mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-03-27 02:30:10 +08:00
hankchow translated
This commit is contained in:
parent
de98a05495
commit
0ac6c8cd63
@ -1,114 +0,0 @@
|
||||
HankChow translating
|
||||
|
||||
Machine learning with Python: Essential hacks and tricks
|
||||
======
|
||||
Master machine learning, AI, and deep learning with Python.
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
It's never been easier to get started with machine learning. In addition to structured massive open online courses (MOOCs), there are a huge number of incredible, free resources available around the web. Here are a few that have helped me.
|
||||
|
||||
2. Learn to clearly differentiate between the buzzwords—for example, machine learning, artificial intelligence, deep learning, data science, computer vision, and robotics. Read or listen to talks by experts on each of them. Watch this [amazing video by Brandon Rohrer][1], an influential data scientist. Or this video about the [clear differences between various roles][2] associated with data science.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
3. Clearly set a goal for what you want to learn. Then go and take [that Coursera course][3]. Or take the one [from the University of Washington][4], which is pretty good too.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
5. If you are enthusiastic about taking online courses, check out this article for guidance on [choosing the right MOOC][5].
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
6. Most of all, develop a feel for it. Join some good social forums, but resist the temptation to latch onto sensationalized headlines and news. Do your own reading to understand what it is and what it is not, where it might go, and what possibilities it can open up. Then sit back and think about how you can apply machine learning or imbue data science principles into your daily work. Build a simple regression model to predict the cost of your next lunch or download your electricity usage data from your energy provider and do a simple time-series plot in Excel to discover some pattern of usage. And after you are thoroughly enamored with machine learning, you can watch this video.
|
||||
|
||||
<https://www.youtube.com/embed/IpGxLWOIZy4>
|
||||
|
||||
### Is Python a good language for machine learning/AI?
|
||||
|
||||
Familiarity and moderate expertise in at least one high-level programming language is useful for beginners in machine learning. Unless you are a Ph.D. researcher working on a purely theoretical proof of some complex algorithm, you are expected to mostly use the existing machine learning algorithms and apply them in solving novel problems. This requires you to put on a programming hat.
|
||||
|
||||
There's a lot of talk about the best language for data science. While the debate rages, grab a coffee and read this insightful FreeCodeCamp article to learn about [data science languages][6] . Or, check out this post on KDnuggets to dive directly into the [Python vs. R debate][7]
|
||||
|
||||
For now, it's widely believed that Python helps developers be more productive from development to deployment and maintenance. Python's syntax is simpler and at a higher level when compared to Java, C, and C++. It has a vibrant community, open source culture, hundreds of high-quality libraries focused on machine learning, and a huge support base from big names in the industry (e.g., Google, Dropbox, Airbnb, etc.).
|
||||
|
||||
### Fundamental Python libraries
|
||||
|
||||
Assuming you go with the widespread opinion that Python is the best language for machine learning, there are a few core Python packages and libraries you need to master.
|
||||
|
||||
#### NumPy
|
||||
|
||||
Short for [Numerical Python][8], NumPy is the fundamental package required for high-performance scientific computing and data analysis in the Python ecosystem. It's the foundation on which nearly all of the higher-level tools, such as [Pandas][9] and [scikit-learn][10], are built. [TensorFlow][11] uses NumPy arrays as the fundamental building blocks underpinning Tensor objects and graphflow for deep learning tasks. Many NumPy operations are implemented in C, making them super fast. For data science and modern machine learning tasks, this is an invaluable advantage.
