mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-02-03 23:40:14 +08:00
finish translating by GitFuture
This commit is contained in:
parent
da5eb60dd8
commit
10e5d95d9c
@ -1,304 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Translating by GitFuture
|
||||
|
||||
Install LEMP with MariaDB 10, PHP 7 and HTTP 2.0 Support for Nginx on Ubuntu 16.04
|
||||
=====================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
The LEMP stack is an acronym which represents is a group of packages (Linux OS, Nginx web server, MySQL\MariaDB database and PHP server-side dynamic programming language) which are used to deploy dynamic web applications and web pages.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>Install Nginx with MariaDB 10, PHP 7 and HTTP 2.0 Support on Ubuntu 16.04
|
||||
|
||||
This tutorial will guide you on how to install a LEMP stack (Nginx with MariaDB and PHP7) on Ubuntu 16.04 server.
|
||||
|
||||
Requirements
|
||||
|
||||
[Installation of Ubuntu 16.04 Server Edition][1]
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 1: Install the Nginx Web Server
|
||||
|
||||
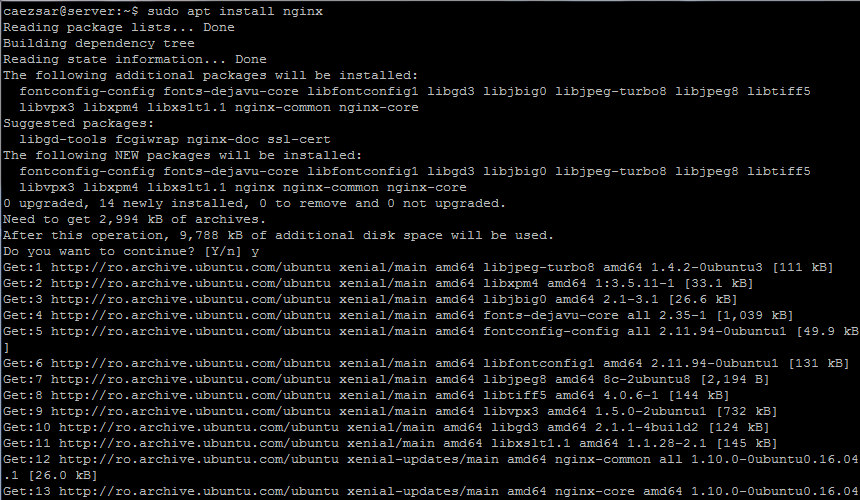
#### 1. Nginx is a modern and resources efficient web server used to display web pages to visitors on the internet. We’ll start by installing Nginx web server from Ubuntu official repositories by using the [apt command line][2].
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install nginx
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
>Install Nginx on Ubuntu 16.04
|
||||
|
||||
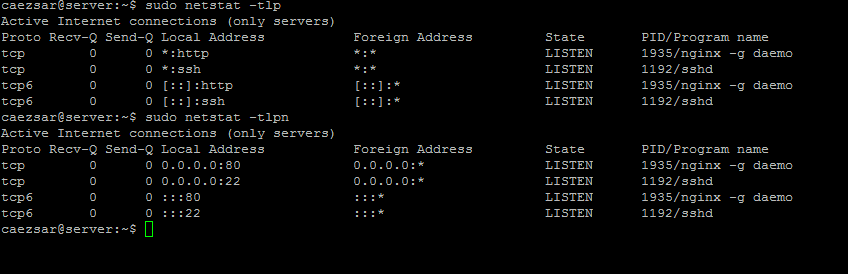
#### 2. Next, issue the [netstat][3] and [systemctl][4] commands in order to confirm if Nginx is started and binds on port 80.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ netstat -tlpn
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
>Check Nginx Network Port Connection
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
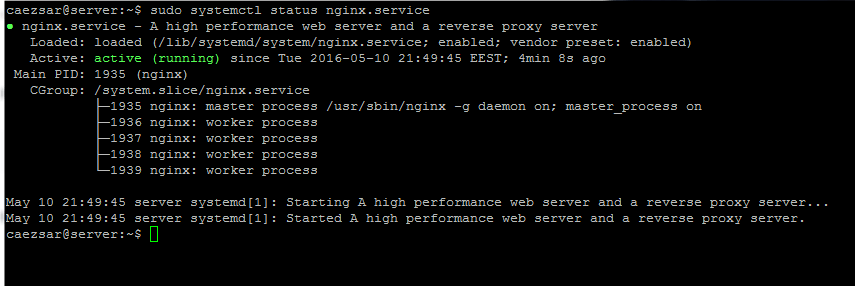
$ sudo systemctl status nginx.service
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
>Check Nginx Service Status
|
||||
|
||||
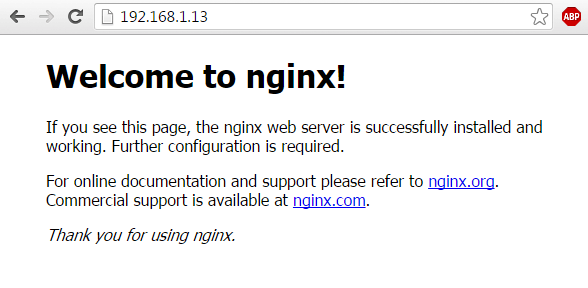
Once you have the confirmation that the server is started you can open a browser and navigate to your server IP address or DNS record using HTTP protocol in order to visit Nginx default web page.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
http://IP-Address
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
>Verify Nginx Webpage
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 2: Enable Nginx HTTP/2.0 Protocol
|
||||
|
||||
#### 3. The HTTP/2.0 protocol which is build by default in the latest release of Nginx binaries on Ubuntu 16.04 works only in conjunction with SSL and promises a huge speed improvement in loading web SSL web pages.
