mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-03-27 02:30:10 +08:00
commit
20102de929
@ -0,0 +1,435 @@
|
||||
如何在 Ubuntu 15.04 中安装 puppet
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
大家好,本教程将学习如何在 ubuntu 15.04 上面安装 puppet,它可以用来管理你的服务器基础环境。puppet 是由puppet 实验室(Puppet Labs)开发并维护的一款开源的配置管理软件,它能够帮我们自动化供给、配置和管理服务器的基础环境。不管我们管理的是几个服务器还是数以千计的计算机组成的业务报表体系,puppet 都能够使管理员从繁琐的手动配置调整中解放出来,腾出时间和精力去提系统的升整体效率。它能够确保所有自动化流程作业的一致性、可靠性以及稳定性。它让管理员和开发者更紧密的联系在一起,使开发者更容易产出付出设计良好、简洁清晰的代码。puppet 提供了配置管理和数据中心自动化的两个解决方案。这两个解决方案分别是 **puppet 开源版** 和 **puppet 企业版**。puppet 开源版以 Apache 2.0 许可证发布,它是一个非常灵活、可定制的解决方案,设置初衷是帮助管理员去完成那些重复性操作工作。pupprt 企业版是一个全平台复杂 IT 环境下的成熟解决方案,它除了拥有开源版本所有优势以外还有移动端 apps、只有商业版才有的加强支持,以及模块化和集成管理等。Puppet 使用 SSL 证书来认证主控服务器与代理节点之间的通信。
|
||||
|
||||
本教程将要介绍如何在运行 ubuntu 15.04 的主控服务器和代理节点上面安装开源版的 puppet。在这里,我们用一台服务器做主控服务器(master),管理和控制剩余的当作 puppet 代理节点(agent node)的服务器,这些代理节点将依据主控服务器来进行配置。在 ubuntu 15.04 只需要简单的几步就能安装配置好 puppet,用它来管理我们的服务器基础环境非常的方便。(LCTT 译注:puppet 采用 C/S 架构,所以必须有至少有一台作为服务器,其他作为客户端处理)
|
||||
|
||||
### 1.设置主机文件 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在本教程里,我们将使用2台运行 ubuntu 15.04 “Vivid Vervet" 的主机,一台作为主控服务器,另一台作为 puppet 的代理节点。下面是我们将用到的服务器的基础信息。
|
||||
|
||||
- puupet 主控服务器 IP:44.55.88.6 ,主机名: puppetmaster
|
||||
- puppet 代理节点 IP: 45.55.86.39 ,主机名: puppetnode
|
||||
|
||||
我们要在代理节点和服务器这两台机器的 hosts 文件里面都添加上相应的条目,使用 root 或是 sudo 访问权限来编辑 /etc/hosts 文件,命令如下:
|
||||
|
||||
# nano /etc/hosts
|
||||
|
||||
45.55.88.6 puppetmaster.example.com puppetmaster
|
||||
45.55.86.39 puppetnode.example.com puppetnode
|
||||
|
||||
注意,puppet 主控服务器必使用 8140 端口来运行,所以请务必保证开启8140端口。
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. 用 NTP 更新时间 ###
|
||||
|
||||
puppet 代理节点所使用系统时间必须要准确,这样可以避免代理证书出现问题。如果有时间差异,那么证书将过期失效,所以服务器与代理节点的系统时间必须互相同步。我们使用 NTP(Network Time Protocol,网络时间协议)来同步时间。**在服务器与代理节点上面分别**运行以下命令来同步时间。
|
||||
|
||||
# ntpdate pool.ntp.org
|
||||
|
||||
17 Jun 00:17:08 ntpdate[882]: adjust time server 66.175.209.17 offset -0.001938 sec
|
||||
|
||||
(LCTT 译注:显示类似的输出结果表示运行正常)
|
||||
|
||||
如果没有安装 ntp,请使用下面的命令更新你的软件仓库,安装并运行ntp服务
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get update && sudo apt-get -y install ntp ; service ntp restart
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. 安装主控服务器软件 ###
|
||||
|
||||
安装开源版本的 puppet 有很多的方法。在本教程中我们在 puppet 实验室官网下载一个名为 puppetlabs-release 的软件包的软件源,安装后它将为我们在软件源里面添加 puppetmaster-passenger。puppetmaster-passenger 包括带有 apache 的 puppet 主控服务器。我们开始下载这个软件包:
|
||||
|
||||
# cd /tmp/
|
||||
# wget https://apt.puppetlabs.com/puppetlabs-release-trusty.deb
|
||||
|
||||
--2015-06-17 00:19:26-- https://apt.puppetlabs.com/puppetlabs-release-trusty.deb
|
||||
Resolving apt.puppetlabs.com (apt.puppetlabs.com)... 192.155.89.90, 2600:3c03::f03c:91ff:fedb:6b1d
|
||||
Connecting to apt.puppetlabs.com (apt.puppetlabs.com)|192.155.89.90|:443... connected.
|
||||
HTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK
|
||||
Length: 7384 (7.2K) [application/x-debian-package]
|
||||
Saving to: ‘puppetlabs-release-trusty.deb’
|
||||
|
||||
puppetlabs-release-tr 100%[===========================>] 7.21K --.-KB/s in 0.06s
|
||||
|
||||
2015-06-17 00:19:26 (130 KB/s) - ‘puppetlabs-release-trusty.deb’ saved [7384/7384]
|
||||
|
||||
下载完成,我们来安装它:
|
||||
|
||||
# dpkg -i puppetlabs-release-trusty.deb
|
||||
|
||||
Selecting previously unselected package puppetlabs-release.
|
||||
(Reading database ... 85899 files and directories currently installed.)
|
||||
Preparing to unpack puppetlabs-release-trusty.deb ...
|
||||
Unpacking puppetlabs-release (1.0-11) ...
|
||||
Setting up puppetlabs-release (1.0-11) ...
|
||||
|
||||
使用 apt 包管理命令更新一下本地的软件源:
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get update
|
||||
|
||||
现在我们就可以安装 puppetmaster-passenger 了
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get install puppetmaster-passenger
|
||||
|
||||
**提示**: 在安装的时候可能会报错:
|
||||
|
||||
Warning: Setting templatedir is deprecated.see http://links.puppetlabs.com/env-settings-deprecations (at /usr/lib/ruby/vendor_ruby/puppet/settings.rb:1139:in `issue_deprecation_warning')
|
||||
|
||||
不过不用担心,忽略掉它就好,我们只需要在设置配置文件的时候把这一项禁用就行了。
|
||||
|
||||
如何来查看puppet 主控服务器是否已经安装成功了呢?非常简单,只需要使用下面的命令查看它的版本就可以了。
|
||||
|
||||
# puppet --version
|
||||
|
||||
3.8.1
|
||||
|
||||
现在我们已经安装好了 puppet 主控服务器。因为我们使用的是配合 apache 的 passenger,由 apache 来控制 puppet 主控服务器,当 apache 运行时 puppet 主控才运行。
|
||||
|
||||
在开始之前,我们需要通过停止 apache 服务来让 puppet 主控服务器停止运行。
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl stop apache2
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. 使用 Apt 工具锁定主控服务器的版本 ###
|
||||
|
||||
现在已经安装了 3.8.1 版的 puppet,我们锁定这个版本不让它随意升级,因为升级会造成配置文件混乱。 使用 apt 工具来锁定它,这里我们需要使用文本编辑器来创建一个新的文件 **/etc/apt/preferences.d/00-puppet.pref**
|
||||
|
||||
# nano /etc/apt/preferences.d/00-puppet.pref
|
||||
|
||||
在新创建的文件里面添加以下内容:
|
||||
|
||||
# /etc/apt/preferences.d/00-puppet.pref
|
||||
Package: puppet puppet-common puppetmaster-passenger
|
||||
Pin: version 3.8*
|
||||
Pin-Priority: 501
|
||||
|
||||
这样在以后的系统软件升级中, puppet 主控服务器将不会跟随系统软件一起升级。
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. 配置 Puppet 主控服务器###
|
||||
|
||||
Puppet 主控服务器作为一个证书发行机构,需要生成它自己的证书,用于签署所有代理的证书的请求。首先我们要删除所有在该软件包安装过程中创建出来的 ssl 证书。本地默认的 puppet 证书放在 /var/lib/puppet/ssl。因此我们只需要使用 rm 命令来整个移除这些证书就可以了。
|
||||
|
||||
# rm -rf /var/lib/puppet/ssl
|
||||
|
||||
现在来配置该证书,在创建 puppet 主控服务器证书时,我们需要包括代理节点与主控服务器沟通所用的每个 DNS 名称。使用文本编辑器来修改服务器的配置文件 puppet.conf
|
||||
|
||||
# nano /etc/puppet/puppet.conf
|
||||
|
||||
输出的结果像下面这样
|
||||
|
||||
[main]
|
||||
logdir=/var/log/puppet
|
||||
vardir=/var/lib/puppet
|
||||
ssldir=/var/lib/puppet/ssl
|
||||
rundir=/var/run/puppet
|
||||
factpath=$vardir/lib/facter
|
||||
templatedir=$confdir/templates
|
||||
|
||||
[master]
|
||||
# These are needed when the puppetmaster is run by passenger
|
||||
# and can safely be removed if webrick is used.
|
||||
ssl_client_header = SSL_CLIENT_S_DN
|
||||
ssl_client_verify_header = SSL_CLIENT_VERIFY
|
||||
|
||||
在这我们需要注释掉 templatedir 这行使它失效。然后在文件的 `[main]` 小节的结尾添加下面的信息。
|
||||
|
||||
server = puppetmaster
|
||||
environment = production
|
||||
runinterval = 1h
|
||||
strict_variables = true
|
||||
certname = puppetmaster
|
||||
dns_alt_names = puppetmaster, puppetmaster.example.com
|
||||
|
||||
还有很多你可能用的到的配置选项。 如果你有需要,在 Puppet 实验室有一份详细的描述文件供你阅读: [Main Config File (puppet.conf)][1]。
|
||||
|
||||
编辑完成后保存退出。
|
||||
|
||||
使用下面的命令来生成一个新的证书。
|
||||
|
||||
# puppet master --verbose --no-daemonize
|
||||
|
||||
Info: Creating a new SSL key for ca
|
||||
Info: Creating a new SSL certificate request for ca
|
||||
Info: Certificate Request fingerprint (SHA256): F6:2F:69:89:BA:A5:5E:FF:7F:94:15:6B:A7:C4:20:CE:23:C7:E3:C9:63:53:E0:F2:76:D7:2E:E0:BF:BD:A6:78
|
||||
...
