mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-01-25 23:11:02 +08:00
merge with latest repo
This commit is contained in:
commit
0936663037
@ -0,0 +1,136 @@
|
||||
又一波你可能不知道的 Linux 命令行网络监控工具
|
||||
===============================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
对任何规模的业务来说,网络监控工具都是一个重要的功能。网络监控的目标可能千差万别。比如,监控活动的目标可以是保证长期的网络服务、安全保护、对性能进行排查、网络使用统计等。由于它的目标不同,网络监控器使用很多不同的方式来完成任务。比如对包层面的嗅探,对数据流层面的统计数据,向网络中注入探测的流量,分析服务器日志等。
|
||||
|
||||
尽管有许多专用的网络监控系统可以365天24小时监控,但您依旧可以在特定的情况下使用命令行式的网络监控器,某些命令行式的网络监控器在某方面很有用。如果您是系统管理员,那您就应该有亲身使用一些知名的命令行式网络监控器的经历。这里有一份**Linux上流行且实用的网络监控器**列表。
|
||||
|
||||
### 包层面的嗅探器 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在这个类别下,监控工具在链路上捕捉独立的包,分析它们的内容,展示解码后的内容或者包层面的统计数据。这些工具在最底层对网络进行监控、管理,同样的也能进行最细粒度的监控,其代价是影响网络I/O和分析的过程。
|
||||
|
||||
1. **dhcpdump**:一个命令行式的DHCP流量嗅探工具,捕捉DHCP的请求/回复流量,并以用户友好的方式显示解码的DHCP协议消息。这是一款排查DHCP相关故障的实用工具。
|
||||
|
||||
2. **[dsniff][1]**:一个基于命令行的嗅探、伪造和劫持的工具合集,被设计用于网络审查和渗透测试。它可以嗅探多种信息,比如密码、NSF流量(LCTT 译注:此处疑为 NFS 流量)、email消息、网络地址等。
|
||||
|
||||
3. **[httpry][2]**:一个HTTP报文嗅探器,用于捕获、解码HTTP请求和回复报文,并以用户友好的方式显示这些信息。(LCTT 译注:[延伸阅读](https://linux.cn/article-4148-1.html)。 )
|
||||
|
||||
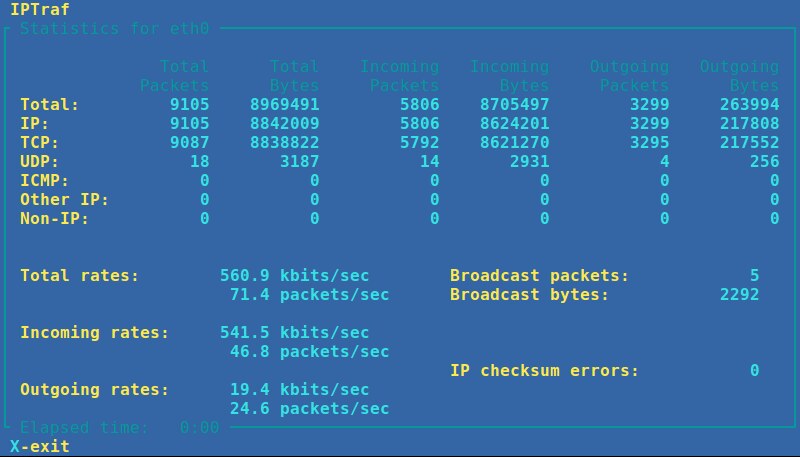
4. **IPTraf**:基于命令行的网络统计数据查看器。它实时显示包层面、连接层面、接口层面、协议层面的报文/字节数。抓包过程由协议过滤器控制,且操作过程全部是菜单驱动的。(LCTT 译注:[延伸阅读](https://linux.cn/article-5430-1.html)。)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
5. **[mysql-sniffer][3]**:一个用于抓取、解码MySQL请求相关的数据包的工具。它以可读的方式显示最频繁或全部的请求。
|
||||
|
||||
6. **[ngrep][4]**:在网络报文中执行grep。它能实时抓取报文,并用正则表达式或十六进制表达式的方式匹配(过滤)报文。它是一个可以对异常流量进行检测、存储或者对实时流中特定模式报文进行抓取的实用工具。
|
||||
|
||||
7. **[p0f][5]**:一个被动的基于包嗅探的指纹采集工具,可以可靠地识别操作系统、NAT或者代理设置、网络链路类型以及许多其它与活动的TCP连接相关的属性。
|
||||
|
||||
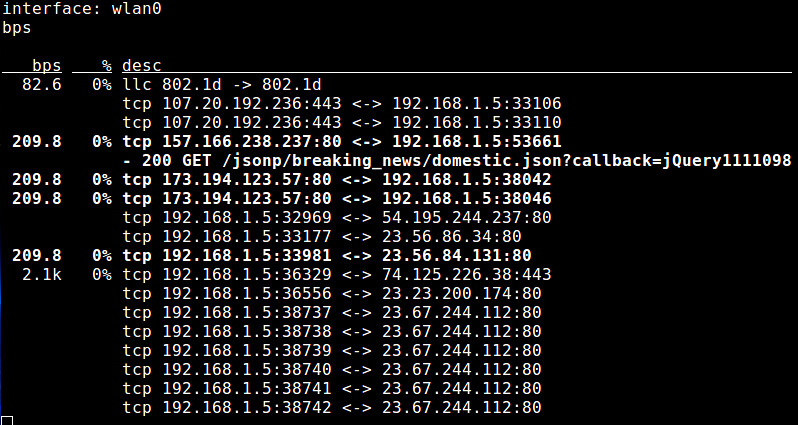
8. **pktstat**:一个命令行式的工具,通过实时分析报文,显示连接带宽使用情况以及相关的协议(例如,HTTP GET/POST、FTP、X11)等描述信息。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
9. **Snort**:一个入侵检测和预防工具,通过规则驱动的协议分析和内容匹配,来检测/预防活跃流量中各种各样的后门、僵尸网络、网络钓鱼、间谍软件攻击。
|
||||
|
||||
10. **tcpdump**:一个命令行的嗅探工具,可以基于过滤表达式抓取网络中的报文,分析报文,并且在包层面输出报文内容以便于包层面的分析。他在许多网络相关的错误排查、网络程序debug、或[安全][6]监测方面应用广泛。
|
||||
|
||||
11. **tshark**:一个与Wireshark窗口程序一起使用的命令行式的嗅探工具。它能捕捉、解码网络上的实时报文,并能以用户友好的方式显示其内容。
|
||||
|
||||
### 流/进程/接口层面的监控 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在这个分类中,网络监控器通过把流量按照流、相关进程或接口分类,收集每个流、每个进程、每个接口的统计数据。其信息的来源可以是libpcap抓包库或者sysfs内核虚拟文件系统。这些工具的监控成本很低,但是缺乏包层面的检视能力。
|
||||
|
||||
12. **bmon**:一个基于命令行的带宽监测工具,可以显示各种接口相关的信息,不但包括接收/发送的总量/平均值统计数据,而且拥有历史带宽使用视图。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
13. **[iftop][7]**:一个带宽使用监测工具,可以实时显示某个网络连接的带宽使用情况。它对所有带宽使用情况排序并通过ncurses的接口来进行可视化。他可以方便的监控哪个连接消耗了最多的带宽。(LCTT 译注:[延伸阅读](https://linux.cn/article-1843-1.html)。)
|
||||
|
||||
14. **nethogs**:一个基于ncurses显示的进程监控工具,提供进程相关的实时的上行/下行带宽使用信息。它对检测占用大量带宽的进程很有用。(LCTT 译注:[延伸阅读](https://linux.cn/article-2808-1.html)。)
|
||||
|
||||
15. **netstat**:一个显示许多TCP/UDP的网络堆栈的统计信息的工具。诸如打开的TCP/UDP连接书、网络接口发送/接收、路由表、协议/套接字的统计信息和属性。当您诊断与网络堆栈相关的性能、资源使用时它很有用。
|
||||
|
||||
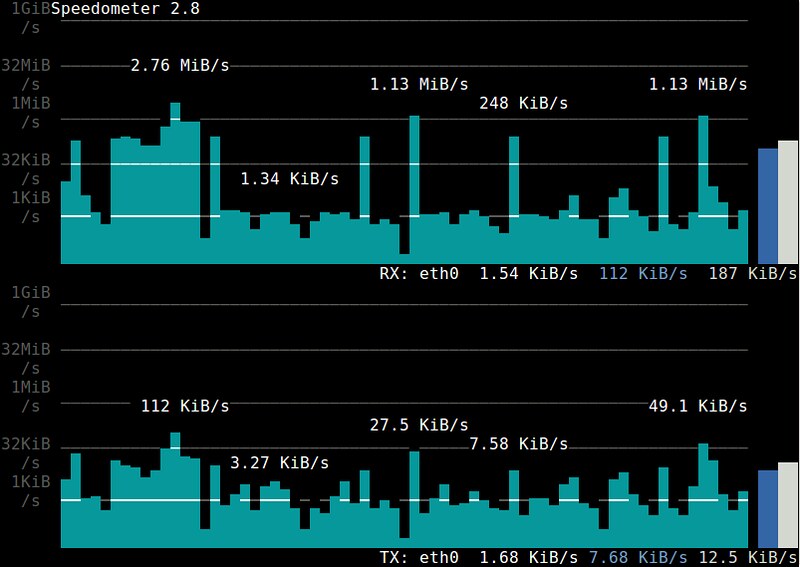
16. **[speedometer][8]**:一个可视化某个接口发送/接收的带宽使用的历史趋势,并且基于ncurses的条状图进行显示的终端工具。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
