mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-02-03 23:40:14 +08:00
Merge remote-tracking branch 'LCTT/master'
This commit is contained in:
commit
24b7019b54
@ -0,0 +1,96 @@
|
||||
[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
|
||||
[#]: translator: (wxy)
|
||||
[#]: reviewer: (wxy)
|
||||
[#]: publisher: (wxy)
|
||||
[#]: url: (https://linux.cn/article-11346-1.html)
|
||||
[#]: subject: (Great News! Firefox 69 Blocks Third-Party Cookies, Autoplay Videos & Cryptominers by Default)
|
||||
[#]: via: (https://itsfoss.com/firefox-69/)
|
||||
[#]: author: (Ankush Das https://itsfoss.com/author/ankush/)
|
||||
|
||||
Firefox 69 默认阻拦第三方 Cookie、自动播放的视频和加密矿工
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||
如果你使用的是 [Mozilla Firefox][1] 并且尚未更新到最新版本,那么你将错过许多新的重要功能。
|
||||
|
||||
### Firefox 69 版本中的一些新功能
|
||||
|
||||
首先,Mozilla Firefox 69 会默认强制执行更强大的安全和隐私选项。以下是新版本的一些主要亮点。
|
||||
|
||||
#### Firefox 69 阻拦视频自动播放
|
||||
|
||||
![][2]
|
||||
|
||||
现在很多网站都提供了自动播放视频。无论是弹出视频还是嵌入在文章中设置为自动播放的视频,默认情况下,Firefox 69 都会阻止它(或者可能会提示你)。
|
||||
|
||||
这个[阻拦自动播放][3]功能可让用户自动阻止任何视频播放。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 禁止第三方跟踪 cookie
|
||||
|
||||
默认情况下,作为<ruby>增强型跟踪保护<rt>Enhanced Tracking Protection</rt></ruby>功能的一部分,它现在将阻止第三方跟踪 Cookie 和加密矿工。这是 Mozilla Firefox 的增强隐私保护功能的非常有用的改变。
|
||||
|
||||
Cookie 有两种:第一方的和第三方的。第一方 cookie 由网站本身拥有。这些是“好的 cookie”,可以让你保持登录、记住你的密码或输入字段等来改善浏览体验。第三方 cookie 由你访问的网站以外的域所有。广告服务器使用这些 Cookie 来跟踪你,并在你访问的所有网站上跟踪广告。Firefox 69 旨在阻止这些。
|
||||
|
||||
当它发挥作用时,你将在地址栏中看到盾牌图标。你可以选择为特定网站禁用它。
|
||||
|
||||
![Firefox Blocking Tracking][4]
|
||||
|
||||
#### 禁止加密矿工消耗你的 CPU
|
||||
|
||||
![][5]
|
||||
|
||||
对加密货币的欲望一直困扰着这个世界。GPU 的价格已经高企,因为专业的加密矿工们使用它们来挖掘加密货币。
|
||||
|
||||
人们使用工作场所的计算机秘密挖掘加密货币。当我说工作场所时,我不一定是指 IT 公司。就在今年,[人们在乌克兰的一家核电站抓住了偷挖加密货币的活动][6]。
|
||||
|
||||
不仅如此。如果你访问某些网站,他们会运行脚本并使用你的计算机的 CPU 来挖掘加密货币。这在 IT 术语中被称为 <ruby>[挖矿攻击][7]<rt>cryptojacking</rt></ruby>。
|
||||
|
||||
好消息是 Firefox 69 会自动阻止这些加密矿工脚本。因此,网站不再能利用你的系统资源进行挖矿攻击了。
|
||||
|
||||
#### Firefox 69 带来的更强隐私保护
|
||||
|
||||
![][8]
|
||||
|
||||
如果你把隐私保护设置得更严格,那么它也会阻止指纹。因此,当你在 Firefox 69 中选择严格的隐私设置时,你不必担心通过[指纹][9]共享计算机的配置信息。
|
||||
|
||||
在[关于这次发布的官方博客文章][10]中,Mozilla 提到,在此版本中,他们希望默认情况下为 100% 的用户提供保护。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 性能改进
|
||||
|
||||
尽管在更新日志中没有提及 Linux,但它提到了在 Windows 10/mac OS 上运行性能、UI 和电池寿命有所改进。如果你发现任何性能改进,请在评论中提及。
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结
|
||||
|
||||
除了所有这些之外,还有很多底层的改进。你可以查看[发行说明][11]中的详细信息。
|
||||
|
||||
Firefox 69 对于关注其隐私的用户来说是一个令人印象深刻的更新。与我们最近对某些[安全电子邮件服务][12]的建议类似,我们建议你更新浏览器以充分受益。新版本已在大多数 Linux 发行版中提供,你只需要更新你的系统即可。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你对阻止广告和跟踪 Cookie 的浏览器感兴趣,请尝试[开源的 Brave 浏览器][13],他们甚至给你提供了加密货币以让你使用他们的浏览器,你可以使用这些加密货币来奖励你最喜爱的发布商。
|
||||
|
||||
你觉得这个版本怎么样?请在下面的评论中告诉我们你的想法。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://itsfoss.com/firefox-69/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Ankush Das][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972][b]
