mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2024-12-26 21:30:55 +08:00
Translated:20140530 Linux script command--A recorder inside your Terminal.md
This commit is contained in:
commit
1fa4191c77
@ -1,37 +0,0 @@
|
||||
alim0x translating
|
||||
|
||||
Fix “Cannot Add PPA” Error In Ubuntu 14.04 & Linux Mint
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
A regular reader of It’s FOSS, Chetan Jain contacted me today with this question: How can I fix “Cannot add PPA” error in Ubuntu 14.04. Chetan was trying to install [TLP (power management tool to reduce overheting)][1] and encountered this error:
|
||||
|
||||
chetan@Inspiron-3521:~$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:linrunner/tlp
|
||||
Cannot add PPA: ‘ppa:linrunner/tlp’.
|
||||
Please check that the PPA name or format is correct.
|
||||
|
||||
If you encounter similar error while adding a PPA in Ubuntu or Mint, don’t worry. It’s one of the (less) common issue with PPA and can be solved easily.
|
||||
|
||||
### Fix Cannot add PPA error in Ubuntu and Linux Mint ###
|
||||
|
||||
There can be mainly two reasons behind this kind of error. Either the CA certificates on your system are broken or there is a proxy set up in your network.
|
||||
|
||||
Let’s first try to reinstall the CA certificates:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install --reinstall ca-certificates
|
||||
|
||||
If the above command doesn’t work, perhaps there is proxy settings involved. To pass proxy settings to sudo, use it with E option in the following manner:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo -E add-apt-repository ppa:linrunner/tlp
|
||||
|
||||
This will get the PPA working. Chetan’s issue was solved with the second solution. I hope this quick tip help you as well to get rid of the PPA error. Any questions or suggestions are always welcomed.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/fix-add-ppa-error-ubuntu-1404-linux-mint/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://itsfoss.com/solve-overheating-issue-battery-life-ubuntu-1304/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,86 @@
|
||||
Translating by GOLinux...
|
||||
Linux script command - A recorder inside your Terminal
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
When you are working on the terminal or console, you may want to record what you have done in the terminal. The recording can be used as a documentation about what happen in terminal. Let say you are working together with some Linux Administrators at the same time. Or you let someone to remote your server. You may want to record about what happen in the terminal. To do this, you can use script command.
|
||||
|
||||
### What is script ###
|
||||
|
||||
script is a command that make a typescript that printed in the terminal. It is useful for everyone who need a hardcopy record of the session that happened in the terminal. This record can be saved and printed out later.
|
||||
|
||||
### How to use it ###
|
||||
|
||||
By default, we can start script with typing script on the terminal.
|
||||
|
||||
pungki@dev-machine:~$ script
|
||||
Script started, file is typescript
|
||||
pungki@dev-machine:~$
|
||||
|
||||
You can also define a destination filename to write the result of typescript.
|
||||
|
||||
pungki@dev-machine:~$ script myfile
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
When you received a command prompt again, it means the terminal will record anything that is printed in terminal.
|
||||
|
||||
You will see in the current directory, there is a file named typescript.
|
||||
|
||||
### Why we use script command ###
|
||||
|
||||
As we mention before, script has main function to record everything. Here’s two samples of scenarios why we are using it.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Collaborate with colleague ####
|
||||
|
||||
When working together with your colleague, we can record your activity with script.
|
||||
Let say we will use a typescript file called **collaborate**. To do that type :
|
||||
|
||||
$ script collaborate
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Then after doing some tasks, let say you need to send your work to another engineer. Just send the file. So when the other engineer need to review what was done, he can just open the file using a text editor.
|
||||
|
||||
If he want to update the file, he can use **-a** option.
|
||||
|
||||
$ script -a collaborate
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Record someone activity in the terminal ####
|
||||
|
||||
You may let your engineer or someone to enter your system remotely. To make sure that your engineer are doing right, you can record what he had done to your system. To make the script command run automatically upon login, we can add it on your shell profile. If you are using **bash** shell, add this line into your bash profile.