|
||||
|
||||
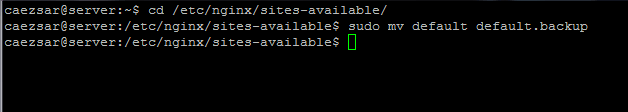
To enable the protocol in Nginx on Ubuntu 16.04, first navigate to Nginx available sites configuration files and backup the default configuration file by issuing the below command.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ cd /etc/nginx/sites-available/
|
||||
$ sudo mv default default.backup
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
>Backup Nginx Sites Configuration File
|
||||
|
||||
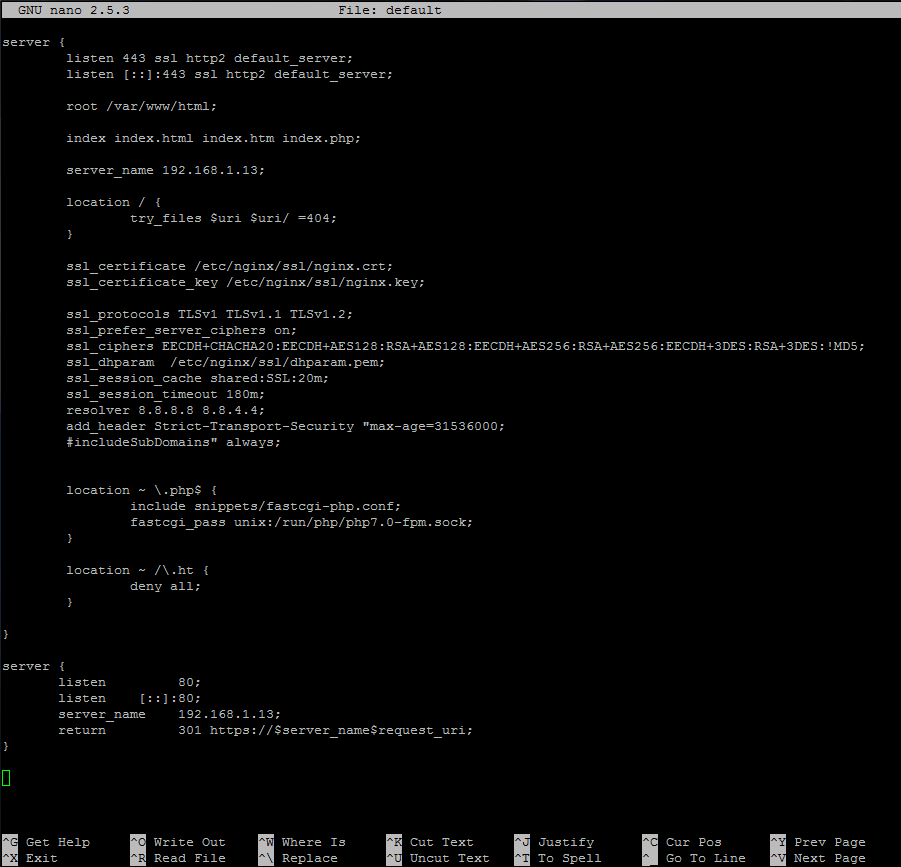
#### 4. Then, using a text editor create a new default page with the below instructions:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
server {
|
||||
listen 443 ssl http2 default_server;
|
||||
listen [::]:443 ssl http2 default_server;
|
||||
|
||||
root /var/www/html;
|
||||
|
||||
index index.html index.htm index.php;
|
||||
|
||||
server_name 192.168.1.13;
|
||||
|
||||
location / {
|
||||
try_files $uri $uri/ =404;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
ssl_certificate /etc/nginx/ssl/nginx.crt;
|
||||
ssl_certificate_key /etc/nginx/ssl/nginx.key;
|
||||
|
||||
ssl_protocols TLSv1 TLSv1.1 TLSv1.2;
|
||||
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
|
||||
ssl_ciphers EECDH+CHACHA20:EECDH+AES128:RSA+AES128:EECDH+AES256:RSA+AES256:EECDH+3DES:RSA+3DES:!MD5;
|
||||
ssl_dhparam /etc/nginx/ssl/dhparam.pem;
|
||||
ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:20m;
|
||||
ssl_session_timeout 180m;
|
||||
resolver 8.8.8.8 8.8.4.4;
|
||||
add_header Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=31536000;
|
||||
#includeSubDomains" always;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
location ~ \.php$ {
|
||||
include snippets/fastcgi-php.conf;
|
||||
fastcgi_pass unix:/run/php/php7.0-fpm.sock;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
location ~ /\.ht {
|
||||
deny all;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
server {
|
||||
listen 80;
|
||||
listen [::]:80;
|
||||
server_name 192.168.1.13;
|
||||
return 301 https://$server_name$request_uri;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
>Enable Nginx HTTP 2 Protocol
|
||||
|
||||
The above configuration snippet enables the use of `HTTP/2.0` by adding the http2 parameter to all SSL listen directives.
|
||||
|
||||
Also, the last part of the excerpt enclosed in server directive is used to redirect all non-SSL traffic to SSL/TLS default host. Also, replace the `server_name` directive to match your own IP address or DNS record (FQDN preferably).
|
||||
|
||||
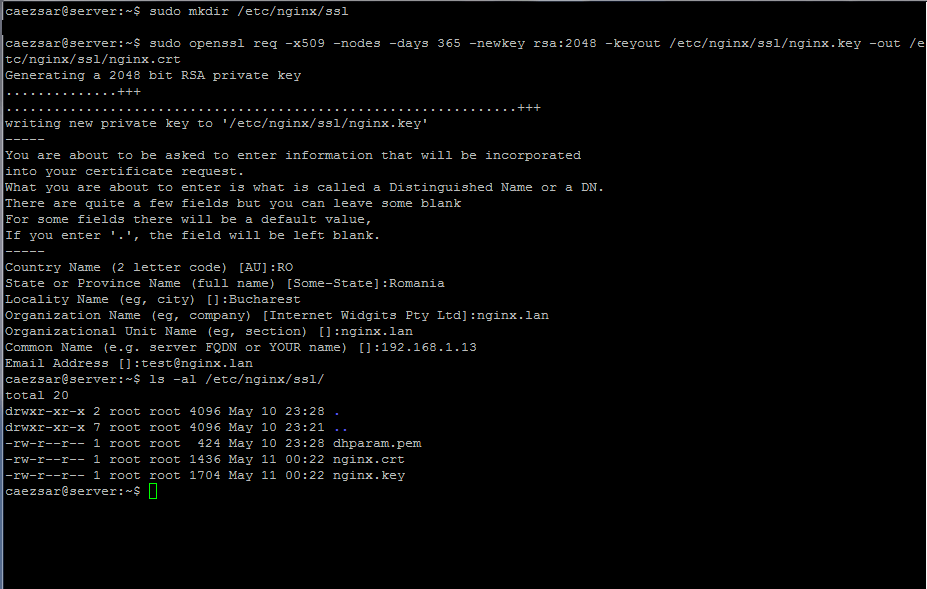
#### 5. Once you finished editing Nginx default configuration file with the above settings, generate and list the SSL certificate file and key by executing the below commands.
