mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-03-24 02:20:09 +08:00
commit
0fa8c006b8
@ -0,0 +1,195 @@
|
||||
“云”是怎么影响着每一位linux用户的?
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
### “云”简介 ###
|
||||
|
||||
不论是报纸、在线资讯、播客、科技博客、科技门户网站,甚至是电台和电视。“云计算”永远都是人们津津乐道的主题。
|
||||
|
||||
然而,因为“云计算”包含了太多的东西,现在并没有一个明确的定义,所以你认为“云计算”应该是什么呢?
|
||||
|
||||
> **云计算** 过去常常被当做是网络计算的一个模型,网络计算就是把用户程序或者是应用运行在一个联网的服务器或是一个服务器集群,而不是像个人电脑、平板以及智能手机这一类运算设备。比如像传统的client-server (客户机-服务器模型) 和老一代的大型机,^[1] 用户通过连接服务器来执行一项任务。这和“云计算”是不同的,“云计算”是利用虚拟化的技术,把运算进程运行在一个或多个服务器上。利用虚拟技术,越来越多的物理化的服务器被配置和划分成多个独立的“虚拟”服务器,每个服务独立运行,对于用户来说,就像是运行在一个独立的物理服务器上一样。虚拟服务器本质上还是从他们的物理服务器中分离出来的,由于这种灵活的配置方式,使得人们可以按照意愿移动服务器和按比例分配资源而不影响最终的用户体验。计算机资源已成“颗粒”,给用户和管理人员提供方便,包括提供按需自助服务,支持更广泛的跨平台之间的访问,资源共享,快速重新部署,可被监控与量测服务。^[2]
|
||||
|
||||
以上引用摘自维基百科。
|
||||
|
||||
在过去,我们要么用哑终端连接大型电脑主机,要么近年来使用桌面电脑连接运行在内部服务器上的应用,就像网站连接数据库一样。
|
||||
|
||||
现在,所有桌面、应用和服务器的管理都已经本地化,都需要来自它们所属公司的技术支持。
|
||||
|
||||
然而这只对软件公司等少数的公司有利,却对其他的一些商业公司不利,比如说银行、保险公司和石油公司。信息技术公司没有银行的职能,就好像是做餐饮的钻不出地下的石油一样。
|
||||
|
||||
大公司早已把很多服务外包给专业的公司。例如,让餐饮公司为他们的员工提供食堂,以及我们所熟知的离岸呼叫中心处理银行业务的客户电话。
|
||||
|
||||
IT 行业的很多服务也逐渐转向外包,许多的技术支持和开发的业务都被打包给中国、印度、马来西亚和东欧。
|
||||
|
||||
云计算与传统的典型模型有很大不同的一方面在于虚拟化,这种虚拟化的技术把服务运行于虚拟服务器上,服务器可以被放置在同一个地方或者是相隔千山万水,但是,这并不重要,你也不用担心,因为那不是你该担心的事情。
|
||||
|
||||
> 现在,“云计算”已经成为云计算基础设施的简称。^[4] 这个术语来源于早年一些网络工程师用云状的符号表示那些对他们来说未知的网络。^[5] 后来,营销者普及了这个云的概念,指的是软件、平台和一些可以买卖的基础设施。比如,远程登录互联网。
|
||||
|
||||
因此,这篇文章讲述了和云相关的所有,对于linux的用户来说,这意味着你想用它做什么和它能为自己做些什么,当然,这有可能也会给我们造成一些误区。
|
||||
|
||||
从一个终端用户和家庭使用者的角度来看,云计算最基本的就是提供在线服务。
|
||||
|
||||
所以,让我们来说一说云能到底能给每一位linux用户提供些什么有用的服务?
|
||||
|
||||
### 电子邮件 ###
|
||||
|
||||
当你读到这里的时候,如果你还没有一个电子邮箱,我只能说你OUT了。
|
||||
|
||||
据PC杂志顾问统计分析,截至2014三月份,电子邮箱的用户最多的前六名分别是Outlook、GMail、Yahoo、icloud、AOL和GMX。
|
||||
|
||||
### 办公套件 ###
|
||||
|
||||
和电子邮件客户端一样,对于每个人来说,另一个最常用的工具之一就是办公套件。
|
||||
|
||||
在以前,当人们刚刚进入电脑世界的时候,买一个电脑会带回一个超大型的机器和半打子CD,刻着几个没用的 Microsoft Works ( 微软工作软件 )。 (LCTT译注:Microsoft Works Mirosoft Works是微软的一种家用综合软件,它主要面向低端的家庭用户,提供基本的能提高生活效率的工具,比如提供简单的文档处理、数据库、电子表格的入门级办公包功能。) 微软工作软件是一个廉价,而且无用到几乎要被砍掉的微软office版本。
|
||||
|
||||
而现在,你甚至不需要在你的电脑上安装任何的办公套件,即便是有LibreOffice和Kingsoft这样好的软件供选择。
|
||||
|
||||
最好的选择当然是Google Docs和Office 365。对于Office 365能否很好的运行于Linux平台,这篇来自2012期专业电脑的文章似乎说明了这个问题。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
有人说这怎么可能呢,我不相信,所以,我注册并登录了Office 365,想看看到底是什么情况。
|
||||
|
||||
注册,可以免费试用一个月,并且会赠送包括Word、Excel、和Outlook等一些在线应用。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
一切看起来都挺好,我打开了Microsoft Word,选择了一个模板来使用,当然根本就没有打开成功。
|
||||
|
||||
Office 365 并没有很好的支持linux设备,况且,说实话,你也不需要这东西。so,咱们继续。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Google Docs对于一般的办公支持非常完美,它能完成很多的事情,并且有很多的模板针对文字处理,演示工具,电子表格等。即使它始终也代替不了Excel,因为他并没有成百上千的开发人员为其创建宏和编写VBA脚本。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
另一个可供选择的办公套件是Zoho。
|
||||
|
||||
和Google Docs一样,Zoho也包含有文字处理工具,演示程序,电子表格程序和电子邮件。
|
||||
|
||||
此外,还有很多金融和客户管理系统。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
这个工具的界面看起来真的很简洁,很棒。
|
||||
|
||||
它和Google Docs和Zoho这些在线服务一样,给予了人们相互协作的便利。
|
||||
|
||||
很多文档被不同的人分享,然后在不同的地方被不同的人修改完善。
|
||||
|
||||
这里会给出一些理由来帮助你从Google Docs和Zoho中选择一个适合你的办公套件。
|
||||
|
||||
### 在线文件存储 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Google Docs和Zoho给我们提供了其他一些很好的服务,就是很好的线上存储能力,你们可以线上存储很多文档和创建很多文件。
|
||||
|
||||
也有一些其他的服务,比如说Dropbox,仅仅只提供在云存储服务。
|
||||
|
||||
像Dropbox这样的云存储的好处是如果你的东西被偷了或者是不小心房子着火了,而这时,你仍然有一份离岸备份是安好无缺的。你仍然可以在任何地方获取你的文件。
|
||||
|
||||
Dropbox对于前2G的容量是免费的,如果你还有更多的东西要存储,每天还有更多的事情要做,每个月只要9.9美刀,你就能拥有100G的存储空间,另外,Dropbox也提供商务版本,每个月15美刀。
|
||||
|
||||
当然,并不是说Dropbox没有可替代的方案,这个网站也提供了很多很好的一些在线备份的方案。
|
||||
|
||||
### 相册 ###
|
||||
|
||||
自从有了数码照相机和智能手机,现在越来越多的人们利用存储卡来保存照片。
|
||||
|
||||
我相信肯定有人因为电话坏了而丢失照片,因为他的照片是存储在电话上的,而不是其他的存储设备,甚至,有些因为丢失了电话而丢失了他们孩子的运动会照片或者是其他一些具有纪念意义的照片资料。
|
||||
|
||||
丢失电话肯定不是什么好事情,如果你放机灵一点,情况可能要好一点,因为很多人的电话和email,facebook,Twitter的账户是同步的,甚至在线存储也是。
|
||||
|
||||
当然,丢失手机时,我们可以更改以上那些账户的密码,可是丢失的照片却是再也找不回来了,这让人有一点点伤心。
|
||||
|
||||
备份资料到电脑当然是一种很好的解决方法,不过要是你的笔记本哪天不小心坏了,你也只能变得一无所有,从头再来。
|
||||
|
||||
在线照片存储的网站是一个很好的资源,因为他们不止要保证你的照片的安全,你也可以很方便的把照片分享给你选择的人。省去了那些把同样的照片做无数次的拷贝分别发给妈妈,奶奶,妹妹,阿姨和岳母等各种亲戚朋友的麻烦。
|
||||
|
||||
我常用的一个是谷歌的Picasa相册工具,但是大家也可能听说过像Flickr这样的网络相册。
|
||||
|
||||
Lifehacker给出了最好的5个网络分享的相册。
|
||||
|
||||
请记住,他们仅仅是被称作相册分享工具,并不是说你一定要分享,你也可以自己保留他们。
|
||||
|
||||
### 音乐 ###
|
||||
|
||||
我得到的第一个唱片是20世纪80年代初“Adam and the Ants”的"Kings of the wild frontier"里的一个12英寸的碟子。
|
||||
|
||||
在20世纪80年代后的很长一段时间里,唱片逐渐被磁带所取代,就好像是我积累了很多的磁带以后,磁带却被CD所取代。
|
||||
|
||||
后来,成百上千的CD和MP3越来越普遍,直至成为了一种潮流。
|
||||
|
||||
而音频流媒体始终也跟着潮流一起进步,比如像Spotify。
|
||||
|
||||
Spotify是一个免费的软件,但是里面包含广告,对于使用的人们而言,它就像是一个你可以定制的私人电台,当然你也可以交月费来去除广告。
|
||||
|
||||
Grooveshark和last.fm也有提供很多相似的服务。
|
||||
|
||||
Techradar给出了7种Spotify的替代方案。
|
||||
|
||||
### 电影 ###
|
||||
|
||||
小飞象 (Dumbo) 是我最早在电影院看的一部电影。而我最早接触录像是“Krull”,它讲述了Dulph Lundgren的年轻时候的经历,录像的格式是Beta Max。(当时我的邻居就有一个) 。
|
||||
|
||||
有一天,爸爸从收音机租赁处带回来一个录像机,我和我的姐姐就轮流去录像店租带子看。我清楚的记得,我第一次租的带子名字叫“黑洞”(The Black Hole)。
|
||||
|
||||
直到有声电影的出现,你就不得不拿一个很大的东西来装电影带子,所以有些天才就发明了DVD,甚至是制造出了蓝光碟片。
|
||||
|
||||
现在,流媒体已经充斥着我们生活的每一天,要是你有个牛X的网络就更完美了。
|
||||
|
||||
其中,最出名的流媒体提供商是Netflix和Lovefilm (Netflix和Lovefilm都是在线的影片租赁公司)。
|
||||
|
||||
linuxnews给了我们一些更好的选择来替代Netflix,因为并不是所有的服务都能无缝的在linux上工作,包括Netflix。
|
||||
|
||||
### 游戏 ###
|
||||
|
||||
继音乐,电影搬到线上以后,游戏也登上了在线的舞台。
|
||||
|
||||
对游戏来说就要困难一些,因为音乐只占用很少的带宽,而电影的要求相对高一点,但是也仅仅是为了得到一幅清晰的画面。
|
||||
|
||||
游戏始终需要很高的帧速支持,不然即使你手上有一个很好玩的游戏,可能也不值得去尝试。
|
||||
|
||||
当前,很多游戏服务商都有提供基于云的游戏,包括OnLive和StreamMyGame也有提供。
|
||||
|
||||
linuxnews给出了6个和OnLive竞争的游戏服务提供商。
|
||||
|
||||
### 争议 ###
|
||||
|
||||
云计算也并不是没有争议。
|
||||
|
||||
首先,最大的问题就是安全问题,如果有人进入了你的在线存储空间和你的电子邮箱,并盗取了你的个人信息。
|
||||
|
||||
那么在线存储你都会存些什么呢?像Megaupload.com这样的网站,上面都有很多有价值的客户资料。
|
||||
|
||||
Megaupload.com这个网站本来提供的大容量文件的存储,而问题却是,很多人用它来分享一些有版权的资料,美国的当局就不依不饶的下来检查,所以这个服务被迫关掉了。
|
||||
|
||||
现在,因为很多人丢失了资料,当局的这样做也是无可厚非的,但是对于那些没有做错事的人来说,他们的数据资料也丢失了,美国当局拒绝还给本人。
|
||||
|
||||
最后给出了一个服务正在维护的答复,如果你的电子邮件停了一天你能应付,那么3天呢?甚至是一个月你还能应付得了吗,那么你也就只能任由服务提供商摆布了。
|
||||
|
||||
很多大公司已经取回了丢失的数据,但是仍然有很多心脏病漏洞(openssl的heartbleed安全漏洞)的消息在,这是ssl应用多年中发现的一个重大的安全漏洞。
|
||||
|
||||
所以说,如果你用了别人提供的在线服务,那么你必须信赖他们技术支持人员,你也必须相信他们不会出现被黑客攻击,硬件故障,缺乏备份和无法恢复系统这样的情况。
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结 ###
|
||||
|
||||
现在云计算早已成了充斥着在线服务的主题,你的浏览器就是一个客户端,连接世界上任意一个地方的服务器或者是服务器集群。重点是你没必要去关注,而且你也不需要知道。
|
||||
|
||||
一般来说,我们仅仅触及的是它的表面,所有我们每天接触到的云,对于我们大多数人来说甚至都不用去关注它。
|
||||
|
||||
至于说云到底是怎样影响着每一位linux用户,事实去证明是有很多的。
|
||||
|
||||
云到底是好是坏?又或许什么都不是。每一种服务的好坏都要看它的优势。
|
||||
|
||||
或许云仅仅是营销人员炒起来的一个概念,也只会让技术新闻感到兴奋。是否还有人记得我们一直在用的“Web 2.0”?
|
||||
|
||||
感谢您的阅读。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxnews.pro/how-does-the-cloud-affect-the-everyday-linux-user/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[barney-ro](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,38 @@
|
||||
保持自由 - GCC应该接受收费插件吗?
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
> GCC邮件列表中在争论GCC是否应该接受收费插件,但是认为GCC是一个免费软件开发的媒介的论调占得了上风
|
||||
|
||||
Gcc以及它在模块化方面的缺失又一次作为一个问题被提出来,并且和市场上的新的编译器LLVM做了对比。GCC巨大而古老:5百万行代码,30年研发时间,并且还在继续增长。相比较而言,LLVM更加年轻,更加模块化,并且允许所有的语言都作为一个模块添加进去。
|
||||
|
||||
LLVM的核心是‘开放源代码’。GCC是反著作权(copyleft)代表,是严格的免费软件,她不允许以任何形式收费的插件的代码进入到GCC的代码中。争论的一种意见,正如Eric Raymond说的,“FSF不可能既阻止持有所有权的供应者添加他们的插件到一个免费编译器中,又让这个编译器得到发展。就像马儿已经偏离了跑道,反对插件策略的战略目标已经彻底的失败了”。
|
||||
|
||||
LLVM已经被苹果公司采用作为OS X和苹果硬件上GCC的替代品,并且正在变得流行起来,特别是在BSD系列操作系统的用户中间。LLVM的拥护者推测LLVM将会在更广阔的应用程序和移动设备开发市场上成为GCC的替代者。GCC的反对者们的观点是GCC太过复杂,并且开发者们必须遵守她的‘反著作权(copyleft)’。这限制了那些不想在‘反著作权(copyleft)’许可证下发布他们的语言或者软件产品。作为典型,苹果公司有一个很长的厌恶免费软件的历史。他们也不允许遵守‘反著作权(copyleft)’的软件通过他们的App Store发布。
|
||||
|
||||
LLVM和GCC之间的争论其实是GNU/Linux和BSD系列、开放源代码和免费软件之间历史差异的翻新版。开放源码的开发者允许代码被以任何形式的使用,免费或者维持版权。免费软件则严格地规定,代码或者针对代码做的更新,必须保持永久免费。免费软件的支持者认为完整的‘反著作权’授权有助于GCC的发展,并且已经将Linux和免费软件带到一个其他方式无法到达的高度,同时保证了免费软件不会被收购或者堕落成商业利益。开放源码的支持者则认为开放源码更加的自由,因为使用这没有受到限制,他们可以随意使用,包括开发非开源的版本。
|
||||
|
||||
GNU编译器集合(GCC)一直是免费软件发展的关键。编译器是稀有且昂贵的商品,版权软件公司也充斥着对不符合标准的特性的需求。让软件兼容不同的机器和操作系统是一个非必需的复杂任务。GCC作为第一个真正免费的跨平台编译器,简化了这个过程。
|
||||
|
||||
GCC对于软件开发者和移动设备开发者来说也是一个划时代的产品,而不仅仅对于那些免费软件概念提出者。GCC不但免费和可移植,她跨越不同硬件架构的普遍性和公用性使得更加容易做到软件的兼容性、鲁棒性和一致性。这和John Gilmore,Michael Tiemann和David Henkel-Wallace在开发GCC时发现的一样。这也是Cygnus Solutions公司主要的卖点,Cygnus Solutions是第一家靠卖免费软件赚钱的公司。[译注:Cygnus Solutions是John Gilmore, Michael Tiemann and David Henkel- Wallace创办的公司,同时也是GNU几个主要产品的贡献者]
|
||||
|
||||
LLVM和GCC之间主要的技术差异集中在组成‘前端’,‘中端’,‘后端’的模块分割。‘前端’用来翻译特定的语言。‘中端’对翻译后产生的代码进行优化。‘后端’将优化后的代码转化成特定硬件架构的机器码。LLVM将这些模块分割成不同的实体,但是由于语义的和历史的原因,GCC模糊了这些模块之间的界限。
|
||||
|
||||
对于一个免费软件项目,添加一种新的语言或者架构到GCC也许是一个非常困难的过程,添加有版权的插件也是不允许的。由于模块间界限非常不明确,最容易的添加方法就是让添加的特性遵循免费软件许可证。最初的开发者也许想保持代码的封闭和版权,但最后不得不将代码以免费软件发布。早期的C++以及Objective C就被认为是其中典型的例子。
|
||||
|
||||
与此相反,LLVM允许,甚至也许可以说是鼓励添加和发展版权语言和架构,比如英伟达基于Clang和LLVM的对于GPU开发的NVCC。NVCC的源代码是免费软件或者开源软件开发者获取不到的。
|
||||
|
||||
Richard Stallman[对这方面的演讲中][1]旗帜鲜明地宣布:“在免费软件运动中,我们为自由而战。免费软件的的价值观从根本上就和开源软件不同,后者以写‘更好的代码’为终极目标。如果GCC从免费的编译器变成非免费的编译器,她将不再能够达成自由的目标。
|
||||
|
||||
“Clang和LLVM的开发者不认可我们的价值观和目标,所以得出了跟我们不一样的结论。他们反对我们采取的捍卫自由的措施,因为他们只看到这对他们造成的不便,却没有看到(或者不关心)他们真正的需求。我猜测他们把他们的工作定义为‘开源’,并且漠视自由。”
|
||||
|
||||
GCC开发者们不可能在许可证的条件上妥协。LLVM在某些行业的部门非常流行,因为它很年轻很新,在编程语言的浪潮中跳跃式发展着。流行的风向着更加开放奔跑,GCC决心跟商业利益死磕也许是这个长期演进路上的一大助力。Unix公司们从80和90年代的Unix战争中学到了一些东西。语言和操作系统都是工具,它们最好是开放和共享的。GCC是免费软件,不属于任何人。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxuser.co.uk/features/staying-free-should-gcc-allow-non-free-plug-ins
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[love\_daisy\_love](https://github.com/CNprober) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://lwn.net/articles/582241
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,58 @@
|
||||
在Ubuntu上要用微软OFFICE?去安装官方的Web应用吧
|
||||
==================================================
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**不论你喜欢与否,微软 Office 及其文件格式是大多数工作和学习环境所必须的,无论是好用还是不好用**
|
||||
|
||||
通过使用[LibreOffice的应用程序套件][1],在Ubuntu上阅读、编辑和保存这些专有文件格式出现是基本可行的。 Writer、Calc和Impress都不同程度的和微软 Office 可以互通,虽然以我的实际经验来看(幸好很短暂),不是很完美。
|
||||
|
||||
有时候你会不得不使用微软Office(虽然我们大多数人都心里向着开放标准,但是我们不应该无视实际问题),但你如果不太想去购买一个完整的微软OFFICE许可证,并通过 WINE来运行它,那么微软的在线网络应用程序就是完美的解决方法。
|
||||
|
||||
###在Ubuntu安装微软在线办公软件上的应用程序###
|
||||
|
||||
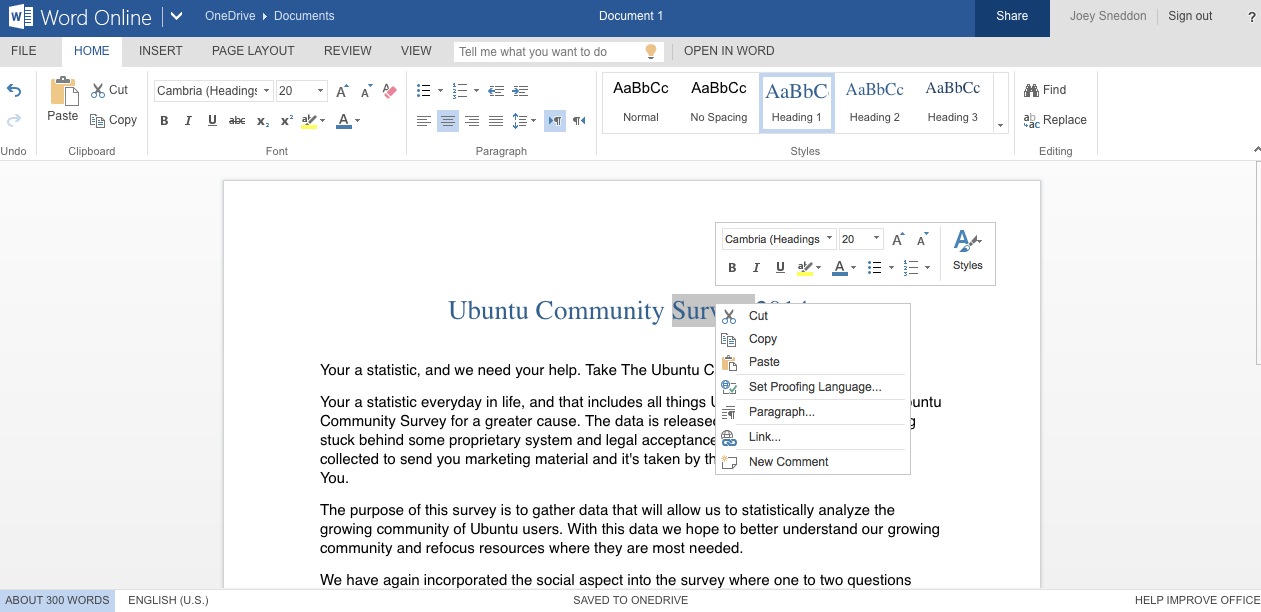
为了更容易地从Ubuntu的桌面访问这些在线版本,“Linux的Web应用项目”创造了一个小的、非官方的安装程序。它可以添加Web应用程序的快捷方式(“漂亮的书签”)到您的应用程序启动器。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
通过快捷方式,可以在你的默认的浏览器中打开相应的Microsoft Web应用,不可能有比这更简单的了。听起来不错吧?你可以找到这些Web 应用的快捷方式:
|
||||
|
||||
- Word
|
||||
- Excel
|
||||
- PowerPoint
|
||||
- Outlook
|
||||
- OneDrive
|
||||
- Calendar
|
||||
- OneNote
|
||||
- People
|
||||
|
||||
该软件包还创建了一个新的应用程序类别来容纳这些链接,不但可以让您把这些快捷方式从其他应用程序单独分开来,而且是直接位于常见的“办公软件”应用程序下。
|
||||
|
||||
这些都是必不可少的吗?不见得。他们有用吗?这取决于你的工作需要。但它是不错的选择吗?一定是的。
|
||||
|
||||
你可以从下面的链接下载.deb文件安装程序。适用于Ubuntu14.04 LTS和更高版本。
|
||||
|
||||
- [下载微软的在线办公应用(.deb)][2]
|
||||
|
||||
###其他可选项###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
类似的替代方案是[安装Chrome官方网上应用商店的在线办公应用程序][3],然后添加应用程序启动器到Linux。这也会在 Dash 中为它们创建启动快捷方式,不过那些可以被设置为打开自己的窗口框架中,而且不需要安装任何第三方软件包。
|
||||
|
||||
同时,谷歌最近在整合完整的Office功能(由于其购买了QuickOffice)[到自己的文档,幻灯片和表单应用][4]。Android应用程序Quickoffice退出了舞台,而以Chrome扩展的方式再次出现。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你是一个深度的谷歌网络硬盘/文档的用户,那么这个解决方案可能对你来说更好。
|
||||
|
||||
-------------------------------------------------- ------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/07/run-microsoft-office-web-apps-ubuntu-desktop
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[cereuz](https://github.com/cereuz)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.libreoffice.org/
|
||||
[2]:https://docs.google.com/file/d/0ByQnaVw7riBQMjNCUFh4ZlM4Y0E/edit?usp=sharing
|
||||
[3]:http://www.omgchrome.com/microsoft-brings-office-online-chrome-web-store/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.omgchrome.com/quickoffice-chrome-extension-gets-name-change/
|
||||
@ -1,22 +1,22 @@
|
||||
diff -u: 内核开发里的新鲜事儿
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
偶尔总会有人指出Linux中的POSIX违规(注:violation此处暂译为违规,若不妥,请修正),通常的回答是修复违规问题,但有时李纳斯·托瓦兹认为POSIX特性是不完整的,至少他们维护Linux特性的情形下是这样的。因此,他们或许应该构建一层POSIX兼容层,即便这个分层会相对较慢和低效。
|
||||
偶尔总会有人指出Linux中的POSIX违规(violation),通常的回答是“修复违规问题”,但有时李纳斯·托瓦兹认为POSIX特性是不完整的,至少他们维护Linux特性的情形下是这样的。因此,他们或许应该构建一层POSIX兼容层,即便这个分层会相对较慢和低效。
|
||||
|
||||
这一次,*迈克尔·凯利斯克*报告了一个影响文件操作的POSIX违规。显然,在多线程操作期间读写文件会导致竞争出现,重写其它操作的改变。
|
||||
这一次,*迈克尔·凯利斯克(Michael Kerrisk)*报告了一个影响文件操作的POSIX违规。显然,在多线程操作期间读写文件会导致竞争出现,重写其它操作的改变。
|
||||
|
||||
关于这是否是POSIX的一个违规存在一些讨论,但到最后又有谁关心呢?数据重写是很糟糕的。在迈克尔提交部分代码去重现这个问题后,讨论的问题集中到该做什么去修复它。但迈克尔确实提出了“Linux从早期开始就与UNIX不一致。(如在1992年版的史蒂夫的APUE的191页讨论到fork()操作后在父进程与子进程之间文件偏移量的共享问题。尽管史蒂夫没有显式地讲清楚一致性的保证,但缺乏这个保证的推论这里的讨论可能有些没意义。)”的观点。
|
||||
关于这是否是POSIX的一个违规存在一些讨论,但到最后又有谁关心呢?数据重写(clobbering)是很糟糕的事情。在迈克尔提交部分代码去重现这个问题后,讨论的问题集中到该做什么去修复它。但迈克尔的观点是:“Linux从早期开始就与UNIX不一致。(如在1992年版的史蒂夫的APUE的191页讨论到fork()操作后在父进程与子进程之间文件偏移量的共享问题。尽管史蒂夫没有显式地讲清楚一致性的保证,但缺乏这个保证的推论这里的讨论可能有些没意义。)”
|
||||
|
||||
艾尔·维洛和李纳斯一起设法解决这个修复。李纳斯尝试引入一个简单的互斥量去锁住文件,以便写操作无法互相重写。艾尔提出了自己的改进以改善李纳斯的补丁。
|
||||
艾尔·维洛(Al Viro)和李纳斯一起设法解决这个修复。李纳斯尝试引入一个简单的互斥量去锁住文件,以便写操作无法互相重写。艾尔提出了自己的改进以改善李纳斯的补丁。
|
||||
|
||||
李纳斯一度解释过这个故障自身的历史。显然,从前这个用来告诉系统去哪里写文件的文件指针已经被锁在一个信号量中,所以只有一个进程可以在某一时刻对这个文件做任何操作。但是,他们从中拿走了这个信号量,以便在任何时候可以适应设备文件和其它非常规文件,因为当用户被禁止写入其中时它们就会陷入竞争状态。
|
||||
|
||||
这就是错误的由来。那时候,它悄悄通过了检查,未被发现。因为实际上对常规文件的读写仍然由内核自动处理。只有文件指针自身可以避免同步。而且,因为高速线程化的文件操作是一个非常罕见的需求,所以对任何人来说都需要很长时间才能遇到这个问题并报告它。
|
||||
这就是错误的由来。那个时候,它悄悄地通过了检查,未被发现。因为实际上对常规文件的读写仍然由内核自动处理。只有文件指针自身可以避免同步。而且,因为高速线程化的文件操作是一个非常罕见的需求,所以对任何人来说都需要很长时间才能遇到这个问题并报告它。
|
||||
|
||||
一个有趣的小细节是当李纳斯和艾尔在寻找一个修复方案时,艾尔一度抱怨李纳斯采用的方法并不能支持确定的架构,包括*ARM*和*PowerPC*。李纳斯的回应是“我怀疑关心这个是否有意义。[...]如果使用ARM/PPC架构的人停止抱怨,他们可以往gcc中加入struct-return的支持。”
|
||||
一个有趣的小细节是当李纳斯和艾尔在寻找一个修复方案时,艾尔一度抱怨李纳斯采用的方法并不能支持一些确定的架构,包括*ARM*和*PowerPC*。李纳斯的回应是“我怀疑关心这个是否有意义。[...]如果使用ARM/PPC架构的人停止抱怨,他们可以往gcc中加入struct-return的支持。”
|
||||
|
||||
看到这些问题突然产生并得到处理通常是很有趣的。在某些情况下,这个修复的部分工作必须在内核中进行,部分在GCC中,部分在其它地方。在这个特例里,艾尔认为整个事情都应该在内核里处理,他在灵感的激发下往补丁中写入了自己的版本,李纳斯也接受了。
|
||||
|
||||
*安迪·克伦*则想为*perf*增加底层CPU事件支持。问题在于这可能会导致大量的底层事件,而且会因CPU的变化而改变。即使为了所有类型的CPU把可能的时间都存储在内存里,也可能会显著地增加内核的运行大小。因此,把这个信息硬编码进内核的方法是有问题的。
|
||||
*安迪·克伦(Andi Kleen)*则想为*perf*增加底层CPU事件支持。问题在于这可能会导致大量的底层事件,而且会因CPU的变化而改变。即使为了所有类型的CPU把可能的时间都存储在内存里,也可能会显著地增加内核的运行大小。因此,把这个信息硬编码进内核的方法是有问题的。
|
||||
|
||||
他也指出*OProfile*工具依赖于这些时间的公开可用列表,尽管他表示OProfile开发者并非总维持他们的列表与最新的可用版本一致。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -24,20 +24,21 @@ diff -u: 内核开发里的新鲜事儿
|
||||
|
||||
有各种各样对安迪代码的反馈,其中大部分涉及到应该在哪个目录下保存事件列表和文件如何命名。这份代码本身的特性似乎得到了很好的回应。一处细节证明了安迪的代码比其他人的更有争议,就是将列表下载到用户家目录下的一个子目录。安迪表示如果不这样做的话,用户可能会以系统管理员的身份去下载事件列表,这会是危害安全的操作。
|
||||
|
||||
萨沙·莱文最近发布了一个脚本来从堆栈转储中把*十六进制的偏移量*翻译成有意义的指向内核源码文件的行号。因此诸如“ffffffff811f0ec8”形式的十六进制表示可以被翻译成“fs/proc/generic.c:445”。
|
||||
萨沙·莱文(Sasha Levin)最近发布了一个脚本来从堆栈转储中把*十六进制的偏移量*翻译成有意义的指向内核源码文件的行号。因此诸如“ffffffff811f0ec8”形式的十六进制表示可以被翻译成“fs/proc/generic.c:445”。
|
||||
|
||||
然而,结果表明李纳斯·托瓦兹正打算从堆栈转储中移除十六进制偏移量,具体原因是他们难以理解。所以萨沙的代码看起来过时了。【译者注:程序媛,伤不起!】
|
||||
然而,结果表明李纳斯·托瓦兹正打算从堆栈转储中移除十六进制偏移量,具体原因是他们难以理解。所以萨沙的代码看起来过时了。[译者注:程序媛,伤不起!:< ]
|
||||
|
||||
他们在这个问题上纠结了一番。起初,萨沙打算依赖存储在System.map文件里的数据区补偿,但李纳斯指出包括他在内的有些人并不会保留System.map文件。李纳斯推荐使用/usr/bin/nm从编译好的内核文件中提取符号表。
|
||||
|
||||
所以,似乎萨沙的脚本可能确实为调试堆栈转储提供了有意义的文件和行号,假设堆栈转储提供足够的信息去完成计算。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxjournal.com/content/diff-u-whats-new-kernel-development-0
|
||||
|
||||
原文作者:[Zack Brown][a]
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[KayGuoWhu](https://github.com/KayGuoWhu) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[KayGuoWhu](https://github.com/KayGuoWhu) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,132 @@
|
||||
10个关于linux中Squid代理服务器的实用面试问答
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
不仅是系统管理员和网络管理员时不时会听到“代理服务器”这个词,我们也经常听到。代理服务器已经成为一种企业常态,而且经常会接触到它。它现在也出现在一些小型的学校或者大型跨国公司的自助餐厅里。Squid(常被视作代理服务的代名词)就是这样一个应用程序,它不但可以被作为代理服务器,其同时也是在该类工具中比较被广泛使用的一种。
|
||||
|
||||
本文旨在提高你在遇到关于代理服务器面试点时的一些基本应对能力。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
以下为面试问答的内容
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. 什么是代理服务器?代理服务器在计算机网络中有什么用途? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **回答** : 代理服务器是指那些作为客户端和资源提供商或服务器之间的中间件的物理机或者应用程序。客户端从代理服务器中寻找文件、页面或者是数据,而且代理服务器能处理客户端与服务器之间所有复杂事务,从而满足客户端的生成的需求。
|
||||
|
||||
代理服务器是WWW(万维网)的支柱,它们其中大部分都是Web代理。一台代理服务器能处理客户端与服务器之间的复杂通信事务。此外,它在网络上提供的是匿名信息(LCTT 译注:指浏览者的 IP、浏览器信息等被隐藏),这就意味着你的身份和浏览痕迹都是安全的。代理可以去配置允许哪些网站的客户能看到,哪些网站被屏蔽了。
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Squid是什么? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **回答** : Squid是一个在GNU/GPL协议下发布的既可作为代理服务器,同时也可作为Web缓存守护进程的应用软件。Squid主要是支持像HTTP和FTP那样的协议,但是对其它的协议比如HTTPS,SSL,TLS等同样也能支持。其特点是Web缓存守护进程通过从经常上访问的网站里缓存Web和DNS数据,从而让上网速度更快。Squid支持所有的主流平台,包括Linux,UNIX,微软公司的Windows和苹果公司的Mac。
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. Squid的默认端口是什么?怎么去修改它的操作端口? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **回答** : Squid运行时的默认端口是3128。我们可以通过编辑它的配置文件来把它的默认端口修改成未被用户使用的端口,路径是 /etc/squid/squid.conf ,建议如下。
|
||||
|
||||
用你的编辑器打开 ‘/etc/squid/squid.conf’ 文件。
|
||||
|
||||
# nano /etc/squid/squid.conf
|
||||
|
||||
现在把它修改成未被使用的其它端口,并保存退出。
|
||||
|
||||
http_port 3128
|
||||
|
||||
重新启动Squid代理服务,如下显示。
|
||||
|
||||
# service squid restart
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. 你的公司管理层要求你通过Squid代理服务器屏蔽掉一些域名,你怎么做? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **回答** : 屏蔽域名是一个在配置文件中实现的功能模块。我们只需要执行一个小的手动配置即可,建议如下。
|
||||
|
||||
a. 在 ‘/etc/squid’ 目录下创建一个名为 ‘blacklist’ 的文件。
|
||||
|
||||
# touch /etc/squid/blacklist
|
||||
|
||||
b. 用nano编辑器打开这个文件。
|
||||
|
||||
# nano /etc/squid/blacklist
|
||||
|
||||
c. 以每行一个域名的方式将想要屏蔽的域名写进这个文件里。
|
||||
|
||||
.facebook.com
|
||||
.twitter.com
|
||||
.gmail.com
|
||||
.yahoo.com
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
d. 保存退出,然后从 ‘/etc/squid/squid.conf’ 打开Squid配置文件。
|
||||
|
||||
# nano /etc/squid/squid.conf
|
||||
|
||||
e. 在配置文件中添加如下行。
|
||||
|
||||
acl BLACKLIST dstdom_regex -i “/etc/squid/blacklist”
|
||||
http_access deny blacklist
|
||||
|
||||
f. 保存配置文件并退出,重启Squid服务让其生效。
|
||||
|
||||
# service squid restart
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. 在Squid中什么是媒体范围限制(Media Range Limitation)和部分下载? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **回答** : 媒体范围限制是Squid的一种特殊的功能,它只从服务器中获取所需要的数据而不是整个文件。这个功能很好的实现了用户在各种视频流媒体网站如YouTube和Metacafe看视频时,可以点击视频中的进度条来选择进度,因此整个视频不用全部都加载,除了一些需要的部分。
|
||||
|
||||
Squid部分下载功能的特点是很好地实现了类似在Windows更新时能以一个个小数据包的形式下载,并可以暂停,正因为它的这个特点,正在下载文件的Windows机器可以重新继续下载,而不用担心数据会丢失。Squid的媒体范围限制和部分下载功能只有在存储了一个完整文件的副本之后才行。此外,当用户访问另一个页面时,除非Squid进行了特定的配置,部分下载下来的文件会被删除且不留在缓存中。
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. 什么是Squid的反向代理? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **回答** : 反向代理是Squid的一个功能,这个功能被用来加快最终用户的上网速度。下面用缩写 ‘RS’ 的表示包含了资源的原服务器,而代理服务器则称作 ‘PS’ 。初次访问时,它会从RS得到其提供的数据,并将其副本按照配置好的时间存储在PS上。这样的话每次从PS上请求的数据就相当于就是从原服务器上获取的。这样就会减轻网络拥堵,减少CPU使用率,降低网络资源的利用率,从而缓解原来实际服务器的负载压力。但是RS统计不了总流量的数据,因为PS分担了部分原服务器的任务。‘X-Forwarded-For HTTP’ 信息能用于记录下通过HTTP代理或负载均衡方式连接到RS的客户端最原始的IP地址。
|
||||
|
||||
从技术上说,用单个Squid服务器同时作为正向代理服务器和反向代理服务器是可行的。
|
||||
|
||||
### 7. 由于Squid能作为一个Web缓存守护进程,那缓存可以删除吗?怎么删除? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **回答** : 当然!作为一个Web缓存守护进程,Squid能加快网页的访问速度,清除缓存也是非常简单的。
|
||||
|
||||
a. 首先停止Squid代理服务,然后从这个 ‘/var/lib/squid/cache’ 目录中删除缓存。
|
||||
|
||||
# service squid stop
|
||||
# rm -rf /var/lib/squid/cache/*<
|
||||
|
||||
b. 创建交换分区目录。
|
||||
|
||||
# squid -z
|
||||
|
||||
### 8. 你有一台工作中的机器可以访问代理服务器,如果想要限制你的孩子的访问时间,你会怎么去设置那个场景? ###
|
||||
|
||||
把允许访问的时间设置成晚上4点到7点三个小时,跨度为星期一到星期五。
|
||||
|
||||
a. 想要限制Web访问时间在星期一到星期五的晚上4点到7点,要先打开Squid的配置文件。
|
||||
|
||||
# nano /etc/squid/squid.conf
|
||||
|
||||
b. 在配置文件中添加如下行,保存文件并退出。
|
||||
|
||||
acl ALLOW_TIME time M T W H F 16:00-19:00
|
||||
shttp_access allow ALLOW_TIME
|
||||
|
||||
c. 重启Squid服务。
|
||||
|
||||
# service squid restart
|
||||
|
||||
### 9. Squid存储的数据是什么文件格式? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **回答** : Squid存储的数据是UFS文件格式的。UFS是一种老的,使用比较广泛的Squid存储格式
|
||||
|
||||
### 10. Squid的缓存会存储到哪里? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **回答** : Squid存储的缓存是位于 ‘/var/spool/squid’ 的特定目录下。
|
||||
|
||||
以上就是全部内容了,很快我还会带着其它有趣的内容回到这里。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/squid-interview-questions/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Avishek Kumar][a]
|
||||
译者:[ZTinoZ](https://github.com/ZTinoZ)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/avishek/
|
||||
@ -13,56 +13,56 @@ shell脚本中的变量是用来**调用**一个**数值**或者**字符值**的
|
||||
<table width="100%" cellspacing="1" cellpadding="1">
|
||||
<tbody>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><strong> System Defined Variables </strong></td>
|
||||
<td><strong> Meaning </strong></td>
|
||||
<td><strong>系统定义的变量 </strong></td>
|
||||
<td><strong>意义 </strong></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td> BASH=/bin/bash </td>
|
||||
<td> Shell Name </td>
|
||||
<td> Bash Shell 名称 </td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td> BASH_VERSION=4.1.2(1) </td>
|
||||
<td> Bash Version </td>
|
||||
<td> Bash 版本 </td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td> COLUMNS=80 </td>
|
||||
<td> No. of columns for our screen </td>
|
||||
<td> 你的屏幕宽度(列数) </td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td> HOME=/home/linuxtechi </td>
|
||||
<td> Home Directory of the User </td>
|
||||
<td> 用户家目录 </td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td> LINES=25 </td>
|
||||
<td> No. of columns for our screen </td>
|
||||
<td> 你的屏幕高度(行数) </td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td> LOGNAME=LinuxTechi </td>
|
||||
<td> LinuxTechi Our logging name </td>
|
||||
<td> 当前登录用户的名字 </td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td> OSTYPE=Linux </td>
|
||||
<td> OS type </td>
|
||||
<td> 操作系统类型 </td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td> PATH=/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin </td>
|
||||
<td> Path Settings </td>
|
||||
<td> 可执行文件搜索路径 </td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td> PS1=[\u@\h \W]\$ </td>
|
||||
<td> Prompt Settings </td>
|
||||
<td> 命令行提示符 </td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td> PWD=/home/linuxtechi </td>
|
||||
<td> Current Working Directory </td>
|
||||
<td> 当前工作目录 </td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td> SHELL=/bin/bash </td>
|
||||
<td> Shell Name </td>
|
||||
<td> Shell 名称 </td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td> USERNAME=linuxtechi </td>
|
||||
<td> User name who is currently login to system </td>
|
||||
<td> 当前登录的用户名 </td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</tbody>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
@ -87,7 +87,7 @@ shell脚本中的变量是用来**调用**一个**数值**或者**字符值**的
|
||||
$ echo “The cost of the item is $15”
|
||||
The cost of the item is 5
|
||||
|
||||
很明显,那不是我们说希望的。无论何时,当脚本遇见引号中的美元符号时,它都会认为你是在调用一个变量。在本例中,改脚本试着显示**变量$1**(而这个变量并没有定义),然后显示数字5。要显示实际上的美元符号,你**必须前置**一个**反斜线字符**:
|
||||
很明显,那不是我们说希望的。无论何时,当脚本遇见引号中的美元符号时,它都会认为你是在调用一个变量。在本例中,该脚本试着显示**变量$1**(而这个变量并没有定义),然后显示数字5。要显示实际上的美元符号,你**必须前置**一个**反斜线字符**:
|
||||
|
||||
$ echo “The cost of the item is \$15”
|
||||
The cost of the item is $15
|
||||
@ -98,7 +98,7 @@ shell脚本中的变量是用来**调用**一个**数值**或者**字符值**的
|
||||
|
||||
这些变量由**用户**定义。shell脚本允许我们在脚本中设置并使用我们**自己的变量**。设置变量允许你**临时存储数据**并在脚本中使用,让shell脚本看起来像一个真正的计算机程序。
|
||||
|
||||
**用户变量**可以是任何不超过**20个字母,数字**的文本字符串,或者**一个下划线字符**。用户变量是大小写敏感的,因此,变量Var1和变量var1是不同的变量。这个小规则常常让新手编写脚本时麻烦重重。
|
||||
**用户变量**可以是任何不超过**20个的字母、数字**或者**下划线字符**的文本字符串(LCTT 译注:变量只能以字母或下划线开头)。用户变量是大小写敏感的,因此,变量Var1和变量var1是不同的变量。这个小规则常常让新手编写脚本时麻烦重重。
|
||||
|
||||
我们可以通过**等于号**为变量赋值。变量,等于号和值(对于新手又是个麻烦的地方)之间不能有空格。下面是几个给用户变量赋值的例子:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -130,7 +130,7 @@ shell脚本为变量值**自动确定数据类型**。shell脚本内定义的变
|
||||
Jessica checked in 5 days ago
|
||||
$
|
||||
|
||||
每次变量被**调用**,它都会产生当前分配给它的值。记住这一点很重要,当调用一个变量值时,你使用**美元符号**,但是当调用一个变量来为其分配一个值时,你不能用美元符号。下面用例子来说明:
|
||||
每次变量被**调用**,它都会变成了当前分配给它的值。有一点很重要,当调用一个变量值时,你使用**美元符号**,但是当为一个变量分配一个值时,你不能用美元符号。下面用例子来说明:
|
||||
|
||||
$ cat test4
|
||||
#!/bin/bash
|
||||
@ -180,7 +180,7 @@ shell会在**反引号**中运行命令,然后将输出结果赋值给变量te
|
||||
$ ./test5
|
||||
The date and time are: Mon Jan 31 20:23:25 EDT 2011
|
||||
|
||||
**注**:在bash中,你也可以选用$(...)语法来替换反引号(`),它有个优点就是可以重用。
|
||||
**注**:在bash中,你也可以选用$(...)语法来替换反引号(`),它有个优点就是可以重用(re-entrant)。
|
||||
|
||||
例:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -192,8 +192,8 @@ shell会在**反引号**中运行命令,然后将输出结果赋值给变量te
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxtechi.com/variables-in-shell-scripting/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Pradeep Kumar][a]
|
||||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[ ](https://github.com/GOLinux)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -8,12 +8,13 @@
|
||||
|
||||
### 添加窗口按钮 ###
|
||||
|
||||
处于一些未知的原因,GNOME的开发者们决定对标准的窗口按钮(关闭,最小化,最大化)不屑一顾,而支持只有单个关闭按钮的窗口了。我缺少了最大化按钮(虽然你可以简单地拖动窗口到屏幕顶部来将它最大化),然而也可以通过在标题栏右击选择最小化或者最大化来进行最小化/最大化操作。这种变化仅仅增加了操作步骤,因此缺少最小化按钮实在搞得人云里雾里。所幸的是,有个简单的修复工具可以解决这个问题,下面说说怎样做吧:
|
||||
出于一些未知的原因,GNOME的开发者们决定对标准的窗口按钮(关闭,最小化,最大化)不屑一顾,而支持只有单个关闭按钮的窗口了。我缺少了最大化按钮(虽然你可以简单地拖动窗口到屏幕顶部来将它最大化),而且也可以通过在标题栏右击选择最小化或者最大化来进行最小化/最大化操作。这种变化仅仅增加了操作步骤,因此缺少最小化按钮实在搞得人云里雾里。所幸的是,有个简单的修复工具可以解决这个问题,下面说说怎样做吧:
|
||||
|
||||
默认情况下,你应该安装了GNOME优化工具。通过该工具,你可以打开最大化或最小化按钮(图1)。
|
||||
默认情况下,你应该安装了GNOME优化工具(GNOME Tweak Tool)。通过该工具,你可以打开最大化或最小化按钮(图1)。
|
||||
|
||||
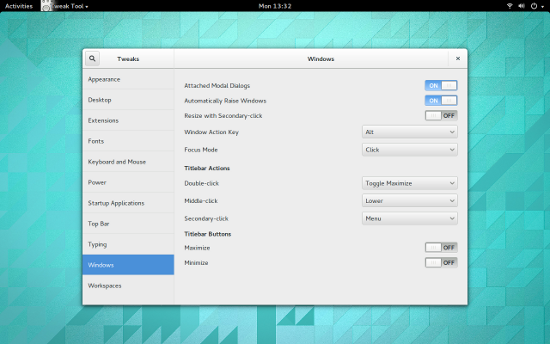
|
||||
Figure 1: 添加回最小化按钮到GNOME 3窗口
|
||||
<center>
|
||||
|
||||
*图 1: 添加回最小化按钮到GNOME 3窗口*</center>
|
||||
|
||||
添加完后,你就可以看到最小化按钮了,它在关闭按钮的左边,等着为你服务呢。你的窗口现在管理起来更方便了。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -27,36 +28,39 @@ Figure 1: 添加回最小化按钮到GNOME 3窗口
|
||||
|
||||
### 添加扩展 ###
|
||||
|
||||
GNOME 3的最佳特性之一,就是shell扩展,这些扩展为GNOME带来了全部种类的有用的特性。关于shell扩展,没必要从包管理器去安装。你可以访问[GNOME Shell扩展][2]站点,搜索你想要添加的扩展,点击扩展列表,点击打开按钮,然后扩展就安装完成了;或者你也可以从GNOME优化工具中添加它们(你在网站上会找到更多可用的扩展)。
|
||||
GNOME 3的最佳特性之一,就是shell扩展,这些扩展为GNOME带来了各种类别的有用特性。关于shell扩展,没必要从包管理器去安装。你可以访问[GNOME Shell扩展][2]站点,搜索你想要添加的扩展,点击扩展列表,点击打开按钮,然后扩展就安装完成了;或者你也可以从GNOME优化工具中添加它们(你在网站上会找到更多可用的扩展)。
|
||||
|
||||
注:你可能需要在浏览器中允许扩展安装。如果出现这样的情况,你会在第一次访问GNOME Shell扩展站点时见到警告信息。当出现提示时,只要点击允许即可。
|
||||
|
||||
令人印象更为深刻的(而又得心应手的扩展)之一,就是[Dash to Dock][3]。
|
||||
令人印象更为深刻的(而又得心应手的)扩展之一,就是[Dash to Dock][3]。
|
||||
|
||||
该扩展将Dash移出应用程序概览,并将它转变为相当标准的停靠栏(图2)。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Figure 2: Dash to Dock添加一个停靠栏到GNOME 3.
|
||||
<center>
|
||||
|
||||
*图 2: Dash to Dock添加一个停靠栏到GNOME 3*</center>
|
||||
|
||||
当你添加应用程序到Dash后,他们也将被添加到Dash to Dock。你也可以通过点击Dock底部的6点图标访问应用程序概览。
|
||||
|
||||
还有大量其它扩展聚焦于讲GNOME 3打造成一个更为高效的桌面,在这些更好的扩展中,包括以下这些:
|
||||
还有大量其它扩展致力于将GNOME 3打造成一个更为高效的桌面,在这些不错的扩展中,包括以下这些:
|
||||
|
||||
- [最近项目][4]: 添加一个最近使用项目的下拉菜单到面板。
|
||||
- [搜索Firefox书签提供者][5]: 从概览搜索(并启动)书签。
|
||||
- [Firefox书签搜索][5]: 从概览搜索(并启动)书签。
|
||||
- [跳转列表][6]: 添加一个跳转列表弹出菜单到Dash图标(该扩展可以让你快速打开和程序关联的新文档,甚至更多)
|
||||
- [待办列表][7]: 添加一个下拉列表到面板,它允许你添加项目到该列表。
|
||||
- [网页搜索对话框][8]: 允许你通过敲击Ctrl+空格来快速搜索网页并输入一个文本字符串(结果在新的浏览器标签页中显示)。
|
||||
- [网页搜索框][8]: 允许你通过敲击Ctrl+空格来快速搜索网页并输入一个文本字符串(结果在新的浏览器标签页中显示)。
|
||||
|
||||
### 添加一个完整停靠栏 ###
|
||||
|
||||
如果Dash to dock对于而言功能还是太有限(你想要通知区域,甚至更多),那么向你推荐我最喜爱的停靠栏之一[Cairo Dock][9](图3)。
|
||||
如果Dash to dock对于你而言功能还是太有限(你想要“通知区域”,甚至更多),那么向你推荐我最喜爱的停靠栏之一[Cairo Dock][9](图3)。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Figure 3: Cairo Dock待命
|
||||
<center>
|
||||
|
||||
在Cairo Dock添加到GNOME 3后,你的体验将成倍地增长。从你的发行版的包管理器中安装这个优秀的停靠栏吧。
|
||||
*图 3: Cairo Dock待命*</center>
|
||||
|
||||
不必将GNOME 3看作是一个效率不高的,用户不友好的桌面。只要稍作调整,GNOME 3可以成为和其它可用的桌面一样强大而用户友好的桌面。
|
||||
在将Cairo Dock添加到GNOME 3后,你的体验将成倍地增长。从你的发行版的包管理器中安装这个优秀的停靠栏吧。
|
||||
|
||||
不要将GNOME 3看作是一个效率不高的,用户不友好的桌面。只要稍作调整,GNOME 3可以成为和其它可用的桌面一样强大而用户友好的桌面。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
@ -64,7 +68,7 @@ via: http://www.linux.com/learn/tutorials/781916-easy-steps-to-make-gnome-3-more
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Jack Wallen][a]
|
||||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[ wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
|
||||
什么时候Linux才能完美
|
||||
什么时候Linux才能完美?
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
前几天我的同事兼损友,Ken Starks,在FOSS Force上发表了[一篇文章][1],关于他最喜欢发牢骚的内容:Linux系统中那些不能正常工作的事情。这次他抱怨的是在Mint里使用KDE时碰到的字体问题。这对于Ken来说也不是什么新鲜事了。过去他写了一些文章,关于各种Linux发行版中的缺陷从来都没有被认真修复过。他的观点是,这些在一次又一次的发布中从没有被修复过的“小问题”,对于Linux桌面系统在赢得大众方面的失败需要负主要责任。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -14,21 +14,21 @@
|
||||
|
||||
### 也不全是这样子的 ###
|
||||
|
||||
早在2002年的时候,我第一次安装使用GNU/Linux,像大多数美国人那样,我搞不定拨号连接,在我呆的这个小地方当时宽带还没普及。我在当地Best Buy商店里花了差不多70美元买了用热缩膜包装的Mandrake 9.0的Powerpack版,当时那里同时在卖Mandrake和Red Hat,现在仍然还在经营桌面业务。
|
||||
早在2002年的时候,我第一次安装使用GNU/Linux,像大多数美国人那样,我搞不定拨号连接,在我呆的这个小地方当时宽带还没普及。我在当地Best Buy商店里花了差不多70美元买了用热缩膜包装的Mandrake 9.0的Powerpack版,当时那里同时在卖Mandrake和Red Hat,现在仍然还在经营桌面PC业务。
|
||||
|
||||
在那个恐龙时代,Mandrake被认为是易用的Linux发行版中做的最好的。它安装简单,还有人说比Windows还简单,它自带的分区工具更是让划分磁盘像切苹果馅饼一样简单。不过实际上,Linux老手们经常公开嘲笑Mandrake,暗示易用的Linux不是真的Linux。
|
||||
|
||||
但是我很喜欢它,感觉来到了一个全新的世界。再也不用担心Windows的蓝屏死机和几乎每天一死了。不幸的是,之前在Windows下“能用”的很多外围设备也随之而去。
|
||||
|
||||
安装完Mandrake之后我要做的第一件事就是,把我的小白盒拿给[Dragonware Computers][2]的Michelle,把便宜的winmodem换成硬件调制解调器。就算,一个硬件猫意味着计算机响应更快,但是计算机商店却在40英里外的地方,并不是很方便,而且费用我也有点压力。
|
||||
安装完Mandrake之后我要做的第一件事就是,把我的小白盒拿给[Dragonware Computers][2]的Michelle,把便宜的winmodem换成硬件调制解调器。就算是一个硬件猫意味着计算机响应更快,但是计算机商店却在40英里外的地方,并不是很方便,而且费用对我也有点压力。
|
||||
|
||||
但是我不介意。我对Microsoft并不感冒--而且使用一个“不同”的操作系统让我感觉自己就像一个计算机天才。
|
||||
|
||||
打印机也是个麻烦,但是这个问题对于Mandrake还好,不像其他大多数发行版还需要命令行里的操作才能解决。Mandrake提供了一个华丽的图形界面来设置打印机-如果你正好幸运的有一台能在Linux下工作的打印机的话。很多,不是大多数,都不行。
|
||||
打印机也是个麻烦,但是这个问题对于Mandrake还好,不像其他大多数发行版还需要命令行里的操作才能解决。Mandrake提供了一个华丽的图形界面来设置打印机-如果你正好幸运的有一台能在Linux下工作的打印机的话。很多打印机——就算不是大多数——都不行。
|
||||
|
||||
我的还在保修期的Lexmark,在Windows下比其他打印机多出很多华而不实的小功能,厂商并不支持Linux版本,但是我找到一个多少能用的开源逆向工程驱动。它能在Mozilla浏览器里正常打印网页,但是在Star Office软件里打印的话会是用很小的字体塞到页面的右上角里。打印机还会发出很大的机械响声,让我想起了汽车变速箱在报废时发出的噪音。
|
||||
|
||||
Star Office问题的变通方案是把所有文字都保存到文本文件,然后在文本编辑器里打印。而对于那个听上去像是打印机处于自解体模式的噪音?我的方法是尽量不要打印。
|
||||
Star Office问题的变通方案是把所有文字都保存到文本文件,然后在文本编辑器里打印。而对于那个听上去像是打印机处于天魔解体模式的噪音?我的方法是尽量不要打印。
|
||||
|
||||
### 更多的其他问题-对我来说太多了都快忘了 ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -36,12 +36,13 @@ Star Office问题的变通方案是把所有文字都保存到文本文件,然
|
||||
|
||||
好吧,我还有个并口扫描仪,在我转移到Linux之前两个星期买的,之后它就基本是块砖了,因为没有Linux下的驱动。
|
||||
|
||||
我的观点是在那个年代里这些都不重要。我们大多数人都习惯了修改配置文件之类的事情,即便是运行微软产品的“IBM兼容”计算机。就像那个年代的大多数用户,我刚学开始接触使用命令行的DOS机器,在它上面打印机需要针对每个程序单独设置,而且写写简单的autoexec.bat是必须的技能。
|
||||
我的观点是在那个年代里这些都不重要。我们大多数人都习惯了修改配置文件之类的事情,即便是运行微软产品的“IBM兼容”计算机。就像那个年代的大多数用户,我刚学开始接触使用命令行的DOS机器,在它上面打印机需要针对每个程序单独设置,而且写写简单的autoexec.bat是必备的技能。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Linux就像1966年的“山羊”
|
||||
<center></center>
|
||||
|
||||
能够摆弄操作系统内部的配置是能够拥有一台计算机的一个简单部分。我们大多数使用计算机的人要么是极客或是希望成为极客。我们为这种能够调整计算机按我们想要的方式运行的能力而感到骄傲。我们就是那个年代里高科技版本的好男孩,他们会在周六下午在树荫下改装他们肌肉车上的排气管,通风管,化油器之类的。
|
||||
<center>Linux就像1966年的“山羊”</center>
|
||||
|
||||
那时,能够摆弄操作系统内部的配置是能够拥有一台计算机的一个简单部分。我们大多数使用计算机的人要么是极客或是希望成为极客。我们为这种能够调整计算机按我们想要的方式运行的能力而感到骄傲。我们就是那个年代里高科技版本的好男孩,他们会在周六下午在树荫下改装他们肌肉车上的排气管,通风管,化油器之类的。
|
||||
|
||||
### 不过现在大家不是这样使用计算机的 ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -59,7 +60,7 @@ via: http://fossforce.com/2014/08/when-linux-was-perfect-enough/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Christine Hall
|
||||
译者:[zpl1025](https://github.com/zpl1025)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,20 +1,17 @@
|
||||
使用Clonezilla对硬盘进行镜像和克隆
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
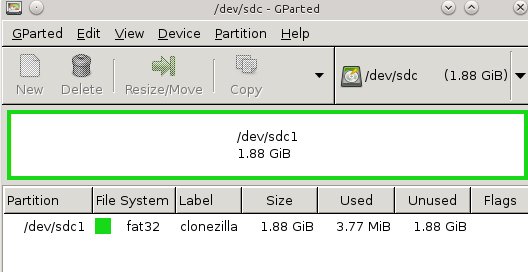
|
||||
|
||||
图1: 在USB存储棒上为Clonezilla创建分区
|
||||
Clonezilla是一个用于Linux,Free-Net-OpenBSD,Mac OS X,Windows以及Minix的分区和磁盘克隆程序。它支持所有主要的文件系统,包括EXT,NTFS,FAT,XFS,JFS和Btrfs,LVM2,以及VMWare的企业集群文件系统VMFS3和VMFS5。Clonezilla支持32位和64位系统,同时支持旧版BIOS和UEFI BIOS,并且同时支持MBR和GPT分区表。它是一个用于完整备份Windows系统和所有安装于上的应用软件的好工具,而我喜欢用它来为Linux测试系统做备份,以便我可以在其上做疯狂的实验搞坏后,可以快速恢复它们。
|
||||
|
||||
Clonezilla是一个用于Linux,Free-Net-,OpenBSD,Mac OS X,Windows以及Minix的分区和磁盘克隆程序。它支持所有主要的文件系统,包括EXT,NTFS,FAT,XFS,JFS和Btrfs,LVM2,以及VMWare的企业集群文件系统VMFS3和VMFS5。Clonezilla支持32位和64位系统,同时支持旧版BIOS和UEFI BIOS,并且同时支持MBR和GPT分区表。它是一个用于完整备份Windows系统和所有安装于上的应用软件的好工具,而我喜欢用它来为Linux测试系统做备份,以便我可以在其上做疯狂的实验搞坏后,可以快速恢复它们。
|
||||
Clonezilla也可以使用dd命令来备份不支持的文件系统,该命令可以复制块而非文件,因而不必在意文件系统。简单点说,就是Clonezilla可以复制任何东西。(关于块的快速说明:磁盘扇区是磁盘上最小的可编址存储单元,而块是由单个或者多个扇区组成的逻辑数据结构。)
|
||||
|
||||
Clonezilla也可以使用dd命令来备份不支持的文件系统,该命令可以复制块而非文件,因而不必弄明白文件系统。因此,简单点说,就是Clonezilla可以复制任何东西。(关于块的快速说明:磁盘扇区是磁盘上最小的可编址存储单元,而块是由单个或者多个扇区组成的逻辑数据结构。)
|
||||
|
||||
Clonezilla分为两个版本:Clonezilla Live和Clonezilla Server Edition(SE)。Clonezilla Live对于将单个计算机克隆岛本地存储设备或者网络共享来说是一流的。而Clonezilla SE则适合更大的部署,用于一次性快速多点克隆整个网络中的PC。Clonezilla SE是一个神奇的软件,我们将在今后讨论。今天,我们将创建一个Clonezilla Live USB存储棒,克隆某个系统,然后恢复它。
|
||||
Clonezilla分为两个版本:Clonezilla Live和Clonezilla Server Edition(SE)。Clonezilla Live对于将单个计算机克隆到本地存储设备或者网络共享来说是一流的。而Clonezilla SE则适合更大的部署,用于一次性快速多点克隆整个网络中的PC。Clonezilla SE是一个神奇的软件,我们将在今后讨论。今天,我们将创建一个Clonezilla Live USB存储棒,克隆某个系统,然后恢复它。
|
||||
|
||||
### Clonezilla和Tuxboot ###
|
||||
|
||||
当你访问下载页时,你会看到[稳定版和可选稳定发行版][1]。也有测试版本,如果你有兴趣帮助改善Clonezilla,那么我推荐你使用此版本。稳定版基于Debian,不含有非自由软件。可选稳定版基于Ubuntu,包含有一些非自由固件,并支持UEFI安全启动。
|
||||
|
||||
在你[下载Clonezilla][2]后,请安装[Tuxboot][3]来复制Clonezilla到USB存储棒。Tuxboot是一个Unetbootin的修改版,它支持Clonezilla;你不能使用Unetbootin,因为它无法工作。安装Tuxboot有点让人头痛,然而Ubuntu用户通过个人包归档压缩包(PPA)方便地安装:
|
||||
在你[下载Clonezilla][2]后,请安装[Tuxboot][3]来复制Clonezilla到USB存储棒。Tuxboot是一个Unetbootin的修改版,它支持Clonezilla;你不能使用Unetbootin,因为它无法配合工作。安装Tuxboot有点让人头痛,然而Ubuntu用户通过个人包归档包(PPA)方便地安装:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-add-repository ppa:thomas.tsai/ubuntu-tuxboot
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get update
|
||||
@ -22,18 +19,24 @@ Clonezilla分为两个版本:Clonezilla Live和Clonezilla Server Edition(SE
|
||||
|
||||
如果你没有运行Ubuntu,并且你的发行版不包含打包好的Tuxboot版本,那么请[下载源代码tarball][4],并遵循README.txt文件中的说明来编译并安装。
|
||||
|
||||
安装完Tuxboot后,就可以使用它来创建你精巧的可直接启动的Clonezilla USB存储棒了。首先,创建一个最小200MB的FAT 32分区;图1(上面)展示了使用GParted来进行分区。我喜欢使用标签,比如“Clonezilla”,这会让我知道它是个什么东西。该例子中展示了将一个2GB的存储棒格式化成一个单个分区。
|
||||
Then fire up Tuxboot (figure 2). Check "Pre-downloaded" and click the button with the ellipsis to select your Clonezilla file. It should find your USB stick automatically, and you should check the partition number to make sure it found the right one. In my example that is /dev/sdd1. Click OK, and when it's finished click Exit. It asks you if you want to reboot now, but don't worry because it won't. Now you have a nice portable Clonezilla USB stick you can use almost anywhere.
