/
-[8]: https://github.com/Orama-Interactive/Pixelorama
-[9]: https://itsfoss.com/unzip-linux/
-[10]: https://github.com/Orama-Interactive/Pixelorama/releases
-[11]: https://i1.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/03/pixelorama.jpg?ssl=1
-[12]: https://itsfoss.com/best-linux-graphic-design-software/
-[13]: https://itsfoss.com/donations-foss/
-[14]: https://www.paypal.me/erevos
diff --git a/sources/tech/20200407 How to avoid man-in-the-middle cyber attacks.md b/sources/tech/20200407 How to avoid man-in-the-middle cyber attacks.md
deleted file mode 100644
index c8a72579ef..0000000000
--- a/sources/tech/20200407 How to avoid man-in-the-middle cyber attacks.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,94 +0,0 @@
-[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
-[#]: translator: (tinyeyeser )
-[#]: reviewer: ( )
-[#]: publisher: ( )
-[#]: url: ( )
-[#]: subject: (How to avoid man-in-the-middle cyber attacks)
-[#]: via: (https://opensource.com/article/20/4/mitm-attacks)
-[#]: author: (Jackie Lam https://opensource.com/users/beenverified)
-
-How to avoid man-in-the-middle cyber attacks
-======
-Understanding MITM attacks is the first step in not being a victim of
-this high-tech style of eavesdropping.
-![Security monster][1]
-
-Whether you're sending data on your computer or talking to someone online, you want to assume some level of security and privacy.
-
-But what if a third party is eavesdropping online, unbeknownst to you? And worse, what if they're impersonating someone from a business you trust in order to gain damaging information? This could put your personal data into the hands of dangerous, would-be thieves.
-
-Welcome to what's called a man-in-the-middle (MITM) attack.
-
-### What are man-in-the-middle attacks?
-
-A man-in-the-middle attack occurs when a cybercriminal inserts themselves into communications between you, the targeted victim, and a device in order to steal sensitive information that can be used for a variety of criminal purposes—most notably identity theft, says Steve J. J. Weisman, founder of Scamicide.
-
-"A man-in-the-middle-attack can also occur when the victim believes he or she is communicating with a legitimate app or website," says Weisman, "when the truth is that the victim is communicating with a phony website or app and thereby providing sensitive information to the criminal."
-
-One of the oldest forms of cyberattacks, MITM attacks have been around since the 1980s. What's more, they're quite common. As Weisman explains, there are a handful of ways a MITM attack can happen:
-
- * **Attacking a WiFi router that is not properly secured:** This typically occurs when someone is using public WiFi. "While home routers might be vulnerable, it's more common for criminals to attack public WiFi networks," says Weisman. The goal is to spy on unsuspecting people who are handling sensitive information, such as their online bank accounts, he adds.
- * **Hacking email accounts of banks, financial advisers, and other companies:** "Once [the criminals] have hacked these email systems, they send out emails that appear to come from the legitimate bank or other company," Weisman says. "[They ask] for personal information, such as usernames and passwords, under the guise of an emergency. The targeted victim is lured into providing that information."
- * **Sending phishing emails:** Thieves might also send emails pretending to be legitimate companies that the targeted victim does business with, asking the recipient for their personal information. "In many instances, the spear-phishing emails will direct the victim to a counterfeit website that appears to be that of a legitimate company with which the victim does business," says Weisman.
- * **Using malicious code in legitimate websites:** Attackers can also place malicious code—usually JavaScript—into a legitimate website by way of a web application. "When the victim loads the legitimate page, the malicious code just sits in the background until the user enters sensitive information, such as account login or credit card details, which the malicious code then copies and sends to the attackers' servers," says Nicholas McBride, a cybersecurity consultant.
-
-
-
-### What is an example of an MITM attack?
-
-The Lenovo case is a well-known example of an MITM attack. In 2014 and 2015, the major computer manufacturer sold consumer laptops with preinstalled software that meddled with how a user's browser communicated with websites. Whenever the user's cursor hovered over a product, this software, called VisualDiscovery, sent pop-up ads from retail partners that sold similar products.
-
-Here's the kicker: This MITM attack allowed VisualDiscovery to access all of the user's personal data, including social security numbers, info about financial transactions, medical info, and logins and passwords. All without the user knowing or granting permission beforehand. The FTC deemed this a deceptive and unfair online scam. Lenovo agreed to pay $8.3 million in a class-action settlement in 2019.
-
-### How can I protect myself from an online attack?
-
- * **Avoid using public WiFi:** Weisman recommends never using public WiFi for financial transactions unless you've installed a reliable virtual private network (VPN) client on your device and have a VPN host you can use and trust. Over a VPN connection, your communications are encrypted, so your information can't be stolen.
-
- * **Be on the lookout:** Be wary of emails or text messages that ask you to update your password or provide your username or personal information. These methods can be used to steal your identity.
-
-If you are unsure of the actual identity of the party sending you the email, you can use tools such as a reverse phone or email search. With a reverse phone number lookup, you may be able to find out more about the identity of an unknown texter. And with a reverse email lookup, you can try to determine who might have sent you a message.
-
-Generally, if something's actually a problem, you'll hear from someone you know and trust within your company, or from someone you can also go and meet, in person, at your bank or school or other organization. Important account information is never the purview of an unknown technician.
-
- * **Don't click on links contained in emails:** If someone sends you an email telling you that you need to sign into an account, don't click on the link provided in the email. Instead, navigate to the site yourself, log in as you normally would, and look for an alert there. If you don't see an alert message in your account settings, contact a representative by phone using contact information on the site and _not_ from the email.
-
- * **Install reliable security software:** If you're on Windows, install good open source antivirus like [ClamAV][2]. On all platforms, keep your software up to date with the latest security patches.
-
- * **Take alerts seriously:** If you're visiting a site that starts with HTTPS, your browser might alert you to an issue, says McBride. For instance, if the domain name on the site's certificate doesn't match the one you're trying to visit. Don't ignore the alert. Heed it and navigate away from the site for now. Verify that you haven't [mistyped it][3], and if the problem persists, contact the site owner if you can.
-
- * **Use an ad blocker:** Pop-up ads (also known as _adware attacks_) can be used to intercept your personal information, so use an ad blocker. "The truth is, as an individual user, it's hard to protect against a MITM attack," says McBride, "as it is designed to leave the victim in the dark and to prevent them from noticing that there is anything wrong."
-
-A good open source ad blocker (or "wide-spectrum blocker," in the developer's words) is [uBlock origin][4]. It's available for both Firefox and Chromium (and all Chromium-based browsers, such as Chrome, Brave, Vivaldi, Edge, and so on), and even Safari.
-
-
-
-
-### Stay alert
-
-Remember, you don't have to click anything online right away, and you don't have to follow random people's instructions, no matter how urgent they may seem. The internet will still be there after you step away from the computer and verify the identity of a person or site demanding your attention.
-
-While MITM attacks can happen to anyone, understanding what they are, knowing how they happen, and actively taking steps to prevent them can safeguard you from being a victim.
-
-* * *
-
-_This article was originally published on [BeenVerified.com][5] under a [CC BY-SA 2.0][6] license._
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: https://opensource.com/article/20/4/mitm-attacks
-
-作者:[Jackie Lam][a]
-选题:[lujun9972][b]
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]: https://opensource.com/users/beenverified
-[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
-[1]: https://opensource.com/sites/default/files/styles/image-full-size/public/lead-images/security_password_chaos_engineer_monster.png?itok=J31aRccu (Security monster)
-[2]: https://www.clamav.net
-[3]: https://opensource.com/article/20/1/stop-typosquatting-attacks
-[4]: https://github.com/gorhill/uBlock
-[5]: https://www.beenverified.com/crime/what-is-a-man-in-the-middle-attack/
-[6]: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.0/
diff --git a/sources/tech/20200416 Learning to love systemd.md b/sources/tech/20200416 Learning to love systemd.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 70243db915..0000000000
--- a/sources/tech/20200416 Learning to love systemd.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,328 +0,0 @@
-[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
-[#]: translator: (messon007)
-[#]: reviewer: ( )
-[#]: publisher: ( )
-[#]: url: ( )
-[#]: subject: (Learning to love systemd)
-[#]: via: (https://opensource.com/article/20/4/systemd)
-[#]: author: (David Both https://opensource.com/users/dboth)
-
-Learning to love systemd
-======
-systemd is the mother of all processes, responsible for bringing the
-Linux host up to a state where productive work can be done.
-![Penguin driving a car with a yellow background][1]
-
-systemd—yes, all lower-case, even at the beginning of a sentence—is the modern replacement for init and SystemV init scripts. It is also much more.
-
-Like most sysadmins, when I think of the init program and SystemV, I think of Linux startup and shutdown and not really much else, like managing services once they are up and running. Like init, systemd is the mother of all processes, and it is responsible for bringing the Linux host up to a state in which productive work can be done. Some of the functions assumed by systemd, which is far more extensive than the old init program, are to manage many aspects of a running Linux host, including mounting filesystems, managing hardware, handling timers, and starting and managing the system services that are required to have a productive Linux host.
-
-This series of articles, which is based in part on excerpts from my three-volume Linux training course, [_Using and administering Linux: zero to sysadmin_][2], explores systemd's functions both at startup and beginning after startup finishes.
-
-### Linux boot
-
-The complete process that takes a Linux host from an off state to a running state is complex, but it is open and knowable. Before getting into the details, I'll give a quick overview from when the host hardware is turned on until the system is ready for a user to log in. Most of the time, "the boot process" is discussed as a single entity, but that is not accurate. There are, in fact, three major parts to the full boot and startup process:
-
- * **Hardware boot:** Initializes the system hardware
- * **Linux boot:** Loads the Linux kernel and then systemd
- * **Linux startup:** Where systemd prepares the host for productive work
-
-
-
-The Linux startup sequence begins after the kernel has loaded either init or systemd, depending upon whether the distribution uses the old or new startup, respectively. The init and systemd programs start and manage all the other processes and are both known as the "mother of all processes" on their respective systems.
-
-It is important to separate the hardware boot from the Linux boot from the Linux startup and to explicitly define the demarcation points between them. Understanding these differences and what part each plays in getting a Linux system to a state where it can be productive makes it possible to manage these processes and better determine where a problem is occurring during what most people refer to as "boot."
-
-The startup process follows the three-step boot process and brings the Linux computer up to an operational state in which it is usable for productive work. The startup process begins when the kernel transfers control of the host to systemd.
-
-### systemd controversy
-
-systemd can evoke a wide range of reactions from sysadmins and others responsible for keeping Linux systems up and running. The fact that systemd is taking over so many tasks in many Linux systems has engendered pushback and discord among certain groups of developers and sysadmins.
-
-SystemV and systemd are two different methods of performing the Linux startup sequence. SystemV start scripts and the init program are the old methods, and systemd using targets is the new method. Although most modern Linux distributions use the newer systemd for startup, shutdown, and process management, there are still some that do not. One reason is that some distribution maintainers and some sysadmins prefer the older SystemV method over the newer systemd.
-
-I think both have advantages.
-
-#### Why I prefer SystemV
-
-I prefer SystemV because it is more open. Startup is accomplished using Bash scripts. After the kernel starts the init program, which is a compiled binary, init launches the **rc.sysinit** script, which performs many system initialization tasks. After **rc.sysinit** completes, init launches the **/etc/rc.d/rc** script, which in turn starts the various services defined by the SystemV start scripts in the **/etc/rc.d/rcX.d**, where "X" is the number of the runlevel being started.
-
-Except for the init program itself, all these programs are open and easily knowable scripts. It is possible to read through these scripts and learn exactly what is taking place during the entire startup process, but I don't think many sysadmins actually do that. Each start script is numbered so that it starts its intended service in a specific sequence. Services are started serially, and only one service starts at a time.
-
-systemd, developed by Red Hat's Lennart Poettering and Kay Sievers, is a complex system of large, compiled binary executables that are not understandable without access to the source code. It is open source, so "access to the source code" isn't hard, just less convenient. systemd appears to represent a significant refutation of multiple tenets of the Linux philosophy. As a binary, systemd is not directly open for the sysadmin to view or make easy changes. systemd tries to do everything, such as managing running services, while providing significantly more status information than SystemV. It also manages hardware, processes, and groups of processes, filesystem mounts, and much more. systemd is present in almost every aspect of the modern Linux host, making it the one-stop tool for system management. All of this is a clear violation of the tenets that programs should be small and that each program should do one thing and do it well.
-
-#### Why I prefer systemd
-
-I prefer systemd as my startup mechanism because it starts as many services as possible in parallel, depending upon the current stage in the startup process. This speeds the overall startup and gets the host system to a login screen faster than SystemV.
-
-systemd manages almost every aspect of a running Linux system. It can manage running services while providing significantly more status information than SystemV. It also manages hardware, processes and groups of processes, filesystem mounts, and much more. systemd is present in almost every aspect of the modern Linux operating system, making it the one-stop tool for system management. (Does this sound familiar?)
-
-The systemd tools are compiled binaries, but the tool suite is open because all the configuration files are ASCII text files. Startup configuration can be modified through various GUI and command-line tools, as well as adding or modifying various configuration files to suit the needs of the specific local computing environment.
-
-#### The real issue
-
-Did you think I could not like both startup systems? I do, and I can work with either one.
-
-In my opinion, the real issue and the root cause of most of the controversy between SystemV and systemd is that there is [no choice][3] on the sysadmin level. The choice of whether to use SystemV or systemd has already been made by the developers, maintainers, and packagers of the various distributions—but with good reason. Scooping out and replacing an init system, by its extreme, invasive nature, has a lot of consequences that would be hard to tackle outside the distribution design process.
-
-Despite the fact that this choice is made for me, my Linux hosts boot up and work, which is what I usually care the most about. As an end user and even as a sysadmin, my primary concern is whether I can get my work done, work such as writing my books and this article, installing updates, and writing scripts to automate everything. So long as I can do my work, I don't really care about the start sequence used on my distro.
-
-I do care when there is a problem during startup or service management. Regardless of which startup system is used on a host, I know enough to follow the sequence of events to find the failure and fix it.
-
-#### Replacing SystemV
-
-There have been previous attempts at replacing SystemV with something a bit more modern. For about two releases, Fedora used a thing called Upstart to replace the aging SystemV, but it did not replace init and provided no changes that I noticed. Because Upstart provided no significant changes to the issues surrounding SystemV, efforts in this direction were quickly dropped in favor of systemd.
-
-Despite the fact that most Linux developers agree that replacing the old SystemV startup is a good idea, many developers and sysadmins dislike systemd for that. Rather than rehash all the so-called issues that people have—or had—with systemd, I will refer you to two good, if somewhat old, articles that should cover most everything. Linus Torvalds, the creator of the Linux kernel, seems disinterested. In a 2014 ZDNet article, _[Linus Torvalds and others on Linux's systemd][4]_, Linus is clear about his feelings.
-
-> "I don't actually have any particularly strong opinions on systemd itself. I've had issues with some of the core developers that I think are much too cavalier about bugs and compatibility, and I think some of the design details are insane (I dislike the binary logs, for example), but those are details, not big issues."
-
-In case you don't know much about Linus, I can tell you that if he does not like something, he is very outspoken, explicit, and quite clear about that dislike. He has become more socially acceptable in his manner of addressing his dislike about things.
-
-In 2013, Poettering wrote a long blog post in which he debunks the [myths about systemd][5] while providing insight into some of the reasons for creating it. This is a very good read, and I highly recommend it.
-
-### systemd tasks
-
-Depending upon the options used during the compile process (which are not considered in this series), systemd can have as many as 69 binary executables that perform the following tasks, among others:
-
- * The systemd program runs as PID 1 and provides system startup of as many services in parallel as possible, which, as a side effect, speeds overall startup times. It also manages the shutdown sequence.
- * The systemctl program provides a user interface for service management.
- * Support for SystemV and LSB start scripts is offered for backward compatibility.
- * Service management and reporting provide more service status data than SystemV.
- * It includes tools for basic system configuration, such as hostname, date, locale, lists of logged-in users, running containers and virtual machines, system accounts, runtime directories and settings, daemons to manage simple network configuration, network time synchronization, log forwarding, and name resolution.
- * It offers socket management.
- * systemd timers provide advanced cron-like capabilities to include running a script at times relative to system boot, systemd startup, the last time the timer was started, and more.
- * It provides a tool to analyze dates and times used in timer specifications.
- * Mounting and unmounting of filesystems with hierarchical awareness allows safer cascading of mounted filesystems.
- * It enables the positive creation and management of temporary files, including deletion.
- * An interface to D-Bus provides the ability to run scripts when devices are plugged in or removed. This allows all devices, whether pluggable or not, to be treated as plug-and-play, which considerably simplifies device handling.
- * Its tool to analyze the startup sequence can be used to locate the services that take the most time.
- * It includes journals for storing system log messages and tools for managing the journals.
-
-
-
-### Architecture
-
-Those tasks and more are supported by a number of daemons, control programs, and configuration files. Figure 1 shows many of the components that belong to systemd. This is a simplified diagram designed to provide a high-level overview, so it does not include all of the individual programs or files. Nor does it provide any insight into data flow, which is so complex that it would be a useless exercise in the context of this series of articles.
-
-![systemd architecture][6]
-
-A full exposition of systemd would take a book on its own. You do not need to understand the details of how the systemd components in Figure 1 fit together; it's enough to know about the programs and components that enable managing various Linux services and deal with log files and journals. But it's clear that systemd is not the monolithic monstrosity it is purported to be by some of its critics.
-
-### systemd as PID 1
-
-systemd is PID 1. Some of its functions, which are far more extensive than the old SystemV3 init program, are to manage many aspects of a running Linux host, including mounting filesystems and starting and managing system services required to have a productive Linux host. Any of systemd's tasks that are not related to the startup sequence are outside the scope of this article (but some will be explored later in this series).
-
-First, systemd mounts the filesystems defined by **/etc/fstab**, including any swap files or partitions. At this point, it can access the configuration files located in **/etc**, including its own. It uses its configuration link, **/etc/systemd/system/default.target**, to determine which state or target it should boot the host into. The **default.target** file is a symbolic link to the true target file. For a desktop workstation, this is typically going to be the **graphical.target**, which is equivalent to runlevel 5 in SystemV. For a server, the default is more likely to be the **multi-user.target**, which is like runlevel 3 in SystemV. The **emergency.target** is similar to single-user mode. Targets and services are systemd units.
-
-The table below (Figure 2) compares the systemd targets with the old SystemV startup runlevels. systemd provides the systemd target aliases for backward compatibility. The target aliases allow scripts—and many sysadmins—to use SystemV commands like **init 3** to change runlevels. Of course, the SystemV commands are forwarded to systemd for interpretation and execution.
-
-**systemd targets** | **SystemV runlevel** | **target aliases** | **Description**
----|---|---|---
-default.target | | | This target is always aliased with a symbolic link to either **multi-user.target** or **graphical.target**. systemd always uses the **default.target** to start the system. The **default.target** should never be aliased to **halt.target**, **poweroff.target**, or **reboot.target**.
-graphical.target | 5 | runlevel5.target | **Multi-user.target** with a GUI
-| 4 | runlevel4.target | Unused. Runlevel 4 was identical to runlevel 3 in the SystemV world. This target could be created and customized to start local services without changing the default **multi-user.target**.
-multi-user.target | 3 | runlevel3.target | All services running, but command-line interface (CLI) only
-| 2 | runlevel2.target | Multi-user, without NFS, but all other non-GUI services running
-rescue.target | 1 | runlevel1.target | A basic system, including mounting the filesystems with only the most basic services running and a rescue shell on the main console
-emergency.target | S | | Single-user mode—no services are running; filesystems are not mounted. This is the most basic level of operation with only an emergency shell running on the main console for the user to interact with the system.
-halt.target | | | Halts the system without powering it down
-reboot.target | 6 | runlevel6.target | Reboot
-poweroff.target | 0 | runlevel0.target | Halts the system and turns the power off
-
-Each target has a set of dependencies described in its configuration file. systemd starts the required dependencies, which are the services required to run the Linux host at a specific level of functionality. When all the dependencies listed in the target configuration files are loaded and running, the system is running at that target level. In Figure 2, the targets with the most functionality are at the top of the table, with functionality declining towards the bottom of the table.
-
-systemd also looks at the legacy SystemV init directories to see if any startup files exist there. If so, systemd uses them as configuration files to start the services described by the files. The deprecated network service is a good example of one that still uses SystemV startup files in Fedora.
-
-Figure 3 (below) is copied directly from the bootup man page. It shows a map of the general sequence of events during systemd startup and the basic ordering requirements to ensure a successful startup.
-
-
-```
- cryptsetup-pre.target
- |
- (various low-level v
- API VFS mounts: (various cryptsetup devices...)
- mqueue, configfs, | |
- debugfs, ...) v |
- | cryptsetup.target |
- | (various swap | | remote-fs-pre.target
- | devices...) | | | |
- | | | | | v
- | v local-fs-pre.target | | | (network file systems)
- | swap.target | | v v |
- | | v | remote-cryptsetup.target |
- | | (various low-level (various mounts and | | |
- | | services: udevd, fsck services...) | | remote-fs.target
- | | tmpfiles, random | | | /
- | | seed, sysctl, ...) v | | /
- | | | local-fs.target | | /
- | | | | | | /
- \\____|______|_______________ ______|___________/ | /
- \ / | /
- v | /
- sysinit.target | /
- | | /
- ______________________/|\\_____________________ | /
- / | | | \ | /
- | | | | | | /
- v v | v | | /
- (various (various | (various | |/
- timers...) paths...) | sockets...) | |
- | | | | | |
- v v | v | |
- timers.target paths.target | sockets.target | |
- | | | | v |
- v \\_______ | _____/ rescue.service |
- \|/ | |
- v v |
- basic.target rescue.target |
- | |
- ________v____________________ |
- / | \ |
- | | | |
- v v v |
- display- (various system (various system |
- manager.service services services) |
- | required for | |
- | graphical UIs) v v
- | | multi-user.target
- emergency.service | | |
- | \\_____________ | _____________/
- v \|/
- emergency.target v
- graphical.target
-```
-
-The **sysinit.target** and **basic.target** targets can be considered checkpoints in the startup process. Although one of systemd's design goals is to start system services in parallel, certain services and functional targets must be started before other services and targets can start. These checkpoints cannot be passed until all of the services and targets required by that checkpoint are fulfilled.
-
-The **sysinit.target** is reached when all of the units it depends on are completed. All of those units, mounting filesystems, setting up swap files, starting udev, setting the random generator seed, initiating low-level services, and setting up cryptographic services (if one or more filesystems are encrypted), must be completed but, within the **sysinit.target**, those tasks can be performed in parallel.
-
-The **sysinit.target** starts up all of the low-level services and units required for the system to be marginally functional and that are required to enable moving onto the **basic.target**.
-
-After the **sysinit.target** is fulfilled, systemd then starts all the units required to fulfill the next target. The basic target provides some additional functionality by starting units that are required for all of the next targets. These include setting up things like paths to various executable directories, communication sockets, and timers.
-
-Finally, the user-level targets, **multi-user.target** or **graphical.target**, can be initialized. The **multi-user.target** must be reached before the graphical target dependencies can be met. The underlined targets in Figure 3 are the usual startup targets. When one of these targets is reached, startup has completed. If the **multi-user.target** is the default, then you should see a text-mode login on the console. If **graphical.target** is the default, then you should see a graphical login; the specific GUI login screen you see depends on your default display manager.
-
-The bootup man page also describes and provides maps of the boot into the initial RAM disk and the systemd shutdown process.
-
-systemd also provides a tool that lists dependencies of a complete startup or for a specified unit. A unit is a controllable systemd resource entity that can range from a specific service, such as httpd or sshd, to timers, mounts, sockets, and more. Try the following command and scroll through the results.
-
-
-```
-`systemctl list-dependencies graphical.target`
-```
-
-Notice that this fully expands the top-level target units list required to bring the system up to the graphical target run mode. Use the **\--all** option to expand all of the other units as well.
-
-
-```
-`systemctl list-dependencies --all graphical.target`
-```
-
-You can search for strings such as "target," "slice," and "socket" using the search tools of the **less** command.
-
-So now, try the following.
-
-
-```
-`systemctl list-dependencies multi-user.target`
-```
-
-and
-
-
-```
-`systemctl list-dependencies rescue.target`
-```
-
-and
-
-
-```
-`systemctl list-dependencies local-fs.target`
-```
-
-and
-
-
-```
-`systemctl list-dependencies dbus.service`
-```
-
-This tool helps me visualize the specifics of the startup dependencies for the host I am working on. Go ahead and spend some time exploring the startup tree for one or more of your Linux hosts. But be careful because the systemctl man page contains this note:
-
-> _"Note that this command only lists units currently loaded into memory by the service manager. In particular, this command is not suitable to get a comprehensive list at all reverse dependencies on a specific unit, as it won't list the dependencies declared by units currently not loaded."_
-
-### Final thoughts
-
-Even before getting very deep into systemd, it's obvious that it is both powerful and complex. It is also apparent that systemd is not a single, huge, monolithic, and unknowable binary file. Rather, it is composed of a number of smaller components and subcommands that are designed to perform specific tasks.
-
-The next article in this series will explore systemd startup in more detail, as well as systemd configuration files, changing the default target, and how to create a simple service unit.
-
-### Resources
-
-There is a great deal of information about systemd available on the internet, but much is terse, obtuse, or even misleading. In addition to the resources mentioned in this article, the following webpages offer more detailed and reliable information about systemd startup.
-
- * The Fedora Project has a good, practical [guide][7] [to systemd][7]. It has pretty much everything you need to know in order to configure, manage, and maintain a Fedora computer using systemd.
- * The Fedora Project also has a good [cheat sheet][8] that cross-references the old SystemV commands to comparable systemd ones.
- * For detailed technical information about systemd and the reasons for creating it, check out [Freedesktop.org][9]'s [description of systemd][10].
- * [Linux.com][11]'s "More systemd fun" offers more advanced systemd [information and tips][12].
-
-
-
-There is also a series of deeply technical articles for Linux sysadmins by Lennart Poettering, the designer and primary developer of systemd. These articles were written between April 2010 and September 2011, but they are just as relevant now as they were then. Much of everything else good that has been written about systemd and its ecosystem is based on these papers.
-
- * [Rethinking PID 1][13]
- * [systemd for Administrators, Part I][14]
- * [systemd for Administrators, Part II][15]
- * [systemd for Administrators, Part III][16]
- * [systemd for Administrators, Part IV][17]
- * [systemd for Administrators, Part V][18]
- * [systemd for Administrators, Part VI][19]
- * [systemd for Administrators, Part VII][20]
- * [systemd for Administrators, Part VIII][21]
- * [systemd for Administrators, Part IX][22]
- * [systemd for Administrators, Part X][23]
- * [systemd for Administrators, Part XI][24]
-
-
-
-Alison Chiaken, a Linux kernel and systems programmer at Mentor Graphics, offers a preview of her...
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: https://opensource.com/article/20/4/systemd
-
-作者:[David Both][a]
-选题:[lujun9972][b]
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]: https://opensource.com/users/dboth
-[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
-[1]: https://opensource.com/sites/default/files/styles/image-full-size/public/lead-images/car-penguin-drive-linux-yellow.png?itok=twWGlYAc (Penguin driving a car with a yellow background)
-[2]: http://www.both.org/?page_id=1183
-[3]: http://www.osnews.com/story/28026/Editorial_Thoughts_on_Systemd_and_the_Freedom_to_Choose
-[4]: https://www.zdnet.com/article/linus-torvalds-and-others-on-linuxs-systemd/
-[5]: http://0pointer.de/blog/projects/the-biggest-myths.html
-[6]: https://opensource.com/sites/default/files/uploads/systemd-architecture.png (systemd architecture)
-[7]: https://docs.fedoraproject.org/en-US/quick-docs/understanding-and-administering-systemd/index.html
-[8]: https://fedoraproject.org/wiki/SysVinit_to_Systemd_Cheatsheet
-[9]: http://Freedesktop.org
-[10]: http://www.freedesktop.org/wiki/Software/systemd
-[11]: http://Linux.com
-[12]: https://www.linux.com/training-tutorials/more-systemd-fun-blame-game-and-stopping-services-prejudice/
-[13]: http://0pointer.de/blog/projects/systemd.html
-[14]: http://0pointer.de/blog/projects/systemd-for-admins-1.html
-[15]: http://0pointer.de/blog/projects/systemd-for-admins-2.html
-[16]: http://0pointer.de/blog/projects/systemd-for-admins-3.html
-[17]: http://0pointer.de/blog/projects/systemd-for-admins-4.html
-[18]: http://0pointer.de/blog/projects/three-levels-of-off.html
-[19]: http://0pointer.de/blog/projects/changing-roots
-[20]: http://0pointer.de/blog/projects/blame-game.html
-[21]: http://0pointer.de/blog/projects/the-new-configuration-files.html
-[22]: http://0pointer.de/blog/projects/on-etc-sysinit.html
-[23]: http://0pointer.de/blog/projects/instances.html
-[24]: http://0pointer.de/blog/projects/inetd.html
diff --git a/sources/tech/20200417 How to compress files on Linux 5 ways.md b/sources/tech/20200417 How to compress files on Linux 5 ways.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 5ce33cd18c..0000000000
--- a/sources/tech/20200417 How to compress files on Linux 5 ways.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,207 +0,0 @@
-[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
-[#]: translator: ( )
-[#]: reviewer: ( )
-[#]: publisher: ( )
-[#]: url: ( )
-[#]: subject: (How to compress files on Linux 5 ways)
-[#]: via: (https://www.networkworld.com/article/3538471/how-to-compress-files-on-linux-5-ways.html)
-[#]: author: (Sandra Henry-Stocker https://www.networkworld.com/author/Sandra-Henry_Stocker/)
-
-How to compress files on Linux 5 ways
-======
-There are a number of tools that you use to compress files on Linux systems, but they don't all behave the same way or yield the same level of compression. In this post, we compare five of them.
-Getty Images
-
-There are quite a few commands on Linux for compressing files. One of the newest and most effective is **xz**, but they all have advantages for both saving disk space and preserving files for later use. In this post, we compare the compression commands and point out the significant differences.
-
-### tar
-
-The tar command is not specifically a compression command. It’s generally used to pull a number of files into a single file for easy transport to another system or to back the files up as a related group. It also provides compression as a feature, which makes a lot of sense, and the addition of the **z** compression option is available to make this happen.
-
-When compression is added to a **tar** command with the **z** option, tar uses **gzip** to do the compressing.
-
-You can use **tar** to compress a single file as easily as a group though this offers no particular advantage over using **gzip** directly. To use **tar** for this, just identify the file as you would a group of files with a “tar cfz newtarfile filename” command like this:
-
-```
-$ tar cfz bigfile.tgz bigfile
- ^ ^
- | |
- +- new file +- file to be compressed
-
-$ ls -l bigfile*
--rw-rw-r-- 1 shs shs 103270400 Apr 16 16:09 bigfile
--rw-rw-r-- 1 shs shs 21608325 Apr 16 16:08 bigfile.tgz
-```
-
-Note the significant reduction in the file size.
-
-If you prefer, you can use the **tar.gz** extension which might make the character of the file a bit more obvious, but most Linux users will probably recognize **tgz** as meaning the same thing – the combination of **tar** and **gz** to indicate that the file is a compressed tar file. You will be left with both the original file and the compressed file once the compression is complete.