|
||||
|
||||
Fill the certificate with your own custom settings and pay attention to Common Name setting to match your DNS FQDN record or your server IP address that will be used to access the web page.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo mkdir /etc/nginx/ssl
|
||||
$ sudo openssl req -x509 -nodes -days 365 -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout /etc/nginx/ssl/nginx.key -out /etc/nginx/ssl/nginx.crt
|
||||
$ ls /etc/nginx/ssl/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
>Generate SSL Certificate and Key for Nginx
|
||||
|
||||
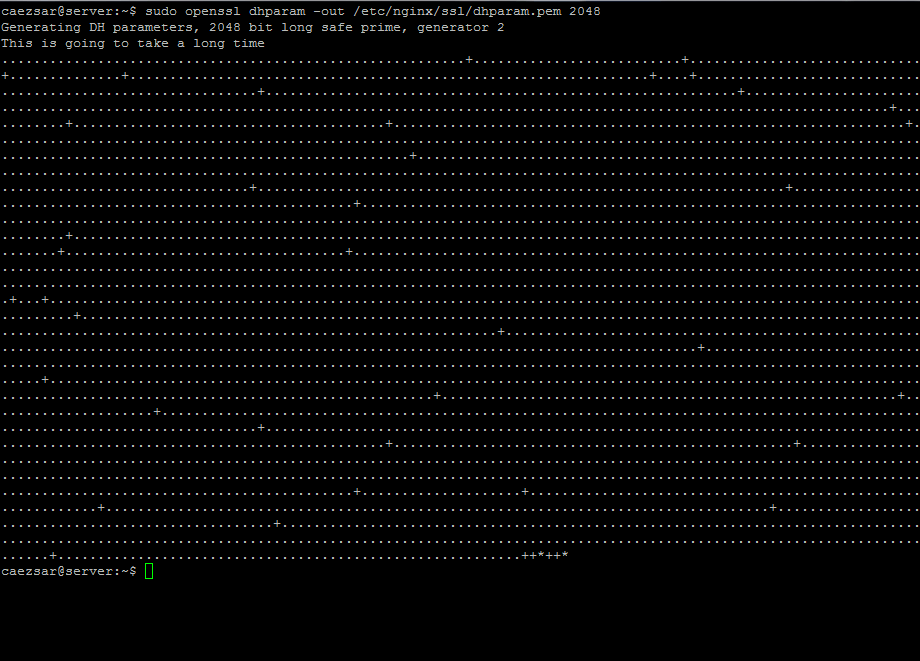
#### 6. Also, create a strong DH cypher, which was changed on the above configuration file on `ssl_dhparam` instruction line, by issuing the below command:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo openssl dhparam -out /etc/nginx/ssl/dhparam.pem 2048
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
>Create Diffie-Hellman Key
|
||||
|
||||
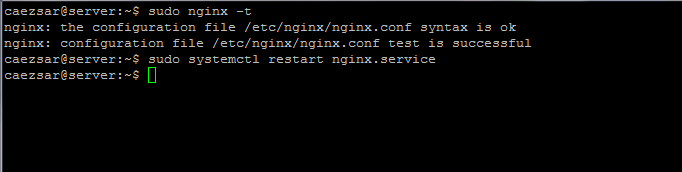
#### 7. Once the `Diffie-Hellman` key has been created, verify if Nginx configuration file is correctly written and can be applied by Nginx web server and restart the daemon to reflect changes by running the below commands.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo nginx -t
|
||||
$ sudo systemctl restart nginx.service
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
>Check Nginx Configuration
|
||||
|
||||
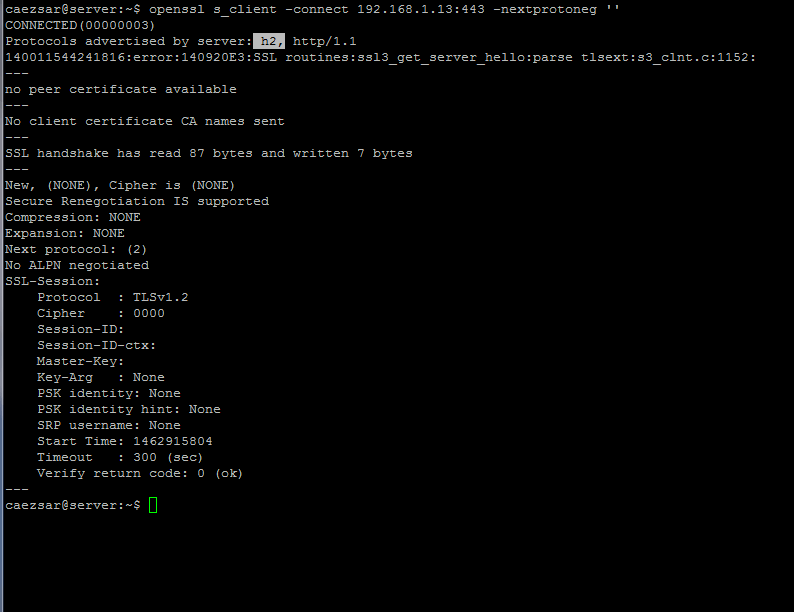
#### 8. In order to test if Nginx uses HTTP/2.0 protocol issue the below command. The presence of `h2` advertised protocol confirms that Nginx has been successfully configured to use HTTP/2.0 protocol. All modern up-to-date browsers should support this protocol by default.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ openssl s_client -connect localhost:443 -nextprotoneg ''
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
>Test Nginx HTTP 2.0 Protocol
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 3: Install PHP 7 Interpreter
|
||||
|
||||
Nginx can be used with PHP dynamic processing language interpreter to generate dynamic web content with the help of FastCGI process manager obtained by installing the php-fpm binary package from Ubuntu official repositories.