|
||||
|
||||
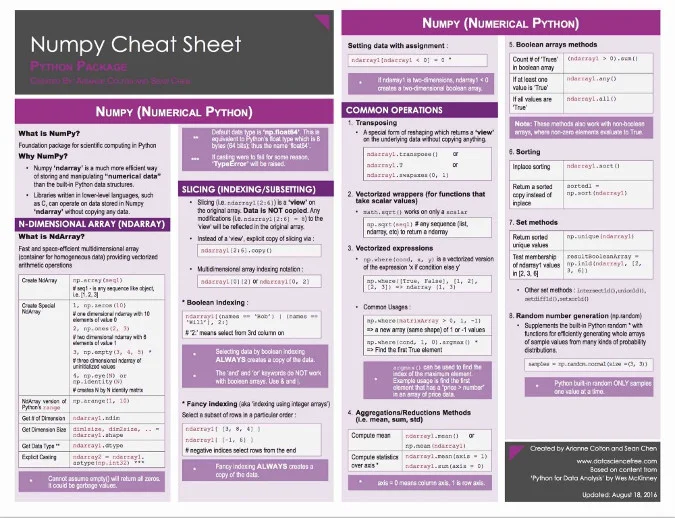
|
||||
|
||||
#### Pandas
|
||||
|
||||
Pandas is the most popular library in the scientific Python ecosystem for doing general-purpose data analysis. Pandas is built upon a NumPy array, thereby preserving fast execution speed and offering many data engineering features, including:
|
||||
|
||||
* Reading/writing many different data formats
|
||||
* Selecting subsets of data
|
||||
* Calculating across rows and down columns
|
||||
* Finding and filling missing data
|
||||
* Applying operations to independent groups within the data
|
||||
* Reshaping data into different forms
|
||||
* Combing multiple datasets together
|
||||
* Advanced time-series functionality
|
||||
* Visualization through Matplotlib and Seaborn
|
||||
|
||||
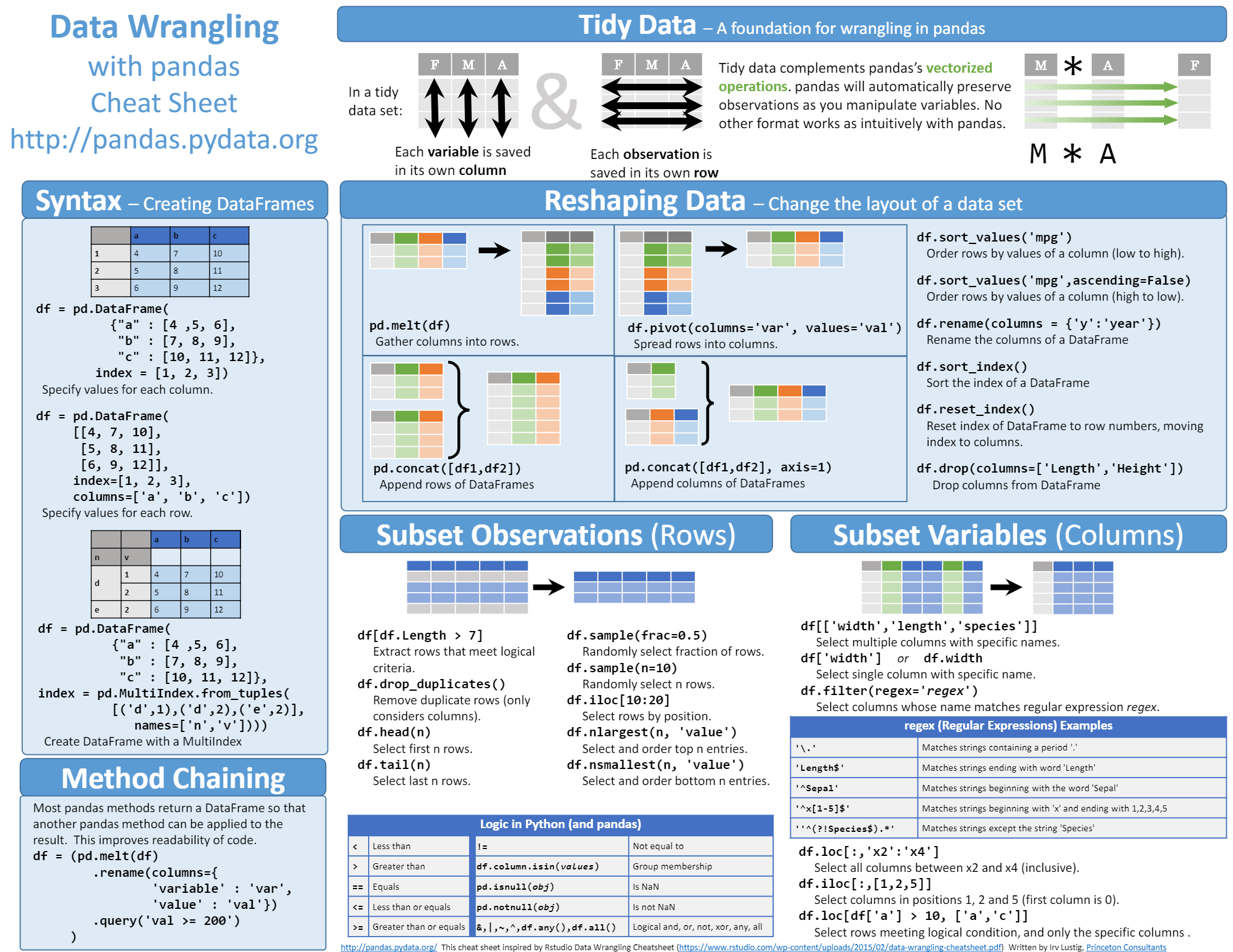
|
||||
|
||||
#### Matplotlib and Seaborn
|
||||
|
||||
Data visualization and storytelling with data are essential skills for every data scientist because it's crtitical to be able to communicate insights from analyses to any audience effectively. This is an equally critical part of your machine learning pipeline, as you often have to perform an exploratory analysis of a dataset before deciding to apply a particular machine learning algorithm.