|
||||
然后,启动Tuxboot(图2)。选中“预下载的(Pre-downloaded)”然后点击带省略号的按钮来选择Clonezilla文件。它会自动发现你的USB存储棒,而你需要选中分区号来确保它找到的是正确的那个,我的例子中是/dev/sdd1。点击确定,然后当它完成后点击退出。它会问你是否要重启动,请不要担心,因为它不会的。现在你有一个精巧的便携式Clonezilla USB存储棒了,你可以随时随地使用它了。
|
||||
<center></center>
|
||||
|
||||
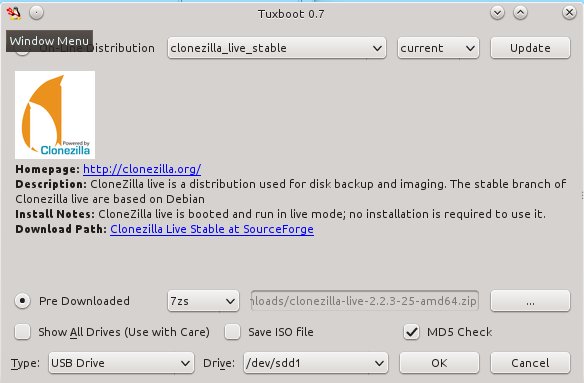
|
||||
图2: 启动Tuxboot
|
||||
<center>*图1: 在USB存储棒上为Clonezilla创建分区*</center>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
安装完Tuxboot后,就可以使用它来创建你精巧的可直接启动的Clonezilla USB存储棒了。首先,创建一个最小200MB的FAT 32分区;图1(上图)展示了使用GParted来进行分区。我喜欢使用类似“Clonezilla”这样的标签,这会让我知道它是个什么东西。该例子中展示了将一个2GB的存储棒格式化成一个单个分区。
|
||||
|
||||
然后,启动Tuxboot(图2)。选中“预下载的(Pre-downloaded)”然后点击带省略号的按钮来选择Clonezilla文件。它会自动发现你的USB存储棒,而你需要选中分区号来确保它找到的是正确的那个,我的例子中是/dev/sdd1。点击确定,然后当它完成后点击退出。它会问你是否要重启动,不要担心,现在不用重启。现在你有一个精巧的便携式Clonezilla USB存储棒了,你可以随时随地使用它了。
|
||||
|
||||
<center></center>
|
||||
|
||||
<center>*图2: 启动Tuxboot*</center>
|
||||
|
||||
### 创建磁盘镜像 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在你想要备份的计算机上启动Clonezilla USB存储棒,第一个映入你眼帘的是常规的启动菜单。启动到默认条目。你会被问及使用何种语言和键盘,而当你到达启动Clonezilla菜单时,请选择启动Clonezilla。在下一级菜单中选择设备镜像,然后进入下一屏。
|
||||
|
||||
这一屏有点让人摸不着头脑,里头有什么local_dev,ssh_server,samba_server,以及nfs_server之类的选项。这里就是要你选择将备份的镜像拷贝到哪里,目标分区或者驱动器必须和你要拷贝的卷要一样大,甚至更大。如果你选择local_dev,那么你需要一个足够大的本地分区来存储你的镜像。附加USB硬盘驱动器是一个不错的,快速而又简单的选项。如果你选择任何服务器选项,你需要有线连接到服务器,并提供IP地址并登录上去。我将使用一个本地分区,这就是说要选择local_dev。
|
||||
这一屏有点让人摸不着头脑,里头有什么local_dev,ssh_server,samba_server,以及nfs_server之类的选项。这里就是要你选择将备份的镜像拷贝到哪里,目标分区或者驱动器必须和你要拷贝的卷要一样大,甚至更大。如果你选择local_dev,那么你需要一个足够大的本地分区来存储你的镜像。附加的USB硬盘驱动器是一个不错的,快速而又简单的选项。如果你选择任何服务器选项,你需要能连接到服务器,并提供IP地址并登录上去。我将使用一个本地分区,这就是说要选择local_dev。
|
||||
|
||||
当你选择local_dev时,Clonezilla会扫描所有连接到本地的存储折本,包括硬盘和USB存储设备。然后,它会列出所有分区。选择你想要存储镜像的分区,然后它会问你使用哪个目录并列出目录。选择你所需要的目录,然后进入下一屏,它会显示所有的挂载以及已使用/可用的空间。按回车进入下一屏,请选择初学者还是专家模式。我选择初学者模式。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -41,12 +44,13 @@ Then fire up Tuxboot (figure 2). Check "Pre-downloaded" and click the button wit
|
||||
|
||||
下一屏中,它会问你新建镜像的名称。在接受默认名称,或者输入你自己的名称后,进入下一屏。Clonezilla会扫描你所有的分区并创建一个检查列表,你可以从中选择你想要拷贝的。选择完后,在下一屏中会让你选择是否进行文件系统检查并修复。我才没这耐心,所以直接跳过了。
|
||||
|
||||
下一屏中,会问你是否想要Clonezilla检查你新创建的镜像,以确保它是可恢复的。选是吧,确保万无一失。接下来,它会给你一个命令行提示,如果你想用命令行而非GUI,那么你必须再次按回车。你需要再次确认,并输入y来确认制作拷贝。
|
||||
下一屏中,会问你是否想要Clonezilla检查你新创建的镜像,以确保它是可恢复的。选“是”吧,确保万无一失。接下来,它会给你一个命令行提示,如果你想用命令行而非GUI,那么你必须再次按回车。你需要再次确认,并输入y来确认制作拷贝。
|
||||
|
||||
在Clonezilla创建新镜像的时候,你可以好好欣赏一下这个友好的红、白、蓝三色的进度屏(图3)。
|
||||
|
||||
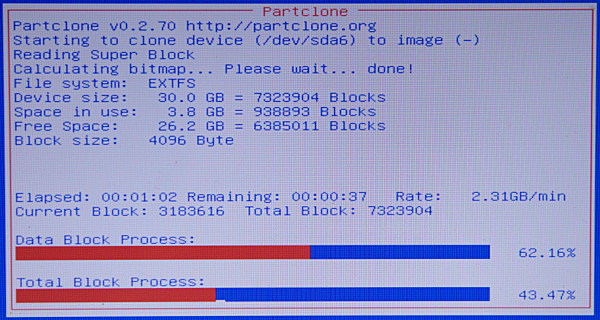
|
||||
图3: 守候创建新镜像
|
||||
<center></center>
|
||||
|
||||
<center>*图3: 守候创建新镜像*</center>
|
||||
|
||||
全部完成后,按回车然后选择重启,记得拔下你的Clonezilla USB存储棒。正常启动计算机,然后去看看你新创建的Clonezilla镜像吧。你应该看到像下面这样的东西:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -81,7 +85,7 @@ via: http://www.linux.com/learn/tutorials/783416-how-to-image-and-clone-hard-dri
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Carla Schroder][a]
|
||||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
|
||||
Linux FAQ -- 如何在VMware ESXi虚拟机上设置静态MAC地址。
|
||||
Linux有问必答:如何在VMware ESXi虚拟机上设置静态MAC地址
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **问题**:我想给VMware ESXi上的一台虚拟机分配一个静态的MAC地址。然而当我开始这么做的时候,虚拟机就不能启动了不且抛出了一个这样一个错误"00:0c:29:1f:4a:ab is not an allowed static Ethernet address. It conflicts with VMware reserved MACs"(00:0c:29:1f:4a:ab不是一个合法的静态以太网地址。它与VMWare的保留MAC地址冲突)。我该如何在VMware ESXi虚拟机上设置静态MAC地址?
|
||||
> **问题**:我想给VMware ESXi上的一台虚拟机分配一个静态的MAC地址。然而当我开始这么做的时候,虚拟机就不能启动了,并且抛出了一个这样一个错误"00:0c:29:1f:4a:ab is not an allowed static Ethernet address. It conflicts with VMware reserved MACs"(00:0c:29:1f:4a:ab不是一个合法的静态以太网地址。它与VMWare的保留MAC地址冲突)。我该如何在VMware ESXi虚拟机上设置静态MAC地址?
|
||||
|
||||
当你在VMware ESXi上创建虚拟机时,虚拟机的每个网络接口就被分配了一个动态的NAC地址。如果你想要改变默认的行为并给你的虚拟机分配一个静态MAC地址时就这样做
|
||||
|
||||
@ -16,7 +16,7 @@ Linux FAQ -- 如何在VMware ESXi虚拟机上设置静态MAC地址。
|
||||
|
||||
首先关闭你想要分配静态MAC地址的虚拟机。
|
||||
|
||||
[对你的ESXi主机启用SSH访问][1]如果你还没这么做的话。接着通过SSH登录ESXi主机。
|
||||
[对你的ESXi主机启用SSH访问][1],如果你还没这么做的话。接着通过SSH登录ESXi主机。
|
||||
|
||||
移到你虚拟机的.vmx文件所在目录。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -35,7 +35,7 @@ Linux FAQ -- 如何在VMware ESXi虚拟机上设置静态MAC地址。
|
||||
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/static-mac-address-vmware-esxi-virtual-machine.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,16 +1,16 @@
|
||||
Linux 下 SSH 命令实例指南
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
如果你已经接触计算机比较长时间, 应该对 SSH 这个了不起的工具及其安全特性有所耳闻吧. 本教程可以让你在短时间内掌握通过 SSH 安全便利地连接到远程计算机的技术.
|
||||
如果你已经在IT圈内混了很长时间, 应该对 SSH 这个了不起的工具及其安全特性有所耳闻吧. 本教程可以让你在短时间内掌握通过 SSH 安全便利地连接到远程计算机的技术.
|
||||
|
||||
如果你对 SSH 还没什么概念, 可以先访问 [维基百科][1] 进行了解.
|
||||
|
||||
### 基本用法 ###
|
||||
|
||||
最简单的 SSH 命令只需要提供用户名和主机名参数即可. 主机名可以是 IP 地址或者域名. 命令格式如下:
|
||||
最简单的 SSH 命令只需要指定用户名和主机名参数即可. 主机名可以是 IP 地址或者域名. 命令格式如下:
|
||||
|
||||
$ ssh user@hostname
|
||||
|
||||
比如要登录到局域网内我的一个树莓派系统, 只需要简单的在命令行输入如下命令:
|
||||
比如要在我的局域网内登录一个树莓派系统, 只需要简单的在命令行输入如下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
$ ssh pi@10.42.0.47
|
||||
|
||||
@ -22,7 +22,7 @@ Linux 下 SSH 命令实例指南
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用其他端口 ###
|
||||
|
||||
SSH 默认连接到目标主机的 22 端口上, 但是由于各种原因你可能需要连接到其他端口.
|
||||
SSH 默认连接到目标主机的 22 端口上,但是由于各种原因你可能需要连接到其他端口.
|
||||
|
||||
$ ssh -p 10022 user@hostname
|
||||
|
||||
@ -30,7 +30,7 @@ SSH 默认连接到目标主机的 22 端口上, 但是由于各种原因你可
|
||||
|
||||
### 远程执行命令 ###
|
||||
|
||||
有时需要很方便地在远程主机执行一条命令并显示到本地, 然后继续本地工作. SSH 就能满足这个需求:
|
||||
有时在远程主机执行一条命令并显示到本地, 然后继续本地工作是很方便的. SSH 就能满足这个需求:
|
||||
|
||||
$ ssh pi@10.42.0.47 ls -l
|
||||
|
||||
@ -38,9 +38,9 @@ SSH 默认连接到目标主机的 22 端口上, 但是由于各种原因你可
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 挂在远程文件系统 ###
|
||||
### 挂载远程文件系统 ###
|
||||
|
||||
有一个很赞的基于 SSH 的工具叫 sshfs. sshfs 可以让你在本地直接挂载远程主机的文件系统.
|
||||
另外一个很赞的基于 SSH 的工具叫 sshfs. sshfs 可以让你在本地直接挂载远程主机的文件系统.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sshfs -o idmap=user user@hostname:/home/user ~/Remote
|
||||
|
||||
@ -50,7 +50,7 @@ SSH 默认连接到目标主机的 22 端口上, 但是由于各种原因你可
|
||||
|
||||
该命令就将远程主机 pi 用户的主目录挂载到本地主目录下的 Pi 文件夹.
|
||||
|
||||
要详细了解可以参考 [sshfs 入门教程][2].
|
||||
要详细了解可以参考 [sshfs 教程][2].
|
||||
|
||||
### X11 图形界面 ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -114,7 +114,7 @@ SSH 提供了多样的转义字符功能. 用 SSH 连接到任意一台远程主
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结 ###
|
||||
|
||||
通过以上的内容你应该可以很轻松的使用 SSH 了. SSH 还有很多功能值得你去发掘, 这就要看你的想象力了.
|
||||
通过以上的内容你应该可以轻松使用 SSH 了. SSH 还有很多功能值得你去发掘, 这就要看你的想象力了。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
@ -123,7 +123,7 @@ via: http://linoxide.com/linux-command/pocket-guide-linux-ssh-command/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Bobbin Zachariah][a]
|
||||
译者:[henryfour](https://github.com/henryfour)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,155 @@
|
||||
15个关于Linux的‘cd’命令的练习例子
|
||||
===========================
|
||||
|
||||
在Linux中,**‘cd‘(改变目录)**命令,是对新手和系统管理员来说,最重要最常用的命令。对管理无图形界面的服务器的管理员,‘**cd**‘是进入目录,检查日志,执行程序/应用软件/脚本和其余每个任务的唯一方法。对新手来说,是他们必须自己动手学习的最初始命令
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*Linux中15个cd命令举例*
|
||||
|
||||
所以,请用心学习,我们在这会带给你**15**个基础的‘**cd**‘命令,它们富有技巧和捷径,学会使用这些了解到的技巧,会大大减少你在终端上花费的努力和时间
|
||||
|
||||
### 课程细节 ###
|
||||
|
||||
- 命令名称:cd
|
||||
- 代表:切换目录
|
||||
- 使用平台:所有Linux发行版本
|
||||
- 执行方式:命令行
|
||||
- 权限:访问自己的目录或者其余指定目录
|
||||
- 级别:基础/初学者
|
||||
|
||||
1. 从当前目录切换到/usr/local
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:~$ cd /usr/local
|
||||
avi@tecmint:/usr/local$
|
||||
|
||||
2. 使用绝对路径,从当前目录切换到/usr/local/lib
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:/usr/local$ cd /usr/local/lib
|
||||
avi@tecmint:/usr/local/lib$
|
||||
|
||||
3. 使用相对路径,从当前路径切换到/usr/local/lib
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:/usr/local$ cd lib
|
||||
avi@tecmint:/usr/local/lib$
|
||||
|
||||
4. **(a)**切换当前目录到上级目录
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:/usr/local/lib$ cd -
|
||||
/usr/local
|
||||
avi@tecmint:/usr/local$
|
||||
|
||||
**(b)**切换当前目录到上级目录
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:/usr/local/lib$ cd ..
|
||||
avi@tecmint:/usr/local$
|
||||
|
||||
5. 显示我们最后一个离开的工作目录(使用‘-’选项)
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:/usr/local$ cd --
|
||||
/home/avi
|
||||
|
||||
6. 从当前目录向上级返回两层
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:/usr/local$ cd ../../
|
||||
avi@tecmint:/$
|
||||
|
||||
7. 从任何目录返回到用户home目录
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:/usr/local$ cd ~
|
||||
avi@tecmint:~$
|
||||
|
||||
或
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:/usr/local$ cd
|
||||
avi@tecmint:~$
|
||||
|
||||
8. 切换工作目录到当前工作目录(LCTT:这有什么意义嘛?!)
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:~/Downloads$ cd .
|
||||
avi@tecmint:~/Downloads$
|
||||
|
||||
或
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:~/Downloads$ cd ./
|
||||
avi@tecmint:~/Downloads$
|
||||
|
||||
9. 你当前目录是“/usr/local/lib/python3.4/dist-packages”,现在要切换到“/home/avi/Desktop/”,要求:一行命令,通过向上一直切换直到‘/’,然后使用绝对路径
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:/usr/local/lib/python3.4/dist-packages$ cd ../../../../../home/avi/Desktop/
|
||||
avi@tecmint:~/Desktop$
|
||||
|
||||
10. 从当前工作目录切换到/var/www/html,要求:不要将命令打完整,使用TAB
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:/var/www$ cd /v<TAB>/w<TAB>/h<TAB>
|
||||
avi@tecmint:/var/www/html$
|
||||
|
||||
11. 从当前目录切换到/etc/v__ _,啊呀,你竟然忘了目录的名字,但是你又不想用TAB
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:~$ cd /etc/v*
|
||||
avi@tecmint:/etc/vbox$
|
||||
|
||||
**请注意:**如果只有一个目录以‘**v**‘开头,这将会移动到‘**vbox**‘。如果有很多目录以‘**v**‘开头,而且命令行中没有提供更多的标准,这将会移动到第一个以‘**v**‘开头的目录(按照他们在标准字典里字母存在的顺序)
|
||||
|
||||
12. 你想切换到用户‘**av**‘(不确定是avi还是avt)目录,不用**TAB**
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:/etc$ cd /home/av?
|
||||
avi@tecmint:~$
|
||||
|
||||
13. Linux下的pushed和poped
|
||||
|
||||
Pushed和poped是Linux bash命令,也是其他几个能够保存当前工作目录位置至内存,并且从内存读取目录作为当前目录的脚本,这些脚本也可以切换目录
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:~$ pushd /var/www/html
|
||||
/var/www/html ~
|
||||
avi@tecmint:/var/www/html$
|
||||
|
||||
上面的命令保存当前目录到内存,然后切换到要求的目录。一旦poped被执行,它会从内存取出保存的目录位置,作为当前目录
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:/var/www/html$ popd
|
||||
~
|
||||
avi@tecmint:~$
|
||||
|
||||
14. 切换到名字带有空格的目录
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:~$ cd test\ tecmint/
|
||||
avi@tecmint:~/test tecmint$
|
||||
|
||||
或
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:~$ cd 'test tecmint'
|
||||
avi@tecmint:~/test tecmint$
|
||||
|
||||
或
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:~$ cd "test tecmint"/
|
||||
avi@tecmint:~/test tecmint$
|
||||
|
||||
15. 从当前目录切换到下载目录,然后列出它所包含的内容(使用一行命令)
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:/usr$ cd ~/Downloads && ls
|
||||
...
|
||||
.
|
||||
service_locator_in.xls
|
||||
sources.list
|
||||
teamviewer_linux_x64.deb
|
||||
tor-browser-linux64-3.6.3_en-US.tar.xz
|
||||
.
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
我们尝试使用最少的词句和一如既往的友好,来让你了解Linux的工作和执行
|
||||
|
||||
这就是所有内容。我很快会带着另一个有趣的主题回来的。
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/cd-command-in-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Avishek Kumar][a]
|
||||
译者:[su-kaiyao](https://github.com/su-kaiyao)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/avishek/
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,67 @@
|
||||
中国将要改变软件购买和销售的方式
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
> 这一切都是关于“开源”.
|
||||
|
||||
**中国并不需要你,也不需要你的软件。具体说来,中国市场并不需要你的工程师日以继夜的工作,也不需要你提供的任何东西。
|
||||
|
||||
中国每年会产生超过100000名新软件工程师。这些工程师会写出一大批令人惊叹的奇妙软件。如果有中国市场上尚未出现的软件,中国的工程师们就会从国外“借鉴”。在2012年,这样的软件掠夺达到了77%之多。对于那些已经面对着开源和云服务的挑战的西方软件卖家来说,中国无疑让他们的日子更苦难了。
|
||||
|
||||
不止是更困难,简直是举步维艰。
|
||||
|
||||
中国正在挑战西方公司在中国及其他地区的赚钱模式。对于那些已经明白如何在中国运营的公司来说,他们的未来看起来一片光明。
|
||||
|
||||
### 抵制中国模式 ###
|
||||
|
||||
当然,并非每家公司都会坐以待毙。以微软为例,微软已经通过[行使美国的国家司法权力来禁止中国公司做生意][1]——除非他们向微软购买许可证。这是一种很聪明的做法,而且它可能会为微软创造数十亿美元的价值,但是最终这一做法看起来与中国市场格格不入。
|
||||
|
||||
原因很简单,中国与微软对待知识产权的态度十分不同。
|
||||
|
||||
正如 [我所提到的][2],“与同在亚洲的印度十分相似,中国的企业更倾向于购买复杂的、面向企业的软件。因为这种软件比服务大众的公司开发出来的更为先进。”但这种形势不会持续太久,因为中国的软件产业正在以一种惊人的速度前进,并毫无颓势。中国将会坚持向西方国家“借鉴”代码,直到有一天有足够的能力可以创造出创新性的软件。
|
||||
|
||||
但即使到那时候,中国的软件公司与美国软件的运营模式还是有所不同,美国的软件大多都已经捆绑在设备、架构在云端或者公司只靠提供软件支持而盈利。而这些运营模式都是无法克隆的。
|
||||
|
||||
不出所料,接下来的问题将是,这些公司将如何通过“开源”来盈利。
|
||||
|
||||
### 开源化中国 ###
|
||||
|
||||
正如CCID的分析师在 [J. Aaron Farr 的关于中国开源化报告][3] 中指出的,中国的开源社区规模很小而且没什么影响力。开源社区中缺少大项目、参与者稀少而且资金匮乏。
|
||||
|
||||
这真是个坏消息。
|
||||
|
||||
而好消息是,华为等公司将开源视为一种战略前景。具体而言,当[华为的开源项目网页][4]过时或疲软之时,就间接显示出了技术大步伐的前进方向。在与参与了开源项目的华为公司内部顾问的谈话中,虽然华为对如何参与到开源社区还处于摸索阶段,但他们总是对华为的开源项目赞不绝口。
|
||||
|
||||
这看起来并不容易坚持长久。
|
||||
|
||||
从一件事就可以看出端倪。中国最大的互联网公司们都纷纷以积极地姿态拥抱开源,这意味着中国开源时代的到来。你若是和任意一位在百度、阿里巴巴、微博的员工谈话,你会发现他们的软件项目都是彻底开源的。这些开源的软件都是运行在这些公司自己研发的硬件上而不是西方的硬件上。
|
||||
|
||||
换句话说,这样的模式已经和美国及西欧的运营模式如出一辙了。
|
||||
|
||||
抬头看看 [现金软件行业内最炙手可热的新公司][5], 你就会知道中国的互联网公司未来的主流趋势,正如发生在西方世界的一样。不出意料的,许多都是关于“开源”。
|
||||
|
||||
### 销售给中国 ###
|
||||
|
||||
所有的一切都表明中国的软件行业不会像美国的软件行业发展历史一般发展。中国不会产生在柜台上卖卖软件就赚上亿美元的公司。因为西方对于知识产权的观念无法简单适用于中国的科技经济。
|
||||
|
||||
所以,商家们需要售卖比软件更丰富的产品。云服务是一大前景。硬件设施看起来也是前途璀璨。软件支持和咨询服务(虽然有一些非主流)也很被公司门看好。总而言之,中国的软件行业将会充满开源味道,而不能靠着简单的售卖专柜软件的形式赚钱。
|
||||
|
||||
图片由 [hackNY.org][6] 提供。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
原文: http://readwrite.com/2014/08/12/china-opensource-software-ip-programmers-united-states
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Matt Asay][a]
|
||||
译者:[chi1shi2](https://github.com/chi1shi2)
|
||||
校对:[reinoir](https://github.com/reinoir)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://readwrite.com/author/matt-asay
|
||||
[1]:http://readwrite.com/2014/03/17/microsoft-anti-piracy-strategy-china
|
||||
[2]:http://readwrite.com/2014/04/11/india-starts-paying-for-software-china-it
|
||||
[3]:http://cdn.oreillystatic.com/en/assets/1/event/12/Open%20Source%20in%20China%20Presentation%201.pdf
|
||||
[4]:http://huawei.com/en/about-huawei/Partner/openathuawei/index.htm
|
||||
[5]:http://codingvc.com/which-technologies-do-startups-use-an-exploration-of-angellist-data
|
||||
[6]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/hackny/8675057448/
|
||||
@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
|
||||
Linux FAQ -- 如何在CentOS或者RHEL上启用Nux Dextop仓库
|
||||
Linux有问必答:如何在CentOS或者RHEL上启用Nux Dextop仓库
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **问题**: 我想要安装一个在Nux Dextop仓库的RPM包。我该如何在CentOS或者RHEL上设置Nux Dextop仓库?
|
||||
|
||||
@ -6,7 +6,7 @@ Linux FAQ -- 如何在CentOS或者RHEL上启用Nux Dextop仓库
|
||||
|
||||
要在CentOS或者RHEL上启用Nux Dextop,遵循下面的步骤。
|
||||
|
||||
首先,要理解Nux Dextop被设计与EPEL仓库共存。因此,你需要使用Nux Dexyop仓库前先[启用 EPEL][2]。
|
||||
首先,要知道Nux Dextop被设计与EPEL仓库共存。因此,你需要在使用Nux Dexyop仓库前先[启用 EPEL][2]。
|
||||
|
||||
启用EPEL后,用下面的命令安装Nux Dextop仓库。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -26,13 +26,13 @@ Linux FAQ -- 如何在CentOS或者RHEL上启用Nux Dextop仓库
|
||||
|
||||
### 对于 Repoforge/RPMforge 用户 ###
|
||||
|
||||
据作者所说,Nux Dextop目前所知会与其他第三方库比如Repoforge和ATrpms相冲突。因此,如果你启用了除了EPEL的其他第三方库,强烈建议你将Nux Dextop仓库设置成“default off”(默认关闭)状态。就是用文本编辑器打开/etc/yum.repos.d/nux-dextop.repo,并且在nux-desktop下面将"enabled=1" 改成 "enabled=0"。
|
||||
据作者所说,目前已知Nux Dextop会与其他第三方库比如Repoforge和ATrpms相冲突。因此,如果你启用了除了EPEL的其他第三方库,强烈建议你将Nux Dextop仓库设置成“default off”(默认关闭)状态。就是用文本编辑器打开/etc/yum.repos.d/nux-dextop.repo,并且在nux-desktop下面将"enabled=1" 改成 "enabled=0"。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo vi /etc/yum.repos.d/nux-dextop.repo
|
||||
$ sudo vi /etc/yum.repos.d/nux-dextop.repo
|
||||
|
||||
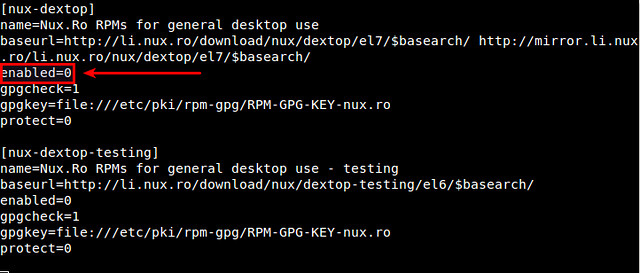
|
||||
|
||||
当你无论何时从Nux Dextop仓库安装包时,显式地用下面的命令启用仓库。
|
||||
无论何时当你从Nux Dextop仓库安装包时,显式地用下面的命令启用仓库。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum --enablerepo=nux-dextop install <package-name>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -41,7 +41,7 @@ $ sudo vi /etc/yum.repos.d/nux-dextop.repo
|
||||
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/enable-nux-dextop-repository-centos-rhel.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[ wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
|
||||
Linux有问必答——如何修复“运行aclocal失败:没有该文件或目录”
|
||||
Linux有问必答:如何修复“运行aclocal失败:没有该文件或目录”
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **问题**:我试着在Linux上构建一个程序,该程序的开发版本是使用“autogen.sh”脚本进行的。当我运行它来创建配置脚本时,却发生了下面的错误:
|
||||
>
|
||||
@ -24,7 +24,7 @@ Linux有问必答——如何修复“运行aclocal失败:没有该文件或
|
||||
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/fix-failed-to-run-aclocal.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
32
published/20140829 Linux Doesn't Need to Own the Desktop.md
Normal file
32
published/20140829 Linux Doesn't Need to Own the Desktop.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,32 @@
|
||||
Linux 应当放弃桌面
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Linus Torvalds 前不久发布了 Linux 3.17 rc-2,这[偏离了他正常的发布时间表][1],因为8月25日是 Linux 的第23个生日。“Hello 大家好,你还在使用minix吗?”,23年前的8月25日,Torvalds 在 Linux 的第一次发布中这样写道。
|
||||
|
||||
与此同时,最近 PCMag.com 网站声称[Linux 的时间已经不多了][2]。但是你们不觉得这样没玩没了地讨论 Linux 在桌面端是否成功其实是毫无意义的吗?Linux 已经广泛应用于超级计算机和车载系统,它构建了 Android 的基础,同时还是最流行的云整合(例如 OpenStack)的运行平台 —— 以上这些还只是 Linux 的一部分成就。桌面并不是 Linux 唯一的战场。
|
||||
|
||||
Jon Buys 在他[最近的文章][3]中谈到了 Linux 专业化以及与桌面有关的内容:
|
||||
|
||||
> “最近,IT业在追问‘[Linus 是否还在执著于 Linux 桌面?][4]’,来自 Teck Republic 的 Matt Asay 也在说‘[拜托不要再讨论 Linux 桌面了行吗?][5]’。这两篇文章都对 Linux 在个人计算机方面的发展空间持怀疑态度,还拿 Android 的成功故事来说事…… 但是它们都忽略了,Linux的灵活性以及它开源许可证的开放性,也许这两者正是拯救 Linux 桌面的关键。”
|
||||
|
||||
也许这是事实,但是 Linux 对于如此众多的桌面用户来说,还是太多余了。Linux 分享庞大市场的最佳机会已经来也匆匆去也匆匆了。
|
||||
|
||||
事实其实很简单,Linux已经改变了世界,获得了无与伦比的成功 —— 除了桌面系统,这毋庸置疑。Android已经不仅仅是一个基于Linux的平台,它已经成为了一个伟大的标志。Linux在服务器端和嵌入式技术领域占有巨大的份额,同时也为平台整合方面不断提供创新动力。Ubuntu已经成为部署搭建 OpenStack 最流行的平台。全世界的超级计算机都运行着 Linux,Chrome OS 也是基于 Linux。
|
||||
|
||||
因此,Linux 正在不断推动着整个世界的巨变,批评家们是时候停下来执著于 Linux 在桌面端的状态了。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ostatic.com/blog/linux-doesnt-need-to-own-the-desktop
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Sam Dean][a]
|
||||
译者:[Mr小眼儿](http://blog.csdn.net/tinyeyeser)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://ostatic.com/member/samdean
|
||||
[1]:http://www.theregister.co.uk/2014/08/26/linux_turns_23_and_linus_torvalds_celebrates_as_only_he_can/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.pcmag.com/article2/0,2817,2465125,00.asp
|
||||
[3]:http://ostatic.com/blog/specialization-and-the-linux-desktop
|
||||
[4]:http://www.itworld.com/open-source/432816/does-it-still-make-sense-linus-want-desktop-linux
|
||||
[5]:http://www.techrepublic.com/article/can-we-please-stop-talking-about-the-linux-desktop/
|
||||
25
published/20140902 Happy Birthday Email.md
Normal file
25
published/20140902 Happy Birthday Email.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,25 @@
|
||||
他发明了 Email ?
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
[编者按:本文所述的 Email 发明人的观点存在很大的争议,请读者留意,以我的观点来看,其更应该被称作为某个 Email 应用系统的发明人,其所发明的一些功能和特性,至今沿用。——wxy]
|
||||
|
||||
**一个印度裔美国人用他天才的头脑发明了电子邮件,而从此以后我们没有哪一天可以离开电子邮件。**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
8月30日,电子邮件满32岁了。现在让我们一起熟悉一下这个快捷迅速的信息传递方式是怎么诞生的。这要感谢以为印度裔美国人,Shiva Ayyadurai。Shiva开发了一个全功能的办公室间邮件系统软件并命名为email。
|
||||
|
||||
在1982年8月30日,他被美国政府正式承认作为这个电脑程序的发明者。Shiva生于孟买的一个泰米尔家庭,发明email系统的时候只有14岁。当时他还在新泽西的利文斯顿高中学习,并开始为新泽西牙科和医科大学开发这个系统。email系统被授予版权,因为当时还没有其他方式被用来保护软件发明。
|
||||
|
||||
Ayyadurai从日常办公室之间的内部邮件往来方式里找到email系统的点子。他尝试复制普遍用来传送办公室之间邮件的‘气动管道系统’。这个系统使用了一个物理的管道网络来传送打印好的邮件给秘书。每一位秘书都有收件箱,发件箱,草稿箱,复写纸,文件夹,地址本,别针,或是附件等等。所有这些都用作建立和处理接收和发送邮件。
|
||||
|
||||
Shiva也记下了一些常用的模板,像“发给”,“来自”,“主题”,“日期”,“正文”,“抄送”,“密送”等等。所有这些模版也都被纳入电子邮件的版本中。电子邮件系统是用FORTRAN编程语言写的,Shiva发明了一个同样系统的电子版本。因为这件非凡的作品,Shiva获得了无数嘉奖,也赢得了1981年度高中毕业生的西屋科学天才奖。如今,由史密森学会美国历史国家博物馆持有“Email”的正式美国版权。但是,也有争论说不是Ayyadurai而是其他什么人发明了email。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.efytimes.com/e1/fullnews.asp?edid=147170
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Sanchari Banerjee
|
||||
译者:[zpl1025](https://github.com/zpl1025)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,111 @@
|
||||
如何在linux上分享你shell命令的输出
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
前段时间我发布了一篇关于[shelr.tv][1]这个网站的文章,它提供一个服务允许你从网站上直接分享你的[终端][2]记录。
|
||||
|
||||
现在shelr.tv这个网站似乎关闭了,然后我四处寻找是否有类似的网站,于是我发现了[commands.com][3]。
|
||||
|
||||
从它的主页上来看,它的服务和其他网站提供的服务是类似的,因此让我们来测试它。
|
||||
|
||||
### 步骤 1 – 在网站上注册 ###
|
||||
|
||||
只需要[注册][4]一个新的 用户名/密码,或者直接使用你的github账户快速登录。
|
||||
|
||||
### 步骤 2 – 下载安装monitor程序 ###
|
||||
|
||||
[Monitor][5]是一个命令行工具,它能捕获命令行的输入输出并且发送到commands.com网站上,这个程序是开源的,并托管在github上。
|
||||
|
||||
Monitor使得仓库的设置/安装变得更简单。通过它,你能方便地向人们展示最常见的错误与命令的输出。
|
||||
|
||||
简而言之,你能方便地和世界分享你的命令及其输出。
|
||||
|
||||
通过如下简单几步来安装它:
|
||||
|
||||
1) 克隆github上的这个项目的仓库,这样你能获得最新的源代码。
|
||||
|
||||
要完成这步,你需要在系统中已经安装了git命令,如果你得到关于这个命令的报错信息,你可以使用包管理工具来安装它,例如:
|
||||
|
||||
基于Debian的发布版:
|
||||
|
||||
apt-get install git
|
||||
|
||||
Redhat/Centos/Fedora发布版:
|
||||
|
||||
yum install git
|
||||
|
||||
现在从终端克隆这个仓库:
|
||||
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/dtannen/monitor.git
|
||||
|
||||
2) 安装readline和curl,这些库是通过源码构建程序的先决条件:
|
||||
|
||||
基于Debian的发布版:
|
||||
|
||||
apt-get install libreadline-dev libcurl4-openssl-dev
|
||||
|
||||
Redhat/Centos/Fedora发布版:
|
||||
|
||||
yum install readline-devel curl-devel
|
||||
|
||||
3) 构建程序:
|
||||
|
||||
要完成这步,你必须进入刚刚用git克隆的目录,然后编译这个c程序:
|
||||
|
||||
cd monitor
|
||||
make
|
||||
sudo make install
|
||||
|
||||
默认安装将把二进制文件放入/usr/local/bin目录下。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 步骤 3 – 使用monitor命令###
|
||||
|
||||
monitor命令特别简单易用:
|
||||
|
||||
monitor {-d} {-h} {-u <username>}
|
||||
|
||||
-d : 不删除/tmp下的文件
|
||||
-h : 帮助
|
||||
-u : commands.com用户名</username>
|
||||
|
||||
要退出monitor程序,需要按ctrl-c。
|
||||
|
||||
对我来说这仅仅意味着打开一个终端然后执行这些命令:
|
||||
|
||||
riccio@mint-desktop ~ $ monitor -u ricciocri
|
||||
Password:
|
||||
|
||||
Successfully logged in...
|
||||
AuthKey saved to /tmp/.riccio.commands.com. Delete file to return to Anonymous posting.
|
||||
monitor$ cd /tmp
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
想知道在这之后我使用过的哪个命令吗?我已经把这个会话公开(默认是私有),因此你可以去这个url查看:[https://commands.com/JTNSHRLQJA][6]
|
||||
|
||||
在这里,你能看我已经使用过的命令以及它们的输出,一个有趣的选项是“fold/expand”你可以折叠(fold)所有的命令的输出或者仅仅展开(expand)你喜欢的那个命令的输出。
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结 ###
|
||||
|
||||
这只是一个简单的安装指南,在这个网站上你能参加更多“社会化”的活动,比如评论脚本/shell会话,派生它们或者选择你的最爱。
|
||||
|
||||
和github一样,你能派生任何一个公开的脚本/命令并能直接在网站上改变它,然后你也能得到一个公开(或私有)的url。你可以直接运行你脚本,就像这样:
|
||||
|
||||
curl commands.io/JTNSHRLQJA | sh
|
||||
|
||||
在网络上储存一些你在电脑/服务器上经常使用到的脚本,这是极好的,通常不要放置任何密码或敏感信息,这样你的信息才足够安全。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linuxaria.com/article/how-to-share-on-linux-the-output-of-your-shell-commands
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[guodongxiaren](https://github.com/guodongxiaren)
|
||||
校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://linuxaria.com/recensioni/shelr-broadcast-your-linux-shell-on-the-net
|
||||
[2]:http://linuxaria.com/tag/shell
|
||||
[3]:https://commands.com/
|
||||
[4]:https://commands.com/Register/Index
|
||||
[5]:https://github.com/dtannen/monitor
|
||||
[6]:https://commands.com/JTNSHRLQJA
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,26 @@
|
||||
Ubuntu商城有了一款 Ubuntu Touch 的 BT 客户端了
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Ubuntu触屏平台已经拥有许多有趣应用程序,甚至看起来很多开发者已经开始实现许多超乎期望的软件,像BT客户端就是个很好的例子。**
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu触屏设备的应用商店在过去几个月一直平稳增长并增添了许多有趣的应用程序。其中大多数都已经满足操作系统的基本需求,但也有不少远远超出普通用户的需求。
|
||||
|
||||
你会发现在大多数手机中BT客户端并不是必备的东西。Android和Windows手机已经已经有这类的应用程序,看起来Ubuntu也将是支持的平台之一。Ubuntu开发者[Alan Pope][1]公布了一张正在为Ubuntu平台开发的应用程序的截图,该程序命名为DowNow。
|
||||
|
||||
这是一个相对较新的应用程序,而且仍然在开发中,你可以在Launchpad点击DowNow 0.3安装包,如果你想要获得更多详情,你也可以从Ubuntu软件中心下载。
|
||||
|
||||
目前,只有Nexus4和Nexus7设备支持,如果你想要在更多手机上尝试Ubuntu,也许还要等待几个月。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/Ubuntu-Touch-Now-Has-a-Torrent-Clinent-in-the-Ubuntu-Store-457538.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Silviu Stahie][a]
|
||||
译者:[disylee](https://github.com/disylee)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://news.softpedia.com/editors/browse/silviu-stahie
|
||||
[1]:https://plus.google.com/u/0/+AlanPope/posts/Ej3vKVxBum8
|
||||
@ -1,5 +1,4 @@
|
||||
2q1w2007翻译中
|
||||
[小贴士] 怎么在Linux发行版下列出所有安装了的包
|
||||
怎么在Linux发行版下列出所有安装了的包
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@ -39,7 +38,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
dpkg -l
|
||||
|
||||
祝你有好的一天。
|
||||
祝你一天好心情。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
@ -47,7 +46,7 @@ via: http://www.unixmen.com/quick-tip-list-installed-packages-linux-distribution
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Enock Seth Nyamador][a]
|
||||
译者:[2q1w2007](https://github.com/2q1w2007)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,59 @@
|
||||
在Ubuntu14.04上安装UberWriterMarkdown编辑器
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
这是一篇快速教程指导我们如何通过官方的PPA源在Ubuntu14.04上安装UberWriter编辑器。
|
||||
|
||||
[UberWriter][1]是一款Ubuntu下的Markdown编辑器,它简洁的界面能让我们更致力于编辑文字。UberWriter利用了[pandoc][3](一个格式转换器)。但由于UberWriter的UI是基于GTK3的,因此不能完全兼容Unity桌面系统。以下是对UberWriter功能的列举:
|
||||
|
||||
- 简洁的界面
|
||||
- 使用pandoc转换markdown
|
||||
- 可预览
|
||||
- 免打扰模式
|
||||
- 拼写检查
|
||||
- 语法高亮,能在html和pdf中出现数学公式
|
||||
- 支持导出到PDF,HTML,ODT等
|
||||
|
||||
### 在Ubuntu14.04上安装UberWriter ###
|
||||
|
||||
UberWriter可以在[Ubuntu软件中心][4]中找到但是安装需要支付5刀。如果你真的喜欢这款编辑器并想为开发者提供一些资金支持的话,我很建议你购买它。
|
||||
|
||||
除此之外,UberWriter也能通过官方的PPA源来免费安装。通过如下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:w-vollprecht/ppa
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install uberwriter
|
||||
|
||||
安装完毕之后,你可以通过Unity的Dash运行使用。如你所见,它支持markdown的语法高亮:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
你可以使用预览功能来查看你的文档:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
我尝试导出到PDF的时候被提示安装texlive。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
虽然导出到HTML和ODT格式是好的。
|
||||
|
||||
在Linux下还有一些其他的markdown编辑器。[Remarkable][5]是一款能够实时预览的编辑器,UberWriter却不能,不过总的来说它是一款很不错的应用。如果你在寻找文本编辑器的话,你可以试试[Texmaker LaTeX editor][6]。
|
||||
|
||||
系统这个教程能够帮你在Ubuntu14.04上成功安装UberWriter。我猜想UberWriter在Ubuntu12.04,Linux Mint 17,Elementary OS和其他在Ubuntu的基础上的Linux发行版上也能成功安装。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/install-uberwriter-markdown-editor-ubuntu-1404/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek][a]
|
||||
译者:[John](https://github.com/johnhoow)
|
||||
校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://itsfoss.com/author/Abhishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://uberwriter.wolfvollprecht.de/
|
||||
[2]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Markdown
|
||||
[3]:http://johnmacfarlane.net/pandoc/
|
||||
[4]:apt://uberwriter
|
||||
[5]:http://itsfoss.com/remarkable-markdown-editor-linux/
|
||||
[6]:http://itsfoss.com/install-latex-ubuntu-1404/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,38 @@
|
||||
如何“上手”体验乌托邦独角兽!
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**想要知道如何在正式发布前上手体验乌托邦独角兽(Utopic Unicorn)?现在你就可以做到!—— 真的是[“上手”][1]体验哦~!**
|
||||
|
||||
显然是为了庆祝即将发布的同名Ubuntu,Canonical上线了一款“手把手教你独角兽折纸指南”。这一活动作为该公司[2014 Deconstruct][2] 大会的一部分出现,大会于九月上旬在英国Brighton举办。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
供图: Alejandra Obregon
|
||||
|
||||
大会为期一天,为富有创造力的专家以及数字文化狂热者们提供了一个理想的交流场所,Canonical将展示一个正在开发中版本的 Ubuntu Phone,内容包括具体的设计以及用户交互界面,用以满足与会观众。
|
||||
|
||||
人们对这一折纸活动的反响很积极。折纸独角兽作品最棒的人,将会获得一部全新的 Ubuntu 手机,这大大激发了人们的积极性。
|
||||
|
||||
### 下载折纸独角兽 ###
|
||||
|
||||
其余没有获奖的朋友,也不要气馁,下载折纸独角兽还是会有惊喜哦~
|
||||
|
||||
如果你有五分钟的休息时间,为什么不玩玩这个折纸娱乐一下呢?如果你认为自己折出来的独角兽非常非常出(la)色(ji),请在[Twitter][3] 或 [Google+][4]上给我们发照片~(译者表示不爽!这是诚心不给我们天朝百姓获奖的机会吗?)
|
||||
|
||||
- [下载 ‘Make a Unicorn’ 手工折纸][5]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/09/unicorn-origami-download-pdf-ubuntu-utopic
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Joey-Elijah Sneddon][a]
|
||||
译者:[Mr小眼儿](http://blog.csdn.net/tinyeyeser)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://plus.google.com/117485690627814051450/?rel=author
|
||||
[1]:http://design.canonical.com/2014/09/canonical-and-ubuntu-at-dconstruct/
|
||||
[2]:http://2014.dconstruct.org/
|
||||
[3]:http://twitter.com/omgubuntu
|
||||
[4]:http://plus.google.com/+omgubuntu
|
||||
[5]:http://design.canonical.com/wp-content/uploads/042_CAN_dConstruct_instructions.pdf
|
||||
@ -1,47 +1,46 @@
|
||||
2q1w2007翻译中
|
||||
QuiteRSS: Linux桌面的RSS阅读器
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
[QuiteRSS][1]是一个自由而[开源][2]的RSS/Atome阅读器。它可以运行在Windows , Linux和Mac上运行。它用C++/QT编写,所以它会有更好的未来。
|
||||
[QuiteRSS][1]是一个免费的[开源][2]RSS/Atome阅读器。它可以在Windows、Linux和Mac上运行。它用C++/QT编写。它有许多的特色功能。
|
||||
|
||||
QuiteRSS的界面让我想起Lotus Notes mail,会有很多RSS信息排列在大小合适的方块上,你可以通过标签分组。需要查找东西时,只需在下面板上打开RSS信息。
|
||||
QuiteRSS的界面让我想起Lotus Notes mail,会有很多RSS信息排列在右侧面板上,你可以通过标签分组。点击一个 RSS 条目时,会在下方的面板里面显示该信息。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
除了上述功能,它还有一个广告屏蔽器,一个报纸输出视图,通过URL特性导入RSS等众多功能。你可以在[这里][3]查找到完整的功能列表。
|
||||
除了上述功能,它还有一个广告屏蔽器,一个报纸视图,通过URL导入RSS源等众多功能。你可以在[这里][3]查找到完整的功能列表。
|
||||
|
||||
### 在 Ubuntu 和 Linux Mint 上安装 QuiteRSS ###
|
||||
|
||||
QuiteRSS在Ubuntu 14.04 和 Linux Mint 17中可用。你可以很简单的通过以下命令行安装:
|
||||
QuiteRSS在Ubuntu 14.04 和 Linux Mint 17中可用。你可以通过以下命令行轻松安装:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install quiterss
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想安装最新的稳定版本,你可以用官方的[QuiteRSS PPA][4]:
|
||||
如果你想安装最新的稳定版本,你可以使用官方的[QuiteRSS PPA][4]:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:quiterss/quiterss
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install quiterss
|
||||
|
||||
上面的命令在所有基于Ubuntu的发行版像 Linux Mint, Elementary OS, Linux Lite, Pinguy OS 都应该好用。在其他Linux发行版和平台上,你可以从 [下载页][5]获得源码来安装.
|
||||
上面的命令支持所有基于Ubuntu的发行版,比如Linux Mint, Elementary OS, Linux Lite, Pinguy OS等等。对于其他Linux发行版和平台上,你可以从 [下载页][5]获得源码来安装。
|
||||
|
||||
### 卸载 QuiteRSS ###
|
||||
|
||||
用下方命令卸载 QuiteRSS:
|
||||
用下列命令卸载 QuiteRSS:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get remove quiterss
|
||||
|
||||
如果你用了PPA,你还需要从源列表中把仓库删除:
|
||||
如果你使用了PPA,你还也应该从源列表中把仓库删除:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository --remove ppa:quiterss/quiterss
|
||||
|
||||
QuiteRSS是一个不错的开源RSS阅读器,尽管我更喜欢[Feedly][6]。尽管现在 Feedly 还没有Linux桌面程序,但是你依然可以在网页浏览器中使用。我希望你会认为QuiteRSS值得一试。
|
||||
QuiteRSS是一个不错的开源RSS阅读器,尽管我更喜欢[Feedly][6]。不过现在 Feedly 还没有Linux桌面程序,但是你依然可以在网页浏览器中使用。希望你会觉得QuiteRSS值得在桌面Linux一试。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/quiterss-rss-reader-desktop-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek][a]
|
||||
译者:[2q1w2007(https://github.com/2q1w2007)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[2q1w2007](https://github.com/2q1w2007)
|
||||
校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -51,4 +50,4 @@ via: http://itsfoss.com/quiterss-rss-reader-desktop-linux/
|
||||
[3]:http://quiterss.org/en/about
|
||||
[4]:https://launchpad.net/~quiterss/+archive/ubuntu/quiterss/
|
||||
[5]:http://quiterss.org/en/download
|
||||
[6]:http://feedly.com/
|
||||
[6]:http://feedly.com/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,127 @@
|
||||
从Windows双启动中卸载Ubuntu Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
我在过去已经多次涉及到[在UEFI模式下安装Ubuntu 14.04与Windows 8/8.1双启动][1]的话题。 但是要怎么从**Windows双启动中卸载Ubuntu呢**?下面我们将看到的教程适用于任意的Linux操作系统,如Ubuntu,Linux Mint,Elementary OS或其它任意Linux发行版。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你认为[在双启动模式下安装Ubuntu与Windows 8共存][2]是件难事,而从Windows双启动中移除Ubuntu将是很简单的,你的想法并不是完全错误的。如果你有个Windows安装介质的话,从Windows双启动中卸载Linux将是轻而易举的。
|
||||
|
||||
这个教程将教你如何在有**Windows 8/8.1安装介质**的情况下将Linux从Windows 8或Windows 8.1双启动中完全移除。
|
||||
|
||||
### 将Ubuntu从Windows 8双启动中安全卸载 ###
|
||||
|
||||
你有没有Windows 8安装介质以及是否已经安装了Windows 8.1在你系统上这都不重要。它同样工作得很好。但是我不能说在Windows 7上也一样。如果你身边有Windows安装盘,让我们开始从Windows双启动中移除Ubuntu的进程吧。
|
||||
|
||||
从双启动中删除Linux分为两部分。第一部分是删除Linux安装的所在分区。第二部分是修复Windows启动引导,因为简单地将Linux分区删除会引起[“Grub rescue”错误][3]。
|
||||
|
||||
### 第一部分:在Windows下删除Linux分区 ###
|
||||
|
||||
**第一步:**
|
||||
|
||||
登录Windows。按下 **Windows+R** 然后在其中运行 diskmgmt.msc 命令。它将会打开Windows磁盘管理工具。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**第二步:**
|
||||
|
||||
在你安装了Linux之后,就能很容易地从大小上分辨出Linux分区。另一个分辨Linux分区的提示是找没有文件系统以及驱动器卷标的分区。Windows分区通常用卷标进行标记,比如C,D,E等等,而且通常是NTFS或FAT文件系统。
|
||||
|
||||
就像你所能看到的,我在这里有三个Linux分区,因为我在安装Ubuntu时单独地创建了根分区(root),交换分区(swap)和家目录(home)。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Step 3:**
|
||||
**第三步:**
|
||||
|
||||
选择Linux分区,右键点击并选择 **删除卷** 选项。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
如果出现了警告,在这里选择是即可。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Step 4:**
|
||||
**第四步:**
|
||||
|
||||
被删除的分区会变成一块可用的空闲空间。你可以用它来扩展已有的卷或创建一个新的Windows分区。我会建议你创建一个新的驱动器(或是卷或者分区,随便你怎么叫),因为这样子万一你将来又想将Linux和Winodws双启动时会简单一点。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### 第二部分:修复Windows启动引导 ####
|
||||
|
||||
一旦你删除了Linux分区,就是时候修复Windows启动引导了。这里的图片看起来可能不是很清楚,因为相对于Windows来说[在Ubuntu下对登录画面进行截图][4]要简单的多。我用手机相机拍下了这些照片。
|
||||
|
||||
**第一步:**
|
||||
|
||||
**插入Windows 8安装介质并重启**你的电脑。在启动的时候按下F10或F12进入BIOS/UEFI,选择**从可移除介质启动(boot from removable disk)**。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**第二步:**
|
||||
|
||||
选择修复你的计算机(repair your computer):
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**第三步:**
|
||||
|
||||
在这里选择疑难解答(Troubleshoot):
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**第四步:**
|
||||
|
||||
在疑难解答页面,选择高级选项(Advanced options):
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**第五步:**
|
||||
|
||||
找到这里的命令提示符(command prompt):
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**第六步:**
|
||||
|
||||
在命令行中输入下列命令来修复Windows启动引导:
|
||||
|
||||
bootrec.exe /fixmbr
|
||||
|
||||
正常情况下,它是立即生效的,你甚至都不用等。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**第七步:**
|
||||
|
||||
一旦完成了这一步,重启你的电脑,这次从硬盘正常启动。你应该能够启动进入Windows。如果你仍然看到Grub rescue错误,试试下面的步骤。
|
||||
|
||||
**第八步:如果第六步中的方法不起作用**
|
||||
|
||||
如果第六步中的命令不起作用,试试高级疑难解答中的自动修复选项。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
它会花点时间查找问题然后修复它。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
现在如果你重启的话,你应该能够正常进入Windows,不再看到任何的Grub rescue错误提示。
|
||||
|
||||
我希望这个指南能够帮助你**将Ubuntu从Windows 8双启动中完全移除**。欢迎提出任何问题与建议。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/uninstall-ubuntu-linux-windows-dual-boot/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek][a]
|
||||
译者:[alim0x](https://github.com/alim0x)
|
||||
校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://itsfoss.com/author/Abhishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://linux.cn/article-3178-1.html
|
||||
[2]:http://itsfoss.com/install-ubuntu-dual-boot-mode-windows/
|
||||
[3]:http://itsfoss.com/solve-error-partition-grub-rescue-ubuntu-linux/
|
||||
[4]:http://itsfoss.com/screenshot-login-screen-ubuntu-linux/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,44 @@
|
||||
Linux有问必答——如何查找并移除Ubuntu上陈旧的PPA仓库
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **问题**:我试着通过运行apt-get update命令来再次同步包索引文件,但是却出现了“404 无法找到”的错误,看起来似乎是我不能从先前添加的第三方PPA仓库中获取最新的索引。我怎样才能清除这些破损而且陈旧的PPA仓库呢?
|
||||
|
||||
Err http://ppa.launchpad.net trusty/main amd64 Packages
|
||||
404 Not Found
|
||||
Err http://ppa.launchpad.net trusty/main i386 Packages
|
||||
404 Not Found
|
||||
W: Failed to fetch http://ppa.launchpad.net/finalterm/daily/ubuntu/dists/trusty/main/binary-amd64/Packages 404 Not Found
|
||||
|
||||
W: Failed to fetch http://ppa.launchpad.net/finalterm/daily/ubuntu/dists/trusty/main/binary-i386/Packages 404 Not Found
|
||||
|
||||
E: Some index files failed to download. They have been ignored, or old ones used instead.
|
||||
|
||||
当你试着更新APT包索引时,“404 无法找到”错误总是会在版本更新之后发生。就是说,在你升级你的Ubuntu发行版后,你在旧的版本上添加的一些第三方PPA仓库就不再受新版本的支持。在此种情况下,你可以像下面这样来**鉴别并清除那些破损的PPA仓库**。
|
||||
|
||||
首先,找出那些引起“404 无法找到”错误的PPA。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get update | grep "Failed"
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在本例中,Ubuntu Trusty不再支持的PPA仓库是“ppa:finalterm/daily”。
|
||||
|
||||
去[移除PPA仓库][1]吧。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo add-apt-repository --remove ppa:finalterm/daily
|
||||
|
||||
你得去重复重复再重复,把上面找到的所有过时的PPA仓库一个一个地移除。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在移除所有过时的PPA仓库后,重新运行“apt-get update”命令来检查它们是否都被成功移除。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/find-remove-obsolete-ppa-repositories-ubuntu.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
|
||||
校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/how-to-remove-ppa-repository-from-command-line-on-ubuntu.html
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,39 @@
|
||||
世界上最小的发行版之一Tiny Core有了更新
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Tiny Core
|
||||
|
||||
**Robert Shingledecker 宣布了最终版本的Tiny Core 5.4 Linux操作系统已经可以即刻下载,这也使它成为世界上最小的发行版之一。**
|
||||
|
||||
发行版的名字说明了一切,但是开发者依然集成了一些有意思的包和一个轻量的桌面来与它相匹配。这次最新的迭代只有一个候选版本,而且它也是迄今为止最安静的版本之一。
|
||||
|
||||
官网上的开发者说"Tiny Core是一个简单的范例来说明核心项目可以提供什么。它提供了一个12MB的FLTK/FLWM桌面。用户对提供的程序和外加的硬件有完整的控制权。你可以把它用在桌面、笔记本或者服务器上,这可以由用户从在线库中安装附加程序时选择,或者用提供的工具编译大多数你需要的。"
|
||||
|
||||
根据更新日志,NFS的入口被添加,'Done'将在新的一行里显示,udev也升级到174来修复竞态条件问题。
|
||||
|
||||
关于修改和升级的完整内容可以在官方的[声明][1]里找到。
|
||||
|
||||
你可以点击以下链接下载Tiny Core Linux 5.4.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Tiny Core Linux 5.4 (ISO)][2][iso] [14 MB]
|
||||
- [Tiny Core Plus 5.4 (ISO)][3][iso] [72 MB]
|
||||
- [Core 5.4 (ISO)][4][iso] [8.90 MB]
|
||||
|
||||
这些发行版都有Live,你可以在安装之前试用。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/One-of-the-Smallest-Distros-in-the-World-Tiny-Core-Gets-a-Fresh-Update-458785.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Silviu Stahie][a]
|
||||
译者:[2q1w2007](https://github.com/2q1w2007)
|
||||
校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://news.softpedia.com/editors/browse/silviu-stahie
|
||||
[1]:http://forum.tinycorelinux.net/index.php/topic,17487.0.html
|
||||
[2]:http://distro.ibiblio.org/pub/linux/distributions/tinycorelinux/5.x/x86/release/TinyCore-5.4.iso
|
||||
[3]:http://repo.tinycorelinux.net/5.x/x86/release/CorePlus-5.4.iso
|
||||
[4]:http://distro.ibiblio.org/tinycorelinux/5.x/x86/release/Core-current.iso
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,44 @@
|
||||
Potenza 图标主题2.0已可下载
|
||||
=================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[Potenza][1]图标主题版本2.0已经发布。Potenza 图标的灵感来自[faenza][2],faenza是我们在[Ubuntu 13.10的最佳图标][3]的列出的一款漂亮的图标主题。
|
||||
|
||||
Potenza 的开发者 Alessandro Bompadre说,他曾试图建立一个适用于Linux的完整图标集,它应该适合各种桌面环境,包括如Unity,Gnome,Cinnamon,KDE等。
|
||||
|
||||
###下载 Potenza 图标###
|
||||
|
||||
Potenza 图标可在 Ubuntu,Linux Mint、Elementary OS、Linux Lite 等环境中通过Noobslab的PPA来安装。只有一点需要提醒你,因为要为所有主要类型的桌面环境提供了大量的图标,所以总下载字节大概是400 MB。
|
||||
|
||||
打开一个终端,使用下面的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:noobslab/potenza
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install potenza-2
|
||||
|
||||
如果你不想使用PPA,您也可以从下面的链接安装该图标主题:
|
||||
|
||||
- [下载 Potenza 图标主题][4]
|
||||
|
||||
解压文件到 ~/.icons 目录。在Ubuntu的Unity环境中,你可以[使用Unity Tweak Tool把当前的图标主题切换][5] 为 Potenza 。
|
||||
|
||||
希望你喜欢Potenza,您也可以试试[Dalisha图标主题][6]或看看我们的[Ubuntu 14.04的最佳图标主题列表][7]。
|
||||
|
||||
-------------------------------------------------- ------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/potenza-icon-themes-20-download/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek][a]
|
||||
译者:[fbigun](https://github.com/fbigun)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://itsfoss.com/author/Abhishek/
|
||||
[1]:https://github.com/AlessandroBompadre/Potenza/
|
||||
[2]:http://tiheum.deviantart.com/art/Faenza-Icons-173323228
|
||||
[3]:http://itsfoss.com/best-icon-themes-ubuntu-1310/
|
||||
[4]:http://gnome-look.org/content/show.php/Potenza+2.0?content=166853
|
||||
[5]:http://itsfoss.com/best-icon-themes-ubuntu-1404/
|
||||
[6]:http://itsfoss.com/dalisha-icon-ubuntu-linux/
|
||||
[7]:http://itsfoss.com/best-icon-themes-ubuntu-1404/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,41 @@
|
||||
GNOME控制中心3.14 RC1修复了大量潜在崩溃问题
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Arch Linux下的GNOME控制中心
|
||||
|
||||
**GNOME控制中心,可以在GNOME中更改你的桌面各个方面设置的主界面,已经升级至3.14 RC1,伴随而来的是大量来自GNOME stack的包。**
|
||||
|
||||
GNOME控制中心是在GNOME生态系统中十分重要的软件之一,尽管不是所有的用户意识到了它的存在。GNOME控制中心是管理由GNOME驱动的操作系统中所有设置的部分,就像你从截图里看到的那样。
|
||||
|
||||
GNOME控制中心不是很经常被宣传,它实际上是GNOME stack中为数不多的源代码包和安装后的应用名称不同的软件包。源代码包的名字为GNOME控制中心,但用户经常看到的应用名称是“设置”或“系统设置”,取决于开发者的选择。
|
||||
|
||||
### GNOME控制中心 3.14 RC1 带来哪些新东西 ###
|
||||
|
||||
通过更新日志可以得知,升级了libgd以修复GdNotification主题,切换视图时背景选择对话框不再重新调整大小,选择对话框由三个不同视图组合而成,修复Flickr支持中的一个内存泄漏,在“日期和时间”中不再使用硬编码的字体大小,修复改换窗口管理器(或重启)时引起的崩溃,更改无线网络启用时可能引起的崩溃也已被修复,以及纠正了更多可能的WWAN潜在崩溃因素。
|
||||
|
||||
此外,现在热点仅在设备活动时运行,所有虚拟桥接现在是隐藏的,不再显示VPN连接的底层设备,默认不显示空文件夹列表,解决了几个UI填充问题,输入焦点现在重新回到了账户对话框,将年份设置为0时导致的崩溃已修复,“Wi-Fi热点”属性居中,修复了打开启用热点时弹出警告的问题,以及现在打开热点失败时将弹出错误信息。
|
||||
|
||||
完整的变动,更新以及bug修复,参见官方[更新日志][1]。
|
||||
|
||||
你可以下载GNOME控制中心 3.14 RC1:
|
||||
|
||||
- [tar.xz (3.12.1 稳定版)][2][sources] [6.50 MB]
|
||||
- [tar.xz (3.14 RC1 开发版)][3][sources] [6.60 MB]
|
||||
|
||||
这里提供的仅仅是源代码包,你必须自己编译以测试GNOME控制中心。除非你真的知道自己在做什么,否则你应该等到完整的GNOME stack在源中可用时再使用。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/GNOME-Control-Center-3-14-RC1-Correct-Lots-of-Potential-Crashes-458986.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Silviu Stahie][a]
|
||||
译者:[alim0x](https://github.com/alim0x)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://news.softpedia.com/editors/browse/silviu-stahie
|
||||
[1]:http://ftp.acc.umu.se/pub/GNOME/sources/gnome-control-center/3.13/gnome-control-center-3.13.92.news
|
||||
[2]:http://ftp.acc.umu.se/pub/GNOME/sources/gnome-control-center/3.12/gnome-control-center-3.12.1.tar.xz
|
||||
[3]:http://ftp.acc.umu.se/pub/GNOME/sources/gnome-control-center/3.13/gnome-control-center-3.13.92.tar.xz
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,36 @@
|
||||
欧洲现在很流行拥抱开源
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
看来拥抱[开源][1]最近在欧洲的国家很流行。上个月我们我只听说[都灵成为意大利首个官方接受开源产品的城市][2]。另一个意大利西北部城市,[乌迪内][3],已经宣布他们正在抛弃微软Office转而迁移到[OpenOffice][4]。
|
||||
|
||||
乌迪内有100,000的人口并且行政部门有大约900台电脑,它们都运行着微软Windows以及它的默认产品套装。根据[预算文档][5],迁移将在大约12月份时进行,从80台新电脑开始。接着将会是旧电脑迁移到OpenOffice。
|
||||
|
||||
迁移估计会节省一笔授权费用,不然将会每台电脑花费大约400欧元,总计360,000欧元。但是节约成本并不是迁移的唯一目的,获得常规的软件升级也是其中一个因素。
|
||||
|
||||
当然从微软的Office到OpenOfifice不会太顺利。不过,全市的培训计划是先让少数员工使用安装了OpenOffice的电脑。
|
||||
|
||||
如我先前说明的,这似乎在欧洲是一个趋势。在今年早些时候在[西班牙的加那利群岛][7]之后[法国城市图卢兹也使用了LibreOffice中从而节省了100万欧元][6]。相邻的法国城市[日内瓦也有开源方面的迹象][8]。在世界的另一边,政府机构[泰米尔纳德邦][9]和印度喀拉拉邦省也抛弃了微软而使用开源软件。
|
||||
|
||||
伴随着经济的萧条,我觉得Windows XP的死亡一直是开源的福音。无论是什么原因,我很高兴看到这份名单越来越大。你看呢?