|
||||
Notice: puppetmaster has a waiting certificate request
|
||||
Notice: Signed certificate request for puppetmaster
|
||||
Notice: Removing file Puppet::SSL::CertificateRequest puppetmaster at '/var/lib/puppet/ssl/ca/requests/puppetmaster.pem'
|
||||
Notice: Removing file Puppet::SSL::CertificateRequest puppetmaster at '/var/lib/puppet/ssl/certificate_requests/puppetmaster.pem'
|
||||
Notice: Starting Puppet master version 3.8.1
|
||||
^CNotice: Caught INT; storing stop
|
||||
Notice: Processing stop
|
||||
|
||||
至此,证书已经生成。一旦我们看到 **Notice: Starting Puppet master version 3.8.1**,就表明证书就已经制作好了。我们按下 CTRL-C 回到 shell 命令行。
|
||||
|
||||
查看新生成证书的信息,可以使用下面的命令。
|
||||
|
||||
# puppet cert list -all
|
||||
|
||||
+ "puppetmaster" (SHA256) 33:28:97:86:A1:C3:2F:73:10:D1:FB:42:DA:D5:42:69:71:84:F0:E2:8A:01:B9:58:38:90:E4:7D:B7:25:23:EC (alt names: "DNS:puppetmaster", "DNS:puppetmaster.example.com")
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. 创建一个 Puppet 清单 ###
|
||||
|
||||
默认的主要清单(Manifest)是 /etc/puppet/manifests/site.pp。 这个主要清单文件包括了用于在代理节点执行的配置定义。现在我们来创建一个清单文件:
|
||||
|
||||
# nano /etc/puppet/manifests/site.pp
|
||||
|
||||
在刚打开的文件里面添加下面这几行:
|
||||
|
||||
# execute 'apt-get update'
|
||||
exec { 'apt-update': # exec resource named 'apt-update'
|
||||
command => '/usr/bin/apt-get update' # command this resource will run
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# install apache2 package
|
||||
package { 'apache2':
|
||||
require => Exec['apt-update'], # require 'apt-update' before installing
|
||||
ensure => installed,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# ensure apache2 service is running
|
||||
service { 'apache2':
|
||||
ensure => running,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
以上这几行的意思是给代理节点部署 apache web 服务。
|
||||
|
||||
### 7. 运行 puppet 主控服务 ###
|
||||
|
||||
已经准备好运行 puppet 主控服务器 了,那么开启 apache 服务来让它启动
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl start apache2
|
||||
|
||||
我们 puppet 主控服务器已经运行,不过它还不能管理任何代理节点。现在我们给 puppet 主控服务器添加代理节点.
|
||||
|
||||
**提示**: 如果报错
|
||||
|
||||
Job for apache2.service failed. see "systemctl status apache2.service" and "journalctl -xe" for details.
|
||||
|
||||
肯定是 apache 服务器有一些问题,我们可以使用 root 或是 sudo 访问权限来运行**apachectl start**查看它输出的日志。在本教程执行过程中, 我们发现一个 **/etc/apache2/sites-enabled/puppetmaster.conf** 的证书配置问题。修改其中的**SSLCertificateFile /var/lib/puppet/ssl/certs/server.pem **为 **SSLCertificateFile /var/lib/puppet/ssl/certs/puppetmaster.pem**,然后注释掉后面这行**SSLCertificateKeyFile** 。然后在命令行重新启动 apache。
|
||||
|
||||
### 8. 安装 Puppet 代理节点的软件包 ###
|
||||
|
||||
我们已经准备好了 puppet 的服务器,现在需要一个可以管理的代理节点,我们将安装 puppet 代理软件到节点上去。这里我们要给每一个需要管理的节点安装代理软件,并且确保这些节点能够通过 DNS 查询到服务器主机。下面将 安装最新的代理软件到 节点 puppetnode.example.com 上。
|
||||
|
||||
在代理节点上使用下面的命令下载 puppet 实验室提供的软件包:
|
||||
|
||||
# cd /tmp/
|
||||
# wget https://apt.puppetlabs.com/puppetlabs-release-trusty.deb\
|
||||
|
||||
--2015-06-17 00:54:42-- https://apt.puppetlabs.com/puppetlabs-release-trusty.deb
|
||||
Resolving apt.puppetlabs.com (apt.puppetlabs.com)... 192.155.89.90, 2600:3c03::f03c:91ff:fedb:6b1d
|
||||
Connecting to apt.puppetlabs.com (apt.puppetlabs.com)|192.155.89.90|:443... connected.
|
||||
HTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK
|
||||
Length: 7384 (7.2K) [application/x-debian-package]
|
||||
Saving to: ‘puppetlabs-release-trusty.deb’
|
||||
|
||||
puppetlabs-release-tr 100%[===========================>] 7.21K --.-KB/s in 0.04s
|
||||
|
||||
2015-06-17 00:54:42 (162 KB/s) - ‘puppetlabs-release-trusty.deb’ saved [7384/7384]
|
||||
|
||||
在 ubuntu 15.04 上我们使用debian包管理系统来安装它,命令如下:
|
||||
|
||||
# dpkg -i puppetlabs-release-trusty.deb
|
||||
|
||||
使用 apt 包管理命令更新一下本地的软件源:
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get update
|
||||
|
||||
通过远程仓库安装:
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get install puppet
|
||||
|
||||
Puppet 代理默认是不启动的。这里我们需要使用文本编辑器修改 /etc/default/puppet 文件,使它正常工作:
|
||||
|
||||
# nano /etc/default/puppet
|
||||
|
||||
更改 **START** 的值改成 "yes" 。
|
||||
|
||||
START=yes
|
||||
|
||||
最后保存并退出。
|
||||
|
||||
### 9. 使用 Apt 工具锁定代理软件的版本 ###
|
||||
|
||||
和上面的步骤一样为防止随意升级造成的配置文件混乱,我们要使用 apt 工具来把它锁定。具体做法是使用文本编辑器创建一个文件 **/etc/apt/preferences.d/00-puppet.pref**
|
||||
|
||||
# nano /etc/apt/preferences.d/00-puppet.pref
|
||||
|
||||
在新建的文件里面加入如下内容
|
||||
|
||||
# /etc/apt/preferences.d/00-puppet.pref
|
||||
Package: puppet puppet-common
|
||||
Pin: version 3.8*
|
||||
Pin-Priority: 501
|
||||
|
||||
这样 puppet 就不会随着系统软件升级而随意升级了。
|
||||
|
||||
### 10. 配置 puppet 代理节点 ###
|
||||
|
||||
我们需要编辑一下代理节点的 puppet.conf 文件,来使它运行。
|
||||
|
||||
# nano /etc/puppet/puppet.conf
|
||||
|
||||
它看起来和服务器的配置文件完全一样。同样注释掉**templatedir**这行。不同的是在这里我们需要删除掉所有关于`[master]` 的部分。
|
||||
|
||||
假定主控服务器可以通过名字“puppet-master”访问,我们的客户端应该可以和它相互连接通信。如果不行的话,我们需要使用完整的主机域名 puppetmaster.example.com
|
||||
|
||||
[agent]
|
||||
server = puppetmaster.example.com
|
||||
certname = puppetnode.example.com
|
||||
|
||||
在文件的结尾增加上面3行,增加之后文件内容像下面这样:
|
||||
|
||||
[main]
|
||||
logdir=/var/log/puppet
|
||||
vardir=/var/lib/puppet
|
||||
ssldir=/var/lib/puppet/ssl
|
||||
rundir=/var/run/puppet
|
||||
factpath=$vardir/lib/facter
|
||||
#templatedir=$confdir/templates
|
||||
|
||||
[agent]
|
||||
server = puppetmaster.example.com
|
||||
certname = puppetnode.example.com
|
||||
|
||||
最后保存并退出。
|
||||
|
||||
使用下面的命令来启动客户端软件:
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl start puppet
|
||||
|
||||
如果一切顺利的话,我们不会看到命令行有任何输出。 第一次运行的时候,代理节点会生成一个 ssl 证书并且给服务器发送一个请求,经过签名确认后,两台机器就可以互相通信了。
|
||||
|
||||
**提示**: 如果这是你添加的第一个代理节点,建议你在添加其他节点前先给这个证书签名。一旦能够通过并正常运行,回过头来再添加其他代理节点。
|
||||
|
||||
### 11. 在主控服务器上对证书请求进行签名 ###
|
||||
|
||||
第一次运行的时候,代理节点会生成一个 ssl 证书并且给服务器发送一个签名请求。在主控服务器给代理节点服务器证书签名之后,主服务器才能和代理服务器通信并且控制代理服务器。
|
||||
|
||||
在主控服务器上使用下面的命令来列出当前的证书请求:
|
||||
|
||||
# puppet cert list
|
||||
"puppetnode.example.com" (SHA256) 31:A1:7E:23:6B:CD:7B:7D:83:98:33:8B:21:01:A6:C4:01:D5:53:3D:A0:0E:77:9A:77:AE:8F:05:4A:9A:50:B2
|
||||
|
||||
因为只设置了一台代理节点服务器,所以我们将只看到一个请求。看起来类似如上,代理节点的完整域名即其主机名。
|
||||
|
||||
注意有没有“+”号在前面,代表这个证书有没有被签名。
|
||||
|
||||
使用带有主机名的**puppet cert sign**这个命令来签署这个签名请求,如下:
|
||||
|
||||
# puppet cert sign puppetnode.example.com
|
||||
Notice: Signed certificate request for puppetnode.example.com
|
||||
Notice: Removing file Puppet::SSL::CertificateRequest puppetnode.example.com at '/var/lib/puppet/ssl/ca/requests/puppetnode.example.com.pem'
|
||||
|
||||
主控服务器现在可以通讯和控制它签名过的代理节点了。
|
||||
|
||||
如果想签署所有的当前请求,可以使用 -all 选项,如下所示:
|
||||
|
||||
# puppet cert sign --all
|
||||
|
||||
### 12. 删除一个 Puppet 证书 ###
|
||||
|
||||
如果我们想移除一个主机,或者想重建一个主机然后再添加它。下面的例子里我们将展示如何删除 puppet 主控服务器上面的一个证书。使用的命令如下:
|
||||
|
||||
# puppet cert clean hostname
|
||||
Notice: Revoked certificate with serial 5
|
||||
Notice: Removing file Puppet::SSL::Certificate puppetnode.example.com at '/var/lib/puppet/ssl/ca/signed/puppetnode.example.com.pem'
|
||||
Notice: Removing file Puppet::SSL::Certificate puppetnode.example.com at '/var/lib/puppet/ssl/certs/puppetnode.example.com.pem'
|
||||
|
||||
如果我们想查看所有的签署和未签署的请求,使用下面这条命令:
|
||||
|
||||
# puppet cert list --all
|
||||
+ "puppetmaster" (SHA256) 33:28:97:86:A1:C3:2F:73:10:D1:FB:42:DA:D5:42:69:71:84:F0:E2:8A:01:B9:58:38:90:E4:7D:B7:25:23:EC (alt names: "DNS:puppetmaster", "DNS:puppetmaster.example.com")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 13. 部署 Puppet 清单 ###
|
||||
|
||||
当配置并完成 puppet 清单后,现在我们需要部署清单到代理节点服务器上。要应用并加载主 puppet 清单,我们可以在代理节点服务器上面使用下面的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
# puppet agent --test
|
||||
|
||||
Info: Retrieving pluginfacts
|
||||
Info: Retrieving plugin
|
||||
Info: Caching catalog for puppetnode.example.com
|
||||
Info: Applying configuration version '1434563858'
|
||||