-
-To collect a number of files together and compress the resultant “tar ball” in one command, use the same basic syntax, but specify the files to be included as a group in place of the single file. Here’s an example:
-
-[][1]
-
-```
-$ tar cfz bin.tgz bin/*
- ^ ^
- | +-- files to include
- + new file
-```
-
-### zip
-
-The **zip** command creates a compressed file while leaving the original file intact. The syntax is straightforward except that, as with **tar**, you have to remember that your original file should be the last argument on the command line.
-
-```
-$ zip ./bigfile.zip bigfile
-updating: bigfile (deflated 79%)
-$ ls -l bigfile bigfile.zip
--rw-rw-r-- 1 shs shs 103270400 Apr 16 11:18 bigfile
--rw-rw-r-- 1 shs shs 21606889 Apr 16 11:19 bigfile.zip
-```
-
-### gzip
-
-The **gzip** command is very simple to use. You just type "gzip" followed by the name of the file you want to compress. Unlike the commands described above, **gzip** will encrypt the files "in place". In other words, the original file will be replaced by the encrypted file.
-
-```
-$ gzip bigfile
-$ ls -l bigfile*
--rw-rw-r-- 1 shs shs 21606751 Apr 15 17:57 bigfile.gz
-```
-
-### bzip2
-
-As with the **gzip** command, **bzip2** will compress the file that you select "in place", leaving only the original file.
-
-```
-$ bzip bigfile
-$ ls -l bigfile*
--rw-rw-r-- 1 shs shs 18115234 Apr 15 17:57 bigfile.bz2
-```
-
-### xz
-
-A relative newcomer to the compression command team, **xz** is a front runner in terms of how well it compresses files. Like the two previous commands, you only need to supply the file name to the command. Again, the original file is compressed in place.
-
-```
-$ xz bigfile
-$ ls -l bigfile*
--rw-rw-r-- 1 shs shs 13427236 Apr 15 17:30 bigfile.xz
-```
-
-For large files, you are likely to notice that **xz** takes longer to run than other compression commands, but the compression results are very impressive.
-
-### Comparisons to consider
-
-Most people have heard it said that "size isn't everything". So, let's compare file size as well as some other issues to be considered when you make plans for how you want to compress your files.
-
-The stats shown below all relate to compressing the single file – bigfile – used in the example commands shown above. This file is a large and fairly random text file. Compression rates will depend to some extent on the content of the files.
-
-#### Size reduction
-
-When compared, the various compression commands shown above yielded the following results. The percentages represent how the compressed files compare with the original file.
-
-```
--rw-rw-r-- 1 shs shs 103270400 Apr 16 14:01 bigfile
-------------------------------------------------------
--rw-rw-r-- 1 shs shs 18115234 Apr 16 13:59 bigfile.bz2 ~17%
--rw-rw-r-- 1 shs shs 21606751 Apr 16 14:00 bigfile.gz ~21%
--rw-rw-r-- 1 shs shs 21608322 Apr 16 13:59 bigfile.tgz ~21%
--rw-rw-r-- 1 shs shs 13427236 Apr 16 14:00 bigfile.xz ~13%
--rw-rw-r-- 1 shs shs 21606889 Apr 16 13:59 bigfile.zip ~21%
-```
-
-The **xz** commands wins, ending up at only 13% the size of the original file, but all of these compression commands reduced the original file size quite significantly.
-
-#### Whether the original files are replaced
-
-The **bzip2**, **gzip** and **xz** commands all replace the original files with compressed versions. The **tar** and **zip** commands to not.
-
-#### Run time
-
-The **xz** command seems to take more time than the other commands to encrypt the files. For bigfile, the approximate times were:
-
-```
-command run-time
-tar 4.9 seconds
-zip 5.2 seconds
-bzip2 22.8 seconds
-gzip 4.8 seconds
-xz 50.4 seconds
-```
-
-Decompression times are likely to be considerably smaller than compression times.
-
-#### File permissions
-
-Regardless of what permissions you have set on your original file, permissions for the compressed file will be based on your **umask** setting, except for **bzip2** which retains the original file's permissions.
-
-#### Compatibility with Windows
-
-The **zip** command creates a file which can be used (i.e., decompressed) on Windows systems as well as Linux and other Unix systems without having to install other tools which may or may not be available.
-
-### Decompressing files
-
-The commands for decompressing files are similar to those used to compress the files. These commands would work for decompressing bigfile after the compression commands shown above were run.
-
- * tar: **tar xf bigfile.tgz**
- * zip: **unzip bigfile.zip**
- * gzip: **gunzip bigfile.gz**
- * bzip2: **bunzip2 bigfile.gz2**
- * xz: **xz -d bigfile.xz** or **unxz bigfile.xz**
-
-
-
-### Running your own compression comparisons
-
-If you'd like to run some tests on your own, grab a large but replaceable file and compress it using each of the commands shown above – preferably using a new subdirectory. You might have to first install **xz** if you want to include it in the tests.This script can make the comparison easier, but will likely take a few minutes to complete.
-
-```
-#!/bin/bash
-
-# ask user for filename
-echo -n "filename> "
-read filename
-
-# you need this because some commands will replace the original file
-cp $filename $filename-2
-
-# clean up first (in case previous results are still available)
-rm $filename.*
-
-tar cvfz ./$filename.tgz $filename > /dev/null
-zip $filename.zip $filename > /dev/null
-bzip2 $filename
-# recover original file
-cp $filename-2 $filename
-gzip $filename
-# recover original file
-cp $filename-2 $filename
-xz $filename
-
-# show results
-ls -l $filename.*
-
-# replace the original file
-mv $filename-2 $filename
-```
-
-Join the Network World communities on [Facebook][2] and [LinkedIn][3] to comment on topics that are top of mind.
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: https://www.networkworld.com/article/3538471/how-to-compress-files-on-linux-5-ways.html
-
-作者:[Sandra Henry-Stocker][a]
-选题:[lujun9972][b]
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]: https://www.networkworld.com/author/Sandra-Henry_Stocker/
-[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
-[1]: https://www.networkworld.com/blog/itaas-and-the-corporate-storage-technology/?utm_source=IDG&utm_medium=promotions&utm_campaign=HPE22140&utm_content=sidebar (ITAAS and Corporate Storage Strategy)
-[2]: https://www.facebook.com/NetworkWorld/
-[3]: https://www.linkedin.com/company/network-world
diff --git a/sources/tech/20200427 How to secure your Linux email services with SSL-TLS.md b/sources/tech/20200427 How to secure your Linux email services with SSL-TLS.md
index 163e6b017f..3dcd2a5dc6 100644
--- a/sources/tech/20200427 How to secure your Linux email services with SSL-TLS.md
+++ b/sources/tech/20200427 How to secure your Linux email services with SSL-TLS.md
@@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
-[#]: translator: ( )
+[#]: translator: (Acceleratorrrr)
[#]: reviewer: ( )
[#]: publisher: ( )
[#]: url: ( )
@@ -7,6 +7,7 @@
[#]: via: (https://opensource.com/article/20/4/securing-linux-email)
[#]: author: (Marc Skinner https://opensource.com/users/marc-skinner)
+
How to secure your Linux email services with SSL/TLS
======
Protect your Linux email services by understanding security
diff --git a/sources/tech/20200427 New zine- How Containers Work.md b/sources/tech/20200427 New zine- How Containers Work.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..fa2198ebbc
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/tech/20200427 New zine- How Containers Work.md
@@ -0,0 +1,121 @@
+[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
+[#]: translator: ( )
+[#]: reviewer: ( )
+[#]: publisher: ( )
+[#]: url: ( )
+[#]: subject: (New zine: How Containers Work!)
+[#]: via: (https://jvns.ca/blog/2020/04/27/new-zine-how-containers-work/)
+[#]: author: (Julia Evans https://jvns.ca/)
+
+New zine: How Containers Work!
+======
+
+On Friday I published a new zine: “How Containers Work!”. I also launched a fun redesign of [wizardzines.com][1].
+
+You can get it for $12 at . If you buy it, you’ll get a PDF that you can either print out or read on your computer. Or you can get a pack of [all 8 zines][2] so far.
+
+Here’s the cover and table of contents:
+
+[![][3]][4]
+
+### why containers?
+
+I’ve spent a lot of time [figuring][5] [out][6] [how to][7] [run][8] [things][9] [in][10] [containers][11] over the last 3-4 years. And at the beginning I was really confused! I knew a bunch of things about Linux, and containers didn’t seem to fit in with anything I thought I knew (“is it a process? what’s a network namespace? what’s happening?“). The whole thing seemed really weird.
+
+It turns out that containers ARE actually pretty weird. They’re not just one thing, they’re what you get when you glue together 6 different features that were mostly designed to work together but have a bunch of confusing edge cases.
+
+As usual, the thing that helped me the most in my container adventures is a good understanding of the **fundamentals** – what exactly is actually happening on my server when I run a container?
+
+So that’s what this zine is about – cgroups, namespaces, pivot_root, seccomp-bpf, and all the other Linux kernel features that make containers work.
+
+Once I understood those ideas, it got a **lot** easier to debug when my containers were doing surprising things in production. I learned a couple of interesting and strange things about containers while writing this zine too – I’ll probably write a blog post about one of them later this week.
+
+### containers aren’t magic
+
+This picture (page 6 of the zine) shows you how to run a fish container image with only 15 lines of bash. This is heavily inspired by [bocker][12], which “implements” Docker in about 100 lines of bash.
+
+
+
+The main things I see missing from that script compared to what Docker actually does when running a container (other than using an actual container image and not just a tarball) are:
+
+ * it doesn’t drop any capabilities – the container is still running as root and has full root privileges (just in a different mount + PID namespace)
+ * it doesn’t block any system calls with seccomp-bpf
+
+
+
+### container command line tools
+
+The zine also goes over a bunch of command line tools & files that you can use to inspect running containers or play with Linux container features. Here’s a list:
+
+ * `mount -t overlay` (create and view overlay filesystems)
+ * `unshare` (create namespaces)
+ * `nsenter` (use an existing namespace)
+ * `getpcaps` (get a process’s capabilities)
+ * `capsh` (drop or add capabilities, etc)
+ * `cgcreate` (create a cgroup)
+ * `cgexec` (run a command in an existing cgroup)
+ * `chroot` (change root directory. not actually what containers use but interesting to play with anyway)
+ * `/sys/fs/cgroups` (for information about cgroups, like `memory.usage_in_bytes`)
+ * `/proc/PID/ns` (all a process’s namespaces)
+ * `lsns` (another way to view namespaces)
+
+
+
+I also made a short youtube video a while back called [ways to spy on a Docker container][13] that demos some of these command line tools.
+
+### container runtime agnostic
+
+I tried to keep this zine pretty container-runtime-agnostic – I mention Docker a couple of times because it’s so widely used, but it’s about the Linux kernel features that make containers work in general, not Docker or LXC or systemd-nspawn or Kubernetes or whatever. If you understand the fundamentals you can figure all those things out!
+
+### we redesigned wizardzines.com!
+
+On Friday I also launched a redesign of [wizardzines.com][1]! [Melody Starling][14] (who is amazing) did the design. I think now it’s better organized but the tiny touch that I’m most delighted by is that now the zines jump with joy when you hover over them.
+
+One cool thing about working with a designer is – they don’t just make things _look_ better, they help _organize_ the information better so the website makes more sense and it’s easier to find things! This is probably obvious to anyone who knows anything about design but I haven’t worked with designers very much (or maybe ever?) so it was really cool to see.
+
+One tiny example of this: Melody had the idea of adding a tiny FAQ on the landing page for each zine, where I can put the answers to all the questions people always ask! Here’s what the little FAQ box looks like:
+
+[![][15]][4]
+
+I probably want to edit those questions & answers over time but it’s SO NICE to have somewhere to put them.
+
+### what’s next: maybe debugging! or working more on flashcards!
+
+The two projects I’m thinking about the most right now are
+
+ 1. a zine about debugging, which I started last summer and haven’t gotten around to finishing yet
+ 2. a [flashcards project][16] that I’ve been adding to slowly over the last couple of months. I think could become a nice way to explain basic ideas.
+
+
+
+Here’s a link to where to [get the zine][4] again :)
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://jvns.ca/blog/2020/04/27/new-zine-how-containers-work/
+
+作者:[Julia Evans][a]
+选题:[lujun9972][b]
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]: https://jvns.ca/
+[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
+[1]: https://wizardzines.com
+[2]: https://wizardzines.com/zines/all-the-zines/
+[3]: https://jvns.ca/images/containers-cover.jpg
+[4]: https://wizardzines.com/zines/containers
+[5]: https://stripe.com/en-ca/blog/operating-kubernetes
+[6]: https://jvns.ca/blog/2016/09/15/whats-up-with-containers-docker-and-rkt/
+[7]: https://jvns.ca/blog/2016/10/10/what-even-is-a-container/
+[8]: https://jvns.ca/blog/2016/12/22/container-networking/
+[9]: https://jvns.ca/blog/2016/10/26/running-container-without-docker/
+[10]: https://jvns.ca/blog/2017/02/17/mystery-swap/
+[11]: https://jvns.ca/blog/2016/10/02/a-list-of-container-software/
+[12]: https://github.com/p8952/bocker
+[13]: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YCVSdnYzH34&t=1s
+[14]: https://melody.dev
+[15]: https://jvns.ca/images/wizardzines-faq.png
+[16]: https://flashcards.wizardzines.com
diff --git a/sources/tech/20200428 Learn Bash with this book of puzzles.md b/sources/tech/20200428 Learn Bash with this book of puzzles.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..08a07b93c5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/tech/20200428 Learn Bash with this book of puzzles.md
@@ -0,0 +1,60 @@
+[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
+[#]: translator: ( )
+[#]: reviewer: ( )
+[#]: publisher: ( )
+[#]: url: ( )
+[#]: subject: (Learn Bash with this book of puzzles)
+[#]: via: (https://opensource.com/article/20/4/bash-it-out-book)
+[#]: author: (Carlos Aguayo https://opensource.com/users/hwmaster1)
+
+Learn Bash with this book of puzzles
+======
+'Bash it out' covers basic, medium, and advanced Bash scripting using 16
+puzzles.
+![Puzzle pieces coming together to form a computer screen][1]
+
+Computers are both my hobby and my profession. I have about 10 of them scattered around my apartment, all running Linux (including my Macs). Since I enjoy upgrading my computers and my computer skills, when I came across [_Bash it out_][2] by Sylvain Leroux, I jumped on the chance to buy it. I use the command line a lot on Debian Linux, and it seemed like a great opportunity to expand my Bash knowledge. I smiled when the author explained in the preface that he uses Debian Linux, which is one of my two favorite distributions.
+
+Bash lets you automate tasks, so it's a labor-saving, interesting, and useful tool. Before reading the book, I already had a fair amount of experience with Bash on Unix and Linux. I'm not an expert, in part because the scripting language is so extensive and powerful. I first became intrigued with Bash when I saw it on the welcome screen of [EndeavourOS][3], an Arch-based Linux distribution.
+
+The following screenshots show some options from EndeavourOS. Beleieve it or not, these panels just point to Bash scripts, each of which accomplish some relatively complex tasks. And because it's all open source, I can modify any of these scripts if I want.
+
+![EndeavourOS after install][4]
+
+![EndeavourOS install apps][5]
+
+### Always something to learn
+
+My impressions of this book are very favorable. It's not long, but it is well-thought-out. The author has very extensive knowledge of Bash and an uncanny ability to explain how to use it. The book covers basic, medium, and advanced Bash scripting using 16 puzzles, which he calls "challenges." This taught me to see Bash scripting as a programming puzzle to solve, which makes it more interesting to play with.
+
+An exciting aspect of Bash is that it's deeply integrated with the Linux system. While part of its power lies in its syntax, it's also powerful because it has access to so much. You can script repetitive tasks, or tasks that are easy but you're just tired of performing manually. Nothing is too great or too small, and _Bash it out_ helps you understand both what you can do, and how to achieve it.
+
+This review would not be complete if I didn't mention David Both's free resource [_A sysadmin's guide to Bash scripting_][6] on Opensource.com. This 17-page PDF guide is different from _Bash it out_, but together they make a winning combination for anyone who wants to learn about it.
+
+I am not a computer programmer, but _Bash it out_ has increased my desire to get into more advanced levels of Bash scripting—I might inadvertently end up as a computer programmer without planning to.
+
+One reason I love Linux is because of how powerful and versatile the operating system is. However much I know about Linux, there is always something new to learn that makes me appreciate Linux even more.
+
+In a competitive and ever-changing job market, it behooves all of us to continuously update our skills. This book helped me learn Bash in a very hands-on way. It almost felt as if the author was in the same room with me, patiently guiding me in my learning.
+
+The author, Leroux, has an uncanny ability to engage readers. This is a rare gift that I think is even more valuable than his technical expertise. In fact, I am writing this book review to thank the author for anticipating my own learning needs; although we have never met, I have benefited in real ways from his gifts.
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://opensource.com/article/20/4/bash-it-out-book
+
+作者:[Carlos Aguayo][a]
+选题:[lujun9972][b]
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]: https://opensource.com/users/hwmaster1
+[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
+[1]: https://opensource.com/sites/default/files/styles/image-full-size/public/lead-images/puzzle_computer_solve_fix_tool.png?itok=U0pH1uwj (Puzzle pieces coming together to form a computer screen)
+[2]: https://www.amazon.com/Bash-Out-Strengthen-challenges-difficulties/dp/1521773262/
+[3]: https://endeavouros.com/
+[4]: https://opensource.com/sites/default/files/uploads/endeavouros-welcome.png (EndeavourOS after install)
+[5]: https://opensource.com/sites/default/files/uploads/endeavouros-install-apps.png (EndeavourOS install apps)
+[6]: https://opensource.com/downloads/bash-scripting-ebook
diff --git a/sources/tech/20200428 Open source has room for everyone.md b/sources/tech/20200428 Open source has room for everyone.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..bab55ddfbe
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/tech/20200428 Open source has room for everyone.md
@@ -0,0 +1,74 @@
+[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
+[#]: translator: ( )
+[#]: reviewer: ( )
+[#]: publisher: ( )
+[#]: url: ( )
+[#]: subject: (Open source has room for everyone)
+[#]: via: (https://opensource.com/article/20/4/interview-Megan-Byrd-Sanicki)
+[#]: author: (Jay Barber https://opensource.com/users/jaybarber)
+
+Open source has room for everyone
+======
+Learn how Megan Byrd-Sanicki, 2020 Women in Open Source Community Award
+winner, brings people together.
+![Dandelion held out over water][1]
+
+"Growing up, I was a bit of a field marshal," Megan Byrd-Sanicki, 2020 [Women in Open Source Community Award][2] winner, says with a smile. "I was always the one pulling classmates together. 'We're going to play a game. Come on, everyone, I'll teach you the rules.' I'd also have an eye to the sidelines, trying to identify who wasn't being included and how I could draw them in."
+
+![Photo by Megan Sanicki, Used with permission][3]
+
+That drive to bring people together and set up a structure for them to excel carries through much of her career and community work. "I look back on who I was in second-grade gym class and have to admit that it's still who I am today."
+
+Megan has been active in open source for a decade, first as Executive Director of the [Drupal Association][4], and now as the Manager of Research and Operations for Google's Open Source Program Office. "I'm fortunate in my current position because it offers a view into Google's more than 2000 open source projects with different objectives, different governance structures, and different strategies. It's been just a phenomenal learning opportunity." Megan was also recently elected to the [Open Source Initiative][5] Board of Directors, where she strives to strengthen the leadership in open source that the organization offers to projects and businesses around the globe.
+
+### Lessons from the basement steps
+
+Far from being set on technology, Megan originally thought she'd go into business. Sitting on the basement steps, listening to her father make sales calls, she knew his entire product line by age 16, but she also internalized other lessons.
+
+"I learned from him that doing business means solving problems and helping people," Megan says. "And I've kept that front-of-mind throughout my career. In some ways, I'm not surprised by this path; it's a natural extension of who I am, but it's also taken me places I would never have dreamed possible."
+
+Open source isn't just a career for Megan; she also uses the same strategies in her community involvement. "Right now, I'm working with a great group of engineers, data scientists, and epidemiologists at [Covid Act Now][6]. The team members are volunteering their expertise, collaborating openly to provide data modeling to public officials so that they can make informed decisions as quickly as possible."
+
+She's also active in [FOSS Responders][7], a group focused on shining a light on open source projects and community members affected by COVID-19-related event cancellations. "In times of turmoil, it can be difficult for projects to find the help they need. We help organizations and individuals who need assistance aggregate and amplify their requests." An important component of the organization is administering the [FOSS Responders Fund][7], a mechanism to capture some of the open source funding requests that may fall through the cracks otherwise.
+
+### Engaging people in a changing world
+
+The twin themes that influence Megan's community engagement are a clear commitment to the principles of open source and a drive to bring people together. "When people have dreams, things they're actively trying to accomplish, it creates a shared sense of purpose and a strong 'why.' People engage easily around why. I know I do," Megan says when asked what drives her in these efforts.
+
+"Whether helping raise funds for Drupal's mission or enabling open source projects to become more sustainable, there's a real human impact. I get really passionate about the butterfly effect that results from helping people meet their goals and realize their dreams and visions."
+
+As open source becomes a larger and larger part of the technology space, Megan is hopeful for the future. "The exciting thing is that the story isn't done. As a community, we're still figuring things out," she says. "There's so much we need to learn about open source, and it can evolve in so many ways, while the landscape changes around us. We need to have the right conversations and figure out how to evolve together, ensuring there's a place at the table for everyone."
+
+In her words, it's possible to hear those same lessons learned from listening to her father's business calls—doing business is about solving problems and helping people. "Helping more people understand how to use and contribute to open source to solve problems is really rewarding. Whether it is to drive innovation, accelerate velocity, or achieve business goals, there are lots of ways to gain value from open source."
+
+### Own your awesome
+
+When asked what advice she has for other women wanting to engage with the open source community, Megan lights up. "Remember that open source has room for everyone. It can be daunting, but in my experience, people want to help. Ask for help when you need it, but also be clear on where you can contribute, how you can contribute, and what your needs are."
+
+She also recognizes that among all the voices in open source, a lack of centralized leadership can sometimes be felt, but she cautions against looking at it as a privileged role, reserved for only a few. "Be the leader you need. When there's a void in leadership, each individual can fill that void for themselves. Every contributor to open source is a leader, whether they're leading others, leading the community, or just leading themselves. Don't wait to be given permission and own your awesome."
+
+The open source journey for Megan has been just that: a trek where her path wasn't always clear. She's never shied away from adventure or run from uncertainty, though. "I look at life as this beautiful tapestry that you're weaving, but day to day, you only get to see the threads in the back. If you could see the full picture, you'd realize that you've contributed to this wonderful work in countless ways just by doing your best every day."
+
+_Also read Jay Barber's [interview with Netha Hussain][8], who won the 2020 Women in Open Source Academic Award._
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://opensource.com/article/20/4/interview-Megan-Byrd-Sanicki
+
+作者:[Jay Barber][a]
+选题:[lujun9972][b]
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]: https://opensource.com/users/jaybarber
+[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
+[1]: https://opensource.com/sites/default/files/styles/image-full-size/public/lead-images/dandelion_blue_water_hand.jpg?itok=QggW8Wnw (Dandelion held out over water)
+[2]: https://www.redhat.com/en/about/women-in-open-source
+[3]: https://opensource.com/sites/default/files/uploads/megan_sanicki_headshot_small_0.png (Photo by Megan Sanicki, Used with permission)
+[4]: https://www.drupal.org/association
+[5]: https://opensource.org/
+[6]: https://www.covidactnow.org/
+[7]: https://fossresponders.com/
+[8]: https://opensource.com/article/20/4/interview-Netha-Hussain
diff --git a/sources/tech/20200428 Upgrading Fedora 31 to Fedora 32.md b/sources/tech/20200428 Upgrading Fedora 31 to Fedora 32.md
index 1807d5e6a7..5dd426ccfc 100644
--- a/sources/tech/20200428 Upgrading Fedora 31 to Fedora 32.md
+++ b/sources/tech/20200428 Upgrading Fedora 31 to Fedora 32.md
@@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
-[#]: translator: ( )
+[#]: translator: (geekpi)
[#]: reviewer: ( )
[#]: publisher: ( )
[#]: url: ( )
diff --git a/sources/tech/20200428 What-s new in Fedora 32 Workstation.md b/sources/tech/20200428 What-s new in Fedora 32 Workstation.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..402a8e63a7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/tech/20200428 What-s new in Fedora 32 Workstation.md
@@ -0,0 +1,89 @@
+[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
+[#]: translator: ( )
+[#]: reviewer: ( )
+[#]: publisher: ( )
+[#]: url: ( )
+[#]: subject: (What’s new in Fedora 32 Workstation)
+[#]: via: (https://fedoramagazine.org/whats-new-fedora-32-workstation/)
+[#]: author: (Ryan Lerch https://fedoramagazine.org/author/ryanlerch/)
+
+What’s new in Fedora 32 Workstation
+======
+
+![][1]
+
+Fedora 32 Workstation is the [latest release][2] of our free, leading-edge operating system. You can download it from [the official website here][3] right now. There are several new and noteworthy changes in Fedora 32 Workstation. Read more details below.
+
+### GNOME 3.36
+
+Fedora 32 Workstation includes the latest release of GNOME Desktop Environment for users of all types. GNOME 3.36 in Fedora 32 Workstation includes many updates and improvements, including:
+
+#### Redesigned Lock Screen
+
+The lock screen in Fedora 32 is a totally new experience. The new design removes the “window shade” metaphor used in previous releases, and focuses on ease and speed of use.
+
+![Unlock screen in Fedora 32][4]
+
+#### New Extensions Application
+
+Fedora 32 features the new Extensions application, to easily manage your GNOME Extensions. In the past, extensions were installed, configured, and enabled using either the Software application and / or the Tweak Tool.
+
+![The new Extensions application in Fedora 32][5]
+
+Note that the Extensions application is not installed by default on Fedora 32. To either use the Software application to search and install, or use the following command in the terminal:
+
+```
+sudo dnf install gnome-extensions-app
+```
+
+#### Reorganized Settings
+
+Eagle-eyed Fedora users will notice that the Settings application has been re-organized. The structure of the settings categories is a lot flatter, resulting in more settings being visible at a glance.
+
+Additionally, the **About** category now has a more information about your system, including which windowing system you are running (e.g. Wayland)
+
+![The reorganized settings application in Fedora 32][6]
+
+#### Redesigned Notifications / Calendar popover
+
+The Notifications / Calendar popover — toggled by clicking on the Date and Time at the top of your desktop — has had numerous small style tweaks. Additionally, the popover now has a **Do Not Disturb** switch to quickly disable all notifications. This quick access is useful when presenting your screen, and not wanting your personal notifications appearing.
+
+![The new Notification / Calendar popover in Fedora 32 ][7]
+
+#### Redesigned Clocks Application
+
+The Clocks application is totally redesigned in Fedora 32. It features a design that works better on smaller windows.
+
+![The Clocks application in Fedora 32][8]
+
+GNOME 3.36 also provides many additional features and enhancements. Check out the [GNOME 3.36 Release Notes][9] for further information
+
+* * *
+
+### Improved Out of Memory handling
+
+Previously, if a system encountered a low-memory situation, it may have encountered heavy swap usage (aka [swap thrashing][10])– sometimes resulting in the Workstation UI slowing down, or becoming unresponsive for periods of time. Fedora 32 Workstation now ships and enables EarlyOOM by default. EarlyOOM enables users to more quickly recover and regain control over their system in low-memory situations with heavy swap usage.
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://fedoramagazine.org/whats-new-fedora-32-workstation/
+
+作者:[Ryan Lerch][a]
+选题:[lujun9972][b]
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]: https://fedoramagazine.org/author/ryanlerch/
+[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
+[1]: https://fedoramagazine.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/fedora32workstation-816x345.jpg
+[2]: https://fedoramagazine.org/announcing-fedora-32/
+[3]: https://getfedora.org/workstation
+[4]: https://fedoramagazine.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/unlock.gif
+[5]: https://fedoramagazine.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/extensions.png
+[6]: https://fedoramagazine.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/settings.png
+[7]: https://fedoramagazine.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/donotdisturb.png
+[8]: https://fedoramagazine.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/clocks.png
+[9]: https://help.gnome.org/misc/release-notes/3.36/
+[10]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thrashing_(computer_science)
diff --git a/sources/tech/20200429 Drop PNG and JPG for your online images- Use WebP.md b/sources/tech/20200429 Drop PNG and JPG for your online images- Use WebP.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..f4e6711933
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/tech/20200429 Drop PNG and JPG for your online images- Use WebP.md
@@ -0,0 +1,144 @@
+[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
+[#]: translator: (lxbwolf)
+[#]: reviewer: ( )
+[#]: publisher: ( )
+[#]: url: ( )
+[#]: subject: (Drop PNG and JPG for your online images: Use WebP)
+[#]: via: (https://opensource.com/article/20/4/webp-image-compression)
+[#]: author: (Jeff Macharyas https://opensource.com/users/jeffmacharyas)
+
+Drop PNG and JPG for your online images: Use WebP
+======
+Get started with this open source image editing tool to save time and
+space.
+![Painting art on a computer screen][1]
+
+WebP is an image format developed by Google in 2010 that provides superior lossless and lossy compression for images on the web. Using WebP, web developers can create smaller, richer images that improve site speed. A faster loading website is critical to the user experience and for the website's marketing effectiveness.
+
+For optimal loading across all devices and users, images on your site should not be larger than 500 KB in file size.
+
+WebP lossless images are often at least 25% smaller in size compared to PNGs. WebP lossy images are often anywhere from 25-34% smaller than comparable JPEG images at equivalent SSIM (structural similarity) quality index.
+
+Lossless WebP supports transparency, as well. For cases when lossy RGB compression is acceptable, lossy WebP also supports transparency, typically providing three times smaller file sizes compared to PNG.
+
+Google reports a 64% reduction in file size for images converted from animated GIFs to lossy WebP, and a 19% reduction when converted to lossless WebP.
+
+The WebP file format is based on the RIFF (resource interchange file format) document format. The file signature is **52 49 46 46** (RIFF), as you can see with [hexdump][2]:
+
+
+```
+$ hexdump --canonical pixel.webp
+00000000 52 49 46 46 26 00 00 00 [...] |RIFF&...WEBPVP8 |
+00000010 1a 00 00 00 30 01 00 9d [...] |....0....*......|
+00000020 0e 25 a4 00 03 70 00 fe [...] |.%...p...`....|
+0000002e
+```
+
+The standalone libwebp library serves as a reference implementation for the WebP specification and is available from Google's [Git repository][3] or as a tarball.
+
+The WebP format is compatible with 80% of the web browsers in use worldwide. At the time of this writing, it is not compatible with Apple's Safari browser. The workaround for this is to serve up a JPG/PNG alongside a WebP, and there are methods and Wordpress plugins to do that.
+
+### Why does this matter?
+
+Part of my job is to design and maintain our organization's website. Since the website is a marketing tool and site speed is a critical aspect of the user experience, I have been working to improve the speed, and reducing image sizes by converting them to WebP has been a good solution.
+
+To test the speed of one of the pages, I turned to **web.dev**, which is powered by Lighthouse, released under the Apache 2.0 license, and can be found at .
+
+According to its official description, "Lighthouse is an open source, automated tool for improving the quality of web pages. You can run it against any web page—public or requiring authentication. It has audits for performance, accessibility, progressive web apps, SEO, and more. You can run Lighthouse in Chrome DevTools, from the command line, or as a Node module. You give Lighthouse a URL to audit, it runs a series of audits against the page, and then it generates a report on how well the page did. From there, use the failing audits as indicators on how to improve the page. Each audit has a reference doc explaining why the audit is important, as well as how to fix it."
