mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-02-28 01:01:09 +08:00
20150615-2 选题
This commit is contained in:
parent
a471b5ddc7
commit
1e2cd00a69
@ -0,0 +1,73 @@
|
||||
Extend Swap Space using Swap file in Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
There are some scenarios where our Linux box is running out of swap space so in that case we can extend the swap space using swap partition but due to unavailability of free partitions on the disk, we are unable to extend it.
|
||||
|
||||
So in such cases we can extend or increase swap space using a swap file
|
||||
|
||||
### Below are the Steps to extend Swap Space using Swap File in Linux ###
|
||||
|
||||
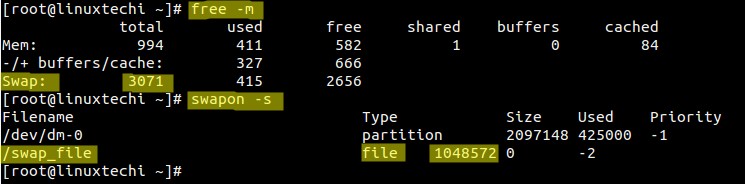
Lets first check the size of existing swap space / partition using the command like ‘**free -m‘** and ‘**swapon -s**‘
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
free-output-with-swap
|
||||
|
||||
In my case size of swap partition is 2 GB. So we will be extending swap space by 1 GB.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step:1 Create a swap file of size 1 GB using below dd Command ####
|
||||
|
||||
[root@linuxtechi ~]# dd if=/dev/zero of=/swap_file bs=1G count=1
|
||||
1+0 records in
|
||||
1+0 records out
|
||||
1073741824 bytes (1.1 GB) copied, 414.898 s, 2.6 MB/s
|
||||
[root@linuxtechi ~]#
|
||||
|
||||
Replace the value of ‘**bs**‘ and ‘**count**‘ according your requirement.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step:2 Secure the swap file with permissions 644. ####
|
||||
|
||||
[root@linuxtechi ~]# chmod 600 /swap_file
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step:3 Enable the Swap Area on the file (swap_file) ####
|
||||
|
||||
Use mkswap command to enable swap area
|
||||
|
||||
[root@linuxtechi ~]# mkswap /swap_file
|
||||
Setting up swapspace version 1, size = 1048572 KiB
|
||||
no label, UUID=f7b3ae59-c09a-4dc2-ba4d-c02abb7db33b
|
||||
[root@linuxtechi ~]#
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step:4 Add the swap file entry in the fstab file ####
|
||||
|
||||
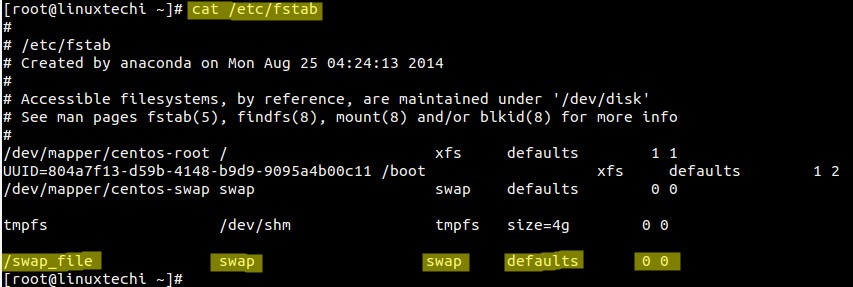
Add the below entry in the fstab file so that swap file become persistent across every reboot.
|
||||
|
||||
/swap_file swap swap defaults 0 0
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step:5 Enable the swap file using ‘mkswap on’ command. ####
|
||||
|
||||
[root@linuxtechi ~]# swapon /swap_file
|
||||
[root@linuxtechi ~]#
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step:6 Now verify the swap space ####
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**: To disable the swap file for any troubleshooting point of view, use swapoff command as shown below and to re-enable swap file then use swapon command as shown in step5.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@linuxtechi ~]# swapoff /swap_file
|
||||
[root@linuxtechi ~]#
|
||||
|
||||
Please share your valuable inputs and comments of this article.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxtechi.com/extend-swap-space-using-swap-file-in-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Pradeep Kumar][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.linuxtechi.com/author/pradeep/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,191 @@
|
||||
Install Plex Media Server On Ubuntu / CentOS 7.1 / Fedora 22
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
In this article we will show you how easily you can setup Plex Home Media Server on major Linux distributions with their latest releases. After its successful installation of Plex you will be able to use your centralized home media playback system that streams its media to many Plex player Apps and the Plex Home will allows you to setup your environment by adding your devices and to setup a group of users that all can use Plex Together. So let’s start its installation first on Ubuntu 15.04.