17. **[sysdig][9]**:一个可以通过统一的界面对各个Linux子系统进行系统级综合性调试的工具。它的网络监控模块可以监控在线或离线、许多进程/主机相关的网络统计数据,例如带宽、连接/请求数等。(LCTT 译注:[延伸阅读](https://linux.cn/article-4341-1.html)。)
|
||||
|
||||
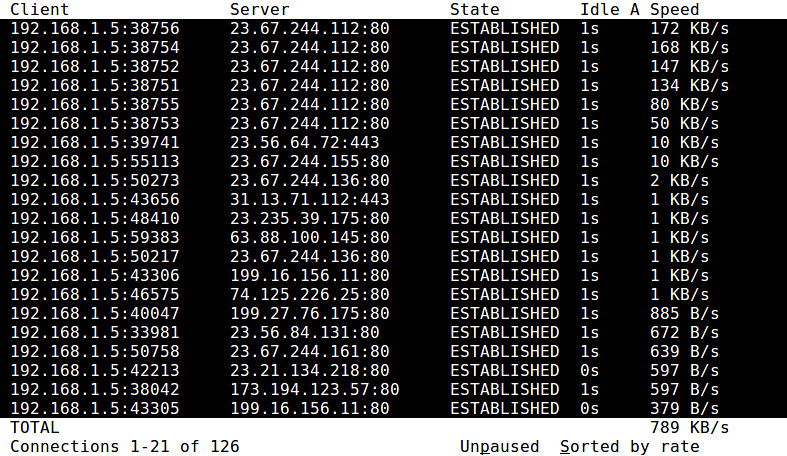
18. **tcptrack**:一个TCP连接监控工具,可以显示活动的TCP连接,包括源/目的IP地址/端口、TCP状态、带宽使用等。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
19. **vnStat**:一个存储并显示每个接口的历史接收/发送带宽视图(例如,当前、每日、每月)的流量监控器。作为一个后台守护进程,它收集并存储统计数据,包括接口带宽使用率和传输字节总数。(LCTT 译注:[延伸阅读](https://linux.cn/article-5256-1.html)。)
|
||||
|
||||
### 主动网络监控器 ###
|
||||
|
||||
不同于前面提到的被动的监听工具,这个类别的工具们在监听时会主动的“注入”探测内容到网络中,并且会收集相应的反应。监听目标包括路由路径、可供使用的带宽、丢包率、延时、抖动(jitter)、系统设置或者缺陷等。
|
||||
|
||||
20. **[dnsyo][10]**:一个DNS检测工具,能够管理跨越多达1500个不同网络的开放解析器的DNS查询。它在您检查DNS传播或排查DNS设置的时候很有用。
|
||||
|
||||
21. **[iperf][11]**:一个TCP/UDP带宽测量工具,能够测量两个端点间最大可用带宽。它通过在两个主机间单向或双向的输出TCP/UDP探测流量来测量可用的带宽。它在监测网络容量、调谐网络协议栈参数时很有用。一个叫做[netperf][12]的变种拥有更多的功能及更好的统计数据。
|
||||
|
||||
22. **[netcat][13]/socat**:通用的网络调试工具,可以对TCP/UDP套接字进行读、写或监听。它通常和其他的程序或脚本结合起来在后端对网络传输或端口进行监听。(LCTT 译注:[延伸阅读](https://linux.cn/article-1171-1.html)。)
|
||||
|
||||
23. **nmap**:一个命令行的端口扫描和网络发现工具。它依赖于若干基于TCP/UDP的扫描技术来查找开放的端口、活动的主机或者在本地网络存在的操作系统。它在你审查本地主机漏洞或者建立维护所用的主机映射时很有用。[zmap][14]是一个类似的替代品,是一个用于互联网范围的扫描工具。(LCTT 译注:[延伸阅读](https://linux.cn/article-2561-1.html)。)
|
||||
|
||||
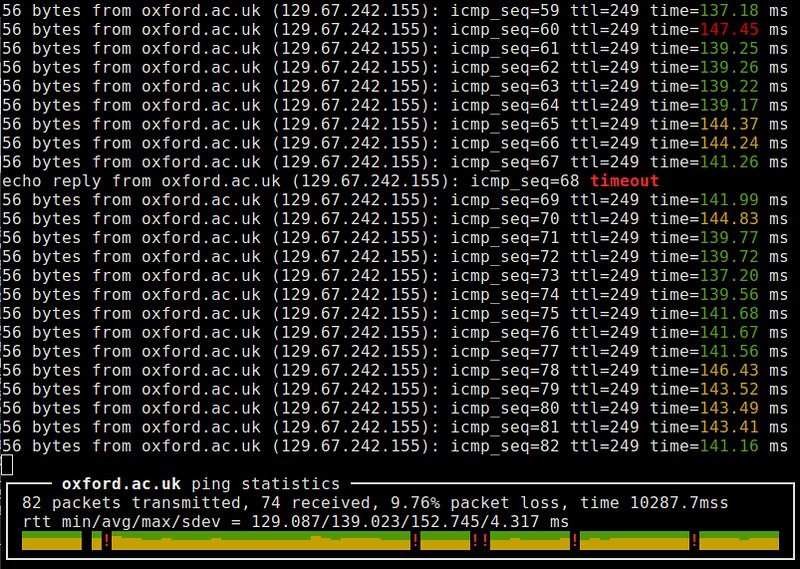
24. ping:一个常用的网络测试工具。通过交换ICMP的echo和reply报文来实现其功能。它在测量路由的RTT、丢包率以及检测远端系统防火墙规则时很有用。ping的变种有更漂亮的界面(例如,[noping][15])、多协议支持(例如,[hping][16])或者并行探测能力(例如,[fping][17])。(LCTT 译注:[延伸阅读](https://linux.cn/article-2303-1.html)。)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
25. **[sprobe][18]**:一个启发式推断本地主机和任意远端IP地址之间的网络带宽瓶颈的命令行工具。它使用TCP三次握手机制来评估带宽的瓶颈。它在检测大范围网络性能和路由相关的问题时很有用。
|
||||
|
||||
26. **traceroute**:一个能发现从本地到远端主机的第三层路由/转发路径的网络发现工具。它发送限制了TTL的探测报文,收集中间路由的ICMP反馈信息。它在排查低速网络连接或者路由相关的问题时很有用。traceroute的变种有更好的RTT统计功能(例如,[mtr][19])。
|
||||
|
||||
### 应用日志解析器 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在这个类别下的网络监测器把特定的服务器应用程序作为目标(例如,web服务器或者数据库服务器)。由服务器程序产生或消耗的网络流量通过它的日志被分析和监测。不像前面提到的网络层的监控器,这个类别的工具能够在应用层面分析和监控网络流量。
|
||||
|
||||
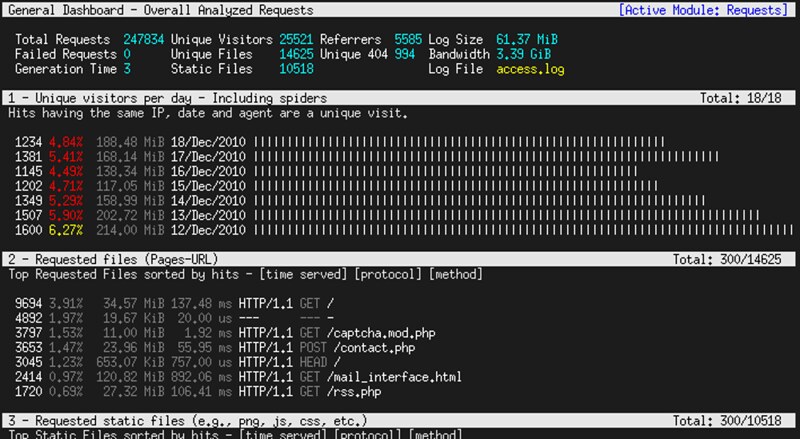
27. **[GoAccess][20]**:一个针对Apache和Nginx服务器流量的交互式查看器。基于对获取到的日志的分析,它能展示包括日访问量、最多请求、客户端操作系统、客户端位置、客户端浏览器等在内的多个实时的统计信息,并以滚动方式显示。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
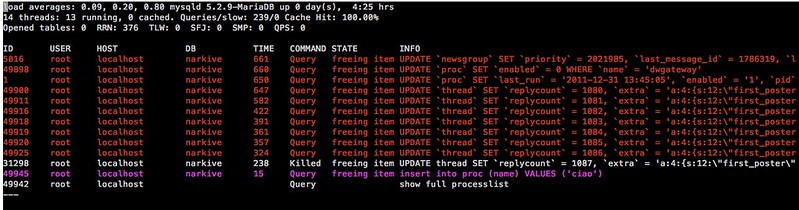
28. **[mtop][21]**:一个面向MySQL/MariaDB服务器的命令行监控器,它可以将成本最大的查询和当前数据库服务器负载以可视化的方式显示出来。它在您优化MySQL服务器性能、调谐服务器参数时很有用。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
29. **[ngxtop][22]**:一个面向Nginx和Apache服务器的流量监测工具,能够以类似top指令的方式可视化的显示Web服务器的流量。它解析web服务器的查询日志文件并收集某个目的地或请求的流量统计信息。
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在这篇文章中,我展示了许多命令行式监测工具,从最底层的包层面的监控器到最高层应用程序层面的网络监控器。了解那个工具的作用是一回事,选择哪个工具使用又是另外一回事。单一的一个工具不能作为您每天使用的通用的解决方案。一个好的系统管理员应该能决定哪个工具更适合当前的环境。希望这个列表对此有所帮助。
|
||||
|
||||
欢迎您通过回复来改进这个列表的内容!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/useful-command-line-network-monitors-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
|
||||
译者:[wwy-hust](https://github.com/wwy-hust)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/nanni
|
||||
[1]:http://www.monkey.org/~dugsong/dsniff/
|
||||
[2]:http://xmodulo.com/monitor-http-traffic-command-line-linux.html
|
||||