+
+### Creating a smaller WebP image
+
+The page I tested returned three images. In the report it generates, it provides recommendations and targets. I chose the "app-graphic" image, which, it reported, is 650 KB. By converting it to WebP, I should save 589 KB, reducing the image to 61 KB. I converted the image in Photoshop and saved it with the default WebP settings, and it returned a file size of 44.9 KB. Better than expected! As the screenshot from Photoshop shows, the images look identical in visual quality.
+
+![WebP vs JPG comparison][4]
+
+On the left: 650 KB (actual size). On the right: 589 KB (target size after conversion).
+
+Of course, the open source image editor [GIMP][5] also supports WebP as an export format. It offers several options for quality and compression profile:
+
+![GIMP dialog for exporting webp, as a webp][6]
+
+A zoomed-in look of another image:
+
+![WebP vs PNG comparison][7]
+
+PNG (left) and WebP (right), both converted from a JPG, shows the WebP, although smaller in size, is superior in visual quality.
+
+### Convert to an image to WebP
+
+To convert images on Linux from JPG/PNG to WebP, you can also use the command-line:
+
+Use **cwebp** on the command line to convert PNG or JPG image files to WebP format. You can convert a PNG image file to a WebP image with a quality range of 80 with the command:
+
+
+```
+`cwebp -q 80 image.png -o image.webp`
+```
+
+Alternatively, you can also use [Image Magick][8], which is probably available in your distribution's software repository. The subcommand for conversion is **convert**, and all that's needed is an input and output file:
+
+
+```
+`convert pixel.png pixel.webp`
+```
+
+### Convert an image to WebP with an editor
+
+To convert images to WebP with a photo editor, use [GIMP][9]. From version 2.10 on, it supports WebP natively.
+
+If you're a Photoshop user, you need a plugin to convert the files, as Photoshop does not include it natively. WebPShop 0.2.1, released under the Apache License 2.0 license, is a Photoshop module for opening and saving WebP images, including animations, and can be found at: .
+
+To use the plugin, put the file found in the **bin** folder inside your Photoshop plugin directory:
+
+Windows x64—C:\Program Files\Adobe\Adobe Photoshop\Plug-ins\WebPShop.8bi
+
+Mac—Applications/Adobe Photoshop/Plug-ins/WebPShop.plugin
+
+### WebP on Wordpress
+
+Many websites are built using Wordpress (that's what I use). So, how does Wordpress handle uploading WebP images? At the time of this writing, it doesn't. But, there are, of course, plugins to enable it so you can serve up both WebP alongside PNG/JPG images (for the Apple crowd).
+
+Or there are these [instructions][10] from [Marius Hosting][11]:
+
+"How about directly uploading WebP images to Wordpress? This is easy. Just add some text line on your theme functions.php file. Wordpress does not natively support viewing and uploading WebP files, but I will explain to you how you can make it work in a few simple steps. Log in to your Wordpress admin area and go to Appearance/Theme Editor and find functions.php. Copy and paste the code below at the end of the file and save it.
+
+
+```
+`//** *Enable upload for webp image files.*/ function webp_upload_mimes($existing_mimes) { $existing_mimes['webp'] = 'image/webp'; return $existing_mimes; } add_filter('mime_types', 'webp_upload_mimes');`
+```
+
+If you want to see the thumbnail image preview when you go to Media/Library, you have to add the code below in the same functions.php file. To find the functions.php file, go to Appearance/Theme Editor and find functions.php, then copy and paste the code below at the end of the file and save it."
+
+
+```
+`//** * Enable preview / thumbnail for webp image files.*/ function webp_is_displayable($result, $path) { if ($result === false) { $displayable_image_types = array( IMAGETYPE_WEBP ); $info = @getimagesize( $path ); if (empty($info)) { $result = false; } elseif (!in_array($info[2], $displayable_image_types)) { $result = false; } else { $result = true; } } return $result; } add_filter('file_is_displayable_image', 'webp_is_displayable', 10, 2);`
+```
+
+### WebP and the future
+
+WebP is a robust and optimized format. It looks better, it has better compression ratio, and it has all the features of most other common image formats. There's no need to wait—start using it now.
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://opensource.com/article/20/4/webp-image-compression
+
+作者:[Jeff Macharyas][a]
+选题:[lujun9972][b]
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]: https://opensource.com/users/jeffmacharyas
+[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
+[1]: https://opensource.com/sites/default/files/styles/image-full-size/public/lead-images/painting_computer_screen_art_design_creative.png?itok=LVAeQx3_ (Painting art on a computer screen)
+[2]: https://opensource.com/article/19/8/dig-binary-files-hexdump
+[3]: https://storage.googleapis.com/downloads.webmproject.org/releases/webp/index.html
+[4]: https://opensource.com/sites/default/files/uploads/webp-vs-jpg-app-graphic.png (WebP vs JPG comparison)
+[5]: http://gimp.org
+[6]: https://opensource.com/sites/default/files/webp-gimp.webp (GIMP dialog for exporting webp, as a webp)
+[7]: https://opensource.com/sites/default/files/uploads/xcompare-png-left-webp-right.png (WebP vs PNG comparison)
+[8]: https://imagemagick.org
+[9]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/GIMP
+[10]: https://mariushosting.com/how-to-upload-webp-files-on-wordpress/
+[11]: https://mariushosting.com/
diff --git a/sources/tech/20200429 Open source live streaming with Open Broadcaster Software.md b/sources/tech/20200429 Open source live streaming with Open Broadcaster Software.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..748786de77
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/tech/20200429 Open source live streaming with Open Broadcaster Software.md
@@ -0,0 +1,137 @@
+[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
+[#]: translator: ( )
+[#]: reviewer: ( )
+[#]: publisher: ( )
+[#]: url: ( )
+[#]: subject: (Open source live streaming with Open Broadcaster Software)
+[#]: via: (https://opensource.com/article/20/4/open-source-live-stream)
+[#]: author: (Seth Kenlon https://opensource.com/users/seth)
+
+Open source live streaming with Open Broadcaster Software
+======
+If you have something to say, a skill to teach, or just something fun to
+share, broadcast it to the world with OBS.
+![An old-fashioned video camera][1]
+
+If you have a talent you want to share with the world, whether it's making your favorite sourdough bread or speedrunning through a level of your favorite video game, live streaming is the modern show-and-tell. It's a powerful way to tell the world about your hobby through a medium once reserved for exclusive and expensive TV studios. Not only is the medium available to anyone with a relatively good internet connection, but the most popular software to make it happen is open source.
+
+[OBS][2] (Open Broadcaster Software) is a cross-platform application that serves as a control center for your live stream. A _stream_, strictly speaking, means _progressive and coherent data_. The data in a stream can be audio, video, graphics, text, or anything else you can represent as digital data. OBS is programmed to accept data as input, combine streams together (technically referred to as _mixing_) into one product, and then broadcast it.
+
+![OBS flowchart][3]
+
+A _broadcast_ is data that can be received by some target. If you're live streaming, your primary target is a streaming service that can host your stream, so other people can find it in a web browser or media player. A live stream is a live event, so people have to "tune in" to your stream when it's happening, or else they miss it. However, you can also target your own hard drive so you can record a presentation and then post it on the internet later for people to watch at their leisure.
+
+### Installing OBS
+
+To install OBS on Windows or macOS, download an installer package from [OBS's website][2].
+
+To install OBS on Linux, either install it with your package manager (such as **dnf**, **zypper**, or **apt**) or [install it as a Flatpak][4].
+
+### Join a streaming service
+
+In order to live stream, you must have a stream broker. That is, you need a central location on the internet for your stream to be delivered, so your viewers can get to what you're broadcasting. There are a few popular streaming services online, like YouTube and Twitch. You can also [set up your own video streaming server][5] using open source software.
+
+Regardless of which option you choose, before you begin streaming, you must have a destination for your stream. If you do use a streaming service, you must obtain a _streaming key_. A streaming key is a hash value (it usually looks something like **2ae2fad4e33c3a89c21**) that is private and unique to you. You use this key to authenticate yourself through your streaming software. Without it, the streaming service can't know you are who you say you are and won't let you broadcast over your user account.
+
+* * *
+
+* * *
+
+* * *
+
+**![Streaming key][6]**
+
+ * In Twitch, your **Primary Stream Key** is available in the **Channel** panel of your **Creator Dashboard**.
+ * On YouTube, you must enable live streaming by verifying your account. Once you've done that, your **Stream Key** is in the **Other Features** menu option of your **Channel Dashboard**.
+ * If you're using your own server, there's no maze-like GUI to navigate. You just [create your own streaming key][7].
+
+
+
+### Enter your streaming key
+
+Once you have a streaming key, launch OBS and go to the **File** > **Settings** menu.
+
+In the **Settings** window, click on the **Stream** category in the left column. Set the **Service** to your stream service (Custom, Twitch, YouTube, etc.), and enter your stream key. Click the **OK** button in the bottom right to save your changes.
+
+### Create sources
+
+In OBS, _sources_ represent any input signal you want to stream. By default, sources are listed at the bottom of the OBS window.
+
+![OBS sources][8]
+
+This might be a webcam, a microphone, an audio stream (such as the sound of a video game you're playing), a screen capture of your computer (a "screencast"), a slideshow you want to present, an image, and so on. Before you start streaming, you should define all the sources you plan on using for your stream. This means you have to do a little pre-production and consider what you anticipate for your show. Any camera you have set up must be defined as a source in OBS. Any extra media you plan on cutting to during your show must be defined as a source. Any sound effects or background music must be defined as a source.
+
+Not all sources "happen" at once. By adding media to your **Sources** panel in OBS, you're just assembling the raw components for your stream. Once you make devices and data available to OBS, you can create your **Scenes**.
+
+#### Setting up audio
+
+Computers have seemingly dozens of ways to route audio. Here's the workflow to follow when setting up sound for your stream:
+
+ 1. Check your cables: verify that your microphone is plugged in.
+ 2. Go to your computer's sound control panel and set the input to whatever microphone you want OBS to treat as the main microphone. This might be a gaming headset or a boom mic or a desktop podcasting mic or a Bluetooth device or a fancy audio interface with XLR ports. Whatever it is, make sure your computer "hears" your main sound input.
+ 3. In OBS, create a source for your main microphone and name it something obvious (e.g., boom mic, master sound, or mic).
+ 4. Do a test. Make sure OBS "hears" your microphone by referring to the audio-level monitors at the bottom of the OBS window. If it's not responding to the input you believe you've set as input, check your cables, check your computer sound control panel, and check OBS.
+
+
+
+I've seen more people panic over audio sources than any other issue when streaming, and we've _all_ made the same dumb mistakes (several times each, probably!) when attempting to set a microphone for a live stream or videoconference call. Breathe deep, check your cables, check your inputs and outputs, and [get comfortable with audio][9]. It'll pay off in the end.
+
+### Create scenes
+
+A **Scene** in OBS is a screen layout and consists of one or more sources.
+
+![Scenes in OBS][10]
+
+For instance, you might create a scene called **Master shot** that shows you sitting at your desk in front of your computer or at the kitchen counter ready to mix ingredients together. The source could be a webcam mounted on a tripod a meter or two in front of you. Because you want to cut to a detail shot, you might create a second scene called **Close-up**, which uses the computer screen and audio as one input source and your microphone as another source, so you can narrate as you demonstrate what you're doing. If you're doing a baking show, you might want to mount a second webcam above the counter, so you can cut to an overhead shot of ingredients being mixed. Here, your source is a different webcam but probably the same microphone (to avoid making changes in the audio).
+
+A _scene_, in other words, is a lot like a _shot_ in traditional production vernacular, but it can be the combination of many shots. The fun thing about OBS is that you can mix and match a lot of different sources together, so when you're adding a **Scene**, you can resize and position different sources to achieve picture-in-picture, or split-screen, or any other effect you might want. It's common in video game "let's play" streams to have the video game in full-screen, with the player inset in the lower right or left. Or, if you're recording a panel or a multi-player game like D&D you might have several cameras covering several players in a _Brady Bunch_ grid.
+
+The possibilities are endless. During streaming, you can cut from one scene to another as needed. This is intended to be a dynamic system, so you can change scenes depending on what the viewer needs to see at any given moment.
+
+Generally, you want to have some preset scenes before you start to stream. Even if you have a friend willing to do video mixing as you stream, you always want a safe scene to fall back to, so take time beforehand to set up at least a master shot that shows you doing whatever it is you're doing. If all else fails, at least you'll have your main shot you can safely and reliably cut to.
+
+### Transitions
+
+When switching from one scene to another, OBS uses a transition. Once you have more than one scene, you can configure what kind of transition it uses in the **Transitions** panel. Simple transitions are usually best. By default, OBS uses a subtle crossfade, but you can experiment with others as you see fit.
+
+### Go live
+
+To start streaming, do your vocal exercises, find your motivation, and press the **Start Streaming** button.
+
+![Start streaming in OBS][11]
+
+As long as you've set up your streaming service correctly, you're on the air (or on the wires, anyway).
+
+If you're the talent (the person in front of the camera), it might be easiest to have someone control OBS during streaming. But if that's not possible, you can control it yourself as long as you've practiced a little in advance. If you're screencasting, it helps to have a two-monitor setup so you can control OBS without it being on screen.
+
+### Streaming for success
+
+Many of us take streaming for granted now that the internet exists and can broadcast media created by _anyone_. It's a hugely powerful means of communication, and we're all responsible for making the most of it.
+
+If you have something positive to say, a skill to teach, words of encouragement, or just something fun that you want to share, and you feel like you want to broadcast to the world, then take the time to learn OBS. You might not get a million viewers, but independent media is a vital part of [free culture][12]. The world can always use empowering and positive open source voices, and yours may be one of the most important of all.
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://opensource.com/article/20/4/open-source-live-stream
+
+作者:[Seth Kenlon][a]
+选题:[lujun9972][b]
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]: https://opensource.com/users/seth
+[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
+[1]: https://opensource.com/sites/default/files/styles/image-full-size/public/lead-images/LIFE_film.png?itok=aElrLLrw (An old-fashioned video camera)
+[2]: http://obsproject.com
+[3]: https://opensource.com/sites/default/files/obs-flowchart.jpg (OBS flowchart)
+[4]: https://flatpak.org/setup
+[5]: https://opensource.com/article/19/1/basic-live-video-streaming-server
+[6]: https://opensource.com/sites/default/files/twitch-key.jpg (Streaming key)
+[7]: https://opensource.com/article/19/1/basic-live-video-streaming-server#obs
+[8]: https://opensource.com/sites/default/files/uploads/obs-sources.jpg (OBS sources)
+[9]: https://opensource.com/article/17/1/linux-plays-sound
+[10]: https://opensource.com/sites/default/files/uploads/obs-scenes.jpg (Scenes in OBS)
+[11]: https://opensource.com/sites/default/files/uploads/obs-stream-start.jpg (Start streaming in OBS)
+[12]: https://opensource.com/article/18/1/creative-commons-real-world
diff --git a/sources/tech/20200429 The life-changing magic of git rebase -i.md b/sources/tech/20200429 The life-changing magic of git rebase -i.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..8afb9d7f8e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/tech/20200429 The life-changing magic of git rebase -i.md
@@ -0,0 +1,80 @@
+[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
+[#]: translator: ( )
+[#]: reviewer: ( )
+[#]: publisher: ( )
+[#]: url: ( )
+[#]: subject: (The life-changing magic of git rebase -i)
+[#]: via: (https://opensource.com/article/20/4/git-rebase-i)
+[#]: author: (Dave Neary https://opensource.com/users/dneary)
+
+The life-changing magic of git rebase -i
+======
+Make everyone think you write perfect code the first time (and make your
+patches easier to review and merge).
+![Hands programming][1]
+
+Software development is messy. So many wrong turns, typos to fix, quick hacks and kludges to correct later, off-by-one errors you find late in the process. With version control, you have a pristine record of every wrong turn and correction made during the process of creating the "perfect" final product—a patch ready to submit upstream. Like the outtakes from movies, they are a little embarrassing and sometimes amusing.
+
+Wouldn't it be great if you could use version control to save your work regularly at waypoints, and then when you have something you are ready to submit for review, you could hide all of that private drafting work and just submit a single, perfect patch? Meet **git rebase -i**, the perfect way to rewrite history and make everyone think that you produce perfect code the first time!
+
+### What does git rebase do?
+
+In case you're not familiar with the intricacies of Git, here is a brief overview. Under the covers, Git associates different versions of your project with a unique identifier, which is made up of a hash of the parent node's unique identifier, and the difference between the new version and its parent node. This creates a tree of revisions, and each person who checks out the project gets their own copy. Different people can take the project in different directions, each starting from potentially different branch points.
+
+![Master branch vs. private branch][2]
+
+The master branch in the "origin" repo on the left and the private branch on your personal copy on the right.
+
+There are two ways to integrate your work back with the master branch in the original repository: one is to use **git merge**, and the other is to use **git rebase**. They work in very different ways.
+
+When you use **git merge**, a new commit is created on the master branch that includes all of the changes from origin plus all of your local changes. If there are any conflicts (for example, if someone else has changed a file you are also working with), these will be marked, and you have an opportunity to resolve the conflicts before committing this merge commit to your local repository. When you push your changes back to the parent repository, all of your local work will appear as a branch for other users of the Git repository.
+
+But **git rebase** works differently. It rewinds your commits and replays those commits again from the tip of the master branch. This results in two main changes. First, since your commits are now branching off a different parent node, their hashes will be recalculated, and anyone who has cloned your repository may now have a broken copy of the repository. Second, you do not have a merge commit, so any merge conflicts are identified as your changes are being replayed onto the master branch, and you need to fix them before proceeding with the rebase. When you push your changes now, your work does not appear on a branch, and it looks as though you wrote all of your changes off the very latest commit to the master branch.
+
+![Merge commits preserve history, and rebase rewrites history.][3]
+
+Merge commits (left) preserve history, while rebase (right) rewrites history.
+
+However, both of these options come with a downside: everyone can see all your scribbles and edits as you worked through problems locally before you were ready to share your code. This is where the **\--interactive** (or **-i** for short) flag to **git rebase** comes into the picture.
+
+### Introducing git rebase -i
+
+The big advantage of **git rebase** is that it rewrites history. But why stop at just pretending you branched off a later point? There is a way to go even further and rewrite how you arrived at your ready-to-propose code: **git rebase -i**, an interactive **git rebase**.
+
+This feature is the "magic time machine" function in Git. The flag allows you to make sophisticated changes to revision history while doing a rebase. You can hide your mistakes! Merge many small changes into one pristine feature patch! Reorder how things appear in revision history!
+
+![output of git rebase -i][4]
+
+When you run **git rebase -i**, you get an editor session listing all of the commits that are being rebased and a number of options for what you can do to them. The default choice is **pick**.
+
+ * **Pick** maintains the commit in your history.
+ * **Reword** allows you to change a commit message, perhaps to fix a typo or add additional commentary.
+ * **Edit** allows you to make changes to the commit while in the process of replaying the branch.
+ * **Squash** merges multiple commits into one.
+ * You can reorder commits by moving them around in the file.
+
+
+
+When you are finished, simply save the final result, and the rebase will execute. At each stage where you have chosen to modify a commit (either with **reword**, **edit**, **squash**, or when there is a conflict), the rebase stops and allows you to make the appropriate changes before continuing.
+
+The example above results in "One-liner bug fix" and "Integrate new header everywhere" being merged into one commit, and "New header for docs website" and "D'oh - typo. Fixed" into another. Like magic, the work that went into the other commits is still there on your branch, but the associated commits have disappeared from your history!
+
+This makes it easy to submit a clean patch to an upstream project using **git send-email** or by creating a pull request against the parent repository with your newly tidied up patchset. This has a number of advantages, including that it makes your code easier to review, easier to accept, and easier to merge.
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://opensource.com/article/20/4/git-rebase-i
+
+作者:[Dave Neary][a]
+选题:[lujun9972][b]
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]: https://opensource.com/users/dneary
+[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
+[1]: https://opensource.com/sites/default/files/styles/image-full-size/public/lead-images/programming-code-keyboard-laptop.png?itok=pGfEfu2S (Hands programming)
+[2]: https://opensource.com/sites/default/files/uploads/master-private-branches.png (Master branch vs. private branch)
+[3]: https://opensource.com/sites/default/files/uploads/merge-commit-vs-rebase.png (Merge commits preserve history, and rebase rewrites history.)
+[4]: https://opensource.com/sites/default/files/uploads/git-rebase-i.png (output of git rebase -i)
diff --git a/sources/tech/20200429 Why strace doesn-t work in Docker.md b/sources/tech/20200429 Why strace doesn-t work in Docker.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..42414ad377
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/tech/20200429 Why strace doesn-t work in Docker.md
@@ -0,0 +1,161 @@
+[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
+[#]: translator: ( )
+[#]: reviewer: ( )
+[#]: publisher: ( )
+[#]: url: ( )
+[#]: subject: (Why strace doesn't work in Docker)
+[#]: via: (https://jvns.ca/blog/2020/04/29/why-strace-doesnt-work-in-docker/)
+[#]: author: (Julia Evans https://jvns.ca/)
+
+Why strace doesn't work in Docker
+======
+
+While editing the capabilities page of the [how containers work][1] zine, I found myself trying to explain why `strace` doesn’t work in a Docker container.
+
+The problem here is – if you run `strace` in a Docker container, this happens:
+
+```
+$ docker run -it ubuntu:18.04 /bin/bash
+$ # ... install strace ...
+[email protected]:/# strace ls
+strace: ptrace(PTRACE_TRACEME, ...): Operation not permitted
+```
+
+strace works using the `ptrace` system call, so if `ptrace` isn’t allowed, it’s definitely not gonna work! This is pretty easy to fix – on my machine, this fixes it:
+
+```
+docker run --cap-add=SYS_PTRACE -it ubuntu:18.04 /bin/bash
+```
+
+But I wasn’t interested in fixing it, I wanted to know why it happens. So why does strace not work, and why does `--cap-add=SYS_PTRACE` fix it?
+
+### hypothesis 1: container processes are missing the `CAP_SYS_PTRACE` capability
+
+I always thought the reason was that Docker container processes by default didn’t have the `CAP_SYS_PTRACE` capability. This is consistent with it being fixed by `--cap-add=SYS_PTRACE`, right?
+
+But this actually doesn’t make sense for 2 reasons.
+
+**Reason 1**: Experimentally, as a regular user, I can strace on any process run by my user. But if I check if my current process has the `CAP_SYS_PTRACE` capability, I don’t:
+
+```
+$ getpcaps $$
+Capabilities for `11589': =
+```
+
+**Reason 2**: `man capabilities` says this about `CAP_SYS_PTRACE`:
+
+```
+CAP_SYS_PTRACE
+ * Trace arbitrary processes using ptrace(2);
+```
+
+So the point of `CAP_SYS_PTRACE` is to let you ptrace **arbitrary** processes owned by any user, the way that root usually can. You shouldn’t need it to just ptrace a regular process owned by your user.
+
+And I tested this a third way – I ran a Docker container with `docker run --cap-add=SYS_PTRACE -it ubuntu:18.04 /bin/bash`, dropped the `CAP_SYS_PTRACE` capability, and I could still strace processes even though I didn’t have that capability anymore. What? Why?
+
+### hypothesis 2: something about user namespaces???
+
+My next (much less well-founded) hypothesis was something along the lines of “um, maybe the process is in a different user namespace and strace doesn’t work because of… reasons?” This isn’t really coherent but here’s what happened when I looked into it.
+
+Is the container process in a different user namespace? Well, in the container:
+
+```
+[email protected]:/# ls /proc/$$/ns/user -l
+... /proc/1/ns/user -> 'user:[4026531837]'
+```
+
+On the host:
+
+```
+[email protected]:~$ ls /proc/$$/ns/user -l
+... /proc/12177/ns/user -> 'user:[4026531837]'
+```
+
+Because the user namespace ID (`4026531837`) is the same, the root user in the container is the exact same user as the root user on the host. So there’s definitely no reason it shouldn’t be able to strace processes that it created!
+
+This hypothesis doesn’t make much sense but I hadn’t realized that the root user in a Docker container is the same as the root user on the host, so I thought that was interesting.
+
+### hypothesis 3: the ptrace system call is being blocked by a seccomp-bpf rule
+
+I also knew that Docker uses seccomp-bpf to stop container processes from running a lot of system calls. And ptrace is in the [list of system calls blocked by Docker’s default seccomp profile][2]! (actually the list of allowed system calls is a whitelist, so it’s just that ptrace is not in the default whitelist. But it comes out to the same thing.)
+
+That easily explains why strace wouldn’t work in a Docker container – if the `ptrace` system call is totally blocked, then of course you can’t call it at all and strace would fail.
+
+Let’s verify this hypothesis – if we disable all seccomp rules, can we strace in a Docker container?
+
+```
+$ docker run --security-opt seccomp=unconfined -it ubuntu:18.04 /bin/bash
+$ strace ls
+execve("/bin/ls", ["ls"], 0x7ffc69a65580 /* 8 vars */) = 0
+... it works fine ...
+```
+
+Yes! It works! Great. Mystery solved, except…
+
+### why does `--cap-add=SYS_PTRACE` fix the problem?
+
+What we still haven’t explained is: why does `--cap-add=SYS_PTRACE` would fix the problem?
+
+The man page for `docker run` explains the `--cap-add` argument this way:
+
+```
+--cap-add=[]
+ Add Linux capabilities
+```
+
+That doesn’t have anything to do with seccomp rules! What’s going on?
+
+### let’s look at the Docker source code.
+
+When the documentation doesn’t help, the only thing to do is go look at the source.
+
+The nice thing about Go is, because dependencies are often vendored in a Go repository, you can just grep the repository to figure out where the code that does a thing is. So I cloned `github.com/moby/moby` and grepped for some things, like `rg CAP_SYS_PTRACE`.
+
+Here’s what I think is going on. In containerd’s seccomp implementation, in [contrib/seccomp/seccomp_default.go][3], there’s a bunch of code that makes sure that if a process has a capability, then it’s also given access (through a seccomp rule) to use the system calls that go with that capability.
+
+```
+case "CAP_SYS_PTRACE":
+ s.Syscalls = append(s.Syscalls, specs.LinuxSyscall{
+ Names: []string{
+ "kcmp",
+ "process_vm_readv",
+ "process_vm_writev",
+ "ptrace",
+ },
+ Action: specs.ActAllow,
+ Args: []specs.LinuxSeccompArg{},
+ })
+```
+
+There’s some other code that seems to do something very similar in [profiles/seccomp/seccomp.go][4] in moby and the [default seccomp profile][5], so it’s possible that that’s what’s doing it instead.
+
+So I think we have our answer!
+
+### `--cap-add` in Docker does a little more than what it says
+
+The upshot seems to be that `--cap-add` doesn’t do exactly what it says it does in the man page, it’s more like `--cap-add-and-also-whitelist-some-extra-system-calls-if-required`. Which makes sense! If you have a capability like `CAP_SYS_PTRACE` which is supposed to let you use the `process_vm_readv` system call but that system call is blocked by a seccomp profile, that’s not going to help you much!
+
+So allowing the `process_vm_readv` and `ptrace` system calls when you give the container `CAP_SYS_PTRACE` seems like a reasonable choice.
+
+### that’s all!
+
+This was a fun small thing to investigate, and I think it’s a nice example of how containers are made of lots of moving pieces that work together in not-completely-obvious ways.
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://jvns.ca/blog/2020/04/29/why-strace-doesnt-work-in-docker/
+
+作者:[Julia Evans][a]
+选题:[lujun9972][b]
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]: https://jvns.ca/
+[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
+[1]: https://wizardzines.com/zines/containers
+[2]: https://docs.docker.com/engine/security/seccomp/
+[3]: https://github.com/containerd/containerd/blob/4be98fa28b62e8a012491d655a4d6818ef87b080/contrib/seccomp/seccomp_default.go#L527-L537
+[4]: https://github.com/moby/moby/blob/cc0dfb6e7b22ad120c60a9ce770ea15415767cf9/profiles/seccomp/seccomp.go#L126-L132
+[5]: https://github.com/moby/moby/blob/master/profiles/seccomp/default.json#L723-L739
diff --git a/sources/tech/20200430 Edit music recordings with Audacity on Linux.md b/sources/tech/20200430 Edit music recordings with Audacity on Linux.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..be6f68f062
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/tech/20200430 Edit music recordings with Audacity on Linux.md
@@ -0,0 +1,161 @@
+[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
+[#]: translator: ( )
+[#]: reviewer: ( )
+[#]: publisher: ( )
+[#]: url: ( )
+[#]: subject: (Edit music recordings with Audacity on Linux)
+[#]: via: (https://opensource.com/article/20/4/audacity)
+[#]: author: (David Both https://opensource.com/users/dboth)
+
+Edit music recordings with Audacity on Linux
+======
+How COVID-19 caused me to learn Audacity on the fly and learn to love
+it.
+![Bird singing and music notes][1]
+
+In this strange and difficult time of a global pandemic, we are all called upon to do things differently, to change our routines, and to learn new things.
+
+I have worked from home for many years, so that is nothing new to me. Even though I am allegedly retired, I write articles for Opensource.com and [Enable Sysadmin][2] and books. I also manage my own home network, which is larger than you might think, and my church's network and Linux hosts, and I help a few friends with Linux. All of this keeps me busy doing what I like to do, and all of it is usually well within my comfort zone.
+
+But COVID-19 has changed all of that. And, like many other types of organizations, my church had to move quickly to a new service-delivery paradigm. And that is what churches do—deliver a specific kind of service. As the church sysadmin and with some knowledge of audio recording and editing (back in the '70s, I mixed the sound and was the only roadie for a couple of regional folk-rock groups in Toledo, Ohio), I decided to learn the open source audio recording and editing software [Audacity][3] to help meet this challenge.
+
+This is not a comprehensive how-to article about using Audacity. It is about my experiences getting started with this powerful audio-editing tool, but there should be enough information here to help you get started.
+
+I have learned just what I need to know in order to accomplish my task: combining several separate audio clips into a single MP3 audio file. If you already know Audacity and do things differently or know things that I don't, that is expected. And if you have any suggestions to help me accomplish my task more easily, please share them in the comments.
+
+### The old way
+
+I try not to use the term "normal" now because it is hard to know exactly what that is—if such a state even exists. But our old method of producing recordings for our shut-ins, members who are traveling, and anyone else was to record the sermon portion of our regular, in-person church services and post them on our website.
+
+To do this, I installed a TASCAM SS-R100 solid-state recorder that stores the sermons as MP3 files on a thumb drive. We uploaded the recordings to a special directory of our website so people could download them. The recordings are uploaded using a Bash [program][4] I wrote for the task. _Automate everything!_ I trained a couple of others to perform these tasks using sudo in case I was not available.
+
+This all worked very well. Until it didn't.
+
+### The new way
+
+As soon as the first restrictions on large gatherings occurred, we made some changes. We could still have small gatherings, so four of us met Sunday mornings and recorded an abbreviated service using our in-house recorder and doing the upload the usual way. This worked, but as the crisis deepened and it became more of a risk to meet with even a few people, we had to make more changes.
+
+Like a huge number of other organizations, we realized we each needed to perform our parts of creating services in separate locations from our own homes.
+
+Now, depending upon the structure of the service, I receive several recordings that I need to combine to create the full church service. Our music director records each anthem and interlude using her iPhone and sends me the recordings in the M4A (MPEG-4 audio) format. They each range in length from seconds to five minutes and are up to 3MB in size. Likewise, our rector sends me two to six recordings, also in M4A format, that contains his portion of the service. Sometimes, other musicians in our church send solos or duets recorded with their significant others; these can be in MP3 or M4A formats.