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/udine-open-source/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek][a]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://itsfoss.com/author/Abhishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://itsfoss.com/category/open-source-software/
|
||||
[2]:http://linux.cn/article-3602-1.html
|
||||
[3]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Udine
|
||||
[4]:https://www.openoffice.org/
|
||||
[5]:http://www.comune.udine.it/opencms/opencms/release/ComuneUdine/comune/Rendicontazione/PEG/PEG_2014/index.html?lang=it&style=1&expfolder=???+NavText+???
|
||||
[6]:http://linux.cn/article-3575-1.html
|
||||
[7]:http://itsfoss.com/canary-islands-saves-700000-euro-open-source/
|
||||
[8]:http://itsfoss.com/170-primary-public-schools-geneva-switch-ubuntu/
|
||||
[9]:http://linux.cn/article-2744-1.html
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
|
||||
来自Ubuntu开发团队关于Mir和Unity 8的状态更新
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> 目前Unity 8和Mir的开发进度很慢,但是仍在进行中
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**和其他项目一样,Canonical也在开发Unity桌面环境与Mir显示服务。开发团队刚刚发布了一个小的更新,据此我们可以知道都有些什么进展**
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu开发者可能刚刚集中精力在一些重要的发布上,就像接下来的Ubuntu 14.10(Utopic Unicorn) 或者是新的面向移动设备的Ubuntu Touch,但是他们同样也涉及像Mir以及Unity 8这样的项目。
|
||||
|
||||
目前这代Ubuntu系统使用的是Unity 7桌面环境,但是新一代已经酝酿了很长一段时间。它与新的显示服务一起,已经在Ubuntu的移动版中了,但最终也要将它带到桌面上。
|
||||
|
||||
这两个项目的领导Kevin Gunn经常发布一些来自开发者的进度信息以及这周以来的一些改变,虽然这些都很粗略。
|
||||
|
||||
根据 [开发团队][1]的消息, 一些关于触摸/触发角的问题已经修正了,也修复了几个翻译问题,一些Dash UI相关的问题已经修复了,目前 团队在开发Mir 0.8,Mir 0.7.2将被升级,同时一些高优先级的bug处理也在进行中。
|
||||
|
||||
你可以[下载 Ubuntu Next][7]来体验新的Unity 8以及Mir的特性,但是还不够稳定。要等到成熟还需要一些时间。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/Mir-and-Unity-8-Update-Arrive-from-Ubuntu-Devs-459263.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Silviu Stahie][a]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://news.softpedia.com/editors/browse/silviu-stahie
|
||||
[1]:https://lists.launchpad.net/ubuntu-phone/msg09875.html
|
||||
[2]:http://cdimage.ubuntu.com/daily-live/current/utopic-desktop-amd64.iso
|
||||
[3]:http://cdimage.ubuntu.com/daily-live/current/utopic-desktop-i386.iso
|
||||
[4]:http://cdimage.ubuntu.com/daily-live/current/utopic-desktop-amd64+mac.iso
|
||||
[5]:http://cdimage.ubuntu.com/ubuntu-desktop-next/daily-live/current/utopic-desktop-amd64.iso
|
||||
[6]:http://cdimage.ubuntu.com/ubuntu-desktop-next/daily-live/current/utopic-desktop-i386.iso
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,48 @@
|
||||
Netflix支持 Ubuntu 上原生回放
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**我们[上个月说的Netflix 的原生Linux支持很接近了][1],现在终于有了,我们只需几个简单的步骤就可以在Ubuntu桌面上启用HTML 5视频流了。
|
||||
|
||||
现在Netflix更近一步提供了支持。它希望给Ubuntu带来真正的开箱即用的Netflix回放。现在只需要更新**网络安全(Network Security Services,NSS)**服务库就行。
|
||||
|
||||
### 原生Netflix? Neato. ###
|
||||
|
||||
在一封发给Ubuntu开发者邮件列表的[邮件中][2],Netflix的Paul Adolph解释了现在的情况:
|
||||
|
||||
> “如果NSS的版本是3.16.2或者更高的话,Netflix可以在Ubuntu 14.04的稳定版Chrome中播放。如果版本超过了14.04,Netflix会作出一些调整,以避免用户必须对浏览器的 User-Agent 参数进行一些修改才能播放。”
|
||||
|
||||
[LCTT 译注:此处原文是“14.02”,疑是笔误,应该是指Ubuntu 14.04。]
|
||||
|
||||
很快要发布的Ubuntu 14.10提供了更新的[NSS v3.17][3], 而目前大多数用户使用的版本 Ubuntu 14.04 LTS 提供的是 v3.15.x。
|
||||
|
||||
NSS是一系列支持多种安全功能的客户端和服务端应用的库,包括SSL,TLS,PKCS和其他安全标准。为了让Ubuntu LTS用户可以尽快用上原生的HTML5 Netflix, Paul 问道:
|
||||
|
||||
>”让一个新的NSS版本进入更新流的过程是什么?或者有人可以给我提供正确的联系方式么?“
|
||||
|
||||
Netflix今年早期时在Windows 8.1和OSX Yosemite上提供了HTML5视频回放,而不需要任何额外的下载或者插件。现在可以通过[加密媒体扩展][4]特性来使用。
|
||||
|
||||
虽然我们等待这讨论取得进展(并且希望可以完全解决),但是你仍可以在Ubuntu上[下面的指导来][5]修改HTML5 Netflix。
|
||||
|
||||
更新:9/19
|
||||
|
||||
本文发表后,Canonical 已经确认所需版本的NSS 库会按计划在下个“安全更新”中更新,预计 Ubuntu 14.04 LTS 将在两周内得到更新。
|
||||
|
||||
这个新闻让 Netflix 的Paul Adolph 很高兴,作为回应,他说当软件包更新后,他将“去掉 Chrome 中回放 Netflix HTML5 视频时的User-Agent 过滤,不再需要修改UA 了”。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/09/netflix-linux-html5-nss-change-request
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Joey-Elijah Sneddon][a]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://plus.google.com/117485690627814051450/?rel=author
|
||||
[1]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/08/netflix-linux-html5-support-plugins
|
||||
[2]:https://lists.ubuntu.com/archives/ubuntu-devel-discuss/2014-September/015048.html
|
||||
[3]:https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Mozilla/Projects/NSS/NSS_3.17_release_notes
|
||||
[4]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Encrypted_Media_Extensions
|
||||
[5]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/08/netflix-linux-html5-support-plugins
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,42 @@
|
||||
Debian 8 "Jessie" 将把GNOME作为默认桌面环境
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> Debian的GNOME团队已经取得了实质进展
|
||||
|
||||
<center></center>
|
||||
|
||||
<center>*GNOME 3.14桌面*</center>
|
||||
|
||||
**Debian项目开发者花了很长一段时间来决定将Xfce,GNOME或一些其他桌面环境中的哪个作为默认环境,不过目前看起来像是GNOME赢了。**
|
||||
|
||||
[我们两天前提到了][1],GNOME 3.14的软件包被上传到 Debian Testing(Debian 8 “Jessie”)的软件仓库中,这是一个令人惊喜的事情。通常情况下,GNOME的维护者对任何类型的软件包都不会这么快地决定添加,更别说桌面环境。
|
||||
|
||||
事实证明,关于即将到来的Debian 8的发行版中所用的默认桌面的争论已经尘埃落定,尽管这个词可能有点过于武断。无论什么情况下,总是有些开发者想要Xfce,另外一些则是喜欢 GNOME,看起来 MATE 也是不少人的备选。
|
||||
|
||||
### 最有可能的是,GNOME将Debian 8“Jessie” 的默认桌面环境###
|
||||
|
||||
我们之所以说“最有可能”是因为协议尚未达成一致,但它看起来GNOME已经遥遥领先了。Debian的维护者和开发者乔伊·赫斯解释了为什么会这样。
|
||||
|
||||
“根据从 https://wiki.debian.org/DebianDesktop/Requalification/Jessie 初步结果看,一些所需数据尚不可用,但在这一点上,我百分之八十地确定GNOME已经领先了。特别是,由于“辅助功能”和某些“systemd”整合的进度。在辅助功能方面:Gnome和Mate都领先了一大截。其他一些桌面的辅助功能改善了在Debian上的支持,部分原因是这一过程推动的,但仍需要上游大力支持。“
|
||||
|
||||
“Systemd /etc 整合方面:Xfce,Mate等尽力追赶在这一领域正在发生的变化,当技术团队停止了修改之后,希望有时间能在冻结期间解决这些问题。所以这并不是完全否决这些桌面,但要从目前的状态看,GNOME是未来的选择,“乔伊·赫斯[补充说][2]。
|
||||
|
||||
开发者在邮件中表示,在Debian的GNOME团队对他们所维护的项目[充满了激情][3],而Debian的Xfce的团队是决定默认桌面的实际阻碍。
|
||||
|
||||
无论如何,Debian 8“Jessie”没有一个具体发布时间,并没有迹象显示何时可能会被发布。在另一方面,GNOME 3.14已经发布了(也许你已经看到新闻了),它将很快应对好进行Debian的测试。
|
||||
|
||||
我们也应该感谢Jordi Mallach,在Debian中的GNOME包的维护者之一,他为我们指引了正确的讯息。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/Debian-8-quot-Jessie-quot-to-Have-GNOME-as-the-Default-Desktop-459665.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Silviu Stahie][a]
|
||||
译者:[fbigun](https://github.com/fbigun)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://news.softpedia.com/editors/browse/silviu-stahie
|
||||
[1]:http://news.softpedia.com/news/Debian-8-quot-Jessie-quot-to-Get-GNOME-3-14-459470.shtml
|
||||
[2]:http://anonscm.debian.org/cgit/tasksel/tasksel.git/commit/?id=dce99f5f8d84e4c885e6beb4cc1bb5bb1d9ee6d7
|
||||
[3]:http://news.softpedia.com/news/Debian-Maintainer-Says-that-Xfce-on-Debian-Will-Not-Meet-Quality-Standards-GNOME-Is-Needed-454962.shtml
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,29 @@
|
||||
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5产品线终结
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
2007年3月,红帽公司首次宣布它的[Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5][1](RHEL)平台。虽然如今看来很普通,RHEL 5特别显著的一点是它是红帽公司第一个强调虚拟化的主要发行版本,而这点是如今现代发行版所广泛接受的特性。
|
||||
|
||||
最初的计划是为RHEL 5提供七年的寿命,但在2012年该计划改变了,红帽为RHEL 5[扩展][2]至10年的标准支持。
|
||||
|
||||
刚刚过去的这个星期,Red Hat发布的RHEL 5.11是RHEL 5.X系列的最后的、次要里程碑版本。红帽现在进入了将持续三年的名为“production 3”的支持周期。在这阶段将没有新的功能被添加到平台中,并且红帽公司将只提供有重大影响的安全修复程序和紧急优先级的bug修复。
|
||||
|
||||
平台事业部副总裁兼总经理Jim Totton在红帽公司在一份声明中说:“红帽公司致力于建立一个长期,稳定的产品生命周期,这将给那些依赖Red Hat Enterprise Linux为他们的关键应用服务的企业客户提供关键的益处。虽然RHEL 5.11是RHEL 5平台的最终次要版本,但它提供了安全性和可靠性方面的增强功能,以保持该平台接下来几年的活力。”
|
||||
|
||||
新的增强功能包括安全性和稳定性更新,包括改进了红帽帮助用户调试系统的方式。
|
||||
|
||||
还有一些新的存储的驱动程序,以支持新的存储适配器和改进在VMware ESXi上运行RHEL的支持。
|
||||
|
||||
在安全方面的巨大改进是OpenSCAP更新到版本1.0.8。红帽在2011年五月的[RHEL5.7的里程碑更新][3]中第一次支持了OpenSCAP。 OpenSCAP是安全内容自动化协议(SCAP)框架的开源实现,用于创建一个标准化方法来维护安全系统。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxplanet.com/news/end-of-the-line-for-red-hat-enterprise-linux-5.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Sean Michael Kerner
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.internetnews.com/ent-news/article.php/3665641
|
||||
[2]:http://www.serverwatch.com/server-news/red-hat-extends-linux-support.html
|
||||
[3]:http://www.internetnews.com/skerner/2011/05/red-hat-enterprise-linux-57-ad.html
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,39 @@
|
||||
KDE Plasma 5的第二个bug修复版本发布,带来了很多的改变
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> 新的Plasma 5发布了,带来了新的外观
|
||||
|
||||
<center></center>
|
||||
|
||||
<center>*KDE Plasma 5*</center>
|
||||
|
||||
### Plasma 5的第二个bug修复版本发布,已可下载###
|
||||
|
||||
KDE Plasma 5的bug修复版本不断来到,它新的桌面体验将会是KDE的生态系统的一个组成部分。
|
||||
|
||||
[公告][1]称:“plasma-5.0.2这个版本,新增了一个月以来来自KDE的贡献者新的翻译和修订。Bug修复通常是很小但是很重要,如修正未翻译的文字,使用正确的图标和修正KDELibs 4软件的文件重复现象。它还增加了一个月以来辛勤的翻译成果,使其支持其他更多的语言”
|
||||
|
||||
这个桌面还没有在任何Linux发行版中默认安装,这将持续一段时间,直到我们测试完成。
|
||||
|
||||
开发者还解释说,更新的软件包可以在Kubuntu Plasma 5的开发版本中进行审查。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你个人需要它们,你也可以下载源码包。
|
||||
|
||||
- [KDE Plasma Packages][2]
|
||||
- [KDE Plasma Sources][3]
|
||||
|
||||
如果你决定去编译它,你必须需要知道 KDE Plasma 5.0.2是一组复杂的软件,可能你需要解决不少问题。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/Second-Bugfix-Release-for-KDE-Plasma-5-Arrives-with-Lots-of-Changes-459688.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Silviu Stahie][a]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://news.softpedia.com/editors/browse/silviu-stahie
|
||||
[1]:http://kde.org/announcements/plasma-5.0.2.php
|
||||
[2]:https://community.kde.org/Plasma/Packages
|
||||
[3]:http://kde.org/info/plasma-5.0.2.php
|
||||
@ -1,37 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Microsoft Lobby Denies the State of Chile Access to Free Software
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
Fuerza Chile
|
||||
|
||||
Fresh on the heels of the entire Munich and Linux debacle, another story involving Microsoft and free software has popped up across the world, in Chile. A prolific magazine from the South American country says that the powerful Microsoft lobby managed to turn around a law that would allow the authorities to use free software.
|
||||
|
||||
The story broke out from a magazine called El Sábado de El Mercurio, which explains in great detail how the Microsoft lobby works and how it can overturn a law that may harm its financial interests.
|
||||
|
||||
An independent member of the Chilean Parliament, Vlado Mirosevic, pushed a bill that would allow the state to consider free software when the authorities needed to purchase or renew licenses. The state of Chile pays $2.7 billion (€2 billion) on licenses from various companies, including Microsoft.
|
||||
|
||||
According to [ubuntizando.com][1], Microsoft representatives met with Vlado Mirosevic shortly after he announced his intentions, but the bill passed the vote, with 64 votes in favor, 12 abstentions, and one vote against it. That one vote was cast by Daniel Farcas, a member of a Chilean party.
|
||||
|
||||
A while later, the same member of the Parliament, Daniel Farcas, proposed another bill that actually nullified the effects of the previous one that had just been adopted. To make things even more interesting, some of the people who voted in favor of the first law also voted in favor of the second one.
|
||||
|
||||
The new bill is even more egregious, because it aggressively pushes for the adoption of proprietary software. Companies that choose to use proprietary software will receive certain tax breaks, which makes it very hard for free software to get adopted.
|
||||
|
||||
Microsoft has been in the news in the last few days because the [German city of Munich that adopted Linux][2] and dropped Windows system from its administration was considering, supposedly, returning to proprietary software.
|
||||
|
||||
This new situation in Chile give us a sample of the kind of pull a company like Microsoft has and it shows us just how fragile laws really are. This is not the first time a company tries to bend the laws in a country to maximize the profits, but the advent of free software and the clear financial advantages that it offers are really making a dent.
|
||||
|
||||
Five years ago, few people or governments would have considered adopting free software, but the quality of that software has risen dramatically and it has become a real competition [for the likes of Microsoft][3].
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/Microsoft-Lobby-Denies-the-State-of-Chile-Access-to-Free-Software-455598.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Silviu Stahie][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://news.softpedia.com/editors/browse/silviu-stahie
|
||||
[1]:http://www.ubuntizando.com/2014/08/20/microsoft-chile-y-el-poder-del-lobby/
|
||||
[2]:http://news.softpedia.com/news/Munich-Disappointed-with-Linux-Plans-to-Switch-Back-to-Windows-455405.shtml
|
||||
[3]:http://news.softpedia.com/news/Munich-Switching-to-Windows-from-Linux-Is-Proof-that-Microsoft-Is-Still-an-Evil-Company-455510.shtml
|
||||
@ -1,40 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Transport Tycoon Deluxe Remake OpenTTD 1.4.2 Is an Almost Perfect Sim
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
Transport Tycoon
|
||||
|
||||
**OpenTTD 1.4.2, an open source simulation game based on the popular Microprose title Transport Tycoon written by Chris Sawyer, has been officially released.**
|
||||
|
||||
Transport Tycoon is a very old game that was originally launched back in 1995, but it made such a huge impact on the gaming community that, even almost 20 years later, it still has a powerful fan base.
|
||||
|
||||
In fact, Transport Tycoon Deluxe had such an impact on the gaming industry that it managed to spawn an entire generation of similar games and it has yet to be surpassed by any new title, even though many have tried.
|
||||
|
||||
Despite the aging graphics, the developers of OpenTTD have tried to provide new challenges for the fans of the original games. To put things into perspective, the original game is already two decades old. That means that someone who was 20 years old back then is now in his forties and he is the main audience for OpenTTD.
|
||||
|
||||
"OpenTTD is modelled after the original Transport Tycoon game by Chris Sawyer and enhances the game experience dramatically. Many features were inspired by TTDPatch while others are original," reads the official announcement.
|
||||
|
||||
OpenTTD features bigger maps (up to 64 times in size), stable multiplayer mode for up to 255 players in 15 companies, a dedicated server mode and an in-game console for administration, IPv6 and IPv4 support for all communication of the client and server, new pathfinding algorithms that makes vehicles go where you want them to, different configurable models for acceleration of vehicles, and much more.
|
||||
|
||||
According to the changelog, awk is now used instead of trying to convince cpp to preprocess nfo files, CMD_CLEAR_ORDER_BACKUP is no longer suppressed by pause modes, the Wrong breakdown sound is no longer played for ships, integer overflow in the acceleration code is no longer causing either too low acceleration or too high acceleration, incorrectly saved order backups are now discarded when clients join, and the game no longer crashes when trying to show an error about vehicle in a NewGRF and the NewGRF was not loaded at all.
|
||||
|
||||
Also, the Slovak language no longer uses space as group separator in numbers, the parameter bound checks are now tighter on GSCargoMonitor functions, the days in dates are not represented by ordinal numbers in all languages, and the incorrect usage of string commands in the base language has been fixed.
|
||||
|
||||
Check out the [changelog][1] for a complete list of updates and fixes.
|
||||
|
||||
Download OpenTTD 1.4.2:
|
||||
|
||||
- [http://www.openttd.org/en/download-stable][2]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/Transport-Tycoon-Deluxe-Remake-OpenTTD-1-4-2-Is-an-Almost-Perfect-Sim-455715.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Silviu Stahie][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://news.softpedia.com/editors/browse/silviu-stahie
|
||||
[1]:http://ftp.snt.utwente.nl/pub/games/openttd/binaries/releases/1.4.2/changelog.txt
|
||||
[2]:http://www.openttd.org/en/download-stable
|
||||
@ -1,41 +0,0 @@
|
||||
[sailing]
|
||||
Munich Council: LiMux Demise Has Been Greatly Exaggerated
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
LiMux – Munich City Council’s Official OS
|
||||
|
||||
A Munich city council spokesman has attempted to clarify the reasons behind its [plan to re-examine the role of open-source][1] software in local government IT systems.
|
||||
|
||||
The response comes after numerous German media outlets revealed that the city’s incoming mayor has asked for a report into the use of LiMux, the open-source Linux distribution used by more than 80% of municipalities.
|
||||
|
||||
Reports quoted an unnamed city official, who claimed employees were ‘suffering’ from having to use open-source software. Others called it an ‘expensive failure’, with the deputy mayor, Josef Schmid, saying the move was ‘driven by ideology’, not financial prudence.
|
||||
|
||||
With Munich often viewed as the poster child for large Linux migrations, news of the potential renege quickly went viral. Now council spokesman Stefan Hauf has attempted to bring clarity to the situation.
|
||||
|
||||
### ‘Plans for the future’ ###
|
||||
|
||||
Hauf confirms that the city’s new mayor has requested a review of the city’s IT systems, including its choice of operating systems. But the report is not, as implied in earlier reports, solely tasked with deciding whether to return to using Microsoft Windows.
|
||||
|
||||
**“It’s about the organisation, the costs, performance and the usability and satisfaction of the users,”** [Techrepublic][2] quote him as saying.
|
||||
|
||||
**“[It's about gathering the] facts so we can decide and make a proposal for the city council how to proceed in future.”**
|
||||
|
||||
Hauf also confirms that council staff have, and do, complain about LiMux, but that the majority of issues stem from compatibility issues in OpenOffice, something a potential switch to LibreOffice could solve.
|
||||
|
||||
So is Munich about to switch back to Windows? As we said in our original coverage: it’s just too early to say, but it’s not being ruled out.
|
||||
|
||||
No final date for the report’s recommendations is yet set, and any binding decision on Munich’s IT infrastructure will need to be made by its elected members, the majority of whom are said to ‘support’ the LiMux initiative.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/08/munich-council-say-talk-limux-demise-greatly-exaggerated
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Joey-Elijah Sneddon][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://plus.google.com/117485690627814051450/?rel=author
|
||||
[1]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/08/munich-city-linux-switching-back-windows
|
||||
[2]:http://www.techrepublic.com/article/no-munich-isnt-about-to-ditch-free-software-and-move-back-to-windows/
|
||||
@ -1,31 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Red Hat Shake-up, Desktop Users, and Outta Time
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Our top story tonight is the seemingly sudden resignation of Red Hat CTO Brian Stevens. In other news, John C. Dvorak says "Linux has run out of time" and Infoworld.com says there may be problems with Red Hat Enterprise 7. OpenSource.com has a couple of interesting interviews and Nick Heath has five big names that use Linux on the desktop.
|
||||
|
||||
**In a late afternoon** [press release][1], Red Hat announced the resignation of long-time CTO Brian Stevens. Paul Cormier will be handling CTO duties until Stevens' replacement is named. No reason for the sudden resignation was given although CEO Whitehurst said, "We want to thank Brian for his years of service and numerous contributions to Red Hat’s business. We wish him well in his future endeavors." However, Steven J. Vaughan-Nichols says some rumors are flying. One says friction between Stevens and Cormier caused the resignation and others say Stevens had higher ambitions than Red Hat could provide. He'd been with Red Hat since 2001 and had been CTO at Mission Critical Linux before that [according to Vaughan-Nichols][2] who also said Stevens' Red Hat page was gone within seconds of the announcement.
|
||||
|
||||
**Speaking of Red Hat**, InfoWorld.com has a review of RHEL 7 available to the general public today. Reviewer Paul Venezia runs down the new features, but soon mentions systemd as one of the many new features "certain to cause consternation." After offering his opinion on several other key features and even throwing in a tip or two, [Venezia concludes][3], "RHEL 7 is a fairly significant departure from the expected full-revision release from Red Hat. This is not merely a reskinning of the previous release with updated packages, a more modern kernel, and some new toolkits and widgets. This is a very different release than RHEL 6 in any form, mostly due to the move to Systemd."
|
||||
|
||||
**Our own Sam Dean** [today said][4] that Linux doesn't need to own the desktop because of its success in many other key areas. While that may be true, Nick Heath today listed "five big names that use Linux on the desktop." He said besides Munich, there's Google for one and they even have their own Ubuntu derivative. He lists a couple of US government agencies and then mentions CERN and others. See that [full story][5] for more.
|
||||
|
||||
Despite that feel-good report, John C. Dvorak said he's tired of waiting for someone to develop that one "killer app" that would bring in the masses or satisfy his needs. [He says][6] he has to make podcasts and "photographic art" and he just can't do that with Linux. Our native applications "do not cut it in the end."
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ostatic.com/blog/red-hat-shake-up-desktop-users-and-outta-time
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Susan Linton][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://ostatic.com/member/susan-linton
|
||||
[1]:http://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20140827006134/en/Brian-Stevens-Step-CTO-Red-Hat#.U_5AlvFdX0p
|
||||
[2]:http://www.zdnet.com/red-hat-chief-technology-officer-resigns-7000033058/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.infoworld.com/d/data-center/review-rhel-7-lands-jolt-249219
|
||||
[4]:http://ostatic.com/blog/linux-doesnt-need-to-own-the-desktop
|
||||
[5]:http://www.techrepublic.com/article/five-big-names-that-use-linux-on-the-desktop/
|
||||
[6]:http://www.pcmag.com/article2/0,2817,2465125,00.asp
|
||||
@ -1,37 +0,0 @@
|
||||
LibreOffice 4.3.1 Has More than 100 Fixes and DOCX Embedded Objects Support
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
LibreOffice selection menu
|
||||
|
||||
**The Document Foundation announces that the stable version of LibreOffice 4.3.1 has been released and is now available for download.**
|
||||
|
||||
The developers from The Document Foundation have released a new update for the 4.3 branch of LibreOffice and they have implemented quite a few fixes and other various changes. The development cycle for this latest update has been rather short and the devs managed to repair most of the issues that have been found.
|
||||
|
||||
LibreOffice 4.3.1 is just maintenance release, which means that the focus has been about the bugs found so far. Don't expect to find anything extraordinary, but you should upgrade the software nonetheless.
|
||||
|
||||
"The Document Foundation announces LibreOffice 4.3.1, the first minor release of LibreOffice 4.3 'fresh' family, with over 100 fixes (including patches for two CVEs, backported to LibreOffice 4.2.6-secfix, which is also available for download now)."
|
||||
|
||||
"All LibreOffice users are invited to update their installation as soon as possible to avoid security issues. This includes users who are running LibreOffice 4.2.6 as originally released on August, 5th 2014. LibreOffice 4.3.1 and LibreOffice 4.2.6 will be shown on stage at the LibreOffice Conference in Bern, from September 3 to September 5, with a large number of sessions about development, community, marketing and migrations," reads the announcement made by The Linux Foundation.
|
||||
|
||||
According to the changelog, editing the text search with expanded fields is now working properly, the static value array for OOXML chart is now handled correctly, bullets now have the color as the following text by default, ww8import no longer creates a pagedesc if a continuous section changes margins, the 0 font height is now handled just like outdev, it's now possible to import OLE objects in the header with background wrapping, the XLSX export of revisions has been fixed in order to get it to work in Excel, and borders around data labels are now supported.
|
||||
|
||||
Also, the table style for lastRow is now correctly applied, the rulers now have app-background by default, the graphics are now swapped in on DrawingML::WriteImage, the redundant 'Preferences' label has been removed in order to save some space, page breaks in tables are now ignored during the RTF import, some of the style hierarchy has been reworked, Data Statistics no longer crashes with any entry, DOCX embedded objects are now supported, and numerous other improvements have been made.
|
||||
|
||||
More details about this release can be found in the official [announcement][1].
|
||||
|
||||
- [Download LibreOffice 4.3.1 for Linux][2]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/LibreOffice-4-3-1-Has-More-Than-100-Fixes-and-DOCX-Embedded-Objects-Support-456916.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Silviu Stahie][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://news.softpedia.com/editors/browse/silviu-stahie
|
||||
[1]:http://blog.documentfoundation.org/2014/08/28/libreoffice-4-3-1-fresh-announced/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.libreoffice.org/download/libreoffice-fresh/
|
||||
@ -1,27 +0,0 @@
|
||||
disylee占个坑!来翻译了!
|
||||
Ubuntu Touch Now Has a Torrent Client in the Ubuntu Store
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**The Ubuntu Touch platform is already the host of many interesting applications, and it looks like the developers have started to implement software that goes beyond what you might expect, like a torrent client for example.**
|
||||
|
||||
The app store for Ubuntu Touch has been growing steadily over the past few months and interesting applications are added all the time. Most of them are covering some of the basic needs of the operating system, but there are quite a few that go well beyond regular users’ needs.
|
||||
|
||||
A torrent client is not something that you will find on most phones. Android and Windows Phone already have this kind of apps and it looks like Ubuntu is now one of those platforms. Ubuntu developer [Alan Pope][1] posted a screenshot with a new application that's being developed for the Ubuntu platforms called DowNow.
|
||||
|
||||
This is a relatively new application and it's still under development. You can find the click package for DowNow 0.3 in Launchpad, if you want to take a closer look, or you can download from Ubuntu Software Center.
|
||||
|
||||
For now, the only supported devices are Nexus 4 and Nexus 7, if you want to test Ubuntu for phones, but that might change in the coming months.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/Ubuntu-Touch-Now-Has-a-Torrent-Clinent-in-the-Ubuntu-Store-457538.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Silviu Stahie][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://news.softpedia.com/editors/browse/silviu-stahie
|
||||
[1]:https://plus.google.com/u/0/+AlanPope/posts/Ej3vKVxBum8
|
||||
@ -1,37 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Jelly Conky Adds Simple, Stylish Stats To Your Linux Desktop
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**I treat Conky setups a bit like wallpapers: I’ll find one I love, only to change it the next week because I’m bored of it and want a change.**
|
||||
|
||||
Part of the impatience is fuelled by the ever-growing catalog of designs available. One of my most recent favourites is Jelly Conky.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Jelly Conky sports the minimal design many of the Conky’s we’ve highlighted recently have followed. It’s not trying to be a kitchen sink. It won’t win favour with those who need constant at-a-glance data on their HDD temperatures and IP addresses.
|
||||
|
||||
It comes with three distinct modes that can all add personality to an otherwise static background image:
|
||||
|
||||
- Clock
|
||||
- Clock plus date
|
||||
- Clock plus date and weather
|
||||
|
||||
Some people don’t understand the point of having a duplicate clock on show on the desktop. That’s understandable. For me, it’s more about form than function (though, personally, I find Conky clocks easier to see than the minuscule digits nestled in my upper panel).
|
||||
|
||||
Chances are if you have a home screen widget on Android with the time, you won’t mind having one on your desktop, either!
|
||||
|
||||
You can download Jelly Conky from the link below. The .zip archive contains a readme with instructions on how to install. For a guided walkthrough, [revisit one of our previous articles][1].
|
||||
|
||||
- [Download Jelly Conky on Deviant Art][2]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/09/jelly-conky-for-linux-desktop
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Joey-Elijah Sneddon][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://plus.google.com/117485690627814051450/?rel=author
|
||||
[1]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/07/conky-circle-theme-nod-lg-quick-cover
|
||||
[2]:http://zagortenay333.deviantart.com/art/Jelly-Conky-442559003
|
||||
@ -1,38 +0,0 @@
|
||||
How to Go Hands On With the Utopic Unicorn – Literally!
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**Looking to go hands-on with the Utopic Unicorn ahead of its release? Now you can — [literally][1]!**
|
||||
|
||||
A step-by-step guide to making your own paper Unicorn (to celebrate the upcoming release of the same name, obviously) has been posted online by Canonical. The instructions were offered as part of the company’s presence at the 2014 [deconstruct][2] event held in Brighton, UK in early September.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Image: Alejandra Obregon
|
||||
|
||||
The one-day conference for creative professionals and digital culture enthusiasts served as an ideal place for Canonical to showcase an in-progress version of the upcoming Ubuntu Phone, its design and the user interaction benefits they believe it offers.
|
||||
|
||||
Reaction was positive, they say. That will have made the prize of a brand new Ubuntu phone to the maker of the best origami unicorn all the more tempting!
|
||||
|
||||
### Download Origami Unicorn ###
|
||||
|
||||
No prizes are on offer to the rest of us attempting to fold our way to frustration, but a download of the how-to is.
|
||||
|
||||
If you have a spare five hours minutes, why not make one for fun? If you make particularly epic success/fail of it be sure to send us a pic on [Twitter][3] or [Google+][4].
|
||||
|
||||
- [Download ‘Make a Unicorn’ Instructions][5]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/09/unicorn-origami-download-pdf-ubuntu-utopic
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Joey-Elijah Sneddon][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://plus.google.com/117485690627814051450/?rel=author
|
||||
[1]:http://design.canonical.com/2014/09/canonical-and-ubuntu-at-dconstruct/
|
||||
[2]:http://2014.dconstruct.org/
|
||||
[3]:http://twitter.com/omgubuntu
|
||||
[4]:http://plus.google.com/+omgubuntu
|
||||
[5]:http://design.canonical.com/wp-content/uploads/042_CAN_dConstruct_instructions.pdf
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,38 @@
|
||||
Translating by ZTinoZ
|
||||
Red Hat Acquires FeedHenry for $82 Million to Advance Mobile Development
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> Red Hat jumps into the mobile development sector with a key acquisition.
|
||||
|
||||
Red Hat's JBoss developer tools division has always focused on enterprise development, but hasn't always been focused on mobile. Today that will start to change as Red Hat announced its intention to acquire mobile development vendor [FeedHenry][1] for $82 million in cash. The deal is set to close in the third quarter of Red Hat's fiscal 2015. Red Hat is set to disclose its second quarter fiscal 2015 earning at 4 ET today.
|
||||
|
||||
Mike Piech, general manager of Middleware at Red Hat, told Datamation that upon the deal's closing FeedHenry's employees will become Red Hat employees
|
||||
|
||||
FeedHenry's development platform enables application developers to rapidly build mobile application for Android, IOS, Windows Phone and BlackBerry. The FeedHenry platform leverages Node.js programming architecture, which is not an area where JBoss has had much exposure in the past.
|
||||
|
||||
"The acquisition of FeedHenry significantly expands Red Hat's support for and engagement in Node.js," Piech said.
|
||||
|
||||
Piech Red Hat's OpenShift Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) technology already has a Node.js cartridge. Additionally Red Hat Enterprise Linux ships a tech preview of node.js as part of the Red Hat Software Collections.
|
||||
|
||||
While node.js itself is open source, not all of FeedHenry's technology is currently available under an open source license. As has been Red Hat's policy throughout its entire history, it is now committing to making FeedHenry open source as well.
|
||||
|
||||
"As we've done with other acquisitions, open sourcing the technology we acquire is a priority for Red Hat, and we have no reason to expect that approach will change with FeedHenry," Piech said.
|
||||
|
||||
Red Hat's last major acquisition of a company with non open source technology was with [ManageIQ][2] for $104 million back in 2012. In May of this year, Red Hat launched the ManageIQ open-source project, opening up development and code of the formerly closed-source cloud management technology.
|
||||
|
||||
From an integration standpoint, Red Hat is not yet providing full details of precisely where FeedHenry will fit it.
|
||||
|
||||
"We've already identified a number of areas where FeedHenry and Red Hat's existing technology and products can be better aligned and integrated," Piech said. "We'll share more details as we develop the roadmap over the next 90 days."
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.datamation.com/mobile-wireless/red-hat-acquires-feedhenry-for-82-million-to-advance-mobile-development.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Sean Michael Kerner][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.datamation.com/author/Sean-Michael-Kerner-4807810.html
|
||||
[1]:http://www.feedhenry.com/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.datamation.com/cloud-computing/red-hat-makes-104-million-cloud-management-bid-with-manageiq-acquisition.html
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,36 @@
|
||||
Wal Commander GitHub Edition 0.17 released
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
> ### Description ###
|
||||
>
|
||||
> Wal Commander GitHub Edition is a multi-platform open source file manager for Windows, Linux, FreeBSD and OS X.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> The purpose of this project is to create a portable file manager mimicking the look-n-feel of Far Manager.
|
||||
|
||||
The next stable version of our Wal Commander GitHub Edition 0.17 is out. Major features include command line autocomplete using the commands history; file associations to bind custom commands to different actions on files; and experimental support of OS X using XQuartz. A lot of new hotkeys were added in this release. Precompiled binaries are available for Windows x64. Linux, FreeBSD and OS X versions can be built directly from the [GitHub source code][1].
|
||||
|
||||
### Major features ###
|
||||
|
||||
- command line autocomplete (use Del key to erase a command)
|
||||
- file associations (Main menu -> Commands -> File associations)
|
||||
- experimental OS X support on top of XQuartz ([https://github.com/corporateshark/WalCommander/issues/5][2])
|
||||
|
||||
### [Downloads][3] ###.
|
||||
|
||||
Source code: [https://github.com/corporateshark/WalCommander][4]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://wcm.linderdaum.com/release-0-17-0/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:https://github.com/corporateshark/WalCommander/releases
|
||||
[2]:https://github.com/corporateshark/WalCommander/issues/5
|
||||
[3]:http://wcm.linderdaum.com/downloads/
|
||||
[4]:https://github.com/corporateshark/WalCommander
|
||||
@ -1,197 +0,0 @@
|
||||
barney-ro translating
|
||||
|
||||
How does the cloud affect the everyday linux user?
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
### Introduction ###
|
||||
|
||||
Cloud computing is one of those terms you hear about and see all the time whether it is in the national newspapers, online news websites, podcasts, technical blogs, technical news sites or on radio and television.
|
||||
|
||||
It is a fairly woolly term that encompasses so many things but what exactly is it?
|
||||
|
||||
> **Cloud computing** is a term used to refer to a model of network computing where a program or application runs on a connected server or servers rather than on a local computing device such as a PC, tablet or smartphone. Like the traditional client-server model or older mainframe computing,[1] a user connects with a server to perform a task. The difference with cloud computing is that the computing process may run on one or many connected computers at the same time, utilizing the concept of virtualization. With virtualization, one or more physical servers can be configured and partitioned into multiple independent “virtual” servers, all functioning independently and appearing to the user to be a single physical device. Such virtual servers are in essence disassociated from their physical server, and with this added flexibility, they can be moved around and scaled up or down on the fly without affecting the end user. The computing resources have become “granular”, which provides end user and operator benefits including on-demand self-service, broad access across multiple devices, resource pooling, rapid elasticity and service metering capability.[2]
|
||||
|
||||
The above quote was obviously taken from Wikipedia.
|
||||
|
||||
In the past we either used dumb terminals to connect to a mainframe or more recently desktop computers connected to applications on in-house servers which in turn connected to databases also kept on site.
|
||||
|
||||
The management of the desktops, applications and servers were all local and all had to be supported by the company who owned them.
|
||||
|
||||
Whilst this might be great for software houses it isn’t good business for other companies such as banks, insurance companies and oil companies. Information Technology is not a banking function in the same way catering isn’t a function of drilling oil out of the ground.
|
||||
|
||||
Large companies have long since outsourced many functions to dedicated companies. For example outside catering companies provide the staff canteen and we all know about the offshore call centres handling customer calls for the banks.
|
||||
|
||||
IT has also become an offshore function with a number of support and development functions shipped out to China, India, Malaysia and Eastern Europe.
|
||||
|
||||
Cloud computing is different to the typical model in that it is all about virtualisation. It is about putting applications on virtual servers which could all be in one location or could be thousands of miles apart but the point is it doesn’t matter because it is somebody else’s job to make sure they work.
|
||||
|
||||
> In common usage the term “the cloud” has become a shorthand way to refer to cloud computing infrastructure.[4] The term came from the cloud symbol that network engineers used on network diagrams to represent the unknown (to them) segments of a network.[5] Marketers have further popularized the phrase “in the cloud” to refer to software, platforms and infrastructure that are sold “as a service”, i.e. remotely through the Internet.
|
||||
|
||||
This article is therefore all about the cloud and what it means for the everyday linux user and what it can do for you and what, if any, pitfalls are there.
|
||||
|
||||
From an end user and home user point of view, cloud computing has basically come to mean any service that is hosted online.
|
||||
|
||||
So here goes, which cloud services are useful for an everyday linux user?
|
||||
|
||||
### Email ###
|
||||
|
||||
I would be very surprised if you are reading this and you don’t have an email account.
|
||||
|
||||
PC Advisor magazine analysed the top 6 emails services back in March, 2014 consisting of Outlook, GMail, Yahoo, iCloud, AOL and GMX.
|
||||
|
||||
### Office Suites ###
|
||||
|
||||
As well as an email client one of the most commonly used tools required by everyone is an office suite.
|
||||
|
||||
In the past people would toddle off down to PC World, buy a computer and come home with a great big machine and half a dozen CDs containing 5 programs you definitely won’t use and Microsoft Works which was a cheap and virtually useless cut down version of Microsoft Office.
|
||||
|
||||
Now you don’t even need an office suite on your computer even though there are some great free choices out there including LibreOffice and Kingsoft.
|
||||
|
||||
The obvious choices are of course Google Docs and Office 365. Does Office 365 work for Linux? Well this article from PC Pro in 2012 seems to suggest that it does.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
I don’t believe everything I read though so I signed up to Office 365 to see what would happen.
|
||||
|
||||
Signing up was free for a month and I was presented with a list of online applications that I could use which included Word, Excel and Outlook.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
All looked to be going well. I started Microsoft Word, chose a template to use and then of course it didn’t work at all.
|
||||
|
||||
Office 365 isn’t yet supported on Linux and to be honest you don’t need it. Move on.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Google Docs works and for home use it is perfect. There are hundreds of templates for the word processing and presentation tools and the spreadsheet application does most things although it doesn’t really replace Excel because you haven’t got hundreds of wannabe developers creating naff macros and VBA scripts everywhere.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Another alternative to Office 365 is Zoho.
|
||||
|
||||
Similar to Google Docs, Zoho includes a word processor, spreadsheet tool, presentation tool and mail.
|
||||
|
||||
There are finance and CRM tools as well.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The interface for the tools is actually very nice and clean.
|
||||
|
||||
Services such as Google Docs and Zoho also give you the power of collaboration.
|
||||
|
||||
Documents can be shared and worked on by different people in different locations.
|
||||
|
||||
This site provides a good list of alternative choices to Google Docs and Zoho.
|
||||
|
||||
### Online File Storage ###
|
||||
|
||||
Another good service provided by Google Docs and Zoho is the ability to store the documents and files you create online.
|
||||
|
||||
There are other services however such as Dropbox that are used to exclusively store your documents in the cloud.
|
||||
|
||||
The benefit of storing files with services like Dropbox is that if your house is burgled or catches fire then you have an offshore backup that remains intact. You can also access your files anywhere.
|
||||
|
||||
Dropbox is free for up to 2 gigabytes of use. If you have a lot more data, and most of us do nowadays, then there is a $ 9.99 monthly plan that is available allowing for 100 gigabytes. There is also a business version available from $ 15 a month.
|
||||
|
||||
There are of course alternatives to Dropbox and this site provides a list of the best online backup solutions.
|
||||
|
||||
### Photos ###
|
||||
|
||||
Since the introduction of digital cameras and more recently smart phones, more and more of us have memory cards full of photos.
|
||||
|
||||
I bet that at some point or other that you have lost photos because your phone died and the photos were on the phone and not the memory card or you lost your phone losing pictures of your child’s sports day or another important occasion.
|
||||
|
||||
Losing a phone is never a good thing. If you are clever you will have set up some sort of security because most people have their phones synchronised with their email accounts, Facebook, Twitter and even online banking.
|
||||
|
||||
All it takes to fix a lost phone is to change the passwords to all of the above accounts but lost photos are just not possible to recover and are a little bit more upsetting when lost.
|
||||
|
||||
One solution of course is to backup to your computer. This is of course a good first step but occasionally laptops break as well and you are back to square one.
|
||||
|
||||
Online photo storage sites are great resources because not only do they keep your photos safe you can also share them with whoever you choose to, eliminating the need to get 5 copies of the same photo developed to send to mum, nan, sister, aunty and mother-in-law.
|
||||
|
||||
The solution I like to use is Google’s Picasa but many of you will have heard of services like Flickr as well.
|
||||
|
||||
Lifehacker has a list of the five best photo sharing services.
|
||||
|
||||
Remember though that just because they are called photo sharing services doesn’t mean you have to share them. You can keep them just to yourself.
|
||||
|
||||
### Music ###
|
||||
|
||||
The first record that I was ever given was a 12 inch vinyl version of “Kings of the wild frontier” by “Adam and the Ants” back in the early 1980s.
|
||||
|
||||
As the 1980s progressed the long play records were replaced by cassettes and just as I had accumulated a decent number of cassettes the compact disc became the thing to have.
|
||||
|
||||
Hundreds of compact discs later and MP3 file sharing became the norm and it even became the legal way of doing things.
|
||||
|
||||
Nothing sits still with technology and the future is now with audio streaming services such as Spotify.
|
||||
|
||||
Spotify is free to use but is supported with the inclusion of adverts. In this regard it is like having your own personal radio station where you choose the playlist. Of course you can pay a monthly fee and have the adverts removed altogether.
|
||||
|
||||
There are dozens of similar services including Grooveshark and last.fm.
|
||||
|
||||
Techradar has a list of 7 alternatives to Spotify.
|
||||
|
||||
### Film ###
|
||||
|
||||
The first film I ever watched in the Cinema was Dumbo. The first video I ever watched was “Krull” which contained a young Dulph Lundgren. The format of the video was on Beta Max. (My next door neighbour had one).
|
||||
|
||||
My dad came home one day with a video recorder from Radio Rentals and my sister and I used to take it in turns to pick a video to hire from the video store. I remember my first choice being “The Black Hole”.
|
||||
|
||||
As with music time moves on. Just as you get large units full of movies, some genius comes along and develops DVDs and then they come out with Bluerays.
|
||||
|
||||
Now of course video streaming is the order of the day especially if you have a decent enough internet connection.
|
||||
|
||||
The most commonly known services are Netflix and Lovefilm.
|
||||
|
||||
This website has a list of good alternatives to Netflix. Not all of these services (including Netflix) work seamlessly on Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
### Gaming ###
|
||||
|
||||
Music, films and now gaming have moved to the online arena.
|
||||
|
||||
Gaming is of course more difficult. Music is relatively low cost in terms of bandwidth and although films require a little more, the stream just needs to remain steady to get a clear picture.
|
||||
|
||||
Games need to run at a consistently high frame rate to be playable and unless you have a decent connection it probably isn’t even worth trying.
|
||||
|
||||
Current services offering a cloud gaming service include OnLive and StreamMyGame.
|
||||
|
||||
This site contains a list of 6 online gaming services to rival OnLive.
|
||||
|
||||
### Pitfalls ###
|
||||
|
||||
Cloud computing isn’t free from issues.
|
||||
|
||||
There is the obvious problem of hacking. If someone gets access to your online banking or your email then you have a real problem.
|
||||
|
||||
What about online file storage? There is currently the high profile case of Megaupload.com.
|
||||
|
||||
Megaupload.com was essentially a file storage site for storing large files. The problem is that a lot of people used the service to share copyright material and the US authorities came down like a ton of bricks and the service was shut down.
|
||||
|
||||
Now a lot of people losing files would perhaps be expecting the inevitable but what about people who genuinely did nothing wrong. Their data has been lost. The US authorities refusing to give it back.
|
||||
|
||||
Finally there is the subject of service maintenance. If your email went down for a day could you cope? What about 3 days? What about a month? You are at the mercy of the service provider.
|
||||
|
||||
A lot has been made about large companies losing data and there has also been a lot of noise regarding heartbleed which is a vulnerability found in SSL left unpatched for years.
|
||||
|
||||
If you have services hosted for you online then you are relying on technical support staff to do their job properly and if they don’t you could be at the mercy of hackers, hardware failures and poor backup and recovery maintenance.
|
||||
|
||||
### Summary ###
|
||||
|
||||
Cloud computing has really become the buzz term for any online service. Your web browser is a client connecting to a server or clusters of servers hosted anywhere in the world. The point is that you don’t care. You don’t need to know.
|
||||
|
||||
Generally speaking I have barely touched the surface. We all use the cloud everyday and most of us don’t even think about it.
|
||||
|
||||
How does the cloud affect the everyday linux user? It turns out quite a bit.
|
||||
|
||||
Is the cloud a good or bad thing? Neither. Each service has to be judged on it’s own merits.
|
||||
|
||||
The term “The Cloud” is just something marketing people and the technical press get excited about. Anyone remember when they kept using the term “Web 2.0″?
|
||||
|
||||
Thankyou for reading.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxnews.pro/how-does-the-cloud-affect-the-everyday-linux-user/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -1,33 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Red Hat's CEO Sees Open Source Cloud Domination
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Red Hat CEO Jim Whitehurst sees the business opportunity of a generation in what he calls a computing paradigm shift from client server to cloud architectures. “In those paradigm shifts, generally new winners emerge,” says Whitehurst and he intends to make sure Red Hat is one of those winners. His logic is sound and simple: disruptive technologies like the cloud that arise every couple decades level the playing field between large, established firms and smaller, innovative challengers since everyone, from corporate behemoth to a couple guys in a garage, starts from the same spot and must play by the same unfamiliar and changeable rules. With the cloud “there’s less of an installed based and an opportunity for new winners to be chosen,” Whitehurst adds. His mission is “to see that open source is the default choice for next generation architecture” and that Red Hat is the preferred choice, particularly for enterprise IT, of open source providers.
|
||||
|
||||
The case for open source dominating the cloud rests on the fact that it’s already the foundation for many popular cloud services and enterprise applications. Whitehurst aptly notes that outside of Microsoft Azure, the underlying infrastructure of all the major public cloud services is built upon open source software. Furthermore, software like Linux, Apache, MySQL, WordPress and many others are already widely used and trusted by most enterprises. “In many cases [open source] already is the default choice for next generation architectures, but it hasn’t fully driven itself through the traditional enterprise data center,” he says. Cloud software is the next and most important software category up for open source disruption.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Yet open source is still saddled with a reputation for widely variable software quality and support, something the recent OpenSSL Heartbleed bug only reinforced. However Whitehurst contends that strong enterprise adoption of Red Hat’s Linux distribution and it’s training and skills certification programs lends credibility to a similar plan for the cloud: [Red Hat’s Cloud Partner Program][1]. He believes such insurance policies alleviate enterprise IT’s fears of adopting open source software for both internal, private clouds and external public cloud services. Red Hat wants its imprimatur to be the Good Housekeeping seal of approval for open source in general and cloud software in specific, namely IT’s assurance that their applications will work and the service is trustworthy and reliable.
|
||||
|
||||
Red Hat’s strategy to make open source clouds safe for the enterprise is mirrors that used to break into the market for enterprise server software. There, “Job one for Red Hat is making sure our operating system and layers above that work well on anyone’s infrastructure underneath,” says Whitehurst. Red Hat is applying this same model of polishing, integrating and supporting open source software to cloud stacks. “One of the most important parts about cloud, public, private or hybrid, is a sense that you can confidently run your applications,” says Whitehurst and he believes Red Hat’s track record on Linux and other open source products will carry over to make Red Hat “the enterprise choice” for cloud architectures.
|
||||
|
||||
### Cloud isn’t just virtualization 2.0 ###
|
||||
|
||||
One of the conundrums for OpenStack advocates like Whitehurst is the entrenchment of Microsoft and VMware in the enterprise market. Although virtual servers are a prerequisite for clouds, they’re sufficient. Countering the notion that enterprise clouds are just a natural extension of virtualized servers and storage, Whitehurst argues that by setting new rules for infrastructure and application design, cloud infrastructure is more than just the natural evolution of server virtualization.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Whitehurst draws an important distinction between traditional client-server and cloud-optimized applications. “One of the big questions will be how much of this [cloud adoption] is moving traditional Windows workloads, which frankly were written as stateful apps in the first place. [Instead] are we talking about a new generation of applications that are actually built with elasticity and scalability in mind.” Whitehurst clearly believes cloud infrastructure is much more appropriate for the latter and that in such Greenfield scenarios, OpenStack and other open source software have established themselves as the preferred platform. Contrasting OpenStack, based on the Linux KVM hypervisor and VMware or Microsoft using their proprietary virtual machine platforms, Whitehurst says, “Longer term, nobody really cares what the hypervisor is, you just expect it to work and bluntly, as long as Red Hat supports you on it, why do you have to care,” adding “more and more, you’ll see the hypervisor mattering less and less.” Of course, VMware and Microsoft probably agree, both having moved their energies to building more sophisticated management platforms and making the hypervisor a baseline feature.
|
||||
|
||||
But in Whitehurst’s view of the world, traditional virtualization platforms like VMware or Microsoft Hyper-V are legacy infrastructure designed for yesterday’s client-server software, not the sort of distributed, rapidly relocatable, elastically scalable applications that define the era of big data, SaaS and social software. “I’m not sure what good you get out of putting Exchange on a cloud,” he quips. Instead, he says this new generation of cloud-optimized applications are the sweet spot for OpenStack. According to Whitehurst, “If you look at where most new applications are getting built, and therefore where so much of the innovation around languages, frameworks and management paradigms are happening, it’s around an open infrastructure.” But there’s obviously some selection bias in Whitehurst’s account, as he lives in an open source world where it’s easy to be unaware, overlook or ignore the innovation happening on proprietary cloud platforms like Azure, AWS and vCloud.
|
||||
|
||||
In sum, Whitehurst hopes and expects OpenStack to do to VMware what Linux did to Windows: to become the first choice of cloud-savvy startups and if not the default choice, at least an accepted and respectable alternative within the enterprise. In my next column I’ll explain that even for an open source champion like Whitehurst, OpenStack versus VMware vCloud or Microsoft Azure isn’t an either/or choice and how he sees the fundamental notion of cloud computing as based on virtual machines as an design model likely to change.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.forbes.com/sites/kurtmarko/2014/06/08/red-hat-ceo-open-source-clouds/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.redhat.com/partners/become/cloud/
|
||||
@ -1,27 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Linux hiring frenzy: Why open source devs are being bombarded with offers to jump ship
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> Summary: Figures from the Linux Foundation suggest skills shortages across disciplines and throughout Europe.
|
||||
|
||||
Nine out of ten (87 percent) of hiring managers in Europe have "hiring Linux talent" on their list of priorities and almost half (48 percent) say they are looking to hire people with Linux skills within the next six months.
|
||||
|
||||
But while they either need or want to hire more people with Linux skills, the data from the Linux Foundation suggests that this is easier said than done. Almost all — 93 percent — of the managers surveyed said they were having difficulty finding IT professionals with the Linux skills required and a quarter (25 percent) said they have "delayed projects as a result".
|
||||
|
||||
All of this makes it a good time to be a Linux expert.
|
||||
|
||||
Seven out of 10 Europe-based Linux professionals have received calls where they were pitched new positions in the past six months, and a third said they had received more calls than in the previous six months. One in three are looking to move anyway, and over half of them said it would be fairly or very easy. Salary is the biggest reason to move jobs, followed by work-life balance and the chance to gain additional skills.
|
||||
|
||||
Employers are trying harder to keep hold of staff too: In the past six months, 29 percent of Linux professionals say they have been offered a higher salary from their current employers, while a quarter said they’ve been offered a flexible work schedule and one in five have been extended additional training opportunities or certification.
|
||||
|
||||
The Linux Foundation, a non-profit organisation which supports the growth of Linux, and Dice Holdings, which provides career sites for technology professionals, produced the research which covers Europe and the US.
|
||||
|
||||
In terms of the specific skills organisations are looking for people with the developer (69 percent) and enterprise management (51 percent) skills. These are followed by 32 percent of respondents who are looking for people with a combination of development and operations skills (DevOps), and 19 percent who are in management/IT management.
|
||||
|
||||
The Linux Job Report has been produced for the last three years by the Linux Foundation and Dice but this is the first time that a specific report on European skills has been separated out of the worldwide report. Some 893 Linux professionals responded to the survey across Europe.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.zdnet.com/linux-hiring-frenzy-why-open-source-devs-are-being-bombarded-with-offers-to-jump-ship-7000030418/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -1,61 +0,0 @@
|
||||
The Companies That Support Linux: Rackspace
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
[][1]
|
||||
|
||||
[Rackspace][1] has lately been in the news for its stock market gains and a [potential acquisition][2]. But over the past 16 years the company has become well known, first as a web hosting provider built on Linux and open source, and later as a [pioneer of the open source cloud][3] and founder of the OpenStack cloud platform.
|
||||
|
||||
In May, Rackspace became a [Xen Project][4] member and was one of [three companies to join the Linux Foundation][5] as a corporate member, along with CoreOS and Cumulus Networks.
|
||||
|
||||
“Many of the applications and infrastructure that we need to run for internal use or for customers run best on Linux,” said Paul Voccio, Senior Director of Software Development at Rackspace, via email. “This includes all the popular language frameworks and open virtualization platforms such as Xen, LXC, KVM, Docker, etc.”
|
||||
|
||||
In this Q&A, Voccio discusses the role of Rackspace in the cloud, how the company uses Linux, why they joined the Linux Foundation, as well as current trends and future technologies in the data center.
|
||||
|
||||
### Linux.com: What is Rackspace? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Paul Voccio: Rackspace is the managed cloud specialist and founder of OpenStack, the open-source operating system for the cloud. Hundreds of thousands of customers look to Rackspace to deliver the best-fit hybrid cloud solutions for their IT needs, leveraging a product and services portfolio that allows workloads to run where they perform best – whether on the public cloud, private cloud, dedicated servers, or a combination of platforms.
|
||||
|
||||
As a managed cloud pioneer, we give our customers 24x7 access to cloud engineers for everything from planning and architecting to building and operating clouds through our award-winning Fanatical Support®. We help customers successfully architect, deploy and run their most critical applications. Or, more plainly put, we’re cloud specialists so you don’t have to be. We are headquartered in San Antonio, Texas, and operate a global support and engineering organization with data centers on four continents.
|
||||
|
||||
### How and why do you use Linux? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Rackspace uses Linux because it provides a stable and flexible platform for our customers' workloads. Our customers trust us to support their mission-critical applications and we need reliable infrastructure – including software and hardware – to meet their expectations. If you look under the hood in our dedicated environments or in our expansive cloud infrastructure, you'll find Linux running there.
|
||||
|
||||
Many of the applications and infrastructure that we need to run for internal use or for customers run best on Linux. This includes all the popular language frameworks and open virtualization platforms such as Xen, LXC, KVM, Docker, etc. Running combinations of these platforms give us the stability and performance we demand for the Rackspace Cloud. Our Cloud Servers product runs OpenStack services that manage tens of thousands of hypervisors – all running Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
Using Linux also allows us to tap into a community of experts to solve problems. When we have an issue, we're comfortable asking questions. When we have a solution, we enjoy sharing it with the community. At Rackspace, we understand how to work and contribute in an open community and Linux has many opportunities to build relationships with other groups that have similar goals.
|
||||
|
||||
### Why did you join the Linux Foundation? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Joining the Linux Foundation allows us to show our support and engage the Linux community in new ways. We've learned plenty from running Linux in highly demanding environments at a large scale and we're eager to share those experiences. Other members of the community have probably run into different challenges than we have and this gives us a greater opportunity to learn from them as well.
|
||||
|
||||
### What interesting or innovative trends are you witnessing in the data center and what role does Linux play in them? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Virtualization and automation have changed how companies deploy hardware and software. Linux gives us several virtualization options and these allow us to automate more of our infrastructure deployments and maintenance tasks. Automation and configuration management frameworks allow us to reduce our costs, improve our testing capabilities, and bring products to market faster. The majority of these open source automation frameworks run best on Linux servers.
|
||||
|
||||
### How is Rackspace participating in that innovation? ###
|
||||
|
||||
We leverage several open-source Linux-based tools and projects to deliver great customer outcomes. One of our largest efforts in this area is with OpenStack. It's the software that runs our public and private clouds and we're actively engaged with the community to improve it. We're using Linux to find new ways to scale our large virtualization platform and deliver infrastructure to customers quickly.
|
||||
|
||||
The open-source nature of Linux inspires us to share the majority of these discoveries with the community. Our customers can improve OpenStack and those improvements will eventually make it into our product offering. We make contributions to a countless number of open source projects either as a company or as individual Rackers (our employees are called "Rackers") and many of these projects are designed to run on Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
### What other future technologies or industries do you think Linux and open source will increasingly become important in and why? ###
|
||||
|
||||
The move to software-defined infrastructure is a big shift. Customers already have access to virtualization platforms like Xen that allow them to define their infrastructure with software. Software-defined networking is quickly becoming more mature and scalable. However, customers want the ability to have a software defined datacenter at their fingertips. This may involve physical servers, virtual servers, and virtual networks that need high performance with flexible configurations. Many of the current technologies are designed to run on Linux due to technology already available in the kernel or userland frameworks provided by the community.
|
||||
|
||||
### Are you hiring? ###
|
||||
|
||||
From hacking on kernels to supporting thousands of virtual machines – we are always looking for talented admins, developers and engineers. You can find more information at Rackertalent.com.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linux.com/news/featured-blogs/200-libby-clark/775890-the-companies-that-support-linux-rackspace/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.rackspace.com/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.bloomberg.com/news/2014-05-15/rackspace-hires-morgan-stanley-to-evaluate-options.html
|
||||
[3]:http://www.informationweek.com/cloud/infrastructure-as-a-service/9-more-cloud-computing-pioneers/d/d-id/1109120
|
||||
[4]:http://www.xenproject.org/
|
||||
[5]:http://www.linuxfoundation.org/news-media/announcements/2014/05/new-linux-foundation-members-advance-massively-scalable-secure
|
||||
@ -1,79 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Fire Phone Dynamic Perspective tracks eyes for 3D UI
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
3D on phones is back, and it's Amazon giving it a try this time with Dynamic Perspective on the new [Fire Phone][1]. Eschewing a "true" 3D display as we've seen before, the Fire Phone's system instead uses four front-facing cameras to track the user's eyes, and adjusts the on-screen UI so that the various layers shift around to give the impression of 3D.
|
||||
|
||||
A combination of physically tilting the phone and moving your head as you hold it can be used to navigate through the interface and apps. So, tilting the Fire Phone can scroll through the browser, rather than having to swipe around with a fingertip.
|
||||
|
||||
youtube视频链接地址:[http://www.youtube.com/embed/iB75HJe8eiI][2]
|
||||
|
||||
Similarly, with a carousel of items in Amazon's store on the phone, tilting the handset left and right pans through the products.
|
||||
|
||||
youtube视频链接地址:[http://www.youtube.com/embed/lwj0hlE8CJc][3]
|
||||
|
||||
In ebooks, the Kindle app can scroll through according to how you're holding it. The settings can be switched between adjusting speed depending on how extreme the tilt angle is, or locking it to a fixed rate if you'd rather have things be predictable.
|
||||
|
||||
### This is the Amazon Fire Phone ###
|
||||
|
||||
Maps, too, get Dynamic Perspective support. Moving the Fire Phone around can show what's "hiding" behind 3D buildings or on different layers. Tilting can also be used to open up menus, in games for motion control, and even to navigate between the now-playing and lyrics UIs in the Prime Music app.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
All that 3D didn't come easy, though. Based on the fact that every face is different, with variations in hair color, shape, whether they wear glasses, and other factors, Amazon had to put Dynamic Perspective through some serious testing.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
In the companies labs, that involved a somewhat nightmarish rubber head on a stick, but then Amazon expanded that to use real-world data from thousands of photos of people. The use of four cameras means that, no matter what may be blocking the screen, the Fire Phone should be able to spot the user properly.
|
||||
|
||||
youtube视频链接地址:[http://www.youtube.com/embed/X-wPOq27iXk][5]
|
||||
|
||||
Whether it'll all work as Bezos says, or be something owners quickly turn off, remains to be seen. We'll know more when we spend some hands-on time with the Fire Phone soon.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.slashgear.com/fire-phone-dynamic-perspective-tracks-eyes-for-3d-ui-18334229/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.slashgear.com/tags/fire-phone
|
||||
[2]:http://www.youtube.com/embed/iB75HJe8eiI
|
||||
[3]:http://www.youtube.com/embed/lwj0hlE8CJc
|
||||
[4]:http://www.slashgear.com/this-is-the-amazon-fire-phone-18334195/
|
||||
[5]:http://www.youtube.com/embed/X-wPOq27iXk
|
||||
@ -1,39 +0,0 @@
|
||||
CNprober translating..
|
||||
|
||||
Staying free – should GCC allow non-free plug ins?
