mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-01-13 22:30:37 +08:00
Translated:How to set up a web-based lightweight system monitor on Linux.md
This commit is contained in:
parent
5354a6ccdc
commit
1c844fb965
@ -1,185 +0,0 @@
|
||||
How to set up a web-based lightweight system monitor on Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Sometimes we, as a normal user or a system admin, need to know how well our system is running. Many questions related to system status can be answered by checking log files generated by active services. However, inspecting every bit of log files is not easy even for seasoned system admins. That is why they rely on monitoring software which is capable of gathering information from different sources, and reporting analysis result in easy to understand formats, such as graphs, visualization, statistics, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
There are many sophisticated monitoring system software such as [Cacti][1], [Nagios][2], Zabbix, Munin, etc. In this article, we pick a lightweight monitoring tool called Monitorix, which is designed to monitor system resources and many well-known third-party applications on Linux/BSD servers. Optimized to run on resource-limited embedded systems, Monitorix boasts of simplicity and small memory footprint. It comes with a built-in HTTP server for web-based interface, and stores time series statistics with RRDtool which is easy to combine with any scripting language such as Perl, Python, shell script, Ruby, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
### Main Features ###
|
||||
|
||||
Here is a list of Monitorix's main features. For a complete list, refer to the [official site][3].
|
||||
|
||||
- System load and system service demand
|
||||
- CPU/GPU temperature sensors
|
||||
- Disk temperature and health
|
||||
- Network/port traffic and netstat statistics
|
||||
- Mail statistics
|
||||
- Web server statistics (Apache, Nginx, Lighttpd)
|
||||
- MySQL load and statistics
|
||||
- Squid proxy statistics
|
||||
- NFS server/client statistics
|
||||
- Raspberry Pi sensor statistics
|
||||
- Memcached statistics
|
||||
|
||||
### Install and Configure Monitorix on Fedora, CentOS or RHEL ###
|
||||
|
||||
First, install required packages as follows. Note that on CentOS, you need to set up [EPEL][4] and [Repoforge][5] repositories first.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install rrdtool rrdtool-perl perl-libwww-perl perl-MailTools perl-MIME-Lite perl-CGI perl-DBI perl-XML-Simple perl-Config-General perl-HTTP-Server-Simple perl-IO-Socket-SSL
|
||||
|
||||
After this, Monitorix can be installed with this command:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install monitorix
|
||||
|
||||
To configure Monitorix, open the configuration file in /etc/monitorix/monitorix.conf, and change the options. The details on Monitorix configuration file can be found at [http://www.monitorix.org/documentation.html][6]
|
||||
|
||||
By default, the built-in HTTP server listens on port 8080. Thus, make sure that your firewall does not block TCP port 8080.
|
||||
|
||||
To start Monitorix, simply type the following.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo service monitorix start
|
||||
|
||||
Start your favorite web browser, and then go to http://<host-ip-address>:8080/monitorix to access Monitorix's web interface.
|
||||
|
||||
### Install and Configure Monitorix on Archlinux ###
|
||||
|
||||
On Archlinux, the Monitorix package can be downloaded from [AUR][7].
|
||||
|
||||
By default, the built-in HTTP server is disabled on Archlinux. To enable built-in HTTP server, edit <httpd_builtin> section in /etc/monitorix.conf as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
<httpd_builtin>
|
||||
enabled = y
|
||||
host =
|
||||
port = 8080
|
||||
user = nobody
|
||||
group = nobody
|
||||
log_file = /var/log/monitorix-httpd
|
||||
hosts_deny =
|
||||
hosts_allow =
|
||||
<auth>
|
||||
enabled = n
|
||||
msg = Monitorix: Restricted access
|
||||
htpasswd = /var/lib/monitorix/htpasswd
|
||||
</auth>
|
||||
</httpd_builtin>
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, start Monitorix service.
|
||||
|
||||
Open your favorite web browser, and go to http://<host-ip-address>:8080/monitorix to access Monitorix.