[3]:https://github.com/zorkian/mysql-sniffer
|
||||
[4]:http://ngrep.sourceforge.net/
|
||||
[5]:http://lcamtuf.coredump.cx/p0f3/
|
||||
[6]:http://xmodulo.com/recommend/firewallbook
|
||||
[7]:http://xmodulo.com/how-to-install-iftop-on-linux.html
|
||||
[8]:https://excess.org/speedometer/
|
||||
[9]:http://xmodulo.com/monitor-troubleshoot-linux-server-sysdig.html
|
||||
[10]:http://xmodulo.com/check-dns-propagation-linux.html
|
||||
[11]:https://iperf.fr/
|
||||
[12]:http://www.netperf.org/netperf/
|
||||
[13]:http://xmodulo.com/useful-netcat-examples-linux.html
|
||||
[14]:https://zmap.io/
|
||||
[15]:http://noping.cc/
|
||||
[16]:http://www.hping.org/
|
||||
[17]:http://fping.org/
|
||||
[18]:http://sprobe.cs.washington.edu/
|
||||
[19]:http://xmodulo.com/better-alternatives-basic-command-line-utilities.html#mtr_link
|
||||
[20]:http://goaccess.io/
|
||||
[21]:http://mtop.sourceforge.net/
|
||||
[22]:http://xmodulo.com/monitor-nginx-web-server-command-line-real-time.html
|
||||
73
published/20150123 How to make a file immutable on Linux.md
Normal file
73
published/20150123 How to make a file immutable on Linux.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,73 @@
|
||||
如何在Linux下创建一个不可变更的文件
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
假如你想对Linux中的一些重要文件做写保护,这样它们就不能被删除或者被篡改成之前的版本或者其他东西,或者在其他情况下,你可能想避免某些配置文件被软件自动修改。使用`chown`和`chmod`命令修改文件的归属关系或者权限位是处理这种情况的一个解决方法,但这并不完美,因为这样无法避免有root权限的操作。这时`chattr`就派上用场了。
|
||||
|
||||
`chattr`是一个可以设置或取消文件的标志位的Linux命令,它和标准的文件权限(读、写、执行)是分离的。与此相关的另一个命令是`lsattr`,它可以显示文件的哪些标志位被设置上了。最初只有EXT文件系统(EXT2/3/4)支持`chattr`和`lsattr`所管理的标志位,但现在很多其他的原生的Linux文件系统都支持了,比如XFS、Btrfs、ReiserFS等等。
|
||||
|
||||
在这个教程中,我会示范如果使用`chattr`来让Linux中的文件不可变更。
|
||||
|
||||
`chattr`和`lsattr`命令是e2fsprogs包的一部分,它在所有现代Linux发行版都预装了。
|
||||
|
||||
下面是`chattr`的基本语法。
|
||||
|
||||
$ chattr [-RVf] [操作符][标志位] 文件...
|
||||
|
||||
其中操作符可以是“+”(把选定的标志位添加到标志位列表)、“-”(从标志位列表中移除选定的标志位)、或者“=”(强制使用选定的标志位)。
|
||||
|
||||
下面是一些可用的标志位。
|
||||
|
||||
- **a**: 只能以追加模式打开。
|
||||
- **A**: 不能更新atime(文件访问时间)。
|
||||
- **c**: 当被写入磁盘时被自动压缩。
|
||||
- **C**: 关掉“写时复制”。
|
||||
- **i**: 不可变更。
|
||||
- **s**: 通过自动归零来安全删除。(LCTT 译注:一般情况文件被删后内容不会被修改,改标志位会使得文件被删后原有内容被“0”取代)
|
||||
|
||||
### “不可变更”标志位 ###
|
||||
|
||||
为了让一个文件不可变更,你需要按照如下方法为这个文件添加“不可变更”标志位。例如,对/etc/passwd文件做写保护:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo chattr +i /etc/passwd
|
||||
|
||||
注意设置或取消一个文件的“不可变更”标志位是需要root用户权限的。现在检查该文件“不可变更”标志位是否被添加上了。
|
||||
|
||||
$ lsattr /etc/passwd
|
||||
|
||||
一旦文件被设置为不可变更,任何用户都将无法修改该文件。即使是root用户也不可以修改、删除、覆盖、移动或者重命名这个文件。如果你想再次修改这个文件,需要先把“不可变更”标志位取消了。
|
||||
|
||||
用如下命令取消“不可变更”标志位:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo chattr -i /etc/passwd
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
如果你想让一个目录(比如/etc)连同它下边的所有内容不可变更,使用“-R”选项:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo chattr -R +i /etc
|
||||
|
||||
### “只可追加”标志位 ###
|
||||
|
||||
另一个有用的的标志位是“只可追加”,它只允许文件内容被追加的方式修改。你不能覆盖或者删除一个设置了“只可追加”标志位的文件。这个标志位在你想避免日志文件被意外清理掉的情况很有用。
|
||||
|
||||
和“不可变更”标志位类似,你可以使用如下命令让文件变成“只可追加”模式:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo chattr +a /var/log/syslog
|
||||
|
||||
注意当你复制一个“不可变更”或者“只可追加”的文件到其他地方后,新文件不会保留这些标志位!
