diff --git a/published/20160518 Cleaning Up Your Linux Startup Process.md b/published/20160518 Cleaning Up Your Linux Startup Process.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..b4f8c3d02d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20160518 Cleaning Up Your Linux Startup Process.md
@@ -0,0 +1,145 @@
+Linux 系统开机启动项清理
+=======
+
+
+
+一般情况下,常规用途的 Linux 发行版在开机启动时拉起各种相关服务进程,包括许多你可能无需使用的服务,例如蓝牙、Avahi、 调制解调管理器、ppp-dns(LCTT 译注:此处作者笔误 ppp-dns 应该为 pppd-dns) 等服务进程,这些都是什么东西?用于哪里,有何功能?
+
+Systemd 提供了许多很好的工具用于查看系统启动情况,也可以控制在系统启动时运行什么。在这篇文章中,我将说明在 Systemd 类发行版中如何关闭一些令人讨厌的进程。
+
+### 查看开机启动项
+
+在过去,你能很容易通过查看 `/etc/init.d` 了解到哪些服务进程会在引导时启动。Systemd 以不同的方式展现,你可以使用如下命令罗列允许开机启动的服务进程。
+
+```
+$ systemctl list-unit-files --type=service | grep enabled
+accounts-daemon.service enabled
+anacron-resume.service enabled
+anacron.service enabled
+bluetooth.service enabled
+brltty.service enabled
+[...]
+```
+
+在此列表顶部,对我来说,蓝牙服务是冗余项,因为在该电脑上我不需要使用蓝牙功能,故无需运行此服务。下面的命令将停止该服务进程,并且使其开机不启动。
+
+```
+$ sudo systemctl stop bluetooth.service
+$ sudo systemctl disable bluetooth.service
+```
+
+你可以通过下面命令确定是否操作成功。
+
+```
+$ systemctl status bluetooth.service
+ bluetooth.service - Bluetooth service
+ Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/bluetooth.service; disabled; vendor preset: enabled)
+ Active: inactive (dead)
+ Docs: man:bluetoothd(8)
+```
+
+停用的服务进程仍然能够被另外一个服务进程启动。如果你真的想在任何情况下系统启动时都不启动该进程,无需卸载该它,只需要把它掩盖起来就可以阻止该进程在任何情况下开机启动。
+
+```
+$ sudo systemctl mask bluetooth.service
+ Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/bluetooth.service to /dev/null.
+```
+
+一旦你对禁用该进程启动而没有出现负面作用感到满意,你也可以选择卸载该程序。
+
+通过执行命令可以获得如下服务列表:
+
+```
+$ systemctl list-unit-files --type=service
+UNIT FILE STATE
+accounts-daemon.service enabled
+acpid.service disabled
+alsa-restore.service static
+alsa-utils.service masked
+```
+
+你不能启用或禁用静态服务,因为静态服务被其他的进程所依赖,并不意味着它们自己运行。
+
+### 哪些服务能够禁止?
+
+如何知道你需要哪些服务,而哪些又是可以安全地禁用的呢?它总是依赖于你的个性化需求。
+
+这里举例了几个服务进程的作用。许多服务进程都是发行版特定的,所以你应该看看你的发行版文档(比如通过 google 或 StackOverflow)。
+
+- **accounts-daemon.service** 是一个潜在的安全风险。它是 AccountsService 的一部分,AccountsService 允许程序获得或操作用户账户信息。我不认为有好的理由能使我允许这样的后台操作,所以我选择掩盖该服务进程。
+- **avahi-daemon.service** 用于零配置网络发现,使电脑超容易发现网络中打印机或其他的主机,我总是禁用它,别漏掉它。
+- **brltty.service** 提供布莱叶盲文设备支持,例如布莱叶盲文显示器。
+- **debug-shell.service** 开放了一个巨大的安全漏洞(该服务提供了一个无密码的 root shell ,用于帮助 调试 systemd 问题),除非你正在使用该服务,否则永远不要启动服务。
+- **ModemManager.service** 该服务是一个被 dbus 激活的守护进程,用于提供移动宽频(2G/3G/4G)接口,如果你没有该接口,无论是内置接口,还是通过如蓝牙配对的电话,以及 USB 适配器,那么你也无需该服务。
+- **pppd-dns.service** 是一个计算机发展的遗物,如果你使用拨号接入互联网的话,保留它,否则你不需要它。
+- **rtkit-daemon.service** 听起来很可怕,听起来像是 rootkit。 但是你需要该服务,因为它是一个实时内核调度器。
+- **whoopsie.service** 是 Ubuntu 错误报告服务。它用于收集 Ubuntu 系统崩溃报告,并发送报告到 https://daisy.ubuntu.com 。 你可以放心地禁止其启动,或者永久的卸载它。
+- **wpa_supplicant.service** 仅在你使用 Wi-Fi 连接时需要。
+
+### 系统启动时发生了什么?
+
+Systemd 提供了一些命令帮助调试系统开机启动问题。该命令会重演你的系统启动的所有消息。
+
+```
+$ journalctl -b
+
+-- Logs begin at Mon 2016-05-09 06:18:11 PDT,
+end at Mon 2016-05-09 10:17:01 PDT. --
+May 16 06:18:11 studio systemd-journal[289]:
+Runtime journal (/run/log/journal/) is currently using 8.0M.
+Maximum allowed usage is set to 157.2M.
+Leaving at least 235.9M free (of currently available 1.5G of space).
+Enforced usage limit is thus 157.2M.
+[...]
+```
+
+通过命令 `journalctl -b -1` 可以复审前一次启动,`journalctl -b -2` 可以复审倒数第 2 次启动,以此类推。
+
+该命令会打印出大量的信息,你可能并不关注所有信息,只是关注其中问题相关部分。为此,系统提供了几个过滤器,用于帮助你锁定目标。让我们以进程号为 1 的进程为例,该进程是所有其它进程的父进程。
+
+```
+$ journalctl _PID=1
+
+May 08 06:18:17 studio systemd[1]: Starting LSB: Raise network interfaces....
+May 08 06:18:17 studio systemd[1]: Started LSB: Raise network interfaces..
+May 08 06:18:17 studio systemd[1]: Reached target System Initialization.
+May 08 06:18:17 studio systemd[1]: Started CUPS Scheduler.
+May 08 06:18:17 studio systemd[1]: Listening on D-Bus System Message Bus Socket
+May 08 06:18:17 studio systemd[1]: Listening on CUPS Scheduler.
+[...]
+```
+
+这些打印消息显示了什么被启动,或者是正在尝试启动。
+
+一个最有用的命令工具之一 `systemd-analyze blame`,用于帮助查看哪个服务进程启动耗时最长。
+
+```
+$ systemd-analyze blame
+ 8.708s gpu-manager.service
+ 8.002s NetworkManager-wait-online.service
+ 5.791s mysql.service
+ 2.975s dev-sda3.device
+ 1.810s alsa-restore.service
+ 1.806s systemd-logind.service
+ 1.803s irqbalance.service
+ 1.800s lm-sensors.service
+ 1.800s grub-common.service
+```
+
+这个特定的例子没有出现任何异常,但是如果存在系统启动瓶颈,则该命令将能发现它。
+
+你也能通过如下资源了解 Systemd 如何工作:
+
+- [理解和使用 Systemd](https://www.linux.com/learn/understanding-and-using-systemd)
+- [介绍 Systemd 运行级别和服务管理命令](https://www.linux.com/learn/intro-systemd-runlevels-and-service-management-commands)
+- [再次前行,另一个 Linux 初始化系统:Systemd 介绍](https://www.linux.com/learn/here-we-go-again-another-linux-init-intro-systemd)
+
+----
+
+via: https://www.linux.com/learn/cleaning-your-linux-startup-process
+
+作者:[David Both](https://www.linux.com/users/cschroder)
+译者:[penghuster](https://github.com/penghuster)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 LCTT 原创编译,Linux中国 荣誉推出
diff --git a/published/20160815 Here are all the Git commands I used last week and what they do.md b/published/20160815 Here are all the Git commands I used last week and what they do.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..da5520275c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20160815 Here are all the Git commands I used last week and what they do.md
@@ -0,0 +1,196 @@
+一周工作所用的日常 Git 命令
+============================================================
+
+
+
+像大多数新手一样,我一开始是在 StackOverflow 上搜索 Git 命令,然后把答案复制粘贴,并没有真正理解它们究竟做了什么。
+
+
+
+*Image credit: [XKCD][7]*
+
+我曾经想过:“如果有一个最常见的 Git 命令的列表,以及它们的功能是什么,这不是极好的吗?”
+
+多年之后,我编制了这样一个列表,并且给出了一些最佳实践,让新手们甚至中高级开发人员都能从中发现有用的东西。
+
+为了保持实用性,我将这个列表与我过去一周实际使用的 Git 命令进行了比较。
+
+几乎每个开发人员都在使用 Git,当然很可能是 GitHub。但大多数开发者大概有 99% 的时间只是使用这三个命令:
+
+```
+git add --all
+git commit -am ""
+git push origin master
+```
+
+如果你只是单枪匹马,或者参加一场黑客马拉松或开发一次性的应用时,它工作得很好,但是当稳定性和可维护性开始成为一个优先考虑的事情后,清理提交、坚持分支策略和提交信息的规范性就变得很重要。
+
+我将从常用命令的列表开始,使新手更容易了解 Git 能做什么,然后进入更高级的功能和最佳实践。
+
+### 经常使用的命令
+
+要想在仓库(repo)中初始化 Git,你只需输入以下命令即可。如果你没有初始化 Git,则不能在该仓库内运行任何其他的 Git 命令。
+
+```
+git init
+```
+
+如果你在使用 GitHub,而且正在将代码推送到在线存储的 GitHub 仓库中,那么你正在使用的就是远程(remote)仓库。该远程仓库的默认名称(也称为别名)为 `origin`。如果你已经从 Github 复制了一个项目,它就有了一个 `origin`。你可以使用命令 `git remote -v` 查看该 `origin`,该命令将列出远程仓库的 URL。
+
+如果你初始化了自己的 Git 仓库,并希望将其与 GitHub 仓库相关联,则必须在 GitHub 上创建一个,复制新仓库提供的 URL,并使用 `git remote add origin ` 命令,这里使用 GitHub 提供的 URL 替换 ``。这样,你就可以添加、提交和推送更改到你的远程仓库了。
+
+最后一条命令用在当你需要更改远程仓库时。如果你从其他人那里复制了一个仓库,并希望将远程仓库从原始所有者更改为你自己的 GitHub 帐户。除了改用 `set-url` 来更改远程仓库外,流程与 `git remote add origin` 相同。
+
+```
+git remote -v
+git remote add origin
+git remote set-url origin
+```
+
+复制仓库最常见的方式是使用 `git clone`,后跟仓库的 URL。
+
+请记住,远程仓库将连接到克隆仓库原属于的帐户。所以,如果你克隆了一个属于别人的仓库,你将无法推送到 GitHub,除非你使用上面的命令改变了 `origin`。
+
+```
+git clone
+```
+
+你很快就会发现自己正在使用分支。如果你还不理解什么是分支,有许多其他更深入的教程,你应该先阅读它们,再继续下面的操作。([这里是一个教程][8])
+
+命令 `git branch` 列出了本地机器上的所有分支。如果要创建一个新的分支,可以使用命令 `git branch `,其中 `` 表示分支的名字,比如说 `master`。
+
+`git checkout ` 命令可以切换到现有的分支。你也可以使用 `git checkout -b` 命令创建一个新的分支并立即切换到它。大多数人都使用此命令而不是单独的 `branch` 和 `checkout` 命令。
+
+```
+git branch
+git branch
+git checkout
+git checkout -b
+```
+
+如果你对一个分支进行了一系列的更改,假如说此分支名为 `develop`,如果想要将该分支合并回主分支(`master`)上,则使用 `git merge ` 命令。你需要先检出(`checkout`)主分支,然后运行 `git merge develop` 将 `develop` 合并到主分支中。
+
+```
+git merge
+```
+
+如果你正在与多个人进行协作,你会发现有时 GitHub 的仓库上已经更新了,但你的本地却没有做相应的更改。如果是这样,你可以使用 `git pull origin ` 命令从远程分支中拉取最新的更改。
+
+```
+git pull origin
+```
+
+如果您好奇地想看到哪些文件已被更改以及哪些内存正在被跟踪,可以使用 `git status` 命令。如果要查看每个文件的更改,可以使用 `git diff` 来查看每个文件中更改的行。
+
+```
+git status
+git diff --stat
+```
+
+### 高级命令和最佳实践
+
+很快你会到达一个阶段,这时你希望你的提交看起来整洁一致。你可能还需要调整你的提交记录,使得提交更容易理解或者能还原一个意外的有破坏性的更改。
+
+`git log` 命令可以输出提交的历史记录。你将使用它来查看提交的历史记录。
+
+你的提交会附带消息和一个哈希值,哈希值是一串包含数字和字母的随机序列。一个哈希值示例如下:`c3d882aa1aa4e3d5f18b3890132670fbeac912f7`。
+
+```
+git log
+```
+
+假设你推送了一些可能破坏了你应用程序的东西。你最好回退一个提交然后再提交一次正确的,而不是修复它和推送新的东西。
+
+如果你希望及时回退并从之前的提交中检出(`checkout`)你的应用程序,则可以使用该哈希作为分支名直接执行此操作。这将使你的应用程序与当前版本分离(因为你正在编辑历史记录的版本,而不是当前版本)。
+
+```
+git checkout c3d88eaa1aa4e4d5f
+```
+
+然后,如果你在那个历史分支中做了更改,并且想要再次推送,你必须使用强制推送。
+
+**注意**:强制推送是危险的,只有在绝对必要的时候才能执行它。它将覆盖你的应用程序的历史记录,你将失去之后版本的任何信息。
+
+```
+git push -f origin master
+```
+
+在其他时候,将所有内容保留在一个提交中是不现实的。也行你想在尝试有潜在风险的操作之前保存当前进度,或者也许你犯了一个错误,但希望在你的版本历史中避免尴尬地留着这个错误。对此,我们有 `git rebase`。
+
+假设你在本地历史记录上有 4 个提交(没有推送到 GitHub),你要回退这是个提交。你的提交记录看起来很乱很拖拉。这时你可以使用 `rebase` 将所有这些提交合并到一个简单的提交中。
+
+```
+git rebase -i HEAD~4
+```
+
+上面的命令会打开你计算机的默认编辑器(默认为 Vim,除非你将默认修改为其他的),提供了几个你准备如何修改你的提交的选项。它看起来就像下面的代码:
+
+```
+pick 130deo9 oldest commit message
+pick 4209fei second oldest commit message
+pick 4390gne third oldest commit message
+pick bmo0dne newest commit message
+```
+
+为了合并这些提交,我们需要将 `pick` 选项修改为 `fixup`(如代码下面的文档所示),以将该提交合并并丢弃该提交消息。请注意,在 Vim 中,你需要按下 `a` 或 `i` 才能编辑文本,要保存退出,你需要按下 `Esc` 键,然后按 `shift + z + z`。不要问我为什么,它就是这样。
+
+```
+pick 130deo9 oldest commit message
+fixup 4209fei second oldest commit message
+fixup 4390gne third oldest commit message
+fixup bmo0dne newest commit message
+```
+
+这将把你的所有提交合并到一个提交中,提交消息为 `oldest commit message`。
+
+下一步是重命名你的提交消息。这完全是一个建议的操作,但只要你一直遵循一致的模式,都可以做得很好。这里我建议使用 [Google 为 Angular.js 提供的提交指南][9]。
+
+为了更改提交消息,请使用 `amend` 标志。
+
+```
+git commit --amend
+```
+
+这也会打开 Vim,文本编辑和保存规则如上所示。为了给出一个良好的提交消息的例子,下面是遵循该指南中规则的提交消息:
+
+```
+feat: add stripe checkout button to payments page
+
+- add stripe checkout button
+- write tests for checkout
+```
+
+保持指南中列出的类型(type)的一个优点是它使编写更改日志更加容易。你还可以在页脚(footer)(再次,在指南中规定的)中包含信息来引用问题(issue)。
+
+**注意:**如果你正在协作一个项目,并将代码推送到了 GitHub,你应该避免重新引用(`rebase`)并压缩(`squash`)你的提交。如果你开始在人们的眼皮子底下更改版本历史,那么你可能会遇到难以追踪的错误,从而给每个人都带来麻烦。
+
+Git 有无数的命令,但这里介绍的命令可能是您最初几年编程所需要知道的所有。
+
+* * *
+
+Sam Corcos 是 [Sightline Maps][10] 的首席开发工程师和联合创始人,Sightline Maps 是最直观的 3D 打印地形图的平台,以及用于构建 Phoenix 和 React 的可扩展生产应用程序的中级高级教程网站 [LearnPhoenix.io][11]。使用优惠码:free_code_camp 取得 LearnPhoenix 的20美元。
+
+(题图:[GitHub Octodex][6])
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://medium.freecodecamp.org/git-cheat-sheet-and-best-practices-c6ce5321f52
+
+作者:[Sam Corcos][a]
+译者:[firmianay](https://github.com/firmianay)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:https://medium.freecodecamp.org/@SamCorcos?source=post_header_lockup
+[1]:https://medium.freecodecamp.org/tagged/git?source=post
+[2]:https://medium.freecodecamp.org/tagged/github?source=post
+[3]:https://medium.freecodecamp.org/tagged/programming?source=post
+[4]:https://medium.freecodecamp.org/tagged/software-development?source=post
+[5]:https://medium.freecodecamp.org/tagged/web-development?source=post
+[6]:https://octodex.github.com/
+[7]:https://xkcd.com/1597/
+[8]:https://guides.github.com/introduction/flow/
+[9]:https://github.com/angular/angular.js/blob/master/CONTRIBUTING.md#-git-commit-guidelines
+[10]:http://sightlinemaps.com/
+[11]:http://learnphoenix.io/
diff --git a/translated/tech/20170123 What I Dont Like About Error Handling in Go and How to Work Around It.md b/published/20170123 What I Dont Like About Error Handling in Go and How to Work Around It.md
similarity index 64%
rename from translated/tech/20170123 What I Dont Like About Error Handling in Go and How to Work Around It.md
rename to published/20170123 What I Dont Like About Error Handling in Go and How to Work Around It.md
index d7b7627e49..dae5a6e6dc 100644
--- a/translated/tech/20170123 What I Dont Like About Error Handling in Go and How to Work Around It.md
+++ b/published/20170123 What I Dont Like About Error Handling in Go and How to Work Around It.md
@@ -1,18 +1,17 @@
我对 Go 的错误处理有哪些不满,以及我是如何处理的
======================
-写 Go 的人往往对它的错误处理模式有一定的看法。根据你对其他语言的经验,你可能习惯于不同的方法。这就是为什么我决定要写这篇文章,尽管有点固执己见,但我认为吸收我的经验在辩论中是有用的。 我想要解决的主要问题是,很难去强制良好的错误处理实践,错误没有堆栈追踪,并且错误处理本身太冗长。不过,我已经看到了一些潜在的解决方案或许能帮助解决一些问题。
+写 Go 的人往往对它的错误处理模式有一定的看法。按不同的语言经验,人们可能有不同的习惯处理方法。这就是为什么我决定要写这篇文章,尽管有点固执己见,但我认为听取我的经验是有用的。我想要讲的主要问题是,很难去强制执行良好的错误处理实践,错误经常没有堆栈追踪,并且错误处理本身太冗长。不过,我已经看到了一些潜在的解决方案,或许能帮助解决一些问题。
### 与其他语言的快速比较
-
-[在 Go 中,所有的错误是值][1]。因为这点,相当多的函数最后会返回一个 `error`, 看起来像这样:
+[在 Go 中,所有的错误都是值][1]。因为这点,相当多的函数最后会返回一个 `error`, 看起来像这样:
```
func (s *SomeStruct) Function() (string, error)
```
-由于这点,调用代码常规上会使用 `if` 语句来检查它们:
+因此这导致调用代码通常会使用 `if` 语句来检查它们:
```
bytes, err := someStruct.Function()
@@ -21,13 +20,13 @@ if err != nil {
}
```
-另外一种是在其他语言中如 Java、C#、Javascript、Objective C、Python 等使用的 `try-catch` 模式。如下你可以看到与先前的 Go 示例类似的 Java 代码,声明 `throws` 而不是返回 `error`:
+另外一种方法,是在其他语言中,如 Java、C#、Javascript、Objective C、Python 等使用的 `try-catch` 模式。如下你可以看到与先前的 Go 示例类似的 Java 代码,声明 `throws` 而不是返回 `error`:
```
public String function() throws Exception
```
- `try-catch` 而不是 `if err != nil`:
+它使用的是 `try-catch` 而不是 `if err != nil`:
```
try {
@@ -39,11 +38,11 @@ catch (Exception e) {
}
```
-当然,还有其他的不同。不如,`error` 不会使你的程序崩溃,然而 `Exception` 会。还有其他的一些,我希望在在本篇中专注在这些上。
+当然,还有其他的不同。例如,`error` 不会使你的程序崩溃,然而 `Exception` 会。还有其他的一些,在本篇中会专门提到这些。
### 实现集中式错误处理
-退一步,让我们看看为什么以及如何在一个集中的地方处理错误。
+退一步,让我们看看为什么要在一个集中的地方处理错误,以及如何做到。
大多数人或许会熟悉的一个例子是 web 服务 - 如果出现了一些未预料的的服务端错误,我们会生成一个 5xx 错误。在 Go 中,你或许会这么实现:
@@ -68,7 +67,7 @@ func viewCompanies(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
}
```
-这并不是一个好的解决方案,因为我们不得不重复在所有的处理函数中处理错误。为了能更好地维护,最好能在一处地方处理错误。幸运的是,[在 Go 的博客中,Andrew Gerrand 提供了一个替代方法][2]可以完美地实现。我们可以错见一个处理错误的类型:
+这并不是一个好的解决方案,因为我们不得不重复地在所有的处理函数中处理错误。为了能更好地维护,最好能在一处地方处理错误。幸运的是,[在 Go 语言的官方博客中,Andrew Gerrand 提供了一个替代方法][2],可以完美地实现。我们可以创建一个处理错误的 Type:
```
type appHandler func(http.ResponseWriter, *http.Request) error
@@ -89,11 +88,11 @@ func init() {
}
```
-接着我们需要做的是修改处理函数的签名来使它们返回 `errors`。这个方法很好,因为我们做到了 [dry][3] 原则,并且没有重复使用不必要的代码 - 现在我们可以在一处返回默认错误了。
+接着我们需要做的是修改处理函数的签名来使它们返回 `errors`。这个方法很好,因为我们做到了 [DRY][3] 原则,并且没有重复使用不必要的代码 - 现在我们可以在单独一个地方返回默认错误了。
### 错误上下文
-在先前的例子中,我们可能会收到许多潜在的错误,它们的任何一个都可能在调用堆栈的许多部分生成。这时候事情就变得棘手了。
+在先前的例子中,我们可能会收到许多潜在的错误,它们中的任何一个都可能在调用堆栈的许多环节中生成。这时候事情就变得棘手了。
为了演示这点,我们可以扩展我们的处理函数。它可能看上去像这样,因为模板执行并不是唯一一处会发生错误的地方:
@@ -109,9 +108,9 @@ func viewUsers(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) error {
调用链可能会相当深,在整个过程中,各种错误可能在不同的地方实例化。[Russ Cox][4]的这篇文章解释了如何避免遇到太多这类问题的最佳实践:
- 在 Go 中错误报告的部分约定是函数包含相关的上下文、包含正在尝试的操作(比如函数名和它的参数)
+> “在 Go 中错误报告的部分约定是函数包含相关的上下文,包括正在尝试的操作(比如函数名和它的参数)。”
-给出的例子是 OS 包中的一个调用:
+这个给出的例子是对 OS 包的一个调用:
```
err := os.Remove("/tmp/nonexist")
@@ -140,11 +139,11 @@ if err != nil {
}
```
-这意味着错误发生时它们没有交流。
+这意味着错误何时发生并没有被传递出来。
应该注意的是,所有这些错误都可以在 `Exception` 驱动的模型中发生 - 糟糕的错误信息、隐藏异常等。那么为什么我认为该模型更有用?
-如果我们在处理一个糟糕的异常消息,_我们仍然能够了解堆栈中发生了什么_。因为堆栈跟踪,这引发了一些我对 Go 不了解的部分 - 你知道 Go 的 `panic` 包含了堆栈追踪,但是 `error` 没有。我认为推论是 `panic` 可能会使你的程序崩溃,因此需要一个堆栈追踪,而处理错误并不会,因为它会假定你在它发生的地方做一些事。
+即便我们在处理一个糟糕的异常消息,_我们仍然能够了解它发生在调用堆栈中什么地方_。因为堆栈跟踪,这引发了一些我对 Go 不了解的部分 - 你知道 Go 的 `panic` 包含了堆栈追踪,但是 `error` 没有。我推测可能是 `panic` 会使你的程序崩溃,因此需要一个堆栈追踪,而处理错误并不会,因为它会假定你在它发生的地方做一些事。
所以让我们回到之前的例子 - 一个有糟糕错误信息的第三方库,它只是输出了调用链。你认为调试会更容易吗?
@@ -170,17 +169,17 @@ github.com/Org/app/core/vendor/github.com/rusenask/goproxy.FuncReqHandler.Handle
如果我们使用 Java 作为一个随意的例子,其中人们犯的一个最愚蠢的错误是不记录堆栈追踪:
```
-LOGGER.error(ex.getMessage()) // Doesn't log stack trace
-LOGGER.error(ex.getMessage(), ex) // Does log stack trace
+LOGGER.error(ex.getMessage()) // 不记录堆栈追踪
+LOGGER.error(ex.getMessage(), ex) // 记录堆栈追踪
```
-但是 Go 设计中似乎没有这个信息
+但是 Go 似乎在设计中就没有这个信息。
-在获取上下文信息方面 - Russ 还提到了社区正在讨论一些潜在的接口用于剥离上下文错误。了解更多这点或许会很有趣。
+在获取上下文信息方面 - Russ 还提到了社区正在讨论一些潜在的接口用于剥离上下文错误。关于这点,了解更多或许会很有趣。
### 堆栈追踪问题解决方案
-幸运的是,在做了一些查找后,我发现了这个出色的[ Go 错误][5]库来帮助解决这个问题,来给错误添加堆栈跟踪:
+幸运的是,在做了一些查找后,我发现了这个出色的 [Go 错误][5]库来帮助解决这个问题,来给错误添加堆栈跟踪:
```
if errors.Is(err, crashy.Crashed) {
@@ -188,7 +187,7 @@ if errors.Is(err, crashy.Crashed) {
}
```
-不过,我认为这个功能能成为语言的一等公民将是一个改进,这样你就不必对类型做一些修改了。此外,如果我们像先前的例子那样使用第三方库,那就可能不必使用 `crashy` - 我们仍有相同的问题。
+不过,我认为这个功能如果能成为语言的第一类公民将是一个改进,这样你就不必做一些类型修改了。此外,如果我们像先前的例子那样使用第三方库,它可能没有使用 `crashy` - 我们仍有相同的问题。
### 我们对错误应该做什么?
@@ -201,7 +200,7 @@ if err != nil {
}
```
-如果我们想要调用大量会返回错误的方法时会发生什么,在同一个地方处理它们么?看上去像这样:
+如果我们想要调用大量方法,它们会产生错误,然后在一个地方处理所有错误,这时会发生什么?看上去像这样:
```
err := doSomething()
@@ -222,7 +221,7 @@ func doSomething() error {
}
```
-这感觉有点冗余,然而在其他语言中你可以将多条语句作为一个整体处理。
+这感觉有点冗余,在其他语言中你可以将多条语句作为一个整体处理。
```
try {
@@ -245,9 +244,9 @@ public void doSomething() throws SomeErrorToPropogate {
}
```
-我个人认为这两个例子实现了一件事情,只有 `Exception` 模式更少冗余更加弹性。如果有什么,我发现 `if err!= nil` 感觉像样板。也许有一种方法可以清理?
+我个人认为这两个例子实现了一件事情,只是 `Exception` 模式更少冗余,更加弹性。如果有什么的话,我觉得 `if err!= nil` 感觉像样板。也许有一种方法可以清理?
-### 将多条语句像一个整体那样发生错误
+### 将失败的多条语句做为一个整体处理错误
首先,我做了更多的阅读,并[在 Rob Pike 写的 Go 博客中][7]发现了一个比较务实的解决方案。
@@ -280,7 +279,7 @@ if ew.err != nil {
}
```
-这也是一个很好的方案,但是我感觉缺少了点什么 - 因为我们不能重复使用这个模式。如果我们想要一个含有字符串参数的方法,我们就不得不改变函数签名。或者如果我们不想执行写会怎样?我们可以尝试使它更通用:
+这也是一个很好的方案,但是我感觉缺少了点什么 - 因为我们不能重复使用这个模式。如果我们想要一个含有字符串参数的方法,我们就不得不改变函数签名。或者如果我们不想执行写操作会怎样?我们可以尝试使它更通用:
```
type errWrapper struct {
@@ -317,11 +316,11 @@ if err != nil {
}
```
-这可以用,但是并没有帮助太大,因为它最后比标准的 `if err != nil` 检查带来了更多的冗余。我有兴趣听到有人能提供其他解决方案。或许语言本身需要一些方法来以不那么臃肿的方式的传递或者组合错误 - 但是感觉似乎是特意设计成不那么做。
+这可以用,但是并没有太大帮助,因为它最终比标准的 `if err != nil` 检查带来了更多的冗余。如果有人能提供其他解决方案,我会很有兴趣听。或许这个语言本身需要一些方法来以不那么臃肿的方式传递或者组合错误 - 但是感觉似乎是特意设计成不那么做。
### 总结
-看完这些之后,你可能会认为我反对在 Go 中使用 `error`。但事实并非如此,我只是描述了如何将它与 `try catch` 模型的经验进行比较。它是一个用于系统编程很好的语言,并且已经出现了一些优秀的工具。仅举几例有 [Kubernetes][8]、[Docker][9]、[Terraform][10]、[Hoverfly][11] 等。还有小型、高性能、本地二进制的优点。但是,`error` 难以适应。 我希望我的推论是有道理的,而且一些方案和解决方法可能会有帮助。
+看完这些之后,你可能会认为我在对 `error` 挑刺儿,由此推论我反对 Go。事实并非如此,我只是将它与我使用 `try catch` 模型的经验进行比较。它是一个用于系统编程很好的语言,并且已经出现了一些优秀的工具。仅举几例,有 [Kubernetes][8]、[Docker][9]、[Terraform][10]、[Hoverfly][11] 等。还有小型、高性能、本地二进制的优点。但是,`error` 难以适应。 我希望我的推论是有道理的,而且一些方案和解决方法可能会有帮助。
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
@@ -336,7 +335,7 @@ via: https://opencredo.com/why-i-dont-like-error-handling-in-go
作者:[Andrew Morgan][a]
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/published/20170531 DNS Infrastructure at GitHub.md b/published/20170531 DNS Infrastructure at GitHub.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..0abec33d5b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20170531 DNS Infrastructure at GitHub.md
@@ -0,0 +1,79 @@
+GitHub 的 DNS 基础设施
+============================================================
+
+在 GitHub,我们最近从头改进了 DNS。这包括了我们[如何与外部 DNS 提供商交互][4]以及我们如何在内部向我们的主机提供记录。为此,我们必须设计和构建一个新的 DNS 基础设施,它可以随着 GitHub 的增长扩展并跨越多个数据中心。
+
+以前,GitHub 的 DNS 基础设施相当简单直接。它包括每台服务器上本地的、只具备转发功能的 DNS 缓存服务器,以及一对被所有这些主机使用的缓存服务器和权威服务器主机。这些主机在内部网络以及公共互联网上都可用。我们在缓存守护程序中配置了区域存根,以在本地进行查询,而不是在互联网上进行递归。我们还在我们的 DNS 提供商处设置了 NS 记录,它们将特定的内部域指向这对主机的公共 IP,以便我们网络外部的查询。
+
+这个配置使用了很多年,但它并非没有缺点。许多程序对于解析 DNS 查询非常敏感,我们遇到的任何性能或可用性问题在最好的情况下也会导致服务排队和性能降级,而最坏情况下客户会遭遇服务中断。配置和代码的更改可能会导致查询率发生大幅度的意外变化。因此超出这两台主机的扩展成为了一个问题。由于这些主机的网络配置,如果我们只是继续添加 IP 和主机的话存在一些本身的问题。在试图解决和补救这些问题的同时,由于缺乏测量指标和可见性,老旧的系统难以识别问题的原因。在许多情况下,我们使用 `tcpdump` 来识别有问题的流量和查询。另一个问题是在公共 DNS 服务器上运行,我们处于泄露内部网络信息的风险之下。因此,我们决定建立更好的东西,并开始确定我们对新系统的要求。
+
+我们着手设计一个新的 DNS 基础设施,以改善上述包括扩展和可见性在内的运维问题,并引入了一些额外的需求。我们希望通过外部 DNS 提供商继续运行我们的公共 DNS 域,因此我们构建的系统需要与供应商无关。此外,我们希望该系统能够服务于我们的内部和外部域,这意味着内部域仅在我们的内部网络上可用,除非另有特别配置,而外部域也不用离开我们的内部网络就可解析。我们希望新的 DNS 架构不但可以[基于部署的工作流进行更改][5],并可以通过我们的仓库和配置系统使用 API 自动更改 DNS 记录。新系统不能有任何外部依赖,太依赖于 DNS 功能将会陷入级联故障,这包括连接到其他数据中心和其中可能有的 DNS 服务。我们的旧系统将缓存服务器和权威服务器在同一台主机上混合使用。我们想转到具有独立角色的分层设计。最后,我们希望系统能够支持多数据中心环境,无论是 EC2 还是裸机。
+
+### 实现
+
+
+
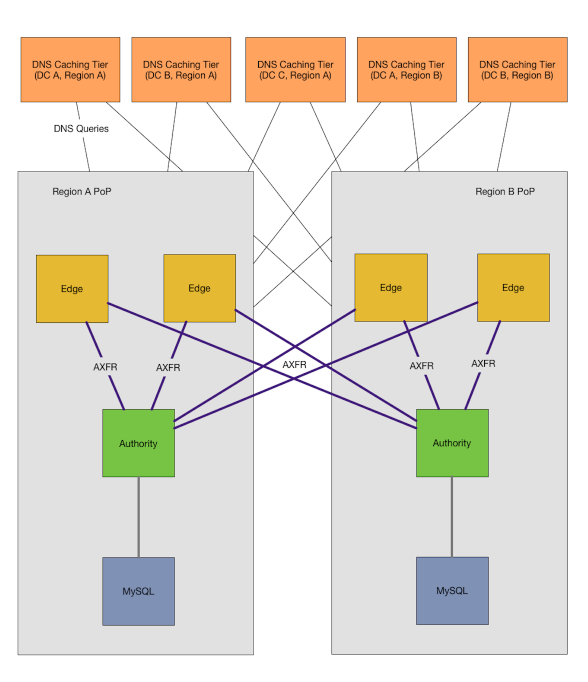
+为了构建这个系统,我们确定了三类主机:缓存主机、边缘主机和权威主机。缓存主机作为递归解析器和 DNS “路由器” 缓存来自边缘层的响应。边缘层运行 DNS 权威守护程序,用于响应缓存层对 DNS 区域的请求,其被配置为来自权威层的区域传输。权威层作为隐藏的 DNS 主服务器,作为 DNS 数据的规范来源,为来自边缘主机的区域传输提供服务,并提供用于创建、修改或删除记录的 HTTP API。
+
+在我们的新配置中,缓存主机存在于每个数据中心中,这意味着应用主机不需要穿过数据中心边界来检索记录。缓存主机被配置为将区域映射到其地域内的边缘主机,以便将我们的内部区域路由到我们自己的主机。未明确配置的任何区域将通过互联网递归解析。
+
+边缘主机是地域性的主机,存在我们的网络边缘 PoP(存在点)内。我们的 PoP 有一个或多个依赖于它们进行外部连接的数据中心,没有 PoP 数据中心将无法访问互联网,互联网也无法访问它们。边缘主机对所有的权威主机执行区域传输,无论它们存在什么地域或位置,并将这些区域存在本地的磁盘上。
+
+我们的权威主机也是地域性的主机,只包含适用于其所在地域的区域。我们的仓库和配置系统决定一个区域存放在哪个地域性权威主机,并通过 HTTP API 服务来创建和删除记录。 OctoDNS 将区域映射到地域性权威主机,并使用相同的 API 创建静态记录,以及确保动态源处于同步状态。对于外部域 (如 github.com),我们有另外一个单独的权威主机,以允许我们可以在连接中断期间查询我们的外部域。所有记录都存储在 MySQL 中。
+
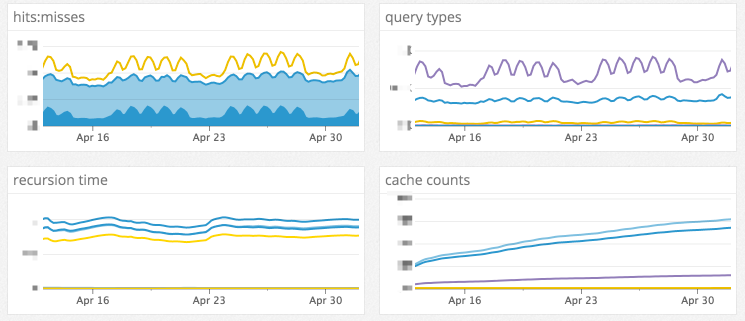
+### 可运维性
+
+
+
+迁移到更现代的 DNS 基础设施的巨大好处是可观察性。我们的旧 DNS 系统几乎没有指标,只有有限的日志。决定使用哪些 DNS 服务器的一个重要因素是它们所产生的指标的广度和深度。我们最终用 [Unbound][6] 作为缓存主机,[NSD][7] 作为边缘主机,[PowerDNS][8] 作为权威主机,所有这些都已在比 GitHub 大得多的 DNS 基础架构中得到了证实。
+
+当在我们的裸机数据中心运行时,缓存通过私有的[任播][9] IP 访问,从而使之可以到达最近的可用缓存主机。缓存主机已经以机架感知的方式部署,在它们之间提供了一定程度的平衡负载,并且与一些电源和网络故障模式相隔离。当缓存主机出现故障时,通常将用其进行 DNS 查询的服务器现在将自动路由到下一个最接近的缓存主机,以保持低延迟并提供对某些故障模式的容错。任播允许我们扩展单个 IP 地址后面的缓存数量,这与先前的配置不同,使得我们能够按 DNS 需求量运行尽可能多的缓存主机。
+
+无论地域或位置如何,边缘主机使用权威层进行区域传输。我们的区域并没有大到在每个地域保留所有区域的副本成为问题。(LCTT 译注:此处原文“Our zones are not large enough that keeping a copy of all of them in every region is a problem.”,根据上下文理解而翻译。)这意味着对于每个区域,即使某个地域处于脱机状态,或者上游服务提供商存在连接问题,所有缓存服务器都可以访问具备所有区域的本地副本的本地边缘服务器。这种变化在面对连接问题方面已被证明是相当有弹性的,并且在不久前本来会导致客户面临停止服务的故障期间帮助保持 GitHub 可用。
+
+那些区域传输包括了内部和外部域从它们相应的权威服务器进行的传输。正如你可能会猜想像 github.com 这样的区域是外部的,像 github.net 这样的区域通常是内部的。它们之间的区别仅在于我们使用的类型和存储在其中的数据。了解哪些区域是内部和外部的,为我们在配置中提供了一些灵活性。
+
+```
+$ dig +short github.com
+192.30.253.112
+192.30.253.113
+```
+
+公共区域被[同步][10]到外部 DNS 提供商,并且是 GitHub 用户每天使用的 DNS 记录。另外,公共区域在我们的网络中是完全可解析的,而不需要与我们的外部提供商进行通信。这意味着需要查询 `api.github.com` 的任何服务都可以这样做,而无需依赖外部网络连接。我们还使用了 Unbound 的 `stub-first` 配置选项,它给了我们第二次查询的机会,如果我们的内部 DNS 服务由于某些原因在外部查询失败,则可以进行第二次查找。
+
+```
+$ dig +short time.github.net
+10.127.6.10
+```
+