|
||||
|
||||
### Install and Configure Monitorix on Debian and Ubuntu ###
|
||||
|
||||
For Debian family, Monitorix can be installed in two ways: manually or through a third party repository.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Manual installation (for Debian) ####
|
||||
|
||||
Install all dependent packages first.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install rrdtool perl libwww-perl libmailtools-perl libmime-lite-perl librrds-perl libdbi-perl libxml-simple-perl libhttp-server-simple-perl libconfig-general-perl libio-socket-ssl-perl
|
||||
|
||||
Download Monitorix package from [http://www.monitorix.org/downloads.html][8], and install it.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo dpkg -i monitorix*.deb
|
||||
|
||||
During installation, you might be asked to configure a backend web server. If you using Apache, make sure to reload Apache configuration by restarting Apache service.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo service apache2 reload
|
||||
|
||||
#### nstallation through repositories (for Ubuntu) ####
|
||||
|
||||
Enable Izzysoft repository by appending the following line in /etc/apt/source.list.
|
||||
|
||||
deb http://apt.izzysoft.de/ubuntu generic universe
|
||||
|
||||
Download and add a GPG key for the repository.
|
||||
|
||||
$ wget http://apt.izzysoft.de/izzysoft.asc
|
||||
$ sudo apt-key add izzysoft.asc
|
||||
|
||||
Install Monitorix with apt-get. All its dependent packages will automatically be installed as well.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get update
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install monitorix
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, start Monitorix service.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo service monitorix start
|
||||
|
||||
To configure Monitorix, edit /etc/monitorix/monitorix.conf with a text editor, and restart Monitorix service.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo service monitorix restart
|
||||
|
||||
The built-in web server of Monitorix for Ubuntu is enabled by default. To access web-based monitoring result, go to http://<host-ip-address>8080/monitorix on your favorite web browser.
|
||||
|
||||
### Install and Configure Monitorix on Raspberry Pi ###
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to install Monitorix on Raspberry Pi (which is Debian-based), you cannot use the Izzysoft repository mentioned above because it does not provide an ARM port of Monitorix. Instead, follow Debian-based manual installation as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
First, install required packages.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install rrdtool perl libwww-perl libmailtools-perl libmime-lite-perl librrds-perl libdbi-perl libxml-simple-perl libhttp-server-simple-perl libconfig-general-perl libio-socket-ssl-perl
|
||||
|
||||
If some of the required packages are not be installed, we need to force install with this command.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get -f install
|
||||
|
||||
Download Monitorix package (monitorix_x.x.x-izzy1_all.deb) from [http://www.monitorix.org/downloads.html][9].
|
||||
|
||||
Install Monitorix package with the command below.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo dpkg -i monitorix_x.x.x-izzy1_all.deb
|
||||
|
||||
After installation is finished, we need to change a small thing in Monitorix configuration as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
Open /etc/monitorix/monitorix.conf with your favorite text editor. Scroll down until you find <graphs enable>. Search for "raspberrypi = n", and replace 'n' with 'y'. This will enable monitoring of Raspberry Pi clock frequency, temperatures and voltages.