|
||||
|
||||
### 结论 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在这个教程中,我展示了如何使用`chattr`和`lsattr`命令来管理额外的文件标志位,来避免文件被篡改(意外或者其他情况)的方法。注意你不能将`chattr`作为一个安全措施,因为“不可变更”标志位可以很容易被取消掉。解决这个问题的一个可能的方式是限制`chattr`命令自身的可用性,或者去掉CAP_LINUX_IMMUTABLE内核权能标志。关于`chattr`以及可用的标志位的更多细节,请参考它的man手册。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/make-file-immutable-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
|
||||
译者:[goreliu](https://github.com/goreliu)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/nanni
|
||||
@ -1,10 +1,10 @@
|
||||
局域网中实现Ubuntu和Windows共享文件夹
|
||||
如何在局域网中将Ubuntu文件夹共享给Windows
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
本文全面详细地向你描述了**在Ubuntu中如何实现局域网内的文件夹共享**。
|
||||
|
||||
你的家中是不是有多台电脑?当你需要从一台Ubuntu电脑向另一台电脑传输数据时,是不是必须用到U盘或SD卡?你是否也觉得这个方法很烦人?我想肯定是。本文的目的就是使你在局域网内快速方便地传输文件、文档和其它较大的数据,来节省你的宝贵时间。只需一次设置,然后轻点鼠标,你就可以自由地**在Ubuntu和Windows之间共享文件**,当然这对其它Linux系统同样使用。不要担心这很容易操作,不会花费太多时间。
|
||||
你的家中是不是有多台电脑?当你需要从一台Ubuntu电脑向另一台电脑传输数据时,是不是必须用到U盘或SD卡?你是否也觉得这个方法很烦人?我想肯定是。本文的目的就是使你在局域网内快速方便地传输文件、文档和其它较大的数据,以节省你的宝贵时间。只需一次设置,然后轻点鼠标,你就可以自由地**在Ubuntu和Windows之间共享文件**,当然这对其它Linux系统同样使用。不要担心,这很容易操作,不会花费太多时间。
|
||||
|
||||
除此之外,尽管本文是在Ubuntu上进行实践,但这个教程在其它Linux系统上同样有用。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -21,11 +21,11 @@
|
||||
|
||||
#### 步骤一:####
|
||||
|
||||
为了在Ubuntu上实现局域网共享文件夹,右键点击打算共享的文件夹,并选择“Local Network Share”:
|
||||
为了在Ubuntu上实现局域网共享文件夹,右键点击打算共享的文件夹,并选择“Local Network Share(本地网络共享)”:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**可能有用的故障方案**:如果在右键菜单中看不到“Local Network Share”的选项,那就新建一个终端,使用下面的命令去安装nautlius-share:
|
||||
**可能有用的故障解决方案**:如果在右键菜单中看不到“Local Network Share”的选项,那就新建一个终端,使用下面的命令去安装nautlius-share插件:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install nautilus-share
|
||||
|
||||
@ -35,17 +35,17 @@
|
||||
|
||||
#### 步骤二:####
|
||||
|
||||
一旦点击“Local Network Share”,就会出现共享文件夹的选项。只需选中“Share this folder”这一项:
|
||||
一旦点击“Local Network Share”,就会出现共享文件夹的选项。只需选中“Share this folder(共享该文件夹)”这一项:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
可能的故障方案:如果提示共享服务还未安装,就像下图所示,那就点击安装服务,按照提示操作。
|
||||
**可能的故障解决方案**:如果提示共享服务还未安装,就像下图所示,那就点击安装服务,按照提示操作。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### 步骤三:####
|
||||
|
||||
一旦选中“Share this folder”的选项,就会看到按钮“Create Share”变成可用了。你也可以允许其他用户在共享文件夹中编辑文件。选项“Guest access”也是如此。
|
||||
当选中“Share this folder”的选项,就会看到按钮“Create Share(创建共享)”变得可以点击了。你也可以“Allow others to create and delete fies in this folder(允许其他用户在共享文件夹中编辑文件)”。选项“Guest access(允许访客访问)”也是如此。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@ -55,13 +55,13 @@
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. 在Ubuntu上使用密码保护实现局域网共享文件夹###
|
||||
|
||||
为了达到目的,首先需要配置Samba服务器。事实上,在这篇教程的前一部分我们已经用到了Samba,只是我们没有刻意强调。在介绍如何在Ubuntu上搭建Samba服务器实现局域网共享的方法之前,先快速预览一下[Samba][1]到底是什么。
|
||||
为了达到这个目的,首先需要配置Samba服务器。事实上,在这篇教程的前一部分我们已经用到了Samba,只是我们没有刻意强调。在介绍如何在Ubuntu上搭建Samba服务器实现局域网共享的方法之前,先快速预览一下[Samba][1]到底是什么。
|
||||
|
||||
#### Samba是什么? ####
|
||||
|
||||
Samba是一个允许用户通过网络共享文件、文档和打印机的软件包,无论是在Linux、Windows,还是Mac上。它适用于所有的主流平台,可以在所有支持系统上流畅运行。下面是维基百科的介绍:
|
||||
|
||||
> Samba是一款重新实现SMB/CIFS网络协议的自由软件,最初由安德鲁·垂鸠开发。在第三版中,Smaba不仅支持通过不同的Windows客户端访问及分享SMB的文件夹及打印机,还可以集成到Windows Server域名,作为主要域名控制站(PDC)或者域名成员。它也可以作为Active Directory域名的一部分。
|
||||
> Samba是一款重新实现SMB/CIFS网络协议的自由软件,最初由安德鲁·垂鸠开发。在第三版中,Smaba不仅支持通过不同的Windows客户端访问及分享SMB的文件夹及打印机,还可以集成到Windows Server域,作为主域控制器(PDC)或者域成员。它也可以作为活动目录域的一部分。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在Ubuntu上安装Samba服务器 ####
|
||||
|
||||
@ -77,7 +77,7 @@ Samba是一个允许用户通过网络共享文件、文档和打印机的软件
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在Ubuntu上配置Samba服务器 ####
|
||||
|
||||
从dash打开Samba配置工具:
|
||||
从dash中打开Samba配置工具:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@ -86,7 +86,7 @@ Samba是一个允许用户通过网络共享文件、文档和打印机的软件
|
||||
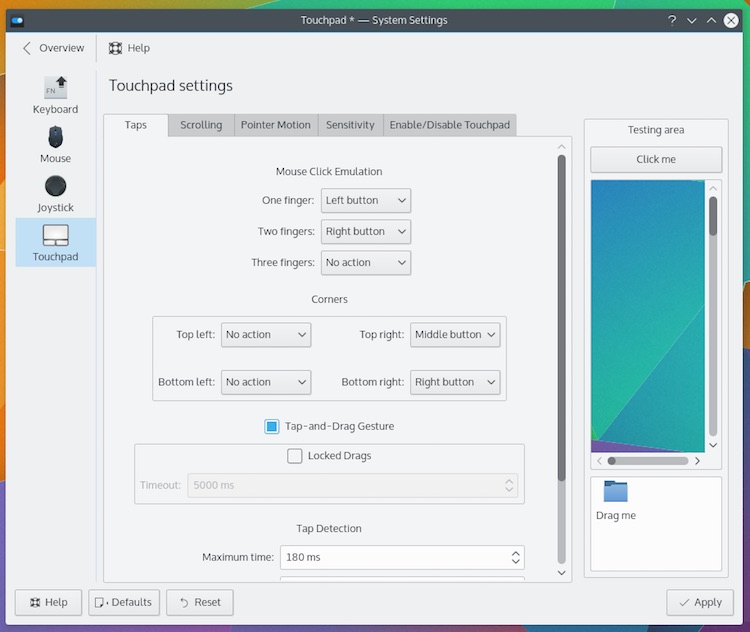
在Server Setting中可以看到两个选项卡,‘Basic’和‘Security’。在Basic选项卡下的选项含义如下:
|
||||
|
||||
- 工作组 - 用户要连接的电脑所在工作组的名字。比如,如果你想连接到一台Windows电脑,你就要输入Windows电脑的工作组名字。在Windows的Samba服务器设置中,已经默认设置好统一的工作组名字。但如果你有不同的工作组名字,就在这个字段中输入自定义的工作组名字。(在Windows 7中获取工作组名字,右击计算机图标,进到属性,就能看到Windows工作组名字。)
|
||||
- 描述 - 其他用户看到的你的电脑名字。不要使用空格或计算机不支持(望更正!)的字符。
|
||||
- 描述 - 其他用户看到的你的电脑名字。不要使用空格或不适用于网络的字符。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@ -101,14 +101,14 @@ Samba是一个允许用户通过网络共享文件、文档和打印机的软件
|
||||
现在我们需要为网络共享文件创建一个系统用户。下面是非常简单的步骤:
|
||||
|
||||
- 在Systems Settings下点击**User Accounts**。
|
||||
- 点击**unlock**使其可用,以及+(**plus**)图标。
|
||||
- 点击+(plus)图标,创建一个新的系统用户。
|
||||
- 点击**unlock**使其可用,以及+(**加号**)图标。
|
||||
- 点击+(加号)图标,创建一个新的系统用户。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
如上图所示,需要输入‘Full name’。当你输入‘Full name’时,Username会自动填充为Full name。因为创建这个用户是为了共享文件,所以还要指定Account Type为‘**Standard**’。
|
||||
|
||||
完成上述步骤,点击添加,你就创建好一个系统用户。这个用户还没有被激活,所以需要为其设置密码来激活。确保Users accounts界面已经解锁。点击Account disabled。输入一个新密码,然后确认密码,点击Change。
|
||||
完成上述步骤,点击添加,你就创建好一个系统用户。这个用户还没有被激活,所以需要为其设置密码来激活。确保Users accounts界面已经解锁。点击尚不可用的账户,输入一个新密码,然后确认密码,点击Change。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@ -132,7 +132,7 @@ Samba是一个允许用户通过网络共享文件、文档和打印机的软件
|
||||
|
||||
#### 通过网络共享文件夹或文件 ####
|
||||
|
||||
在图形用户界面下通过Samba共享文件是很简单的。点击Plus图标,会看到如图所示的对话框:
|
||||
在图形用户界面下通过Samba共享文件是很简单的。点击加号图标,会看到如图所示的对话框:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@ -157,9 +157,8 @@ Samba是一个允许用户通过网络共享文件、文档和打印机的软件
|
||||
|
||||
全部搞定!我们也可以使用终端进行网络文件共享,但这样没有本文介绍的方法这么容易。如果你确实想知道命令行操作,我会再写一篇关于在Linux上使用命令行实现网络文件共享的文章。
|
||||
|
||||
所以,你是怎么找到这篇教程的呢?我希望看了这篇教程你可以**很容易地在Ubuntu和Windows之间共享文件**。如果你有任何问题或建议,请再评论里说出来。
|
||||
所以,你是怎么找到这篇教程的呢?我希望看了这篇教程你可以**很容易地在Ubuntu和Windows之间共享文件**。如果你有任何问题或建议,请在评论里说出来。
|
||||
|
||||
这篇教程是在Kalc的请求下写出的。如果你也想,你可以[请求你自己的教程][2]。我们很乐意帮助你和面临同样问题的读者解决问题。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
@ -167,7 +166,7 @@ via: http://itsfoss.com/share-folders-local-network-ubuntu-windows/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Mohd Sohail][a]
|
||||
译者:[KayGuoWhu](https://github.com/KayGuoWhu)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,117 +0,0 @@
|
||||
translating by wwy-hust
|
||||
|
||||
Guake 0.7.0 Released – A Drop-Down Terminal for Gnome Desktops
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Linux commandline is the best and most powerful thing that fascinates a new user and provides extreme power to experienced users and geeks. For those who work on Server and Production, they are already aware of this fact. It would be interesting to know that Linux console was one of those first features of the kernel that was written by Linus Torvalds way back in the year 1991.