|
||||
译者:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: https://itsfoss.com/author/ankush/
|
||||
[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
|
||||
[1]: https://itsfoss.com/why-firefox/
|
||||
[2]: https://i1.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/09/auto-block-firefox.png?ssl=1
|
||||
[3]: https://support.mozilla.org/en-US/kb/block-autoplay
|
||||
[4]: https://i1.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/09/firefox-blocking-tracking.png?ssl=1
|
||||
[5]: https://i0.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/09/firefox-shield.png?ssl=1
|
||||
[6]: https://thenextweb.com/hardfork/2019/08/22/ukrainian-nuclear-powerplant-mine-cryptocurrency-state-secrets/
|
||||
[7]: https://hackernoon.com/cryptojacking-in-2019-is-not-dead-its-evolving-984b97346d16
|
||||
[8]: https://i0.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/09/firefox-secure.jpg?ssl=1
|
||||
[9]: https://clearcode.cc/blog/device-fingerprinting/
|
||||
[10]: https://blog.mozilla.org/blog/2019/09/03/todays-firefox-blocks-third-party-tracking-cookies-and-cryptomining-by-default/
|
||||
[11]: https://www.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/69.0/releasenotes/
|
||||
[12]: https://itsfoss.com/secure-private-email-services/
|
||||
[13]: https://itsfoss.com/brave-web-browser/
|
||||
@ -1,96 +0,0 @@
|
||||
[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
|
||||
[#]: translator: ( )
|
||||
[#]: reviewer: ( )
|
||||
[#]: publisher: ( )
|
||||
[#]: url: ( )
|
||||
[#]: subject: (Great News! Firefox 69 Blocks Third-Party Cookies, Autoplay Videos & Cryptominers by Default)
|
||||
[#]: via: (https://itsfoss.com/firefox-69/)
|
||||
[#]: author: (Ankush Das https://itsfoss.com/author/ankush/)
|
||||
|
||||
Great News! Firefox 69 Blocks Third-Party Cookies, Autoplay Videos & Cryptominers by Default
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||
If you’re using [Mozilla Firefox][1] and haven’t updated yet to the latest version, you are missing a lot of new and important features.
|
||||
|
||||
### Awesome new features in Firefox 69 release
|
||||
|
||||
To start with, Mozilla Firefox 69 enforces stronger security and privacy options by default. Here are some of the major highlights of the new release.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Firefox 69 blocks autoplay videos
|
||||
|
||||
![][2]
|
||||
|
||||
A lot of websites offer auto-play videos nowadays. No matter whether it is a pop-up video or a video embedded in an article set to autoplay, it is blocked by default (or you may be prompted about it).
|
||||
|
||||
The [Block Autoplay][3] feature gives users to block any video playing automatically.
|
||||
|
||||
#### No more third party tracking cookies
|
||||
|
||||
By default, as part of the Enhanced Tracking Protection feature, it will now block third-party tracking cookies and crypto miners. This is a very useful change to enhance privacy protection while using Mozilla Firefox.