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> Arguments in favour of the use of non-free plug-ins in GCC have again been raised on GCC mailing-lists, but are trumped by the arguments for GCC as a vehicle for free software development
|
||||
|
||||
Once again, Gcc and its lack of modularity has been raised as an issue and contrasted with LLVm, the new compiler on the block. GCC is huge and venerable: 5 million lines, 30 years, and growing. LLVM, in contrast, is relatively youthful and modular and allows free and proprietary languages to be added as modules.
|
||||
|
||||
The core of LLVM is ‘open source’. GCC is copyleft and unreservedly free software and doesn’t allow plug-ins or other means to add proprietary extensions to the GCC code. The argument, as delivered by Eric Raymond, is that “FSF can no longer prevent proprietary vendors from plugging into a free compiler to improve their tools. That horse has left the barn; the strategic goal of the anti-plug-in policy has been definitively busted.”
|
||||
|
||||
LLVM has been sponsored by Apple as a replacement for GCC on OS X and Apple hardware and has grown in popularity, especially among users of the BSDs. Advocates of LLVM see it as a putative replacement for GCC in the wider market for applications developers and mobile devices. The argument against GCC is that its complexity, and the commitment of its developers to copyleft licensing, constrains the possibilities for proprietary developers, who do not want to release their language or architectural specifications under a copyleft licence. Apple, of course, has a long history of antipathy to free software, and doesn’t allow applications licensed under copyleft licences to be distributed through its App Store.
|
||||
|
||||
To this extent, the argument between LLVM and GCC is a retread of the historic differences between GNU/Linux and the BSDs, between ‘open source’ and free software. Open source developers allow the code to be reused in any context, free or proprietary. Free software is restrictive in that it insists that the code, and any modifications to the code, must remain free in perpetuity. Advocates of free software would argue that the integrity of copyleft licensing has been instrumental in the spread of GCC, and has taken Linux and free software into places it would not otherwise have reached, and that free software cannot be bought or corrupted by commercial or corporate interests. Open source advocates argue that open source is more free because the user has no restrictions and can do what he or she likes, including developing closed source versions of the code.
|
||||
|
||||
Since the beginning, the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC) was vital to the spread of free software. Compilers were a rare and expensive commodity and the compilers of the proprietary software companies were rife with ‘features’ that were non-compliant with ANSI programming standards. Porting software between different machines and operating systems was an unnecessarily complicated task. GCC, the first truly free cross-platform compiler, commoditised this process.
|
||||
|
||||
GCC was a breakthrough product for applications developers and mobile device developers – not just those who were committed to the idea of free software. Not only was GCC free and portable, its ubiquity and commonality across different architectures made it easier to port software between machines and to expect robust and consistent results – as the likes of John Gilmore, Michael Tiemann and David Henkel- Wallace were to discover when they made GCC and its development the key selling point of Cygnus Solutions, the first company to make money by selling free software.
|
||||
|
||||
The primary technical difference between LLVM and GCC emerges in the separation between the modules that form the ‘front ends’, ‘middle end’ and ‘back ends’ of both GCC and LLVM. ‘Front ends’ are used to interpret the code specific to the translation of a particular language. The ‘middle end’ optimises the translated code. The ‘back ends’ take the optimised code and apply the results to a specific target architecture. LLVM separates these modules into distinct entities, but for semantic and historical reasons, GCC obfuscates the separation between the modules.
|
||||
|
||||
Perhaps untypically for a free software project, it is a difficult process to add a new language or architecture to GCC and the adding of proprietary plug-ins is not allowed. There is little clear separation between the modules, and the path of least resistance is to add any feature under a free software licence. The early ports of C++ and Objective C (via Apple) are cited as examples where the original developers might have preferred to keep the code in-house and proprietary, and instead released the code as free software.
|
||||
|
||||
In contrast, LLVM has allowed, or perhaps even encouraged, the addition and development of proprietary languages and architectures – one example being Nvidia’s NVCC for GPU computing, based on Clang and LLVM. The source code of NVCC is inaccessible to free software or ‘open source’ developers.
|
||||
|
||||
Richard Stallman’s [take on this][1] is characteristically resolute: “In the free software movement, we campaign for the freedom of the users of computing. The values of free software are fundamentally different from the values of open source, which make‘bettercode’theultimategoal. IfGCCwere to change from a free compiler into a platform for non-free compilers, it would no longer serve the goal of freedom very well.
|
||||
|
||||
“The Clang and LLVM developers reach different conclusions from ours because they do not share our values and goals. They object to the measures we have taken to defend freedom because they see the inconvenience of them and do not recognise (or don’t care about) the need for them. I would guess they describe their work as ‘open source’ and do not talk about freedom.”
|
||||
|
||||
The GCC developers are unlikely to compromise on the licensing terms. While LLVM is fashionable among certain sectors of industry, because it is young and new and has been quicker to jump on developing trands in programming languages, the prevailing wind is towards greater openness, and GCC’s resolve to be incorruptible and free from commercial interests, may be the greater asset in the long term. The Unix companies learnt something from the Unix wars of the Eighties and Nineties. Languages and operating systems are tools, and are better open and shared. GCC is free software and belongs to nobody.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxuser.co.uk/features/staying-free-should-gcc-allow-non-free-plug-ins
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://lwn.net/articles/582241
|
||||
@ -1,37 +0,0 @@
|
||||
$2400 Valued Introduction To Linux Course Is Available For Free On edX
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Probably you have already heard it. [Linux Foundation][1] has tied up with [edX][2] (a major online learning platform founded by MIT and Harvard University) to provide its Introduction to Linux course, which usually costs $2400, for free.
|
||||
|
||||
edX has over 200 courses from over 50 elite universities, corporations and organizations worldwide. Over 2.5 million users attend these online courses across the globe.
|
||||
|
||||
**Introduction to Linux course is starting from 1st August**. There are three ways one can take this course (or most other edX courses):
|
||||
|
||||
- **Audit the course**: Simple register for **free** and get access to study material. Participate in course as per your own pace. There is no compulsion or penalty if you cannot complete the course.
|
||||
- **Honor code certificate**: It certifies that you have successfully completed the course, however, it doesn’t verify your identity. This too is for free.
|
||||
- **Verified certificate of achievement**: This certificates validates your identity and costs $250 for **Introduction to Linux** course.
|
||||
|
||||
Introduction to Linux requires a working knowledge of computers and common software. Program aims to provide experienced computer users, who may or may not have previous Linux experience, a good working knowledge of Linux, from both a graphical and command line perspective. It consists a course work of 40 to 60 hours and is designed by Dr. Jerry Cooperstein, who manages training content at Linux Foundation.
|
||||
|
||||
If you are planning to attend Introduction to Linux, it is advised to have Linux installed on your computer beforehand. Linux Foundation has [prepared a guide to set up the computer][3] to help users out.
|
||||
|
||||
What are you waiting for? If you ever wanted to learn Linux, this is the time and best of all, it’s FREE! Sign up to the course with the link below:
|
||||
|
||||
- [Introduction to Linux course at edX][4]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/introduction-linux-free-edx/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://itsfoss.com/author/Abhishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.linuxfoundation.org/
|
||||
[2]:https://www.edx.org/
|
||||
[3]:https://training.linuxfoundation.org/images/pdfs/Preparing_Your_Computer_for_LFS101x.pdf
|
||||
[4]:https://www.edx.org/course/linuxfoundationx/linuxfoundationx-lfs101x-introduction-1621#.U9gJ5nWSyb8
|
||||
@ -1,28 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Microsoft’s Raspberry Pi Will Cost $300
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
I presume that you have heard of [Raspberry Pi][1]. A $35 microcomputer that has revolutionized the low cost computing and has cult following among hardware hobbyist and do-it-yourself enthusiasts. Several other followed in the footsteps of Raspberry Pi to provide low cost micro computers, [Arduino][2] is one of the successful examples.
|
||||
|
||||
Microsoft has decided to enter the world of “System on Chip” and to come up with its “own Raspberry Pi”. Teamed up with Intel and [CircuitCo][3], [Microsoft will be launching a micro computer named “Sharks Cove“][4].
|
||||
|
||||
Sharks Cove boasts of Intel Atom Z3735G, a quad-core chip with speeds up to 1.83GHz, 1GB of RAM, 16GB of flash storage and a MicroSD slot among many other things. You can read the full specifications [here][5]. The main aim of Shark Cove is to provide a platform to develop hardware and drivers for Windows and Android.
|
||||
|
||||
Everything sounds fine till it comes to price. Sharks Cove will cost $299 with a Windows 8.1 license. While Arduino costs around $55 and Raspberry Pi $35, I don’t think there will be many buyers for such a high price in a domain which is dominated by low cost Linux based devices. What do you think?
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/microsofts-raspberry-pi/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://itsfoss.com/author/Abhishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.raspberrypi.org/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.arduino.cc/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.circuitco.com/
|
||||
[4]:http://blogs.msdn.com/b/windows_hardware_and_driver_developer_blog/archive/2014/07/26/the-sharks-cove-is-now-available-for-pre-order.aspx
|
||||
[5]:http://www.sharkscove.org/docs/
|
||||
@ -1,94 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Nostalgic Gaming On Linux With Good Old Games
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Thanks to the recent Linux support provided by DRM-free classic games provider, GOG.com, getting that nostalgic kick on Linux has never been easier. In this article I'll also detail a few of my favourite classic games that are now available to play in Linux.**
|
||||
|
||||
It's not all nostalgia, though. Some of the classic games you might think of are genuinely classic, amazing games no matter their age. Others, you might need to imagine you're back in, say, 1995 and look at the game from that point of view to appreciate how good it must have seemed at that time. Whatever the case though, there's no shortage of these old games out there to enjoy and thankfully it's recently gotten even easier with [GOG.com][1] recently announcing Linux support.
|
||||
|
||||
A lot of these old classic games actually run in [DOSBox][2], so a seasoned Linux gamer who has experience with such games may bring up the point that you could play a lot of these games provided by services such as GOG.com for years already, well before that recent announcement. Which is correct, I've done the same thing myself, but it does involve a bit of fiddling with files, so at the very least we now have a "turn-key" solution even with the DOSBox powered games - you download them, you launch them, they should just work. If you just want to purchase a game and play it right away, that's no bad thing.
|
||||
|
||||
Then there's the non-DOS games. A lot of old Windows 95/98 games do often work fine in WINE, but not always, or perhaps need workarounds to be manually applied or even a special version of WINE itself. Some old games just won't work at all no matter what you try, even on modern versions of Windows itself! So again, having an alternative available that is designed to work out-of-the-box (and DRM-free, no less) is a nice thing.
|
||||
|
||||
GOG.com initially provided 50 Linux compatible games on their penguin-friendly launch, but that number is and will keep growing. In coming months they say they hope to reach 100 games, and who knows how many thereafter, but it should grow to be a fairly considerable library.
|
||||
|
||||
Here are a few of my favourites so far, that are available right now:
|
||||
|
||||
### Rise Of The Triads Dark War (1994) ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
If you crave some 90's style shoot-em-up action where you get to blow the hell out of, well, everything and everyone, Rise Of The Triads (ROTT) is one of the best choices and a favourite to many.
|
||||
|
||||
If you know these kinds of shooters, you probably know what to expect. There is a storyline, but really it's about blowing everything up and/or riddling enemies full of bullet holes. As a member of an elite group of operatives you are sent to a remote island to stop a mad cult leader, where typically everything goes pear-shaped and you have to kill everything and successfully navigate levels to save the day and get out alive in the process.
|
||||
|
||||
True to the arcade-style shooter of this vintage, weapons are all about being big, high-tech and fun. You might be in an elite operations group, but you ain't stuck with peashooters and standard rifles - no there's duel pistols all the way to heat seeking missiles and the Flamewall cannon and many more. It's all about genuine fun and doesn't take itself too seriously.
|
||||
|
||||
*Verdict: A blast (literally)*
|
||||
|
||||
### Realms Of The Haunting (1996) ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
This one is actually fairly new to me and isn't a game I remember from years back. Which is my loss really, as I can imagine this game must have seemed pretty incredible all the way back in 1996.
|
||||
|
||||
Realms Of The Haunting is something of a first-person shooter/point-and-click adventure combination. The controls at first seem a bit strange because of this (keyboard to control movement and attack etc. Mouse to move the context indicator/cursor around the screen and interact with objects) but you soon get used to it. The storyline, although I have not experienced all of it yet myself, is apparently very good and certainly my impressions of it have been good. This is also one of those classic games that uses good old FMV (Full Motion Video) for cutscenes.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Basically you play as a young man who receives a suitably vague letter from your recently deceased father about a strange deserted mansion and it's curious happenings inside. Naturally, said young man decides to visit the mansion and discovers his father's spirit being held captive by the forces of evil and then sets out to try free him. That sounds like a pretty standard storyline at first but the difference lays in the execution and how it progresses.
|
||||
|
||||
From the moment the main character picks up a lantern and gazes around the dark, creepy surroundings of the mansion, it actually reminds me a bit of Amnesia: The Dark Descent. Sure, the gameplay and amount of actual combat means the comparison somewhat ends after that, but ROTH does also have it's fair share of exploration and puzzles. Despite a very dated looking graphics engine (it is based on the DOOM engine after all!) it strikes me how much attention to detail the game creators managed to pack into the environment, which further adds to the atmosphere and immersion despite the constant pixel party happening on screen.
|
||||
|
||||
All in all, Realms Of The Haunting is a creepy but very intriguing old game that is very much worth checking out. And if you love games that feature old-school FMV, there is heaps on offer here too.
|
||||
|
||||
*Verdict: Ahead of it's time?*
|
||||
|
||||
### Sid Meier's Colonization (1994) ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Think Civilization, but with a colonial twist. Instead of building a nation from a mound of dirt in the middle of nowhere, Colonization tasks you with controlling either the forces of England, France, Spain or The Netherlands as you set about managing expansion across the Atlantic for your nation of choice. The aim of the game, as far as winning goes, is to achieve independence from your mother country and defeat the angry Royal Expeditionary Force that comes your way.
|
||||
|
||||
If big chunky pixels, even in text, is something that hurts your eyes you may want to avoid this one but the simple old graphics belie the actual gameplay and depth available here. If you have experience with the more modern Sid Meier turn-based strategy games like the Civilization series, you may be surprised just how much familiar elements and gameplay there is in this old game.
|
||||
|
||||
It may appear ancient and a little clunky, but like most of the classic Sid Meier games, you can sink hours upon hours into this game. Which considering it's price nowadays, no more than a piece of cake and a coffee, is fantastic value that is hard to beat. Do try it.
|
||||
|
||||
*Verdict: Superb turn-based strategy, all the way from 1994*
|
||||
|
||||
### Sword Of The Samurai (1989) ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
This one is a little more obscure and may surprise. For me, and this will sound a little cliché given the Japanese theme and setting, but there is something rather Zen about Sword Of The Samurai. A product in the year 1989, the graphics are obviously simple and have a very limited colour palette. Yet, I think even today the graphics work for this particular game and add to its charm and, again, the Zen.
|
||||
|
||||
Describing SOTS is difficult though. It's sort of... a strategy, war, dating, stealth, melee, dueling, diplomacy, choose-your-own adventure Samurai sim.
|
||||
|
||||
Seriously.
|
||||
|
||||
Somehow this old game, which weighs in less than 20 megabytes, fits in an incredible amount of different gameplay (and surprisingly smart artificial intelligence) and approaches you can take to achieve your goal. The core goal is get a very important thing called Honor. In the world of feudal Japan, Honor is a big, big thing and you must get more Honor any way you can in order to achieve the goal of unifying Japan under your rule, as Shogun.
|
||||
|
||||
While you can of course be the "good guy" and do everything you think is right to get Honor, the game is inherently deep and clever enough to allow you to achieve Honor even with, shall we say, more underhanded tactics.
|
||||
|
||||
It's difficult to truly describe all the ways you can play this game but my advice is to simply do so - play it, let it wash over you and soak in the Japanese culture and atmosphere that the game exudes in a really classy way, without being over-the-top. And yes, the game can also be educational! You can't beat that.
|
||||
|
||||
*Verdict: An under-appreciated masterpiece*
|
||||
|
||||
### Get your game on ###
|
||||
|
||||
So there we have it, there's some of my favourites that I've been (re)playing recently, on my Fedora 20 system no less. Some of these games may be older than Linux (the kernel) itself, but thanks to the likes of GOG.com and especially emulators like DOSBox, you can still enjoy the classic titles you remember from years gone by.
|
||||
|
||||
What are some of your favourite classic games? Are you also playing them now in your favourite Linux distro? Let us know in the comments!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://thelinuxrain.com/articles/nostalgic-gaming-on-linux-with-good-old-games
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Andrew Powell
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://gog.com/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.dosbox.com/
|
||||
@ -1,132 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Five Awesome GOG.com Linux Games Everyone Should Play Once
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
GOG AKA ILU TUX NAO
|
||||
|
||||
**Ardent Linux gamers will have seen last week as a good one, as rising game distribution service [GOG.com brought a batch of more than 50 classic PC and indie titles to the platform][1], many for the very first time.**
|
||||
|
||||
Against the 775 DRM-free offerings offered to Windows users, not to mention the 600 strong Linux catalog on Steam, it might not sound like much. But the company says this is only the first wave and that another 50 games are set to land later in the year.
|
||||
|
||||
Last week [we asked][2] our Facebook fans which five games being sold by GOG they consider ‘must have’ titles.
|
||||
|
||||
After pruning the titles often found warming the shelves of the Humble Bundle (*e.g., Uplink: Hacker Elite, Darwinia, Don’t Starve and Anomaly Warzone Earth*), and throwing in a free title for good measure, we came up with the following list.
|
||||
|
||||
It’s not comprehensive, it’s not definitive and it’s certainly not going to be the five you’d pick. But for those either too young to have experienced some of these games for the first time, or old enough to level up nostalgia, it’s a great jumping in point.
|
||||
|
||||
Because we know it matters to some of you, we’ve listed the ‘port’ type for each entry, so you can avoid Wine or DOSBox where needed.
|
||||
|
||||
Finally (though it really should go without saying) if you’re looking for full HD immersive 3D worlds with GPU melting graphics requirements, this is not the list for you.
|
||||
|
||||
Now to hark back to rainy days spent cooped up inside, eyes firmly fixed on a CRT monitor…
|
||||
|
||||
### FlatOut ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Year**: 2005. **Genre**: Racing. **Port**: Wine. **Price**: $5.99 (inc. extras).
|
||||
|
||||
Unbuckle up and prepare for one bad-ass and throughly bumpy ride.
|
||||
|
||||
Trying to condense why FlatOut is a classic demolition rally game into just a few short sentences is traumatic. Almost as traumatic as being a driver in it must be.
|
||||
|
||||
Its premise — carnage, destruction, more carnage — reads fairly standard these days. Virtually every racing game (at least those worth their tread) implements an element of off-road mayhem. But FlatOut was one of the first, and even today remains one of the best.
|
||||
|
||||
With 36 course littered with more than 3000 items to crash and smash, plus 16 upgradeable vehicles, each made up of 40 “deformable pieces” for ultimate on-screen obliteration, FlatOut is flat out one of the best raucous racing games available on Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
*Also check out Flat Out 2, released in 2011 and costing $9.99.*
|
||||
|
||||
- [Buy “FlatOut” on GOG][3]
|
||||
|
||||
### Duke Nukem 3D: Atomic Edition ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Year**: 1995. **Genre**: First-Person Shooter. **Port**: DOSBox. **Price**: $5.99 (inc. extras).
|
||||
|
||||
Politically incorrect, full of female objectification, and featuring more cheesy one-liners than the script of a straight-to-VHS Jean-Claude Van Damme action film. Yep, it’s Duke Nukem.
|
||||
|
||||
But c’mon; no list of retro PC classics would be complete without a least one Duke Nukem entry, right? They are bona fide classics. Along with Doom and Quake, it kickstarted the gory corridor crawling shooter genre.
|
||||
|
||||
Most of its strengths are in the pastiche; it is camp, cheesy and kaleidoscopically brash, and takes itself about as seriously as a Sega MegaCD video cutscene from Night Trap.
|
||||
|
||||
The environments are varied and rich. The gameplay mechanics easy to get to grips with. And while the less than subtle humour laced throughout may rile the easily offended, those of a certain age won’t be able to resist smirking at the pop-culture satire.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Buy “Duke Nukem: Atomic Edition” on GOG][4]
|
||||
|
||||
### The Last Federation ###
|
||||
|
||||
Youtobe 视频地址:
|
||||
https://www.youtube.com/embed/5RKXWpyf1i4?feature=oembed
|
||||
|
||||
**Year**: 2014. **Genre**: Strategy. **Port**: Native. Price: $19.99.
|
||||
|
||||
The Last Federation is the most expensive title on this list and also the most modern, having debuted this year.
|
||||
|
||||
It’s a turn-based tactical combat set in space that burdens you with the task of ‘forging a lasting federation of planets and usher in an era of peace and prosperity to the solar system.’
|
||||
|
||||
But to forge a lasting truce you must indulge your inner machiavellian monsters.
|
||||
|
||||
*“Remember, when helping civilizations evolve, sometimes they evolve faster when a large multi-headed monster is glaring menacingly at them,” reads the game’s synopsis.*
|
||||
|
||||
Pricey, but one of the standout strategy games of 2014.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Buy “The Last Federation” on GOG][5]
|
||||
|
||||
### StarGunner ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Year**: 1996. **Genre**: Arcade. **Port**: DOSBox. Price: Free.
|
||||
|
||||
StarGunner is one of two Linux games available for free on GOG. It’s a space-based side scrolling shoot ‘em up, similar to thousands of mid-nineties arcade games now resting in a land fill somewhere.
|
||||
|
||||
That’s not to say it’s not any good; it’s great fun but just a little familiar.
|
||||
|
||||
Gameplay is fast, battlefields switch between space, ground and water often enough to maintain interest, and with more than 75 different enemy crafts (plus over 30 super adaptive bosses) things never get visually tired, either.
|
||||
|
||||
Look out for weapons and other power-ups littered through levels.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Download “StarGunner” for free on GOG][6]
|
||||
|
||||
### Blocks That Matter ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Year**: 2011. **Price**: $2.99. **Genre**: Platformer. **Port**: Wine, 32-bit only.
|
||||
|
||||
Take some blocks, drop them into an isometrical world, add bit of jumping and a whole lot of puzzle solving. Finally, coat it all in a layer of cuteness. Aside from an needlessly drawn out introduction, you should end up with **Blocks That Matter**. And boy do these blocks matter.
|
||||
|
||||
Playing as a robot called Tetrobot, your sole aim is to waddle about each level drilling blocks of various materials (sand, ice, etc.) one by one. Blocks can be collected and inserted into the game to help you complete levels, but depending on the material this can often be a hindrance rather than a help.
|
||||
|
||||
An innovative 2D platform-puzzler, it offers up 40 levels in standard Adventure Mode with another 20 waiting to be unlocked. It’s cute, clever and cheap.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Buy “Blocks that Matter” on GOG][7]
|
||||
|
||||
### Honourable Mentions ###
|
||||
|
||||
####DarkLands####
|
||||
|
||||
**Year**: 1992. **Genre**: RPG. **Port**: DOSBox. **Price**: $5.99 (inc. extras).
|
||||
|
||||
#### Sid Meier’s Covert Action ####
|
||||
|
||||
**Year**: 1990. **Genre**: Action/Strategy. **Port**: DOSBox. **Price**: $5.99 (inc. extras).
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/08/five-best-linux-gog-com-games-available-now
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Joey-Elijah Sneddon][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://plus.google.com/117485690627814051450/?rel=author
|
||||
[1]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/07/50-classic-pc-games-now-available-linux-gog
|
||||
[2]:https://www.facebook.com/omgubuntu/posts/830930706919468
|
||||
[3]:http://www.gog.com/game/flatout
|
||||
[4]:http://www.gog.com/game/duke_nukem_3d_atomic_edition
|
||||
[5]:http://www.gog.com/game/last_federation_the
|
||||
[6]:http://www.gog.com/game/stargunner
|
||||
[7]:http://www.gog.com/game/blocks_that_matter
|
||||
@ -1,105 +0,0 @@
|
||||
zpl1025
|
||||
Where And How To Code: Choosing The Best Free Code Editor
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
A close look at Cloud9, Koding and Nitrous.IO.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Ready to start your first coding project? Great! Just configure** Terminal or Command Prompt, learn to use it and then install all the languages, add-on libraries and APIs you’ll need. When you're finally through with all that, you can get started with installing [Visual Studio][1] so you can preview your work.
|
||||
|
||||
At least that's how you used to have to do it.
|
||||
|
||||
No wonder beginning coders are increasingly turning to online integrated development environments (IDEs). An IDE is a code editor that comes ready to work with languages and all their dependencies, saving you the hassle of installing them on your computer.
|
||||
|
||||
I wanted to learn more about what constitutes the typical IDE, so I took a look at the free tier for three of the most popular integrated development environments out there: [Cloud9][2], [Koding][3], and [Nitrous.IO][4]. In the process, I learned a lot about the cases in which programmers would and would not want to use IDEs.
|
||||
|
||||
### Why Use An IDE? ###
|
||||
|
||||
If a text editor is like Microsoft Word, think of an IDE as Google Drive. You get similar functionality, but it's accessible from any computer and ready to share. As the Internet becomes an increasingly influential part of project workflow, IDEs make life easier.
|
||||
|
||||
I used Nitrous.IO for my last ReadWrite tutorial, the Python app in [Create Your Own Obnoxiously Simple Messaging App Just Like Yo][5]. When you use an IDE, you select the language you want to work in so you can test and preview how it looks on the IDE’s Virtual Machine (VM) designed to run programs written specifically in that language.
|
||||
|
||||
If you read the tutorial, you'll see there are only two API libraries that my app depended on—messaging service Twilio and Python microframework Flask. That would have been easy to build using a text editor and Terminal on my computer, but I chose an IDE for yet another convenience: when everyone is using the same developer environment, it’s easier to follow along with a tutorial.
|
||||
|
||||
### What An IDE Is Not ###
|
||||
|
||||
Still, an IDE is not a long term hosting solution.
|
||||
|
||||
When you’re working on an IDE, you’re able to build, test and preview your app in the cloud. You’re even able to share the final draft via link.
|
||||
|
||||
But you can’t use an IDE to store your project permanently. You wouldn't ditch your blog in favor of hosting your posts as Google Drive documents. Like Google Drive, IDEs allow you to link and share content, but neither are equipped to replace real hosting.
|
||||
|
||||
What's more, IDEs aren't designed for wide-spread sharing. Despite the increased functionality IDEs add to the preview capability of most text editors, stick with showing off your app preview to friends and coworkers, not with, say, the front page of Hacker News. In that case, your IDE would probably shut you down for excessive traffic.
|
||||
|
||||
Think of it this way: an IDE is a place to build and test your app; a host is a place for it to live. So once you’ve finalized your app, you’ll want to deploy it on a cloud-based service that lets you host apps long term, preferably one with a free hosting option like [Heroku][6].
|
||||
|
||||
### Choosing An IDE ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
As IDEs become more popular, more are popping up all the time. In my opinion, there’s no perfect IDE. However, some IDEs are better for certain work process priorities than others.
|
||||
|
||||
I took a look at the free tier for three of the most popular integrated development environments out there: Cloud9, Koding, and Nitrous.IO. Each has its benefits, depending on what you're working on. Here's what I found.
|
||||
|
||||
### Cloud9: Ready To Collaborate ###
|
||||
|
||||
When I signed up for Cloud9, one of the first things it prompted me to do was integrate my GitHub and BitBucket accounts. Instantly, all my GitHub projects, solo and collaborative, were ready to clone and work on in Cloud9’s development tool. Other IDEs have nowhere near this level of GitHub integration.
|
||||
|
||||
Out of the three IDEs I looked at, Cloud9 seemed most intent on ensuring an environment where I could work seamlessly with co-coders. Here, it’s not just a chat function in the corner. In fact, said CEO Ruben Daniels, Cloud9 collaborators can see each others coding in real time, just like co-authors are able to on Google Drive.
|
||||
|
||||
“Most services’ collaborative features only work on a single file,” said Daniels. “Ours work on multiples throughout the project. Collaboration is fully integrated within the IDE.”
|
||||
|
||||
### Koding: Help When You Need It ###
|
||||
|
||||
IDEs give you the tools you need to build and test applications in the gamut of open source languages. For a beginner, that can be a little bit intimidating. For example, if I’m working on a project with both Python and Ruby components, which VM do I use for testing?
|
||||
|
||||
The answer is both, though on a free account, you can only turn on one VM for testing at a time. I was able to find that out right on my Koding dashboard, which doubles as a place for users to give and get advice on their Koding projects. Of the three, it’s the most transparent when it comes to where you can ask for assistance and hear back in minutes.
|
||||
|
||||
“We have an active community built into the application,” said Nitin Gupta, Chief Business Officer at Koding. “We wanted to create an environment that is extremely attractive to people who need help and who want to help.”
|
||||
|
||||
### Nitrous.IO: An IDE Wherever You Want ###
|
||||
|
||||
The ultimate advantage of using an IDE over your own desktop environment is that it’s self-contained. You don’t have to install anything to use it. On the other hand, the ultimate advantage of using your own desktop environment is that you can work locally, even without Internet.
|
||||
|
||||
Nitrous.IO gives you the best of both worlds. You can use the IDE on the Web, or you can download it to your own computer, said cofounder AJ Solimine. The advantage is that you can merge the integrations of Nitrous with the familiarity of your preferred text editor.
|
||||
|
||||
“You can access Nitrous.IO from any modern web browser via our online Web IDE, but we also have handy desktop applications for Windows and Mac that let you edit with your favorite editor,” he said.
|
||||
|
||||
### The Bottom Line ###
|
||||
|
||||
The most surprising thing I learned from a week of [using][7] three different IDEs? How similar they are. [When it comes to the basics of coding][8], they’re all equally helpful.
|
||||
|
||||
Cloud9, Koding, [and Nitrous.IO all support][9] every major open source language, from Ruby to Python to PHP to HTML5. You can choose from any of those VMs.
|
||||
|
||||
Both Cloud9 and Nitrous.IO have built-in one-click GitHub integration. For Koding there are a [couple more steps][10], but it can be done.
|
||||
|
||||
Each integrated easily with the APIs I needed. Each let me install my preferred package installers, too (and Koding made me do it as a superuser). They all have a built in Terminal for easily testing and deploying projects. All three allow you to easily preview your project. And of course, they all hosted my project in the cloud so I could work on it anywhere.
|
||||
|
||||
On the downside, they all had the same negatives, which is reasonable when you consider they're free. You can only run one VM at a time to test a program written in a particular language. When you’re not using your VM for a while, the IDE preserves bandwidth by putting it into hibernation and you have to wait for it to reload next time you use it (and Cloud9 was especially laborious). None of them make a good permanent host for your finished projects.
|
||||
|
||||
So to answer those who ask me if there’s a perfect free IDE out there, probably not. But depending on your priorities, there might be one that’s perfect for your project.
|
||||
|
||||
Lead image courtesy of [Shutterstock][11]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://readwrite.com/2014/08/14/cloud9-koding-nitrousio-integrated-development-environment-ide-coding
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Lauren Orsini][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://readwrite.com/author/lauren-orsini
|
||||
[1]:http://www.visualstudio.com/
|
||||
[2]:http://c9.io/
|
||||
[3]:https://koding.com/
|
||||
[4]:http://nitrous.io/
|
||||
[5]:http://readwrite.com/2014/07/11/one-click-messaging-app
|
||||
[6]:http://heroku.com/
|
||||
[7]:http://help.nitrous.io/ide-general/
|
||||
[8]:https://www.nitrous.io/desktop
|
||||
[9]:https://www.nitrous.io/desktop
|
||||
[10]:https://koding.com/Activity/steps-clone-projects-github-koding-1-create-account-github-2-open-your-terminal-3
|
||||
[11]:http://www.shutterstock.com/
|
||||
@ -1,68 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Why Your Company Needs To Write More Open Source Software - ReadWrite
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> Real innovation doesn't happen behind closed doors.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**The Wall Street Journal [thinks][1] it's news that Zulily is developing** "more software in-house." It's not. At all. As [Eric Raymond wrote][2] years ago, 95% of the world's software is written for use, not for sale. The reasons are many, but one stands out: as Zulily CIO Luke Friang declares, it's "nearly impossible for a [off the shelf] solution to keep up with our pace."
|
||||
|
||||
True now, just as it was true 20 years ago.
|
||||
|
||||
But one thing is different, and it's something the WSJ completely missed. Historically software developed in-house was zealously kept proprietary because, the reasoning went, it was the source of a firm's competitive advantage. Today, however, companies increasingly realize the opposite: there is far more to be gained by open sourcing in-house software than keeping it closed.
|
||||
|
||||
Which is why your company needs to contribute more open-source code. Much more.
|
||||
|
||||
We've gone through an anomalous time these past 20 years. While most software continued to be written for internal use, most of the attention has been focused on vendors like SAP and Microsoft that build solutions that apply to a wide range of companies.
|
||||
|
||||
That's the theory, anyway.
|
||||
|
||||
In practice, buyers spent a small fortune on license fees, then a 5X multiple on top of that to make the software fit their requirements. For example, a company may spend $100,000 on an ERP system, but they're going to spend another $500,000 making it work.
|
||||
|
||||
One of the reasons open source took off, even in applications, was that companies could get a less functional product for free (or a relatively inexpensive fee) and then spend their implementation dollars tuning it to their needs. Either way, customization was necessary, but the open source approach was less costly and arguably more likely to result in a more tailored result.
|
||||
|
||||
Meanwhile, technology vendors doubled-down on "sameness," as Redmonk analyst [Stephen O'Grady describes][3]:
|
||||
|
||||
> The mainstream technology industry has, in recent years, eschewed specialization. Virtual appliances, each running a version of the operating system customized for an application or purpose, have entirely failed to dent the sales of general purpose alternatives such as RHEL or Windows. For better than twenty years, the answer to any application data persistence requirement has meant one thing: a relational database. If you were talking about enterprise application development, you were talking about Java. And so on.
|
||||
|
||||
Along the way, however, companies discovered that vendors weren't really meeting their needs, even for well-understood product categories like Content Management Systems. They needed different, not same.
|
||||
|
||||
So the customers went rogue. They became vendors. Sort of.
|
||||
|
||||
As is often the case, [O'Grady nails][4] this point. Writing in 2010, O'Grady uncovers an interesting trend: "Software vendors are facing a powerful new market competitor: their customers."
|
||||
|
||||
Think about the most visible technologies today. Most are open source, and nearly all of them were originally written for some company's internal use, or some developer's hobby. Linux, Git, Hadoop, Cassandra, MongoDB, Android, etc. None of these technologies were originally written to be sold as products.
|
||||
|
||||
Instead, they were developed by companies—usually Web companies—building software to "[scratch their own itches][5]," to use the open source phrase. And unlike previous generations of in-house software developed at banks, hospitals and other organizations, they open sourced the code.
|
||||
|
||||
While [some companies eschew developing custom software][6] because they don't want to maintain it, open source (somewhat) mitigates this by letting a community grow up to extend and maintain a project, thereby amortizing the costs of development for the code originators. Yahoo! started Hadoop, but its biggest contributors today are Cloudera and Hortonworks. Facebook kickstarted Cassandra, but DataStax primarily maintains it today. And so on.
|
||||
|
||||
Today real software innovation doesn't happen behind closed doors. Or, if it does, it doesn't stay there. It's open source, and it's upending decades of established software orthodoxy.
|
||||
|
||||
Not that it's for the faint of heart.
|
||||
|
||||
The best open-source projects [innovate very fast][7]. Which is not the same as saying anyone will care about your open-source code. There are [significant pros and cons to open sourcing your code][8]. But one massive "pro" is that the best developers want to work on open code: if you need to hire quality developers, you need to give them an open source outlet for their work. (Just [ask Netflix][9].)
|
||||
|
||||
But that's no excuse to sit on the sidelines. It's time to get involved, and not for the good of some ill-defined "community." No, the primary beneficiary of open-source software development is you and your company. Better get started.
|
||||
|
||||
Lead image courtesy of Shutterstock.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://readwrite.com/2014/08/16/open-source-software-business-zulily-erp-wall-street-journal
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Matt Asay][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://readwrite.com/author/matt-asay
|
||||
[1]:http://blogs.wsj.com/cio/2014/08/08/zulily-calls-in-house-software-a-differentiator-for-competitive-advantage/
|
||||
[2]:http://oreilly.com/catalog/cathbazpaper/chapter/ch05.html
|
||||
[3]:http://redmonk.com/sogrady/2010/01/12/roll-your-own/#ixzz3ATBuZsef
|
||||
[4]:http://redmonk.com/sogrady/2010/01/12/roll-your-own/
|
||||
[5]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/The_Cathedral_and_the_Bazaar
|
||||
[6]:http://www.abajournal.com/magazine/article/roll_your_own_software_hidden_dangers_on_the_road_less_traveled/
|
||||
[7]:http://readwrite.com/2013/12/12/open-source-innovation
|
||||
[8]:http://readwrite.com/2014/07/07/open-source-software-pros-cons
|
||||
[9]:http://techblog.netflix.com/2012/07/open-source-at-netflix-by-ruslan.html
|
||||
@ -1,31 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Linus Torvalds Promotes Linux for Desktops, Embedded Computing
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> Linux kernel developer and open source leader Linus Torvalds spoke recently about the future of desktop Linux and Linux for embedded devices.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
What's the future of Linux for desktop computers and embedded devices? That's a question up for debate, but Linux founder and open source superstar Linus Torvalds provided some intriguing viewpoints in a discussion at the [Linux Foundation's][1] recent LinuxCon event.
|
||||
|
||||
As the guy who wrote the first Linux kernel code and shared it publicly over the Internet back in 1991, Torvalds is without doubt among the most famous developers of open source software—or any software, really—alive today. And while Torvalds is only one individual among many thousands of people and organizations guiding the development of Linux, his opinions tend to be influential with the open source community, and his role as a lead kernel developer places him in a powerful position for deciding which features and code make it into the operating system.
|
||||
|
||||
So it's worth paying attention when Torvalds says, "I still want the desktop," as he [did last week][2] at LinuxCon. It's a sign that he still sees a future for Linux as an operating system for powering personal PCs, even though desktop Linux market share has remained minuscule and relatively flat for more than a decade, and most of the commercial activity around Linux these days involves servers or Android-powered mobile hardware.
|
||||
|
||||
But, Torvalds added, ensuring a strong future for desktop Linux means solving an "infrastructure problem" that stems, he seems to believe, from the broader open source software ecosystem and the hardware world. It's not the core Linux code itself that's at issue, and making the channel friendly for desktop Linux is a feat Torvalds and his fellow kernel developers probably have little power to achieve on their own. That's up to app developers, hardware manufacturers and other parties who have the power to deliver computing platforms based on Linux that people will readily use.
|
||||
|
||||
On the other hand, Torvalds also mentioned a hope that kernel developers might streamline the Linux code for embedded devices—a task that might be at odds in some ways with making the kernel more desktop-friendly. But that's not necessarily the case, and at any rate, given that Linux is designed to be so modular, there's no reason a single kernel code base can't meet the needs of desktop users and embedded developers equally well, depending on which chunks they choose to use.
|
||||
|
||||
As a longtime desktop Linux user who would also like to see more Linux-powered embedded devices, I'm hoping Torvalds's aspirations in both regards will be realized, and that I will one day be able to do everything I need using only Linux, whether it's on a desktop computer, a mobile phone, the car or anywhere else.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://thevarguy.com/open-source-application-software-companies/082514/linus-torvalds-promotes-linux-desktops-and-embedded-compu
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Christopher Tozzi][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://thevarguy.com/author/christopher-tozzi
|
||||
[1]:http://linuxfoundation.org/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.eweek.com/enterprise-apps/linux-founder-linus-torvalds-still-wants-the-desktop.html
|
||||
@ -1,85 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Interesting facts about Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Today, August, 25th, is the 23rd birthday of Linux. The modest [Usenet post][1] made by a 21 year old student at the University of Helsinki on August 25th, 1991, marks the birth of the venerable Linux as we know it today.
|
||||
|
||||
Fast forward 23 years, and now Linux is everywhere, not only installed on end user desktops, [smartphones][2] and embedded systems, but also fulfilling the needs of [leading enterprises][3] and powering mission-critical systems such as [US Navy's nuclear submarines][4] and [FAA's air traffic control][5]. Entering the era of ubiquitous cloud computing, Linux is continuing [its dominance][6] as by far the most popular platform for the cloud.
|
||||
|
||||
Celebrating the 23rd birthday of Linux today, let me show you **some interesting facts and history you may not know about Linux**. If there is anything to add, feel free to share it in the comments. In this article, I will use the terms "Linux", "kernel" or "Linux kernel" interchangeably to mean the same thing.
|
||||
|
||||
1. There is a never-ending debate on whether or not Linux is an operating system. Technically, the term "Linux" refers to the kernel, a core component of an operating system. Folks who argue that Linux is not an operating system are operating system purists who think that the kernel alone does not make the whole operating system, or free software ideologists who believe that the largest free operating system should be named "[GNU/Linux][7]" to give credit where credit is due (i.e., [GNU project][8]). On the other hand, some developers and programmers have a view that Linux qualifies as an operating system in a sense that it implements the [POSIX standard][9].
|
||||
|
||||
2. According to openhub.net, the majority (95%) of Linux is written in C language. The second popular language for Linux is assembly language (2.8%). The dominance of C lanaguage over C++ is no surprise given Linus's stance on C++. Here is the programming language breakdown for Linux.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
3. Linux has been built by a total of [13,036 contributors][10] worldwide. The most prolific contributor is, of course, Linus Torvalds himself, who has committed code more than 20,000 times over the course of the lifetime of Linux. The following figures show the all-time top-10 contributors of Linux in terms of commit counts.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
4. The total source lines of code (SLOC) of Linux is over 17 million. The estimated cost for the entire code base is 5,526 person-years, or over 300M USD according to [basic COCOMO model][11].
|
||||
|
||||
5. Enterprises have not been simply consumers of Linux. Their employees have been [actively participated][12] in the development of Linux. The figure below shows the top-10 corporate sponsors of Linux kernel development, in terms of total commit counts from their employees, as of year 2013. They include commercial Linux distributors (Red Hat, SUSE), chip/embedded system makers (Intel, Texas Instruments, Wolfson), non-profits (Linaro), and other IT power houses (IBM, Samsung, Google).
|
||||
|
||||
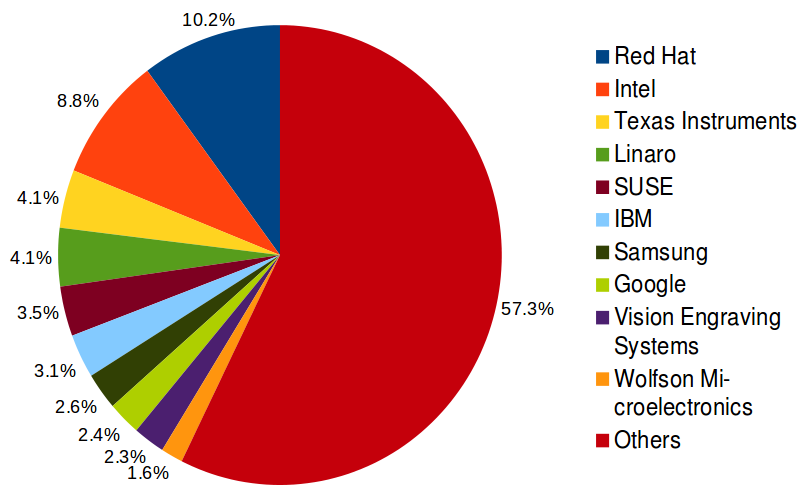
|
||||
|
||||
6. The official mascot of Linux is "Tux", a friendly penguin character. The idea of using a cuddly penguin as a mascot/logo was in fact [first conceived and asserted][13] by Linus himself. Why penguin? Personally Linus is fond of penguins, despite the fact that he once was bitten by a ferocious penguin, causing him infected with a disease.
|
||||
|
||||
7. A Linux "distribution" contains the Linux kernel, supporting GNU utilities/libraries, and other third-party applications. According to [distrowatch.com][14], there are a total of 286 actively maintained Linux distrutions. The oldest among them is [Slackware][15] whose very first release 1.0 became available in 1993.
|
||||
|
||||
8. Kernel.org, which is the main repository of Linux source code, was [compromised][16] by an unknown attacker in August, 2011, who managed to tamper with several kernel.org's servers. In an effort to tighten up access policies of the Linux kernel, Linux foundation recently [turned on][17] two-factor authentication at the official Git repositories hosting the Linux kernel.
|
||||
|
||||
9. The dominance of Linux on top 500 supercomputers [continues to rise][18]. As of June 2014, 97% of the world-fastest computers are powered by Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
10. Spacewatch, a research group of Lunar and Planetary Laboratory at the University of Arizona, named several asteroids ([9793 Torvalds][19], [9882 Stallman][20], [9885 Linux][21] and [9965 GNU][22]) after GNU/Linux and their creators, in recognition of the free operating system which was instrumental in their asteroid survey activities.
|
||||
|
||||
11. In the modern history of Linux kernel development, there was a big jump in kernel version: from 2.6 to 3.0. The [renumbering to version 3][23] actually did not signify any major restructuring in kernel code, but was simply to celebrate the 20 year milestone of the Linux kernel.
|
||||
|
||||
12. In 2000, Steve Jobs at Apple Inc. [tried to hire][24] Linus Torvalds to have him drop Linux development and instead work on "Unix for the biggest user base," which was OS X back then. Linus declined the offer.
|
||||
|
||||
13. The [reboot()][25] system call in the Linux kernel requires two magic numbers. The second magic number comes from the [birth dates][26] of Linus Torvalds and his three daughters.
|
||||
|
||||
14. With so many fans of Linux around the world, there are [criticisms][27] on current Linux distributions (mainly desktops), such as limited hardware support, lack of standardization, instability due to short upgrade/release cycles, etc. During the [Linux kernel panel][28] at LinuxCon 2014, Linus was quoted as saying "I still want the desktop" when asked where he thinks Linux should go next.
|
||||
|
||||
If you know any interesting facts about Linux, feel free to share them in the comments.
|
||||
|
||||
Happy birthday, Linux!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/08/interesting-facts-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/nanni
|
||||
[1]:https://groups.google.com/forum/message/raw?msg=comp.os.minix/dlNtH7RRrGA/SwRavCzVE7gJ
|
||||
[2]:http://developer.android.com/about/index.html
|
||||
[3]:http://fortune.com/2013/05/06/how-linux-conquered-the-fortune-500/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.linuxjournal.com/article/7789
|
||||
[5]:http://fcw.com/Articles/2006/05/01/FAA-manages-air-traffic-with-Linux.aspx
|
||||
[6]:http://thecloudmarket.com/stats
|
||||
[7]:http://www.gnu.org/gnu/why-gnu-linux.html
|
||||
[8]:http://www.gnu.org/gnu/gnu-history.html
|
||||
[9]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/POSIX
|
||||
[10]:https://www.openhub.net/p/linux/contributors/summary
|
||||
[11]:https://www.openhub.net/p/linux/estimated_cost
|
||||
[12]:http://www.linuxfoundation.org/publications/linux-foundation/who-writes-linux-2013
|
||||
[13]:http://www.sjbaker.org/wiki/index.php?title=The_History_of_Tux_the_Linux_Penguin
|
||||
[14]:http://distrowatch.com/search.php?ostype=All&category=All&origin=All&basedon=All¬basedon=None&desktop=All&architecture=All&status=Active
|
||||
[15]:http://www.slackware.com/info/
|
||||
[16]:http://pastebin.com/BKcmMd47
|
||||
[17]:http://www.linux.com/news/featured-blogs/203-konstantin-ryabitsev/784544-linux-kernel-git-repositories-add-2-factor-authentication
|
||||
[18]:http://www.top500.org/statistics/details/osfam/1
|
||||
[19]:http://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/sbdb.cgi?sstr=9793
|
||||
[20]:http://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/sbdb.cgi?sstr=9882
|
||||
[21]:http://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/sbdb.cgi?sstr=9885
|
||||
[22]:http://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/sbdb.cgi?sstr=9965
|
||||
[23]:https://lkml.org/lkml/2011/5/29/204
|
||||
[24]:http://www.wired.com/2012/03/mr-linux/2/
|
||||
[25]:http://lxr.free-electrons.com/source/kernel/reboot.c#L199
|
||||
[26]:http://www.nndb.com/people/444/000022378/
|
||||
[27]:http://linuxfonts.narod.ru/why.linux.is.not.ready.for.the.desktop.current.html
|
||||
[28]:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8myENKt8bD0
|
||||
@ -1,32 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Linux Doesn't Need to Own the Desktop
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Linus Torvalds issued Linux 3.17 rc-2 on Monday of this week, and [he deviated from his normal schedule][1] in doing so, because August 25 happens to mark the 23rd anniversary of the original Linux announcement. "Hello everybody out there using minix," Torvalds wrote.
|
||||
|
||||
Meanwhile, PCMag.com has proclaimed that [Linux has run out of time][2]. But isn't it true that the endless discussions of whether Linux is a success on the desktop are moot? Linux is in supercomputers and cars, it formed the basis for Android and is the most popular platform to run emerging cloud platforms like OpenStack on--just to name a few of its successes. The desktop is not the only battleground for Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
Jon Buys took note of specialization and the Linux desktop [in a recent post][3], where he wrote:
|
||||
|
||||
> "Recently, IT World asked “[Does it still make sense for Linus to want the desktop for Linux?][4]”, and Matt Asay from Tech Repubic asked “[Can we please stop talking about the Linux desktop?][5]”. Both publishers are critical of the claim that there is still room for Linux on Personal Computers, and point to Android as a Linux success story...What both articles miss though is that the flexibility of Linux, and the permissiveness of its open source license may be the things that save Linux on the desktop."
|
||||
|
||||
That may be true, but Linux is so much to so many people beyond the desktop. Linux's opportunity for great market share on the desktop has come and gone.
|
||||
|
||||
The simple fact is that Linux has changed the world and been a tremendous success outside the desktop, and there is nothing wrong with that. Android is hardly the only Linux-based platform that has made a big mark. Linux is huge on servers, in embedded technology, and is a constant prompt for innovation on emerging platforms. Ubuntu is the most popular platform for building OpenStack deployments on. Supercomputers all over the world run Linux, and Chrome OS is based on it.
|
||||
|
||||
So Linux is making a huge difference globally, and it is time for detractors to stop focusing exclusively on its status on the desktop.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ostatic.com/blog/linux-doesnt-need-to-own-the-desktop
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Sam Dean][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://ostatic.com/member/samdean
|
||||
[1]:http://www.theregister.co.uk/2014/08/26/linux_turns_23_and_linus_torvalds_celebrates_as_only_he_can/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.pcmag.com/article2/0,2817,2465125,00.asp
|
||||
[3]:http://ostatic.com/blog/specialization-and-the-linux-desktop
|
||||
[4]:http://www.itworld.com/open-source/432816/does-it-still-make-sense-linus-want-desktop-linux
|
||||
[5]:http://www.techrepublic.com/article/can-we-please-stop-talking-about-the-linux-desktop/
|
||||
@ -1,23 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Happy Birthday Email
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**An Indian American had the brain to invent electronic mail without which we cannot figure out a single day in this era.**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
30 August, email turned 32. Now we wonder how this fast and quick method of message transfer came into existence. The credit goes to an Indian American, Shiva Ayyadurai. Shiva developed a full-scale software of the interoffice mail system and it was named email.
|
||||
|
||||
He was officially acknowledged as the inventor of the computer programme on 30 August, 1982, by the US government. Born to Tamil family in Bombay, Shiva was just 14 years old when he invented the email system. He was studying at Livingston High School in New Jersey and he began working on this system for the University of Medicine and Dentistry of New Jersey. A copyright was given to the email system as no other way was known to protect software inventions at that time.
|
||||
|
||||
Ayyadurai got the idea of the email system from the way mail was transported internally in offices. He tried to make a copy of ‘Pneumatic Tube System’ which was mostly used to send interoffice mails across offices. This system used a physical network of tubes which used to transport typed mails to secretaries. Each secretary used to have inbox, outbox, drafts, carbon copy paper, folders, address book, paper clips or attachments etc. All these were used to create and process incoming and outgoing mails.
|
||||
|
||||
Shiva also took a note of the common templates like “To”, “From”, “Subject”, “Date”, “Body”, “CC”, “BCC” and so on. All these templates were incorporated in the version of the electronic mail too. Mail was written FORTRAN programming language and Shiva discovered an electronic version of the same. Shiva received many accolades for his extraordinary work and also won a Westinghouse Science Talent Search Award for high school seniors in 1981. Now Smithsonian Institution National Museum of American History (SINMAH) has the official US copyright for “Email”. But there is a controversy that not Ayyadurai but some other people have invented email.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.efytimes.com/e1/fullnews.asp?edid=147170
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Sanchari Banerjee
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -1,378 +0,0 @@
|
||||
[Translating by SteveArcher]
|
||||
The Masked Avengers
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> How Anonymous incited online vigilantism from Tunisia to Ferguson.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Anyone can join Anonymous simply by claiming affiliation. An anthropologist says that participants “remain subordinate to a focus on the epic win—and, especially, the lulz.”
|
||||
|
||||
Paper Sculpture by Jeff Nishinaka / Photograph by Scott Dunbar
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
In the mid-nineteen-seventies, when Christopher Doyon was a child in rural Maine, he spent hours chatting with strangers on CB radio. His handle was Big Red, for his hair. Transmitters lined the walls of his bedroom, and he persuaded his father to attach two directional antennas to the roof of their house. CB radio was associated primarily with truck drivers, but Doyon and others used it to form the sort of virtual community that later appeared on the Internet, with self-selected nicknames, inside jokes, and an earnest desire to effect change.
|
||||
|
||||
Doyon’s mother died when he was a child, and he and his younger sister were reared by their father, who they both say was physically abusive. Doyon found solace, and a sense of purpose, in the CB-radio community. He and his friends took turns monitoring the local emergency channel. One friend’s father bought a bubble light and affixed it to the roof of his car; when the boys heard a distress call from a stranded motorist, he’d drive them to the side of the highway. There wasn’t much they could do beyond offering to call 911, but the adventure made them feel heroic.
|
||||
|
||||
Small and wiry, with a thick New England accent, Doyon was fascinated by “Star Trek” and Isaac Asimov novels. When he saw an ad in Popular Mechanics for a build-your-own personal-computer kit, he asked his grandmother to buy it for him, and he spent months figuring out how to put it together and hook it up to the Internet. Compared with the sparsely populated CB airwaves, online chat rooms were a revelation. “I just click a button, hit this guy’s name, and I’m talking to him,” Doyon recalled recently. “It was just breathtaking.”
|
||||
|
||||
At the age of fourteen, he ran away from home, and two years later he moved to Cambridge, Massachusetts, a hub of the emerging computer counterculture. The Tech Model Railroad Club, which had been founded thirty-four years earlier by train hobbyists at M.I.T., had evolved into “hackers”—the first group to popularize the term. Richard Stallman, a computer scientist who worked in M.I.T.’s Artificial Intelligence Laboratory at the time, says that these early hackers were more likely to pass around copies of “Gödel, Escher, Bach” than to incite technological warfare. “We didn’t have tenets,” Stallman said. “It wasn’t a movement. It was just a thing that people did to impress each other.” Some of their “hacks” were fun (coding video games); others were functional (improving computer-processing speeds); and some were pranks that took place in the real world (placing mock street signs near campus). Michael Patton, who helped run the T.M.R.C. in the seventies, told me that the original hackers had unwritten rules and that the first one was “Do no damage.”
|
||||
|
||||
In Cambridge, Doyon supported himself through odd jobs and panhandling, preferring the freedom of sleeping on park benches to the monotony of a regular job. In 1985, he and a half-dozen other activists formed an electronic “militia.” Echoing the Animal Liberation Front, they called themselves the Peoples Liberation Front. They adopted aliases: the founder, a towering middle-aged man who claimed to be a military veteran, called himself Commander Adama; Doyon went by Commander X. Inspired by the Merry Pranksters, they sold LSD at Grateful Dead shows and used some of the cash to outfit an old school bus with bullhorns, cameras, and battery chargers. They also rented a basement apartment in Cambridge, where Doyon occasionally slept.
|
||||
|
||||
Doyon was drawn to computers, but he was not an expert coder. In a series of conversations over the past year, he told me that he saw himself as an activist, in the radical tradition of Abbie Hoffman and Eldridge Cleaver; technology was merely his medium of dissent. In the eighties, students at Harvard and M.I.T. held rallies urging their schools to divest from South Africa. To help the protesters communicate over a secure channel, the P.L.F. built radio kits: mobile FM transmitters, retractable antennas, and microphones, all stuffed inside backpacks. Willard Johnson, an activist and a political scientist at M.I.T., said that hackers were not a transformative presence at rallies. “Most of our work was still done using a bullhorn,” he said.
|
||||
|
||||
In 1992, at a Grateful Dead concert in Indiana, Doyon sold three hundred hits of acid to an undercover narcotics agent. He was sentenced to twelve years in Pendleton Correctional Facility, of which he served five. While there, he developed an interest in religion and philosophy and took classes from Ball State University.
|
||||
|
||||
Netscape Navigator, the first commercial Web browser, was released in 1994, while Doyon was incarcerated. When he returned to Cambridge, the P.L.F. was still active, and their tools had a much wider reach. The change, Doyon recalls, “was gigantic—it was the difference between sending up smoke signals and being able to telegraph someone.” Hackers defaced an Indian military Web site with the words “Save Kashmir.” In Serbia, hackers took down an Albanian site. Stefan Wray, an early online activist, defended such tactics at an “anti-Columbus Day” rally in New York. “We see this as a form of electronic civil disobedience,” he told the crowd.
|
||||
|
||||
In 1999, the Recording Industry Association of America sued Napster, the file-sharing service, for copyright infringement. As a result, Napster was shut down in 2001. Doyon and other hackers disabled the R.I.A.A. site for a weekend, using a Distributed Denial of Service, or DDoS, attack, which floods a site with so much data that it slows down or crashes. Doyon defended his actions, employing the heightened rhetoric of other “hacktivists.” “We quickly came to understand that the battle to defend Napster was symbolic of the battle to preserve a free internet,” he later wrote.
|
||||
|
||||
One day in 2008, Doyon and Commander Adama met at the P.L.F.’s basement apartment in Cambridge. Adama showed Doyon the Web site of the Epilepsy Foundation, on which a link, instead of leading to a discussion forum, triggered a series of flashing colored lights. Some epileptics are sensitive to strobes; out of sheer malice, someone was trying to induce seizures in innocent people. There had been at least one victim already.
|
||||
|
||||
Doyon was incensed. He asked Adama who would do such a thing.
|
||||
|
||||
“Ever hear of a group called Anonymous?” Adama said.
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
In 2003, Christopher Poole, a fifteen-year-old insomniac from New York City, launched 4chan, a discussion board where fans of anime could post photographs and snarky comments. The focus quickly widened to include many of the Internet’s earliest memes: LOLcats, Chocolate Rain, RickRolls. Users who did not enter a screen name were given the default handle Anonymous.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
“I need to talk about my inner life.”
|
||||
|
||||
Poole hoped that anonymity would keep things irreverent. “We have no intention of partaking in intelligent discussions concerning foreign affairs,” he wrote on the site. One of the highest values within the 4chan community was the pursuit of “lulz,” a term derived from the acronym LOL. Lulz were often achieved by sharing puerile jokes or images, many of them pornographic or scatological. The most shocking of these were posted on a part of the site labelled /b/, whose users called themselves /b/tards. Doyon was aware of 4chan, but considered its users “a bunch of stupid little pranksters.” Around 2004, some people on /b/ started referring to “Anonymous” as an independent entity.
|
||||
|
||||
It was a new kind of hacker collective. “It’s not a group,” Mikko Hypponen, a leading computer-security researcher, told me—rather, it could be thought of as a shape-shifting subculture. Barrett Brown, a Texas journalist and a well-known champion of Anonymous, has described it as “a series of relationships.” There was no membership fee or initiation. Anyone who wanted to be a part of Anonymous—an Anon—could simply claim allegiance.
|
||||
|
||||
Despite 4chan’s focus on trivial topics, many Anons considered themselves crusaders for justice. They launched vigilante campaigns that were purposeful, if sometimes misguided. More than once, they posed as underage girls in order to entrap pedophiles, whose personal information they sent to the police. Other Anons were apolitical and sowed chaos for the lulz. One of them posted images on /b/ of what looked like pipe bombs; another threatened to blow up several football stadiums and was arrested by the F.B.I. In 2007, a local news affiliate in Los Angeles called Anonymous “an Internet hate machine.”
|
||||
|
||||
In January, 2008, Gawker Media posted a video in which Tom Cruise enthusiastically touted the benefits of Scientology. The video was copyright-protected, and the Church of Scientology sent a cease-and-desist letter to Gawker, asking that the video be removed. Anonymous viewed the church’s demands as attempts at censorship. “I think it’s time for /b/ to do something big,” someone posted on 4chan. “I’m talking about ‘hacking’ or ‘taking down’ the official Scientology Web site.” An Anon used YouTube to issue a “press release,” which included stock footage of storm clouds and a computerized voice-over. “We shall proceed to expel you from the Internet and systematically dismantle the Church of Scientology in its present form,” the voice said. “You have nowhere to hide.” Within a few weeks, the YouTube video had been viewed more than two million times.
|
||||
|
||||
Anonymous had outgrown 4chan. The hackers met in dedicated Internet Relay Chat channels, or I.R.C.s, to coördinate tactics. Using DDoS attacks, they caused the main Scientology Web site to crash intermittently for several days. Anons created a “Google bomb,” so that a search for “dangerous cult” would yield the main Scientology site at the top of the results page. Others sent hundreds of pizzas to Scientology centers in Europe, and overwhelmed the church’s Los Angeles headquarters with all-black faxes, draining the machines of ink. The Church of Scientology, an organization that reportedly has more than a billion dollars in assets, could withstand the depletion of its ink cartridges. But its leaders, who had also received death threats, contacted the F.B.I. to request an investigation into Anonymous.
|
||||
|
||||
On March 15, 2008, several thousand Anons marched past Scientology churches in more than a hundred cities, from London to Sydney. In keeping with the theme of anonymity, the organizers decided that all the protesters should wear versions of the same mask. After considering Batman, they settled on the Guy Fawkes mask worn in “V for Vendetta,” a dystopian movie from 2005. “It was available in every major city, in large quantities, for cheap,” Gregg Housh, one of the organizers of the protests and a well-known Anon, told me. The mask was a caricature of a man with rosy cheeks, a handlebar mustache, and a wide grin.
|
||||
|
||||
Anonymous did not “dismantle” the Church of Scientology. Still, the Tom Cruise video remained online. Anonymous had proved its tenacity. The collective adopted a bombastic slogan: “We are Legion. We do not forgive. We do not forget. Expect us.”
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
In 2010, Doyon moved to Santa Cruz, California, to join a local movement called Peace Camp. Using wood that he stole from a lumberyard, he built a shack in the mountains. He borrowed WiFi from a nearby mansion, drew power from salvaged solar panels, and harvested marijuana, which he sold for cash.
|
||||
|
||||
At the time, the Peace Camp activists were sleeping on city property as a protest against a Santa Cruz anti-homelessness law that they considered extreme. Doyon appeared at Peace Camp meetings and offered to promote their cause online. He had an unkempt red beard and wore a floppy beige hat and quasi-military fatigues. Some of the activists called him Curbhugger Chris.
|
||||
|
||||
Kelley Landaker, a member of Peace Camp, spoke with Doyon several times about hacking. Doyon sometimes bragged about his technical aptitude, but Landaker, an expert programmer, was unimpressed. “He was more of a spokesman than a hands-on-the-keyboard type of person,” Landaker told me. But the movement needed a passionate leader more than it needed a coder. “He was very enthusiastic and very outspoken,” Robert Norse, also a member of Peace Camp, told me. “He created more media attention for the issue than anyone I’ve seen, and I’ve been doing this for twenty years.”
|
||||
|
||||
Commander Adama, Doyon’s superior in the P.L.F., who still lived in Cambridge and communicated with him via e-mail, had ordered Doyon to monitor Anonymous. Doyon’s brief was to observe their methods and to recruit members to the P.L.F. Recalling his revulsion at the Epilepsy Foundation hack, Doyon initially balked. Adama argued that the malicious hackers were a minority within Anonymous, and that the collective might inspire powerful new forms of activism. Doyon was skeptical. “The biggest movement in the world is going to come from 4chan?” he said. But, out of loyalty to the P.L.F., he obeyed Adama.
|
||||
|
||||
Doyon spent much of his time at the Santa Cruz Coffee Roasting Company, a café downtown, hunched over an Acer laptop. The main Anonymous I.R.C. did not require a password. Doyon logged in using the name PLF and followed along. Over time, he discovered back channels where smaller, more dedicated groups of Anons had dozens of overlapping conversations. To participate, you had to know the names of the back channels, which could be changed to deflect intruders. It was not a highly secure system, but it was adaptable. “These simultaneous cabals keep centralization from happening,” Gabriella Coleman, an anthropologist at McGill University, told me.
|
||||
|
||||
Some Anons proposed an action called Operation Payback. As the journalist Parmy Olson wrote in a 2012 book, “We Are Anonymous,” Operation Payback started as another campaign in support of file-sharing sites like the Pirate Bay, a successor to Napster, but the focus soon broadened to include political speech. In late 2010, at the behest of the State Department, several companies, including MasterCard, Visa, and PayPal, stopped facilitating donations to WikiLeaks, the vigilante organization that had released hundreds of thousands of diplomatic cables. In an online video, Anonymous called for revenge, promising to lash out at the companies that had impeded WikiLeaks. Doyon, attracted by the anti-corporate spirit of the project, decided to participate.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
During Operation Payback, in early December, Anonymous directed new recruits, or noobs, to a flyer headed “How to Join the Fucking Hive,” in which participants were instructed to “FIX YOUR GODDAMN INTERNET. THIS IS VERY FUCKING IMPORTANT.” They were also asked to download Low Orbit Ion Cannon, an easy-to-use tool that is publicly available. Doyon downloaded the software and watched the chat rooms, waiting for a cue. When the signal came, thousands of Anons fired at once. Doyon entered a target URL—say, www.visa.com—and, in the upper-right corner, clicked a button that said “IMMA CHARGIN MAH LAZER.” (The operation also relied on more sophisticated hacking.) Over several days, Operation Payback disabled the home pages of Visa, MasterCard, and PayPal. In court filings, PayPal claimed that the attack had cost the company five and a half million dollars.
|
||||
|
||||
To Doyon, this was activism made tangible. In Cambridge, protesting against apartheid, he could not see immediate results; now, with the tap of a button, he could help sabotage a major corporation’s site. A banner headline on the Huffington Post read “MasterCard DOWN.” One gloating Anon tweeted, “There are some things WikiLeaks can’t do. For everything else, there’s Operation Payback.”