|
||||
|
||||
Terminal is a powerful tool that is very reliable as it does not have any movable part. Terminal serves as an intermediate between console and GUI environment. Terminal themselves are GUI application that run on top of a desktop environment. There are a lot of terminal application some of which are Desktop Environment specific and rest are universal. Terminator, Konsole, Gnome-Terminal, Terminology, XFCE terminal, xterm are a few terminal emulators to name.
|
||||
|
||||
You may get a list of most widely used Terminal Emulator follow the below link.
|
||||
|
||||
- [20 Useful Terminals for Linux][1]
|
||||
|
||||
Last day while surfing web, I came across a terminal namely ‘guake‘ which is a terminal for gnome. Though this is not the first time I have learned about Guake. I’d known this application nearly one year ago but somehow I could not write on this and later it was out of my mind until I heard it again. So finally the article is here. We will be taking you to Guake features, installation on Debian, Ubuntu and Fedora followed by quick testing.
|
||||
|
||||
#### What is Guake? ####
|
||||
|
||||
Guake is a Drop Down Terminal for Gnome Environment. Written from scratch mostly in Python and a little in C this application is released under GPLv2+ and is available for Linux and alike systems. Guake is inspired by a console in computer game Quake which slides down from the top by pressing a specially Key (Default is F12) and then slides-up when the same key is pressed.
|
||||
|
||||
Important to mention that Guake is not the first of this kind. Yakuake which stands for Yet Another Kuake, a terminal emulator for KDE Desktop Environment and Tilda which is a GTK+ terminal Emulator are also inspired by the same slide up/down console of computer game Quake.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Features of Guake ####
|
||||
|
||||
- Lightweight
|
||||
- Simple Easy and Elegant
|
||||
- Functional
|
||||
- Powerful
|
||||
- Good Looking
|
||||
- Smooth integration of terminal into GUI
|
||||
- Appears when you call and disappear once you are done by pressing a predefined hot key
|
||||
- Support for hotkeys, tabs, background transparency makes it a brilliant application, must for every Gnome User.
|
||||
- Extremely configurable
|
||||
- Plenty of color palette included, fixed and recognized
|
||||
- Shortcut for transparency level
|
||||
- Run a script when Guake starts via Guake Preferences.
|
||||
- Able to run on more than one monitor
|
||||
|
||||
Guake 0.7.0 was released recently, which brings numerous fixes as well as some new features as discussed above. For complete Guake 0.7.0 changelog and source tarball packages can be found [Here][2].
|
||||
|
||||
### Installing Guake Terminal in Linux ###
|
||||
|
||||
If you are interested in compiling Guake from source you may download the source from the link above, build it yourself before installing.
|
||||
|
||||
However Guake is available to be installed on most of the distributions from repository or by adding an additional repository. Here, we will be installing Guake on Debian, Ubuntu, Linux Mint and Fedora systems.
|
||||
|
||||
First get the latest software package list from the repository and then install Guake from the default repository as shown below.
|
||||
|
||||
---------------- On Debian, Ubuntu and Linux Mint ----------------
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get update
|
||||
$ apt-get install guake
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
---------------- On Fedora 19 Onwards ----------------
|
||||
# yum update
|
||||
# yum install guake
|
||||
|
||||
After installation, start the Guake from another terminal as:
|
||||
|
||||
$ guake
|
||||
|
||||
After starting it, use F12 (Default) to roll down and roll up the terminal on your Gnome Desktop.
|
||||
|
||||
Seems very beautiful specially the transparent background. Roll down… Roll up… Roll down… Roll up…. run command. Open another tab run command… Roll up… Roll down…
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Guake Terminal in Action
|
||||
|
||||
If your wallpaper or working windows color don’t match you may like to change your wallpaper or reduce the transparency of the Guake terminal color.
|
||||
|
||||
Next is to look into Guake Properties to edit settings as per requirements. Run Guake Preferences either by running it from Application Menu or by running the below command.
|
||||
|
||||
$ guake --preferences
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Guake Terminal Properties
|
||||
|
||||
Scrolling Properties..
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Guake Scrolling Settings
|
||||
|
||||
Appearance Properties – Here you can modify text and background color as well as tune transparency.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Appearance Properties
|
||||
|
||||
Keyboard Shortcuts – Here you may edit and Modify Toggle key for Guage Visibility (default is F12).
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Keyboard Shortcuts
|
||||
|
||||
Compatibility Setting – Perhaps you won’t need to edit it.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Compatibility Setting
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
This Project is not too young and not too old, hence has reached certain level of maturity and is quiet solid and works out of the box. For someone like me who need to switch between GUI and Console very often Guake is a boon. I don’t need to manage an extra window, open and close frequently, use tab among a huge pool of opened applications to find terminal or switch to different workspace to manage terminal now all I need is F12.
|
||||
|
||||
I think this is a must tool for any Linux user who makes use of GUI and Console at the same time, equally. I am going to recommend it to anyone who want to work on a system where interaction between GUI and Console is smooth and hassle free.
|
||||
|
||||
That’s all for now. Let us know if there is any problem in installing and running. We will be here to help you. Also tell us your’s experience about Guake. Provide us with your valuable feedback in the comments below. Like and share us and help us get spread.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/install-guake-terminal-ubuntu-mint-fedora/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Avishek Kumar][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/avishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/linux-terminal-emulators/
|
||||
[2]:https://github.com/Guake/guake/releases/tag/0.7.0
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
||||
[translating by KayGuoWhu]
|
||||
Open Source History: Why Did Linux Succeed?
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> Why did Linux, the Unix-like operating system kernel started by Linus Torvalds in 1991 that became central to the open source world, succeed where so many similar projects, including GNU HURD and the BSDs, fail?