+大部分的 `github.net` 区域是完全私有的,无法从互联网访问,它只包含 [RFC 1918][11] 中规定的 IP 地址。每个地域和站点都划分了私有区域。每个地域和/或站点都具有适用于该位置的一组子区域,子区域用于管理网络、服务发现、特定的服务记录,并且还包括在我们仓库中的配置主机。私有区域还包括 PTR 反向查找区域。
+
+### 总结
+
+用一个新系统替换可以为数百万客户提供服务的旧系统并不容易。使用实用的、基于需求的方法来设计和实施我们的新 DNS 系统,才能打造出一个能够迅速有效地运行、并有望与 GitHub 一起成长的 DNS 基础设施。
+
+想帮助 GitHub SRE 团队解决有趣的问题吗?我们很乐意你加入我们。[在这申请][12]。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://githubengineering.com/dns-infrastructure-at-github/
+
+作者:[Joe Williams][a]
+译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:https://github.com/joewilliams
+[1]:https://githubengineering.com/dns-infrastructure-at-github/
+[2]:https://github.com/joewilliams
+[3]:https://github.com/joewilliams
+[4]:https://githubengineering.com/enabling-split-authority-dns-with-octodns/
+[5]:https://githubengineering.com/enabling-split-authority-dns-with-octodns/
+[6]:https://unbound.net/
+[7]:https://www.nlnetlabs.nl/projects/nsd/
+[8]:https://powerdns.com/
+[9]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anycast
+[10]:https://githubengineering.com/enabling-split-authority-dns-with-octodns/
+[11]:http://www.faqs.org/rfcs/rfc1918.html
+[12]:https://boards.greenhouse.io/github/jobs/669805#.WPVqJlPyvUI
diff --git a/published/20170718 Integrate Ubuntu to Samba4 AD DC with SSSD and Realm – Part 15.md b/published/20170718 Integrate Ubuntu to Samba4 AD DC with SSSD and Realm – Part 15.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..cf322790a7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20170718 Integrate Ubuntu to Samba4 AD DC with SSSD and Realm – Part 15.md
@@ -0,0 +1,384 @@
+Samba 系列(十五):用 SSSD 和 Realm 集成 Ubuntu 到 Samba4 AD DC
+============================================================
+
+本教程将告诉你如何将 Ubuntu 桌面版机器加入到带有 SSSD 和 Realm 服务的 Samba4 活动目录域中,以在活动目录中认证用户。
+
+### 要求:
+
+1. [在 Ubuntu 上用 Samba4 创建一个活动目录架构][1]
+
+### 第 1 步:初始配置
+
+1、 在把 Ubuntu 加入活动目录前确保主机名被正确设置了。使用 `hostnamectl` 命令设置机器名字或者手动编辑 `/etc/hostname` 文件。
+
+```
+$ sudo hostnamectl set-hostname your_machine_short_hostname
+$ cat /etc/hostname
+$ hostnamectl
+```
+
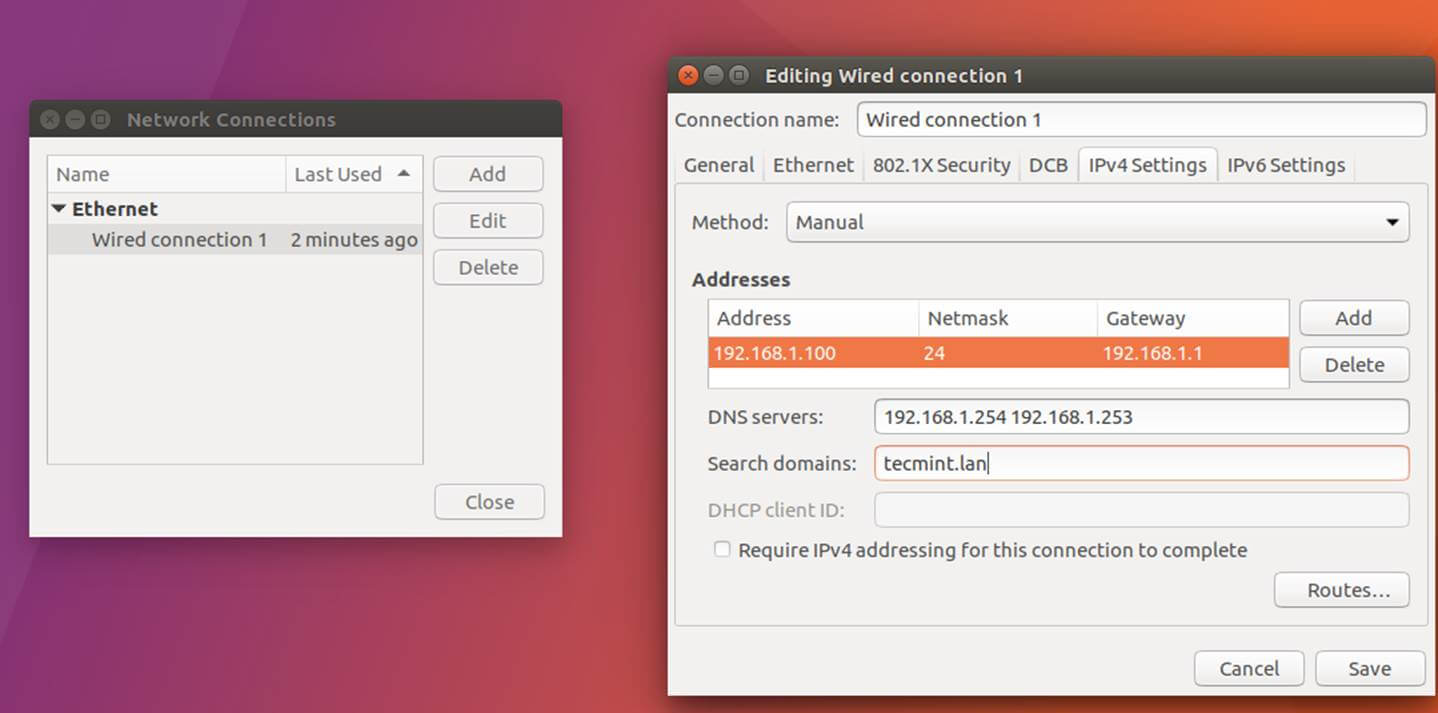
+2、 接下来,编辑机器网络接口设置并且添加合适的 IP 设置,并将正确的 DNS IP 服务器地址指向 Samba 活动目录域控制器,如下图所示。
+
+如果你已经配置了 DHCP 服务来为局域网机器自动分配包括合适的 AD DNS IP 地址的 IP 设置,那么你可以跳过这一步。
+
+[][2]
+
+*设置网络接口*
+
+上图中,`192.168.1.254` 和 `192.168.1.253` 代表 Samba4 域控制器的 IP 地址。
+
+3、 用 GUI(图形用户界面)或命令行重启网络服务来应用修改,并且对你的域名发起一系列 ping 请求来测试 DNS 解析如预期工作。 也用 `host` 命令来测试 DNS 解析。
+
+```
+$ sudo systemctl restart networking.service
+$ host your_domain.tld
+$ ping -c2 your_domain_name
+$ ping -c2 adc1
+$ ping -c2 adc2
+```
+
+4、 最后, 确保机器时间和 Samba4 AD 同步。安装 `ntpdate` 包并用下列指令和 AD 同步时间。
+
+```
+$ sudo apt-get install ntpdate
+$ sudo ntpdate your_domain_name
+```
+
+### 第 2 步:安装需要的包
+
+5、 这一步将安装将 Ubuntu 加入 Samba4 活动目录域控制器所必须的软件和依赖:Realmd 和 SSSD 服务。
+
+```
+$ sudo apt install adcli realmd krb5-user samba-common-bin samba-libs samba-dsdb-modules sssd sssd-tools libnss-sss libpam-sss packagekit policykit-1
+```
+
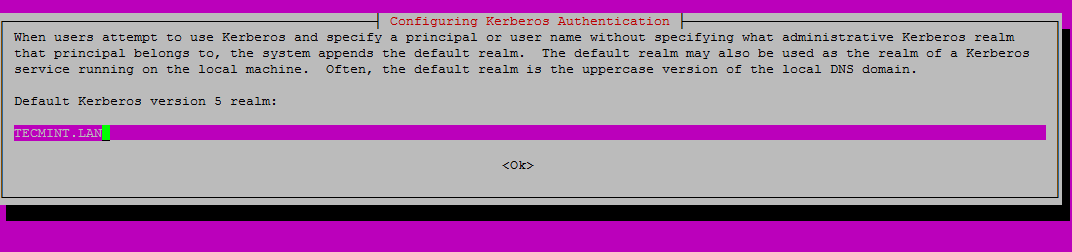
+6、 输入大写的默认 realm 名称,然后按下回车继续安装。
+
+[][3]
+
+*输入 Realm 名称*
+
+7、 接着,创建包含以下内容的 SSSD 配置文件。
+
+```
+$ sudo nano /etc/sssd/sssd.conf
+```
+
+加入下面的内容到 `sssd.conf` 文件。
+
+```
+[nss]
+filter_groups = root
+filter_users = root
+reconnection_retries = 3
+[pam]
+reconnection_retries = 3
+[sssd]
+domains = tecmint.lan
+config_file_version = 2
+services = nss, pam
+default_domain_suffix = TECMINT.LAN
+[domain/tecmint.lan]
+ad_domain = tecmint.lan
+krb5_realm = TECMINT.LAN
+realmd_tags = manages-system joined-with-samba
+cache_credentials = True
+id_provider = ad
+krb5_store_password_if_offline = True
+default_shell = /bin/bash
+ldap_id_mapping = True
+use_fully_qualified_names = True
+fallback_homedir = /home/%d/%u
+access_provider = ad
+auth_provider = ad
+chpass_provider = ad
+access_provider = ad
+ldap_schema = ad
+dyndns_update = true
+dyndsn_refresh_interval = 43200
+dyndns_update_ptr = true
+dyndns_ttl = 3600
+```
+
+确保你对应地替换了下列参数的域名:
+
+```
+domains = tecmint.lan
+default_domain_suffix = TECMINT.LAN
+[domain/tecmint.lan]
+ad_domain = tecmint.lan
+krb5_realm = TECMINT.LAN
+```
+
+8、 接着,用下列命令给 SSSD 配置文件适当的权限:
+
+```
+$ sudo chmod 700 /etc/sssd/sssd.conf
+```
+
+9、 现在,打开并编辑 Realmd 配置文件,输入下面这行:
+
+```
+$ sudo nano /etc/realmd.conf
+```
+
+`realmd.conf` 文件摘录:
+
+```
+[active-directory]
+os-name = Linux Ubuntu
+os-version = 17.04
+[service]
+automatic-install = yes
+[users]
+default-home = /home/%d/%u
+default-shell = /bin/bash
+[tecmint.lan]
+user-principal = yes
+fully-qualified-names = no
+```
+
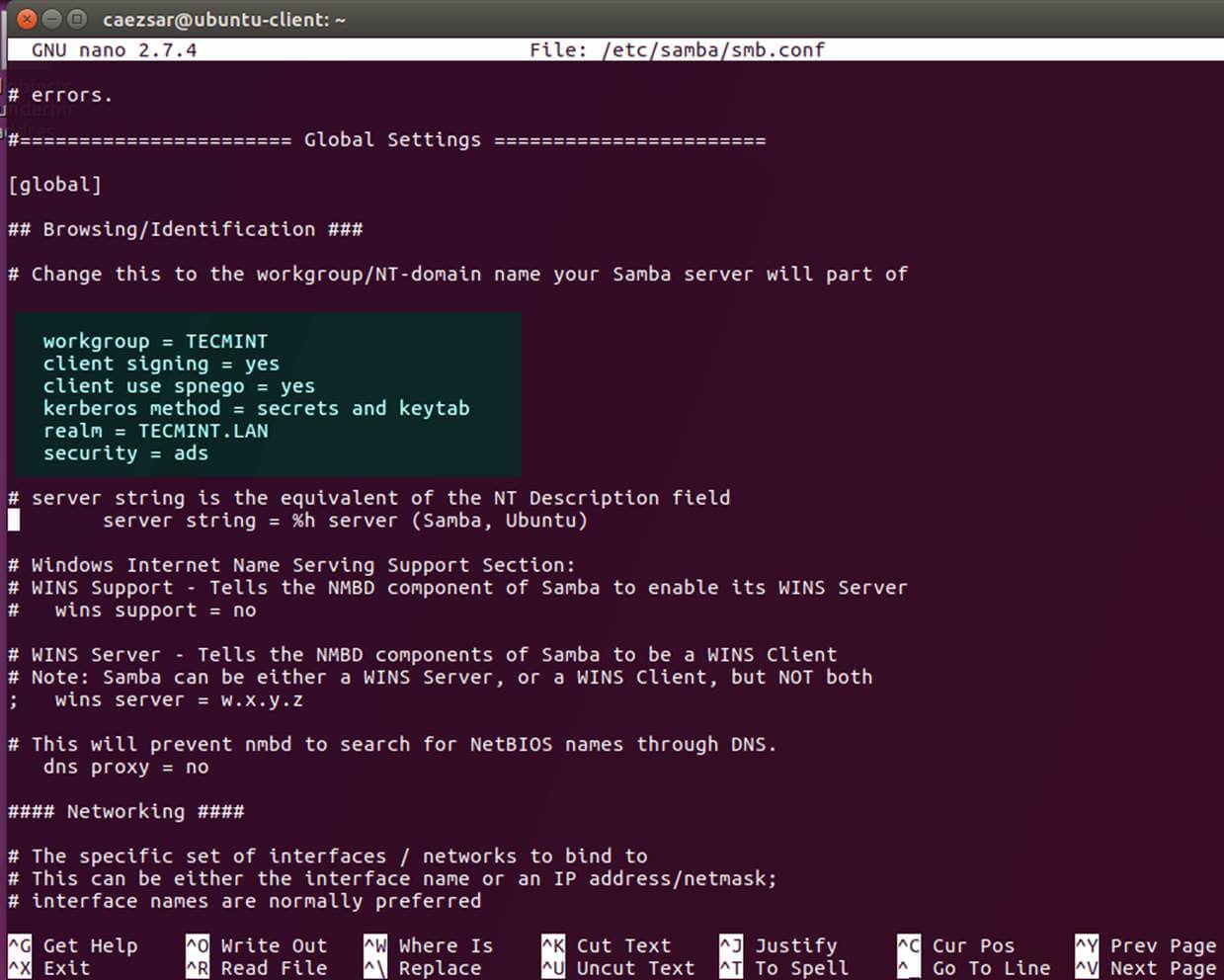
+10、 最后需要修改的文件属于 Samba 守护进程。 打开 `/etc/samba/smb.conf` 文件编辑,然后在文件开头加入下面这块代码,在 `[global]` 之后的部分如下图所示。
+
+```
+workgroup = TECMINT
+client signing = yes
+client use spnego = yes
+kerberos method = secrets and keytab
+realm = TECMINT.LAN
+security = ads
+```
+
+[][4]
+
+*配置 Samba 服务器*
+
+确保你替换了域名值,特别是对应域名的 realm 值,并运行 `testparm` 命令检验设置文件是否包含错误。
+
+```
+$ sudo testparm
+```
+
+[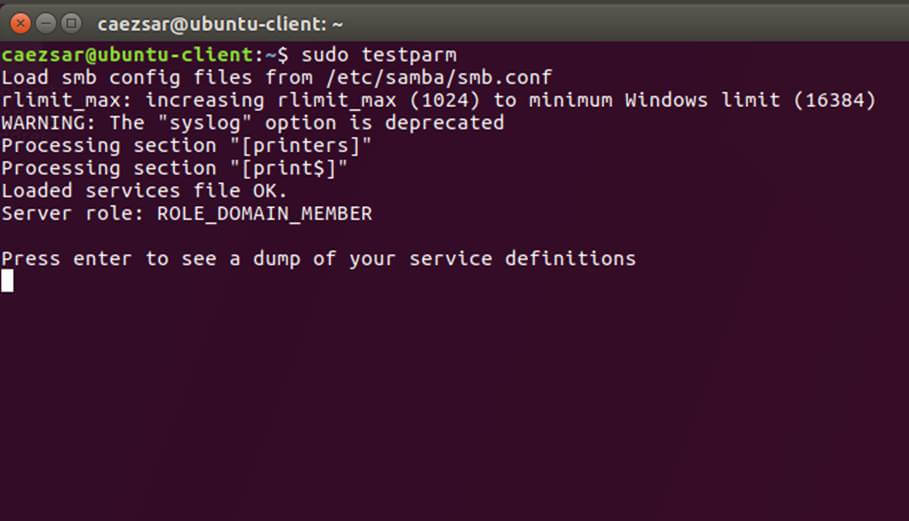][5]
+
+*测试 Samba 配置*
+
+11、 在做完所有必需的修改之后,用 AD 管理员帐号验证 Kerberos 认证并用下面的命令列出票据。
+
+```
+$ sudo kinit ad_admin_user@DOMAIN.TLD
+$ sudo klist
+```
+
+[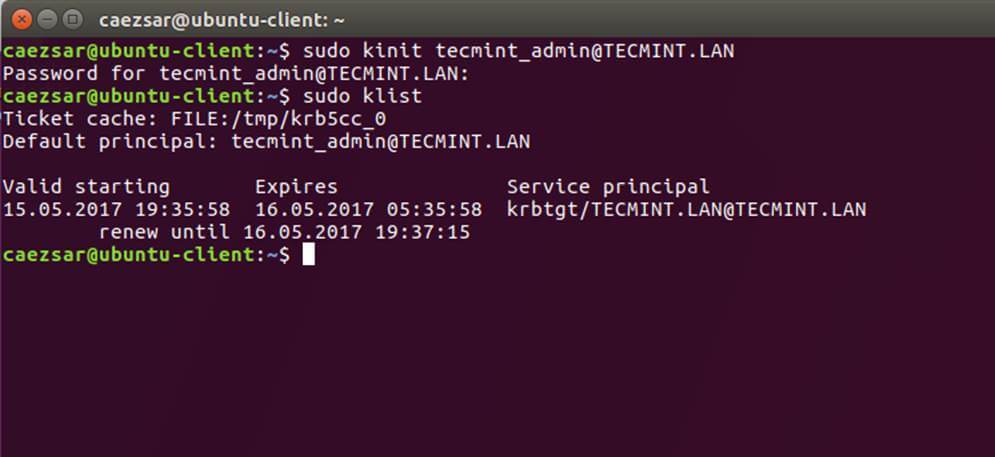][6]
+
+*检验 Kerberos 认证*
+
+### 第 3 步: 加入 Ubuntu 到 Samba4 Realm
+
+12、 键入下列命令将 Ubuntu 机器加入到 Samba4 活动目录。用有管理员权限的 AD DC 账户名字,以便绑定 realm 可以如预期般工作,并替换对应的域名值。
+
+```
+$ sudo realm discover -v DOMAIN.TLD
+$ sudo realm list
+$ sudo realm join TECMINT.LAN -U ad_admin_user -v
+$ sudo net ads join -k
+```
+
+[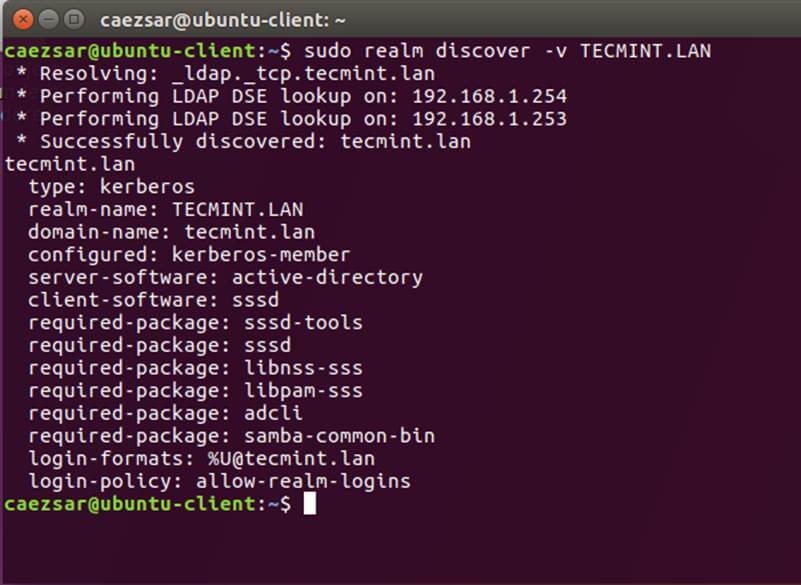][7]
+
+*加入 Ubuntu 到 Samba4 Realm*
+
+[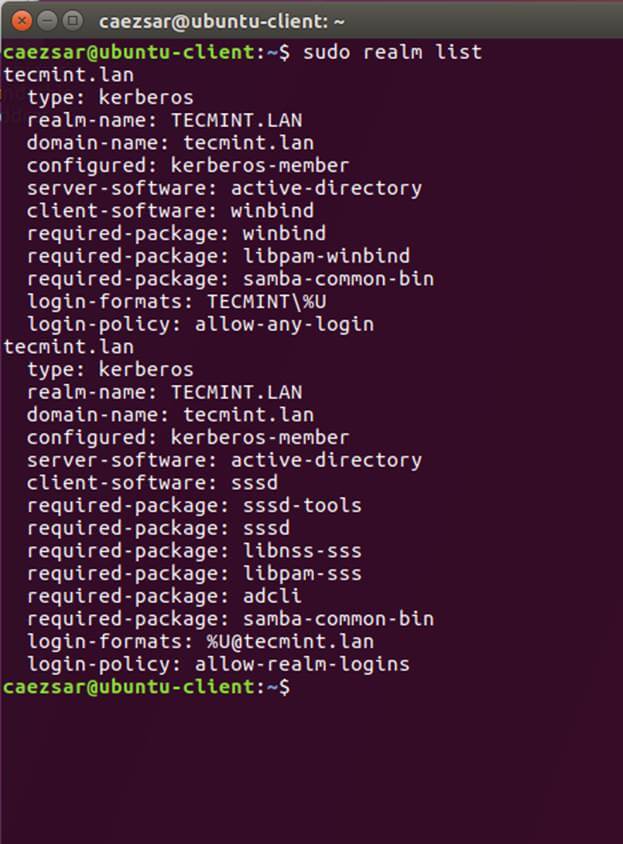][8]
+
+*列出 Realm Domain 信息*
+
+[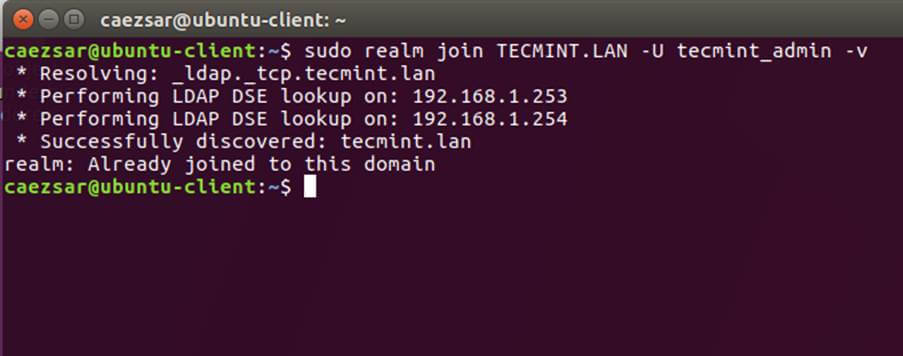][9]
+
+*添加用户到 Realm Domain*
+
+[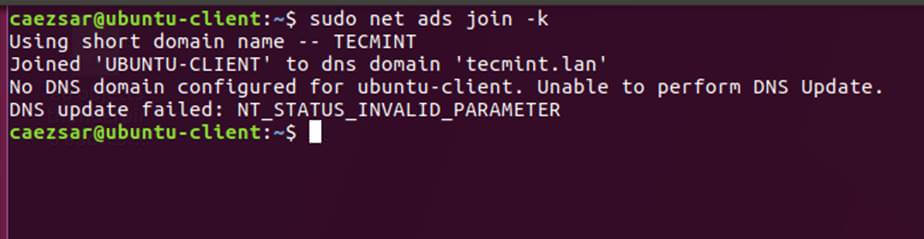][10]
+
+*添加 Domain 到 Realm*
+
+13、 区域绑定好了之后,运行下面的命令确保所有域账户允许在这台机器上认证。
+
+```
+$ sudo realm permit -all
+```
+
+然后你可以使用下面举例的 `realm` 命令允许或者禁止域用户帐号或群组访问。
+
+```
+$ sudo realm deny -a
+$ realm permit --groups ‘domain.tld\Linux Admins’
+$ realm permit user@domain.lan
+$ realm permit DOMAIN\\User2
+```
+
+14、 从一个 [安装了 RSAT 工具的][11] Windows 机器上你可以打开 AD UC 并浏览“电脑”容器,并检验是否有一个使用你机器名的对象帐号已经创建。
+
+[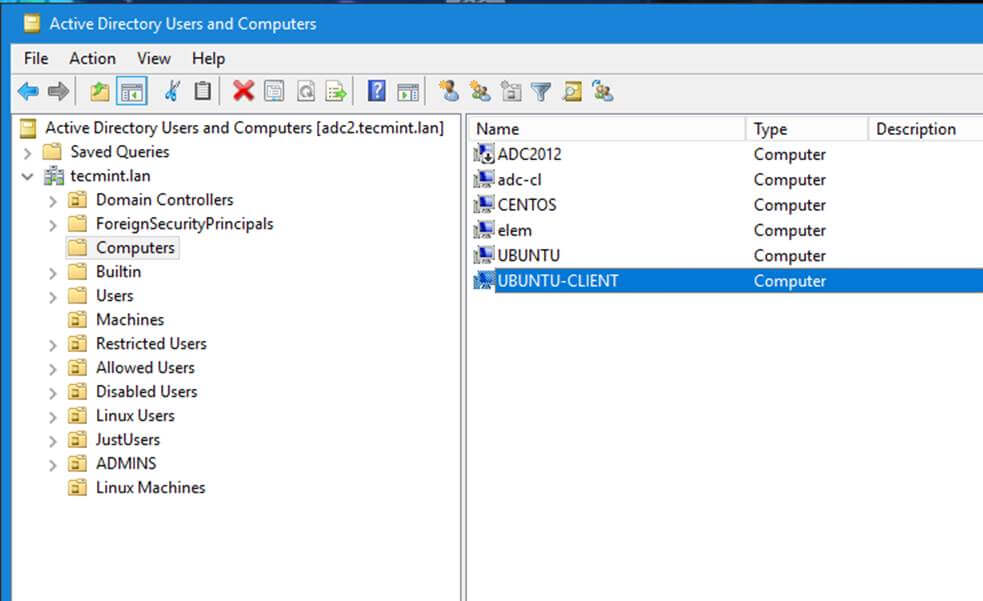][12]
+
+*确保域被加入 AD DC*
+
+### 第 4 步:配置 AD 账户认证
+
+15、 为了在 Ubuntu 机器上用域账户认证,你需要用 root 权限运行 `pam-auth-update` 命令并允许所有 PAM 配置文件,包括为每个域账户在第一次注册的时候自动创建家目录的选项。
+
+按 [空格] 键检验所有配置项并点击 ok 来应用配置。
+
+```
+$ sudo pam-auth-update
+```
+
+[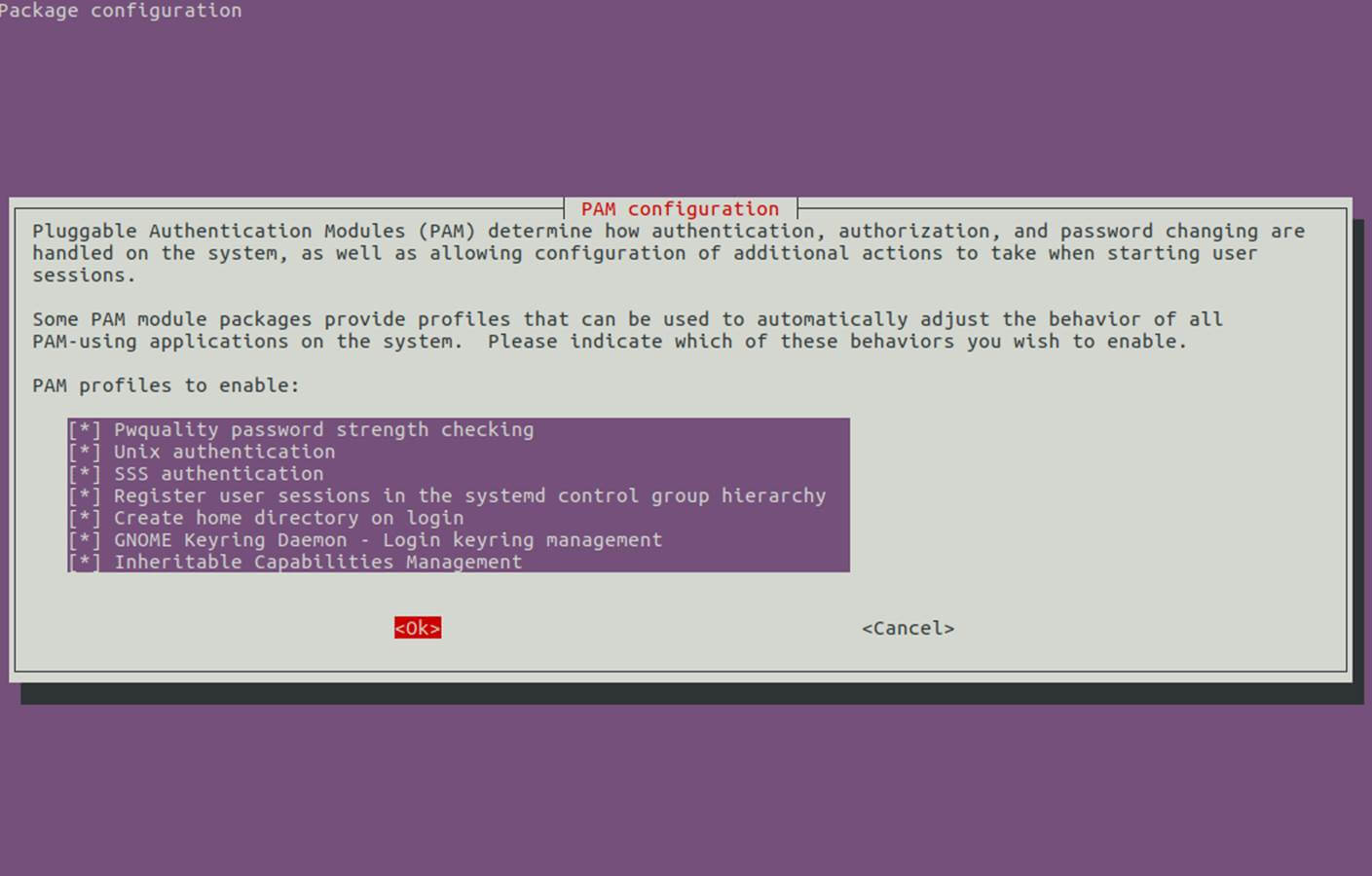][13]
+
+*PAM 配置*
+
+16、 在系统上手动编辑 `/etc/pam.d/common-account` 文件,下面这几行是为了给认证过的域用户自动创建家目录。
+
+```
+session required pam_mkhomedir.so skel=/etc/skel/ umask=0022
+```
+
+17、 如果活动目录用户不能用 linux 命令行修改他们的密码,打开 `/etc/pam.d/common-password` 文件并在 `password` 行移除 `use_authtok` 语句,最后如下:
+
+```
+password [success=1 default=ignore] pam_winbind.so try_first_pass
+```
+
+18、 最后,用下面的命令重启并启用以应用 Realmd 和 SSSD 服务的修改:
+
+```
+$ sudo systemctl restart realmd sssd
+$ sudo systemctl enable realmd sssd
+```
+
+19、 为了测试 Ubuntu 机器是是否成功集成到 realm ,安装 winbind 包并运行 `wbinfo` 命令列出域账户和群组,如下所示。
+
+```
+$ sudo apt-get install winbind
+$ wbinfo -u
+$ wbinfo -g
+```
+
+[][14]
+
+*列出域账户*
+
+20、 同样,也可以针对特定的域用户或群组使用 `getent` 命令检验 Winbind nsswitch 模块。
+
+```
+$ sudo getent passwd your_domain_user
+$ sudo getent group ‘domain admins’
+```
+
+[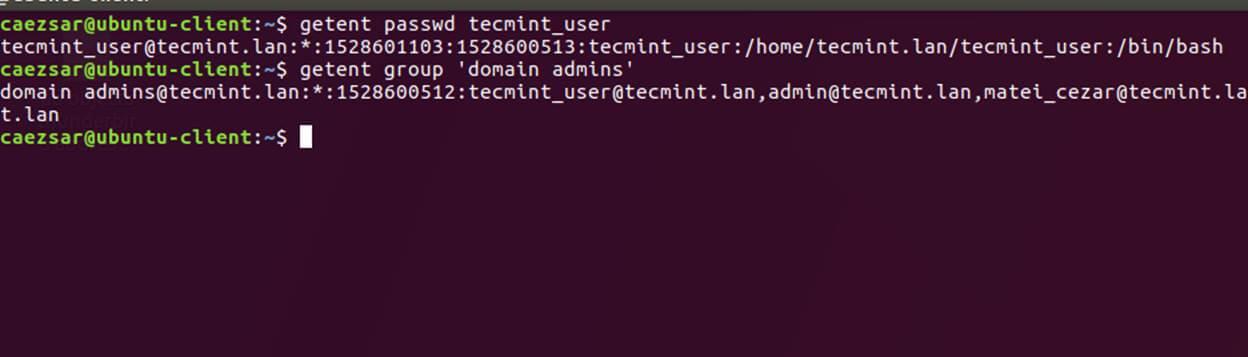][15]
+
+*检验 Winbind Nsswitch*
+
+21、 你也可以用 Linux `id` 命令获取 AD 账户的信息,命令如下:
+
+```
+$ id tecmint_user
+```
+
+[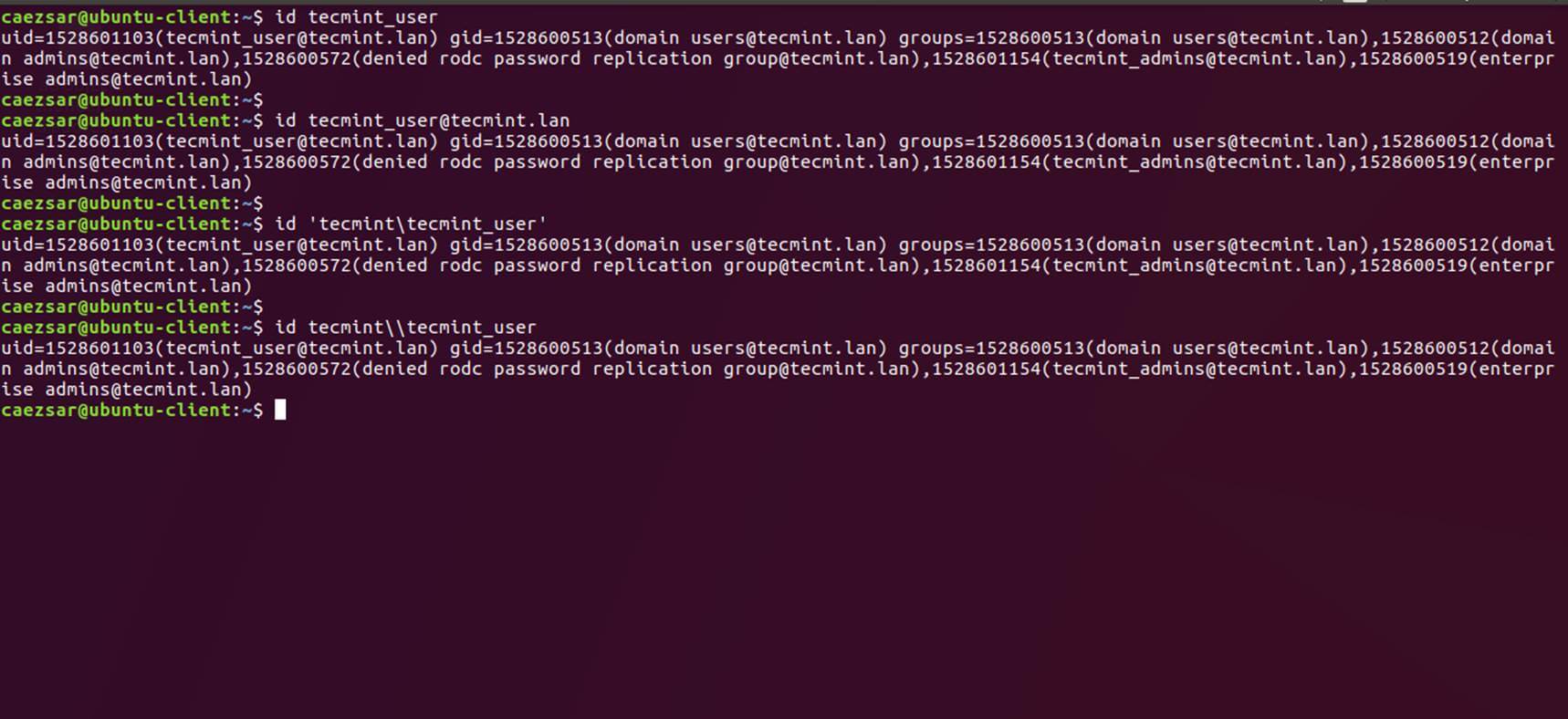][16]
+
+*检验 AD 用户信息*
+
+22、 用 `su -` 后跟上域用户名参数来认证 Ubuntu 主机的一个 Samba4 AD 账户。运行 `id` 命令获取该 AD 账户的更多信息。
+
+```
+$ su - your_ad_user
+```
+
+[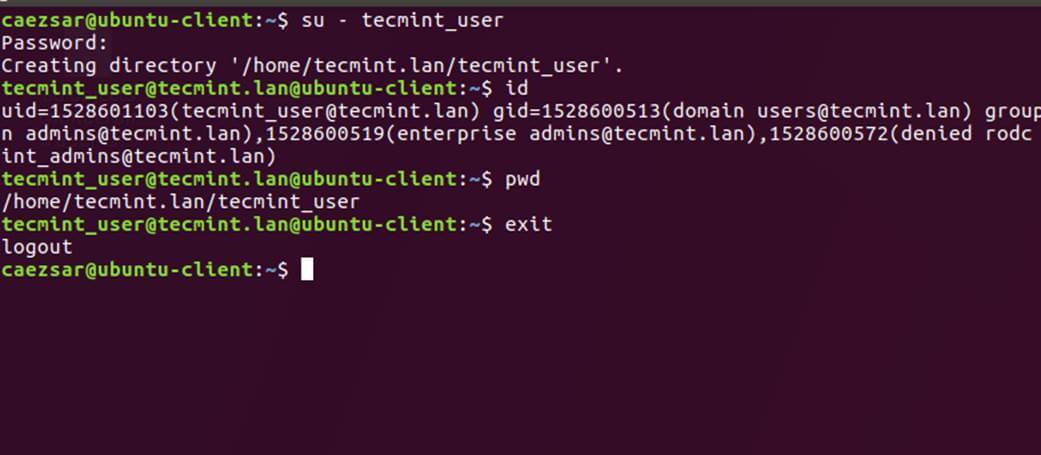][17]
+
+*AD 用户认证*
+
+用 `pwd` 命令查看你的域用户当前工作目录,和用 `passwd` 命令修改密码。
+
+23、 在 Ubuntu 上使用有 root 权限的域账户,你需要用下面的命令添加 AD 用户名到 sudo 系统群组:
+
+```
+$ sudo usermod -aG sudo your_domain_user@domain.tld
+```
+
+用域账户登录 Ubuntu 并运行 `apt update` 命令来更新你的系统以检验 root 权限。
+
+24、 给一个域群组 root 权限,用 `visudo` 命令打开并编辑 `/etc/sudoers` 文件,并加入如下行:
+
+```
+%domain\ admins@tecmint.lan ALL=(ALL:ALL) ALL
+```
+
+25、 要在 Ubuntu 桌面使用域账户认证,通过编辑 `/usr/share/lightdm/lightdm.conf.d/50-ubuntu.conf` 文件来修改 LightDM 显示管理器,增加以下两行并重启 lightdm 服务或重启机器应用修改。
+
+```
+greeter-show-manual-login=true
+greeter-hide-users=true
+```
+
+域账户用“你的域用户”或“你的域用户@你的域” 格式来登录 Ubuntu 桌面。
+
+26、 为使用 Samba AD 账户的简称格式,编辑 `/etc/sssd/sssd.conf` 文件,在 `[sssd]` 块加入如下几行命令。
+
+```
+full_name_format = %1$s
+```
+
+并重启 SSSD 守护进程应用改变。
+
+```
+$ sudo systemctl restart sssd
+```
+
+你会注意到 bash 提示符会变成了没有附加域名部分的 AD 用户名。
+
+27、 万一你因为 `sssd.conf` 里的 `enumerate=true` 参数设定而不能登录,你得用下面的命令清空 sssd 缓存数据:
+
+```
+$ rm /var/lib/sss/db/cache_tecmint.lan.ldb
+```
+
+这就是全部了!虽然这个教程主要集中于集成 Samba4 活动目录,同样的步骤也能被用于把使用 Realm 和 SSSD 服务的 Ubuntu 整合到微软 Windows 服务器活动目录。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+作者简介:
+
+Matei Cezar - 我是一名网瘾少年,开源和基于 linux 系统软件的粉丝,有4年经验在 linux 发行版桌面、服务器和 bash 脚本。
+
+------------------
+
+via: https://www.tecmint.com/integrate-ubuntu-to-samba4-ad-dc-with-sssd-and-realm/
+
+作者:[Matei Cezar][a]
+译者:[XYenChi](https://github.com/XYenChi)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:https://www.tecmint.com/author/cezarmatei/
+[1]:https://linux.cn/article-8065-1.html
+[2]:https://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/Configure-Network-Interface.jpg
+[3]:https://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/Set-realm-name.png
+[4]:https://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/Configure-Samba-Server.jpg
+[5]:https://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/Test-Samba-Configuration.jpg
+[6]:https://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/Check-Kerberos-Authentication.jpg
+[7]:https://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/Join-Ubuntu-to-Samba4-Realm.jpg
+[8]:https://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/List-Realm-Domain-Info.jpg
+[9]:https://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/Add-User-to-Realm-Domain.jpg
+[10]:https://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/Add-Domain-to-Realm.jpg
+[11]:https://linux.cn/article-8097-1.html
+[12]:https://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/Confirm-Domain-Added.jpg
+[13]:https://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/PAM-Configuration.jpg
+[14]:https://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/List-Domain-Accounts.jpg
+[15]:https://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/check-Winbind-nsswitch.jpg
+[16]:https://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/Check-AD-User-Info.jpg
+[17]:https://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/AD-User-Authentication.jpg
+[18]:https://www.tecmint.com/author/cezarmatei/
+[19]:https://www.tecmint.com/10-useful-free-linux-ebooks-for-newbies-and-administrators/
+[20]:https://www.tecmint.com/free-linux-shell-scripting-books/
diff --git a/published/20170813 An Intro to Compilers.md b/published/20170813 An Intro to Compilers.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..8d9e9a3f60
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20170813 An Intro to Compilers.md
@@ -0,0 +1,216 @@
+编译器简介: 在 Siri 前时代如何与计算机对话
+============================================================
+
+
+
+简单说来,一个编译器不过是一个可以翻译其他程序的程序。传统的编译器可以把源代码翻译成你的计算机能够理解的可执行机器代码。(一些编译器将源代码翻译成别的程序语言,这样的编译器称为源到源翻译器或转化器。)[LLVM][7] 是一个广泛使用的编译器项目,包含许多模块化的编译工具。
+
+传统的编译器设计包含三个部分:
+
+
+
+* 前端将源代码翻译为中间表示 (IR)* 。[clang][1] 是 LLVM 中用于 C 家族语言的前端工具。
+* 优化器分析 IR 然后将其转化为更高效的形式。[opt][2] 是 LLVM 的优化工具。
+* 后端通过将 IR 映射到目标硬件指令集从而生成机器代码。[llc][3] 是 LLVM 的后端工具。
+
+注:LLVM 的 IR 是一种和汇编类似的低级语言。然而,它抽离了特定硬件信息。
+
+### Hello, Compiler
+
+下面是一个打印 “Hello, Compiler!” 到标准输出的简单 C 程序。C 语法是人类可读的,但是计算机却不能理解,不知道该程序要干什么。我将通过三个编译阶段使该程序变成机器可执行的程序。
+
+```
+// compile_me.c
+// Wave to the compiler. The world can wait.
+
+#include
+
+int main() {
+ printf("Hello, Compiler!\n");
+ return 0;
+}
+```
+
+#### 前端
+
+正如我在上面所提到的,`clang` 是 LLVM 中用于 C 家族语言的前端工具。Clang 包含 C 预处理器、词法分析器、语法解析器、语义分析器和 IR 生成器。
+
+**C 预处理器**在将源程序翻译成 IR 前修改源程序。预处理器处理外部包含文件,比如上面的 `#include `。 它将会把这一行替换为 `stdio.h` C 标准库文件的完整内容,其中包含 `printf` 函数的声明。
+
+通过运行下面的命令来查看预处理步骤的输出:
+
+```
+clang -E compile_me.c -o preprocessed.i
+```
+
+**词法分析器**(或扫描器或分词器)将一串字符转化为一串单词。每一个单词或记号,被归并到五种语法类别之一:标点符号、关键字、标识符、文字或注释。
+
+compile_me.c 的分词过程:
+
+
+
+**语法分析器**确定源程序中的单词流是否组成了合法的句子。在分析记号流的语法后,它会输出一个抽象语法树(AST)。Clang 的 AST 中的节点表示声明、语句和类型。
+
+compile_me.c 的语法树:
+
+
+
+**语义分析器**会遍历抽象语法树,从而确定代码语句是否有正确意义。这个阶段会检查类型错误。如果 `compile_me.c` 的 main 函数返回 `"zero"`而不是 `0`, 那么语义分析器将会抛出一个错误,因为 `"zero"` 不是 `int` 类型。
+
+**IR 生成器**将抽象语法树翻译为 IR。
+
+对 compile_me.c 运行 clang 来生成 LLVM IR:
+
+```
+clang -S -emit-llvm -o llvm_ir.ll compile_me.c
+```
+
+在 `llvm_ir.ll` 中的 main 函数:
+
+```
+; llvm_ir.ll
+@.str = private unnamed_addr constant [18 x i8] c"Hello, Compiler!\0A\00", align 1
+
+define i32 @main() {
+ %1 = alloca i32, align 4 ; <- memory allocated on the stack
+ store i32 0, i32* %1, align 4
+ %2 = call i32 (i8*, ...) @printf(i8* getelementptr inbounds ([18 x i8], [18 x i8]* @.str, i32 0, i32 0))
+ ret i32 0
+}
+
+declare i32 @printf(i8*, ...)
+```
+
+#### 优化程序
+
+优化程序的工作是基于其对程序的运行时行为的理解来提高代码效率。优化程序将 IR 作为输入,然后生成改进后的 IR 作为输出。LLVM 的优化工具 `opt` 将会通过标记 `-O2`(大写字母 `o`,数字 2)来优化处理器速度,通过标记 `Os`(大写字母 `o`,小写字母 `s`)来减少指令数目。
+
+看一看上面的前端工具生成的 LLVM IR 代码和运行下面的命令生成的结果之间的区别:
+
+```
+opt -O2 -S llvm_ir.ll -o optimized.ll
+```
+
+在 `optimized.ll` 中的 main 函数:
+
+```
+optimized.ll
+
+@str = private unnamed_addr constant [17 x i8] c"Hello, Compiler!\00"
+
+define i32 @main() {
+ %puts = tail call i32 @puts(i8* getelementptr inbounds ([17 x i8], [17 x i8]* @str, i64 0, i64 0))
+ ret i32 0
+}
+
+declare i32 @puts(i8* nocapture readonly)
+```
+
+优化后的版本中, main 函数没有在栈中分配内存,因为它不使用任何内存。优化后的代码中调用 `puts` 函数而不是 `printf` 函数,因为程序中并没有使用 `printf` 函数的格式化功能。
+
+当然,优化程序不仅仅知道何时可以把 `printf` 函数用 `puts` 函数代替。优化程序也能展开循环并内联简单计算的结果。考虑下面的程序,它将两个整数相加并打印出结果。
+
+```
+// add.c
+#include
+
+int main() {
+ int a = 5, b = 10, c = a + b;
+ printf("%i + %i = %i\n", a, b, c);
+}
+```
+
+下面是未优化的 LLVM IR:
+
+```
+@.str = private unnamed_addr constant [14 x i8] c"%i + %i = %i\0A\00", align 1
+
+define i32 @main() {
+ %1 = alloca i32, align 4 ; <- allocate stack space for var a
+ %2 = alloca i32, align 4 ; <- allocate stack space for var b
+ %3 = alloca i32, align 4 ; <- allocate stack space for var c
+ store i32 5, i32* %1, align 4 ; <- store 5 at memory location %1
+ store i32 10, i32* %2, align 4 ; <- store 10 at memory location %2
+ %4 = load i32, i32* %1, align 4 ; <- load the value at memory address %1 into register %4
+ %5 = load i32, i32* %2, align 4 ; <- load the value at memory address %2 into register %5
+ %6 = add nsw i32 %4, %5 ; <- add the values in registers %4 and %5\. put the result in register %6
+ store i32 %6, i32* %3, align 4 ; <- put the value of register %6 into memory address %3
+ %7 = load i32, i32* %1, align 4 ; <- load the value at memory address %1 into register %7
+ %8 = load i32, i32* %2, align 4 ; <- load the value at memory address %2 into register %8
+ %9 = load i32, i32* %3, align 4 ; <- load the value at memory address %3 into register %9
+ %10 = call i32 (i8*, ...) @printf(i8* getelementptr inbounds ([14 x i8], [14 x i8]* @.str, i32 0, i32 0), i32 %7, i32 %8, i32 %9)
+ ret i32 0
+}
+
+declare i32 @printf(i8*, ...)
+```
+
+下面是优化后的 LLVM IR:
+
+```
+@.str = private unnamed_addr constant [14 x i8] c"%i + %i = %i\0A\00", align 1
+
+define i32 @main() {
+ %1 = tail call i32 (i8*, ...) @printf(i8* getelementptr inbounds ([14 x i8], [14 x i8]* @.str, i64 0, i64 0), i32 5, i32 10, i32 15)
+ ret i32 0
+}
+
+declare i32 @printf(i8* nocapture readonly, ...)
+```
+
+优化后的 main 函数本质上是未优化版本的第 17 行和 18 行,伴有变量值内联。`opt` 计算加法,因为所有的变量都是常数。很酷吧,对不对?
+
+#### 后端
+
+LLVM 的后端工具是 `llc`。它分三个阶段将 LLVM IR 作为输入生成机器代码。
+
+* **指令选择**是将 IR 指令映射到目标机器的指令集。这个步骤使用虚拟寄存器的无限名字空间。
+* **寄存器分配**是将虚拟寄存器映射到目标体系结构的实际寄存器。我的 CPU 是 x86 结构,它只有 16 个寄存器。然而,编译器将会尽可能少的使用寄存器。
+* **指令安排**是重排操作,从而反映出目标机器的性能约束。
+
+运行下面这个命令将会产生一些机器代码:
+
+```
+llc -o compiled-assembly.s optimized.ll
+```
+
+```
+_main:
+ pushq %rbp
+ movq %rsp, %rbp
+ leaq L_str(%rip), %rdi
+ callq _puts
+ xorl %eax, %eax
+ popq %rbp
+ retq
+L_str:
+ .asciz "Hello, Compiler!"
+```
+
+这个程序是 x86 汇编语言,它是计算机所说的语言,并具有人类可读语法。某些人最后也许能理解我。
+
+* * *
+
+相关资源:
+
+1. [设计一个编译器][4]
+2. [开始探索 LLVM 核心库][5]
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://nicoleorchard.com/blog/compilers
+
+作者:[Nicole Orchard][a]
+译者:[ucasFL](https://github.com/ucasFL)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:https://nicoleorchard.com/
+[1]:http://clang.llvm.org/
+[2]:http://llvm.org/docs/CommandGuide/opt.html
+[3]:http://llvm.org/docs/CommandGuide/llc.html
+[4]:https://www.amazon.com/Engineering-Compiler-Second-Keith-Cooper/dp/012088478X
+[5]:https://www.amazon.com/Getting-Started-LLVM-Core-Libraries/dp/1782166920
+[6]:https://twitter.com/norchard/status/864246049266958336
+[7]:http://llvm.org/
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/tech/20170815 Getting Started with Headless Chrome.md b/published/20170815 Getting Started with Headless Chrome.md
similarity index 50%
rename from sources/tech/20170815 Getting Started with Headless Chrome.md
rename to published/20170815 Getting Started with Headless Chrome.md
index 6d4c9bc3cc..fc65331a10 100644
--- a/sources/tech/20170815 Getting Started with Headless Chrome.md
+++ b/published/20170815 Getting Started with Headless Chrome.md
@@ -1,20 +1,20 @@
-Getting Started with Headless Chrome
+Headless Chrome 入门
============================================================
-### TL;DR
+### 摘要
-[Headless Chrome][9] is shipping in Chrome 59\. It's a way to run the Chrome browser in a headless environment. Essentially, running Chrome without chrome! It brings **all modern web platform features** provided by Chromium and the Blink rendering engine to the command line.
+在 Chrome 59 中开始搭载 [Headless Chrome][9]。这是一种在无需显示的环境下运行 Chrome 浏览器的方式。从本质上来说,就是不用 chrome 浏览器来运行 Chrome 的功能!它将 Chromium 和 Blink 渲染引擎提供的所有现代 Web 平台的功能都带入了命令行。
-Why is that useful?
+它有什么用?
-A headless browser is a great tool for automated testing and server environments where you don't need a visible UI shell. For example, you may want to run some tests against a real web page, create a PDF of it, or just inspect how the browser renders an URL.
+无需显示的浏览器对于自动化测试和不需要可视化 UI 界面的服务器环境是一个很好的工具。例如,你可能需要对真实的网页运行一些测试,创建一个 PDF,或者只是检查浏览器如何呈现 URL。
-
+> **注意:** Mac 和 Linux 上的 Chrome 59 都可以运行无需显示模式。[对 Windows 的支持][2]将在 Chrome 60 中提供。要检查你使用的 Chrome 版本,请在浏览器中打开 `chrome://version`。
-### Starting Headless (CLI)
+### 开启无需显示模式(命令行界面)
-The easiest way to get started with headless mode is to open the Chrome binary from the command line. If you've got Chrome 59+ installed, start Chrome with the `--headless` flag:
+开启无需显示模式最简单的方法是从命令行打开 Chrome 二进制文件。如果你已经安装了 Chrome 59 以上的版本,请使用 `--headless` 标志启动 Chrome:
```
chrome \
@@ -24,11 +24,11 @@ chrome \
https://www.chromestatus.com # URL to open. Defaults to about:blank.
```
-
+> **注意:**目前你仍然需要使用 `--disable-gpu` 标志。但它最终会不需要的。
-`chrome` should point to your installation of Chrome. The exact location will vary from platform to platform. Since I'm on Mac, I created convenient aliases for each version of Chrome that I have installed.
+`chrome` 二进制文件应该指向你安装 Chrome 的位置。确切的位置会因平台差异而不同。当前我在 Mac 上操作,所以我为安装的每个版本的 Chrome 都创建了方便使用的别名。
-If you're on the stable channel of Chrome and cannot get the Beta, I recommend using `chrome-canary`:
+如果您使用 Chrome 的稳定版,并且无法获得测试版,我建议您使用 `chrome-canary` 版本:
```
alias chrome="/Applications/Google\ Chrome.app/Contents/MacOS/Google\ Chrome"
@@ -36,31 +36,31 @@ alias chrome-canary="/Applications/Google\ Chrome\ Canary.app/Contents/MacOS/Goo
alias chromium="/Applications/Chromium.app/Contents/MacOS/Chromium"
```
-Download Chrome Canary [here][10].
+在[这里][10]下载 Chrome Cannary。
-### Command line features
+### 命令行的功能
-In some cases, you may not need to [programmatically script][11] Headless Chrome. There are some [useful command line flags][12] to perform common tasks.
+在某些情况下,你可能不需要[以脚本编程的方式][11]操作 Headless Chrome。可以使用一些[有用的命令行标志][12]来执行常见的任务。
-### Printing the DOM
+#### 打印 DOM
-The `--dump-dom` flag prints `document.body.innerHTML` to stdout:
+`--dump-dom` 标志将打印 `document.body.innerHTML` 到标准输出:
```
chrome --headless --disable-gpu --dump-dom https://www.chromestatus.com/
```
-### Create a PDF
+#### 创建一个 PDF
-The `--print-to-pdf` flag creates a PDF of the page:
+`--print-to-pdf` 标志将页面转出为 PDF 文件:
```
chrome --headless --disable-gpu --print-to-pdf https://www.chromestatus.com/
```
-### Taking screenshots
+#### 截图
-To capture a screenshot of a page, use the `--screenshot` flag:
+要捕获页面的屏幕截图,请使用 `--screenshot` 标志:
```
chrome --headless --disable-gpu --screenshot https://www.chromestatus.com/
@@ -72,11 +72,11 @@ chrome --headless --disable-gpu --screenshot --window-size=1280,1696 https://www
chrome --headless --disable-gpu --screenshot --window-size=412,732 https://www.chromestatus.com/
```
-Running with `--screenshot` will produce a file named `screenshot.png` in the current working directory. If you're looking for full page screenshots, things are a tad more involved. There's a great blog post from David Schnurr that has you covered. Check out [Using headless Chrome as an automated screenshot tool ][13].