|
||||
|
||||
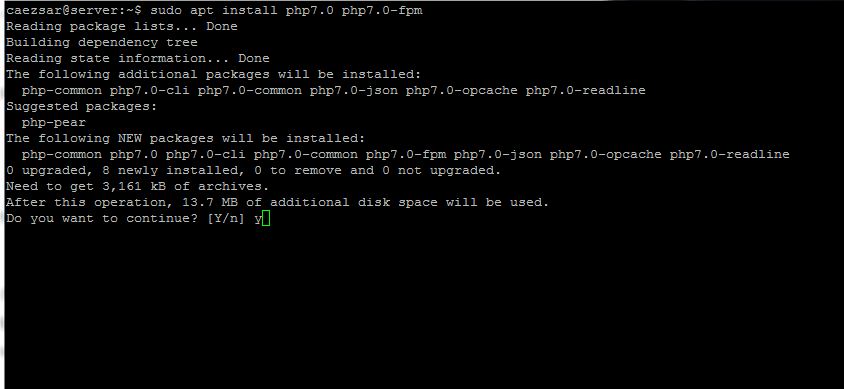
#### 9. In order to grab PHP7.0 and the additional packages that will allow PHP to communicate with Nginx web server issue the below command on your server console:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo apt install php7.0 php7.0-fpm
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
>Install PHP 7 and PHP-FPM for Ngin
|
||||
|
||||
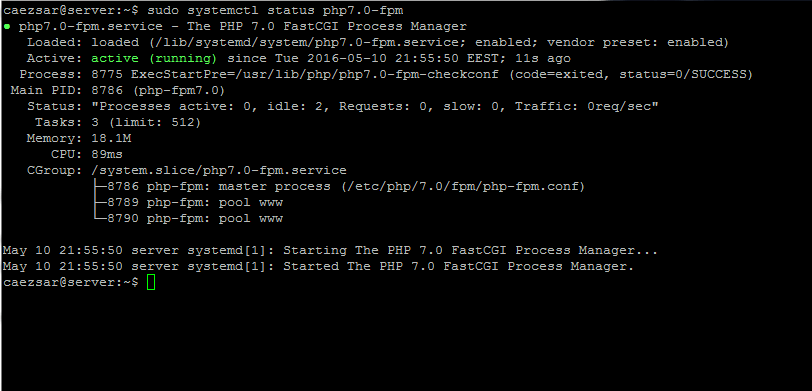
#### 10. Once the PHP7.0 interpreter has been successfully installed on your machine, start and check php7.0-fpm daemon by issuing the below command:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo systemctl start php7.0-fpm
|
||||
$ sudo systemctl status php7.0-fpm
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
>Start and Verify php-fpm Service
|
||||
|
||||
#### 11. The current configuration file of Nginx is already configured to use PHP FastCGI process manager in order to server dynamic content.
|
||||
|
||||
The server block that enables Nginx to use PHP interpreter is presented on the below excerpt, so no further modifications of default Nginx configuration file are required.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
location ~ \.php$ {
|
||||
include snippets/fastcgi-php.conf;
|
||||
fastcgi_pass unix:/run/php/php7.0-fpm.sock;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Below is a screenshot of what instructions you need to uncomment and modify is case of an original Nginx default configuration file.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
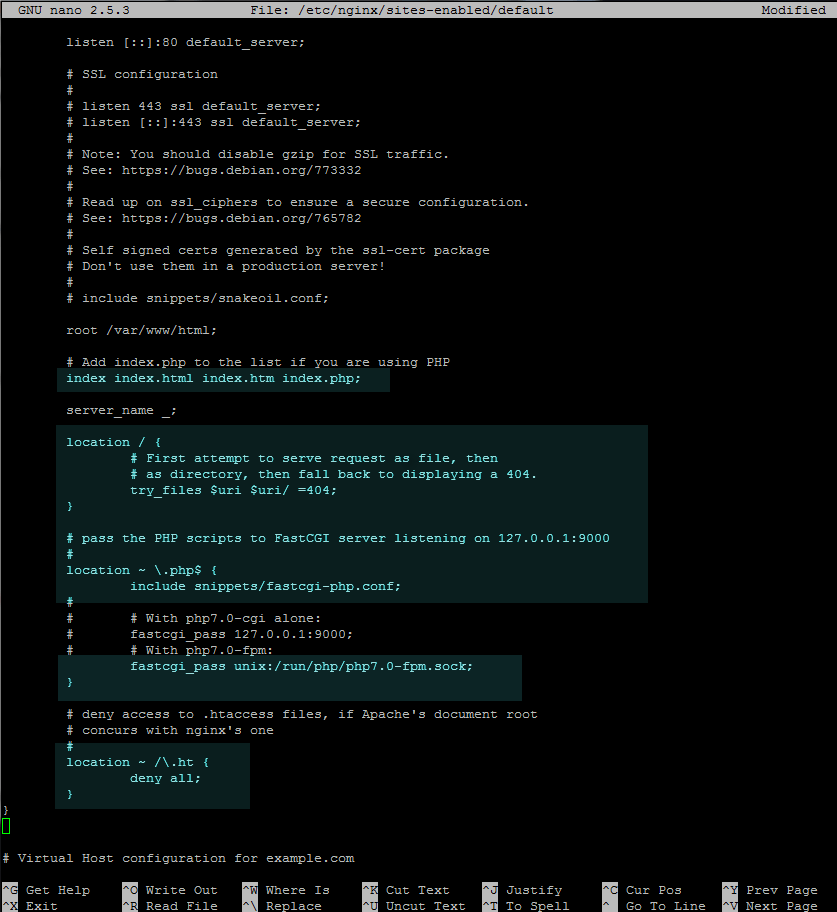
|
||||
>Enable PHP FastCGI for Nginx
|
||||
|
||||
#### 12. To test Nginx web server relation with PHP FastCGI process manager create a PHP `info.php` test configuration file by issuing the below command and verify the settings by visiting this configuration file using the below address: `http://IP_or domain/info.php`.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo su -c 'echo "<?php phpinfo(); ?>" |tee /var/www/html/info.php'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
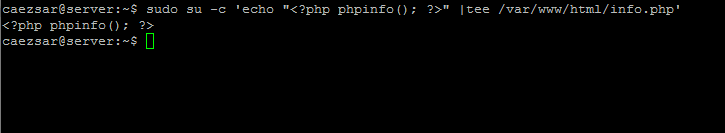
|
||||
>Create PHP Info File
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>Verify PHP FastCGI Info
|
||||
|
||||
Also check if HTTP/2.0 protocol is advertised by the server by locating the line `$_SERVER[‘SERVER_PROTOCOL’]` on PHP Variables block as illustrated on the below screenshot.
