mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2024-12-26 21:30:55 +08:00
20151204-2 选题
20151204-2 选题
This commit is contained in:
parent
b73766ccc0
commit
09a694c649
195
sources/tech/20151204 Linux or Unix--jobs Command Examples.md
Normal file
195
sources/tech/20151204 Linux or Unix--jobs Command Examples.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,195 @@
|
|||||||
|
Linux / Unix: jobs Command Examples
|
||||||
|
================================================================================
|
||||||
|
I am new Linux and Unix user. How do I show the active jobs on Linux or Unix-like systems using BASH/KSH/TCSH or POSIX based shell? How can I display status of jobs in the current session on Unix/Linux?
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Job control is nothing but the ability to stop/suspend the execution of processes (command) and continue/resume their execution as per your requirements. This is done using your operating system and shell such as bash/ksh or POSIX shell.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
You shell keeps a table of currently executing jobs and can be displayed with jobs command.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### Purpose ###
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
> Displays status of jobs in the current shell session.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### Syntax ###
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
The basic syntax is as follows:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
jobs
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
OR
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
jobs jobID
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
OR
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
jobs [options] jobID
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### Starting few jobs for demonstration purpose ###
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Before you start using jobs command, you need to start couple of jobs on your system. Type the following commands to start jobs:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## Start xeyes, calculator, and gedit text editor ###
|
||||||
|
xeyes &
|
||||||
|
gnome-calculator &
|
||||||
|
gedit fetch-stock-prices.py &
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Finally, run ping command in foreground:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
ping www.cyberciti.biz
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
To suspend ping command job hit the **Ctrl-Z** key sequence.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### jobs command examples ###
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
To display the status of jobs in the current shell, enter:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
$ jobs
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Sample outputs:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
[1] 7895 Running gpass &
|
||||||
|
[2] 7906 Running gnome-calculator &
|
||||||
|
[3]- 7910 Running gedit fetch-stock-prices.py &
|
||||||
|
[4]+ 7946 Stopped ping cyberciti.biz
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
To display the process ID or jobs for the job whose name begins with "p," enter:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
$ jobs -p %p
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
OR
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
$ jobs %p
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Sample outputs:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
[4]- Stopped ping cyberciti.biz
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
The character % introduces a job specification. In this example, you are using the string whose name begins with suspended command such as %ping.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### How do I show process IDs in addition to the normal information? ###
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Pass the -l(lowercase L) option to jobs command for more information about each job listed, run:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
$ jobs -l
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Sample outputs:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
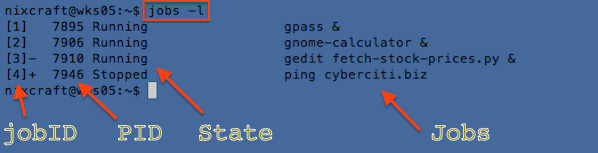
|
||||||
|
Fig.01: Displaying the status of jobs in the shell
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### How do I list only processes that have changed status since the last notification? ###
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
First, start a new job as follows:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
$ sleep 100 &
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Now, only show jobs that have stopped or exited since last notified, type:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
$ jobs -n
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Sample outputs:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
[5]- Running sleep 100 &
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### Display lists process IDs (PIDs) only ###
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Pass the -p option to jobs command to display PIDs only:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
$ jobs -p
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Sample outputs:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
7895
|
||||||
|
7906
|
||||||
|
7910
|
||||||
|
7946
|
||||||
|
7949
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### How do I display only running jobs? ###
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Pass the -r option to jobs command to display only running jobs only, type:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
$ jobs -r
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Sample outputs:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
[1] Running gpass &
|
||||||
|
[2] Running gnome-calculator &
|
||||||
|
[3]- Running gedit fetch-stock-prices.py &
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### How do I display only jobs that have stopped? ###
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Pass the -s option to jobs command to display only stopped jobs only, type:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
$ jobs -s
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Sample outputs:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
[4]+ Stopped ping cyberciti.biz
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
To resume the ping cyberciti.biz job by entering the following bg command:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
$ bg %4
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### jobs command options ###
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
From the [bash(1)][1] command man page:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
注:表格
|
||||||
|
<table border="1">
|
||||||
|
<tbody>
|
||||||
|
<tr>
|
||||||
|
<td>Option</td>
|
||||||
|
<td>Description</td>
|
||||||
|
</tr>
|
||||||
|
<tr>
|
||||||
|
<td><kbd><strong>-l</strong></kbd></td>
|
||||||
|
<td>Show process id's in addition to the normal information.</td>
|
||||||
|
</tr>
|
||||||
|
<tr>
|
||||||
|
<td><kbd><strong>-p</strong></kbd></td>
|
||||||
|
<td>Show process id's only.</td>
|
||||||
|
</tr>
|
||||||
|
<tr>
|
||||||
|
<td><kbd><strong>-n</strong></kbd></td>
|
||||||
|
<td>Show only processes that have changed status since the last notification are printed.</td>
|
||||||
|
</tr>
|
||||||
|
<tr>
|
||||||
|
<td><kbd><strong>-r</strong></kbd></td>
|
||||||
|
<td>Restrict output to running jobs only.</td>
|
||||||
|
</tr>
|
||||||
|
<tr>
|
||||||
|
<td><kbd><strong>-s</strong></kbd></td>
|
||||||
|
<td>Restrict output to stopped jobs only.</td>
|
||||||
|
</tr>
|
||||||
|
<tr>
|
||||||
|
<td><kbd><strong>-x</strong></kbd></td>
|
||||||
|
<td>COMMAND is run after all job specifications that appear in ARGS have been replaced with the process ID of that job's process group leader./td></td>
|
||||||
|
</tr>
|
||||||
|
</tbody>
|
||||||
|
</table>
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### A note about /usr/bin/jobs and shell builtin ###
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Type the following type command to find out whether jobs is part of shell, external command or both:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
$ type -a jobs
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Sample outputs:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
jobs is a shell builtin
|
||||||
|
jobs is /usr/bin/jobs
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
In almost all cases you need to use the jobs command that is implemented as a BASH/KSH/POSIX shell built-in. The /usr/bin/jobs command can not be used in the current shell. The /usr/bin/jobs command operates in a different environment and does not share the parent bash/ksh's shells understanding of jobs.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
via:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
作者:Vivek Gite
|
||||||
|
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||||
|
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
[1]:http://www.manpager.com/linux/man1/bash.1.html
|
||||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user