|
||||
|
||||
[Matplotlib][12] is the most widely used 2D Python visualization library. It's equipped with a dazzling array of commands and interfaces for producing publication-quality graphics from your data. This amazingly detailed and rich article will help you [get started with Matplotlib][13].
|
||||
|
||||
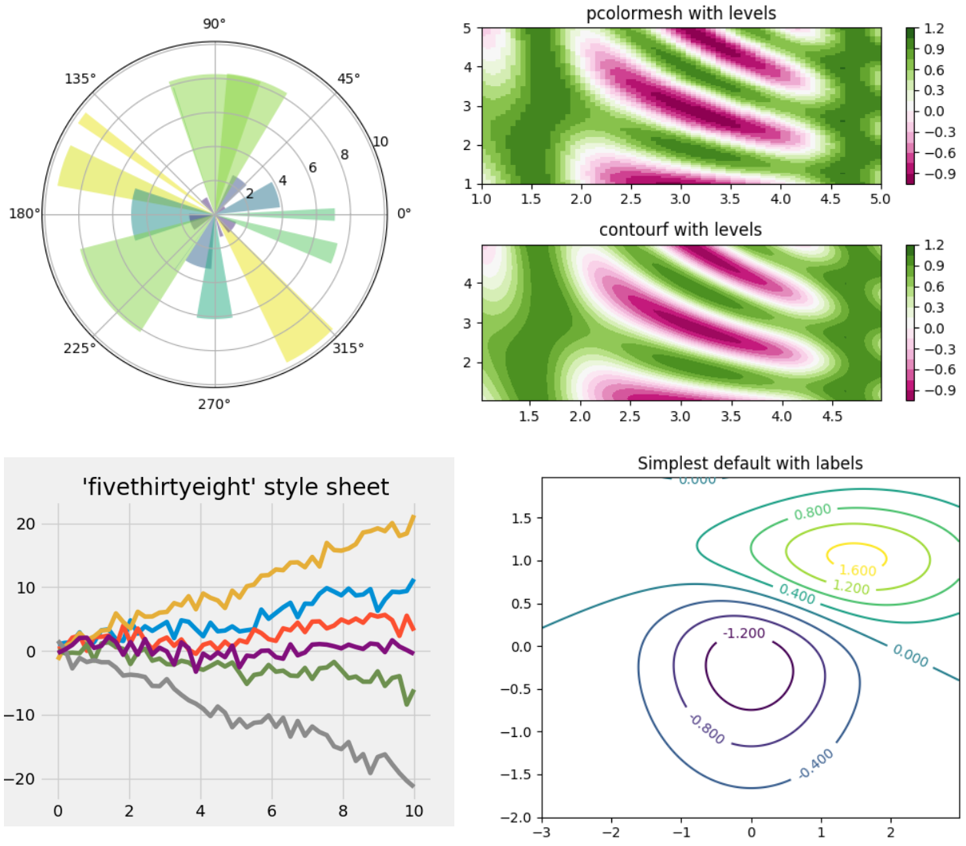
|
||||
[Seaborn][14] is another great visualization library focused on statistical plotting. It provides an API (with flexible choices for plot style and color defaults) on top of Matplotlib, defines simple high-level functions for common statistical plot types, and integrates with functionality provided by Pandas. You can start with this great tutorial on [Seaborn for beginners][15].