|
||||
|
||||
$ vi ~/.profile
|
||||
|
||||
# run the script command to record everything
|
||||
# use -q for quite and -a option to append the script
|
||||
#
|
||||
/usr/bin/script -qa /usr/local/script/log_record_script
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Then save it. Next time he logged in to your system, script command will automatically run and put the log on the **/usr/local/script/log_record_script**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The option **-q** will run script command in quite mode. The user who logged in will not have any notification that the script command is run. While **-a** option will add the record without erasing the previous record.
|
||||
|
||||
If we don’t use **-q** option, then when the user logged on, the user will get a notification about script as the picture below.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Quit recording ###
|
||||
|
||||
To exit the record activity, we can press **Ctrl+D** button or type **exit** from the terminal. Before you exit from script, you will find the size of the record file is 0 Kb. After you exit from script, the file size will change.
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
Script command may useful when you need to record or documenting what happen in the terminal. The record file will be stored as a text file, so it will easy to open it with any text editor. As usual, we can always type **man script** or **script -h** to display its manual page and explore it more detail.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/linux-command/script-command-recorder/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -1,60 +1,60 @@
|
||||
翻译中...
|
||||
|
||||
Install RainLoop Webmail (A Web Based Email Client) using ‘Nginx and Apache’ in Arch Linux
