mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-02-28 01:01:09 +08:00
完成翻译 Part 11 - How to Allow Awk to Use Shell Variables
This commit is contained in:
parent
b45e17341f
commit
1200da7909
@ -1,97 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Being translated by ChrisLeeGit
|
||||
|
||||
How to Allow Awk to Use Shell Variables – Part 11
|
||||
==================================================
|
||||
|
||||
When we write shell scripts, we normally include other smaller programs or commands such as Awk operations in our scripts. In the case of Awk, we have to find ways of passing some values from the shell to Awk operations.
|
||||
|
||||
This can be done by using shell variables within Awk commands, and in this part of the series, we shall learn how to allow Awk to use shell variables that may contain values we want to pass to Awk commands.
|
||||
|
||||
There possibly two ways you can enable Awk to use shell variables:
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Using Shell Quoting
|
||||
|
||||
Let us take a look at an example to illustrate how you can actually use shell quoting to substitute the value of a shell variable in an Awk command. In this example, we want to search for a username in the file /etc/passwd, filter and print the user’s account information.
|
||||
|
||||
Therefore, we can write a `test.sh` script with the following content:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
#!/bin/bash
|
||||
|
||||
#read user input
|
||||
read -p "Please enter username:" username
|
||||
|
||||
#search for username in /etc/passwd file and print details on the screen
|
||||
cat /etc/passwd | awk "/$username/ "' { print $0 }'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Thereafter, save the file and exit.
|
||||
|
||||
Interpretation of the Awk command in the test.sh script above:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
cat /etc/passwd | awk "/$username/ "' { print $0 }'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
`"/$username/ "` – shell quoting used to substitute value of shell variable username in Awk command. The value of username is the pattern to be searched in the file /etc/passwd.
|
||||
|
||||
Note that the double quote is outside the Awk script, `‘{ print $0 }’`.
|
||||
|
||||
Then make the script executable and run it as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ chmod +x test.sh
|
||||
$ ./text.sh
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
After running the script, you will be prompted to enter a username, type a valid username and hit Enter. You will view the user’s account details from the /etc/passwd file as below:
|
||||
|
||||
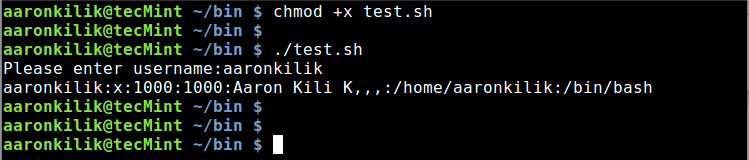
|
||||
>Shell Script to Find Username in Password File
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Using Awk’s Variable Assignment
|
||||
|
||||
This method is much simpler and better in comparison to method one above. Considering the example above, we can run a simple command to accomplish the job. Under this method, we use the -v option to assign a shell variable to a Awk variable.
|
||||
|
||||
Firstly, create a shell variable, username and assign it the name that we want to search in the /etc/passswd file:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
username="aaronkilik"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then type the command below and hit Enter:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# cat /etc/passwd | awk -v name="$username" ' $0 ~ name {print $0}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
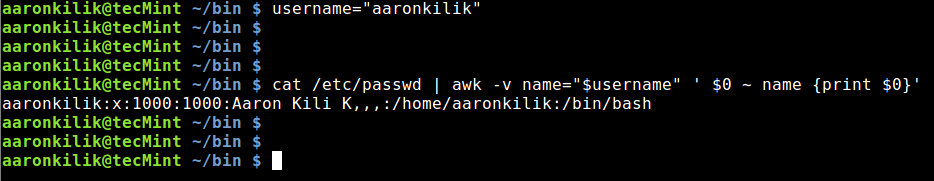
|
||||
>Find Username in Password File Using Awk
|
||||
|
||||
Explanation of the above command:
|
||||
|
||||
- `-v` – Awk option to declare a variable
|
||||
- `username` – is the shell variable
|
||||
- `name` – is the Awk variable
|
||||
Let us take a careful look at `$0 ~ name` inside the Awk script, `' $0 ~ name {print $0}'`. Remember, when we covered Awk comparison operators in Part 4 of this series, one of the comparison operators was value ~ pattern, which means: true if value matches the pattern.
|
||||
|
||||
The `output($0)` of cat command piped to Awk matches the pattern `(aaronkilik)` which is the name we are searching for in /etc/passwd, as a result, the comparison operation is true. The line containing the user’s account information is then printed on the screen.