+
+Then, I pull all of this together into a single recording that can be uploaded to our server for people to download. I use Audacity for this because it was available in my repo, and it was easy to get started.
+
+### Getting started with Audacity
+
+I had never used [Audacity][5] before this, so, like many others these days, I needed to learn something new just in time to accomplish what I needed to do. I struggled a bit at first, but it turned out to be fun and very enlightening.
+
+Audacity was easy to install on my Fedora 31 workstation because, as in many distros, it is available from the Fedora repository.
+
+The first time I opened Audacity with the program launcher icon, the application's window was empty with no projects nor tracks present. Audacity projects have an AUP extension, so if you have an existing project, you could click on the file in your favorite file manager and launch Audacity that way.
+
+### Convert M4A to MP3
+
+As installed by Fedora, Audacity does not recognize M4A files. Regardless of how you proceed, you need to install the [LAME][6] MP3 encoder and [FFmpeg][7] import/export library, both of which are available from the Fedora repository and, most likely, any other distro's repository.
+
+There are websites that explain how to configure Audacity to use these tools to import and convert audio files from M4A to other types (such as MP3), but I decided to write a script to do it from the command line. For one reason, using a script is faster than doing a lot of extra clicking in a GUI interface, and for another, the file names need some work, so I already needed a script to rename the files. Many people use non-alphanumeric characters to name files, but I don't like dealing with special keyboard characters from the command line. It's easier to manage files with simple alphanumeric names, so my script removes all non-alphanumeric characters from the file names and then converts the files to MP3 format.
+
+You may choose a different approach, but I like the scripted solution. It is fast, and I only need to run the script once, no matter how many files need to be renamed and converted to MP3.
+
+### Create a new project
+
+You can create a new project whether or not any audio tracks are loaded. I recommend creating the project first, before importing any audio files (aka "clips"). From the Menu bar, select **File > Save Project > Save Project As**. This opens a warning dialog window that says, _"'Save project' is for an Audacity project, not an audio file."_ Click the **OK** button to continue to a standard file-save dialog.
+
+I found that I needed to do this twice. The first time, the warning dialog did not display any buttons, so I had to close the dialog using the window menu or the x icon in the Title bar.
+
+Name the project whatever you like, and Audacity automatically adds the AUP extension. You now have an empty project.
+
+### Add audio files to your project
+
+The first step is to add your audio files to the project. Using the Menu bar, open **File > Import > Audio** and then use the file dialog to select one or more files to import. For my first test project, I loaded all the files at once without sorting the tracks nor aligning the clips in the desired sequence along the timeline. This time, I started by loading the audio files one at a time in the sequence I wanted them from top to bottom. As each file is imported, it is placed into a new track below any existing tracks. The following image shows the files loaded all at one time in the sequence they appear in the working directory.
+
+![Tracks loaded in Audacity][8]
+
+There is a timeline across the top of the window's track area. There is also a scroll bar at the bottom of the window, so you can scroll along the timeline when the tracks extend beyond the width of the Audacity window. There is also a vertical scroll bar if there are more tracks than fit into the window.
+
+Notice the names in the upper-left corner of the waveform section of each track—they are the file names of each track without the extension. These are not there by default, but I find them helpful. To display these names, use the Menu bar to select **Edit > Preferences** and place a check in the **Show Audio Track Name As Overlay** box.
+
+### Order your audio clips
+
+Once you have some files loaded into the Audacity workspace, you can start manipulating them. To order your audio clips, select one and use the **Time-Shift** tool (↔︎) to slide them horizontally along the tracks; continue doing this until all the clips line up end to end in the order you want them. Note that the clip you are moving is book-ended by a pair of vertical alignment lines. When they line up perfectly, the end lines of the two aligned tracks change color to alert you.
+
+You can hover the mouse pointer over the tool icons in the Audacity toolbars to see a pop-up that displays the name of that tool. This helps beginners understand what each tool does.
+
+![Audacity toolbox][9]
+
+Here, the **Selection** tool** **is selected in the Audacity toolbar. The **Time-Shift** tool is second from the left on the bottom row.
+
+The following image shows what happens when you slide the audio clips into place on the project timeline without sorting the tracks into a particular sequence. This may not be optimal for how you like to work. It is not for me.
+
+![Audio clips in Audacity][10]
+
+To remove segments of (or complete) audio clips, select them with the **Selection** tool—you can also select multiple adjacent tracks. Then you can press the **Delete** button on your keyboard to delete the selected segment(s).
+
+In the image above, you can see a vertical black line in track 1 and a vertical green line crossing all the tracks. These are the audio cursors that show the playback positions of a track or the entire project. Choose the **Selection** tool and click the desired position within a track, then click the **Play** button on the transport controls (in the upper-left of the Audacity window) to begin playback. Playback will continue past the end of the selected track and all the way to the end of the project. If tracks overlap on the timeline, they will play simultaneously.
+
+To begin playback immediately, click the desired starting point on the timeline. To play part of a track, hold down the Left mouse button to select a short segment of the track, and then click the **Play** button. The other transport buttons—Pause, Stop, and so—on are identified with universal icons and work as you would expect.
+
+You can also click the **Silence Audio Selection** button—the fifth button from the left on the **Edit** toolbar (shown below)—to completely silence a selected segment while leaving it in place for timing purposes. This is how I silenced a number of background clicks and noises.
+
+![Audacity edit tools][11]
+
+It took me a while to figure out how to sort the tracks vertically, and it turns out there are a few different ways to accomplish the task.
+
+You can use the track menu to reorder arrangement. Each track has its own Control Panel on the left side (shown below). The track drop-down Menu bar at the top of the Control Panel opens a menu that provides several track-sequencing options to move a track up, down, to the top, or to the bottom.
+
+![Moving tracks in Audacity][12]
+
+The items to move a track up or down move the track one position at a time, so you have to select it as many times as necessary to get the track in the desired position.
+
+To drag and drop tracks, you must click on the space occupied by the track details. In this screenshot, that's "Mono, 48000Hz 32 bit float". It can be tricky, because if you click too high, you adjust the panning (the left and right stereo position) and if you click too low, you may collapse or select the track. Target the "Mono" or "Stereo" label (whatever your track happens to be) label, and then click and drag the track up or down to reposition it in your workspace.
+
+### Apply amplification and noise reduction effects
+
+Some tracks need the overall volume to be adjusted. I used the **Selection** tool to double-click and select the entire track (but you could also select a portion of a track). On the Menu bar, select **Effect > Amplify** to display a small dialog window. You can use the slider or enter a value to specify the amount of amplification. Negative numbers decrease the volume. If you try to increase the volume, you need to place a check in the **Allow Clipping** box. Then click OK.
+
+I found that amplification is a bit tricky; it is easy to use too much or too little. Start by using small numbers to see the results. You can always use **Ctrl+Z** to undo your changes if you go too far in either direction.
+
+Another effect I find useful is noise reduction. One of the tracks was recorded with a noticeable 60Hz hum, which is usually due to poor grounding of the microphone or recorder. Fortunately, there were only several seconds of hum and no other sound at the beginning of the recording.
+
+Applying the noise reduction effect was a little confusing at first. First, I selected a few samples of the humming sound to tell Audacity what sound needed to be reduced, and then I navigated to **Effect > Noise Reduction**. This opens the **Noise Reduction** dialog. I clicked on the **Get Noise Profile** button in the Step 1 section of the dialog, which uses the selected sample as the basis for a set of filter presets. After it gathers the selected sample, though, the dialog disappeared (this is by design). I re-opened the dialog, used the slider to select the noise reduction level in decibels (I set it to 15dB and left the other sliders alone), and then clicked **OK**.
+
+This worked well—you can hear the residual hum only if you know it is there. I need to experiment with this some more, but since the result was acceptable, so I did not play with the settings any further.
+
+The reason the dialog box closes after getting a noise profile is actually for the sake of expediency. If you're processing many tracks or segments of audio, each with a different noise profile, you can open the **Noise Reduction** effect, get the current noise profile, and then select the audio you want to clean. You can then run the Noise Reduction filter using **Ctrl+R**, the keyboard shortcut for running the most recent filter. Instead of getting a new noise profile, however, Audacity uses the one you've just stored, and performs the filter instead. This way, you can get a sample with a few clicks but clean lots of audio with just one keyboard shortcut.
+
+### And so much more
+
+I have only worked with a few of the basics and have not even begun to scratch the surface of Audacity. I can already see that it has so many more features and tools that will enable me to create even more professional-sounding projects.
+
+For example, in addition to working with existing audio files, Audacity can make recordings from line inputs, the desktop sound stream, and microphone inputs. It can do special effects like fade in and out and cross-fades. And I have not even tried to figure out what many of the other effects and tools are capable of.
+
+I have a feeling I will need to learn more in the near future. Hopefully, this story of my very limited experience with Audacity will prompt you to check it out. For much more information, you can find the [Audacity manual][13] online.
+
+Using Audacity, you can quickly clean up audio file so that any background noise becomes tolerable.
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://opensource.com/article/20/4/audacity
+
+作者:[David Both][a]
+选题:[lujun9972][b]
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]: https://opensource.com/users/dboth
+[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
+[1]: https://opensource.com/sites/default/files/styles/image-full-size/public/lead-images/music-birds-recording-520.png?itok=UoM7brl0 (Bird singing and music notes)
+[2]: https://www.redhat.com/sysadmin/
+[3]: https://www.audacityteam.org/
+[4]: https://opensource.com/article/17/12/using-sudo-delegate
+[5]: https://opensource.com/education/16/9/audacity-classroom
+[6]: https://manual.audacityteam.org/man/installing_and_updating_audacity_on_linux.html#linlame
+[7]: https://manual.audacityteam.org/man/installing_and_updating_audacity_on_linux.html#linff
+[8]: https://opensource.com/sites/default/files/uploads/audacity1_tracksloaded.png (Tracks loaded in Audacity)
+[9]: https://opensource.com/sites/default/files/uploads/audacity2_tools.png (Audacity toolbox)
+[10]: https://opensource.com/sites/default/files/uploads/audacity3_audioclips.png (Audio clips in Audacity)
+[11]: https://opensource.com/sites/default/files/uploads/audacity4_edittoolbar.png (Audacity edit tools)
+[12]: https://opensource.com/sites/default/files/uploads/audacity5_trackmovement.png (Moving tracks in Audacity)
+[13]: https://manual.audacityteam.org/#
diff --git a/sources/tech/20200430 Linux and Kubernetes- Serving The Common Goals of Enterprises.md b/sources/tech/20200430 Linux and Kubernetes- Serving The Common Goals of Enterprises.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..c3c0c36b66
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/tech/20200430 Linux and Kubernetes- Serving The Common Goals of Enterprises.md
@@ -0,0 +1,77 @@
+[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
+[#]: translator: ( )
+[#]: reviewer: ( )
+[#]: publisher: ( )
+[#]: url: ( )
+[#]: subject: (Linux and Kubernetes: Serving The Common Goals of Enterprises)
+[#]: via: (https://www.linux.com/articles/linux-and-kubernetes-serving-the-common-goals-of-enterprises/)
+[#]: author: (Swapnil Bhartiya https://www.linux.com/author/swapnil/)
+
+Linux and Kubernetes: Serving The Common Goals of Enterprises
+======
+
+[![][1]][2]
+
+For [Stefanie Chiras,][3] VP & GM, Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) Business Unit at [Red Hat][4], aspects such as security and resiliency have always been important for Red Hat. More so, in the current situation when everyone has gone fully remote and it’s much harder to get people in front of the hardware for carrying out updates, patching, etc.
+
+“As we look at our current situation, never has it been more important to have an operating system that is resilient and secure, and we’re focused on that,” she said.
+
+The recently released version of [Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) 8.2][5] inadvertently address these challenge as it makes it easier for technology leaders to embrace the latest, production-ready innovations swiftly which offering security and resilience that their IT teams need.
+
+RHEL’s embrace of a predictable 6-month minor release cycle also helped customers plan upgrades more efficiently.
+
+“There is value for customers in having predictability of minor releases on a six-month cycle. Without knowing when they were coming was causing disruptions for them. The launch of 8.2 is now the second time we have delivered on our commitment of having minor releases every six months,” said Stefanie Chiras.
+
+In addition to offering security updates, the new version adds insights capabilities and forays into newer areas of innovation.
+
+The upgrade has expanded the earlier capability called ‘Adviser’ dramatically. Additional functionalities such as drift monitoring and CVE coverage allow for a much deeper granularity into how the infrastructure is running.
+
+“It really amplifies the skills that are already present in ops and sysadmin teams, and this provides a Red Hat consultation, if you will, directly into the data center,” claimed Charis.
+
+As containers are increasingly being leveraged for digital transformation, RHEL 8.2 offers an updated application stream of Red Hat’s container tools. It also has new, containerized versions of Buildah and Skopeo.
+
+[Skopeo][6] is an open-source image copying tool, while Buildah is a tool for building Docker- and Kubernetes-compatible images easily and quickly.
+
+RHEL has also ensured in-place upgrades in the new version. Customers can now directly in-place upgrade from version 7 to version 8.2.
+
+Chiras believes Linux has emerged as the go-to-platform for innovations such as Machine Learning, Deep Learning, and Artificial Intelligence.
+
+“Linux has now become the springboard of innovation,” she argued. “AI, machine learning, and deep learning are driving a real change in not just the software but also the hardware. In the context of these emerging technologies, it’s all about making them consumable into an enterprise.”
+
+“We’re very focused on our ecosystem, making sure that we’re working in the right upstream communities with the right ISVs, with the right hardware partners to make all of that magic come together,” Chiras said.
+
+Towards this end, Red Hat has been partnering with multiple architectures for a long time — be it an x86 architecture, ARM, Power, or mainframe with IBM Z. Its partnership with Nvidia pulls in capabilities such as FPGAs, and GPU.
+
+**Synergizing Kubernetes and Linux **
+
+Kubernetes is fast finding favor in enterprises. So how do Linux and Kubernetes serve the common goals of enterprises?
+
+“Kubernetes is a new way to deploy Linux. We’re very focused on providing operational consistency by leveraging our technology in RHEL and then bringing in that incredible capability of Kubernetes within our OpenShift product line,” Chiras said.
+
+The deployment of Linux within a Kubernetes environment is much more complicated than in a traditional deployment. RHEL, therefore, made some key changes. The company created Red Hat Enterprise Linux CoreOS — an optimized version of RHEL for the OpenShift experience.
+
+“It’s deployed as an immutable. It’s tailored, narrow, and gets updated as part of your OpenShift update to provide consistent user experience and comprehensive security.
+
+The launch of the Red Hat Universal Base Image (UBI) offers users greater security, reliability, and performance of official Red Hat container images where OCI-compliant Linux containers run.
+
+“Kubernetes is a new way to deploy Linux. It really is a tight collaboration but what we’re really focused on is the customer experience. We want them to get easy updates with consistency and reliability, resilience and security. We’re pulling all of that together. With such advancements going on, it’s a fascinating space to watch,” added Chiras.
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://www.linux.com/articles/linux-and-kubernetes-serving-the-common-goals-of-enterprises/
+
+作者:[Swapnil Bhartiya][a]
+选题:[lujun9972][b]
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]: https://www.linux.com/author/swapnil/
+[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
+[1]: https://www.linux.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/12/computer-2930704_1280-1068x634.jpg (computer-2930704_1280)
+[2]: https://www.linux.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/12/computer-2930704_1280.jpg
+[3]: https://www.linkedin.com/in/stefanie-chiras-9022144/
+[4]: https://www.redhat.com/en
+[5]: https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_enterprise_linux/8/html-single/8.2_release_notes/index
+[6]: https://github.com/containers/skopeo
diff --git a/sources/tech/20200501 How to Handle Automatic Updates in Ubuntu.md b/sources/tech/20200501 How to Handle Automatic Updates in Ubuntu.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..b62af6da74
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/tech/20200501 How to Handle Automatic Updates in Ubuntu.md
@@ -0,0 +1,125 @@
+[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
+[#]: translator: ( )
+[#]: reviewer: ( )
+[#]: publisher: ( )
+[#]: url: ( )
+[#]: subject: (How to Handle Automatic Updates in Ubuntu)
+[#]: via: (https://itsfoss.com/auto-updates-ubuntu/)
+[#]: author: (Abhishek Prakash https://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/)
+
+How to Handle Automatic Updates in Ubuntu
+======
+
+_**Brief: This tutorial teaches you how to handle the unattended upgrade i.e. the automatic system updates in Ubuntu Linux.**_
+
+Sometimes, when you try to [shutdown your Ubuntu system][1], you may come across this screen that stops you from shutting down:
+
+**Unattended-upgrade in progress during shutdown, please don’t turn off the computer.**
+
+![Unattended Upgrade In Progress In Ubuntu][2]
+
+You might wonder what is this “unattended upgrade” and how come it is running without your knowledge.
+
+The reason is that [Ubuntu][3] takes your system’s security very seriously. By default, it automatically checks for system updates daily and if it finds any security updates, it downloads those updates and install them on its own. For normal system and application updates, it notifies you via the Software Updater tool.
+
+Since all this happens in the background, you don’t even realize it until you try to shutdown your system or try to install applications on your own.
+
+Trying to install a new software when these unattended upgrades are in progress leads to the famous [could not get lock error][4].
+
+![][5]
+
+As you can see, the automatic updates present a couple of minor annoyance. You may choose to disable the auto updates but that would mean that you’ll have to check and [update your Ubuntu system][6] manually all the time.
+
+Do you really need to disable auto updates?
+
+Please note that this is a security feature. Linux allows you to do practically everything in your system even disabling these security features.
+But in my opinion, as a regular user, _**you should not disable the automatic updates**_. It keeps your system safe after all.
+For the sake of your system’s security, you may tolerate the minor annoyances that come with the automatic updates.
+
+Now that you have been warned and you think it is better to take up the additional task of manually updating your system, let’s see how to handle the auto updates.
+
+As always, there are two ways to do it: GUI and command line. I’ll show you both methods.
+
+I have used Ubuntu 20.04 here but the steps are valid for Ubuntu 18.04 and any other Ubuntu version.
+
+### Method 1: Disable automatic updates in Ubuntu graphically
+
+Go to the menu and look for ‘software & updates’ tool.
+
+![Software & Updates Settings][7]
+
+In here, go to Updates tab. Now look for the “Automatically check for updates”. By default it is set to Daily.
+
+You can change it to Never and your system will never check for updates on its own again. And if it won’t check for updates, it won’t find new updates to install.
+
+![Disable Auto Updates in Ubuntu Completely][8]
+
+If you do this, you must manually update your system from time to time. But that’s an additional chore to do and you may not remember it all the time.
+
+#### Slightly better way to handle auto updates in Ubuntu
+
+Personally, I would suggest to let it check for updates on its own. If you don’t want it installing the updates automatically, you can change that behavior to get notified about the availability of security updates.
+
+Keep “Automatically check for updates” to Daily and change “When there are security updates” option to “Display immediately” instead of “Download and install automatically”.
+
+![Get notified for security updates instead of automatically installing them][9]
+
+This way, it checks for updates and if there are updates, instead of installing them automatically in the background, the Software Updater tool notifies you that updates are available for your system. Your system already does that for normal system and software updates.
+
+![Get notified about security updates][10]
+
+With this setup, you won’t see the “unattended upgrades in progress” when you shutdown your system However, you may still encounter the ‘could not get lock’ error because two separate processes cannot use apt package manager at the same time.
+
+I believe this is a better solution, don’t you you think?
+
+As I promised both GUI and command line methods, let me show you how to disable unattended upgrades in the terminal.
+
+### How to disable automatic updates in Ubuntu using command line
+
+You’ll find the auto-upgrades settings in the **/etc/apt/apt.conf.d/20auto-upgrades** file. The default text editor in Ubuntu terminal is Nano so you can use this command to edit this configuration file:
+
+```
+sudo nano /etc/apt/apt.conf.d/20auto-upgrades
+```
+
+Now, if you don’t want your system to check for updates automatically, you can change the value of APT::Periodic::Update-Package-Lists to 0.
+
+```
+APT::Periodic::Update-Package-Lists "0";
+APT::Periodic::Unattended-Upgrade "0";
+```
+
+If you want it to check for updates but don’t install the unattended-upgrades automatically, you can choose to set it like this:
+
+```
+APT::Periodic::Update-Package-Lists "1";
+APT::Periodic::Unattended-Upgrade "0";
+```
+
+**In the end…**
+
+The automatic security updates are enabled automatically for a reason and I recommend you keep it like this. A couple of minor annoyances are not really worth risking the security of your system. What do you think?
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://itsfoss.com/auto-updates-ubuntu/
+
+作者:[Abhishek Prakash][a]
+选题:[lujun9972][b]
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]: https://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/
+[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
+[1]: https://itsfoss.com/schedule-shutdown-ubuntu/
+[2]: https://i0.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/unattended-upgrade-in-progress-in-ubuntu.png?ssl=1
+[3]: https://ubuntu.com/
+[4]: https://itsfoss.com/could-not-get-lock-error/
+[5]: https://i1.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/12/Could_not_get_lock.jpg?ssl=1
+[6]: https://itsfoss.com/update-ubuntu/
+[7]: https://i0.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/software-updates-settings-ubuntu-20-04.jpg?ssl=1
+[8]: https://i2.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/disable-auto-updates-ubuntu.jpg?ssl=1
+[9]: https://i1.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/handle-auto-updates-ubuntu.jpg?ssl=1
+[10]: https://i2.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/updates-available-ubuntu.png?ssl=1
diff --git a/sources/tech/20200501 Transparent, open source alternative to Google Analytics.md b/sources/tech/20200501 Transparent, open source alternative to Google Analytics.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..d4ce222a39
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/tech/20200501 Transparent, open source alternative to Google Analytics.md
@@ -0,0 +1,123 @@
+[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
+[#]: translator: ( )
+[#]: reviewer: ( )
+[#]: publisher: ( )
+[#]: url: ( )
+[#]: subject: (Transparent, open source alternative to Google Analytics)
+[#]: via: (https://opensource.com/article/20/5/plausible-analytics)
+[#]: author: (Marko Saric https://opensource.com/users/markosaric)
+
+Transparent, open source alternative to Google Analytics
+======
+Plausible Analytics is a leaner, more transparent option, with the
+essential data you need but without all the privacy baggage.
+![Digital creative of a browser on the internet][1]
+
+Google Analytics is the most popular website analytics tool. Millions of developers and creators turn to it to collect and analyze their website statistics.
+
+More than 53% of all sites on the web track their visitors using Google Analytics. [84%][2] of sites that do use a known analytics script use Google Analytics.
+
+Google Analytics has, for years, been one of the first tools I installed on a newly launched site. It is a powerful and useful analytics tool. Installing Google Analytics was a habit I didn't think much about until the introduction of the [GDPR][3] (General Data Protection Regulation) and other privacy regulations.
+
+Using Google Analytics these days comes with several pitfalls, including the need for a privacy policy, the need for cookie banners, and the need for a GDPR consent prompt. All these may negatively impact the site loading time and visitor experience.
+
+This has made me try to [de-Google-ify websites][4] that I work on, and it's made me start working on independent solutions that are open source and more privacy-friendly. This is where Plausible Analytics enters the story.
+
+[Plausible Analytics][5] is an open source and lightweight alternative to Google Analytics. It doesn't use cookies and it doesn't collect any personal data, so you don't need to show any cookie banners or get GDPR or CCPA consent. Let's take a closer look.
+
+### Main differences between Google Analytics and Plausible
+
+Plausible Analytics is not designed to be a clone of Google Analytics. It is meant as a simple-to-use replacement and a privacy-friendly alternative. Here are the main differences between the two web analytics tools:
+
+#### Open source vs. closed source
+
+Google Analytics may be powerful and useful, but it is closed source. It is a proprietary tool run by one of the largest companies in the world, a company that is a key player in the ad-tech industry. There's simply no way of knowing what's going on behind the scenes. You have to put your trust in Google.
+
+Plausible is a fully open source tool. You can read our code [on GitHub][6]. We're "open" in other ways, too, such as our [public roadmap][7], which is based around the feedback and features submitted by the members of our community.
+
+#### Privacy of your website visitors
+
+Google Analytics places [several cookies][8] on the devices of your visitors, and it tracks and collects a lot of data. This means that there are several requirements if you want to use Google Analytics and be compliant with the different regulations:
+
+ * You need to have a privacy policy about analytics
+ * You need to show a cookie banner
+ * You need to obtain a GDPR/CCPA consent
+
+
+
+Plausible is made to be fully compliant with the privacy regulations. No cookies are used, and no personal data is collected. This means that you don't need to display the cookie banner, you don't need a privacy policy, and you don't need to ask for the GDPR/CCPA consent when using Plausible.
+
+#### Page weight and loading time
+
+The recommended way of installing Google Analytics is to use the Google Tag Manager. Google Tag Manager script weights 28 KB, and it downloads another JavaScript file called the Google Analytics tag, which adds an additional 17.7 KB to your page size. That's 45.7 KB of page weight combined.
+
+Plausible script weights only 1.4 KB. That's 33 times smaller than the Google Analytics Global Site Tag. Every KB matters when you want to keep your site fast to load.
+
+#### Accuracy of visitor stats
+
+Google Analytics is being blocked by an increasing number of web users. It's blocked by those who use open source browsers such as [Firefox][9] and [Brave][10]. It's also blocked by those who use open source browser add-ons such as the [uBlock Origin][11]. It's not uncommon to see 40% or more of the audience on a tech site blocking Google Analytics.
+
+Plausible is a new player on this market and it's privacy-friendly by default, so it doesn't see the same level of blockage.
+
+#### Simple vs. complex web analytics
+
+[Google Analytics is overkill][12] for many website owners. It's a complex tool that takes time to understand and requires training. Google Analytics presents hundreds of different reports and metrics for you to get insights from. Many users end up creating custom dashboards while ignoring all the rest.
+
+Plausible cuts through all the noise that Google Analytics creates. It presents everything you need to know on one single page—all the most valuable metrics at a glance. You can get an overview of the most actionable insights about your website in one minute.
+
+### A guided tour of Plausible Analytics
+
+Plausible Analytics is not a full-blown replacement and a feature-by-feature reproduction of Google Analytics. It's not designed for all the different use-cases of Google Analytics.
+
+It's built with simplicity and speed in mind. There is no navigational menu. There are no additional sub-menus. There is no need to create custom reports. You get one simple and useful web analytics dashboard out of the box.
+
+Rather than tracking every metric imaginable, many of them that you will never find a use for, Plausible focuses on the essential website stats only. It is easy to use and understand with no training or prior experience:
+
+![Plausible analytics in action][13]
+
+ * Choose the time range that you want to analyze. The visitor numbers are automatically presented on an hourly, daily, or monthly graph. The default time frame is set at the last 30 days.
+ * See the number of unique visitors, total page views, and the bounce rate. These metrics include a percentage comparison to the previous time period, so you understand if the trends are going up or down.
+ * See all the referral sources of traffic and all the most visited pages on your site. Bounce rates of the individual referrals and pages are included too.
+ * See the list of countries your traffic is coming from. You can also see the device, browser, and operating system your visitors are using.
+ * Track events and goals to identify the number of converted visitors, the conversion rate, and the referral sites that send the best quality traffic.
+
+
+
+Take a look at the [live demo][14] where you can follow the traffic to the Plausible website.
+
+### Give Plausible Analytics a chance
+
+With Plausible Analytics, you get all the important web analytics at a glance so you can focus on creating a better site without needing to annoy your visitors with all the different banners and prompts.
+
+You can try Plausible Analytics on your site alongside Google Analytics. [Register today][15] to try it out, and see what you like and what you don't. Share your feedback with the community. This helps us learn and improve. We'd love to hear from you.
+
+Take a look at five great open source alternatives to Google Docs.
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://opensource.com/article/20/5/plausible-analytics
+
+作者:[Marko Saric][a]
+选题:[lujun9972][b]
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]: https://opensource.com/users/markosaric
+[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
+[1]: https://opensource.com/sites/default/files/styles/image-full-size/public/lead-images/browser_web_internet_website.png?itok=g5B_Bw62 (Digital creative of a browser on the internet)
+[2]: https://w3techs.com/technologies/details/ta-googleanalytics
+[3]: https://gdpr-info.eu/
+[4]: https://markosaric.com/degoogleify/
+[5]: https://plausible.io/
+[6]: https://github.com/plausible-insights/plausible
+[7]: https://feedback.plausible.io/roadmap
+[8]: https://developers.google.com/analytics/devguides/collection/analyticsjs/cookie-usage
+[9]: https://www.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/new/
+[10]: https://brave.com/
+[11]: https://github.com/gorhill/uBlock
+[12]: https://plausible.io/vs-google-analytics
+[13]: https://opensource.com/sites/default/files/plausible-analytics.png (Plausible analytics in action)
+[14]: https://plausible.io/plausible.io
+[15]: https://plausible.io/register
diff --git a/sources/tech/20200501 Using mergerfs to increase your virtual storage.md b/sources/tech/20200501 Using mergerfs to increase your virtual storage.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..06f26abf51
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/tech/20200501 Using mergerfs to increase your virtual storage.md
@@ -0,0 +1,147 @@
+[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
+[#]: translator: ( )
+[#]: reviewer: ( )
+[#]: publisher: ( )
+[#]: url: ( )
+[#]: subject: (Using mergerfs to increase your virtual storage)
+[#]: via: (https://fedoramagazine.org/using-mergerfs-to-increase-your-virtual-storage/)
+[#]: author: (Curt Warfield https://fedoramagazine.org/author/rcurtiswarfield/)
+
+Using mergerfs to increase your virtual storage
+======
+
+![][1]
+
+What happens if you have multiple disks or partitions that you’d like to use for a media project and you don’t want to lose any of your existing data, but you’d like to have everything located or mounted under one drive. That’s where mergerfs can come to your rescue!
+
+[mergerfs][2] is a union filesystem geared towards simplifying storage and management of files across numerous commodity storage devices.
+
+You will need to grab the latest RPM from their github page [here][3]. The releases for Fedora have _**fc**_ and the version number in the name. For example here is the version for Fedora 31:
+
+[mergerfs-2.29.0-1.fc31.x86_64.rpm][4]
+
+### Installing and configuring mergerfs
+
+Install the mergerfs package that you’ve downloaded using sudo:
+
+```
+$ sudo dnf install mergerfs-2.29.0-1.fc31.x86_64.rpm
+```
+
+You will now be able to mount multiple disks as one drive. This comes in handy if you have a media server and you’d like all of your media files to show up under one location. If you upload new files to your system, you can copy them to your mergerfs directory and mergerfs will automatically copy them to which ever drive has enough free space available.
+
+Here is an example to make it easier to understand:
+
+```
+$ df -hT | grep disk
+/dev/sdb1 ext4 23M 386K 21M 2% /disk1
+/dev/sdc1 ext4 44M 1.1M 40M 3% /disk2
+
+$ ls -l /disk1/Videos/
+total 1
+-rw-r--r--. 1 curt curt 0 Mar 8 17:17 Our Wedding.mkv
+
+$ ls -l /disk2/Videos/
+total 2
+-rw-r--r--. 1 curt curt 0 Mar 8 17:17 Baby's first Xmas.mkv
+-rw-rw-r--. 1 curt curt 0 Mar 8 17:21 Halloween hijinks.mkv
+```
+
+In this example there are two disks mounted as _disk1_ and _disk2_. Both drives have a _**Videos**_ directory with existing files.
+
+Now we’re going to mount those drives using mergerfs to make them appear as one larger drive.