|
||||
|
||||
There are two kind of cookies: first party and third party. The first party cookies are owned by the website itself. These are the ‘good cookies’ that improve your browsing experience by keeping you logged in, remembering your password or entry fields etc. The third party cookies are owned by domains other than the website you visit. Ad servers use these cookies to track you and serve you tracking ads on all the website you visit. Firefox 69 aims to block these.
|
||||
|
||||
You will observe the shield icon in the address bar when it’s active. You may choose to disable it for specific websites.
|
||||
|
||||
![Firefox Blocking Tracking][4]
|
||||
|
||||
#### No more cryptomining off your CPU
|
||||
|
||||
![][5]
|
||||
|
||||
The lust for cryptocurrency has plagued the world. The cost of GPU has gone high because the professional cryptominers use them for mining cryptocurrency.
|
||||
|
||||
People are using computers at work to secretly mine cryptocurrency. And when I say work, I don’t necessarily mean an IT company. Only this year, [people got caught mining cryptocurency at a nuclear plant in Ukrain][6][.][6]
|
||||
|
||||
That’s not it. If you visit some websites, they run scripts and use your computer’s CPU to mine cryptocurrency. This is called [cryptojacking][7] in IT terms.
|
||||
|
||||
The good thing is that Firefox 69 will automatically blocking cryptominers. So websites should not be able to exploit your system resources for cryptojacking.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Stronger Privacy with Firefox 69
|
||||
|
||||
![][8]
|
||||
|
||||
If you take it up a notch with a stricter setting, it will block fingerprinters as well. So, you won’t have to worry about sharing your computer’s configuration info via [fingerprinters][9] when you choose the strict privacy setting in Firefox 69.
|
||||
|
||||
In the [official blog post about the release][10], Mozilla mentions that with this release, they expect to provide protection for 100% of our users by default.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Performance Improvements
|
||||
|
||||
Even though Linux hasn’t been mentioned in the changelog – it mentions performance, UI, and battery life improvements for systems running on Windows 10/mac OS. If you observe any performance improvements, do mention it in comments.
|
||||
|
||||
**Wrapping Up**
|
||||
|
||||
In addition to all these, there’s a lot of under-the-hood improvements as well. You can check out the details in the [release notes][11].
|
||||
|
||||
Firefox 69 is an impressive update for users concerned about their privacy. Similar to our recommendation on some of the [secure email services][12] recently, we recommend you to update your browser to get the best out of it. The new update is already available in most Linux distributions. You just have to update your system.
|
||||
|
||||
If you are interested in browsers that block ads and tracking cookies, try [open source Brave browser][13]. They are even giving you their own cryptocurrency for using their web browser. You can use it to reward your favorite publishers.
|
||||
|
||||
What do you think about this release? Let us know your thoughts in the comments below.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://itsfoss.com/firefox-69/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Ankush Das][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972][b]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: https://itsfoss.com/author/ankush/
|
||||
[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
|
||||
[1]: https://itsfoss.com/why-firefox/
|
||||
[2]: https://i1.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/09/auto-block-firefox.png?ssl=1
|
||||
[3]: https://support.mozilla.org/en-US/kb/block-autoplay
|
||||
[4]: https://i1.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/09/firefox-blocking-tracking.png?ssl=1
|
||||
[5]: https://i0.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/09/firefox-shield.png?ssl=1
|
||||
[6]: https://thenextweb.com/hardfork/2019/08/22/ukrainian-nuclear-powerplant-mine-cryptocurrency-state-secrets/
|
||||
[7]: https://hackernoon.com/cryptojacking-in-2019-is-not-dead-its-evolving-984b97346d16
|
||||
[8]: https://i0.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/09/firefox-secure.jpg?ssl=1
|
||||
[9]: https://clearcode.cc/blog/device-fingerprinting/
|
||||
[10]: https://blog.mozilla.org/blog/2019/09/03/todays-firefox-blocks-third-party-tracking-cookies-and-cryptomining-by-default/
|
||||
[11]: https://www.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/69.0/releasenotes/
|
||||
[12]: https://itsfoss.com/secure-private-email-services/
|
||||
[13]: https://itsfoss.com/brave-web-browser/
|
||||
@ -1,95 +0,0 @@
|
||||
How blockchain can complement open source
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[The Cathedral and The Bazaar][1] is a classic open source story, written 20 years ago by Eric Steven Raymond. In the story, Eric describes a new revolutionary software development model where complex software projects are built without (or with a very little) central management. This new model is open source.