|
||||
|
||||
### Basic System Resources ###
|
||||
|
||||
System resources mainly depend on the type and number of devices that you are planning to connect with the server. So according to our requirements we will be using as following system resources and software for a standalone server.
|
||||
|
||||
注:表格
|
||||
<table width="666" style="height: 181px;">
|
||||
<tbody>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td width="670" colspan="2"><b>Plex Home Media Server</b></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td width="236"><b>Base Operating System</b></td>
|
||||
<td width="425">Ubuntu 15.04 / CentOS 7.1 / Fedora 22 Work Station</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td width="236"><b>Plex Media Server</b></td>
|
||||
<td width="425">Version 0.9.12.3.1173-937aac3</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td width="236"><b>RAM and CPU</b></td>
|
||||
<td width="425">1 GB , 2.0 GHZ</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td width="236"><b>Hard Disk</b></td>
|
||||
<td width="425">30 GB</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</tbody>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
|
||||
### Plex Media Server 0.9.12.3 on Ubuntu 15.04 ###
|
||||
|
||||
We are now ready to start the installations process of Plex Media Server on Ubuntu so let’s start with the following steps to get it ready.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 1: System Update ####
|
||||
|
||||
Login to your server with root privileges Make your that your system is upto date if not then do by using below command.
|
||||
|
||||
root@ubuntu-15:~#apt-get update
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 2: Download the Latest Plex Media Server Package ####
|
||||
|
||||
Create a new directory and download .deb plex Media Package in it from the official website of Plex for Ubuntu using wget command.
|
||||
|
||||
root@ubuntu-15:~# cd /plex/
|
||||
root@ubuntu-15:/plex#
|
||||
root@ubuntu-15:/plex# wget https://downloads.plex.tv/plex-media-server/0.9.12.3.1173-937aac3/plexmediaserver_0.9.12.3.1173-937aac3_amd64.deb
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 3: Install the Debian Package of Plex Media Server ####
|
||||
|
||||
Now within the same directory run following command to start installation of debian package and then check the status of plekmediaserver.
|
||||
|
||||
root@ubuntu-15:/plex# dpkg -i plexmediaserver_0.9.12.3.1173-937aac3_amd64.deb
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
root@ubuntu-15:~# service plexmediaserver status
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Plex Home Media Web App Setup on Ubuntu 15.04 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Let's open your web browser within your localhost network and open the Web Interface with your localhost IP and port 32400 and do following steps to configure it:
|
||||
|
||||
http://172.25.10.179:32400/web
|
||||
http://localhost:32400/web
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 1:Sign UP before Login ####
|
||||
|
||||
After you have access to the web interface of Plesk Media Server make sure to Sign Up and set your username email ID and Password to login as.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 2: Enter Your Pin to Secure Your Plex Media Home User ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Now you have successfully configured your user under Plex Home Media.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Opening Plex Web App on Devices Other than Localhost Server ###
|
||||
|
||||
As we have seen in our Plex media home page that it indicates that "You do not have permissions to access this server". Its because of we are on a different network than the Server computer.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Now we need to resolve this permissions issue so that we can have access to server on the devices other than the hosted server by doing following setup.
|
||||
|
||||
### Setup SSH Tunnel for Windows System to access Linux Server ###
|
||||
|
||||
First we need to set up a SSH tunnel so that we can access things as if they were local. This is only necessary for the initial setup.
|
||||
|
||||
If you are using Windows as your local system and server on Linux then we can setup SSH-Tunneling using Putty as shown.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Once you have the SSH tunnel set up:**
|
||||
|
||||
Open your Web browser window and type following URL in the address bar.