|
||||
|
||||
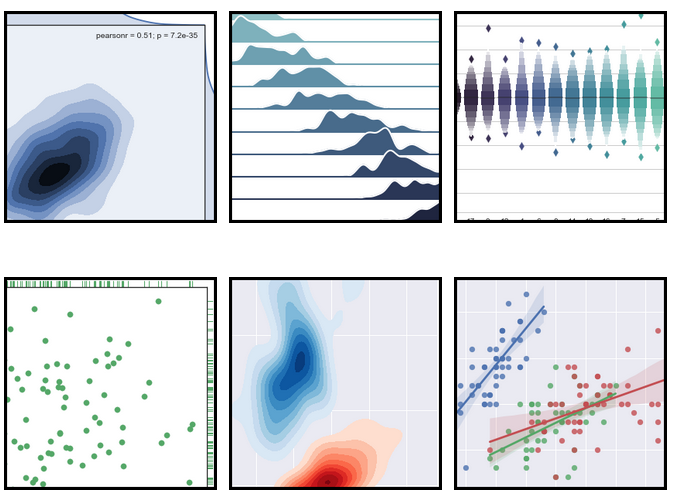
|
||||
|
||||
#### Scikit-learn
|
||||
|
||||
Scikit-learn is the most important general machine learning Python package to master. It features various [classification][16], [regression][17], and [clustering][18] algorithms, including [support vector machines][19], [random forests][20], [gradient boosting][21], [k-means][22], and [DBSCAN][23], and is designed to interoperate with the Python numerical and scientific libraries NumPy and [SciPy][24]. It provides a range of supervised and unsupervised learning algorithms via a consistent interface. The library has a level of robustness and support required for use in production systems. This means it has a deep focus on concerns such as ease of use, code quality, collaboration, documentation, and performance. Look at this [gentle introduction to machine learning vocabulary][25] used in the Scikit-learn universe or this article demonstrating [a simple machine learning pipeline][26] method using Scikit-learn.
|
||||
|
||||
This article was originally published on [Heartbeat][27] under [CC BY-SA 4.0][28].
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://opensource.com/article/18/10/machine-learning-python-essential-hacks-and-tricks
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Tirthajyoti Sarkar][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972][b]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: https://opensource.com/users/tirthajyoti
|
||||
[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
|
||||
[1]: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tKa0zDDDaQk
|
||||
[2]: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ura_ioOcpQI
|
||||
[3]: https://www.coursera.org/learn/machine-learning
|
||||
[4]: https://www.coursera.org/specializations/machine-learning
|
||||
[5]: https://towardsdatascience.com/how-to-choose-effective-moocs-for-machine-learning-and-data-science-8681700ed83f
|
||||
[6]: https://medium.freecodecamp.org/which-languages-should-you-learn-for-data-science-e806ba55a81f
|
||||
[7]: https://www.kdnuggets.com/2017/09/python-vs-r-data-science-machine-learning.html
|
||||
[8]: http://numpy.org/
|
||||
[9]: https://pandas.pydata.org/
|
||||
[10]: http://scikit-learn.org/
|
||||
[11]: https://www.tensorflow.org/
|
||||
[12]: https://matplotlib.org/
|
||||
[13]: https://realpython.com/python-matplotlib-guide/
|
||||
[14]: https://seaborn.pydata.org/
|
||||
[15]: https://www.datacamp.com/community/tutorials/seaborn-python-tutorial
|
||||
[16]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Statistical_classification
|
||||
[17]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Regression_analysis
|
||||
[18]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cluster_analysis
|
||||
[19]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Support_vector_machine
|
||||
[20]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Random_forests
|
||||
[21]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gradient_boosting
|
||||
[22]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/K-means_clustering
|
||||
[23]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/DBSCAN
|
||||
[24]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/SciPy
|
||||
[25]: http://scikit-learn.org/stable/tutorial/basic/tutorial.html
|
||||