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
In the fall of 2010, the Peace Camp protests ended. With slight concessions, the anti-homelessness law remained in effect. Doyon hoped to use the tactics of Anonymous to reinvigorate the movement. He recalls thinking, “I could wield Anonymous against this tiny little city government and they would just be fucking wrecked. Plan was we were finally going to solve this homelessness problem, once and for all.”
|
||||
|
||||
Joshua Covelli, a twenty-five-year-old Anon who went by the nickname Absolem, admired Doyon’s decisiveness. “Anonymous had been this clusterfuck of chaos,” Covelli told me. With Commander X, “there seemed to be a structure set up.” Covelli worked as a receptionist at a college in Fairborn, Ohio, and knew nothing about Santa Cruz politics. But when Doyon asked for help with Operation Peace Camp, Covelli e-mailed back immediately: “I’ve been waiting to join something like that my entire life.”
|
||||
|
||||
Doyon, under the name PLF, invited Covelli into a private I.R.C.:
|
||||
|
||||
> Absolem: Sorry to be so rude . . . Is PLF part of Anonymous or separate?
|
||||
>
|
||||
> Absolem: I was just asking because you all seem very organized in chat.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> PLF: You are not in the least rude. I am pleased to meet you. PLF is 22 year old hacker group originally from Boston. I started hacking in 81, not with computers but PBX (telephones).
|
||||
>
|
||||
> PLF: We are all older 40 or over. Some of us are former military or intelligence. One of us, Commander Adama is currently sought by an alphabet soup of cops and spooks and in hiding.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> Absolem: Wow that’s legit. I am really interested in helping this out in some way and Anonymous just seems too chaotic. I have some computer skills but very noob in hacking. I have some tools but no Idea how to use them.
|
||||
|
||||
With ritual solemnity, Doyon accepted Covelli’s request to join the P.L.F.:
|
||||
|
||||
> PLF: Encrypt the fuck out of all sensitive material that might incriminate you.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> PLF: Yep, work with any PLFer to get a message to me. Call me . . . Commander X for now.
|
||||
|
||||
In 2012, the Associated Press called Anonymous “a group of expert hackers”; Quinn Norton, in Wired, wrote that “Anonymous had figured out how to infiltrate anything,” resulting in “a wild string of brilliant hacks.” In fact some Anons are gifted coders, but the vast majority possess little technical skill. Coleman, the anthropologist, told me that only a fifth of Anons are hackers—the rest are “geeks and protesters.”
|
||||
|
||||
On December 16, 2010, Doyon, as Commander X, sent an e-mail to several reporters. “At exactly noon local time tomorrow, the Peoples Liberation Front and Anonymous will remove from the Internet the Web site of the Santa Cruz County government,” he wrote. “And exactly 30 minutes later, we will return it to normal function.”
|
||||
|
||||
The data-center staff for Santa Cruz County saw the warning and scrambled to prepare for the attack. They ran security scans on the servers and contacted A.T. & T., the county’s Internet provider, which suggested that they alert the F.B.I.
|
||||
|
||||
The next day, Doyon entered a Starbucks and booted up his laptop. Even for a surfing town, he was notably eccentric: a homeless-looking man wearing fatigues and typing furiously. Covelli met him in a private chat room.
|
||||
|
||||
> PLF: Go to Forum, sign in—and look at top right menu bar “chat.” Thats Ops for today. Thank you for standing with us.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> Absolem: Anything for PLF, sir.
|
||||
|
||||
They both opened DDoS software. Though only a handful of people were participating in Operation Peace Camp, Doyon gave orders as if he were addressing legions of troops:
|
||||
|
||||
> PLF: ATTENTION: Everyone who supports the PLF or considers us their friend—or who cares about defeating evil and protecting the innocent: Operation Peace Camp is LIVE and an action is underway. TARGET: www.co.santa-cruz.ca.us. Fire At Will. Repeat: FIRE!
|
||||
>
|
||||
> Absolem: got it, sir.
|
||||
|
||||
The data-center staff watched their servers, which showed a flurry of denial-of-service requests. Despite their best efforts, the site crashed. Twenty-five minutes later, Doyon decided that he had made his point. He typed “CEASE FIRE,” and the county’s site flickered back to life. (Despite the attack, the city’s anti-homelessness law did not change.)
|
||||
|
||||
Doyon hardly had time to celebrate before he grew anxious. “I got to leave,” he typed to Covelli. He fled to his shack in the mountains. Doyon was right to be wary: an F.B.I. agent had been snooping in the I.R.C. The F.B.I. obtained a warrant to search Doyon’s laptop.
|
||||
|
||||
A few weeks later, Doyon’s food ran out, and he returned to town. While he was at the Santa Cruz Coffee Roasting Company, two federal agents entered the shop. They brought him to the county police station. Doyon called Ed Frey, a lawyer and the founder of Peace Camp, who met him at the station. Doyon told Frey about his alter ego as Commander X.
|
||||
|
||||
Doyon was released, but the F.B.I. kept his laptop, which was full of incriminating evidence. Frey, a civil-rights lawyer who knew little about cybersecurity, drove Doyon back to his hillside encampment. “What are you going to do?” Frey asked.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
“Zach is in the gifted-and-talented-and-you’re-not class.”
|
||||
|
||||
He spoke in cinematic terms. “Run like hell,” he said. “I will go underground, try to stay free as long as I can, and keep fighting the bastards any way possible.” Frey gave him two twenty-dollar bills and wished him luck.
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
Doyon hitchhiked to San Francisco and stayed there for three months. He spent his days at Coffee to the People, a quirky café in the Haight-Ashbury district, where he would sit for hours in front of his computer, interrupted only by outdoor cigarette breaks.
|
||||
|
||||
In January, 2011, Doyon contacted Barrett Brown, the journalist and Anon. “What are we going to do next?” Doyon asked.
|
||||
|
||||
“Tunisia,” Brown said.
|
||||
|
||||
“Yeah, it’s a country in the Middle East,” Doyon said. “What about it?”
|
||||
|
||||
“We’re gonna take down its dictator,” Brown said.
|
||||
|
||||
“Oh, they have a dictator?” Doyon said.
|
||||
|
||||
A couple of days later, Operation Tunisia began. Doyon volunteered to spam Tunisian government e-mail addresses in an attempt to clog their servers. “I would take the text of the press release for that op and just keep sending it over and over again,” he said. “Sometimes, I was so busy that I would just put ‘fuck you’ and send it.” In one day, the Anons brought down the Web sites of the Tunisian Stock Exchange, the Ministry of Industry, the President, and the Prime Minister. They replaced the Web page of the President’s office with an image of a pirate ship and the message “Payback is a bitch, isn’t it?”
|
||||
|
||||
Doyon often spoke of his online battles as if he had just crawled out of a foxhole. “Dude, I turned black from doing it,” he told me. “My face, from all the smoke—it would cling to me. I would look up and I would literally be like a raccoon.” Most nights, he camped out in Golden Gate Park. “I would look at myself in the mirror and I’d be like, O.K., it’s been four days—maybe I should eat, bathe.”
|
||||
|
||||
Anonymous-affiliated operations continued to be announced on YouTube: Operation Libya, Operation Bahrain, Operation Morocco. As protesters filled Tahrir Square, Doyon participated in Operation Egypt. A Facebook page disseminated information, including links to a “care package” for protesters on the ground. The package, distributed through the file-sharing site Megaupload, contained encryption software and a primer on defending against tear gas. Later, when the Egyptian government disabled Internet and cellular networks within the country, Anonymous helped the protesters find alternative ways to get online.
|
||||
|
||||
In the summer of 2011, Doyon succeeded Adama as Supreme Commander of the P.L.F. Doyon recruited roughly half a dozen new members and attempted to position the P.L.F. as an élite squad within Anonymous. Covelli became one of his technical advisers. Another hacker, Crypt0nymous, made YouTube videos; others did research or assembled electronic care packages. Unlike Anonymous, the P.L.F. had a strict command structure. “X always called the shots on everything,” Covelli said. “It was his way or no way.” A hacker who founded a blog called AnonInsiders told me over encrypted chat that Doyon was willing to act unilaterally—a rare thing within Anonymous. “When we wanted to start an op, he didn’t mind if anyone would agree or not,” he said. “He would just write the press release by himself, list all the targets, open the I.R.C. channel, tell everyone to go in there, and start the DDoSing.”
|
||||
|
||||
Some Anons viewed the P.L.F. as a vanity project and Doyon as a laughingstock. “He’s known for his exaggeration,” Mustafa Al-Bassam, an Anon who went by Tflow, told me. Others, even those who disapproved of Doyon’s egotism, grudgingly acknowledged his importance to the Anonymous movement. “He walks that tough line of sometimes being effective and sometimes being in the way,” Gregg Housh said, adding that he and other prominent Anons had faced similar challenges.
|
||||
|
||||
Publicly, Anonymous persists in claiming to be non-hierarchical. In “We Are Legion,” a 2012 documentary about Anonymous by Brian Knappenberger, one activist uses the metaphor of a flock of birds, with various individuals taking turns drifting toward the front. Gabriella Coleman told me that, despite such claims, something resembling an informal leadership class did emerge within Anonymous. “The organizer is really important,” she said. “There are four or five individuals who are really good at it.” She counted Doyon among them. Still, Anons tend to rebel against institutional structure. In a forthcoming book about Anonymous, “Hacker, Hoaxer, Whistleblower, Spy,” Coleman writes that, among Anons, “personal identity and the individual remain subordinate to a focus on the epic win—and, especially, the lulz.”
|
||||
|
||||
Anons who seek individual attention are often dismissed as “egofags” or “namefags.” (Many Anons have yet to outgrow their penchant for offensive epithets.) “There are surprisingly few people who violate the rule” against attention-seeking, Coleman says. “Those who do, like X, are marginalized.” Last year, in an online discussion forum, a commenter wrote, “I stopped reading his BS when he started comparing himself to Batman.”
|
||||
|
||||
Peter Fein, an online activist known by the nickname n0pants, was among the many Anons who were put off by Doyon’s self-aggrandizing rhetoric. Fein browsed the P.L.F. Web site, which featured a coat of arms and a manifesto about the group’s “epic battle for the very soul of humanity.” Fein was dismayed to find that Doyon had registered the site using his real name, leaving himself and possibly other Anons vulnerable to prosecution. “I’m basically okay with people DDoSing,” Fein recalls telling Doyon over private chat. “But if you’re going to do it, you’ve got to cover your ass.”
|
||||
|
||||
On February 5, 2011, the Financial Times reported that Aaron Barr, the C.E.O. of a cybersecurity firm called HBGary Federal, had identified the “most senior” members of Anonymous. Barr’s research suggested that one of the top three was Commander X, a hacker based in California, who could “manage some significant firepower.” Barr contacted the F.B.I. and offered to share his work with them.
|
||||
|
||||
Like Fein, Barr had seen that the P.L.F. site was registered to Christopher Doyon at an address on Haight Street. Based on Facebook and I.R.C. activity, Barr concluded that Commander X was Benjamin Spock de Vries, an online activist who had lived near the Haight Street address. Barr approached de Vries on Facebook. “Please tell the folks there that I am not out to get you guys,” Barr wrote. “Just want the ‘leadership’ to know what my intent is.”
|
||||
|
||||
“ ‘Leadership’ lmao,” de Vries responded.
|
||||
|
||||
Days after the Financial Times story appeared, Anonymous struck back. HBGary Federal’s Web site was defaced. Barr’s personal Twitter account was hijacked, thousands of his e-mails were leaked online, and Anons released his address and other personal information—a punishment known as doxing. Barr resigned from HBGary Federal within the month.
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
In April, 2011, Doyon left San Francisco and hitchhiked around the West, camping in parks at night and spending his days at Starbucks outlets. In his backpack he kept his laptop, his Guy Fawkes mask, and several packs of Pall Malls.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
“This is what I learned during my summer at TED camp.”
|
||||
|
||||
He followed internal Anonymous news. That spring, six élite Anons, all of whom had been instrumental in deflecting Barr’s investigation, formed a group called Lulz Security, or LulzSec. As their name indicated, they felt that Anonymous had become too self-serious; they aimed to bring the lulz back. While Anonymous continued supporting Arab Spring protesters, LulzSec hacked the Web site of PBS and posted a fake story claiming that the late rapper Tupac Shakur was alive in New Zealand.
|
||||
|
||||
Anons often share text through the Web site Pastebin.com. On the site, LulzSec issued a statement that read, “It has come to our unfortunate attention that NATO and our good friend Barrack Osama-Llama 24th-century Obama have recently upped the stakes with regard to hacking. They now treat hacking as an act of war.” The loftier the target, the greater the lulz. On June 15th, LulzSec took credit for crashing the C.I.A.’s Web site, tweeting, “Tango down—cia.gov—for the lulz.”
|
||||
|
||||
On June 20, 2011, Ryan Cleary, a nineteen-year-old member of LulzSec, was arrested for the DDoS attacks on the C.I.A. site. The next month, F.B.I. agents arrested fourteen other hackers for DDoS attacks on PayPal seven months earlier. Each of the PayPal Fourteen, as they became known, faced fifteen years in prison and a five-hundred-thousand-dollar fine. They were charged with conspiracy and intentional damage to protected computers under the Computer Fraud and Abuse Act. (The law allows for wide prosecutorial discretion and was widely criticized after Aaron Swartz, an Internet activist who was facing thirty-five years in prison, committed suicide last year.)
|
||||
|
||||
A petition was circulated on behalf of Jake (Topiary) Davis, a member of LulzSec, who needed help paying his legal fees. Doyon entered an I.R.C. to promote Davis’s cause:
|
||||
|
||||
> CommanderX: Please sign the petition and help Topiary…
|
||||
>
|
||||
> toad: you are an attention whore
|
||||
>
|
||||
> toad: so you get attention
|
||||
>
|
||||
> CommanderX: Toad your an asshole.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> katanon: sigh
|
||||
|
||||
Doyon had grown increasingly brazen. He DDoS’ed the Web site of the Chamber of Commerce of Orlando, Florida, after activists there were arrested for feeding the homeless. He launched the attacks from public WiFi networks, using his personal laptop, without making much effort to cover his tracks. “That’s brave but stupid,” a senior member of the P.L.F. who asked to be called Kalli told me. “He didn’t seem to care if he was caught. He was a suicide hacker.”
|
||||
|
||||
Two months later, Doyon participated in a DDoS strike against San Francisco’s Bay Area Rapid Transit, protesting an incident in which a BART police officer had killed a homeless man named Charles Hill. Doyon appeared on the “CBS Evening News” to defend the action, his voice disguised and his face obscured by a bandanna. He compared DDoS attacks to civil disobedience. “It’s no different, really, than taking up seats at the Woolworth lunch counters,” he said. Bob Schieffer, the CBS anchor, snickered and said, “It’s not quite the civil-rights movement, as I see it.”
|
||||
|
||||
On September 22, 2011, in a coffee shop in Mountain View, California, Doyon was arrested and charged with causing intentional damage to a protected computer. He was detained for a week and released on bond. Two days later, against his lawyer’s advice, he called a press conference on the steps of the Santa Cruz County Courthouse. His hair in a ponytail, he wore dark sunglasses, a black pirate hat, and a camouflage bandanna around his neck.
|
||||
|
||||
In characteristically melodramatic fashion, Doyon revealed his identity. “I am Commander X,” he told reporters. He raised his fist. “I am immensely proud, and humbled to the core, to be a part of the idea called Anonymous.” He told a journalist, “All you need to be a world-class hacker is a computer and a cool pair of sunglasses. And the computer is optional.”
|
||||
|
||||
Kalli worried that Doyon was placing his ego above the safety of other Anons. “It’s the weakest link in the chain that ends up taking everyone down,” he told me. Josh Covelli, the Anon who had been eager to help Doyon with Operation Peace Camp, told me that his “jaw dropped” when he saw a video of Doyon’s press conference online. “The way he presented himself and the way he acted had become more unhinged,” Covelli said.
|
||||
|
||||
Three months later, Doyon’s pro-bono lawyer, Jay Leiderman, was in a federal court in San Jose. Leiderman had not heard from Doyon in a couple of weeks. “I’m inquiring as to whether there’s a reason for that,” the judge said. Leiderman had no answer. Doyon was absent from another hearing two weeks later. The prosecutor stated the obvious: “It appears as though the defendant has fled.”
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
Operation Xport was the first Anonymous operation of its kind. The goal was to smuggle Doyon, now a fugitive wanted for two felonies, out of the country. The coördinators were Kalli and a veteran Anon who had met Doyon at an acid party in Cambridge during the eighties. A retired software executive, he was widely respected within Anonymous.
|
||||
|
||||
Doyon’s ultimate destination was the software executive’s house, deep in rural Canada. In December, 2011, he hitchhiked to San Francisco and made his way to an Occupy encampment downtown. He found his designated contact, who helped him get to a pizzeria in Oakland. At 2 A.M., Doyon, using the pizzeria’s WiFi, received a message on encrypted chat.
|
||||
|
||||
“Are you near a window?” the message read.
|
||||
|
||||
“Yeah,” Doyon typed.
|
||||
|
||||
“Look across the street. Do you see the green mailbox? In exactly fifteen minutes, go and stand next to that mailbox and set your backpack down, and lay your mask on top of it.”
|
||||
|
||||
For a few weeks, Doyon shuttled among safe houses in the Bay Area, following instructions through encrypted chat. Eventually, he took a Greyhound bus to Seattle, where he stayed with a friend of the software executive. The friend, a wealthy retiree, spent hours using Google Earth to help Doyon plot a route to Canada. They went to a camping-supplies store, and the friend spent fifteen hundred dollars on gear for Doyon, including hiking boots and a new backpack. Then he drove Doyon two hours north and dropped him off in a remote area, several hundred miles from the border, where Doyon met up with Amber Lyon.
|
||||
|
||||
Months earlier, Lyon, a broadcast journalist, had interviewed Doyon for a CNN segment about Anonymous. He liked her report, and they stayed in touch. Lyon asked to join Doyon on his escape, to shoot footage for a possible documentary. The software executive thought that it was “nuts” to take the risk, but Doyon invited her anyway. “I think he wanted to make himself a face of the movement,” Lyon told me. For four days, she filmed him as he hiked north, camping in the woods. “It wasn’t very organized,” Lyon recalls. “He was functionally homeless, so he just kind of wandered out of the country.”
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
“This is the barn where we keep our feelings. If a feeling comes to you, bring it out here and lock it up.”
|
||||
|
||||
On February 11, 2012, a press release appeared on Pastebin. “The PLF is delighted to announce that Commander X, aka Christopher Mark Doyon, has fled the jurisdiction of the USA and entered the relative safety of the nation of Canada,” it read. “The PLF calls upon the government of the USA to come to its senses and cease the harassment, surveillance—and arrest of not only Anonymous, but all activists.”
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
In Canada, Doyon spent a few days with the software executive in a small house in the woods. In a chat with Barrett Brown, Doyon was effusive.
|
||||
|
||||
> BarrettBrown: you have enough safe houses, etc? . . .
|
||||
>
|
||||
> CommanderX: Yes I am good here, money and houses a plenty in Canada.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> CommanderX: Amber Lyon asked me on camera about you.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> CommanderX: I think you will like my reply, and fuck the trolls Barrett. I have always loved you and always will.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> CommanderX: :-)
|
||||
>
|
||||
> CommanderX: I told her you were a hero.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> BarrettBrown: you’re a hero . . .
|
||||
>
|
||||
> BarrettBrown: glad you’re safe for now
|
||||
>
|
||||
> BarrettBrown: let me know if you need anything
|
||||
>
|
||||
> CommanderX: I am, and if this works we can get others out to . . . .
|
||||
>
|
||||
> BarrettBrown: good, we’re going to need that
|
||||
|
||||
Ten days after Doyon’s escape, the Wall Street Journal reported that Keith Alexander, then the N.S.A. and U.S. Cyber Command director, had held classified meetings in the White House and elsewhere during which he expressed concern about Anonymous. Within two years, Alexander warned, the group might be capable of destabilizing national power grids. General Martin Dempsey, the chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff, told the Journal that an enemy of the U.S. “could give cyber malware capability to some fringe group,” adding, “We have to get after this.”
|
||||
|
||||
On March 8th, a briefing on cybersecurity was held for members of Congress at a Sensitive Compartmented Information Facility near the Capitol Building. Many of the country’s top security officials attended the briefing, including Alexander, Dempsey, Robert Mueller, the head of the F.B.I., and Janet Napolitano, the Secretary of Homeland Security. Attendees were shown a computer simulation of what a cyberattack on the Eastern Seaboard’s electrical supply might look like. Anonymous was not yet capable of mounting an attack on this scale, but security officials worried that they might join forces with other, more sophisticated groups. “As we were dealing with this ever-increasing presence on the Net and ever-increasing risk, the government nuts and bolts were still being worked out,” Napolitano told me. When discussing potential cybersecurity threats, she added, “We often used Anonymous as Exhibit A.”
|
||||
|
||||
Anonymous might be the most powerful nongovernmental hacking collective in the world. Even so, it has never demonstrated an ability or desire to damage any key elements of public infrastructure. To some cybersecurity experts, the dire warnings about Anonymous sounded like fearmongering. “There’s a big gap between declaring war on Orlando and pulling off a Stuxnet attack,” James Andrew Lewis, a senior fellow at the Center for Strategic and International Studies, told me, referring to the elaborate cyberstrike carried out by the U.S. and Israel against Iranian nuclear sites in 2007. Yochai Benkler, a professor at Harvard Law School, told me, “What we’ve seen is the use of drumbeating as justification for major defense spending of a form that would otherwise be hard to justify.”
|
||||
|
||||
Keith Alexander, who recently retired from the government, declined to comment for this story, as did representatives from the N.S.A., the F.B.I., the C.I.A., and the D.H.S. Although Anons have never seriously compromised government computer networks, they have a record of seeking revenge against individuals who anger them. Andy Purdy, the former head of the national-cybersecurity division of the D.H.S., told me that “a fear of retaliation,” both institutional and personal, prevents government representatives from speaking out against Anonymous. “Everyone is vulnerable,” he said.
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
On March 6, 2012, Hector Xavier Monsegur, a key member of LulzSec with the screen name Sabu, was revealed to be an F.B.I. informant. In exchange for a reduced sentence, Monsegur had spent several months undercover, helping to gather evidence against other LulzSec members. The same day, five leading Anons were arrested and charged with several crimes, including computer conspiracy. An F.B.I. official told Fox News, “This is devastating to the organization. We’re chopping off the head of LulzSec.” Over the next ten months, Barrett Brown was indicted on seventeen federal charges, most of which were later dropped. (He will be sentenced in October.)
|
||||
|
||||
Doyon was distraught, but he continued to hack—and to seek attention. He appeared, masked, at a Toronto screening of a documentary about Anonymous. He gave an interview to a reporter from the National Post and boasted, without substantiation, “We have access to every classified database in the U.S. government. It’s a matter of when we leak the contents of those databases, not if.”
|
||||
|
||||
In January, 2013, after another Anon started an operation about the rape of a teen-age girl in Steubenville, Ohio, Doyon repurposed LocalLeaks, a site he had created two years earlier, as a clearinghouse for information about the rape. Like many Anonymous efforts, LocalLeaks was both influential and irresponsible. It was the first site to widely disseminate the twelve-minute video of a Steubenville High School graduate joking about the rape, which inflamed public outrage about the story. But the site also perpetuated several false rumors about the case and it failed to redact a court document, thus accidentally revealing the rape victim’s name. Doyon admitted to me that his strategy of releasing unexpurgated materials was controversial, but he recalled thinking, “We could either gut the Steubenville Files . . . or we could release everything we know, basically, with the caveat, Hey, you’ve got to trust us.”
|
||||
|
||||
In May, 2013, the Rustle League, a group of online trolls who often provoke Anonymous, hacked Doyon’s Twitter account. Shm00p, one of the leaders of Rustle League, told me, “We’re not trying to cause harm to the guy, but, just, the shit he was saying—it was comical to me.” The Rustle League implanted racist and anti-Semitic messages into Doyon’s account, such as a link to www.jewsdid911.org.
|
||||
|
||||
On August 27, 2013, Doyon posted a note announcing his retirement from Anonymous. “My entire life has been dedicated to fighting for justice and freedom,” he wrote. “ ‘Commander X’ may be invincible, but I am extremely ill from the exhaustion and stress of fighting in this epic global cyber war.” Reactions varied from compassion (“you deserve a rest”) to ridicule (“poor crazy old gnoll. Maybe he has some time for bathing now”). Covelli told me, “The persona has consumed him to the point where he can’t handle it anymore.”
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
August 17, 1998 “We still have Paris? Just thought I’d check.”
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
The first Million Mask March took place on November 5, 2013. Several thousand people marched in support of Anonymous, in four hundred and fifty cities around the world. In a sign of how deeply Anonymous had penetrated popular culture, one protester in London removed his Guy Fawkes mask to reveal that he was the actor Russell Brand.
|
||||
|
||||
While I attended the rally in Washington, D.C., Doyon watched a livestream in Canada. I exchanged e-mails with him on my phone. “It is so surreal to sit here, sidelined and out of the game—and watch something that you helped create turn into this,” he wrote. “At least it all made a difference.”
|
||||
|
||||
We arranged a face-to-face meeting. Doyon insisted that I submit to elaborate plans made over encrypted chat. I was to fly to an airport several hours away, rent a car, drive to a remote location in Canada, and disable my phone.
|
||||
|
||||
I found him in a small, run-down apartment building in a quiet residential neighborhood. He wore a green Army-style jacket and a T-shirt featuring one of Anonymous’s logos: a black-suited man with a question mark instead of a face. The apartment was sparsely furnished and smelled of cigarette smoke. He discussed U.S. politics (“I have not voted in many elections—it’s all a rigged game”), militant Islam (“I believe that people in the Nigerian government essentially colluded to create a completely phony Al Qaeda affiliate called Boko Haram”), and his tenuous position within Anonymous (“These people who call themselves trolls are really just rotten, mean, evil people”).
|
||||
|
||||
Doyon had shaved his beard, and he looked gaunt. He told me that he was ill and that he rarely went outside. On his small desk were two laptops, a stack of books about Buddhism, and an overflowing ashtray. A Guy Fawkes mask hung on an otherwise bare yellow wall. He told me, “Underneath the whole X persona is a little old man who is in absolute agony at times.”
|
||||
|
||||
This past Christmas, the founder of the news site AnonInsiders visited him, bearing pie and cigarettes. Doyon asked the friend to succeed him as Supreme Commander of the P.L.F., offering “the keys to the kingdom”—all his passwords, as well as secret files relating to several Anonymous operations. The friend gently declined. “I have a life,” he told me.
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
On August 9, 2014, at 5:09 P.M. local time, Kareem (Tef Poe) Jackson, a rapper and activist from Dellwood, Missouri, a suburb of St. Louis, tweeted about a crisis unfolding in a neighboring town. “Basically martial law is taking place in Ferguson all perimeters blocked coming and going,” he wrote. “National and international friends Help!!!” Five hours earlier in Ferguson, an unarmed eighteen-year-old African-American, Michael Brown, had been shot to death by a white police officer. The police claimed that Brown had reached for the officer’s gun. Brown’s friend Dorian Johnson, who was with him at the time, said that Brown’s only offense was refusing to leave the middle of the street.
|
||||
|
||||
Within two hours, Jackson received a reply from a Twitter account called CommanderXanon. “You can certainly expect us,” the message read. “See if you can get us some live streams going, that would be useful.” In recent weeks, Doyon, still in Canada, had come out of retirement. In June, two months before his fiftieth birthday, he quit smoking (“#hacktheaddiction #ecigaretteswork #old,” he later tweeted). The following month, after fighting broke out in Gaza, he tweeted in support of Anonymous’s Operation Save Gaza, a series of DDoS strikes against Israeli Web sites. Doyon found the events in Ferguson even more compelling. Despite his idiosyncrasies, he had a knack for being early to a cause.
|
||||
|
||||
“Start collecting URLs for cops, city government,” Doyon tweeted. Within ten minutes, he had created an I.R.C. channel. “Anonymous Operation Ferguson is engaged,” he tweeted. Only two people retweeted the message.
|
||||
|
||||
The next morning, Doyon posted a link to a rudimentary Web site, which included a message to the people of Ferguson—“You are not alone, we will support you in every way possible”—and an ultimatum to the police: “If you abuse, harass or harm in any way the protesters in Ferguson, we will take every Web based asset of your departments and governments off line. That is not a threat, it is a promise.” Doyon appealed to the most visible Anonymous Twitter account, YourAnonNews, which has 1.3 million followers. “Please support Operation Ferguson,” he wrote. A minute later, YourAnonNews complied. That day, the hashtag #OpFerguson was tweeted more than six thousand times.
|
||||
|
||||
The crisis became a top news story, and Anons rallied around Operation Ferguson. As with the Arab Spring operations, Anonymous sent electronic care packages to protesters on the ground, including a riot guide (“Pick up the gas emitter and lob it back at the police”) and printable Guy Fawkes masks. As Jackson and other protesters marched through Ferguson, the police attempted to subdue them with rubber bullets and tear gas. “It looked like a scene from a Bruce Willis movie,” Jackson told me. “Barack Obama hasn’t supported us to the degree Anonymous has,” he said. “It’s comforting to know that someone out there has your back.”
|
||||
|
||||
One site, www.opferguson.com, turned out to be a honeypot—a trap designed to collect the Internet Protocol addresses of visitors and turn them over to law-enforcement agencies. Some suspected Commander X of being a government informant. In the #OpFerguson I.R.C., someone named Sherlock wrote, “Everyone got me scared clicking links. Unless it’s from a name I’ve seen a lot, I just avoid them.”
|
||||
|
||||
Protesters in Ferguson asked the police to reveal the name of the officer who had shot Brown. Several times, Anons echoed this demand. Someone tweeted, “Ferguson police better release the shooter’s name before Anonymous does the work for them.” In a community meeting on August 12th, Jon Belmar, the Chief of the St. Louis Police Department, refused. “We do not do that until they’re charged with an offense,” he said.
|
||||
|
||||
In retaliation, a hacker with the handle TheAnonMessage tweeted a link to what he claimed was a two-hour audio file of a police radio scanner, recorded around the time of Brown’s death. TheAnonMessage also doxed Belmar, tweeting what he purported to be the police chief’s home address, phone number, and photographs of his family—one of his son sleeping on a couch, another of Belmar posing with his wife. “Nice photo, Jon,” TheAnonMessage tweeted. “Your wife actually looks good for her age. Have you had enough?” An hour later, TheAnonMessage threatened to dox Belmar’s daughter.
|
||||
|
||||
Richard Stallman, the first-generation hacker from M.I.T., told me that though he supports many of Anonymous’s causes, he considered these dox attacks reprehensible. Even internally, TheAnonMessage’s actions were divisive. “Why bother doxing people who weren’t involved?” one Anon asked over I.R.C., adding that threatening Belmar’s family was “beyond stupid.” But TheAnonMessage and other Anons continued to seek information that could be used in future dox attacks. The names of Ferguson Police Department employees were available online, and Anons scoured the Internet, trying to suss out which of the officers had killed Brown.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
April 12, 1999“Which thing do I press?”
|
||||
|
||||
In the early morning of August 14th, a few Anons became convinced, based on Facebook photos and other disparate clues, that Brown’s shooter was a thirty-two-year-old man named Bryan Willman. According to a transcript of an I.R.C., one Anon posted a photo of Willman with a swollen face; another noted, “The shooter claimed to have been hit in the face.” Another user, Anonymous|11057, acknowledged that his suspicion of Willman involved “a leap of probably bad logic.” Still, he wrote, “i just can’t shake it. i really truly honestly and without a shred of hard evidence think it’s him.”
|
||||
|
||||
TheAnonMessage seemed amused by the conversation, writing, “#RIPBryanWillman.” Other Anons urged caution. “Please be sure,” Anonymous|2252 wrote. “It’s not just about a man’s life, Anon can easily be turned on by the public if something truly unjust comes of this.”
|
||||
|
||||
The debate went on for more than an hour. Several Anons pointed out that there was no way to confirm that Willman had ever been a Ferguson police officer.
|
||||
|
||||
> Anonymous|3549: @gs we still don’t have a confirmation that bry is even on PD
|
||||
>
|
||||
> Intangir: tensions are high enough right now where there is a slim chance someone might care enough to kill him
|
||||
>
|
||||
> Anonymous|11057: the only real way to get a confirmation would be an eyewitness report from the scene of the crime. otherwise it’s hearsay and shillery
|
||||
>
|
||||
> Anonymous|11057: the fastest way to eliminate a suspect is to call him a suspect . . . we are all terrified of being unjust, but the pegs keep fitting in the holes . . .
|
||||
|
||||
Many Anons remained uncomfortable with the idea of a dox. But around 7 A.M. a vote was taken. According to chat logs, of the eighty or so people in the I.R.C., fewer than ten participated. They decided to release Willman’s personal information.
|
||||
|
||||
> Anonymous|2252: is this going on twitter?
|
||||
>
|
||||
> anondepp: lol
|
||||
>
|
||||
> Anonymous|2252: via @theanonmessage ?
|
||||
>
|
||||
> TheAnonMessage: yup
|
||||
>
|
||||
> TheAnonMessage: just did
|
||||
>
|
||||
> anondepp: its up
|
||||
>
|
||||
> Anonymous|2252: shit
|
||||
>
|
||||
> TheAnonMessage: Lord in heaven…
|
||||
>
|
||||
> Anonymous|3549: . . .have mercy on our souls
|
||||
>
|
||||
> anondepp: lol
|
||||
|
||||
At 9:45 A.M., the St. Louis Police Department responded to TheAnonMessage. “Bryan Willman is not even an officer with Ferguson or St. Louis County PD,” the tweet read. “Do not release more info on this random citizen.” (The F.B.I. later opened an investigation into the hacking of police computers in Ferguson.) Twitter quickly suspended TheAnonMessage, but Willman’s name and address had been reported widely.
|
||||
|
||||
Willman is the head police dispatcher in St. Ann, a suburb west of Ferguson. When the St. Louis Police Department’s Intelligence Unit called to tell him that he had been named as the killer, Willman told me, “I thought it was the weirdest joke.” Within hours, he received hundreds of death threats on his social-media accounts. He stayed in his house for nearly a week, alone, under police protection. “I just want it all to go away,” he told me. He thinks that Anonymous has irreparably harmed his reputation. “I don’t see how they can ever think they can be trusted again,” he said.
|
||||
|
||||
“We are not perfect,” OpFerguson tweeted. “Anonymous makes mistakes, and we’ve made a few in the chaos of the past few days. For those, we apologize.” Though Doyon was not responsible for the errant dox attack, other Anons took the opportunity to shame him for having launched an operation that spiralled out of control. A Pastebin message, distributed by YourAnonNews, read, “You may notice contradictory tweets and information about #Ferguson and #OpFerguson from various Anonymous twitter accounts. Part of why there is dissension about this particular #op is that CommanderX is considered a ‘namefag/facefag’—a known entity who enjoys or at least doesn’t shun publicity—which is considered by most Anonymous to be bad form, for some probably fairly obvious reasons.”
|
||||
|
||||
On his personal Twitter account, Doyon denied any involvement with Op Ferguson and wrote, “I hate this shit. I don’t want drama and I don’t want to fight with people I thought were friends.” Within a couple of days, he was sounding hopeful again. He recently retweeted messages reading, “You call them rioters, we call them voices of the oppressed” and “Free Tibet.”
|
||||
|
||||
Doyon is still in hiding. Even Jay Leiderman, his attorney, does not know where he is. Leiderman says that, in addition to the charges in Santa Cruz, Doyon may face indictment for his role in the PayPal and Orlando attacks. If he is arrested and convicted on all counts, he could spend the rest of his life in prison. Following the example of Edward Snowden, he hopes to apply for asylum with the Russians. When we spoke, he used a lit cigarette to gesture around his apartment. “How is this better than a fucking jail cell? I never go out,” he said. “I will never speak with my family again. . . . It’s an incredibly high price to pay to do everything you can to keep people alive and free and informed.”
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.newyorker.com/magazine/2014/09/08/masked-avengers
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[David Kushner][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.newyorker.com/contributors/david-kushner
|
||||
@ -1,100 +0,0 @@
|
||||
5 Reasons Why I Hate GNU/Linux – Do You Hate (Love) Linux?
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
This part of Linux, I don’t like to talk very often but sometimes I do really feel some of the aspects related to Linux is real pain. Here are the five points which I come across on a daily basis, almost.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
5 Reasons Why I Hate Linux
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Choose from Too Many Good Distros ###
|
||||
|
||||
While reading several on-line forum (a part of my hobby), I very often come across a question like – Hi, I am new to Linux, just [switched over from Windows to Linux][1]. Which Linux Distribution, I should get my hands dirty with? Oh! forgot to mention, I am an Engineering Student.
|
||||
|
||||
As soon as someone posted such question, there is a flood of comments. each distribution’s fan boy tries to make sense that the distro he is using leads all the rest, a few comments may look like:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Get your hands upon Linux Mint or Ubuntu, they are easy to use specially for newbies like you.
|
||||
1. Ubuntu is Sh** better go with Mint.
|
||||
1. If you want something like windows, better stay there.
|
||||
1. Nothing is better than Debian. It is easy to use and contains all the packages you may need.
|
||||
1. Slackware, for the point, if you learn slack you learn Linux.
|
||||
At this point, the student who asked question really gets confused and annoyed.
|
||||
1. CentOS – Nothing like this, when comes to stability.
|
||||
1. I will recommend Fedora, Bleeding edge technology implementation, you will get a lot to learn.
|
||||
1. Puppy Linux, SUSE, BSD, Manjaro, Megia, Kali, RedHat Beta, etc,……
|
||||
|
||||
At the end of discussion, the discussion forum may be used as a paper for research based upon the facts and figure provided in the comments.
|
||||
|
||||
Now think the same in Windows or Mac – One may say are you Insane? Still using Windows XP or Vista but no one will try to prove that windows 8 is better than XP and XP is more on a User Friendly side. You won’t get a fan boy in Mac as well, who is trying to jump into the discussion just to make his point sounds louder.
|
||||
|
||||
You may frequently come across points like – Distros are like religion. These things makes the newbie puzzled. Anyone who have used Linux for a considerable time would be knowing that all the distros are same at the base. It is only the working interface and the way to perform task differs and that too rarely. You are using apt, yum, portage, emerge, spike or ABS who cares as far as the things are done and user is comfortable with it.
|
||||
|
||||
Well the above scenario is not only true in forums and groups on-line, it is sometimes taken to the corporate world.
|
||||
|
||||
I was recently being Interviewed by a company based in Mumbai (India). The person interviewing, asked me several questions and technologies, I have worked with. As per their requirements, I have worked with nearly half of the technologies they were looking for. A few of last conversation as mentioned below.
|
||||
|
||||
**Interviewer**: Do you know kernel editing? (Then he talked to himself for a couple of seconds – no, no not kernel editing, it is a very different thing.) Do you know how to compile a kernel on a monolithic side?
|
||||
|
||||
**Me**: Yes, we just need to make sure what we need to run in future. We need to select those options only that supports our need before compiling the kernel.
|
||||
|
||||
**Interviewer**: How do you compile a kernel?
|
||||
|
||||
**Me**: make menuconfig, fire it as………..(interrupted)
|
||||
|
||||
**Interviewer**: When have you compiled the kernel lastly without any help?
|
||||
|
||||
**Me**: Very recently on my Debian…..(Interrupted)
|
||||
|
||||
**Interviewer**: Debian? Do you know what we does? Debian-Febian is not of our use. We use CentOS. Ok, I will tell the management the result. They will call you.
|
||||
|
||||
**Not to Mention**: I didn’t get the call or job, but certainly the phrase **Debian-febian** forces me to think over and over again. He could have said we don’t use Debian, we use CentOS. The tone of him, was a bit racist, it is spread-ed all over.
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Some of the very important software has no support in Linux ###
|
||||
|
||||
No! I am not talking about Photoshop. I understand Linux is not build to perform such task. But some backbone softwares required to connect your Android phone to PC for Updation – PC Suite certainly means a lot. I have been looking for a windows PC.
|
||||
|
||||
I know Linux is more like a server side OS. Really? Is not it trying to make a point that, it has been used as a Desktop as well? If Yes! It should have other developed desktop features. For a desktop user security, stability, RAID, Kernel does not mean much. They should get their work done with little or no effort.
|
||||
|
||||
Moreover the companies like Samsung, Sony, Micromax, etc are dealing with Android (Linux) Phones and they have no support to get their phone connected over a Linux PC.
|
||||
|
||||
Don’t drag me in PC suite discussion. For Linux to be a Desktop OS, it still lacks several things, Little or no gaming support – I mean high end gaming. No professional Video and Photo Editing Tools, I Said Professional. And yeah I remember Titanic and Avatar Movies were maid using some kind of FOSS video editor, I am coming to that point.
|
||||
|
||||
Agree or not, Linux still has to go a long way to be a distro for everyone.
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. Linuxer have a habit of living in virtual world ###
|
||||
|
||||
I am a Linux user, and I am superior than you. I can handle terminal much better than you. You know Linux is Everywhere in your wrist watch, mobile phones, remote control. You know what, Hacker’s use Linux. Are you aware as soon as you boot Linux you become hacker. You can do several things from Linux you can’t even think of using Windows and Mac.
|
||||
|
||||
Let me tell you, Linux is now being used in International Space Station. The world’s most successful movies Avatar and Titanic were build using Linux. Last but not the least, world’s 90% supercomputers are using Linux. World’s Top 5 fastest computer are using Linux. Facebook, Linkedin, Google, Yahoo all have their server based on Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
I don’t mean they are wrong. I only mean they keeps on talking about the thing they very little know about.
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. The long hours of compilation and dependency resolution ###
|
||||
|
||||
I am aware of automatic dependency resolution and the program getting smart day by day. Still think from corporate view, I was installing a program say ‘y‘, it had one dependency say ‘**x**‘ which was unable to be resolved automatically. While resolving ‘**x**‘ I came across 8 other dependency, a few of other were dependent on a few other libraries and program. Isn’t it painful?
|
||||
|
||||
The rule of corporate is to have the work done efficiently with less man power and as much less time as possible. Who cares if your piece of codes are coming from Windows or Mac or Linux as far as the work is done.
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. Too much manual work ###
|
||||
|
||||
No matter which distro you choose, you have to manually do a lot a things time-to-time. Lets say you are installing proprietary Nvidia Driver. Now you need to kill **X** manually, may need to edit **Xorg.conf** manually and still may have a broken **X**. Furthermore, you have to make sure that the next time kernel updates, it still be in working condition.
|
||||
|
||||
Think of same on Windows. You have nothing to do other than firing the executables and click** Next, Next, I Agree, Next, Forward, Finish, Reboot** and your system may very rarely have broken GUI. Though the demerit is a broken GUI is not possible to be repaired on Windows but easily on Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
Hey don’t tell me its because of security implementation. If you are installing something using ‘**root**‘, and still needs a lot of things done manually that not security. Some may have a point that it gives you power to configure your system to any extent. My friend at least give him a working interface from where he can configure it to next best level. Why Installer laves him to re-invent the wheel every-time in the name of security and configurability.
|
||||
|
||||
I myself is a Linux fan and have been working on this platform for nearly half a decades. I myself have used Distros of several kind and came to the above conclusion. You may have used a different distro’s and might you’ve came to a such conclusion, where you feel that Linux is not upto the mark.
|
||||
|
||||
Please do share with us, why do you hate (Love) Linux? via our comment section below.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/why-i-hate-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Avishek Kumar][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/avishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/useful-linux-commands-for-newbies/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,87 @@
|
||||
10 Open Source Cloning Software For Linux Users
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> These cloning software take all disk data, convert them into a single .img file and you can copy it to another hard drive.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Disk cloning means copying data from a hard disk to another one and you can do this by simple copy & paste. But you cannot copy the hidden files and folders and not the in-use files too. That's when you need a cloning software which can also help you in saving a back-up image from your files and folders. The cloning software takes all disk data, convert them into a single .img file and you can copy it to another hard drive. Here we give you the best 10 Open Source Cloning software:
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. [Clonezilla][1]: ###
|
||||
|
||||
Clonezilla is a Live CD based on Ubuntu and Debian. It clones all your hard drive data and take a backup just like Norton Ghost on Windows but in a more effective way. Clonezilla support many filesystems like ext2, ext3, ext4, btrfs, xfs and others. It also supports BIOS, UEFI, MPR and GPT partitions.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 2. [Redo Backup][2]: ###
|
||||
|
||||
Redo Bakcup is another Live CD tool which clones your drivers easily. It is free and Open Source Live System which has its licence under GPL 3. Its main features include easy GUI boots from CD, no installation, restoration of Linux and Windows systems, access to files with out any log-in, recovery of deleted files and more.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 3. [Mondo Rescue][3]: ###
|
||||
|
||||
Mondo doesn't work like other software. It doesn’t convert your hard drivers into an .img file. It converts them into an .iso image and with Mondo you can also create a custom Live CD using “mindi” which is a special tool developed by Mondo Rescue to clone your data from the Live CD. It supports most Linux distributions, FreeBSD, and it is licensed under GPL.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 4. [Partimage][4]: ###
|
||||
|
||||
This is an open-source software backup, which works under Linux system, by default. It's also available to install from the package manager for most Linux distributions and if you don’t have a Linux system then you can use “SystemRescueCd”. It is a Live CD which includes Partimage by default to do the cloning process that you want. Partimage is very fast in cloning hard drivers.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 5. [FSArchiver][5]: ###
|
||||
|
||||
FSArchiver is a follow-up to Partimage, and it is again a good tool to clone hard disks. It supports cloning Ext4 partitions and NTFS partitions, basic file attributes like owner, permissions, extended attributes like those used by SELinux, basic file system attributes for all Linux file systems and so on.
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. [Partclone][6]: ###
|
||||
|
||||
Partclone is a free tool which clones and restores partitions. Written in C it first appeared in 2007 and it supports many filesystems like ext2, ext3, ext4, xfs, nfs, reiserfs, reiser4, hfs+, btrfs. It is very simple to use and it's licensed under GPL.
|
||||
|
||||
### 7. [doClone][7]: ###
|
||||
|
||||
doClone is a free software project which is developed to clone Linux system partitions easily. It's written in C++ and it supports up to 12 different filesystems. It can preform Grub bootloader restoration and can also transform the clone image to another computer via LAN. It also provides support to live cloning which means you will eb able to clone from the system even if it's running.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 8. [Macrium Reflect Free Edition][8]: ###
|
||||
|
||||
Macrium Reflect Free Edition is claimed to be one of the fastest disk cloning utilities which supports only Windows file systems. It is a fairly straightforward user interface. This software does disk imaging and disk cloning and also allows you to access images from the file manager. It allows you to create a Linux rescue CD and it is compatible with Windows Vista and 7.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 9. [DriveImage XML][9]: ###
|
||||
|
||||
DriveImage XML uses Microsoft VSS for creation of images, quite reliably. With this software you can create "hot" images from a disk, which is still running. XML files store images, which means you can access them from any supporting third-party software. DriveImage XML also allows restoring an image to a machine without any reboot. This software is also compatible with Windows XP, Windows Server 2003, Vista, and 7.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 10. [Paragon Backup & Recovery Free][10]: ###
|
||||
|
||||
Paragon Backup & Recovery Free does a great job when it comes to managing scheduled imaging. This is a free software but it's for personal use only.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.efytimes.com/e1/fullnews.asp?edid=148039
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Sanchari Banerjee
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://clonezilla.org/
|
||||
[2]:http://redobackup.org/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.mondorescue.org/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.partimage.org/Main_Page
|
||||
[5]:http://www.fsarchiver.org/Main_Page
|
||||
[6]:http://www.partclone.org/
|
||||
[7]:http://doclone.nongnu.org/
|
||||
[8]:http://www.macrium.com/reflectfree.aspx
|
||||
[9]:http://www.runtime.org/driveimage-xml.htm
|
||||
[10]:http://www.paragon-software.com/home/br-free/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,67 @@
|
||||
barney-ro translating
|
||||
|
||||
7 killer open source monitoring tools
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Looking for greater visibility into your network? Look no further than these excellent free tools
|
||||
|
||||
Network and system monitoring is a broad category. There are solutions that monitor for the proper operation of servers, network gear, and applications, and there are solutions that track the performance of those systems and devices, providing trending and analysis. Some tools will sound alarms and notifications when problems are detected, while others will even trigger actions to run when alarms sound. Here is a collection of open source solutions that aim to provide some or all of these capabilities.
|
||||
|
||||
### Cacti ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Cacti is a very extensive performance graphing and trending tool that can be used to track just about any monitored metric that can be plotted on a graph. From disk utilization to fan speeds in a power supply, if it can be monitored, Cacti can track it -- and make that data quickly available.
|
||||
|
||||
### Nagios ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Nagios is the old guard of system and network monitoring. It is fast, reliable, and extremely customizable. Nagios can be a challenge for newcomers, but the rather complex configuration is also its strength, as it can be adapted to just about any monitoring task. What it may lack in looks it makes up for in power and reliability.
|
||||
|
||||
### Icinga ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Icinga is an offshoot of Nagios that is currently being rebuilt anew. It offers a thorough monitoring and alerting framework that\u2019s designed to be as open and extensible as Nagios is, but with several different Web UI options. Icinga 1 is closely related to Nagios, while Icinga 2 is the rewrite. Both versions are currently supported, and Nagios users can migrate to Icinga 1 very easily.
|
||||
|
||||
### NeDi ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
NeDi may not be as well known as some of the others, but it\u2019s a great solution for tracking devices across a network. It continuously walks through a network infrastructure and catalogs devices, keeping track of everything it discovers. It can provide the current location of any device, as well as a history.
|
||||
|
||||
NeDi can be used to locate stolen or lost devices by alerting you if they reappear on the network. It can even display all known and discovered connections on a map, showing how every network interconnect is laid out, down to the physical port level.
|
||||
|
||||
### Observium ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Observium combines system and network monitoring with performance trending. It uses both static and auto discovery to identify servers and network devices, leverages a variety of monitoring methods, and can be configured to track just about any available metric. The Web UI is very clean, well thought out, and easy to navigate.
|
||||
|
||||
As shown, Observium can also display the physical location of monitored devices on a geographical map. Note too the heads-up panels showing active alarms and device counts.
|
||||
|
||||
### Zabbix ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Zabbix monitors servers and networks with an extensive array of tools. There are Zabbix agents for most operating systems, or you can use passive or external checks, including SNMP to monitor hosts and network devices. You'll also find extensive alerting and notification facilities, and a highly customizable Web UI that can be adapted to a variety of heads-up displays. In addition, Zabbix has specific tools that monitor Web application stacks and virtualization hypervisors.
|
||||
|
||||
Zabbix can also produce logical interconnection diagrams detailing how certain monitored objects are interconnected. These maps are customizable, and maps can be created for groups of monitored devices and hosts.
|
||||
|
||||
### Ntop ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Ntop is a packet sniffing tool with a slick Web UI that displays live data on network traffic passing by a monitoring interface. Instant data on network flows is available through an advanced live graphing function. Host data flows and host communication pair information is also available in real-time.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.networkworld.com/article/2686794/asset-management/164219-7-killer-open-source-monitoring-tools.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Paul Venezia][a]
|
||||
译者:[barney-ro](https://github.com/barney-ro)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.networkworld.com/author/Paul-Venezia/
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,5 @@
|
||||
alim0x translating
|
||||
|
||||
The history of Android
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
@ -106,4 +108,4 @@ via: http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/06/building-android-a-40000-word-histor
|
||||
[2]:http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=y3z7Tw1K17A
|
||||
[3]:http://arstechnica.com/information-technology/2009/02/google-tries-location-based-social-networking-with-latitude/
|
||||
[a]:http://arstechnica.com/author/ronamadeo
|
||||
[t]:https://twitter.com/RonAmadeo
|
||||
[t]:https://twitter.com/RonAmadeo
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,132 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Translating by ZTinoZ
|
||||
10 Useful “Squid Proxy Server” Interview Questions and Answers in Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
It’s not only to System Administrator and Network Administrator, who listens the phrase Proxy Server every now and then but we too. Proxy Server is now a corporate culture and is the need of the hour. Proxy server now a days is implemented from small schools, cafeteria to large MNCs. Squid (also known as proxy) is such an application which acts as proxy server and one of the most widely used tool of its kind.
|
||||
|
||||
This Interview article aims at strengthening your base from Interview point on the ground of proxy server and squid.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Squid Interview Questions
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. What do you mean by Proxy Server? What is the use of Proxy Server in Computer Networks? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : A Proxy Server refers to physical machine or Application which acts intermediate between client and resource provider or server. A client seeks for file, page or data from the the proxy server and proxy server manages to get the requested demand of client fulfilled by handling all the complexities in between.
|
||||
|
||||
Proxy servers are the backbone of WWW (World Wide Web). Most of the proxies of today are web proxies. A proxy server handles the complexity in between the Communication of client and Server. Moreover it provides anonymity on the web which simply means your identity and digital footprints are safe. Proxies can be configured to allow which sites client can see and which sites are blocked.
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. What is Squid? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : Squid is an Application software released under GNU/GPL which acts as a proxy server as well as web cache Daemon. Squid primarily supports Protocol like HTTP and FTP however other protocols like HTTPS, SSL,TLS, etc are well supported. The feature web cache Daemon makes web surfing faster by caching web and DNS for frequently visited websites. Squid is known to support all major platforms including Linux, UNIX, Microsoft Windows and Mac.
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. What is the default port of squid and how to change its operating port? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : The default port on which squid runs is 3128. We can change the operating port of squid from default to any custom unused port by editing its configuration file which is located at /etc/squid/squid.conf as suggested below.
|
||||
|
||||
Open ‘/etc/squid/squid.conf’ file and with your choice of editor.
|
||||
|
||||
# nano /etc/squid/squid.conf
|
||||
|
||||
Now change this port to any other unused port. Save the editor and exit.
|
||||
|
||||
http_port 3128
|
||||
|
||||
Restart the squid service as shown below.
|
||||
|
||||
# service squid restart
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. You works for a company the management of which ask you to block certain domains through squid proxy server. What are you going to do? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : Blocking domain is a module which is implemented well in the configuration file. We just need to perform a little manual configuration as suggested below.
|
||||
|
||||
a. Create a file say ‘blacklist’ under directory ‘/etc/squid’.
|
||||
|
||||
# touch /etc/squid/blacklist
|
||||
|
||||
b. Open the file ‘/etc/squid/blacklist’ with nano editor.
|
||||
|
||||
# nano /etc/squid/blacklist
|
||||
|
||||
c. Add all the domains to the file blacklist with one domain per line.
|
||||
|
||||
.facebook.com
|
||||
.twitter.com
|
||||
.gmail.com
|
||||
.yahoo.com
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
d. Save the file and exit. Now open the Squid configuration file from location ‘/etc/squid/squid.conf’.
|
||||
|
||||
# nano /etc/squid/squid.conf
|
||||
|
||||
e. Add the lines below to the Squid configuration file.
|
||||
|
||||
acl BLACKLIST dstdom_regex -i “/etc/squid/blacklist”
|
||||
http_access deny blacklist
|
||||
|
||||
f. Save the configuration file and exit. Restart Squid service to make the changes effective.
|
||||
|
||||
# service squid restart
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. What is Media Range Limitation and partial download in Squid? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : Media Range Limitation is a special feature of squid in which just the required data is requested from the server and not the whole file. This feature is very well implemented in various videos streaming websites like Youtube and Metacafe where a user can click on the middle of progress bar hence whole video need not be fetched except for the requested part.
|
||||
|
||||
The squid’s feature of partial download is implemented well within windows update where downloads are requested in the form of small packets which can be paused. Because of this feature a update downloading windows machine can be restarted without any fear of data loss. Squid makes the Media Range Limitation and Partial Download possible only after storing a copy of whole data in it. Moreover the partial download gets deleted and not cached when user points to another page until Squid is specially configured somehow.
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. What is reverse proxy in squid? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : Reverse proxy is a feature of Squid which is used to accelerate the web surfing for end user. Say the Real server ‘RS’ contains the resource and ‘PS’ is the proxy Server. The client seek some data which is available at RS. It will rely on RS for the specified data for the first time and the copy of that specified data gets stored on PS for configurable amount of time. For every request for that data from now PS becomes the real source. This results in Less traffic, Lesser CPU usages, Lesser web resource utilization and hence lesser load to actual server RS. But RS has no statistics for the total traffic since PS acted as actual server and no Client reached RS. ‘X-Forwarded-For HTTP’ can be used to log the client IP although on RS.
|
||||
|
||||
Technically it is feasible to use single squid server to act both as normal proxy server and reverse proxy server at the same point of time.
|
||||
|
||||
### 7. Since Squid can be used as web-cache Daemon, is it possible to Clear its Cache? How? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : No Doubt! Squid acts as web-cache Daemon which is used to accelerate web surfing still it is possible to clear its cache and that too very easily.
|
||||
|
||||
a. First stop Squid proxy server and delete cache from the location ‘/var/lib/squid/cache’ directory.
|
||||
|
||||
# service squid stop
|
||||
# rm -rf /var/lib/squid/cache/*<
|
||||
|
||||
b. Create Swap directories.
|
||||
|
||||
# squid -z
|
||||
|
||||
### 8. A client approaches you, who is working. They want the web access time be restricted for their children. How will you achieve this scenario? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Say the web access allow time be 4′o clock to 7′o clock in the evening for three hours, sharply form Monday to Friday.
|
||||
|
||||
a. To restrict web access between 4 to 7 from Monday to Friday, open the Squid configuration file.
|
||||
|
||||
# nano /etc/squid/squid.conf
|
||||
|
||||
b. Add the following lines and save the file and exit.
|
||||
|
||||
acl ALLOW_TIME time M T W H F 16:00-19:00
|
||||
shttp_access allow ALLOW_TIME
|
||||
|
||||
c. Restart the Squid Service.
|
||||
|
||||
# service squid restart
|
||||
|
||||
### 9. Squid stores data in which file format? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : Data stored by Squid is in ufs format. Ufs is the old well-known Squid storage format.
|
||||
|
||||
### 10. Where do cache gets stored by squid? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : A squid stores cache in special folder at the location ‘/var/spool/squid’.
|
||||
|
||||
That’s all for now. I’ll be here again with another interesting article soon. Till then stay tuned and connected to Tecmint. Don’t forget to provide us with your valuable feedback the comment section below.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/squid-interview-questions/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Avishek Kumar][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/avishek/
|
||||
@ -1,77 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Check how much do you type with WhatPulse on Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
If, like me, you are a statistics freak you must install this small application on all your computers: [WhatPulse][1]
|
||||
|
||||
The software tracks a user’s pressed keys, mouse clicks and used [bandwidth][2] and the uptime of the system. Periodically, or by hand, the user can upload to the server the number of keystrokes made; this is called “pulsing”.
|
||||
|
||||
Users can see where they are in a leaderboard of people who have joined the program and compare themselves against people from their own countries. Users can also join teams, which enables them to compare themselves against people with similar interests (Go Linux Users !!).
|
||||
|
||||
There is a basic, and free, version where you can easily see and check all the basic statistics and a premium account where you can see some more stats.
|
||||
|
||||
The software is available for Linux, Windows and Mac.
|
||||
|
||||
### Registration on the website ###
|
||||
|
||||
As first step you have to register your account on the [WhatPulse Website][1] or as alternative when you first start the WhatPulse client there is a practical wizard through which each user has the option to create an account to upload their own statistics (you can also log in with Facebook).
|
||||
|
||||
You will be prompted to login, once you login, you have to search for your computers name, this is because you can login to several computers with this and they’ll all collectively go to the same statistic count. Once you’ve logged in, a small W will appear in your system tray, that’s it, your set up!
|
||||
|
||||
### Installation of WhatPulse on Linux ###
|
||||
|
||||
The official website offer on the [download page][3] a generic version distributed via a .tar.gz archive (available for 32 and 64 bit) and a debian package.
|
||||
|
||||
Personally I’ve installed the debian package on my Mint Qiana and the [Aur Package][4] on My Arch Linux, no problems at all.
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to go with the generic installation please keep in mind that WhatPulse requires several libraries to function. Mainly Qt, because WhatPulse is built on Qt. Here’s a list of requirements:
|
||||
|
||||
- libQtCore
|
||||
- libQtWebKit
|
||||
- libqt4-sql
|
||||
- libqt4-sql-sqlite
|
||||
- openssl-devel (libssl-dev)
|
||||
- libQtScript
|
||||
|
||||
#### Input Statistics ####
|
||||
|
||||
The client needs permissions to be allowed to read your keyboard/mouse input. Run the included interactive .sh script to set up these permissions.
|
||||
|
||||
#### [Network][5] Statistics ####
|
||||
|
||||
To enable the network measurements, you also need the package **libpcap** to allow WhatPulse to hook into the network traffic. If WhatPulse does not find libpcap, it will run but it will not display any network statistics.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Using the Application ###
|
||||
|
||||
By default WhatPulse will start automatically at the login of your graphical session and clicking on the W on your systray you’ll go to the Overview tab that gives a birds-eye view of all the different information gathered about your machine, for instance, the Linux version installed on your PC, processor model, RAM, GPU, total click counts, keystrokes and bandwidth usage. Clicking ‘Pulse’ under these information will upload the gathered data to the main server.
|
||||
|
||||
It’s also possible to select when automatically ‘Pulse’ the data to the server, such as every 50.000 clicks or 1 GB downloaded.
|
||||
|
||||
For further details, you can switch to each category’s pertaining tab. For example, the Input tab shows you the amount of key strokes and clicks your PC has registered during a certain time period. The time period can be sorted on a daily, weekly, monthly, yearly and all-time basis. The ‘all’ setting will show stats since the program was installed.
|
||||
|
||||
Below the keystrokes, you’ll find the keyboard heat map, which basically uses light and warm colors to shows what keys were used more than others during the selected time period, as shown in the screenshot above. Below that, the app displays the total amount of clicks registered in the selected period.
|
||||
|
||||
Under the Network tab, it’s possible to view the daily Internet usage. The application can monitor bandwidth usage of all the network devices, and even shows you bandwidth usage by country. Once again, you can navigate between available data using the arrow buttons at the top-right.
|
||||
|
||||
On the website you’ll see the sum of all your computer statistics with the same information available on the client.
|
||||
|
||||
Disclaimer: The link above to the WhatPulse website contains my referral link, using it when you register will give me a premium account for some time.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linuxaria.com/recensioni/check-how-much-do-you-type-with-whatpulse-on-linux
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[linuxari][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://plus.google.com/100563597940685405833?rel=author
|
||||
[1]:http://whatpulse.org/ref/833872/
|
||||
[2]:http://linuxaria.com/article/tool-command-line-bandwidth-linux
|
||||
[3]:http://www.whatpulse.org/downloads/
|
||||
[4]:https://aur.archlinux.org/packages/whatpulse/
|
||||
[5]:http://linuxaria.com/tag/network
|
||||
@ -1,44 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Disable reboot using Ctrl-Alt-Del Keys in RHEL / CentOS
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
In Linux , It's a security concern for us to allow anyone to **reboot** the server using **Ctrl-Alt-Del keys**. It is always recommended in production boxes that one should disable reboot uisng Ctrl-Alt-Del keys.
|
||||
|
||||
In this article we will discuss how can we disable reboot via above keys in RHEL & CentOS
|
||||
|
||||
### For RHEL 5.X & CentOS 5.X ###
|
||||
|
||||
To prevent the **init** process from handling **Ctrl-Alt-Del**, edit the file '**/etc/inittab**' comment the line which begins with '**ca::ctrlaltdel**:' as shown below :
|
||||
|
||||
[root@localhost ~]# cat /etc/inittab
|
||||
# Trap CTRL-ALT-DELETE
|
||||
#ca::ctrlaltdel:/sbin/shutdown -t3 -r now
|
||||
|
||||
We can also modify the line 'ca::ctrlaltdel:' to generate logs , if anybody try to reboot the server using the keys ,
|
||||
|
||||
[root@localhost ~]# cat /etc/inittab
|
||||
# Trap CTRL-ALT-DELETE
|
||||
ca::ctrlaltdel:/bin/logger -p authpriv.warning -t init "Console-invoked Ctrl-Alt-Del was ignored"
|
||||
|
||||
### For RHEL6.X & CentOS 6.X ###
|
||||
|
||||
In RHEL 6.X / CentOS 6.X , reboot using the keys are handled by the file '**/etc/init/control-alt-delete.conf**'.
|
||||
|
||||
**Step:1** Before making the changes , first take the backup using below command
|
||||
|
||||
[root@localhost ~]# cp -v /etc/init/control-alt-delete.conf /etc/init/control-alt-delete.override
|
||||
|
||||
**Step:2** Edit the file , replacing the 'exec /sbin/shutdown' line with the following, which will simply generate a log entry each time Ctrl-Alt-Del is pressed:
|
||||
|
||||
[root@localhost ~]# cat /etc/init/control-alt-delete.conf
|
||||
exec /usr/bin/logger -p authpriv.notice -t init "Ctrl-Alt-Del was pressed and ignored"
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxtechi.com/disable-reboot-using-ctrl-alt-del-keys/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Pradeep Kumar][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.linuxtechi.com/author/pradeep/
|
||||
@ -1,200 +0,0 @@
|
||||
How to Take ‘Snapshot of Logical Volume and Restore’ in LVM – Part III
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**LVM Snapshots** are space efficient pointing time copies of lvm volumes. It works only with lvm and consume the space only when changes are made to the source logical volume to snapshot volume. If source volume has a huge changes made to sum of 1GB the same changes will be made to the snapshot volume. Its best to always have a small size of changes for space efficient. Incase the snapshot runs out of storage, we can use lvextend to grow. And if we need to shrink the snapshot we can use lvreduce.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Take Snapshot in LVM
|
||||
|
||||
If we have accidentally deleted any file after creating a Snapshot we don’t have to worry because the snapshot have the original file which we have deleted. It is possible if the file was there when the snapshot was created. Don’t alter the snapshot volume, keep as it while snapshot used to do a fast recovery.
|
||||
|
||||
Snapshots can’t be use for backup option. Backups are Primary Copy of some data’s, so we cant use snapshot as a backup option.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Requirements ####
|
||||
|
||||
注:此两篇文章如果发布后可换成发布后链接,原文在前几天更新中
|
||||
|
||||
- [Create Disk Storage with LVM in Linux – PART 1][1]
|
||||
- [How to Extend/Reduce LVM’s in Linux – Part II][2]
|
||||
|
||||
### My Server Setup ###
|
||||
|
||||
- Operating System – CentOS 6.5 with LVM Installation
|
||||
- Server IP – 192.168.0.200
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 1: Creating LVM Snapshot ####
|
||||
|
||||
First, check for free space in volume group to create a new snapshot using following ‘**vgs**‘ command.
|
||||
|
||||
# vgs
|
||||
# lvs
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Check LVM Disk Space
|
||||
|
||||
You see, there is 8GB of free space left in above **vgs** output. So, let’s create a snapshot for one of my volume named **tecmint_datas**. For demonstration purpose, I am going to create only 1GB snapshot volume using following commands.
|
||||
|
||||
# lvcreate -L 1GB -s -n tecmint_datas_snap /dev/vg_tecmint_extra/tecmint_datas
|
||||
|
||||
OR
|
||||
|
||||
# lvcreate --size 1G --snapshot --name tecmint_datas_snap /dev/vg_tecmint_extra/tecmint_datas
|
||||
|
||||
Both the above commands does the same thing:
|
||||
|
||||
- **-s** – Creates Snapshot
|
||||
- **-n** – Name for snapshot
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Create LVM Snapshot
|
||||
|
||||
Here, is the explanation of each point highlighted above.
|
||||
|
||||
- Size of snapshot Iam creating here.
|
||||
- Creates snapshot.
|
||||
- Creates name for the snapshot.
|
||||
- New snapshots name.
|
||||
- Volume which we are going to create a snapshot.