|
||||
|
||||
Eric's story compares two models:
|
||||
|
||||
* The classic model (represented by the cathedral), in which software is crafted by a small group of individuals in a closed and controlled environment through slow and stable releases.
|
||||
* And the new model (represented by the bazaar), in which software is crafted in an open environment where individuals can participate freely but still produce a stable and coherent system.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Some of the reasons open source is so successful can be traced back to the founding principles Eric describes. Releasing early, releasing often, and accepting the fact that many heads are inevitably better than one allows open source projects to tap into the world’s pool of talent (and few companies can match that using the closed source model).
|
||||
|
||||
Two decades after Eric's reflective analysis of the hacker community, we see open source becoming dominant. It is no longer a model only for scratching a developer’s personal itch, but instead, the place where innovation happens. Even the world's [largest][2] software companies are transitioning to this model in order to continue dominating.
|
||||
|
||||
### A barter system
|
||||
|
||||
If we look closely at how the open source model works in practice, we realize that it is a closed system, exclusive only to open source developers and techies. The only way to influence the direction of a project is by joining the open source community, understanding the written and the unwritten rules, learning how to contribute, the coding standards, etc., and doing it yourself.
|
||||
|
||||
This is how the bazaar works, and it is where the barter system analogy comes from. A barter system is a method of exchanging services and goods in return for other services and goods. In the bazaar—where the software is built—that means in order to take something, you must also be a producer yourself and give something back in return. And that is by exchanging your time and knowledge for getting something done. A bazaar is a place where open source developers interact with other open source developers and produce open source software the open source way.
|
||||
|
||||
The barter system is a great step forward and an evolution from the state of self-sufficiency where everybody must be a jack of all trades. The bazaar (open source model) using the barter system allows people with common interests and different skills to gather, collaborate, and create something that no individual can create on their own. The barter system is simple and lacks complex problems of the modern monetary systems, but it also has some limitations, such as:
|
||||
|
||||
* Lack of divisibility: In the absence of a common medium of exchange, a large indivisible commodity/value cannot be exchanged for a smaller commodity/value. For example, if you want to do even a small change in an open source project, you may sometimes still need to go through a high entry barrier.
|
||||
* Storing value: If a project is important to your company, you may want to have a large investment/commitment in it. But since it is a barter system among open source developers, the only way to have a strong say is by employing many open source committers, and that is not always possible.
|
||||
* Transferring value: If you have invested in a project (trained employees, hired open source developers) and want to move focus to another project, it is not possible to transfer expertise, reputation, and influence quickly.
|
||||
* Temporal decoupling: The barter system does not provide a good mechanism for deferred or advance commitments. In the open source world, that means a user cannot express commitment or interest in a project in a measurable way in advance, or continuously for future periods.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Below, we will explore how to address these limitations using the back door to the bazaar.
|
||||
|
||||
### A currency system
|
||||
|
||||
People are hanging at the bazaar for different reasons: Some are there to learn, some are there to scratch a personal developer's itch, and some work for large software farms. Because the only way to have a say in the bazaar is to become part of the open source community and join the barter system, in order to gain credibility in the open source world, many large software companies employ these developers and pay them in monetary value. This represents the use of a currency system to influence the bazaar. Open source is no longer only for scratching the personal developer itch. It also accounts for a significant part of the overall software production worldwide, and there are many who want to have an influence.
|
||||
|
||||
Open source sets the guiding principles through which developers interact and build a coherent system in a distributed way. It dictates how a project is governed, how software is built, and how the output distributed to users. It is an open consensus model for decentralized entities for building quality software together. But the open source model does not cover how open source is subsidized. Whether it is sponsored, directly or indirectly, through intrinsic or extrinsic motivators is irrelevant to the bazaar.