|
||||
|
||||
http://localhost:8888/web
|
||||
|
||||
The browser will connect to the server and load the Plex Web App with same functionality as on local.
|
||||
Agree to the terms of Services and start
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Now a fully functional Plex Home Media Server is ready to add new media libraries, channels, playlists etc.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Plex Media Server 0.9.12.3 on CentOS 7.1 ###
|
||||
|
||||
We will follow the same steps on CentOS-7.1 that we did for the installation of Plex Home Media Server on Ubuntu 15.04.
|
||||
|
||||
So lets start with Plex Media Servers Package Installation.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 1: Plex Media Server Installation ####
|
||||
|
||||
To install Plex Media Server on centOS 7.1 we need to download the .rpm package from the official website of Plex. So we will use wget command to download .rpm package for this purpose in a new directory.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@linux-tutorials ~]# cd /plex
|
||||
[root@linux-tutorials plex]# wget https://downloads.plex.tv/plex-media-server/0.9.12.3.1173-937aac3/plexmediaserver-0.9.12.3.1173-937aac3.x86_64.rpm
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 2: Install .RPM Package ####
|
||||
|
||||
After completion of complete download package we will install this package using rpm command within the same direcory where we installed the .rpm package.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@linux-tutorials plex]# ls
|
||||
plexmediaserver-0.9.12.3.1173-937aac3.x86_64.rpm
|
||||
[root@linux-tutorials plex]# rpm -i plexmediaserver-0.9.12.3.1173-937aac3.x86_64.rpm
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 3: Start Plexmediaservice ####
|
||||
|
||||
We have successfully installed Plex Media Server Now we just need to restart its service and then enable it permanently.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@linux-tutorials plex]# systemctl start plexmediaserver.service
|
||||
[root@linux-tutorials plex]# systemctl enable plexmediaserver.service
|
||||
[root@linux-tutorials plex]# systemctl status plexmediaserver.service
|
||||
|
||||
### Plex Home Media Web App Setup on CentOS-7.1 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Now we just need to repeat all steps that we performed during the Web app setup of Ubuntu.
|
||||
So let's Open a new window in your web browser and access the Plex Media Server Web app using localhost or IP or your Plex server.
|
||||
|
||||
http://172.20.3.174:32400/web
|
||||
http://localhost:32400/web
|
||||
|
||||
Then to get full permissions on the server you need to repeat the steps to create the SSH-Tunnel.
|
||||
After signing up with new user account we will be able to access its all features and can add new users, add new libraries and setup it per our needs.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Plex Media Server 0.9.12.3 on Fedora 22 Work Station ###
|
||||
|
||||
The Basic steps to download and install Plex Media Server are the same as its we did for in CentOS 7.1.
|
||||
We just need to download its .rpm package and then install it with rpm command.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Plex Home Media Web App Setup on Fedora 22 Work Station ###
|
||||
|
||||
We had setup Plex Media Server on the same host so we don't need to setup SSH-Tunnel in this time scenario. Just open the web browser in your Fedora 22 Workstation with default port 32400 of Plex Home Media Server and accept the Plex Terms of Services Agreement.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Welcome to Plex Home Media Server on Fedora 22 Workstation**
|
||||
|
||||
Lets login with your plex account and start with adding your libraries for your favorite movie channels , create your playlists, add your photos and enjoy with many other features of Plex Home Media Server.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
We had successfully installed and configured Plex Media Server on Major Linux Distributions. So, Plex Home Media Server has always been a best choice for media management. Its so simple to setup on cross platform as we did for Ubuntu, CentOS and Fedora. It has simplifies the tasks of organizing your media content and streaming to other computers and devices then to share it with your friends.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/tools/install-plex-media-server-ubuntu-centos-7-1-fedora-22/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Kashif Siddique][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/kashifs/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,176 @@
|
||||
Lolcat – A Command Line Tool to Output Rainbow Of Colors in Linux Terminal
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
For those who believe that Linux Command Line is boring and there isn’t any fun, then you’re wrong here are the articles on Linux, that shows how funny and naughty is Linux..