|
||||
使用`Nginx和Apache`安装RainLoop Webmail(一个网页邮件客户端)
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Rainloop is a free Open Source web application written in PHP which provides a fast modern web interface to access your emails on all major domain mail providers like Yahoo, Gmail, Outlook and many others as well as your own local mail servers, and, also, acts as a MUA (Mail User Agent) by accessing domain mail servers through IMAP and SMTP protocols.
|
||||
Rainloop是一个使用PHP编写的,开源免费的网页邮件客户端。他支持包括Google,Yahoo,OutLook在内的主流的邮件服务器,当然,他也支持你自己的本地邮件服务器。他主要的表现看起来像使用IMAP和SMTP协议的MUA(邮件客户端)。
|
||||
|
||||
#### RainLoop Demo ####
|
||||
#### RainLoop 示例 ####
|
||||
|
||||
Have a quick look at the demo page setup by the author at [http://demo.rainloop.net/][1].
|
||||
可以看一下作者编写的安装文档: [http://demo.rainloop.net/][1].
|
||||
|
||||
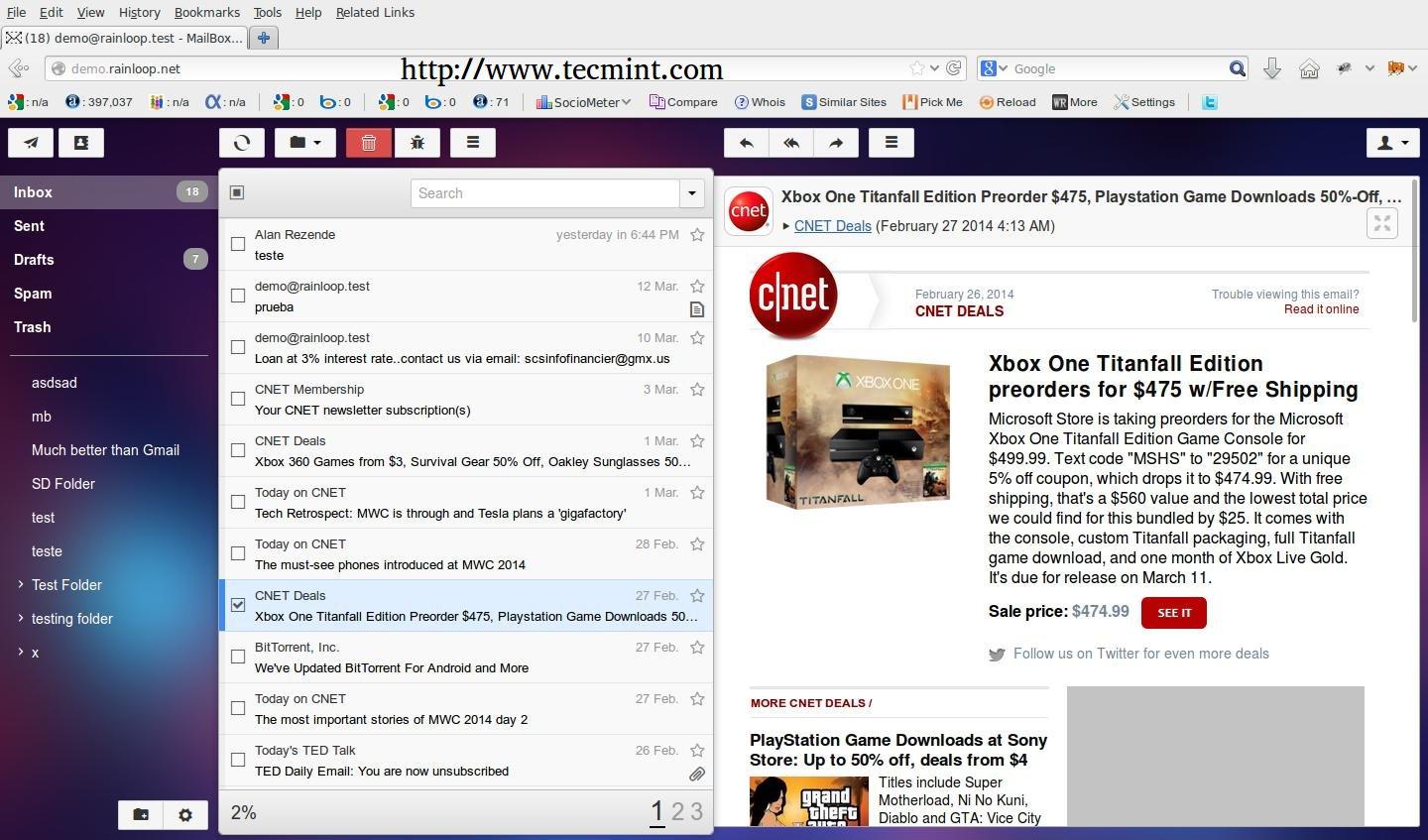
|
||||
Install RainLoop in Arch Linux
|
||||

|
||||
在Arch Linux上安装RainLoop
|
||||
|
||||
Once you have deployed Rainloop on your servers the only thing remaining to do is to access your Rainloop domain through a web browser and provide credentials for your enabled domain mail server.
|
||||
一旦在您的服务器部署上Rainloop,剩余要做的唯一的事情是通过Web浏览器访问您的Rainloop,并提供你正在使用的邮件服务器信息。
|
||||
|
||||
This tutorial covers **Rainloop** webmail installation process on **Arch Linux** from both point of view configuration files for **Apache** and **Nginx**, using a virtual local domain configured through local hosts file, without a DNS server.
|
||||
本教程包含了在 **Arch Linux**上的**Rainloop** 网页客户端的安装流程,包括如何进行配置 **Apache** 或 **Nginx**, 当然本教程使用修改Hosts的方式,从而避免了DNS的访问。
|
||||
|
||||
If you also need references on installing Rainloop on **Debian** and **Red Hat** systems visit the previous RainLoop Webmail article at.
