mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-03-21 02:10:11 +08:00
translated
This commit is contained in:
parent
78b4961b8c
commit
09f2ee0599
@ -1,50 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Translating---geekpi
|
||||
|
||||
Linux FAQs with Answers--How to get the process ID (PID) of a shell script
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **Question**: I want to know the process ID (PID) of the subshell under which my shell script is running. How can I find a PID in a bash shell script?
|
||||
|
||||
When you execute a shell script, it will launch a process known as a subshell. As a child process of the main shell, a subshell executes a list of commands in a shell script as a batch (so-called "batch processing").
|
||||
|
||||
In some cases, you may want to know the process ID (PID) of the subshell where your shell script is running. This PID information can be used under different circumstances. For example, you can create a unique temporary file in /tmp by naming it with the shell script PID. In case a script needs to examine all running processes, it can exclude its own subshell from the process list.
|
||||
|
||||
In bash, the **PID of a shell script's subshell process** is stored in a special variable called '$$'. This variable is read-only, and you cannot modify it in a shell script. For example:
|
||||
|
||||
#!/bin/bash
|
||||
|
||||
echo "PID of this script: $$"
|
||||
|
||||
The above script will show the following output.
|
||||
|
||||
PID of this script: 6583
|
||||
|
||||
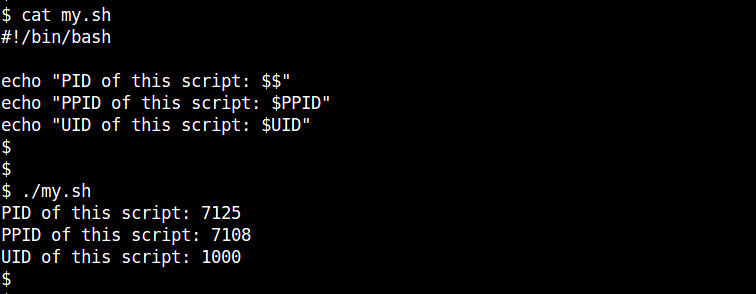
Besides $$, bash shell exports several other read-only variables. For example, PPID stores the process ID of the subshell's parent process (i.e., main shell). UID stores the user ID of the current user who is executing the script. For example:
|
||||
|
||||
#!/bin/bash
|
||||
|
||||
echo "PID of this script: $$"
|
||||
echo "PPID of this script: $PPID"
|
||||
echo "UID of this script: $UID"
|
||||
|
||||
Its output will be:
|
||||
|
||||
PID of this script: 6686
|
||||
PPID of this script: 4656
|
||||
UID of this script: 1000
|
||||
|
||||
In the above, PID will keep changing every time you invoke a script. That is because each invocation of a script will create a new subshell. On the other hand, PPID will remain the same as long as you run a script inside the same shell.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
For a complete list of built-in bash variables, refer to its man page.
|
||||
|
||||
$ man bash
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/process-id-pid-shell-script.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,48 @@
|
||||
Linux有问必答:如何在脚本中获取进程ID(PID)
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **提问**: 我想要知道运行中脚本subshell的进程id。我该如何在shell脚本中得到PID。
|
||||
|
||||
当我在执行shell脚本时,它会启动一个叫subshell的进程。作为主shell的子进程,subshell将shell脚本中的命令作为批处理运行(因此称为“批处理进程”)。
|
||||
|
||||
在某些情况下,你也许想要知道运行中的subshell的PID。这个PID信息可以在不同的情况下使用。比如,你可以使用shell脚本的PID在/tmp下创建一个唯一的临时文件。有时侯脚本需要检测所有运行的进程,它可以从进程列表中排除自身的subshell。
|
||||
|
||||
在bash中,**subshell进程的PID**存储在一个特殊的变量‘$$’中。这个变量只读,你不可以在脚本中修改它。比如:
|
||||
|
||||
#!/bin/bash
|
||||
|
||||
echo "PID of this script: $$"
|
||||
|
||||
上面的脚本会得到下面的输出:
|
||||
|
||||
PID of this script: 6583
|
||||
|
||||
除了$$, bash shell还会导出其他的只读变量。比如,PPID存储subshell父进程的ID(也就是主shell)。UID存储了执行这个脚本的当前用户ID。比如:
|
||||
|
||||
#!/bin/bash
|
||||
|
||||
echo "PID of this script: $$"
|
||||
echo "PPID of this script: $PPID"
|
||||
echo "UID of this script: $UID"
|
||||
|
||||
输出是:
|
||||
|
||||
PID of this script: 6686
|
||||
PPID of this script: 4656
|
||||
UID of this script: 1000
|
||||
|
||||
上面输出中,PID每次执行都会变化。这个因为每次运行都会创建一个新的shell。另一方面,PPID每次都会一样只要你在同一个shell中运行。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
对于所有bash内置变量列表,参考man页。
|
||||
|
||||
$ man bash
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/process-id-pid-shell-script.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user