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to remove a snapshot, you can use ‘**lvremove**‘ command.
|
||||
|
||||
# lvremove /dev/vg_tecmint_extra/tecmint_datas_snap
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Remove LVM Snapshot
|
||||
|
||||
Now, list the newly created snapshot using following command.
|
||||
|
||||
# lvs
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Verify LVM Snapshot
|
||||
|
||||
You see above, a snapshot was created successfully. I have marked with an arrow where snapshots origin from where its created, Its **tecmint_datas**. Yes, because we have created a snapshot for **tecmint_datas l-volume**.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Check LVM Snapshot Space
|
||||
|
||||
Let’s add some new files into **tecmint_datas**. Now volume has some data’s around 650MB and our snapshot size is 1GB. So there is enough space to backup our changes in snap volume. Here we can see, what is the status of our snapshot using below command.
|
||||
|
||||
# lvs
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Check Snapshot Status
|
||||
|
||||
You see, **51%** of snapshot volume was used now, no issue for more modification in your files. For more detailed information use command.
|
||||
|
||||
# lvdisplay vg_tecmint_extra/tecmint_data_snap
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
View Snapshot Information
|
||||
|
||||
Again, here is the clear explanation of each point highlighted in the above picture.
|
||||
|
||||
- Name of Snapshot Logical Volume.
|
||||
- Volume group name currently under use.
|
||||
- Snapshot volume in read and write mode, we can even mount the volume and use it.
|
||||
- Time when the snapshot was created. This is very important because snapshot will look for every changes after this time.
|
||||
- This snapshot belongs to tecmint_datas logical volume.
|
||||
- Logical volume is online and available to use.
|
||||
- Size of Source volume which we took snapshot.
|
||||
- Cow-table size = copy on Write, that means whatever changes was made to the tecmint_data volume will be written to this snapshot.
|
||||
- Currently snapshot size used, our tecmint_datas was 10G but our snapshot size was 1GB that means our file is around 650 MB. So what its now in 51% if the file grow to 2GB size in tecmint_datas size will increase more than snapshot allocated size, sure we will be in trouble with snapshot. That means we need to extend the size of logical volume (snapshot volume).
|
||||
- Gives the size of chunk for snapshot.
|
||||
|
||||
Now, let’s copy more than 1GB of files in **tecmint_datas**, let’s see what will happen. If you do, you will get error message saying ‘**Input/output error**‘, it means out of space in snapshot.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Add Files to Snapshot
|
||||
|
||||
If the logical volume become full it will get dropped automatically and we can’t use it any more, even if we extend the size of snapshot volume. It is the best idea to have the same size of Source while creating a snapshot, **tecmint_datas** size was 10G, if I create a snapshot size of 10GB it will never over flow like above because it has enough space to take snap of your volume.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 2: Extend Snapshot in LVM ####
|
||||
|
||||
If we need to extend the snapshot size before overflow we can do it using.
|
||||
|
||||
# lvextend -L +1G /dev/vg_tecmint_extra/tecmint_data_snap
|
||||
|
||||
Now there was totally 2GB size for snapshot.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Extend LVM Snapshot
|
||||
|
||||
Next, verify the new size and COW table using following command.
|
||||
|
||||
# lvdisplay /dev/vg_tecmint_extra/tecmint_data_snap
|
||||
|
||||
To know the size of snap volume and usage **%**.
|
||||
|
||||
# lvs
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Check Size of Snapshot
|
||||
|
||||
But if, you have snapshot volume with the same size of Source volume we don’t need to worry about these issues.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 3: Restoring Snapshot or Merging ####
|
||||
|
||||
To restore the snapshot, we need to un-mount the file system first.
|
||||
|
||||
# unmount /mnt/tecmint_datas/
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Un-mount File System
|
||||
|
||||
Just check for the mount point whether its unmounted or not.
|
||||
|
||||
# df -h
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Check File System Mount Points
|
||||
|
||||
Here our mount has been unmounted, so we can continue to restore the snapshot. To restore the snap using command **lvconvert**.
|
||||
|
||||
# lvconvert --merge /dev/vg_tecmint_extra/tecmint_data_snap
|
||||
|
||||
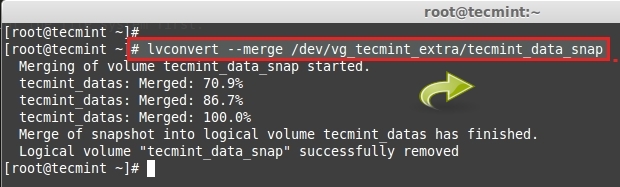
|
||||
Restore LVM Snapshot
|
||||
|
||||
After the merge is completed, snapshot volume will be removed automatically. Now we can see the space of our partition using **df** command.
|
||||
|
||||
# df -Th
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
After the snapshot volume removed automatically. You can see the size of logical volume.
|
||||
|
||||
# lvs
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Check Size of Logical Volume
|
||||
|
||||
**Important**: To Extend the Snapshots automatically, we can do it using some modification in conf file. For manual we can extend using lvextend.
|
||||
|
||||
Open the lvm configuration file using your choice of editor.
|
||||
|
||||
# vim /etc/lvm/lvm.conf
|
||||
|
||||
Search for word autoextend. By Default the value will be similar to below.
|
||||
|
||||
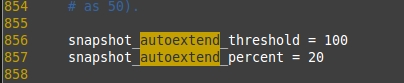
|
||||
LVM Configuration
|
||||
|
||||
Change the **100** to **75** here, if so auto extend threshold is **75** and auto extend percent is 20, it will expand the size more by **20 Percent**
|
||||
|
||||
If the snapshot volume reach **75%** it will automatically expand the size of snap volume by **20%** more. Thus,we can expand automatically. Save and exit the file using **wq!**.
|
||||
|
||||
This will save snapshot from overflow drop. This will also help you to save more time. LVM is the only Partition method in which we can expand more and have many features as thin Provisioning, Striping, Virtual volume and more Using thin-pool, let us see them in the next topic.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/take-snapshot-of-logical-volume-and-restore-in-lvm/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Babin Lonston][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/babinlonston/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/create-lvm-storage-in-linux/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/extend-and-reduce-lvms-in-linux/
|
||||
@ -1,112 +0,0 @@
|
||||
8 Options to Trace/Debug Programs using Linux strace Command
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
The strace is the tool that helps in debugging issues by tracing system calls executed by a program. It is handy when you want to see how the program interacts with the operating system, like what system calls are executed in what order.
|
||||
|
||||
This simple yet very powerful tool is available for almost all the Linux based operating systems and can be used to debug a large number of programs.
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Command Usage ###
|
||||
|
||||
Let’s see how we can use strace command to trace the execution of a program.
|
||||
|
||||
In the simplest form, any command can follow strace. It will list a whole lot of system calls. Not all of it would make sence at first, but if you’re really looking for something particular, then you should be able to figure something out of this output.
|
||||
Lets see the system calls trace for simple ls command.
|
||||
|
||||
raghu@raghu-Linoxide ~ $ strace ls
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
This output shows the first few lines for strace command. The rest of the output is truncated.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The above part of the output shows the write system call where it outputs to STDOUT the current directory’s listing. Following image shows the listing of the directoy by ls command (without strace).
|
||||
|
||||
raghu@raghu-Linoxide ~ $ ls
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### 1.1 Find configuration file read by program ####
|
||||
|
||||
One use of strace (Except debugging some problem) is that you can find out which configuration files are read by a program. For example,
|
||||
|
||||
raghu@raghu-Linoxide ~ $ strace php 2>&1 | grep php.ini
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### 1.2 Trace specific system call ####
|
||||
|
||||
The -e option to strace command can be used to display certain system calls only (for example, open, write etc.)
|
||||
|
||||
Lets trace only ‘open’ system call for cat command.
|
||||
|
||||
raghu@raghu-Linoxide ~ $ strace -e open cat dead.letter
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### 1.3 Stracing a process ####
|
||||
|
||||
The strace command can not only be used on the commands, but also on the running processes with -p option.
|
||||
|
||||
raghu@raghu-Linoxide ~ $ sudo strace -p 1846
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### 1.4 Statistical summary of strace ####
|
||||
|
||||
The summary of the system calls, time of execution, errors etc. can be displayed in a neat manner with -c option:
|
||||
|
||||
raghu@raghu-Linoxide ~ $ strace -c ls
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### 1.5 Saving output ####
|
||||
|
||||
The output of strace command can be saved into a file with -o option.
|
||||
|
||||
raghu@raghu-Linoxide ~ $ sudo strace -o process_strace -p 3229
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The above command is run with sudo as it will display error in case the user ID does not match with the process owner.
|
||||
|
||||
### 1.6 Displaying timestamp ###
|
||||
|
||||
The timestamp can be displayed before each output line with -t option.
|
||||
|
||||
raghu@raghu-Linoxide ~ $ strace -t ls
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### 1.7 The Finer timestamp ####
|
||||
|
||||
The -tt option displays timestamp followed by microsecond.
|
||||
|
||||
raghu@raghu-Linoxide ~ $ strace -tt ls
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The -ttt displays microseconds like above, but instead of printing surrent time, it displays the number of seconds since the epoch.
|
||||
|
||||
raghu@raghu-Linoxide ~ $ strace -ttt ls
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### 1.8 Relative Time ####
|
||||
|
||||
The -r option displays the relative timestamp between the system calls.
|
||||
|
||||
raghu@raghu-Linoxide ~ $ strace -r ls
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/linux-command/linux-strace-command-examples/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Raghu][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/raghu/
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
||||
zpl1025
|
||||
Build a Raspberry Pi Arcade Machine
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**Relive the golden majesty of the 80s with a little help from a marvel of the current decade.**
|
||||
@ -132,4 +133,4 @@ via: http://www.linuxvoice.com/arcade-machine/
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.linuxvoice.com/author/ben_everard/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.ultimarc.com/jpac.html
|
||||
[1]:http://www.ultimarc.com/jpac.html
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,106 +0,0 @@
|
||||
[translating by KayGuoWhu]
|
||||
How to Encrypt Email in Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
Kgpg provides a nice GUI for creating and managing your encryption keys.
|
||||
|
||||
If you've been thinking of encrypting your email, it is a rather bewildering maze to sort through thanks to the multitude of email services and mail clients. There are two levels of encryption to consider: SSL/TLS encryption protects your login and password to your mailserver. [GnuPG][1] is the standard strong Linux encryption tool, and it encrypts and authenticates your messages. It is best if you manage your own GPG encryption and not leave it up to third parties, which we will discuss in a moment.
|
||||
|
||||
Encrypting messages still leaves you vulnerable to traffic analysis, as message headers must be in the clear. So that necessitates yet another tool such as the [Tor network][2] for hiding your Internet footprints. Let's look at various mail services and clients, and the pitfalls and benefits therein.
|
||||
|
||||
### Forget Webmail ###
|
||||
|
||||
If you use GMail, Yahoo, Hotmail, or another Web mail provider, forget about it. Anything you type in a Web browser is vulnerable to JavaScript attacks, and whatever mischiefs the service provider engages in. GMail, Yahoo, and Hotmail all offer SSL/TLS encryption to protect your messages from wiretapping. But they offer no protections from their own data-mining habits, so they don't offer end-to-end encryption. Yahoo and Google both claim they're going to roll out end-to-end encryption next year. Color me skeptical, because they will wither and die if anything interferes with the data-mining that is their core business.
|
||||
|
||||
There are various third-party email security services such as [Virtru][3] and [SafeMess][4] that claim to offer secure encryption for all types of email. Again I am skeptical, because whoever holds your encryption keys has access to your messages, so you're still depending on trust rather than technology.
|
||||
|
||||
Peer messaging avoids many of the pitfalls of using centralized services. [RetroShare][5] and [Bitmessage][6] are two popular examples of this. I don't know if they live up to their claims, but the concept certainly has merit.
|
||||
|
||||
What about Android and iOS? It's safest to assume that the majority of Android and iOS apps are out to get you. Don't take my word for it-- read their terms of service and examine the permissions they require to install on your devices. And even if their terms are acceptable when you first install them, unilateral TOS changes are industry standard, so it is safest to assume the worst.
|
||||
|
||||
### Zero Knowledge ###
|
||||
|
||||
[Proton Mail][7] is a new email service that claims zero-knowledge message encryption. Authentication and message encryption are two separate steps, Proton is under Swiss privacy laws, and they do not log user activity. Zero knowledge encryption offers real security. This means that only you possess your encryption keys, and if you lose them your messages are not recoverable.
|
||||
|
||||
There are many encrypted email services that claim to protect your privacy. Read the fine print carefully and look for red flags such as limited user data collection, sharing with partners, and cooperation with law enforcement. These indicate that they collect and share user data, and have access to your encryption keys and can read your messages.
|
||||
|
||||
### Linux Mail Clients ###
|
||||
|
||||
A standalone open source mail client such as KMail, Thunderbird, Mutt, Claws, Evolution, Sylpheed, or Alpine, set up with your own GnuPG keys that you control gives you the most protection. (The easiest way to set up more secure email and Web surfing is to run the TAILS live Linux distribution. See [Protect Yourself Online With Tor, TAILS, and Debian][8].)
|
||||
|
||||
Whether you use TAILS or a standard Linux distro, managing GnuPG is the same, so let's learn how to encrypt messages with GnuPG.
|
||||
|
||||
### How to Use GnuPG ###
|
||||
|
||||
First, a quick bit of terminology. OpenPGP is an open email encryption and authentication protocol, based on Phil Zimmerman's Pretty Good Privacy (PGP). GNU Privacy Guard (GnuPG or GPG) is the GPL implementation of OpenPGP. GnuPG uses symmetric public key cryptography. This means that you create pairs of keys: a public key that anyone can use to encrypt messages to send to you, and a private key that only you possess to decrypt them. GnuPG performs two separate functions: digitally-signing messages to prove they came from you, and encrypting messages. Anyone can read your digitally-signed messages, but only people you have exchanged keys with can read your encrypted messages. Remember, never share your private keys! Only public keys.
|
||||
|
||||
Seahorse is GNOME's graphical front-end to GnuPG, and KGpg is KDE's graphical GnuPG tool.
|
||||
|
||||
Now let's run through the basic steps of creating and managing GnuPG keys. This command creates a new key:
|
||||
|
||||
$ gpg --gen-key
|
||||
|
||||
This is a multi-step process; just answer all the questions, and the defaults are fine for most people. When you create your passphrase, write it down and keep it in a secure place because if you lose it you cannot decrypt anything. All that advice about never writing down your passwords is wrong. Most of us have dozens of logins and passwords to track, including some that we rarely use, so it's not realistic to remember all of them. You know what happens when people don't write down their passwords? They create simple passwords and re-use them. Anything you store on your computer is potentially vulnerable; a nice little notebook kept in a locked drawer is impervious to everything but a physical intrusion, if an intruder even knew to look for it.
|
||||
|
||||
I must leave it as your homework to figure out how to configure your mail client to use your new key, as every one is different. You can list your key or keys:
|
||||
|
||||
$ gpg --list-keys
|
||||
/home/carla/.gnupg/pubring.gpg
|
||||
------------------------------
|
||||
pub 2048R/587DD0F5 2014-08-13
|
||||
uid Carla Schroder (my gpg key)
|
||||
sub 2048R/AE05E1E4 2014-08-13
|
||||
|
||||
This is a fast way to grab necessary information like the location of your keys, and your key name, which is the UID. Suppose you want to upload your public key to a keyserver; this is how it looks using my example key:
|
||||
|
||||
$ gpg --send-keys 'Carla Schroder' --keyserver http://example.com
|
||||
|
||||
When you create a new key for upload to public key servers, you should also create a revocation certificate. Don't do it later-- create it when you create your new key. You can give it any arbitrary name, so instead of revoke.asc you could give it a descriptive name like mycodeproject.asc:
|
||||
|
||||
$ gpg --output revoke.asc --gen-revoke 'Carla Schroder'
|
||||
|
||||
Now if your key ever becomes compromised you can revoke it by first importing the revocation certificate into your keyring:
|
||||
|
||||
$ gpg --import ~/.gnupg/revoke.asc
|
||||
|
||||
Then create and upload a new key to replace it. Any users of your old key will be notified as they refresh their key databases.
|
||||
|
||||
You must guard your revocation certificate just as zealously as your private key. Copy it to a CD or USB stick and lock it up, and delete it from your computer. It is a plain-text key, so you could even print it on paper.
|
||||
|
||||
If you ever need a copy-and-paste key, for example on public keyrings that allow pasting your key into a web form, or if you want to post your public key on your Web site, then you must create an ASCII-armored version of your public key:
|
||||
|
||||
$ gpg --output carla-pubkey.asc --export -a 'Carla Schroder'
|
||||
|
||||
This creates the familiar plain-text public key you've probably seen, like this shortened example:
|
||||
|
||||
-----BEGIN PGP PUBLIC KEY BLOCK-----
|
||||
Version: GnuPG v1
|
||||
mQENBFPrn4gBCADeEXKdrDOV3AFXL7QQQ+i61rMOZKwFTxlJlNbAVczpawkWRC3l
|
||||
IrWeeJiy2VyoMQ2ZXpBLDwGEjVQ5H7/UyjUsP8h2ufIJt01NO1pQJMwaOMcS5yTS
|
||||
[...]
|
||||
I+LNrbP23HEvgAdNSBWqa8MaZGUWBietQP7JsKjmE+ukalm8jY8mdWDyS4nMhZY=
|
||||
=QL65
|
||||
-----END PGP PUBLIC KEY BLOCK-----
|
||||
|
||||
That should get you started learning your way around GnuPG. [The GnuPG manuals][9] have complete details on using GnuPG and all of its options.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linux.com/learn/tutorials/784165-how-to-encrypt-email-in-linux
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Carla Schroder][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.linux.com/component/ninjaboard/person/3734
|
||||
[1]:http://www.openpgp.org/members/gnupg.shtml
|
||||
[2]:https://www.torproject.org/
|
||||
[3]:https://www.virtru.com/
|
||||
[4]:https://www.safemess.com/
|
||||
[5]:http://retroshare.sourceforge.net/
|
||||
[6]:http://retroshare.sourceforge.net/
|
||||
[7]:https://protonmail.ch/
|
||||
[8]:http://www.linux.com/learn/docs/718398-protect-yourself-online-with-tor-+tails-and-debian
|
||||
[9]:https://www.gnupg.org/documentation/manuals.html
|
||||
@ -1,103 +0,0 @@
|
||||
How to sniff HTTP traffic from the command line on Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Suppose you want to sniff live HTTP web traffic (i.e., HTTP requests and responses) on the wire for some reason. For example, you may be testing experimental features of a web server. Or you may be debugging a web application or a RESTful service. Or you may be trying to troubleshoot [PAC (proxy auto config)][1] or check for any malware files surreptitiously downloaded from a website. Whatever the reason is, there are cases where HTTP traffic sniffing is helpful, for system admins, developers, or even end users.
|
||||
|
||||
While [packet sniffing tools][2] such as tcpdump are popularly used for live packet dump, you need to set up proper filtering to capture HTTP traffic, and even then, their raw output typically cannot be interpreted on the HTTP protocol level so easily. Real-time web server log parsers such as [ngxtop][3] provide human-readable real-time web traffic traces, but only applicable with a full access to live web server logs.
|
||||
|
||||
What will be nice is to have tcpdump-like traffic sniffing tool, but targeting HTTP traffic only. In fact, [httpry][4] is extactly that: **HTTP packet sniffing tool**. httpry captures live HTTP packets on the wire, and displays their content at the HTTP protocol level in a human-readable format. In this tutorial, let's see how we can sniff HTTP traffic with httpry.
|
||||
|
||||
### Install httpry on Linux ###
|
||||
|
||||
On Debian-based systems (Ubuntu or Linux Mint), httpry is not available in base repositories. So build it from the source:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install gcc make git libpcap0.8-dev
|
||||
$ git clone https://github.com/jbittel/httpry.git
|
||||
$ cd httpry
|
||||
$ make
|
||||
$ sudo make install
|
||||
|
||||
On Fedora, CentOS or RHEL, you can install httpry with yum as follows. On CentOS/RHEL, enable [EPEL repo][5] before running yum.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install httpry
|
||||
|
||||
If you still want to build httpry from the source, you can easily do that by:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install gcc make git libpcap-devel
|
||||
$ git clone https://github.com/jbittel/httpry.git
|
||||
$ cd httpry
|
||||
$ make
|
||||
$ sudo make install
|
||||
|
||||
### Basic Usage of httpry ###
|
||||
|
||||
The basic use case of httpry is as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo httpry -i <network-interface>
|
||||
|
||||
httpry then listens on a specified network interface, and displays captured HTTP requests/responses in real time.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
In most cases, however, you will be swamped with the fast scrolling output as packets are coming in and out. So you want to save captured HTTP packets for offline analysis. For that, use either '-b' or '-o' options. The '-b' option allows you to save raw HTTP packets into a binary file as is, which then can be replayed with httpry later. On the other hand, '-o' option saves human-readable output of httpry into a text file.
|
||||
|
||||
To save raw HTTP packets into a binary file:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo httpry -i eth0 -b output.dump
|
||||
|
||||
To replay saved HTTP packets:
|
||||
|
||||
$ httpry -r output.dump
|
||||
|
||||
Note that when you read a dump file with '-r' option, you don't need root privilege.
|
||||
|
||||
To save httpr's output to a text file:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo httpry -i eth0 -o output.txt
|
||||
|
||||
### Advanced Usage of httpry ###
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to monitor only specific HTTP methods (e.g., GET, POST, PUT, HEAD, CONNECT, etc), use '-m' option:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo httpry -i eth0 -m get,head
|
||||
|
||||
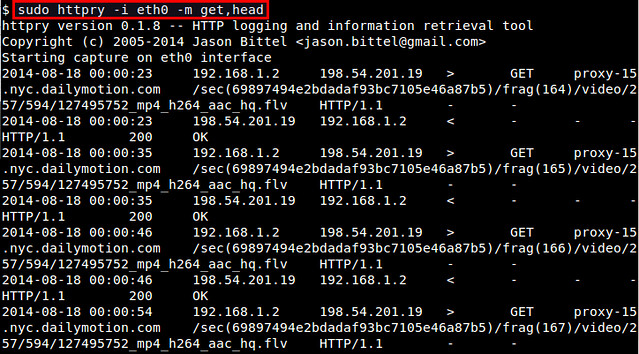
|
||||
|
||||
If you downloaded httpry's source code, you will notice that the source code comes with a collection of Perl scripts which aid in analyzing httpry's output. These scripts are found in httpry/scripts/plugins directory. If you want to write a custom parser for httpry's output, these scripts can be good examples to start from. Some of their capabilities are:
|
||||
|
||||
- **hostnames**: Displays a list of unique host names with counts.
|
||||
- **find_proxies**: Detect web proxies.
|
||||
- **search_terms**: Find and count search terms entered in search services.
|
||||
- **content_analysis**: Find URIs which contain specific keywords.
|
||||
- **xml_output**: Convert output into XML format.
|
||||
- **log_summary**: Generate a summary of log.
|
||||
- **db_dump**: Dump log file data into a database.
|
||||
|
||||
Before using these scripts, first run httpry with '-o' option for some time. Once you obtained the output file, run the scripts on it at once by using this command:
|
||||
|
||||
$ cd httpry/scripts
|
||||
$ perl parse_log.pl -d ./plugins <httpry-output-file>
|
||||
|
||||
You may encounter warnings with several plugins. For example, db_dump plugin may fail if you haven't set up a MySQL database with DBI interface. If a plugin fails to initialize, it will automatically be disabled. So you can ignore those warnings.
|
||||
|
||||
After parse_log.pl is completed, you will see a number of analysis results (*.txt/xml) in httpry/scripts directory. For example, log_summary.txt looks like the following.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
To conclude, httpry can be a life saver if you are in a situation where you need to interpret live HTTP packets. That might not be so common for average Linux users, but it never hurts to be prepared. What do you think of this tool?
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/08/sniff-http-traffic-command-line-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/nanni
|
||||
[1]:http://xmodulo.com/2012/12/how-to-set-up-proxy-auto-config-on-ubuntu-desktop.html
|
||||
[2]:http://xmodulo.com/2012/11/what-are-popular-packet-sniffers-on-linux.html
|
||||
[3]:http://xmodulo.com/2014/06/monitor-nginx-web-server-command-line-real-time.html
|
||||
[4]:http://dumpsterventures.com/jason/httpry/
|
||||
[5]:http://xmodulo.com/2013/03/how-to-set-up-epel-repository-on-centos.html
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
||||
DoubleC is translating
|
||||
How to create a site-to-site IPsec VPN tunnel using Openswan in Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
A virtual private network (VPN) tunnel is used to securely interconnect two physically separate networks through a tunnel over the Internet. Tunneling is needed when the separate networks are private LAN subnets with globally non-routable private IP addresses, which are not reachable to each other via traditional routing over the Internet. For example, VPN tunnels are often deployed to connect different NATed branch office networks belonging to the same institution.
|
||||
@ -215,4 +216,4 @@ via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/08/create-site-to-site-ipsec-vpn-tunnel-openswan-li
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/sarmed
|
||||
[1]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IPsec
|
||||
[2]:https://www.openswan.org/
|
||||
[2]:https://www.openswan.org/
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,107 +0,0 @@
|
||||
wangjiezhe translating
|
||||
6 Interesting Funny Commands of Linux (Fun in Terminal) – Part II
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
In our past following articles, we’ve shown some useful articles on some funny commands of Linux, which shows that Linux is not as complex as it seems and can be fun if we know how to use it. Linux command line can perform any complex task very easily and with perfection and can be interesting and joyful.
|
||||
|
||||
- [20 Funny Commands of Linux – Part I][1]注,此篇的原文应该翻译过,文件名应该是:20 Funny Commands of Linux or Linux is Fun in Terminal
|
||||
- [Fun in Linux Terminal – Play with Word and Character Counts][2]注:这篇文章刚刚补充上
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Funny Linux Commands
|
||||
|
||||
The former Post comprises of 20 funny Linux Commands/Script (and subcommands) which was highly appreciated by our readers. The other post, though not that much popular as former comprises of Commands/ Scripts and Tweaks which lets you play with text files, words and strings.
|
||||
|
||||
This post aims at bringing some new fun commands and one-liner scripts which is going to rejoice you.
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. pv Command ###
|
||||
|
||||
You might have seen simulating text in movies. It appears as, it is being typed in real time. Won’t it be nice, if you can have such an effect in terminal?
|
||||
|
||||
This can be achieved, by installing ‘**pv**‘ command in your Linux system by using ‘**apt**‘ or ‘**yum**‘ tool. Let’s install ‘**pv**‘ command as shown.
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install pv [On RedHat based Systems]
|
||||
|
||||
# sudo apt-get install pv [On Debian based Systems]
|
||||
|
||||
Once, ‘**pv**‘ command installed successfully on your system, let’s try to run the following one liner command to see the real time text effect on the screen.
|
||||
|
||||
$ echo "Tecmint[dot]com is a community of Linux Nerds and Geeks" | pv -qL 10
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
pv command in action
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**: The ‘**q**‘ option means ‘quite’, no output information and option ‘**L**‘ means the Limit of Transfer of bytes per second. The number value can be adjusted in either direction (must be integer) to get desired simulation of text.
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. toilet Command ###
|
||||
|
||||
How about printing text with border in terminal, using an one-liner script command ‘**toilet**‘. Again, you must have ‘**toilet**‘ command installed on your system, if not use apt or yum to install it.
|
||||
|
||||
$ while true; do echo “$(date | toilet -f term -F border –Tecmint)”; sleep 1; done
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
toilet command in action
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**: The above script needs to be suspended using **ctrl+z** key.
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. rig Command ###
|
||||
|
||||
This command generates a random identity and address, every time. To run, this command you need to install ‘**rig**‘ using apt or yum.
|
||||
|
||||
# rig
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
rig command in action
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. aview Command ###
|
||||
|
||||
How about viewing an image in ASCII format on the terminal? We must have a package ‘**aview**‘ installed, just apt or yum it. I’ve an image named ‘**elephant.jpg**‘ in my current working directory and I want view it on terminal as ASCII format.
|
||||
|
||||
$ asciiview elephant.jpg -driver curses
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
aview command in action
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. xeyes Command ###
|
||||
|
||||
In last article we introduced a command ‘**oneko**‘ which attaches jerry with mouse pointer and keeps on chasing it. A similar program ‘**xeyes**‘ which is a graphical programs and as soon as you fire the command you will see two monster eyes chasing your movement.
|
||||
|
||||
$ xeyes
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
xeyes command in action
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. cowsay Command ###
|
||||
|
||||
Do you remember last time we introduced command, which is useful in output of desired text with animated character cow. What if you want other animal in place of cow? Check a list of available animals.
|
||||
|
||||
$ cowsay -l
|
||||
|
||||
How about Elephant inside ASCII Snake?
|
||||
|
||||
$ cowsay -f elephant-in-snake Tecmint is Best
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
cowsay command in action
|
||||
|
||||
How about Elephant inside ASCII goat?
|
||||
|
||||
$ cowsay -f gnu Tecmint is Best
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
cowsay goat in action
|
||||
|
||||
That’s all for now. I’ll be here again with another interesting article. Till then stay update and connected to Tecmint. Don’t forget to provide us with your valuable feedback in the comments below.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/linux-funny-commands/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Avishek Kumar][a]
|
||||
译者:[wangjiezhe](https://github.com/wangjiezhe)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/avishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/20-funny-commands-of-linux-or-linux-is-fun-in-terminal/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/play-with-word-and-character-counts-in-linux/
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,5 @@
|
||||
chi1shi2 is translating.
|
||||
|
||||
How to use on-screen virtual keyboard on Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
On-screen virtual keyboard is an alternative input method that can replace a real hardware keyboard. Virtual keyboard may be a necessity in various cases. For example, your hardware keyboard is just broken; you do not have enough keyboards for extra machines; your hardware does not have an available port left to connect a keyboard; you are a disabled person with difficulty in typing on a real keyboard; or you are building a touchscreen-based web kiosk.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,112 +0,0 @@
|
||||
How to share on linux the output of your shell commands
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Some time ago I posted an article about [shelr.tv][1] a website and a service that was made to allow you to share your [terminal][2] records directly from the website.
|
||||
|
||||
Now the website of shelr.tv seems dead and so I’ve took a look around to see if there are similar websites and I’ve found [commands.com][3].
|
||||
|
||||
For what I can see from their homepage it’s a service similar to the other, so let’s test it.
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 1 – Register on the website ###
|
||||
|
||||
Just [register][4] with a new username/password or use your github account to do it quickly.
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 2 – download and install the program monitor ###
|
||||
|
||||
[Monitor][5] is a command-line tool that captures command-line input/output and sends it to commands.com, the program it’s open source and hosted on github.
|
||||
|
||||
Monitor makes it easy to automate set-up/install of repos. With it you can easily show at people the most common errors and output from commands.
|
||||
|
||||
In short with it you can easily share your commands and their output with the world.
|
||||
|
||||
To install it follow these simple steps:
|
||||
|
||||
1) Clone the github repository of this project, in this way you’ll get the latest source code.
|
||||
|
||||
To do this you need the git command installed on your system, if you get an error with this command install it with your package manager, such as
|
||||
|
||||
Debian based distributions:
|
||||
|
||||
apt-get install git
|
||||
|
||||
Redhat/Centos/Fedora distributions
|
||||
|
||||
yum install git
|
||||
|
||||
And now from a terminal clone the repository with:
|
||||
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/dtannen/monitor.git
|
||||
|
||||
2) Install readline and curl, these libraries are a pre-requisite for building the program from the sources:
|
||||
|
||||
Debian based distributions:
|
||||
|
||||
apt-get install libreadline-dev libcurl4-openssl-dev
|
||||
|
||||
Redhat/Centos/Fedora distributions
|
||||
|
||||
yum install readline-devel curl-devel
|
||||
|
||||
3) Build the program:
|
||||
|
||||
To do this you have to go to the directory we just cloned with git and compile the c program:
|
||||
|
||||
cd monitor
|
||||
make
|
||||
sudo make install
|
||||
|
||||
The default installation will put the binary in /usr/local/bin
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Step 3 – using the monitor command ###
|
||||
|
||||
The command monitor it’s pretty easy to use:
|
||||
|
||||
monitor {-d} {-h} {-u <username>}
|
||||
|
||||
-d : do not delete /tmp files
|
||||
-h : help
|
||||
-u : commands.com username</username>
|
||||
|
||||
To exit the monitor program you just have to use ctrl-c.
|
||||
|
||||
So for me this means just opening a terminal and give these commands:
|
||||
|
||||
riccio@mint-desktop ~ $ monitor -u ricciocri
|
||||
Password:
|
||||
|
||||
Successfully logged in...
|
||||
AuthKey saved to /tmp/.riccio.commands.com. Delete file to return to Anonymous posting.
|
||||
monitor$ cd /tmp
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
Want to see which command I’ve used after these ?
|
||||
I’ve made this session public (the default it’s private) so you can simply check this url: [https://commands.com/JTNSHRLQJA][6]
|
||||
|
||||
From there you can see the commands I’ve used and their output, an interesting options it’s the “fold/expand” so you could fold all commands and just expand the output of the one you like more.
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusions ###
|
||||
|
||||
This is just the a basic startup guide, from the website you can make more “social” activity such as comment script/shell sessions, fork them or choose your favorites.
|
||||
|
||||
Like github, you can fork any public script/command and change it directly from the website and after that you can also get a public (or private url) that you can use to run directly your script with something like this:
|
||||
|
||||
curl commands.io/JTNSHRLQJA | sh
|
||||
|
||||
That’s great to store on the net some scripts that you run frequently on different computers/server, as usual don’t put anything with passwords or sensible information on the net and you’ll be safe enough.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linuxaria.com/article/how-to-share-on-linux-the-output-of-your-shell-commands
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://linuxaria.com/recensioni/shelr-broadcast-your-linux-shell-on-the-net
|
||||
[2]:http://linuxaria.com/tag/shell
|
||||
[3]:https://commands.com/
|
||||
[4]:https://commands.com/Register/Index
|
||||
[5]:https://github.com/dtannen/monitor
|
||||
[6]:https://commands.com/JTNSHRLQJA
|
||||
@ -1,46 +0,0 @@
|
||||
johnhoow translating...
|
||||
Use LaTeX In Ubuntu 14.04 and Linux Mint 17 With Texmaker
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[LaTeX][1] is a document markup language and document preparation system. It is widely used as a standard in universities and academics to write professional scientific papers, thesis and other such documents. In this quick post, we shall see **how to use LaTeX in Ubuntu 14.04**.
|
||||
|
||||
### Install Texmaker to use LaTeX in Ubuntu 14.04 & Linux Mint 17 ###
|
||||
|
||||
[Texmaker][2] is a free and open source LaTeX editor which is available for all major desktop OS i.e. Windows, Linux and OS X. Followings are the salient features of the Texmaker:
|
||||
|
||||
- Unicode editor
|
||||
- Spell checker
|
||||
- Code folding
|
||||
- Code completion
|
||||
- Fast navigation
|
||||
- Integrated Pdf viewer
|
||||
- Easy compilation
|
||||
- 370 Mathematical symbols
|
||||
- LaTeX documentation
|
||||
- Export to html and odt via TeX4ht
|
||||
- Regex support
|
||||
|
||||
You can install Texmaker in Ubuntu 14.04 by downloading the binaries from the given link:
|
||||
|
||||
- [Download Texmaker LaTeX editor][3]
|
||||
|
||||
Since it is .deb packaging, same installation files can be used n any other Debian based distribution such as Linux Mint, Elementary OS, Pinguy OS etc.
|
||||
|
||||
If you want a Github type markdown editor, you should check [Remarkable editor][4]. I hope Texmaker helps you with **LaTeX in Ubuntu** and Linux Mint.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/install-latex-ubuntu-1404/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://itsfoss.com/author/Abhishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.latex-project.org/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.xm1math.net/texmaker/index.html
|
||||
[3]:http://www.xm1math.net/texmaker/download.html#linux
|
||||
[4]:http://itsfoss.com/remarkable-markdown-editor-linux/
|
||||
@ -1,4 +1,6 @@
|
||||
>>Linchenguang is translating
|
||||
|
||||
》》延期申请
|
||||
Linux TCP/IP networking: net-tools vs. iproute2
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Many sysadmins still manage and troubleshoot various network configurations by using a combination of ifconfig, route, arp and netstat command-line tools, collectively known as net-tools. Originally rooted in the BSD TCP/IP toolkit, the net-tools was developed to configure network functionality of older Linux kernels. Its development in the Linux community so far has ceased since 2001. Some Linux distros such as Arch Linux and CentOS/RHEL 7 have already deprecated net-tools in favor of iproute2.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
||||
translating by cvsher
|
||||
20 Useful Commands of ‘Sysstat’ Utilities (mpstat, pidstat, iostat and sar) for Linux Performance Monitoring
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
In our last article, we have learned about installing and upgrading the **sysstat** package and understanding briefly about the utilities which comes with the package.
|
||||
@ -401,4 +402,4 @@ via: http://www.tecmint.com/sysstat-commands-to-monitor-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/kuldeepsharma47/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/install-sysstat-in-linux/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/linux-performance-monitoring-with-vmstat-and-iostat-commands/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/linux-performance-monitoring-with-vmstat-and-iostat-commands/
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,61 +0,0 @@
|
||||
johnhoow translating...
|
||||
Install UberWriter Markdown Editor In Ubuntu 14.04
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Quick tutorial to show you **how to install UberWriter markdown editor in Ubuntu 14.04** for free via official PPA.
|
||||
|
||||
[UberWriter][1] is a [markdown][2] editor for Ubuntu with a clean interface with focus on writing only. UberWriter utilizes [pandoc][3] markdown. The UI is based on GTK3 which is not yet fully integrated with Unity. A quick list of features for UberWriter is as following:
|
||||
|
||||
- Clean interface
|
||||
- pandoc markdown
|
||||
- Preview option
|
||||
- Distraction free “focus mode”
|
||||
- Spell check
|
||||
- Syntax highlighting and math in html and pdf
|
||||
- Option to export as PDF, HTML, ODT etc
|
||||
|
||||
### Install UberWriter in Ubuntu 14.04 ###
|
||||
|
||||
UberWriter is available in [Ubuntu Software Center][4] but it costs $5. I would really recommend that you buy it, if you like it and if you can afford it to support the developer.
|
||||
|
||||
UberWriter is also available for free via its official PPA. You can install it using the following commands in terminal:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:w-vollprecht/ppa
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install uberwriter
|
||||
|
||||
Once installed, you can run it from Unity Dash. Write down your document in UberWriter. As you can see, it highlights the markdown syntax:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
You can use the preview feature to see how your document will actually look like:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
I tried to export it as PDF but it asked me to install texlive.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Export to HTML and ODT was fine though.
|
||||
|
||||
There are several other markdown editors available for Linux. [Remarkable][5] is one of them which has the feature of real time preview, which is not in UberWriter. But overall it is a nice application. If you are looking for document writing tool, you can also use [Texmaker LaTeX editor][6].
|
||||
|
||||
I hope this tutorial helped you to **install UberWriter in Ubuntu 14.04**. I haven’t tried but I presume that it should also work in Ubuntu 12.04, Linux Mint 17, Elementary OS and other Linux distributions based on Ubuntu.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/install-uberwriter-markdown-editor-ubuntu-1404/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://itsfoss.com/author/Abhishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://uberwriter.wolfvollprecht.de/
|
||||
[2]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Markdown
|
||||
[3]:http://johnmacfarlane.net/pandoc/
|
||||
[4]:apt://uberwriter
|
||||
[5]:http://itsfoss.com/remarkable-markdown-editor-linux/
|
||||
[6]:http://itsfoss.com/install-latex-ubuntu-1404/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,224 @@
|
||||
|
||||
How to create a software RAID-1 array with mdadm on Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID) is a storage technology that combines multiple hard disks into a single logical unit to provide fault-tolerance and/or improve disk I/O performance. Depending on how data is stored in an array of disks (e.g., with striping, mirroring, parity, or any combination thereof), different RAID levels are defined (e.g., RAID-0, RAID-1, RAID-5, etc). RAID can be implemented either in software or with a hardware RAID card. On modern Linux, basic software RAID functionality is available by default.
|
||||
|
||||
In this post, we'll discuss the software setup of a RAID-1 array (also known as a "mirroring" array), where identical data is written to the two devices that form the array. While it is possible to implement RAID-1 with partitions on a single physical hard drive (as with other RAID levels), it won't be of much use if that single hard drive fails. In fact, that's why most RAID levels normally use multiple physical drives to provide redundancy. In the event of any single drive failure, the virtual RAID block device should continue functioning without issues, and allow us to replace the faulty drive without significant production downtime and, more importantly, with no data loss. However, it does not replace the need to save periodic system backups in external storage.
|
||||
|
||||
Since the actual storage capacity (size) of a RAID-1 array is the size of the smallest drive, normally (if not always) you will find two identical physical drives in RAID-1 setup.
|
||||
|
||||
### Installing mdadm on Linux ###
|
||||
|
||||
The tool that we are going to use to create, assemble, manage, and monitor our software RAID-1 is called mdadm (short for **m**ultiple **d**isks **adm**in). On Linux distros such as Fedora, CentOS, RHEL or Arch Linux, mdadm is available by default. On Debian-based distros, mdadm can be installed with aptitude or apt-get.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Fedora, CentOS or RHEL ####
|
||||
|
||||
As mdadm comes pre-installed, all you have to do is to start RAID monitoring service, and configure it to auto-start upon boot:
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl start mdmonitor
|
||||
# systemctl enable mdmonitor
|
||||
|
||||
For CentOS/RHEL 6, use these commands instead:
|
||||
|
||||
# service mdmonitor start
|
||||
# chkconfig mdmonitor on
|
||||
|
||||
#### Debian, Ubuntu or Linux Mint ####
|
||||
|
||||
On Debian and its derivatives, mdadm can be installed with **aptitude or apt-get**:
|
||||
|
||||
# aptitude install mdadm
|
||||
|
||||
On Ubuntu, you will be asked to configure postfix MTA for sending out email notifications (as part of RAID monitoring). You can skip it for now.
|
||||
|
||||
On Debian, the installation will start with the following explanatory message to help us decide whether or not we are going to install the root filesystem on a RAID array. What we need to enter on the next screen will depend on this decision. Read it carefully:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Since we will not use our RAID-1 for the root filesystem, we will leave the answer blank:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
When asked whether we want to start (reassemble) our array automatically during each boot, choose "Yes". Note that we will need to add an entry to the /etc/fstab file later in order for the array to be properly mounted during the boot process as well.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Partitioning Hard Drives ###
|
||||
|
||||
Now it's time to prepare the physical devices that will be used in our array. For this setup, I have plugged in two 8 GB USB drives that have been identified as /dev/sdb and /dev/sdc from dmesg output:
|
||||
|
||||
# dmesg | less
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
[ 60.014863] sd 3:0:0:0: [sdb] 15826944 512-byte logical blocks: (8.10 GB/7.54 GiB)
|
||||
[ 75.066466] sd 4:0:0:0: [sdc] 15826944 512-byte logical blocks: (8.10 GB/7.54 GiB)
|
||||
|
||||
We will use fdisk to create a primary partition on each disk that will occupy its entire size. The following steps show how to perform this task on /dev/sdb, and assume that this drive hasn't been partitioned yet (otherwise, we can delete the existing partition(s) to start off with a clean disk):
|
||||
|
||||
# fdisk /dev/sdb
|
||||
|
||||
Press 'p' to print the current partition table:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
(if one or more partitions are found, they can be deleted with 'd' option. Then 'w' option is used to apply the changes).
|
||||
|
||||
Since no partitions are found, we will create a new primary partition ['n'] as a primary partition ['p'], assign the partition number = ['1'] to it, and then indicate its size. You can press Enter key to accept the proposed default values, or enter a value of your choosing, as shown in the image below.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Now repeat the same process for /dev/sdc.
|
||||
|
||||
If we have two drives of different sizes, say 750 GB and 1 TB for example, we should create a primary partition of 750 GB on each of them, and use the remaining space on the bigger drive for another purpose, independent of the RAID array.
|
||||
|
||||
### Create a RAID-1 Array ###
|
||||
|
||||
Once you are done with creating the primary partition on each drive, use the following command to create a RAID-1 array:
|
||||
|
||||
# mdadm -Cv /dev/md0 -l1 -n2 /dev/sdb1 /dev/sdc1
|
||||
|
||||
Where:
|
||||
|
||||
- **-Cv**: creates an array and produce verbose output.
|
||||
- **/dev/md0**: is the name of the array.
|
||||
- **-l1** (l as in "level"): indicates that this will be a RAID-1 array.
|
||||
- **-n2**: indicates that we will add two partitions to the array, namely /dev/sdb1 and /dev/sdc1.
|
||||
|
||||
The above command is equivalent to:
|
||||
|
||||
# mdadm --create --verbose /dev/md0 --level=1 --raid-devices=2 /dev/sdb1 /dev/sdc1
|
||||
|
||||
If alternatively you want to add a spare device in order to replace a faulty disk in the future, you can add '--spare-devices=1 /dev/sdd1' to the above command.
|
||||
|
||||
Answer "y" when prompted if you want to continue creating an array, then press Enter:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
You can check the progress with the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
# cat /proc/mdstat
|
||||
|
||||
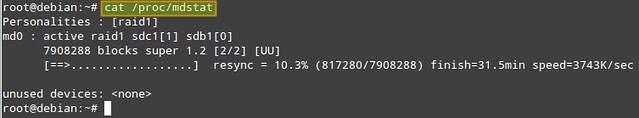
|
||||
|
||||
Another way to obtain more information about a RAID array (both while it's being assembled and after the process is finished) is:
|
||||
|
||||
# mdadm --query /dev/md0
|
||||
# mdadm --detail /dev/md0 (or mdadm -D /dev/md0)
|
||||
|
||||
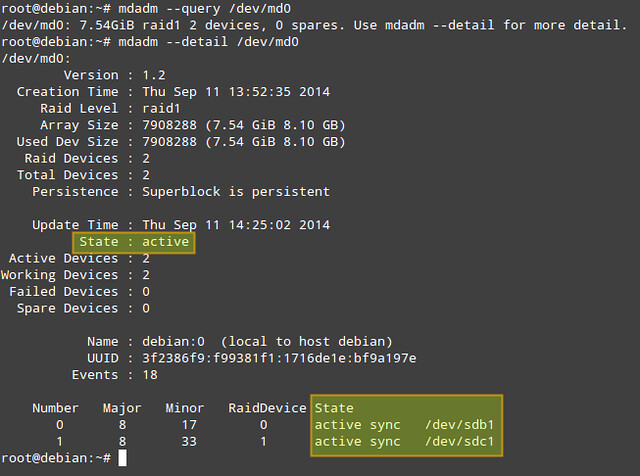
|
||||
|
||||
Of the information provided by 'mdadm -D', perhaps the most useful is that which shows the state of the array. The active state means that there is currently I/O activity happening. Other possible states are clean (all I/O activity has been completed), degraded (one of the devices is faulty or missing), resyncing (the system is recovering from an unclean shutdown such as a power outage), or recovering (a new drive has been added to the array, and data is being copied from the other drive onto it), to name the most common states.
|
||||
|
||||
### Formatting and Mounting a RAID Array ###
|
||||
|
||||
The next step is formatting (with ext4 in this example) the array:
|
||||
|
||||
# mkfs.ext4 /dev/md0
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Now let's mount the array, and verify that it was mounted correctly:
|
||||
|
||||
# mount /dev/md0 /mnt
|
||||
# mount
|
||||
|
||||
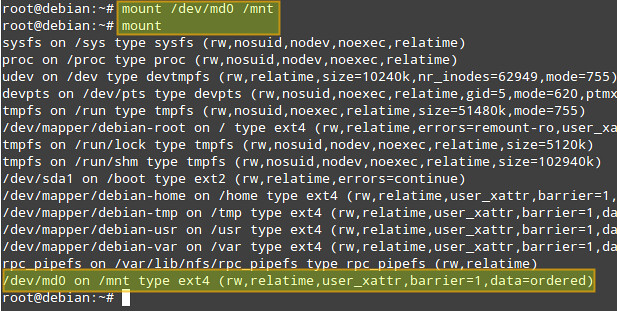
|
||||
|
||||
### Monitor a RAID Array ###
|
||||
|
||||
The mdadm tool comes with RAID monitoring capability built in. When mdadm is set to run as a daemon (which is the case with our RAID setup), it periodically polls existing RAID arrays, and reports on any detected events via email notification or syslog logging. Optionally, it can also be configured to invoke contingency commands (e.g., retrying or removing a disk) upon detecting any critical errors.
|
||||
|
||||
By default, mdadm scans all existing partitions and MD arrays, and logs any detected event to /var/log/syslog. Alternatively, you can specify devices and RAID arrays to scan in mdadm.conf located in /etc/mdadm/mdadm.conf (Debian-based) or /etc/mdadm.conf (Red Hat-based), in the following format. If mdadm.conf does not exist, create one.
|
||||
|
||||
DEVICE /dev/sd[bcde]1 /dev/sd[ab]1
|
||||
|
||||
ARRAY /dev/md0 devices=/dev/sdb1,/dev/sdc1
|
||||
ARRAY /dev/md1 devices=/dev/sdd1,/dev/sde1
|
||||
.....
|
||||
|
||||
# optional email address to notify events
|
||||
MAILADDR your@email.com
|
||||
|
||||
After modifying mdadm configuration, restart mdadm daemon:
|
||||
|
||||
On Debian, Ubuntu or Linux Mint:
|
||||
|
||||
# service mdadm restart
|
||||
|
||||
On Fedora, CentOS/RHEL 7:
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl restart mdmonitor
|
||||
|
||||
On CentOS/RHEL 6:
|
||||
|
||||
# service mdmonitor restart
|
||||
|
||||
### Auto-mount a RAID Array ###
|
||||
|
||||
Now we will add an entry in the /etc/fstab to mount the array in /mnt automatically during boot (you can specify any other mount point):
|
||||
|
||||
# echo "/dev/md0 /mnt ext4 defaults 0 2" << /etc/fstab
|
||||
|
||||
To verify that mount works okay, we now unmount the array, restart mdadm, and remount. We can see that /dev/md0 has been mounted as per the entry we just added to /etc/fstab:
|
||||
|
||||
# umount /mnt
|
||||
# service mdadm restart (on Debian, Ubuntu or Linux Mint)
|
||||
or systemctl restart mdmonitor (on Fedora, CentOS/RHEL7)
|
||||
or service mdmonitor restart (on CentOS/RHEL6)
|
||||
# mount -a
|
||||
|
||||
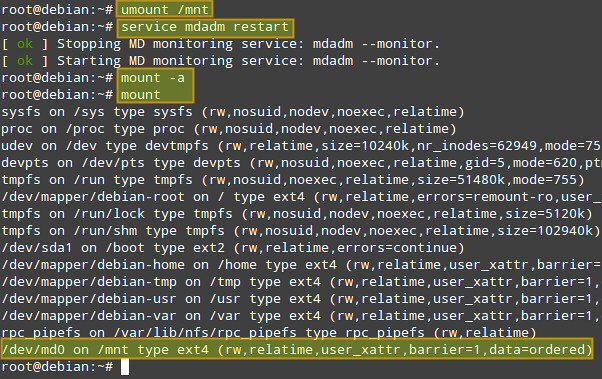
|
||||
|
||||
Now we are ready to access the RAID array via /mnt mount point. To test the array, we'll copy the /etc/passwd file (any other file will do) into /mnt:
|
||||
|
||||
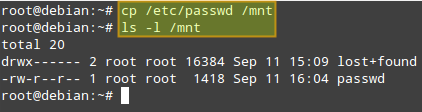
|
||||
|
||||
On Debian, we need to tell the mdadm daemon to automatically start the RAID array during boot by setting the AUTOSTART variable to true in the /etc/default/mdadm file:
|
||||
|
||||
AUTOSTART=true
|
||||
|
||||
### Simulating Drive Failures ###
|
||||
|
||||
We will simulate a faulty drive and remove it with the following commands. Note that in a real life scenario, it is not necessary to mark a device as faulty first, as it will already be in that state in case of a failure.
|
||||
|
||||
First, unmount the array:
|
||||
|
||||
# umount /mnt
|
||||
|
||||
Now, notice how the output of 'mdadm -D /dev/md0' indicates the changes after performing each command below.
|
||||
|
||||
# mdadm /dev/md0 --fail /dev/sdb1 #Marks /dev/sdb1 as faulty
|
||||
# mdadm --remove /dev/md0 /dev/sdb1 #Removes /dev/sdb1 from the array
|
||||
|
||||
Afterwards, when you have a new drive for replacement, re-add the drive again:
|
||||
|
||||
# mdadm /dev/md0 --add /dev/sdb1
|
||||
|
||||
The data is then immediately started to be rebuilt onto /dev/sdb1:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Note that the steps detailed above apply for systems with hot-swappable disks. If you do not have such technology, you will also have to stop a current array, and shutdown your system first in order to replace the part:
|
||||
|
||||
# mdadm --stop /dev/md0
|
||||
# shutdown -h now
|
||||
|
||||
Then add the new drive and re-assemble the array:
|
||||
|
||||
# mdadm /dev/md0 --add /dev/sdb1
|
||||
# mdadm --assemble /dev/md0 /dev/sdb1 /dev/sdc1
|
||||
|
||||
Hope this helps.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/09/create-software-raid1-array-mdadm-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Gabriel Cánepa][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/gabriel
|
||||
124
sources/tech/20140924 Unix----stat -- more than ls.md
Normal file
124
sources/tech/20140924 Unix----stat -- more than ls.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,124 @@
|
||||
wangjiezhe translating
|
||||
|
||||
Unix: stat -- more than ls
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> Tired of ls and want to see more interesting information on your files? Try stat!
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The ls command is probably one of the first commands that anyone using Unix learns, but it only shows a small portion of the information that is available with the stat command.
|
||||
|
||||
The stat command pulls information from the file's inode. As you might be aware, there are actually three sets of dates and times that are stored for every file on your system. These include the date the file was last modified (i.e., the date and time that you see when you use the ls -l command), the time the file was last changed (which includes renaming the file), and the time that file was last accessed.
|
||||
|
||||
View a long listing for a file and you will see something like this:
|
||||
|
||||
$ ls -l trythis
|
||||
-rwx------ 1 shs unixdweebs 109 Nov 11 2013 trythis
|
||||
|
||||
Use the stat command and you see all this:
|
||||
|
||||
$ stat trythis
|
||||
File: `trythis'
|
||||
Size: 109 Blocks: 8 IO Block: 262144 regular file
|
||||
Device: 18h/24d Inode: 12731691 Links: 1
|
||||
Access: (0700/-rwx------) Uid: ( 263/ shs) Gid: ( 100/ unixdweebs)
|
||||
Access: 2014-09-09 19:27:58.000000000 -0400
|
||||
Modify: 2013-11-11 08:40:10.000000000 -0500
|
||||
Change: 2013-11-11 08:40:10.000000000 -0500
|
||||
|
||||
The file's change and modify dates/times are the same in this case, while the access time is fairly recent. We can also see that the file is using 8 blocks and we see the permissions in each of the two formats -- the octal (0700) format and the rwx format. The inode number, shown in the third line of the output, is 12731681. There are no additional hard links (Links: 1). And the file is a regular file.
|
||||
|
||||
Rename the file and you will see that the change time will be updated.
|
||||
|
||||
This, the ctime information, was originally intended to hold the creation date and time for the file, but the field was turned into the change time field somewhere a while back.
|
||||
|
||||
$ mv trythis trythat
|
||||
$ stat trythat
|
||||
File: `trythat'
|
||||
Size: 109 Blocks: 8 IO Block: 262144 regular file
|
||||
Device: 18h/24d Inode: 12731691 Links: 1
|
||||
Access: (0700/-rwx------) Uid: ( 263/ shs) Gid: ( 100/ unixdweebs)
|
||||
Access: 2014-09-09 19:27:58.000000000 -0400
|
||||
Modify: 2013-11-11 08:40:10.000000000 -0500
|
||||
Change: 2014-09-21 12:46:22.000000000 -0400
|
||||
|
||||
Changing the file's permissions would also register in the ctime field.
|
||||
|
||||
You can also use wilcards with the stat command and list your files' stats in a group:
|
||||
|
||||
$ stat myfile*
|
||||
File: `myfile'
|
||||
Size: 20 Blocks: 8 IO Block: 262144 regular file
|
||||
Device: 18h/24d Inode: 12731803 Links: 1
|
||||
Access: (0640/-rw-r-----) Uid: ( 263/ shs) Gid: ( 100/ unixdweebs)
|
||||
Access: 2014-08-23 03:00:36.000000000 -0400
|
||||
Modify: 2014-08-22 12:02:12.000000000 -0400
|
||||
Change: 2014-08-22 12:02:12.000000000 -0400
|
||||
File: `myfile2'
|
||||
Size: 20 Blocks: 8 IO Block: 262144 regular file
|
||||
Device: 18h/24d Inode: 12731806 Links: 1
|
||||
Access: (0640/-rw-r-----) Uid: ( 263/ shs) Gid: ( 100/ unixdweebs)
|
||||
Access: 2014-08-23 03:00:36.000000000 -0400
|
||||
Modify: 2014-08-22 12:03:30.000000000 -0400
|
||||
Change: 2014-08-22 12:03:30.000000000 -0400
|
||||
File: `myfile3'
|
||||
Size: 40 Blocks: 8 IO Block: 262144 regular file
|
||||
Device: 18h/24d Inode: 12730533 Links: 1
|
||||
Access: (0640/-rw-r-----) Uid: ( 263/ shs) Gid: ( 100/ unixdweebs)
|
||||
Access: 2014-08-23 03:00:36.000000000 -0400
|
||||
Modify: 2014-08-22 12:03:59.000000000 -0400
|
||||
Change: 2014-08-22 12:03:59.000000000 -0400
|
||||
|
||||
We can get some of this information with other commands if we like.
|
||||
|
||||
Add the "u" option to a long listing and you'll see something like this. Notice this shows us the last access time while adding "c" shows us the change time (in this example, the time when we renamed the file).
|
||||
|
||||
$ ls -lu trythat
|
||||
-rwx------ 1 shs unixdweebs 109 Sep 9 19:27 trythat
|
||||
$ ls -lc trythat
|
||||
-rwx------ 1 shs unixdweebs 109 Sep 21 12:46 trythat
|
||||
|
||||
The stat command can also work against directories.
|
||||
|
||||
In this case, we see that there are a number of links.
|
||||
|
||||
$ stat bin
|
||||
File: `bin'
|
||||
Size: 12288 Blocks: 24 IO Block: 262144 directory
|
||||
Device: 18h/24d Inode: 15089714 Links: 9
|
||||
Access: (0700/drwx------) Uid: ( 263/ shs) Gid: ( 100/ unixdweebs)
|
||||
Access: 2014-09-21 03:00:45.000000000 -0400
|
||||
Modify: 2014-09-15 17:54:41.000000000 -0400
|
||||
Change: 2014-09-15 17:54:41.000000000 -0400
|
||||
|
||||
Here, we're looking at a file system.
|
||||
|
||||
$ stat -f /dev/cciss/c0d0p2
|
||||
File: "/dev/cciss/c0d0p2"
|
||||
ID: 0 Namelen: 255 Type: tmpfs
|
||||
Block size: 4096Fundamental block size: 4096
|
||||
Blocks: Total: 259366 Free: 259337 Available: 259337
|
||||
Inodes: Total: 223834 Free: 223531
|
||||
|
||||
Notice the Namelen (name length) field. Good luck if you had your heart set on file names with greater than 255 characters!
|
||||
|
||||
The stat command can also display some of its information a field at a time for those times when that's all you want to see, In the example below, we just want to see the file type and then the number of hard links.
|
||||
|
||||
$ stat --format=%F trythat
|
||||
regular file
|
||||
$ stat --format=%h trythat
|
||||
1
|
||||
|
||||
In the examples below, we look at permissions -- in each of the two available formats -- and then the file's SELinux security context.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.itworld.com/operating-systems/437351/unix-stat-more-ls
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Sandra Henry-Stocker][a]
|
||||
译者:[wangjiezhe](https://github.com/wangjiezhe)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.itworld.com/sandra-henry-stocker
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,84 @@
|
||||
Linux FAQs with Answers--How to build a RPM or DEB package from the source with CheckInstall
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **Question**: I would like to install a software program by building it from the source. Is there a way to build and install a package from the source, instead of running "make install"? That way, I could uninstall the program easily later if I want to.
|
||||
|
||||
If you have installed a Linux program from its source by running "make install", it becomes really tricky to remove it completely, unless the author of the program provides an uninstall target in the Makefile. You will have to compare the complete list of files in your system before and after installing the program from source, and manually remove all the files that were added during the installation.
|
||||
|
||||
That is when CheckInstall can come in handy. CheckInstall keeps track of all the files created or modified by an install command line (e.g., "make install" "make install_modules", etc.), and builds a standard binary package, giving you the ability to install or uninstall it with your distribution's standard package management system (e.g., yum for Red Hat or apt-get for Debian). It has been also known to work with Slackware, SuSe, Mandrake and Gentoo as well, as per the [official documentation][1].
|
||||
|
||||
In this post, we will only focus on Red Hat and Debian based distributions, and show how to build a RPM or DEB package from the source using CheckInstall.
|
||||
|
||||
### Installing CheckInstall on Linux ###
|
||||
|
||||
To install CheckInstall on Debian derivatives:
|
||||
|
||||
# aptitude install checkinstall
|
||||
|
||||
To install CheckInstall on Red Hat-based distributions, you will need to download a pre-built .rpm of CheckInstall (e.g., searchable from [http://rpm.pbone.net][2]), as it has been removed from the Repoforge repository. The .rpm package for CentOS 6 works in CentOS 7 as well.
|
||||
|
||||
# wget ftp://ftp.pbone.net/mirror/ftp5.gwdg.de/pub/opensuse/repositories/home:/ikoinoba/CentOS_CentOS-6/x86_64/checkinstall-1.6.2-3.el6.1.x86_64.rpm
|
||||
# yum install checkinstall-1.6.2-3.el6.1.x86_64.rpm
|
||||
|
||||
Once checkinstall is installed, you can use the following format to build a package for particular software.
|
||||
|
||||
# checkinstall <install-command>
|
||||
|
||||
Without <install-command> argument, the default install command "make install" will be used.
|
||||
|
||||
### Build a RPM or DEB Pacakge with CheckInstall ###
|
||||
|
||||
In this example, we will build a package for [htop][3], an interactive text-mode process viewer for Linux (like top on steroids).
|
||||
|
||||
First, let's download the source code from the official website of the project. As a best practice, we will store the tarball in /usr/local/src, and untar it.
|
||||
|
||||
# cd /usr/local/src
|
||||
# wget http://hisham.hm/htop/releases/1.0.3/htop-1.0.3.tar.gz
|
||||
# tar xzf htop-1.0.3.tar.gz
|
||||
# cd htop-1.0.3
|
||||
|
||||
Let's find out the install command for htop, so that we can invoke checkinstall with the command. As shown below, htop is installed with 'make install' command.
|
||||
|
||||
# ./configure
|
||||
# make install
|
||||
|
||||
Therefore, to build a htop package, we can invoke checkinstall without any argument, which will then use 'make install' command to build a package. Along the process, the checkinstall command will ask you a series of questions.
|
||||
|
||||
In short, here are the commands to build a package for **htop**:
|
||||
|
||||
# ./configure
|
||||
# checkinstall
|
||||
|
||||
Answer 'y' to "Should I create a default set of package docs?":
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
You can enter a brief description of the package, then press Enter twice:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Enter a number to modify any of the following values or Enter to proceed:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Then checkinstall will create a .rpm or a .deb package automatically, depending on what your Linux system is:
|
||||
|
||||
On CentOS 7:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
On Debian 7:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/build-rpm-deb-package-source-checkinstall.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://checkinstall.izto.org/docs/README
|
||||
[2]:http://rpm.pbone.net/
|
||||
[3]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/install-htop-centos-rhel.html
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,30 @@
|
||||
Linux FAQs with Answers--How to catch and handle a signal in Perl
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **Question**: I need to handle an interrupt signal by using a custom signal handler in Perl. In general, how can I catch and handle various signals (e.g., INT, TERM) in a Perl program?
|
||||
|
||||
As an asynchronous notification mechanism in the POSIX standard, a signal is sent by an operating system to a process to notify it of a certain event. When a signal is generated, the target process's execution is interrupted by an operating system, and the signal is delivered to the process's signal handler routine. One can define and register a custom signal handler or rely on the default signal handler.
|
||||
|
||||
In Perl, signals can be caught and handled by using a global %SIG hash variable. This %SIG hash variable is keyed by signal numbers, and contains references to corresponding signal handlers. Therefore, if you want to define a custom signal handler for a particular signal, you can simply update the hash value of %SIG for the signal.
|
||||
|
||||
Here is a code snippet to handle interrupt (INT) and termination (TERM) signals using a custom signal handler.
|
||||
|
||||
$SIG{INT} = \&signal_handler;
|
||||
$SIG{TERM} = \&signal_handler;
|
||||
|
||||
sub signal_handler {
|
||||
print "This is a custom signal handler\n";
|
||||
die "Caught a signal $!";
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Other valid hash values for %SIG are 'IGNORE' and 'DEFAULT'. When an assigned hash value is 'IGNORE' (e.g., $SIG{CHLD}='IGNORE'), the corresponding signal will be ignored. Assigning 'DEFAULT' hash value (e.g., $SIG{HUP}='DEFAULT') means that we will be using a default signal handler.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/catch-handle-interrupt-signal-perl.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,69 @@
|
||||
Linux FAQs with Answers--How to change a network interface name on CentOS 7
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **Question**: On CentOS 7, I would like to change the assigned name of a network interface to something else. What is a proper way to rename a network interface on CentOS or RHEL 7?
|
||||
|
||||
Traditionally, network interfaces in Linux are enumerated as eth[0123...], but these names do not necessarily correspond to actual hardware slots, PCI geography, USB port number, etc. This introduces a unpredictable naming problem (e.g., due to undeterministic device probing behavior) which can cause various network misconfigurations (e.g., disabled interface or firewall bypass resulting from unintentional interface renaming). MAC address based udev rules are not so much helpful in a virtualized environment where MAC addresses are as euphemeral as port numbers.
|
||||
|
||||
CentOS/RHEL 6 has introduced a method for [consistent and predictable network device naming][1] for network interfaces. These features uniquely determine the name of network interfaces in order to make locating and differentiating the interfaces easier and in such a way that it is persistent across later boots, time, and hardware changes. However, this naming rule is not turned on by default on CentOS/RHEL 6.
|
||||
|
||||
Starting with CentOS/RHEL 7, the predictable naming rule is adopted by default. Under this rule, interface names are automatically determined based on firmware, topology, and location information. Now interface names stay fixed even if NIC hardware is added or removed without re-enumeration, and broken hardware can be replaced seamlessly.
|
||||
|
||||
* Two character prefixes based on the type of interface:
|
||||
* en -- ethernet
|
||||
* sl -- serial line IP (slip)
|
||||
* wl -- wlan
|
||||
* ww -- wwan
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Type of names:
|
||||
* b<number> -- BCMA bus core number
|
||||
* ccw<name> -- CCW bus group name
|
||||
* o<index> -- on-board device index number
|
||||
* s<slot>[f<function>][d<dev_port>] -- hotplug slot index number
|
||||
* x<MAC> -- MAC address
|
||||
* [P<domain>]p<bus>s<slot>[f<function>][d<dev_port>]
|
||||
* -- PCI geographical location
|
||||
* [P<domain>]p<bus>s<slot>[f<function>][u<port>][..]1[i<interface>]
|
||||
* -- USB port number chain
|
||||
|
||||
A minor disadvantage of this new naming scheme is that the interface names are somewhat harder to read than the traditional names. For example, you may find names like enp0s3. Besides, you no longer have any control over such interface names.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
If, for some reason, you prefer the old way, and want to be able to assign any arbitrary name of your choice to an interface on CentOS/RHEL 7, you need to override the default predictable naming rule, and define a MAC address based udev rule.
|
||||
|
||||
**Here is how to rename a network interface on CentOS or RHEL 7.**
|
||||
|
||||
First, let's disable the predictable naming rule. For that, you can pass "net.ifnames=0" kernel parameter during boot. This is achieved by editing /etc/default/grub and adding "net.ifnames=0" to GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX variable.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Then run this command to regenerate GRUB configuration with updated kernel parameters.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo grub2-mkconfig -o /boot/grub2/grub.cfg
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Next, edit (or create) a udev network naming rule file (/etc/udev/rules.d/70-persistent-net.rules), and add the following line. Replace MAC address and interface with your own.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo vi /etc/udev/rules.d/70-persistent-net.rules
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
SUBSYSTEM=="net", ACTION=="add", DRIVERS=="?*", ATTR{address}=="08:00:27:a9:7a:e1", ATTR{type}=="1", KERNEL=="eth*", NAME="sushi"
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, reboot the machine, and verify the new interface name.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Note that it is still your responsibility to configure the renamed interface. If the network configuration (e.g., IPv4 settings, firewall rules) is based on the old name (before change), you need to update network configuration to reflect the name change.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/change-network-interface-name-centos7.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-US/Red_Hat_Enterprise_Linux/6/html/Deployment_Guide/appe-Consistent_Network_Device_Naming.html
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,78 @@
|
||||
Linux FAQs with Answers--How to configure a static IP address on CentOS 7
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **Question**: On CentOS 7, I want to switch from DHCP to static IP address configuration with one of my network interfaces. What is a proper way to assign a static IP address to a network interface permanently on CentOS or RHEL 7?