[26]: https://towardsdatascience.com/machine-learning-with-python-easy-and-robust-method-to-fit-nonlinear-data-19e8a1ddbd49
|
||||
[27]: https://heartbeat.fritz.ai/some-essential-hacks-and-tricks-for-machine-learning-with-python-5478bc6593f2
|
||||
[28]: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,123 @@
|
||||
Python 机器学习的必备技巧
|
||||
======
|
||||
> 尝试使用 Python 掌握机器学习、人工智能和深度学习。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
想要入门机器学习并不难。除了<ruby>大规模网络公开课<rt>Massive Open Online Courses</rt></ruby>(MOOCs)之外,还有很多其它优秀的免费资源。下面我分享一些我觉得比较有用的方法。
|
||||
|
||||
1. 阅览一些关于这方面的视频、文章或者书籍,例如 [The Master Algorithm: How the Quest for the Ultimate Learning Machine Will Remake Our World][29],你肯定会喜欢这些[关于机器学习的互动页面][30]。
|
||||
|
||||
2. 对于“机器学习”、“人工智能”、“深度学习”、“数据科学”、“计算机视觉”和“机器人技术”这一堆新名词,你需要知道它们之前的区别。你可以阅览这些领域的专家们的演讲,例如[数据科学家 Brandon Rohrer 的这个视频][1]。
|
||||
|
||||
3. 明确你自己的学习目标,并选择合适的 [Coursera 课程][3],或者参加高校的网络公开课。例如[华盛顿大学的课程][4]就很不错。
|
||||
|
||||
4. 关注优秀的博客:例如 [KDnuggets][32] 的博客、[Mark Meloon][33] 的博客、[Brandon Rohrer][34] 的博客、[Open AI][35] 的博客,这些都值得推荐。
|
||||
|
||||
5. 如果你对在线课程有很大兴趣,后文中会有如何[正确选择 MOOC 课程][31]的指导。
|
||||
|
||||
6. 最重要的是,培养自己对这些技术的兴趣。加入一些优秀的社交论坛,专注于阅读和了解,将这些技术的背景知识和发展方向理解透彻,并积极思考在日常生活和工作中如何应用机器学习或数据科学的原理。例如建立一个简单的回归模型来预测下一次午餐的成本,又或者是从电力公司的网站上下载历史电费数据,在 Excel 中进行简单的时序分析以发现某种规律。在你对这些技术产生了浓厚兴趣之后,可以观看以下这个视频。
|
||||
|
||||
<https://www.youtube.com/embed/IpGxLWOIZy4>
|
||||
|
||||
### Python 是机器学习和人工智能方面的最佳语言吗?
|
||||
|
||||
除非你是一名专业的研究一些复杂算法纯理论证明的研究人员,否则,对于一个机器学习的入门者来说,需要熟悉至少一种高级编程语言一家相关的专业知识。因为大多数情况下都是需要考虑如何将机器学习算法应用于解决实际问题,而这需要有一定的编程能力作为基础。
|
||||
|
||||
哪一种语言是数据科学的最佳语言?这个讨论一直没有停息过。对于这方面,你可以提起精神来看一下 FreeCodeCamp 上这一篇关于[数据科学语言][6]的文章,又或者是 KDnuggets 关于 [Python 和 R][7] 之间的深入探讨。
|
||||
|
||||
目前人们普遍认为 Python 在开发、部署、维护各方面的效率都是比较高的。与 Java、C 和 C++ 这些较为传统的语言相比,Python 的语法更为简单和高级。而且 Python 拥有活跃的社区群体、广泛的开源文化、数百个专用于机器学习的优质代码库,以及来自业界巨头(包括Google、Dropbox、Airbnb 等)的强大技术支持。
|
||||
|
||||
### 基础 Python 库
|
||||
|
||||
如果你打算使用 Python 实施机器学习,你必须掌握一些 Python 包和库的使用方法。
|
||||
|
||||
#### NumPy
|
||||
|
||||
NumPy 的完整名称是 [Numerical Python][8],它是 Python 生态里高性能科学计算和数据分析都需要用到的基础包,几乎所有高级工具(例如 [Pandas][9] 和 [scikit-learn][10])都依赖于它。[TensorFlow][11] 使用了 NumPy 数组作为基础构建块以支持 Tensor 对象和深度学习的图形流。很多 NumPy 操作的速度都非常快,因为它们都是通过 C 实现的。高性能对于数据科学和现代机器学习来说是一个非常宝贵的优势。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Pandas
|
||||
|
||||
Pandas 是 Python 生态中用于进行通用数据分析的最受欢迎的库。Pandas 基于 NumPy 数组构建,在保证了可观的执行速度的同时,还提供了许多数据工程方面的功能,包括:
|
||||
|
||||
* 对多种不同数据格式的读写操作
|
||||
* 选择数据子集
|
||||
* 跨行列计算
|
||||
* 查找并补充缺失的数据
|
||||
* 将操作应用于数据中的独立组
|
||||
* 按照多种格式转换数据
|
||||
* 组合多个数据集
|
||||
* 高级时间序列功能
|
||||
* 通过 Matplotlib 和 Seaborn 进行可视化
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Matplotlib 和 Seaborn
|
||||
|
||||
数据可视化和数据分析是数据科学家的必备技能,毕竟仅凭一堆枯燥的数据是无法有效地将背后蕴含的信息向受众传达的。这两项技能对于机器学习来说同样重要,因为首先要对数据集进行一个探索性分析,才能更准确地选择合适的机器学习算法。
|
||||
|
||||
[Matplotlib][12] 是应用最广泛的 2D Python 可视化库。它包含海量的命令和接口,可以让你根据数据生成高质量的图表。要学习使用 Matplotlib,可以参考这篇详尽的[文章][13]。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[Seaborn][14] 也是一个强大的用于统计和绘图的可视化库。它在 Matplotlib 的基础上提供样式灵活的 API、用于统计和绘图的常见高级函数,还可以和 Pandas 提供的功能相结合。要学习使用 Seaborn,可以参考这篇优秀的[教程][15]。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Scikit-learn
|
||||
|
||||