|
||||
|
||||
如果你还是需要一篇在**Debian** 和 **Red Hat** 安装 RainLoop Webmail 的教程,你可以看这篇文章:
|
||||
|
||||
- [Install RainLoop Webmail on Debian and Red Hat based Systems][2]
|
||||
|
||||
### Requirements ###
|
||||
### 系统要求 ###
|
||||
|
||||
#### For Nginx ####
|
||||
#### 对 Nginx ####
|
||||
|
||||
- [Install LEMP (Nginx, PHP, MySQL with MariaDB engine and PhpMyAdmin) in Arch Linux][3]
|
||||
- [Create Virtual Hosts in Nginx Web Server][4]
|
||||
|
||||
#### For Apache ####
|
||||
#### 对 Apache ####
|
||||
|
||||
- [Install LAMP (Linux, Apache, MySQL/MariaDB, and PHP/PhpMyAdmin) in Arch Linux][5]
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 1: Create Virtual Hosts for Nginx or Apache ###
|
||||
### Step 1:为 Nginx 或者 Apache 提供虚拟Host###
|
||||
|
||||
**1.** Assuming that you have configured your servers (**Nginx** or **Apache**) as described in upper presentations links, the first thing you need to do is to create a rudimentary **DNS** entry on local **hosts** file that points to **Arch Linux** system IP.
|
||||
**1.** 假设你已经配置您的服务器(**Nginx**或**Apache**),如上面介绍的链接描述的,你需要做的第一件事是在Hosts文件里创建一个指向**的Arch Linux*系统的IP。
|
||||
|
||||
On Linux system edit **/etc/hosts** file and include your Rainloop virtual domain after localhost entry.
|
||||
对与Linux系统,修改 **/etc/hosts** 文件并且在你得localhost下添加 Rainloop virtual 域。如下:
|
||||
|
||||
127.0.0.1 localhost.localdomain localhost rainloop.lan
|
||||
192.168.1.33 rainloop.lan
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Add Domain Host Entry
|
||||
添加域信息
|
||||
|
||||
On Windows system edit **C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts** and add the following line at the bottom.
|
||||
对于Windows系统,则修改 **C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts** 并且将接下来的内容添加到你的文件里:
|
||||
|
||||
192.168.1.33 rainloop.lan
|
||||
|
||||
**2.** After you verify local domain using **ping** command, create the necessary **Virtual Hosts** and **SSL** configurations for **Apache** or **Nginx**.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Nginx Virtual Hosts ####
|
||||
#### Nginx 虚拟主机 ####
|
||||
|
||||
Create a file named **rainloop.lan** in **/etc/nginx/sites-available/** path with the following configuration.
|
||||
在**/etc/nginx/sites-available/** 目录下使用如下命令创建一个名叫**rainloop.lan**的文件:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo nano /etc/nginx/sites-available/rainloop.conf
|
||||
|
||||
Add the following file content.
|
||||
添加如下的文件内容:
|
||||
|
||||
server {
|
||||
listen 80;
|
||||
@ -90,11 +90,11 @@ Add the following file content.
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Then create the SSL equivalent file content.
|
||||
接下来创建SSL配置文件:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo nano /etc/nginx/sites-available/rainloop-ssl.conf
|
||||
|
||||
Add the following file content.
|
||||
添加如下内容:
|
||||
|
||||
server {
|
||||
listen 443 ssl;
|
||||
@ -137,14 +137,14 @@ Add the following file content.
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
On the next step generate **Certificate** file and **Keys** for **SSL Virtual Host** and add your virtual domain name (**rainloop.lan**) on Certificate **Common Name**.
|
||||
接下来将会自动生成**Certificate**和**Keys**文件,然后在文件中叫**Common Name*的证书里中添加您的虚拟域名(** rainloop.lan**)。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo nginx_gen_ssl.sh
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Generate Certificate and Keys
|
||||
生成证书和密钥
|
||||
|
||||
After the Certificate and SSL keys are generated, create Rainloop **root** webserver file path ( place where Rainloop PHP files reside), then enable Virtual Hosts and restart Nginx daemon to apply configurations.
|
||||
生成证书和SSL密钥后,创建Rainloop**根**网络服务器的文件路径(Rainloop PHP文件所在的位置),然后启用虚拟主机,并重新启动Nginx的守护进程,应用配置。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo mkdir -p /srv/www/rainloop
|
||||
$ sudo n2ensite rainloop
|
||||
@ -152,15 +152,15 @@ After the Certificate and SSL keys are generated, create Rainloop **root** webse
|
||||
$ sudo systemctl restart nginx
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Create RainLoop Web Director
|
||||
创建RainLoop 网页向导
|
||||
|
||||
#### Apache Virtual Hosts ####
|
||||
#### Apache 虚拟主机 ####
|
||||
|
||||
Create a new file named **rainloop.conf** in **/etc/httpd/conf/sites-available/** with the following content.