|
||||
|
||||
- [20 Funny Commands of Linux or Linux is Fun in Terminal][1]
|
||||
- [6 Interesting Funny Commands of Linux (Fun in Terminal)][2]
|
||||
- [Fun in Linux Terminal – Play with Word and Character Counts][3]
|
||||
|
||||
Here in this article, I will be discussing about a small utility called “lolcat” – Which produce rainbow of colors in terminal.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Lolcat Command to Output Rainbow of Colors for Terminal
|
||||
|
||||
#### What is lolcat? ####
|
||||
|
||||
Lolcat is an utility for Linux, BSD and OSX which concatenates like similar to [cat command][4] and adds rainbow coloring to it. Lolcat is primarily used for rainbow coloring of text in Linux Terminal.
|
||||
|
||||
### Installation of Lolcat in Linux ###
|
||||
|
||||
**1. Lolcat utility is available in the repository of lots of Linux distributions, but the available version bit older. Alternatively you can download and install latest version of lolcat from git repository.**
|
||||
|
||||
Lolcat is a ruby gem hence it is essential to have latest version of RUBY installed on your system.
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get install ruby [On APT based Systems]
|
||||
# yum install ruby [On Yum based Systems]
|
||||
# dnf install ruby [On DNF based Systems]
|
||||
|
||||
Once ruby package has been installed, make sure to verify the version of ruby installed.
|
||||
|
||||
# ruby --version
|
||||
|
||||
ruby 2.1.5p273 (2014-11-13) [x86_64-linux-gnu]
|
||||
|
||||
**2. Next download and install the most recent version of lolcat from the git repository using following commands.**
|
||||
|
||||
# wget https://github.com/busyloop/lolcat/archive/master.zip
|
||||
# unzip master.zip
|
||||
# cd lolcat-master/bin
|
||||
# gem install lolcat
|
||||
|
||||
Once lolcat is installed, you can check the version.
|
||||
|
||||
# lolcat --version
|
||||
|
||||
lolcat 42.0.99 (c)2011 moe@busyloop.net
|
||||
|
||||
### Usage of Lolcat ###
|
||||
|
||||
**3. Before starting usage of lolcat, make sure to know the available options and help using following command.**
|
||||
|
||||
# lolcat -h
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Lolcat Help
|
||||
|
||||
**4. Next, pipeline lolcat with commads say ps, date and cal as:**
|
||||
|
||||
# ps | lolcat
|
||||
# date | lolcat
|
||||
# cal | lolcat
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
ps Command Output
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Date Output
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Calendar Output
|
||||
|
||||
**5. 3. Use lolcat to display codes of a script file as:**
|
||||
|
||||
# lolcat test.sh
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Display Codes with Lolcat
|
||||
|
||||
**6. Pipeline lolcat with figlet command. Figlet is a utility which displays large characters made up of ordinary screen characters. We can pipeline the output of figlet with lolcat to make the output colorful as:**
|
||||
|
||||
# echo I ❤ Tecmint | lolcat
|
||||
# figlet I Love Tecmint | lolcat
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Colorful Texts
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**: Not to mention that ❤ is an unicode character and to install figlet you have to yum and apt to get the required packages as:
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get figlet
|
||||
# yum install figlet
|
||||
# dnf install figlet
|
||||
|
||||
**7. Animate a text in rainbow of colours, as:**
|
||||
|
||||
$ echo I ❤ Tecmit | lolcat -a -d 500
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Animated Text
|
||||
|
||||
Here the option -a is for Animation and -d is for duration. In the above example duration count is 500.