|
||||
|
||||
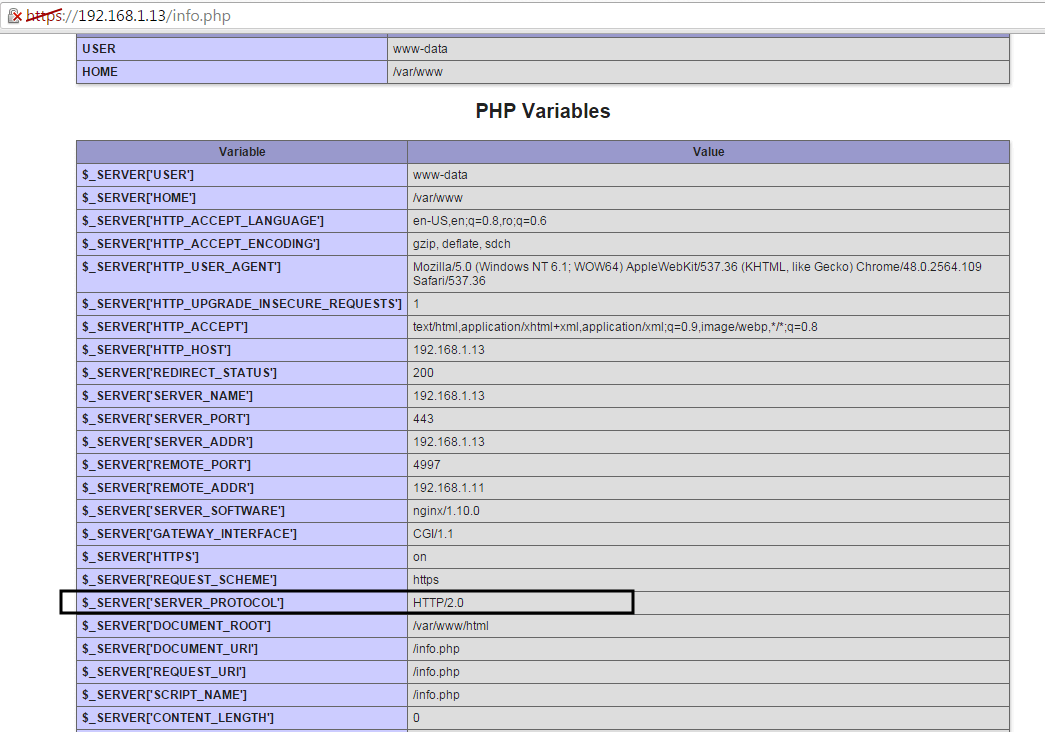
|
||||
>Check HTTP 2.0 Protocol Info
|
||||
|
||||
#### 13. In order to install extra PHP7.0 modules use the `apt search php7.0` command to find a PHP module and install it.
|
||||
|
||||
Also, try to install the following PHP modules which can come in handy in case you are planning to [install WordPress][5] or other CMS.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo apt install php7.0-mcrypt php7.0-mbstring
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
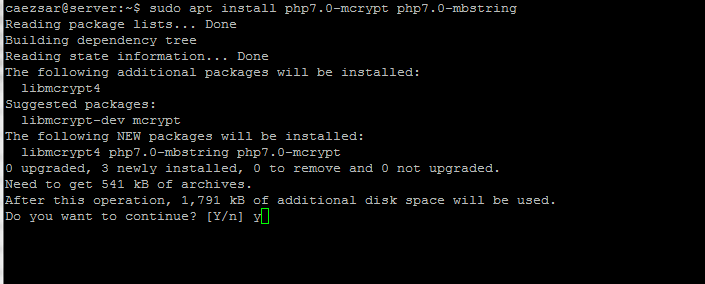
|
||||
>Install PHP 7 Modules
|
||||
|
||||
#### 14. To register the PHP extra modules just restart PHP-FPM daemon by issuing the below command.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo systemctl restart php7.0-fpm.service
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 4: Install MariaDB Database
|
||||
|
||||
#### 15. Finally, in order to complete our LEMP stack we need the MariaDB database component to store and manage website data.
|
||||
|
||||
Install MariaDB database management system by running the below command and restart PHP-FPM service in order to use MySQL module to access the database.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo apt install mariadb-server mariadb-client php7.0-mysql
|
||||
$ sudo systemctl restart php7.0-fpm.service
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
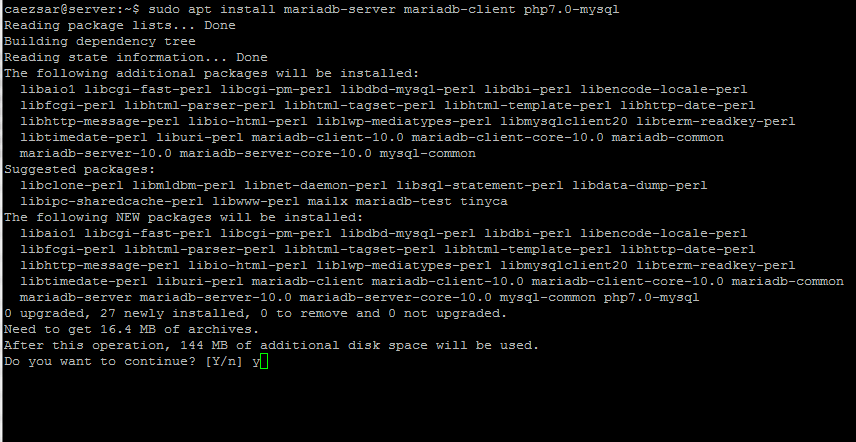
|
||||
>Install MariaDB for Nginx
|
||||
|
||||
#### 16. To secure the MariaDB installation, run the security script provided by the binary package from Ubuntu repositories which will ask you set a root password, remove anonymous users, disable root login remotely and remove test database.