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,72 +0,0 @@
|
||||
How to make a file immutable on Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Suppose you want to write-protect some important files on Linux, so that they cannot be deleted or tampered with by accident or otherwise. In other cases, you may want to prevent certain configuration files from being overwritten automatically by software. While changing their ownership or permission bits on the files by using chown or chmod is one way to deal with this situation, this is not a perfect solution as it cannot prevent any action done with root privilege. That is when chattr comes in handy.
|
||||
|
||||
chattr is a Linux command which allows one to set or unset attributes on a file, which are separate from the standard (read, write, execute) file permission. A related command is lsattr which shows which attributes are set on a file. While file attributes managed by chattr and lsattr are originally supported by EXT file systems (EXT2/3/4) only, this feature is now available on many other native Linux file systems such as XFS, Btrfs, ReiserFS, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
In this tutorial, I am going to demonstrate how to use chattr to make files immutable on Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
chattr and lsattr commands are a part of e2fsprogs package which comes pre-installed on all modern Linux distributions.
|
||||
|
||||
Basic syntax of chattr is as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
$ chattr [-RVf] [operator][attribute(s)] files...
|
||||
|
||||
The operator can be '+' (which adds selected attributes to attribute list), '-' (which removes selected attributes from attribute list), or '=' (which forces selected attributes only).
|
||||
|
||||
Some of available attributes are the following.
|
||||
|
||||
- **a**: can be opened in append mode only.
|
||||
- **A**: do not update atime (file access time).
|
||||
- **c**: automatically compressed when written to disk.
|
||||
- **C**: turn off copy-on-write.
|
||||
- **i**: set immutable.
|
||||
- **s**: securely deleted with automatic zeroing.
|
||||
|
||||
### Immutable Attribute ###
|
||||
|
||||
To make a file immutable, you can add "immutable" attribute to the file as follows. For example, to write-protect /etc/passwd file:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo chattr +i /etc/passwd
|
||||
|
||||
Note that you must use root privilege to set or unset "immutable" attribute on a file. Now verify that "immutable" attribute is added to the file successfully.
|
||||
|
||||
$ lsattr /etc/passwd
|
||||
|
||||
Once the file is set immutable, this file is impervious to change for any user. Even the root cannot modify, remove, overwrite, move or rename the file. You will need to unset the immutable attribute before you can tamper with the file again.
|
||||
|
||||
To unset the immutable attribute, use the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo chattr -i /etc/passwd
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
If you want to make a whole directory (e.g., /etc) including all its content immutable at once recursively, use "-R" option:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo chattr -R +i /etc
|
||||
|
||||
### Append Only Attribute ###
|
||||
|
||||
Another useful attribute is "append-only" attribute which forces a file to grow only. You cannot overwrite or delete a file with "append-only" attribute set. This attribute can be useful when you want to prevent a log file from being cleared by accident.
|
||||
|
||||
Similar to immutable attribute, you can turn a file into "append-only" mode by:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo chattr +a /var/log/syslog
|
||||
|
||||
Note that when you copy an immutable or append-only file to another file, those attributes will not be preserved on the newly created file.
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
In this tutorial, I showed how to use chattr and lsattr commands to manage additional file attributes to prevent (accidental or otherwise) file tampering. Beware that you cannot rely on chattr as a security measure as one can easily undo immutability. One possible way to address this limitation is to restrict the availability of chattr command itself, or drop kernel capability CAP_LINUX_IMMUTABLE. For more details on chattr and available attributes, refer to its man page.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/make-file-immutable-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/nanni
|
||||
@ -1,63 +0,0 @@
|
||||
zBackup – A versatile deduplicating backup tool
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
zbackup is a globally-deduplicating backup tool, based on the ideas found in rsync. Feed a large .tar into it, and it will store duplicate regions of it only once, then compress and optionally encrypt the result. Feed another .tar file, and it will also re-use any data found in any previous backups. This way only new changes are stored, and as long as the files are not very different, the amount of storage required is very low. Any of the backup files stored previously can be read back in full at any time.
|
||||
|
||||
### zBackup Features ###
|
||||
|
||||
Parallel LZMA or LZO compression of the stored data
|
||||
Built-in AES encryption of the stored data
|
||||
Possibility to delete old backup data
|
||||
Use of a 64-bit rolling hash, keeping the amount of soft collisions to zero
|
||||
Repository consists of immutable files. No existing files are ever modified
|
||||
Written in C++ only with only modest library dependencies
|
||||
Safe to use in production
|
||||
Possibility to exchange data between repos without recompression
|
||||
|
||||
### Install zBackup in ubuntu ###
|
||||
|
||||
Open the terminal and run the following command
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install zbackup
|
||||
|
||||
### Using zBackup ###
|
||||
|
||||
zbackup init initializes a backup repository for the backup files to be stored.
|
||||
|
||||
zbackup init [--non-encrypted] [--password-file ~/.my_backup_password ] /my/backup/repo
|
||||
|
||||
zbackup backup backups a tar file generated by tar c to the repository initialized using zbackup init
|
||||
|
||||
zbackup [--password-file ~/.my_backup_password ] [--threads number_of_threads ] backup /my/backup/repo/backups/backup-`date ‘+%Y-%m-%d'`
|
||||
|
||||
zbackup restore restores the backup file to a tar file.
|
||||
|
||||
zbackup [--password-file ~/.my_backup_password [--cache-size cache_size_in_mb restore /my/backup/repo/backups/backup-`date ‘+%Y-%m-%d'` > /my/precious/backup-restored.tar
|
||||
|
||||
### Available Options ###
|
||||
|
||||
- -non-encrypted -- Do not encrypt the backup repository.
|
||||
- --password-file ~/.my_backup_password -- Use the password file specified at ~/.my_backup_password to encrypt the repository and backup file, or to decrypt the backup file.
|
||||
- --threads number_of_threads -- Limit the partial LZMA compression to number_of_threads needed. Recommended for 32-bit architectures.
|
||||
- --cache-size cache_size_in_mb -- Use the cache size provided by cache_size_in_mb to speed up the restoration process.
|
||||
|
||||
### zBackup files ###
|
||||
|
||||
~/.my_backup_password Used to encrypt the repository and backup file, or to decrypt the backup file. See zbackup for further details.
|
||||
|
||||
/my/backup/repo The directory used to hold the backup repository.
|
||||
|
||||
/my/precious/restored-tar The tar used for restoring the backup.
|
||||
|
||||
/my/backup/repo/backups/backup-`date ‘+%Y-%m-%d'` Specifies the backup file.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.ubuntugeek.com/zbackup-a-versatile-deduplicating-backup-tool.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[ruchi][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.ubuntugeek.com/author/ubuntufix
|
||||
@ -1,115 +0,0 @@
|
||||
[translating by KayGuoWhu]
|
||||
Enjoy Android Apps on Ubuntu using ARChon Runtime
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Before, we gave try to many android app emulating tools like Genymotion, Virtualbox, Android SDK, etc to try to run android apps on it. But, with this new Chrome Android Runtime, we are able to run Android Apps on our Chrome Browser. So, here are the steps we'll need to follow to install Android Apps on Ubuntu using ARChon Runtime.
|
||||
|
||||
Google had [announced the first set of Android apps is ready to run natively on Chrome OS][1], a feature made possible using a new ‘**Android Runtime**’ extension. Now, a developer named Vlad Filippov has figured out a way to bring Android Apps to Chrome on the desktop. His chromeos-apk script and ARChon Android Runtime extension work hand-in-hand to bring Android apps to Chrome browser on the Windows, Mac and Linux desktop.
|
||||
|
||||
Performance of this apps through the runtime is not pretty good. Similarly, as its both an unofficial repackaging of the official runtime and running outside of Google's Chrome OS, system integration like webcam, speakers, etc. may be patchy or non-existent.
|
||||
|
||||
### Installing Chrome ###
|
||||
|
||||
First of all, we'll need Chrome installed in our machine, Chrome version 37 or higher is required. We can download them from the [download page of Chrome Browser][2].
|
||||
|
||||
If you wanna install a Dev Channel version you'll need to follow below procedure.
|
||||
|
||||
We'll need to add repository source list for Google Chrome which can be done my using the following command.
|
||||
|
||||
$ wget -q -O - https://dl-ssl.google.com/linux/linux_signing_key.pub | sudo apt-key add -
|
||||
$ sudo sh -c 'echo "deb http://dl.google.com/linux/chrome/deb/ stable main" >> /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome.list'
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
After adding the repository source list, we'll need to update the local repository index by the command below.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get update
|
||||
|
||||
Now, we'll gonna install google chrome unstable which is dev version.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install google-chrome-unstable
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Installing Archon Runtime ###
|
||||
|
||||
Next we'll need to download the custom-made ergo officially not endorsed by Google or Chromium Android Runtime created by Vlad Filippov. This differs from the official version in a number of ways, the chief being it can be used on desktop versions of the browser. Here below is the runtime we need to download, please select anyone of the following according to your bit of Ubuntu installed.