+使用 `--screenshot` 标志运行 Headless Chrome 将在当前工作目录中生成一个名为 `screenshot.png` 的文件。如果你正在寻求整个页面的截图,那么会涉及到很多事情。来自 David Schnurr 的一篇很棒的博文已经介绍了这一内容。请查看 [使用 headless Chrome 作为自动截屏工具][13]。
-### REPL mode (read-eval-print loop)
+#### REPL 模式 (read-eval-print loop)
-The `--repl` flag runs Headless in a mode where you can evaluate JS expressions in the browser, right from the command line:
+`--repl` 标志可以使 Headless Chrome 运行在一个你可以使用浏览器评估 JS 表达式的模式下。执行下面的命令:
```
$ chrome --headless --disable-gpu --repl https://www.chromestatus.com/
@@ -84,35 +84,35 @@ $ chrome --headless --disable-gpu --repl https://www.chromestatus.com/
>>> location.href
{"result":{"type":"string","value":"https://www.chromestatus.com/features"}}
>>> quit
-$
```
-### Debugging Chrome without a browser UI?
+### 在没有浏览器界面的情况下调试 Chrome
-When you run Chrome with `--remote-debugging-port=9222`, it starts an instance with the [DevTools protocol][14] enabled. The protocol is used to communicate with Chrome and drive the headless browser instance. It's also what tools like Sublime, VS Code, and Node use for remote debugging an application. #synergy
+当你使用 `--remote-debugging-port=9222` 运行 Chrome 时,它会启动一个支持 [DevTools 协议][14]的实例。该协议用于与 Chrome 进行通信,并且驱动 Headless Chrome 浏览器实例。它也是一个类似 Sublime、VS Code 和 Node 的工具,可用于应用程序的远程调试。#协同效应
-Since you don't have browser UI to see the page, navigate to `http://localhost:9222` in another browser to check that everything is working. You'll see a list of inspectable pages where you can click through and see what Headless is rendering:
+由于你没有浏览器用户界面可用来查看网页,请在另一个浏览器中输入 `http://localhost:9222`,以检查一切是否正常。你将会看到一个可检查的页面的列表,可以点击它们来查看 Headless Chrome 正在呈现的内容:

-DevTools remote debugging UI
-From here, you can use the familiar DevTools features to inspect, debug, and tweak the page as you normally would. If you're using Headless programmatically, this page is also a powerful debugging tool for seeing all the raw DevTools protocol commands going across the wire, communicating with the browser.
+*DevTools 远程调试界面*
-### Using programmatically (Node)
+从这里,你就可以像往常一样使用熟悉的 DevTools 来检查、调试和调整页面了。如果你以编程方式使用 Headless Chrome,这个页面也是一个功能强大的调试工具,用于查看所有通过网络与浏览器交互的原始 DevTools 协议命令。
-### The Puppeteer API
+### 使用编程模式 (Node)
-[Puppeteer][15] is a Node library developed by the Chrome team. It provides a high-level API to control headless (or full) Chrome. It's similar to other automated testing libraries like Phantom and NightmareJS, but it only works with the latest versions of Chrome.
+#### Puppeteer 库 API
-Among other things, Puppeteer can be used to easily take screenshots, create PDFs, navigate pages, and fetch information about those pages. I recommend the library if you want to quickly automate browser testing. It hides away the complexities of the DevTools protocol and takes care of redundant tasks like launching a debug instance of Chrome.
+[Puppeteer][15] 是一个由 Chrome 团队开发的 Node 库。它提供了一个高层次的 API 来控制无需显示版(或 完全版)的 Chrome。它与其他自动化测试库,如 Phantom 和 NightmareJS 相类似,但是只适用于最新版本的 Chrome。
-Install it:
+除此之外,Puppeteer 还可用于轻松截取屏幕截图,创建 PDF,页面间导航以及获取有关这些页面的信息。如果你想快速地自动化进行浏览器测试,我建议使用该库。它隐藏了 DevTools 协议的复杂性,并可以处理诸如启动 Chrome 调试实例等繁冗的任务。
+
+安装:
```
yarn add puppeteer
```
-**Example** - print the user agent
+**例子** - 打印用户代理:
```
const puppeteer = require('puppeteer');
@@ -124,7 +124,7 @@ const puppeteer = require('puppeteer');
})();
```
-**Example** - taking a screenshot of the page
+**例子** - 获取页面的屏幕截图:
```
const puppeteer = require('puppeteer');
@@ -140,19 +140,19 @@ browser.close();
})();
```
-Check out [Puppeteer's documentation][16] to learn more about the full API.
+查看 [Puppeteer 的文档][16],了解完整 API 的更多信息。
-### The CRI library
+#### CRI 库
-[chrome-remote-interface][17] is a lower-level library than Puppeteer's API. I recommend it if you want to be close to the metal and use the [DevTools protocol][18] directly.
+[chrome-remote-interface][17] 是一个比 Puppeteer API 更低层次的库。如果你想要更接近原始信息和更直接地使用 [DevTools 协议][18]的话,我推荐使用它。
-#### Launching Chrome
+**启动 Chrome**
-chrome-remote-interface doesn't launch Chrome for you, so you'll have to take care of that yourself.
+chrome-remote-interface 不会为你启动 Chrome,所以你要自己启动它。
-In the CLI section, we [started Chrome manually][19] using `--headless --remote-debugging-port=9222`. However, to fully automate tests, you'll probably want to spawn Chrome _from_ your application.
+在前面的 CLI 章节中,我们使用 `--headless --remote-debugging-port=9222` [手动启动了 Chrome][19]。但是,要想做到完全自动化测试,你可能希望从你的应用程序中启动 Chrome。
-One way is to use `child_process`:
+其中一种方法是使用 `child_process`:
```
const execFile = require('child_process').execFile;
@@ -168,19 +168,19 @@ launchHeadlessChrome('https://www.chromestatus.com', (err, stdout, stderr) => {
});
```
-But things get tricky if you want a portable solution that works across multiple platforms. Just look at that hard-coded path to Chrome :(
+但是如果你想要在多个平台上运行可移植的解决方案,事情会变得很棘手。请注意 Chrome 的硬编码路径:
-##### Using ChromeLauncher
+**使用 ChromeLauncher**
-[Lighthouse][20] is a marvelous tool for testing the quality of your web apps. A robust module for launching Chrome was developed within Lighthouse and is now extracted for standalone use. The [`chrome-launcher` NPM module][21] will find where Chrome is installed, set up a debug instance, launch the browser, and kill it when your program is done. Best part is that it works cross-platform thanks to Node!
+[Lighthouse][20] 是一个令人称奇的网络应用的质量测试工具。Lighthouse 内部开发了一个强大的用于启动 Chrome 的模块,现在已经被提取出来单独使用。[chrome-launcher NPM 模块][21] 可以找到 Chrome 的安装位置,设置调试实例,启动浏览器和在程序运行完之后将其杀死。它最好的一点是可以跨平台工作,感谢 Node!
-By default, **`chrome-launcher` will try to launch Chrome Canary** (if it's installed), but you can change that to manually select which Chrome to use. To use it, first install from npm:
+默认情况下,**chrome-launcher 会尝试启动 Chrome Canary**(如果已经安装),但是你也可以更改它,手动选择使用的 Chrome 版本。要想使用它,首先从 npm 安装:
```
yarn add chrome-launcher
```
-**Example** - using `chrome-launcher` to launch Headless
+**例子** - 使用 `chrome-launcher` 启动 Headless Chrome:
```
const chromeLauncher = require('chrome-launcher');
@@ -214,23 +214,21 @@ launchChrome().then(chrome => {
});
```
-Running this script doesn't do much, but you should see an instance of Chrome fire up in the task manager that loaded `about:blank`. Remember, there won't be any browser UI. We're headless.
+运行这个脚本没有做太多的事情,但你应该能在任务管理器中看到启动了一个 Chrome 的实例,它加载了页面 `about:blank`。记住,它不会有任何的浏览器界面,我们是无需显示的。
-To control the browser, we need the DevTools protocol!
+为了控制浏览器,我们需要 DevTools 协议!
-#### Retrieving information about the page
+#### 检索有关页面的信息
-
+> **警告:** DevTools 协议可以做一些有趣的事情,但是起初可能有点令人生畏。我建议先花点时间浏览 [DevTools 协议查看器][3]。然后,转到 `chrome-remote-interface` 的 API 文档,看看它是如何包装原始协议的。
-Let's install the library:
+我们来安装该库:
```
yarn add chrome-remote-interface
```
-##### Examples
-
-**Example** - print the user agent
+**例子** - 打印用户代理:
```
const CDP = require('chrome-remote-interface');
@@ -243,9 +241,9 @@ launchChrome().then(async chrome => {
});
```
-Results in something like: `HeadlessChrome/60.0.3082.0`
+结果是类似这样的东西:`HeadlessChrome/60.0.3082.0`。
-**Example** - check if the site has a [web app manifest][22]
+**例子** - 检查网站是否有 [Web 应用程序清单][22]:
```
const CDP = require('chrome-remote-interface');
@@ -282,7 +280,7 @@ Page.loadEventFired(async () => {
})();
```
-**Example** - extract the `` of the page using DOM APIs.
+**例子** - 使用 DOM API 提取页面的 `<title>`:
```
const CDP = require('chrome-remote-interface');
@@ -316,21 +314,21 @@ Page.loadEventFired(async () => {
})();
```
-### Using Selenium, WebDriver, and ChromeDriver
+### 使用 Selenium、WebDriver 和 ChromeDriver
-Right now, Selenium opens a full instance of Chrome. In other words, it's an automated solution but not completely headless. However, Selenium can be configured to run headless Chrome with a little work. I recommend [Running Selenium with Headless Chrome][23] if you want the full instructions on how to set things up yourself, but I've dropped in some examples below to get you started.
+现在,Selenium 开启了 Chrome 的完整实例。换句话说,这是一个自动化的解决方案,但不是完全无需显示的。但是,Selenium 只需要进行小小的配置即可运行 Headless Chrome。如果你想要关于如何自己设置的完整说明,我建议你阅读“[使用 Headless Chrome 来运行 Selenium][23]”,不过你可以从下面的一些示例开始。
-#### Using ChromeDriver
+#### 使用 ChromeDriver
-[ChromeDriver][24] 2.3.0 supports Chrome 59 and later and works with headless Chrome. In some cases, you may need Chrome 60 to work around bugs. For example, there are known issues with taking screenshots in Chrome 59.
+[ChromeDriver][24] 2.3.0 支持 Chrome 59 及更新版本,可与 Headless Chrome 配合使用。在某些情况下,你可能需要等到 Chrome 60 以解决 bug。例如,Chrome 59 中屏幕截图已知存在问题。
-Install:
+安装:
```
yarn add selenium-webdriver chromedriver
```
-Example:
+例子:
```
const fs = require('fs');
@@ -368,17 +366,17 @@ driver.takeScreenshot().then(base64png => {
driver.quit();
```
-#### Using WebDriverIO
+#### 使用 WebDriverIO
-[WebDriverIO][25] is a higher level API on top of Selenium WebDriver.
+[WebDriverIO][25] 是一个在 Selenium WebDrive 上构建的更高层次的 API。
-Install:
+安装:
```
yarn add webdriverio chromedriver
```
-Example: filter CSS features on chromestatus.com
+例子:过滤 chromestatus.com 上的 CSS 功能:
```
const webdriverio = require('webdriverio');
@@ -435,71 +433,69 @@ browser.end();
})();
```
-### Further resources
+### 更多资源
-Here are some useful resources to get you started:
+以下是一些可以带你入门的有用资源:
-Docs
+文档
-* [DevTools Protocol Viewer][4] - API reference docs
+* [DevTools Protocol Viewer][4] - API 参考文档
-Tools
+工具
-* [chrome-remote-interface][5] - node module that wraps the DevTools protocol
+* [chrome-remote-interface][5] - 基于 DevTools 协议的 node 模块
+* [Lighthouse][6] - 测试 Web 应用程序质量的自动化工具;大量使用了协议
+* [chrome-launcher][7] - 用于启动 Chrome 的 node 模块,可以自动化
-* [Lighthouse][6] - automated tool for testing web app quality; makes heavy use of the protocol
+样例
-* [chrome-launcher][7] - node module for launching Chrome, ready for automation
+* "[The Headless Web][8]" - Paul Kinlan 发布的使用了 Headless 和 api.ai 的精彩博客
-Demos
+### 常见问题
-* "[The Headless Web][8]" - Paul Kinlan's great blog post on using Headless with api.ai.
+**我需要 `--disable-gpu` 标志吗?**
-### FAQ
+目前是需要的。`--disable-gpu` 标志在处理一些 bug 时是需要的。在未来版本的 Chrome 中就不需要了。查看 [https://crbug.com/546953#c152][26] 和 [https://crbug.com/695212][27] 获取更多信息。
-**Do I need the `--disable-gpu` flag?**
+**所以我仍然需要 Xvfb 吗?**
-Yes, for now. The `--disable-gpu` flag is a temporary requirement to work around a few bugs. You won't need this flag in future versions of Chrome. See [https://crbug.com/546953#c152][26] and [https://crbug.com/695212][27] for more information.
+不。Headless Chrome 不使用窗口,所以不需要像 Xvfb 这样的显示服务器。没有它你也可以愉快地运行你的自动化测试。
-**So I still need Xvfb?**
+什么是 Xvfb?Xvfb 是一个用于类 Unix 系统的运行于内存之内的显示服务器,可以让你运行图形应用程序(如 Chrome),而无需附加的物理显示器。许多人使用 Xvfb 运行早期版本的 Chrome 进行 “headless” 测试。
-No. Headless Chrome doesn't use a window so a display server like Xvfb is no longer needed. You can happily run your automated tests without it.
+**如何创建一个运行 Headless Chrome 的 Docker 容器?**
-What is Xvfb? Xvfb is an in-memory display server for Unix-like systems that enables you to run graphical applications (like Chrome) without an attached physical display. Many people use Xvfb to run earlier versions of Chrome to do "headless" testing.
+查看 [lighthouse-ci][28]。它有一个使用 Ubuntu 作为基础镜像的 [Dockerfile 示例][29],并且在 App Engine Flexible 容器中安装和运行了 Lighthouse。
-**How do I create a Docker container that runs Headless Chrome?**
+**我可以把它和 Selenium / WebDriver / ChromeDriver 一起使用吗?**
-Check out [lighthouse-ci][28]. It has an [example Dockerfile][29] that uses Ubuntu as a base image, and installs + runs Lighthouse in an App Engine Flexible container.
+是的。查看 [Using Selenium, WebDrive, or ChromeDriver][30]。
-**Can I use this with Selenium / WebDriver / ChromeDriver**?
+**它和 PhantomJS 有什么关系?**
-Yes. See [Using Selenium, WebDrive, or ChromeDriver][30].
+Headless Chrome 和 [PhantomJS][31] 是类似的工具。它们都可以用来在无需显示的环境中进行自动化测试。两者的主要不同在于 Phantom 使用了一个较老版本的 WebKit 作为它的渲染引擎,而 Headless Chrome 使用了最新版本的 Blink。
-**How is this related to PhantomJS?**
+目前,Phantom 提供了比 [DevTools protocol][32] 更高层次的 API。
-Headless Chrome is similar to tools like [PhantomJS][31]. Both can be used for automated testing in a headless environment. The main difference between the two is that Phantom uses an older version of WebKit as its rendering engine while Headless Chrome uses the latest version of Blink.
+**我在哪儿提交 bug?**
-At the moment, Phantom also provides a higher level API than the [DevTools protocol][32].
+对于 Headless Chrome 的 bug,请提交到 [crbug.com][33]。
-**Where do I report bugs?**
-
-For bugs against Headless Chrome, file them on [crbug.com][33].
-
-For bugs in the DevTools protocol, file them at [github.com/ChromeDevTools/devtools-protocol][34].
+对于 DevTools 协议的 bug,请提交到 [github.com/ChromeDevTools/devtools-protocol][34]。
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
作者简介
-[Eric Bidelman][1]Engineer @ Google working on Lighthouse, Web Components, Chrome, and the web
+[Eric Bidelman][1] 谷歌工程师,Lighthouse 开发,Web 和 Web 组件开发,Chrome 开发
-----------------------------------
via: https://developers.google.com/web/updates/2017/04/headless-chrome
-作者:[Eric Bidelman ][a]
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+作者:[Eric Bidelman][a]
+译者:[firmianay](https://github.com/firmianay)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/published/20170821 Getting started with ImageMagick.md b/published/20170821 Getting started with ImageMagick.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..14d25f8eff
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20170821 Getting started with ImageMagick.md
@@ -0,0 +1,184 @@
+ImageMagick 入门:使用命令行来编辑图片
+============================================================
+
+> 了解使用此轻量级图像编辑器查看和修改图像的常见方法。
+
+
+
+
+在最近一篇关于[轻量级图像查看器][8]的文章中,作者 Scott Nesbitt 提到了 `display`,它是 [ImageMagick][9] 中的一个组件。ImageMagick 不仅仅是一个图像查看器,它还提供了大量的图像编辑工具和选项。本教程将详细介绍如何在 ImageMagick 中使用 `display` 命令和其他命令行工具。
+
+现在有许多优秀的图像编辑器可用,你可能会想知道为什么有人会选择一个非 GUI 的、基于命令行的程序,如 ImageMagick。一方面,它非常可靠。但更大的好处是,它允许你建立一个以特定的方式编辑大量图像的方式。
+
+这篇对于常见的 ImageMagick 命令的介绍应该让你入门。
+
+### display 命令
+
+让我们从 Scott 提到的命令开始:`display`。假设你有一个目录,其中有很多想要查看的图像。使用以下命令开始 `display`:
+
+```
+cd Pictures
+display *.JPG
+```
+
+这将按照字母数字顺序顺序加载你的 JPG 文件,每张放在一个简单的窗口中。左键单击图像可以打开一个简单的独立菜单(ImageMagick 中唯一的 GUI 功能)。
+
+
+
+你可以在 **display** 菜单中找到以下内容:
+
+* **File** 包含选项 Open、Next、Former、Select、Save、Print、Delete、New、Visual Directory 和 Quit。 _Select_ 来选择要显示的特定文件,_Visual Directory_ 显示当前工作目录中的所有文件(而不仅仅是图像)。如果要滚动显示所有选定的图像,你可以使用 _Next_ 和 _Former_,但使用键盘快捷键(下一张图像用空格键,上一张图像用退格)更容易。
+* **Edit** 提供 Undo、Redo、Cut、Copy 和 Paste,它们只是辅助命令进行更具体的编辑过程。 当你进行不同的编辑功能看看它们做什么时 _Undo_ 特别有用。
+* **View** 有 Half Size、Original Size、Double Size、Resize、Apply、Refresh 和 Restore。这些大多是不用说明的,除非你在应用其中之一后保存图像,否则图像文件不会更改。_Resize_ 会打开一个对话框,以像素为单位,带有或者不带尺寸限制,或者是百分比指定图片大小。我不知道 _Apply_ 会做什么。
+* **Transform** 显示 Crop、Chop、Flop、Flip、Rotate Right、Rotate Left、Rotate、Shear、Roll 和 Trim Edges。_Chop_ 使用点击拖动操作剪切图像的垂直或水平部分,将边缘粘贴在一起。了解这些功能如何工作的最佳方法是操作它们,而不是看看。
+* **Enhance** 提供 Hue、Saturation、Brightness、Gamma、Spiff、Dull、Contrast Stretch、Sigmoidal Contrast、Normalize、Equalize、Negate、Grayscale、Map 和 Quantize。这些是用于颜色和调整亮度和对比度的操作。
+* **效果** 有 Despeckle、Emboss、Reduce Noise、Add Noise、Sharpen、Blur、Threshold、Edge Detect、Spread、Shade、Raise 和 Segment。这些是相当标准的图像编辑效果。
+* **F/X** 选项有 Solarize、Sepia Tone、Swirl、Implode、Vignette、Wave、Oil Paint 和 Charcoal Draw,在图像编辑器中也是非常常见的效果。
+* **Image Edit** 包含 Annotate、Draw、Color、Matte、Composite、Add Border、Add Frame、Comment、Launch 和 Region of Interest。_Launch _ 将打开 GIMP 中的当前图像(至少在我的 Fedora 中是这样)。 _Region of Interest_ 允许你选择一个区域来应用编辑。按下 Esc 取消选择该区域。
+* **Miscellany** 提供 Image Info、Zoom Image、Show Preview、Show Histogram、Show Matte、Background、Slide Show 和 Preferences。 _Show Preview_ 似乎很有趣,但我努力让它工作。
+* **Help** 有 Overview、Browse Documentation 和 About Display。 _Overview_ 提供了大量关于 display 的基本信息,并且包含大量内置的键盘快捷键,用于各种命令和操作。在我的 Fedora 中,_Browse Documentation_ 没有作用。
+
+虽然 `display` 的 GUI 界面提供了一个称职的图像编辑器,但 ImageMagick 还提供了 89 个命令行选项,其中许多与上述菜单项相对应。例如,如果我显示的数码相片目录中的图像大于我的屏幕尺寸,我不用在显示后单独调整大小,我可以指定:
+
+```
+display -resize 50% *.JPG
+```
+
+上面菜单中的许多操作都可以通过在命令行中添加一个选项来完成。但是还有其他的选项在菜单中没有,包括 `-monochrome`,将图像转换为黑白(不是灰度),还有 `-colors`,你可以指定在图像中使用多少种颜色。例如,尝试这些:
+
+```
+display -resize 50% -monochrome *.JPG
+```
+
+```
+display -resize 50% -colors 8 *.JPG
+```
+
+这些操作会创建有趣的图像。试试增强颜色或进行其他编辑后减少颜色。记住,除非你保存并覆盖它们,否则原始文件保持不变。
+
+### convert 命令
+
+`convert` 命令有 237 个选项 - 是的, 237 个! - 它提供了你可以做的各种各样的事情(其中一些 `display` 也可以做)。我只会覆盖其中的几个,主要是图像操作。你可以用 `convert` 做的两件简单的事情是:
+
+```
+convert DSC_0001.JPG dsc0001.png
+```
+
+```
+convert *.bmp *.png
+```
+
+第一个命令将单个文件(DSC_0001)从 JPG 转换为 PNG 格式,而不更改原始文件。第二个将对目录中的所有 BMP 图像执行此操作。
+
+如果要查看 ImageMagick 可以使用的格式,请输入:
+
+```
+identify -list format
+```
+
+我们来看几个用 `convert` 命令来处理图像的有趣方法。以下是此命令的一般格式:
+
+```
+convert inputfilename [options] outputfilename
+```
+
+你有多个选项,它们按照从左到右排列的顺序完成。
+
+以下是几个简单的选项:
+
+```
+convert monochrome_source.jpg -monochrome monochrome_example.jpg
+```
+
+
+
+
+```
+convert DSC_0008.jpg -charcoal 1.2 charcoal_example.jpg
+```
+
+
+
+`-monochrome` 选项没有关联的设置,但 `-charcoal` 变量需要一个相关因子。根据我的经验,它需要一个小的数字(甚至小于 1)来实现类似于炭笔绘画的东西,否则你会得到很大的黑色斑点。即使如此,图像中的尖锐边缘也是非常明显的,与炭笔绘画不同。
+
+现在来看看这些:
+
+```
+convert DSC_0032.JPG -edge 3 edge_demo.jpg
+```
+
+```
+convert DSC_0032.JPG -colors 4 reduced4_demo.jpg
+```
+
+```
+convert DSC_0032.JPG -colors 4 -edge 3 reduced+edge_demo.jpg
+```
+
+
+
+原始图像位于左上方。在第一个命令中,我使用了一个 `-edge` 选项,设置为 3(见右上角的图像) - 对于我的喜好而言小于它的数字都太精细了。在第二个命令(左下角的图像)中,我们将颜色的数量减少到了 4 个,与原来没有什么不同。但是看看当我们在第三个命令中组合这两个时,会发生什么(右下角的图像)!也许这有点大胆,但谁能预期到从原始图像或任何一个选项变成这个结果?
+
+`-canny` 选项提供了另外一个惊喜。这是另一种边缘检测器,称为“多阶算法”。单独使用 `-canny` 可以产生基本黑色的图像和一些白线。我后面跟着一个 `-negate` 选项:
+
+```
+convert DSC_0049.jpg -canny 0x1 -negate canny_egret.jpg
+convert DSC_0023.jpg -canny 0x1 -negate canny_ship.jpg
+```
+
+
+
+这有点极简主义,但我认为它类似于一种笔墨绘画,与原始照片有相当显著的差异。它并不能用于所有图片。一般来说,它对有锐利线条的图像效果最好。不是焦点的元素可能会消失。注意白鹭图片中的背景沙滩没有显示,因为它是模糊的。同样注意下船舶图片,虽然大多数边缘显示得非常好,因为没有颜色,我们失去了图片的整体形象,所以也许这可以作为一些数字着色,甚至在印后着色的基础。
+
+### montage 命令
+
+最后,我想谈一下 `montage` (蒙太奇)命令。我已经在上面展示了这个例子,我将单个图像组合成复合图片。
+
+这是我如何生成炭笔的例子(请注意,它们都在一行):
+
+```
+montage -label %f DSC_0008.jpg charcoal_example.jpg -geometry +10+10
+ -resize 25% -shadow -title 'charcoal demo' charcoal_demo.jpg
+```
+
+`-label` 选项会在每个图像下方标记它的文件名(`%f`)。不用 `-geometry` 选项,所有的图像将是缩略图大小(120 像素宽),`+10+10` 负责边框大小。接下来,我调整了整个最终组合的大小(`-resize 25%`),并添加了一个阴影(没有设置,因此是默认值),最后为这次 montage 操作创建了一个标题(`-title`)。
+
+你可以将所有图像名称放在最后,最后一个图像的名称将是 `montage` 操作所保存的文件名。这可用于为命令及其所有选项创建别名,然后我可以简单地键入该别名、输入适当的文件名即可。我偶尔会这么做来减少 `montage` 操作需要输入的命令长度。
+
+在 `-canny` 的例子中,我对 4 张图像进行了蒙太奇操作。我添加了 `-tile` 选项,确切地说是 `-tile 2x`,它创建了有两列的蒙太奇。我可以指定一个 `matrix`、`-tile 2x2` 或 `-tile x2` 来产生相同的结果。
+
+ImageMagick 还有更多可以了解,所以我打算写更多关于它的文章,甚至可能使用 [Perl][10] 脚本运行 ImageMagick 命令。ImageMagick 具有丰富的[文档][11],尽管该网站在示例或者显示结果上还不足,我认为最好的学习方式是通过实验和更改各种设置和选项来学习。
+
+(题图: opensource.com)
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+作者简介:
+
+Greg Pittman - Greg 是肯塔基州路易斯维尔的一名退休的神经科医生,对计算机和程序设计有着长期的兴趣,从 1960 年代的 Fortran IV 开始。当 Linux 和开源软件相继出现时,他开始学习更多,并最终做出贡献。他是 Scribus 团队的成员。
+
+---------------------
+
+via: https://opensource.com/article/17/8/imagemagick
+
+作者:[Greg Pittman][a]
+译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:https://opensource.com/users/greg-p
+[1]:https://opensource.com/file/367401
+[2]:https://opensource.com/file/367391
+[3]:https://opensource.com/file/367396
+[4]:https://opensource.com/file/367381
+[5]:https://opensource.com/file/367406
+[6]:https://opensource.com/article/17/8/imagemagick?rate=W2W3j4nu4L14gOClu1RhT7GOMDS31pUdyw-dsgFNqYI
+[7]:https://opensource.com/user/30666/feed
+[8]:https://opensource.com/article/17/7/4-lightweight-image-viewers-linux-desktop
+[9]:https://www.imagemagick.org/script/index.php
+[10]:https://opensource.com/sitewide-search?search_api_views_fulltext=perl
+[11]:https://imagemagick.org/script/index.php
+[12]:https://opensource.com/users/greg-p
+[13]:https://opensource.com/users/greg-p
+[14]:https://opensource.com/article/17/8/imagemagick#comments
diff --git a/published/20170823 Using Ansible for deploying serverless applications.md b/published/20170823 Using Ansible for deploying serverless applications.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..2c435b3a45
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20170823 Using Ansible for deploying serverless applications.md
@@ -0,0 +1,116 @@
+使用 Ansible 部署无服务(serverless)应用
+============================================================
+
+> <ruby>无服务<rt>serverless</rt></ruby>是<ruby>托管服务<rt>managed service</rt></ruby>发展方向的又一步,并且与 Ansible 的无代理体系结构相得益彰。
+
+
+
+[Ansible][8] 被设计为实际工作中的最简化的部署工具。这意味着它不是一个完整的编程语言。你需要编写定义任务的 YAML 模板,并列出任何需要自动完成的任务。
+
+大多数人认为 Ansible 是一种更强大的“处于 for 循环中的 SSH”,在简单的使用场景下这是真的。但其实 Ansible 是_任务_,而非 SSH。在很多情况下,我们通过 SSH 进行连接,但它也支持 Windows 机器上的 Windows 远程管理(WinRM),以及作为云服务的通用语言的 HTTPS API 之类的东西。
+
+在云中,Ansible 可以在两个独立的层面上操作:<ruby>控制面<rt>control plane</rt></ruby>和<ruby>实例资源<rt>on-instance resource</rt></ruby>。控制面由所有_没有_运行在操作系统上的东西组成。包括设置网络、新建实例、供给更高级别的服务,如亚马逊的 S3 或 DynamoDB,以及保持云基础设施安全和服务客户所需的一切。
+
+实例上的工作是你已经知道 Ansible 可以做的:启动和停止服务、配置文件<ruby>模版化<rt>templating</rt></ruby>、安装软件包以及通过 SSH 执行的所有与操作系统相关的操作。
+
+现在,什么是<ruby>[无服务][9]<rt>serverless</rt></ruby>呢?这要看你问谁,无服务要么是对公有云的无限延伸,或者是一个全新的范例,其中所有的东西都是 API 调用,以前从来没有这样做过。
+
+Ansible 采取第一种观点。在 “无服务” 是专门术语之前,用户不得不管理和配置 EC2 实例、虚拟私有云 (VPC) 网络以及其他所有内容。无服务是托管服务方向迈出的另一步,并且与 Ansible 的无代理体系结构相得益彰。
+
+在我们开始 [Lambda][10] 示例之前,让我们来看一个简单的配置 CloudFormation 栈任务:
+
+```
+- name: Build network
+ cloudformation:
+ stack_name: prod-vpc
+ state: present
+ template: base_vpc.yml
+```
+
+编写这样的任务只需要几分钟,但它是构建基础架构所涉及的最后的半手动步骤 - 点击 “Create Stack” - 这将 playbook 与其他放在一起。现在你的 VPC 只是在建立新区域时可以调用的另一项任务了。
+
+由于云提供商是你帐户中发生些什么的真相来源,因此 Ansible 有许多方法来取回并使用 ID、名称和其他参数来过滤和查询运行的实例或网络。以 `cloudformation_facts` 模块为例,我们可以从我们刚刚创建的模板中得到子网 ID、网络范围和其他数据。
+
+```
+- name: Pull all new resources back in as a variable
+ cloudformation_facts:
+ stack_name: prod-vpc
+ register: network_stack
+```
+
+对于无服务应用,除了 DynamoDB 表,S3 bucket 和其他任何其他功能之外,你肯定还需要一个 Lambda 函数的补充。幸运的是,通过使用 `lambda` 模块, Lambda 函数可以以上次任务的堆栈相同的方式创建:
+
+```
+- lambda:
+ name: sendReportMail
+ zip_file: "{{ deployment_package }}"
+ runtime: python3.6
+ handler: report.send
+ memory_size: 1024
+ role: "{{ iam_exec_role }}"
+ register: new_function
+```
+
+如果你有其他想用来交付无服务应用的工具,这也是可以的。开源的[无服务框架][11]有自己的 Ansible 模块,它也可以工作:
+
+```
+- serverless:
+ service_path: '{{ project_dir }}'
+ stage: dev
+ register: sls
+- name: Serverless uses CloudFormation under the hood, so you can easily pull info back into Ansible
+ cloudformation_facts:
+ stack_name: "{{ sls.service_name }}"
+ register: sls_facts
+```
+
+这不是你需要的全部,因为无服务项目也必须存在,你将在那里大量的定义你的函数和事件源。对于此例,我们将制作一个响应 HTTP 请求的函数。无服务框架使用 YAML 作为其配置语言(和 Ansible 一样),所以这应该看起来很熟悉。
+
+```
+# serverless.yml
+service: fakeservice
+
+provider:
+ name: aws
+ runtime: python3.6
+
+functions:
+ main:
+ handler: test_function.handler
+ events:
+ - http:
+ path: /
+ method: get
+```
+
+在 [AnsibleFest][12] 中,我将介绍这个例子和其他深入的部署策略,以最大限度地利用你已经拥有的 playbook 和基础设施,还有新的无服务实践。无论你是否能到,我希望这些例子可以让你开始使用 Ansible,无论你是否有任何服务要管理。
+
+_AnsibleFest 是一个单日会议,汇集了数百名 Ansible 用户、开发人员和行业合作伙伴。加入我们吧,这里有产品更新、鼓舞人心的交谈、技术深度潜水,动手演示和整天的网络。_
+
+(题图: opensource.com)
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://opensource.com/article/17/8/ansible-serverless-applications
+
+作者:[Ryan Scott Brown][a]
+译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:https://opensource.com/users/ryansb
+[1]:https://www.ansible.com/how-ansible-works?intcmp=701f2000000h4RcAAI
+[2]:https://www.ansible.com/ebooks?intcmp=701f2000000h4RcAAI
+[3]:https://www.ansible.com/quick-start-video?intcmp=701f2000000h4RcAAI
+[4]:https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/latest/intro_installation.html?intcmp=701f2000000h4RcAAI
+[5]:https://opensource.com/article/17/8/ansible-serverless-applications?rate=zOgBPQUEmiTctfbajpu_TddaH-8b-ay3pFCK0b43vFw
+[6]:https://www.eventbrite.com/e/ansiblefest-san-francisco-2017-tickets-34008433139
+[7]:https://opensource.com/user/12043/feed
+[8]:https://www.ansible.com/
+[9]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Serverless_computing
+[10]:https://aws.amazon.com/lambda/
+[11]:https://serverless.com/
+[12]:https://www.ansible.com/ansiblefest?intcmp=701f2000000h4RcAAI
+[13]:https://opensource.com/users/ryansb
+[14]:https://opensource.com/users/ryansb
diff --git a/published/20170823 Using Kubernetes for Local Development — Minikube.md b/published/20170823 Using Kubernetes for Local Development — Minikube.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..438e2df530
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20170823 Using Kubernetes for Local Development — Minikube.md
@@ -0,0 +1,273 @@
+Minikube:使用 Kubernetes 进行本地开发
+============================================================
+
+如果你的运维团队在使用 Docker 和 Kubernetes,那么建议开发上采用相同或相似的技术。这将减少不兼容性和可移植性问题的数量,并使每个人都会认识到应用程序容器是开发和运维团队的共同责任。
+
+
+
+这篇博客文章介绍了 Kubernetes 在开发模式中的用法,它的灵感来自于一个视频教程,你可以在“[无痛 Docker 教程][10]”中找到它。
+
+
+
+Minikube 是一个允许开发人员在本地使用和运行 Kubernetes 集群的工具,从而使开发人员的生活变得轻松。
+
+在这篇博客中,对于我测试的例子,我使用的是 Linux Mint 18,但其它 Linux 发行版在安装部分没有区别。
+
+```
+cat /etc/lsb-release
+```
+
+```
+DISTRIB_ID=LinuxMint
+DISTRIB_RELEASE=18.1
+DISTRIB_CODENAME=serena
+DISTRIB_DESCRIPTION=”Linux Mint 18.1 Serena”
+```
+
+
+
+### 先决条件
+
+为了与 Minkube 一起工作,我们应该安装 Kubectl 和 Minikube 和一些虚拟化驱动程序。
+
+* 对于 OS X,安装 [xhyve 驱动][2]、[VirtualBox][3] 或者 [VMware Fusion][4],然后再安装 Kubectl 和 Minkube。
+
+ ```
+ curl -LO https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/$(curl -s https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/stable.txt)/bin/darwin/amd64/kubectl
+
+ chmod +x ./kubectl
+
+ sudo mv ./kubectl /usr/local/bin/kubectl
+
+ curl -Lo minikube https://storage.googleapis.com/minikube/releases/v0.21.0/minikube-darwin-amd64 && chmod +x minikube && sudo mv minikube /usr/local/bin/
+ ```
+
+* 对于 Windows,安装 [VirtualBox][6] 或者 [Hyper-V][7],然后再安装 Kubectl 和 Minkube。
+
+ ```
+ curl -LO https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/v1.7.0/bin/windows/amd64/kubectl.exe
+ ```
+
+ 将二进制文件添加到你的 PATH 中(这篇[文章][11]解释了如何修改 PATH)
+
+ 下载 `minikube-windows-amd64.exe`,将其重命名为 `minikube.exe`,并将其添加到你的 PATH 中。[在这][12]可以找到最新版本。
+
+* 对于 Linux,安装 [VirtualBox][8] 或者 [KVM][9],然后再安装 Kubectl 和 Minkube。
+
+ ```
+ curl -LO https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/$(curl -s https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/stable.txt)/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl
+
+ chmod +x ./kubectl
+
+ sudo mv ./kubectl /usr/local/bin/kubectl
+
+ curl -Lo minikube https://storage.googleapis.com/minikube/releases/v0.21.0/minikube-linux-amd64 && chmod +x minikube && sudo mv minikube /usr/local/bin/
+ ```
+
+### 使用 Minikube
+
+我们先从这个 Dockerfile 创建一个镜像:
+
+```
+FROM busybox
+ADD index.html /www/index.html
+EXPOSE 8000
+CMD httpd -p 8000 -h /www; tail -f /dev/null
+```
+
+添加你希望在 index.html 中看到的内容。
+
+构建镜像:
+
+```
+docker build -t eon01/hello-world-web-server .
+```
+
+我们来运行容器来测试它:
+
+```
+docker run -d --name webserver -p 8000:8000 eon01/hello-world-web-server
+```
+
+这是 `docker ps` 的输出:
+
+```
+docker ps
+
+CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
+2ad8d688d812 eon01/hello-world-web-server "/bin/sh -c 'httpd..." 3 seconds ago Up 2 seconds 0.0.0.0:8000->8000/tcp webserver
+```
+
+让我们提交镜像并将其上传到公共 Docker Hub 中。你也可以使用自己的私有仓库:
+
+```
+docker commit webserver
+docker push eon01/hello-world-web-server
+```
+
+删除容器,因为我们将与 Minikube 一起使用它。
+
+```
+docker rm -f webserver
+```
+
+启动 Minikube:
+
+```
+minkube start
+```
+
+检查状态:
+
+```
+minikube status
+```
+
+我们运行一个单一节点:
+
+```
+kubectl get node
+```
+
+运行 webserver:
+
+```
+kubectl run webserver --image=eon01/hello-world-web-server --port=8000
+```
+
+webserver 应该会暴露它的端口:
+
+```
+kubectl expose deployment webserver --type=NodePort
+```
+
+为了得到服务 url 输入:
+
+```
+minikube service webserver --url
+```
+
+使用下面的命令得到 Web 页面的内容:
+
+```
+curl $(minikube service webserver --url)
+```
+
+显示运行中集群的摘要:
+
+```
+kubectl cluster-info
+```
+
+更多细节:
+
+```
+kubectl cluster-info dump
+```
+
+我们还可以使用以下方式列出 pod:
+
+```
+kubectl get pods
+```
+
+使用下面的方式访问面板:
+
+```
+minikube dashboard
+```
+
+如果你想访问 Web 程序的前端,输入:
+
+```
+kubectl proxy
+```
+
+如果我们要在容器内部执行一个命令,请使用以下命令获取 pod id:
+
+```
+kubetctl get pods
+```
+
+然后像这样使用:
+
+```
+kubectl exec webserver-2022867364-0v1p9 -it -- /bin/sh
+```
+
+最后完成了,请删除所有部署:
+
+```
+kubectl delete deployments --all
+```
+
+删除所有 pod:
+
+```
+kubectl delete pods --all
+```
+
+并且停止 Minikube。
+
+```
+minikube stop
+```
+
+我希望你享受这个介绍。
+
+### 更加深入
+
+如果你对本文感到共鸣,您可以在[无痛 Docker 教程][13]中找到更多有趣的内容。
+
+我们 [Eralabs][14] 将很乐意为你的 Docker 和云计算项目提供帮助,[联系我们][15],我们将很乐意听到你的项目。
+
+请订阅 [DevOpsLinks][16]:成千上万的 IT 专家和 DevOps 爱好者在线社区。
+
+你可能也有兴趣加入我们的新闻订阅 [Shipped][17],一个专注于容器,编排和无服务技术的新闻订阅。
+
+你可以在 [Twitter][18]、[Clarity][19] 或我的[网站][20]上找到我,你也可以看看我的书:[SaltStack For DevOps][21]。
+
+不要忘记加入我的最后一个项目 [DevOps 的职位][22]!
+
+如果你喜欢本文,请推荐它,并与你的关注者分享。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+作者简介:
+
+Aymen El Amri - 云和软件架构师、企业家、作者、www.eralabs.io 的 CEO、www.devopslinks.com 的创始人,个人页面:www.aymenelamri.com
+
+-------------------
+
+
+via: https://medium.com/devopslinks/using-kubernetes-minikube-for-local-development-c37c6e56e3db
+
+作者:[Aymen El Amri][a]
+译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:https://medium.com/@eon01
+[1]:http://painlessdocker.com/
+[2]:https://git.k8s.io/minikube/docs/drivers.md#xhyve-driver
+[3]:https://www.virtualbox.org/wiki/Downloads
+[4]:https://www.vmware.com/products/fusion
+[5]:https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/stable.txt%29/bin/darwin/amd64/kubectl
+[6]:https://www.virtualbox.org/wiki/Downloads
+[7]:https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/virtualization/hyperv_on_windows/quick_start/walkthrough_install
+[8]:https://www.virtualbox.org/wiki/Downloads
+[9]:http://www.linux-kvm.org/
+[10]:http://painlessdocker.com/
+[11]:https://www.windows-commandline.com/set-path-command-line/
+[12]:https://github.com/kubernetes/minikube/releases
+[13]:http://painlessdocker.com/
+[14]:http://eralabs.io/
+[15]:http://eralabs.io/
+[16]:http://devopslinks.com/
+[17]:http://shipped.devopslinks.com/
+[18]:https://twitter.com/eon01
+[19]:https://clarity.fm/aymenelamri/
+[20]:http://aymenelamri.com/
+[21]:http://saltstackfordevops.com/
+[22]:http://jobsfordevops.com/
diff --git a/published/20170823 Why open source should be the first choice for cloud-native environments.md b/published/20170823 Why open source should be the first choice for cloud-native environments.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..ed47aa5710
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20170823 Why open source should be the first choice for cloud-native environments.md
@@ -0,0 +1,110 @@
+为什么开源应该是云原生环境的首选
+============================================================
+
+> 基于 Linux 击败了专有软件一样的原因,开源应该成为云原生环境的首选。
+
+
+
+让我们回溯到上世纪 90 年代,当时专有软件大行其道,而开源才刚开始进入它自己的时代。是什么导致了这种转变?更重要的是,而今天我们转到云原生环境时,我们能从中学到什么?
+
+### 基础设施的历史经验
+
+我将以一个高度武断的、开源的视角开始,来看看基础设施过去 30 年的历史。在上世纪 90 年代,Linux 只是大多数组织视野中一个微不足道的小光点而已——如果他们听说过它的话。你早早购入股票的那些公司们很快就发现了 Linux 的好处,它主要是作为专有的 Unix 的廉价替代品,而部署服务器的标准方式是使用专有的 Unix,或者日渐增多的使用 Microsoft Windows NT。
+
+这种模式的专有本性为更专有的软件提供了一个肥沃的生态系统。软件被装在盒子里面放在商店出售。甚至开源软件也参与了这种装盒游戏;你可以在货架上买到 Linux,而不是用你的互联网连接免费下载。去商店和从你的软件供应商那里只是你得到软件的不同方式而已。
+
+
+
+*Ubuntu 包装盒出现在百思买的货架上*
+
+我认为,随着 LAMP 系列(Linux、Apache、MySQL 和 PHP / Perl / Python)的崛起,情况发生了变化。LAMP 系列非常成功。它是稳定的、可伸缩的和相对用户友好的。与此同时,我开始看到对专有解决方案的不满。一旦客户在 LAMP 系列中尝过了开源的甜头,他们就会改变他们对软件的期望,包括:
+
+* 不愿被供应商绑架,
+* 关注安全,
+* 希望自己来修复 bug ,以及
+* 孤立开发的软件意味着创新被扼杀。
+
+在技术方面,我们也看到了各种组织在如何使用软件上的巨大变化。忽然有一天,网站的宕机变成不可接受的了。这就对扩展性和自动化有了更多的依赖。特别是在过去的十年里,我们看到了基础设施从传统的“宠物”模式到“群牛”模式的转变,在这种模式中,服务器可以被换下和替换,而不是一直运行和被指定。公司使用大量的数据,更注重数据留存和数据到用户的处理和返回速度。
+
+开源和开源社区,以及来自大公司的日益增多的投入,为我们改变如何使用软件提供了基础。系统管理员的岗位要求开始 要求 Linux 技能和对开源技术和理念的熟悉。通过开源类似 Chef cookbooks 和 Puppet 模块这样东西,管理员可以分享他们的模式配置。我们不再单独配置和调优 MySQL;我们创建了一个掌控基础部分的系统,我们现在可以专注于更有趣的、可以给我们雇主带来更高价值的工程作业。
+
+开源现在无处不在,围绕它的模式也无处不在。曾经仇视这个想法的公司不仅通过协同项目与外界拥抱开源,而且进一步地,还发布了他们自己的开源软件项目并且围绕它们构建了社区。
+
+
+
+### 转向云端
+
+今天,我们生活在一个 DevOps 和云端的世界里。我们收获了开源运动带来的创新成果。在公司内部采用开源软件开发实践的情况下, Tim O'reilly 所称的 “[内部开源][11]” 有了明显增长。我们为云平台共享部署配置。像 Terraform 这样的工具甚至允许我们编写和分享我们如何部署特定的平台。
+
+但这些平台本身呢?
+
+> “大多数人想都不想就使用了云……许多用户将钱投入到根本不属于他们的基础设施中,而对放弃他们的数据和信息毫无顾虑。"
+> —Edward Snowden, OpenStack Summit, May 9, 2017
+
+现在是时候要更多地想想本能地转移或扩展到云上的事情了。
+
+就像 Snowden 强调的那样,现在我们正面临着对我们的用户和客户的数据的失控风险。抛开安全不谈,如果我们回顾一下我们转向开源的原因,个中原因还包括被厂商绑架的担忧、创新难以推动、甚至修复 bug 的考虑。
+
+在把你自己和/或你的公司锁定在一个专有平台之前,考虑以下问题:
+
+* 我使用的服务是遵循开放标准,还是被厂商绑架的?
+* 如果服务供应商破产或被竞争对手收购,什么是我可以依赖的?
+* 关于停机、安全等问题,供应商与其客户沟通中是否有一个明确而真诚的历史过往?
+* 供应商是否响应 bug 和特性请求,即使那是来自小客户?
+* 供应商是否会在我不知情的情况下使用我们的数据(或者更糟,即便我们的客户协议所不同意)?
+* 供应商是否有一个计划来处理长期的,不断上升的增长成本,特别是如果最初的成本很低呢?
+
+您可以通过这个问卷,讨论每个要点,而仍然决定使用专有的解决方案。这很好,很多公司一直都在这么做。然而,如果你像我一样,宁愿找到一个更开放的解决方案而仍然受益于云,你确实有的选择。
+
+### 基于私有云
+
+当您寻找私有云解决方案时,您的首选是开源,投资一个云提供商,其核心运行在开源软件上。 [OpenStack][12] 是行业领袖,在其 7 年的历史中,有 100 多个参与组织和成千上万的贡献者(包括我)。 OpenStack 项目已经证明,结合多个基于 OpenStack 云不仅是可行的,而且相对简单。云公司之间的 API 是相似的,所以您不必局限于特定的 OpenStack 供应商。作为一个开放源码项目,您仍然可以影响该基础设施的特性、bug 请求和发展方向。
+
+第二种选择是继续在基础层面上使用私有云,但在一个开源容器编排系统中。无论您选择 [DC/OS][13](基于[Apache Mesos][14]) 、[Kubernetes][15] 或 [Docker Swarm 模式][16] ,这些平台都允许您将私有云系统提供的虚拟机作为独立的 Linux 机器,并在此之上安装您的平台。您所需要的只是 Linux 而已,不会立即被锁定在特定云的工具或平台上。可以根据具体情况来决定是否使用特定的专属后端,但如果你这样做,就应该着眼于未来。
+
+有了这两种选择,你也可以选择完全离开云服务商。您可以部署自己的 OpenStack 云,或者将容器平台内部架构移动到您自己的数据中心。
+
+### 做一个登月计划
+
+最后,我想谈一谈开源项目基础设施。今年 3 月,在召开的 [南加州 Linux 展会][17] 上,多个开放源码项目的参与者讨论了为他们的项目运行开源基础设施。(更多的,请阅读我的 [关于该会议的总结][18])我认为这些项目正在做的这个工作是基础设施开源的最后一步。除了我们现在正在做的基本分享之外,我相信公司和组织们可以在不放弃与竞争对手相区分的“独门秘方”的情况下,进一步充分利用他们的基础设施开源。
+
+开源了他们的基础设施的开源项目,已经证明了允许多个公司和组织向他们的基础设施提交训练有素的 bug 报告,甚至是补丁和特定论文的价值。突然之间,你可以邀请兼职的贡献者。你的客户可以通过了解你的基础设施,“深入引擎盖子之下”,从而获得信心。
+
+想要更多的证据吗?访问 [开源基础设施][19] 的网站了解开源基础设施的项目(以及他们已经发布的大量基础设施)。
+
+可以在 8 月 26 日在费城举办的 FOSSCON 大会上 Elizabeth K. Joseph 的演讲“[基础架构开源][4]”上了解更多。
+
+(题图:[Jason Baker][6]. [CC BY-SA 4.0][7]. Source: [Cloud][8], [Globe][9]. Both [CC0][10].)