|
||||
|
||||
After editing is done, restart Monitorix service.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo service monitorix restart
|
||||
|
||||
By default, Monitorix's built-in HTTP web server is enabled. To access Monitorix's web interface, go to http://<raspberrypi-ip-address>:8080/monitorix
|
||||
|
||||
### Monitorix Screenshots (on Raspberry Pi) ###
|
||||
|
||||
Monitorix home screen:
|
||||
|
||||
[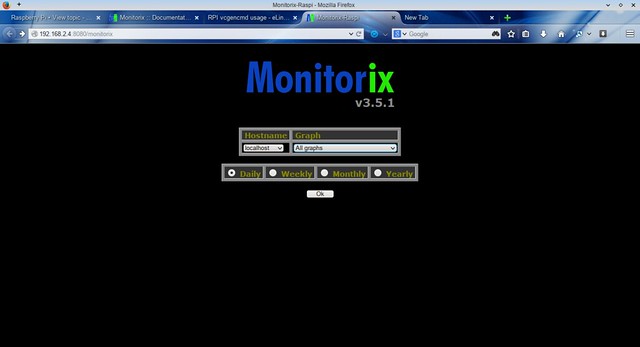][10]
|
||||
|
||||
System load average and usage in graph option:
|
||||
|
||||
[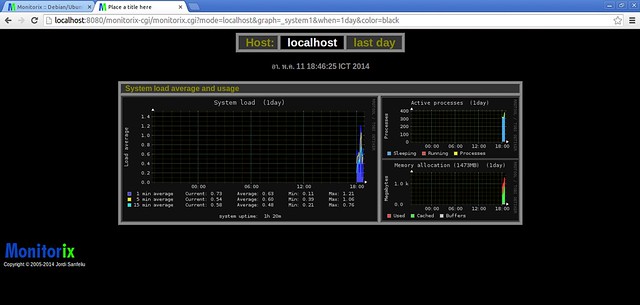][11]
|
||||
|
||||
Active process graph option:
|
||||
|
||||
[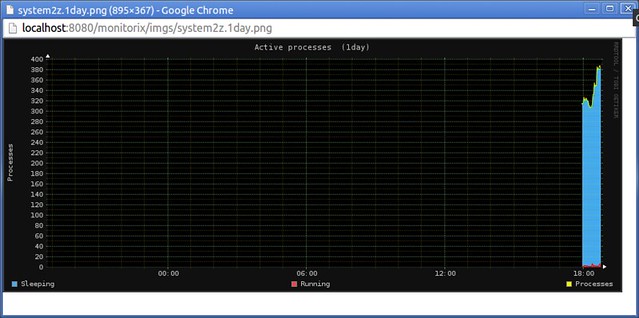][12]
|
||||
|
||||
Choose "Clock Frequency" under "Raspberry Pi" section in the home screen, and you will see clock frequency, temperature, and voltage graphs for [Raspberry Pi][13].
|
||||
|
||||
[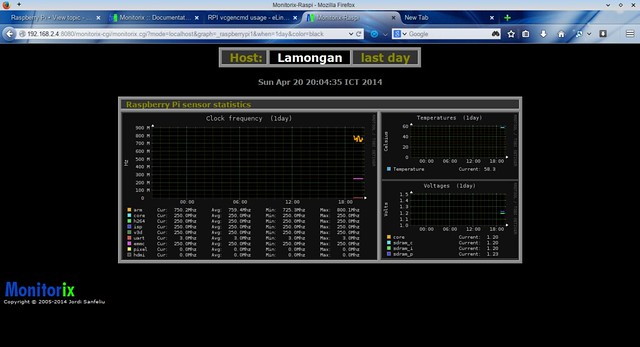][14]
|
||||
|
||||
All monitoring graphs:
|
||||
|
||||
[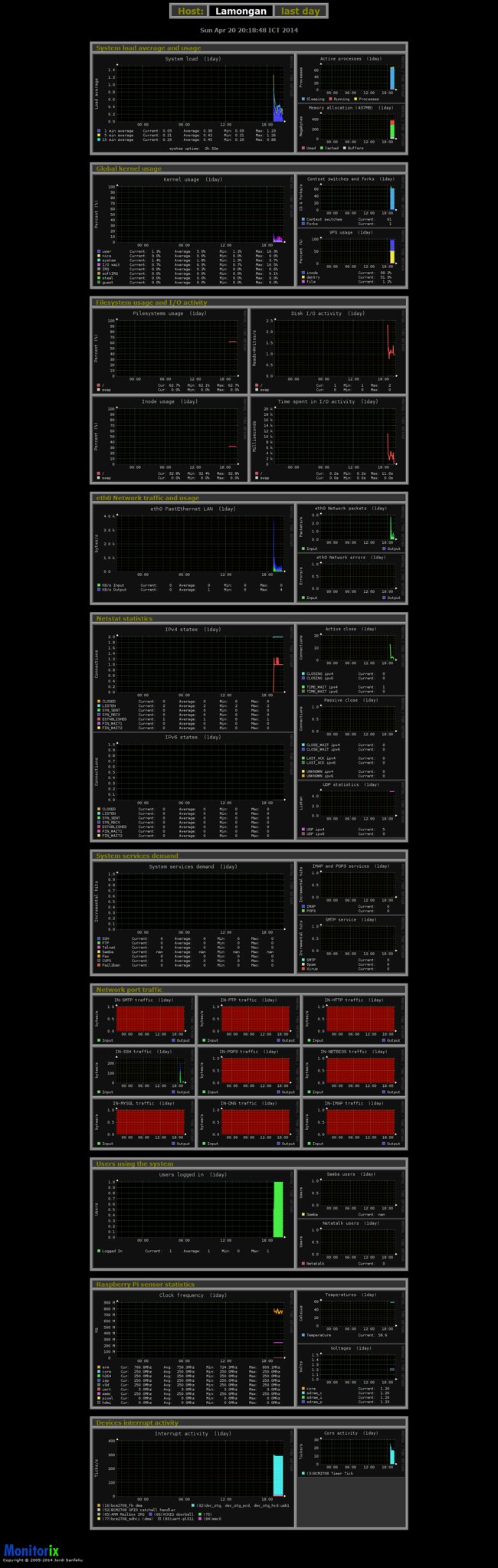][15]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/05/web-based-lightweight-system-monitor-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://xmodulo.com/2013/11/install-configure-cacti-linux.html
|
||||
[2]:http://xmodulo.com/tag/nagios
|
||||
[3]:http://www.monitorix.org/features.html
|
||||
[4]:http://xmodulo.com/2013/03/how-to-set-up-epel-repository-on-centos.html
|
||||
[5]:http://xmodulo.com/2013/01/how-to-set-up-rpmforge-repoforge-repository-on-centos.html
|
||||
[6]:http://www.monitorix.org/documentation.html
|
||||
[7]:http://aur.archlinux.org/packages.php?ID=33911
|