Notice: /Stage[main]/Main/Exec[apt-update]/returns: executed successfully
|
||||
Notice: Finished catalog run in 10.53 seconds
|
||||
|
||||
这里向我们展示了主清单如何立即影响到了一个单一的服务器。
|
||||
|
||||
如果我们打算运行的 puppet 清单与主清单没有什么关联,我们可以简单使用 puppet apply 带上相应的清单文件的路径即可。它仅将清单应用到我们运行该清单的代理节点上。
|
||||
|
||||
# puppet apply /etc/puppet/manifest/test.pp
|
||||
|
||||
### 14. 为特定节点配置清单 ###
|
||||
|
||||
如果我们想部署一个清单到某个特定的节点,我们需要如下配置清单。
|
||||
|
||||
在主控服务器上面使用文本编辑器编辑 /etc/puppet/manifest/site.pp:
|
||||
|
||||
# nano /etc/puppet/manifest/site.pp
|
||||
|
||||
添加下面的内容进去
|
||||
|
||||
node 'puppetnode', 'puppetnode1' {
|
||||
# execute 'apt-get update'
|
||||
exec { 'apt-update': # exec resource named 'apt-update'
|
||||
command => '/usr/bin/apt-get update' # command this resource will run
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# install apache2 package
|
||||
package { 'apache2':
|
||||
require => Exec['apt-update'], # require 'apt-update' before installing
|
||||
ensure => installed,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# ensure apache2 service is running
|
||||
service { 'apache2':
|
||||
ensure => running,
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
这里的配置显示我们将在名为 puppetnode 和 puppetnode1 的2个指定的节点上面安装 apache 服务。这里可以添加其他我们需要安装部署的具体节点进去。
|
||||
|
||||
### 15. 配置清单模块 ###
|
||||
|
||||
模块对于组合任务是非常有用的,在 Puppet 社区有很多人贡献了自己的模块组件。
|
||||
|
||||
在主控服务器上, 我们将使用 puppet module 命令来安装 **puppetlabs-apache** 模块。
|
||||
|
||||
# puppet module install puppetlabs-apache
|
||||
|
||||
**警告**: 千万不要在一个已经部署 apache 环境的机器上面使用这个模块,否则它将清空你没有被 puppet 管理的 apache 配置。
|
||||
|
||||
现在用文本编辑器来修改 **site.pp** :
|
||||
|
||||
# nano /etc/puppet/manifest/site.pp
|
||||
|
||||
添加下面的内容进去,在 puppetnode 上面安装 apache 服务。
|
||||
|
||||
node 'puppet-node' {
|
||||
class { 'apache': } # use apache module
|
||||
apache::vhost { 'example.com': # define vhost resource
|
||||
port => '80',
|
||||
docroot => '/var/www/html'
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
保存退出。然后重新运行该清单来为我们的代理节点部署 apache 配置。
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结 ###
|
||||
|
||||
现在我们已经成功的在 ubuntu 15.04 上面部署并运行 puppet 来管理代理节点服务器的基础运行环境。我们学习了puppet 是如何工作的,编写清单文件,节点与主机间使用 ssl 证书认证的认证过程。使用 puppet 开源软件配置管理工具在众多的代理节点上来控制、管理和配置重复性任务是非常容易的。如果你有任何的问题,建议,反馈,与我们取得联系,我们将第一时间完善更新,谢谢。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/linux-how-to/install-puppet-ubuntu-15-04/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Arun Pyasi][a]
|
||||
译者:[ivo-wang](https://github.com/ivo-wang)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arunp/
|
||||
[1]:https://docs.puppetlabs.com/puppet/latest/reference/config_file_main.html
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
||||
translated by ivo-wang
|
||||
How to Configure OpenNMS on CentOS 7.x
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Systems management and monitoring services are very important that provides information to view important systems management information that allow us to to make decisions based on this information. To make sure the network is running at its best and to minimize the network downtime we need to improve application performance. So, in this article we will make you understand the step by step procedure to setup OpenNMS in your IT infrastructure. OpenNMS is a free open source enterprise level network monitoring and management platform that provides information to allow us to make decisions in regards to future network and capacity planning.
|
||||
@ -216,4 +217,4 @@ via: http://linoxide.com/monitoring-2/install-configure-opennms-centos-7-x/
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/kashifs/
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/kashifs/
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
||||
translated by ivo-wang
|
||||
How to install Suricata intrusion detection system on Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
With incessant security threats, intrusion detection system (IDS) has become one of the most critical requirements in today's data center environments. However, as more and more servers upgrade their NICs to 10GB/40GB Ethernet, it is increasingly difficult to implement compute-intensive intrusion detection on commodity hardware at line rates. One approach to scaling IDS performance is **multi-threaded IDS**, where CPU-intensive deep packet inspection workload is parallelized into multiple concurrent tasks. Such parallelized inspection can exploit multi-core hardware to scale up IDS throughput easily. Two well-known open-source efforts in this area are [Suricata][1] and [Bro][2].
|
||||
@ -194,4 +195,4 @@ via: http://xmodulo.com/install-suricata-intrusion-detection-system-linux.html
|
||||
[6]:https://redmine.openinfosecfoundation.org/projects/suricata/wiki/Runmodes
|
||||
[7]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/view-threads-process-linux.html
|
||||
[8]:http://xmodulo.com/how-to-compile-and-install-snort-from-source-code-on-ubuntu.html
|
||||
[9]:https://redmine.openinfosecfoundation.org/projects/suricata/wiki
|
||||
[9]:https://redmine.openinfosecfoundation.org/projects/suricata/wiki
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
||||
ictlyh Translating
|
||||
How to install Android Studio on Ubuntu 15.04 / CentOS 7
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
With the advancement of smart phones in the recent years, Android has become one of the biggest phone platforms and all the tools required to build Android applications are also freely available. Android Studio is an Integrated Development Environment (IDE) for developing Android applications based on [IntelliJ IDEA][1]. It is a free and open source software by Google released in 2014 and succeeds Eclipse as the main IDE.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,230 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Flowsnow translating...
|
||||
Part 9 - LFCS: Linux Package Management with Yum, RPM, Apt, Dpkg, Aptitude and Zypper
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Last August, the Linux Foundation announced the LFCS certification (Linux Foundation Certified Sysadmin), a shiny chance for system administrators everywhere to demonstrate, through a performance-based exam, that they are capable of succeeding at overall operational support for Linux systems. A Linux Foundation Certified Sysadmin has the expertise to ensure effective system support, first-level troubleshooting and monitoring, including finally issue escalation, when needed, to engineering support teams.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Linux Foundation Certified Sysadmin – Part 9
|
||||
|
||||
Watch the following video that explains about the Linux Foundation Certification Program.
|
||||
|
||||
注:youtube 视频
|
||||
<iframe width="720" height="405" frameborder="0" allowfullscreen="allowfullscreen" src="//www.youtube.com/embed/Y29qZ71Kicg"></iframe>
|
||||
|
||||
This article is a Part 9 of 10-tutorial long series, today in this article we will guide you about Linux Package Management, that are required for the LFCS certification exam.
|
||||
|
||||
### Package Management ###
|
||||
|
||||
In few words, package management is a method of installing and maintaining (which includes updating and probably removing as well) software on the system.
|
||||
|
||||
In the early days of Linux, programs were only distributed as source code, along with the required man pages, the necessary configuration files, and more. Nowadays, most Linux distributors use by default pre-built programs or sets of programs called packages, which are presented to users ready for installation on that distribution. However, one of the wonders of Linux is still the possibility to obtain source code of a program to be studied, improved, and compiled.