|
||||
|
||||
**8. Read a man page (say man ls) in rainbow of colors as:**
|
||||
|
||||
# man ls | lolcat
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
List Files Colorfully
|
||||
|
||||
**9. Pipeline lolcat with cowsay. cowsay is a configurable thinking and/or speaking cow, which supports a lot of other animals as well.**
|
||||
|
||||
Install cowsay as:
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get cowsay
|
||||
# yum install cowsay
|
||||
# dnf install cowsay
|
||||
|
||||
After install, print the list of all the animals in cowsay as:
|
||||
|
||||
# cowsay -l
|
||||
|
||||
**Sample Output**
|
||||
|
||||
Cow files in /usr/share/cowsay/cows:
|
||||
apt beavis.zen bong bud-frogs bunny calvin cheese cock cower daemon default
|
||||
dragon dragon-and-cow duck elephant elephant-in-snake eyes flaming-sheep
|
||||
ghostbusters gnu head-in hellokitty kiss kitty koala kosh luke-koala
|
||||
mech-and-cow meow milk moofasa moose mutilated pony pony-smaller ren sheep
|
||||
skeleton snowman sodomized-sheep stegosaurus stimpy suse three-eyes turkey
|
||||
turtle tux unipony unipony-smaller vader vader-koala www
|
||||
|
||||
Output of cowsay pipelined with lolcat and ‘gnu‘ cowfile is used.
|
||||
|
||||
# cowsay -f gnu ☛ Tecmint ☚ is the best Linux Resource Available online | lolcat
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Cowsay with Lolcat
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**: You can use lolcat with any other command in pipeline and get colored output in terminal.
|
||||
|
||||
**10. You may create alias for the most frequently used commands to get command output in rainbow of colors. You can alias ‘ls -l‘ command which is used for long list the contents of directory as below.**
|
||||
|
||||
# alias lolls="ls -l | lolcat"
|
||||
# lolls
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Alias Commands with Colorful
|
||||
|
||||
You may create alias for any command as suggested above. To create permanent alias, you have to add the relevant code (above code for ls -l alias) to ~/.bashrc file and also make sure to logout and login back for the changes to be taken into effect.
|
||||
|
||||
That’s all for now. I would like to know if you were aware of lolcat previously? Did you like the post? And suggestion and feedback is welcome in the comment section below. Like and share us and help us get spread.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/lolcat-command-to-output-rainbow-of-colors-in-linux-terminal/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Avishek Kumar][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/avishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/20-funny-commands-of-linux-or-linux-is-fun-in-terminal/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/linux-funny-commands/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/play-with-word-and-character-counts-in-linux/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.tecmint.com/13-basic-cat-command-examples-in-linux/
|
||||
91
sources/tech/20150615 How to combine two graphs on Cacti.md
Normal file
91
sources/tech/20150615 How to combine two graphs on Cacti.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,91 @@
|
||||
How to combine two graphs on Cacti
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
[Cacti][1] a fantastic open source network monitoring system that is widely used to graph network elements like bandwidth, storage, processor and memory utilization. Using its web based interface, you can create and organize graphs easily. However, some advanced features like merging graphs, creating aggregate graphs using multiple sources, migration of Cacti to another server are not provided by default. You might need some experience with Cacti to pull these off. In this tutorial, we will see how we can merge two Cacti graphs into one.
|
||||
|
||||
Consider this example. Client-A has been connected to port 5 of switch-A for the last six months. Port 5 becomes faulty, and so the client is migrated to Port 6. As Cacti uses different graphs for each interface/element, the bandwidth history of the client would be split into port 5 and port 6. So we end up with two graphs for one client - one with six months' worth of old data, and the other that contains ongoing data.
|
||||
|
||||
In such cases, we can actually combine the two graphs so the old data is appended to the new graph, and we get to keep a single graph containing historic and new data for one customer. This tutorial will explain exactly how we can achieve that.
|
||||
|
||||
Cacti stores the data of each graph in its own RRD (round robin database) file. When a graph is requested, the values stored in a corresponding RRD file are used to generate the graph. RRD files are stored in `/var/lib/cacti/rra` in Ubuntu/Debian systems and in `/var/www/cacti/rra` in CentOS/RHEL systems.
|
||||
|
||||
The idea behind merging graphs is to alter these RRD files so the values from the old RRD file are appended to the new RRD file.
|
||||
|
||||
### Scenario ###
|
||||
|
||||
The services for a client is running on eth0 for over a year. Because of hardware failure, the client has been migrated to eth1 interface of another server. We want to graph the bandwidth of the new interface, while retaining the historic data for over a year. The client would see only one graph.