+
+```
+$ sudo mergerfs -o defaults,allow_other,use_ino,category.create=mfs,moveonenospc=true,minfreespace=1M /disk1:/disk2 /media
+```
+
+The mergerfs man page is quite extensive and complex so we’ll break down the options that were specified.
+
+ * _defaults_: This will use the default settings unless specified.
+ * _allow_other_: allows users besides sudo or root to see the filesystem.
+ * _use_ino_: Causes mergerfs to supply file/directory inodes rather than libfuse. While not a default it is recommended it be enabled so that linked files share the same inode value.
+ * _category.create=mfs_: Spreads files out across your drives based on available space.
+ * _moveonenospc=true_: If enabled, if writing fails, a scan will be done looking for the drive with the most free space.
+ * _minfreespace=1M_: The minimum space value used.
+ * _disk1_: First hard drive.
+ * _disk2_: Second hard drive.
+ * _/media_: The directory folder where the drives are mounted.
+
+
+
+Here is what it looks like:
+
+```
+$ df -hT | grep disk
+/dev/sdb1 ext4 23M 386K 21M 2% /disk1
+/dev/sdc1 ext4 44M 1.1M 40M 3% /disk2
+
+$ df -hT | grep media
+1:2 fuse.mergerfs 66M 1.4M 60M 3% /media
+```
+
+You can see that the mergerfs mount now shows a total capacity of 66M which is the combined total of the two hard drives.
+
+Continuing with the example:
+
+There is a 30Mb video called _Baby’s second Xmas.mkv_. Let’s copy it to the _/media_ folder which is the mergerfs mount.
+
+```
+$ ls -lh "Baby's second Xmas.mkv"
+-rw-rw-r--. 1 curt curt 30M Apr 20 08:45 Baby's second Xmas.mkv
+$ cp "Baby's second Xmas.mkv" /media/Videos/
+```
+
+Here is the end result:
+
+```
+$ df -hT | grep disk
+/dev/sdb1 ext4 23M 386K 21M 2% /disk1
+/dev/sdc1 ext4 44M 31M 9.8M 76% /disk2
+
+$ df -hT | grep media
+1:2 fuse.mergerfs 66M 31M 30M 51% /media
+```
+
+You can see from the disk space utilization that mergerfs automatically copied the file to disk2 because disk1 did not have enough free space.
+
+Here is a breakdown of all of the files:
+
+```
+$ ls -l /disk1/Videos/
+total 1
+-rw-r--r--. 1 curt curt 0 Mar 8 17:17 Our Wedding.mkv
+
+$ ls -l /disk2/Videos/
+total 30003
+-rw-r--r--. 1 curt curt 0 Mar 8 17:17 Baby's first Xmas.mkv
+-rw-rw-r--. 1 curt curt 30720000 Apr 20 08:47 Baby's second Xmas.mkv
+-rw-rw-r--. 1 curt curt 0 Mar 8 17:21 Halloween hijinks.mkv
+
+$ ls -l /media/Videos/
+total 30004
+-rw-r--r--. 1 curt curt 0 Mar 8 17:17 Baby's first Xmas.mkv
+-rw-rw-r--. 1 curt curt 30720000 Apr 20 08:47 Baby's second Xmas.mkv
+-rw-rw-r--. 1 curt curt 0 Mar 8 17:21 Halloween hijinks.mkv
+-rw-r--r--. 1 curt curt 0 Mar 8 17:17 Our Wedding.mkv
+```
+
+When you copy files to your mergerfs mount, it will always copy the files to the hard disk that has enough free space. If none of the drives in the pool have enough free space, then you won’t be able to copy them.
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://fedoramagazine.org/using-mergerfs-to-increase-your-virtual-storage/
+
+作者:[Curt Warfield][a]
+选题:[lujun9972][b]
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]: https://fedoramagazine.org/author/rcurtiswarfield/
+[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
+[1]: https://fedoramagazine.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/mergerfs-816x346.png
+[2]: https://github.com/trapexit/mergerfs
+[3]: https://github.com/trapexit/mergerfs/releases
+[4]: https://github.com/trapexit/mergerfs/releases/download/2.29.0/mergerfs-2.29.0-1.fc31.x86_64.rpm
diff --git a/sources/tech/20200503 13 tips for getting your talk accepted at a tech conference.md b/sources/tech/20200503 13 tips for getting your talk accepted at a tech conference.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..b260116fb6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/tech/20200503 13 tips for getting your talk accepted at a tech conference.md
@@ -0,0 +1,127 @@
+[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
+[#]: translator: ( )
+[#]: reviewer: ( )
+[#]: publisher: ( )
+[#]: url: ( )
+[#]: subject: (13 tips for getting your talk accepted at a tech conference)
+[#]: via: (https://opensource.com/article/20/5/tips-conference-proposals)
+[#]: author: (Todd Lewis https://opensource.com/users/toddlewis)
+
+13 tips for getting your talk accepted at a tech conference
+======
+Before you respond to an event's call for papers, make sure your talk's
+proposal aligns with these best practices.
+![All Things Open check-in at registration booth][1]
+
+As tech conference organizers ramp up for the fall season, you may be seeing calls for papers (CFP) landing in your email box or social media feeds. We at [All Things Open][2] (ATO) have seen a lot of presentation proposals over the years, and we've learned a few things about what makes them successful.
+
+As we prepare for the eighth annual ATO in October 2020, we thought we'd offer a few best practices for writing successful CFP responses. If you're considering submitting a talk to ATO or another tech event, we hope these tips will help improve the chances that your proposal will be accepted.
+
+### 1\. Know the event you're submitting a talk to
+
+This seems like the proverbial _no-brainer_, but some people don't take the time to research an event before they submit a talk. Peruse the conference's website and review the talks, speakers, topics, etc. featured in the last couple of years. You can also find a lot of information simply by googling. The time you invest here will help you avoid a submission that is completely out of context for the event.
+
+### 2\. Understand what the event is looking for
+
+Look for information about what the event is looking for and what types of topics or talks it expects will be a good fit. We try to provide as much information as possible about the [ATO conference][3], [why someone would want to speak][4], and [what we're looking for][5] (both general and special interest topics). We also try to make the submission process as easy as possible (no doubt, there is room for improvement), in part because we believe this improves the quality of submissions and makes our review process go more smoothly.
+
+### 3\. Reach out to the organizer and ask questions
+
+If you're considering submitting a talk, don't hesitate to reach out and ask the event organizers any questions you have and for guidance specific to the event. If there is no or little response, that should be a red flag. If you have any questions about All Things Open, please reach out directly at [info@allthingsopen.org][6].
+
+### 4\. Be clear about what attendees will learn from your talk
+
+This is one of the most common mistakes we see. Only about 25% of the proposals we receive clearly explain the proposed talk's takeaways. One reason you should include this is that nearly every event attendee makes their schedule based on what they will learn if they go to a session. But for organizers and proposal reviewers, having this information clearly stated upfront is pure gold. It simplifies and speeds up the assessment process, which gets you one step closer to being accepted as a speaker. A paragraph titled "Attendee Takeaways" with bullet points is the holy grail for everyone involved.
+
+### 5\. Keep recommended word counts in mind
+
+This is another mistake we see a lot. Many talks are submitted with either a single sentence description in the abstract or an extraordinary long volume of text. Neither is a good idea. The only exception we can think of is when a topic is very popular or topical, and that alone is enough to win the day even if the abstract is extremely short (but this is rare). Most abstracts should be between 75 and 250 words, and perhaps more for an extended workshop with prerequisites (e.g., preexisting knowledge or required downloads). Even then, try to keep your proposal as sharp, concise, and on-point as possible.
+
+Disregard this advice at your own risk; otherwise, there's a high likelihood that your proposal will be met with one of these reactions from reviewers: "They didn't take the time to write any more than this?" or "Sheesh, there's no way I have the time to read all that. I'm going to give it the lowest score and move on."
+
+### 6\. Choose a good title
+
+This is a debate we see all the time: Should a talk's title describe what the talk is about, or should it be written to stand out and get attention (e.g., evoking emotion, anchoring to a popular pop culture topic, or asking a compelling question)? There isn't a single correct answer to this question, but we definitely know when a title "works" and when it doesn't. We've seen some very creative titles work well and generate interest, and we've seen very straightforward titles work well, also.
+
+Here is our rule of thumb: If the talk covers a topic that has been around a while and is not particularly _hot_ right now, try getting creative and spicing it up a bit. If the topic is newer, a more straightforward title describing the talk in plain terms should be good.
+
+Titles on an event schedule may be the only thing attendees use to decide what talks to attend. So, run your potential talk titles by colleagues and friends, and seek their opinions. Ask: "If you were attending an event and saw this title on the schedule, would it pique your interest?"
+
+### 7\. Know the basic criteria that reviewers and organizers use to make decisions
+
+While this isn't a comprehensive list of review criteria, most reviewers and organizers consider one or more of the following when evaluating talk proposals. Therefore, at minimum, consider this list when you're creating a talk and the components that go with it.
+
+ 1. **Timeliness of and estimated interest in the topic:** Is the topic applicable to the session's target audience? Will it deliver value? Is it timely?
+ 2. **Educational value:** Based on the abstract and speaker, is it clear that attendees will learn something from the talk? As mentioned in item 4 above, including an "Attendee Takeaways" section is really helpful to establish educational value.
+ 3. **Technical value:** Is the technology you intend to showcase applicable, unique, or being used in a new and creative way? Is there a live demo or a hands-on component? While some topics don't lend themselves to a demo, most people are visual learners and are better off if a presentation includes one (if it's relevant). For this reason, we place a lot of value on demos and hands-on content.
+ 4. **Diversity:** Yes, there are exceptions, but the majority of events, reviewers, and organizers agree that having a diverse speaker lineup is optimal and results in a better overall event in multiple ways. A topic delivered from a different perspective can often lead to creative breakthroughs for attendees, which is a huge value-add. See item 10 below for more on this.
+ 5. **Talk difficulty level:** We identify All Things Open talks as introductory, intermediate, or advanced. Having a good mix of talk levels ensures everyone in attendance can access applicable content. See item 9 below for more on this, but in general, it's smart to indicate your talk's level, whether or not the CFP requests it.
+
+
+
+### 8\. Stay current on the event's industry or sector
+
+Submitting a proposal on a relevant topic increases the probability your talk will be accepted. But how do you know what topics are of interest, especially if the CFP doesn't spell it out in simple terms? The best way to know what's timely and interesting is to deeply understand the sector the event focuses on.
+
+Yes, this requires time and effort, and it implies you enjoy the sector enough to stay current on it, but it will pay off. This knowledge will result in a higher _sector IQ_, which will be reflected in your topic, title, and abstract. It will be recognized by reviewers and immediately set you apart from others. At All Things Open, we spend the majority of our time reading about and staying current on the "open" space so that we can feature relevant, substantive, and informed content. Submitting a talk that is relevant, substantive, and informed greatly enhances the chance it will be accepted.
+
+### 9\. Describe whether the talk is introductory, intermediate, or advanced
+
+Some CFPs don't ask for this information, but you should offer it anyway. It will make the reviewers and organizer very happy for multiple reasons, including these:
+
+ 1. Unless the event targets attendees with a certain skill or experience level (and most do not), organizers must include content that is appealing to a wide audience, including people of all skill, experience, and expertise levels. Even if an event focuses on a specific type of attendee (perhaps people with higher levels of experience or skills), most want to offer something a little different. Listing the talk level makes this much easier for organizers.
+ 2. News flash: Reviewers and organizers don't know everything and are not experts in every possible topic area. As a result, reviewers will sometimes look for a few keywords or other criteria, and adding the talk level can "seal the deal" and get your talk confirmed.
+
+
+
+### 10\. Tell organizers if you're a member of a historically underrepresented group
+
+A growing number of events are getting better at recognizing the value of diversity and ensuring their speaker lineup reflects it. If you're part of a group that hasn't typically been included in tech events and leadership, look to see if there is a place to indicate that on the submission form. If not, mention it in a conspicuous place somewhere in the abstract. This does not guarantee approval in any way—your proposal must still be well-written and relevant—but it does give reviewers and organizers pertinent information they may value and take into consideration.
+
+### 11\. Don't be ashamed of your credentials or speaking experience if it is light
+
+We talk to a lot of people who would like to deliver a presentation and have a lot to offer, but they never submit a talk because they don't feel they're qualified to speak. _Not true._ Some of the best talks we've seen are from first-time speakers or those very early in their speaking careers. Go ahead and submit the talk, and be honest when discussing your background. Most reviewers and organizers will focus on the substance of the submission over your experience and recognize that new ways of approaching and using technology often come from newbies rather than industry veterans.
+
+One caveat here: It still pays to know yourself. By this, we mean if you absolutely hate public speaking, have no desire to do it, and are only considering submitting a talk due to, for example, pressure from an employer, the talk is not likely to go well. It's better, to be honest, on the frontend than force something you have no desire to do.
+
+### 12\. Consider panel sessions carefully
+
+If you've got an idea for a panel session, please consider it carefully. In more than 10 years of hosting events we've seen some really good panel sessions, but we've seen far more that didn't go so well. Perhaps too many people were on the panel and not everyone had a chance to speak, perhaps a single panel member dominated the entire conversation, or perhaps the moderator didn't keep the dialogue and engagement flowing smoothly. Regardless of the issue, panels have the potential to go very wrong.
+
+That said, panels can still work and deliver a lot of value to attendees. If you do submit a panel session be sure to keep in mind the amount of time allotted for the session and confirm the number of panel members accordingly. Remember, less is always more when it comes to the panel format. Also, be sure the moderator understands the subject matter being discussed and doesn't mind enforcing format parameters and speaking time limits. Finally, let organizers know panel members and the moderator will engage in a pre-conference walk-through/preparation call before the event to ensure a smooth process in front of a live audience. Remember, organizers are well aware panels can be terrific but can also go in the opposite direction and very easily lead to a lot of negative feedback.
+
+### 13\. This is not an opportunity to sell
+
+This is a sensitive topic, but one that absolutely must be mentioned. Over the years we've seen literally hundreds of talks "disqualified" by reviewers because they viewed the talk as a sales pitch. Few things evoke such a visceral response. Yes, there are events, tracks, and session slots where a sales pitch is appropriate (and maybe even required by the company paying your costs). However, make it a priority to know when and where this is appropriate and acceptable. And always, and we mean always, err on the side of making substance the focus of the talk rather than a sales angle.
+
+It might sound like a cliche, but when a talk is delivered effectively with a focus on substance, people will **want** to buy what you're selling. And if you're not selling anything, they'll want to follow you on social media and generally engage with you—because you delivered value to them. Meaning: You gave them something they can apply themselves (education) or because your delivery style was entertaining and engaging. With rare exceptions, always focus any abstract on substance, and the rest will take care of itself.
+
+### Go for it!
+
+We greatly admire and respect anyone who submits a talk for consideration—it takes a lot of time, thought, and courage. Therefore, we go to great lengths to thank everyone who goes through the process; we give free event passes to everyone who applies (regardless of approval or rejection), and we make every effort to host Q&A sessions to provide as much guidance as possible on the front end. Again, the more time and consideration speakers put into the submission process, the easier the lives of reviewers and organizers. We need to make all of this as easy as possible.
+
+While this is not a comprehensive list of best practices, it includes some of the things we think people can benefit from knowing before submitting a talk. There are a lot of people out there with more knowledge and experience, so please share your best tips for submitting conference proposals in the comments, so we can all learn from you.
+
+* * *
+
+_[All Things Open][2] is a universe of platforms and events focusing on open source, open tech, and the open web. It hosts the [All Things Open conference][3], the largest open source/tech/web event on the US East Coast. The conference regularly hosts thousands of attendees and many of the world's most influential companies from a wide variety of industries and sectors. In 2019, nearly 5,000 people attended from 41 US states and 24 countries. Please direct inquiries about ATO to the team at [info@allthingsopen.org][6]._
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://opensource.com/article/20/5/tips-conference-proposals
+
+作者:[Todd Lewis][a]
+选题:[lujun9972][b]
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]: https://opensource.com/users/toddlewis
+[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
+[1]: https://opensource.com/sites/default/files/styles/image-full-size/public/lead-images/ato2016_checkin_conference.jpg?itok=DJtoSS6t (All Things Open check-in at registration booth)
+[2]: https://www.allthingsopen.org/
+[3]: https://2020.allthingsopen.org/
+[4]: https://2020.allthingsopen.org/call-for-speakers
+[5]: https://www.allthingsopen.org/what-were-looking-for/
+[6]: mailto:info@allthingsopen.org
diff --git a/translated/talk/20200401 The ins and outs of high-performance computing as a service.md b/translated/talk/20200401 The ins and outs of high-performance computing as a service.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..948d985765
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/talk/20200401 The ins and outs of high-performance computing as a service.md
@@ -0,0 +1,101 @@
+[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
+[#]: translator: (messon007)
+[#]: reviewer: ( )
+[#]: publisher: ( )
+[#]: url: ( )
+[#]: subject: (The ins and outs of high-performance computing as a service)
+[#]: via: (https://www.networkworld.com/article/3534725/the-ins-and-outs-of-high-performance-computing-as-a-service.html)
+[#]: author: (Josh Fruhlinger https://www.networkworld.com/author/Josh-Fruhlinger/)
+
+高性能计算即服务的来龙去脉
+======
+高性能计算(HPC)服务可能是一种满足不断增长的超级计算需求的方式,但依赖于使用场景,它们不一定比使用本地超级计算机好。
+
+戴尔EMC
+导弹和军用直升机上的电子设备需要工作在极端条件下。国防承包商麦考密克·史蒂文森公司(McCormick Stevenson Corp.)在部署任何物理设备之前都会事先模拟它所能承受的真实条件。模拟依赖于像Ansys这样的有限元素分析软件,该软件需要强大的算力。
+
+几年前的一天,它出乎意料地超出了计算极限。
+[世界上最快的10个超级计算机][1]
+
+麦考密克·史蒂文森(McCormick Stevenson)的首席工程师迈克·克劳奇奇(Mike Krawczyk)说:“我们的一些工作会使办公室的计算机不堪重负。购买机器并安装软件在经济上或计划上都不划算。” 相反,该公司与Rescale签约,从其购买在超级计算机系统上运行的周期(cycles),而这只花费了他们购买新硬件上所需的一小部分。
+
+麦考密克·史蒂文森(McCormick Stevenson)已成为被称为超级计算即服务或高性能计算(HPC)即服务(两个紧密相关的术语)市场的早期采用者之一。根据国家计算科学研究所(的定义),HPC是超级计算机在计算复杂问题上的应用,而超级计算机是处理能力最先进的那些计算机。
+
+无论叫它什么,这些服务都在颠覆传统的超级计算市场,并将HPC能力带给以前买不起的客户。但这不是万能的,而且绝对不是即插即用的,至少现在还不是。
+
+### HPC服务实践
+
+从最终用户的角度来看,HPC即服务类似于早期大型机时代的批处理模型。 “我们创建一个Ansys批处理文件并将其发送过去,运行它,然后将结果文件取下来并在本地导入它们,” Krawczyk说。
+
+在HPC服务背后,云提供商在其自己的数据中心中运行超级计算基础设施,尽管这不一定意味着当您听到“超级计算机”时你就会看到最先进的硬件。正如IBM OpenPOWER计算技术副总裁Dave Turek解释的那样,HPC服务的核心是“相互互连的服务器集合。您可以调用该虚拟计算基础设施,它能够在您提出问题时,使得许多不同的服务器并行工作来解决问题。”
+[][2]
+
+理论听起来很简单。但都柏林城市大学数字业务教授西奥·林恩(Theo Lynn)表示,要使其在实践中可行,需要解决一些技术问题。普通计算与HPC的区别在于那些互连-高速的,低延时的而且昂贵的-因此需要将这些互连引入云基础设施领域。在HPC服务可行之前,至少需要将存储性能和数据传输也提升到与本地HPC相同的水平。
+
+但是林恩说,一些制度创新相比技术更好的帮助了HPC服务的起飞。特别是,“我们现在看到越来越多的传统HPC应用采用云友好的许可模式-过去是采用这种模式的障碍。”
+
+他说,经济也改变了潜在的客户群。 “云服务提供商通过向那些负担不起传统HPC所需的投资成本的低端HPC买家开放,进一步开放了市场。随着市场的开放,超大规模经济模型变得越来越多,更可行,成本开始下降。”
+
+避免本地资本支出**
+**
+
+HPC服务对有志于传统超级计算长期把持的领域的私营行业客户具有吸引力。这些客户包括严重依赖复杂数学模型的行业,包括麦考密克·史蒂文森(McCormick Stevenson)等国防承包商,以及油气公司,金融服务公司和生物技术公司。都柏林城市大学的Lynn补充说,松耦合的工作负载是一个特别好的用例,这意味着许多早期采用者将其用于3D图像渲染和相关应用。
+
+但是,何时考虑HPC服务而不是本地HPC才有意义?对于德国的模拟烟雾在建筑物中的蔓延和火灾对建筑物结构部件的破坏的hhpberlin公司来说,答案是在它超出了其现有资源时。
+
+Hpberlin公司数值模拟的科学负责人Susanne Kilian说:“几年来,我们一直在运行自己的小型集群,该集群具有多达80个处理器核。” “但是,随着应用复杂性的提高,这种架构(constellation)已经越来越不足以支撑;可用容量并不总是够快速地处理项目。”
+
+她说:“但是,仅仅花钱买一个新的集群并不是一个理想的解决方案:鉴于我们公司的规模和管理环境,强制持续维护该集群(定期进行软件和硬件升级)是不现实的。另外,需要模拟的项目数量会出现很大的波动,因此集群的利用率并不是真正可预测的。通常,使用率很高的阶段与很少使用或不使用的阶段交替出现。”通过转换为HPC服务模式,hhpberlin释放了过剩的容量,并无需支付升级费用。
+
+IBM的Turek解释了不同公司在评估其需求时所经历的计算过程。对于拥有30名员工的生物科学初创公司来说,“您需要计算,但您实在负担不起15%的员工专门从事它。这就像您可能也说过,您不想拥有在职法律代表,因此您也可以通过服务获得它。”但是,对于一家较大的公司而言,最终归结为权衡HPC服务的运营费用与购买内部超级计算机或HPC集群的费用。
+
+到目前为止,这些都是您采用任何云服务时都会遇到的类似的争论。但是,可以HPC市场的某些特点将使得衡量运营支出与资本支出时选择前者。超级计算机不是诸如存储或x86服务器之类的商用硬件;它们非常昂贵,技术进步很快会使其过时。正如麦考密克·史蒂文森(McCormick Stevenson)的克拉维奇(Krawczyk)所说,“这就像买车:只要车一开走,它就会开始贬值。”对于许多公司,尤其是规模较大,灵活性较差的公司,购买超级计算机的过程可能会陷入无望的泥潭。 IBM的Turek说:“您陷入了计划问题,建筑问题,施工问题,培训问题,然后必须执行RFP。您必须得到CIO的支持。您必须与内部客户合作以确保服务的连续性。这是一个非常非常复杂的过程,并没有很多机构有非常出色的执行力。”
+
+一旦您选择了HPC服务的路线后,您会发现您会得到您期望从云服务中得到的许多好处,特别是仅在业务需要时才需付费的能力,从而可以带来资源的高效利用。 Gartner高级总监兼分析师Chirag Dekate表示,当您对高性能计算有短期需求时的突发性负载是推动选择HPC服务的关键用例。
+
+他说:“在制造业中,在产品设计阶段,HPC活动往往会达到很高的峰值。但是,一旦产品设计完成,在其余产品开发周期中,HPC资源的利用率就会降低。” 相比之下,他说:“当您拥有大量长期运行的工作时,云的经济性就会逐渐减弱。”
+
+通过巧妙的系统设计,您可以将这些HPC服务突发活动与您自己的内部常规计算集成在一起。 埃森哲(Accenture)实验室常务董事Teresa Tung举了一个例子:“通过API访问HPC可以无缝地与传统计算混合。在模型构建阶段,传统的AI流水线可能会在高端超级计算机上进行训练,但是最终经过反复按预期运行的训练好的模型将部署在云中的其他服务上,甚至部署在边缘设备上。”
+
+### 它并不适合所有的应用场景 **
+
+**
+
+HPC服务适合批处理和松耦合的场景。这与HPC的普遍缺点有关:数据传输问题。高性能计算本身通常涉及庞大的数据集,而将所有这些信息通过Internet发送到云服务提供商并不容易。IBM的Turek说:“我们与生物技术行业的客户交流,他们每月仅在数据费用上就花费1000万美元。”
+
+钱并不是唯一的潜在问题。已制定的需要使用数据的工作流可能会使您在数据传输所需的时间内无法工作。hhpberlin的Kilian说:“当我们拥有自己的HPC集群时,当然可以随时访问已经产生的仿真结果,从而进行交互式的临时评估。我们目前正努力达到在仿真的任意时刻都可以更高效地,交互地访问和评估云中生成的数据,而无需下载大量的模拟数据。”
+
+Mike Krawczyk提到了另一个绊脚石:合规性问题。国防承包商使用的任何服务都需要遵从(原文是complaint, 应该是笔误)《国际武器交易条例》(ITAR),麦考密克·史蒂文森(McCormick Stevenson)之所以选择Rescale,部分原因是因为这是他们发现的唯一符合的供应商。如今,尽管有更多的公司(使用云服务),但任何希望使用云服务的公司都应该意识到使用其他人的基础设施时所涉及的法律和数据保护问题,而且许多HPC场景的敏感性使得更HPC即服务的这个问题更加突出。
+
+此外,HPC服务所需的IT治理超出了目前的监管范围。例如,您需要跟踪您的软件许可证是否允许云使用 –尤其是专门为本地HPC群集上运行而编写的软件包。通常,您需要跟踪HPC服务的使用方式,它可能是一个诱人的资源,尤其是当您从员工习惯的内部系统过渡到有可用的空闲的HPC能力时。例如,Avanade全球平台高级主管兼Azure平台服务全球负责人Ron Gilpin建议,回调您用于时间不敏感任务的处理核心数量。他说:“如果一项工作只需要用一小时来完成而不需要在十分钟内就完成,那么它可以使用165个处理器而不是1,000个,从而节省了数千美元。”
+
+### 独特的HPC技能**
+
+**
+
+一直以来,采用HPC的最大障碍之一就是其所需的独特的内部技能,而HPC服务并不能使这种障碍消失。Gartner的Dekate表示:“许多CIO将许多工作负载迁移到了云上,他们看到了成本的节约,敏捷性和效率的提升,因此相信在HPC生态中也可以达成类似的效果。一个普遍的误解是,他们可以通过彻底地免去系统管理员,并聘用能解决其HPC工作负载的新的云专家,从而以某种方式优化人力成本。”
+
+“但是HPC并不是一个主流的企业环境。” 他说。“您正在处理通过高带宽,低延迟的网络互联的高端计算节点,以及相当复杂的应用和中间件技术栈。许多情况下,甚至连文件系统层也是HPC环境所独有的。没有对应的技能可能会破坏稳定性。”
+
+但是超级计算技能的供给却在减少,Dekate将其称为劳动力“灰化”,这是因为一代开发人员将目光投向了新兴的初创公司,而不是学术界或使用HPC的更老套的公司。因此,HPC服务供应商正在尽其所能地弥补差距。 IBM的Turek表示,许多HPC老手将总是想运行他们自己精心调整过的代码,将需要专门的调试器和其他工具来帮助他们在云上实现这一目标。但是,即使是HPC新手也可以调用供应商构建的代码库,以利用超级计算的并行处理能力。第三方软件提供商出售的交钥匙软件包可以减少HPC的许多复杂性。
+
+埃森哲的Tung表示,该行业需要进一步加大投入才能真正繁荣。她说:“HPCaaS已经创建了具有重大影响力的新功能,但还需要做的是使它易于被数据科学家,企业架构师或软件开发人员使用。这包括易用的API,文档和示例代码。它包括用户支持来解答问题。仅仅提供API是不够的,API需要适合特定的用途。对于数据科学家而言,这可能是以python形式提供,并容易更换她已经在使用的框架。其价值来自使这些用户最综只有在使用新功能时才能够改进效率和性能。” 如果供应商能够做到这一点,那么HPC服务才能真正将超级计算带给大众。
+
+加入[Facebook][3]和[LinkedIn][4]上的Network World社区,探讨最前沿的话题。
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://www.networkworld.com/article/3534725/the-ins-and-outs-of-high-performance-computing-as-a-service.html
+
+作者:[Josh Fruhlinger][a]
+选题:[lujun9972][b]
+译者:[messon007](https://github.com/messon007)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]: https://www.networkworld.com/author/Josh-Fruhlinger/
+[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
+[1]: https://www.networkworld.com/article/3236875/embargo-10-of-the-worlds-fastest-supercomputers.html
+[2]: https://www.networkworld.com/blog/itaas-and-the-corporate-storage-technology/?utm_source=IDG&utm_medium=promotions&utm_campaign=HPE22140&utm_content=sidebar (ITAAS and Corporate Storage Strategy)
+[3]: https://www.facebook.com/NetworkWorld/
+[4]: https://www.linkedin.com/company/network-world
diff --git a/translated/tech/20180612 Systemd Services- Reacting to Change.md b/translated/tech/20180612 Systemd Services- Reacting to Change.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..22c176ee80
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20180612 Systemd Services- Reacting to Change.md
@@ -0,0 +1,273 @@
+Systemd服务:响应变更
+======
+
+
+
+[我有一个这样的电脑棒][1](图1),并将其用作通用服务器。它很小且安静,由于它是基于x86架构,因此我为我的打印机安装驱动没有任何问题,而且这就是它大多数时候干的事:与客厅的共享打印机和扫描仪通信。
+
+![ComputeStick][3]
+
+一个英特尔电脑棒。欧元硬币大小。
+
+[Used with permission][4]
+
+大多数时候,它都闲着,尤其是当我们外出时,因此我认为用它作监视系统是个好主意。该设备没有自带的摄像头,也不需要一直监视。我也不想手动启动图像捕获,因为这样就意味着在出门前必须通过SSH登录,并在shell中编写命令来启动该进程。
+
+因此,我以为应该这么做:抓住USB摄像头,然后只需插入它即可自动启动监视系统。如果Stick重启后发现连接了摄像头也启动监视系统就更加分了。
+
+在先前的文章中,我们看到[systemd服务可以手动启动或停止][5]或[在满足某些条件时][6]。这些条件不限于操作系统在启动或关机时序中达到某种状态,还可以在您插入新硬件或文件系统发生变化时进行。您可以通过将Udev规则与systemd服务结合起来实现。
+
+### 有Udev(支持)的热插拔
+
+Udev规则位于 _/etc/udev/rules_ 目录中,通常是由导致一个 _动作(action)_ 的 _条件(conditions)_ 和 _赋值(assignments)_ 的单行语句来描述。
+
+有点神秘。让我们再试一次:
+
+通常,在Udev规则中,您告诉systemd当连接一个设备时需要查看什么信息。例如,您可能想检查刚插入的设备的品牌和型号是否与您让Udev等待的设备的品牌和型号相对应。这些就是前面提到的条件。
+
+然后,您可能想要更改一些内容,以便以后可以轻松使用该设备。例如,更改设备的读写权限:如果插入USB打印机,您将希望用户能够从打印机读取信息(用户的打印应用程序需要知道其模型,制造商,以及是否准备好接受打印作业)并向其写入内容,即发送要打印的内容。更改设备的读写权限是通过您之前阅读的 _赋值(assignments)_ 之一完成的。
+
+最后,您可能希望系统在满足上述条件时执行某些动作,例如在插入某个外接硬盘时启动备份程序以复制重要文件。这就是上面提到的 _动作(action)_ 的例子。
+
+了解这些之后, 来看看以下几点:
+
+```
+ACTION=="add", SUBSYSTEM=="video4linux", ATTRS{idVendor}=="03f0", ATTRS{idProduct}=="e207",
+SYMLINK+="mywebcam", TAG+="systemd", MODE="0666", ENV{SYSTEMD_WANTS}="webcam.service"
+```
+
+规则的第一部分,
+
+```
+ACTION=="add", SUBSYSTEM=="video4linux", ATTRS{idVendor}=="03f0",
+ATTRS{idProduct}=="e207" [etc... ]
+```
+
+表明了执行您想让系统执行的其他动作之前设备必须满足的条件。设备必须被添加到(`ACTION=="add"`)机器上,并且必须添加到 `video4linux` 子系统中。为了确保仅在插入正确的设备时才应用该规则,您必须确保Udev正确识别设备的制造商(`ATTRS{idVendor}=="03f0"`)和型号(`ATTRS{idProduct}=="e207"`)。
+
+在本例中,我们讨论的是这个设备(图2):
+
+![webcam][8]
+
+这个试验使用的是HP的摄像头。
+
+[Used with permission][4]
+
+注意怎样用 `==` 来表示这是一个逻辑操作。您应该像这样阅读上面的简要规则:
+
+```
+如果添加了一个设备并且该设备由video4linux子系统控制
+而且该设备的制造商是03f0,型号是e207,那么...