|
||||
|
||||
Run the script by issuing the below command and answer all questions with yes. Use the below screenshot as a guide.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo mysql_secure_installation
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
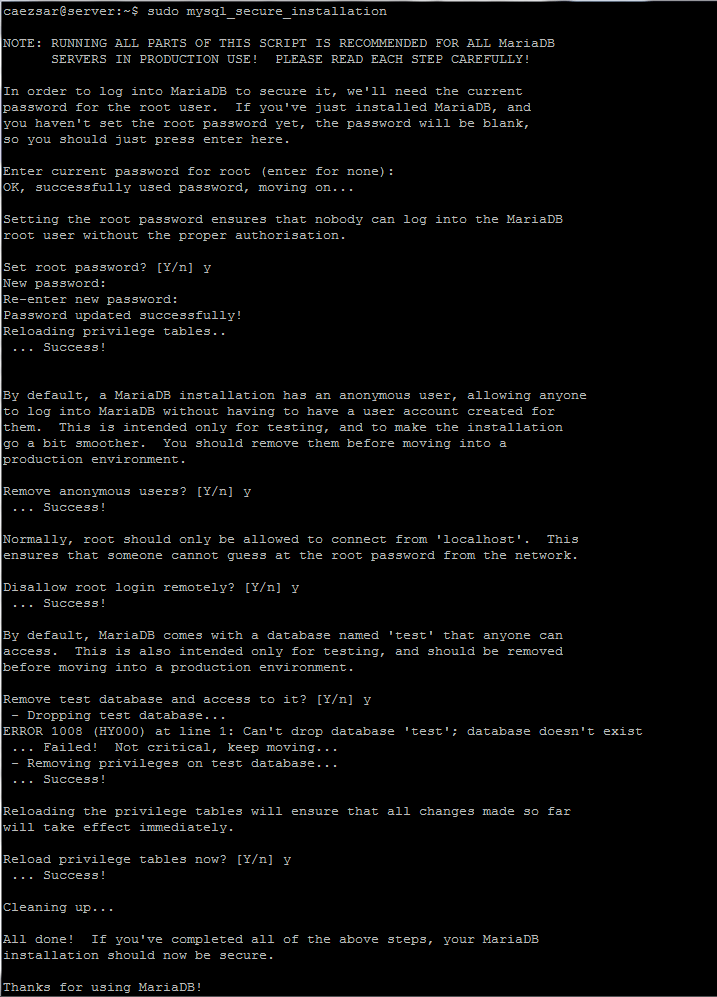
|
||||
>Secure MariaDB Installation for Nginx
|
||||
|
||||
#### 17. To configure MariaDB so that ordinary users can access the database without system sudo privileges, go to MySQL command line interface with root privileges and run the below commands on MySQL interpreter:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo mysql
|
||||
MariaDB> use mysql;
|
||||
MariaDB> update user set plugin=’‘ where User=’root’;
|
||||
MariaDB> flush privileges;
|
||||
MariaDB> exit
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
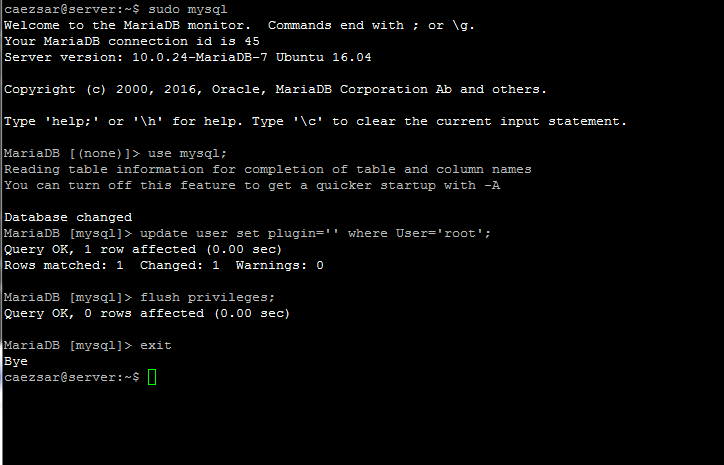
|
||||
>MariaDB User Permissions
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, login to MariaDB database and run an arbitrary command without root privileges by executing the below command:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ mysql -u root -p -e 'show databases'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
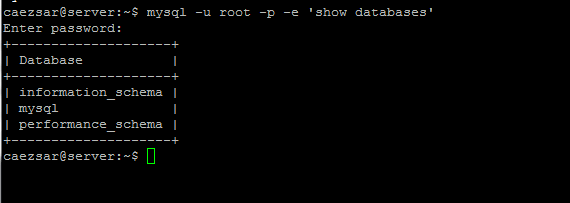
|
||||
>Check MariaDB Databases
|
||||
|
||||
That’ all! Now you have a **LEMP** stack configured on **Ubuntu 16.04** server that allows you to deploy complex dynamic web applications that can interact with databases.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/install-nginx-mariadb-php7-http2-on-ubuntu-16-04/?utm_source=feedburner&utm_medium=feed&utm_campaign=Feed%3A+tecmint+%28Tecmint%3A+Linux+Howto%27s+Guide%29
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Matei Cezar ][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: http://www.tecmint.com/author/cezarmatei/
|
||||
[1]: http://www.tecmint.com/installation-of-ubuntu-16-04-server-edition/
|
||||
[2]: http://www.tecmint.com/apt-advanced-package-command-examples-in-ubuntu/
|
||||
[3]: http://www.tecmint.com/20-netstat-commands-for-linux-network-management/
|
||||
[4]: http://www.tecmint.com/manage-services-using-systemd-and-systemctl-in-linux/
|
||||
[5]: http://www.tecmint.com/install-wordpress-using-lamp-or-lemp-on-rhel-centos-fedora/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,302 @@
|
||||
在 Ubuntu 16.04 为 Nginx 服务器安装 LEMP 环境(MariaDB, PHP 7 并且支持 HTTP 2.0)
|
||||
=====================
|
||||
|
||||
LEMP 是字首组合词,代表一组软件包(Linux OS,Nginx 网络服务器,MySQL\MariaDB 数据库和 PHP 服务端动态编程语言),它被用来搭建动态的网络应用和网页。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>在 Ubuntu 16.04 安装 Nginx 以及 MariaDB,PHP7 并且支持 HTTP 2.0
|
||||
|
||||
这篇教程会教你怎么在 Ubuntu 16.04 的服务器上安装 LEMP (Nginx 和 MariaDB 以及 PHP7)。
|
||||
|
||||
准备
|
||||
|
||||
[安装 Ubuntu 16.04 服务器版本][1]
|
||||
|
||||
### 步骤 1:安装 Nginx 服务器
|
||||
|
||||
#### 1. Nginx 是一个先进的、资源优化的网络服务器程序,用来向因特网上的访客展示网页。我们从 Nginx 服务器的安装开始介绍,使用 [apt 命令][2] 从 Ubuntu 的官方软件仓库中获取 Nginx 程序。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install nginx
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>在 Ubuntu 16.04 安装 Nginx
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2. 然后输入 [netstat][3] 和 [systemctl][4] 命令,确认 Nginx 进程已经启动并且绑定在 80 端口。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ netstat -tlpn
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>检查 Nginx 网络端口连接
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo systemctl status nginx.service
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>检查 Nginx 服务状态
|
||||
|
||||
当你确认服务进程已经启动了,你可以打开一个浏览器,使用 HTTP 协议访问你的服务器 IP 地址或者域名,浏览 Nginx 的默认网页。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
http://IP-Address
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>验证 Nginx 网页
|
||||
|
||||
### 步骤 2:启用 Nginx HTTP/2.0 协议
|
||||
|
||||
#### 3. HTTP/2.0 协议默认包含在 Ubuntu 16.04 最新发行版的 Nginx 二进制文件中,它只能通过 SSL 连接并且保证加载网页的速度有巨大提升。
|
||||
|
||||