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion
|
||||
|
||||
We have covered an important section of Awk features, that can help us use shell variables within Awk commands. Many times, you will write small Awk programs or commands within shell scripts and therefore, you need to have a clear understanding of how to use shell variables within Awk commands.
|
||||
|
||||
In the next part of the Awk series, we shall dive into yet another critical section of Awk features, that is flow control statements. So stay tunned and let’s keep learning and sharing.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/use-shell-script-variable-in-awk/?utm_source=feedburner&utm_medium=feed&utm_campaign=Feed%3A+tecmint+%28Tecmint%3A+Linux+Howto%27s+Guide%29
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Aaron Kili][a]
|
||||
译者:[ChrisLeeGit](https://github.com/chrisleegit)
|
||||
校对:[校对ID](https://github.com/校对ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,95 @@
|
||||
awk 系列:如何让 awk 使用 Shell 变量
|
||||
==================================================
|
||||
|
||||
当我们编写 shell 脚本时,我们通常会在脚本中包含其它小程序或命令,例如 awk 操作。对于 awk 而言,我们需要找一些将某些值从 shell 传递到 awk 操作中的方法。
|
||||
|
||||
我们可以通过在 awk 命令中使用 shell 变量达到目的,在 awk 系列的这一节中,我们将学习如何让 awk 使用 shell 变量,这些变量可能包含我们希望传递给 awk 命令的值。
|
||||
|
||||
有两种可能的方法可以让 awk 使用 shell 变量:
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. 使用 Shell 引用
|
||||
|
||||
让我们用一个示例来演示如何在一条 awk 命令中使用 shell 引用替代一个 shell 变量。在该示例中,我们希望在文件 /etc/passwd 中搜索一个用户名,过滤并输出用户的账户信息。
|
||||
|
||||
因此,我们可以编写一个 `test.sh` 脚本,内容如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
#!/bin/bash
|
||||
|
||||
# 读取用户名
|
||||
read -p "请输入用户名:" username
|
||||
|
||||
# 在 /etc/passwd 中搜索用户名,然后在屏幕上输出详细信息
|
||||
cat /etc/passwd | awk "/$username/ "' { print $0 }'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
然后,保存文件并退出。
|
||||
|
||||
上述 `test.sh` 脚本中 awk 命令的说明:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
cat /etc/passwd | awk "/$username/ "' { print $0 }'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
`"/$username/ "`:在 awk 命令中使用 shell 引用来替代 shell 变量 `username` 的值。`username` 的值就是要在文件 /etc/passwd 中搜索的模式。
|
||||
|
||||
注意,双引号位于 awk 脚本 `'{ print $0 }'` 之外。
|
||||
|
||||
接下来给脚本添加可执行权限并运行它,操作如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ chmod +x test.sh
|
||||
$ ./text.sh
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
运行脚本后,它会提示你输入一个用户名,然后你输入一个合法的用户名并回车。你将会看到来自 /etc/passwd 文件中详细的用户账户信息,如下图所示:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
> *在 Password 文件中查找用户名的 shell 脚本*
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. 使用 awk 进行变量赋值
|
||||
|
||||
和上面介绍的方法相比,该方法更加单,并且更好。考虑上面的示例,我们可以运行一条简单的命令来完成同样的任务。
|
||||
在该方法中,我们使用 `-v` 选项将一个 shell 变量的值赋给一个 awk 变量。
|
||||
首先,创建一个 shell 变量 `username`,然后给它赋予一个我们希望在 /etc/passwd 文件中搜索的名称。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
username="aaronkilik"
|
||||
```
|
||||
然后输入下面的命令并回车:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# cat /etc/passwd | awk -v name="$username" ' $0 ~ name {print $0}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
> *使用 awk 在 Password 文件中查找用户名*
|
||||
|
||||
上述命令的说明:
|
||||
|
||||
- `-v`:awk 选项之一,用于声明一个变量
|
||||
- `username`:是 shell 变量
|
||||
- `name`:是 awk 变量
|
||||
|
||||
让我们仔细瞧瞧 awk 脚本 `' $0 ~ name {print $0}'` 中的 `$0 ~ name`。还记得么,当我们在 awk 系列第四节中介绍 awk 比较运算符时,`value ~ pattern` 便是比较运算符之一,它是指:如果 `value` 匹配了 `pattern` 则返回 `true`。
|
||||
|
||||
cat 命令通过管道传给 awk 的 `output($0)` 与模式 `(aaronkilik)` 匹配,该模式即为我们在 /etc/passwd 中搜索的名称,最后,比较操作返回 `true`。接下来会在屏幕上输出包含用户账户信息的行。
|
||||
|
||||
### 结论
|
||||
|
||||
我们已经介绍了 awk 功能的一个重要部分,它能帮助我们在 awk 命令中使用 shell 变量。很多时候,你都会在 shell 脚本中编写小的 awk 程序或命令,因此,你需要清晰地理解如何在 awk 命令中使用 shell 变量。
|
||||
|
||||
在 awk 系列的下一个部分,我们将会深入学习 awk 功能的另外一个关键部分,即流程控制语句。所以请继续保持关注,并让我们坚持学习与分享。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/use-shell-script-variable-in-awk/?utm_source=feedburner&utm_medium=feed&utm_campaign=Feed%3A+tecmint+%28Tecmint%3A+Linux+Howto%27s+Guide%29
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Aaron Kili][a]
|
||||
译者:[ChrisLeeGit](https://github.com/chrisleegit)
|
||||
校对:[校对ID](https://github.com/校对ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user