+```
+
+但是,您从哪里获取的这些信息? 您在哪里找到触发事件的动作,制造商,模型等等?您可能必须使用多个来源。您可以通过将摄像头插入机器并运行 `lsusb` 来获得 `IdVendor` 和 `idProduct` :
+
+```
+lsusb
+Bus 002 Device 002: ID 8087:0024 Intel Corp. Integrated Rate Matching Hub
+Bus 002 Device 001: ID 1d6b:0002 Linux Foundation 2.0 root hub
+Bus 004 Device 001: ID 1d6b:0003 Linux Foundation 3.0 root hub
+Bus 003 Device 003: ID 03f0:e207 Hewlett-Packard
+Bus 003 Device 001: ID 1d6b:0002 Linux Foundation 2.0 root hub
+Bus 001 Device 003: ID 04f2:b1bb Chicony Electronics Co., Ltd
+Bus 001 Device 002: ID 8087:0024 Intel Corp. Integrated Rate Matching Hub
+Bus 001 Device 001: ID 1d6b:0002 Linux Foundation 2.0 root hub
+```
+
+我用的摄像头是HP的,您在上面的列表中只能看到一个HP设备。 `ID` 告诉了制造商和型号,它们以冒号( `:` )分隔。如果您有同一制造商的多个设备,不确定哪个是哪个设备,请拔下摄像头,再次运行 `lsusb` , 看看少了什么。
+
+或者...
+
+拔下摄像头,等待几秒钟,运行命令 `udevadmin monitor --environment` ,然后重新插入摄像头。当您使用的是HP摄像头时,您将看到:
+
+```
+udevadmin monitor --environment
+UDEV [35776.495221] add /devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:1c.3/0000:04:00.0
+ /usb3/3-1/3-1:1.0/input/input21/event11 (input)
+.MM_USBIFNUM=00
+ACTION=add
+BACKSPACE=guess
+DEVLINKS=/dev/input/by-path/pci-0000:04:00.0-usb-0:1:1.0-event
+ /dev/input/by-id/usb-Hewlett_Packard_HP_Webcam_HD_2300-event-if00
+DEVNAME=/dev/input/event11
+DEVPATH=/devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:1c.3/0000:04:00.0/
+ usb3/3-1/3-1:1.0/input/input21/event11
+ID_BUS=usb
+ID_INPUT=1
+ID_INPUT_KEY=1
+ID_MODEL=HP_Webcam_HD_2300
+ID_MODEL_ENC=HP\x20Webcam\x20HD\x202300
+ID_MODEL_ID=e207
+ID_PATH=pci-0000:04:00.0-usb-0:1:1.0
+ID_PATH_TAG=pci-0000_04_00_0-usb-0_1_1_0
+ID_REVISION=1020
+ID_SERIAL=Hewlett_Packard_HP_Webcam_HD_2300
+ID_TYPE=video
+ID_USB_DRIVER=uvcvideo
+ID_USB_INTERFACES=:0e0100:0e0200:010100:010200:030000:
+ID_USB_INTERFACE_NUM=00
+ID_VENDOR=Hewlett_Packard
+ID_VENDOR_ENC=Hewlett\x20Packard
+ID_VENDOR_ID=03f0
+LIBINPUT_DEVICE_GROUP=3/3f0/e207:usb-0000:04:00.0-1/button
+MAJOR=13
+MINOR=75
+SEQNUM=3162
+SUBSYSTEM=input
+USEC_INITIALIZED=35776495065
+XKBLAYOUT=es
+XKBMODEL=pc105
+XKBOPTIONS=
+XKBVARIANT=
+```
+
+可能看起来有很多信息要处理,但是,看一下这个:列表前面的 `ACTION` 字段, 它告诉您刚刚发生了什么事件,即一个设备被添加到系统中。您还可以在几行中看到设备名称的拼写,因此可以非常确定它就是您要找的设备。输出里还显示了制造商的ID(`ID_VENDOR_ID = 03f0`)和型号(`ID_VENDOR_ID = 03f0`)。
+
+这为您提供了规则条件部分需要的四个值中的三个。您可能也会想到它还给了您第四个,因为还有一行这样写道:
+
+```
+SUBSYSTEM=input
+```
+
+小心!尽管USB摄像头确实是提供输入的设备(键盘和鼠标也是),但它也属于 _usb_ 子系统和其他几个子系统。这意味着您的摄像头被添加到了多个子系统,并且看起来像多个设备。如果您选择了错误的子系统,那么您的规则可能无法按您期望的那样工作,或者根本无法工作。
+
+因此,您必须检查的第三件事是摄像头添加到的所有子系统,并选择正确的那个。为此,请再次拔下摄像头,然后运行:
+
+```
+ls /dev/video*
+```
+
+这将向您显示连接到本机的所有视频设备。如果您使用的是笔记本,大多数笔记本都带有内置摄像头,它可能会显示为 `/dev/video0` 。重新插入摄像头,然后再次运行 `ls /dev/video*` 。
+
+现在,您应该看到多一个视频设备(可能是`/dev/video1`)。
+
+现在,您可以通过运行`udevadm info -a /dev/video1`找出它所属的所有子系统:
+
+```
+udevadm info -a /dev/video1
+
+Udevadm info starts with the device specified by the devpath and then
+walks up the chain of parent devices. It prints for every device
+found, all possible attributes in the udev rules key format.
+A rule to match, can be composed by the attributes of the device
+and the attributes from one single parent device.
+
+ looking at device '/devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:1c.3/0000:04:00.0
+ /usb3/3-1/3-1:1.0/video4linux/video1':
+ KERNEL=="video1"
+ SUBSYSTEM=="video4linux"
+ DRIVER==""
+ ATTR{dev_debug}=="0"
+ ATTR{index}=="0"
+ ATTR{name}=="HP Webcam HD 2300: HP Webcam HD"
+
+[etc...]
+```
+
+输出持续了一段时间,但是您感兴趣的只是开始:`SUBSYSTEM =="video4linux"`。您可以将这行按文本复制并粘贴到规则中。输出的其余部分(为简便起见未显示)为您提供了更多的块,例如制造商和模型ID,您也可以以同样的格式复制并粘贴到规则中。
+
+现在,您有了识别设备的方式并明确了什么事件应该触发该动作,该对设备进行修改了。
+
+规则的下一部分,`SYMLINK+="mywebcam", TAG+="systemd", MODE="0666"`告诉Udev做三件事:首先,您要创建设备的符号链接(例如 _/dev/video1_ 到 _/dev/mywebcam_ 。这是因为您无法预测系统默认情况下会把那个设备叫什么。当您拥有内置摄像头并热插拔一个新的时,内置摄像头通常为 _/dev/video0_ ,而外部摄像头通常为 _/dev/video1_ 。但是,如果您在插入外部USB摄像头的情况下重启计算机,则可能会相反,内部摄像头可能会变成 _/dev/video1_ ,而外部摄像头会变成 _/dev/video0_ 。这想告诉您的是,尽管您的图像捕获脚本(稍后将看到)总是需要指向外部摄像头设备,但是您不能依赖它是 _/dev/video0_ 或 _/dev/video1_ 。为了解决这个问题,您告诉Udev创建一个符号链接,该链接在设备被添加到 _video4linux_ 子系统的那一刻起就不会再变,您将使您的脚本指向该链接。
+
+您要做的第二件事是将 `"systemd"` 添加到与此规则关联的Udev标记列表中。这告诉Udev,该规则触发的动作将由systemd管理,即它将是某种systemd服务。
+
+注意在两种情况下该如何使用 `+=` 运算符。这会将值添加到列表中,这意味着您可以向 `SYMLINK` 和 `TAG` 添加多个值。
+
+另一方面,`MODE` 值只能包含一个值(因此,您可以使用简单的 `=` 赋值运算符)。`MODE` 的作用是告诉Udev谁可以读或写该设备。如果您熟悉 `chmod`(您读到此文, 应该会熟悉),您就也会熟悉[如何用数字表示权限][9]。这就是它的含义: `0666` 的含义是 “ _向所有人授予对设备的读写权限_ ”。
+
+最后, `ENV{SYSTEMD_WANTS}="webcam.service"` 告诉Udev要运行什么systemd服务。
+
+将此规则保存到 _/etc/udev/rules.d_ 目录名为 _90-webcam.rules_ (或类似的名称)的文件中,您可以通过重启机器或运行以下命令来加载它:
+
+```
+sudo udevadm control --reload-rules && udevadm trigger
+```
+
+## 最后描述服务
+
+Udev规则触发的服务非常简单:
+```
+# webcam.service
+
+[Service]
+Type=simple
+ExecStart=/home/[user name]/bin/checkimage.sh
+```
+
+基本上,它只是运行存储在您个人 _bin/_ 中的 _checkimage.sh_ 脚本并将其放到后台。 [这是您在先前的部分中看过的内容][5]。 它看起来似乎很小,但那只是因为它是被Udev规则调用的,您刚刚创建了一种特殊的systemd单元,称为 _device_ 单元。 恭喜。
+
+至于 _webcam.service_ 调用的 _checkimage.sh_ 脚本,有几种方法从摄像头抓取图像并将其与前一个图像进行比较以检查变化(这是 _checkimage.sh_ 所做的事),但这是我的方法:
+
+```
+#!/bin/bash
+# This is the checkimage.sh script
+
+mplayer -vo png -frames 1 tv:// -tv driver=v4l2:width=640:height=480:device=
+ /dev/mywebcam &>/dev/null
+mv 00000001.png /home/[user name]/monitor/monitor.png
+
+while true
+do
+ mplayer -vo png -frames 1 tv:// -tv driver=v4l2:width=640:height=480:device=/dev/mywebcam &>/dev/null
+ mv 00000001.png /home/[user name]/monitor/temp.png
+
+ imagediff=`compare -metric mae /home/[user name]/monitor/monitor.png /home/[user name]
+ /monitor/temp.png /home/[user name]/monitor/diff.png 2>&1 > /dev/null | cut -f 1 -d " "`
+ if [ `echo "$imagediff > 700.0" | bc` -eq 1 ]
+ then
+ mv /home/[user name]/monitor/temp.png /home/[user name]/monitor/monitor.png
+ fi
+
+ sleep 0.5
+done
+```
+
+首先使用[MPlayer][10]从摄像头抓取一帧(_00000001.png_)。注意,我们怎样将 `mplayer` 指向Udev规则中创建的 `mywebcam` 符号链接,而不是指向 `video0` 或 `video1` 。然后,将图像传输到主目录中的 _monitor/_ 目录。然后执行一个无限循环,一次又一次地执行相同的操作,但还使用了[Image Magick的_compare_工具][11]来查看最后捕获的图像与 _monitor/_ 目录中已有的图像之间是否存在差异。
+
+如果图像不同,则表示摄像头的镜框里某些东西动了。该脚本将新图像覆盖原始图像,并继续比较以等待更多变动。
+
+### 插线
+
+所有东西准备好后,当您插入摄像头后,您的Udev规则将被触发并启动 _webcam.service_ 。 _webcam.service_ 将在后台执行 _checkimage.sh_ ,而 _checkimage.sh_ 将开始每半秒拍一次照。您会感觉到,因为摄像头的LED在每次拍照时将开始闪。
+
+与往常一样,如果出现问题,请运行
+
+```
+systemctl status webcam.service
+```
+
+检查您的服务和脚本正在做什么。
+
+### 接下来
+
+您可能想知道:为什么要覆盖原始图像? 当然,系统检测到任何动静,您都想知道发生了什么,对吗?您是对的,但是如您在下一部分中将看到的那样,将它们保持原样,并使用另一种类型的systemd单元处理图像将更好,更清晰和更简单。
+
+请稍等。
+
+通过Linux基金会和edX的免费["Linux简介"][12]课程了解有关Linux的更多信息。
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://www.linux.com/blog/intro-to-linux/2018/6/systemd-services-reacting-change
+
+作者:[Paul Brown][a]
+选题:[lujun9972][b]
+译者:[messon007](https://github.com/messon007)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]: https://www.linux.com/users/bro66
+[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
+[1]: https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/products/boards-kits/compute-stick/stk1a32sc.html
+[2]: https://www.linux.com/files/images/fig01png
+[3]: https://www.linux.com/sites/lcom/files/styles/floated_images/public/fig01.png?itok=cfEHN5f1 (ComputeStick)
+[4]: https://www.linux.com/licenses/category/used-permission
+[5]: https://www.linux.com/blog/learn/intro-to-linux/2018/5/writing-systemd-services-fun-and-profit
+[6]: https://www.linux.com/blog/learn/2018/5/systemd-services-beyond-starting-and-stopping
+[7]: https://www.linux.com/files/images/fig02png
+[8]: https://www.linux.com/sites/lcom/files/styles/floated_images/public/fig02.png?itok=esFv4BdM (webcam)
+[9]: https://chmod-calculator.com/
+[10]: https://mplayerhq.hu/design7/news.html
+[11]: https://www.imagemagick.org/script/compare.php
+[12]: https://training.linuxfoundation.org/linux-courses/system-administration-training/introduction-to-linux
diff --git a/translated/tech/20190915 How to Configure SFTP Server with Chroot in Debian 10.md b/translated/tech/20190915 How to Configure SFTP Server with Chroot in Debian 10.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..a30b6ee817
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20190915 How to Configure SFTP Server with Chroot in Debian 10.md
@@ -0,0 +1,197 @@
+[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
+[#]: translator: (robsean)
+[#]: reviewer: ( )
+[#]: publisher: ( )
+[#]: url: ( )
+[#]: subject: (How to Configure SFTP Server with Chroot in Debian 10)
+[#]: via: (https://www.linuxtechi.com/configure-sftp-chroot-debian10/)
+[#]: author: (Pradeep Kumar https://www.linuxtechi.com/author/pradeep/)
+
+如何在 Debian 10 中使用 Chroot 配置 SFTP 服务
+======
+
+**SFTP** 代表安全文件传输协议 / SSH 文件传输协议,它是最常用的一个方法,用于通过ssh将文件从本地系统安全地传输到远程服务器,反之亦然。sftp 的主要优点是,除 ‘**openssh-server**’ 之外,我们不需要安装任何额外的软件包,在大多数的 Linux 发行版中,‘openssh-server’ 软件包是默认安装的一部分。sftp 的另外一个好处是,我们可以允许用户使用 sftp ,而不允许使用 ssh 。
+
+[![配置-sftp-debian10][1]][2]
+
+当前 Debian 10 ,代号‘Buster’,已经发布,在这篇文章中,我们将演示如何在 Debian 10 系统中使用 Chroot ‘Jail’ 类似的环境配置 sftp 。在这里,Chroot Jail 类似环境意味着,用户不能超出各自的 home 目录,或者用户不能从各自的 home 目录更改目录。下面实验的详细情况:
+
+ * OS = Debian 10
+ * IP 地址 = 192.168.56.151
+
+
+
+让我们跳转到 SFTP 配置步骤,
+
+### 步骤:1) 为 sftp 使用 groupadd 命令创建一个组
+
+打开终端,使用下面的 groupadd 命令创建一个名为的“**sftp_users**”组,
+
+```
+root@linuxtechi:~# groupadd sftp_users
+```
+
+### 步骤:2) 添加用户到组 ‘sftp_users’ 并设置权限
+
+假设你想创建新的用户,并且想添加该用户到 ‘sftp_users’ 组中,那么运行下面的命令,
+
+**语法:** # useradd -m -G sftp_users
+
+让我们假设用户名是 ’Jonathan’
+
+```
+root@linuxtechi:~# useradd -m -G sftp_users jonathan
+```
+
+使用下面的 chpasswd 命令设置密码,
+
+```
+root@linuxtechi:~# echo "jonathan:" | chpasswd
+```
+
+假设你想添加现有的用户到 ‘sftp_users’ 组中,那么运行下面的 usermod 命令,让我们假设已经存在的用户名称是 ‘chris’
+
+```
+root@linuxtechi:~# usermod -G sftp_users chris
+```
+
+现在设置用户所需的权限,
+
+```
+root@linuxtechi:~# chown root /home/jonathan /home/chris/
+```
+
+在各用户的 home 目录中都创建一个上传目录,并设置正确地所有权,
+
+```
+root@linuxtechi:~# mkdir /home/jonathan/upload
+root@linuxtechi:~# mkdir /home/chris/upload
+root@linuxtechi:~# chown jonathan /home/jonathan/upload
+root@linuxtechi:~# chown chris /home/chris/upload
+```
+
+**注意:** 像 Jonathan 和 Chris 之类的用户可以从他们的本地系统上传文件和目录。
+
+### 步骤:3) 编辑 sftp 配置文件 (/etc/ssh/sshd_config)
+
+正如我们已经陈述的,sftp 操作是通过 ssh 完成的,所以它的配置文件是 “**/etc/ssh/sshd_config**“, 在做任何更改前,我建议首先备份文件,然后再编辑该文件,接下来添加下面的内容,
+
+```
+root@linuxtechi:~# cp /etc/ssh/sshd_config /etc/ssh/sshd_config-org
+root@linuxtechi:~# vim /etc/ssh/sshd_config
+………
+#Subsystem sftp /usr/lib/openssh/sftp-server
+Subsystem sftp internal-sftp
+
+Match Group sftp_users
+ X11Forwarding no
+ AllowTcpForwarding no
+ ChrootDirectory %h
+ ForceCommand internal-sftp
+…………
+```
+
+保存并退出文件。
+
+为使上述更改生效,使用下面的 systemctl 命令来重新启动 ssh 服务
+
+```
+root@linuxtechi:~# systemctl restart sshd
+```
+
+在上面的 ‘sshd_config’ 文件中,我们已经注释掉了以 “Subsystem”开头的行,并添加了新的条目 “Subsystem sftp internal-sftp” 和新的行,像,
+
+“**Match Group sftp_users”** –> 它意味着如果用户是 ‘sftp_users’ 组中的一员,那么将应用下面提到的规则到这个条目。
+
+“**ChrootDierctory %h**” –> 它意味着用户只能在他们自己各自的 home 目录中更改目录,而不能超出他们各自的 home 目录。或者换句话说,我们可以说用户是不允许更改目录的。他们将在他们的目录中获得 jai 类似环境,并且不能访问其他用户的目录和系统的目录。
+
+“**ForceCommand internal-sftp**” –> 它意味着用户仅被限制到 sftp 命令。
+
+### 步骤:4) 测试和验证 sftp
+
+登录到你的 sftp 服务器的同一个网络上的任何其它的 Linux 系统,然后通过我们在 ‘sftp_users’ 组中映射的用户来尝试 ssh sftp 服务。
+
+```
+[root@linuxtechi ~]# ssh root@linuxtechi
+root@linuxtechi's password:
+Write failed: Broken pipe
+[root@linuxtechi ~]# ssh root@linuxtechi
+root@linuxtechi's password:
+Write failed: Broken pipe
+[root@linuxtechi ~]#
+```
+
+以上操作证实用户不允许 SSH ,现在使用下面的命令尝试 sftp ,
+
+```
+[root@linuxtechi ~]# sftp root@linuxtechi
+root@linuxtechi's password:
+Connected to 192.168.56.151.
+sftp> ls -l
+drwxr-xr-x 2 root 1001 4096 Sep 14 07:52 debian10-pkgs
+-rw-r--r-- 1 root 1001 155 Sep 14 07:52 devops-actions.txt
+drwxr-xr-x 2 1001 1002 4096 Sep 14 08:29 upload
+```
+
+让我们使用 sftp ‘**get**‘ 命令来尝试下载一个文件
+
+```
+sftp> get devops-actions.txt
+Fetching /devops-actions.txt to devops-actions.txt
+/devops-actions.txt 100% 155 0.2KB/s 00:00
+sftp>
+sftp> cd /etc
+Couldn't stat remote file: No such file or directory
+sftp> cd /root
+Couldn't stat remote file: No such file or directory
+sftp>
+```
+
+上面的输出证实我们能从我们的 sftp 服务器下载文件到本地机器,除此之外,我们也必需测试用户不能更改目录。
+
+让我们在 **upload**”目录下尝试上传一个文件,
+
+```
+sftp> cd upload/
+sftp> put metricbeat-7.3.1-amd64.deb
+Uploading metricbeat-7.3.1-amd64.deb to /upload/metricbeat-7.3.1-amd64.deb
+metricbeat-7.3.1-amd64.deb 100% 38MB 38.4MB/s 00:01
+sftp> ls -l
+-rw-r--r-- 1 1001 1002 40275654 Sep 14 09:18 metricbeat-7.3.1-amd64.deb
+sftp>
+```
+
+这证实我们已经成功地从我们的本地系统上传一个文件到 sftp 服务中。
+
+现在使用 winscp 工具来测试 SFTP 服务,输入 sftp 服务器 ip 地址和用户的凭证,
+
+[![Winscp-sftp-debian10][1]][3]
+
+在 Login 上单击,然后尝试下载和上传文件
+
+[![下载-文件-winscp-debian10-sftp][1]][4]
+
+现在,在 upload 文件夹中尝试上传文件,
+
+[![使用-winscp-Debian10-sftp-上传-文件][1]][5]
+
+上面的窗口证实上传是完好地工作的,这就是这篇文章的全部。如果这些步骤能帮助你在 Debian 10 中使用 chroot 环境配置 SFTP 服务器s,那么请分享你的反馈和评论。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://www.linuxtechi.com/configure-sftp-chroot-debian10/
+
+作者:[Pradeep Kumar][a]
+选题:[lujun9972][b]
+译者:[robsean](https://github.com/robsean)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]: https://www.linuxtechi.com/author/pradeep/
+[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
+[1]: data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7
+[2]: https://www.linuxtechi.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/09/Configure-sftp-debian10.jpg
+[3]: https://www.linuxtechi.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/09/Winscp-sftp-debian10.jpg
+[4]: https://www.linuxtechi.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/09/Download-file-winscp-debian10-sftp.jpg
+[5]: https://www.linuxtechi.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/09/Upload-File-using-winscp-Debian10-sftp.jpg
diff --git a/translated/tech/20200407 How to avoid man-in-the-middle cyber attacks.md b/translated/tech/20200407 How to avoid man-in-the-middle cyber attacks.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..7ccce7c3bd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20200407 How to avoid man-in-the-middle cyber attacks.md
@@ -0,0 +1,84 @@
+[#]: collector: "lujun9972"
+[#]: translator: " "
+[#]: reviewer: " "
+[#]: publisher: " "
+[#]: url: " "
+[#]: subject: "How to avoid man-in-the-middle cyber attacks"
+[#]: via: "https://opensource.com/article/20/4/mitm-attacks"
+[#]: author: "Jackie Lam https://opensource.com/users/beenverified"
+
+如何避免中间人攻击
+======
+
+首先搞明白到底什么是中间人攻击,才能避免成为此类高科技窃听的受害者。
+
+![Security monster][1]
+
+当你使用电脑发送数据或与某人在线通话的时候,你一定采取了某种程度的安全隐私手段。
+
+但如果有第三方在你不知情的情况下窃听,甚至冒充某个你信任的商业伙伴窃取破坏性的信息呢?你的私人数据就这样被放在了危险分子的手中。
+
+这就是臭名昭著的中间人攻击。
+
+### 到底什么是中间人攻击?
+
+黑客潜入到你与受害者或是某个设备间的通信过程中,窃取敏感信息——多数是身份信息——进而从事各种违法行为的过程,就是一次中间人攻击。Scamicide公司创始人Steve J. J. Weisman介绍说:
+
+“中间人攻击也可以发生在受害者与某个合法app或网页中间。当受害者以为自己面对的是正常app或网页时,其实Ta 正在与一个仿冒的app或网页互动,将自己的敏感信息透露给不法分子。”
+
+中间人攻击诞生于1980年代,是最古老的网络攻击形式之一。但它却更为常见。Weisman解释道,发生中间人攻击的场景有很多种:
+
+ * **攻陷一个未有效加密的WiFi路由器**:该场景多见于人们使用公共WiFi的时候。“虽然家用路由器也很脆弱,但黑客攻击公共WiFi网络的情况更为常见。”Weisman说,“黑客的目标就是从毫无戒心的人们那里窃取在线银行账户这样的敏感信息。”
+ * **攻陷银行、金融顾问等机构的电子邮件账户**:“一旦黑客攻陷了这些电子邮件系统,他们就会冒充银行或此类公司给受害者发邮件”,Weisman说,”他们以紧急情况的名义索要个人信息,诸如用户名和密码。受害者很容易被诱骗交出这些信息。“
+ * **发送钓鱼邮件**:窃贼们还可能冒充成与受害者有合作关系的公司,向其索要个人信息。”在多个案例中,钓鱼邮件会引导受害者访问一个伪造的网页,这个伪造的网页看起来就和受害者常常访问的合法公司网页一模一样。“Weisman说道。
+ * **在合法网页中嵌入恶意代码**:攻击者还会把恶意代码——通常是JavaScript——嵌入到一个合法的网页中。”当受害者加载这个合法网页时,恶意代码首先按兵不动,直到用户输入账户登录或是信用卡信息时,恶意代码就会复制这些信息并将其发送至攻击者的服务器。“网络安全专家Nicholas McBride介绍说。
+
+### 有哪些中间人攻击的著名案例?
+
+联想作为主流的计算机制造厂商,在2014到2015年售卖的消费级笔记本电脑中预装了一款叫做 VisualDiscovery 的软件,拦截用户的网页浏览行为。当用户的鼠标在某个产品页面经过时,这款软件就会弹出一个来自合作伙伴的类似产品的广告。
+
+这起中间人攻击事件的关键在于:VisualDiscovery 拥有访问用户所有私人数据的权限,包括身份证号、金融交易信息、医疗信息、登录名和密码等等。所有这些访问行为都是在用户不知情和未获得授权的情况下进行的。联邦交易委员会(FTC)认定此次事件为欺诈与不公平竞争。2019年,联想同意为此支付8300万美元的集体诉讼罚款。
+
+### 我如何才能避免遭受中间人攻击?