Scikit-learn 是机器学习方面通用的重要 Python 包。它实现了多种[分类][16]、[回归][17]和[聚类][18]算法,包括[支持向量机][19]、[随机森林][20]、[梯度增强][21]、[k-means 算法][22]和 [DBSCAN 算法][23],可以与 Python 的数值库 NumPy 和科学计算库 [SciPy][24] 结合使用。它通过兼容的接口提供了有监督和无监督的学习算法。Scikit-learn 的强壮性让它可以稳定运行在生产环境中,同时它在易用性、代码质量、团队协作、文档和性能等各个方面都有良好的表现。可以参考这篇基于 Scikit-learn 的[机器学习入门][25],或者这篇基于 Scikit-learn 的[简单机器学习用例演示][26]。
|
||||
|
||||
本文使用 [CC BY-SA 4.0][28] 许可,在 [Heartbeat][27] 上首发。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://opensource.com/article/18/10/machine-learning-python-essential-hacks-and-tricks
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Tirthajyoti Sarkar][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972][b]
|
||||
译者:[HankChow](https://github.com/HankChow)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: https://opensource.com/users/tirthajyoti
|
||||
[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
|
||||
[1]: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tKa0zDDDaQk
|
||||
[2]: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ura_ioOcpQI
|
||||
[3]: https://www.coursera.org/learn/machine-learning
|
||||
[4]: https://www.coursera.org/specializations/machine-learning
|
||||
[5]: https://towardsdatascience.com/how-to-choose-effective-moocs-for-machine-learning-and-data-science-8681700ed83f
|
||||
[6]: https://medium.freecodecamp.org/which-languages-should-you-learn-for-data-science-e806ba55a81f
|
||||
[7]: https://www.kdnuggets.com/2017/09/python-vs-r-data-science-machine-learning.html
|
||||
[8]: http://numpy.org/
|
||||
[9]: https://pandas.pydata.org/
|
||||
[10]: http://scikit-learn.org/
|
||||
[11]: https://www.tensorflow.org/
|
||||
[12]: https://matplotlib.org/
|
||||
[13]: https://realpython.com/python-matplotlib-guide/
|
||||
[14]: https://seaborn.pydata.org/
|
||||
[15]: https://www.datacamp.com/community/tutorials/seaborn-python-tutorial
|
||||
[16]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Statistical_classification
|
||||
[17]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Regression_analysis
|
||||
[18]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cluster_analysis
|
||||
[19]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Support_vector_machine
|
||||
[20]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Random_forests
|
||||
[21]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gradient_boosting
|
||||
[22]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/K-means_clustering
|
||||
[23]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/DBSCAN
|
||||
[24]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/SciPy
|
||||
[25]: http://scikit-learn.org/stable/tutorial/basic/tutorial.html
|
||||
[26]: https://towardsdatascience.com/machine-learning-with-python-easy-and-robust-method-to-fit-nonlinear-data-19e8a1ddbd49
|
||||
[27]: https://heartbeat.fritz.ai/some-essential-hacks-and-tricks-for-machine-learning-with-python-5478bc6593f2
|
||||
[28]: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/
|
||||
[29]: https://www.goodreads.com/book/show/24612233-the-master-algorithm
|
||||
[30]: http://www.r2d3.us/visual-intro-to-machine-learning-part-1/
|
||||
[31]: https://towardsdatascience.com/how-to-choose-effective-moocs-for-machine-learning-and-data-science-8681700ed83f
|
||||
[32]: https://www.kdnuggets.com/
|
||||
[33]: http://www.markmeloon.com/
|
||||
[34]: https://brohrer.github.io/blog.html
|
||||
[35]: https://blog.openai.com/
|
||||
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user