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://opensource.com/article/17/8/open-sourcing-infrastructure
+
+作者:[Elizabeth K. Joseph][a]
+译者:[wenzhiyi](https://github.com/wenzhiyi)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:https://opensource.com/users/pleia2
+[1]:https://opensource.com/file/366596
+[2]:https://opensource.com/file/366591
+[3]:https://opensource.com/article/17/8/open-sourcing-infrastructure?rate=PdT-huv5y5HFZVMHOoRoo_qd95RG70y4DARqU5pzgkU
+[4]:https://fosscon.us/node/12637
+[5]:https://opensource.com/user/25923/feed
+[6]:https://opensource.com/users/jason-baker
+[7]:https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/
+[8]:https://pixabay.com/en/clouds-sky-cloud-dark-clouds-1473311/
+[9]:https://pixabay.com/en/globe-planet-earth-world-1015311/
+[10]:https://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/
+[11]:https://opensource.com/life/16/11/create-internal-innersource-community
+[12]:https://www.openstack.org/
+[13]:https://dcos.io/
+[14]:http://mesos.apache.org/
+[15]:https://kubernetes.io/
+[16]:https://docs.docker.com/engine/swarm/
+[17]:https://www.socallinuxexpo.org/
+[18]:https://opensource.com/article/17/3/growth-open-source-project-infrastructures
+[19]:https://opensourceinfra.org/
+[20]:https://opensource.com/users/pleia2
+[21]:https://opensource.com/users/pleia2
diff --git a/published/20170825 Happy anniversary Linux A look back at where it all began.md b/published/20170825 Happy anniversary Linux A look back at where it all began.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..037b7b7203
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20170825 Happy anniversary Linux A look back at where it all began.md
@@ -0,0 +1,153 @@
+Linux 1.0 之旅:回顾这一切的开始
+============================================================
+
+> 通过安装 SLS 1.05 展示了 Linux 内核在这 26 年间走过了多远。
+
+
+
+我第一次安装 Linux 是在 1993 年。那时我跑的是 MS-DOS,但我真的很喜欢学校机房电脑的 Unix 系统,就在那里度过了我大学本科时光。 当我听说了 Linux,一个 Unix 的免费版本,可以在我家的 386 电脑上运行的时候,我立刻就想要试试。我的第一个 Linux 发行版是 [Softlanding Linux System][27] (SLS) 1.03,带有 11 级补丁的 0.99 alpha 版本的 Linux 内核。它要求高达 2 MB 的内存,如果你想要编译项目需要 4 MB,运行 X windows 则需要 8 MB。
+
+我认为 Linux 相较于 MS-DOS 世界是一个巨大的进步。 尽管 Linux 缺乏运行在 MS-DOS 上的广泛的应用及游戏,但我发现 Linux 带给我的是巨大的灵活性。不像 MS-DOS ,现在我可以进行真正的多任务,同时运行不止一个程序。并且 Linux 提供了丰富的工具,包括一个 C 语言编译器,让我可以构建自己的项目。
+
+一年后,我升级到了 SLS 1.05,它支持全新的 Linux 内核 1.0。 更重要的,Linux 引入了内核模块。通过内核模块,你不再需要为支持新硬件而编译整个内核;取而代之,只需要从包含 Linux 内核之内的 63 个模块里加载一个就行。在 SLS 1.05 的发行自述文件中包含这些关于模块的注释:
+
+> 内核的模块化旨在正视减少并最终消除重新编译内核的要求,无论是变更、修改设备驱动或者为了动态访问不常用的驱动。也许更为重要的是,个别工作小组的工作不再影响到内核的正确开发。事实上,这让以二进制发布官方内核现在成为了可能。
+
+在 8 月 25 日,Linux 内核将迎来它的第 26 周年(LCTT 译注:已经过去了 =.= )。为了庆祝,我重新安装了 SLS 1.05 来提醒自己 Linux 1.0 内核是什么样子,去认识 Linux 自二十世纪 90 年代以来走了多远。和我一起踏上 Linux 的怀旧之旅吧!
+
+### 安装
+
+SLS 是第一个真正的 “发行版”,因为它包含一个安装程序。 尽管安装过程并不像现代发行版一样顺畅。 不能从 CD-ROM 启动安装,我需要从安装软盘启动我的系统,然后从 **login** 提示中运行安装程序。
+
+
+
+在 SLS 1.05 中引入的一个漂亮的功能是支持彩色的文本模式安装器。当我选择彩色模式时,安装器切换到一个带有黑色文字的亮蓝色背景,不再是我们祖祖辈辈们使用的原始的普通黑白文本。
+
+
+
+SLS 安装器是个简单的东西,文本从屏幕底部滚动而上,显示其做的工作。通过对一些简单的提示的响应,我能够创建一个 Linux 分区,挂载上 ext2 文件系统,并安装 Linux 。 安装包含了 X windows 和开发工具的 SLS 1.05,需要大约 85 MB 的磁盘空间。依照今天的标准这听起来可能不是很多,但在 Linux 1.0 出来的时候,120 MB 的硬件设备才是主流设备。
+
+
+
+
+
+### 系统级别
+
+当我第一次启动到 Linux 时,让我想起来了一些关于这个早期版本 Linux 系统的事情。首先,Linux 没有占据很多的空间。在启动系统之后运行一些程序来检查的时候,Linux 占用了不到 4 MB 的内存。在一个拥有 16MB 内存的系统中,这就意味着节省了很多内存用来运行程序。
+
+
+
+熟悉的 `/proc` 元文件系统在 Linux 1.0 就存在了,尽管对比我们今天在现代系统上看到的,它并不能提供许多信息。在 Linux 1.0, `/proc` 包含一些接口来探测类似 `meminfo` 和 `stat` 之类的基本系统状态。
+
+
+
+在这个系统上的 `/etc` 文件目录非常简单。值得一提的是,SLS 1.05 借用了来自 [BSD Unix][28] 的 **rc** 脚本来控制系统启动。 初始化是通过 **rc** 脚本进行的,由 `rc.local` 文件来定义本地系统的调整。后来,许多 Linux 发行版采用了来自 [Unix System V][29] 的很相似的 **init** 脚本,后来又是 [systemd][30] 初始化系统。
+
+
+
+### 你能做些什么
+
+随着我的系统的启动运行,接下来就可以使用了了。那么,在这样的早期 Linux 系统上你能做些什么?
+
+让我们从基本的文件管理开始。 每次在你登录的时候,SLS 会让你使用 Softlanding 菜单界面(MESH),这是一个文件管理程序,现代的用户们可能觉得它和 [Midnight Commander][31] 很相似。 而二十世纪 90 年代的用户们可能会拿 MESH 与更为接近的 [Norton Commander][32] 相比,这个可以说是在 MS-DOS 上最流行的第三方文件管理程序。
+
+")
+
+除了 MESH 之外,在 SLS 1.05 中还少量包含了一些全屏应用程序。你可以找到熟悉的用户工具,包括 Elm 邮件阅读器、GNU Emacs 可编程编辑器,以及古老的 Vim 编辑器。
+
+
+
+
+
+SLS 1.05 甚至包含了一个可以让你在终端玩的俄罗斯方块版本。
+
+
+
+在二十世纪 90 年代,多数住宅的网络接入是通过拨号连接的,所以 SLS 1.05 包含了 Minicom 调制解调器拨号程序。Minicom 提供一个与调制解调器的直接连接,并需要用户通过贺氏调制解调器的 **AT** 命令来完成一些像是拨号或挂电话这样的基础功能。Minicom 同样支持宏和其他简单功能来使连接你的本地调制解调器池更容易。
+
+
+
+但如果你想要写一篇文档时怎么办? SLS 1.05 的存在要比 LibreOffice 或者 OpenOffice 早很长时间。在二十世纪 90 年代,Linux 还没有这些应用。相反,如果你想要使用一个文字处理器,可能需要引导你的系统进入 MS-DOS,然后运行你喜欢的文字处理器程序,如 WordPerfect 或者共享软件 GalaxyWrite。
+
+但是所有的 Unix 系统都包含一套简单的文本格式化程序,叫做 nroff 和 troff。在 Linux 系统中,他们被合并成 GNU groff 包,而 SLS 1.05 包含了 groff 的一个版本。我在 SLS 1.05 上的一项测试就是用 nroff 生成一个简单的文本文档。
+
+
+
+
+
+### 运行 X windows
+
+获取安装 X windows 并不特别容易,如 SLS 安装文件承诺的那样:
+
+> 在你的 PC 上获取安装 X windows 可能会有一些发人深省的体验,主要是因为 PC 的显示卡类型太多。Linux X11 仅支持 VGA 类型的显示卡,但在许多类型的 VGA 中仅有个别的某些类型是完全支持的。SLS 存在两种 X windows 服务器。全彩的 XFree86,支持一些或所有 ET3000、ET400、PVGA1、GVGA、Trident、S3、8514、Accelerated cards、ATI plus 等。
+>
+> 另一个服务器 XF86_Mono,能够工作在几乎所有的 VGA 卡上,但只提供单色模式。因此,相比于彩色服务器,它会占用更少的内存并拥有更快的速度。当然就是看起来不怎么漂亮。
+>
+> X windows 的配置信息都堆放在目录 “/usr/X386/lib/X11/”。需要注意的是,“Xconfig” 文件为监视器和显示卡定义了时序。默认情况下,X windows 设置使用彩色服务器,如果彩色服务器出现问题,你可以切换到单色服务器 x386mono,因为它已经支持各种标准的 VGA。本质上,这只是将 /usr/X386/bin/X 链接到它。
+>
+> 只需要编辑 Xconfig 来设置鼠标驱动类型和时序,然后键入 “startx” 即可。
+
+这些听起来令人困惑,但它就是这样。手工配置 X windows 真的可以是一个发人深省的体验。幸好,SLS 1.05 包含了 syssetup 程序来帮你确定系统组件的种类,包括了 X windows 的显示设置。在一些提示过后,经过一些实验和调整,最终我成功启动了 X windows!
+
+
+
+但这是来自于 1994 年的 X windows,它仍然并没有桌面的概念。我可以从 FVWM (一个虚拟窗口管理器)或 TWM (选项卡式的窗口管理器)中选择。TWM 直观地设置提供一个功能简单的图形环境。
+
+
+
+### 关机
+
+我已经在我的 Linux 寻根之旅沉浸许久,是时候最终回到我的现代桌面上了。最初我跑 Linux 的是一台仅有 8MB 内存和 一个 120MB 硬盘驱动器的 32 位 386 电脑,而我现在的系统已经足够强大了。拥有双核 64 位 Intel Core i5 处理器,4 GB 内存和一个 128 GB 的固态硬盘,我可以在我的运行着 Linux 内核 4.11.11 的系统上做更多事情。那么,在我的 SLS 1.05 的实验结束之后,是时候离开了。
+
+
+
+再见,Linux 1.0。很高兴看到你的茁壮成长。
+
+(题图:图片来源:[litlnemo][25]。由 Opnesource.com 修改。[CC BY-SA 2.0.][26])
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://opensource.com/article/17/8/linux-anniversary
+
+作者:[Jim Hall][a]
+译者:[softpaopao](https://github.com/softpaopao)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:https://opensource.com/users/jim-hall
+[1]:https://opensource.com/resources/what-is-linux?intcmp=70160000000h1jYAAQ&utm_source=intcallout&utm_campaign=linuxcontent
+[2]:https://opensource.com/resources/what-are-linux-containers?intcmp=70160000000h1jYAAQ&utm_source=intcallout&utm_campaign=linuxcontent
+[3]:https://developers.redhat.com/promotions/linux-cheatsheet/?intcmp=70160000000h1jYAAQ&utm_source=intcallout&utm_campaign=linuxcontent
+[4]:https://developers.redhat.com/cheat-sheet/advanced-linux-commands-cheatsheet?intcmp=70160000000h1jYAAQ&utm_source=intcallout&utm_campaign=linuxcontent
+[5]:https://opensource.com/tags/linux?intcmp=70160000000h1jYAAQ&utm_source=intcallout&utm_campaign=linuxcontent
+[6]:https://opensource.com/file/365166
+[7]:https://opensource.com/file/365171
+[8]:https://opensource.com/file/365176
+[9]:https://opensource.com/file/365161
+[10]:https://opensource.com/file/365221
+[11]:https://opensource.com/file/365196
+[12]:https://opensource.com/file/365156
+[13]:https://opensource.com/file/365181
+[14]:https://opensource.com/file/365146
+[15]:https://opensource.com/file/365151
+[16]:https://opensource.com/file/365211
+[17]:https://opensource.com/file/365186
+[18]:https://opensource.com/file/365191
+[19]:https://opensource.com/file/365226
+[20]:https://opensource.com/file/365206
+[21]:https://opensource.com/file/365236
+[22]:https://opensource.com/file/365201
+[23]:https://opensource.com/article/17/8/linux-anniversary?rate=XujKSFS7GfDmxcV7Jf_HUK_MdrW15Po336fO3G8s1m0
+[24]:https://opensource.com/user/126046/feed
+[25]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/litlnemo/19777182/
+[26]:https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.0/
+[27]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Softlanding_Linux_System
+[28]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Berkeley_Software_Distribution
+[29]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/UNIX_System_V
+[30]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Systemd
+[31]:https://midnight-commander.org/
+[32]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Norton_Commander
+[33]:https://opensource.com/users/jim-hall
+[34]:https://opensource.com/users/jim-hall
+[35]:https://opensource.com/article/17/8/linux-anniversary#comments
diff --git a/published/20170901 An economically efficient model for open source software license compliance.md b/published/20170901 An economically efficient model for open source software license compliance.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..abc27f2a84
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20170901 An economically efficient model for open source software license compliance.md
@@ -0,0 +1,61 @@
+一个开源软件许可证合规的经济高效模式
+============================================================
+
+> 使用开源的方式有利于你的盈亏底线以及开源生态系统。
+
+
+
+
+
+“<ruby>合规性工业联合体<rt>The Compliance Industrial Complex</rt></ruby>” 是一个术语,它会唤起那些组织参与精心设计并且花费昂贵流程的以遵守开源许可条款的反乌托邦想象。由于“生活经常模仿艺术”,许多组织采用了这种做法,可惜的是它们剥夺了许多开源模型的好处。本文介绍了一种经济高效的开源软件许可证合规性方法。
+
+开源许可证通常对从第三方授权的代码分发者有三个要求:
+
+1. 提供开源许可证的副本
+2. 包括版权声明
+3. 对于 copyleft 许可证(如 GPL),将相应的源代码提供给接受者。
+
+_(与任何一般性声明一样,可能会有例外情况,因此始终建议审查许可条款,如有需要,请咨询律师的意见。)_
+
+因为源代码(以及任何相关的文件,例如:许可证、README)通常都包含所有这些信息,所以最简单的遵循方法就是随着二进制/可执行程序一起提供源代码。
+
+替代方案更加困难并且昂贵,因为在大多数情况下,你仍然需要提供开源许可证的副本并保留版权声明。提取这些信息来结合你的二进制/可执行版本并不简单。你需要流程、系统和人员来从源代码和相关文件中复制此信息,并将其插入到单独的文本文件或文档中。
+
+不要低估创建此文件的时间和费用。虽然有工具也许可以自动化部分流程,但这些工具通常需要人力资源(例如工程师、质量经理、发布经理)来准备代码来扫描并对结果进行评估(没有完美的工具,几乎总是需要审查)。你的组织资源有限,将其转移到此活动会增加机会成本。考虑到这笔费用,每个后续版本(主要或次要)的成本将需要进行新的分析和修订。
+
+也有因不选择发布不能被很好识别的源码而导致增加的其他成本。这些根源在于不向开源项目的原始作者和/或维护者发布源代码, 这一活动称为上游化。独自上游化一般不满足大多数开源许可证的要求,这就是为什么这篇文章主张与你的二进制/可执行文件一起发布源代码。然而,上游化和提供源代码以及二进制/可执行文件都能提供额外的经济效益。这是因为你的组织不再需要保留随着每次发布合并开源代码修改而产生的私有分支 - 由于你的内部代码库与社区项目不同,这将是越来越消耗和凌乱的工作。上游化还增强了开源生态系统,它会鼓励社区创新,从中你的组织或许也会得到收益。
+
+那么为什么大量的组织不会为其产品发布源代码来简化其合规性工作?在许多情况下,这是因为他们认为这可能会暴露他们竞争优势的信息。考虑到这些专有产品中的大量代码可能是开源代码的直接副本,以支持诸如 WiFi 或云服务这些当代产品的基础功能,这种信念可能是错误的。
+
+即使对这些开源作品进行了修改来适配其专有产品,这些更改也往往是微不足道的,并包含了很少的新的版权部分或可用来专利的内容。因此,任何组织都应该通过这种方式来查看其代码,因为它可能会发现其代码库中绝大部分是开源的,只有一小部分是真正专有的、与竞争对手区分开来的部分。那么为什么不分发和向上游提交这些没有差别的代码呢?
+
+考虑一下拒绝遵从工业联合体的思维方式, 以降低成本并大大简化合规性。使用开源的方式,并体验发布你的源代码的乐趣,以造福于你的盈亏底线和开源生态系统,从中你将继续收获更多的利益。
+
+------------------------
+
+作者简介
+
+Jeffrey Robert Kaufman - Jeffrey R. Kaufman 是全球领先的开源软件解决方案提供商红帽公司的开源知识产权律师。Jeffrey 还担任着 Thomas Jefferson 法学院的兼职教授。 在加入红帽前,Jeffrey 在高通担任专利法律顾问,为首席科学家办公室提供开源顾问。 Jeffrey 在 RFID、条形码、图像处理和打印技术方面拥有多项专利。[更多关于我][2]
+
+(题图: opensource.com)
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://opensource.com/article/17/9/economically-efficient-model
+
+作者:[Jeffrey Robert Kaufman][a]
+译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:https://opensource.com/users/jkaufman
+[1]:https://opensource.com/article/17/9/economically-efficient-model?rate=0SO3DeFAxtgLdmZxE2ZZQyTRTTbu2OOlksFZSUXmjJk
+[2]:https://opensource.com/users/jkaufman
+[3]:https://opensource.com/user/74461/feed
+[4]:https://opensource.com/users/jkaufman
+[5]:https://opensource.com/users/jkaufman
+[6]:https://opensource.com/users/jkaufman
+[7]:https://opensource.com/tags/law
+[8]:https://opensource.com/tags/licensing
+[9]:https://opensource.com/participate
diff --git a/sources/talk/20170310 How to use pull requests to improve your code reviews.md b/sources/talk/20170310 How to use pull requests to improve your code reviews.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 4e84a4a2fd..0000000000
--- a/sources/talk/20170310 How to use pull requests to improve your code reviews.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,95 +0,0 @@
-How to use pull requests to improve your code reviews
-============================================================
-
-Spend more time building and less time fixing with GitHub Pull Requests for proper code review.
-
- 
-
-
->Take a look Brent and Peter’s book, [ _Introducing GitHub_ ][5], for more on creating projects, starting pull requests, and getting an overview of your team’s software development process.
-
-
-If you don’t write code every day, you may not know some of the problems that software developers face on a daily basis:
-
-* Security vulnerabilities in the code
-* Code that causes your application to crash
-* Code that can be referred to as “technical debt” and needs to be re-written later
-* Code that has already been written somewhere that you didn’t know about
-
-
-Code review helps improve the software we write by allowing other people and/or tools to look it over for us. This review can happen with automated code analysis or test coverage tools — two important pieces of the software development process that can save hours of manual work — or peer review. Peer review is a process where developers review each other's work. When it comes to developing software, speed and urgency are two components that often result in some of the previously mentioned problems. If you don’t release soon enough, your competitor may come out with a new feature first. If you don’t release often enough, your users may doubt whether or not you still care about improvements to your application.
-
-### Weighing the time trade-off: code review vs. bug fixing
-
-If someone is able to bring together multiple types of code review in a way that has minimal friction, then the quality of that software written over time will be improved. It would be naive to think that the introduction of new tools or processes would not at first introduce some amount of delay in time. But what is more expensive: time to fix bugs in production, or improving the software before it makes it into production? Even if new tools introduce some lag time in which a new feature can be released and appreciated by customers, that lag time will shorten as the software developers improve their own skills and the software release cycles will increase back to previous levels while bugs should decrease.
-
-One of the keys for achieving this goal of proactively improving code quality with code review is using a platform that is flexible enough to allow software developers to quickly write code, plug in the tools they are familiar with, and do peer review of each others’ code. [GitHub][9] is a great example of such a platform. However, putting your code on GitHub doesn’t just magically make code review happen; you have to open a pull request to start down this journey.
-
-### Pull requests: a living discussion about code
-
-[Pull requests][10] are a tool on GitHub that allows software developers to discuss and propose changes to the main codebase of a project that later can be deployed for all users to see. They were created back in February of 2008 for the purpose of suggesting a change on to someone’s work before it would be accepted (merged) and later deployed to production for end-users to see that change.
-
-Pull requests started out as a loose way to offer your change to someone’s project, but they have evolved into:
-
-* A living discussion about the code you want merged
-* Added functionality of increasing the visibility of what changed
-* Integration of your favorite tools
-* Explicit pull request reviews that can be required as part of a protected branch workflow
-
-### Considering code: URLs are forever
-
-Looking at the first two bullet points above, pull requests foster an ongoing code discussion that makes code changes very visible, as well as making it easy to pick up where you left off on your review. For both new and experienced developers, being able to refer back to these previous discussions about why a feature was developed the way it was or being linked to another conversation about a related feature should be priceless. Context can be so important when coordinating features across multiple projects and keeping everyone in the loop as close as possible to the code is great too. If those features are still being developed, it’s important to be able to just see what’s changed since you last reviewed. After all, it’s far easier to [review a small change than a large one][11], but that’s not always possible with large features. So, it’s important to be able to pick up where you last reviewed and only view the changes since then.
-
-### Integrating tools: software developers are opinionated
-
-Considering the third point above, GitHub’s pull requests have a lot of functionality but developers will always have a preference on additional tools. Code quality is a whole realm of code review that involves the other component to code reviews that aren’t necessarily human. Detecting code that’s “inefficient” or slow, a potential security vulnerability, or just not up to company standards is a task best left to automated tools. Tools like [SonarQube][12] and [Code Climate][13]can analyse your code, while tools like [Codecov][14] and [Coveralls][15] can tell you if the new code you just wrote is not well tested. The wonder of these tools is that they can plug into GitHub and report their findings right back into the pull request! This means the conversation not only has people reviewing the code, but the tools are reporting there too. Everyone can stay in the loop of exactly how a feature is developing.
-
-Lastly, depending on the preference of your team, you can make the tools and the peer review required by leveraging the required status feature of the [protected branch workflow][16].
-
-Though you may just be getting started on your software development journey, a business stakeholder who wants to know how a project is doing, or a project manager who wants to ensure the timeliness and quality of a project, getting involved in the pull request by setting up an approval workflow and thinking about integration with additional tools to ensure quality is important at any level of software development.
-
-Whether it’s for your personal website, your company’s online store, or the latest combine to harvest this year’s corn with maximum yield, writing good software involves having good code review. Having good code review involves the right tools and platform. To learn more about GitHub and the software development process, take a look at the O’Reilly book, [ _Introducing GitHub_ ][17], where you can understand creating projects, starting pull requests, and getting an overview of your team's’ software development process.
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-作者简介:
-
-**Brent Beer**
-
-Brent Beer has used Git and GitHub for over 5 years through university classes, contributions to open source projects, and professionally as a web developer. While working as a trainer for GitHub, he also became a published author of “Introducing GitHub” for O’Reilly. He now works as a solutions engineer for GitHub in Amsterdam to help bring Git and GitHub to developers across the world.
-
-**Peter Bell**
-
-Peter Bell is the founder and CTO of Ronin Labs. Training is broken - we're fixing it through technology enhanced training! He is an experienced entrepreneur, technologist, agile coach and CTO specializing in EdTech projects. He wrote "Introducing GitHub" for O'Reilly, created the "Mastering GitHub" course for code school and "Git and GitHub LiveLessons" for Pearson. He has presented regularly at national and international conferences on ruby, nodejs, NoSQL (especially MongoDB and neo4j), cloud computing, software craftsmanship, java, groovy, j...
-
-
--------------
-
-
-via: https://www.oreilly.com/ideas/how-to-use-pull-requests-to-improve-your-code-reviews?imm_mid=0ee8ca&cmp=em-prog-na-na-newsltr_20170311
-
-作者:[Brent Beer][a],[Peter Bell][b]
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:https://www.oreilly.com/people/acf937de-cdf4-4b0e-85bd-b559404c580e
-[b]:https://www.oreilly.com/people/2256f119-7ea0-440e-99e8-65281919e952
-[1]:https://pixabay.com/en/measure-measures-rule-metro-106354/
-[2]:http://conferences.oreilly.com/oscon/oscon-tx?intcmp=il-prog-confreg-update-ostx17_new_site_oscon_17_austin_right_rail_cta
-[3]:https://www.oreilly.com/people/acf937de-cdf4-4b0e-85bd-b559404c580e
-[4]:https://www.oreilly.com/people/2256f119-7ea0-440e-99e8-65281919e952
-[5]:https://www.safaribooksonline.com/library/view/introducing-github/9781491949801/?utm_source=newsite&utm_medium=content&utm_campaign=lgen&utm_content=how-to-use-pull-requests-to-improve-your-code-reviews
-[6]:http://conferences.oreilly.com/oscon/oscon-tx?intcmp=il-prog-confreg-update-ostx17_new_site_oscon_17_austin_right_rail_cta
-[7]:http://conferences.oreilly.com/oscon/oscon-tx?intcmp=il-prog-confreg-update-ostx17_new_site_oscon_17_austin_right_rail_cta
-[8]:https://www.oreilly.com/ideas/how-to-use-pull-requests-to-improve-your-code-reviews?imm_mid=0ee8ca&cmp=em-prog-na-na-newsltr_20170311
-[9]:https://github.com/about
-[10]:https://help.github.com/articles/about-pull-requests/
-[11]:https://blog.skyliner.io/ship-small-diffs-741308bec0d1
-[12]:https://github.com/integrations/sonarqube
-[13]:https://github.com/integrations/code-climate
-[14]:https://github.com/integrations/codecov
-[15]:https://github.com/integrations/coveralls
-[16]:https://help.github.com/articles/about-protected-branches/
-[17]:https://www.safaribooksonline.com/library/view/introducing-github/9781491949801/?utm_source=newsite&utm_medium=content&utm_campaign=lgen&utm_content=how-to-use-pull-requests-to-improve-your-code-reviews-lower
diff --git a/sources/tech/20160815 Here are all the Git commands I used last week and what they do.md b/sources/tech/20160815 Here are all the Git commands I used last week and what they do.md
deleted file mode 100644
index dd044d3c34..0000000000
--- a/sources/tech/20160815 Here are all the Git commands I used last week and what they do.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,214 +0,0 @@
-translating by firmianay
-
-Here are all the Git commands I used last week, and what they do.
-============================================================
-
-Image credit: [GitHub Octodex][6]
-
-Like most newbies, I started out searching StackOverflow for Git commands, then copy-pasting answers, without really understanding what they did.
-
-
-
-Image credit: [XKCD][7]
-
-I remember thinking,“Wouldn’t it be nice if there were a list of the most common Git commands along with an explanation as to why they are useful?”
-
-Well, here I am years later to compile such a list, and lay out some best practices that even intermediate-advanced developers should find useful.
-
-To keep things practical, I’m basing this list off of the actual Git commands I used over the past week.
-
-Almost every developer uses Git, and most likely GitHub. But the average developer probably only uses these three commands 99% of the time:
-
-```
-git add --all
-git commit -am "<message>"
-git push origin master
-```
-
-That’s all well and good when you’re working on a one-person team, a hackathon, or a throw-away app, but when stability and maintenance start to become a priority, cleaning up commits, sticking to a branching strategy, and writing coherent commit messages becomes important.
-
-I’ll start with the list of commonly used commands to make it easier for newbies to understand what is possible with Git, then move into the more advanced functionality and best practices.
-
-#### Regularly used commands
-
-To initialize Git in a repository (repo), you just need to type the following command. If you don’t initialize Git, you cannot run any other Git commands within that repo.
-
-```
-git init
-```
-
-If you’re using GitHub and you’re pushing code to a GitHub repo that’s stored online, you’re using a remote repo. The default name (also known as an alias) for that remote repo is origin. If you’ve copied a project from Github, it already has an origin. You can view that origin with the command git remote -v, which will list the URL of the remote repo.
-
-If you initialized your own Git repo and want to associate it with a GitHub repo, you’ll have to create one on GitHub, copy the URL provided, and use the command git remote add origin <URL>, with the URL provided by GitHub replacing “<URL>”. From there, you can add, commit, and push to your remote repo.
-
-The last one is used when you need to change the remote repository. Let’s say you copied a repo from someone else and want to change the remote repository from the original owner’s to your own GitHub account. Follow the same process as git remote add origin, except use set-url instead to change the remote repo.
-
-```
-git remote -v
-git remote add origin <url>
-git remote set-url origin <url>
-```
-
-The most common way to copy a repo is to use git clone, followed by the URL of the repo.
-
-Keep in mind that the remote repository will be linked to the account from which you cloned the repo. So if you cloned a repo that belongs to someone else, you will not be able to push to GitHub until you change the originusing the commands above.
-
-```
-git clone <url>
-```
-
-You’ll quickly find yourself using branches. If you don’t understand what branches are, there are other tutorials that are much more in-depth, and you should read those before proceeding ([here’s one][8]).
-
-The command git branch lists all branches on your local machine. If you want to create a new branch, you can use git branch <name>, with <name> representing the name of the branch, such as “master”.
-
-The git checkout <name> command switches to an existing branch. You can also use the git checkout -b <name> command to create a new branch and immediately switch to it. Most people use this instead of separate branch and checkout commands.
-
-```
-git branch
-git branch <name>
-git checkout <name>
-git checkout -b <name>
-```
-
-If you’ve made a bunch of changes to a branch, let’s call it “develop”, and you want to merge that branch back into your master branch, you use the git merge <branch> command. You’ll want to checkout the master branch, then run git merge develop to merge develop into the master branch.
-
-```
-git merge <branch>
-```
-
-If you’re working with multiple people, you’ll find yourself in a position where a repo was updated on GitHub, but you don’t have the changes locally. If that’s the case, you can use git pull origin <branch> to pull the most recent changes from that remote branch.
-
-```
-git pull origin <branch>
-```
-
-If you’re curious to see what files have been changed and what’s being tracked, you can use git status. If you want to see _how much_ each file has been changed, you can use git diff to see the number of lines changed in each file.
-
-```
-git status
-git diff --stat
-```
-
-### Advanced commands and best practices
-
-Soon you reach a point where you want your commits to look nice and stay consistent. You might also have to fiddle around with your commit history to make your commits easier to comprehend or to revert an accidental breaking change.
-
-The git log command lets you see the commit history. You’ll want to use this to see the history of your commits.
-
-Your commits will come with messages and a hash, which is random series of numbers and letters. An example hash might look like this: c3d882aa1aa4e3d5f18b3890132670fbeac912f7
-
-```
-git log
-```
-
-Let’s say you pushed something that broke your app. Rather than fix it and push something new, you’d rather just go back one commit and try again.
-
-If you want to go back in time and checkout your app from a previous commit, you can do this directly by using the hash as the branch name. This will detach your app from the current version (because you’re editing a historical record, rather than the current version).
-
-```
-git checkout c3d88eaa1aa4e4d5f
-```
-
-Then, if you make changes from that historical branch and you want to push again, you’d have to do a force push.
-
-Caution: Force pushing is dangerous and should only be done if you absolutely must. It will overwrite the history of your app and you will lose whatever came after.
-
-```
-git push -f origin master
-```
-
-Other times it’s just not practical to keep everything in one commit. Perhaps you want to save your progress before trying something potentially risky, or perhaps you made a mistake and want to spare yourself the embarrassment of having an error in your version history. For that, we have git rebase.
-
-Let’s say you have 4 commits in your local history (not pushed to GitHub) in which you’ve gone back and forth. Your commits look sloppy and indecisive. You can use rebase to combine all of those commits into a single, concise commit.
-
-```
-git rebase -i HEAD~4
-```
-
-The above command will open up your computer’s default editor (which is Vim unless you’ve set it to something else), with several options for how you can change your commits. It will look something like the code below:
-
-```
-pick 130deo9 oldest commit message
-pick 4209fei second oldest commit message
-pick 4390gne third oldest commit message
-pick bmo0dne newest commit message
-```
-
-In order to combine these, we need to change the “pick” option to “fixup” (as the documentation below the code says) to meld the commits and discard the commit messages. Note that in vim, you need to press “a” or “i” to be able to edit the text, and to save and exit, you need to type the escapekey followed by “shift + z + z”. Don’t ask me why, it just is.
-
-```
-pick 130deo9 oldest commit message
-fixup 4209fei second oldest commit message
-fixup 4390gne third oldest commit message
-fixup bmo0dne newest commit message
-```
-
-This will merge all of your commits into the commit with the message “oldest commit message”.
-
-The next step is to rename your commit message. This is entirely a matter of opinion, but so long as you follow a consistent pattern, anything you do is fine. I recommend using the [commit guidelines put out by Google for Angular.js][9].
-
-In order to change the commit message, use the amend flag.
-
-```
-git commit --amend
-```
-
-This will also open vim, and the text editing and saving rules are the same as above. To give an example of a good commit message, here’s one following the rules from the guideline:
-
-```
-feat: add stripe checkout button to payments page
-```
-
-```
-- add stripe checkout button
-- write tests for checkout
-```
-
-One advantage to keeping with the types listed in the guideline is that it makes writing change logs easier. You can also include information in the footer (again, specified in the guideline) that references issues.
-
-Note: you should avoid rebasing and squashing your commits if you are collaborating on a project, and have code pushed to GitHub. If you start changing version history under people’s noses, you could end up making everyone’s lives more difficult with bugs that are difficult to track.
-
-There are an almost endless number of possible commands with Git, but these commands are probably the only ones you’ll need to know for your first few years of programming.
-
-* * *
-
- _Sam Corcos is the lead developer and co-founder of _ [_Sightline Maps_][10] _, the most intuitive platform for 3D printing topographical maps, as well as _ [_LearnPhoenix.io_][11] _, an intermediate-advanced tutorial site for building scalable production apps with Phoenix and React. Get $20 off of LearnPhoenix with the coupon code: _ _free_code_camp_
-
-
-* [Git][1]
-
-* [Github][2]
-
-* [Programming][3]
-
-* [Software Development][4]
-
-* [Web Development][5]
-
-Show your support
-
-Clapping shows how much you appreciated Sam Corcos’s story.
-
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: https://medium.freecodecamp.org/git-cheat-sheet-and-best-practices-c6ce5321f52
-
-作者:[Sam Corcos][a]
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:https://medium.freecodecamp.org/@SamCorcos?source=post_header_lockup
-[1]:https://medium.freecodecamp.org/tagged/git?source=post
-[2]:https://medium.freecodecamp.org/tagged/github?source=post
-[3]:https://medium.freecodecamp.org/tagged/programming?source=post
-[4]:https://medium.freecodecamp.org/tagged/software-development?source=post
-[5]:https://medium.freecodecamp.org/tagged/web-development?source=post
-[6]:https://octodex.github.com/
-[7]:https://xkcd.com/1597/
-[8]:https://guides.github.com/introduction/flow/
-[9]:https://github.com/angular/angular.js/blob/master/CONTRIBUTING.md#-git-commit-guidelines
-[10]:http://sightlinemaps.com/
-[11]:http://learnphoenix.io/
diff --git a/sources/tech/20161031 An introduction to Linux filesystems.md b/sources/tech/20161031 An introduction to Linux filesystems.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..92aed3b557
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/tech/20161031 An introduction to Linux filesystems.md
@@ -0,0 +1,214 @@
+ucasFL translating
+
+An introduction to Linux filesystems
+============================================================
+
+
+Image credits : Original photo by Rikki Endsley. [CC BY-SA 4.0][9]
+
+This article is intended to be a very high-level discussion of Linux filesystem concepts. It is not intended to be a low-level description of how a particular filesystem type, such as EXT4, works, nor is it intended to be a tutorial of filesystem commands.
+
+More Linux resources
+
+* [What is Linux?][1]
+
+* [What are Linux containers?][2]
+
+* [Download Now: Linux commands cheat sheet][3]
+
+* [Advanced Linux commands cheat sheet][4]
+
+* [Our latest Linux articles][5]
+
+Every general-purpose computer needs to store data of various types on a hard disk drive (HDD) or some equivalent, such as a USB memory stick. There are a couple reasons for this. First, RAM loses its contents when the computer is switched off. There are non-volatile types of RAM that can maintain the data stored there after power is removed (such as flash RAM that is used in USB memory sticks and solid state drives), but flash RAM is much more expensive than standard, volatile RAM like DDR3 and other, similar types.
+
+The second reason that data needs to be stored on hard drives is that even standard RAM is still more expensive than disk space. Both RAM and disk costs have been dropping rapidly, but RAM still leads the way in terms of cost per byte. A quick calculation of the cost per byte, based on costs for 16GB of RAM vs. a 2TB hard drive, shows that the RAM is about 71 times more expensive per unit than the hard drive. A typical cost for RAM is around $0.0000000043743750 per byte today.
+
+For a quick historical note to put present RAM costs in perspective, in the very early days of computing, one type of memory was based on dots on a CRT screen. This was very expensive at about $1.00 _per bit_ !
+
+### Definitions
+
+You may hear people talk about filesystems in a number of different and confusing ways. The word itself can have multiple meanings, and you may have to discern the correct meaning from the context of a discussion or document.
+
+I will attempt to define the various meanings of the word "filesystem" based on how I have observed it being used in different circumstances. Note that while attempting to conform to standard "official" meanings, my intent is to define the term based on its various usages. These meanings will be explored in greater detail in the following sections of this article.
+
+1. The entire Linux directory structure starting at the top (/) root directory.
+
+2. A specific type of data storage format, such as EXT3, EXT4, BTRFS, XFS, and so on. Linux supports almost 100 types of filesystems, including some very old ones as well as some of the newest. Each of these filesystem types uses its own metadata structures to define how the data is stored and accessed.
+
+3. A partition or logical volume formatted with a specific type of filesystem that can be mounted on a specified mount point on a Linux filesystem.
+
+### Basic filesystem functions
+
+Disk storage is a necessity that brings with it some interesting and inescapable details. Obviously, a filesystem is designed to provide space for non-volatile storage of data; that is its ultimate function. However, there are many other important functions that flow from that requirement.
+
+All filesystems need to provide a namespace—that is, a naming and organizational methodology. This defines how a file can be named, specifically the length of a filename and the subset of characters that can be used for filenames out of the total set of characters available. It also defines the logical structure of the data on a disk, such as the use of directories for organizing files instead of just lumping them all together in a single, huge conglomeration of files.
+
+Once the namespace has been defined, a metadata structure is necessary to provide the logical foundation for that namespace. This includes the data structures required to support a hierarchical directory structure; structures to determine which blocks of space on the disk are used and which are available; structures that allow for maintaining the names of the files and directories; information about the files such as their size and times they were created, modified or last accessed; and the location or locations of the data belonging to the file on the disk. Other metadata is used to store high-level information about the subdivisions of the disk, such as logical volumes and partitions. This higher-level metadata and the structures it represents contain the information describing the filesystem stored on the drive or partition, but is separate from and independent of the filesystem metadata.
+
+Filesystems also require an Application Programming Interface (API) that provides access to system function calls which manipulate filesystem objects like files and directories. APIs provide for tasks such as creating, moving, and deleting files. It also provides algorithms that determine things like where a file is placed on a filesystem. Such algorithms may account for objectives such as speed or minimizing disk fragmentation.
+
+Modern filesystems also provide a security model, which is a scheme for defining access rights to files and directories. The Linux filesystem security model helps to ensure that users only have access to their own files and not those of others or the operating system itself.
+
+The final building block is the software required to implement all of these functions. Linux uses a two-part software implementation as a way to improve both system and programmer efficiency.
+
+<center>
+
+
+Figure 1: The Linux two-part filesystem software implementation.</center>
+
+The first part of this two-part implementation is the Linux virtual filesystem. This virtual filesystem provides a single set of commands for the kernel, and developers, to access all types of filesystems. The virtual filesystem software calls the specific device driver required to interface to the various types of filesystems. The filesystem-specific device drivers are the second part of the implementation. The device driver interprets the standard set of filesystem commands to ones specific to the type of filesystem on the partition or logical volume.
+
+### Directory structure
+
+As a usually very organized Virgo, I like things stored in smaller, organized groups rather than in one big bucket. The use of directories helps me to be able to store and then locate the files I want when I am looking for them. Directories are also known as folders because they can be thought of as folders in which files are kept in a sort of physical desktop analogy.
+
+In Linux and many other operating systems, directories can be structured in a tree-like hierarchy. The Linux directory structure is well defined and documented in the [Linux Filesystem Hierarchy Standard][10] (FHS). Referencing those directories when accessing them is accomplished by using the sequentially deeper directory names connected by forward slashes (/) such as /var/log and /var/spool/mail. These are called paths.
+
+The following table provides a very brief list of the standard, well-known, and defined top-level Linux directories and their purposes.
+
+| Directory | Description |
+| --- | --- |
+| / (root filesystem) | The root filesystem is the top-level directory of the filesystem. It must contain all of the files required to boot the Linux system before other filesystems are mounted. It must include all of the required executables and libraries required to boot the remaining filesystems. After the system is booted, all other filesystems are mounted on standard, well-defined mount points as subdirectories of the root filesystem. |
+| /bin | The /bin directory contains user executable files. |
+| /boot | Contains the static bootloader and kernel executable and configuration files required to boot a Linux computer. |
+| /dev | This directory contains the device files for every hardware device attached to the system. These are not device drivers, rather they are files that represent each device on the computer and facilitate access to those devices. |
+| /etc | Contains the local system configuration files for the host computer. |
+| /home | Home directory storage for user files. Each user has a subdirectory in /home. |
+| /lib | Contains shared library files that are required to boot the system. |
+| /media | A place to mount external removable media devices such as USB thumb drives that may be connected to the host. |
+| /mnt | A temporary mountpoint for regular filesystems (as in not removable media) that can be used while the administrator is repairing or working on a filesystem. |
+| /opt | Optional files such as vendor supplied application programs should be located here. |
+| /root | This is not the root (/) filesystem. It is the home directory for the root user. |
+| /sbin | System binary files. These are executables used for system administration. |
+| /tmp | Temporary directory. Used by the operating system and many programs to store temporary files. Users may also store files here temporarily. Note that files stored here may be deleted at any time without prior notice. |
+| /usr | These are shareable, read-only files, including executable binaries and libraries, man files, and other types of documentation. |
+| /var | Variable data files are stored here. This can include things like log files, MySQL, and other database files, web server data files, email inboxes, and much more. |
+
+<center>Table 1: The top level of the Linux filesystem hierarchy.</center>
+
+The directories and their subdirectories shown in Table 1, along with their subdirectories, that have a teal background are considered an integral part of the root filesystem. That is, they cannot be created as a separate filesystem and mounted at startup time. This is because they (specifically, their contents) must be present at boot time in order for the system to boot properly.
+
+The /media and /mnt directories are part of the root filesystem, but they should never contain any data. Rather, they are simply temporary mount points.
+
+The remaining directories, those that have no background color in Table 1 do not need to be present during the boot sequence, but will be mounted later, during the startup sequence that prepares the host to perform useful work.
+
+Be sure to refer to the official [Linux Filesystem Hierarchy Standard][11] (FHS) web page for details about each of these directories and their many subdirectories. Wikipedia also has a good description of the [FHS][12]. This standard should be followed as closely as possible to ensure operational and functional consistency. Regardless of the filesystem types used on a host, this hierarchical directory structure is the same.
+
+### Linux unified directory structure
+
+In some non-Linux PC operating systems, if there are multiple physical hard drives or multiple partitions, each disk or partition is assigned a drive letter. It is necessary to know on which hard drive a file or program is located, such as C: or D:. Then you issue the drive letter as a command, **D:**, for example, to change to the D: drive, and then you use the **cd** command to change to the correct directory to locate the desired file. Each hard drive has its own separate and complete directory tree.
+
+The Linux filesystem unifies all physical hard drives and partitions into a single directory structure. It all starts at the top–the root (/) directory. All other directories and their subdirectories are located under the single Linux root directory. This means that there is only one single directory tree in which to search for files and programs.
+
+This can work only because a filesystem, such as /home, /tmp, /var, /opt, or /usr can be created on separate physical hard drives, a different partition, or a different logical volume from the / (root) filesystem and then be mounted on a mountpoint (directory) as part of the root filesystem tree. Even removable drives such as a USB thumb drive or an external USB or ESATA hard drive will be mounted onto the root filesystem and become an integral part of that directory tree.
+
+One good reason to do this is apparent during an upgrade from one version of a Linux distribution to another, or changing from one distribution to another. In general, and aside from any upgrade utilities like dnf-upgrade in Fedora, it is wise to occasionally reformat the hard drive(s) containing the operating system during an upgrade to positively remove any cruft that has accumulated over time. If /home is part of the root filesystem it will be reformatted as well and would then have to be restored from a backup. By having /home as a separate filesystem, it will be known to the installation program as a separate filesystem and formatting of it can be skipped. This can also apply to /var where database, email inboxes, website, and other variable user and system data are stored.
+
+There are other reasons for maintaining certain parts of the Linux directory tree as separate filesystems. For example, a long time ago, when I was not yet aware of the potential issues surrounding having all of the required Linux directories as part of the / (root) filesystem, I managed to fill up my home directory with a large number of very big files. Since neither the /home directory nor the /tmp directory were separate filesystems but simply subdirectories of the root filesystem, the entire root filesystem filled up. There was no room left for the operating system to create temporary files or to expand existing data files. At first, the application programs started complaining that there was no room to save files, and then the OS itself started to act very strangely. Booting to single-user mode and clearing out the offending files in my home directory allowed me to get going again. I then reinstalled Linux using a pretty standard multi-filesystem setup and was able to prevent complete system crashes from occurring again.
+
+I once had a situation where a Linux host continued to run, but prevented the user from logging in using the GUI desktop. I was able to log in using the command line interface (CLI) locally using one of the [virtual consoles][13], and remotely using SSH. The problem was that the /tmp filesystem had filled up and some temporary files required by the GUI desktop could not be created at login time. Because the CLI login did not require files to be created in /tmp, the lack of space there did not prevent me from logging in using the CLI. In this case, the /tmp directory was a separate filesystem and there was plenty of space available in the volume group the /tmp logical volume was a part of. I simply [expanded the /tmp logical volume][14] to a size that accommodated my fresh understanding of the amount of temporary file space needed on that host and the problem was solved. Note that this solution did not require a reboot, and as soon as the /tmp filesystem was enlarged the user was able to login to the desktop.
+
+Another situation occurred while I was working as a lab administrator at one large technology company. One of our developers had installed an application in the wrong location (/var). The application was crashing because the /var filesystem was full and the log files, which are stored in /var/log on that filesystem, could not be appended with new messages due to the lack of space. However, the system remained up and running because the critical / (root) and /tmp filesystems did not fill up. Removing the offending application and reinstalling it in the /opt filesystem resolved that problem.
+
+### Filesystem types
+
+Linux supports reading around 100 partition types; it can create and write to only a few of these. But it is possible—and very common—to mount filesystems of different types on the same root filesystem. In this context we are talking about filesystems in terms of the structures and metadata required to store and manage the user data on a partition of a hard drive or a logical volume. The complete list of filesystem partition types recognized by the Linux **fdisk**command is provided here, so that you can get a feel for the high degree of compatibility that Linux has with very many types of systems.