||||
[8]:http://www.monitorix.org/downloads.html
|
||||
[9]:http://www.monitorix.org/downloads.html
|
||||
[10]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/14215953893/
|
||||
[11]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/14009175290/
|
||||
[12]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/14195746084/
|
||||
[13]:http://xmodulo.com/go/raspberrypi
|
||||
[14]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/14009143189/
|
||||
[15]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/14192525721/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,180 @@
|
||||
在Linux上配置基于web的轻量级系统监控
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
有时候,我们作为普通用户或者系统管理员,需要知道系统运行是否良好。与系统状态相关的许多问题,都可以通过检查活动服务生成的日志文件来获得答案。然而,即便对于历经数个春秋的系统管理员而言,要检查日志文件的每个细节都不是件容易的事。这也是为什么他们依赖于监控软件的原因,监控软件能够从不同的源收集信息,并以易于理解的格式给出分析报告,如图表、可视化图像、统计数据等。
|
||||
|
||||
市面上流传着许多复杂的系统监控软件,诸如[Cacti][1], [Nagios][2], Zabbix, Munin此类。在本文中,我们选取了一个轻量级的监控工具——Monitorix,该工具设计用于在Linux/BSD上监控系统资源和许多熟知的第三方应用程序。由于专为资源有限的嵌入式系统而优化,Monitorix以使用简单,消耗内存资源少而著称。它内建了一个HTTP服务器用于提供web界面,并使用PRDtool来存储时间序列统计数据,该PRDtoo可以很容易地和任何脚本语言整合,如Perl,Python,shell脚本,Ruby等。
|
||||
### 主要特性 ###
|
||||
这里列出了Monitorix的主要特性。要查看完整列表,请参阅[官方网站][3]
|
||||
|
||||
- 系统负载和系统服务需求
|
||||
- CPU/GPU温度传感器
|
||||
- 磁盘温度和健康
|
||||
- 网络/端口流量和网络状况统计
|
||||
- 邮件统计
|
||||
- Web服务器统计(Apache,Nginx,Light图片的)
|
||||
- MySQL负载和统计
|
||||
- Squid代理统计
|
||||
- NFS服务器/客户端统计
|
||||
- Raspberry Pi传感器统计
|
||||
- Memcached统计
|
||||
|
||||
### 在Fedora, CentOS或者RHEL上安装并配置Monitorix ###
|
||||
|
||||