|
||||
|
||||
### Identifying the RRD for the Graph ###
|
||||
|
||||
The first step during graph merging is to identify the RRD file associated with a graph. We can check the file by opening the graph in debug mode. To do this, go to Cacti's menu: Console > Graph Management > Select Graph > Turn On Graph Debug Mode.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Old graph: ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### New graph: ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
From the example output (which is based on a Debian system), we can identify the RRD files for two graphs:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Old graph**: /var/lib/cacti/rra/old_graph_traffic_in_8.rrd
|
||||
- **New graph**: /var/lib/cacti/rra/new_graph_traffic_in_10.rrd
|
||||
|
||||
### Preparing a Script ###
|
||||
|
||||
We will merge two RRD files using a [RRD splice script][2]. Download this PHP script, and install it as /var/lib/cacti/rra/rrdsplice.php (for Debian/Ubuntu) or /var/www/cacti/rra/rrdsplice.php (for CentOS/RHEL).
|
||||
|
||||
Next, make sure that the file is owned by Apache user.
|
||||
|
||||
On Debian or Ubuntu, run the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
# chown www-data:www-data rrdsplice.php
|
||||
|
||||
and update rrdsplice.php accordingly. Look for the following line:
|
||||
|
||||
chown($finrrd, "apache");
|
||||
|
||||
and replace it with:
|
||||
|
||||
chown($finrrd, "www-data");
|
||||
|
||||
On CentOS or RHEL, run the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
# chown apache:apache rrdsplice.php
|
||||
|
||||
### Merging Two Graphs ###
|
||||
|
||||
The syntax usage of the script can easily be found by running it without any parameters.
|
||||
|
||||
# cd /path/to/rrdsplice.php
|
||||
# php rrdsplice.php
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
USAGE: rrdsplice.php --oldrrd=file --newrrd=file --finrrd=file
|
||||
|
||||
Now we are ready to merge two RRD files. Simply supply the names of an old RRD file and a new RRD file. We will overwrite the merged result back to the new RRD file.
|
||||
|
||||
# php rrdsplice.php --oldrrd=old_graph_traffic_in_8.rrd --newrrd=new_graph_traffic_in_10.rrd --finrrd=new_graph_traffic_in_10.rrd
|
||||
|
||||
Now the data from the old RRD file should be appended to the new RRD. Any new data will continue to be written by Cacti to the new RRD file. If we click on the graph, we should be able to verify that the weekly, monthly and yearly records have also been added from the old graph. The second graph in the following diagram shows weekly records from the old graph.
|
||||
|
||||
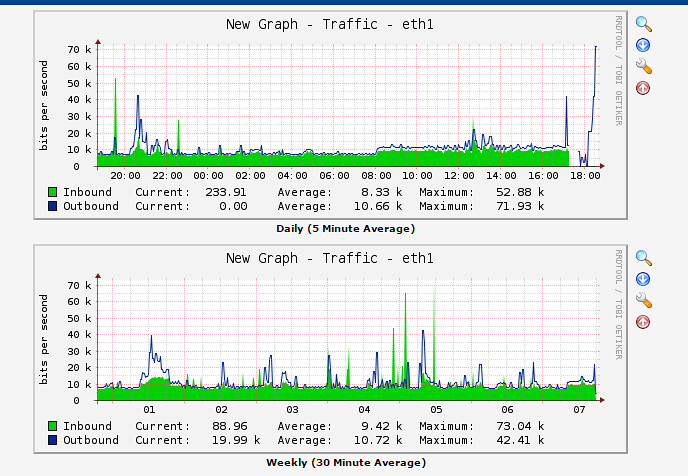
|
||||
|
||||
To sum up, this tutorial showed how we can easily merge two Cacti graphs into one. This trick is useful when a service is migrated to another device/interface and we want to deal with only one graph instead of two. The script is very handy as it can join graphs regardless of the source device e.g., Cisco 1800 router and Cisco 2960 switch.
|
||||
|
||||
Hope this helps.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/combine-two-graphs-cacti.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Sarmed Rahman][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/sarmed
|
||||
[1]:http://xmodulo.com/install-configure-cacti-linux.html
|
||||
[2]:http://svn.cacti.net/viewvc/developers/thewitness/rrdsplice/rrdsplice.php
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user