mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-03-24 02:20:09 +08:00
commit
0b98f9392f
@ -1,165 +0,0 @@
|
||||
CoreFreq – A Powerful CPU Monitoring Tool for Linux Systems
|
||||
============================================================
|
||||
|
||||
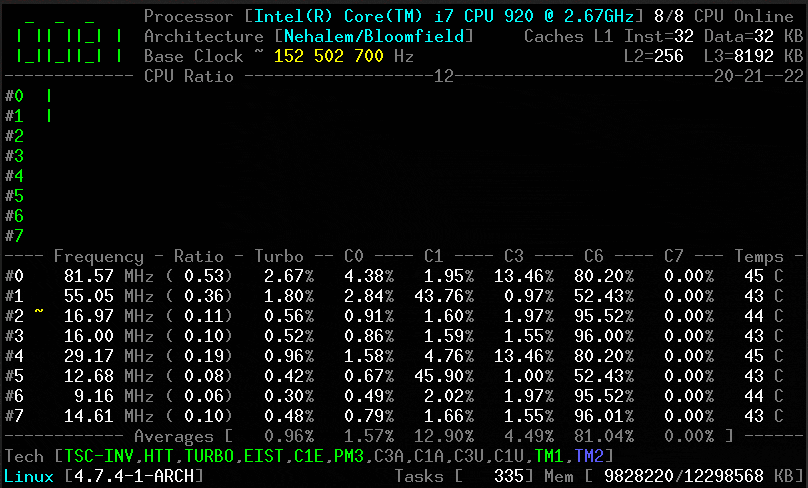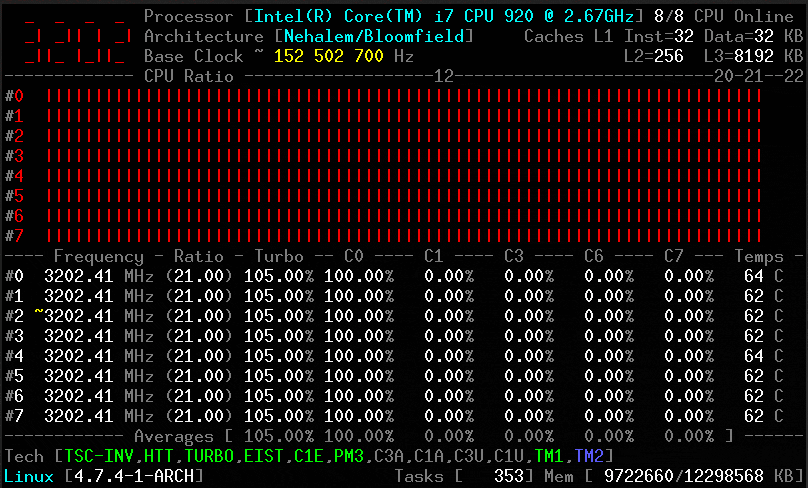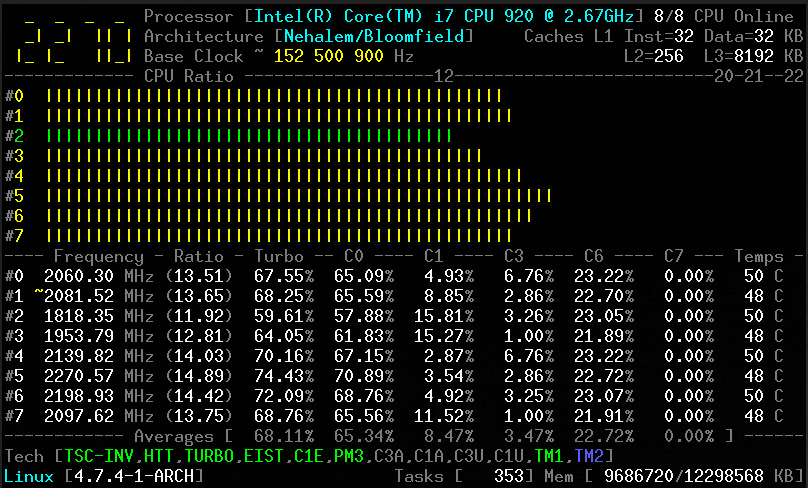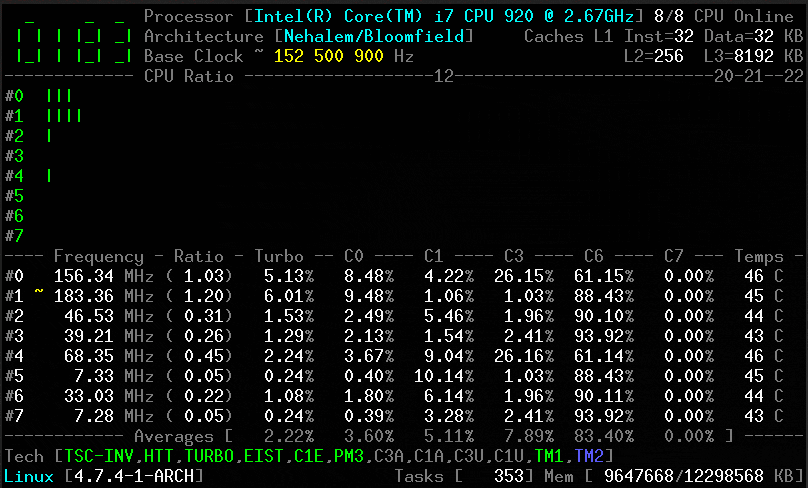
CoreFreq is a [CPU monitoring program][1] intended for the Intel 64-bits processor and supports architectures such as Atom, Core2, Nehalem, SandyBridge and above, AMD Family 0F.
