mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2024-12-26 21:30:55 +08:00
2014018-1 选题
This commit is contained in:
parent
f55cf524b8
commit
157fae0cc3
@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
|
||||
Mir Display Server May Not Arrive on Desktops As Default Until 2016
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**Ubuntu’s next generation display server Mir, developed by Canonical as a flexible alternative to Wayland and XServer, could be facing another delay on its way to the desktop. **
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The technology was initially positioned as a candidate for shipping by default on the desktop later this year but, [in a video address][1] to developers, Mark Shuttleworth has now intimated that Mir may not find its way on to the Ubuntu desktop until the release of Ubuntu 16.04 LTS — in 2016.
|
||||
|
||||
Responding to a question asking when users could expect to find it available on PCs, Shuttleworth replied:
|
||||
|
||||
> “I expect Mir to be the display server [to be default] as soon as it’s rock solid and we have a story we’re really proud of on it. You can run it on your desktop [now], but we don’t want to let a love of technology interfere with our mission to be great for the user. This is a great place for us to set the bar very high in terms of performance…where we have freedom to get it right, without having to worry too much about compatibility.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> By 16.04 it’ll be the default display server…That’s the kind of timeline we’re looking at.”
|
||||
|
||||
### Mir Oh Mir ###
|
||||
|
||||
It’s not immediately clear what impact, if any, such a delay would mean for Unity 8, scheduled to arrive on desktops this October.
|
||||
|
||||
Similarly, it’s also not clear from his words whether the ‘by 16.04′ references a pure Mir experience or something akin to the Mir + Xmir hybrid proposed for Ubuntu 13.10. Either way a slip in timeframe is a hazard of any development process. Display servers are not easy technologies to build, particularly when designing one to span all manner of screen sizes and form factors.
|
||||
|
||||
This delay, if as assured as some news outlets are reporting it as being, won’t be the first to scupper Canonical’s plans. Ubuntu [originally intended to land a Mir Hybrid in Ubuntu 13.10][2], but technical flaws prevented that from happened. Its inclusion in the upcoming release of 14.04 LTS [was also ruled][3] out early on.
|
||||
|
||||
### Mir As It Is ###
|
||||
|
||||
As disappointing as the above may read Mir is continuing to evolve at breakneck pace. In fact, while it won’t be default, it will be possible to install a Mir session in Ubuntu 14.04 LTS, bundled with an in-progress version of the Unity 8 desktop. It’s also rocking out as the default on Ubuntu Touch for both phones and tablets.
|
||||
|
||||
But on the desktop it looks like things may take a little longer. Unlike on phones and tablets, where Ubuntu is able to make use of Android device drivers [via Hybris][4], there are currently no proprietary AMD, Intel or Nvidia desktop graphics drivers supporting Mir. Upstream support in open-source drivers remain patchy at best, with Canonical [being forced][5] to carry patches to enable functionality.
|
||||
|
||||
**The more time Canonical has to refine, iterate and improve on the technology in its desktop form, the better the end user experience of it will be.**
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/03/mir-default-display-server-ubuntu-2016
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dWTVe5Mdv0Y&feature=share&t=29m19s
|
||||
[2]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2013/10/xmir-longer-default-supported-cards-13-10
|
||||
[3]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2013/11/expect-ubuntu-14-04-lts
|
||||
[4]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hybris_(software)
|
||||
[5]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2013/09/intel-remove-xmir-support-in-xorg-video-driver
|
||||
268
sources/tech/Linux or Unix--chroot Command Examples.md
Normal file
268
sources/tech/Linux or Unix--chroot Command Examples.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,268 @@
|
||||
Linux / Unix: chroot Command Examples
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
I am a new Linux and Unix user. How do I change the root directory of a command? How do I change the root directory of a process such as web-server using a chroot command to isolate file system? How do I use a chroot to recover password or fix the damaged Linux/Unix based environment?