+
+```
+0 Empty 24 NEC DOS 81 Minix / old Lin bf Solaris 1 FAT12 27 Hidden NTFS Win 82 Linux swap / So c1 DRDOS/sec (FAT- 2 XENIX root 39 Plan 9 83 Linux c4 DRDOS/sec (FAT- 3 XENIX usr 3c PartitionMagic 84 OS/2 hidden or c6 DRDOS/sec (FAT- 4 FAT16 <32M 40 Venix 80286 85 Linux extended c7 Syrinx 5 Extended 41 PPC PReP Boot 86 NTFS volume set da Non-FS data 6 FAT16 42 SFS 87 NTFS volume set db CP/M / CTOS / . 7 HPFS/NTFS/exFAT 4d QNX4.x 88 Linux plaintext de Dell Utility 8 AIX 4e QNX4.x 2nd part 8e Linux LVM df BootIt 9 AIX bootable 4f QNX4.x 3rd part 93 Amoeba e1 DOS access a OS/2 Boot Manag 50 OnTrack DM 94 Amoeba BBT e3 DOS R/O b W95 FAT32 51 OnTrack DM6 Aux 9f BSD/OS e4 SpeedStor c W95 FAT32 (LBA) 52 CP/M a0 IBM Thinkpad hi ea Rufus alignment e W95 FAT16 (LBA) 53 OnTrack DM6 Aux a5 FreeBSD eb BeOS fs f W95 Ext'd (LBA) 54 OnTrackDM6 a6 OpenBSD ee GPT 10 OPUS 55 EZ-Drive a7 NeXTSTEP ef EFI (FAT-12/16/ 11 Hidden FAT12 56 Golden Bow a8 Darwin UFS f0 Linux/PA-RISC b 12 Compaq diagnost 5c Priam Edisk a9 NetBSD f1 SpeedStor 14 Hidden FAT16 <3 61 SpeedStor ab Darwin boot f4 SpeedStor 16 Hidden FAT16 63 GNU HURD or Sys af HFS / HFS+ f2 DOS secondary 17 Hidden HPFS/NTF 64 Novell Netware b7 BSDI fs fb VMware VMFS 18 AST SmartSleep 65 Novell Netware b8 BSDI swap fc VMware VMKCORE 1b Hidden W95 FAT3 70 DiskSecure Mult bb Boot Wizard hid fd Linux raid auto 1c Hidden W95 FAT3 75 PC/IX bc Acronis FAT32 L fe LANstep 1e Hidden W95 FAT1 80 Old Minix be Solaris boot ff BBT
+```
+
+The main purpose in supporting the ability to read so many partition types is to allow for compatibility and at least some interoperability with other computer systems' filesystems. The choices available when creating a new filesystem with Fedora are shown in the following list.
+
+* btrfs
+
+* **cramfs**
+
+* **ext2**
+
+* **ext3**
+
+* **ext4**
+
+* fat
+
+* gfs2
+
+* hfsplus
+
+* minix
+
+* **msdos**
+
+* ntfs
+
+* reiserfs
+
+* **vfat**
+
+* xfs
+
+Other distributions support creating different filesystem types. For example, CentOS 6 supports creating only those filesystems highlighted in bold in the above list.
+
+### Mounting
+
+The term "to mount" a filesystem in Linux refers back to the early days of computing when a tape or removable disk pack would need to be physically mounted on an appropriate drive device. After being physically placed on the drive, the filesystem on the disk pack would be logically mounted by the operating system to make the contents available for access by the OS, application programs and users.
+
+A mount point is simply a directory, like any other, that is created as part of the root filesystem. So, for example, the home filesystem is mounted on the directory /home. Filesystems can be mounted at mount points on other non-root filesystems but this is less common.
+
+The Linux root filesystem is mounted on the root directory (/) very early in the boot sequence. Other filesystems are mounted later, by the Linux startup programs, either **rc** under SystemV or by **systemd** in newer Linux releases. Mounting of filesystems during the startup process is managed by the /etc/fstab configuration file. An easy way to remember that is that fstab stands for "file system table," and it is a list of filesystems that are to be mounted, their designated mount points, and any options that might be needed for specific filesystems.
+
+Filesystems are mounted on an existing directory/mount point using the **mount**command. In general, any directory that is used as a mount point should be empty and not have any other files contained in it. Linux will not prevent users from mounting one filesystem over one that is already there or on a directory that contains files. If you mount a filesystem on an existing directory or filesystem, the original contents will be hidden and only the content of the newly mounted filesystem will be visible.
+
+### Conclusion
+
+I hope that some of the possible confusion surrounding the term filesystem has been cleared up by this article. It took a long time and a very helpful mentor for me to truly understand and appreciate the complexity, elegance, and functionality of the Linux filesystem in all of its meanings.
+
+If you have questions, please add them to the comments below and I will try to answer them.
+
+### Next month
+
+Another important concept is that for Linux, everything is a file. This concept has some interesting and important practical applications for users and system admins. The reason I mention this is that you might want to read my "[Everything is a file][15]" article before the article I am planning for next month on the /dev directory.
+
+-----------------
+
+作者简介:
+
+David Both - David Both is a Linux and Open Source advocate who resides in Raleigh, North Carolina. He has been in the IT industry for over forty years and taught OS/2 for IBM where he worked for over 20 years. While at IBM, he wrote the first training course for the original IBM PC in 1981\. He has taught RHCE classes for Red Hat and has worked at MCI Worldcom, Cisco, and the State of North Carolina. He has been working with Linux and Open Source Software for almost 20 years. David has written articles for[More about me][7]
+
+* [Learn how you can contribute][22]
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://opensource.com/life/16/10/introduction-linux-filesystems
+
+作者:[David Both][a]
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:https://opensource.com/users/dboth
+[1]:https://opensource.com/resources/what-is-linux?intcmp=70160000000h1jYAAQ&utm_source=intcallout&utm_campaign=linuxcontent
+[2]:https://opensource.com/resources/what-are-linux-containers?intcmp=70160000000h1jYAAQ&utm_source=intcallout&utm_campaign=linuxcontent
+[3]:https://developers.redhat.com/promotions/linux-cheatsheet/?intcmp=70160000000h1jYAAQ&utm_source=intcallout&utm_campaign=linuxcontent
+[4]:https://developers.redhat.com/cheat-sheet/advanced-linux-commands-cheatsheet?intcmp=70160000000h1jYAAQ&utm_source=intcallout&utm_campaign=linuxcontent
+[5]:https://opensource.com/tags/linux?intcmp=70160000000h1jYAAQ&utm_source=intcallout&utm_campaign=linuxcontent
+[6]:https://opensource.com/life/16/10/introduction-linux-filesystems?rate=Qyf2jgkdgrj5_zfDwadBT8KsHZ2Gp5Be2_tF7R-s02Y
+[7]:https://opensource.com/users/dboth
+[8]:https://opensource.com/user/14106/feed
+[9]:https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/
+[10]:http://www.pathname.com/fhs/
+[11]:http://www.pathname.com/fhs/
+[12]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Filesystem_Hierarchy_Standard
+[13]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Virtual_console
+[14]:https://opensource.com/business/16/9/linux-users-guide-lvm
+[15]:https://opensource.com/life/15/9/everything-is-a-file
+[16]:https://opensource.com/users/dboth
+[17]:https://opensource.com/users/dboth
+[18]:https://opensource.com/users/dboth
+[19]:https://opensource.com/life/16/10/introduction-linux-filesystems#comments
+[20]:https://opensource.com/tags/linux
+[21]:https://opensource.com/tags/sysadmin
+[22]:https://opensource.com/participate
diff --git a/sources/tech/20161108 How to create an internal innersource community.md b/sources/tech/20161108 How to create an internal innersource community.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..15a3d70ec4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/tech/20161108 How to create an internal innersource community.md
@@ -0,0 +1,110 @@
+How to create an internal innersource community
+============================================================
+
+
+
+Image by : opensource.com
+
+In recent years, we have seen more and more interest in a variance of open source known as _innersource_ . Put simply, innersource is taking the principles of open source and bringing them inside the walls of an organization. As such, you build collaboration and community that may look and taste like open source, but in which all code and community is private within the walls of the organization.
+
+As a [community strategy and leadership consultant][5], I work with many companies to help build their innersource communities. As such, I thought it could be fun to share some of the most important principles that map to most of my clients and beyond. This could be a helpful primer if you are considering exploring innersource inside your organization.
+
+### Culture then code
+
+For most companies, their innersource journey starts out life as a pilot project. Typically the project will focus on a few specific teams who may be more receptive to the experiment. As such, innersource is almost always a new workflow and methodology being brought into an existing culture. Making this cultural adjustment is key to being successful and the biggest challenge.
+
+There is an understandable misconception that the key to doing innersource well is to focus on building the open source software development lifecycle in your company. That is, open code repositories and communication channels, encouraging forking, code review, and continuous integration/deployment. This is definitely an essential part of the innersource approach, but think of these pieces as lego bricks. The real trick is building an environment where people have the permission and incentive to build incredible things with those bricks.
+
+As such, doing innersource well is more about building a culture, environment, and set of incentives that encourage and reward the behavior we often associate with open source. Building that culture from scratch is much easier, but adapting to this culture, particularly for traditional organizations is where most of the work lies.
+
+Cultural change can't be dictated, it is the amalgamation of individual actions that build social conventions that the wider group are influenced by. To do this well you need to look at the problem from the vantage-point of your staff. How can you make their work easier, more efficient, more rewarding, and more collaborative?
+
+When you understand the existing cultural pain points and your staff associate the new innersource culture as a way to relieve those issues, the adaptation goes much more smoothly.
+
+### Methodology
+
+Given that innersource is largely a cultural adjustment that incorporates some proven open source workflow methodologies, it begs an interesting question: How do you manage the rollout of an innersource program?
+
+I have seen good and bad ways in which organizations do this. Some take a top-down approach and announce to their staff that things are going to be different and teams and staff need to fall in line given a specific innersource schedule. Other companies take a more bottom-up approach where a dedicated innersource team informally tries to get people on board with the innersource program.
+
+I wouldn't recommend either approach explicitly, but instead a combination. For any cultural change you are going to need a top-down approach in emphasizing and encouraging a new way of working from your executive team and company leaders. Rather than dictating rules, these leaders should instead be supporting an environment where your staff can help shape the workings and implementation of your innersource program in a more bottom-up way.
+
+Let's be honest, everyone hates these kind of cultural adjustments. We have all lived through company executives bringing in new ways of working—agile, kanban, pair-programming, or whatever else. Often these new ways of working are pushed onto staff and it sets the dynamic off on the wrong foot: Instead of encouraging your staff to shape the culture you are instead mandating it to them.
+
+The approach I recommend here is to put in place a regular cadence that iterates your innersource strategy.
+
+For example, every six months a new cycle begins. Prior to the end of the previous cycle the leadership team will survey staff to get their perspectives on how the innersource program is working, review their feedback, and set out core goals for the new cycle. Staff will then have structured ways in which they can play a role in helping to shape how these goals can be accomplished. For example, this could be individual teams/groups that focus on communication, peer review, QA, community growth and engagement, and more. Throughout the entire process a core innersource team will facilitate these conversations, mentor and guide the leadership team, support individual staff in making worthwhile contributions, and keep the train moving forward.
+
+This is how it works in open source. If you hack on a project you don't just get to submit code, but you can also play a role in the operational dynamics of the project too. It is important you bring this sense of influence into your innersource program and your staff—the most rewarding companies are the ones where the staff feel they can influence the culture in a positive way.
+
+### Asynchronous and remote working
+
+One of the most interesting challenges with innersource is that it depends on asynchronous collaboration extensively. That is, you can collaborate digitally without requiring participants to be in the same timezone or location.
+
+As an example, some companies require all staff members to work from the same office and much of the business that gets done takes place in in-person meetings in conference rooms, on conference calls, and via email. This can make it difficult for the company to grow and hire remote workers or for staff to be productive when they are on the road at conferences or at home.
+
+A core component of what makes open source work well is that participants can work asynchronously. All communication, development (code submission, issue management, and code review), QA, and release management can often be performed entirely online and from any timezone. The asynchronous with semi-regular in-person sprints/meetings combo is a hugely productive and efficient methodology.
+
+This can be a difficult transition for companies. For example, some of my clients will have traditionally had in-person meetings to plan projects, perform code review over a board-room table, and don't have the infrastructure and communication channels to operate asynchronously. To do innersource well, it is important to put in place a plan to work as asynchronously as possible, while blending the benefits of in-person communication at the office, while also supporting digital collaboration.
+
+The side benefit of doing this is that you build an environment that can support remote working. As anyone who works in technology will likely agree, hiring good people is _hard_ , and a blocker can often be a relocation to your city. Thus, your investment in innersource will also make it easier to not just hire people remotely (anyone can do that), but importantly to have an environment where remote workers can be successful.
+
+### Peer review and workflow
+
+For companies making the adjustment to innersource, one of the most interesting "sticking points" is the peer review process.
+
+For those of you familiar with open source, there are two important principles that take place in everyday collaboration. Firstly, all contributions are reviewed by other developers (both new features and bug fixes), and secondly, this peer review takes place out in the open for other people to see. This open peer review element can be a tough pill to swallow for people new to open source. If your engineers have either not conducted code review or it took place privately, it can be socially awkward and unsettling to move over to a more open review process.
+
+This adjustment is something that needs to be carefully managed. A large part of this is building a culture in which critique is something that should be favored not avoided, that we celebrate failure, and we cherish our peers helping us to be better at what we do. Again, this is about framing these adjustments to the benefit of your staff so that while it may be awkward at first, they will feel the ultimate benefits soon after.
+
+As you can probably see, a core chunk of building communities (whether public communities or innersource communities in companies) is understanding the psychology of your community members and converting those psychological patterns into workflow that helps you encourage the behavior you want to see.
+
+As an example, there are two behavioral economics principles that play a key role with peer review and workflow. The first is the _Ikea Effect_ . This is where if you and I were to put together the exact same Ikea table (or build something else), we will each think our respective table is somehow better or more valuable. Thus, we put more value into the things we make, often overstated value. Secondly, there is the principle of _autonomy_ , which is essentially that _choice_ is critically important to people. If we don't feel we have control of our destiny, that we can make choices, we feel boxed in and restricted.
+
+Just these two principles have an important impact on workflow and peer review. In terms of the Ikea effect we should expect that most people's pull requests and fixes will likely be seen as very valuable to them. As such, we need to use the peer review process to objectively define the value of the contribution in an independent and unemotional way (e.g. reviewing specific pieces of the diff, requiring at least two reviewers, encouraging specific implementation feedback, etc). With the autonomy principle, we should ensure staff can refine, customize, and hack on their toolchain and workflow as much as possible, and regularly give them an opportunity to provide feedback and input on making it better.
+
+### Reputation, incentives, and engagement
+
+Another key element of building an innersource culture in a company is to carefully carve out how you will track great work and incentivize and encourage that kind of behavior.
+
+This piece has three core components.
+
+Firstly, we need to have a way of getting a quantitative representation of the quality of that person's work. This can be as involved as building a complex system for tracking individual actions and weighting their value, or as simple as observationally watching how people work. What is important here is that people should be judged on their merit, and not factors such as how much they schmooze with the bosses, or how many donuts they bring to the office.
+
+Secondly, based on this representation of their work we need to provide different incentives and rewards to encourage the behavior we want to see.
+
+There are two core types of rewards. _Extrinsic_ rewards are material in nature, such as T-shirts, hoodies, gift cards, money, and more. _Intrinsic_ rewards are of the more touchy-feely kind such as respect, recognition, and admiration. Both are important and it is important to get the right balance of these rewards. Based on the behavior you want to encourage, I recommend putting together incentives that inspire action and rewards that validate those actions.
+
+Finally, it can be helpful to sub-divide your staff into different groups based on their work and engage them in different ways. For example, people who are new will benefit from mentoring, support, and wider guidance. On the other hand, the most active and accomplished staff members can be used as a tremendous source of insight, guidance, and them enjoying playing a role in helping to shape the company culture further.
+
+So, there are a few starting points for broader brushstrokes that typically need to be made when painting an innersource picture inside your organization. As usual, let me know your thoughts in the comments and feel free to reach out to me with questions!
+
+-----------------
+
+作者简介
+
+Jono Bacon - Jono Bacon is a leading community manager, speaker, author, and podcaster. He is the founder of [Jono Bacon Consulting][2] which provides community strategy/execution, developer workflow, and other services. He also previously served as director of community at GitHub, Canonical, XPRIZE, OpenAdvantage, and consulted and advised a range of organizations.[More about me][3]
+
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://opensource.com/life/16/11/create-internal-innersource-community
+
+作者:[Jono Bacon ][a]
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:https://opensource.com/users/jonobacon
+[1]:https://opensource.com/life/16/11/create-internal-innersource-community?rate=QnpszlpgMXpNG5m2OLbZPYAg_RV_DA1i48tI00CPyTc
+[2]:http://www.jonobacon.com/consulting
+[3]:https://opensource.com/users/jonobacon
+[4]:https://opensource.com/user/26312/feed
+[5]:http://www.jonobacon.org/consulting
+[6]:https://opensource.com/users/jonobacon
+[7]:https://opensource.com/users/jonobacon
+[8]:https://opensource.com/users/jonobacon
+[9]:https://opensource.com/tags/community-management
+[10]:https://opensource.com/tags/six-degrees-column
+[11]:https://opensource.com/participate
diff --git a/sources/tech/20170403 Introduction to functional programming.md b/sources/tech/20170403 Introduction to functional programming.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 73fb97fe79..0000000000
--- a/sources/tech/20170403 Introduction to functional programming.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,254 +0,0 @@
-MonkeyDEcho translating
-
-Introduction to functional programming
-============================================================
-
-> We explain what functional programming is, explore its benefits, and look at resources for learning functional programming.
-
-
- 
-Image by :
-
-opensource.com
-
-Depending on whom you ask, _functional programming_ (FP) is either an enlightened approach to programming that should be spread far and wide, or an overly academic approach to programming with few real-world benefits. In this article, I will explain what functional programming is, explore its benefits, and recommend resources for learning functional programming.
-
-### Syntax primer
-
-Code examples in this article are in the [Haskell][40] programming language. All that you need to understand for this article is the basic function syntax:
-
-```
- even :: Int -> Bool
- even = ... -- implementation goes here
-```
-
-This defines a one-argument function named **even**. The first line is the _type declaration_ , which says that **even** takes an **Int** and returns a **Bool**. The implementation follows and consists of one or more _equations_ . We'll ignore the implementation (the name and type tell us enough):
-
-```
- map :: (a -> b) -> [a] -> [b]
- map = ...
-```
-
-In this example, **map** is a function that takes two arguments:
-
-1. **(a -> b)**: a functions that turns an **a** into a **b**
-2. **[a]**: a list of **a**
-
-and returns a list of **b**. Again, we don't care about the definition—the type is more interesting! **a** and **b** are _type variables_ that could stand for any type. In the expression below, **a** is **Int** and **b** is **Bool**:
-
-```
- map even [1,2,3]
-```
-
-It evaluates to a **[Bool]**:
-
-```
- [False,True,False]
-```
-
-If you see other syntax that you do not understand, don't panic; full comprehension of the syntax is not essential.
-
-### Myths about functional programming
-
-Programming and development
-
-* [Our latest JavaScript articles][1]
-* [Recent Perl posts][2]
-* [New Python content][3]
-* [Red Hat Developers Blog][4]
-* [Tools for Red Hat Developers][5]
-
-Let's begin by dispelling common misconceptions:
-
-* Functional programming is not the rival or antithesis of imperative or object-oriented programming. This is a false dichotomy.
-* Functional programming is not just the domain of academics. It is true that the history of functional programming is steeped in academia, and languages such as like Haskell and OCaml are popular research languages. But today many companies use functional programming for large-scale systems, small specialized programs, and everything in between. There's even an annual conference for [Commercial Users of Functional Programming][33]; past programs give an insight into how functional programming is being used in industry, and by whom.
-* Functional programming has nothing to do with [monads][34], nor any other particular abstraction. For all the hand-wringing around this topic, monad is just an abstraction with laws. Some things are monads, others are not.
-* Functional programming is not especially hard to learn. Some languages may have different syntax or evaluation semantics from those you already know, but these differences are superficial. There are dense concepts in functional programming, but this is also true of other approaches.
-
-### What is functional programming?
-
-At its core, functional programming is just programming with functions— _pure_ mathematical functions. The result of a function depends only on the arguments, and there are no side effects, such as I/O or mutation of state. Programs are built by combining functions together. One way of combining functions is _function composition_ :
-
-```
- (.) :: (b -> c) -> (a -> b) -> (a -> c)
- (g . f) x = g (f x)
-```
-
-This _infix_ function combines two functions into one, applying **g** to the output of **f**. We'll see it used in an upcoming example. For comparison, the same function in Python looks like:
-
-```
- def compose(g, f):
- return lambda x: g(f(x))
-```
-
-The beauty of functional programming is that because functions are deterministic and have no side effects, you can always replace a function application with the result of the application. This substitution of equals for equals enables _equational reasoning_ . Every programmer has to reason about their code and others', and equational reasoning is a great tool for doing that. Let's look at an example. You encounter the expression:
-
-```
- map even . map (+1)
-```
-
-What does this program do? Can it be simplified? Equational reasoning lets you analyze the code through a series of substitutions:
-
-```
- map even . map (+1)
- map (even . (+1)) -- from definition of 'map'
- map (\x -> even (x + 1)) -- lambda abstraction
- map odd -- from definition of 'even'
-```
-
-We can use equational reasoning to understand programs and optimize for readability. The Haskell compiler uses equational reasoning to perform many kinds of program optimizations. Without pure functions, equational reasoning either isn't possible, or requires an inordinate effort from the programmer.
-
-### Functional programming languages
-
-What do you need from a programming language to be able to do functional programming?
-
-Doing functional programming meaningfully in a language without _higher-order functions_ (the ability to pass functions as arguments and return functions), _lambdas_ (anonymous functions), and _generics_ is difficult. Most modern languages have these, but there are differences in _how well_ different languages support functional programming. The languages with the best support are called _functional programming languages_ . These include _Haskell_ , _OCaml_ , _F#_ , and _Scala_ , which are statically typed, and the dynamically typed _Erlang_ and _Clojure_ .
-
-Even among functional languages there are big differences in how far you can exploit functional programming. Having a type system helps a lot, especially if it supports _type inference_ (so you don't always have to type the types). There isn't room in this article to go into detail, but suffice it to say, not all type systems are created equal.
-
-As with all languages, different functional languages emphasize different concepts, techniques, or use cases. When choosing a language, considering how well it supports functional programming and whether it fits your use case is important. If you're stuck using some non-FP language, you will still benefit from applying functional programming to the extent the language supports it.
-
-### Don't open that trap door!
-
-Recall that the result of a function depends only on its inputs. Alas, almost all programming languages have "features" that break this assumption. Null values, type case (**instanceof**), type casting, exceptions, side-effects, and the possibility of infinite recursion are trap doors that break equational reasoning and impair a programmer's ability to reason about the behavior or correctness of a program. ( _Total languages_ , which do not have any trap doors, include Agda, Idris, and Coq.)
-
-Fortunately, as programmers, we can choose to avoid these traps, and if we are disciplined, we can pretend that the trap doors do not exist. This idea is called _fast and loose reasoning_ . It costs nothing—almost any program can be written without using the trap doors—and by avoiding them you win back equational reasoning, composability and reuse.
-
-Let's discuss exceptions in detail. This trap door breaks equational reasoning because the possibility of abnormal termination is not reflected in the type. (Count yourself lucky if the documentation even mentions the exceptions that could be thrown.) But there is no reason why we can't have a return type that encompasses all the failure modes.
-
-Avoiding trap doors is an area in which language features can make a big difference. For avoiding exceptions, _algebraic data types_ can be used to model error conditions, like so:
-
-```
- -- new data type for results of computations that can fail
- --
- data Result e a = Error e | Success a
-
- -- new data type for three kinds of arithmetic errors
- --
- data ArithError = DivByZero | Overflow | Underflow
-
- -- integer division, accounting for divide-by-zero
- --
- safeDiv :: Int -> Int -> Result ArithError Int
- safeDiv x y =
- if y == 0
- then Error DivByZero
- else Success (div x y)
-```
-
-The trade-off in this example is that you must now work with values of type **Result ArithError Int** instead of plain old **Int**, but there are abstractions for dealing with this. You no longer need to handle exceptions and can use fast and loose reasoning, so overall it's a win.
-
-### Theorems for free
-
-Most modern statically typed languages have _generics_ (also called _parametric polymorphism_ ), where functions are defined over one or more abstract types. For example, consider a function over lists:
-
-```
- f :: [a] -> [a]
- f = ...
-```
-
-The same function in Java looks like:
-
-```
- static <A> List<A> f(List<A> xs) { ... }
-```
-
-The compiled program is a proof that this function will work with _any_ choice for the type **a**. With that in mind, and employing fast and loose reasoning, can you work out what the function does? Does knowing the type help?
-
-In this case, the type doesn't tell us exactly what the function does (it could reverse the list, drop the first element, or many other things), but it does tell us a lot. Just from the type, we can derive theorems about the function:
-
-* **Theorem 1**: Every element in the output appears in the input; it couldn't possibly add an **a** to the list because it has no knowledge of what **a** is or how to construct one.
-* **Theorem 2**: If you map any function over the list then apply **f**, the result is the same as applying **f** then mapping.
-
-Theorem 1 helps us understand what the code is doing, and Theorem 2 is useful for program optimization. We learned all this just from the type! This result—the ability to derive useful theorems from types—is called _parametricity_ . It follows that a type is a partial (sometimes complete) specification of a function's behavior, and a kind of machine-checked documentation.
-
-Now it's your turn to exploit parametricity. What can you conclude from the types of **map** and **(.)**, or the following functions?
-
-* **foo :: a -> (a, a)**
-* **bar :: a -> a -> a**
-* **baz :: b -> a -> a**
-
-### Resources for learning functional programming
-
-Perhaps you have been convinced that functional programming is a better way to write software, and you are wondering how to get started? There are several approaches to learning functional programming; here are some I recommend (with, I admit, a strong bias toward Haskell):
-
-* UPenn's [CIS 194: Introduction to Haskell][35] is a solid introduction to functional programming concepts and real-world Haskell development. The course material is available, but the lectures are not (you could view Brisbane Functional Programming Group's [series of talks covering CIS 194][36] from a few years ago instead).
-* Good introductory books include _[Functional Programming in Scala][30]_ , _[Thinking Functionally with Haskell][31]_ , and _[Haskell Programming from first principles][32]_ .
-* The [Data61 FP course][37] (f.k.a., _NICTA_ course) teaches foundational abstractions and data structures through _type-driven development_ . The payoff is huge, but it is _difficult by design_ , having its origins in training workshops, so only attempt it if you know a functional programmer who is willing to mentor you.
-* Start practicing functional programming in whatever code you're working on. Write pure functions (avoid non-determinism and mutation), use higher-order functions and recursion instead of loops, exploit parametricity for improved readability and reuse. Many people start out in functional programming by experimenting and experiencing the benefits in all kinds of languages.
-* Join a functional programming user group or study group in your area—or start one—and look out for functional programming conferences (new ones are popping up all the time).
-
-### Conclusion
-
-In this article, I discussed what functional programming is and is not, and looked at advantages of functional programming, including equational reasoning and parametricity. We learned that you can do _some_ functional programming in most programming languages, but the choice of language affects how much you can benefit, with _functional programming languages_ , such as Haskell, having the most to offer. I also recommended resources for learning functional programming.
-
-Functional programming is a rich field and there are many deeper (and denser) topics awaiting exploration. I would be remiss not to mention a few that have practical implications, such as:
-
-* lenses and prisms (first-class, composable getters and setters; great for working with nested data);
-* theorem proving (why test your code when you could _prove it correct_ instead?);
-* lazy evaluation (lets you work with potentially infinite data structures);
-* and category theory (the origin of many beautiful and practical abstractions in functional programming).
-
-I hope that you have enjoyed this introduction to functional programming and are inspired to dive into this fun and practical approach to software development.
-
- _This article is published under the [CC BY 4.0][38] license._
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-作者简介:
-
-Software Engineer at Red Hat. Interested in functional programming, category theory and other intersections of math and programming. Crazy about jalapeños.
-
-----------------------
-
-via: https://opensource.com/article/17/4/introduction-functional-programming
-
-作者:[Fraser Tweedale ][a]
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:https://opensource.com/users/frasertweedale
-[1]:https://opensource.com/tags/javascript?src=programming_resource_menu
-[2]:https://opensource.com/tags/perl?src=programming_resource_menu
-[3]:https://opensource.com/tags/python?src=programming_resource_menu
-[4]:https://developers.redhat.com/?intcmp=7016000000127cYAAQ&src=programming_resource_menu
-[5]:https://developers.redhat.com/products/#developer_tools?intcmp=7016000000127cYAAQ&src=programming_resource_menu
-[6]:http://haskell.org/ghc/docs/latest/html/libraries/base/Prelude.html#t:Int
-[7]:http://haskell.org/ghc/docs/latest/html/libraries/base/Prelude.html#t:Int
-[8]:http://haskell.org/ghc/docs/latest/html/libraries/base/Prelude.html#t:Int
-[9]:http://haskell.org/ghc/docs/latest/html/libraries/base/Prelude.html#v:div
-[10]:http://haskell.org/ghc/docs/latest/html/libraries/base/Prelude.html#v:even
-[11]:http://haskell.org/ghc/docs/latest/html/libraries/base/Prelude.html#t:Int
-[12]:http://haskell.org/ghc/docs/latest/html/libraries/base/Prelude.html#t:Bool
-[13]:http://haskell.org/ghc/docs/latest/html/libraries/base/Prelude.html#v:even
-[14]:http://haskell.org/ghc/docs/latest/html/libraries/base/Prelude.html#v:map
-[15]:http://haskell.org/ghc/docs/latest/html/libraries/base/Prelude.html#v:map
-[16]:http://haskell.org/ghc/docs/latest/html/libraries/base/Prelude.html#v:map
-[17]:http://haskell.org/ghc/docs/latest/html/libraries/base/Prelude.html#v:even
-[18]:http://haskell.org/ghc/docs/latest/html/libraries/base/Prelude.html#v:map
-[19]:http://haskell.org/ghc/docs/latest/html/libraries/base/Prelude.html#v:even
-[20]:http://haskell.org/ghc/docs/latest/html/libraries/base/Prelude.html#v:map
-[21]:http://haskell.org/ghc/docs/latest/html/libraries/base/Prelude.html#v:map
-[22]:http://haskell.org/ghc/docs/latest/html/libraries/base/Prelude.html#v:even
-[23]:http://haskell.org/ghc/docs/latest/html/libraries/base/Prelude.html#v:map
-[24]:http://haskell.org/ghc/docs/latest/html/libraries/base/Prelude.html#v:map
-[25]:http://haskell.org/ghc/docs/latest/html/libraries/base/Prelude.html#v:even
-[26]:http://haskell.org/ghc/docs/latest/html/libraries/base/Prelude.html#v:map
-[27]:http://haskell.org/ghc/docs/latest/html/libraries/base/Prelude.html#v:even
-[28]:http://haskell.org/ghc/docs/latest/html/libraries/base/Prelude.html#v:map
-[29]:http://haskell.org/ghc/docs/latest/html/libraries/base/Prelude.html#v:odd
-[30]:https://www.manning.com/books/functional-programming-in-scala
-[31]:http://www.cambridge.org/gb/academic/subjects/computer-science/programming-languages-and-applied-logic/thinking-functionally-haskell
-[32]:http://haskellbook.com/
-[33]:http://cufp.org/
-[34]:https://www.haskell.org/tutorial/monads.html
-[35]:https://www.cis.upenn.edu/~cis194/fall16/
-[36]:https://github.com/bfpg/cis194-yorgey-lectures
-[37]:https://github.com/data61/fp-course
-[38]:https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/
-[39]:https://opensource.com/article/17/4/introduction-functional-programming?rate=_tO5hNzT4hRKNMJtWwQM-K3Jmxm10iPeqoy3bbS12MQ
-[40]:https://wiki.haskell.org/Introduction
-[41]:https://opensource.com/user/123116/feed
-[42]:https://opensource.com/users/frasertweedale
diff --git a/sources/tech/20170427 Enabling DNS split authority with OctoDNS.md b/sources/tech/20170427 Enabling DNS split authority with OctoDNS.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..2b543efaef
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/tech/20170427 Enabling DNS split authority with OctoDNS.md
@@ -0,0 +1,144 @@
+[Enabling DNS split authority with OctoDNS][1]
+============================================================
+
+Building robust systems involves designing for failure. As Site Reliability Engineers at GitHub, we’re always on the lookout for places where redundancy can help to mitigate problems, and today we’ll be talking about steps we’ve recently taken to shore up how you locate our servers via DNS.
+
+Large [DNS][4] providers have many levels of redundancy built into their services, but issues will arise causing outages and there are steps that can be taken to lessen their impact. One of the best options available is to split authority for your zones across multiple providers. Enabling split authority is straightforward, you just configure two or more sets of [name servers][5] for your zones in the registrar and DNS requests will be split across the full list. However, the catch is that you now have to keep the records for those zones in sync across multiple providers and depending on the details, that can either be complex to set up or a completely manual process.
+
+```
+$ dig NS github.com. @a.gtld-servers.net.
+
+...
+
+;; QUESTION SECTION:
+;github.com. IN NS
+
+;; AUTHORITY SECTION:
+github.com. 172800 IN NS ns4.p16.dynect.net.
+github.com. 172800 IN NS ns-520.awsdns-01.net.
+github.com. 172800 IN NS ns1.p16.dynect.net.
+github.com. 172800 IN NS ns3.p16.dynect.net.
+github.com. 172800 IN NS ns-421.awsdns-52.com.
+github.com. 172800 IN NS ns-1283.awsdns-32.org.
+github.com. 172800 IN NS ns2.p16.dynect.net.
+github.com. 172800 IN NS ns-1707.awsdns-21.co.uk.
+
+...
+
+```
+
+The above query is asking a [TLD name server][6] for `github.com.` `NS` records. It returns the values configured in our registrar, in this case four each of two providers. If one of those providers was to experience an outage, the other would hopefully still be available to service requests. We keep our records in sync in further places and can safely change over to them without having to worry about stale or incorrect state.
+
+The last piece of fully configuring split authority is to add all of the name servers as apex `NS` records, the root of the zone, in both providers.
+
+```
+$ dig NS github.com. @ns1.p16.dynect.net.
+
+...
+
+;; QUESTION SECTION:
+;github.com. IN NS
+
+;; ANSWER SECTION:
+github.com. 551 IN NS ns1.p16.dynect.net.
+github.com. 551 IN NS ns2.p16.dynect.net.
+github.com. 551 IN NS ns-520.awsdns-01.net.
+github.com. 551 IN NS ns3.p16.dynect.net.
+github.com. 551 IN NS ns-421.awsdns-52.com.
+github.com. 551 IN NS ns4.p16.dynect.net.
+github.com. 551 IN NS ns-1283.awsdns-32.org.
+github.com. 551 IN NS ns-1707.awsdns-21.co.uk.
+
+```
+
+At GitHub we have dozens of zones and thousands of records, and while the majority of those aren’t critical enough to require redundancy, we have a fair number that do. We wanted a solution that was able to keep these records in sync in multiple providers and more generally manage all of our DNS records, both internal and external. So today we’re announcing [OctoDNS][7].
+
+
+
+#### Configuration
+
+OctoDNS has allowed us to revamp our DNS workflow. Our zones and records are laid out in config files stored in a Git repo. Changes now use the [GitHub Flow][8] and are [branch deployed just like the site][9]. We can even do “noop” deploys to preview what records will be modified by a change. The config files are yaml dictionaries, one per zone, where the top-level keys are record names and the values lay out the ttl, type, and type-specific data. For example, the following config will create the `A` record `octodns.github.com.` when included in the zone file `github.com.yaml`.
+
+```
+octodns:
+ type: A
+ values:
+ - 1.2.3.4
+ - 1.2.3.5
+
+```
+
+The second piece of configuration maps sources of record data to providers. The snippet below tells OctoDNS to load the zone `github.com` from the `config` provider and to sync the results to `dyn` and `route53`.
+
+```
+zones:
+ github.com.:
+ sources:
+ - config
+ targets:
+ - dyn
+ - route53
+
+```
+
+#### Synchronizing
+
+Once our configuration is in place OctoDNS can evaluate the current state and build a plan listing the set of changes it would need to match the targets’ state to the source’s. In the example below, `octodns.github.com` is a new record so the required action is to create the record in both.
+
+```
+$ octodns-sync --config-file=./config/production.yaml
+...
+********************************************************************************
+* github.com.
+********************************************************************************
+* route53 (Route53Provider)
+* Create <ARecord A 60, octodns.github.com., [u'1.2.3.4', '1.2.3.5']>
+* Summary: Creates=1, Updates=0, Deletes=0, Existing Records=0
+* dyn (DynProvider)
+* Create <ARecord A 60, octodns.github.com., [u'1.2.3.4', '1.2.3.5']>
+* Summary: Creates=1, Updates=0, Deletes=0, Existing Records=0
+********************************************************************************
+...
+
+```
+
+By default `octodns-sync` is in dry-run mode, so no action was taken. Once we’ve reviewed the changes and we’re happy with them, we can run the command again and add the `--doit` flag. OctoDNS will run through it’s process and this time continue on to make the necessary changes in Route53 and Dynect so that the new record exists.
+
+```
+$ octodns-sync --config-file=./config/production.yaml --doit
+...
+
+```
+
+At this point we have consistent record data stored in both providers and can comfortably split our DNS requests across them knowing they’ll be providing the accurate results. While we’re running OctoDNS commands directly above, our internal workflow relies on deploy scripts and chatops. You can find more about that in the [workflow section of the README][10].
+
+#### Conclusion
+
+Split authority is something we feel most sites can benefit from and the hope is that with [OctoDNS][11], one of the biggest obstacles to enabling it has been removed. Even if split authority isn’t of interest, OctoDNS may still be worth a look as it brings the benefits of [Infrastructure as Code][12] to DNS.
+
+Want to help the GitHub SRE team solve interesting problems like this? We’d love for you to join us. [Apply Here][13]
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://githubengineering.com/enabling-split-authority-dns-with-octodns/
+
+作者:[ross ][a]
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:https://github.com/ross
+[1]:https://githubengineering.com/enabling-split-authority-dns-with-octodns/
+[2]:https://github.com/ross
+[3]:https://github.com/ross
+[4]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Domain_Name_System
+[5]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Name_server
+[6]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Top-level_domain
+[7]:https://github.com/github/octodns/
+[8]:https://guides.github.com/introduction/flow/
+[9]:https://githubengineering.com/deploying-branches-to-github-com/
+[10]:https://github.com/github/octodns#workflow
+[11]:https://github.com/github/octodns/
+[12]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Infrastructure_as_Code
+[13]:https://boards.greenhouse.io/github/jobs/669805#.WPVqJlPyvUI
diff --git a/sources/tech/20170531 DNS Infrastructure at GitHub.md b/sources/tech/20170531 DNS Infrastructure at GitHub.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 5feb4c5873..0000000000
--- a/sources/tech/20170531 DNS Infrastructure at GitHub.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,82 +0,0 @@
-[DNS Infrastructure at GitHub][1]
-============================================================
-
-
-At GitHub we recently revamped how we do DNS from the ground up. This included both how we [interact with external DNS providers][4] and how we serve records internally to our hosts. To do this, we had to design and build a new DNS infrastructure that could scale with GitHub’s growth and across many data centers.
-
-Previously GitHub’s DNS infrastructure was fairly simple and straightforward. It included a local, forwarding only DNS cache on every server and a pair of hosts that acted as both caches and authorities used by all these hosts. These hosts were available both on the internal network as well as public internet. We configured zone stubs in the caching daemon to direct queries locally rather than recurse on the internet. We also had NS records set up at our DNS providers that pointed specific internal zones to the public IPs of this pair of hosts for queries external to our network.
-
-This configuration worked for many years but was not without its downsides. Many applications are highly sensitive to resolving DNS queries and any performance or availability issues we ran into would cause queuing and degraded performance at best and customer impacting outages at worst. Configuration and code changes can cause large unexpected changes in query rates. As such scaling beyond these two hosts became an issue. Due to the network configuration of these hosts we would just need to keep adding IPs and hosts which has its own problems. While attempting to fire fight and remediate these issues, the old system made it difficult to identify causes due to a lack of metrics and visibility. In many cases we resorted to `tcpdump` to identify traffic and queries in question. Another issue was running on public DNS servers we run the risk of leaking internal network information. As a result we decided to build something better and began to identify our requirements for the new system.
-
-We set out to design a new DNS infrastructure that would improve the aforementioned operational issues including scaling and visibility, as well as introducing some additional requirements. We wanted to continue to run our public DNS zones via external DNS providers so whatever system we build needed to be vendor agnostic. Additionally, we wanted this system to be capable of serving both our internal and external zones, meaning internal zones were only available on our internal network unless specifically configured otherwise and external zones are resolvable without leaving our internal network. We wanted the new DNS architecture to allow both a [deploy-based workflow for making changes][5] as well as API access to our records for automated changes via our inventory and provisioning systems. The new system could not have any external dependencies; too much relies on DNS functioning for it to get caught in a cascading failure. This includes connectivity to other data centers and DNS services that may reside there. Our old system mixed the use of caches and authorities on the same host; we wanted to move to a tiered design with isolated roles. Lastly, we wanted a system that could support many data center environments whether it be EC2 or bare metal.
-
-### Implementation
-
-
-
-To build this system we identified three classes of hosts: caches, edges, and authorities. Caches serve as recursive resolvers and DNS “routers” caching responses from the edge tier. The edge tier, running a DNS authority daemon, responds to queries from the caching tier for zones it is configured to zone transfer from the authority tier. The authority tier serve as hidden DNS masters as our canonical source for DNS data, servicing zone transfers from the edge hosts as well as providing an HTTP API for creating, modifying or deleting records.
-
-In our new configuration, caches live in each data center meaning application hosts don’t need to traverse a data center boundary to retrieve a record. The caches are configured to map zones to the edge hosts within their region in order to route our internal zones to our own hosts. Any zone that is not explicitly configured will recurse on the internet to resolve an answer.
-
-The edge hosts are regional hosts, living in our network edge PoPs (Point of Presence). Our PoPs have one or more data centers that rely on them for external connectivity, without the PoP the data center can’t get to the internet and the internet can’t get to them. The edges perform zone transfers with all authorities regardless of what region or location they exist in and store those zones locally on their disk.
-
-Our authorities are also regional hosts, only containing zones applicable to the region it is contained in. Our inventory and provisioning systems determine which regional authority a zone lives in and will create and delete records via an HTTP API as servers come and go. OctoDNS maps zones to regional authorities and uses the same API to create static records and to ensure dynamic sources are in sync. We have an additional separate authority for external domains, such as github.com, to allow us to query our external domains during a disruption to connectivity. All records are stored in MySQL.
-
-### Operability
-
-
-
-One huge benefit of moving to a more modern DNS infrastructure is observability. Our old DNS system had little to no metrics and limited logging. A large factor in deciding which DNS servers to use was the breadth and depth of metrics they produce. We finalized on [Unbound][6] for the caches, [NSD][7] for the edge hosts and [PowerDNS][8] for the authorities, all of which have been proven in DNS infrastructures much larger than at GitHub.
-
-When running in our bare metal data centers, caches are accessed via a private [anycast][9] IP resulting in it reaching the nearest available cache host. The caches have been deployed in a rack aware manner that provides some level of balanced load between them and isolation against some power and network failure modes. When a cache host fails, servers that would normally use it for lookups will now automatically be routed to the next closest cache, keeping latency low as well as providing tolerance to some failure modes. Anycast allows us to scale the number of caches behind a single IP address unlike our previous configuration, giving us the ability to run as many caching hosts as DNS demand requires.
-
-Edge hosts perform zone transfers with the authority tier, regardless of region or location. Our zones are not large enough that keeping a copy of all of them in every region is a problem. This means for every zone, all caches will have access to a local edge server with a local copy of all zones even when a region is offline or upstream providers are having connectivity issues. This change alone has proven to be quite resilient in the face of connectivity issues and has helped keep GitHub available during failures that not long ago would have caused customer facing outages.
-
-These zone transfers include both our internal and external zones from their respective authorities. As you might guess zones like github.com are external and zones like github.net are generally internal. The difference between them is only the types of use and data stored in them. Knowing which zones are internal and external gives us some flexibility in our configuration.
-
-```
-$ dig +short github.com
-192.30.253.112
-192.30.253.113
-
-```
-
-Public zones are [sync’d][10] to external DNS providers and are records GitHub users use everyday. Addtionally, public zones are completely resolvable within our network without needing to communicate with our external providers. This means any service that needs to look up `api.github.com` can do so without needing to rely on external network connectivity. We also use the stub-first configuration option of Unbound which gives a lookup a second chance if our internal DNS service is down for some reason by looking it up externally when it fails.
-
-```
-$ dig +short time.github.net
-10.127.6.10
-
-```
-
-Most of the `github.net` zone is completely private, inaccessible from the internet and only contains [RFC 1918][11] IP addresses. Private zones are split up per region and site. Each region and/or site has a set of sub-zones applicable to that location, sub-zones for management network, service discovery, specific service records and yet to be provisioned hosts that are in our inventory. Private zones also include reverse lookup zones for PTRs.
-
-### Conclusion
-
-Replacing an old system with a new one that is ready to serve millions of customers is never easy. Using a pragmatic, requirements based approach to designing and implementing our new DNS system resulted in a DNS infrastructure that was able to hit the ground running and will hopefully grow with GitHub into the future.
-
-Want to help the GitHub SRE team solve interesting problems like this? We’d love for you to join us. [Apply Here][12]
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: https://githubengineering.com/dns-infrastructure-at-github/
-
-作者:[Joe Williams ][a]
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:https://github.com/joewilliams
-[1]:https://githubengineering.com/dns-infrastructure-at-github/
-[2]:https://github.com/joewilliams
-[3]:https://github.com/joewilliams
-[4]:https://githubengineering.com/enabling-split-authority-dns-with-octodns/
-[5]:https://githubengineering.com/enabling-split-authority-dns-with-octodns/
-[6]:https://unbound.net/
-[7]:https://www.nlnetlabs.nl/projects/nsd/
-[8]:https://powerdns.com/
-[9]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anycast
-[10]:https://githubengineering.com/enabling-split-authority-dns-with-octodns/
-[11]:http://www.faqs.org/rfcs/rfc1918.html
-[12]:https://boards.greenhouse.io/github/jobs/669805#.WPVqJlPyvUI
diff --git a/sources/tech/20170617 Top 8 IDEs for Raspberry Pi.md b/sources/tech/20170617 Top 8 IDEs for Raspberry Pi.md
index 8091a1e04a..7d59525f50 100644
--- a/sources/tech/20170617 Top 8 IDEs for Raspberry Pi.md
+++ b/sources/tech/20170617 Top 8 IDEs for Raspberry Pi.md
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
Top 8 IDEs for Raspberry Pi
============================================================
-
+translating by softpaopao
__
diff --git a/sources/tech/20170706 MySQL infrastructure testing automation at GitHub.md b/sources/tech/20170706 MySQL infrastructure testing automation at GitHub.md
index def24a3b0f..32d4a82db9 100644
--- a/sources/tech/20170706 MySQL infrastructure testing automation at GitHub.md
+++ b/sources/tech/20170706 MySQL infrastructure testing automation at GitHub.md
@@ -1,3 +1,5 @@
+MonkeyDEcho translated
+
[MySQL infrastructure testing automation at GitHub][31]
============================================================
diff --git a/sources/tech/20170817 Creating better disaster recovery plans.md b/sources/tech/20170817 Creating better disaster recovery plans.md
index 7827b417e5..7d934d2676 100644
--- a/sources/tech/20170817 Creating better disaster recovery plans.md
+++ b/sources/tech/20170817 Creating better disaster recovery plans.md
@@ -1,3 +1,5 @@
+translating---geekpi
+
Creating better disaster recovery plans
============================================================
diff --git a/sources/tech/20170818 Orchestration tools fully exploit Linux container technology.md b/sources/tech/20170818 Orchestration tools fully exploit Linux container technology.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..3b7e728c5d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/tech/20170818 Orchestration tools fully exploit Linux container technology.md
@@ -0,0 +1,86 @@
+Orchestration tools fully exploit Linux container technology
+============================================================
+
+### Once companies get past the “let’s see how these container things work” stage, they end up with a lot of containers running in a lot of different places
+
+
+>Thinkstock
+
+Companies that need to deliver applications quickly and efficiently—and today, what company doesn’t need to do this?— are turning to Linux containers. What they are also finding is that once they get past the “let’s see how these container things work” stage, they are going to end up with a lot of containers running in a lot of different places.
+
+Linux container technology is not new, but it has increased in popularity due to factors including the innovative packaging format (now [Open Container Initiative (OCI) format][3]) originally invented by Docker, as well as the competitive requirement for continual development and deployment of new applications. In a May 2016 Forrester study commissioned by Red Hat, 48 percent of respondents said they were already using containers in development, a figure projected to rise to 53 percent this year. Only one-fifth of respondents said that they wouldn’t leverage containers in development processes in 2017.
+
+Like Lego blocks, container images enable easy reuse of code and services. Each container image is like a separate Lego block, designed to do one part of the job really well. This could be a database, a data store, or even a booking service, or analytics service. By packaging each part separately, they can be used in different applications. But, without some sort of application definition (the instruction booklet), it’s difficult to create copies of the full application in different environments. That’s where container orchestration comes in.
+
+
+ Scott McCarty
+
+Container orchestration provides an infrastructure like the Lego system – the developer can provide simple instructions for how to build the application. The orchestration engine will know how to run it. This makes it easy to create multiple copies of the same application, spanning developer laptops, CI/CD system, and even production data centers and cloud provider environments.
+
+Linux container images allow companies to package and isolate the building blocks of applications with their entire runtime environment (operating system pieces). Building on this, container orchestration makes it easy to define and run all of the blocks together as a full applications. Once the work has been invested to define the full application, they can be moved between different environments (dev, test, production, and so on) without breaking them, and without changing how they behave.