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to set up a static IP address on a network interface in CentOS 7, there are several different ways to do it, varying depending on whether or not you want to use Network Manager for that.
|
||||
|
||||
Network Manager is a dynamic network control and configuration system that attempts to keep network devices and connections up and active when they are available). CentOS/RHEL 7 comes with Network Manager service installed and enabled by default.
|
||||
|
||||
To verify the status of Network Manager service:
|
||||
|
||||
$ systemctl status NetworkManager.service
|
||||
|
||||
To check which network interface is managed by Network Manager, run:
|
||||
|
||||
$ nmcli dev status
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
If the output of nmcli shows "connected" for a particular interface (e.g., enp0s3 in the example), it means that the interface is managed by Network Manager. You can easily disable Network Manager for a particular interface, so that you can configure it on your own for a static IP address.
|
||||
|
||||
Here are **two different ways to assign a static IP address to a network interface on CentOS 7**. We will be configuring a network interface named enp0s3.
|
||||
|
||||
### Configure a Static IP Address without Network Manager ###
|
||||
|
||||
Go to the /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts directory, and locate its configuration file (ifcfg-enp0s3). Create it if not found.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Open the configuration file and edit the following variables:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
In the above, "NM_CONTROLLED=no" indicates that this interface will be set up using this configuration file, instead of being managed by Network Manager service. "ONBOOT=yes" tells the system to bring up the interface during boot.
|
||||
|
||||
Save changes and restart the network service using the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl restart network.service
|
||||
|
||||
Now verify that the interface has been properly configured:
|
||||
|
||||
# ip add
|
||||
|
||||
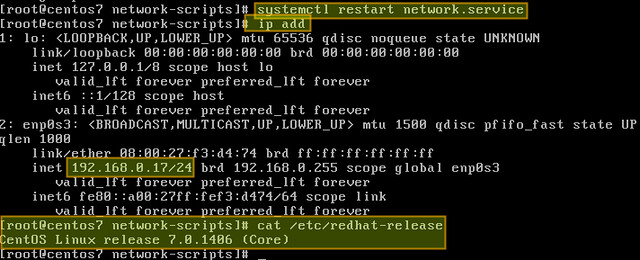
|
||||
|
||||
### Configure a Static IP Address with Network Manager ###
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to use Network Manager to manage the interface, you can use nmtui (Network Manager Text User Interface) which provides a way to configure Network Manager in a terminal environment.
|
||||
|
||||
Before using nmtui, first set "NM_CONTROLLED=yes" in /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-enp0s3.
|
||||
|
||||
Now let's install nmtui as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install NetworkManager-tui
|
||||
|
||||
Then go ahead and edit the Network Manager configuration of enp0s3 interface:
|
||||
|
||||
# nmtui edit enp0s3
|
||||
|
||||
The following screen will allow us to manually enter the same information that is contained in /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-enp0s3.
|
||||
|
||||
Use the arrow keys to navigate this screen, press Enter to select from a list of values (or fill in the desired values), and finally click OK at the bottom right:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Finally, restart the network service.
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl restart network.service
|
||||
|
||||
and you're ready to go.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/configure-static-ip-address-centos7.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,53 @@
|
||||
Linux FAQs with Answers--How to detect a Linux distribution in Perl
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **Question**: I need to write a Perl program which contains Linux distro-dependent code. For that, the Perl program needs to be able to automatically detect what Linux distribution (e.g., Ubuntu, CentOS, Debian, Fedora, etc) it is running on, and what version number it is. How can I identify Linux distribution in Perl?
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to detect Linux distribution within a Perl script, you can use a Perl module named [Linux::Distribution][1]. This module guesses the underlying Linux operating system by examining /etc/lsb-release, and other distro-specific files under /etc directory. It supports detecting all major Linux distributions, including Fedora, CentOS, Arch Linux, Debian, Ubuntu, SuSe, Red Hat, Gentoo, Slackware, Knoppix, and Mandrake.
|
||||
|
||||
To use this module in a Perl program, you need to install it first.
|
||||
|
||||
### Install Linux::Distribution on Debian or Ubuntu ###
|
||||
|
||||
Installation on Debian-based system is straightforward with apt-get:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install liblinux-distribution-packages-perl
|
||||
|
||||
### Install Linux::Distribution on Fedora, CentOS or RHEL ###
|
||||
|
||||
If Linux::Distribution module is not available as a package in your Linux (such as on Red Hat based systems), you can use CPAN to build it.
|
||||
|
||||
First, make sure that you have CPAN installed on your Linux system:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum -y install perl-CPAN
|
||||
|
||||
Then use this command to build and install the module:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo perl -MCPAN -e 'install Linux::Distribution'
|
||||
|
||||
### Identify a Linux Distribution in Perl ###
|
||||
|
||||
Once Linux::Distribution module is installed, you can use the following code snippet to identify on which Linux distribution you are running.
|
||||
|
||||
use Linux::Distribution qw(distribution_name distribution_version);
|
||||
|
||||
my $linux = Linux::Distribution->new;
|
||||
|
||||
if ($linux) {
|
||||
my $distro = $linux->distribution_name();
|
||||
my $version = $linux->distribution_version();
|
||||
print "Distro: $distro $version\n";
|
||||
}
|
||||
else {
|
||||
print "Distro: unknown\n";
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/detect-linux-distribution-in-perl.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:https://metacpan.org/pod/Linux::Distribution
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,39 @@
|
||||
Linux FAQs with Answers--How to embed all fonts in a PDF document generated with LaTex
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **Question**: I generated a PDF document by compiling LaTex source files. However, I noticed that not all fonts used are embedded in the PDF document. How can I make sure that all fonts are embedded in a PDF document generated from LaTex?
|
||||
|
||||
When you create a PDF file, it is a good idea to embed fonts in the PDF file. If you don't embed fonts, a PDF viewer can replace a font with something else if the font is not available on the computer. This will cause the document to be rendered differently across different PDF viewers or OS platforms. Missing fonts can also be an issue when you print out the document.
|
||||
|
||||
When you generate a PDF document from LaTex (for example with pdflatex or dvipdfm), it's possible that not all fonts are embedded in the PDF document. For example, the following output of [pdffonts][1] says that there are missing fonts (e.g., Helvetica) in a PDF document.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
To avoid this kind of problems, here is how to embed all fonts at LaTex compile time.
|
||||
|
||||
$ latex document.tex
|
||||
$ dvips -Ppdf -G0 -t letter -o document.ps document.dvi
|
||||
$ ps2pdf -dPDFSETTINGS=/prepress \
|
||||
-dCompatibilityLevel=1.4 \
|
||||
-dAutoFilterColorImages=false \
|
||||
-dAutoFilterGrayImages=false \
|
||||
-dColorImageFilter=/FlateEncode \
|
||||
-dGrayImageFilter=/FlateEncode \
|
||||
-dMonoImageFilter=/FlateEncode \
|
||||
-dDownsampleColorImages=false \
|
||||
-dDownsampleGrayImages=false \
|
||||
document.ps document.pdf
|
||||
|
||||
Now you will see that all fonts are properly embedded in the PDF file.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/embed-all-fonts-pdf-document-latex.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/check-which-fonts-are-used-pdf-document.html
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,36 @@
|
||||
Jelly Conky给你的Linux桌面加入了简约、时尚的状态
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**我把Conky设置成有点像壁纸:我会找出一张我喜欢的,只在下一周更换因为我厌倦了并且想要一点改变。**
|
||||
|
||||
不耐烦的一部分原因是由于日益增长的设计目录。我最近最喜欢的是Jelly Conky。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
我们最近强调的许多Conky所夸耀的最小设计都遵循了。它并不想成为一个厨房水槽。它不会被那些需要一眼需要看到他们硬盘温度和IP地址的人所青睐
|
||||
|
||||
它配备了三种不同的模式,它们都可以添加个性的或者静态背景图像:
|
||||
|
||||
- 时钟
|
||||
- 时钟加日期
|
||||
- 时钟加日期和天气
|
||||
|
||||
一些人不理解为什么要在桌面上拥有重复的时钟。这是很好理解的。对于我而言,这不仅仅是功能(虽然,个人而言,Conky的时钟比挤在上部面板上那渺小的数字要更容易看清)。
|
||||
|
||||
机会是如果你的Android主屏幕有一个时间小部件的话,你不会介意在你的桌面上也有这么一个
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- [从Deviant Art上下载 Jelly Conky][2]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/09/jelly-conky-for-linux-desktop
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Joey-Elijah Sneddon][a]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://plus.google.com/117485690627814051450/?rel=author
|
||||
[1]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/07/conky-circle-theme-nod-lg-quick-cover
|
||||
[2]:http://zagortenay333.deviantart.com/art/Jelly-Conky-442559003
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,37 @@
|
||||
Canonical在Ubuntu 14.04 LTS中关闭了一个nginx漏洞
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> 用户不得不升级他们的系统来修复这个漏洞
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu 14.04 LTS
|
||||
|
||||
**Canonical已经在安全公告中公布了这个影响到Ubuntu 14.04 LTS (Trusty Tahr)的nginx漏洞的细节。这个问题已经被确定并被修复了**
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu的开发者已经修复了nginx的一个小漏洞。他们解释nginx可能已经被用来暴露网络上的敏感信息。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
根据安全公告,“Antoine Delignat-Lavaud和Karthikeyan Bhargavan发现nginx错误地重复使用了缓存的SSL会话。攻击者可能利用此问题,在特定的配置下,可以从不同的虚拟主机获得信息“。
|
||||
|
||||
对于这些问题的更详细的描述,可以看到Canonical的安全[公告][1]。用户应该升级自己的Linux发行版以解决此问题。
|
||||
|
||||
这个问题可以通过在系统升级到最新nginx包(和依赖v包)进行修复。要应用该补丁,你可以直接运行升级管理程序。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你不想使用软件更新器,您可以打开终端,输入以下命令(需要root权限):
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get dist-upgrade
|
||||
|
||||
在一般情况下,一个标准的系统更新将会进行必要的更改。要应用此修补程序您不必重新启动计算机。
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/Canonical-Closes-Nginx-Exploit-in-Ubuntu-14-04-LTS-459677.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Silviu Stahie][a]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://news.softpedia.com/editors/browse/silviu-stahie
|
||||
[1]:http://www.ubuntu.com/usn/usn-2351-1/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,104 @@
|
||||
在哪儿以及怎么写代码:选择最好的免费代码编辑器
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
深入了解一下Cloud9,Koding和Nitrous.IO。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**已经准备好开始你的第一个编程项目了吗?很好!只要配置一下**终端或命令行,学习如何使用并安装所有要用到的编程语言,插件库和API函数库。当最终准备好一切以后,再安装好[Visual Studio][1]就可以开始了,然后才可以预览自己的工作。
|
||||
|
||||
至少这是大家过去已经熟悉的方式。
|
||||
|
||||
也难怪初学程序员们逐渐喜欢上在线集成开发环境(IDE)了。IDE是一个代码编辑器,不过已经准备好编程语言以及所有需要的依赖,可以让你避免把它们一一安装到电脑上的麻烦。
|
||||
|
||||
我想搞清楚到底是哪些因素能组成一个典型的IDE,所以我试用了一下免费级别的时下最受欢迎的三款集成开发环境:[Cloud9][2],[Koding][3]和[Nitrous.IO][4]。在这个过程中,我了解了许多程序员应该或不应该使用IDE的各种情形。
|
||||
|
||||
### 为什么要用IDE? ###
|
||||
|
||||
假如有一个像Microsoft Word那样的文字编辑器,想想类似Google Drive那样的IDE吧。你可以拥有类似的功能,但是它还能支持从任意电脑上访问,还能随时共享。因为因特网在项目工作流中的影响已经越来越重要,IDE也让生活更轻松。
|
||||
|
||||
在我最近的一篇ReadWrite教程中我使用了Nitrous.IO,这是在文章[创建一个你自己的像Yo那样的极端简单的聊天应用][5]里的一个Python应用。当使用IDE的时候,你只要选择你要用的编程语言,然后通过IDE特别设计用来运行这种语言程序的虚拟机(VM),你就可以测试和预览你的应用了。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你读过那篇教程,就会知道我的那个应用只用到了两个API库-信息服务Twilio和Python微框架Flask。在我的电脑上就算是使用文字编辑器和终端来做也是很简单的,不过我选择使用IDE还有一个方便的地方:如果大家都使用同样的开发环境,跟着教程一步步走下去就更简单了。
|
||||
|
||||
### IDE不能做的事情 ###
|
||||
|
||||
到目前为止,IDE还不是一个长期托管方案。
|
||||
|
||||
当你使用IDE工作的时候,你可以在云上构建,测试和预览你的应用。你甚至还可以直接通过链接共享你的最终作品。
|
||||
|
||||
但是不能用IDE来永久存储你的整个项目。把帖子保存在Google Drive文件中不会让你的博客丢失。类似Google Drive,IDE可以让你创建链接用于共享内容,但是任何一个都还不足以替代真正的托管服务器。
|
||||
|
||||
还有,IDE并不是设计成方便广泛共享。尽管各种IDE都在不断改善大多数文字编辑器的预览功能,还只能用来给你的朋友或同事展示一下应用预览,而不是,比如说,类似Hacker News的主页。那样的话,占用太多带宽的IDE也许会让你崩溃。
|
||||
|
||||
这样说吧:IDE只是构建和测试你的应用的地方,托管服务器才是它们生存的地方。所以一旦完成了你的应用,你会希望把它布置到能长期托管的云服务器上,最好是能免费托管的那种,例如[Heroku][6]。
|
||||
|
||||
### 选择一个IDE ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
随着IDE变得越来越流行,选择也越来越多。在我眼里,没有一个是完美的。不过,还是有些IDE在完成某些工作方面相对来说有些优势。
|
||||
|
||||
我尝试了一下免费级别的三个最受欢迎的集成开发环境:Cloud9,Koding和Nitrous.IO。每一个都有自己的优点,当然跟你用来做的事情有关系。下面就是我的发现。
|
||||
|
||||
### Cloud9:乐于协作 ###
|
||||
|
||||
当我完成了Cloud9的注册后,它提示的第一件事情就是添加我的GitHub和BitBucket账号。马上,所有我的GitHub项目,个人的和协作的,都可以直接克隆到本地并使用Cloud9的开发工具开始工作。其他的IDE在和GitHub集成的方面都没有达到这种水准。
|
||||
|
||||
在我测试的这三款IDE中,Cloud9看起来更加侧重于一个可以让协同工作的人们无缝衔接工作的环境。在这里,它并不是角落里放个聊天窗口。实际上,按照CEO Ruben Daniels说的,试用Cloud9的协作者可以互相看到其他人实时的编码情况,就像Google Drive上的合作者那样。
|
||||
|
||||
“大多数IDE服务的协同功能只能操作单一文件”,Daniels说,“而我们的产品可以支持整个项目中的不同文件。协同功能被完美集成到了我们的IDE中。”
|
||||
|
||||
### Koding:在你需要的时候能提供帮助 ###
|
||||
|
||||
IDE可以提供你所需的工具来构建和测试所有开源编程语言的应用。对于初学者来说,看起来有点吓人。举个例子,如果我要做一个项目同时用到Python和Ruby组件,那我要用哪个VM来测试?
|
||||
|
||||
答案是两个都要,尽管使用免费账号的话,只能够同时打开一个VM用于测试。我就在Koding的控制面板里找到了答案,一个折叠起来的地方,用户可以提供或获得他们Koding项目的各种经验。在这三者中间,它是最容易使用的,拥有一个你可以寻求帮助并很快有人回答的地方。
|
||||
|
||||
“我们在这款产品里加入了一个积极的社区功能”,Koding的首席商务官Nitin Gupta说,“我们希望搭建一个环境,真正吸引那些希望得到帮助和愿意提供帮助的人们。”
|
||||
|
||||
### Nitrous.IO: An IDE Wherever You Want ###
|
||||
|
||||
相对于自己的桌面环境,使用IDE的最大优势是它是自包含的。你不需要安装任何其他的就可以使用。而另一方面,使用自己的桌面环境的最大优势就是你可以在本地工作,甚至在没有互联网的情况下。
|
||||
|
||||
Nitrous.IO结合了这两个优势。你可以在网站上在线使用这个IDE,你也可以把它下载到自己的饿电脑上,共同创始人AJ Solimine这样说。优点是你可以结合Nitrous的集成性和你最喜欢的文字编辑器的熟悉。
|
||||
|
||||
他说:“你可以使用任意当代浏览器访问Nitrous.IO的在线IDE网站,但我们仍然提供了方便的Windows和Mac桌面应用,可以让你使用你最喜欢的编辑器来写代码。”
|
||||
|
||||
### 底线 ###
|
||||
|
||||
这一个星期的[使用][7]三个不同IDE的最让我意外的收获?它们是如此相似。[当用来做最基本的代码编辑的时候][8],它们都一样的好用。
|
||||
|
||||
Cloud9,Koding,[和Nitrous.IO都支持][9]所有主流的开源编程语言,从Ruby到Python到PHP到HTML5。你可以选择任何一种VM。
|
||||
|
||||
Cloud9和Nitrous.IO都实现了GitHub的一键集成。Koding需要[多几个步骤][10],不过也是可以实现的。
|
||||
|
||||
每一个都轻松地集成了我需要的API。每一个也都可以让我自己安装喜欢的包(Koding需要超级用户权限)。它们都带有内置的终端,可以用来轻松地测试和布置项目。三个都支持轻松地预览项目。当然,它们也都把我的项目托管在云服务器中,所以我在任意地方都可以在上边工作。
|
||||
|
||||
不好的一面,它们都有相同的缺陷,不过考虑到它们都是免费的也还合理。你每次只能同时运行一个VM来测试特定编程语言写出的程序。而当你一段时间没有使用VM之后,IDE会把VM切换成休眠模式以节省带宽,而下次要用的时候就得等它重新加载(Cloud9在这一点上更加费力)。它们中也没有任何一个为已完成的项目提供像样的永久托管服务。
|
||||
|
||||
所以,对咨询我是否有一个完美的免费IDE的人,答案是可能没有。但是这也要看你侧重的地方,对你的某个项目来说也许有一个完美的IDE。
|
||||
|
||||
图片由[Shutterstock][11]友情提供
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://readwrite.com/2014/08/14/cloud9-koding-nitrousio-integrated-development-environment-ide-coding
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Lauren Orsini][a]
|
||||
译者:[zpl1025](https://github.com/zpl1025)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://readwrite.com/author/lauren-orsini
|
||||
[1]:http://www.visualstudio.com/
|
||||
[2]:http://c9.io/
|
||||
[3]:https://koding.com/
|
||||
[4]:http://nitrous.io/
|
||||
[5]:http://readwrite.com/2014/07/11/one-click-messaging-app
|
||||
[6]:http://heroku.com/
|
||||
[7]:http://help.nitrous.io/ide-general/
|
||||
[8]:https://www.nitrous.io/desktop
|
||||
[9]:https://www.nitrous.io/desktop
|
||||
[10]:https://koding.com/Activity/steps-clone-projects-github-koding-1-create-account-github-2-open-your-terminal-3
|
||||
[11]:http://www.shutterstock.com/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,68 @@
|
||||
为什么你的公司需要参与更多开源软件的编写
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
>闭关锁国是产生不了创新的。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**华尔街日报 [称][1],有消息表明,Zulily正在开发** 更多的内部软件,但实际上根本不是。多年前[Eric Raymond写道][2],全世界95%的软件写来用的,而不是售卖。原因很多,但是其中有一个比较突出:正如Zulily的CIO Luke Friang所说,几乎没有一个[非定制]软件解决方案能跟上我们的步伐。
|
||||
|
||||
20年前是这样,现在也是这样。
|
||||
|
||||
但是有一点是不同的,这也正是华尔街日报完全忽略的地方。而这也正是历史上开发的内部软件始终保持着专有的原因了,因为她是一个公司的 核心竞争力。然而今天,越来越多的公司意识到另一面:开源内部软件将会比保持专有获益更多。
|
||||
|
||||
这也就是为什么你的公司需要为开源项目做出更多的贡献。记住是更多。
|
||||
|
||||
我们刚刚经历了一个很不一样的20年,那时很多软件的开发都是为了内部的使用,大多数人的精力都放在由SAP和微软这样的厂商建立的应用广泛的企业级解决方案。
|
||||
|
||||
不管怎么说,这都是一个理论。
|
||||
|
||||
在实践中,买方花费很少的钱购买license,然后至少付出5倍以上的代价来使软件符合他们的需求。比如说,一个公司可能在一个ERP系统上花费 100,000美元,但是他们还得继续花费500,000来维持软件正常运行。
|
||||
|
||||
开源软件甚至是应用程序正式发展起来的原因之一是很多公司可以免费获得一些功能性的产品(或者是以一个相对便宜的费用获得产品), 然后定制为他们所需要的。不管怎样,定制是有必要的,而且开源的根本是使成本更低,或许,这样的定制或许能产生更好的结果。
|
||||
|
||||
同时,开发者尽量的减少同类之间的相似之处。作为Redmonk分析师,[Stephen O'Grady认为][3]:
|
||||
|
||||
> 从最近几年看,主流技术产业都有意避开专业化。运行在定制操作系统上的虚拟设备,已经彻底败给了RHEL和Windowns这些通用的操作系统。 最快20年,任何程序的数据保存都意味着一件事:一个关联的数据库,如果你要做的是企业级应用开发,那么你首先要接触的是Java,等等。
|
||||
|
||||
然而,开源的道路上,一些公司也发现,有些销售商不能很好地描述他们所想要的,即便是很好理解的产品类别,如像内容管理系统,他们需要 知道的是产品亮点,而不希望是一个模子刻出来的。
|
||||
|
||||
所以顾客没了,他们中有一部分上转变变成了供应商。
|
||||
|
||||
这也是常有的事,[O'Grady指出了][4]这一点。2010年,O'Grady发现了一个有趣的现象:“软件提供商正面对着一个强有力的市场竞争者:他们 的顾客。”
|
||||
|
||||
回想一下今天的高科技,大多数都是开源的,几乎所有的项目一开始都是某些公司的内部项目,或者仅仅是有些开发者的爱好,Linux,Git,Hadoop,Cassandra,MongDB,Android,等等。没有一个项目起初是为了售卖而产生的。
|
||||
|
||||
相反,这些项目通常是由一些公司维护,他们使用开源的资源来构建软件并[完善软件][5],这主要是一些Web公司。不像以前银行,医院和一些组织开发的软件只供内部使用,他们开源源码。
|
||||
|
||||
虽然,[有些公司避免定制软件][6],因为他们不想自己维护它,开源(稍微)减轻了这些发展中公司来维护一个项目的压力。从而为项目发起人均摊项目的开发成本,Yahoo,开始于Hadoop,但是现在最大的贡献者是Cloudera和Hortonworks。Facebook开始于Cassandra,但是现在主要是靠DataStax在维护。等等。
|
||||
|
||||
今天,真正的软件创新并不是闭门造车能造出来的,即便是可以,它也不会在那儿,开源项目颠覆了几十年的软件开发传统。
|
||||
|
||||
这不仅仅是一个人的一点点力量。
|
||||
|
||||
最好的开源项目都[发展得很快][7],但是这并不意味着别人在乎你的开源代码。[开放你的源码有显著的优缺点][8],其中一个很重要的优点是 很多伟大的开发者都希望为开源做出贡献:如果你也想找一个伟大的开发者跟你一起,你需要给他们一个开放的源代码来让他们工作。([Netflix][9]说)
|
||||
|
||||
但是,我们没有理由站在一边看,现在正是时候参与开源社区了,而不是一些不清楚的社区。是的,开源最大的参与者正是你们和你们的公司。 赶紧开始吧。
|
||||
|
||||
主要图片来自于Shutterstock. (注:Shutterstock是美国的一家摄影图片网站。)
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://readwrite.com/2014/08/16/open-source-software-business-zulily-erp-wall-street-journal
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Matt Asay][a]
|
||||
译者:[barney-ro](https://github.com/barney-ro)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://readwrite.com/author/matt-asay
|
||||
[1]:http://blogs.wsj.com/cio/2014/08/08/zulily-calls-in-house-software-a-differentiator-for-competitive-advantage/
|
||||
[2]:http://oreilly.com/catalog/cathbazpaper/chapter/ch05.html
|
||||
[3]:http://redmonk.com/sogrady/2010/01/12/roll-your-own/#ixzz3ATBuZsef
|
||||
[4]:http://redmonk.com/sogrady/2010/01/12/roll-your-own/
|
||||
[5]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/The_Cathedral_and_the_Bazaar
|
||||
[6]:http://www.abajournal.com/magazine/article/roll_your_own_software_hidden_dangers_on_the_road_less_traveled/
|
||||
[7]:http://readwrite.com/2013/12/12/open-source-innovation
|
||||
[8]:http://readwrite.com/2014/07/07/open-source-software-pros-cons
|
||||
[9]:http://techblog.netflix.com/2012/07/open-source-at-netflix-by-ruslan.html
|
||||
@ -1,67 +0,0 @@
|
||||
中国将要改变软件购买和销售的方式
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
> 这一切都是关于“开源”.
|
||||
|
||||
**中国并不需要开源,也不需要你的软件。具体说来,中国市场并不需要你的工程师日以继夜的工作,也不需要你提供的任何东西。
|
||||
|
||||
中国每年会产生超过100000名新软件工程师们,这些工程师会写出一大批令人惊叹的奇妙软件。如果有中国市场上尚未出现的软件,中国的工程师们就会从国外“借鉴”。在2012年,这样的软件掠夺达到了77%之多。对于那些已经面对着开源和云服务的挑战的软件卖家来说,中国无疑让他们的日子更苦难了。
|
||||
|
||||
不止是更困难,简直是举步维艰。
|
||||
|
||||
中国正在挑战西方公司在中国或者其他地方赚钱的模式。对于那些已经明白如何在中国运营的公司来说,他们的未来看起来一片光明。
|
||||
|
||||
### 抵制中国模式 ###
|
||||
|
||||
当然,并非每家公司都会坐以待毙。以微软为例,微软通用美国的国家司法权力来禁止中国公司做生意——除非他们像微软购买许可证。这是一种很聪明的做法,而且它可能会为微软创造数以十亿计的价值。但是最终这一做法看起来与中国市场格格不入。
|
||||
|
||||
原因很简单,中国与微软对待知识产权的态度十分不同。
|
||||
|
||||
正如 [我所提到的][2],“中国的企业更倾向于购买复杂的,面向企业的软件。因为这种软件比服务大众的公司设计出来的软件更先进,就像同在亚洲的印度。”但这种形势不会持续太久,因为中国的软件产业正在以一种惊人的速度前进,并毫无颓势。中国一定会坚持向西方国家“借鉴”代码直到有一天有足够的能力可以创造出有创新能力的软件。
|
||||
|
||||
但是即使这样,中国的软件公司与美国软件的运营模式还是有所不同,美国的软件大多都已经捆绑在设备、架构在云端或者公司只因为提供软件支持而要价。而这些运营模式中国是无法克隆的。
|
||||
|
||||
不出所料的,每一个收费模式是公司门使用“开源”进行盈利。
|
||||
|
||||
### 开源化中国 ###
|
||||
|
||||
正如CCID的分析师在 [J. Aaron Farr 的关于中国开源化报告][3] 中指出的,中国的开源社区规模很小而且没什么影响力。开源社区们没有大项目、参与者稀少而且资金匮乏。
|
||||
|
||||
这真是个坏消息。
|
||||
|
||||
好消息是,像华为这样的公司就把开源作为一种战略前景。具体而言,当华为的开源项目过时或者不是很强势的时候,这种现象就证明了他们的科技步伐是错误的。在与参与了开源项目的华为公司内部顾问的谈话中,虽然华为对如何参与到开源社区还处于摸索阶段,但他们总是对华为的开源项目赞不绝口。
|
||||
|
||||
这种无人关注开源的现象不会长久地持续下去。
|
||||
|
||||
从一件事就可以看出端倪。中国最大的互联网公司们都纷纷以积极地姿态拥抱开源,这意味着中国开源时代的到来。你若是和任意一位在百度、阿里巴巴、微博的员工谈话,你会发现他们的软件项目都是彻底开源的。这些开源的软件都是运行在这些公司自己研发的硬件上而不是西方的硬件上。
|
||||
|
||||
换句话说,这样的模式已经和西方的运营模式如出一辙了。
|
||||
|
||||
抬头看看 [现金软件行业内最炙手可热的新公司][5], 你就会知道中国的互联网公司未来的主流趋势,正如发生在西方世界的一样。不出意料的,许多都是关于“开源”。
|
||||
|
||||
### 销售给中国 ###
|
||||
|
||||
所有的一切都表明中国的软件行业不会像美国的软件行业发展历史一般发展。中国不会产生在柜台上卖卖软件就赚上亿美元的公司。因为西方对于知识产权的观念就是不适于中国的科技经济。
|
||||
|
||||
所以,软件卖家们需要售卖币软件更丰富的产品。云服务是一大前景。硬件设施看起来也是前途璀璨。软件支持和咨询服务(虽然有一些非主流)也很被公司门看好。总而言之,中国的软件行业会充满了开源味道,而不能靠着简单的售卖专柜软件的形式赚钱。
|
||||
|
||||
图片由 [hackNY.org][6] 提供。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
原文: http://readwrite.com/2014/08/12/china-opensource-software-ip-programmers-united-states
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Matt Asay][a]
|
||||
译者:[chi1shi2](https://github.com/chi1shi2)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://readwrite.com/author/matt-asay
|
||||
[1]:http://readwrite.com/2014/03/17/microsoft-anti-piracy-strategy-china
|
||||
[2]:http://readwrite.com/2014/04/11/india-starts-paying-for-software-china-it
|
||||
[3]:http://cdn.oreillystatic.com/en/assets/1/event/12/Open%20Source%20in%20China%20Presentation%201.pdf
|
||||
[4]:http://huawei.com/en/about-huawei/Partner/openathuawei/index.htm
|
||||
[5]:http://codingvc.com/which-technologies-do-startups-use-an-exploration-of-angellist-data
|
||||
[6]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/hackny/8675057448/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
|
||||
Linus Torvalds推动Linux的桌面与嵌入式计算的发展
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> Linux的内核开发者和开源领袖Linus Torvalds最近表达了关于Linux桌面和嵌入式设备中Linux的未来的看法。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
什么是Linux桌面和嵌入式设备中Linux的未来?这是个值得讨论的问题,不过Linux的创始人和开源巨人Linus Torvalds在最近一届 [Linux 基金会][1] 的LinuxCon大会上,在一次对话中表达了一些有趣的观点。
|
||||
|
||||
作为敲出第一版Linux内核代码并且在1991年将它们共享在互联网上的家伙,Torvalds毫无疑问是开源软件甚至是任何软件中最著名的开发者,如今他依然活跃在其中。在此期间,Torvalds是许多人和组织中唯一一个引领着Linux发展的个体,它的观点往往能影响着开源社区,而且,作为一个内核开发者的角色赋予了他能决定哪些特点和代码能被放进操作系统内部的强大权利。
|
||||
|
||||
所以说,关注Torvalds所说的话是很值得的, "我还是挺想要桌面的。" [上周他在LinuxCon大会上这样说道][2] 那标志着他仍然着眼于作为使个人机更加强大的操作系统Linux的未来,尽管十年来Linux桌面市场的分享一直很少,而且大部分围绕Linux的商业活动都去涉及服务器或者安卓手机硬件去了。
|
||||
|
||||
但是,Torvalds还说,确保Linux桌面能有个宏伟的未来意味着解决了受阻的 “基础设施问题”,好像庞大的开源软件生态系统和硬件世界让他充满信心。这不是Linux核心代码本身的问题,而是要让Linux桌面渠道友好,这可能是伟大的Torvalds和他开发同伴们所需要花精力去达到的目标。这取决于app的开发者、硬件制造商和其它有志于实现人们能方便使用基于Linux的计算平台的各方力量。
|
||||
|
||||
另一方面,Torvalds也提到了他的憧憬,就是内核开发者们能简化嵌入式装置中的Linux代码——一个在让内核更加桌面友好化上会导致很多分歧的任务。但这也不一定,因为无论如何,Linux都是以模块化设计的,单内核代码库不能同时满足桌面用户和嵌入式开发者的需求,这是没有道理的,因为这取决于他们使用的模块。
|
||||
|
||||
作为一个长时间想看到更多搭载Linux的嵌入式设备出现的Linux桌面用户,我希望Torvalds的所有愿望都可以实现,到那时我就能只用Liunx来做所有我想做的事情,无论是在电脑桌面上、手机上、车上,或者是任何其它的地方。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://thevarguy.com/open-source-application-software-companies/082514/linus-torvalds-promotes-linux-desktops-and-embedded-compu
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Christopher Tozzi][a]
|
||||
译者:[ZTinoZ](https://github.com/ZTinoZ)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://thevarguy.com/author/christopher-tozzi
|
||||
[1]:http://linuxfoundation.org/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.eweek.com/enterprise-apps/linux-founder-linus-torvalds-still-wants-the-desktop.html
|
||||
85
translated/talk/20140828 Interesting facts about Linux.md
Normal file
85
translated/talk/20140828 Interesting facts about Linux.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,85 @@
|
||||
Linux趣事
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
今天,8月25号,是Linux的第23个生日。1991年,8月25日,21岁的赫尔辛基大学的学生发布了举世闻名的[新闻组][1](Usenet post),标志着现在世界著名的Linux正式诞生。
|
||||
|
||||
23年以后的今天,linux已经无处不在,不仅仅被安装于桌面系统,[智能手机][2]和嵌入式系统,甚至也被[龙头企业][3]用于他们的关键系统,比如说像[美国海军的核潜艇][4](US Navy's nuclear submarines)和[联邦航空局的空中管制系统][5](FAA's air traffic control)。进入无处不在的云计算时代,linux在云计算平台方面仍然保持着它的优势。
|
||||
|
||||
今天,我们一起庆祝linux 23岁生日,就让我们告诉你**一些你可能不知道的linux趣事和linux历史**。如果有什么要补充的,请在评论中分享出来。在这篇文章里,我可能用会用“linux”,“kernel”和“Linux kernel”来表示同一个意思。
|
||||
|
||||
1.关于linux是否是一个开源的操作系统这种争论一直是无休无止的。事实上,“Linux”操作系统的核心组件参照的是Linux kernel(内核)。而反派认为Linux不是一个纯粹的操作系统,因为他们认为仅仅一个内核(kernel),并不是一个操作系统,自由软件的推崇者认为最大的操作系统应叫做“[GNU/Linux][7]”把功劳归于应得的人。(比如:[GNU project][8])。另一方面,一些linux的开发者认为,linux拥有成为一个操作系统的资格,因为它实现了[POSIX标准][9]。
|
||||
|
||||
2.从openhub网站的统计来看,绝大部分(95%)的Linux是用C语言写的。第二(2.8%)受欢迎的是汇编语言。毫无疑问,C语言比C++ 的更受欢迎,也表明了linus对C++的立场。下面是Linus编程语言的分类。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
3.在世界上,Linux已经被[13,036个贡献者][10]创建和修改。当然,贡献最多的还是Linus Torvalds自己。直到目前,他提交了20,000次以上的代码。下图显示了所有提交次数最多的前十位Linux贡献者。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
4.Linux的代码行(SLOC)有超过1700万行。估计整个代码库的花费大概是5,526人年,或者是超过300M(1M=10*1000万亿)美元,[基于模型的基本估算法][11](basic COCOMO model)。
|
||||
|
||||
5.企业并不是单纯的Linux消费者。他们的员工也在[积极参与][12]Linux的开发。下图显示了前十的Linux内核开发参与的企业员工2013年提交次数的总和。他们包括linux的商业版发行者(Red Hat,SUSE),芯片/嵌入式系统制造商(Intel,Texas Instrument,wolfson),非盈利性组织(Linaro)和其他的IT公司(IBM,Samsung,Google)。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
6.Linux的官方吉祥物是“小企鹅”,一个非常可爱的企鹅标志。[第一次提出][13]并决定小企鹅作为Linux吉祥物/标志这个想法的是Linus自己。为什么是小企鹅呢?因为Linus本人很喜欢企鹅,尽管他曾经被一只凶猛的企鹅咬伤过,还导致他得了一场病。
|
||||
|
||||
7.一个Linux系统“包括”Linux内核、支持GUN的组件和库、和一些第三方的应用。[distrowatch网站][14]显示,现在总共有286个活跃的Linux发行版。其中最老的一个版本叫[Slackware][15],它是从1993年正式发布出来的一个可用的版本。
|
||||
|
||||
8.Kernel.org是一个Linux源码的主要仓库,曾经在2011年8月被一个匿名的攻击者[攻陷][16],攻击者打算篡改kernel.org的服务器。为了加强linux内核的访问策略的安全性,Linux基金会最近在Linux内核的Git官方托管的仓库上[开启了][17]双重认证。
|
||||
|
||||
9.Linux在500强超级计算机中的优势还在[增加][18]。截至2014年6月,运算速度最快的计算机97%都是运行在Linux上面的。
|
||||
|
||||
10.太空监视(spacewatch),是亚利桑那大学月球与行星实验室的一个研究项目,在GNU/Linux和它的创造者们出现之后,用他们名字命名了几颗小行星([小行星9793 Torvalds][19],[小行星9882 Stallman][20],[小行星9885 Linux][21],[小行星9965 GUN][22]),以表彰他们把开源操作系统用于他们的小行星调查活动。
|
||||
|
||||
11.纵观Linux内核发展得近代史,版本从2.6到3.0有一个很大的跳跃。这个[重编的版本号3][23]实际上并不是意味着Linux内核有什么重大的构建,但却标志着Linux 20周年的一个里程碑。
|
||||
|
||||
12.在2000年的时候,乔帮主还在苹果。他当时就[尝试雇佣][24]Linus Torvalds,让他放弃Linux的开发,转而为“Unix最大的用户群工作”,这个项目后面发展成了MAC OS X。当时,linus拒绝了乔帮主的邀请。
|
||||
|
||||
13.Linux 内核的重启函数[reboot()][25]要求两个神奇的数字,而这第二个数字来自Linus Torvalds和他的3个女儿的出生日期。
|
||||
|
||||
14.虽然全世界都有Linux的很多粉丝,但是也仍然存在很多对Linux的批评(主要是桌面系统),如缺乏硬件支持,缺乏标准化,由于很短的升级和发布周期导致系统的不稳定,等。2014年Linux内核小组在linuxCon大会上,当Linus被问及Linux的未来将何去何从,他表示“I still want the desktop”(我仍然希望桌面化)。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你还知道些关于Linux的趣事,请写在评论里。
|
||||
|
||||
生日快乐,Linux!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/08/interesting-facts-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
|
||||
译者:[barney-ro](https://github.com/barney-ro)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/nanni
|
||||
[1]:https://groups.google.com/forum/message/raw?msg=comp.os.minix/dlNtH7RRrGA/SwRavCzVE7gJ
|
||||
[2]:http://developer.android.com/about/index.html
|
||||
[3]:http://fortune.com/2013/05/06/how-linux-conquered-the-fortune-500/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.linuxjournal.com/article/7789
|
||||
[5]:http://fcw.com/Articles/2006/05/01/FAA-manages-air-traffic-with-Linux.aspx
|
||||
[6]:http://thecloudmarket.com/stats
|
||||
[7]:http://www.gnu.org/gnu/why-gnu-linux.html
|
||||
[8]:http://www.gnu.org/gnu/gnu-history.html
|
||||
[9]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/POSIX
|
||||
[10]:https://www.openhub.net/p/linux/contributors/summary
|
||||
[11]:https://www.openhub.net/p/linux/estimated_cost
|
||||
[12]:http://www.linuxfoundation.org/publications/linux-foundation/who-writes-linux-2013
|
||||
[13]:http://www.sjbaker.org/wiki/index.php?title=The_History_of_Tux_the_Linux_Penguin
|
||||
[14]:http://distrowatch.com/search.php?ostype=All&category=All&origin=All&basedon=All¬basedon=None&desktop=All&architecture=All&status=Active
|
||||
[15]:http://www.slackware.com/info/
|
||||
[16]:http://pastebin.com/BKcmMd47
|
||||
[17]:http://www.linux.com/news/featured-blogs/203-konstantin-ryabitsev/784544-linux-kernel-git-repositories-add-2-factor-authentication
|
||||
[18]:http://www.top500.org/statistics/details/osfam/1
|
||||
[19]:http://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/sbdb.cgi?sstr=9793
|
||||
[20]:http://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/sbdb.cgi?sstr=9882
|
||||
[21]:http://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/sbdb.cgi?sstr=9885
|
||||
[22]:http://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/sbdb.cgi?sstr=9965
|
||||
[23]:https://lkml.org/lkml/2011/5/29/204
|
||||
[24]:http://www.wired.com/2012/03/mr-linux/2/
|
||||
[25]:http://lxr.free-electrons.com/source/kernel/reboot.c#L199
|
||||
[26]:http://www.nndb.com/people/444/000022378/
|
||||
[27]:http://linuxfonts.narod.ru/why.linux.is.not.ready.for.the.desktop.current.html
|
||||
[28]:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8myENKt8bD0
|
||||
377
translated/talk/20140904 The Masked Avengers.md
Normal file
377
translated/talk/20140904 The Masked Avengers.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,377 @@
|
||||
<h1>戴着面具的复仇者 —— 揭秘:激进黑客组织“匿名者”</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
<blockquote><em>从“<a href="https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E8%8C%89%E8%8E%89%E8%8A%B1%E9%9D%A9%E5%91%BD">突尼斯政变</a>”到“<a href="https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E9%82%81%E5%85%8B%E7%88%BE%C2%B7%E5%B8%83%E6%9C%97%E6%A7%8D%E6%93%8A%E6%A1%88">弗格森枪击事件</a>”,“匿名者”组织是如何煽动起网络示威活动的。</em></blockquote>
|
||||
|
||||
<center><img src="https://www.newyorker.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/09/140908_r25419-690.jpg" /></center>
|
||||
|
||||
<blockquote><em>通过入会声明,任何人都能轻易加入“匿名者”组织。某人类学家称,组织成员会“根据影响程度对重大事件保持着不同关注,特别是那些能挑起强烈争端的事件”。</em></blockquote>
|
||||
|
||||
<small>布景:Jeff Nishinaka / 摄影:Scott Dunbar</small>
|
||||
|
||||
<h2>1</h2>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>上世纪七十年代中期,当 Christopher Doyon 还是一个生活在缅因州乡村的孩童时,就终日泡在 CB radio 上与各种陌生人聊天。他的昵称是“大红”,因为他有一头红色的头发。Christopher Doyon 把发射机挂在了卧室的墙壁上,并且说服了父亲在自家屋顶安装了两根天线。CB radio 主要用于卡车司机间的联络,但 Doyon 和一些人却将之用于不久后出现在 Internet 上的虚拟社交——自定义昵称、成员间才懂的笑话,以及施行变革的强烈愿望。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>Doyon 很小的时候母亲就去世了,兄妹二人由父亲抚养长大,他俩都说受到过父亲的虐待。由此 Doyon 在 CB radio 社区中找到了慰藉和归属感。他和他的朋友们轮流监听当地紧急事件频道。其中一个朋友的父亲买了一个气泡灯并安装在了他的车顶上;每当这个孩子收听到来自孤立无援的乘车人的求助后,都会开车载着所有人到求助者所在的公路旁。除了拨打 911 外他们基本没有什么可做的,但这足以让他们感觉自己成为了英雄。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>短小精悍的 Doyon 有着一口浓厚的新英格兰口音,并且非常喜欢《星际迷航》和阿西莫夫的小说。当他在《大众机械》上看到一则“组装你的专属个人计算机”构件广告时,就央求祖父给他买一套,接下来 Doyon 花了数月的时间把计算机组装起来并连接到 Internet 上去。与鲜为人知的 CB 电波相比,在线聊天室确实不可同日而语。“我只需要点一下按钮,再选中某个家伙的名字,然后我就可以和他聊天了,” Doyon 在最近回忆时说道,“这真的很惊人。”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>十四岁那年,Doyon 离家出走,两年后他搬到了马萨诸塞州的剑桥,那里是一个新出现的计算机反主流文化的中心。同一时间,早在 34 年前就已由麻省理工学院的铁路狂热爱好者们创立的铁路模型技术俱乐部,已经演变成了“黑客”——也是推广该词的第一个组织。Richard Stallman,在那时还是一名任职于麻省理工学院人工智能实验室的计算机科学家,指出早期黑客们比起引发技术战争更乐于讨论“哥德尔、艾舍尔、巴赫”之类的话题。“我们没有任何约束”,Stallman 说,“这不是一项运动,而是一种可以让人们相互留下深刻印象的行为。”其中有些“行为”很有趣(制作电子游戏);有些非常实用(提高计算机处理速度);还有些则属于发生在真实世界里的恶作剧(在校园内放置模拟街道标识)。Michael Patton,在七十年代里管理着铁路模型技术俱乐部的人,谈起初代黑客间不成文的规定,说第一条就是“不要搞破坏”。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>在剑桥,Doyon 以打零工和乞讨为生,他宁愿为了自由而睡在公园的长椅上,也不愿被单调的固定工作所束缚。1985 年,他和其他六个活跃分子共同组建了一支电子“义勇军”。模仿“动物解放阵线”,他们称呼自己为“人民解放阵线”(Peoples Liberation Front,PLF)。所有人都使用化名:如组织的创建者,声称自己是老兵的一位高大中年男子,自称“Commander Adama”;Doyon 则选择了“Commander X”这个称呼。受 “Merry Pranksters” 启示,他们在 Grateful Dead 的演唱会上出售 LSD(lysergic acid diethylamide,麦角酸酰二乙胺,一种迷幻药),并用收入的一部分购置了一辆二手校车,以及扩音器、相机,还有电源充电器。同时在剑桥租了一间地下公寓,Doyon 偶尔会在那里歇息。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>Doyon 深深地沉溺于计算机中,虽然他并不是一位专业的程序员。在过去一年的几次谈话中,他告诉我他将自己视为激进主义分子,继承了 Abbie Hoffman 和 Eldridge Cleaver 的激进传统;技术不过是他抗议的工具。八十年代,哈佛大学和麻省理工学院的学生们举行集会,强烈抗议他们的学校从南非撤资。为了帮助抗议者通过安全渠道进行交流,PLF 制作了无线电套装:移动调频发射器、伸缩式天线,还有麦克风,所有部件都内置于背包内。Willard Johnson,麻省理工学院的一位激进分子和政治学家,表示黑客们出席集会并不意味着一次变革。“我们的大部分工作仍然是通过扩音器来完成的,”他解释道。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>1992 年,在 Grateful Dead 的一场印第安纳的演唱会上,Doyon 秘密地向一位瘾君子出售了 300 粒药。由此他被判决在印第安纳州立监狱服役十二年,后来改为五年。服役期间,他对宗教和哲学产生了浓厚的兴趣,并于鲍尔州立大学学习了相应课程。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>1994 年,第一款商业 Web 浏览器网景领航员正式发布,同一年 Doyon 被捕入狱。当他出狱并再次回到剑桥后,PLF 依然活跃着,并且他们的工具有了实质性的飞跃。Doyon 回忆起和他入狱之前的变化,“非常巨大——好比是‘烽火狼烟’跟‘电报传信’之间那么大的差距。”黑客们入侵了一个印度的军事网站,并修改其首页文字为“拯救克什米尔”。在塞尔维亚,黑客们攻陷了一个阿尔巴尼亚网站。Stefan Wray,一位早期网络激进主义分子,为一次纽约“反哥伦布日”集会上的黑客行径辩护。“我们视之为电子形式的公众抗议,”他告诉大家。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>1999 年,美国唱片业协会因为版权侵犯问题起诉了 Napster,一款文件共享软件。最终,Napster 于 2001 年关闭。Doyon 与其他黑客使用分布式拒绝服务(Distributed Denial of Service,DDoS,使大量数据涌入网站导致其响应速度减缓直至奔溃)的手段,攻击了美国唱片业协会的网站,使之停运时间长达一星期之久。Doyon为自己的行为进行了辩解,并高度赞扬了其他的“黑客主义者”。“我们很快意识到保卫 Napster 的战争象征着保卫 Internet 自由的战争,”他在后来写道。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>2008 年的一天,Doyon 和 “Commander Adama” 在剑桥的 PLE 地下公寓相遇。Adama 当着 Doyon 的面点击了癫痫基金会的一个链接,与意料中将要打开的论坛不同,出现的是一连串闪烁的彩光。有些癫痫病患者对闪光灯非常敏感——这完全是出于恶意,有人想要在无辜群众中诱发癫痫病。已经出现了至少一名受害者。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>Doyon 愤怒了。他质问 Adama 什么样的人才会做出这样的事来。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>“你听说过‘匿名者’组织吗?” Adama 问。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<h2>2</h2>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>2003 年,一位来自纽约的已经患病 15 年的失眠症患者 Christopher Poole,推出了 4chan 讨论社区,在这里用户们可以随意发布照片或者尖锐评论。随后其关注点迅速从动漫延伸到许多 Internet 的早期文化基因,如:LOLcats、Chocolate Rain、RickRolls。当用户没有按照屏幕上的要求输入昵称时,将会得到系统默认的“匿名者”(Anonymous)称呼。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<center><img src="http://www.newyorker.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/09/140908_a18505-600.jpg" /></center>
|
||||
|
||||
<center><small>“我得谈谈我的感受。”</small></center>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>Poole 希望匿名这一举措可以延续社区的尖锐性因素。“我们无意参与理智的涉外事件讨论,”他在网站上写道。4chan 社区里最具价值的事之一便是寻求“挑起强烈的争端”(lulz),这个词源自缩写 LOL。Lulz 经常是通过分享充满孩子气的笑话或图片来实现的,它们中的大部分不是色情的就是下流的。其中最令人震惊的部分被贴在了网站的“/b/”版块上,这里的用户们称呼自己为“/b/tards”。Doyon 知道 4chan 这个社区,但他认为那些用户是“一群愚昧无知的顽童”。2004 年前后,/b/ 上的部分用户开始把“匿名者”视为一个独立的实体。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>这是一个全新的黑客团体。“这不是一个传统意义上的组织,”一位领导计算机安全工作的研究员 Mikko Hypponen 告诉我——倒不如,视之为一个非传统的亚文化群体。Barrett Brown,德克萨斯州的一名记者,同时也是众所周知的“匿名者”高层领导,把“匿名者”描述为“一连串前仆后继的伟大友谊”。无需任何会费或者入会仪式。任何想要加入“匿名者”组织,成为一名匿名者(Anon)的人,都可以通过简短的象征性的宣誓加入。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>尽管 4chan 的关注焦点是一些琐碎的话题,但许多匿名者认为自己就是“正义的十字军”。如果网上有不良迹象出现,他们就会发起具有针对性的治安维护行动。不止一次,他们以未成年少女的身份套取恋童癖的私人信息,然后把这些信息交给警察局。其他匿名者则是政治的厌恶者,为了挑起争端想方设法散布混乱的信息。他们中的一些人在 /b/ 上发布看着像是雷管炸弹的图片;另一些则叫嚣着要炸毁足球场并因此被联邦调查局逮捕。2007 年,一家洛杉矶当地的新闻联盟机构称呼“匿名者”组织为“互联网负能量制造机”。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>2008 年 1 月,Gawker Media 上传了一段关于汤姆克鲁斯大力吹捧山达基优点的视频。这段视频是受版权保护的,山达基教会致信 Gawker,勒令其删除这段视频。“匿名者”组织认为教会企图控制网络信息。“是时候让 /b/ 来干票大的了,”有人在 4chan 上写道。“我说的是‘入侵’或者‘攻陷’山达基官方网站。”一位匿名者使用 YouTube 放出一段“新闻稿”,其中包括暴雨云视频和经过计算机处理的语音。“我们要立刻把你们从 Internet 上赶出去,并且在现有规模上逐渐瓦解山达基教会,”那个声音说,“你们无处可躲。”不到一个星期,这段 YouTube 视频的点击率就超过了两百万次。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>“匿名者”组织已经不仅限于 4chan 社区。黑客们在专用的互联网中继聊天(Internet Relay Chat channels,IRC 聊天室)频道内进行交流,协商策略。通过 DDoS 攻击手段,他们使山达基的主网站间歇性崩溃了好几天。匿名者们制造了“谷歌炸弹”,由此导致 “dangerous cult” 的搜索结果中的第一条结果就是山达基主网站。其余的匿名者向山达基的欧洲总部寄送了数以百计的披萨,并用大量全黑的传真单耗干了洛杉矶教会总部的传真机墨盒。山达基教会,据报道拥有超过十亿美元资产的组织,当然能经得起墨盒耗尽的考验。但山达基教会的高层可不这么认为,他们还收到了严厉的恐吓,由此他们不得不向 FBI 申请逮捕“匿名者”组织的成员。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>2008 年 3 月 15 日,在从伦敦到悉尼的一百多个城市里,数以千计匿名者们游行示威山达基教会。为了切合“匿名”这个主题,组织者下令所有的抗议者都应该佩戴相同的面具。深思熟虑过蝙蝠侠后,他们选定了 2005 年上映的反乌托邦电影《 V 字仇杀队》中 Guy Fawkes 的面具。“在每个大城市里都能以很便宜的价格大量购买,”广为人知的匿名者、游行组织者之一 Gregg Housh 告诉我说道。漫画式的面具上是一个的脸颊红润的男人,八字胡,有着灿烂的笑容。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>匿名者们并未“瓦解”山达基教会。并且汤姆克鲁斯的那段视频任然保留在网络上。匿名者们证明了自己的顽强。组织选择了一个相当浮夸的口号:“我们是一体。绝不宽恕。永不遗忘。相信我们。”(We are Legion. We do not forgive. We do not forget. Expect us.)</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<h2>3</h2>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>2010 年,Doyon 搬到了加利福尼亚州的圣克鲁斯,并加入了当地的“和平阵营”组织。利用从木材堆置场偷来的木头,他在山上盖起了一间简陋的小屋,“借用”附近住宅的 WiFi,使用太阳能电池板发电,并通过贩卖种植的大麻换取现金。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>与此同时,“和平阵营”维权者们每天晚上开始在公共场所休息,以此抗议圣克鲁斯政府此前颁布的“流浪者管理法案”,他们认为这项法案严重侵犯了流浪者的生存权。Doyon 出席了“和平阵营”的会议,并在网上发起了抗议活动。他留着蓬乱的红色山羊胡,戴一顶米黄色软呢帽,像军人那样不知疲倦。因此维权者们送给了他“罪恶制裁克里斯”的称呼。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>“和平阵营”的成员之一 Kelley Landaker 曾几次和 Doyong 讨论入侵事宜。Doyon 有时会吹嘘自己的技术是多么的厉害,但作为一名资深程序员的 Landaker 却不为所动。“他说得很棒,但却不是行动派的,”Landaker 告诉我。不过在那种场合下,的确更需要一位富有激情的领导者,而不是埋头苦干的技术员。“他非常热情并且坦率,”另一位成员 Robert Norse 如是对我说。“他创造出了大量的能够吸引媒体眼球的话题。我从事这行已经二十年了,在这一点上他比我见过的任何人都要厉害。”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>Doyon 在 PLF 的上司,Commander Adama 仍然住在剑桥,并且通过电子邮件和 Doyon 保持着联络,他下令让 Doyon 潜入“匿名者”组织。以此获知其运作方式,并伺机为 PLF 招募新成员。因为癫痫基金会网站入侵事件的那段不愉快回忆,Doyon 拒绝了 Adama。Adama 给 Doyon 解释说,在“匿名者”组织里不怀好意的黑客只占极少数,与此相反,这个组织经常会有一些的轰动世界举动。Doyon 对这点表示怀疑。“4chan 怎么可能会轰动世界?”他质问道。但出于对 PLF 的忠诚,他还是答应了 Adama 的请求。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>Doyon 经常带着一台宏基笔记本电脑出入于圣克鲁斯的一家名为 Coffee Roasting Company 的咖啡厅。“匿名者”组织的 IRC 聊天室主频道无需密码就能进入。Doyon 使用 PLF 的昵称进行登录并加入了聊天室。一段时间后,他发现了组织内大量的专用匿名者行动聊天频道,这些频道的规模更小,并相互重复。要想参与行动,你必须知道行动的专用聊天频道名称,并且聊天频道随时会因为陌生的闯入者而进行变更。这套交流系统并不具备较高的安全系数,但它的确很凑效。“这些专用行动聊天频道确保了行动机密的高度集中,”麦吉尔大学的人类学家 Gabriella Coleman 告诉我。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>有些匿名者提议了一项行动,名为“反击行动”。如同新闻记者 Parmy Olson 于 2012 年在书中写道的,“我们是匿名者,”这项行动成为了又一次支援文件共享网站,如 Napster 的后继者海盗湾(Pirate Bay),的行动的前奏,但随后其目标却扩展到了政治领域。2010 年末,在美国国务院的要求下,包括万事达、Visa、PayPal 在内的几家公司终止了对维基解密,一家公布了成百上千份外交文件的民间组织,的捐助。在一段网络视频中,“匿名者”组织扬言要进行报复,发誓会对那些阻碍维基解密发展的公司进行惩罚。Doyon 被这种抗议企业的精神所吸引,决定参加这次行动。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<center><img src="http://www.newyorker.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/09/140908_a18473-600.jpg" /></center>
|
||||
|
||||