|
||||
在**/etc/httpd/conf/sites-available/**中创建 **rainloop.conf**文件:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo nano /etc/httpd/conf/sites-available/rainloop.conf
|
||||
|
||||
Add the following file content.
|
||||
添加如下内容:
|
||||
|
||||
<VirtualHost *:80>
|
||||
ServerName rainloop.lan
|
||||
@ -180,13 +180,13 @@ Add the following file content.
|
||||
</VirtualHost>
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Create Apache Virtual Host
|
||||
创建Apache虚拟主机
|
||||
|
||||
Then create the SSL equivalent file content for Apache.
|
||||
为Apache添加SSL支持:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo nano /etc/httpd/conf/sites-available/rainloop-ssl.conf
|
||||
|
||||
Add the following file content.
|
||||
添加如下文件内容:
|
||||
|
||||
<VirtualHost *:443>
|
||||
ServerName rainloop.lan
|
||||
@ -220,17 +220,19 @@ Add the following file content.
|
||||
|
||||
</VirtualHost>
|
||||
|
||||
The next step is to create **SSL Certificate** file and **Keys** for **SSL Virtual Host** and add put your virtual domain name (**rainloop.lan**) on Certificate **Common Name**.
|
||||
|
||||
接下来将会自动生成**Certificate**和**Keys**文件,然后在文件中叫**Common Name*的证书里中添加您的虚拟域名(** rainloop.lan**)。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apache_gen_ssl
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Create SSL Certificate and Keys
|
||||
创建SSL证书和密钥
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Enter Organization Details
|
||||
输入组织信息
|
||||
|
||||
After the Certificate and SSL keys are created, add Rainloop **DocumentRoot** path, then enable Virtual Hosts and restart Apache daemon to apply configurations.
|
||||
在证书和密钥建立之后,添加RainLoop **DocumentRoot**目录,之后激活虚拟主机,并且重启Apache应用设置。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo mkdir -p /srv/www/rainloop
|
||||
$ sudo a2ensite rainloop
|
||||
@ -238,15 +240,15 @@ After the Certificate and SSL keys are created, add Rainloop **DocumentRoot** pa
|
||||
$ sudo systemctl restart httpd
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Enable Virtual Hosts
|
||||
激活虚拟主机
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 2: Add necessary PHP Extensions ###
|
||||
### Step 2: 添加必要的PHP支持 ###
|
||||
|
||||
**3.** Whether you are using **Apache** or **Nginx** webserver, you need to enable the following PHP extensions on **php.ini** file and, also, include the new webserver **DocumentRoot** path to open_basedir directive.
|
||||
**3.** 无论您使用的是**Apache**或**Nginx**Web服务器,您需要激活**php.ini**文件下中的PHP扩展,包括新的服务器**DocumentRoot**目录。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo nano /etc/php/php.ini
|
||||
|
||||
Locate and uncomment the following PHP extensions.
|
||||
找到并且取消如下的PHP扩展的注释:
|
||||
|
||||
extension=iconv.so
|
||||
extension=imap.so
|
||||
@ -256,73 +258,74 @@ Locate and uncomment the following PHP extensions.
|
||||
extension=openssl.so ( enables IMAPS and SMTP SSL protocols on mail servers)
|
||||
extension=pdo_mysql.so
|
||||
|
||||
Also open_basedir statement should look like this.
|
||||
open_basedir语句应该看起来和这个一样。
|
||||
|
||||
open_basedir = /srv/http/:/home/:/tmp/:/usr/share/pear/:/usr/share/webapps/:/etc/webapps/:/srv/www/
|
||||
|
||||
**4.** After the **php.ini** file was modified restart your server than check **phpinfo** file to see if **SSL** protocols are enabled.