|
||||
|
||||
**How package management systems work**
|
||||
|
||||
If a certain package requires a certain resource such as a shared library, or another package, it is said to have a dependency. All modern package management systems provide some method of dependency resolution to ensure that when a package is installed, all of its dependencies are installed as well.
|
||||
|
||||
**Packaging Systems**
|
||||
|
||||
Almost all the software that is installed on a modern Linux system will be found on the Internet. It can either be provided by the distribution vendor through central repositories (which can contain several thousands of packages, each of which has been specifically built, tested, and maintained for the distribution) or be available in source code that can be downloaded and installed manually.
|
||||
|
||||
Because different distribution families use different packaging systems (Debian: *.deb / CentOS: *.rpm / openSUSE: *.rpm built specially for openSUSE), a package intended for one distribution will not be compatible with another distribution. However, most distributions are likely to fall into one of the three distribution families covered by the LFCS certification.
|
||||
|
||||
**High and low-level package tools**
|
||||
|
||||
In order to perform the task of package management effectively, you need to be aware that you will have two types of available utilities: low-level tools (which handle in the backend the actual installation, upgrade, and removal of package files), and high-level tools (which are in charge of ensuring that the tasks of dependency resolution and metadata searching -”data about the data”- are performed).
|
||||
|
||||
注:表格
|
||||
|
||||
<table cellspacing="0" border="0">
|
||||
<colgroup width="200">
|
||||
</colgroup>
|
||||
<colgroup width="200">
|
||||
</colgroup>
|
||||
<colgroup width="200">
|
||||
</colgroup>
|
||||
<tbody>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td bgcolor="#AEA79F" align="CENTER" height="18" style="border: 1px solid #000001;"><b><span style="color: black;">DISTRIBUTION</span></b></td>
|
||||
<td bgcolor="#AEA79F" align="CENTER" style="border: 1px solid #000001;"><b><span style="color: black;">LOW-LEVEL TOOL</span></b></td>
|
||||
<td bgcolor="#AEA79F" align="CENTER" style="border: 1px solid #000001;"><b><span style="color: black;">HIGH-LEVEL TOOL</span></b></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td bgcolor="#FFFFFF" align="LEFT" height="18" style="border: 1px solid #000001;"><span style="color: black;"> Debian and derivatives</span></td>
|
||||
<td bgcolor="#FFFFFF" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000001;"><span style="color: black;"> dpkg</span></td>
|
||||
<td bgcolor="#FFFFFF" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000001;"><span style="color: black;"> apt-get / aptitude</span></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td bgcolor="#FFFFFF" align="LEFT" height="18" style="border: 1px solid #000001;"><span style="color: black;"> CentOS</span></td>
|
||||
<td bgcolor="#FFFFFF" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000001;"><span style="color: black;"> rpm</span></td>
|
||||
<td bgcolor="#FFFFFF" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000001;"><span style="color: black;"> yum</span></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td bgcolor="#FFFFFF" align="LEFT" height="18" style="border: 1px solid #000001;"><span style="color: black;"> openSUSE</span></td>
|
||||
<td bgcolor="#FFFFFF" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000001;"><span style="color: black;"> rpm</span></td>
|
||||
<td bgcolor="#FFFFFF" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000001;"><span style="color: black;"> zypper</span></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</tbody>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
|
||||
Let us see the descrption of the low-level and high-level tools.
|
||||
|
||||
dpkg is a low-level package manager for Debian-based systems. It can install, remove, provide information about and build *.deb packages but it can’t automatically download and install their corresponding dependencies.
|
||||
|
||||
- Read More: [15 dpkg Command Examples][1]
|
||||
|
||||
apt-get is a high-level package manager for Debian and derivatives, and provides a simple way to retrieve and install packages, including dependency resolution, from multiple sources using the command line. Unlike dpkg, apt-get does not work directly with *.deb files, but with the package proper name.
|
||||
|
||||
- Read More: [25 apt-get Command Examples][2]
|
||||
|
||||
aptitude is another high-level package manager for Debian-based systems, and can be used to perform management tasks (installing, upgrading, and removing packages, also handling dependency resolution automatically) in a fast and easy way. It provides the same functionality as apt-get and additional ones, such as offering access to several versions of a package.
|
||||
|
||||
rpm is the package management system used by Linux Standard Base (LSB)-compliant distributions for low-level handling of packages. Just like dpkg, it can query, install, verify, upgrade, and remove packages, and is more frequently used by Fedora-based distributions, such as RHEL and CentOS.
|
||||
|
||||
- Read More: [20 rpm Command Examples][3]
|
||||
|
||||
yum adds the functionality of automatic updates and package management with dependency management to RPM-based systems. As a high-level tool, like apt-get or aptitude, yum works with repositories.
|
||||
|
||||
- Read More: [20 yum Command Examples][4]
|
||||
-
|
||||
### Common Usage of Low-Level Tools ###
|
||||
|
||||
The most frequent tasks that you will do with low level tools are as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
**1. Installing a package from a compiled (*.deb or *.rpm) file**
|
||||
|
||||
The downside of this installation method is that no dependency resolution is provided. You will most likely choose to install a package from a compiled file when such package is not available in the distribution’s repositories and therefore cannot be downloaded and installed through a high-level tool. Since low-level tools do not perform dependency resolution, they will exit with an error if we try to install a package with unmet dependencies.
|
||||
|
||||
# dpkg -i file.deb [Debian and derivative]
|
||||
# rpm -i file.rpm [CentOS / openSUSE]
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**: Do not attempt to install on CentOS a *.rpm file that was built for openSUSE, or vice-versa!
|
||||
|
||||
**2. Upgrading a package from a compiled file**
|
||||
|
||||
Again, you will only upgrade an installed package manually when it is not available in the central repositories.
|
||||
|
||||
# dpkg -i file.deb [Debian and derivative]
|
||||
# rpm -U file.rpm [CentOS / openSUSE]
|
||||
|
||||
**3. Listing installed packages**
|
||||
|
||||
When you first get your hands on an already working system, chances are you’ll want to know what packages are installed.
|
||||
|
||||
# dpkg -l [Debian and derivative]
|
||||
# rpm -qa [CentOS / openSUSE]
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to know whether a specific package is installed, you can pipe the output of the above commands to grep, as explained in [manipulate files in Linux – Part 1][6] of this series. Suppose we need to verify if package mysql-common is installed on an Ubuntu system.
|
||||
|
||||
# dpkg -l | grep mysql-common
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Check Installed Packages
|
||||
|
||||
Another way to determine if a package is installed.
|
||||
|
||||
# dpkg --status package_name [Debian and derivative]
|
||||
# rpm -q package_name [CentOS / openSUSE]
|
||||
|
||||
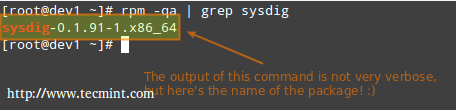
For example, let’s find out whether package sysdig is installed on our system.
|
||||
|
||||
# rpm -qa | grep sysdig
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Check sysdig Package
|
||||
|
||||
**4. Finding out which package installed a file**
|
||||
|
||||
# dpkg --search file_name
|
||||
# rpm -qf file_name
|
||||
|
||||
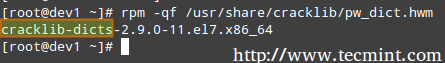
For example, which package installed pw_dict.hwm?
|
||||
|
||||
# rpm -qf /usr/share/cracklib/pw_dict.hwm
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Query File in Linux
|
||||
|
||||
### Common Usage of High-Level Tools ###
|
||||
|
||||
The most frequent tasks that you will do with high level tools are as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
**1. Searching for a package**
|
||||
|
||||
aptitude update will update the list of available packages, and aptitude search will perform the actual search for package_name.
|
||||
|
||||
# aptitude update && aptitude search package_name
|
||||
|
||||
In the search all option, yum will search for package_name not only in package names, but also in package descriptions.
|
||||
|
||||
# yum search package_name
|
||||
# yum search all package_name
|
||||
# yum whatprovides “*/package_name”
|
||||
|
||||
Let’s supposed we need a file whose name is sysdig. To know that package we will have to install, let’s run.
|
||||
|
||||
# yum whatprovides “*/sysdig”
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Check Package Description
|
||||
|
||||
whatprovides tells yum to search the package the will provide a file that matches the above regular expression.
|
||||
|
||||
# zypper refresh && zypper search package_name [On openSUSE]
|
||||
|
||||
**2. Installing a package from a repository**
|
||||
|
||||
While installing a package, you may be prompted to confirm the installation after the package manager has resolved all dependencies. Note that running update or refresh (according to the package manager being used) is not strictly necessary, but keeping installed packages up to date is a good sysadmin practice for security and dependency reasons.
|
||||
|
||||
# aptitude update && aptitude install package_name [Debian and derivatives]
|
||||
# yum update && yum install package_name [CentOS]
|
||||
# zypper refresh && zypper install package_name [openSUSE]
|
||||
|
||||
**3. Removing a package**
|
||||
|
||||
The option remove will uninstall the package but leaving configuration files intact, whereas purge will erase every trace of the program from your system.
|
||||
# aptitude remove / purge package_name
|
||||
# yum erase package_name
|
||||
|
||||
---Notice the minus sign in front of the package that will be uninstalled, openSUSE ---
|
||||
|
||||
# zypper remove -package_name
|
||||
|
||||
Most (if not all) package managers will prompt you, by default, if you’re sure about proceeding with the uninstallation before actually performing it. So read the onscreen messages carefully to avoid running into unnecessary trouble!
|
||||
|
||||
**4. Displaying information about a package**
|
||||
|
||||
The following command will display information about the birthday package.