要启用Nginx 的这个协议,首先找到 Nginx 提供的网站配置文件,输入下面这个命令备份配置文件。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ cd /etc/nginx/sites-available/
|
||||
$ sudo mv default default.backup
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>备份 Nginx 的网站配置文件
|
||||
|
||||
#### 4. 然后,用文本编辑器新建一个默认文件,输入以下内容:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
server {
|
||||
listen 443 ssl http2 default_server;
|
||||
listen [::]:443 ssl http2 default_server;
|
||||
|
||||
root /var/www/html;
|
||||
|
||||
index index.html index.htm index.php;
|
||||
|
||||
server_name 192.168.1.13;
|
||||
|
||||
location / {
|
||||
try_files $uri $uri/ =404;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
ssl_certificate /etc/nginx/ssl/nginx.crt;
|
||||
ssl_certificate_key /etc/nginx/ssl/nginx.key;
|
||||
|
||||
ssl_protocols TLSv1 TLSv1.1 TLSv1.2;
|
||||
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
|
||||
ssl_ciphers EECDH+CHACHA20:EECDH+AES128:RSA+AES128:EECDH+AES256:RSA+AES256:EECDH+3DES:RSA+3DES:!MD5;
|
||||
ssl_dhparam /etc/nginx/ssl/dhparam.pem;
|
||||
ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:20m;
|
||||
ssl_session_timeout 180m;
|
||||
resolver 8.8.8.8 8.8.4.4;
|
||||
add_header Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=31536000;
|
||||
#includeSubDomains" always;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
location ~ \.php$ {
|
||||
include snippets/fastcgi-php.conf;
|
||||
fastcgi_pass unix:/run/php/php7.0-fpm.sock;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
location ~ /\.ht {
|
||||
deny all;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
server {
|
||||
listen 80;
|
||||
listen [::]:80;
|
||||
server_name 192.168.1.13;
|
||||
return 301 https://$server_name$request_uri;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>启用 Nginx HTTP 2 协议
|
||||
|
||||
上面的配置片段向所有的 SSL 监听指令中添加 http2 参数来启用 `HTTP/2.0`。
|
||||
|
||||
添加到服务器配置的最后一段,是用来将所有非 SSL 的流量重定向到 SSL/TLS 默认主机。然后用你主机的 IP 地址或者 DNS 记录(优先 FQDN)替换掉 `server_name` 选项。 (directive 的翻译是指令,但我觉得翻译成选项更好)
|
||||
|
||||
#### 5. 当你按照以上步骤编辑完 Nginx 的默认配置文件之后,用下面这些命令来生成、查看 SSL 证书和密钥。
|
||||
|
||||
用你自定义的设置完成证书的制作,注意常用名设置成和你的 DNS FQDN 记录或者服务器 IP 地址相匹配,DNS 记录或者 IP 地址是用来访问网页的。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo mkdir /etc/nginx/ssl
|
||||
$ sudo openssl req -x509 -nodes -days 365 -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout /etc/nginx/ssl/nginx.key -out /etc/nginx/ssl/nginx.crt
|
||||
$ ls /etc/nginx/ssl/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>生成 Nginx 的 SSL 证书和密钥
|
||||
|
||||
#### 6. 通过输入以下命令使用一个强 DH 加密算法,在之前的配置文件 `ssl_dhparam` 这一行中进行修改。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo openssl dhparam -out /etc/nginx/ssl/dhparam.pem 2048
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>创建 Diffie-Hellman 密钥
|
||||
|
||||
#### 7. 当 `Diffie-Hellman` 密钥生成之后,验证 Nginx 的配置文件是否正确、能否被 Nginx 网络服务程序应用。然后运行以下命令重启守护进程来观察有什么变化。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo nginx -t
|
||||
$ sudo systemctl restart nginx.service
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>检查 Nginx 的配置
|
||||
|
||||
#### 8. 键入下面的命令来测试 Nginx 使用的是 HTTP/2.0 协议。看到协议中有 `h2` 的话,表明 Nginx 已经成功配置使用 HTTP/2.0 协议。所有最新的浏览器默认都能够支持这个协议。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ openssl s_client -connect localhost:443 -nextprotoneg ''
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>测试 Nginx HTTP 2.0 协议
|
||||
|
||||
### 第 3 步:安装 PHP 7 解释器
|
||||
|
||||
通过 FastCGI 进程管理程序的协助,Nginx 能够使用 PHP 动态语言解释器生成动态网络内容。FastCGI 能够从 Ubuntu 官方仓库中安装 php-fpm 二进制包来获取。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 9. 在你的服务器控制台里输入下面的命令来获取 PHP7.0 和扩展包,这能够让 PHP 与 Nginx 网络服务进程通信,
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo apt install php7.0 php7.0-fpm
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>安装 PHP 7 以及 PHP-FPM
|
||||
|
||||
#### 10. 当 PHP7.0 解释器安装成功后,输入以下命令启动或者检查 php7.0-fpm 守护进程:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo systemctl start php7.0-fpm
|
||||
$ sudo systemctl status php7.0-fpm