|
||||
|
||||
Its core is established on a kernel module which helps to retrieve internal performance counters from each CPU core, and works in relation with a daemon which gathers the data and a small console client links to the daemon and displays collected data.
|
||||
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||
][2]
|
||||
|
||||
It offers a groundwork to recapture CPU data with a high degree of accuracy:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Core frequencies & ratios; SpeedStep (EIST), Turbo Boost, Hyper-Threading (HTT) as well as Base Clock.
|
||||
2. Performance counters in conjunction with Time Stamp Counter (TSC), Unhalted Core Cycles (UCC), Unhalted Reference Cycles (URC).
|
||||
3. Number of instructions per cycle or second, IPS, IPC, or CPI.
|
||||
4. CPU C-States C0 C1 C3 C6 C7 – C1E – Auto/UnDemotion of C1 C3.
|
||||
5. DTS Temperature along with Tjunction Max, Thermal Monitoring TM1 TM2 state.
|
||||
6. Topology map including Caches for boostrap together with application CPU.
|
||||
7. Processor features, brand plus architecture strings.
|
||||
|
||||
Note: This tool is more useful and appropriate for expert Linux users and experienced system administrators, however, novice users can gradually learn how to purposefully use it.
|
||||
|
||||
#### How Does CoreFreq Works
|
||||
|
||||
It functions by invoking a Linux Kernel module which then uses:
|
||||
|
||||
1. asm code to keep the readings of the performance counters as close as possible.
|
||||
2. per-CPU, effects slab data memory plus high-resolution timer.
|
||||
3. compliant with suspend / resume and CPU Hot-Plug.
|
||||
4. a shared memory to protect kernel from the user-space part of the program.
|
||||
5. atomic synchronization of threads to do away with mutexes and deadlock.
|
||||
|
||||
### How to Install CoreFreq in Linux
|
||||
|
||||
To install CoreFreq, first you need to install the prerequisites (Development Tools) to compile and build the program from source.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo yum group install 'Development Tools' [On CentOS/RHEL]
|
||||
$ sudo dnf group install 'Development Tools' [On Fedora 22+ Versions]
|
||||
# sudo apt-get install dkms git libpthread-stubs0-dev [On Debian/Ubuntu]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Next clone the CoreFreq source code from the Github repository, move into the download folder and compile and build the program:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ git clone https://github.com/cyring/CoreFreq.git
|
||||
$ cd CoreFreq
|
||||
$ make
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||
][3]
|
||||
|
||||
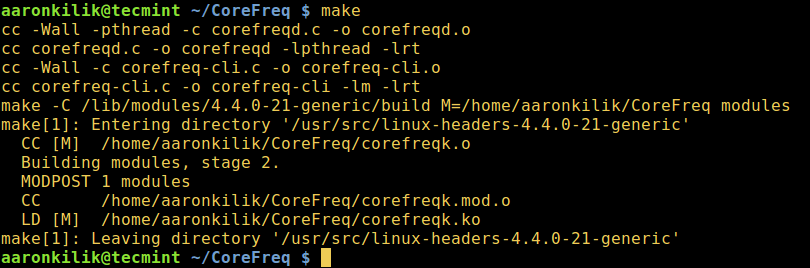
Build CoreFreq Program
|
||||
|
||||
Note: Arch Linux users can install [corefreq-git][4] from the AUR.