|
||||
|
||||
# aptitude show birthday
|
||||
# yum info birthday
|
||||
# zypper info birthday
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Check Package Information
|
||||
|
||||
### Summary ###
|
||||
|
||||
Package management is something you just can’t sweep under the rug as a system administrator. You should be prepared to use the tools described in this article at a moment’s notice. Hope you find it useful in your preparation for the LFCS exam and for your daily tasks. Feel free to leave your comments or questions below. We will be more than glad to get back to you as soon as possible.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/linux-package-management/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Gabriel Cánepa][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/gacanepa/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/dpkg-command-examples/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/useful-basic-commands-of-apt-get-and-apt-cache-for-package-management/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/20-practical-examples-of-rpm-commands-in-linux/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.tecmint.com/20-linux-yum-yellowdog-updater-modified-commands-for-package-mangement/
|
||||
[5]:http://www.tecmint.com/sed-command-to-create-edit-and-manipulate-files-in-linux/
|
||||
@ -1,425 +0,0 @@
|
||||
如何在Ubuntu 15.04中安装puppet
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
大家好,本教程将教各位如何在ubuntu 15.04上面安装puppet,用它来管理你的服务器基础环境。puppet是由puppet实验室开发并维护的一款开源软件,它能够帮我们自动的管理配置服务器的基础环境。不管我们管理的是几个服务器还是数以千计的计算机组成的业务报表体系,puppet都能够使管理员从繁琐的手动配置调整中解放出来,腾出时间和精力去提系统的升整体效率。它能够确保所有自动化流程作业的一致性,可靠性以及稳定性。它让管理员和开发者更紧密的联系在一起,使开发者更容易产出付出设计良好,简洁清晰的代码。puppet提供了管理配置和自动化数据中心的2个解决方案。这两个解决方案分别是**puppet开源项目 和 puppet商业版**。puppet开源项目依赖于apache2.0,它是一个非常灵活可随意定制的解决方案,设置初衷是帮助管理员去完成那些重复性操作工作。pupprt商业版是一个全平台复杂IT环境下的成熟解决方案,它除了拥有开源版本所有优势以外还有移动端apps,只有商业版才有的加强支持,以及模块化和集成管理等。Puppet使用SSL证书来认证主机与代理节点之间的通信。
|
||||
|
||||
本教程将要介绍如何在ubuntu 15.04的主机和代理节点上面安装开源版的puppet。在这我们用一台服务器做主机,管理和控制剩余当作puppet的代理节点的服务器,这些代理节点将依据服务器来进行配置。在ubuntu 15.04只需要简单的几步就能安装配置好puppet,用它来管理我们的服务器基础环境非常的方便。(译者注:puppet采用的C/S架构所以必须有至少有一台作为服务端,其他作为客户端处理)
|
||||
### 1.设置主机###
|
||||
在本教程里,我们将使用用2台运行ubuntu 15.04 "Vivid Vervet"的主机,一台作为服务端,另一台作为puppet的代理节点。下面是我们将用到的服务器的基础信息。
|
||||
|
||||
puupet服务器IP:44.55.88.6,主机名: puppetmaster
|
||||
puppet代理节点IP: 45.55.86.39 ,主机名: puppetnode
|
||||
|
||||
我们要在代理节点和服务器这两天机器的hosts里面都添加上相应的条目,使用root或是sudo访问权限来编辑/etc/hosts文件,命令如下:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# nano /etc/hosts
|
||||
|
||||
45.55.88.6 puppetmaster.example.com puppetmaster
|
||||
45.55.86.39 puppetnode.example.com puppetnode
|
||||
|
||||
注意,puppet服务端必使用8140端口来运行,所以请务必保证开启8140端口。
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. 用NTP更新时间 ###
|
||||
|
||||
puppet代理节点所使用系统时间必须要准确,这样可以避免代理证书出现问题。如果有时间差异,那么证书将过期失效,所以服务器与代理节点的系统时间必须互相同步。我们使用NTP(Network Time Protocol,网络时间协议)来同步时间。在服务器与代理节点上面分别运行以下命令来同步时间。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# ntpdate pool.ntp.org
|
||||
|
||||
17 Jun 00:17:08 ntpdate[882]: adjust time server 66.175.209.17 offset -0.001938 sec (译者注:显示类似的输出结果表示运行正常)
|
||||
|
||||
如果没有ntp,请使用下面的命令更新你的软件仓库,安装并运行ntp服务
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get update && sudo apt-get -y install ntp ; service ntp restart
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. 安装服务器软件 ###
|
||||
|
||||
安装开源版本的puppet有很多的方法。在本教程中我们在puppet实验室官网下载一个名为puppetlabs-release的软件包,安装后它将为我们在软件源里面添加puppetmaster-passenger。puppetmaster-passenger依赖于apache的puppet服务端。我们开始下载这个软件包
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# cd /tmp/
|
||||
# wget https://apt.puppetlabs.com/puppetlabs-release-trusty.deb
|
||||
|
||||
--2015-06-17 00:19:26-- https://apt.puppetlabs.com/puppetlabs-release-trusty.deb
|
||||
Resolving apt.puppetlabs.com (apt.puppetlabs.com)... 192.155.89.90, 2600:3c03::f03c:91ff:fedb:6b1d
|
||||
Connecting to apt.puppetlabs.com (apt.puppetlabs.com)|192.155.89.90|:443... connected.
|
||||
HTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK
|
||||
Length: 7384 (7.2K) [application/x-debian-package]
|
||||
Saving to: ‘puppetlabs-release-trusty.deb’
|
||||
|
||||
puppetlabs-release-tr 100%[===========================>] 7.21K --.-KB/s in 0.06s
|
||||
|
||||
2015-06-17 00:19:26 (130 KB/s) - ‘puppetlabs-release-trusty.deb’ saved [7384/7384]
|
||||
|
||||
下载完成,我们来安装它
|
||||
|
||||
# dpkg -i puppetlabs-release-trusty.deb
|
||||
|
||||
Selecting previously unselected package puppetlabs-release.
|
||||
(Reading database ... 85899 files and directories currently installed.)
|
||||
Preparing to unpack puppetlabs-release-trusty.deb ...
|
||||
Unpacking puppetlabs-release (1.0-11) ...
|
||||
Setting up puppetlabs-release (1.0-11) ...
|
||||
|
||||
使用apt包管理命令更新一下本地的软件源
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get update
|
||||
|
||||
现在我们就可以安装puppetmaster-passenger了
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get install puppetmaster-passenger
|
||||
|
||||
**提示**: 在安装的时候可能会报错**Warning: Setting templatedir is deprecated.请查看 http://links.puppetlabs.com/env-settings-deprecations (at /usr/lib/ruby/vendor_ruby/puppet/settings.rb:1139:in `issue_deprecation_warning')** 不过不用担心,忽略掉它就好,我们只需要在设置配置文件的时候把这一项disable就行了。
|
||||
|
||||
如何来查看puppet master是否已经安装成功了呢?非常简单,只需要使用下面的命令查看它的版本就可以了。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# puppet --version
|
||||
|
||||
3.8.1
|
||||
|
||||
现在我们已经安装好了puppet master。要想使用puppet master apache服务就必须运行起来,因为puppet master进程的运行是依赖于apache的。
|
||||
在开始之前,我们将apache服务停止,这样puppet muster也会停止运行。
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl stop apache2
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. 使用Apt工具锁定Master(服务端)版本 ###
|
||||
|
||||
现在已经安装了 3.8.1版的puppet,我们锁定这个版本不让它随意升级,因为升级会造成配置文件混乱。 使用apt工具来锁定它,这里我们需要使用文本编辑器来创建一个新的文件 **/etc/apt/preferences.d/00-puppet.pref**
|
||||
|
||||
# nano /etc/apt/preferences.d/00-puppet.pref
|
||||
|
||||
在新创建的文件里面添加以下内容
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# /etc/apt/preferences.d/00-puppet.pref
|
||||
Package: puppet puppet-common puppetmaster-passenger
|
||||
Pin: version 3.8*
|
||||
Pin-Priority: 501
|
||||
|
||||
这样在以后的系统软件升级中puppet master将被锁住不会跟随系统软件一起升级。
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. 配置 Puppet Master###
|
||||
Puppet master作为一个证书发行机构,所有代理证书的请求都将由它来处理。首先我们要删除所有在软件包安装过程中创建出来的ssl证书。本地默认的puppet证书在/var/lib/puppet/ssl。因此我们只需要使用rm命令来移除这些证书就可以了。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# rm -rf /var/lib/puppet/ssl
|
||||
|
||||
现在来配置这些证书,在创建puppet master证书的时候,需要用使用DNS能查找到的代理节点名称。使用文本编辑器来修改服务器的配置文件puppet.conf
|
||||
# nano /etc/puppet/puppet.conf
|
||||
|
||||
输出的结果像下面这样
|
||||
|
||||
[main]
|
||||
logdir=/var/log/puppet
|
||||
vardir=/var/lib/puppet
|
||||
ssldir=/var/lib/puppet/ssl
|
||||
rundir=/var/run/puppet
|
||||
factpath=$vardir/lib/facter
|
||||
templatedir=$confdir/templates
|
||||
|
||||
[master]
|
||||
# These are needed when the puppetmaster is run by passenger
|
||||
# and can safely be removed if webrick is used.
|
||||
ssl_client_header = SSL_CLIENT_S_DN
|
||||
ssl_client_verify_header = SSL_CLIENT_VERIFY
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
在这我们需要注释掉templatedir 这行使它失效。然后在文件的结尾添加下面的信息。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
server = puppetmaster
|
||||
environment = production
|
||||
runinterval = 1h
|
||||
strict_variables = true
|
||||
certname = puppetmaster
|
||||
dns_alt_names = puppetmaster, puppetmaster.example.com
|
||||
|
||||
还有很多你可能用的到的配置选项。 如果你有需要,在Puppet实验室有一份详细的描述文件供你阅读。 [Main Config File (puppet.conf)][1].
|
||||
|
||||
编辑完成后保存退出。
|
||||
|
||||
使用下面的命令来生成一个新的证书。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# puppet master --verbose --no-daemonize
|
||||
|
||||
Info: Creating a new SSL key for ca
|
||||
Info: Creating a new SSL certificate request for ca
|
||||
Info: Certificate Request fingerprint (SHA256): F6:2F:69:89:BA:A5:5E:FF:7F:94:15:6B:A7:C4:20:CE:23:C7:E3:C9:63:53:E0:F2:76:D7:2E:E0:BF:BD:A6:78
|
||||
...