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Each process/command on Linux and Unix-like system has current working directory called root directory of a process/command. You can change the root directory of a command using `chroot` command, which ends up changing the root directory for both current running process and its children.
|
||||
|
||||
chroot command details
|
||||
Description:Change root directory
|
||||
Category:Processes Management
|
||||
Difficulty:Advanced
|
||||
Root privileges:Yes
|
||||
|
||||
A process/command that is run in such a modified environment cannot access files outside the root directory. This modified environment is commonly known as "jailed directory" or "chroot jail". Only a privileged process and root user can use chroot command. This is useful to:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Privilege separation for unprivileged process such as Web-server or DNS server.
|
||||
1. Setting up a test environment.
|
||||
1. Run old programs or ABI in-compatibility programs without crashing application or system.
|
||||
1. System recovery.
|
||||
1. Reinstall the bootloader such as Grub or Lilo.
|
||||
1. Password recovery Reset a forgotten password and more.
|
||||
|
||||
### Purpose ###
|
||||
|
||||
> The chroot command **changes its current and root directories to the provided directory and then run command**, if supplied, or an interactive copy of the user's login shell. Please note that not every application can be chrooted.
|
||||
|
||||
### Syntax ###
|
||||
|
||||
The basic syntax is as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
chroot /path/to/new/root command
|
||||
|
||||
OR
|
||||
|
||||
chroot /path/to/new/root /path/to/server
|
||||
|
||||
OR
|
||||
|
||||
chroot [options] /path/to/new/root /path/to/server
|
||||
|
||||
#### chroot command examples ####
|
||||
|
||||
In this example, build a mini-jail for testing purpose with bash and ls command only. First, set jail location using mkdir command:
|
||||
|
||||
$ J=$HOME/jail
|
||||
|
||||
Create directories inside $J:
|
||||
|
||||
$ mkdir -p $J
|
||||
$ mkdir -p $J/{bin,lib64,lib}
|
||||
$ cd $J
|
||||
|
||||
Copy /bin/bash and /bin/ls into $J/bin/ location using [cp command][1]:
|
||||
|
||||
$ cp -v /bin/{bash,ls} $J/bin
|
||||
|
||||
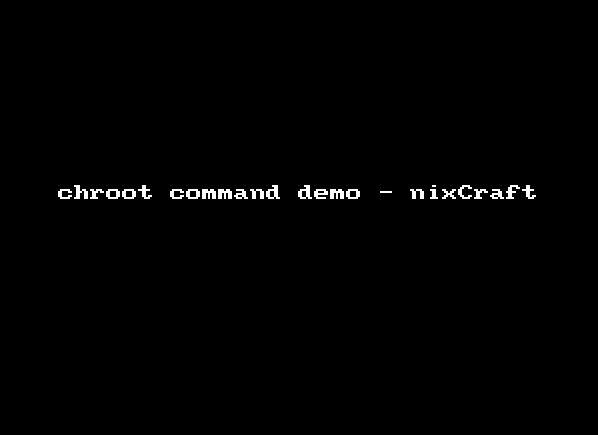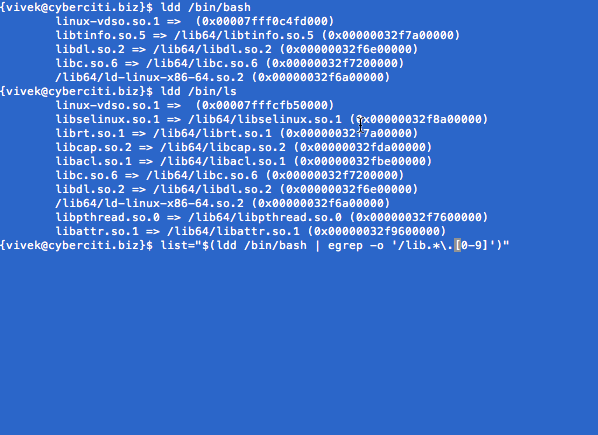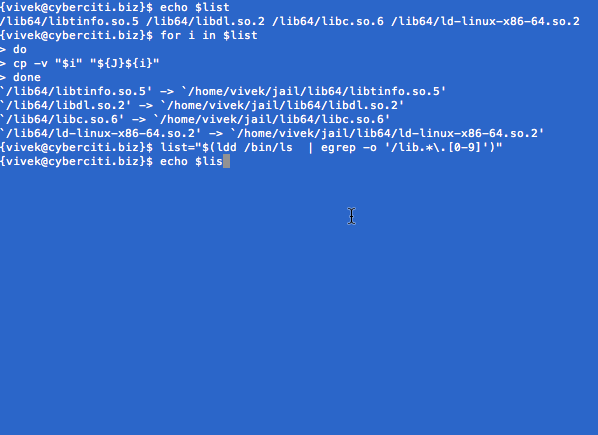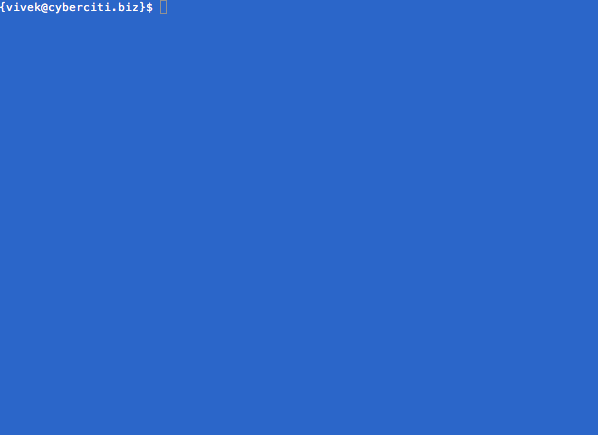
Copy required libs in $J. Use ldd command to print shared library dependencies for bash:
|
||||
|
||||
$ ldd /bin/bash
|
||||
|
||||
Sample outputs:
|
||||
|
||||
linux-vdso.so.1 => (0x00007fff8d987000)
|
||||
libtinfo.so.5 => /lib64/libtinfo.so.5 (0x00000032f7a00000)
|
||||
libdl.so.2 => /lib64/libdl.so.2 (0x00000032f6e00000)
|
||||
libc.so.6 => /lib64/libc.so.6 (0x00000032f7200000)
|
||||
/lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 (0x00000032f6a00000)
|
||||
|
||||
Copy libs in $J correctly from the above output:
|
||||
|
||||
$ cp -v /lib64/libtinfo.so.5 /lib64/libdl.so.2 /lib64/libc.so.6 /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 $J/lib64/
|
||||
|
||||
Sample outputs:
|
||||
|
||||
`/lib64/libtinfo.so.5' -> `/home/vivek/jail/lib64/libtinfo.so.5'
|
||||
`/lib64/libdl.so.2' -> `/home/vivek/jail/lib64/libdl.so.2'
|
||||
`/lib64/libc.so.6' -> `/home/vivek/jail/lib64/libc.so.6'
|
||||
`/lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2' -> `/home/vivek/jail/lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2'
|
||||
|
||||
Copy required libs in $J for ls command. Use ldd command to print shared library dependencies for ls command:
|
||||
|
||||
$ ldd /bin/ls
|
||||
|
||||
Sample outputs:
|
||||
|
||||
linux-vdso.so.1 => (0x00007fff68dff000)
|
||||
libselinux.so.1 => /lib64/libselinux.so.1 (0x00000032f8a00000)
|
||||
librt.so.1 => /lib64/librt.so.1 (0x00000032f7a00000)
|
||||
libcap.so.2 => /lib64/libcap.so.2 (0x00000032fda00000)
|
||||
libacl.so.1 => /lib64/libacl.so.1 (0x00000032fbe00000)
|
||||
libc.so.6 => /lib64/libc.so.6 (0x00000032f7200000)
|
||||
libdl.so.2 => /lib64/libdl.so.2 (0x00000032f6e00000)
|
||||
/lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 (0x00000032f6a00000)
|
||||
libpthread.so.0 => /lib64/libpthread.so.0 (0x00000032f7600000)
|
||||
libattr.so.1 => /lib64/libattr.so.1 (0x00000032f9600000)
|
||||
|
||||
You can copy libs one-by-one or try [bash shell for loop][2] as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
list="$(ldd /bin/ls | egrep -o '/lib.*\.[0-9]')"
|
||||
for i in $list; do cp -v "$i" "${J}${i}"; done
|
||||
|
||||
Sample outputs:
|
||||
|
||||
`/lib64/libselinux.so.1' -> `/home/vivek/jail/lib64/libselinux.so.1'
|
||||
`/lib64/librt.so.1' -> `/home/vivek/jail/lib64/librt.so.1'
|
||||
`/lib64/libcap.so.2' -> `/home/vivek/jail/lib64/libcap.so.2'
|
||||
`/lib64/libacl.so.1' -> `/home/vivek/jail/lib64/libacl.so.1'
|
||||
`/lib64/libc.so.6' -> `/home/vivek/jail/lib64/libc.so.6'
|
||||
`/lib64/libdl.so.2' -> `/home/vivek/jail/lib64/libdl.so.2'
|
||||
`/lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2' -> `/home/vivek/jail/lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2'
|
||||
`/lib64/libpthread.so.0' -> `/home/vivek/jail/lib64/libpthread.so.0'