+
+### Kicking the tires on containers
+
+It’s clear that containers make sense, and more and more companies are figuratively kicking the tires on containers. In the beginning, it might be one developer working with a single container, or a team of developers working with multiple containers. In the latter scenario, the developers are likely writing home-grown code to deal with the complexities that quickly arise once a container deployment grows beyond a single instance.
+
+This is all well and good: They’re developers, after all – they’ve got this. But it’s going to get messy, even in the developer world, and the home-grown code model is just not going to fly once containers move to QA and [dun, dun, duuuuunnnnn] production.
+
+Orchestration tools do essentially two things. First, they help developers define what their application looks like – the set of services it takes to build up an instance of their application – the databases, data stores, web servers, etc., for each application instance. Orchestrators help standardize what all the parts of an application look like, running together and communicating to each other, what I would call a standardized application definition. Second, they manage the process of starting, stopping, upgrading and running these multiple containers in a cluster of compute resources, which is especially useful when running multiple copies of any given application, for things like continuous integration (CI) and continuous delivery (CD).
+
+
+Think about it like an apartment building. Everyone who lives there has the same street address, but each person has a number or letter or combination of both that specifically identifies him or her. This is necessary, for example, for the delivery of the right mail and packages to the right tenants.
+
+Likewise with containers, as soon as you have two containers or two hosts that you want to run those containers on, you have to keep track of things like where developers go to test a database connect or where users go to connect to a service running in a container. Container orchestration tools essentially help manage the logistics of containers across multiple hosts. They extend life cycle management capabilities to full applications, made of multiple containers, deployed on a cluster of machines, allowing users to treat the entire cluster as a single deployment target.
+
+It’s really that simple—and that complicated. Orchestration tools provide a number of capabilities, ranging from provisioning containers, to identifying and rescheduling failed containers, to exposing containers to systems and services outside the cluster, to adding and removing containers on demand.
+
+While container technology has been around for a while, container orchestration tools have been available only for a few years. Orchestrators were developed from lessons learned with high-performance computing (HPC) and application management internally at Google. In essence, to deal with the monstrosity that is, running a bunch of stuff (batch jobs, services, etc.) on a bunch of servers. Since then, orchestrators have evolved to enable companies to strategically leverage containers.
+
+Once your company determines that it needs container orchestration, the next step is figuring out which platform makes the most sense for the business. When evaluating container orchestrators, look closely at (among other things):
+
+* Application definition language
+
+* Existing capability set
+
+* Rate at which new capabilities are being added
+
+* Whether it is open source or proprietary
+
+* Community health (how active/productive members are, the quality/quantity of member submissions, diversity of contributors – individuals and companies)
+
+* Hardening efforts
+
+* Reference architectures
+
+* Certifications
+
+* Process for productization
+
+There are three major container orchestration platforms, which seem to be ahead of the others, each with its own history.
+
+1. **Docker Swarm:** Swarm is an add-on to Docker – arguably, the container poster child. Swarm allows users to establish and manage a cluster of Docker nodes as a single virtual system. The challenge with Swarm is it seems on track to become a single-vendor project.
+
+2. **Mesos**: Mesos grew up from Apache and high-performance computing, and thus serves as an excellent scheduler. Mesos is also very technically advanced, although it doesn’t seem to have the velocity or investment compared to others.
+
+3. **Kubernetes:** Developed by Google, with lessons from an internal orchestrator named Borg, Kubernetes is widely used and has a robust community around it. In fact, it’s the No. 1 project on GitHub. Mesos may currently have a slight technical advantage over Kubernetes, but Kubernetes is a fast-moving project, which is also making architectural investments for long-term technical gains. It should catch up and surpass Mesos in terms of technical capabilities in the very near future.
+
+### The future of orchestration
+
+Looking ahead, companies can expect to see orchestration tools moving in an application- and service-focused direction. Because, in reality, rapid application development today is really about quickly leveraging a mix of services, code, and data. Whether those services are open source and deployed by your internal team or consumed from a cloud provider, the future looks like a mix of both. Since today’s orchestrators are also tackling the application definition challenge, expect to see them tackle the integration of external services more and more.
+
+For the here and now, companies that want to take full advantage of containers must take advantage of container orchestration.
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://www.infoworld.com/article/3205304/containers/orchestration-tools-enable-companies-to-fully-exploit-linux-container-technology.html
+
+作者:[ Scott McCarty][a]
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:https://www.infoworld.com/author/Scott-McCarty/
+[1]:https://www.infoworld.com/article/3204171/what-is-docker-linux-containers-explained.html#tk.ifw-infsb
+[2]:https://www.infoworld.com/resources/16373/application-virtualization/the-beginners-guide-to-docker.html#tk.ifw-infsb
+[3]:https://github.com/opencontainers/image-spec
diff --git a/sources/tech/20170821 Getting started with ImageMagick.md b/sources/tech/20170821 Getting started with ImageMagick.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 219a216e97..0000000000
--- a/sources/tech/20170821 Getting started with ImageMagick.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,200 +0,0 @@
-Getting started with ImageMagick
-============================================================
-
-### Learn common ways to view and modify images with this lightweight image editor.
-
-
-Image by : opensource.com
-
-In a recent article about [lightweight image viewers][8], author Scott Nesbitt mentioned display, one of the components in [ImageMagick][9]. ImageMagick is not merely an image viewer—it offers a large number of utilities and options for image editing. This tutorial will explain more about using the **display** command and other command-line utilities in ImageMagick.
-
-With a number of excellent image editors available, you may be wondering why someone would choose a mainly non-GUI, command-line based program like ImageMagick. For one thing, it is rock-solid dependable. But an even bigger benefit is that it allows you to set up methods to edit a large number of images in a particular way.
-
-This introduction to common ImageMagick commands should get you started.
-
-### The display command
-
-Let's start with the command Scott mentioned: **display**. Say you have a directory with a lot of images you want to look at. Start **display** with the following command:
-
-```
-cd Pictures
-display *.JPG
-```
-
-This will load your JPG files sequentially in alphanumeric order, one at a time in a simple window. Left-clicking on an image brings up a simple, standalone menu (the only GUI feature you'll see in ImageMagick).
-
-### [display_menu.png][1]
-
-
-
-Here's what you'll find in the **display** menu:
-
-* **File** contains the options _Open, Next, Former, Select, Save, Print, Delete, New, Visual Directory_ , and _Quit_ . _Select _ picks a specific image file to display, _Visual Directory_ shows all of the files (not just the images) in the current working directory. If you want to scroll through all the selected images, you can use _Next_ and _Former_ , but it's easier to use their keyboard shortcuts (Spacebar for the next image and Backspace for the previous).
-
-* **Edit** offers _Undo, Redo, Cut, Copy_ , and _Paste_ , which are just auxiliary commands to more specific editing process. _Undo _ is especially useful when you're playing around with different edits to see what they do.
-
-* **View** has _Half Size, Original Size, Double Size, Resize, Apply, Refresh_ , and _Restore_ . These are mostly self-explanatory and, unless you save the image after applying one of them, the image file isn't changed. _Resize_ brings up a dialog to name a specific size either in pixels, with or without constrained dimensions, or a percentage. I'm not sure what _Apply _ does.
-
-* **Transform** shows _Crop, Chop, Flop, Flip, Rotate Right, Rotate Left, Rotate, Shear, Roll_ , and _Trim Edges_ . _Chop _ uses a click-drag operation to cut out a vertical or horizontal section of the image, pasting the edges together. The best way to learn how these features work is to play with them, rather than reading about them.
-
-* **Enhance** provides _Hue, Saturation, Brightness, Gamma, Spiff, Dull, Contrast Stretch, Sigmoidal Contrast, Normalize, Equalize, Negate, Grayscale, Map_ , and _Quantize_ . These are operations for color manipulation and adjusting brightness and contrast.
-
-* **Effects** has _Despeckle, Emboss, Reduce Noise, Add Noise, Sharpen, Blur, Threshold, Edge Detect, Spread, Shade, Raise_ , and _Segment_ . These are fairly standard image editing effects.
-
-* **F/X** options are _Solarize, Sepia Tone, Swirl, Implode, Vignette, Wave, Oil Paint_ , and _Charcoal Draw_ , also very common effects in image editors.
-
-* **Image Edit** contains _Annotate, Draw, Color, Matte, Composite, Add Border, Add Frame, Comment, Launch_ , and _Region of Interest_ . _Launch _ will open the current image in GIMP (in my Fedora at least). _Region of Interest_ allows you to select an area to apply editing; press Esc to deselect the region.
-
-* **Miscellany** offers _Image Info, Zoom Image, Show Preview, Show Histogram, Show Matte, Background, Slide Show_ , and _Preferences_ . _Show Preview_ seems interesting, but I struggled to get it to work.
-
-* **Help** shows _Overview, Browse Documentation_ , and _About Display_ . _Overview_ gives a lot of basic information about display and includes a large number of built-in keyboard equivalents for various commands and operations. In my Fedora, _Browse Documentation_ took me nowhere.
-
-Although **display**'s GUI interface provides a reasonably competent image editor, ImageMagick also provides 89 command-line options, many of which correspond to the menu items above. For example, if I'm displaying a directory of digital images that are larger than my screen size, rather than resizing them individually after they appear on my screen, I can specify:
-
-```
- display -resize 50% *.JPG
-```
-
-Many of the operations in the menus above can also be done by adding an option in the command line. But there are others that aren't available from the menu, including **‑monochrome**, which converts the image to black and white (not grayscale), and **‑colors**, where you can specify how many colors to use in the image. For example, try these out:
-
-```
- display -resize 50% -monochrome *.JPG
-```
-
-```
- display -resize 50% -colors 8 *.JPG
-```
-
-These operations create interesting images. Try enhancing colors or making other edits after reducing colors. Remember, unless you save and overwrite them, the original files remain unchanged.
-
-### The convert command
-
-The **convert** command has 237 options—yes 237—that provide a wide range of things you can do (some of which display can also do). I'll only cover a few of them, mostly sticking with image manipulation. Two simple things you can do with **convert** would be:
-
-```
- convert DSC_0001.JPG dsc0001.png
-```
-
-```
- convert *.bmp *.png
-```
-
-The first command would convert a single file (DSC_0001) from JPG to PNG format without changing the original. The second would do this operation on all the BMP images in a directory.
-
-If you want to see the formats ImageMagick can work with, type:
-
-```
- identify -list format
-```
-
-Let's pick through a few interesting ways we can use the **convert** command to manipulate images. Here is the general format for this command:
-
-```
- convert inputfilename [options] outputfilename
-```
-
-You can have multiple options, and they are done in the order they are arranged, from left to right.
-
-Here are a couple of simple options:
-
-```
- convert monochrome_source.jpg -monochrome monochrome_example.jpg
-```
-
-### [monochrome_demo.jpg][2]
-
-
-
-```
- convert DSC_0008.jpg -charcoal 1.2 charcoal_example.jpg
-```
-
-### [charcoal_demo.jpg][3]
-
-
-
-The **‑monochrome** option has no associated setting, but the **‑charcoal** variable needs an associated factor. In my experience, it needs to be a small number (even less than 1) to achieve something that resembles a charcoal drawing, otherwise you get pretty heavy blobs of black. Even so, the sharp edges in an image are quite distinct, unlike in a charcoal drawing.
-
-Now let's look at these:
-
-```
- convert DSC_0032.JPG -edge 3 edge_demo.jpg
-```
-
-```
- convert DSC_0032.JPG -colors 4 reduced4_demo.jpg
-```
-
-```
- convert DSC_0032.JPG -colors 4 -edge 3 reduced+edge_demo.jpg
-```
-
-### [reduced_demo.jpg][4]
-
-
-
-The original image is in the upper left. In the first command, I applied an **‑edge**option with a setting of 3 (see the upper-right image)—anything less than that was too subtle for my liking. In the second command (the lower-left image), we have reduced the number of colors to four, which doesn't look much different from the original. But look what happens when we combine these two in the third command (lower-right image)! Perhaps it's a bit garish, but who would have expected this result from the original image or either option on its own?
-
-The **‑canny** command provided another surprise. This is another kind of edge detector, called a "multi-stage algorithm." Using **‑canny** alone produces a mostly black image and some white lines. I followed that with a **‑negate** command:
-
-```
- convert DSC_0049.jpg -canny 0x1 -negate canny_egret.jpg
- convert DSC_0023.jpg -canny 0x1 -negate canny_ship.jpg
-```
-
-### [canny_demos.jpg][5]
-
-
-
-It's a bit minimalist, but I think it resembles a pen-and-ink drawing, a rather remarkable difference from the original photos. It doesn't work well with all images; generally, it works best with images with sharp lines. Elements that are out of focus are likely to disappear; notice how the background sandbar in the egret picture doesn't show up because it is blurred. Also notice in the ship picture, while most edges show up very well, without colors we lose the gestalt of the picture, so perhaps this could be the basis for some digital coloration or even coloring after printing.
-
-### The montage command
-
-Finally, I want to talk about the **montage** command. I've already shown examples of it above, where I have combined single images into composites.
-
-Here's how I generated the charcoal example (note that it would all be on one line):
-
-```
- montage -label %f DSC_0008.jpg charcoal_example.jpg -geometry +10+10
- -resize 25% -shadow -title 'charcoal demo' charcoal_demo.jpg
-```
-
-The **-label** option labels each image with its filename (**%f**) underneath. Without the **‑geometry** option, all the images would be thumbnail size (120 pixels wide), and **+10+10** manages the border size. Next, I resized the entire final composite (**‑resize 25%**) and added a shadow (with no settings, so it's the default), and finally created a **title** for the montage.
-
-You can place all the image names at the end, with the last image name the file where the montage is saved. This might be useful to create an alias for the command and all its options, then I can simply type the alias followed by the appropriate filenames. I've done this on occasion to reduce the typing needed to create a series of montages.
-
-In the **‑canny** examples, I had four images in the montage. I added the **‑tile**option, specifically **‑tile 2x**, which created a montage of two columns. I could have specified a **matrix**, **‑tile 2x2**, or **‑tile x2** to produce the same result.
-
-There is a lot more to learn about ImageMagick, so I plan to write more about it, maybe even about using [Perl][10] to script ImageMagick commands. ImageMagick has extensive [documentation][11], although the site is short on examples or showing results, and I think the best way to learn is by experimenting and changing various settings and options.
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-作者简介:
-
-Greg Pittman - Greg is a retired neurologist in Louisville, Kentucky, with a long-standing interest in computers and programming, beginning with Fortran IV in the 1960s. When Linux and open source software came along, it kindled a commitment to learning more, and eventually contributing. He is a member of the Scribus Team.
-
----------------------
-
-via: https://opensource.com/article/17/8/imagemagick
-
-作者:[Greg Pittman ][a]
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:https://opensource.com/users/greg-p
-[1]:https://opensource.com/file/367401
-[2]:https://opensource.com/file/367391
-[3]:https://opensource.com/file/367396
-[4]:https://opensource.com/file/367381
-[5]:https://opensource.com/file/367406
-[6]:https://opensource.com/article/17/8/imagemagick?rate=W2W3j4nu4L14gOClu1RhT7GOMDS31pUdyw-dsgFNqYI
-[7]:https://opensource.com/user/30666/feed
-[8]:https://opensource.com/article/17/7/4-lightweight-image-viewers-linux-desktop
-[9]:https://www.imagemagick.org/script/index.php
-[10]:https://opensource.com/sitewide-search?search_api_views_fulltext=perl
-[11]:https://imagemagick.org/script/index.php
-[12]:https://opensource.com/users/greg-p
-[13]:https://opensource.com/users/greg-p
-[14]:https://opensource.com/article/17/8/imagemagick#comments
diff --git a/sources/tech/20170822 Running WordPress in a Kubernetes Cluster.md b/sources/tech/20170822 Running WordPress in a Kubernetes Cluster.md
index ada30bdb01..c4f492b4e9 100644
--- a/sources/tech/20170822 Running WordPress in a Kubernetes Cluster.md
+++ b/sources/tech/20170822 Running WordPress in a Kubernetes Cluster.md
@@ -1,3 +1,5 @@
+translating by StdioA
+
Running WordPress in a Kubernetes Cluster
============================================================
@@ -170,7 +172,7 @@ via: https://deliciousbrains.com/running-wordpress-kubernetes-cluster/
[9]:https://kubernetes.io/
[10]:https://docs.docker.com/engine/swarm/
[11]:http://mesos.apache.org/
-[12]:https://mesosphere.com/blog/docker-vs-kubernetes-vs-apache-mesos/
+[12]:https://mesosphere.com/blog/docker-vs-kubernetes-vs-apache-mesos/
[13]:https://kubernetes.io/docs/tutorials/kubernetes-basics/
[14]:https://kubernetes.io/docs/getting-started-guides/minikube/
[15]:https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/tools/install-kubectl/
diff --git a/sources/tech/20170823 Using Ansible for deploying serverless applications.md b/sources/tech/20170823 Using Ansible for deploying serverless applications.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 114a6bc0da..0000000000
--- a/sources/tech/20170823 Using Ansible for deploying serverless applications.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,127 +0,0 @@
-translating----geekpi
-
-Using Ansible for deploying serverless applications
-============================================================
-
-### Serverless is another step in the direction of managed services and plays nice with Ansible's agentless architecture.
-
-
-Image by : opensource.com
-
-[Ansible][8] is designed as the simplest deployment tool that actually works. What that means is that it's not a full programming language. You write YAML templates that define tasks and list whatever tasks you need to automate your job.
-
-Most people think of Ansible as a souped-up version of "SSH in a 'for' loop," and that's true for simple use cases. But really Ansible is about _tasks_ , not about SSH. For a lot of use cases, we connect via SSH but also support things like Windows Remote Management (WinRM) for Windows machines, different protocols for network devices, and the HTTPS APIs that are the lingua franca of cloud services.
-
-More on Ansible
-
-* [How Ansible works][1]
-
-* [Free Ansible eBooks][2]
-
-* [Ansible quick start video][3]
-
-* [Download and install Ansible][4]
-
-In a cloud, Ansible can operate on two separate layers: the control plane and the on-instance resources. The control plane consists of everything _not_ running on the OS. This includes setting up networks, spawning instances, provisioning higher-level services like Amazon's S3 or DynamoDB, and everything else you need to keep your cloud infrastructure secure and serving customers.
-
-On-instance work is what you already know Ansible for: starting and stopping services, templating config files, installing packages, and everything else OS-related that you can do over SSH.
-
-Now, what about [serverless][9]? Depending who you ask, serverless is either the ultimate extension of the continued rush to the public cloud or a wildly new paradigm where everything is an API call, and it's never been done before.
-
-Ansible takes the first view. Before "serverless" was a term of art, users had to manage and provision EC2 instances, virtual private cloud (VPC) networks, and everything else. Serverless is another step in the direction of managed services and plays nice with Ansible's agentless architecture.
-
-Before we go into a [Lambda][10] example, let's look at a simpler task for provisioning a CloudFormation stack:
-
-```
-- name: Build network
- cloudformation:
- stack_name: prod-vpc
- state: present
- template: base_vpc.yml
-```
-
-Writing a task like this takes just a couple minutes, but it brings the last semi-manual step involved in building your infrastructure—clicking "Create Stack"—into a playbook with everything else. Now your VPC is just another task you can call when building up a new region.
-
-Since cloud providers are the real source of truth when it comes to what's really happening in your account, Ansible has a number of ways to pull that back and use the IDs, names, and other parameters to filter and query running instances or networks. Take for example the **cloudformation_facts** module that we can use to get the subnet IDs, network ranges, and other data back out of the template we just created.
-
-```
-- name: Pull all new resources back in as a variable
- cloudformation_facts:
- stack_name: prod-vpc
- register: network_stack
-```
-
-For serverless applications, you'll definitely need a complement of Lambda functions in addition to any other DynamoDB tables, S3 buckets, and whatever else. Fortunately, by using the **lambda** modules, Lambda functions can be created in the same way as the stack from the last tasks:
-
-```
-- lambda:
- name: sendReportMail
- zip_file: "{{ deployment_package }}"
- runtime: python3.6
- handler: report.send
- memory_size: 1024
- role: "{{ iam_exec_role }}"
- register: new_function
-```
-
-If you have another tool that you prefer for shipping the serverless parts of your application, that works as well. The open source [Serverless Framework][11] has its own Ansible module that will work just as well:
-
-```
-- serverless:
- service_path: '{{ project_dir }}'
- stage: dev
- register: sls
-- name: Serverless uses CloudFormation under the hood, so you can easily pull info back into Ansible
- cloudformation_facts:
- stack_name: "{{ sls.service_name }}"
- register: sls_facts
-```
-
-That's not quite everything you need, since the serverless project also must exist, and that's where you'll do the heavy lifting of defining your functions and event sources. For this example, we'll make a single function that responds to HTTP requests. The Serverless Framework uses YAML as its config language (as does Ansible), so this should look familiar.
-
-```
-# serverless.yml
-service: fakeservice
-
-provider:
- name: aws
- runtime: python3.6
-
-functions:
- main:
- handler: test_function.handler
- events:
- - http:
- path: /
- method: get
-```
-
-At [AnsibleFest][12], I'll be covering this example and other in-depth deployment strategies to take the best advantage of the Ansible playbooks and infrastructure you already have, along with new serverless practices. Whether you're able to be there or not, I hope these examples can get you started using Ansible—whether or not you have any servers to manage.
-
- _AnsibleFest is a _ _day-long_ _ conference bringing together hundreds of Ansible users, developers, and industry partners. Join us for product updates, inspirational talks, tech deep dives, hands-on demos and a day of networking. Get your tickets to AnsibleFest in San Francisco on September 7\. Save 25% on [**registration**][6] with the discount code **OPENSOURCE**._
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: https://opensource.com/article/17/8/ansible-serverless-applications
-
-作者:[Ryan Scott Brown ][a]
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:https://opensource.com/users/ryansb
-[1]:https://www.ansible.com/how-ansible-works?intcmp=701f2000000h4RcAAI
-[2]:https://www.ansible.com/ebooks?intcmp=701f2000000h4RcAAI
-[3]:https://www.ansible.com/quick-start-video?intcmp=701f2000000h4RcAAI
-[4]:https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/latest/intro_installation.html?intcmp=701f2000000h4RcAAI
-[5]:https://opensource.com/article/17/8/ansible-serverless-applications?rate=zOgBPQUEmiTctfbajpu_TddaH-8b-ay3pFCK0b43vFw
-[6]:https://www.eventbrite.com/e/ansiblefest-san-francisco-2017-tickets-34008433139
-[7]:https://opensource.com/user/12043/feed
-[8]:https://www.ansible.com/
-[9]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Serverless_computing
-[10]:https://aws.amazon.com/lambda/
-[11]:https://serverless.com/
-[12]:https://www.ansible.com/ansiblefest?intcmp=701f2000000h4RcAAI
-[13]:https://opensource.com/users/ryansb
-[14]:https://opensource.com/users/ryansb
diff --git a/sources/tech/20170823 Using Kubernetes for Local Development — Minikube.md b/sources/tech/20170823 Using Kubernetes for Local Development — Minikube.md
deleted file mode 100644
index b517ca5c2a..0000000000
--- a/sources/tech/20170823 Using Kubernetes for Local Development — Minikube.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,294 +0,0 @@
-Using Kubernetes for Local Development — Minikube
-============================================================
-
-If you ops team are using Docker and Kubernetes, it is recommended to adopt the same or similar technologies in development. This will reduce the number of incompatibility and portability problems and makes everyone consider the application container a common responsibility of both Dev and Ops teams.
-
-
-
-
-
-This blog post introduces the usage of Kubernetes in development mode and it is inspired from a screencast that you can find in [Painless Docker Course][10].
-
-][1]
-
-Minikube is a tool that makes developers’ life easy by allowing them to use and run a Kubernetes cluster in a local machine.
-
-In this blog post, for the examples that I tested, I am using Linux Mint 18, but it doesn’t change nothing apart the installation part.
-
-```
-cat /etc/lsb-release
-```
-
-```
-DISTRIB_ID=LinuxMint
-DISTRIB_RELEASE=18.1
-DISTRIB_CODENAME=serena
-DISTRIB_DESCRIPTION=”Linux Mint 18.1 Serena”
-```
-
-
-
-
-#### Prerequisites
-
-In order to work with Minkube, we should have Kubectl and Minikube installed + some virtualization drivers.
-
-* For OS X, install [xhyve driver][2], [VirtualBox][3], or [VMware Fusion][4], then Kubectl and Minkube
-
-```
-curl -LO https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/$(curl -s https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/stable.txt)/bin/darwin/amd64/kubectl
-```
-
-```
-chmod +x ./kubectl
-```
-
-```
-sudo mv ./kubectl /usr/local/bin/kubectl
-```
-
-```
-curl -Lo minikube https://storage.googleapis.com/minikube/releases/v0.21.0/minikube-darwin-amd64 && chmod +x minikube && sudo mv minikube /usr/local/bin/
-```
-
-* For Windows, install [VirtualBox][6] or [Hyper-V][7] then Kubectl and Minkube
-
-```
-curl -LO https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/v1.7.0/bin/windows/amd64/kubectl.exe
-```
-
-Add the binary to your PATH (This [article][11] explains how to modify the PATH)
-
-Download the `minikube-windows-amd64.exe` file, rename it to `minikube.exe`and add it to your path.
-
-Find the last release [here][12].
-
-* For Linux, install [VirtualBox][8] or [KVM][9] then Kubectl and Minkube
-
-```
-curl -LO https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/$(curl -s https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/stable.txt)/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl
-```
-
-```
-chmod +x ./kubectl
-```
-
-```
-sudo mv ./kubectl /usr/local/bin/kubectl
-```
-
-```
-curl -Lo minikube https://storage.googleapis.com/minikube/releases/v0.21.0/minikube-linux-amd64 && chmod +x minikube && sudo mv minikube /usr/local/bin/
-```
-
-#### Using Minikube
-
-Let’s start by creating an image from this Dockerfile:
-
-```
-FROM busybox
-ADD index.html /www/index.html
-EXPOSE 8000
-CMD httpd -p 8000 -h /www; tail -f /dev/null
-```
-
-Add something you’d like to see in the index.html page.
-
-Build the image:
-
-```
-docker build -t eon01/hello-world-web-server .
-```
-
-Let’s run the container to test it:
-
-```
-docker run -d --name webserver -p 8000:8000 eon01/hello-world-web-server
-```
-
-This is the output of docker ps:
-
-```
-docker ps
-```
-
-```
-
-CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
-2ad8d688d812 eon01/hello-world-web-server "/bin/sh -c 'httpd..." 3 seconds ago Up 2 seconds 0.0.0.0:8000->8000/tcp webserver
-```
-
-Let’s commit the image and upload it to the public Docker Hub. You can use your own private registry:
-
-```
-docker commit webserver
-docker push eon01/hello-world-web-server
-```
-
-Remove the container since we will use it with Minikube
-
-```
-docker rm -f webserver
-```
-
-Time to start Minikube:
-
-```
-minkube start
-```
-
-Check the status:
-
-```
-minikube status
-```
-
-We are running a single node:
-
-```
-kubectl get node
-```
-
-Run the webserver:
-
-```
-kubectl run webserver --image=eon01/hello-world-web-server --port=8000
-```
-
-A webserver should have it’s port exposed:
-
-```
-kubectl expose deployment webserver --type=NodePort
-```
-
-In order to get the service url type:
-
-```
-minikube service webserver --url
-```
-
-We can see the content of the web page using :
-
-```
-curl $(minikube service webserver --url)
-```
-
-To show a summary of the running cluster run:
-
-```
-kubectl cluster-info
-```
-
-For more details:
-
-```
-kubectl cluster-info dump
-```
-
-We can also list the pods using:
-
-```
-kubectl get pods
-```
-
-And to access to the dashboard use:
-
-```
-minikube dashboard
-```
-
-If you would like to access the frontend of the web application type:
-
-```
-kubectl proxy
-```
-
-If we want to execute a command inside the container, get the pod id using:
-
-```
-kubetctl get pods
-```
-
-Then use it like :
-
-```
-kubectl exec webserver-2022867364-0v1p9 -it -- /bin/sh
-```
-
-To finish, delete all deployments:
-
-```
-kubectl delete deployments --all
-```
-
-Delete all pods:
-
-```
-kubectl delete pods --all
-```
-
-And stop Minikube
-
-```
-minikube stop
-```
-
-I hope you enjoyed this introduction.
-
-### Connect Deeper
-
-If you resonated with this article, you can find more interesting contents in [Painless Docker Course][13].
-
-We, [Eralabs][14], will be happy to help you on your Docker and Cloud Computing projects, [contact us][15] and we will be happy to hear about your projects.
-
-Please subscribe to [DevOpsLinks][16] : An Online Community Of Thousands Of IT Experts & DevOps Enthusiast From All Over The World.
-
-You may be also interested in joining our newsletter [Shipped][17], a newsletter focused on containers, orchestration and serverless technologies.
-
-You can find me on [Twitter][18], [Clarity][19] or my [website][20] and you can also check my books: [SaltStack For DevOps][21].
-
-Don’t forget to join my last project [Jobs For DevOps][22] !
-
-If you liked this post, please recommend it and share it with your followers.
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-作者简介:
-
-Aymen El Amri
-Cloud & Software Architect, Entrepreneur, Author, CEO www.eralabs.io, Founder www.devopslinks.com, Personal Page : www.aymenelamri.com
-
--------------------
-
-
-via: https://medium.com/devopslinks/using-kubernetes-minikube-for-local-development-c37c6e56e3db
-
-作者:[Aymen El Amri ][a]
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:https://medium.com/@eon01
-[1]:http://painlessdocker.com/
-[2]:https://git.k8s.io/minikube/docs/drivers.md#xhyve-driver
-[3]:https://www.virtualbox.org/wiki/Downloads
-[4]:https://www.vmware.com/products/fusion
-[5]:https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/stable.txt%29/bin/darwin/amd64/kubectl
-[6]:https://www.virtualbox.org/wiki/Downloads
-[7]:https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/virtualization/hyperv_on_windows/quick_start/walkthrough_install
-[8]:https://www.virtualbox.org/wiki/Downloads
-[9]:http://www.linux-kvm.org/
-[10]:http://painlessdocker.com/
-[11]:https://www.windows-commandline.com/set-path-command-line/
-[12]:https://github.com/kubernetes/minikube/releases
-[13]:http://painlessdocker.com/
-[14]:http://eralabs.io/
-[15]:http://eralabs.io/
-[16]:http://devopslinks.com/
-[17]:http://shipped.devopslinks.com/
-[18]:https://twitter.com/eon01
-[19]:https://clarity.fm/aymenelamri/
-[20]:http://aymenelamri.com/
-[21]:http://saltstackfordevops.com/
-[22]:http://jobsfordevops.com/
diff --git a/sources/tech/20170825 Happy anniversary Linux A look back at where it all began.md b/sources/tech/20170825 Happy anniversary Linux A look back at where it all began.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 87eb7d4e6b..0000000000
--- a/sources/tech/20170825 Happy anniversary Linux A look back at where it all began.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,199 +0,0 @@
-Happy anniversary, Linux: A look back at where it all began
-============================================================
-Translating by softpaopao
-
-### Installing SLS 1.05 shows just how far the Linux kernel has come in 26 years.
-
-
-Image by : [litlnemo][25]. Modified by Opensource.com. [CC BY-SA 2.0.][26]
-
-I first installed Linux in 1993\. I ran MS-DOS at the time, but I really liked the Unix systems in our campus computer lab, where I spent much of my time as an undergraduate university student. When I heard about Linux, a free version of Unix that I could run on my 386 computer at home, I immediately wanted to try it out. My first Linux distribution was [Softlanding Linux System][27] (SLS) 1.03, with Linux kernel 0.99 alpha patch level 11\. That required a whopping 2MB of RAM, or 4MB if you wanted to compile programs, and 8MB to run X windows.
-
-More Linux resources
-
-* [What is Linux?][1]
-
-* [What are Linux containers?][2]
-
-* [Download Now: Linux commands cheat sheet][3]
-
-* [Advanced Linux commands cheat sheet][4]
-
-* [Our latest Linux articles][5]
-
-I thought Linux was a huge step up from the world of MS-DOS. While Linux lacked the breadth of applications and games available on MS-DOS, I found Linux gave me a greater degree of flexibility. Unlike MS-DOS, I could now do true multi-tasking, running more than one program at a time. And Linux provided a wealth of tools, including a C compiler that I could use to build my own programs.
-
-A year later, I upgraded to SLS 1.05, which sported the brand-new Linux kernel 1.0\. More importantly, Linux 1.0 introduced kernel modules. With modules, you no longer needed to completely recompile your kernel to support new hardware; instead you loaded one of the 63 included Linux kernel modules. SLS 1.05 included this note about modules in the distribution's README file:
-
-> Modularization of the kernel is aimed squarely at reducing, and eventually eliminating, the requirements for recompiling the kernel, either for changing/modifying device drivers or for dynamic access to infrequently required drivers. More importantly, perhaps, the efforts of individual working groups need no longer affect the development of the kernel proper. In fact, a binary release of the official kernel should now be possible.
-
-On August 25, the Linux kernel will reach its 26th anniversary. To celebrate, I reinstalled SLS 1.05 to remind myself what the Linux 1.0 kernel was like and to recognize how far Linux has come since the 1990s. Join me on this journey into Linux nostalgia!
-
-### Installation
-
-Softlanding Linux System was the first true "distribution" that included an install program. Yet the install process isn't the same smooth process you find in modern distributions. Instead of booting from an install CD-ROM, I needed to boot my system from an install floppy, then run the install program from the **login** prompt.
-
-### [install1.png][6]
-
-
-
-A neat feature introduced in SLS 1.05 was the color-enabled text-mode installer. When I selected color mode, the installer switched to a light blue background with black text, instead of the plain white-on-black text used by our primitive forbearers.
-
-### [install2.png][7]
-
-
-
-The SLS installer is a simple affair, scrolling text from the bottom of the screen, but it does the job. By responding to a few simple prompts, I was able to create a partition for Linux, put an ext2 filesystem on it, and install Linux. Installing SLS 1.05, including X windows and development tools, required about 85MB of disk space. That may not sound like much space by today's standards, but when Linux 1.0 came out, 120MB hard drives were still common.
-
-### [install10.png][8]
-
-
-
-### [firstboot1.png][9]
-
-
-
-### System level
-
-When I first booted into Linux, my memory triggered a few system things about this early version of Linux. First, Linux doesn't take up much space. After booting the system and running a few utilities to check it out, Linux occupied less than 4MB of memory. On a system with 16MB of memory, that meant lots left over to run programs.
-
-### [uname-df.png][10]
-
-
-
-The familiar **/proc** meta filesystem exists in Linux 1.0, although it doesn't provide much information compared to what you see in modern systems. In Linux 1.0, **/proc** includes interfaces to probe basic system statistics like **meminfo** and **stat**.
-
-### [proc.png][11]
-
-
-
-The **/etc** directory on this system is pretty bare. Notably, SLS 1.05 borrows the **rc** scripts from [BSD Unix][28] to control system startup. Everything gets started via **rc**scripts, with local system changes defined in the **rc.local** file. Later, most Linux distributions would adopt the more familiar **init** scripts from [Unix System V][29], then the [systemd][30] initialization system.
-
-### [etc.png][12]
-
-
-
-### What you can do
-
-With my system up and running, it was time to get to work. So, what can you do with this early Linux system?
-
-Let's start with basic file management. Every time you log in, SLS reminds you about the Softlanding menu shell (MESH), a file-management program that modern users might recognize as similar to [Midnight Commander][31]. Users in the 1990s would have compared MESH more closely to [Norton Commander][32], arguably the most popular third-party file manager available on MS-DOS.
-
-### [mesh.png][13]
-
-")
-
-Aside from MESH, there are relatively few full-screen applications included with SLS 1.05\. But you can find the familiar user tools, including the Elm mail reader, the GNU Emacs programmable editor, and the venerable Vim editor.
-
-### [elm.png][14]
-
-
-
-### [emacs19.png][15]
-
-
-
-SLS 1.05 even included a version of Tetris that you could play at the terminal.
-
-### [tetris.png][16]
-
-
-
-In the 1990s, most residential internet access was via dial-up connections, so SLS 1.05 included the Minicom modem-dialer application. Minicom provided a direct connection to the modem and required users to navigate the Hayes modem **AT** commands to do basic functions like dial a number or hang up the phone. Minicom also supported macros and other neat features to make it easier to connect to your local modem pool.
-
-### [minicom.png][17]
-
-
-
-But what if you wanted to write a document? SLS 1.05 existed long before the likes of LibreOffice or OpenOffice. Linux just didn't have those applications in the early 1990s. Instead, if you wanted to use a word processor, you likely booted your system into MS-DOS and ran your favorite word processor program, such as WordPerfect or the shareware GalaxyWrite.
-
-But all Unix systems include a set of simple text formatting programs, called nroff and troff. On Linux systems, these are combined into the GNU groff package, and SLS 1.05 includes a version of groff. One of my tests with SLS 1.05 was to generate a simple text document using nroff.
-
-### [paper-me-emacs.png][18]
-
-
-
-### [paper-me-out.png][19]
-
-
-
-### Running X windows
-
-Getting X windows to perform was not exactly easy, as the SLS install file promised:
-
-> Getting X windows to run on your PC can sometimes be a bit of a sobering experience, mostly because there are so many types of video cards for the PC. Linux X11 supports only VGA type video cards, but there are so many types of VGAs that only certain ones are fully supported. SLS comes with two X windows servers. The full color one, XFree86, supports some or all ET3000, ET4000, PVGA1, GVGA, Trident, S3, 8514, Accelerated cards, ATI plus, and others.
->
-> The other server, XF86_Mono, should work with virtually any VGA card, but only in monochrome mode. Accordingly, it also uses less memory and should be faster than the color one. But of course it doesn't look as nice.
->
-> The bulk of the X windows configuration information is stored in the directory "/usr/X386/lib/X11/". In particular, the file "Xconfig" defines the timings for the monitor and the video card. By default, X windows is set up to use the color server, but you can switch to using the monochrome server x386mono, if the color one gives you trouble, since it should support any standard VGA. Essentially, this just means making /usr/X386/bin/X a link to it.
->
-> Just edit Xconfig to set the mouse device type and timings, and enter "startx".
-
-If that sounds confusing, it is. Configuring X windows by hand really can be a sobering experience. Fortunately, SLS 1.05 included the syssetup program to help you define various system components, including display settings for X windows. After a few prompts, and some experimenting and tweaking, I was finally able to launch X windows!
-
-### [syssetup.png][20]
-
-
-
-But this is X windows from 1994, and the concept of a desktop didn't exist yet. My options were either FVWM (a virtual window manager) or TWM (the tabbed window manager). TWM was straightforward to set up and provided a simple, yet functional, graphical environment.
-
-### [twm_720.png][21]
-
-
-
-### Shutdown
-
-As much as I enjoyed exploring my Linux roots, eventually it was time to return to my modern desktop. I originally ran Linux on a 32-bit 386 computer with just 8MB of memory and a 120MB hard drive, and my system today is much more powerful. I can do so much more on my dual-core, 64-bit Intel Core i5 CPU with 4GB of memory and a 128GB solid-state drive running Linux kernel 4.11.11\. So, after my experiments with SLS 1.05 were over, it was time to leave.
-
-### [shutdown-h.png][22]
-
-
-
-So long, Linux 1.0\. It's good to see how well you've grown up.
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: https://opensource.com/article/17/8/linux-anniversary
-
-作者:[Jim Hall ][a]
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:https://opensource.com/users/jim-hall
-[1]:https://opensource.com/resources/what-is-linux?intcmp=70160000000h1jYAAQ&utm_source=intcallout&utm_campaign=linuxcontent
-[2]:https://opensource.com/resources/what-are-linux-containers?intcmp=70160000000h1jYAAQ&utm_source=intcallout&utm_campaign=linuxcontent
-[3]:https://developers.redhat.com/promotions/linux-cheatsheet/?intcmp=70160000000h1jYAAQ&utm_source=intcallout&utm_campaign=linuxcontent
-[4]:https://developers.redhat.com/cheat-sheet/advanced-linux-commands-cheatsheet?intcmp=70160000000h1jYAAQ&utm_source=intcallout&utm_campaign=linuxcontent
-[5]:https://opensource.com/tags/linux?intcmp=70160000000h1jYAAQ&utm_source=intcallout&utm_campaign=linuxcontent
-[6]:https://opensource.com/file/365166
-[7]:https://opensource.com/file/365171
-[8]:https://opensource.com/file/365176
-[9]:https://opensource.com/file/365161
-[10]:https://opensource.com/file/365221
-[11]:https://opensource.com/file/365196
-[12]:https://opensource.com/file/365156
-[13]:https://opensource.com/file/365181
-[14]:https://opensource.com/file/365146
-[15]:https://opensource.com/file/365151
-[16]:https://opensource.com/file/365211
-[17]:https://opensource.com/file/365186
-[18]:https://opensource.com/file/365191
-[19]:https://opensource.com/file/365226
-[20]:https://opensource.com/file/365206
-[21]:https://opensource.com/file/365236
-[22]:https://opensource.com/file/365201
-[23]:https://opensource.com/article/17/8/linux-anniversary?rate=XujKSFS7GfDmxcV7Jf_HUK_MdrW15Po336fO3G8s1m0
-[24]:https://opensource.com/user/126046/feed
-[25]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/litlnemo/19777182/
-[26]:https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.0/
-[27]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Softlanding_Linux_System
-[28]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Berkeley_Software_Distribution
-[29]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/UNIX_System_V
-[30]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Systemd
-[31]:https://midnight-commander.org/
-[32]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Norton_Commander
-[33]:https://opensource.com/users/jim-hall
-[34]:https://opensource.com/users/jim-hall
-[35]:https://opensource.com/article/17/8/linux-anniversary#comments
diff --git a/sources/tech/20170905 Maneuvering around run levels on Linux.md b/sources/tech/20170905 Maneuvering around run levels on Linux.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..605d5a058d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/tech/20170905 Maneuvering around run levels on Linux.md
@@ -0,0 +1,180 @@
+@penghuster is translating
+
+Maneuvering around run levels on Linux
+============================================================
+
+### Learn how run levels are configured and how you can change the run level interactively or modify what services are available.
+
+
+[Vincent Desjardins][15] [(CC BY 2.0)][16]
+
+
+On Linux systems, run levels are operational levels that describe the state of the system with respect to what services are available.
+
+One run level is restrictive and used only for maintenance; network connections will not be operational, but admins can log in through a console connection.
+
+Others allow anyone to log in and work, but maybe with some differences in the available services. This post examines how run levels are configured and how you can change the run level interactively or modify what services are available.
+
+The default run state on Linux systems — the one that will be used when the system starts up (unless instructed otherwise) — is usually configured in the **/etc/inittab** file, which generally looks something like this:
+
+```
+id:3:initdefault:
+```
+
+Some, including Debian systems, default to run state 2, rather than 3, and don’t generally have an /etc/inittab file at all.
+
+How run levels are set up by default and how they are configured depends in part on the particular distribution you are running. On some systems, for example, run level 2 is multi-user, and run level 3 is multi-user with NFS (file system sharing) support. On others, run levels 2-5 are basically identical. Run level 1 is single-user mode. Run levels on Debian systems, for example, will default to this kind of setup:
+
+Run levels on Debian systems default to this kind of setup:
+
+```
+0 = halted
+1 = single user (maintenance mode)
+2 = multi-user mode
+3-5 = same as 2
+6 = reboot
+```
+
+On Linux systems that use run level 3 to share file systems with other systems, it easy to start or stop file system sharing without changing anything about the system but the run level. Changing run level from 2 to 3 would allow the file systems to be shared. Changing the run level from 3 to 2 would disable sharing.
+
+<aside class="nativo-promo tablet desktop" id="" style="overflow: hidden; margin-bottom: 16px; max-width: 620px;"></aside>
+
+What processes are run in any run level depends on the contents of the /etc/rc?.d directory where ? might be 2, 3, 4, or 5 (corresponding to the run level).
+
+On the system used in the example below (an Ubuntu system), we can see that the content of the directories for these four run states are all set up the same — because the configuration of the directories are the same.
+
+```
+/etc/rc2.d$ ls
+README S20smartmontools S50saned S99grub-common
+S20kerneloops S20speech-dispatcher S70dns-clean S99ondemand
+S20rsync S20sysstat S70pppd-dns S99rc.local
+/etc/rc2.d$ cd ../rc3.d
+/etc/rc3.d$ ls
+README S20smartmontools S50saned S99grub-common
+S20kerneloops S20speech-dispatcher S70dns-clean S99ondemand
+S20rsync S20sysstat S70pppd-dns S99rc.local
+/etc/rc3.d$ cd ../rc4.d
+/etc/rc4.d$ ls
+README S20smartmontools S50saned S99grub-common
+S20kerneloops S20speech-dispatcher S70dns-clean S99ondemand
+S20rsync S20sysstat S70pppd-dns S99rc.local
+/etc/rc4.d$ cd ../rc5.d
+/etc/rc5.d$ ls
+README S20smartmontools S50saned S99grub-common
+S20kerneloops S20speech-dispatcher S70dns-clean S99ondemand
+S20rsync S20sysstat S70pppd-dns S99rc.local
+```
+
+And what are these files? They’re all symbolic links that point to scripts in the /etc/init.d directory that start services. And the names of the files are important because they determine the order in which the scripts are run. For example, S20 scripts are run before S50 scripts.
+
+```
+$ ls -l
+total 4
+-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 677 Feb 16 2016 README
+lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 20 Aug 30 14:40 S20kerneloops -> ../init.d/kerneloops
+lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 15 Aug 30 14:40 S20rsync -> ../init.d/rsync
+lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 23 Aug 30 16:10 S20smartmontools -> ../init.d/smartmontools
+lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 27 Aug 30 14:40 S20speech-dispatcher -> ../init.d/speech-dispatcher
+lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 17 Aug 31 14:12 S20sysstat -> ../init.d/sysstat
+lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 15 Aug 30 14:40 S50saned -> ../init.d/saned
+lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 19 Aug 30 14:40 S70dns-clean -> ../init.d/dns-clean
+lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 18 Aug 30 14:40 S70pppd-dns -> ../init.d/pppd-dns
+lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 21 Aug 30 14:40 S99grub-common -> ../init.d/grub-common
+lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 18 Aug 30 14:40 S99ondemand -> ../init.d/ondemand
+lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 18 Aug 30 14:40 S99rc.local -> ../init.d/rc.local
+```
+
+The /etc/rc1.d directory, as you’d probably suspect, is different because run level 1 is so different. It contains symbolic links that point to a very different set of scripts. Notice, too, that some of the symbolic links start with the letter K, while others start with the more normal S. This is because some services need to **_stop_** when a system enters single user mode. While some of these links point to the same scripts that are used in other run levels, the K (kill) indicates that these scripts will be run with an argument that instructs the services to stop rather than one that instructs them to start.
+
+```
+/etc/rc1.d$ ls -l
+total 4
+lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 20 Aug 30 14:40 K20kerneloops -> ../init.d/kerneloops
+lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 15 Aug 30 14:40 K20rsync -> ../init.d/rsync
+lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 15 Aug 30 14:40 K20saned -> ../init.d/saned
+lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 23 Aug 30 16:10 K20smartmontools -> ../init.d/smartmontools
+lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 27 Aug 30 14:40 K20speech-dispatcher -> ../init.d/speech-dispatcher
+-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 369 Mar 12 2014 README
+lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 19 Aug 30 14:40 S30killprocs -> ../init.d/killprocs
+lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 19 Aug 30 14:40 S70dns-clean -> ../init.d/dns-clean
+lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 18 Aug 30 14:40 S70pppd-dns -> ../init.d/pppd-dns
+lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 16 Aug 30 14:40 S90single -> ../init.d/single
+```
+
+You can change the default run level on a system, though there is rarely a need to do so. For example, you could configure a Debian system to default to a run level of 3 (rather than 2) by setting up an /etc/inittab file that looks, for example, like this one:
+
+```
+id:3:initdefault:
+```
+
+Once you make the change and reboot, the runlevel command would show you this:
+
+```
+$ runlevel
+N 3
+```
+
+Alternately, if you used the **init 3** command, you would also change run levels (rebooting is not required to change run states) and your runlevel output would look like this:
+
+```
+$ runlevel
+2 3
+```
+
+Of course, there’s little reason to change your default state by creating or modifying **/etc/inittab** unless you modify the symbolic links in the corresponding /etc/rc?.d directory to differentiate what will be running in the modified run state.
+
+### How to use run levels on Linux
+
+To recap, here's a quick Q&A on run levels:
+
+#### How do you tell what run level you are in?
+
+Use the **runlevel** command.
+
+#### How do you see what processes are associated with a particular run level?
+
+Look at the associated run level start directory (e.g., /etc/rc2.d for run level 2).
+
+#### How do you know what the default run level is?
+
+Check **/etc/inittab** if it exists. If not, just ask runlevel. You’re likely already in that run level.
+
+#### How do you change run levels?
+
+Use the **init** command (e.g., init 3) to change it temporarily. Modify or set up /etc/inittab to make a permanent change.
+
+#### Can you change what services run in some particular run level?
+
+Of course — by modifying the symbolic links in the associated /etc/rc?.d directory.
+
+#### What else should you consider?
+
+You should always exercise some caution when changing run levels on a Linux server to ensure that you’re not going to be affecting services that are currently in use or users who are logged in.