首先,安装需要的软件包。注意,在CentOS上,你需要先设置 [EPEL][4]和[Repoforge][5]仓库。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install rrdtool rrdtool-perl perl-libwww-perl perl-MailTools perl-MIME-Lite perl-CGI perl-DBI perl-XML-Simple perl-Config-General perl-HTTP-Server-Simple perl-IO-Socket-SSL
|
||||
|
||||
完成上一步后,可以通过以下命令来安装Monitorix:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install monitorix
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
要配置Monitorix,打开/etc/monitorix/monitorix.conf配置文件,并修改选项。关于Monitorix的配置文件细节,可以查阅[http://www.monitorix.org/documentation.html][6]。
|
||||
|
||||
默认情况下,内建的HTTP服务器监听8080端口。因此,确保你的防火墙没有阻止TCP 8080端口。
|
||||
|
||||
要启动Monitorix,只需输入以下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo service monitorix start
|
||||
|
||||
启动你喜爱的Web浏览器,然后通过http://<host-ip-address>:8080/monitorix来访问Monitorix的Web界面。
|
||||
|
||||
### 在Archlinux上安装并配置Monitorix ###
|
||||
在Archlinux上,可以从[AUR][7]上下载Monitorix包。
|
||||
|
||||
默认情况下,Archlinux上是禁用内建HTTP服务器的。要启用内建的HTTP服务器,请编辑/etc/monitorix.conf文件的如下区块。
|
||||
|
||||
<httpd_builtin>
|
||||
enabled = y
|
||||
host =
|
||||
port = 8080
|
||||
user = nobody
|
||||
group = nobody
|
||||
log_file = /var/log/monitorix-httpd
|
||||
hosts_deny =
|
||||
hosts_allow =
|
||||
<auth>
|
||||
enabled = n
|
||||
msg = Monitorix: Restricted access
|
||||
htpasswd = /var/lib/monitorix/htpasswd
|
||||
</auth>
|
||||
</httpd_builtin>
|
||||
|
||||
最后,启动Monitorix服务。
|
||||
|
||||
打开你喜欢的Web浏览器,然后通过http://<host-ip-address>:8080/monitorix来访问Monitorix的Web界面。
|
||||
|
||||
### 在Debian和Ubuntu上安装并配置Monitorix ###
|
||||
对于Debian家族,Monitorix可以通过两种方式安装:手工安装或通过第三方软件仓库。
|
||||
#### 手工安装(用于Debian) ####
|
||||
|
||||
Install all dependent packages first.