|
||||
|
||||
For **32-bit** Ubuntu Distributions:
|
||||
|
||||
- [Download Archron for 32-bit Ubuntu][3]
|
||||
|
||||
For **64-bit** Ubuntu Distributions:
|
||||
|
||||
- [Download Archron for 64-bit Ubuntu][4]
|
||||
|
||||
Once the runtime has fully downloaded you will need to extract the contents from the .zip files and move the resulting directory to Home. Here is the gist commands for this steps to download and extract the contents.
|
||||
|
||||
$ wget https://github.com/vladikoff/chromeos-apk/releases/download/v3.0.0/ARChon-v1.1-x86_32.zip
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
$ unzip ARChon-v1.1-x86_32.zip ~/
|
||||
|
||||
Now to install the runtime, we'll gonna Open our latest Google Chrome and goto the url **chrome://extensions/** then, we'll need to check ‘**Enable developer mode**’. Finally, we'll gonna click on the ‘**load unpacked extension**’ button and select the folder which was placed into **~/Home**.
|
||||
|
||||
### Installing ChromeOS-APK ###
|
||||
|
||||
To convert APKs manually is something you really don’t need to do any more if you use one of the apps mentioned above — you will need to install the ‘[chromeos-apk][5]’ command line JavaScript utility. This is available to install through the Node Packaged Modules (npm) manager. To install nmp and chromeos-apk, we'll need to run the following command in a shell or terminal.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install npm nodejs nodejs-legacy
|
||||
|
||||
**If you are running 64 bit OS**, you should grab the following library, to do so run the below commands in a shell or terminal.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install lib32stdc++6
|
||||
|
||||
Now run the command to install the the latest chromeos-apk is:
|
||||
|
||||
$ npm install -g chromeos-apk@latest
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Depending on your system configuration you may need to need to run this latter command as sudo.
|
||||
|
||||
Now, we'll gonna for Google to find an APK of an app to give it a try, bearing in mind **not all Android apps will work**, and those that do may be unstable or lack features. Most of the messenger out of the box are not working.
|
||||
|
||||
### Converting APK ###
|
||||
|
||||
Place your **Android APK in ~/Home**, then return to **Terminal** to convert it using the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
$ chromeos-apk myapp.apk --archon
|
||||
|
||||
If you want the app in fullscreen mode then run the following instead:
|
||||
|
||||
$ chromeos-apk myapp.apk --archon --tablet
|
||||
|
||||
Note: Please replace myapp.apk to the Android APK app filename you want to convert.
|
||||
|
||||
For our ease, we can also use [Twerk][6] for the conversion process if we want to skip this step.
|
||||
|
||||
### Running Android Apk ###
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, we'll need to open our chrome browser and then goto chrome://extensions page and enable developer mode then tap the ‘load unpacked extension’ button and select the folder the script above created.
|
||||
|
||||
Now, we can Open the Chrome App Launcher to run it.
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
Hurray! We have successfully installed Android Apk App in our favorite desktop browser ie Chrome Browser. This article is all about the popular Chrome Android Runtime called Archon created by Vlad Filippov. This runtime allows us to run converted Apk files in our Chrome browser. It has not yet supported messaging apps like Whatsapp, etc. So, if you have any questions, suggestions, feedback please write them in the comment box below. Thank you ! Enjoy Archon :-)
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/ubuntu-how-to/android-apps-ubuntu-archon-runtime/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Arun Pyasi][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arunp/
|
||||
[1]:http://chrome.blogspot.com/2014/09/first-set-of-android-apps-coming-to.html
|
||||
[2]:https://www.google.com/chrome/browser
|
||||
[3]:https://github.com/vladikoff/chromeos-apk/releases/download/v3.0.0/ARChon-v1.1-x86_32.zip
|
||||
[4]:https://github.com/vladikoff/chromeos-apk/releases/download/v3.0.0/ARChon-v1.1-x86_64.zip
|
||||
[5]:https://github.com/vladikoff/chromeos-apk/blob/master/README.md
|
||||
[6]:https://chrome.google.com/webstore/detail/twerk/jhdnjmjhmfihbfjdgmnappnoaehnhiaf
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,5 @@
|
||||
Translating by goreliu ...
|
||||
|
||||
5 Interesting Command Line Tips and Tricks in Linux – Part 1
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Are you making most out of the Linux? There are lots of helpful features which appears to be Tips and Tricks for many of Linux Users. Sometimes Tips and Tricks become the need. It helps you get productive with the same set of commands yet with enhanced functionality.
|
||||
@ -112,4 +114,4 @@ via: http://www.tecmint.com/5-linux-command-line-tricks/
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/avishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/history-command-examples/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/check-linux-disk-usage-of-files-and-directories/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/check-linux-disk-usage-of-files-and-directories/
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,86 +0,0 @@
|
||||
KDE Plasma 5.3 Released, Here’s How To Upgrade in Kubuntu 15.04
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**KDE [has announced][1] the stable release of Plasma 5.3, which comes charged with a slate of new power management features. **
|
||||
|
||||
Having impressed and excited [with an earlier beta release in April][2], the latest update to the new stable update to the Plasma 5 desktop environments is now considered stable and ready for download.
|
||||
|
||||
Plasma 5.3 continues to refine and finesse the new-look KDE desktop. It sees plenty of feature additions for desktop users to enjoy and **almost 400 bug fixes** packed in it should also improvements the performance and overall stability, too.
|
||||
|
||||
### What’s New in Plasma 5.3 ###
|
||||
|
||||
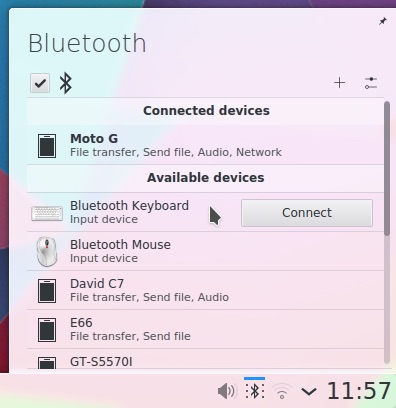
|
||||
Better Bluetooth Management in Plasma 5.3
|
||||
|
||||
While we touched on the majority of the **new features** [in Plasma 5.3 in an earlier article][3] many are worth reiterating.
|
||||
|
||||
**Enhanced power management** features and configuration options, including a **new battery applet, energy usage monitor** and **animated changes in screen brightness**, will help KDE last longer on portable devices.
|
||||
|
||||
Closing a laptop when an external monitor is connected no longer triggers ‘suspend’. This new behaviour is called ‘**cinema mode**‘ and comes enabled by default, but can be disabled using an option in power management settings.
|
||||
|
||||
**Bluetooth functionality is improved**, with a brand new panel applet making connecting and configuring paired bluetooth devices like smartphones, keyboards and speakers easier than ever.
|
||||
|
||||
Similarly, **trackpad configuration in KDE is easier** with Plasma 5.3 thanks to a new set-up and settings module.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Trackpad, Touchpad. Tomato, Tomayto.
|
||||
|
||||
For Plasma widget fans there is a new **Press and Hold** gesture. When enabled this hides the settings handle that appears when on mouseover. Instead making it only appear when long-clicking on widget.
|
||||
|
||||
On the topic of widget-y things, several **old Plasmoid favourites are reintroduced** with this release, including a useful system monitor, handy hard-drive stats and a comic reader.
|
||||
|
||||
### Learning More & Trying It Out ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
A full list of everything — and I mean everything — that is new and improved in Plasma 5.3 is listed [in the official change log][4].
|
||||
|
||||
Live images that let you try Plasma 5.3 on a Kubuntu base **without affecting your own system** are available from the KDE community:
|
||||
|
||||
- [Download KDE Plasma Live Images][5]
|
||||
|
||||
If you need super stable system you can use these live images to try the features but stick with the version of KDE that comes with your distribution on your main computer.
|
||||
|
||||
However, if you’re happy to experiment — read: can handle any package conflicts or system issues resulting from attempting to upgrade your desktop environment — you can.
|
||||
|
||||
### Install Plasma 5.3 in Kubuntu 15.04 ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
To **install Plasma 5.3 in Kubuntu 15.04** you need to add the KDE Backports PPA, run the Software Updater tool and install any available updates.
|
||||
|
||||
The Kubuntu backports PPA may/will also upgrade other parts of the KDE Platform other than Plasma that are installed on your system including KDE applications, frameworks and Kubuntu specific configuration files.
|
||||
|
||||
Using the command line is by far the fastest way to upgrade to Plasma 5.3 in Kubuntu:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:kubuntu-ppa/backports
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get dist-upgrade
|
||||
|
||||
After the upgrade process has completed, and assuming everything went well, you should reboot your computer.