|
||||
|
||||
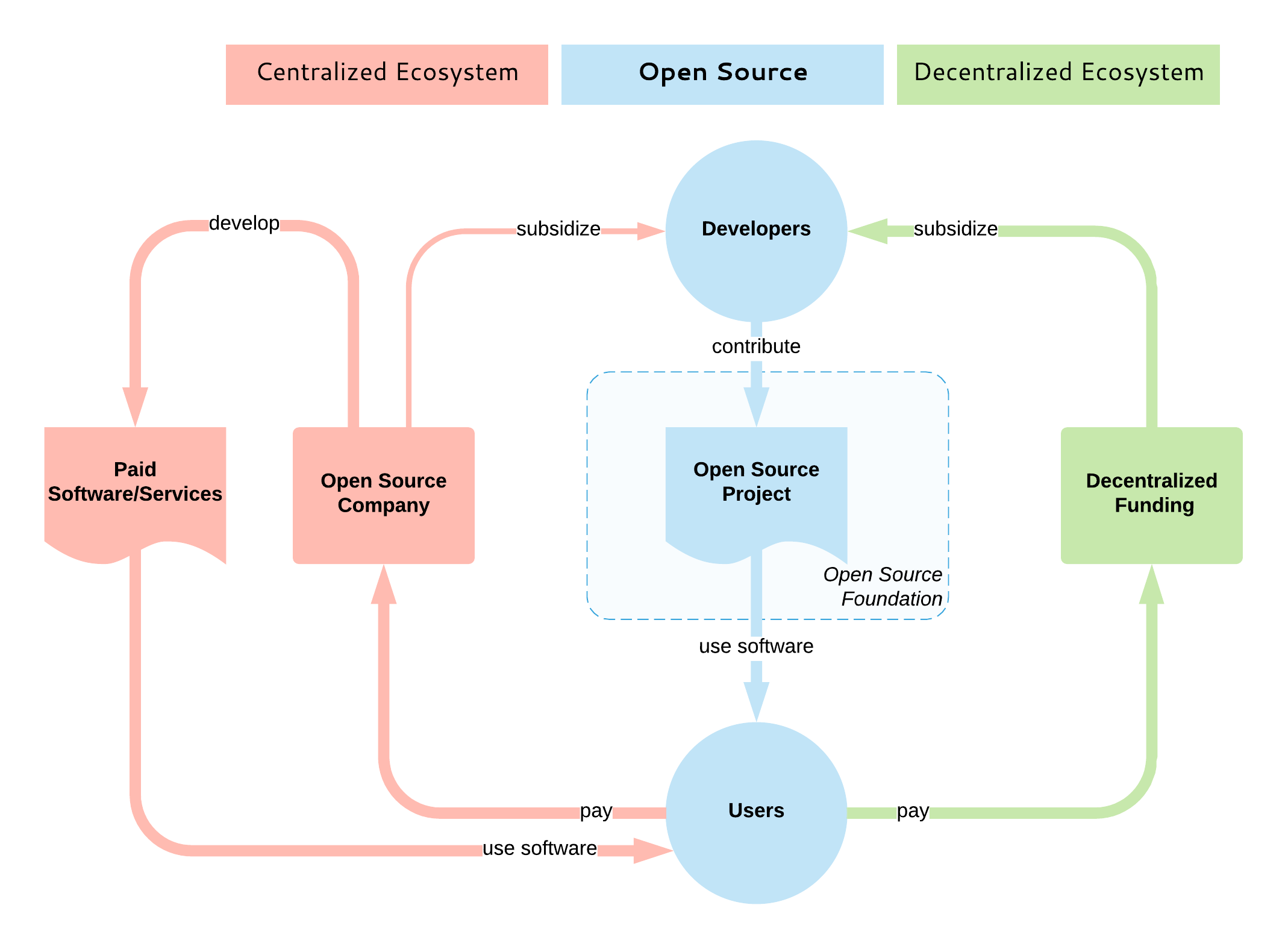
|
||||
|
||||
Currently, there is no equivalent of the decentralized open source development model for subsidization purposes. The majority of open source subsidization is centralized, where typically one company dominates a project by employing the majority of the open source developers of that project. And to be honest, this is currently the best-case scenario, as it guarantees that the developers will be paid for a long period and the project will continue to flourish.