|
||||
`/lib64/libattr.so.1' -> `/home/vivek/jail/lib64/libattr.so.1'
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, chroot into your new jail:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo chroot $J /bin/bash
|
||||
|
||||
Try browsing /etc or /var:
|
||||
|
||||
# ls /
|
||||
# ls /etc/
|
||||
# ls /var/
|
||||
|
||||
A chrooted bash and ls application is locked into a particular directory called $HOME/$J and unable to wander around the rest of the directory tree, and sees that directory as its "/" (root) directory. This is a tremendous boost to security if configured properly. I usually lock down the following applications using the same techniques:
|
||||
|
||||
1. [Apache - Red Hat / CentOS: Chroot Apache 2 Web Server][3]
|
||||
1. [Nginx - Linux nginx: Chroot (Jail) Setup][4]
|
||||
1. [Chroot Lighttpd web server on a Linux based system][5]
|
||||
1. Chroot mail server.
|
||||
1. Chroot Bind DNS server and more.
|
||||
|
||||
### How do I exit from chrooted jail? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Type exit
|
||||
|
||||
$ exit
|
||||
|
||||
Sample session from above commands:
|
||||
|
||||
[][6]
|
||||
|
||||
Animated gif 01: Linux / Unix: Bash Chroot ls Command Demo
|
||||
|
||||
### Find out if service in chrooted jail or not ###
|
||||
|
||||
You can [easily find out if Postfix mail server is chrooted or not][7] using the following two commands:
|
||||
|
||||
pid=$(pidof -s master)
|
||||
ls -ld /proc/$pid/root
|
||||
|
||||
Sample outputs from my Linux based server:
|
||||
|
||||
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 0 Mar 9 11:16 /proc/8613/root -> /
|
||||
|
||||
The PID 8613 pointing out to / (root) i.e. the root directory for application is not changed or chrooted. This is a quick and dirty way to find out if application is chrooted or not without opening configuration files. Here is another example from chrooted nginx server:
|
||||
|
||||
pid=$(pidof -s master)
|
||||
ls -ld /proc/$pid/root
|
||||
|
||||
Sample outputs:
|
||||
|
||||
lrwxrwxrwx 1 nginx nginx 0 Mar 9 11:17 /proc/4233/root -> /nginxjail
|
||||
|
||||
The root directory for application is changed to /nginxjail.
|
||||
|
||||
### Rescue and fix software RAID system with chroot ###
|
||||
|
||||
I'm assuming that software RAID based Linux system is not booting. So you [booted system either using the Live CD or networked based remote rescue kernel mode][8] to fix the system. In this example, I booting RHEL based system using live Linux DVD/CD and chroot into /dev/sda1 and/or /dev/md0 to fix the problem:
|
||||
|
||||
## Recover data, at live cd prompt type the following commands. ##
|
||||
## /dev/sda1 main system partition ##
|
||||
## /dev/md0 /data partition ##
|
||||
# Set jail dir
|
||||
d=/chroot
|
||||
mkdir $d
|
||||
|
||||
# Mount sda1 and required dirs
|
||||
mount /dev/sda1 $d
|
||||
mount -o bind /dev $d/dev
|
||||
mount -o bind /sys $d/sys
|
||||
mount -o bind /dev/shm $d/dev/shm
|
||||
mount -o bind /proc $d/proc
|
||||
|
||||
# Mount software raid /dev/md0
|
||||
mount /dev/md0 $d/data
|
||||
|
||||
# Chroot to our newly created jail. This allows us to fix bootloader or grab data before everything goes to /dev/null
|
||||
chroot $d
|
||||
|
||||
# Can you see?
|
||||
ls
|
||||
df
|
||||
|
||||
# Get files to safe location
|
||||
rsync -avr /path/to/my_precious_data_dir user@safe.location.cyberciti.biz:/path/to/dest
|
||||
|
||||
# Get out of chrooted jail and reboot or format the server as per your needs ;)
|
||||
exit
|
||||
umount {dev,sys,[...],}
|
||||
reboot
|
||||
|
||||
But wait, there's more!
|
||||
|
||||
See all other chroot command related examples on nixCraft:
|
||||
|
||||
1. [Ubuntu: Mount Encrypted Home Directory (~/.private) From an Ubuntu Live CD][9]
|
||||
1. [Linux Configure rssh Chroot Jail To Lock Users To Their Home Directories Only][10]
|
||||
1. [Fix a dual boot MS-Windows XP/Vista/7/Server and Linux problem][11]
|
||||
1. [Restore Debian Linux Grub boot loader][12]
|
||||
|
||||
### A note about chrooting apps on a Linux or Unix-like systems ###
|
||||
|
||||
Should you use the chroot feature all the time? In the above example, the program is fairly simple but you may end up with several different kinds of problems such as:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Missing libs in jail can result into broken jail.
|
||||
1. Complex program are difficult to chroot. I suggest you either try real [jail such as provided by FreeBSD][13] or use virtualization soultuon such as [KVM on Linux][14].
|
||||
1. App running in jail can not run any other programs, can not alter any files, and can not assume another user's identity. Loosen these restrictions, you have lessened your security, chroot or no chroot.
|
||||
|
||||
Also note that:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Do not forgot, to updated chrooted apps when you upgrade apps locally.
|
||||
1. Not every app can or should be chrooted.
|
||||
1. Any app which has to assume root privileges to operate is pointless to attempt to chroot, as root can generally escape a chroot.
|
||||
1. Chroot is not a silver bullet. Learn [how to secure and harden rest of the system too][15].
|
||||
|
||||
### chroot command options ###
|
||||
|
||||
From the [chroot(8)][16] command man page:
|
||||
|
||||
--userspec=USER:GROUP specify user and group (ID or name) to use
|
||||
--groups=G_LIST specify supplementary groups as g1,g2,..,gN
|
||||
--help display this help and exit
|
||||
--version output version information and exit
|
||||
|
||||
### See also ###
|
||||
|
||||
- [chroot(8) Linux/Unix command man page][17]
|
||||
- [Man pages chroot(2)][18]
|
||||
- [OpenBSD documentation See Apache chrooting faq for more information.][19]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via:
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/cp-copy-command-in-unix-examples/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/bash-for-loop/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/chroot-apache-under-rhel-fedora-centos-linux.html
|
||||
[4]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/howto-run-nginx-in-a-chroot-jail/
|
||||
[5]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/howto-setup-lighttpd-php-mysql-chrooted-jail.html
|
||||
[6]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/?attachment_id=28148
|
||||
[7]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/linux-chroot-service.html
|
||||
[8]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/centos-rhel-linux-mount-raid-hard-disk-from-livecd/
|
||||
[9]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/ubuntu-mounting-your-encrypted-home-from-livecd/
|
||||
[10]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/howto-linux-unix-rssh-chroot-jail-setup.html
|
||||
[11]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/howto-fix-dual-boot-windows-vista-linux.html
|
||||
[12]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/restore-debian-linux-grub-boot-loader.html
|
||||
[13]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/how-to-upgrade-freebsd-jail-vps/
|
||||
[14]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/kvm-virtualization-in-redhat-centos-scientific-linux-6/
|
||||
[15]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/linux-security.html
|
||||
[16]:http://www.manpager.com/linux/man8/chroot.8.html
|
||||
[17]:http://www.manpager.com/linux/man8/chroot.8.html
|
||||
[18]:http://www.manpager.com/linux/man2/chroot.2.html
|
||||
[19]:http://www.openbsd.org/faq/
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user