mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-01-25 23:11:02 +08:00
PUB:20170104 5 Ways to Find a Binary Command Description and Location on File System
@geekpi
This commit is contained in:
parent
b5d4be7d73
commit
2250e2d0f2
@ -1,33 +1,34 @@
|
|||||||
5个找出“二进制命令”描述和系统中位置的方法
|
5 个找出“二进制命令”描述和系统中位置的方法
|
||||||
============================================================
|
============================================================
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
在数千个[ Linux 系统可用的命令/程序][1]中,知道给定命令的类型和目的以及其在系统上的位置(绝对路径)对于新手来说可能是一个挑战。
|
在数千个 [Linux 系统上的命令/程序][1]中,知道给定命令的类型和目的以及其在系统上的位置(绝对路径)对于新手来说可能是一个挑战。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
知道命令/程序的一些细节不仅有助于[ Linux 用户掌握大量命令][2],还能使用户理解命令行或脚本在系统上的操作。
|
知道命令/程序的一些细节不仅有助于 [Linux 用户掌握大量命令][2],还能使用户理解命令行或脚本在系统上的操作。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
因此,在本文中我们将向你解释五个有用的命令,用于显示给定命令的简短描述和位置。
|
因此,在本文中我们将向你解释五个有用的命令,用于显示给定命令的简短描述和位置。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
要在系统上发现新命令,请查看 PATH 环境变量中的所有目录。这些目录存储系统上安装的所有命令/程序。
|
要在系统上发现新命令,请查看 PATH 环境变量中的所有目录。这些目录存储系统上安装的所有命令/程序。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
一旦你找到一个有趣的命令名,在继续阅读更多关于它的手册页之前,请尝试如下收集一些简要的信息。
|
一旦你找到一个有趣的命令,在继续阅读更多关于它的手册页之前,请尝试如下收集一些简要的信息。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
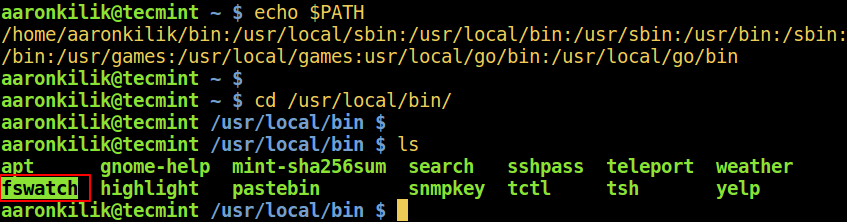
假设你输出了 PATH 的值,并进到目录 /usr/local/bin,注意到一个名为[ fswatch(监视文件修改更改)][3]的新命令:
|
假设你输出了 `PATH` 的值,然后进到其中的一个目录 `/usr/local/bin`,注意到一个名为 [`fswatch`(监视文件修改更改)][3]的新命令:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
$ echo $PATH
|
$ echo $PATH
|
||||||
$ cd /usr/local/bin
|
$ cd /usr/local/bin
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
[
|
[
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
][4]
|
][4]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
*在 Linux 中找出新命令*
|
*在 Linux 中找出新命令*
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
现在让我们在 Linux 中用不同的方法找出 fswatch 命令的描述和位置。
|
现在让我们在 Linux 中用不同的方法找出 `fswatch` 命令的描述和位置。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### 1\. whatis 命令
|
### 1、 whatis 命令
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
whatis 用于显示你作为参数输入的命令名的单行描述(例如下面命令中的fswatch)。
|
`whatis` 用于显示你作为参数输入的命令名的单行描述(例如下面命令中的 `fswatch`)。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
如果描述太长,一些部分在默认情况下会被省略,使用 `-l` 标志来显示完整的描述。
|
如果描述太长,一些部分在默认情况下会被省略,使用 `-l` 标志来显示完整的描述。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@ -41,9 +42,9 @@ $ whatis -l fswatch
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
*Linux whatis 命令示例*
|
*Linux whatis 命令示例*
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### 2\. apropos 命令
|
### 2、 apropos 命令
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
**apropos** 会搜索手册页名称和关键字描述(命令名作为正则)。
|
`apropos` 会搜索手册页名称和关键字描述(以命令名作为正则表达式搜索)。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
使用 `-l` 标志来显示完整的描述。
|
使用 `-l` 标志来显示完整的描述。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@ -51,13 +52,14 @@ $ whatis -l fswatch
|
|||||||
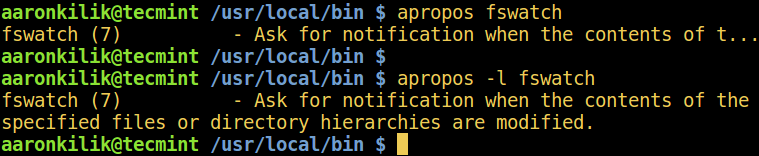
$ apropos fswatch
|
$ apropos fswatch
|
||||||
$ apropos -l fswatch
|
$ apropos -l fswatch
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
[
|
[
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
][6]
|
][6]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
*Linux apropos 命令示例*
|
*Linux apropos 命令示例*
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
默认上,apropos 会如示例那样输出所有匹配的行。你可以使用 `-e` 选项来精确匹配:
|
默认上,`apropos` 会如示例那样输出所有匹配的行。你可以使用 `-e` 选项来精确匹配:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
$ apropos fmt
|
$ apropos fmt
|
||||||
@ -69,54 +71,57 @@ $ apropos -e fmt
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
*Linux apropos 命令根据关键词显示*
|
*Linux apropos 命令根据关键词显示*
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### 3\. type 命令
|
### 3、 type 命令
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
**type** 命令会输出给定命令的完整路径名,此外,如果输入的命令名不是做为独立磁盘文件存在的程序,type 还会告诉你命令分类:
|
`type` 命令会输出给定命令的完整路径名,此外,如果输入的命令名不是做为独立存储在磁盘的文件的程序,`type` 还会告诉你命令分类:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- shell 内置命令 或
|
- shell 内置命令
|
||||||
- shell 关键字或保留字 或
|
- shell 关键字或保留字
|
||||||
- 别名
|
- 别名
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
$ type fswatch
|
$ type fswatch
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
[
|
[
|
||||||