<center><small>潘多拉的魔盒</small></center>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>在十二月初的“反击行动”中,“匿名者”组织指导那些新成员,或者说新兵,关于“如何他【哔~】加入组织”,教程中提到“首先配置你【哔~】的网络,这他【哔~】的很重要。”同时他们被要求下载“低轨道离子炮”,一款易于使用的开源软件。Doyon 下载了软件并在聊天室内等待着下一步指示。当开始的指令发出后,数千名匿名者将同时发动进攻。Doyon 收到了含有目标网址的指令——目标是,www.visa.com——同时,在软件的右上角有个按钮,上面写着“IMMA CHARGIN MAH LAZER.”(“反击行动”同时也发动了大量的复杂精密的入侵进攻。)几天后,“反击行动”攻陷了万事达、Visa、PayPal 公司的主页。在法院的控告单上,PayPal 称这次攻击给公司造成了 550 万美元的损失。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>但对 Doyon 来说,这是切实的激进主义体现。在剑桥反对种族隔离的行动中,他不能立即看到结果;而现在,只需指尖轻轻一点,就可以在攻陷大公司网站的行动中做出自己的贡献。隔天,赫芬顿邮报上出现了“万事达沦陷”的醒目标题。一位得意洋洋的匿名者发推特道:“有些事情维基解密是无能为力的。但这些事情却可以由‘反击行动’来完成。”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<h2>4</h2>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>2010 年的秋天,“和平阵营”的抗议活动终止,政府只做出了轻微的让步,“流浪者管理法案”仍然有效。Doyon 希望通过借助“匿名者”组织的方略扭转局势。他回忆当时自己的想法,“也许我可以发动‘匿名者’组织来教训这种看似不堪一击的市政府网站,这些人绝对会【哔~】地赞同我的提议。最终我们将使得市政府永久性的废除‘流浪者管理法案’。”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>Joshua Covelli 是一位 25 岁的匿名者,他的昵称是“Absolem”,他非常钦佩 Doyon 的果敢。“现在我们的组织完全是他【哔~】各种混乱的一盘散沙,”Covelli 告诉我道。在“Commander X”加入之后,“组织似乎开始变得有模有样了。”Covelli 的工作是俄亥俄州费尔伯恩的一所大学接待员,他从不了解任何有关圣克鲁斯的政治。但是当 Doyon 提及帮助“和平阵营”抗击活动的计划后,Covelli 立即回复了一封表示赞同的电子邮件:“我期待这样的行动很久了。”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>Doyon 使用 PLF 的昵称邀请 Covelli 在 IRC 聊天室进行了一次秘密谈话:</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<blockquote>Absolem:抱歉,有个比较冒犯的问题...请问 PLF 也是组织的一员吗?</blockquote>
|
||||
|
||||
<blockquote>Absolem:我会这么问,是因为我在频道里看过你的聊天记录,你像是一名训练有素的黑客,不太像是来自组织里的成员。</blockquote>
|
||||
|
||||
<blockquote>PLF:不不不,你的问题一点也不冒犯。很高兴遇到你。PLF 是一个来自波士顿的黑客组织,已经成立 22 年了。我在 1981 年就开始了我的黑客生涯,但那时我并没有使用计算机,而是使用的 PBX(Private Branch Exchange,电话交换机)。</blockquote>
|
||||
|
||||
<blockquote>PLF:我们组织内所有成员的年龄都超过了 40 岁。我们当中有退伍士兵和学者。并且我们的成员“Commander Adama”,正在躲避一大帮警察还有间谍的追捕。</blockquote>
|
||||
|
||||
<blockquote>Absolem:听起来很棒!我对这次行动很感兴趣,不知道我是否可以提供一些帮助,我们的组织实在是太混乱了。我的电脑技术还不错,但我在入侵技术上还完全是一个新手。我有一些小工具,但不知道怎么去使用它们。</blockquote>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>庄重的入会仪式后,Doyon 正式接纳 Covelli 加入 PLF:</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<blockquote>PLF:把所有可能对你不利的【哔~】敏感文件加密。</blockquote>
|
||||
|
||||
<blockquote>PLF:还有,想要联系任何一位 PLF 成员的话,给我发消息就行。从现在起,请叫我... Commander X。</blockquote>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>2012 年,美联社称“匿名者”组织为“一伙训练有素的黑客”;Quinn Norton 在《连线》杂志上发文称“‘匿名者’组织可以入侵任何坚不可摧的网站”,并在文末赞扬他们为“一群卓越的民间黑客”。事实上,有些匿名者的确是很有天赋的程序员,但绝大部分成员根本不懂任何技术。人类学家 Coleman 告诉我只有大约五分之一的匿名者是真正的黑客——其他匿名者则是“极客与抗议者”。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>2010 年 12 月 16 日,Doyon 以 Commander X 的身份向几名记者发送了电子邮件。“明天当地时间 12:00 的时候,‘人民解放阵线’组织与‘匿名者’组织将大举进攻圣克鲁斯政府网站”,他在邮件中写道,“12:30 之后我们将恢复网站的正常运行。”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>圣克鲁斯数据中心的工作人员收到了警告,匆忙地准备应对攻击。他们在服务器上运行起安全扫描软件,并向当地的互联网供应商 AT & T 求助,后者建议他们向 FBI 报警。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>第二天,Doyon 走进了一家星巴克并启动了笔记本电脑。即便是在这样一个小镇上,Doyon 也显得格外醒目:一个疲惫的流浪汉疯狂地敲击着键盘。随后,Covelli 和他在一间秘密聊天室碰头。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<blockquote>PLF:去社区,登录——检查一下右上角的“聊天”菜单栏,上面有今天的具体方案。感谢你对我们的支持。</blockquote>
|
||||
|
||||
<blockquote>Absolem:一切为了 PLF,长官。</blockquote>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>他们都打开了 DDoS 软件。尽管只有少数人参加了这次“和平阵营”的行动,但 Doyon 好似统率千军万马般下令:</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<blockquote>PLF:注意:每一位支持 PLF 或者站在我们这边的朋友——还有那些对抗邪恶保卫正义的勇士们:‘和平阵营’行动进行中,战斗的号角已经响起!目标:www.co.santa-cruz.ca.us。随意开火。重复指令:开火!</blockquote>
|
||||
|
||||
<blockquote>Absolem:收到,长官。</blockquote>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>数据中心的工作人员紧张地盯着服务器,上面反馈出一连串拒绝服务的请求。尽管他们尽了最大的努力,网站还是崩溃了。25 分钟后,Doyon 决定遵守承诺。他下令“停止攻击”,政府网站开始恢复了正常运行。(这次攻击后,“流浪者管理法案”依旧没有废除。)</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>Doyon 没有时间去庆祝胜利,他显得焦躁不安。“我得走了,”他告诉 Covelli。他飞一般得逃回了山中小屋。Doyon 的感觉是正确的:一位 FBI 的探员早就在 IRC 上盯住了他。这位 FBI 的探员已经获许搜查 Doyon 的笔记本电脑。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>几周后,Doyon 的食物吃完了,他不得不下山进行采购。当 Doyon在 Coffee Roasting Company 咖啡厅逗留的时候,两位联邦探员走了进来将他拘捕。Doyon 给“和平阵营”的创建者,同时也是一名律师的 Ed Frey 打了一个电话,Ed Frey 来到了警察局。Doyon 告诉了 Frey 他的另一个身份“Commander X”的事。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>随后 Doyon 被释放,但 FBI 没收了他的笔记本电脑,里面满是犯罪证据。Frey 一个几乎不了解网络世界的维权律师,把 Doyon 载回了他的山边露营。“接着你要怎么办?”Frey 问道。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<center><img src="http://www.newyorker.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/09/140908_a18447-600.jpg" /></center>
|
||||
|
||||
<center><small>“Zach 很聪明... 并且... 是一个天才... 但.. 你们... 不在一个班。”</small></center>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>Doyon 引用了一句电影台词。“拼命地跑,”他说。“我会躲起来,尽可能保持我的行动自由,用尽全力和这帮杂种们作斗争。”Frey 给了他两张 20 美元的钞票并祝他好运。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<h2>5</h2>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>Doyon 搭着便车来到了旧金山,并在这里呆了三个月。他经常混迹于 Haight 大街 Ashbury 区的一家杂乱的咖啡馆里,在计算机前一坐就是几个小时,只有在抽烟时他才会起身走到室外活动。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>2011 年 1 月,Doyon 联系了新闻记者兼匿名者的 Barrett Brown。“我们的下一步计划是什么?”Doyon 问道。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>“突尼斯,” Brown 答道。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>“我知道,那是中东地区的一个国家,” Doyon 继续问,“然后呢?”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>“我们准备打倒那里的独裁者,” Brown 再次答道。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>“啊?!那里有一位独裁者吗?” Doyon 有点惊讶。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>几天后,“突尼斯行动”正式展开。Doyon 作为参与者向突尼斯政府域名下的电子邮箱发送了大量的垃圾邮件,以此阻塞其服务器。“我会提前写好关于那次行动邮件,接着一次又一次地把它们发送出去,” Doyon 说,“有时候实在没有时间,我就只简短的写上一句问候对方母亲的的话,然后发送出去。”短短一天时间里,匿名者们就攻陷了包括突尼斯证券交易所、工业部、总统办公室、总理办公室在内的多个网站。他们把总统办公室网站的首页替换成了一艘海盗船的图片,并配以文字“‘报复’是个贱人,不是吗?”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>Doyon 不时会谈起他的网上“战斗”经历,似乎他刚从弹坑里爬出来一样。“伙计,自从干了这行我就变黑了,”他向我诉苦道。“你看我的脸,全是抽烟的时候熏的——而且可能已经粘在我的脸上了。我仔细地照过镜子,毫不夸张地说我简直就是一头棕熊。”很多个夜晚,Doyon 都是在 Golden Gate 公园里露营过夜的。“我就那样干了四天,我看了看镜子里的‘我’,感觉还可以——但其实我觉得‘我’也许应该去吃点东西、洗个澡了。”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>“匿名者”组织接着又在 YouTube 上声明了将要进行的一系列行动:“利比亚行动”、“巴林行动”、“摩洛哥行动”。作为解放广场事件的抗议者,Doyon 参与了“埃及行动”。在 Facebook 针对这次行动的宣传专页中,有一个为当地示威者准备的“行动套装”链接。“行动套装”通过文件共享网站 Megaupload 进行分发,其中含有一份加密软件以及应对瓦斯袭击的保护措施。并且在不久后,埃及政府关闭了埃及的所有互联网及子网络的时候,继续向当地抗议者们提供连接网络的方法。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>2011 年夏季,Doyon 接替 Adama 成为 PLF 的最高指挥官。Doyon 招募了六个新成员,并力图发展 PLF 成为“匿名者”组织的中坚力量。Covelli 成为了他的其中一技位术顾问。另一名黑客 Crypt0nymous 负责在 YouTube 上发布视频;其余的人负责研究以及组装电子设备。与松散的“匿名者”组织不同,PLF 内部有一套极其严格的管理体系。“Commander X 事必躬亲,”Covelli 说。“这是他的行事风格,也许不能称之为一种风格。”一位创立了 AnonInsiders 博客的黑客通过加密聊天告诉我,他认为 Doyon 总是一意孤行——这在“匿名者”组织中是很罕见的现象。“当我们策划发起一项行动时,他并不在乎其他人是否同意,”这位黑客补充道,“他会一个人列出行动方案,确定攻击目标,登录 IRC 聊天室,接着告诉所有人在哪里‘碰头’,然后发起 DDoS 攻击。”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>一些匿名者把 PLF 视为可有可无的部分,认为 Doyon 的所作所为完全是个天大的笑柄。“他是因为吹牛出名的,”另一名昵称为 Tflow 的匿名者 Mustafa Al-Bassam 告诉我。不过,即使是那些极度反感 Doyon 的狂妄自大的人,也不得不承认他在“匿名者”组织发展过程中的重要性。“他所倡导的强硬路线有时很凑效,有时则完全不起作用,” Gregg Housh 说,并且补充道自己和其他优秀的匿名者都曾遇到过相同的问题。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>“匿名者”组织对外坚持声称自己是不分层次的平等组织。在由 Brian Knappenberger 制作的一部纪录片,《我们是一个团体》中,一名成员使用“一群鸟”来比喻组织,它们轮流领飞带动整个组织不断前行。Gabriella Coleman 告诉我,这个比喻不太切合实际,“匿名者”组织内实际上早就出现了一个非正式的领导阶层。“领导者非常重要,”她说。“有四五个人可以看做是我们的领头羊。”她把 Doyon 也算在了其中。但是匿名者们仍然倾向于反抗这种具有体系的组织结构。在一本即将出版的关于“匿名者”组织的书,《黑客、骗子、告密者、间谍》中,Coleman 这么写道,在匿名者中,“成员个体以及那些特立独行的人依然在一些重大事件上保持着服从的态度,优先考虑集体——特别是那些能引发强烈争端的事件。”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>匿名者们谑称那些特立独行的成员为“自尊心超强的疯子”和“想让自己出名的疯子”。(不过许多匿名者已经不会再随便给他人取那种具有冒犯性的称号了。)“但还是有令人惊讶的极少数成员违反规则”打破传统上的看法,Coleman 说。“这么做的人,像 Commander X 这样的,都会在组织里受到排斥。”去年,在一家网络论坛上,有人写道,“当他开始把自己比作‘蝙蝠侠’的时候我就不想理他了。”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>Peter Fein,是一位以 n0pants 为昵称而出名的网络激进分子,也是众多反对 Doyon 的浮夸行为的众多匿名者之一。Fein 浏览了 PLF 的网站,其封面上有一个徽章,还有关于组织的宣言——“为了解放众多人类的灵魂而不断战斗”。Fein 沮丧的发现 Doyon 早就使用真名为这家网站注册过了,使他这种,以及其他想要找事的匿名者们无机可乘。“如果有人要对我的网站进行 DDoS 攻击,那完全可以,” Fein 回想起通过私密聊天告诉 Doyon 时的情景,“但如果你要这么做了的话,我会揍扁你的屁股。”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>2011 年 2 月 5 日,《金融时报》报道了在一家名为 HBGary Federal 的网络安全公司里,首席执行官 HBGary Federal 已经得到了“匿名者”组织骨干成员名单的消息。Barr 的调查结果表明,三位最高领导人其中之一就是‘ Commander X’,这位潜伏在加利福尼亚州的黑客有能力“策划一些大型网络攻击事件”。Barr 联系了 FBI 并提交了自己的调查结果。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>和 Fein 一样,Barr 也发现了 PLF 网站的注册法人名为 Christopher Doyon,地址是 Haight 大街。基于 Facebook 和 IRC 聊天室的调查,Barr 断定‘ Commander X’的真实身份是一名家庭住址在 Haight 大街附近的网络激进分子 Benjamin Spock de Vries。Barr 通过 Facebook 和 de Vries 取得了联系。“请告诉组织里的普通阶层,我并不是来抓你们的,” Barr 留言道,“只是想让‘领导阶层’知晓我的意图。”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>“‘领导阶层’? 2333,笑死我了,” de Vries 回复道。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>《金融时报》发布报道的第二天,“匿名者”组织就进行了反击。HBGary Federal 的网站被进行了恶意篡改。Barr 的私人 Twitter 账户被盗取,他的上千封电子邮件被泄漏到了网上,同时匿名者们还公布了他的住址以及其他私人信息——这是一系列被称作“doxing”的惩罚。不到一个月后,Barr 就从 HBGary Federal 辞职了。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<h2>6</h2>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>2011 年 4 月,Doyon 离开了旧金山搭便车向西部前行,过着夜晚露宿公园、白天混迹于星巴克的生活。他的背包里只有一台笔记本电脑、Guy Fawkes 面具,还有在 Pall 超市里购买的一些东西。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<center><img src="http://www.newyorker.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/09/140908_a18563-600.jpg" /></center>
|
||||
|
||||
<center><small>“这是我在 TED 夏令营里学到的东西。”</small></center>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>他时刻关注着“匿名者”组织的内部消息。那年春季,在 Barr 调查报告中提到的六位匿名者精锐成员,组建了“LulzSec 安全”组织(Lulz Security),简称 LulzSec。这个组织正如其名,这些成员认为“匿名者”组织已经变得太过严肃;他们的目标是重新引发起那些“能挑起强烈争端”的事件。当“匿名者”组织还在继续支持“阿拉伯之春”的抗议者的时候,LulzSec 入侵了公共电视网(Public Broadcasting Service,PBS)网站,并发布了一则虚假声明称已故说唱歌手 Tupac Shakur 仍然生活在新西兰。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>匿名者之间会通过 Pastebin.com 网站来共享文字。在这个网站上,LulzSec 发表了一则声明,称“很不幸,我们注意到北约和我们的好总统巴拉克,奥萨马·本·美洲驼(拉登同学)的好朋友,来自 24 世纪的奥巴马,最近明显提高了对我们这些黑客的关注程度。他们把黑客入侵行为视作一种战争的表现。”目标越高远,挑起的纷争就越大。6 月 15 日,LulzSec 表示对 CIA 网站受到的袭击行为负责,他们发表了一条推特,上面写道“目标击毙(Tango down,亦即target down)—— cia.gov ——这是起挑衅行为。”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>2011 年 6 月 20 日,LulzSec 的一名十九岁的成员 Ryan Cleary 因为对 CIA 的网站进行了 DDoS 攻击而被捕。7 月,FBI 探员逮捕了七个月前对 PayPal 进行 DDoS 攻击的其他十四名黑客。这十四名黑客,每人都面临着 15 年的牢狱之灾以及 500 万美元的罚款。他们因为图谋不轨以及故意破坏互联网,而被控违反了计算机欺诈与滥用处理条例。(该法案允许检察官进行酌情处置,并在去年网络激进分子 Aaron Swartz 因为被判处 35 年牢狱之灾而自杀身亡之后,受到了广泛的质疑和批评。)</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>LulzSec 的成员之一 Jake (Topiary) Davis 因为付不起法律诉讼费,给组织的成员们写了一封请求帮助的信件。Doyon 进入了 IRC 聊天室把 Davis 需要帮助的消息进行了扩散:</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<blockquote>CommanderX:那么请大家阅读信件并给予 Topiary 帮助...</blockquote>
|
||||
|
||||
<blockquote>Toad:你真是和【哔~】一样消息灵通。</blockquote>
|
||||
|
||||
<blockquote>Toad:这么说你得到 Topiary 的消息了?</blockquote>
|
||||
|
||||
<blockquote>CommanderX:Toad 你这个混蛋!</blockquote>
|
||||
|
||||
<blockquote>Katanon:唉...</blockquote>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>Doyon 越来越大胆。他在佛罗里达州当局逮捕了支持流浪者的激进分子后,就 DDoS 了奥兰多商务部商会网站。他使用个人笔记本电脑通过公用无线网络实施了攻击,并且没有花费太多精力来隐藏自己的网络行踪。“这种做法很勇敢,但也很愚蠢,”一位自称 Kalli 的 PLF 的资深成员告诉我。“他看起来并不在乎是否会被抓。他完全是一名自杀式黑客。”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>两个月后,Doyon 参与了针对旧金山湾区快速交通系统(Bay Area Rapid Transit)的 DDoS 攻击,以此抗议一名 BART 的警官杀害一名叫做 Charles Hill 的流浪者的事件。随后 Doyon 现身“CBS 晚间新闻”为这次行动辩护,当然,他处理了自己的声音,把自己的脸用香蕉进行替代。他把 DDoS 攻击比作为公民的抗议行为。“与占用 Woolworth 午餐柜台的座位相比,这真的没什么不同,真的,”他说道。CBS 的主播 Bob Schieffer 笑称:“就我所见,它并不完全是一项民权运动。”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>2011 年 9 月 22 日,在加利福尼亚州的一家名为 Mountain View 的咖啡店里,Doyon 被捕,同时面临着“使用互联网非法破坏受保护的计算机”罪名指控。他被拘留了一个星期的时间,接着在签署协议之后获得假释。两天后,他不顾律师的反对,宣布将在圣克鲁斯郡法院召开新闻发布会。他梳起了马尾辫,戴着一副墨镜、一顶黑色海盗帽,同时还在脖子上围了一条五彩手帕。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>Doyon 通过非常夸大的方式披露了自己的身份。“我就是 Commander X,”他告诉蜂拥的记者。他举起了拳头。“作为‘匿名者’组织的一员,作为一名核心成员,我感到非常的骄傲。”他在接受一名记者的采访时说,“想要成为一名顶尖黑客的话,你只需要准备一台电脑以及一副墨镜。任何一台电脑都行。”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>Kalli 非常担心 Doyon 会不小心泄露组织机密或者其他匿名者的信息。“这是所有环节中最薄弱的地方,如果这里出问题了,那么组织就完了,”他告诉我。曾在“和平阵营行动”中给予 Doyon 大力帮助的匿名者 Josh Covelli 告诉我,当他在网上看见 Doyon 的新闻发布会视频的时候,他感觉瞬间“下巴掉地下了”。“他的所作所为变得越来越不可捉摸,” Covelli 评价道。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>三个月后,Doyon 的指定律师 Jay Leiderman 出席了圣荷西联邦法庭的辩护。Leiderman 已经好几个星期没有得到 Doyon 的消息了。“我需要得知被告无法出席的具体原因,”法官说。Leiderman 无法回答。Doyon 再次缺席了两星期后的另一场听证会。检控方表示:“很明显,看来被告已经逃跑了。”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<h2>7</h2>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>“Xport 行动”是“匿名者”组织进行的所有同类行动中的第一个行动。这次行动的目标是协助如今已经背负两项罪名的通缉犯 Doyon 潜逃出国。负责调度的人是 Kalli 以及另一位曾在八十年代剑桥的迷幻药派对上和 Doyon 见过面的匿名者老兵。这位老兵是一位已经退休的软件主管,在组织内部威望很高。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>Doyon 的终点站是这位软件主管的家,位于加拿大的偏远乡村。2011 年 12 月,他搭便车前往旧金山,并辗转来到了市区组织大本营。他找到了他的指定联系人,后者带领他到达了奥克兰的一家披萨店。凌晨 2 点,Doyon 通过披萨店的无线网络,接收了一条加密聊天消息。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>“你现在靠近窗户吗?”那条消息问道。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>“是的,” Doyon 回复道。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>“往大街对面看。看见一个绿色的邮箱了吗?十五分钟后,你去站到那个邮箱旁边,把你的背包取下来,然后把你的面具放在上面。”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>一连几个星期的时间,Doyon 穿梭于海湾地区的安全屋之间,按照加密聊天那头的指示不断行动。最后,他搭上了前往西雅图的长途公交车,软件主管的一个朋友在那里接待了他。这个朋友是一名非常富有的退休人员,他花费了通过谷歌地球来帮助 Doyon 规划前往加拿大的路线。他们共同前往了一家野外用品供应商店,这位朋友为 Doyon 购置了价值 1500 美元的商品,包括登山鞋以及一个全新的背包。接着他又开车载着 Doyon 北上,两小时后到达距离国界只有几百英里的偏僻地区。随后 Doyon 见到了 Amber Lyon。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>几个月前,广播新闻记者 Lyon 曾在 CNN 的关于“匿名者”组织的节目里采访过 Doyon。Doyon 很欣赏她的报道,他们一直保持着联络。Lyon 要求加入 Doyon 的逃亡行程,为一部可能会发行的纪录片拍摄素材。软件主管认为这样太过冒险,但 Doyon 还是接受了她的请求。“我觉得他是想让自己出名,” Lyon 告诉我。四天的时间里,她用影像记录下了 Doyon 徒步北上,在林间露宿的行程。“那一切看起来不太像是仔细规划过的,” Lyon 回忆说。“他实在是无家可归了,所以他才会想要逃到国外去。”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<center><img src="http://www.newyorker.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/09/140908_a18506-600.jpg" /></center>
|
||||
|
||||
<center><small>“这里是我们存放各种感觉的仓库。如果你发现了某种感觉,把它带到这里然后锁起来。”</small></center>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>2012 年 2 月 11 日,Pastebin 上出现了一条消息。“PLF 很高兴的宣布‘ Commander X’,也就是 Christopher Mark Doyon,已经离开了美国的司法管辖区,抵达了加拿大一个比较安全的地方,”上面写着,“PLF 呼吁美国政府,希望政府能够醒悟过来并停止无谓的骚扰与监视行为——不要仅仅逮捕‘匿名者’组织的成员,对所有的激进组织应该一视同仁。”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<h2>8</h2>
|
||||
|
||||
Doyon 和软件主管在加拿大的小木屋里呆了几天。在一次同 Barrett Brown 的聊天中,Doyon 难掩内心的喜悦之情。
|
||||
|
||||
<blockquote>BarrettBrown:你现在应该足够安全了吧,其他的呢?...</blockquote>
|
||||
|
||||
<blockquote>CommanderX:是的,我现在很安全,现在加拿大既不缺钱也不缺藏身的地方。</blockquote>
|
||||
|
||||
<blockquote>CommanderX:Amber Lyon 想要你的一张照片。</blockquote>
|
||||
|
||||
<blockquote>CommanderX:去他【哔~】的怪人,Barrett,相信你会喜欢我告诉她应该怎样评价你的。</blockquote>
|
||||
|
||||
<blockquote>CommanderX::-)</blockquote>
|
||||
|
||||
<blockquote>CommanderX:我告诉她你是一个英雄。</blockquote>
|
||||
|
||||
<blockquote>BarrettBrown:你才是真正的英雄...</blockquote>
|
||||
|
||||
<blockquote>BarrettBrown:很高兴你现在安全了</blockquote>
|
||||
|
||||
<blockquote>BarrettBrown:如果你还需要什么,告诉我一声就可以了</blockquote>
|
||||
|
||||
<blockquote>CommanderX:我会的,如果这种方式的确很凑效的话,可以让其他被通缉的人也这样逃出来....</blockquote>
|
||||
|
||||
<blockquote>BarrettBrown:当然,估计我们不久后也得这样了</blockquote>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>在 Doyon 出逃十天后,《华尔街日报》上刊登了关于不久后升职为美国国家安全局及网络指挥部主任的 Keith Alexander 的报道,他在白宫举行的秘密会晤以及其他场合下,表达了对“匿名者”组织的高度关注。Alexander 发出警告,两年内,该组织必将会是国家电网改造的大患。参谋长联席会议的主席 General Martin Dempsey 告诉记者,这群人是国家的敌人。“他们有能力把这些使用恶意软件造成破坏的技术扩散到其他的边缘组织去,”随后又补充道,“我们必须防范这种情况发生。”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>3 月 8 日,国会议员们在国会大厦附近的一个敏感信息隔离设施附近举行了关于网络安全的会议。包括 Alexander、Dempsey、美国联邦调查局局长 Robert Mueller,以及美国国土安全部部长 Janet Napolitano 在内的多名美国安全方面的高级官员出席了这次会议。会议上,通过计算机向与会者模拟了东部沿海地区电力设施可能会遭受到的网络攻击时的情境。“匿名者”组织目前应该还不具备发动此种规模攻击的能力,但安全方面的官员担心他们会联合其他更加危险的组织来共同发动攻击。“在我们着手于不断增加的网络风险事故时,政府仍在就具体的处理细节进行不断协商讨论,” Napolitano 告诉我。当谈及潜在的网络安全隐患时,她补充道,“我们通常会把‘匿名者’组织的行动当做 A 级威胁来应对。”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>“匿名者”也许是当今世界上最强大的无政府主义黑客组织。即使如此,它却从未表现出过任何的会对公共基础设施造成破坏的迹象或意愿。一些网络安全专家称,那些关于“匿名者”组织的谣传太过危言耸听。“在奥兰多发布战前宣言和实际发动 Stuxnet 蠕虫病毒攻击之间是有很大的差距的,” Internet 研究与战略中心的一位职员 James Andrew Lewis 告诉我,这和 2007 年美国与以色列对伊朗原子能网站发动的黑客袭击有关。哈佛大学法学院的教授 Yochai Benkler 告诉我,“我们所看见的只是以主要防御为理由而进行的开销,否则,将很难自圆其说。”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>Keith Alexander 最近刚从政府部门退休,他拒绝就此事发表评论,因为他并不能代表国家安全局、联邦调查局、中央情报局以及国土安全部。尽管匿名者们从未真正盯上过政府部门的计算机网络,但他们对于那些激怒他们的人有着强烈的报复心理。前国土安全部国家网络安全部门负责人 Andy Purdy 告诉我他们“害怕被报复,”无论机构还是个人,都不同意政府公然反对“匿名者”组织。“每个人都非常脆弱,”他说。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<h2>9</h2>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>2012 年 3 月 6 日,Hector Xavier Monsegur,昵称为 Sabu 的 LulzSec 骨干成员,被发现是 FBI 派来的卧底。为了换取减刑,Monsegur 花费了数月的时间卧底,协助搜集其他 LulzSec 成员的罪证。同一天,五位匿名者领导被捕,同时面临着包括“计算机某犯罪”在内的多项罪名指控。联邦调查局的一名官员在接受福克斯新闻记者采访时说道,“这对那个组织是一个毁灭性的打击。我们的行动如同砍掉了 LulzSec 组织的头。”接下来的十个月里, Barrett Brown 收到了 17 项联邦罪名的指控,其中的大部分后来被撤销了。(他将在十月被宣判最终结果。)</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>Doyon 感到很烦躁,但他还是继续扮演着一名黑客——以此吸引关注。他在多伦多上映的纪录片上以戴着面具的匿名者形象出现。在接受《National Post》的采访时,他向记者大肆吹嘘未经证实的消息,“我们已经入侵了美国政府的所有机密数据库。现在的问题是我们该何时泄露这些机密数据,而不是我们是否会泄露。”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>2013 年 1 月,在另一名匿名者介入俄亥俄州<a href="https://gist.githubusercontent.com/SteveArcher/cdffc917a507f875b956/raw/c7b49cc11ae1e790d30c87f7b8de95482c18ec74/%E6%96%AF%E6%89%98%E6%9C%AC%E7%BB%B4%E5%B0%94%E8%BD%AE%E5%A5%B8%E6%A1%88%E5%86%8D%E8%B5%B7%E9%A3%8E%E6%B3%A2%20%E9%BB%91%E5%AE%A2%E7%BB%84%E7%BB%87%E4%BB%8B%E5%85%A5">斯托本维尔未成年少女轮奸案</a>,发起抗议行动之后,Doyon 重新启用了他两年前创办的网站 LocalLeaks,作为那起轮奸事件的信息汇总处理中心。如同许多其他“匿名者”组织的所作所为一样,LocalLeaks 网站非常具有影响力,但却也不承担任何责任。LocalLeaks 网站是第一家公布 12 分钟斯托本维尔高中毕业生猥亵视频的网站,这激起了众多当事人的愤怒。LocalLeaks 网站上同时披露了几份未被法庭收录的关于案件的材料,并且由此不小心透漏出了案件受害人的名字。Doyon向我承认他公开这些未经证实的信息的策略是存在争议的,但他同时回忆起自己当时的想法,“我们可以选择去除这些斯托本维尔案件的材料...也可以选择公开所有我们搜集的信息,基本上,给公众以提醒,不过,前提是你们得相信我们。”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>2013 年 3 月,一个名为 Rustle League 的组织入侵了 Doyon 的 Twitter 账户,该组织此前经常挑衅“匿名者”组织。Rustle League 的领导者之一 Shm00p 告诉我,“我们的本意并不是伤害那些家伙,只不过,哦,那些家伙说的话你就当是在放屁好了——我会这么做只是因为我感到很好笑。” Rustle League 组织使用 Doyon 的账户发布了含有如 www.jewsdid911.org 链接这样的,种族主义和反犹太主义的信息。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>2013 年 8 月 27 日,Doyon 发布了一则退出“匿名者”组织的声明。“我的一生都用在了追求正义和自由上,”他写道,“也许‘ Commander X’是无敌的,但我在这种高节奏的全球网络斗争中已经感到很累了,感觉自己好像病了。”各界对此反应不一,有同情的(“你是该休息了”),也有嘲讽的(“可怜的疯狂小老头。也许他现在有时间洗澡了”)。 Covelli 告诉我,“‘匿名者’的身份对他产生了较大的影响,他已经不能再应付了。”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<cneter><img src="http://www.newyorker.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/09/140908_roberts-1998-08-17-600.jpg" /></center>
|
||||
|
||||
<center><small>1998 年 8 月 17 日 “我们还有‘巴黎’吗?仔细想想,我等会儿去检查一下。”</small></center>
|
||||
|
||||
<h2>10</h2>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>2013 年 11 月 5 日举行了第一次“百万面具游行”活动。在全世界四百五十个城市里,发起了数千人的支持“匿名者”组织的游行。伦敦的一名抗议者摘下了盖伊·福克斯面具后,露出了演员罗素·布兰德的脸。这种的迹象表明,“匿名者”组织已经深入到了流行文化中。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>我参加了华盛顿的集会,Doyon 则呆在了加拿大观看现场直播。通过移动电话,我和 Doyon 不断交换着电子邮件。“只能坐在这里看直播而不能亲自去现场真的很令人沮丧——尤其是当这里面包含有你努力的结果的时候,”他在邮件里写道。“不过至少一切都已有所改变。”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>我们约定了一次面谈。Doyon 坚持让我通过加密聊天把面谈的详细情况提前告诉他。我坐了几个小时的飞机,租车来到了加拿大的一个偏远小镇,并且禁用了我的电话。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>最后,我在一个狭小安静的住宅区公寓里见到了 Doyon。他穿了一件绿色的军人夹克衫以及印有“匿名者”组织 logo 的 T 恤衫:一个脸被问号所替代的黑衣人形象。公寓里基本上没有什么家具,充满了一股烟味。他谈论起了美国政治(“我基本没怎么在众多的选举中投票——它们不过是暗箱操作的游戏罢了”),好战的伊斯兰教(“我相信,尼日利亚政府的人不过是相互勾结,以创建一个名为‘博科圣地’的基地组织的下属机构罢了”),以及他对“匿名者”组织的小小看法(“那些自称为怪人的人是真的是烂透了,意思是,邪恶的人”)。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>Doyon 剃去了他的胡须,但他却显得更加憔悴了。他说那是因为他病了的原因,他几乎很少出去。很小的写字台上有两台笔记本电脑、一摞关于佛教的书,还有一个堆满烟灰的烟灰缸。另一面裸露的泛黄墙壁上挂着盖伊·福克斯面具。他告诉我,“所谓‘Commander X’不过是一个处于极度痛苦中的小老头罢了。”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>在刚过去的圣诞节里,匿名者的新网站 AnonInsiders 的创建者拜访了 Doyon,并给他带来了馅饼和香烟。Doyon 询问来访的朋友是否可以继承自己的衣钵成为 PLF 的最高指挥官,同时希望能够递交出自己手里的“王国钥匙”——手里的所有密码,以及几份关于“匿名者”组织的机密文件。这位朋友委婉的拒绝了。“我有自己的生活,”他告诉了我拒绝的理由。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<h2>11</h2>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>2014 年 8 月 9 日,当地时间下午 5 时 09 分,来自密苏里州圣路易斯郊区德尔伍德的一位说唱歌手同时也是激进分子的 Kareem (Tef Poe) Jackson,在 Twitter 上谈起了邻近城镇的一系列令人担忧的举措。“基本可以断定弗格森已经实施了戒严,任何人都无法出入,”他在 Twitter 上写道。“国内的朋友还有因特网上的朋友请帮助我们!!!”五个小时前,弗格森,一位十八岁的手无寸铁的非裔美国人 Michael Brown,被一位白人警察射杀。射杀警察声称自己这么做的原因是 Brown 意图伸手抢夺自己的枪支。而事发当时和 Brown 在一起的朋友 Dorian Johnson 却说,Brown 唯一做得不对的地方在于他当时拒绝离开街道中间。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>不到两小时,Jackson 就收到了一位名为 CommanderXanon 的 Twitter 用户的回复。“你完全可以相信我们,”回复信息里写道。“你是否可以给我们详细描述一下现场情况,那样会对我们很有帮助。”近几周的时间里,仍然呆在加拿大的 Doyon 复出了。六月,他在还有两个月满 50 岁的时候,成功戒烟(“#戒瘾成功 #电子香烟功不可没 #老了,”他在戒烟成功后在 Twitter 上写道)。七月,在加沙地带爆发武装对抗之后,Doyon 发表 Twiter 支持“匿名者”组织的“拯救加沙行动”,并发动了一系列针对以色列网站的 DDoS 攻击。Doyon 认为弗格森枪击事件更加令人关注。抛开他本人的个性,他有在事件发展到引人注目之前的早期,就迅速注意该事件的能力。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>“正在网上搜索关于那名警察以及当地政府的信息,” Doyon 发 Twitter 道。不到十分钟,他就为此专门在 IRC 聊天室里创建了一个频道。“‘匿名者’组织‘弗格森’行动正式启动,”他又发了一条 Twitter。但只有两个人转推了此消息。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>次日早晨,Doyon 发布了一条链接,链接指向的是一个初具雏形的网站,网站首页有一条致弗格森市民的信息——“你们并不孤单,我们将尽一切努力支持你们”——以及致当地警察的警告:“如果你们对对弗格森的抗议者们滥用职权、骚扰,或者伤害了他们,我们绝对会让你们所有政府部门的网站瘫痪。这不是威胁,这是承诺。”同时 Doyon 呼吁有 130 万粉丝的“匿名者”组织的 Twitter 账号 YourAnonNews 给与支持。“请支持‘弗格森’行动”,他发送了消息。一分钟后,YourAnonNews 回复表示同意。当天,包含话题 #OpFerguson 的 Twitter 发表/转推了超过六千次。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>这个事件迅速成为头条新闻,同时匿名者们在弗格森周围进行了大集会。与“阿拉伯之春行动”类似,“匿名者”组织向抗议者们发送了电子关怀包,包括抗暴指导(“把瓦斯弹捡起来回丢给警察”)与可打印的盖伊·福克斯面具。Jackson 和其他示威者在弗格森进行示威游行时,警察企图通过橡皮子弹和催泪瓦斯来驱散他们。“当时的情景真像是布鲁斯·威利斯的电影里的情节,” Jackson 后来告诉我。“不过巴拉克·奥巴马应该并不会支持‘匿名者’组织传授给我们的这些知识,”他笑称道。“让那些警察赶到束手无策真的是太爽了。”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>有个域名是 www.opferguson.com 的网站,后来发现不过是一个骗局——一个用来收集访问者 ip 地址的陷阱,随后这些地址会被移交给执法机构。有些人怀疑 Commander X 是政府的线人。在 IRC 聊天室 #OpFerguson 频道,一个名叫 Sherlock 写道,“现在频道里每个人说的已经让我害怕去点击任何陌生的链接了。除非是一个我非常熟悉的网址,否则我绝对不会去点击。”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>弗格森的抗议者要求当局公布射杀 Brown 的警察的名字。几天后,匿名者们附和了抗议者们的请求。有人在 Twitter 上写道,“弗格森警察局最好公布肇事警察的名字,否则‘匿名者’组织将会替他们公布。”8 月 12 的新闻发布会上,圣路易斯警察局的局长 Jon Belmar 拒绝了这个请求。“我们不会这样做,除非他们被某个罪名所指控,”他说道。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>作为报复,一名黑客使用名为 TheAnonMessage 的 Twitter 账户公布了一条链接,该链接指向一段来自警察的无线电设备所记录的音频文件,文件记录时间是 Brown 被枪杀的两小时左右。TheAnonMessage 同时也把矛头指向了 Belmar,在 Twitter 上公布了这位警察局长的家庭住址、电话号码以及他的家庭照片——一张是他的儿子在长椅上睡觉,另一张则是 Belmar 和他的妻子的合影。“不错的照片,Jon,” TheAnonMessage 在 Twitter 上写道。“你的妻子在她这个年龄算是一个美人了。你已经爱她爱得不耐烦了吗?”一个小时后,TheAnonMessage 又以 Belmar 的女儿为把柄进行了恐吓。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>Richard Stallman,来自 MIT 的初代黑客,告诉我虽然他在很多地方赞同“匿名者”组织的行为,但他认为这些泄露私人信息的攻击行为是要受到谴责的。即使是在国内,TheAnonMessage 的行为也受到了谴责。“为何要泄露无辜的人的信息到网上?”一位匿名者通过 IRC 发问,并且表示威胁 Belmar 的家人实在是“相当愚蠢的行为”。但是 TheAnonMessage 和其他的一些匿名者仍然进行着不断搜寻,并企图在将来再次进行泄露信息的攻击。在互联网上可以得到所有弗格森警察局警员的名字,匿名者们不断地搜索着信息,企图找出具体是哪一个警察找出杀害了 Brown。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<center><img src="http://www.newyorker.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/09/140908_steig-1999-04-12-600.jpg" /></center>
|
||||
|
||||
<center><small></small>1999 年 4 月 12 日 “我应该把镜头对向谁?”</center>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>8 月 14 日清晨,及位匿名者基于 Facebook 上的照片还有其他的证据,确定了射杀 Brown 的凶手是一位名叫 Bryan Willman 的 32 岁男子。根据一份 IRC 聊天记录,一位匿名者贴出了 Willman 的浮夸面孔的照片;另一位匿名者提醒道,“凶手声称自己的脸没有被任何人看到。”另一位昵称为 Anonymous|11057 的匿名者承认他对 Willman 的怀疑确实是“跳跃性的可能错误的逻辑过程推导出来的。”不过他还是写道,“我只是无法动摇自己的想法。虽然我没有任何证据,但我非常非常地确信就是他。”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>TheAnonMessage 看起来被这次对话逗乐了,写道,“#愿逝者安息,凶手是 BryanWillman。”另一位匿名者发出了强烈警告。“请务必确认,” Anonymous|2252 写道。“这不仅仅关乎到一个人的性命,我们可以不负责任地向公众公布我们的结果,但却很可能有无辜的人会因此受到不应受到的对待。”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>争论超过了一个小时。一些匿名者指出没有证据表明 Willman 曾经在弗格森警察局任过职。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<blockquote>Anonymous|3549:@gs 我们依旧没有证据能够证明 Bryan 曾在警局呆过</blockquote>
|
||||
|
||||
<blockquote>Intangir:现在的形势已经够紧张的了,一旦我们把这个消息公布出去,可能就会有人因此去杀了他</blockquote>
|
||||
|
||||
<blockquote>Anonymous|11057:唯一的证明方法是犯罪现场目击者报告。否则我们的结果只是一个谣言</blockquote>
|
||||
|
||||
<blockquote>Anonymous|11057:最快的排除嫌疑的方法是称他为嫌疑犯...我们都害怕犯下不公正的错误,但这种方法恰好可以避免这些...</blockquote>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>大部分匿名者都反对在网上泄露他人信息。但是早晨七点左右匿名者们进行了一次投票。聊天记录显示,当时聊天室里有 80 人左右,只有不到十人参与了投票表决。因此他们决定在互联网上公布 Willman 的私人信息。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<blockquote>Anonymous|2252:还在 Twitter 上公布?</blockquote>
|
||||
|
||||
<blockquote>anondepp:lol</blockquote>
|
||||
|
||||
<blockquote>Anonymous|2252:用 @theanonmessage 公布?</blockquote>
|
||||
|
||||
<blockquote>TheAnonMessage:当然</blockquote>
|
||||
|
||||
<blockquote>TheAnonMessage:去发吧</blockquote>
|
||||
|
||||
<blockquote>anondepp:搞定了</blockquote>
|
||||
|
||||
<blockquote>Anonymous|2252:我去</blockquote>
|
||||
|
||||
<blockquote>TheAnonMessage:上帝保佑...</blockquote>
|
||||
|
||||
<blockquote>Anonymous|3549:...请拯救我们的灵魂</blockquote>
|
||||
|
||||
<blockquote>anondepp:lol</blockquote>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>早晨 9 时 45 分,圣路易斯警察局对 TheAnonMessage 进行了答复。“Bryan Willman 从来没有在弗格森警察局或者圣路易斯警察局任过职,” 他们在 Twitter 上写道。“请不要再公布这位无辜市民的信息了。”(随后 FBI 对弗格森警察的电脑遭黑客入侵的事情展开了调查。)Twitter 管理员迅速封禁了 TheAnonMessage 的账户,但 Willman 的名字和家庭住址仍然被广泛传开。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>实际上,Willman 是弗格森西郊圣安区的警察外勤负责人。当圣路易斯警察局的情报处打电话告诉 Willman,他已经被“确认”为凶手时,他告诉我,“我以为不过是个奇怪的笑话。”几小时后,他的社交账号上就收到了数百条要杀死他的威胁。他在警察的保护下,独自一人在家里呆了将近一个星期。“我只希望这一切都尽快过去,”他告诉我他的感受。他认为“匿名者”组织已经不可挽回地损害了他的名誉。“我不知道他们怎么会以为自己可以被再次信任的,”他说。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>“我们并不完美,” OpFerguson 在 Twitter 上说道。“‘匿名者’组织确实犯错了,过去的几天我们制造一些混乱。为此,我们道歉。”尽管 Doyon 并不应该为这次错误的信息泄露攻击负责,但其他的匿名者却因为他发起了一次无法控制的行动,而归咎他。YourAnonNews 在 Pastebin 上发表了一则消息,上面写道,“你们也许注意到了组织不同的 Twitter 账户发表的话题 #Ferguson 和 #OpFerguson,这两个话题下的 Twitter 与信息是相互矛盾的。为什么会在这些关键话题上出现分歧,部分原因是因为 CommanderX 是一个‘想让自己出名的疯子/想让公众认识自己的疯子’——这种人喜欢,或者至少不回避媒体的宣传——并且显而易见的,组织内大部分成员并不喜欢这样。”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>在个人 Twitter 上,Doyon 否认了所有关于“弗格森行动”的职责,他写道,“我讨厌这样。我不希望这样的情况发生,我也不希望和我认为是朋友的人战斗。”沉寂了几天后,他又再度获吹响了战斗的号角。他最近在 Twitter 上写道,“你们称他们是暴民,我们却称他们是压迫下的反抗之声”以及“解放西藏”。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>Doyon 仍然处于藏匿状态。甚至连他的律师 Jay Leiderman 也不知道他在哪里。Leiderman 表示,除了在圣克鲁斯受到的指控,Doyon 很有可能因为攻击了 PayPal 和奥兰多而面临新的指控。一旦他被捕,所有的刑期加起来,他的余生就要在监狱里度过了。借鉴 Edward Snowden 的先例,他希望申请去俄罗斯避难。我们谈话时,他用一支点燃的香烟在他的公寓里比划着。“这里比他【哔~】的牢房强多了吧?我绝对不会出去,”他愤愤道。“我不会再联系我的家人了....这是相当高的代价,但我必须这么做,我会尽我的努力让所有人活得自由、明白。”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>via: http://www.newyorker.com/magazine/2014/09/08/masked-avengers</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>作者:<a href="http://www.newyorker.com/contributors/david-kushner">David Kushner</a></p>
|
||||
<p>译者:<a href="https://github.com/SteveArcher">SteveArcher</a></p>
|
||||
<p>校对:<a href="https://github.com/校对者ID">校对者ID</a></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>本文由 <a href="https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject">LCTT</a> 原创翻译,<a href="http://linux.cn/">Linux中国</a>荣誉推出</p>
|
||||
189
translated/talk/20140915 Make Downloading Files Effortless.md
Normal file
189
translated/talk/20140915 Make Downloading Files Effortless.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,189 @@
|
||||
让下载更方便
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
下载管理器是一个电脑程序,专门处理下载文件,优化带宽占用,以及让下载更有条理等任务。有些网页浏览器,例如Firefox,也集成了一个下载管理器作为功能,但是它们的方式还是没有专门的下载管理器(或者浏览器插件)那么专业,没有最佳地使用带宽,也没有好用的文件管理功能。
|
||||
|
||||
对于那些经常下载的人,使用一个好的下载管理器会更有帮助。它能够最大化下载速度(加速下载),断点续传以及制定下载计划,让下载更安全也更有价值。下载管理器已经没有之前流行了,但是最好的下载管理器还是很实用,包括和浏览器的紧密结合,支持类似YouTube的主流网站,以及更多。
|
||||
|
||||
有好几个能在Linux下工作都非常优秀的开源下载管理器,以至于让人无从选择。我整理了一个摘要,是我喜欢的下载管理器,以及Firefox里的一个非常好用的下载插件。这里列出的每一个程序都是开源许可发布的。
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
uGet是一个轻量级,容易使用,功能完备的开源下载管理器。uGet允许用户从不同的源并行下载来加快速度,添加文件到下载序列,暂停或继续下载,提供高级分类管理,和浏览器集成,监控剪贴板,批量下载,支持26种语言,以及其他许多功能。
|
||||
|
||||
uGet是一个成熟的软件;保持开发超过11年。在这个时间里,它发展成一个非常多功能的下载管理器,拥有一套很高价值的功能集,还保持了易用性。
|
||||
|
||||
uGet是用C语言开发的,使用了cURL作为底层支持,以及应用库libcurl。uGet有非常好的平台兼容性。它一开始是Linux系统下的项目,但是被移植到在Mac OS X,FreeBSD,Android和Windows平台运行。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 功能点: ####
|
||||
|
||||
- 容易使用
|
||||
- 下载队列可以让下载任务按任意多或少或你希望的数量同时进行。
|
||||
- 断点续传
|
||||
- 默认分类
|
||||
- 完美实现的剪贴板监控功能
|
||||
- 批量下载
|
||||
- 支持从HTML文件导入下载任务
|
||||
- 支持通过HTTP,HTTPS,FTP,BitTorrent和Metalink下载
|
||||
- 多线程下载(也被称为分块下载):每个下载任务支持最多20个线程同时连接,支持自适应的分块管理,意味着如果某个下载块中断了,那么会其他连接会把它捡起来,以时刻保证最佳的下载速度。
|
||||
- 多镜像下载
|
||||
- FTP登录和匿名FTP
|
||||
- 强大的计划任务
|
||||
- 通过FlashGot和FireFox集成
|
||||
- Aria2插件
|
||||
- 多变的主题
|
||||
- 安静模式
|
||||
- 键盘快捷键
|
||||
- 支持命令行/终端控制
|
||||
- 自动创建目录
|
||||
- 下载历史管理
|
||||
- 支持GnuTLS
|
||||
- 支持26种语言,包括:阿拉伯语,白俄罗斯语,简体中文,繁体中文,捷克语,丹麦语,英语(默认),法语,格鲁吉亚语,德语,匈牙利语,印尼语,意大利语,波兰语,葡萄牙语(巴西),俄语,西班牙语,土耳其语,乌克兰语,以及越南语。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- 网站:[ugetdm.com][1]
|
||||
- 开发人员:C.H. Huang and contributors
|
||||
- 许可:GNU LGPL 2.1
|
||||
- 版本:1.10.5
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
DownThemAll!是一个小巧的,可靠的以及易用的,开源下载管理器/加速器,是Firefox的一个组件。它可以让用户下载一个页面上所有链接和图片以及更多功能。它可以让用户完全控制下载任务,随时分配下载速度以及同时下载的任务数量。通过使用Metalinks或者手动添加镜像的方式,可以同时从不同的服务器下载同一个文件。
|
||||
|
||||
DownThemAll会根据你要下载的文件大小,切割成不同的部分,然后并行下载。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 功能点: ####
|
||||
|
||||
- 和Firefox的完全集成
|
||||
- 分块下载,允许用户下载不同的文件块,完成之后再拼接成完整的文件;这样的话当连接到一个缓慢的服务器的时候可以加快下载速度。
|
||||
- 支持Metalink,允许发送下载文件的多个URL以及它的校验值和其他信息到DTA
|
||||
- 支持爬虫方式通过一个单独的链接遍历整个网页
|
||||
- 下载过滤
|
||||
- 高级重命名选项
|
||||
- 暂停和继续下载任务
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- 网站:[addons.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/addon/downthemall][2]
|
||||
- 开发人员:Federico Parodi, Stefano Verna, Nils Maier
|
||||
- 许可:GNU GPL v2
|
||||
- 版本:2.0.17
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
JDownloader是一个免费,开源的下载管理工具,拥有一个大型社区的开发者支持,让下载更简单和快捷。用户可以开始,停止或暂停下载,设置带宽限制,自动解压缩包,以及更多功能。它提供了一个容易扩展的框架。
|
||||
|
||||
JDownloader简化了从一键下载网站下载文件。它还支持从不同并行资源下载,手势识别,自动文件解压缩以及更多功能。另外,还支持许多“加密链接”网站-所以你只需要复制粘贴“加密的”链接,然后JDownloader会处理剩下的事情。JDownloader还能导入CCF,RSDF和DLC文件。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 功能点: ####
|
||||
|
||||
- 一次下载多个文件
|
||||
- 从多个连接同时下载
|
||||
- JD有一个自己实现的强大的OCR模块
|
||||
- 自动解压(包括密码搜索)(RAR压缩包)
|
||||
- 支持主题
|
||||
- 支持多国语言
|
||||
- 大约110个站点以及超过300个解密插件
|
||||
- 通过JDLiveHeaderScripts重连:(支持1400路由)
|
||||
- 网页更新
|
||||
- 集成包管理器支持额外模块(例如,Webinterface,Shutdown)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- 网站:[jdownloader.org][3]
|
||||
- 开发人员:AppWork UG
|
||||
- 许可:GNU GPL v3
|
||||
- 版本:0.9.581
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
FreeRapid Downloader是一个易用的开源下载程序,支持从Rapidshare,Youtube,Facebook,Picasa和其他文件分享网站下载。他的下载引擎基于一些插件,所以可以从特殊站点下载。
|
||||
|
||||
对于需要针对特定文件分享网站的下载管理器用户来说,FreeRapid Downloader是理想的选择。
|
||||
|
||||
FreeRapid Downloader使用Java语言编写。需要至少Sun Java 7.0版本才可以运行。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 功能点: ####
|
||||
|
||||
- 容易使用
|
||||
- 支持从不同服务站点并行下载
|
||||
- 支持断点续传
|
||||
- 支持通过代理列表下载
|
||||
- 支持流视频或图片
|
||||
- 下载历史
|
||||
- 聪明的剪贴板监控
|
||||
- 自动检查服务器文件后缀
|
||||
- 自动关机选项
|
||||
- 插件自动更新
|
||||
- 简单验证码识别
|
||||
- 支持跨平台
|
||||
- 支持多国语言:英语,保加利亚语,捷克语,芬兰语,葡萄牙语,斯洛伐克语,匈牙利语,简体中文,以及其他
|
||||
- 支持超过700个站点
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- 网站:[wordrider.net/freerapid/][4]
|
||||
- 开发人员:Vity and contributors
|
||||
- 许可:GNU GPL v2
|
||||
- 版本:0.9u4
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
FlashGot是一个Firefox和Thunderbird的免费组件,旨在通过外置下载管理器来处理单个和大规模(“所有”和“已选”)下载。
|
||||
|
||||
FlashGot把所支持的所有下载管理器统一成Firefox中的一个下载管理器。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 功能点: ####
|
||||
|
||||
- Linux下支持:Aria, Axel Download Accelerator, cURL, Downloader 4 X, FatRat, GNOME Gwget, FatRat, JDownloader, KDE KGet, pyLoad, SteadyFlow, uGet, wxDFast, 和wxDownload Fast
|
||||
- 支持图库功能,可以帮助把原来分散在不同页面的系列资源,整合到一个所有媒体库页面中,然后可以轻松迅速地“下载所有”
|
||||
- FlashGot Link会使用默认下载管理器下载当前鼠标选中的链接
|
||||
- FlashGot Selection
|
||||
- FlashGot All
|
||||
- FlashGot Tabs
|
||||
- FlashGot Media
|
||||
- 抓取页面里所有链接
|
||||
- 抓取所有标签栏的所有链接
|
||||
- 链接过滤(例如,只下载指定类型文件)
|
||||
- 在网页上抓取点击所产生的所有链接
|
||||
- 支持从大多数链接保护和文件托管服务器直接和批量下载
|
||||
- 隐私选项
|
||||
- 支持国际化
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- 网站:[flashgot.net][5]
|
||||
- 开发人员:Giorgio Maone
|
||||
- 许可:GNU GPL v2
|
||||
- 版本:1.5.6.5
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxlinks.com/article/20140913062041384/DownloadManagers.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Frazer Kline
|
||||
译者:[zpl1025](https://github.com/zpl1025)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://ugetdm.com/
|
||||
[2]:https://addons.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/addon/downthemall/
|
||||
[3]:http://jdownloader.org/
|
||||
[4]:http://wordrider.net/freerapid/
|
||||
[5]:http://flashgot.net/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,104 @@
|
||||
10个 Ubuntu 用户一定要知道的博客
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**想要了解更多关于 ubuntu 的资讯,我们应该追哪些网站呢?**
|
||||
|
||||
这是初学者经常会问的一个问题,在这里,我会告诉你们10个我最喜欢的博客,这些博客可以帮助我们解决问题,能让我们及时了解所有 Ubuntu 版本的更新消息。不,我谈论的不是通常的 Linux 和 shell 脚本一类的东东。我是在说一个流畅的 Linux 桌面系统和一个普通的用户所要的关于 Ubuntu 的经验。
|
||||
|
||||
这些网站帮助你解决你正遇到的问题,提醒你关注各种应用和提供给你来自 Ubuntu 世界的最新消息。这个网站可以让你对 Ubuntu 更了解,所以,下面列出的10个我最喜欢的网站覆盖 Ubuntu 的方方面面。
|
||||
|
||||
###10个Ubutun用户一定要知道的博客###
|
||||
|
||||
从我开始在 itsfoss 网站上写作开始,我特意把他排除在外,没有列入名单。我也并没有把[Planet Ubuntu][1]列入名单,因为他不适合初学的同学。废话不多说,让我们一起来看下**最好的乌邦图(ubuntu)博客**(排名不分先后):
|
||||
|
||||
### [OMG! Ubuntu!][2] ###
|
||||
|
||||
这是一个只针对 ubuntu 爱好者的网站。任何和乌邦图有关系的想法,不管成不成熟,OMG!Ubuntu上都会有收集!他主要包括新闻和应用。你也可以再这里找到一些关于 Ubuntu 的教程,但是不是很多。
|
||||
|
||||
这个博客会让你知道 Ubuntu 的世界是怎么样的。
|
||||
|
||||
### [Web Upd8][3] ###
|
||||
|
||||
Web Upd8 是我最喜欢的博客。除了涵盖新闻,他有很多容易理解的教程。Web Upd8 还维护了几个PPAs。博主[Andrei][4]有时会在评论里回答你的问题,这对你来说也会是很有帮助的。
|
||||
|
||||
一个你可以追新闻资讯和教程的网站。
|
||||
|
||||
### [Noobs Lab][5] ###
|
||||
|
||||
和Web Upd8一样,Noobs Lab上也有很多教程,新闻,并且它可能是PPA里最大的主题和图标集。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你是个小白,跟着Noobs Lab。
|
||||
|
||||
### [Linux Scoop][6] ###
|
||||
|
||||
这里,大多数的博客都是“文字博客”。你通过看说明和截图来学习教程。而 Linux Scoop 上有很多录像来帮助初学者来学习,是一个实实在在的录像博客。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你更喜欢看,而不是阅读的话,Linux Scoop应该是最适合你的。
|
||||
|
||||
### [Ubuntu Geek][7] ###
|
||||
|
||||
这是一个相对比较老的博客。覆盖面很广,并且有很多快速安装的教程和说明。虽然,有时我发现其中的一些教程文章缺乏深度,当然这也许只是我个人的观点。
|
||||
|
||||
想要快速的小贴士,去Ubuntu Geek。
|
||||
|
||||
### [Tech Drive-in][8] ###
|
||||
|
||||
这个网站的更新好像没有以前那么勤快了,可能是 Manuel 在忙于他的工作,但是仍然给我们提供了很多的东西。新闻,教程,应用评论是这个博客的重点。
|
||||
|
||||
博客经常被收入到[Ubuntu的新闻邮件请求][9],Tech Drive-in肯定是一个很值得你去追的网站。
|
||||
|
||||
### [UbuntuHandbook][10] ###
|
||||
|
||||
快速小贴士,新闻和教程是UbuntuHandbook的USP。[Ji m][11]最近也在参与维护一些PPAS。我必须很认真的说,这个站界面其实可以做得更好看点,纯属个人观点。
|
||||
|
||||
UbuntuHandbook 真的很方便。
|
||||
|
||||
### [Unixmen][12] ###
|
||||
|
||||
这个网站是由很多人一起维护的,而且并不仅仅局限于Ubuntu,它也覆盖了很多的其他的Linux发行版。他用他自己的方式来帮助用户。
|
||||
|
||||
紧跟着 Unixmen 的步伐。。
|
||||
|
||||
### [The Mukt][13] ###
|
||||
|
||||
The Mukt是Muktware新的代表。Muktware是一个逐渐消亡的Linux组织,并以Mukt重生。Muktware是一个很严谨的Linux开源的博客,The Mukt涉及很多广泛的主题,包括,科技新闻,古怪的新闻,有时还有娱乐新闻(听起来是否有一种混搭风的感觉?)The Mukt也包括很多Ubuntu的新闻,有些可能是你感兴趣的。
|
||||
|
||||
The Mukt 不仅仅是一个博客,它是一种文化潮流。
|
||||
|
||||
### [LinuxG][14] ###
|
||||
|
||||
LinuxG是一个你可以找到所有关于“怎样安装”文章的站点。几乎所有的文章都开始于一句话“你好,Linux geeksters,正如你所知道的。。。”,博客可以在不同的主题上做得更好。我经常发现有些是文章缺乏深度,并且是急急忙忙写出来的,但是它仍然是一个关注应用更新的好地方。
|
||||
|
||||
它很好的平衡了新的应用和他们最新的版本。
|
||||
|
||||
### 你还有什么好的站点吗? ###
|
||||
|
||||
This was my list of best Ubuntu blogs which I regularly follow. I know there are plenty more out there, perhaps better than some of those listed here. So why don’t you mention your favorite Ubuntu blog in the comment section below?
|
||||
|
||||
这些就是我平时经常浏览的 Ubuntu 博客。我知道还有很多我不知道的站点,可能会比我列出来的这些更好。所以,欢迎把你最喜爱的 Ubuntu 博客在下面评论的位置写出来。
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/ten-blogs-every-ubuntu-user-must-follow/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek][a]
|
||||
译者:[barney-ro](https://github.com/barney-ro)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://itsfoss.com/author/Abhishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://planet.ubuntu.com/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.webupd8.org/
|
||||
[4]:https://plus.google.com/+AlinAndrei
|
||||
[5]:http://www.noobslab.com/
|
||||
[6]:http://linuxscoop.com/
|
||||
[7]:http://www.ubuntugeek.com/
|
||||
[8]:http://www.techdrivein.com/
|
||||
[9]:https://lists.ubuntu.com/mailman/listinfo/ubuntu-news
|
||||
[10]:http://ubuntuhandbook.org/
|
||||
[11]:https://plus.google.com/u/0/+JimUbuntuHandbook
|
||||
[12]:http://www.unixmen.com/
|
||||
[13]:http://www.themukt.com/
|
||||
[14]:http://linuxg.net/
|
||||
@ -1,58 +0,0 @@
|
||||
需要在Ubuntu上安装微软办公软件?去安装官方的网络应用程序
|
||||
================================================== ==============================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**这是微软办公软件及其一贯繁琐的文件指令,而不是每个人的一杯咖啡。同时这是许多工作和教育环境的主要依靠——无论是好还是坏**
|
||||
|
||||
通过使用[LibreOffice的应用程序套件][1],阅读、编辑和保存这些专有指令出现在Ubuntu上是有着某种程度的可能。在作家中,Calc和Impress都不同程度的夸耀微软办公软件文件的协作性,但在我自己的实际操作经验中(谢天谢地,它很简洁!)它并不完美。
|
||||
|
||||
时不时的,你会不得不使用微软办公软件,(虽然我们大多数人都心里向着开放标准,但是我们不应该无视实际问题)但你已经没有意愿去购买一个完整的微软办公软件许可证来运行这个窗口模拟器,那么微软的在线网络应用程序是完美的解决方法。
|
||||
|
||||
###安装微软在线办公软件上的应用程序在Ubuntu###
|
||||
|
||||
为了使从Ubuntu的桌面访问这些在线版本更容易,“Linux的网络应用程序项目”创造了一个小的、非官方的安装程序。它可以添加网络应用程序的快捷方式(“荣耀书签”)到您的应用程序启动器。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
通过快捷方式,相应的Microsoft Web应用程序在你默认的系统浏览器中打开,不可能有比这更精美的了。听起来漂亮吗?下面是你的应用程序的快捷方式:
|
||||
|
||||
- 文档
|
||||
- 表格
|
||||
- 幻灯片
|
||||
- Outlook
|
||||
- OneDrive
|
||||
- 日历
|
||||
- OneNote
|
||||
- 通讯录
|
||||
|
||||
该软件包还创建了一个新的应用程序类别来容纳这些链接,不但可以让您把这些快捷方式从其他应用程序单独分开来,而且是直接位于常见的“办公软件”应用程序下。
|
||||
|
||||
这些都是必不可少的吗?不见得。他们有用吗?这取决于你的工作流程。但它是不错的选择吗?一定是的。
|
||||
|
||||
你可以从下面的链接保存含有.deb文件安装程序,其中有安装链接。适用于Ubuntu14.04 LTS和更高版本。
|
||||
|
||||
- [下载微软的在线办公应用(.deb)][2]
|
||||
|
||||
###其他可选项###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
类似的替代方案是[安装Chrome官方网上应用商店的在线办公应用程序][3],然后添加应用程序启动器到Linux。这次短跑中仍然会为它们创建可启动的快捷方式,但那些可以被设置为打开自己的窗框,而且不需要安装任何第三方软件包。
|
||||
|
||||
同时,谷歌最近在整合完整的Office功能(由于其购买了QuickOffice)[到自己的文档,幻灯片和床单应用][4]。Android应用程序Quickoffice退出了舞台,同时Chrome也实现了扩展。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你是一个深度的谷歌网络硬盘/文档的用户,那么这个解决方案可能对你是更加好了。
|
||||
|
||||
-------------------------------------------------- ------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/07/run-microsoft-office-web-apps-ubuntu-desktop
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[cereuz](https://github.com/cereuz)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.libreoffice.org/
|
||||
[2]:https://docs.google.com/file/d/0ByQnaVw7riBQMjNCUFh4ZlM4Y0E/edit?usp=sharing
|
||||
[3]:http://www.omgchrome.com/microsoft-brings-office-online-chrome-web-store/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.omgchrome.com/quickoffice-chrome-extension-gets-name-change/
|
||||
Some files were not shown because too many files have changed in this diff Show More
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user