|
||||
Notice: puppetmaster has a waiting certificate request
|
||||
Notice: Signed certificate request for puppetmaster
|
||||
Notice: Removing file Puppet::SSL::CertificateRequest puppetmaster at '/var/lib/puppet/ssl/ca/requests/puppetmaster.pem'
|
||||
Notice: Removing file Puppet::SSL::CertificateRequest puppetmaster at '/var/lib/puppet/ssl/certificate_requests/puppetmaster.pem'
|
||||
Notice: Starting Puppet master version 3.8.1
|
||||
^CNotice: Caught INT; storing stop
|
||||
Notice: Processing stop
|
||||
|
||||
至此,证书已经生成。一旦我们看到 **Notice: Starting Puppet master version 3.8.1**, 表明证书就已经制作好了.我们按下 CTRL-C 回到shell命令行。
|
||||
|
||||
查看新生成证书的信息,可以使用下面的命令。
|
||||
|
||||
# puppet cert list -all
|
||||
|
||||
+ "puppetmaster" (SHA256) 33:28:97:86:A1:C3:2F:73:10:D1:FB:42:DA:D5:42:69:71:84:F0:E2:8A:01:B9:58:38:90:E4:7D:B7:25:23:EC (alt names: "DNS:puppetmaster", "DNS:puppetmaster.example.com")
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. 创建一个Puppet清单 ###
|
||||
|
||||
默认的主要清单是/etc/puppet/manifests/site.pp。 这个主要清单文件定义着控制哪些代理节点。现在我们来创建一个清单文件
|
||||
|
||||
# nano /etc/puppet/manifests/site.pp
|
||||
|
||||
在刚打开的文件里面添加下面这几行
|
||||
|
||||
# execute 'apt-get update'
|
||||
exec { 'apt-update': # exec resource named 'apt-update'
|
||||
command => '/usr/bin/apt-get update' # command this resource will run
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# install apache2 package
|
||||
package { 'apache2':
|
||||
require => Exec['apt-update'], # require 'apt-update' before installing
|
||||
ensure => installed,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# ensure apache2 service is running
|
||||
service { 'apache2':
|
||||
ensure => running,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
以上这几行的意思是给代理节点部署apache web 服务
|
||||
### 7. 运行puppet Master服务 ###
|
||||
|
||||
已经准备好运行puppet master了,那么开启apache服务来让它启动
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl start apache2
|
||||
|
||||
我们puppet master已经运行,不过它还不能管理任何代理节点。现在我们给puppet master添加代理节点.
|
||||
|
||||
**提示**: 如果报错 **Job for apache2.service failed. 查看"systemctl status apache2.service" and "journalctl -xe" 所给出的信息.** 肯定是apache server有一些问题. 我们可以使用root或是sudo访问权限来运行**apachectl start**查看它输出的日志。 在本教程执行过程中, 我们发现一个证书配置的问题,解决方法如下**/etc/apache2/sites-enabled/puppetmaster.conf**. 修改其中的**SSLCertificateFile /var/lib/puppet/ssl/certs/server.pem 为 SSLCertificateFile /var/lib/puppet/ssl/certs/puppetmaster.pem** 然后注释掉后面这行**SSLCertificateKeyFile** . 然后在命令行启动apache
|
||||
### 8. Puppet客户端安装 ###
|
||||
|
||||
我们已经准备好了puppet的服务端,现在来为代理节点安装客户端。这里我们要给每一个需要管理的节点安装客户端,并且确保这些节点能够通过DNS查询到服务器主机。下面将 puppetnode.example.com作为代理节点安装客户端
|
||||
在代理节点服务器上,使用下面的命令下载puppet实验室提供的软件包。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# cd /tmp/
|
||||
# wget https://apt.puppetlabs.com/puppetlabs-release-trusty.deb\
|
||||
|
||||
--2015-06-17 00:54:42-- https://apt.puppetlabs.com/puppetlabs-release-trusty.deb
|
||||
Resolving apt.puppetlabs.com (apt.puppetlabs.com)... 192.155.89.90, 2600:3c03::f03c:91ff:fedb:6b1d
|
||||
Connecting to apt.puppetlabs.com (apt.puppetlabs.com)|192.155.89.90|:443... connected.
|
||||
HTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK
|
||||
Length: 7384 (7.2K) [application/x-debian-package]
|
||||
Saving to: ‘puppetlabs-release-trusty.deb’
|
||||
|
||||
puppetlabs-release-tr 100%[===========================>] 7.21K --.-KB/s in 0.04s
|
||||
|
||||
2015-06-17 00:54:42 (162 KB/s) - ‘puppetlabs-release-trusty.deb’ saved [7384/7384]
|
||||
|
||||
在ubuntu 15.04上我们使用debian包管理系统来安装它,命令如下:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# dpkg -i puppetlabs-release-trusty.deb
|
||||
|
||||
使用apt包管理命令更新一下本地的软件源
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get update
|
||||
|
||||
通过远程仓库安装
|
||||
# apt-get install puppet
|
||||
|
||||
Puppet客户端默认是不启动的。这里我们需要使用文本编辑器修改/etc/default/puppet文件,使它正常工作。
|
||||
# nano /etc/default/puppet
|
||||
|
||||
更改 **START** 的值改成 "yes" 。
|
||||
|
||||
START=yes
|
||||
|
||||
最后保存并退出。
|
||||
|
||||
### 9. 使用APT工具锁定Agent(客户端)版本 ###
|
||||
|
||||
和上面的步骤一样为防止随意升级造成的配置文件混乱,我们要使用apt工具来把它锁定。具体做法是使用文本编辑器创建一个文件 **/etc/apt/preferences.d/00-puppet.pref**
|
||||
|
||||
# nano /etc/apt/preferences.d/00-puppet.pref
|
||||
|
||||
在新建的文件里面加入如下内容
|
||||
|
||||
# /etc/apt/preferences.d/00-puppet.pref
|
||||
Package: puppet puppet-common
|
||||
Pin: version 3.8*
|
||||
Pin-Priority: 501
|
||||
|
||||
这样puppet就不会随着系统软件升级而随意升级了。
|
||||
|
||||
### 10. 配置puppet代理节点 ###
|
||||
|
||||
我们需要编辑一下代理节点的puppet.conf文件,来使它运行。
|
||||
|
||||
# nano /etc/puppet/puppet.conf
|
||||
|
||||
它看起来和服务端的配置文件完全一样。同样注释掉**templatedir**这行。不同的是在这里我们需要删除掉所有关于[master]的部分。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
假定服务端可用,我们的客户端应该是可以和它相互连接通信的。如果不行我们需要使用完整的主机域名puppetmaster.example.com
|
||||
|
||||
[agent]
|
||||
server = puppetmaster.example.com
|
||||
certname = puppetnode.example.com
|
||||
|
||||
在文件的结尾增加上面3行,增加之后文件内容像下面这样。
|
||||
|
||||
[main]
|
||||
logdir=/var/log/puppet
|
||||
vardir=/var/lib/puppet
|
||||
ssldir=/var/lib/puppet/ssl
|
||||
rundir=/var/run/puppet
|
||||
factpath=$vardir/lib/facter
|
||||
#templatedir=$confdir/templates
|
||||
|
||||
[agent]
|
||||
server = puppetmaster.example.com
|
||||
certname = puppetnode.example.com
|
||||
|
||||
最后保存并退出。
|
||||
|
||||
使用下面的命令来启动客户端软件
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl start puppet
|
||||
|
||||
如果一切顺利的话,我们不会看到命令行有任何输出。 第一次运行的时候,代理节点会生成一个ssl证书并且给服务端发送一个请求,经过签名确认后,两台机器就可以互相通信了。
|
||||
|
||||
**提示**: 如果这是你添加的第一个代理节点,建议你在添加其他节点前先给这个证书签名。一旦能够通过并正常运行,回过头来再添加其他代理节点。
|
||||
|
||||
### 11. 服务器上的签名证书请求 ###
|
||||
|
||||
第一次运行的时候,代理节点会生成一个ssl证并且给服务端发送一个请求。在主服务器给代理节点服务器证书签名之后,主服务器才能和代理服务器通信并且控制代理服务器。
|
||||
|
||||
在主服务器上使用下面的命令来列出当前的证书请求
|
||||
|
||||
# puppet cert list
|
||||
"puppetnode.example.com" (SHA256) 31:A1:7E:23:6B:CD:7B:7D:83:98:33:8B:21:01:A6:C4:01:D5:53:3D:A0:0E:77:9A:77:AE:8F:05:4A:9A:50:B2
|
||||
|
||||
因为只设置了一台代理节点服务器,所以我们将只看到一个请求。
|
||||
注意有没有“+”号在前面,代表这个证书有没有被签名。
|
||||
|
||||
使用**puppet cert sign**到**hostname**这个命令来签署这个签名请求。
|
||||
|
||||
# puppet cert sign puppetnode.example.com
|
||||
Notice: Signed certificate request for puppetnode.example.com
|
||||