+
+ * **避免使用公共WiFi:**Weisman建议,从来都不要使用公开的WiFi进行金融交易,除非你安装了可靠的VPN客户端并连接至可信任的VPN服务器。通过VPN连接,你的通信是加密的,信息也就不会失窃。
+ * **时刻注意:**对要求你更新密码或是提供用户名等私人信息的邮件或文本消息要时刻保持警惕。这些手段很可能被用来窃取你的身份信息。
+
+如果不确定收到的邮件来自于确切哪一方,你可以使用诸如电话反查或是邮件反查等工具。通过电话反查,你可以找出未知发件人的更多身份信息。通过邮件反查,你可以尝试确定谁给你发来了这条消息。
+
+通常来讲,如果发现某些方面确实有问题,你可以听从公司中某个你认识或是信任的人的意见。或者,你也可以去你的银行、学校或其他某个组织,当面寻求他们的帮助。总之,重要的账户信息绝对不要透露给不认识的“技术人员”。
+
+ * **不要点击邮件中的链接:**如果有人给你发了一封邮件,说你需要登录某个账户,不要点击邮件中的链接。相反,要通过平常习惯的方式自行去访问,并留意是否有告警信息。如果在账户设置中没有看到告警信息,给客服打电话的时候也_不要_联系邮件中留的电话,而是站点页面中的联系人信息。
+ * **安装可靠的安全软件:**如果你使用的是Windows操作系统,安装开源的杀毒软件,如[ClamAV][2]。如果使用的是其他平台,要保持你的软件安装有最新的安全补丁。
+ * **认真对待告警信息:**如果你正在访问的页面以HTTPS开头,浏览器可能会出现一则告警信息。例如,站点证书的域名与你尝试访问的站点域名不相匹配。千万不要忽视此类告警信息。听从告警建议,迅速关掉页面。确认域名没有输入错误的情况下,如果情况依旧,要立刻联系站点所有者。
+ * **使用广告屏蔽软件:**弹窗广告(也叫广告软件攻击)可被用于窃取个人信息,因此你还可以使用广告屏蔽类软件。对个人用户来说,中间人攻击其实是很难防范的,因为它被设计出来的时候,就是为了让受害者始终蒙在鼓里,意识不到任何异常。有一款不错的开源广告屏蔽软件叫 [uBlock origin][4]。可以同时支持Firefox和Chromium(以及所有基于Chromium的浏览器,例如Chrome、Brave、Vivaldi、Edge等),甚至还支持Safari。
+
+### 保持警惕
+
+要时刻记住,你并不需要立刻就点击某些链接,你也并不需要跟随某个陌生人的建议,无论这些信息看起来有多么紧急。互联网始终都在。你大可以先离开电脑,去证实一下这些人的真实身份,看看这些”无比紧急“的页面到底是真是假。
+
+尽管任何人都可能遭遇中间人攻击,只要弄明白何为中间人攻击,理解中间人攻击如何发生,并采取有效的防范措施,就可以保护自己避免成为其受害者。
+
+* * *
+
+_This article was originally published on [BeenVerified.com][5] under a [CC BY-SA 2.0][6] license._
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://opensource.com/article/20/4/mitm-attacks
+
+作者:[Jackie Lam][a]
+选题:[lujun9972][b]
+译者:[tinyeyeser](https://github.com/tinyeyeser)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]: https://opensource.com/users/beenverified
+[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
+[1]: https://opensource.com/sites/default/files/styles/image-full-size/public/lead-images/security_password_chaos_engineer_monster.png?itok=J31aRccu "Security monster"
+[2]: https://www.clamav.net
+[3]: https://opensource.com/article/20/1/stop-typosquatting-attacks
+[4]: https://github.com/gorhill/uBlock
+[5]: https://www.beenverified.com/crime/what-is-a-man-in-the-middle-attack/
+[6]: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.0/
diff --git a/translated/tech/20200416 Learning to love systemd.md b/translated/tech/20200416 Learning to love systemd.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..34bc8ea314
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20200416 Learning to love systemd.md
@@ -0,0 +1,325 @@
+[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
+[#]: translator: (messon007)
+[#]: reviewer: ( )
+[#]: publisher: ( )
+[#]: url: ( )
+[#]: subject: (Learning to love systemd)
+[#]: via: (https://opensource.com/article/20/4/systemd)
+[#]: author: (David Both https://opensource.com/users/dboth)
+
+学会爱上systemd
+======
+
+systemd是所有进程的源头,负责将Linux主机启动到可以做生产性任务的状态。
+![Penguin driving a car with a yellow background][1]
+
+systemd(是的,全小写,即使在句子开头也是小写),是init和SystemV init脚本的现代替代者。它还有更多功能。
+
+当我想到init和SystemV时,像大多数系统管理员一样,我想到的是Linux的启动和关闭,而没有太多其他的,例如在服务启动和运行后对其进行管理。像init一样,systemd是所有进程的源头,它负责使Linux主机启动到可以做生产性任务的状态。 systemd设定的一些功能比老的init要广泛得多,它要管理正在运行的Linux主机的许多方面,包括挂载文件系统,管理硬件,处理定时器以及启动和管理生产性主机所需的系统服务。
+
+本系列文章是基于我的部分三期Linux培训课程[_使用和管理Linux:从零开始进行学习系统管理_][2]的摘录,探讨了systemd在启动和启动完成后的功能。
+
+### Linux启动
+
+Linux主机从关机状态到运行状态的完整启动过程很复杂,但它是开放的并且是可知的。在详细介绍之前,我将简要介绍一下从主机硬件被上电到系统准备好用户登录(的过程)。大多数时候,“启动过程”被作为单个概念来讨论,但这是不准确的。实际上,完整的引导和启动过程包含三个主要部分:
+
+ * **硬件引导:** 初始化系统硬件
+ * **Linux引导:** 加载Linux内核和systemd
+ * **Linux启动:** systemd启动, 为生产工作做准备
+
+
+Linux启动阶段在内核加载了init或systemd(取决于具体发行版使用的是旧的方式还是还是新的方式)之后开始。init和systemd程序启动并管理所有其他进程,他们在各自的系统上都被称为“所有进程之母”。
+
+将硬件引导与Linux引导及Linux启动区分开,并明确定义它们之间的分界点是很重要的。理解他们的差异以及他们每一个在使Linux系统进入生产准备状态所起的作用,才能够管理这些进程并更好地确定大部分人所谓的“启动”问题出在哪里。
+
+启动过程按照三步引导流程使Linux计算机进入可进行生产工作的状态。当内核将主机的控制权转移到systemd时,启动环节开始。
+
+### systemd之争
+
+systemd引起了系统管理员和其他负责维护Linux系统正常运行人员的广泛回应。systemd正在许多Linux系统中接管大量任务的事实造成了某些开发人群和系统管理员群组之间的阻挠和争议。
+
+SystemV和systemd是执行Linux启动环节的两种不同的方法。 SystemV启动脚本和init程序是老的方法,而使用目标(targets)的systemd是新方法。尽管大多数现代Linux发行版都使用较新的systemd进行启动,关机和进程管理,但仍有一些发行版未采用。原因之一是某些发行版维护者和系统管理员喜欢老的SystemV方法,而不是新的systemd。
+
+我认为两者都有其优势。
+
+#### 为何我更喜欢SystemV
+
+我更喜欢SystemV,因为它更开放。使用Bash脚本来完成启动。内核启动init程序(编译后的二进制)后,init启动 **rc.sysinit** 脚本,该脚本执行许多系统初始化任务。 **rc.sysinit** 执行完后,init启动 **/etc/rc.d/rc** 脚本,该脚本依次启动 **/etc/rc.d/rcX.d** 中由SystemV启动脚本定义的各种服务。 其中“ X”是待启动的运行级别号。
+
+除了init程序本身之外,所有这些程序都是开放且易于理解的脚本。可以通读这些脚本并确切了解整个启动过程中发生的事情,但是我不认为有太多系统管理员会实际这样做。每个启动脚本都被编了号,以便按特定顺序启动预期的服务。服务是串行启动的,一次只能启动一个服务。
+
+由Red Hat的Lennart Poettering和Kay Sievers开发的systemd是一个由大的已编译的二进制可执行文件构成的复杂系统,不访问其源码就无法理解。它是开源的,因此“访问其源代码”并不难,只是不太方便。systemd似乎表现出对Linux哲学多个原则的重大驳斥。作为二进制文件,systemd无法被直接打开供系统管理员查看或进行简单更改。systemd试图做所有事情,例如管理正在运行的服务,同时提供比SystemV更多的状态信息。它还管理硬件,进程,进程组,文件系统挂载等。 systemd几乎涉足于现代Linux主机的每方面,使它成为系统管理的一站式工具。所有这些都明显违反了"程序应该小且每个程序都应该只做一件事并且做好"的原则。
+
+#### 为何我更喜欢systemd
+
+我更喜欢用systemd作为启动机制,因为它会根据启动阶段并行地启动尽可能多的服务。这样可以加快整个的启动速度,使得主机系统比SystemV更快地到达登录屏幕。
+
+systemd几乎可以管理正在运行的Linux系统的各个方面。它可以管理正在运行的服务,同时提供比SystemV多得多的状态信息。它还管理硬件,进程和进程组,文件系统挂载等。 systemd几乎涉足于现代Linux操作系统的每方面,使其成为系统管理的一站式工具。(听起来熟悉吧?)
+
+systemd工具是编译后的二进制文件,但该工具包是开放的,因为所有配置文件都是ASCII文本文件。可以通过各种GUI和命令行工具来修改启动配置,也可以添加或修改各种配置文件来满足特定的本地计算环境的需求。
+
+#### 真正的问题
+
+您认为我不能喜欢两种启动系统吗?我能,我会用它们中的任何一个。
+
+我认为,SystemV和systemd之间大多数争议的真正问题和根本原因在于,系统管理阶段[没有选择权][3]。使用SystemV还是systemd已经由各种发行版的开发人员,维护人员和打包人员选择了(但有充分的理由)。由于init极端的侵入性, 挖出(scooping out)并替换init系统会带来很多影响,发行版设计过程之外(的环节)很难处理这些影响。
+
+尽管该选择实际上是为我而选的,我通常最关心的是我的Linux主机仍然可以启动并正常工作。作为最终用户,甚至是系统管理员,我主要关心的是我是否可以完成我的工作,例如写我的书和这篇文章,安装更新以及编写脚本来自动化所有事情。只要我能做我的工作,我就不会真正在意发行版中使用的启动系统。
+
+在启动或服务管理出现问题时,我会在意。无论主机上使用哪种启动系统,我都足够了解如何沿着事件顺序来查找故障并进行修复。
+
+#### 替换SystemV
+
+以前曾有过用更现代的东西替代SystemV的尝试。在大约两个版本中,Fedora使用了一个叫作Upstart的东西来替换老化的SystemV,但是它没有替换init并且没有我能感知到的变化。由于Upstart并未对SystemV的问题进行任何重大更改,因此这个方向的努力很快就被systemd放弃了。
+
+尽管大部分Linux开发人员都认可替换旧的SystemV启动系统是个好主意,但许多开发人员和系统管理员并不喜欢systemd。与其重新讨论人们在systemd中遇到的或曾经遇到过的所有所谓的问题,不如带您去看两篇好文章,尽管有些陈旧,但它们涵盖了大多数内容。Linux内核的创建者Linus Torvalds对systemd似乎不感兴趣。在2014年ZDNet的文章_[Linus Torvalds和其他人对Linux上的systemd的看法][4]_中,Linus清楚地表达了他的感受。
+
+>“实际上我对systemd本身没有任何特别强烈的意见。我对一些核心开发人员有一些意见,我认为它们在对待bugs和兼容性方面过于轻率,而且我认为某些设计细节是疯狂的(例如,我不喜欢二进制日志),但这只是细节,不是大问题。”
+
+如果您对Linus不太了解,我可以告诉您,如果他不喜欢某事,那么他非常直率,坦率,并且非常清楚这种不喜欢。他解决自己对事物不满的方式已经被社会更好地接受了。
+
+2013年,Poettering写了一篇很长的博客,其中他在揭穿[systemd的神话][5]的同时透露了创建它的一些原因。这是一本很好的读物,我强烈建议您阅读。
+
+### systemd任务
+
+根据编译过程中使用的选项(不在本系列中介绍),systemd可以有多达69个二进制可执行文件用于执行任务,其中包括:
+
+ * systemd程序以1号进程(PID 1)运行,并提供使尽可能多服务并行启动的系统启动能力,它额外加快了总体启动时间。它还管理关机顺序。
+ * systemctl程序提供了服务管理的用户接口。
+ * 支持SystemV和LSB启动脚本,以便向后兼容。
+ * 服务管理和报告提供了比SystemV更多的服务状态数据。
+ * 提供基本的系统配置工具,例如主机名,日期,语言环境,已登录用户的列表,正在运行的容器和虚拟机,系统帐户,运行时目录和设置;用于简易网络配置,网络时间同步,日志转发和名称解析的守护程序。
+ * 提供套接字管理。
+ * systemd定时器提供类似cron的高级功能,包括在相对于系统启动,systemd启动,定时器上次启动时刻的某个时间点运行脚本。
+ * 提供了一个工具来分析定时器规格中使用的日期和时间。
+ * 能感知层次的文件系统挂载和卸载可以更安全地级联挂载的文件系统。
+ * 允许主动的创建和管理临时文件,包括删除文件。
+ * D-Bus的接口提供在插入或移除设备时运行脚本的能力。这允许将所有设备(无论是否可插拔)都被视为即插即用,从而大大简化了设备的处理。
+ * 分析启动顺序的工具可用于查找耗时最多的服务。
+ * 包括用于存储系统消息的日志以及管理日志的工具。
+
+
+### 架构
+
+这些和更多的任务通过许多守护程序,控制程序和配置文件来支持。图1显示了许多属于systemd的组件。这是一个简化的图,旨在提供概要描述,因此它并不包括所有独立的程序或文件。它也不提供数据流的视角,数据流是如此复杂,因此在本系列文章的背景下没用。
+
+![系统架构][6]
+
+完整的systemd讲解就需要一本书。您不需要了解图1中的systemd组件是如何组合在一起的细节。了解支持各种Linux服务管理以及日志文件和日志处理的程序和组件就够了。 但是很明显,systemd并不是某些批评者所说的那样的庞然大物。
+
+### 作为1号进程的systemd
+
+systemd是1号进程(PID 1)。它的一些功能(比老的SystemV3 init要广泛得多)用于管理正在运行的Linux主机的许多方面,包括挂载文件系统以及启动和管理Linux生产主机所需的系统服务。与启动顺序无关的任何systemd任务都不在本文讨论范围之内(但本系列后面的一些文章将探讨其中的一些任务)。
+
+首先,systemd挂载 **/etc/fstab** 所定义的文件系统,包括所有交换文件或分区。此时,它可以访问位于 **/etc** 中的配置文件,包括它自己的配置文件。它使用其配置链接 **/etc/systemd/system/default.target** 来确定将主机引导至哪个状态或目标。 **default.target** 文件是指向真实目标文件的符号链接。对于桌面工作站,通常是 **graphical.target**,它相当于SystemV中的运行级别5。对于服务器,默认值更可能是 **multi-user.target**,相当于SystemV中的运行级别3。 **emergency.target** 类似于单用户模式。目标(targets)和服务(services)是systemd的单位。
+
+下表(图2)将systemd目标与老的SystemV启动运行级别进行了比较。systemd提供systemd目标别名以便向后兼容。目标别名允许脚本(以及许多系统管理员)使用SystemV命令(如**init 3**)更改运行级别。当然,SystemV命令被转发给systemd进行解释和执行。
+
+**systemd目标** | **SystemV运行级别** | **目标别名** | **描述**
+--- | --- | ---- |-
+default.target | | |此目标总是通过符号连接的方式成为“多用户目标”或“图形化目标”的别名。systemd始终使用 **default.target** 来启动系统。 ** default.target** 绝不应该设为 **halt.target**,**poweroff.target** 或 **reboot.target** 的别名
+graphic.target | 5 | runlevel5.target |带有GUI的 **Multi-user.target**
+| 4 | runlevel4.target |未用。在SystemV中运行级别4与运行级别3相同。可以创建并自定义此目标以启动本地服务,而无需更改默认的 **multi-user.target**
+multi-user.target | 3 | runlevel3.target |所有服务在运行,但仅有命令行界面(CLI)
+| 2 | runlevel2.target |多用户,没有NFS,其他所有非GUI服务在运行
+rescue.target | 1 | runlevel1.target |基本系统,包括挂载文件系统,运行最基本的服务和主控制台的恢复shell
+Emergency.target | S | |单用户模式-没有服务运行;不挂载文件系统。这是最基本的工作级别,只有主控制台上运行的一个紧急Shell供用户与系统交互
+halt.target | | |在不关电源的情况下停止系统
+reboot.target | 6 | runlevel6.target |重启
+poweroff.target | 0 | runlevel0.target |停止系统并关闭电源
+
+每个目标在其配置文件中都描述了一个依赖集。systemd启动必须的依赖,这些依赖是运行Linux主机到特定功能级别所需的服务。当目标配置文件中列出的所有依赖项被加载并运行后,系统就在该目标级别运行了。 在图2中,功能最多的目标位于表的顶部,从顶向下,功能逐步递减。
+
+systemd还会检查老的SystemV init目录,以确认是否存在任何启动文件。如果有,systemd会将它们作为配置文件以启动它们描述的服务。网络服务是一个很好的例子,在Fedora中它仍然使用SystemV启动文件。
+
+图3(如下)是直接从启动手册页复制来的。它显示了systemd启动期间普遍的事件顺序以及确保成功启动的基本顺序要求。
+
+```
+ cryptsetup-pre.target
+ |
+ (various low-level v
+ API VFS mounts: (various cryptsetup devices...)
+ mqueue, configfs, | |
+ debugfs, ...) v |
+ | cryptsetup.target |
+ | (various swap | | remote-fs-pre.target
+ | devices...) | | | |
+ | | | | | v
+ | v local-fs-pre.target | | | (network file systems)
+ | swap.target | | v v |
+ | | v | remote-cryptsetup.target |
+ | | (various low-level (various mounts and | | |
+ | | services: udevd, fsck services...) | | remote-fs.target
+ | | tmpfiles, random | | | /
+ | | seed, sysctl, ...) v | | /
+ | | | local-fs.target | | /
+ | | | | | | /
+ \\____|______|_______________ ______|___________/ | /
+ \ / | /
+ v | /
+ sysinit.target | /
+ | | /
+ ______________________/|\\_____________________ | /
+ / | | | \ | /
+ | | | | | | /
+ v v | v | | /
+ (various (various | (various | |/
+ timers...) paths...) | sockets...) | |
+ | | | | | |
+ v v | v | |
+ timers.target paths.target | sockets.target | |
+ | | | | v |
+ v \\_______ | _____/ rescue.service |
+ \|/ | |
+ v v |
+ basic.target rescue.target |
+ | |
+ ________v____________________ |
+ / | \ |
+ | | | |
+ v v v |
+ display- (various system (various system |
+ manager.service services services) |
+ | required for | |
+ | graphical UIs) v v
+ | | multi-user.target
+ emergency.service | | |
+ | \\_____________ | _____________/
+ v \|/
+ emergency.target v
+ graphical.target
+```
+
+**sysinit.target** 和 **basic.target** 目标可以看作启动过程中的检查点。尽管systemd的设计目标之一是并行启动系统服务,但是某些服务和功能目标必须先启动,然后才能启动其他服务和目标。直到该检查点所需的所有服务和目标被满足后才能通过这些检查点。
+
+当它依赖的所有单元都完成时,将到达 **sysinit.target**。所有这些单元,挂载文件系统,设置交换文件,启动udev,设置随机数生成器种子,启动低层服务以及配置安全服务(如果一个或多个文件系统是加密的)都必须被完成,但 **sysinit.target** 的这些任务可以并行执行。
+
+**sysinit.target** 将启动系统接近正常运行所需的所有低层服务和单元,以及转移到 **basic.target** 所需的服务和单元。
+
+在完成 **sysinit.target** 目标之后,systemd会启动实现下一个目标所需的所有单元。基本目标通过启动所有下一目标所需的单元来提供一些其他功能。包括设置如PATHs为各种可执行程序的路径,设置通信套接字和计时器之类。
+
+最后,用户级目标 **multi-user.target** 或 **graphical.target** 被初始化。要满足图形目标的依赖必须先达到**multi-user.target**。图3中带下划线的目标是通常的启动目标。当达到这些目标之一时,启动就完成了。如果 **multi-user.target** 是默认设置,那么您应该在控制台上看到文本模式的登录界面。如果 **graphical.target** 是默认设置,那么您应该看到图形的登录界面。您看到的特定的GUI登录界面取决于您默认的显示管理器。
+
+引导手册页还描述并提供了引导到初始RAM磁盘和systemd关机过程的地图。
+
+systemd还提供了一个工具,该工具列出了完整启动或指定单元的依赖。单元是可控制的systemd资源实体,其范围从特定服务(例如httpd或sshd)到计时器,挂载,套接字等。尝试以下命令并滚动查看结果。
+
+```
+`systemctl list-dependencies graphical.target`
+```
+
+注意,这完全展开了使系统进入图形目标运行模式所需的顶层目标单元列表。 也可以使用 **\-all** 选项来展开所有其他单元。
+
+```
+`systemctl list-dependencies --all graphical.target`
+```
+
+您可以使用 **less** 命令来搜索诸如“target”,“slice”和“ socket”之类的字符串。
+
+现在尝试下面的方法。
+
+```
+`systemctl list-dependencies multi-user.target`
+```
+
+和
+
+
+```
+`systemctl list-dependencies rescue.target`
+```
+
+和
+
+
+```
+`systemctl list-dependencies local-fs.target`
+```
+
+和
+
+
+```
+`systemctl list-dependencies dbus.service`
+```
+```
+`systemctl list-dependencies graphic.target`
+```
+
+
+
+这个工具帮助我可视化我正用的主机的启动依赖细节。继续花一些时间探索一个或多个Linux主机的启动树。但是要小心,因为systemctl手册页包含以下注释:
+
+> _“请注意,此命令仅列出当前被服务管理器加载到内存的单元。尤其是,此命令根本不适合用于获取特定单元的全部反向依赖列表,因为它不会列出被单元声明了但是未加载的依赖项。” _
+
+### 结尾语
+
+即使在深入研究systemd之前,很明显能看出它既强大又复杂。显然,systemd不是单一,庞大,整体且不可知的二进制文件。相反,它是由许多较小的组件和旨在执行特定任务的子命令组成。
+
+本系列的下一篇文章将更详细地探讨systemd的启动,以及systemd的配置文件,更改默认的目标以及如何创建简单服务单元。
+
+### 资源
+
+互联网上有大量关于systemd的信息,但是很多都简短,晦涩甚至是误导。除了本文提到的资源外,以下网页还提供了有关systemd启动的更详细和可靠的信息。
+
+ * Fedora项目有一个很好的,实用的[guide to systemd][7]。它有你需要知道的通过systemd来配置,管理和维护Fedora主机所需的几乎所有知识。
+ * Fedora项目还有一个不错的[cheat sheet][8],将老的SystemV命令与对比的systemd命令相互关联。
+ * 有关systemd及其创建原因的详细技术信息,请查看[Freedesktop.org][9]的[systemd描述][10]。
+ * [Linux.com][11]的“systemd的更多乐趣”提供了更高级的systemd [信息和技巧][12]。
+
+
+还有systemd的设计师和主要开发者Lennart Poettering撰写的针对Linux系统管理员的一系列技术文章。这些文章是在2010年4月至2011年9月之间撰写的,但它们现在和那时一样有用。关于systemd及其生态的其他许多好文都基于这些论文。
+
+ * [重新思考1号进程][13]
+ * [systemd之系统管理员, I][14]
+ * [systemd之系统管理员, II][15]
+ * [systemd之系统管理员, III][16]
+ * [systemd之系统管理员, IV][17]
+ * [systemd之系统管理员, V][18]
+ * [systemd之系统管理员, VI][19]
+ * [systemd之系统管理员, VII][20]
+ * [systemd之系统管理员, VIII][21]
+ * [systemd之系统管理员, IX][22]
+ * [systemd之系统管理员, X][23]
+ * [systemd之系统管理员, XI][24]
+
+
+
+Mentor Graphics的Linux内核和系统程序员Alison Chiaken预览了此文...
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://opensource.com/article/20/4/systemd
+
+作者:[David Both][a]
+选题:[lujun9972][b]
+译者:[messon007](https://github.com/messon007)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]: https://opensource.com/users/dboth
+[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
+[1]: https://opensource.com/sites/default/files/styles/image-full-size/public/lead-images/car-penguin-drive-linux-yellow.png?itok=twWGlYAc (Penguin driving a car with a yellow background)
+[2]: http://www.both.org/?page_id=1183
+[3]: http://www.osnews.com/story/28026/Editorial_Thoughts_on_Systemd_and_the_Freedom_to_Choose
+[4]: https://www.zdnet.com/article/linus-torvalds-and-others-on-linuxs-systemd/
+[5]: http://0pointer.de/blog/projects/the-biggest-myths.html
+[6]: https://opensource.com/sites/default/files/uploads/systemd-architecture.png (systemd architecture)
+[7]: https://docs.fedoraproject.org/en-US/quick-docs/understanding-and-administering-systemd/index.html
+[8]: https://fedoraproject.org/wiki/SysVinit_to_Systemd_Cheatsheet
+[9]: http://Freedesktop.org
+[10]: http://www.freedesktop.org/wiki/Software/systemd
+[11]: http://Linux.com
+[12]: https://www.linux.com/training-tutorials/more-systemd-fun-blame-game-and-stopping-services-prejudice/
+[13]: http://0pointer.de/blog/projects/systemd.html
+[14]: http://0pointer.de/blog/projects/systemd-for-admins-1.html
+[15]: http://0pointer.de/blog/projects/systemd-for-admins-2.html
+[16]: http://0pointer.de/blog/projects/systemd-for-admins-3.html
+[17]: http://0pointer.de/blog/projects/systemd-for-admins-4.html
+[18]: http://0pointer.de/blog/projects/three-levels-of-off.html
+[19]: http://0pointer.de/blog/projects/changing-roots
+[20]: http://0pointer.de/blog/projects/blame-game.html
+[21]: http://0pointer.de/blog/projects/the-new-configuration-files.html
+[22]: http://0pointer.de/blog/projects/on-etc-sysinit.html
+[23]: http://0pointer.de/blog/projects/instances.html
+[24]: http://0pointer.de/blog/projects/inetd.html
diff --git a/translated/tech/20200417 How to compress files on Linux 5 ways.md b/translated/tech/20200417 How to compress files on Linux 5 ways.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..e9ef6af572
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20200417 How to compress files on Linux 5 ways.md
@@ -0,0 +1,207 @@
+[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
+[#]: translator: (robsean)
+[#]: reviewer: ( )
+[#]: publisher: ( )
+[#]: url: ( )
+[#]: subject: (How to compress files on Linux 5 ways)
+[#]: via: (https://www.networkworld.com/article/3538471/how-to-compress-files-on-linux-5-ways.html)
+[#]: author: (Sandra Henry-Stocker https://www.networkworld.com/author/Sandra-Henry_Stocker/)
+
+在 Linux 上压缩文件的 5 种方法
+======
+在 Linux 系统上有很多可以用于压缩文件的工具,但是它们表现的行为或产生相同程度的压缩等级并不相同,在这篇文章中,我们比较其中的五个工具。
+Getty Images
+
+在 Linux 上有不少用于压缩文件的命令。最新最有效的一个方法是 **xz** ,但是所有的方法都有节省磁盘空间和为后期使用维护备份文件的优点。在这篇文章中,我们将比较压缩命令并指出显著的不同 。
+
+### tar
+
+tar 命令不是专门的压缩命令。它通常用于将多个文件拉入一单个文件中,以便容易地传输到另一个系统,或者备份文件为一个相关的组。它也提供压缩作为一个功能,这是很明智的,附加的 **z** 压缩选项能够实现压缩文件。
+
+当压缩过程被附加到一个使用 **z** 选项的 **tar** 命令时,tar 使用 **gzip** 来进行压缩。
+
+你可以使用 **tar** 来压缩一个单个文件,就像压缩一个组一样容易,尽管这种操作与直接使用 **gzip** 相比没有特别的优势。为此,要使用 **tar** ,只需要使用一个 “tar cfz newtarfile filename” 命令来像你标识一个组一样标识文件,像这样:
+
+```
+$ tar cfz bigfile.tgz bigfile
+ ^ ^
+ | |
+ +- 新的文件 +- 将被压缩的文件
+
+$ ls -l bigfile*
+-rw-rw-r-- 1 shs shs 103270400 Apr 16 16:09 bigfile
+-rw-rw-r-- 1 shs shs 21608325 Apr 16 16:08 bigfile.tgz
+```
+
+注意,文件的大小显著减少。
+
+如果你喜欢,你可以使用 **tar.gz** 扩展名,这可能会使文件的特征更加明显,但是大多数的 Linux 用户将很可能会意识到与 **tgz** 的意思是相同的东西 – **tar** 和 **gz** 的组合来显示文件是一个压缩的 tar 文件。在压缩完成后,将留下原始文件和压缩文件。
+
+为收集很多文件在一起并在一个命令中压缩生成的 “tar ball” ,使用相同的语法,但是要指明将要被包含的文件来作为一个组,而不是单个文件。这里有一个示例:
+
+[][1]
+
+```
+$ tar cfz bin.tgz bin/*
+ ^ ^
+ | +-- 将被包含的文件
+ + 新的文件
+```
+
+### zip
+
+**zip** 命令创建一个压缩文件,与此同时保留原始文件的完整性。语法像使用 **tar** 一样简单,只是你必需记住,你的原始文件名称应该是命令行上的最后一个参数。
+
+```
+$ zip ./bigfile.zip bigfile
+updating: bigfile (deflated 79%)
+$ ls -l bigfile bigfile.zip
+-rw-rw-r-- 1 shs shs 103270400 Apr 16 11:18 bigfile
+-rw-rw-r-- 1 shs shs 21606889 Apr 16 11:19 bigfile.zip
+```
+
+### gzip
+
+**gzip** 命令非常容易使用。你只需要键入 "gzip" ,紧随其后的是你想要压缩的文件名称。不像上述描述的命令,**gzip** 将“就地”加密文件。换句话说,原始文件将被加密文件替换。
+
+```
+$ gzip bigfile
+$ ls -l bigfile*
+-rw-rw-r-- 1 shs shs 21606751 Apr 15 17:57 bigfile.gz
+```
+
+### bzip2
+
+像使用 **gzip** 命令一样,**bzip2** 将在你选的“合适位置”压缩文件,只留下原始文件保持原样离开。
+
+```
+$ bzip bigfile
+$ ls -l bigfile*
+-rw-rw-r-- 1 shs shs 18115234 Apr 15 17:57 bigfile.bz2
+```
+
+### xz
+
+压缩命令组中的一个相对较新的成员,**xz** 就如何更好的压缩文件而言是领跑者。像先前的两个命令一样,你只需要将文件名称补给到命令中。再强调一次,原始文件被就地压缩。
+
+```
+$ xz bigfile
+$ ls -l bigfile*
+-rw-rw-r-- 1 shs shs 13427236 Apr 15 17:30 bigfile.xz
+```
+
+对于大文件来说,你可能会注意到 **xz** 将比其它的压缩命令花费更多的运行时间,但是压缩的结果却是非常令人赞叹的。
+
+### 考虑对比性
+
+大多数人都听说过 "文件大小不是万能的"。所以,让我们比较一下文件大小以及一些当你计划如何压缩文件时的问题。
+
+下面显示的统计数据都与压缩单个文件相关,在上面显示的示例中使用 – bigfile – 。这个文件是一个大的且相当随机的文本文件。压缩率在一定程度上取决于文件的内容。
+
+#### 大小减缩率
+
+在比较期间,上面显示的各种压缩命产生下面的结果。百分比表示压缩文件对比原始文件。
+
+```
+-rw-rw-r-- 1 shs shs 103270400 Apr 16 14:01 bigfile
+------------------------------------------------------
+-rw-rw-r-- 1 shs shs 18115234 Apr 16 13:59 bigfile.bz2 ~17%
+-rw-rw-r-- 1 shs shs 21606751 Apr 16 14:00 bigfile.gz ~21%
+-rw-rw-r-- 1 shs shs 21608322 Apr 16 13:59 bigfile.tgz ~21%
+-rw-rw-r-- 1 shs shs 13427236 Apr 16 14:00 bigfile.xz ~13%
+-rw-rw-r-- 1 shs shs 21606889 Apr 16 13:59 bigfile.zip ~21%
+```
+
+**xz** 命令获胜,最终只有压缩文件大小的13%,但是这些所有的压缩命令都相当显著地减少原始文件的大小。
+
+#### 是否替换原始文件
+
+**bzip2**,**gzip** 和 **xz** 命令都将使用压缩文件替换原始文件。**tar** 和 **zip** 命令不替换。
+
+#### 运行时间
+
+**xz** 命令似乎比其它命令需要花费更多的时间来加密文件。对于 bigfile 来说,近似时间是:
+
+```
+命令 运行时间
+tar 4.9 秒
+zip 5.2 秒
+bzip2 22.8 秒
+gzip 4.8 秒
+xz 50.4 秒
+```
+
+解压缩文件很可能比压缩时间要短得多。
+
+#### 文件权限
+
+不管你对压缩文件设置什么权限,压缩文件的权限将基于你的 **umask** 设置,除 **bzip2** 维持原始文件的权限外。
+
+#### 与 Windows 的兼容性
+
+**zip** 命令将创建一个可被使用的文件(例如,解压缩),在 Windows 系统上以及 Linux 和其它 Unix 系统上,无需安装其它可能可用或不可用的工具。
+
+### 解压缩文件
+
+解压缩文件的命令类似于这些压缩文件的命令。这些命令将在我们运行上述压缩命令后用于解压缩 bigfile 。
+
+ * tar: **tar xf bigfile.tgz**
+ * zip: **unzip bigfile.zip**
+ * gzip: **gunzip bigfile.gz**
+ * bzip2: **bunzip2 bigfile.gz2**
+ * xz: **xz -d bigfile.xz** 或 **unxz bigfile.xz**
+
+
+
+### 对比你自己运行的压缩
+
+如果你想自己运行一些测试,抓取一个大的且可以替换的文件,并使用上面显示的每个命令来压缩它 – 最好使用一个新的子目录。你可能必需先安装 **xz** ,如果你想在测试中包含它的话。这个脚本可能更容易地压缩,但是将可能花费几分钟来完成。
+
+```
+#!/bin/bash
+
+# 询问用户文件名称
+echo -n "filename> "
+read filename
+
+# 你需要这个,因为一些命令将替换原始文件
+cp $filename $filename-2
+
+# 先清理(以免先前的结果仍然可用)
+rm $filename.*
+
+tar cvfz ./$filename.tgz $filename > /dev/null
+zip $filename.zip $filename > /dev/null
+bzip2 $filename
+# 恢复原始文件
+cp $filename-2 $filename
+gzip $filename
+# 恢复原始文件
+cp $filename-2 $filename
+xz $filename
+
+# 显示结果
+ls -l $filename.*
+
+# 替换原始文件
+mv $filename-2 $filename
+```
+
+加入 [Facebook][2] 和 [LinkedIn][3] 网络世界社区来评论那些最重要的话题。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://www.networkworld.com/article/3538471/how-to-compress-files-on-linux-5-ways.html