|
||||
|
||||
There are also exceptions for the project monopoly scenario: For example, some Cloud Native Computing Foundation projects are developed by a large number of competing companies. Also, the Apache Software Foundation aims for their projects not to be dominated by a single vendor by encouraging diverse contributors, but most of the popular projects, in reality, are still single-vendor projects.
|
||||
|
||||
What we are missing is an open and decentralized model that works like the bazaar without a central coordination and ownership, where consumers (open source users) and producers (open source developers) interact with each other, driven by market forces and open source value. In order to complement open source, such a model must also be open and decentralized, and this is why I think the blockchain technology would [fit best here][3].
|
||||
|
||||
Most of the existing blockchain (and non-blockchain) platforms that aim to subsidize open source development are targeting primarily bug bounties, small and piecemeal tasks. A few also focus on funding new open source projects. But not many aim to provide mechanisms for sustaining continued development of open source projects—basically, a system that would emulate the behavior of an open source service provider company, or open core, open source-based SaaS product company: ensuring developers get continued and predictable incentives and guiding the project development based on the priorities of the incentivizers; i.e., the users. Such a model would address the limitations of the barter system listed above:
|
||||
|
||||
* Allow divisibility: If you want something small fixed, you can pay a small amount rather than the full premium of becoming an open source developer for a project.
|
||||
* Storing value: You can invest a large amount into a project and ensure both its continued development and that your voice is heard.
|
||||
* Transferring value: At any point, you can stop investing in the project and move funds into other projects.
|
||||
* Temporal decoupling: Allow regular recurring payments and subscriptions.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
There would be also other benefits, purely from the fact that such a blockchain-based system is transparent and decentralized: to quantify a project’s value/usefulness based on its users’ commitment, open roadmap commitment, decentralized decision making, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion
|
||||
|
||||
On the one hand, we see large companies hiring open source developers and acquiring open source startups and even foundational platforms (such as Microsoft buying GitHub). Many, if not most, long-running successful open source projects are centralized around a single vendor. The significance of open source and its centralization is a fact.
|
||||
|
||||
On the other hand, the challenges around [sustaining open source][4] software are becoming more apparent, and many are investigating this space and its foundational issues more deeply. There are a few projects with high visibility and a large number of contributors, but there are also many other still-important projects that lack enough contributors and maintainers.