|
||||
|
||||
Now run the following commands to load the Linux kernel module from local directory followed by the daemon:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo insmod corefreqk.ko
|
||||
$ sudo ./corefreqd
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then, start the client, as a user.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ ./corefreq-cli
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][5]
|
||||
|
||||
CoreFreq Linux CPU Monitoring
|
||||
|
||||
From the interface above, you can use shortcut keys:
|
||||
|
||||
1. `F2` to display a usage menu as seen at the top section of the screen.
|
||||
2. `Right` and `Left` arrows to move over the menu tabs.
|
||||
3. `Up` and `Down` arrows to select a menu item, then click [Enter].
|
||||
4. `F4` will close the program.
|
||||
5. `h` will open a quick reference.
|
||||
|
||||
To view all usage options, type the command below:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ ./corefreq-cli -h
|
||||
```
|
||||
CoreFreq Options
|
||||
```
|
||||
CoreFreq. Copyright (C) 2015-2017 CYRIL INGENIERIE
|
||||
usage: corefreq-cli [-option <arguments>]
|
||||
-t Show Top (default)
|
||||
-d Show Dashboard
|
||||
arguments: <left> <top> <marginWidth> <marginHeight>
|
||||
-c Monitor Counters
|
||||
-i Monitor Instructions
|
||||
-s Print System Information
|
||||
-M Print Memory Controller
|
||||
-m Print Topology
|
||||
-u Print CPUID
|
||||
-k Print Kernel
|
||||
-h Print out this message
|
||||
Exit status:
|
||||
0 if OK,
|
||||
1 if problems,
|
||||
>1 if serious trouble.
|
||||
Report bugs to labs[at]cyring.fr
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To print info about the kernel, run:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ ./corefreq-cli -k
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Print CPU identification details:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ ./corefreq-cli -u
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can as well monitor CPU instructions in real-time:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ ./corefreq-cli -i
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Enable tracing of counters as below:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ ./corefreq-cli -c
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For more information and usage, visit the CoreFreq Github repository: [https://github.com/cyring/CoreFreq][6]
|
||||
|
||||
In this article, we reviewed a powerful CPU monitoring tool, which may be more useful to Linux experts or experienced system administrators as compared to novice users.
|
||||
|
||||
Share your thoughts about this command tool or any related ideas with us via the feedback form below.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
作者简介:
|
||||
|
||||
Aaron Kili is a Linux and F.O.S.S enthusiast, an upcoming Linux SysAdmin, web developer, and currently a content creator for TecMint who loves working with computers and strongly believes in sharing knowledge.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/corefreq-linux-cpu-monitoring-tool/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Aaron Kili][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/bcc-best-linux-performance-monitoring-tools/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/CoreFreq-CPU-Monitoring.gif
|
||||
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/make-corefreq.png
|
||||
[4]:https://aur.archlinux.org/packages/corefreq-git
|
||||
[5]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/CoreFreq-Linux-CPU-Monitoring.gif
|
||||
[6]:https://github.com/cyring/CoreFreq
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,167 @@
|
||||
CoreFreq - 一款强大的 Linux 下监控 CPU 的工具
|
||||
============================================================
|
||||
|
||||
CoreFreq 是一个用于英特尔64位处理器的[ CPU 监控程序][1],并且支持Atom、Core2、Nehalem、SandyBridge 及以上、还有 AMD 0F 家族。
|
||||
|
||||
它的核心建立在内核模块上,帮助从每个 CPU 核心检索内部性能计数器,并且与收集数据的守护进程一起工作,并用一个小型控制台客户端链接到守护程序并显示收集的数据。
|
||||
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][2]
|
||||
|
||||
它提供了以高精度重新捕获 CPU 数据的基础工作:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 核心频率和比率; SpeedStep(EIST)、Turbo Boost、超线程(HTT)以及基本时钟。
|
||||
2. 性能计数器结合时间戳计数器(TSC)、未分配的核心循环(UCC)、未赋值的引用循环(URC)。
|
||||
3. 每周期或每秒的指令数、IPS、IPC 或 CPI。