|
||||
**4.** 在修改好**php.ini**之后,重启你得服务器,然后检查 **phpinfo** 文件,去看看**SSL**协议是否已经激活。
|
||||
|
||||
----------On Apache Web Server----------
|
||||
----------对于 Apache Web 服务器----------
|
||||
$ sudo systemctl restart httpd
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
----------On Nginx Web Server----------
|
||||
----------对于 Nginx Web 服务器----------
|
||||
$ sudo systemctl restart nginx
|
||||
$ sudo systemctl restart php-fpm
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Check PHP Information
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 3: Download and Install RainLoop Webmail ###
|
||||
### Step 3: 下载和安装 RainLoop Webmail ###
|
||||
|
||||
**5.** Now it’s time to download and extract Rainloop application from official website to Document Root directory but first install **wget** and **unzip** system utilities.
|
||||
**5.**现在是时候从官方网站下载并解压缩Rainloop应用到文档根目录,但是需要首先安装**wget的**和**unzip**程序。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo pacman -S unzip wget
|
||||
|
||||
**6.** Download latest source package Rainloop zip archive using **wget** command or by using a browser to navigate to [http://rainloop.net/downloads/][6].
|
||||
**6.** 使用**wget**命令或通过使用浏览器导航到[http://rainloop.net/downloads/] [6]下载最新的源码包Rainloop zip归档。
|
||||
|
||||
$ wget http://repository.rainloop.net/v1/rainloop-latest.zip
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Download RainLoop Package
|
||||
下载 RainLoop 包
|
||||
|
||||
**7.** After the download process finishes, extract Rainloop archive to Virtual Host Document Root path ( **/srv/www/rainloop/** ).
|
||||
**7.** 下载过程完成后,解压Rainloop归档到虚拟主机文档根目录路径( **/srv/www/rainloop/** )。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo unzip rainloop-latest.zip -d /srv/www/rainloop/
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Extract Rainloop Archive
|
||||
解压
|
||||
|
||||
**8.** Then set the following permissions on application default path.
|
||||
**8.** 然后设置应用程序的默认路径下的权限。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo chmod -R 755 /srv/www/rainloop/
|
||||
$ sudo chown -R http:http /srv/www/rainloop/
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Set Permission on RainLoop
|
||||
设置权限
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 4: Configure Rainloop via Web Interface ###
|
||||
### Step 4: 通过网页配置RainLoop###
|
||||
|
||||
**9.** Rainloop application can be configured in two ways: using a system shell of via browser. If you want to configure over terminal open and edit **application.ini** file located in **/srv/www/rainloop/data/_data_da047852f16d2bc7352b24240a2f1599/_default_/configs/**.
|
||||
**9.** Rainloop应用程序可以通过两种方式进行配置:使用浏览器或者系统shell。如果要在终端配置就打开和编辑位于**/ srv/www/rainloop/data/_data_da047852f16d2bc7352b24240a2f1599/_default_/configs/**的application.ini**文件。
|
||||
|
||||
**10.** To access Admin Interface from browser, use the following URL address **https://rainloop.lan/?admin**, then provide the default application credentials.
|
||||
**10.** 若要从浏览器访问管理界面,使用下面的URL地址** https://rainloop.lan/?admin**,然后提供默认的应用程序用户名密码。
|
||||
|
||||
User= admin
|
||||
Password= 12345
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Rainloop Web Interface
|
||||
Rainloop Web 界面
|
||||
|
||||
**11.** After initial login you will be warn to change the default password, so I advise you to do it.
|
||||
**11.** 首次登录后,你将被警告更改默认密码,所以我劝你做这一点。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Change Default Password
|
||||
修改默认 Password
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Set New Admin Password
|
||||
设置新的 Admin Password
|
||||
|
||||
**12.** If you want to enable **contacts** login to MySQL database and create a new database with a privileged user on it, then provide database credentials on **Contacts** fields.