|
||||
|
||||
There are [many efforts][3] trying to address the challenges of open source through blockchain. These projects should improve the transparency, decentralization, and subsidization and establish a direct link between open source users and developers. This space is still very young, but it is progressing quickly, and with time, the bazaar is going to have a cryptocurrency system.
|
||||
|
||||
Given enough time and adequate technology, decentralization is happening at many levels:
|
||||
|
||||
* The internet is a decentralized medium that has unlocked the world’s potential for sharing and acquiring knowledge.
|
||||
* Open source is a decentralized collaboration model that has unlocked the world’s potential for innovation.
|
||||
* Similarly, blockchain can complement open source and become the decentralized open source subsidization model.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Follow me on [Twitter][5] for other posts in this space.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://opensource.com/article/18/9/barter-currency-system
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Bilgin lbryam][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: https://opensource.com/users/bibryam
|
||||
[1]: http://catb.org/
|
||||
[2]: http://oss.cash/
|
||||
[3]: https://opensource.com/article/18/8/open-source-tokenomics
|
||||
[4]: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VS6IpvTWwkQ
|
||||
[5]: http://twitter.com/bibryam
|
||||
@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
|
||||
[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
|
||||
[#]: translator: ( )
|
||||
[#]: translator: (heguangzhi)
|
||||
[#]: reviewer: ( )
|
||||
[#]: publisher: ( )
|
||||
[#]: url: ( )
|
||||
@ -159,7 +159,7 @@ via: https://opensource.com/article/19/8/using-conda-ansible-administration-maco
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[James Farrell][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972][b]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/heguangzhi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,87 @@
|
||||
区块链是如何补充开源的
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[大教堂与集市][1]是 20 年前由<ruby>埃里克·史蒂文·雷蒙德<rt>Eric Steven Raymond<rt></ruby>(ESR)撰写的经典开源故事。在这个故事中,ESR 描述了一种新的革命性软件开发模型,其中复杂的软件项目是在没有(或者很少的)集中管理的情况下构建的。这个新模型就是开源。
|
||||
|
||||
ESR 的故事比较了两种模式:
|
||||
|
||||
* 经典模型(由“大教堂”代表),其中软件由一小群人在封闭和受控的环境中通过缓慢而稳定的发布版本制作而成。
|
||||
* 以及新模式(由“集市”代表),其中软件是在开放的环境中制作的,个人可以自由参与,但仍然可以产生一个稳定和连贯的系统。
|
||||
|
||||
开源如此成功的一些原因可以追溯到 ESR 所描述的基础原则。尽早发布、经常发布,并接受许多头脑必然比一个更好的事实,会让开源项目进入全世界的人才库(很少有公司能够使用闭源模式与之匹敌)。
|
||||
|
||||
在 ESR 对黑客社区的反思分析 20 年后,我们看到开源成为占据主导地位的的模式。它不再仅仅是开发人员的个人癖好的模式,而是创新发生的地方。即使是全球[最大][2]软件公司也正在转向这种模式,以便继续占据主导地位。
|
||||
|
||||
### 易货系统
|
||||
|
||||
如果我们仔细研究开源模型在实践中的运作方式,我们就会发现它是一个封闭的系统,专属于开源开发人员和技术人员。影响项目方向的唯一方法是加入开源社区,了解成文和不成文的规则,学习如何贡献,编码标准等,并自己亲力完成。
|
||||
|
||||
这就是集市的运作方式,也是易货系统类比的来源。易货系统是一种交换服务和货物以换取其他服务和货物的方法。在市场中(即软件的构建)这意味着为了获取某些东西,你必须自己也是一个生产者并回馈一些东西——那就是通过交换你的时间和知识来完成任务。集市是开源开发人员与其他开源开发人员交互并以开源方式生成开源软件的地方。