Notice: Removing file Puppet::SSL::CertificateRequest puppetnode.example.com at '/var/lib/puppet/ssl/ca/requests/puppetnode.example.com.pem'
|
||||
|
||||
服务端只能控制它签名过的代理节点。
|
||||
|
||||
如想我们想签署所有的请求, 需要使用-all选项,如下所示。
|
||||
|
||||
# puppet cert sign --all
|
||||
|
||||
### 12.删除一个Puppet证书 ###
|
||||
|
||||
如果我们想移除一个主机,或者想重建一个主机然后再添加它。下面的例子里我们将展示如何删除puppet master上面的一个证书。使用的命令如下:
|
||||
|
||||
# puppet cert clean hostname
|
||||
Notice: Revoked certificate with serial 5
|
||||
Notice: Removing file Puppet::SSL::Certificate puppetnode.example.com at '/var/lib/puppet/ssl/ca/signed/puppetnode.example.com.pem'
|
||||
Notice: Removing file Puppet::SSL::Certificate puppetnode.example.com at '/var/lib/puppet/ssl/certs/puppetnode.example.com.pem'
|
||||
|
||||
如果我们想查看所有的签署和未签署的请求,使用下面这条命令
|
||||
|
||||
# puppet cert list --all
|
||||
+ "puppetmaster" (SHA256) 33:28:97:86:A1:C3:2F:73:10:D1:FB:42:DA:D5:42:69:71:84:F0:E2:8A:01:B9:58:38:90:E4:7D:B7:25:23:EC (alt names: "DNS:puppetmaster", "DNS:puppetmaster.example.com")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 13. 部署代理节点Puppet清单 ###
|
||||
|
||||
当配置并完成主puppet清单后,现在我们需要署代理节点服务器清单。要应用并加载主puppet清单,我们可以在代理节点服务器上面使用下面的命令
|
||||
|
||||
# puppet agent --test
|
||||
|
||||
Info: Retrieving pluginfacts
|
||||
Info: Retrieving plugin
|
||||
Info: Caching catalog for puppetnode.example.com
|
||||
Info: Applying configuration version '1434563858'
|
||||
Notice: /Stage[main]/Main/Exec[apt-update]/returns: executed successfully
|
||||
Notice: Finished catalog run in 10.53 seconds
|
||||
|
||||
这里像我们展示了主清单如何去管理一个单一的服务器。
|
||||
|
||||
如果我们打算运行的puppet清单与主puppet清单没有什么关联,那么需要使用puppet apply 到相应的路径。它仅适用于该代理节点。
|
||||
|
||||
# puppet apply /etc/puppet/manifest/test.pp
|
||||
|
||||
### 14. 配置特殊节点清单 ###
|
||||
|
||||
如果我们想部署一个清单到某个特定的节点,我们需要进行以下操作。
|
||||
|
||||
在主服务器上面使用文本编辑器编辑/etc/puppet/manifest/site.pp
|
||||
|
||||
# nano /etc/puppet/manifest/site.pp
|
||||
|
||||
添加下面的内容进去
|
||||
|
||||
node 'puppetnode', 'puppetnode1' {
|
||||
# execute 'apt-get update'
|
||||
exec { 'apt-update': # exec resource named 'apt-update'
|
||||
command => '/usr/bin/apt-get update' # command this resource will run
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# install apache2 package
|
||||
package { 'apache2':
|
||||
require => Exec['apt-update'], # require 'apt-update' before installing
|
||||
ensure => installed,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# ensure apache2 service is running
|
||||
service { 'apache2':
|
||||
ensure => running,
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
这里的配置显示我们将在名为puppetnode and puppetnode1的2个特殊节点上面安装apache服务. 这里可以添加其他我们需要安装部署的具体节点进去。
|
||||
### 15. 配置清单模块 ###
|
||||
|
||||
模块化组件组是非常实用的,在Puppet社区有很多人贡献自己的模块组件。
|
||||
|
||||
在主puppet服务器上, 我们将使用puppet module命令来安装**puppetlabs-apache** 模块。
|
||||
|
||||
# puppet module install puppetlabs-apache
|
||||
|
||||
**警告**: 千万不要在一个已经部署apache环境的机器上面使用这个模块,否则它将清空你的apache配置。
|
||||
|
||||
现在用文本编辑器来修改 **site.pp**
|
||||
|
||||
# nano /etc/puppet/manifest/site.pp
|
||||
|
||||
添加下面的内容进去,意思是在 puppetnode上面安装apache服务。
|
||||
|
||||
node 'puppet-node' {
|
||||
class { 'apache': } # use apache module
|
||||
apache::vhost { 'example.com': # define vhost resource
|
||||
port => '80',
|
||||
docroot => '/var/www/html'
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
保存退出。这样为我们的代理服务器重新配置部署基础环境。
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结 ###
|
||||
|
||||
现在我们已经成功的在ubuntu 15.04上面部署并运行puppet来管理代理节点服务器的基础运行环境。我们学习了puppet是如何工作的,编写清单文件,节点与主机间使用ssl证书认证的认证过程。使用puppet管理配置众多的代理节点服务器是非常容易的。如果你有任何的问题,建议,反馈,与我们取得联系,我们将第一时间完善更新,谢谢。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/linux-how-to/install-puppet-ubuntu-15-04/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Arun Pyasi][a]
|
||||
译者:[ivo-wang](https://github.com/ivo-wang)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arunp/
|
||||
[1]:https://docs.puppetlabs.com/puppet/latest/reference/config_file_main.html
|
||||
@ -1,12 +1,12 @@
|
||||
How to Remove Banned IP from Fail2ban on CentOS 6 / CentOS 7
|
||||
如何在CentOS 6/7 上移除被Fail2ban禁止的IP
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[Fail2ban][1] is an intrusion prevention software framework that able to protect your server from brute-force attacks. Fail2ban written in the Python programming language and is widely used by most of the VPS servers. Fail2ban will scan log files and IP blacklists that shows signs of malicious, too many password failures, web server exploitation, WordPress plugin attacks and other vulnerabilities. If you already installed and used fail2ban to protect your web server, you may be wondering how to find the IP banned or blocked by Fail2ban, or you may want to remove banned ip from fail2ban jail on CentOS 6, CentOS 7, RHEL 6, RHEL 7 and Oracle Linux 6/7.
|
||||
[Fail2ban][1]是一款用于保护你的服务器免于暴力攻击的入侵保护软件。Fail2ban用python写成,并被广泛用户大多数服务器上。Fail2ban将扫描日志文件和IP黑名单来显示恶意软件、过多的密码失败、web服务器利用、Wordpress插件攻击和其他漏洞。如果你已经安装并使用了fail2ban来保护你的web服务器,你也许会想知道如何在CentOS 6、CentOS 7、RHEL 6、RHEL 7 和 Oracle Linux 6/7中找到被Fail2ban阻止的IP,或者你想将ip从fail2ban监狱中移除。
|
||||
|
||||
### How to List of Banned IP address ###
|
||||
### 如何列出被禁止的IP ###
|
||||
|
||||
To see all the blocked ip addresses, run the following command :
|
||||
要查看所有被禁止的ip地址,运行下面的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
# iptables -L
|
||||
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT)
|
||||
@ -40,11 +40,11 @@ To see all the blocked ip addresses, run the following command :
|
||||
REJECT all -- 104.194.26.205 anywhere reject-with icmp-port-unreachable
|
||||
RETURN all -- anywhere anywhere
|
||||
|
||||
### How to Remove Banned IP from Fail2ban jail ###
|
||||
### 如何从Fail2ban中移除IP ###
|
||||
|
||||
# iptables -D f2b-NoAuthFailures -s banned_ip -j REJECT
|
||||
|
||||
I hope this article gives you some ideas and quick guide on remove banned IP from Fail2ban jail on on CentOS 6, CentOS 7, RHEL 6, RHEL 7 and Oracle Linux 6/7.
|
||||
我希望这篇教程可以给你在CentOS 6、CentOS 7、RHEL 6、RHEL 7 和 Oracle Linux 6/7中移除被禁止的ip一些指导。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,230 @@
|
||||
Flowsnow translating...