|
||||
**12.** 如果您要启用**Contact**,就登录到MySQL数据库并创建上有一个特权用户和一个新的数据库,然后提供**Contacts**字段的数据库凭据。
|
||||
|
||||
mysql -u root -p
|
||||
create database if not exists rainloop;
|
||||
@ -332,39 +335,39 @@ Set New Admin Password
|
||||
exit;
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Enable Contacts in RainLoop
|
||||
在 RainLoop 中激活联系人
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Enter Contact Database Details
|
||||
添加联系人数据
|
||||
|
||||
**13.** By default Rainloop provides **Gmail**, **Yahoo** and **Outlook** domains mail server configuration files, but you can add other mail server domains if you like.
|
||||
**13.** 默认情况下Rainloop提供** Gmail**,**Yahoo**和**Outlook**的邮件服务器的配置文件,但是你如果愿意,你也可以添加其他的邮件服务器域。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Default Mail Domains
|
||||
默认 Mail 域
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Add New Domain
|
||||
添加新域
|
||||
|
||||
**14.** To login on your mail server point your browser to **https://rainloop.lan** and provide your domain server credentials.
|
||||
**14.** 登录你的邮件服务器,浏览** https://rainloop.lan**,并提供您的域名服务器验证信息。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Login to Mail Domain
|
||||
登录到邮件页面
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Login to Gmail Domain
|
||||
登录Gmail
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
RainLoop Email Interface
|
||||
RainLoop Email 界面
|
||||
|
||||
For further configurations please visit official Rainloop documentation page at [http://rainloop.net/docs/][7].
|
||||
想要了解更多的文件,可以访问:[http://rainloop.net/docs/][7].
|
||||
|
||||
With Rainloop you can access mail servers from any device that has a browser as long as your server has Internet connectivity, the only minus of using Rainloop application in Arch Linux so far is the lack of poppassd plugin package needed to change email account password.
|
||||
通过Rainloop你可以从浏览器中访问具有Internet连接的任何邮件服务器。唯一的缺憾就是在Arch Linux下使用Rainloop应用的人缺乏修改电子邮件帐户密码的poppassd插件包。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/install-rainloop-webmail-in-arch-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[MikeCoder](https://github.com/MikeCoder) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
|
||||
修复Ubuntu 14.04和Linux Mint中无法添加PPA源的错误
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
一名It’s FOSS的普通读者Chetan Jain今天联系了我,并询问道:我要怎样修复Ubuntu 14.04中无法添加PPA源的错误。Chetan在尝试安装[TLP (一个用于减少过热发生的电源管理工具)][1]的时候遇到了这个错误:
|
||||
|
||||
chetan@Inspiron-3521:~$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:linrunner/tlp
|
||||
Cannot add PPA: ‘ppa:linrunner/tlp’.
|
||||
Please check that the PPA name or format is correct.
|
||||
|
||||
如果你在Ubuntu或Mint上添加PPA源时遇到了类似的情况,别担心。这是PPA源的一个常见情况(一般很少发生)之一,很容易就能够得到解决。
|
||||
|
||||
### 修复Ubuntu 14.04和Linux Mint中无法添加PPA源的错误 ###
|
||||
|
||||
发生这种错误主要有两种原因。一种是您电脑中的CA证书已经损坏,或者是您的网络设置了一个代理。
|
||||
|
||||
首先让我们重新安装一下CA证书:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install --reinstall ca-certificates
|
||||
|
||||
如果上面的命令不起作用,可能是网络使用了一个代理设置。要略过代理设置,使用sudo命令并加上参数E,就像下面这样:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo -E add-apt-repository ppa:linrunner/tlp
|
||||
|
||||
这样PPA源应该就能正常工作了。Chetan的情况通过第二种方法解决了。我希望这个快速指南同样能够帮助您摆脱PPA源错误。欢迎您提出任何问题或是建议来帮助我们改进。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/fix-add-ppa-error-ubuntu-1404-linux-mint/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[alim0x](https://github.com/alim0x) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://itsfoss.com/solve-overheating-issue-battery-life-ubuntu-1304/
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user