|
||||
|
||||
易货系统向前迈出了一大步,从自给自足的状态演变而来,而在自给自足的状态下,每个人都必须成为所有行业的杰出人选。使用易货系统的集市(开源模式)允许具有共同兴趣和不同技能的人们收集、协作和创造个人无法自己创造的东西。易货系统简单,而不像现代货币系统那么复杂,但也有一些局限性,例如:
|
||||
|
||||
* 缺乏可分性:在没有共同的交换媒介的情况下,不能将较大的不可分割的商品/价值换成较小的商品/价值。例如,如果你想在开源项目中进行一些小的更改,有时你可能仍需要经历一个高进入门槛。
|
||||
* 存储价值:如果项目对贵公司很重要,你可能想要投入大量投资/承诺。但由于它是开源开发人员之间的易货系统,因此拥有强大发言权的唯一方法是雇佣许多开源贡献者,但这并非总是可行的。
|
||||
* 转移价值:如果你投资了一个项目(受过培训的员工、雇用开源开发人员)并希望将重点转移到另一个项目,却不可能快速转移(你在上一个项目中拥有的)专业知识、声誉和影响力。
|
||||
* 时间脱钩:易货系统没有为延期或提前承诺提供良好的机制。在开源世界中,这意味着用户无法提前或在未来期间以可衡量的方式表达对项目的承诺或兴趣。
|
||||
|
||||
下面,我们将探讨如何使用集市的后门解决这些限制。
|
||||
|
||||
### 货币系统
|
||||
|
||||
人们因为不同的原因勾连在集市上:有些人在那里学习,有些是出于满足开发人员个人的喜好,有些人在大型软件工厂工作。因为在集市中拥有发言权的唯一方法是成为开源社区的一份子并加入这个易货系统,为了在开源世界获得信誉,许多大型软件公司雇用这些开发者并以货币方式支付薪酬。这代表使用货币系统来影响集市。开源不再只是为了满足开发人员个人的喜好。它也占据全球整体软件生产的重要部分,并且有许多人想要产生影响。
|
||||
|
||||
开源设置了开发人员交互的指导原则,并以分布式方式构建一致的系统。它决定了项目的治理方式、软件的构建方式以及其成果如何分配给用户。它是分散实体共同构建高质量软件的开放共识模型。但是开源模型并没有包括如何补贴开源。无论是直接还是间接地通过内在或外在动机的赞助,都与集市无关。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
目前,没有相当于以补贴为目的的去中心化式开源开发模型。大多数开源补贴都是集中式的,通常一家公司通过雇用该项目的主要开源开发人员来支配该项目。说实话,这是目前最好的情况,因为它保证了开发人员将长期获得报酬,项目也将继续蓬勃发展。
|
||||
|
||||
项目垄断情景也有例外情况:例如,一些云原生计算基金会(CNCF)项目是由大量的竞争公司开发的。此外,Apache 软件基金会(ASF)旨在通过鼓励不同的贡献者来使他们的项目不被单一供应商所主导,但实际上大多数受欢迎的项目仍然是单一供应商项目。
|
||||
|
||||
我们缺少的是一个开放的、去中心化的模式,就像一个没有集中协调和所有权的集市一样,消费者(开源用户)和生产者(开源开发者)在市场力量和开源价值的驱动下相互作用。为了补充开源,这样的模型也必须是开放和去中心化的,这就是为什么我认为区块链技术[最适合][3]的原因。
|
||||
|
||||
旨在补贴开源开发的大多数现有区块链(和非区块链)平台主要针对的是错误赏金、小型和零碎的任务。少数人还专注于资助新的开源项目。但并没有很多人的目标是提供维持开源项目持续开发的机制 —— 基本上,这个系统可以模仿开源服务提供商公司或开放核心、基于开源的 SaaS 产品公司的行为:确保开发人员继续进行可预测的激励措施,并根据激励者(即用户)的优先事项指导项目开发。这种模型将解决上面列出的易货系统的局限性:
|
||||
|
||||
* 允许可分性:如果你想要一些小的修复,你可以支付少量费用,而不是成为项目的开源开发人员的全部费用。
|
||||
* 存储价值:你可以在项目中投入大量资金,并确保其持续发展和你的发言权。
|
||||
* 转移价值:在任何时候,你都可以停止投资项目并将资金转移到其他项目中。
|
||||
* 时间脱钩:允许定期定期付款和订阅。
|
||||
|
||||
还有其他好处,纯粹是因为这种基于区块链的系统是透明和去中心化的:根据用户的承诺、开放的路线图承诺、去中心化决策等来量化项目的价值/实用性。
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结
|
||||
|
||||
一方面,我们看到大公司雇用开源开发人员并收购开源初创公司甚至基础平台(例如微软收购 GitHub)。许多(甚至大多数)长期成功的开源项目集中在一个供应商周围。开源的重要性及其集中化是一个事实。
|
||||
|
||||
另一方面,围绕[持续开源][4]软件的挑战正变得越来越明显,许多人正在更深入地研究这个领域及其基础问题。有一些项目具有很高的知名度和大量的贡献者,但还有许多其他一样重要的项目缺乏足够的贡献者和维护者。
|
||||
|
||||
有[许多努力][3]试图通过区块链来解决开源的挑战。这些项目应提高透明度、去中心化和补贴,并在开源用户和开发人员之间建立直接联系。这个领域还很年轻,但是进展很快,随着时间的推移,集市将会有一个加密货币系统。
|
||||
|
||||
如果有足够的时间和足够的技术,去中心化就会发生在很多层面:
|
||||
|
||||
* 互联网是一种去中心化的媒介,它释放了全球分享和获取知识的潜力。
|
||||
* 开源是一种去中心化的协作模式,它释放了全球的创新潜力。
|
||||
* 同样,区块链可以补充开源,成为去中心化的开源补贴模式。
|
||||
|
||||
请在[推特][5]上关注我在这个领域的其他帖子。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://opensource.com/article/18/9/barter-currency-system
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Bilgin lbryam][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
|
||||
译者:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: https://opensource.com/users/bibryam
|
||||
[1]: http://catb.org/
|
||||
[2]: http://oss.cash/
|
||||
[3]: https://opensource.com/article/18/8/open-source-tokenomics
|
||||
[4]: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VS6IpvTWwkQ
|
||||
[5]: http://twitter.com/bibryam
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user