|
||||
LFCS系列第九讲: 使用Yum, RPM, Apt, Dpkg, Aptitude, Zypper进行Linux包管理
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
去年八月, Linux基金会宣布了一个全新的LFCS(Linux Foundation Certified Sysadmin,Linux基金会认证系统管理员)认证计划,这对广大系统管理员来说是一个很好的机会,管理员们可以通过绩效考试来表明自己可以成功支持Linux系统的整体运营。 当需要的时候一个Linux基金会认证的系统管理员有足够的专业知识来确保系统高效运行,提供第一手的故障诊断和监视,并且为工程师团队在问题升级时提供智能决策。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Linux基金会认证系统管理员 – 第九讲
|
||||
|
||||
请观看下面关于Linux基金会认证计划的演示。
|
||||
|
||||
注:youtube 视频
|
||||
<iframe width="720" height="405" frameborder="0" allowfullscreen="allowfullscreen" src="http://www.youtube.com/embed/Y29qZ71Kicg"></iframe>
|
||||
|
||||
本文是本系列十套教程中的第九讲,今天在这篇文章中我们会引导你学习Linux包管理,这也是LFCS认证考试所需要的。
|
||||
|
||||
### 包管理 ###
|
||||
|
||||
简单的说,包管理是系统中安装和维护软件的一种方法,其中维护也包含更新和卸载。
|
||||
|
||||
在Linux早期,程序只以源代码的方式发行,还带有所需的用户使用手册和必备的配置文件,甚至更多。现如今,大多数发行商使用默认的预装程序或者被称为包的程序集合。用户使用这些预装程序或者包来安装该发行版本。然而,Linux最伟大的一点是我们仍然能够获得程序的源代码用来学习、改进和编译。
|
||||
|
||||
**包管理系统是如何工作的**
|
||||
|
||||
如果某一个包需要一定的资源,如共享库,或者需要另一个包,据说就会存在依赖性问题。所有现在的包管理系统提供了一些解决依赖性的方法,以确保当安装一个包时,相关的依赖包也安装好了
|
||||
|
||||
**打包系统**
|
||||
|
||||
几乎所有安装在现代Linux系统上的软件都会在互联网上找到。它要么能够通过中央库(中央库能包含几千个包,每个包都已经构建、测试并且维护好了)发行商得到,要么能够直接得到可以下载和手动安装的源代码。
|
||||
|
||||
由于不同的发行版使用不同的打包系统(Debian的*.deb文件/ CentOS的*.rpm文件/ openSUSE的专门为openSUSE构建的*.rpm文件),因此为一个发行版本开发的包会与其他发行版本不兼容。然而,大多数发行版本都可能是LFCS认证的三个发行版本之一。
|
||||
|
||||
**高级和低级打包工具**
|
||||
|
||||
为了有效地进行包管理的任务,你需要知道,你将有两种类型的实用工具:低级工具(能在后端实际安装,升级,卸载包文件),以及高级工具(负责确保能很好的执行依赖性解决和元数据检索的任务,元数据也称为关于数据的数据)。
|
||||
|
||||
注:表格
|
||||
|
||||
<table cellspacing="0" border="0">
|
||||
<colgroup width="200">
|
||||
</colgroup>
|
||||
<colgroup width="200">
|
||||
</colgroup>
|
||||
<colgroup width="200">
|
||||
</colgroup>
|
||||
<tbody>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td bgcolor="#AEA79F" align="CENTER" height="18" style="border: 1px solid #000001;"><b><span style="color: black;">发行版</span></b></td>
|
||||
<td bgcolor="#AEA79F" align="CENTER" style="border: 1px solid #000001;"><b><span style="color: black;">低级工具</span></b></td>
|
||||
<td bgcolor="#AEA79F" align="CENTER" style="border: 1px solid #000001;"><b><span style="color: black;">高级工具</span></b></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td bgcolor="#FFFFFF" align="LEFT" height="18" style="border: 1px solid #000001;"><span style="color: black;"> Debian版及其衍生版</span></td>
|
||||
<td bgcolor="#FFFFFF" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000001;"><span style="color: black;"> dpkg</span></td>
|
||||
<td bgcolor="#FFFFFF" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000001;"><span style="color: black;"> apt-get / aptitude</span></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td bgcolor="#FFFFFF" align="LEFT" height="18" style="border: 1px solid #000001;"><span style="color: black;"> CentOS版</span></td>
|
||||
<td bgcolor="#FFFFFF" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000001;"><span style="color: black;"> rpm</span></td>
|
||||
<td bgcolor="#FFFFFF" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000001;"><span style="color: black;"> yum</span></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td bgcolor="#FFFFFF" align="LEFT" height="18" style="border: 1px solid #000001;"><span style="color: black;"> openSUSE版</span></td>
|
||||
<td bgcolor="#FFFFFF" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000001;"><span style="color: black;"> rpm</span></td>
|
||||
<td bgcolor="#FFFFFF" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000001;"><span style="color: black;"> zypper</span></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</tbody>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
|
||||
让我们来看下低级工具和高级工具的描述。
|
||||
|
||||
dpkg的是基于Debian系统中的一个低级包管理器。它可以安装,删除,提供有关资料,并建立*.deb包,但它不能自动下载并安装它们相应的依赖包。
|
||||
|
||||
- 阅读更多: [15个dpkg命令实例][1]
|
||||
|
||||
apt-get是Debian和衍生版的高级包管理器,并提供命令行方式从多个来源检索和安装软件包,其中包括解决依赖性。和dpkg不同的是,apt-get不是直接基于.deb文件工作,而是基于包的正确名称。
|
||||
|
||||
- 阅读更多: [25个apt-get命令实力][2]
|
||||
|
||||
Aptitude是基于Debian的系统的另一个高级包管理器,它可用于快速简便的执行管理任务(安装,升级和删除软件包,还可以自动处理解决依赖性)。与atp-get和额外的包管理器相比,它提供了相同的功能,例如提供对包的几个版本的访问。
|
||||
|
||||
rpm是Linux标准基础(LSB)兼容发布版使用的一种包管理器,用来对包进行低级处理。就像dpkg,rpm可以查询,安装,检验,升级和卸载软件包,并能被基于Fedora的系统频繁地使用,比如RHEL和CentOS。
|
||||
|
||||
- 阅读更多: [20个rpm命令实例][3]
|
||||
|
||||
相对于基于RPM的系统,yum增加了系统自动更新的功能和带依赖性管理的包管理功能。作为一个高级工具,和apt-get或者aptitude相似,yum基于库工作。
|
||||
|
||||
- 阅读更多: [20个yum命令实例][4]
|
||||
-
|
||||
### 低级工具的常见用法 ###
|
||||
|
||||
你用低级工具处理最常见的任务如下。
|
||||
|
||||
**1. 从已编译(*.deb或*.rpm)的文件安装一个包**
|
||||
|
||||
这种安装方法的缺点是没有提供解决依赖性的方案。当你在发行版本库中无法获得某个包并且又不能通过高级工具下载安装时,你很可能会从一个已编译文件安装该包。因为低级工具不需要解决依赖性问题,所以当安装一个没有解决依赖性的包时会出现出错并且退出。
|
||||
|
||||
# dpkg -i file.deb [Debian版和衍生版]
|
||||
# rpm -i file.rpm [CentOS版 / openSUSE版]
|
||||
|
||||
**注意**: 不要试图在CentOS中安装一个为openSUSE构建的.rpm文件,反之亦然!
|
||||
|
||||
**2. 从已编译文件中更新一个包**
|
||||
|
||||
同样,当中央库中没有某安装包时,你只能手动升级该包。
|
||||
|
||||
# dpkg -i file.deb [Debian版和衍生版]
|
||||
# rpm -U file.rpm [CentOS版 / openSUSE版]
|
||||
|
||||
**3. 列举安装的包**
|
||||
|
||||
当你第一次接触一个已经在工作中的系统时,很可能你会想知道安装了哪些包。
|
||||
|
||||
# dpkg -l [Debian版和衍生版]
|
||||
# rpm -qa [CentOS版 / openSUSE版]
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想知道一个特定的包安装在哪儿, 你可以使用管道命令从以上命令的输出中去搜索,这在这个系列的[操作Linux文件 – 第一讲][5] 中有介绍。假定我们需要验证mysql-common这个包是否安装在Ubuntu系统中。
|
||||
|
||||
# dpkg -l | grep mysql-common
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
检查安装的包
|
||||
|
||||
另外一种方式来判断一个包是否已安装。
|
||||
|
||||
# dpkg --status package_name [Debian版和衍生版]
|
||||
# rpm -q package_name [CentOS版 / openSUSE版]
|
||||
|
||||
例如,让我们找出sysdig包是否安装在我们的系统。
|
||||
|
||||
# rpm -qa | grep sysdig
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
检查sysdig包
|
||||
|
||||
**4. 查询一个文件是由那个包安装的**
|
||||
|
||||
# dpkg --search file_name
|
||||
# rpm -qf file_name
|
||||
|
||||
例如,pw_dict.hwm文件是由那个包安装的?
|
||||
|
||||
# rpm -qf /usr/share/cracklib/pw_dict.hwm
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Linux中查询文件
|
||||
|
||||
### 高级工具的常见用法 ###
|
||||
|
||||
你用高级工具处理最常见的任务如下。
|
||||
|
||||
**1. 搜索包**
|
||||
|
||||
aptitude更新将会更新可用的软件包列表,并且aptitude搜索会根据包名进行实际性的搜索。
|
||||
|
||||
# aptitude update && aptitude search package_name
|
||||
|
||||
在搜索所有选项中,yum不仅可以通过包名还可以通过包的描述搜索程序包。
|
||||
|
||||
# yum search package_name
|
||||
# yum search all package_name
|
||||
# yum whatprovides “*/package_name”
|
||||
|
||||
假定我们需要一个名为sysdig的包,要知道的是我们需要先安装然后才能运行。
|
||||
|
||||
# yum whatprovides “*/sysdig”
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
检查包描述
|
||||
|
||||
whatprovides告诉yum搜索一个含有能够匹配上述正则表达式的文件的包。
|
||||
|
||||
# zypper refresh && zypper search package_name [在openSUSE上]
|
||||
|
||||
**2. 从仓库安装一个包**
|
||||
|
||||
当安装一个包时,在包管理器解决了所有依赖性问题后,可能会提醒你确认安装。需要注意的是运行更新或刷新(根据所使用的软件包管理器)不是绝对必要,但是考虑到安全性和依赖性的原因,保持安装的软件包是最新的是一个好的系统管理员的做法。
|
||||
|
||||
# aptitude update && aptitude install package_name [Debian版和衍生版]
|
||||
# yum update && yum install package_name [CentOS版]
|
||||
# zypper refresh && zypper install package_name [openSUSE版]
|
||||
|
||||
**3. 卸载包**
|
||||
|
||||
按选项卸载将会卸载软件包,但把配置文件保留完好,然而清除包从系统中完全删去该程序。
|
||||
# aptitude remove / purge package_name
|
||||
# yum erase package_name
|
||||
|
||||
---注意要卸载的openSUSE包前面的减号 ---
|
||||
|
||||
# zypper remove -package_name
|
||||
|
||||
在默认情况下,大部分(如果不是全部)的包管理器会提示你,在你实际卸载之前你是否确定要继续卸载。所以,请仔细阅读屏幕上的信息,以避免陷入不必要的麻烦!
|
||||
|
||||
**4. 显示包的信息**
|
||||
|
||||
下面的命令将会显示birthday这个包的信息。
|
||||
|
||||
# aptitude show birthday
|
||||
# yum info birthday
|
||||
# zypper info birthday
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
检查包信息
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结 ###
|
||||
|
||||
作为一个系统管理员,包管理器是你不能回避的东西。你应该立即准备使用本文中介绍的这些工具。希望你在准备LFCS考试和日常工作中会觉得这些工具好用。欢迎在下面留下您的意见或问题,我们将尽可能快的回复你。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/linux-package-management/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Gabriel Cánepa][a]
|
||||
译者:[Flowsnow](https://github.com/Flowsnow)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/gacanepa/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/dpkg-command-examples/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/useful-basic-commands-of-apt-get-and-apt-cache-for-package-management/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/20-practical-examples-of-rpm-commands-in-linux/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.tecmint.com/20-linux-yum-yellowdog-updater-modified-commands-for-package-mangement/
|
||||
[5]:http://www.tecmint.com/sed-command-to-create-edit-and-manipulate-files-in-linux/
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user