|
||||
首先安装所有依赖包。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install rrdtool perl libwww-perl libmailtools-perl libmime-lite-perl librrds-perl libdbi-perl libxml-simple-perl libhttp-server-simple-perl libconfig-general-perl libio-socket-ssl-perl
|
||||
|
||||
从[http://www.monitorix.org/downloads.html][8]下载Monitorix包,并安装。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo dpkg -i monitorix*.deb
|
||||
|
||||
在安装期间,会要求你配置一个后端Web服务器。如果你正是用Apache,确保重启Apache服务来重新加载Apache配置。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo service apache2 reload
|
||||
|
||||
#### 通过软件仓库安装 (用于Ubuntu) ####
|
||||
在/etc/apt/source.list中添加以下行来启用Izzysoft仓库。
|
||||
|
||||
deb http://apt.izzysoft.de/ubuntu generic universe
|
||||
|
||||
下载并为软件仓库添加GPG密钥。
|
||||
|
||||
$ wget http://apt.izzysoft.de/izzysoft.asc
|
||||
$ sudo apt-key add izzysoft.asc
|
||||
|
||||
使用apt-get安装Monitorix,所有依赖包也将自动安装。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get update
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install monitorix
|
||||
|
||||
最后,启动Monitorix服务。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo service monitorix start
|
||||
|
||||
要配置Monitorix,请使用文本编辑器编辑/etc/monitorix/monitorix.conf,并重启Monitorix服务。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo service monitorix restart
|
||||
|
||||
用于Ubuntu的内建Web服务器默认将被启用。要从Web查看监控结果,在你喜爱的Web浏览器中访问http://<host-ip-address>8080/monitorix。
|
||||
|
||||
### 在Raspberry Pi上安装并配置Monitorix ###
|
||||
如果想要在Raspberry Pi(基于Debian)上安装Monitorix,你不能使用上面提到的Izzysoft仓库,因为它不提供Monitorix的ARM端口。取而代之的是,你可以参照如下基于Debian的手工安装。
|
||||
|
||||
首先,安装需要的软件包。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install rrdtool perl libwww-perl libmailtools-perl libmime-lite-perl librrds-perl libdbi-perl libxml-simple-perl libhttp-server-simple-perl libconfig-general-perl libio-socket-ssl-perl
|
||||
|
||||
如果某些需要的软件包没有安装,我们需要使用此命令来强制安装。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get -f install
|
||||
|
||||
从[http://www.monitorix.org/downloads.html][9]下载Monitorix软件包(monitorix_x.x.x-izzy1_all.deb)。
|
||||
|
||||
使用下面的命令来安装Monitorix包。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo dpkg -i monitorix_x.x.x-izzy1_all.deb
|
||||
|
||||
安装完成后,我们需要像下面这样对Monitorix配置稍作修改。
|
||||
|
||||
用你喜爱的文本编辑器打开/etc/monitorix/monitorix.conf,向下滚动文本直到你找到<graphs enable>。搜索“raspberrypi = n”,并用“y”替换“n”,这将启用对Raspberry Pi时钟频率、温度和电压的监控。
|
||||
|
||||
编辑完成后,重启Monitorix服务。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo service monitorix restart
|
||||
|
||||
默认情况下,Monitorix的内建HTTP Web服务器会被启用。要访问Monitorix的Web界面,访问此地址http://<raspberrypi-ip-address>:8080/monitorix。
|
||||
|
||||
### Monitorix截图(Raspberry Pi上) ###
|
||||
|
||||
Monitorix主屏幕:
|
||||
|
||||
[][10]
|
||||
|
||||
系统平均负载和使用情况图示:
|
||||
|
||||
[][11]
|
||||
|
||||
活动进程图示:
|
||||
|
||||
[][12]
|
||||
|
||||
在主屏幕中选择“Raspberry Pi”部分下的“时钟频率”,你会看到[Raspberry Pi][13]的时钟频率、温度和电压的图示:
|
||||
|
||||
[][14]
|
||||
|
||||
所有监控图示:
|
||||
|
||||
[][15]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/05/web-based-lightweight-system-monitor-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://xmodulo.com/2013/11/install-configure-cacti-linux.html
|
||||
[2]:http://xmodulo.com/tag/nagios
|
||||
[3]:http://www.monitorix.org/features.html
|
||||
[4]:http://xmodulo.com/2013/03/how-to-set-up-epel-repository-on-centos.html
|
||||
[5]:http://xmodulo.com/2013/01/how-to-set-up-rpmforge-repoforge-repository-on-centos.html
|
||||
[6]:http://www.monitorix.org/documentation.html
|
||||
[7]:http://aur.archlinux.org/packages.php?ID=33911
|
||||
[8]:http://www.monitorix.org/downloads.html
|
||||
[9]:http://www.monitorix.org/downloads.html
|
||||
[10]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/14215953893/
|
||||
[11]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/14009175290/
|
||||
[12]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/14195746084/
|
||||
[13]:http://xmodulo.com/go/raspberrypi
|
||||
[14]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/14009143189/
|
||||
[15]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/14192525721/
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user