+
+作者:[Sandra Henry-Stocker][a]
+选题:[lujun9972][b]
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]: https://www.networkworld.com/author/Sandra-Henry_Stocker/
+[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
+[1]: https://www.networkworld.com/blog/itaas-and-the-corporate-storage-technology/?utm_source=IDG&utm_medium=promotions&utm_campaign=HPE22140&utm_content=sidebar (ITAAS and Corporate Storage Strategy)
+[2]: https://www.facebook.com/NetworkWorld/
+[3]: https://www.linkedin.com/company/network-world
diff --git a/translated/tech/20200424 16 Things to do After Installing Ubuntu 20.04.md b/translated/tech/20200424 16 Things to do After Installing Ubuntu 20.04.md
deleted file mode 100644
index a221ef6a34..0000000000
--- a/translated/tech/20200424 16 Things to do After Installing Ubuntu 20.04.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,283 +0,0 @@
-[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
-[#]: translator: (qfzy1233)
-[#]: reviewer: ( )
-[#]: publisher: ( )
-[#]: url: ( )
-[#]: subject: (16 Things to do After Installing Ubuntu 20.04)
-[#]: via: (https://itsfoss.com/things-to-do-after-installing-ubuntu-20-04/)
-[#]: author: (Abhishek Prakash https://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/)
-
-安装完 Ubuntu 20.04 后要做的 16 件事
-======
-
-_**以下是安装 Ubuntu 20.04 之后需要做的一些调整和事项,它将使你获得更流畅、更好的桌面 Linux 体验。**_
-
-[Ubuntu 20.04 LTS (长期支持版)带来了许多新的特性][1] 和观感上的变化。 如果你要安装 Ubuntu 20.04 ,让我向你展示一些推荐步骤便于你的使用。
-
-### 安装完 Ubuntu 20.04 LTS “Focal Fossa”后要做的 16 件事
-
-![][2]
-
-我在这里要提到的步骤仅是我的建议。如果一些定制或调整不适合你的需要和兴趣,你可以忽略它们。
-
-同样的,有些步骤看起来很简单,但是对于一个 Ubuntu 新手来说是必要的。
-
-这里的一些建议适用于启用 GNOME 作为默认桌面Ubuntu 20.04。所以请检查[Ubuntu版本][3]和[桌面环境][4]。
-
-以下列表便是安装了代号为 Focal Fossa 的 Ubuntu 20.04 LTS 之后要做的事。
-
-#### 1\. 通过更新和启用额外的 repos 来准备您的系统
-
-安装Ubuntu或任何其他Linux发行版之后,你应该做的第一件事就是更新它。Linux 的可用包数据库工作于本地。这个缓存需要同步以便你能够安装任何软件。
-
-升级Ubuntu非常简单。你可以运行软件更新从菜单( 按 Win 键并搜索软件更新):
-
-![Ubuntu 20.04 的软件升级中心][5]
-
-你也可以在终端使用以下命令更新你的系统:
-
-```
-sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade
-```
-
-接下来,您应该确保启用了[universe和multiverse存储库][6]。使用这些存储库,你可以访问更多的软件。我还推荐阅读关于[Ubuntu软件库][6]的书籍,以了解它背后的基本概念。
-
-搜索软件和放大器;更新菜单:
-
-![软件及更新设置项][7]
-
-请务必选中存储库前面的方框:
-
-![启用额外的存储库][8]
-
-#### 2\. 安装媒体解码器来播放MP3、MPEG4和其他格式媒体文件
-
-如果你想播放媒体文件,如MP3, MPEG4, AVI等,你需要安装媒体解码器。由于不同国家的版权问题,Ubuntu在默认情况下不会安装它。
-
-作为个人,你可以很容易地安装这些媒体编解码器[使用 Ubuntu 额外安装包][9]。这将安装媒体编解码器,Adobe Flash播放器和[微软 True Type 字体在您的Ubuntu系统][10]。
-
-你可以通过[点击这个链接][11](它将要求打开软件中心)来安装它,或者使用以下命令:
-
-```
-sudo apt install ubuntu-restricted-extras
-```
-
-如果遇到EULA或许可证界面,请记住使用tab键在选项之间进行选择,然后按enter键确认你的选择。
-
-![按tab键选择OK并按enter键][12]
-
-#### 3\. 从软件中心或网络上安装软件
-
-现在已经设置了存储库并更新了包缓存,应该开始安装所需的软件了。
-
-有几种方法可以在Ubuntu中安装应用程序。最简单和正式的方法是使用软件中心。
-
-![Ubuntu 软件中心][14]
-
-如果你想要一些关于软件的建议,请参考这个扩展的[不同用途的Ubuntu应用程序列表][15]。
-
-一些软件供应商提供 .deb 文件来方便地安装他们的应用程序。你可以从他们的网站获得 deb 文件。例如,要[在 Ubuntu 上安装谷歌 Chrome ][16],你可以从它的网站上获得 deb 文件,双击它开始安装。
-
-#### 4\. 享受 Steam Proton 和 GameModeEnjoy 上的游戏
-
-[ Linux 上的游戏][17] 已经有了长足的发展。你不受限于自带的少数游戏。你可以[在 Ubuntu 上安装 Steam ][18]并享受许多游戏。
-
-[Steam 新的 Proton 项目][19]可以让你在Linux上玩许多只适用于windows的游戏。除此之外,Ubuntu 20.04还默认安装了[Feral Interactive的游戏][20]。
-
-游戏模式会自动调整Linux系统的性能,使游戏具有比其他后台进程更高的优先级。
-
-这意味着一些支持游戏模式的游戏(如[古墓丽影崛起][21])在 Ubuntu 上的性能应该有所提高。
-
-#### 5\. 管理自动更新(适用于进阶和专家)
-
-最近,Ubuntu 已经开始自动下载和安装对你的系统至关重要的安全更新。这是一个安全功能,作为一个普通用户,你应该让它保持默认,
-
-但是,如果你喜欢自己进行配置更新,而这个自动更新经常导致你[“无法锁定管理目录”错误][22],也许你可以改变自动更新行为。
-
-你可以选择更新是提示,以便它通知你的安全更新是否可用,而不是自动安装。
-
-![管理自动更新设置][23]
-
-#### 6\. 控制电脑的自动挂起和屏幕锁定
-
-如果你在笔记本电脑上使用Ubuntu 20.04,那么你可能需要注意一些电源和屏幕锁定设置。
-
-如果你的笔记本电脑是电池模式,Ubuntu会在20分钟不工作后休眠系统。这样做是为了节省电池电量。就我个人而言,我不喜欢它,因此我禁用了它。
-
-类似地,如果您离开系统几分钟,它会自动锁定屏幕。我也不喜欢这种行为,所以我宁愿禁用它。
-
-![Ubuntu 20.04的电源设置][24]
-
-#### 7\. 享受夜间模式
-
-一个[谈论最多的 Ubuntu 20.04 特性][25]是夜间模式。你可以通过进入设置并在外观部分中选择它来启用夜间模式。
-
-![开启夜间主题 Ubuntu ][26]
-
-你可能需要做一些额外的调整来启用 Ubuntu 20.04 的深度夜间模式。
-
-#### 8\. 控制桌面图标和启动程序
-
-如果你想要一个最简的桌面,你可以禁用桌面上的图标。您还可以从左侧禁用启动程序,并在顶部面板中禁用软件状态栏。
-
-所有这些都可以通过默认的新 GNOME 扩展来控制。
-
-![][28]
-
-顺便说一下,你也可以通过设置-外观来改变启动栏的位置到底部或者右边。
-
-#### 9\. 使用emojis(表情)和特殊字符,或从搜索中禁用它
-
-Ubuntu提供了一个使用 emojis 或表情符号的简单方法。在默认情况下,有一个专用的应用程序叫做 Characters。它可以给你基本表情符号的[Unicode][29]码。
-
-不仅是表情符号,你还可以使用它来获得法语、德语、俄语和拉丁语字符的 unicode 。单击符号你可以复制 unicode ,当你粘贴这段代码时,你所选择的符号便被插入。
-
-! [Emoji Ubuntu] [30]
-
-你也能在桌面搜索中找到这些特殊的字符和表情符号。也可以从搜索结果中复制它们。
-
-![Emojis 出现在桌面搜索中][31]
-
-如果你不想在搜索结果中看到它们,你应该禁用搜索功能对它们的访问。下一节将讨论如何做到这一点。
-
-#### 10\. 掌握桌面搜索
-
-GNOME桌面拥有强大的搜索功能。大多数人使用它来搜索已安装的应用程序,但它不仅限于此。
-
-按超级键(Win键)并搜索一些东西。它将显示与搜索词匹配的任何应用程序,然后是系统设置和软件中心提供的匹配应用程序。
-
-![桌面搜索][32]
-
-不仅如此,搜索还可以找到文件中的文本。如果你正在使用日历,它也可以找到你的会议和提醒。你甚至可以在搜索中进行快速计算并复制其结果。
-
-![Ubuntu搜索的快速计算][33]
-
-你可以通过进入设置来控制搜索的内容和顺序。
-
-![][34]
-
-#### 11\. 使用夜灯功能,减少夜间眼睛疲劳
-
-如果你在晚上使用电脑或智能手机,你应该使用夜灯功能来减少眼睛疲劳。我觉得这很有帮助。
-
-夜灯的特点是在屏幕上增加了一种黄色的色调,比白光少了一些挤压感。
-
-你可以在设置->显示并切换到夜灯选项卡。你可以根据自己的喜好设置“黄色”。
-
-![夜灯功能][35]
-
-#### 12\.使用 2K/4K 显示器? 使用分辨率缩放得到更大的图标和字体
-
-如果你觉得图标、字体、文件夹在你的高分辨率屏幕上看起来都太小了,你可以利用分辨率缩放。
-
-启用分级缩放可以让你有更多的选项来从100%增加到200%。你可以选择适合自己喜好的缩放尺寸。
-
-![启用高分缩放从设置->显示][36]
-
-#### 13\. 探索GNOME扩展以扩展GNOME桌面的可用性
-
-GNOME桌面有称为扩展的小插件或附加组件。你应该[学习使用 GNOM E扩展][37]来扩展系统的可用性。
-
-如下图所示,天气扩展顶部面板中显示了天气信息。不起眼但十分有用。您也可以在这里查看一些[最佳 GNOME 扩展][38]。不要全部安装,只使用那些对你有用的。
-
-![天气 扩展][39]
-
-#### 14\.启用“勿扰”模式,专注于工作
-
-如果你想专注于工作,禁用桌面通知会很方便。你可以轻松地启用“勿扰”模式,并静音所有通知。
-
-![启用“请勿打扰”清除桌面通知][40]
-
-这些通知仍然会在消息栏中,以便您以后可以阅读它们,但是它们不会在桌面上弹出。
-
-#### 15\. 清理你的系统
-
-这是你安装Ubuntu后不需要马上做的事情。但是记住它会对你有帮助。
-
-随着时间的推移,你的系统将有大量不再需要的包。你可以用这个命令一次性删除它们:
-
-```
-sudo apt autoremove
-```
-
-还有其他[清理 Ubuntu 以释放磁盘空间的方法][41],但这是最简单和最安全的。
-
-#### 16\. 根据您的喜好调整和定制 GNOME 桌面
-
-我强烈推荐[安装 GNOME 设置工具][42]。这将让你可以通过额外的设置来进行定制。
-
-![Gnome 设置工具][43]
-
-比如,你可以[以百分比形式显示电池容量][44],[修正在touchpad中右键问题][45],改变 Shell 主题,改变鼠标指针速度,显示日期和星期数,改变应用程序窗口行为等。
-
-定制是没有尽头的,我可能仅使用了它的一小部分功能。这就是为什么我推荐[阅读这些文章]关于[自定义GNOME桌面][46]的[42]。
-
-你也可以[在Ubuntu中安装新主题][47],不过就我个人而言,我喜欢这个版本的默认主题。这是我第一次在Ubuntu发行版中使用默认的图标和主题。
-
-#### 安装 Ubuntu 之后你会做什么?
-
-如果你是Ubuntu的初学者,我建议你[阅读这一系列Ubuntu教程][48]开始学习。
-
-这就是我的建议。安装Ubuntu之后你要做什么?分享你最喜欢的东西,我可能根据你的建议来更新这篇文章。
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: https://itsfoss.com/things-to-do-after-installing-ubuntu-20-04/
-
-作者:[Abhishek Prakash][a]
-选题:[lujun9972][b]
-译者:[qfzy1233](https://github.com/qfzy1233)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]: https://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/
-[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
-[1]: https://itsfoss.com/ubuntu-20-04-release-features/
-[2]: https://i2.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/things-to-do-after-installing-ubuntu-20-04.jpg?ssl=1
-[3]: https://itsfoss.com/how-to-know-ubuntu-unity-version/
-[4]: https://itsfoss.com/find-desktop-environment/
-[5]: https://i0.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/software-updater-ubuntu-20-04.jpg?ssl=1
-[6]: https://itsfoss.com/ubuntu-repositories/
-[7]: https://i0.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/software-updates-settings-ubuntu-20-04.jpg?ssl=1
-[8]: https://i1.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/extra-repositories-ubuntu-20.jpg?ssl=1
-[9]: https://itsfoss.com/install-media-codecs-ubuntu/
-[10]: https://itsfoss.com/install-microsoft-fonts-ubuntu/
-[11]: https://ubuntu-restricted-extras/
-[12]: https://i2.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/02/installing_ubuntu_restricted_extras.jpg?ssl=1
-[13]: https://itsfoss.com/remove-install-software-ubuntu/
-[14]: https://i0.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/software-center-ubuntu-20.png?resize=800%2C509&ssl=1
-[15]: https://itsfoss.com/best-ubuntu-apps/
-[16]: https://itsfoss.com/install-chrome-ubuntu/
-[17]: https://itsfoss.com/linux-gaming-guide/
-[18]: https://itsfoss.com/install-steam-ubuntu-linux/
-[19]: https://itsfoss.com/steam-play/
-[20]: https://github.com/FeralInteractive/gamemode
-[21]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rise_of_the_Tomb_Raider
-[22]: https://itsfoss.com/could-not-get-lock-error/
-[23]: https://i0.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/auto-updates-ubuntu.png?resize=800%2C361&ssl=1
-[24]: https://i0.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/power-settings-ubuntu-20-04.png?fit=800%2C591&ssl=1
-[25]: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lpq8pm_xkSE
-[26]: https://i1.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/enable-dark-theme-ubuntu.png?ssl=1
-[27]: https://itsfoss.com/dark-mode-ubuntu/
-[28]: https://i0.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/disable-dock-ubuntu-20-04.png?ssl=1
-[29]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_Unicode_characters
-[30]: https://i2.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/emoji-ubuntu.jpg?ssl=1
-[31]: https://i2.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/emojis-desktop-search-ubuntu.jpg?ssl=1
-[32]: https://i1.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/ubuntu-desktop-search-1.jpg?ssl=1
-[33]: https://i2.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/quick-calculations-ubuntu-search.jpg?ssl=1
-[34]: https://i1.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/search-settings-control-ubuntu.png?resize=800%2C534&ssl=1
-[35]: https://i2.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/nightlight-ubuntu-20-04.png?ssl=1
-[36]: https://i1.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/fractional-scaling-ubuntu.jpg?ssl=1
-[37]: https://itsfoss.com/gnome-shell-extensions/
-[38]: https://itsfoss.com/best-gnome-extensions/
-[39]: https://i2.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/weather-extension-ubuntu.jpg?ssl=1
-[40]: https://i1.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/03/do-not-distrub-option-ubuntu-20-04.png?ssl=1
-[41]: https://itsfoss.com/free-up-space-ubuntu-linux/
-[42]: https://itsfoss.com/gnome-tweak-tool/
-[43]: https://i1.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/gnome-tweaks-tool-ubuntu-20-04.png?fit=800%2C551&ssl=1
-[44]: https://itsfoss.com/display-battery-ubuntu/
-[45]: https://itsfoss.com/fix-right-click-touchpad-ubuntu/
-[46]: https://itsfoss.com/gnome-tricks-ubuntu/
-[47]: https://itsfoss.com/install-themes-ubuntu/
-[48]: https://itsfoss.com/getting-started-with-ubuntu/
diff --git a/translated/tech/20200430 10 ways to analyze binary files on Linux.md b/translated/tech/20200430 10 ways to analyze binary files on Linux.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..80577dfbcf
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20200430 10 ways to analyze binary files on Linux.md
@@ -0,0 +1,314 @@
+[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
+[#]: translator: (wxy)
+[#]: reviewer: ( )
+[#]: publisher: ( )
+[#]: url: ( )
+[#]: subject: (10 ways to analyze binary files on Linux)
+[#]: via: (https://opensource.com/article/20/4/linux-binary-analysis)
+[#]: author: (Gaurav Kamathe https://opensource.com/users/gkamathe)
+
+在 Linux 上分析二进制文件的 10 种方法
+======
+
+> 这些简单的命令和工具可以帮助你轻松完成分析二进制文件的任务。
+
+![Tux with binary code background][1]
+
+“这个世界上有 10 种人:懂二进制的人和不懂二进制的人。”
+
+我们每天都在与二进制文件打交道,但我们对二进制文件却知之甚少。我所说的二进制,是指你每天运行的可执行文件,从你的命令行工具到成熟的应用程序都是。
+
+Linux 提供了一套丰富的工具,让分析二进制文件变得轻而易举。无论你的工作角色是什么,如果你在 Linux 上工作,了解这些工具的基本知识将帮助你更好地理解你的系统。
+
+在这篇文章中,我们将介绍其中一些最流行的 Linux 工具和命令,其中大部分都是 Linux 发行版的一部分。如果没有找到,你可以随时使用你的软件包管理器来安装和探索它们。请记住:学习在正确的场合使用正确的工具需要大量的耐心和练习。
+
+### file
+
+它的作用:帮助确定文件类型。
+
+这将是你进行二进制分析的出发点。我们每天都在与文件打交道。并非所有的文件都是可执行类型,除此之外还有各种各样的文件类型。在你开始之前,你需要了解要分析的文件类型。它是二进制文件、库文件、ASCII 文本文件、视频文件、图片文件、PDF、数据文件等等。
+
+`file` 命令将帮助你确定你所处理的文件类型。
+
+```
+$ file /bin/ls
+/bin/ls: ELF 64-bit LSB executable, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked (uses shared libs), for GNU/Linux 2.6.32, BuildID[sha1]=94943a89d17e9d373b2794dcb1f7e38c95b66c86, stripped
+$
+$ file /etc/passwd
+/etc/passwd: ASCII text
+$
+```
+
+### ldd
+
+它的作用:打印共享对象依赖关系。
+
+如果你已经在一个可执行的二进制文件上使用了上面的 `file` 命令,你肯定会看到输出中的“动态链接”信息。它是什么意思呢?
+
+在开发软件的时候,我们尽量不要重造轮子。有一组常见的任务是大多数软件程序需要的,比如打印输出或从标准输入/打开的文件中读取等。所有这些常见的任务都被抽象成一组通用的函数,然后每个人都可以使用,而不是写出自己的变体。这些常用的函数被放在一个叫 `libc` 或 `glibc` 的库中。
+
+如何找到可执行程序所依赖的库?这就是 `ldd` 命令的作用了。对动态链接的二进制文件运行该命令会显示出所有依赖库和它们的路径。
+
+```
+$ ldd /bin/ls
+ linux-vdso.so.1 => (0x00007ffef5ba1000)
+ libselinux.so.1 => /lib64/libselinux.so.1 (0x00007fea9f854000)
+ libcap.so.2 => /lib64/libcap.so.2 (0x00007fea9f64f000)
+ libacl.so.1 => /lib64/libacl.so.1 (0x00007fea9f446000)
+ libc.so.6 => /lib64/libc.so.6 (0x00007fea9f079000)
+ libpcre.so.1 => /lib64/libpcre.so.1 (0x00007fea9ee17000)
+ libdl.so.2 => /lib64/libdl.so.2 (0x00007fea9ec13000)
+ /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 (0x00007fea9fa7b000)
+ libattr.so.1 => /lib64/libattr.so.1 (0x00007fea9ea0e000)
+ libpthread.so.0 => /lib64/libpthread.so.0 (0x00007fea9e7f2000)
+$
+```
+
+### ltrace
+
+它的作用:一个库调用跟踪器。
+
+我们现在知道如何使用 `ldd` 命令找到一个可执行程序所依赖的库。然而,一个库可以包含数百个函数。在这几百个函数中,哪些是我们的二进制程序正在使用的实际函数?
+
+`ltrace` 命令可以显示在运行时从库中调用的所有函数。在下面的例子中,你可以看到被调用的函数名称,以及传递给该函数的参数。你也可以在输出的最右边看到这些函数返回的内容。
+
+```
+$ ltrace ls
+__libc_start_main(0x4028c0, 1, 0x7ffd94023b88, 0x412950
+strrchr("ls", '/') = nil
+setlocale(LC_ALL, "") = "en_US.UTF-8"
+bindtextdomain("coreutils", "/usr/share/locale") = "/usr/share/locale"
+textdomain("coreutils") = "coreutils"
+__cxa_atexit(0x40a930, 0, 0, 0x736c6974756572) = 0
+isatty(1) = 1
+getenv("QUOTING_STYLE") = nil
+getenv("COLUMNS") = nil
+ioctl(1, 21523, 0x7ffd94023a50) = 0
+<< snip >>
+fflush(0x7ff7baae61c0) = 0
+fclose(0x7ff7baae61c0) = 0
++++ exited (status 0) +++
+$
+```
+
+### hexdump
+
+它的作用:以 ASCII、十进制、十六进制或八进制显示文件内容。
+
+通常情况下,当你用一个应用程序打开一个文件,而它不知道如何处理该文件时,就会出现这种情况。尝试用 `vim` 打开一个可执行文件或视频文件,你会看到的只是屏幕上抛出的乱码。
+
+在 `hexdump` 中打开未知文件,可以帮助你看到文件的具体内容。你也可以选择使用一些命令行选项来查看用 ASCII 表示的文件数据。这可能会帮助你了解到它是什么类型的文件。
+
+```
+$ hexdump -C /bin/ls | head
+00000000 7f 45 4c 46 02 01 01 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |.ELF............|
+00000010 02 00 3e 00 01 00 00 00 d4 42 40 00 00 00 00 00 |..>......B@.....|
+00000020 40 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 f0 c3 01 00 00 00 00 00 |@...............|
+00000030 00 00 00 00 40 00 38 00 09 00 40 00 1f 00 1e 00 |....@.8...@.....|
+00000040 06 00 00 00 05 00 00 00 40 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |........@.......|
+00000050 40 00 40 00 00 00 00 00 40 00 40 00 00 00 00 00 |@.@.....@.@.....|
+00000060 f8 01 00 00 00 00 00 00 f8 01 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
+00000070 08 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 03 00 00 00 04 00 00 00 |................|
+00000080 38 02 00 00 00 00 00 00 38 02 40 00 00 00 00 00 |8.......8.@.....|
+00000090 38 02 40 00 00 00 00 00 1c 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |8.@.............|
+$
+```
+
+### strings
+
+它的作用:打印文件中的可打印字符的字符串。
+
+如果你只是在二进制中寻找可打印的字符,那么 `hexdump` 对于你的使用场景来说似乎有点矫枉过正,你可以使用 `strings` 命令。
+
+在开发软件的时候,各种文本/ASCII 信息会被添加到其中,比如打印信息、调试信息、帮助信息、错误等。只要这些信息都存在于二进制文件中,就可以用 `strings` 命令将其转储到屏幕上。
+
+```
+$ strings /bin/ls
+```
+
+### readelf
+
+它的作用:显示有关 ELF 文件的信息。
+
+ELF(可执行和可链接文件格式)是可执行文件或二进制文件的主流格式,不仅是 Linux 系统,也是各种 UNIX 系统的主流文件格式。如果你已经使用了像 `file` 命令这样的工具,它告诉你文件是 ELF 格式,那么下一步就是使用 `readelf` 命令和它的各种选项来进一步分析文件。
+
+在使用 `readelf` 命令时,有一个实际的 ELF 规范的参考是非常有用的。你可以在[这里][2]找到规范。
+
+```
+$ readelf -h /bin/ls
+ELF Header:
+ Magic: 7f 45 4c 46 02 01 01 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
+ Class: ELF64
+ Data: 2's complement, little endian
+ Version: 1 (current)
+ OS/ABI: UNIX - System V
+ ABI Version: 0
+ Type: EXEC (Executable file)
+ Machine: Advanced Micro Devices X86-64
+ Version: 0x1
+ Entry point address: 0x4042d4
+ Start of program headers: 64 (bytes into file)
+ Start of section headers: 115696 (bytes into file)
+ Flags: 0x0
+ Size of this header: 64 (bytes)
+ Size of program headers: 56 (bytes)
+ Number of program headers: 9
+ Size of section headers: 64 (bytes)
+ Number of section headers: 31
+ Section header string table index: 30
+$
+```
+
+### objdump
+
+它的作用:从对象文件中显示信息。
+
+二进制文件是通过你编写源码的创建的,这些源码会通过一个叫做编译器的工具进行编译。这个编译器会生成相当于源代码的机器语言指令,然后由 CPU 执行,以执行特定的任务。这些机器语言代码可以通过被称为汇编语言的助记词来解读。汇编语言是一组指令,它可以帮助你理解由程序所进行并最终在 CPU 上执行的操作。
+
+`objdump` 实用程序读取二进制或可执行文件,并将汇编语言指令转储到屏幕上。汇编语言知识对于理解 `objdump` 命令的输出是至关重要的。
+
+请记住:汇编语言是特定于体系结构的。
+
+```
+$ objdump -d /bin/ls | head
+
+/bin/ls: file format elf64-x86-64
+
+
+Disassembly of section .init:
+
+0000000000402150 <_init@@Base>:
+ 402150: 48 83 ec 08 sub $0x8,%rsp
+ 402154: 48 8b 05 6d 8e 21 00 mov 0x218e6d(%rip),%rax # 61afc8 <__gmon_start__>
+ 40215b: 48 85 c0 test %rax,%rax
+$
+```
+
+### strace
+
+它的作用:跟踪系统调用和信号。
+
+如果你用过前面提到的 `ltrace`,那就把 `strace` 想成是类似的。唯一的区别是,`strace` 工具不是追踪调用的库,而是追踪系统调用。系统调用是你与内核对接来完成工作的。
+
+举个例子,如果你想把一些东西打印到屏幕上,你会使用标准库 `libc` 中的 `printf` 或 `puts` 函数;但是,在底层,最终会有一个名为 `write` 的系统调用来实际把东西打印到屏幕上。
+
+```
+$ strace -f /bin/ls
+execve("/bin/ls", ["/bin/ls"], [/* 17 vars */]) = 0
+brk(NULL) = 0x686000
+mmap(NULL, 4096, PROT_READ|PROT_WRITE, MAP_PRIVATE|MAP_ANONYMOUS, -1, 0) = 0x7f967956a000
+access("/etc/ld.so.preload", R_OK) = -1 ENOENT (No such file or directory)
+open("/etc/ld.so.cache", O_RDONLY|O_CLOEXEC) = 3
+fstat(3, {st_mode=S_IFREG|0644, st_size=40661, ...}) = 0
+mmap(NULL, 40661, PROT_READ, MAP_PRIVATE, 3, 0) = 0x7f9679560000
+close(3) = 0
+<< snip >>
+fstat(1, {st_mode=S_IFCHR|0620, st_rdev=makedev(136, 1), ...}) = 0
+mmap(NULL, 4096, PROT_READ|PROT_WRITE, MAP_PRIVATE|MAP_ANONYMOUS, -1, 0) = 0x7f9679569000
+write(1, "R2 RH\n", 7R2 RH
+) = 7
+close(1) = 0
+munmap(0x7f9679569000, 4096) = 0
+close(2) = 0
+exit_group(0) = ?
++++ exited with 0 +++
+$
+```
+
+### nm
+
+它的作用:列出对象文件中的符号。
+
+如果你所使用的二进制文件没有被剥离,`nm` 命令将为你提供在编译过程中嵌入到二进制文件中的有价值的信息。`nm` 可以帮助你从二进制文件中识别变量和函数。你可以想象一下,如果你无法访问二进制文件的源代码,这将是多么有用。
+
+为了展示 `nm`,我们快速编写了一个小程序,用 `-g` 选项编译,我们会看到这个二进制文件没有被剥离。
+
+```
+$ cat hello.c
+#include
+
+int main() {
+ printf("Hello world!");
+ return 0;
+}
+$
+$ gcc -g hello.c -o hello
+$
+$ file hello
+hello: ELF 64-bit LSB executable, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked (uses shared libs), for GNU/Linux 2.6.32, BuildID[sha1]=3de46c8efb98bce4ad525d3328121568ba3d8a5d, not stripped
+$
+$ ./hello
+Hello world!$
+$
+
+
+$ nm hello | tail
+0000000000600e20 d __JCR_END__
+0000000000600e20 d __JCR_LIST__
+00000000004005b0 T __libc_csu_fini
+0000000000400540 T __libc_csu_init
+ U __libc_start_main@@GLIBC_2.2.5
+000000000040051d T main
+ U printf@@GLIBC_2.2.5
+0000000000400490 t register_tm_clones
+0000000000400430 T _start
+0000000000601030 D __TMC_END__
+$
+```
+
+### gdb
+
+它的作用:GNU 调试器。
+
+好吧,不是所有的二进制文件中的东西都可以进行静态分析。我们确实执行了一些运行二进制文件(进行分析)的命令,比如 `ltrace` 和 `strace`;然而,软件由各种条件组成,这些条件可能会导致执行不同的替代路径。
+
+分析这些路径的唯一方法是在运行时环境,在任何给定的位置停止或暂停程序,并能够分析信息,然后再往下执行。
+
+这就是调试器的作用,在 Linux 上,`gdb` 就是调试器的事实标准。它可以帮助你加载程序,在特定的地方设置断点,分析内存和 CPU 的寄存器,还有更多的功能。它是对上面提到的其他工具的补充,可以让你做更多的运行时分析。
+
+有一点需要注意的是,一旦你使用 `gdb` 加载一个程序,你会看到它自己的 `(gdb)` 提示符。所有进一步的命令都将在这个 `gdb` 命令提示符中运行,直到你退出。
+
+我们将使用我们之前编译的 `hello` 程序,使用 `gdb` 来看看它的工作原理。
+
+```
+$ gdb -q ./hello
+Reading symbols from /home/flash/hello...done.
+(gdb) break main
+Breakpoint 1 at 0x400521: file hello.c, line 4.
+(gdb) info break
+Num Type Disp Enb Address What
+1 breakpoint keep y 0x0000000000400521 in main at hello.c:4
+(gdb) run
+Starting program: /home/flash/./hello
+
+Breakpoint 1, main () at hello.c:4
+4 printf("Hello world!");
+Missing separate debuginfos, use: debuginfo-install glibc-2.17-260.el7_6.6.x86_64
+(gdb) bt
+#0 main () at hello.c:4
+(gdb) c
+Continuing.
+Hello world![Inferior 1 (process 29620) exited normally]
+(gdb) q
+$```
+
+### 结语
+
+一旦你习惯了使用这些原生的 Linux 二进制分析工具,并理解了它们提供的输出,你就可以转向更高级和专业的开源二进制分析工具,比如 [radare2][3]。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://opensource.com/article/20/4/linux-binary-analysis
+
+作者:[Gaurav Kamathe][a]
+选题:[lujun9972][b]
+译者:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]: https://opensource.com/users/gkamathe
+[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
+[1]: https://opensource.com/sites/default/files/styles/image-full-size/public/lead-images/tux_linux_penguin_code_binary.jpg?itok=TxGxW0KY (Tux with binary code background)
+[2]: http://www.skyfree.org/linux/references/ELF_Format.pdf
+[3]: https://github.com/radareorg/radare2