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://www.networkworld.com/article/3222070/linux/maneuvering-around-run-levels-on-linux.html
+
+作者:[Sandra Henry-Stocker][a]
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:https://www.networkworld.com/author/Sandra-Henry_Stocker/
+[1]:https://www.networkworld.com/article/3218728/linux/how-log-rotation-works-with-logrotate.html
+[2]:https://www.networkworld.com/article/3219684/linux/half-a-dozen-clever-linux-command-line-tricks.html
+[3]:https://www.networkworld.com/article/3219736/linux/how-to-use-the-motd-file-to-get-linux-users-to-pay-attention.html
+[4]:https://www.networkworld.com/video/51206/solo-drone-has-linux-smarts-gopro-mount
+[5]:https://www.networkworld.com/article/3222828/home-tech/52-off-299-piece-all-purpose-first-aid-kit-deal-alert.html
+[6]:https://www.networkworld.com/article/3222847/mobile/save-a-whopping-100-on-amazon-echo-right-now-by-going-refurbished-deal-alert.html
+[7]:https://www.networkworld.com/article/3221348/mobile/35-off-etekcity-smart-plug-2-pack-energy-monitoring-and-alexa-compatible-deal-alert.html
+[8]:https://www.networkworld.com/article/3218728/linux/how-log-rotation-works-with-logrotate.html
+[9]:https://www.networkworld.com/article/3219684/linux/half-a-dozen-clever-linux-command-line-tricks.html
+[10]:https://www.networkworld.com/article/3219736/linux/how-to-use-the-motd-file-to-get-linux-users-to-pay-attention.html
+[11]:https://www.networkworld.com/video/51206/solo-drone-has-linux-smarts-gopro-mount
+[12]:https://www.networkworld.com/video/51206/solo-drone-has-linux-smarts-gopro-mount
+[13]:https://www.networkworld.com/article/3222847/mobile/save-a-whopping-100-on-amazon-echo-right-now-by-going-refurbished-deal-alert.html
+[14]:https://www.networkworld.com/article/3221348/mobile/35-off-etekcity-smart-plug-2-pack-energy-monitoring-and-alexa-compatible-deal-alert.html
+[15]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/endymion120/4824696883/in/photolist-8mkQi2-8vtyRx-8vvYZS-i31xQj-4TXTS2-S7VRNC-azimYK-dW8cYu-Sb5b7S-S7VRES-fpSVvo-61Zpn8-WxFwGi-UKKq3x-q6NSnC-8vsBLr-S3CPxn-qJUrLr-nDnpNu-8d7a6Q-T7mGpN-RE26wj-SeEXRa-5mZ7LG-Vp7t83-fEG5HS-Vp7sU7-6JpNBi-RCuR8P-qLzCL5-6WsfZx-5nU1tF-6ieGFi-3P5xwh-8mnxpo-hBXwSj-i3iCur-9dmrST-6bXk8d-8vtDb4-i2KLwU-5jhfU6-8vwbrN-ShAtNm-XgzXmb-8rad18-VfXm4L-8tQTrh-Vp7tcb-UceVDB
+[16]:https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0/legalcode
diff --git a/sources/tech/20170906 The Incredible Growth of Python.md b/sources/tech/20170906 The Incredible Growth of Python.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..d24f766147
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/tech/20170906 The Incredible Growth of Python.md
@@ -0,0 +1,96 @@
+The Incredible Growth of Python
+============================================================
+
+We [recently explored][3] how wealthy countries (those defined as [high-income][4] by the World Bank) tend to visit a different set of technologies than the rest of the world. Among the largest differences we saw was in the programming language Python. When we focus on high-income countries, the growth of Python is even larger than it might appear from tools like [Stack Overflow Trends][5], or in other rankings that consider global software development.
+
+In this post, we’ll explore the extraordinary growth of the Python programming language in the last five years, as seen by Stack Overflow traffic within high-income countries. The term “fastest-growing” can be [hard to define precisely][6], but we make the case that Python has a solid claim to being the fastest-growing major programming language.
+
+All the numbers discussed in this post are for high-income countries; they’re generally representative of trends in the United States, United Kingdom, Germany, Canada, and other such countries, which in combination make up about 64% of Stack Overflow’s traffic. Many other countries such as India, Brazil, Russia, and China also make enormous contributions to the global software development ecosystem, and this post is less descriptive of those economies, though we’ll see that Python has shown growth there as well.
+
+It’s worth emphasizing up front that the number of users of a language isn’t a measure of the language’s quality: we’re _describing_ the languages developers use, but not prescribing anything. (Full disclosure: I [used to program][7]primarily in Python, though I have since switched entirely to R).
+
+### Python’s growth in high-income countries
+
+You can see on [Stack Overflow Trends][8] that Python has been growing rapidly in the last few years. But for this post we’ll focus on high-income countries, and consider visits to questions rather than questions asked (this tends to give similar results, but has less month-by-month noise, especially for smaller tags).
+
+We have data on Stack Overflow question views going back to late 2011, and in this time period we can consider the growth of Python relative to five other major programming languages. (Note that this is therefore a shorter time scale than the Trends tool, which goes back to 2008). These are currently six of the ten most-visited Stack Overflow tags in high-income countries; the four we didn’t include are CSS, HTML, Android, and JQuery.
+
+
+
+June 2017 was the first month that Python was the most visited tag on Stack Overflow within high-income nations. This included being the most visited tag within the US and the UK, and in the top 2 in almost all other high income nations (next to either Java or JavaScript). This is especially impressive because in 2012, it was less visited than any of the other 5 languages, and has grown by 2.5-fold in that time.
+
+Part of this is because of the seasonal nature of traffic to Java. Since it’s [heavily taught in undergraduate courses][9], Java traffic tends to rise during the fall and spring and drop during the summer. Will it catch up with Python again by the end of the year? We can try forecasting the next two years of growth with a [model called “STL”][10], which combines growth with seasonal trends to make a prediction about future values.
+
+
+
+According to this model, Python could either stay in the lead or be overtaken by Java in the fall (it’s roughly within the variation of the model’s predictions), but it’s clearly on track to become the most visited tag in 2018\. STL also suggests that JavaScript and Java will remain at similar levels of traffic among high income countries, just as they have for the last two years.
+
+### What tags are growing the fastest overall?
+
+The above was looking only at the six most-visited programming languages. Among other notable technologies, which are currently growing the fastest in high-income countries?
+
+We defined the growth rate in terms of the ratio between 2017 and 2016 share of traffic. We decided to consider only programming languages (like Java and Python) and platforms (such as iOS, Android, Windows and Linux) in this analysis, as opposed to frameworks like [Angular][11] or libraries like [TensorFlow][12] (although many of those showed notable growth that may be examined in a future post).
+
+Because of the challenges in defining “fastest-growing” described in [this comic][13], we compare the growth to the overall average in a [mean-difference plot][14].
+
+
+
+With a 27% year-over year-growth rate, Python stands alone as a tag that is both large and growing rapidly; the next-largest tag that shows similar growth is R. We see that traffic to most other large tags has stayed pretty steady within high-income countries, with visits to Android, iOS, and PHP decreasing slightly. We previously examined some of the shrinking tags like Objective-C, Perl and Ruby in our [post on the death of Flash][15]). We can also notice that among functional programming languages, Scala is the largest and growing, while F# and Clojure are smaller and shrinking, with Haskell in between and remaining steady.
+
+There’s an important omission from the above chart: traffic to TypeScript questions grew by an impressive 142% in the last year, enough that we left it off to avoid overwhelming the rest of the scale. You can also see that some other smaller languages are growing similarly or faster than Python (like R, Go and Rust), and there are a number of tags like Swift and Scala that are also showing impressive growth. How does their traffic over time compare to Python’s?
+
+
+
+The growth of languages like R and Swift is indeed impressive, and TypeScript has shown especially rapid expansion in an even shorter time. Many of these smaller languages grew from getting almost no question traffic to become notable presences in the software ecosystem. But as this graph shows, it’s easier to show rapid growth when a tag started relatively small.
+
+Note that we’re not saying these languages are in any way “competing” with Python. Rather, we’re explaining why we’d treat their growth in a separate category; these were lower-traffic tags to start with. Python is an unusual case for being both one of the most visited tags on Stack Overflow and one of the fastest-growing ones. (Incidentally, it is also accelerating! Its year-over-year growth has become faster each year since 2013).
+
+### Rest of the world
+
+So far in this post we’ve been analyzing the trends in high-income countries. Does Python show a similar growth in the rest of the world, in countries like India, Brazil, Russia and China?
+
+Indeed it does.
+
+
+
+Outside of high-income countries Python is _still_ the fastest growing major programming language; it simply started at a lower level and the growth began two years later (in 2014 rather than 2012). In fact, the year-over-year growth rate of Python in non-high-income countries is slightly _higher_ than it is in high-income countries. We don’t examine it here, but R, the [other language whose usage is positively correlated with GDP][16], is growing in these countries as well.
+
+Many of the conclusions in this post about the growth and decline of tags (as opposed to the absolute rankings) in high-income countries hold true for the rest of the world; there’s a 0.979 Spearman correlation between the growth rates in the two segments. In some cases, you can see a “lagging” phenomenon similar to what happened with Python, where a technology was widely adopted within high-income countries a year or two before it expanded in the rest of the world. (This is an interesting phenomenon and may be the subject of a future blog post!)
+
+### Next time
+
+We’re not looking to contribute to any “language war.” The number of users of a language doesn’t imply anything about its quality, and certainly can’t tell you which language is [more appropriate for a particular situation][17]. With that perspective in mind, however, we believe it’s worth understanding what languages make up the developer ecosystem, and how that ecosystem might be changing.
+
+This post demonstrated that Python has shown a surprising growth in the last five years, especially within high-income countries. In our next post, we’ll start to explore the _“why”_ . We’ll segment the growth by country and by industry, and examine what other technologies tend to be used alongside Python (to estimate, for example, how much of the growth has been due to increased usage of Python for web development versus for data science).
+
+In the meantime, if you work in Python and are looking to take the next step in your career, here are [some companies hiring Python developers right now on Stack Overflow Jobs][18].
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://stackoverflow.blog/2017/09/06/incredible-growth-python/?cb=1
+
+作者:[David Robinson][a]
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:https://stackoverflow.blog/authors/drobinson/
+[1]:https://stackoverflow.blog/authors/drobinson/
+[2]:https://stackoverflow.blog/authors/drobinson/
+[3]:https://stackoverflow.blog/2017/08/29/tale-two-industries-programming-languages-differ-wealthy-developing-countries/?utm_source=so-owned&utm_medium=blog&utm_campaign=gen-blog&utm_content=blog-link&utm_term=incredible-growth-python
+[4]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/World_Bank_high-income_economy
+[5]:https://insights.stackoverflow.com/trends?tags=python%2Cjavascript%2Cjava%2Cc%23%2Cphp%2Cc%2B%2B&utm_source=so-owned&utm_medium=blog&utm_campaign=gen-blog&utm_content=blog-link&utm_term=incredible-growth-python
+[6]:https://xkcd.com/1102/
+[7]:https://stackoverflow.com/search?tab=newest&q=user%3a712603%20%5bpython%5d
+[8]:https://insights.stackoverflow.com/trends?tags=python%2Cjavascript%2Cjava%2Cc%23%2Cphp%2Cc%2B%2B&utm_source=so-owned&utm_medium=blog&utm_campaign=gen-blog&utm_content=blog-link&utm_term=incredible-growth-python
+[9]:https://stackoverflow.blog/2017/02/15/how-do-students-use-stack-overflow/
+[10]:http://otexts.org/fpp2/sec-6-stl.html
+[11]:https://stackoverflow.com/questions/tagged/angular
+[12]:https://stackoverflow.com/questions/tagged/tensorflow
+[13]:https://xkcd.com/1102/
+[14]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bland%E2%80%93Altman_plot
+[15]:https://stackoverflow.blog/2017/08/01/flash-dead-technologies-might-next/?utm_source=so-owned&utm_medium=blog&utm_campaign=gen-blog&utm_content=blog-link&utm_term=incredible-growth-python
+[16]:https://stackoverflow.blog/2017/08/29/tale-two-industries-programming-languages-differ-wealthy-developing-countries/?utm_source=so-owned&utm_medium=blog&utm_campaign=gen-blog&utm_content=blog-link&utm_term=incredible-growth-python
+[17]:https://stackoverflow.blog/2011/08/16/gorilla-vs-shark/?utm_source=so-owned&utm_medium=blog&utm_campaign=gen-blog&utm_content=blog-link&utm_term=incredible-growth-python
+[18]:https://stackoverflow.com/jobs/developer-jobs-using-python?utm_source=so-owned&utm_medium=blog&utm_campaign=gen-blog&utm_content=blog-link&utm_term=incredible-growth-python
diff --git a/translated/talk/20170310 How to use pull requests to improve your code reviews.md b/translated/talk/20170310 How to use pull requests to improve your code reviews.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..ffe2ccb430
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/talk/20170310 How to use pull requests to improve your code reviews.md
@@ -0,0 +1,95 @@
+如何使用 pull requests 来改善你的代码审查
+============================================================
+
+在 Github 上使用 pull requests 来做代码审查,花费更多的时间去构建,而更少的时间去修改。
+
+ 
+
+
+>看看 Brent 和 Peter’s 的[ _Introducing GitHub_ ][5]的书, 了解更多有关创建项目,开始 pull requests 和团队软件开发流程的概述。
+
+
+如果你每天不编写代码,你可能不知道软件开发人员每天面临的一些问题。
+
+* 代码中的安全漏洞
+* 导致应用程序崩溃的代码
+* 被称作 “技术债务” 和之后需要重写的代码
+* 已经重写在你所不知道地方的代码
+
+
+代码审查可以允许其他人和工具检查来帮助我们改善所编写的软件。这种审查通过自动化代码分析或者测试覆盖工具来进行软件开发过程中重要的二个部分,节省数小时的手工劳动或同行评审。同行的审查是开发人员审查彼此工作的过程。在软件开发的过程中,速度和紧迫性是经常面临的问题中二个重要的部分。如果你没有尽快的发布,你的竞争对手可能会在你之前发布相似的产品。如果你不经常发不新的版本,你的用户可能会怀疑您是否仍然关心你的应用程序的改进优化。
+
+### 衡量时间权衡:代码审查 vs. bug 修复
+
+如果有人能够以最小争议的方式汇集多种类型的代码审查,那么随着时间的推移,该软件的质量将会得到改善。认为引入新的工具或流程在最初不会推迟时间,这是天真的想法。但是更昂贵的是:修复生产中的错误的时候,在还是软件生产之前改进软件,即使新工具延迟了时间,客户可以发布和欣赏新功能,随着软件开发人员提高自己的技能,软件开发周期将会回升到以前的水平,同时应该减少错误。
+
+通过代码审查实现提升代码质量目标的关键之一就是使用一个足够灵活的平台,允许软件开发人员快速编写代码,使用他们熟悉的工具,并行彼此进行同行评审码。 GitHub 就是这样一个平台的。然而,把你的代码放在 [GitHub][9] 上并不只是神奇地使代码审查发生; 你必须使用 pull requests ,来开始这个美妙的旅程。
+
+### Pull requests: 一个代码的生活讨论的工具
+
+[Pull requests][10] 是 Github 上的一个工具,允许软件开发人员讨论并提出对项目的主要代码库的更改,稍后可以让所用用户看到。它们在 2008 年 2 月创建的,目的是在接受(合并)某人之前的建议进行更改,然后在部署到生产中,供最终用户看到这种变化。
+
+Pull requests 开始是一种松散的方式为某人的项目提供改变,但是它已经演变成:
+
+* 关于你想要合并的代码的生活讨论
+* 增加功能,这种可见性的修改(更改)
+* 整合你最喜爱的工具
+* 作为受保护的分支工作流程的一部分可能需要显式提取请求评估
+
+### 考虑带代码: URL 是永久的
+
+看看上面的前两个点,pull requests 促成了一个正在进行的代码讨论,使代码变化非常明显,并且使您很容易在回顾的过程中找到所需的代码。对于新人和有经验的开发人员来说,能够回顾以前的讨论,了解为什么一个功能被开发出来,或者与另一个关于相关功能的讨论这样的联系方式是便捷的。当跨多个项目协调功能并使每个人尽可能接近代码时,前后讨论的内容也非常重要。如果这些功能仍在开发中,重要的是能够看到上次审查以来更改了哪些内容。毕竟,[对小的更改比大的修改要容易得多][11],但大的功能并不总是可能的。因此,重要的是能够拿起你上次审查,并只看到从那时以来的变化。
+
+### 集成工具: 软件开发人员的建议
+
+考虑到上述第三点,GitHub 上的 pull requests 有很多功能,但开发人员将始终对第三方工具有偏好。代码质量是代码审查的整个领域,涉及到其他组件的代码评审,而这些评审不一定是人的。检测“低效”或缓慢、潜在的安全漏洞或不符合公司标准的代码是留给自动化工具的任务。
+[SonarQube][12] 和 [Code Climatecan][13] 分析你的代码的工具,而像 [Codecov][14] 和 [Coveralls][15] 的工具可以告诉你如果你只是写新代码没有得到很好的测试。这些令人惊奇工具最大的特点就是,他们可以插到 GitHub 和 pull requests 报告他们的发现!这意味着不仅让人们检查代码,而且工具也在那里报告情况。每个人都可以停留在一个如何发展循环中的功能。
+
+最后,根据您的团队的偏好,您可以利用[受保护的分支工作流][16]所需的状态特性来进行工具和同行评审。
+
+虽然您可能只是开始您的软件开发之旅,一个希望知道一个项目正在做什么的业务利益相关者,或者是想要确保项目的及时性和质量的项目经理,可以通过设置参与 pull requests 批准工作流程,并考虑与其他工具集成以确保质量,在任何级别的软件开发中都很重要。
+
+无论是为您的个人网站,贵公司的在线商店,还是最新的组合,以最大的收益收获今年的玉米,编写好的软件都需要进行良好的代码审查。良好的代码审查涉及到正确的工具和平台。要了解有关 GitHub 和软件开发过程的更多信息,请参阅 O'Reilly 的 [ _GitHub 简介_ ][17] 一书, 您可以在其中了解创建项目,启动拉取请求以及概述团队的“软件开发流程”。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+作者简介:
+
+**Brent Beer**
+
+Brent Beer 使用 Git 和 GitHub 已经超过五年了,通过大学的课程,对开源项目的贡献,以及专业网站开发人员。在担任 GitHub 上的培训师时,他也成为 O’Reilly 的 “GitHub简介” 的出版作者。他现在担任 Amsterdam GitHub 上的解决方案工程师,帮助 Git 和 GitHub 向世界各地的开发人员提供服务。
+
+**Peter Bell**
+
+Peter Bell 是 Ronin 实验室的创始人以及 CTO。Training is broken - we're fixing it through technology enhanced training!他是一位有经验的企业家,技术专家,敏捷教练和CTO,专门从事 EdTech 项目。他为 O'Reilly 撰写了 “ GitHub 简介” ,为代码学校创建了“掌握 GitHub ”课程,为 Pearson 创建了“ Git 和 GitHub LiveLessons ”课程。他经常在国际和国际会议上提供 ruby , nodejs , NoSQL (尤其是 MongoDB 和 neo4j ),云计算,软件工艺,java,groovy,j ...
+
+-------------
+
+
+via: https://www.oreilly.com/ideas/how-to-use-pull-requests-to-improve-your-code-reviews?imm_mid=0ee8ca&cmp=em-prog-na-na-newsltr_20170311
+
+作者:[Brent Beer][a],[Peter Bell][b]
+译者:[MonkeyDEcho](https://github.com/MonkeyDEcho)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:https://www.oreilly.com/people/acf937de-cdf4-4b0e-85bd-b559404c580e
+[b]:https://www.oreilly.com/people/2256f119-7ea0-440e-99e8-65281919e952
+[1]:https://pixabay.com/en/measure-measures-rule-metro-106354/
+[2]:http://conferences.oreilly.com/oscon/oscon-tx?intcmp=il-prog-confreg-update-ostx17_new_site_oscon_17_austin_right_rail_cta
+[3]:https://www.oreilly.com/people/acf937de-cdf4-4b0e-85bd-b559404c580e
+[4]:https://www.oreilly.com/people/2256f119-7ea0-440e-99e8-65281919e952
+[5]:https://www.safaribooksonline.com/library/view/introducing-github/9781491949801/?utm_source=newsite&utm_medium=content&utm_campaign=lgen&utm_content=how-to-use-pull-requests-to-improve-your-code-reviews
+[6]:http://conferences.oreilly.com/oscon/oscon-tx?intcmp=il-prog-confreg-update-ostx17_new_site_oscon_17_austin_right_rail_cta
+[7]:http://conferences.oreilly.com/oscon/oscon-tx?intcmp=il-prog-confreg-update-ostx17_new_site_oscon_17_austin_right_rail_cta
+[8]:https://www.oreilly.com/ideas/how-to-use-pull-requests-to-improve-your-code-reviews?imm_mid=0ee8ca&cmp=em-prog-na-na-newsltr_20170311
+[9]:https://github.com/about
+[10]:https://help.github.com/articles/about-pull-requests/
+[11]:https://blog.skyliner.io/ship-small-diffs-741308bec0d1
+[12]:https://github.com/integrations/sonarqube
+[13]:https://github.com/integrations/code-climate
+[14]:https://github.com/integrations/codecov
+[15]:https://github.com/integrations/coveralls
+[16]:https://help.github.com/articles/about-protected-branches/
+[17]:https://www.safaribooksonline.com/library/view/introducing-github/9781491949801/?utm_source=newsite&utm_medium=content&utm_campaign=lgen&utm_content=how-to-use-pull-requests-to-improve-your-code-reviews-lower
diff --git a/translated/tech/20160518 Cleaning Up Your Linux Startup Process.md b/translated/tech/20160518 Cleaning Up Your Linux Startup Process.md
deleted file mode 100644
index c406431690..0000000000
--- a/translated/tech/20160518 Cleaning Up Your Linux Startup Process.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,123 +0,0 @@
-Linux 系统开机启动项清理
-=======
-
-
-一般情况下, Linux 发行版在开机启动时拉起所有的相关服务进程, 包括许多你可能无需使用的服务, 例如<ruby>蓝牙<rt>bluetooth</rt></ruby>, Avahi, <ruby>调制解调管理器<rt>ModemManager</rt></ruby>, ppp-dns((LCTT 译注:此处作者笔误 ppp-dns 应该为 pppd-dns) 等服务进程, 用于哪里, 有何功能?
-
-systemd 提供了许多很好的工具, 用于查看系统启动情况, 控制系统启动工作. 该文章中将说明在 systemd 控制系统启动的过程中如何关闭一些<ruby>令人讨厌<rt>cruft</rt></ruby>的进程。
-
-###查看开机启动项
-在老式系统启动方式 systemV 中,在 /etc/init.d 中你能很容易看到服务进程是否被设置为开机启动项。Systemd 以不同的方式展现,可以使用如下命令罗列允许开机启动的服务进程。
-```
-$ systemctl list-unit-files --type=service | grep enabled
-accounts-daemon.service enabled
-anacron-resume.service enabled
-anacron.service enabled
-bluetooth.service enabled
-brltty.service enabled
-[...]
-```
-在此列表中, 对我来说, 蓝牙服务是冗余项, 因为在该电脑上我不需要使用蓝牙功能, 故无需运行此服务. 下面的命令将停止该服务进程,并且使其开机不启动。
-```
-$ sudo systemctl stop bluetooth.service
-$ sudo systemctl disable bluetooth.service
-```
-你可以通过下面命令确定是否操作成功。
-```
-$ systemctl status bluetooth.service
- bluetooth.service - Bluetooth service
- Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/bluetooth.service; disabled; vendor preset: enabled)
- Active: inactive (dead)
- Docs: man:bluetoothd(8)
-```
-一个开机不启动的服务进程仍然能够被另外一个服务进程启动。如果你真的想在任何情况下系统启动时都不启动该进程,你可以卸载该程序;若在不卸载程序的情况达到此效果,你可以执行如下命令在任何情况下阻止该进程开机启动。
-```
-$ sudo systemctl mask bluetooth.service
- Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/bluetooth.service to /dev/null.
-```
-一旦你对禁止该进程启动的效果感到满意时,你也可以选择卸载该程序。
-
-通过执行命令可以获得如下服务列表:
-```
-$ systemctl list-unit-files --type=service
-UNIT FILE STATE
-accounts-daemon.service enabled
-acpid.service disabled
-alsa-restore.service static
-alsa-utils.service masked
-```
-你不能使能或使不能静态服务,因为静态服务是依赖于其他的进程,意味着其不能自启动。
-
-###哪些服务能够禁止?
-
-如何知道你是否能够禁止某服务或需要何服务?它总是依赖于你的个性化需求。
-
-这里有列出了几个服务进程的作用,所有服务进程都可以在发行版规范中找到,你也可以通过搜索方式查询起作用。
-
-- accounts-daemon. 该服务存在潜在的安全威胁。它是账号服务的一部分,它被允许获得或操作用户账户信息。我不认为存在一个好的理由能使我允许这样的后台操作,所以我选择<ruby>掩盖<rt>mask</rt></ruby>该服务进程。
-- avahi-daemon. 该服务用于零配置网络发现,使电脑极易发现网络中打印机或其他的主机,我总是使其开机不启动,并从未不习惯于此。
-- brltty.service. 该服务提供布莱叶盲文设备支持,例如布莱叶盲文显示器。
-- debug-shell.service. 该服务打开一个重要的安全漏洞(该服务提供了一个无密码的 root 用户用于帮助 systemd 问题的调试。),除非你正在使用该服务,否则永远不要启动服务。
-- ModemManager.service. 该服务是一个被 dbus 激活的守护进程,用于提供移动<ruby>宽频<rt>broadband</rt></ruby>(2G/3G/4G)接口,如果你不需要该内置接口通过如蓝牙、USB 适配器等来连接手机,那么你也无需该服务。
-- pppd-dns.service. 该是一个计算机发展的遗物,如果你需要通过互联网打电话的话,保留它,否则<ruby>掩盖<rt>mask</rt></ruby>它。
-- rtkit-daemon.service. 该服务听起来很可怕, 其发音与 rootkit 相似. 但是你需要该服务, 因为它是一个<ruby>实时内核调度器<rt>real-time kernel scheduler</rt></ruby>.
-- whoopsie.service. 该服务是 Ubuntu 错误报告服务. 它用于收集 Ubuntu 系统崩溃报告,并发送报告到 https://daisy.ubuntu.com. 你可以放心地禁止其启动, 或者永久的卸载它.
-- wpa_supplicant.service. 该服务仅仅在 Wi-Fi 连接时需要.
-
-###系统<ruby>启动<rt>bootup</rt></ruby>时发生什么?
-systemd 提供了一些命令帮助调试系统开机启动问题. 该命令重演系统启动的消息打印.
-```
-$ journalctl -b
-
--- Logs begin at Mon 2016-05-09 06:18:11 PDT,
-end at Mon 2016-05-09 10:17:01 PDT. --
-May 16 06:18:11 studio systemd-journal[289]:
-Runtime journal (/run/log/journal/) is currently using 8.0M.
-Maximum allowed usage is set to 157.2M.
-Leaving at least 235.9M free (of currently available 1.5G of space).
-Enforced usage limit is thus 157.2M.
-[...]
-```
-通过命令 `journalctl -b -1` 可以复审前一次启动, `journalctl -b -2` 可以复审倒数第2次启动, 以此类推.
-
-该命令打印出大量的信息. 你可能并不关注所有信息, 只是关注其中问题相关部分. 为此, 系统提供了几个过滤命令, 用于帮助你锁定目标. 让我们以进程号为 1 的进程为例, 该进程是所有其他进程的父进程.
-```
-$ journalctl _PID=1
-
-May 08 06:18:17 studio systemd[1]: Starting LSB: Raise network interfaces....
-May 08 06:18:17 studio systemd[1]: Started LSB: Raise network interfaces..
-May 08 06:18:17 studio systemd[1]: Reached target System Initialization.
-May 08 06:18:17 studio systemd[1]: Started CUPS Scheduler.
-May 08 06:18:17 studio systemd[1]: Listening on D-Bus System Message Bus Socket
-May 08 06:18:17 studio systemd[1]: Listening on CUPS Scheduler.
-[...]
-```
-这些打印消息显示了什么被启动, 或者是正在尝试启动.
-
-一个最有用的命令工具之一 `systemd-analyze blame`, 用于帮助查看哪个服务进程启动耗时最长.
-```
-$ systemd-analyze blame
- 8.708s gpu-manager.service
- 8.002s NetworkManager-wait-online.service
- 5.791s mysql.service
- 2.975s dev-sda3.device
- 1.810s alsa-restore.service
- 1.806s systemd-logind.service
- 1.803s irqbalance.service
- 1.800s lm-sensors.service
- 1.800s grub-common.service
-```
-这是一个没有任何异常的特殊样例, 但是如果存在系统启动<ruby>瓶颈<rt>bottleneck</rt></ruby>, 则该命令将发现它.
-
-你也能了解 systemd 如何工作通过如下资源:
-- [Understanding and Using Systemd](https://www.linux.com/learn/understanding-and-using-systemd)
-- [Intro to Systemd Runlevels and Service Management Commands](https://www.linux.com/learn/intro-systemd-runlevels-and-service-management-commands)
-- [Here We Go Again, Another Linux Init: Intro to systemd](https://www.linux.com/learn/here-we-go-again-another-linux-init-intro-systemd)
-
-via: https://www.linux.com/learn/cleaning-your-linux-startup-process
-
-作者:[David Both](https://www.linux.com/users/cschroder)
-译者:[penghuster](https://github.com/penghuster)
-校对:校对者ID
-
-本文由 LCTT 原创编译,Linux中国 荣誉推出
diff --git a/translated/tech/20161216 The truth about traditional JavaScript benchmarks.md b/translated/tech/20161216 The truth about traditional JavaScript benchmarks.md
index 5b0ea6b2de..3786efbeeb 100644
--- a/translated/tech/20161216 The truth about traditional JavaScript benchmarks.md
+++ b/translated/tech/20161216 The truth about traditional JavaScript benchmarks.md
@@ -1,35 +1,35 @@
探索传统 JavaScript 基准测试
============================================================
-可以很公平地说,[JavaScript][22] 是当下软件工程最重要的技术。对于那些深入接触过编程语言、编译器和虚拟机的人来说,这仍然有点令人惊讶,因为在语言设计者们看来,JavaScript 不是十分优雅;在编译器工程师们看来,它没有多少可优化的地方;而且还没有一个伟大的标准库。这取决于你和谁吐槽,JavaScript 的缺点你花上数周都枚举不完,不过你总会找到一些你从所未知的神奇的东西。尽管这看起来明显困难重重,不过 JavaScript 还是成为了当今 web 的核心,并且还(通过 [Node.js][23])成为服务器端/云端的主导技术,甚至还开辟了进军物联网空间的道路。
+可以很公平地说,[JavaScript][22] 是当下软件工程中*最重要的技术*。对于那些深入接触过编程语言、编译器和虚拟机的人来说,这仍然有点令人惊讶,因为在语言设计者们看来,JavaScript 不是十分优雅;在编译器工程师们看来,它没有多少可优化的地方;甚至还没有一个伟大的标准库。这取决于你和谁吐槽,JavaScript 的缺点你花上数周都枚举不完,而你总会找到一些你从所未知的奇怪的东西。尽管这看起来明显困难重重,不过 JavaScript 还是成为了当今 web 的核心,并且还(通过 [Node.js][23])成为服务器端和云端的主导技术,甚至还开辟了进军物联网领域的道路。
-问题来了,为什么 JavaScript 如此受欢迎?或者说如此成功?我知道没有一个很好的答案。如今我们有许多使用 JavaScript 的好理由,或许最重要的是围绕其构建的庞大的生态系统,以及今天大量可用的资源。但所有这一切实际上是发展到一定程度的后果。为什么 JavaScript 变得流行起来了?嗯,你或许会说,这是 web 多年来的通用语了。但是在很长一段时间里,人们极其讨厌 JavaScript。回顾过去,似乎第一波 JavaScript 浪潮爆发在上个年代的后半段。那个时候 JavaScript 引擎加速了各种不同的任务的执行,很自然的,这可能让很多人对 JavaScript 刮目相看。
+那么问题来了,为什么 JavaScript 如此受欢迎?或者说如此成功?我知道没有一个很好的答案。如今我们有许多使用 JavaScript 的好理由,或许最重要的是围绕其构建的庞大的生态系统,以及现今大量可用的资源。但所有这一切实际上是发展到一定程度的后果。为什么 JavaScript 变得流行起来了?嗯,你或许会说,这是 web 多年来的通用语了。但是在很长一段时间里,人们极其讨厌 JavaScript。回顾过去,似乎第一波 JavaScript 浪潮爆发在上个年代的后半段。那个时候 JavaScript 引擎加速了各种不同的任务的执行,很自然的,这可能让很多人对 JavaScript 刮目相看。
-回到过去那些日子,这些加速测试使用了现在所谓的传统 JavaScript 基准——从苹果的 [SunSpider 基准][24](JavaScript 微基准之母)到 Mozilla 的 [Kraken 基准][25] 和谷歌的 V8 基准。后来,V8 基准被 [Octane 基准][26] 取代,而苹果发布了新的 [JetStream 基准][27]。这些传统的 JavaScript 基准测试驱动了无数人的努力,使 JavaScript 的性能达到了本世纪初没人能预料到的水平。据报道其性能加速达到了 1000 倍,一夜之间在网站使用 `<script>` 标签不再是魔鬼的舞蹈,做客户端不再仅仅是可能的了,甚至是被鼓励的。
+回到过去那些日子,这些加速使用了现在所谓的传统 JavaScript 基准进行测试——从苹果的 [SunSpider 基准][24](JavaScript 微基准之母)到 Mozilla 的 [Kraken 基准][25] 和谷歌的 V8 基准。后来,V8 基准被 [Octane 基准][26] 取代,而苹果发布了新的 [JetStream 基准][27]。这些传统的 JavaScript 基准测试驱动了无数人的努力,使 JavaScript 的性能达到了本世纪初没人能预料到的水平。据报道其性能加速达到了 1000 倍,一夜之间在网站使用 `<script>` 标签不再是与魔鬼共舞,做客户端不再仅仅是可能的了,甚至是被鼓励的。
[][28]
(来源: [Advanced JS performance with V8 and Web Assembly](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PvZdTZ1Nl5o), Chrome Developer Summit 2016, @s3ththompson。)
-现在是 2016 年,所有(相关的)JavaScript 引擎的性能都达到了一个令人难以置信的水平,web 应用像原生应用一样快(或者能够像原生应用一样快)。引擎配有复杂的优化编译器,通过收集之前的关于类型/形状的反馈来推测某些操作(例如属性访问、二进制操作、比较、调用等),生成高度优化的机器代码的短序列。大多数优化是由 SunSpider 或 Kraken 等微基准以及 Octane 和 JetStream 等静态测试套件驱动的。由于有像 [asm.js][29] 和 [Emscripten][30] 这样的 JavaScript 技术,我们甚至可以将大型 C++ 应用程序编译成 JavaScript,并在你的浏览器上运行,而无需下载或安装任何东西。例如,现在你可以在 web 上玩 [AngryBots][31],无需沙盒,而过去的 web 游戏需要安装一堆诸如 Adobe Flash 或 Chrome PNaCl 的插件。
+现在是 2016 年,所有(相关的)JavaScript 引擎的性能都达到了一个令人难以置信的水平,web 应用像原生应用一样快(或者能够像原生应用一样快)。引擎配有复杂的优化编译器,通过收集之前的关于类型/形状的反馈来推测某些操作(例如属性访问、二进制操作、比较、调用等),生成高度优化的机器代码的短序列。大多数优化是由 SunSpider 或 Kraken 等微基准以及 Octane 和 JetStream 等静态测试套件驱动的。由于有像 [asm.js][29] 和 [Emscripten][30] 这样的 JavaScript 技术,我们甚至可以将大型 C++ 应用程序编译成 JavaScript,并在你的浏览器上运行,而无需下载或安装任何东西。例如,现在你可以在 web 上玩 [AngryBots][31],无需沙盒,而过去的 web 游戏需要安装一堆诸如 Adobe Flash 或 Chrome PNaCl 的特殊插件。
-这些成就绝大多数都要归功于这些微基准和静态性能测试套件的出现,以及与这些传统 JavaScript 基准间的竞争的结果。你可以对 SunSpider 表示不满,但很显然,没有 SunSpider,JavaScript 的性能可能达不到今天的高度。好吧,赞美到此为止。现在看看另一方面,所有静态性能测试——无论是微基准还是大型应用的宏基准,都注定要随着时间的推移变成噩梦!为什么?因为在开始摆弄它之前,基准只能教你这么多。一旦达到某个阔值以上(或以下),那么有益于特定基准的优化的一般适用性将呈指数下降。例如,我们将 Octane 作为现实世界中 web 应用性能的代表,并且在相当长的一段时间里,它可能做得很不错,但是现在,Octane 与现实场景中的时间分布是截然不同的,因此即使眼下再优化 Octane 乃至超越自身,可能在现实世界中还是得不到任何显著的改进(无论是通用 web 还是 Node.js 的工作负载)。
+这些成就绝大多数都要归功于这些微基准和静态性能测试套件的出现,以及与这些传统的 JavaScript 基准间的竞争的结果。你可以对 SunSpider 表示不满,但很显然,没有 SunSpider,JavaScript 的性能可能达不到今天的高度。好吧,赞美到此为止。现在看看另一方面,所有的静态性能测试——无论是<ruby>微基准<rt>micro-benchmark</rt></ruby>还是大型应用的<ruby>宏基准<rt>macro-benchmark</rt></ruby>,都注定要随着时间的推移变成噩梦!为什么?因为在开始摆弄它之前,基准只能教你这么多。一旦达到某个阔值以上(或以下),那么有益于特定基准的优化的一般适用性将呈指数级下降。例如,我们将 Octane 作为现实世界中 web 应用性能的代表,并且在相当长的一段时间里,它可能做得很不错,但是现在,Octane 与现实场景中的时间分布是截然不同的,因此即使眼下再优化 Octane 乃至超越自身,可能在现实世界中还是得不到任何显著的改进(无论是通用 web 还是 Node.js 的工作负载)。
[][32]
(来源:[Real-World JavaScript Performance](https://youtu.be/xCx4uC7mn6Y),BlinkOn 6 conference,@tverwaes)
-由于传统 JavaScript 基准(包括最新版的 JetStream 和 Octane)可能已经背离其有用性变得越来越远,我们开始在年初寻找新的方法来测量现实场景的性能,为 V8 和 Chrome 添加了大量新的性能追踪钩子。我们还特意添加一些机制来查看我们在浏览 web 时的时间开销,例如,是否是脚本执行、垃圾回收、编译等,并且这些调查的结果非常有趣和令人惊讶。从上面的幻灯片可以看出,运行 Octane 花费超过 70% 的时间去执行 JavaScript 和回收垃圾,而浏览 web 的时候,通常执行 JavaScript 花费的时间不到 30%,垃圾回收占用的时间永远不会超过 5%。在 Octane 中并没有体现出它花费了大量时间来解析和编译。因此,将更多的时间用在优化 JavaScript 执行上将提高你的 Octane 跑分,但不会对加载 [youtube.com][33] 有任何积极的影响。事实上,花费更多的时间来优化 JavaScript 执行甚至可能有损你现实场景的性能,因为编译器需要更多的时间,或者你需要跟踪更多的反馈,最终在编译、IC 和运行时桶开销了更多的时间。
+由于传统 JavaScript 基准(包括最新版的 JetStream 和 Octane)可能已经背离其有用性变得越来越远,我们开始在 2016 年初寻找新的方法来测量现实场景的性能,为 V8 和 Chrome 添加了大量新的性能追踪钩子。我们还特意添加一些机制来查看我们在浏览 web 时的时间究竟开销在哪里,例如,是脚本执行、垃圾回收、编译,还是什么地方?而这些调查的结果非常有趣和令人惊讶。从上面的幻灯片可以看出,运行 Octane 花费了 70% 以上的时间去执行 JavaScript 和垃圾回收,而浏览 web 的时候,通常执行 JavaScript 花费的时间不到 30%,垃圾回收占用的时间永远不会超过 5%。在 Octane 中并没有体现出它花费了大量时间来解析和编译。因此,将更多的时间用在优化 JavaScript 执行上将提高你的 Octane 跑分,但不会对加载 [youtube.com][33] 有任何积极的影响。事实上,花费更多的时间来优化 JavaScript 执行甚至可能有损你现实场景的性能,因为编译器需要更多的时间,或者你需要跟踪更多的反馈,最终在编译、垃圾回收和<ruby>运行时桶<rt>Runtime bucket</rt></ruby>等方面开销了更多的时间。
[][34]
-还有另外一组基准测试用于测量浏览器整体性能(包括 JavaScript 和 DOM 性能),最新推出的是 [Speedometer 基准][35]。该基准试图通过运行一个用不同的主流 web 框架实现的简单的 [TodoMVC][36] 应用(现在看来有点过时了,不过新版本正在研发中)以捕获真实性能。上述幻灯片中的各种测试 (Angular、Ember、React、Vanilla、Flight 和 Backbone)挨着放在 Octane 之后,你可以看到这些测试似乎更好地代表了现在的性能指标。但是请注意,这些数据收集在本文撰写将近 6 个月以前,而且我们优化了更多的现实场景模式(例如我们正在重构垃圾回收系统以显著地降低开销,并且 [解析器也正在重新设计][37])。还要注意的是,虽然这看起来像是只和浏览器相关,但我们有非常强有力的证据表明传统的峰值性能基准也不能很好的代表现实场景中 Node.js 应用性能。
+还有另外一组基准测试用于测量浏览器整体性能(包括 JavaScript 和 DOM 性能),最新推出的是 [Speedometer 基准][35]。该基准试图通过运行一个用不同的主流 web 框架实现的简单的 [TodoMVC][36] 应用(现在看来有点过时了,不过新版本正在研发中)以捕获更真实的现实场景的性能。上述幻灯片中的各种测试 (Angular、Ember、React、Vanilla、Flight 和 Backbone)挨着放在 Octane 之后,你可以看到,此时此刻这些测试似乎更好地代表了现实世界的性能指标。但是请注意,这些数据收集在本文撰写将近 6 个月以前,而且我们优化了更多的现实场景模式(例如我们正在重构垃圾回收系统以显著地降低开销,并且 [解析器也正在重新设计][37])。还要注意的是,虽然这看起来像是只和浏览器相关,但我们有非常强有力的证据表明传统的峰值性能基准也不能很好的代表现实场景中 Node.js 应用性能。
[][38]
(来源: [Real-World JavaScript Performance](https://youtu.be/xCx4uC7mn6Y), BlinkOn 6 conference, @tverwaes.)
-所有这一切可能已经路人皆知了,因此我将用本文剩下的部分强调一些具体案例,它们对关于我为什么认为这不仅有用,而且必须停止关注某一阔值的静态峰值性能基准测试对于 JavaScript 社区的健康是很关键的。让我通过一些例子说明 JavaScript 引擎怎样来玩弄基准的。
+所有这一切可能已经路人皆知了,因此我将用本文剩下的部分强调一些具体案例,它们对关于我为什么认为这不仅有用,而且必须停止关注某一阈值的静态峰值性能基准测试对于 JavaScript 社区的健康是很关键的。让我通过一些例子说明 JavaScript 引擎怎样来玩弄基准的。
### 臭名昭著的 SunSpider 案例
@@ -560,7 +560,6 @@ $
作者简介:
-
我是 Benedikt Meurer,住在 Ottobrunn(德国巴伐利亚州慕尼黑东南部的一个市镇)的一名软件工程师。我于 2007 年在锡根大学获得应用计算机科学与电气工程的文凭,打那以后的 5 年里我在编译器和软件分析领域担任研究员(2007 至 2008 年间还研究过微系统设计)。2013 年我加入了谷歌的慕尼黑办公室,我的工作目标主要是 V8 JavaScript 引擎,目前是 JavaScript 执行性能优化团队的一名技术领导。
diff --git a/translated/tech/20170403 Introduction to functional programming.md b/translated/tech/20170403 Introduction to functional programming.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..4ef2742efb
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20170403 Introduction to functional programming.md
@@ -0,0 +1,253 @@
+函数式编程简介
+============================================================
+
+> 我们来解释函数式编程的什么,它的优点是哪些,并且寻找一些函数式编程的学习资源。
+
+
+ 
+图片来源于:
+
+opensource.com
+
+根据您的问题来回答, _函数式编程_ (FP) 是一种开放的程序设计方法,理应广泛传播或者流行于理论学术中,在现实中没有实际的作用。在这篇文章中我来讲解函数式编程,探究其优点,并推荐学习函数式编程的资源。
+
+### 语法入门
+
+本文的代码示例使用的是 [Haskell][40] 编程语言。因而你需要理解这篇文章的基本函数语法:
+
+```
+ even :: Int -> Bool
+ even = ... -- implementation goes here
+```
+
+示例定义了含有一个参数的函数 **even** ,第一行是 _类型声明_ 具体来说就是 **even** 函数接受一个 int 类型的参数返回一个 bool 类型的值,由一个或多个方法实现,在这里我们将忽略具体实现方法(名称和类型已经足够了):
+
+```
+ map :: (a -> b) -> [a] -> [b]
+ map = ...
+```
+
+这个示例, **map** 是一个有两个参数的函数:
+
+1. **(a -> b)** : 将**a** 转换成 **b** 的匿名函数
+2. **[a]**: 将匿名函数作用到 **[a]** (List 序列与其它语言的数组对应)的每一个元素上,将每次所得结果放到另一个 **[b]** ,最后返回这个结果 **[b]** 。
+
+同样我们不去关心是要如何实现,我们只感兴趣它的定义类型。
+**a** 和 **b** 是任何一种的的 _类型变量_ 。就像上一个示例中, **a** 是 **Int** 类型, **b** 是 **Bool** 类型:
+
+```
+ map even [1,2,3]
+```
+
+这个是一个bool类型的序列:
+
+```
+ [False,True,False]
+```
+
+如果你看到你不理解的其他语法,不要惊慌;对语法的充分理解不是必要的。
+
+### 函数式编程的误区
+
+编程与开发
+
+* [我们最新的 JavaScript 文章][1]
+* [最近 Perl 的帖子][2]
+* [新的 Python 内容][3]
+* [红帽开发者博客][4]
+* [红帽开发者工具][5]
+
+我们先来解释一下常见的误区:
+
+* 函数式编程不是像命令行编程或者面向对象编程一样对立,这些都是虚假的。
+* 函数式编程不仅仅是学术领域在其他领域也有使用。这是真的,在函数式编程的历史中,如像Haskell和OCaml语言是最流行的研究。但是今天许多公司使用函数式编程来处理大型系统,小型专业程序,以及两者之间的一切。甚至还有一个面向函数式编程的商业用户的年度会议;过去的程序让我们了解了函数式编程在工业中的用途,以及由谁来使用它。
+* 函数式编程与monads无关 ,也不是任何其他特殊的抽象。对于围绕这个monad只是一个抽象的规定,有些是有些也的不是。
+* 函数式编程不是特别难学的。有些语言可能与您已经知道的语法不同,但这些差异是浅显的。函数式编程中有dense的概念,但其他方法也是如此。(这里的dense不懂什么意思,校对者注意一下)
+
+### 什么是函数式编程?