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>开启、验证 php-fpm 服务
|
||||
|
||||
#### 11. 当前的 Nginx 配置文件已经配置了使用 PHP FPM 来提供动态内容。
|
||||
|
||||
下面给出的这部分服务器配置让 Nginx 能够使用 PHP 解释器,所以不需要对 Nginx 配置文件作别的修改。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
location ~ \.php$ {
|
||||
include snippets/fastcgi-php.conf;
|
||||
fastcgi_pass unix:/run/php/php7.0-fpm.sock;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
下面是的截图是 Nginx 默认配置文件的内容。你可能需要对其中的代码进行修改或者取消注释。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>启用 PHP FastCGI
|
||||
|
||||
#### 12. 要测试启用了 PHP-FPM 的 Nginx 服务器,用下面的命令创建一个 PHP 测试配置文件 `info.php`。接着用 `http://IP_or domain/info.php` 这个网址来查看配置。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo su -c 'echo "<?php phpinfo(); ?>" |tee /var/www/html/info.php'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>创建 PHP Info 文件
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>检查 PHP FastCGI 的信息
|
||||
|
||||
检查服务器是否应用 HTTP/2.0 协议,定位到 PHP 变量区域中的 `$_SERVER[‘SERVER_PROTOCOL’]` 就像下面这张截图一样。(advertised by server 翻译不清楚,这里翻译成服务器应用了 HTTP/2.0 协议)
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>检查 HTTP2.0 协议信息
|
||||
|
||||
#### 13. 为了安装其它的 PHP7.0 模块,使用 `apt search php7.0` 命令查找 php 的模块然后安装。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想要 [安装 WordPress][5] 或者别的 CMS,需要安装以下的 PHP 模块,这些模块迟早有用。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo apt install php7.0-mcrypt php7.0-mbstring
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>安装 PHP 7 模块
|
||||
|
||||
#### 14. 注册 PHP 额外的模块,输入下面的命令重启 PHP-FPM 守护进程。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo systemctl restart php7.0-fpm.service
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 第 4 步:安装 MariaDB 数据库
|
||||
|
||||
#### 15. 最后,我们需要 MariaDB 数据库来存储、管理网站数据来完成搭建 LEMP
|
||||
|
||||
运行下面的命令安装 MariaDB 数据库管理系统,重启 PHP-FPM 服务使用 MySQL 模块与数据库通信。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo apt install mariadb-server mariadb-client php7.0-mysql
|
||||
$ sudo systemctl restart php7.0-fpm.service
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>安装 MariaDB
|
||||
|
||||
#### 16. 为了保证 MariaDB 的安装,运行来自 Ubuntu 软件仓库中的二进制包提供的安全脚本,这会询问你设置一个根用户密码,移除匿名用户,禁用根用户远程登陆,移除测试数据库。
|
||||
|
||||
输入下面的命令运行脚本,并且确认所有的选择。参照下面的截图。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo mysql_secure_installation
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>MariaDB 的安全安装
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 17. 配置 MariaDB 以便普通用户能够不使用 系统的 sudo 权限来访问数据库。用根用户权限打开 MySQL 命令行界面,运行下面的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo mysql
|
||||
MariaDB> use mysql;
|
||||
MariaDB> update user set plugin=’‘ where User=’root’;
|
||||
MariaDB> flush privileges;
|
||||
MariaDB> exit
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>MariaDB 的用户权限
|
||||
|
||||
最后登陆到 MariaDB 数据库,通过以下命令不使用 root 权限执行任意一个命令:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ mysql -u root -p -e 'show databases'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>查看 MariaDB 数据库
|
||||
|
||||
好了!现在你拥有了配置在 **Ubuntu 16.04** 服务器上的 **LEMP** 环境,你能够部署能够与数据库交互的复杂动态网络应用。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/install-nginx-mariadb-php7-http2-on-ubuntu-16-04/?utm_source=feedburner&utm_medium=feed&utm_campaign=Feed%3A+tecmint+%28Tecmint%3A+Linux+Howto%27s+Guide%29
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Matei Cezar ][a]
|
||||
译者:[GitFuture](https://github.com/GitFuture)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: http://www.tecmint.com/author/cezarmatei/
|
||||
[1]: http://www.tecmint.com/installation-of-ubuntu-16-04-server-edition/
|
||||
[2]: http://www.tecmint.com/apt-advanced-package-command-examples-in-ubuntu/
|
||||
[3]: http://www.tecmint.com/20-netstat-commands-for-linux-network-management/
|
||||
[4]: http://www.tecmint.com/manage-services-using-systemd-and-systemctl-in-linux/
|
||||
[5]: http://www.tecmint.com/install-wordpress-using-lamp-or-lemp-on-rhel-centos-fedora/
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user