|

|
||||||
][8]
|
][8]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
*Linux type 命令示例*
|
*Linux type 命令示例*
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
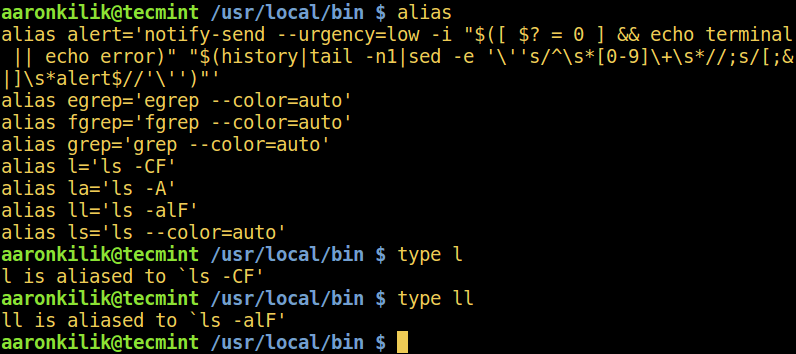
当命令是另外一个命令的别名时,**type** 会显示运行别名时执行的命令。使用 **alias** 命令查看你系统上创建的所有别名:
|
当命令是另外一个命令的别名时,`type` 会显示运行别名时所执行的命令。使用 `alias` 命令可以查看你系统上创建的所有别名:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
$ alias
|
$ alias
|
||||||
$ type l
|
$ type l
|
||||||
$ type ll
|
$ type ll
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
[
|
[
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
][9]
|
][9]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
*显示 Linux 中所有别名*
|
*显示 Linux 中所有别名*
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### 4\. which 命令
|
### 4、 which 命令
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
**which** 帮助命令定位,它打印出命令的绝对路径:
|
`which` 可以帮助命令定位命令,它会打印出命令的绝对路径:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
$ which fswatch
|
$ which fswatch
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
[
|
[
|
||||||

|

|
||||||
][10]
|
][10]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
*找出 Linux 命令位置*
|
*找出 Linux 命令位置*
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
一些二进制文件存在于 PATH 中的多个目录,使用 `-a` 标志来找出所有匹配的路径名。
|
一些二进制文件存在于 `PATH` 环境变量中的多个目录,使用 `-a` 标志来找出所有匹配的路径名。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### 5\. whereis 命令
|
### 5、 whereis 命令
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
**whereis** 定位指定命令名的二进制、源和帮助页文件,如下所示:
|
`whereis` 定位指定命令名的二进制、源和帮助页文件,如下所示:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
$ whereis fswatch
|
$ whereis fswatch
|
||||||
@ -148,7 +153,7 @@ Aaron Kili 是 Linux 和 F.O.S.S 爱好者,将来的 Linux SysAdmin、web 开
|
|||||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/find-linux-command-description-and-location/
|
via: http://www.tecmint.com/find-linux-command-description-and-location/
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
作者:[Aaron Kili ][a]
|
作者:[Aaron Kili][a]
|
||||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||||
校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
|
校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user