+
+核心是函数式编程是只使用_纯粹_的数学函数编程,函数的结果取决于参数,就像 I/O 或者状态转换这样。程序是通过 _组合函数_ 的方法构建的:
+
+```
+ (.) :: (b -> c) -> (a -> b) -> (a -> c)
+ (g . f) x = g (f x)
+```
+
+这个_(.)_ 表示的是二个函数组合成一个,将 **g** 作用到 **f** 上。我们将在下一个示例中看到它的使用。这里使用 Python 中的函数:
+
+```
+ def compose(g, f):
+ return lambda x: g(f(x))
+```
+
+函数式编程的优点在于:由于函数是确定的,所以可以用应用程序的结果替换函数,这种替代等价于使用使 _等式推理_ 。每个程序员都有使用自己代码和别人代码的理由,而等式推理就是解决这样问题不错的工具。来看一个示例。等你遇到这个问题:
+
+```
+ map even . map (+1)
+```
+
+这段代码是做什么的?可以简化吗?通过等式推理,可以通过一系列替换来分析代码:
+
+```
+ map even . map (+1)
+ map (even . (+1)) -- from definition of 'map'
+ map (\x -> even (x + 1)) -- lambda abstraction
+ map odd -- from definition of 'even'
+```
+
+我们可以使用等式推理来理解程序并优化。Haskell编译器使用等式推理进行多种方案的优化。没有纯粹的函数,等式推理是不可能的,或者需要程序员更多的努力。
+
+### 函数式编程语言
+
+你需要一种编程语言来做函数式编程。
+
+在没有高阶函数(传递函数作为参数和返回函数的能力)的语言中有意义地进行函数式编程, _lambdas_ (匿名函数)和泛型是困难的。 大多数现代语言都有这些,但在不同语言支持函数式编程方面存在差异。 具有最佳支持的语言称为函数式编程语言。 这些包括静态类型的 _Haskell_, _OCaml_ , _F#_ 和 _Scala_ ,动态类型的 _Erlang_ 和 _Clojure_。
+
+在函数式语言之间可以在多大程度上利用函数编程有很大差异。有一个类型系统会有很大的帮助,特别是它支持 _类型推断_ (所以你并不总是必须键入类型)。这篇文章中没有详细介绍这部分,但足以说明,并非所有类型的系统都是平等的。
+
+与所有语言一样,不同的函数的语言强调不同的概念,技术或用例。选择语言时,考虑到它支持函数式编程的程度以及是否适合您的用例很重要。如果您使用某些非 FP 语言,会受益于在语言支持的范围内的函数式编程。
+
+### 不要打开表面没什么但却是陷阱的门
+
+回想一下,函数的结果只取决于它的输入。几乎所有的编程语言都有这个。空值,类型case(instanceof),类型转换,异常以及无限递归的可能性都是陷阱,它打破等式推理,并削弱程序员对程序行为正确性的理解能力。(没有任何陷阱的语言包括Agda,Idris和Coq。)
+
+幸运的是,作为程序员,我们可以选择避免这些陷阱,如果我们受到严格的规范,我们可以假装陷阱不存在。 这个方法叫做 _快速推理_ 。它不需要任何条件,几乎任何程序都可以在不使用陷阱的情况下进行编写,并且通过避免这些程序可以进行等式推理,可组合性和可重用性。
+
+让我们详细讨论一下。 这个陷阱打破了等式推理,因为异常终止的可能性没有反映在类型中。(如果文档中提到可能抛出的异常,请自己计算一下)。但是没有理由我们无法包含所有故障模式的返回类型。
+
+避开陷阱是语言特征中产生巨大影响的一个领域。为避免例外, 代数数据类型可用于模型误差的条件下,就像:
+
+```
+ -- new data type for results of computations that can fail
+ --
+ data Result e a = Error e | Success a
+
+ -- new data type for three kinds of arithmetic errors
+ --
+ data ArithError = DivByZero | Overflow | Underflow
+
+ -- integer division, accounting for divide-by-zero
+ --
+ safeDiv :: Int -> Int -> Result ArithError Int
+ safeDiv x y =
+ if y == 0
+ then Error DivByZero
+ else Success (div x y)
+```
+
+在这个例子中的权衡你现在必须使用ArithError 或者 Int 类型为结果,而不是旧的 Int 的值,但这也是解决这个问题的一种方式。你不再需要处理异常,使用 _快速推理_ ,总体来说这是一个胜利。
+
+### 免费的定理
+
+大多数现代静态类型语言具有 _范型_(也称为 _参数多态性_ ),其中函数是通过一个或多个抽象类型定义的。 例如,考虑List(序列)上的函数:
+
+```
+ f :: [a] -> [a]
+ f = ...
+```
+
+Java中的相同函数如下所示:
+
+```
+ static <A> List<A> f(List<A> xs) { ... }
+```
+
+编译程序的过程是一个证明的过程是将 _a_ 类型做出选择的过程。考虑到这一点,采用快速推理的方法,你能够创造出怎样的函数。
+
+在这种情况下,该类型并不能告诉我们函数的功能(它可以改变序列,删除第一个元素或许多其他的东西),但它确实告诉了我们很多信息。只是从类型,我们可以得出关于函数的定理:
+
+* **Theorem 1**: 输入决定输出;不可能在输入的序列 **a** 中添加值,因为你不知道它的数据结构。
+* **Theorem 2**: If you map any function over the list then apply **f**, the result is the same as applying **f** then mapping.
+
+定理1帮助我们了解代码的作用,定理2对于程序优化提供了帮助。我们从类型中学到了这一切!从类型中获取有用的信息称为参数。因此,类型是函数行为的部分(有时是完整的)规范,也是一种检查机制。
+
+现在你可以利用参数话了探寻了。你可以从 **map** **(.)** 或者下面的这些函数中发现什么呢?
+
+* **foo :: a -> (a, a)**
+* **bar :: a -> a -> a**
+* **baz :: b -> a -> a**
+
+### 学习功能编程的资源
+
+也许你已经相信函数式编程是编写软件不错的方式,你想知道如何开始?有几种学习功能编程的方法; 这里有一些我推荐(我承认,我对 Haskell 偏爱:
+
+* UPenn's 的 [CIS 194: 介绍 Haskell][35] 是函数式编程概念和 Haskell 开发的不错选择。可以当课程材料使用,讲座(您可以查看几年前 Brisbane 函数式编程小组的 [系列 CIS 194 讲座][36]。
+* 不错的入门书籍有 _[ Scala 的函数式编程][30]_ , _[ Haskell 对函数的思考][31]_ , 和 _[ Haskell 编程原理][32]_ .
+* [Data61 FP 课程][37] (f.k.a., _NICTA_ 课程) 通过 _类型驱动_ 开发来教授抽象和数据结构的概念。这是十分困难,但收获也是丰富的,如果你有一名愿意引导你函数式编程的程序员,你可以尝试。
+* 在你的工作学习中使用函数式编程书写代码,写一些纯粹的函数(避免不确定性和异常的出现),使用高阶函数而不是循环和递归,利用参数化来提高可读性和重用性。许多人从函数式编程开始,体验各种语言的美妙。
+* 加入到你区域中的一些函数式编程小组或者学习小组中,也可以是参加一些函数式编程的会议(新的会议总是不断的出现)。
+
+### 总结
+
+在本文中,我讨论了什么是函数式编程,而不是函数式编程的优点,包括等式推理和参数化。我们了解到在大多数编程语言中执行一些函数编程,但是语言的选择会影响受益的程度,而 Haskell 是函数式编程中语言最受欢迎的语言。我也推荐学习函数式编程的资源。
+
+函数式编程是一个丰富的领域,还有许多更深入(更神秘)的主题正在等待探索。我没有提到那些具有实际意义的事情,比如:
+
+* lenses and prisms (是一流的设置值的方式;非常适合使用嵌套数据);
+* 定理证明 (当测试你代码的时候你可以你代码的正确性);
+* 懒惰评估 (让您处理潜在无数的数据结构);
+* 类型理论 (函数式编程中许多美丽实用的抽象的起源).
+
+我希望你喜欢这个函数式编程的介绍,并且启发你使用这个有趣和实用的软件开发方法。
+
+ _本文根据 [CC BY 4.0][38] 许可证发布。_
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+作者简介:
+
+红帽软件工程师。对函数式编程,分类理论,数学感兴趣。Crazy about jalapeños.
+
+----------------------
+
+via: https://opensource.com/article/17/4/introduction-functional-programming
+
+作者:[Fraser Tweedale ][a]
+译者:[MonkeyDEcho](https://github.com/MonkeyDEcho)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:https://opensource.com/users/frasertweedale
+[1]:https://opensource.com/tags/javascript?src=programming_resource_menu
+[2]:https://opensource.com/tags/perl?src=programming_resource_menu
+[3]:https://opensource.com/tags/python?src=programming_resource_menu
+[4]:https://developers.redhat.com/?intcmp=7016000000127cYAAQ&src=programming_resource_menu
+[5]:https://developers.redhat.com/products/#developer_tools?intcmp=7016000000127cYAAQ&src=programming_resource_menu
+[6]:http://haskell.org/ghc/docs/latest/html/libraries/base/Prelude.html#t:Int
+[7]:http://haskell.org/ghc/docs/latest/html/libraries/base/Prelude.html#t:Int
+[8]:http://haskell.org/ghc/docs/latest/html/libraries/base/Prelude.html#t:Int
+[9]:http://haskell.org/ghc/docs/latest/html/libraries/base/Prelude.html#v:div
+[10]:http://haskell.org/ghc/docs/latest/html/libraries/base/Prelude.html#v:even
+[11]:http://haskell.org/ghc/docs/latest/html/libraries/base/Prelude.html#t:Int
+[12]:http://haskell.org/ghc/docs/latest/html/libraries/base/Prelude.html#t:Bool
+[13]:http://haskell.org/ghc/docs/latest/html/libraries/base/Prelude.html#v:even
+[14]:http://haskell.org/ghc/docs/latest/html/libraries/base/Prelude.html#v:map
+[15]:http://haskell.org/ghc/docs/latest/html/libraries/base/Prelude.html#v:map
+[16]:http://haskell.org/ghc/docs/latest/html/libraries/base/Prelude.html#v:map
+[17]:http://haskell.org/ghc/docs/latest/html/libraries/base/Prelude.html#v:even
+[18]:http://haskell.org/ghc/docs/latest/html/libraries/base/Prelude.html#v:map
+[19]:http://haskell.org/ghc/docs/latest/html/libraries/base/Prelude.html#v:even
+[20]:http://haskell.org/ghc/docs/latest/html/libraries/base/Prelude.html#v:map
+[21]:http://haskell.org/ghc/docs/latest/html/libraries/base/Prelude.html#v:map
+[22]:http://haskell.org/ghc/docs/latest/html/libraries/base/Prelude.html#v:even
+[23]:http://haskell.org/ghc/docs/latest/html/libraries/base/Prelude.html#v:map
+[24]:http://haskell.org/ghc/docs/latest/html/libraries/base/Prelude.html#v:map
+[25]:http://haskell.org/ghc/docs/latest/html/libraries/base/Prelude.html#v:even
+[26]:http://haskell.org/ghc/docs/latest/html/libraries/base/Prelude.html#v:map
+[27]:http://haskell.org/ghc/docs/latest/html/libraries/base/Prelude.html#v:even
+[28]:http://haskell.org/ghc/docs/latest/html/libraries/base/Prelude.html#v:map
+[29]:http://haskell.org/ghc/docs/latest/html/libraries/base/Prelude.html#v:odd
+[30]:https://www.manning.com/books/functional-programming-in-scala
+[31]:http://www.cambridge.org/gb/academic/subjects/computer-science/programming-languages-and-applied-logic/thinking-functionally-haskell
+[32]:http://haskellbook.com/
+[33]:http://cufp.org/
+[34]:https://www.haskell.org/tutorial/monads.html
+[35]:https://www.cis.upenn.edu/~cis194/fall16/
+[36]:https://github.com/bfpg/cis194-yorgey-lectures
+[37]:https://github.com/data61/fp-course
+[38]:https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/
+[39]:https://opensource.com/article/17/4/introduction-functional-programming?rate=_tO5hNzT4hRKNMJtWwQM-K3Jmxm10iPeqoy3bbS12MQ
+[40]:https://wiki.haskell.org/Introduction
+[41]:https://opensource.com/user/123116/feed
+[42]:https://opensource.com/users/frasertweedale
diff --git a/translated/tech/20170718 Integrate Ubuntu to Samba4 AD DC with SSSD and Realm – Part 15.md b/translated/tech/20170718 Integrate Ubuntu to Samba4 AD DC with SSSD and Realm – Part 15.md
deleted file mode 100644
index d960657582..0000000000
--- a/translated/tech/20170718 Integrate Ubuntu to Samba4 AD DC with SSSD and Realm – Part 15.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,377 +0,0 @@
-Samba 系列(十五):用 SSSD 和 Realm 集成 Ubuntu 到 Samba4 AD DC
-============================================================
-
-
-本教程将告诉你如何将 Ubuntu 桌面版机器加入到 Samba4 活动目录域中,用 SSSD 和 Realm 服务来针对活动目录认证用户。
-
-#### 要求:
-
-1. [在 Ubuntu 上用 Samba4 创建一个活动目录架构][1]
-
-### 第 1 步: 初始配置
-
-1. 在把 Ubuntu 加入活动目录前确保主机名被正确设置了。使用 hostnamectl 命令设置机器名字或者手动编辑 /etc/hostname 文件。
-
-```
-$ sudo hostnamectl set-hostname your_machine_short_hostname
-$ cat /etc/hostname
-$ hostnamectl
-```
-
-2. 接下来,编辑机器网络接口设置并且添加合适的 IP 设置和正确的 DNS IP 服务地址指向 Samba 活动目录域控制器如下图所示。
-
-如果你已经在本地配置了 DHCP 服务来自动分配 IP 设置,给你局域网内机器合适的 AD DNS IP 地址,那么你可以跳过这一步。
-
- [][2]
-
-设置网络接口
-
-上图中,192.168.1.254 和 192.168.1.253 代表 Samba4 域控制器的 IP 地址。
-
-3. 用 GUI(图形用户界面) 或命令行重启网络服务来应用修改并且对你的域名发起一系列 ping 请求来测试 DNS 解析如期工作。 也用 host 命令来测试 DNS 解析。
-
-```
-$ sudo systemctl restart networking.service
-$ host your_domain.tld
-$ ping -c2 your_domain_name
-$ ping -c2 adc1
-$ ping -c2 adc2
-```
-
-4. 最后, 确保机器时间和 Samba4 AD 同步。安装 ntpdate 包并用下列指令和 AD 同步时间。
-
-```
-$ sudo apt-get install ntpdate
-$ sudo ntpdate your_domain_name
-```
-
-### 第 2 步:安装需要的包
-
-5. 这一步安装将 Ubuntu 加入 Samba4 活动目录域控制器所必须的软件和依赖: Realmd 和 SSSD 服务.
-
-```
-$ sudo apt install adcli realmd krb5-user samba-common-bin samba-libs samba-dsdb-modules sssd sssd-tools libnss-sss libpam-sss packagekit policykit-1
-```
-
-6. 输入大写的默认 realm 名称然后按下回车继续安装。
-
- [][3]
-
-输入 Realm 名称
-
-7. 接着,创建包含以下内容的 SSSD 配置文件。
-
-```
-$ sudo nano /etc/sssd/sssd.conf
-```
-
-加入下面的内容到 sssd.conf 文件。
-
-```
-[nss]
-filter_groups = root
-filter_users = root
-reconnection_retries = 3
-[pam]
-reconnection_retries = 3
-[sssd]
-domains = tecmint.lan
-config_file_version = 2
-services = nss, pam
-default_domain_suffix = TECMINT.LAN
-[domain/tecmint.lan]
-ad_domain = tecmint.lan
-krb5_realm = TECMINT.LAN
-realmd_tags = manages-system joined-with-samba
-cache_credentials = True
-id_provider = ad
-krb5_store_password_if_offline = True
-default_shell = /bin/bash
-ldap_id_mapping = True
-use_fully_qualified_names = True
-fallback_homedir = /home/%d/%u
-access_provider = ad
-auth_provider = ad
-chpass_provider = ad
-access_provider = ad
-ldap_schema = ad
-dyndns_update = true
-dyndsn_refresh_interval = 43200
-dyndns_update_ptr = true
-dyndns_ttl = 3600
-```
-
-确保你对应地替换了域名在下面的参数:
-
-```
-domains = tecmint.lan
-default_domain_suffix = TECMINT.LAN
-[domain/tecmint.lan]
-ad_domain = tecmint.lan
-krb5_realm = TECMINT.LAN
-```
-
-8. 接着,用下列命令给 SSSD 文件适当的权限:
-
-```
-$ sudo chmod 700 /etc/sssd/sssd.conf
-```
-
-9. 现在, 打开并编辑 Realmd 配置文件输入下面这行。
-
-```
-$ sudo nano /etc/realmd.conf
-```
-
-Realmd.conf 文件摘录:
-
-```
-[active-directory]
-os-name = Linux Ubuntu
-os-version = 17.04
-[service]
-automatic-install = yes
-[users]
-default-home = /home/%d/%u
-default-shell = /bin/bash
-[tecmint.lan]
-user-principal = yes
-fully-qualified-names = no
-```
-
-10. 最后需要修改的文件属于 Samba daemon. 打开 /etc/samba/smb.conf 文件编辑然后在文件开头加入下面这块代码,在 [global]部分如下图所示之后。
-
-```
- workgroup = TECMINT
-client signing = yes
-client use spnego = yes
-kerberos method = secrets and keytab
-realm = TECMINT.LAN
-security = ads
-```
- [][4]
-
-配置 Samba 服务器
-
-确保你替换了域名值,特别是对应域名的 realm 值并运行 testparm 命令检验设置文件是否包含错误。
-
-```
-$ sudo testparm
-```
- [][5]
-
-测试 Samba 配置
-
-11. 在做完所有必需的修改之后,用 AD 管理员帐号验证 Kerberos 认证并用下面的命令列出票据。
-
-```
-$ sudo kinit ad_admin_user@DOMAIN.TLD
-$ sudo klist
-```
- [][6]
-
-检验 Kerberos 认证
-
-### 第 3 步: 加入 Ubuntu 到 Samba4 Realm
-
-12. 加入 Ubuntu 机器到 Samba4 活动目录键入下列命令。用有管理员权限的 AD DC 账户名字绑定 realm 以照常工作并替换对应的域名值。
-
-```
-$ sudo realm discover -v DOMAIN.TLD
-$ sudo realm list
-$ sudo realm join TECMINT.LAN -U ad_admin_user -v
-$ sudo net ads join -k
-```
- [][7]
-
-加入 Ubuntu 到 Samba4 Realm
-
- [][8]
-
-表列 Realm Domain 信息
-
- [][9]
-
-添加用户到 Realm Domain
-
- [][10]
-
-添加 Domain 到 Realm
-
-13. 区域绑定好了之后,运行下面的命令确保所有域账户在这台机器上允许认证。
-
-```
-$ sudo realm permit -all
-```
-
-然后你可以使用下面例举的 realm 命令允许或者禁止域用户帐号或群组访问。
-
-```
-$ sudo realm deny -a
-$ realm permit --groups ‘domain.tld\Linux Admins’
-$ realm permit user@domain.lan
-$ realm permit DOMAIN\\User2
-```
-
-14. 从一个 [安装了 RSAT 工具的][11]Windows 机器你可以打开 AD UC 浏览电脑容器并检验是否有一个使用你机器名的对象帐号已经被创建。
-
- [][12]
-
-确保域被加入 AD DC
-
-### 第 4 步: 配置 AD 账户认证
-
-15. 为了用域账户认证 Ubuntu 机器,你需要用 root 权限运行 pam-auth-update 命令并允许所有 PAM 配置文件,包括为每个区域账户在第一次注册的时候自动创建起始目录的选项。
-
-按 [空格] 键检验所有入口并敲 ok 来应用配置。
-
-```
-$ sudo pam-auth-update
-```
- [][13]
-
-PAM 配置
-
-16. 系统上手动编辑 /etc/pam.d/common-account 文件,下面这几行是为了自动创建起始位置给认证过的区域用户。
-
-```
-session required pam_mkhomedir.so skel=/etc/skel/ umask=0022
-```
-
-17. 如果活动目录用户不能用 linux 命令行修改他们的密码,打开 /etc/pam.d/common-password 文件并在 password 行移除 use_authtok 语句最后如下摘要。
-
-```
-password [success=1 default=ignore] pam_winbind.so try_first_pass
-```
-
-18. 最后,用下面的命令重启并应用 Realmd 和 SSSD 服务的修改:
-
-```
-$ sudo systemctl restart realmd sssd
-$ sudo systemctl enable realmd sssd
-```
-
-19. 为了测试 Ubuntu 机器是是否成功集成到 realm 运行安装 winbind 包并运行 wbinfo 命令列出区域账户和群组如下所示。
-
-```
-$ sudo apt-get install winbind
-$ wbinfo -u
-$ wbinfo -g
-```
- [][14]
-
-列出区域账户
-
-20. 同样, 也可以针对特定的域用户或群组使用 getent 命令检验 Winbind nsswitch 模式。
-
-```
-$ sudo getent passwd your_domain_user
-$ sudo getent group ‘domain admins’
-```
- [][15]
-
-检验 Winbind Nsswitch
-
-21. 你也可以用 Linux id 命令获取 AD 账户的信息,命令如下。
-
-```
-$ id tecmint_user
-```
- [][16]
-
-检验 AD 用户信息
-
-22. 用 su – 后跟域用户名参数命令来认证 Ubuntu 主机的一个 Samba4 AD 账户。运行 id 命令获取 AD 账户的更多信息。
-
-```
-$ su - your_ad_user
-```
- [][17]
-
-AD 用户认证
-
-用 pwd 命令查看你的域用户当前工作目录和 passwd 命令修改密码。
-
-23. 在 Ubuntu 上使用有 root 权限的域账户,你需要用下面的命令添加 AD 用户名到 sudo 系统群组:
-
-```
-$ sudo usermod -aG sudo your_domain_user@domain.tld
-```
-
-用域账户登录 Ubuntu 并运行 apt updatecommand 来更新你的系统以检验 root 权限。
-
-24. 给一个域群组 root 权限,用 visudocommand 打开并编辑 /etc/sudoers 文件并加入如下行。
-
-```
-%domain\ admins@tecmint.lan ALL=(ALL:ALL) ALL
-```
-
-25. Ubuntu 桌面使用域账户认证修正 LightDM 显示管理,通过编辑 /usr/share/lightdm/lightdm.conf.d/50-ubuntu.conf 文件,增加以下两行并重启 lightdm 服务或重启机器应用修改。
-
-```
-greeter-show-manual-login=true
-greeter-hide-users=true
-```
-
-域账户用 your_domain_username 或 your_domain_username@your_domain.tld 语句登录 Ubuntu 桌面版。
-
-26. 为使用 Samba AD 账户的简称格式,编辑 /etc/sssd/sssd.conf 文件, 在 [sssd] 块加入如下几行命令。
-
-```
-full_name_format = %1$s
-```
-
-并重启 SSSD 后台程序应用改变。
-
-```
-$ sudo systemctl restart sssd
-```
-
-你会注意到 bash 提示符会变化,对于没有增生域名副本的 AD 用户的简称。
-
-27. 万一你因为 sssd.conf 里的 enumerate=true 参数设定而不能登录,你得用下面的命令清空 sssd 缓存数据:
-
-```
-$ rm /var/lib/sss/db/cache_tecmint.lan.ldb
-```
-
-这就是全部了!虽然这个教程主要集中于集成 Samba4 活动目录,同样的步骤也能被用于用 Realm 和 SSSD 服务的 Ubuntu 整合到微软 Windows 服务器活动目录。
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-作者简介:
-
-Matei Cezar
-我是一名网瘾少年,开源和基于 linux 系统软件的粉丝,有4年经验在 linux 发行版桌面、服务器和 bash 脚本。
-
-------------------
-
-via: https://www.tecmint.com/integrate-ubuntu-to-samba4-ad-dc-with-sssd-and-realm/
-
-作者:[ Matei Cezar][a]
-译者:[XYenChi](https://github.com/XYenChi)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:https://www.tecmint.com/author/cezarmatei/
-[1]:https://www.tecmint.com/install-samba4-active-directory-ubuntu/
-[2]:https://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/Configure-Network-Interface.jpg
-[3]:https://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/Set-realm-name.png
-[4]:https://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/Configure-Samba-Server.jpg
-[5]:https://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/Test-Samba-Configuration.jpg
-[6]:https://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/Check-Kerberos-Authentication.jpg
-[7]:https://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/Join-Ubuntu-to-Samba4-Realm.jpg
-[8]:https://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/List-Realm-Domain-Info.jpg
-[9]:https://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/Add-User-to-Realm-Domain.jpg
-[10]:https://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/Add-Domain-to-Realm.jpg
-[11]:https://www.tecmint.com/manage-samba4-ad-from-windows-via-rsat/
-[12]:https://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/Confirm-Domain-Added.jpg
-[13]:https://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/PAM-Configuration.jpg
-[14]:https://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/List-Domain-Accounts.jpg
-[15]:https://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/check-Winbind-nsswitch.jpg
-[16]:https://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/Check-AD-User-Info.jpg
-[17]:https://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/AD-User-Authentication.jpg
-[18]:https://www.tecmint.com/author/cezarmatei/
-[19]:https://www.tecmint.com/10-useful-free-linux-ebooks-for-newbies-and-administrators/
-[20]:https://www.tecmint.com/free-linux-shell-scripting-books/
diff --git a/translated/tech/20170813 An Intro to Compilers.md b/translated/tech/20170813 An Intro to Compilers.md
deleted file mode 100644
index f4dc8ec31a..0000000000
--- a/translated/tech/20170813 An Intro to Compilers.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,219 +0,0 @@
-编译器简介
-============================================================
-
-### 如何对计算机说话 - Pre-Siri
-
-简单说来,一个编译器不过是一个可以翻译其他程序的程序。传统的编译器可以把源代码翻译成你的机器能够理解的可执行机器代码。(一些编译器将源代码翻译成别的程序语言,这样的编译器称为源到源翻译器或转化器。)[LLVM][7] 是一个广泛使用的编译器项目,包含许多模块化的编译工具。
-
-传统的编译器设计包含三个部分:
-
-
-
-* 通过前端翻译将源代码转化为中间表示: (IR)* 。[`clang`][1] 是 LLVM 中用于 C 家族语言的前端工具。
-* 优化程序分析指令然后将其转化为更高效的形式。[`opt`][2]是 LLVM 的优化工具。
-* 后端工具通过将指令映射到目标硬件指令集从而生成机器代码。[`11c`][3]是 LLVM 的后端工具。
-* LLVM IR 是一种和汇编类似的低级语言。然而,它抽象出了特定硬件信息。
-
-### Hello, Compiler
-
-下面是一个打印 "Hello, Compiler!" 到标准输出的简单 C 程序。C 语法是人类可读的,但是计算机却不能理解,不知道该程序要干什么。我将通过三个编译阶段使该程序变成机器可执行的程序。
-
-```
-// compile_me.c
-// Wave to the compiler. The world can wait.
-
-#include <stdio.h>
-
-int main() {
- printf("Hello, Compiler!\n");
- return 0;
-}
-```
-
-### 前端
-
-正如我在上面所提到的,`clang` 是 LLVM 中用于 C 家族语言的前端工具。Clang 包含一个 C 预处理器、词法分析器、语法解析器、语义分析器和 IR生成器。
-
-* C 预处理器在将源程序翻译成 IR 前修改源程序。预处理器处理外部包含文件,比如上面的 `#include <stdio.h>`。 它将会把这一行替换为 `stdio.h` C 标准库文件的完整内容,其中包含 `printf` 函数的声明。
-
- *通过运行下面的命令来查看预处理步骤的输出:*
-
- ```
- clang -E compile_me.c -o preprocessed.i
-
- ```
-
-* 词法分析器(或扫描器或分词器)将一串字符转化为一串单词。每一个单词或记号,被归并到五种语法目录中的一个:标点符号、关键字、标识符、文字或注释。
-
- *compile_me.c 的分词过程*
- 
-
-* 语法分析器确定源程序中的单词流是否组成了合法的句子。在分析标识符流的语法后,它会输出一个抽象语法树(AST)。在 Clang 的 AST 中的节点表示声明、语句和类型。
-
- _compile_me.c 的语法树_
-
-
-
-* 语义分析器遍历抽象语法树,从而确定代码语句是否有正确意义。这个阶段会检查类型错误。如果 compile_me.c 的 main 函数返回 `"zero"`而不是 `0`, 那么语义分析器将会抛出一个错误,因为 `"zero"` 不是 `int` 类型。
-
-* IR 生成器将抽象语法树翻译为 IR 。
-
- *对 compile_me.c 运行 clang 来生成 LLVM IR:*
-
- ```
- clang -S -emit-llvm -o llvm_ir.ll compile_me.c
-
- ```
-
- 在 llvm_ir.ll 中的 main 函数
-
- ```
- ; llvm_ir.ll
- @.str = private unnamed_addr constant [18 x i8] c"Hello, Compiler!\0A\00", align 1
-
- define i32 @main() {
- %1 = alloca i32, align 4 ; <- memory allocated on the stack
- store i32 0, i32* %1, align 4
- %2 = call i32 (i8*, ...) @printf(i8* getelementptr inbounds ([18 x i8], [18 x i8]* @.str, i32 0, i32 0))
- ret i32 0
- }
-
- declare i32 @printf(i8*, ...)
- ```
-
-### 优化程序
-
-优化程序的工作是基于程序的运行时行为来提高代码效率。优化程序将 IR 作为输入然后生成改进后的 IR 作为输出。LLVM 的优化工具 opt 将会通过标记 `-O2`(大写 o,数字 2)来优化处理器速度,通过标记 `Os`(大写 o,小写 s)来减少指令数目。
-
-看一看上面的前端工具生成的 LLVM IR 代码和运行下面的命令生成的结果之间的区别:
-
-```
-opt -O2 -S llvm_ir.ll -o optimized.ll
-
-```
-
- _在 optimized.ll 中的 main 函数_
-
-```
-optimized.ll
-
-@str = private unnamed_addr constant [17 x i8] c"Hello, Compiler!\00"
-
-define i32 @main() {
- %puts = tail call i32 @puts(i8* getelementptr inbounds ([17 x i8], [17 x i8]* @str, i64 0, i64 0))
- ret i32 0
-}
-
-declare i32 @puts(i8* nocapture readonly)
-```
-
-优化后的版本中, main 函数没有在栈中分配内存,因为它不使用任何内存。优化后的代码中调用 `puts` 函数而不是 `printf` 函数,因为程序中并没有使用 `printf` 函数的格式化功能。
-
-当然,优化程序不仅仅知道何时可以把 `printf` 函数用 `puts` 函数代替。优化程序也能展开循环和内联简单计算的结果。考虑下面的程序,它将两个整数相加并打印出结果。
-
-```
-// add.c
-#include <stdio.h>
-
-int main() {
- int a = 5, b = 10, c = a + b;
- printf("%i + %i = %i\n", a, b, c);
-}
-```
-
-_下面是未优化的 LLVM IR:_
-
-```
-@.str = private unnamed_addr constant [14 x i8] c"%i + %i = %i\0A\00", align 1
-
-define i32 @main() {
- %1 = alloca i32, align 4 ; <- allocate stack space for var a
- %2 = alloca i32, align 4 ; <- allocate stack space for var b
- %3 = alloca i32, align 4 ; <- allocate stack space for var c
- store i32 5, i32* %1, align 4 ; <- store 5 at memory location %1
- store i32 10, i32* %2, align 4 ; <- store 10 at memory location %2
- %4 = load i32, i32* %1, align 4 ; <- load the value at memory address %1 into register %4
- %5 = load i32, i32* %2, align 4 ; <- load the value at memory address %2 into register %5
- %6 = add nsw i32 %4, %5 ; <- add the values in registers %4 and %5\. put the result in register %6
- store i32 %6, i32* %3, align 4 ; <- put the value of register %6 into memory address %3
- %7 = load i32, i32* %1, align 4 ; <- load the value at memory address %1 into register %7
- %8 = load i32, i32* %2, align 4 ; <- load the value at memory address %2 into register %8
- %9 = load i32, i32* %3, align 4 ; <- load the value at memory address %3 into register %9
- %10 = call i32 (i8*, ...) @printf(i8* getelementptr inbounds ([14 x i8], [14 x i8]* @.str, i32 0, i32 0), i32 %7, i32 %8, i32 %9)
- ret i32 0
-}
-
-declare i32 @printf(i8*, ...)
-```
-
-_下面是优化后的 LLVM IR_
-
-```
-@.str = private unnamed_addr constant [14 x i8] c"%i + %i = %i\0A\00", align 1
-
-define i32 @main() {
- %1 = tail call i32 (i8*, ...) @printf(i8* getelementptr inbounds ([14 x i8], [14 x i8]* @.str, i64 0, i64 0), i32 5, i32 10, i32 15)
- ret i32 0
-}
-
-declare i32 @printf(i8* nocapture readonly, ...)
-```
-
-优化后的 main 函数本质上是未优化版本的第 17 行和 18 行,伴有变量值内联。`opt` 计算加法,因为所有的变量都是常数。很酷吧,对不对?
-
-### 后端
-
-LLVM 的后端工具是 `11c`。它分三个阶段将 LLVM IR 作为输入生成机器代码。
-
-* 指令选择是将 IR 指令映射到目标机器的指令集。这个步骤使用虚拟寄存器的无限名字空间。
-* 寄存器分配是将虚拟寄存器映射到目标体系结构的实际寄存器。我的 CPU 是 x86 结构,它只有 16 个寄存器。然而,编译器将会尽可能少的使用寄存器。
-* 指令安排是重排操作,从而反映出目标机器的性能约束。
-
-_运行下面这个命令将会产生一些机器代码:_
-
-```
-llc -o compiled-assembly.s optimized.ll
-
-```
-
-```
-_main:
- pushq %rbp
- movq %rsp, %rbp
- leaq L_str(%rip), %rdi
- callq _puts
- xorl %eax, %eax
- popq %rbp
- retq
-L_str:
- .asciz "Hello, Compiler!"
-```
-
-这个程序是 x86 汇编语言,它是计算机所说的语言,并具有人类可读语法。某些人最后也许能理解我。
-
-* * *
-
-相关资源:
-
-1. [设计一个编译器][4]
-
-2. [开始探索 LLVM 核心库][5]
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: https://nicoleorchard.com/blog/compilers
-
-作者:[Nicole Orchard][a]
-译者:[ucasFL](https://github.com/ucasFL)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:https://nicoleorchard.com/
-[1]:http://clang.llvm.org/
-[2]:http://llvm.org/docs/CommandGuide/opt.html
-[3]:http://llvm.org/docs/CommandGuide/llc.html
-[4]:https://www.amazon.com/Engineering-Compiler-Second-Keith-Cooper/dp/012088478X
-[5]:https://www.amazon.com/Getting-Started-LLVM-Core-Libraries/dp/1782166920
-[6]:https://twitter.com/norchard/status/864246049266958336
-[7]:http://llvm.org/
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/tech/20170815 Automated testing with Headless Chrome.md b/translated/tech/20170815 Automated testing with Headless Chrome.md
similarity index 54%
rename from sources/tech/20170815 Automated testing with Headless Chrome.md
rename to translated/tech/20170815 Automated testing with Headless Chrome.md
index 44d1bd489c..c751e55e3e 100644
--- a/sources/tech/20170815 Automated testing with Headless Chrome.md
+++ b/translated/tech/20170815 Automated testing with Headless Chrome.md
@@ -1,42 +1,42 @@
-Automated testing with Headless Chrome
+使用 Headless Chrome 进行自动化测试
============================================================
-If you want to run automated tests using Headless Chrome, look no further! This article will get you all set up using Karma as a runner and Mocha+Chai for authoring tests.
+如果你想使用 Headless Chrome 进行自动化测试,就看下去吧!这篇文章将让你完全使用 Karma 作为 runner,并且使用 Mocha+Chai 进行 authoring 测试。
-**What are these things?**
+**这些东西是什么?**
Karma, Mocha, Chai, Headless Chrome, oh my!
-[Karma][2] is a testing harness that works with any of the the most popular testing frameworks ([Jasmine][3], [Mocha][4], [QUnit][5]).
+[Karma][2] 是一个测试工具,可以和所有最流行的测试框架([Jasmine][3], [Mocha][4], [QUnit][5])配合使用。
-[Chai][6] is an assertion library that works with Node and in the browser. We need the latter.
+[Chai][6] 是一个断言库,可以与 Node 和浏览器一起使用。这里我们需要后者。
-[Headless Chrome][7] is a way to run the Chrome browser in a headless environment without the full browser UI. One of the benefits of using Headless Chrome (as opposed to testing directly in Node) is that your JavaScript tests will be executed in the same environment as users of your site. Headless Chrome gives you a real browser context without the memory overhead of running a full version of Chrome.
+[Headless Chrome][7] 是一种在没有浏览器用户界面的 headless 环境中运行 Chrome 浏览器的方法。使用 Headless Chrome(而不是直接在 Node 中测试) 的一个好处是 JavaScript 测试将在与你的网站用户相同的环境中执行。Headless Chrome 为你提供了真正的浏览器环境,却没有运行完整版本的 Chrome 一样的内存开销。
### Setup
-### Installation
+### 安装
-Install Karma, the relevant, plugins, and the test runners using `yarn`:
+使用 `yarn` 安装 Karma、相关插件和测试用例:
```
yarn add --dev karma karma-chrome-launcher karma-mocha karma-chai
yarn add --dev mocha chai
```
-or use `npm`:
+或者使用 `npm`:
```
npm i --save-dev karma karma-chrome-launcher karma-mocha karma-chai
npm i --save-dev mocha chai
```
-I'm using [Mocha][8] and [Chai][9] in this post, but if you're not a fan, choose your favorite assertion library that works in the browser.
+在这篇文章中我使用 [Mocha][8] 和 [Chai][9],但是你也可以选择自己最喜欢的在浏览器中工作的断言库。
-### Configure Karma
+### 配置 Karma
-Create a `karma.config.js` file that uses the `ChromeHeadless` launcher.
+创建一个使用 `ChromeHeadless` 启动器的 `karma.config.js` 文件。
**karma.conf.js**
@@ -57,11 +57,11 @@ module.exports = function(config) {
}
```
-<aside class="note" style="box-sizing: inherit; font-size: 14px; margin-top: 16px; margin-bottom: 16px; padding: 12px 24px 12px 60px; background: rgb(225, 245, 254); color: rgb(2, 136, 209);">**Note:** Run `./node_modules/karma/bin/ init karma.conf.js` to generate the Karma configuration file.</aside>
+<aside class="note" style="box-sizing: inherit; font-size: 14px; margin-top: 16px; margin-bottom: 16px; padding: 12px 24px 12px 60px; background: rgb(225, 245, 254); color: rgb(2, 136, 209);">**注意:** 运行 `./node_modules/karma/bin/ init karma.conf.js` 生成 Karma 的配置文件。</aside>
-### Write a test
+### 写一个测试
-Create a test in `/test/test.js`.
+在 `/test/test.js` 中写一个测试:
**/test/test.js**
@@ -75,9 +75,9 @@ describe('Array', () => {
});
```
-### Run your tests
+### 运行你的测试
-Add a `test` script in `package.json` that runs Karma with our settings.
+在我们设置好用于运行 Karma 的 `package.json` 中添加一个测试脚本。
**package.json**
@@ -87,15 +87,15 @@ Add a `test` script in `package.json` that runs Karma with our settings.
}
```
-When you run your tests (`yarn test`), Headless Chrome should fire up and output the results to the terminal:
+当你运行你的测试(`yarn test`)时,Headless Chrome 会启动并将运行结果输出到终端:

-### Creating your own Headless Chrome launcher
+### 创建你自己的 Headless Chrome 启动器
-The `ChromeHeadless` launcher is great because it works out of the box for testing on Headless Chrome. It includes the appropriate Chrome flags for you and launches a remote debugging version of Chrome on port `9222`.
+`ChromeHeadless` 启动器非常棒,因为它可以在 Headless Chrome 上进行测试。它包含了适合你的 Chrome 标志,并在端口 `9222` 上启动 Chrome 的远程调试版本。
-However, sometimes you may want to pass custom flags to Chrome or change the remote debugging port the launcher uses. To do that, create a `customLaunchers` field that extends the base `ChromeHeadless` launcher:
+但是,有时你可能希望将自定义的标志传递给 Chrome 或更改启动器使用的远程调试端口。要做到这一点,可以通过创建一个 `customLaunchers` 字段来扩展基础的 `ChromeHeadless` 启动器:
**karma.conf.js**
@@ -116,11 +116,11 @@ module.exports = function(config) {
};
```
-### Running it all on Travis CI
+### 在 Travis CI 上运行它
-Configuring Karma to run your tests in Headless Chrome is the hard part. Continuous integration in Travis is just a few lines away!
+在 Headless Chrome 中配置 Karma 运行测试是很困难的。而在 Travis 中持续整合就只有几种!
-To run your tests in Travis, use `dist: trusty` and install the Chrome stable addon:
+要在 Travis 中运行测试,请使用 `dist: trusty` 并安装稳定版 Chrome 插件:
**.travis.yml**
@@ -146,14 +146,14 @@ script:
作者简介
-[Eric Bidelman][1]Engineer @ Google working on Lighthouse, Web Components, Chrome, and the web
+[Eric Bidelman][1] 谷歌工程师,Lighthouse 开发,Web 和 Web 组件开发,Chrome 开发
----------------
via: https://developers.google.com/web/updates/2017/06/headless-karma-mocha-chai
作者:[ Eric Bidelman][a]
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+译者:[firmianay](https://github.com/firmianay)
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/translated/tech/20170823 Why open source should be the first choice for cloud-native environments.md b/translated/tech/20170823 Why open source should be the first choice for cloud-native environments.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 2c5bda6774..0000000000
--- a/translated/tech/20170823 Why open source should be the first choice for cloud-native environments.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,143 +0,0 @@
-为什么开源应该是云原生环境的首选
-============================================================
-
-
-### 基于相同的原因,Linux 击败了闭源软件,开源应该成为云原生环境的首选。
-
-
-
-Image by :
-
-[Jason Baker][6]. [CC BY-SA 4.0][7]. Source: [Cloud][8], [Globe][9]. Both [CC0][10].
-
-让我们回溯到上世纪 90 年代,当时闭源软件大行其道,而开源才刚开始进入它自己的时代。是什么导致了这种转变,更重要的是,当我们转变为云原生环境时,我们能从今天学到什么?
-
-
-### 基础设施的历史教训
-
-
-我将从一个高度武断、开放基础设施的过去30年历史开始。如果他们知道什么的话,在 20 世纪 90 年代,Linux 只是大多数组织的雷达上的一个闪光点。从那些很快看到 Linux 好处的公司中,你已经得到了早期的支持,它主要是作为私有 Unix 的廉价替代品,但是即使 UNIX 与日俱增,使用 Microsoft Windows NT 来部署服务器依旧是一种标准方式。
-
-这种工具的专有特性为更专有的软件提供了一个肥沃的生态系统。软件被装箱出售。甚至开源也参与了包装游戏;你可以在书架上买到Linux,而不是把你的互联网连接从免费的来源下载。去商店或者和你的软件供应商一起工作只是你得到软件的方式。
-
-### [ubuntu_box.png][1]
-
-
-
-Ubuntu盒包装在最好的买架上
-
-我认为,随着 LAMP 系列 (Linux、Apache、MySQL 和 PHP / Perl / Python) 的兴起,情况发生了变化。
-
-我认为,随着 LAMP 系列 (Linux、Apache、MySQL 和 PHP / Perl / Python) 的兴起,情况发生了变化。LAMP系列是一个巨大的成功故事。它是稳定的、可伸缩的、友好的。与此同时,我开始看到对闭源解决方案的不满。一旦客户在LAMP系列中有了这种开源的念头,他们就会改变他们对软件的期望,包括:
-
-* 不愿被供应商绑架,
-
-* 关注安全,
-
-* 希望修复 bug ,以及
-
-* 当软件被孤立开发时,意味着创新被扼杀了。
-
-在技术方面,我们也看到了组织者在如何使用软件上的巨大变化。突如其来一个网站的宕机是不可预测和接受的。这会对扩展性和自动化造成影响。特别是在过去的十年里,我们看到了从传统的基础设施模型到“牛”模型的转变,在这种模式中,服务器可以被替换和替换,而不是保存和命名。公司使用大量的数据,更注重数据保留和处理速度,并将数据返回给用户。
-
-开源社区,开放社区和来自大公司的增持投资,为我们如何开始使用软件提供了基础。系统管理员的工作职责开始需要使用 Linux 的技能,熟悉开源技术和方法。通过开源,如 Chef cookbooks 和 Puppet 模块,管理员可以共享他们工具的配置。我们不再单独配置和调优 MySQL ;我们创建了一个用于处理以上问题的系统。
-
-开源现在无处不在,围绕它的工具也无处不在。我们可以把重点放在更有趣的工程上,从而为我们的雇主带来更大的价值。
-
-开源现在无处不在,围绕它的工具也无处不在。曾经对这个想法怀有敌意的公司不仅通过互操作性项目与外界拥抱开源,而且还通过发布他们自己的开源软件项目并且围绕它们构建社区。
-
-### [microsoft_linux_stick.png][2]
-
-
-
-A "Microsoft
-
- Linux" USB stick
-
-
-### 转向云端
-
-
-今天,我们生活在一个 DevOps 和云端的世界里。我们收获了开源运动带来的创新成果。 Tim O ' reilly 所称的 “[inner-sourcing][11]” ,在公司内部采用开源软件开发实践。我们正在为云平台共享部署配置。像 Terraform 这样的工具甚至允许我们编写和分享我们如何部署到特定的平台。
-
-今天,我们生活在一个 DevOps 和云端的世界里。但这些平台本身呢?
-
-> "Most people just consume the cloud without thinking ... many users are sinking cost into infrastructure that is not theirs, and they are giving up data and information about themselves without thinking."
-> —Edward Snowden, OpenStack Summit, May 9, 2017
-
-现在是时候把更多的想法放入我们的本能反应中来部署扩展到云上。
-
-就像 Snowden 强调的那样,现在我们有可能失去对用户数据的控制。抛开安全不谈,如果我们回顾一下我们转向开源的原因,个中原因还包括对厂商锁定的担忧,创新难以推动,以及无法修复bug。
-
-在你把自己和/或你的公司锁定在一个专有平台之前,考虑以下问题:
-
-* 我使用的服务是遵循开放标准,还是闭源?
-
-* 如果服务供应商破产或被竞争对手收购,我的追索权是什么?
-
-* 关于停机、安全等问题,供应商在与客户沟通中是否有一个明确而真诚的历史过往?
-
-* 供应商是否响应bug和特性请求,即使那是来自小客户?
-
-* 供应商是否会在我不知情的情况下使用我们的数据(或者更糟,不让我们反对的客户协议)?
-
-* 供应商是否有一个计划来处理长期的,不断上升的增长成本,特别是如果最初的成本很低呢?
-
-您可以通过这个问卷,讨论每个要点,仍然决定使用专有的解决方案。这很好,公司一直都在这么做。然而,如果你像我一样,宁愿找到一个更开放的解决方案,而仍然受益于云,你确实有选择。
-
-
-### 基于私有云
-
-
-当您寻找私有云解决方案时,您的第一个选择是投资一个云提供商,它的核心运行在开源软件上。 [OpenStack][12] 是行业领袖,在其7年的历史中,有100多个参与组织和成千上万的贡献者(包括我)。 OpenStack 项目已经证明,与多个 openstackbased 云的接口不仅是可以实现,而且相对简单。云公司之间的 api 是相似的,所以您不必局限于特定的 OpenStack 供应商。作为一个开放源码项目,您仍然可以影响基础设施的特性、bug请求和方向。
-
-第二种选择是继续在一个基本级别上使用专有云,但在一个开源容器编排系统中。无论您选择 [DC / OS][13](基于[Apache Mesos][14]) ,[Kubernetes][15] ,或[Docker in swarm mode][16] ,这些平台都允许您将专有云系统提供的虚拟机作为独立的 Linux 机器,并在此之上安装您的平台。您所需要的只是 linux 不会立即被锁定在特定于云的工具或平台上。决策可以根据具体情况来决定是否使用特定的私有后端,但如果你这样做,就应该着眼于未来。
-
-有了这两种选择,你也可以选择完全离开云。您可以部署自己的 OpenStack 云,或者将容器平台内部架构移动到您自己的数据中心。
-
-
-### 做一个月球探测器
-
-
-最后,我想谈一谈开源项目基础设施。今年3月,来自 [Southern California Linux Expo][17] 的多个开放源码项目的参与者讨论了为他们的项目运行开源基础设施。(更多的,请阅读我的 [summary of this event][18]。)我认为这些项目的工作是基础设施开放采购的最后一步。除了我们现在正在做的基本分享之外,我相信公司和组织可以在不放弃与竞争对手较劲的情况下,充分利用他们的基础设施开源。
-
-开源项目已经公开了他们的基础设施,已经证明了允许多个公司和组织向他们的基础设施提交有系统知识的 bug 报告,甚至是补丁和特定论文。突然之间,你可以邀请兼职的贡献者。你的客户可以通过了解你的基础设施在“引擎”而使用放心。
-
-
-想要更多的证据吗?访问 [Open Source Infrastructure][19] 的网站,了解更多的项目,使其基础设施开放源代码(以及他们已经发布的大量基础设施)。
-
-
-8 月 26 日在费城的 FOSSCON 网站上,伊丽莎白·k·约瑟夫的演讲[The Open Sourcing of Infrastructure][4]。
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: https://opensource.com/article/17/8/open-sourcing-infrastructure
-
-作者:[ Elizabeth K. Joseph][a]
-译者:[ wenzhiyi ](https://github.com/wenzhiyi)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:https://opensource.com/users/pleia2
-[1]:https://opensource.com/file/366596
-[2]:https://opensource.com/file/366591
-[3]:https://opensource.com/article/17/8/open-sourcing-infrastructure?rate=PdT-huv5y5HFZVMHOoRoo_qd95RG70y4DARqU5pzgkU
-[4]:https://fosscon.us/node/12637
-[5]:https://opensource.com/user/25923/feed
-[6]:https://opensource.com/users/jason-baker
-[7]:https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/
-[8]:https://pixabay.com/en/clouds-sky-cloud-dark-clouds-1473311/
-[9]:https://pixabay.com/en/globe-planet-earth-world-1015311/
-[10]:https://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/
-[11]:https://opensource.com/life/16/11/create-internal-innersource-community
-[12]:https://www.openstack.org/
-[13]:https://dcos.io/
-[14]:http://mesos.apache.org/
-[15]:https://kubernetes.io/
-[16]:https://docs.docker.com/engine/swarm/
-[17]:https://www.socallinuxexpo.org/
-[18]:https://opensource.com/article/17/3/growth-open-source-project-infrastructures
-[19]:https://opensourceinfra.org/
-[20]:https://opensource.com/users/pleia2
-[21]:https://opensource.com/users/pleia2