|
||||
4. CPU C 的状态 C0 C1 C3 C6 C7 - C1E - C1、C3 的自动/降级。
|
||||
5. 带有 Tjunction Max 的 DTS 温度、热监测 TM1、TM2 的状态。
|
||||
6. 包括用于自举的高速缓存和应用程序 CPU 拓扑图。
|
||||
7. 处理器特性、品牌、架构字符串。
|
||||
|
||||
注意:此工具更适用于专家 Linux 用户和经验丰富的系统管理员,但新手用户可以逐步学习如何使用它。
|
||||
|
||||
#### CoreFreq 如何工作
|
||||
|
||||
它通过调用一个 Linux 内核模块,然后使用:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 汇编代码保持性能计数器的读数尽可能接近。
|
||||
2. 每个 CPU 影响 slab 数据内存加上高分辨率定时器。
|
||||
3. 可以暂停/恢复和 CPU 热插拔。
|
||||
4. 使用共享内存来保护内核免受来自用户空间程序的损害。
|
||||
5. 使用原子同步的线程来消除互斥和死锁。
|
||||
|
||||
### 如何在 Linux 中安装 CoreFreq
|
||||
|
||||
要安装 CoreFreq,你首先需要安装依赖程序(开发工具)来编译并从源码构建程序。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo yum group install 'Development Tools' [On CentOS/RHEL]
|
||||
$ sudo dnf group install 'Development Tools' [On Fedora 22+ Versions]
|
||||
# sudo apt-get install dkms git libpthread-stubs0-dev [On Debian/Ubuntu]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
接下来克隆 Github 上 CoreFreq 源码,进入下载文件夹并编译构建程序:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ git clone https://github.com/cyring/CoreFreq.git
|
||||
$ cd CoreFreq
|
||||
$ make
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][3]
|
||||
|
||||
构建 CoreFreq 程序
|
||||
|
||||
注意:Arch Linux 用户可以从 AUR 中安装 [corefreq-git][4]。
|
||||
|
||||
现在运行以下命令从本地目录加载 Linux 内核模块,接着运行守护程序:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo insmod corefreqk.ko
|
||||
$ sudo ./corefreqd
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
接着使用普通用户启动客户端。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ ./corefreq-cli
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][5]
|
||||
|
||||
CoreFreq Linux CPU 监控
|
||||
|
||||
在上面的界面中,你可以使用这些快捷键:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 使用 `F2` 显示屏幕顶部显示的使用菜单。
|
||||
2. 使用 `右` 和 `左` 箭头移动菜单选项卡。
|
||||
3. 使用 `上`和 `下` 箭头选择菜单项,然后单击[Enter]。
|
||||
4. 使用 `F4` 关闭程序。
|
||||
5. 使用 `h` 打开快速参考。
|
||||
|
||||
要查看所有的使用选项,请输入以下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ ./corefreq-cli -h
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
CoreFreq 选项
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
CoreFreq. Copyright (C) 2015-2017 CYRIL INGENIERIE
|
||||
usage: corefreq-cli [-option <arguments>]
|
||||
-t Show Top (default)
|
||||
-d Show Dashboard
|
||||
arguments: <left> <top> <marginWidth> <marginHeight>
|
||||
-c Monitor Counters
|
||||
-i Monitor Instructions
|
||||
-s Print System Information
|
||||
-M Print Memory Controller
|
||||
-m Print Topology
|
||||
-u Print CPUID
|
||||
-k Print Kernel
|
||||
-h Print out this message
|
||||
Exit status:
|
||||
0 if OK,
|
||||
1 if problems,
|
||||
>1 if serious trouble.
|
||||
Report bugs to labs[at]cyring.fr
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
要打印内核的信息,运行:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ ./corefreq-cli -k
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
打印 CPU 细节信息:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ ./corefreq-cli -u
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
你也可以实时监控 CPU 指令:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ ./corefreq-cli -i
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如下启用计数器追踪:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ ./corefreq-cli -c
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
有关更多信息和用法,请访问 CoreFreq Github 仓库:[https://github.com/cyring/CoreFreq][6]
|
||||
|
||||
在本文中,我们回顾了一个强大的 CPU 监控工具,这对于 Linux 专家或经验丰富的系统管理员来说可能比新手用户更有用。
|
||||
|
||||
通过下面的评论栏与我们分享你对这个工具或任何相关的想法。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
作者简介:
|
||||
|
||||
Aaron Kili 是 Linux 和 F.O.S.S 爱好者,将来的 Linux 系统管理员和网络开发人员,目前是 TecMint 的内容创作者,他喜欢用电脑工作,并坚信分享知识。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/corefreq-linux-cpu-monitoring-tool/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Aaron Kili][a]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/bcc-best-linux-performance-monitoring-tools/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/CoreFreq-CPU-Monitoring.gif
|
||||
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/make-corefreq.png
|
||||
[4]:https://aur.archlinux.org/packages/corefreq-git
|
||||
[5]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/CoreFreq-Linux-CPU-Monitoring.gif
|
||||
[6]:https://github.com/cyring/CoreFreq
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user