|
||||
|
||||
If you’re using an alternative desktop environment, like LXDE, Unity or GNOME, you will need to install the Kubuntu desktop package (you’ll find it in the Ubuntu Software Centre) after running both of the commands above.
|
||||
|
||||
To downgrade to the stock version of Plasma in 15.04 you can use the PPA-Purge tool:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install ppa-purge
|
||||
|
||||
sudo ppa-purge ppa:kubuntu-ppa/backports
|
||||
|
||||
Let us know how your upgrade/testing goes in the comments below and don’t forget to mention the features you hope to see added to the Plasma 5 desktop next.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2015/04/kde-plasma-5-3-released-heres-how-to-upgrade-in-kubuntu-15-04
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Joey-Elijah Sneddon][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://plus.google.com/117485690627814051450/?rel=author
|
||||
[1]:https://www.kde.org/announcements/plasma-5.3.0.php
|
||||
[2]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2015/04/beta-plasma-5-3-features
|
||||
[3]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2015/04/beta-plasma-5-3-features
|
||||
[4]:https://www.kde.org/announcements/plasma-5.2.2-5.3.0-changelog.php
|
||||
[5]:https://community.kde.org/Plasma/Live_Images
|
||||
@ -1,136 +0,0 @@
|
||||
FSSlc translating
|
||||
|
||||
Install uGet Download Manager 2.0 in Debian, Ubuntu, Linux Mint and Fedora
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
After a long development period, which includes more than 11 developement releases, finally uGet project team pleased to announce the immediate availability of the latest stable version of uGet 2.0. The latest version includes numerous attractive features, such as a new setting dialog, improved BitTorrent and Metalink support added in the aria2 plugin, as well as better support for uGet RSS messages in the banner, other features include:
|
||||
|
||||
- A new “Check for Updates” button informs you about new released versions.
|
||||
- Added new languages & updated existing languages.
|
||||
- Added a new “Message Banner” that allows developers to easily provide uGet related information to all users.
|
||||
- Enhanced the Help Menu by including links to the Documentation, to submit Feedback & Bug Reports and more.
|
||||
- Integrated uGet download manager into the two major browsers on the Linux platform, Firefox and Google Chrome.
|
||||
- Improved support for Firefox Addon ‘FlashGot’.
|
||||
|
||||
### What is uGet ###
|
||||
|
||||
uGet (formerly known ad UrlGfe) is an open source, free and very powerful multi-platform GTK based download manager application was written in C language, that released and licensed under GPL. It offers large collection of features such as resuming downloads, multiple download support, categories support with an independent configuration, clipboard monitoring, download scheduler, import URLs from HTML files, integrated Flashgot plugin with Firefox and download torrent and metalink files using aria2 (a command-line download manager) that integrated with uGet.
|
||||
|
||||
I have listed down all the key features of uGet Download Manager in detailed explanation.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Key Features of uGet Download Manager ####
|
||||
|
||||
- Downloads Queue: Place all your downloads into a Queue. As downloads finishes, the remaining queue files will automatically start downloading.
|
||||
- Resume Downloads: If in case, your network connection disconnected, don’t worry you can start or resume download where it was left.
|
||||
- Download Categories: Support for unlimited categories to manage downloads.
|
||||
- Clipboard Monitor: Add the types of files to clipboard that automatically prompt you to download copied files.
|
||||
- Batch Downloads: Allows you to easily add unlimited number of files at once for downloading.
|
||||
- Multi-Protocol: Allows you to easily download files through HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, BitTorrent and Metalink using arial2 command-line plugin.
|
||||
- Multi-Connection: Support for up to 20 simultaneous connections per download using aria2 plugin.
|
||||
- FTP Login & Anonymous FTP: Added support for FTP login using username and password, as well as anonymous FTP.
|
||||
- Scheduler: Added support for scheduled downloads, now you can schedule all your downloads.
|
||||
- FireFox Integration via FlashGot: Integrated FlashGot as an independent supported Firefox extension that handles single or massive selection of files for downloading.
|
||||
- CLI / Terminal Support: Offers command line or terminal option to download files.
|
||||
- Folder Auto-Creation: If you have provided the save path for the download, but the save path doesn’t exist, uget will automatically create them.
|
||||
- Download History Management: Keeps a track of finished download and recycled entries, per list 9,999 files. Entries which are older than the custom limit will be deleted automatically.
|
||||
- Multi-Language Support: By default uGet uses English, but it support more than 23 languages.
|
||||
- Aria2 Plugin: uGet integrated with Aria2 plugin to give more user friendly GUI.
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to know a complete list of available features, see the official uGet [features page][1].
|
||||
|
||||
### Install uGet in Debian, Ubuntu, Linux Mint and Fedora ###
|
||||
|
||||
The uGet developers added latest version in various repos throughout the Linux platform, so you can able to install or upgrade uGet using supported repository under your Linux distribution.
|
||||
|
||||
Currently, a few Linux distributions are not up-to-date, but you can get the status of your distribution by going to the [uGet Download page][2] and selecting your preferred distro from there for more details.
|
||||
|
||||
#### On Debian ####
|
||||
|
||||
In Debian Testing (Jessie) and Debian Unstable (Sid), you can easily install and update using the official repository on a fairly reliable basis.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get update
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install uget
|
||||
|
||||
#### On Ubuntu & Linux Mint ####
|
||||
|
||||
In Ubuntu and Linux Mint, you can install and update uGet using official PPA repository ‘ppa:plushuang-tw/uget-stable‘. By using this PPA, you automatically be kept up-to-date with the latest versions.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:plushuang-tw/uget-stable
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get update
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install uget
|
||||
|
||||
#### On Fedora ####
|
||||
|
||||
In Fedora 20 – 21, latest version of uGet (2.0) available from the official repositories, installing from these repo is fairly reliable.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install uget
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**: On older versions of Debian, Ubuntu, Linux Mint and Fedora, users can also install uGet. but the available version is 1.10.4. If you are looking for updated version (i.e. 2.0) you need to upgrade your system and add uGet PPA to get latest stable version.
|
||||
|
||||
### Installing aria2 plugin ###
|
||||
|
||||
[aria2][3] is a excellent command-line download utility, that is used by uGet as a aria2 plugin to add even more great functionality such as downloading torrent files, metalinks, multi-protocol & multi-source download.
|
||||
|
||||
By default uGet uses CURL as backend in most of the today’s Linux systems, but the aria2 Plugin replaces CURL with aria2 as the backend.
|
||||
|
||||
aria2 is a separate package that needs to be installed separately. You can easily install latest version of aria2 using supported repository under your Linux distribution or you can also use [downloads-aria2][4] that explains how to install aria2 on each distro.
|
||||
|
||||
#### On Debian, Ubuntu and Linux Mint ####
|
||||
|
||||
Use the official aria2 PPA repository to install latest version of aria2 using the following commands.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:t-tujikawa/ppa
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get update
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install aria2
|
||||
|
||||
#### On Fedora ####
|
||||
|
||||
Fedora’s official repositories already added aria2 package, so you can easily install it using the following yum command.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install aria2
|
||||
|
||||
#### Starting uGet ####
|
||||
|
||||
To start uGet application, from the desktop “Menu” on search bar type “uget“. Refer below screenshot.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Start uGet Download Manager
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
uGet Version: 2.0
|
||||
|
||||
#### Activate aria2 Plugin in uGet ####
|
||||
|
||||
To active the aria2 plugin, from the uGet menu go to Edit –> Settings –> Plug-in tab, from the drop-down select “arial2“.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Enable Aria2 Plugin for uGet
|
||||
|
||||
### uGet 2.0 Screenshot Tour ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Download Files Using Aria2
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Download Torrent File Using uGet
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Batch Downloads Using uGet
|
||||
|
||||
uGet source files and RPM packages also available for other Linux distributions and Windows at [download page][5].
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/install-uget-download-manager-in-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Ravi Saive][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/admin/
|
||||
[1]:http://uget.visuex.com/features
|
||||
[2]:http://ugetdm.com/downloads
|
||||
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/install-aria2-a-multi-protocol-command-line-download-manager-in-rhel-centos-fedora/
|
||||
[4]:http://ugetdm.com/downloads-aria2
|
||||
[5]:http://ugetdm.com/downloads
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,193 @@
|
||||
10 Amazing and Mysterious Uses of (!) Symbol or Operator in Linux Commands
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
The `'!'` symbol or operator in Linux can be used as Logical Negation operator as well as to fetch commands from history with tweaks or to run previously run command with modification. All the commands below have been checked explicitly in bash Shell. Though I have not checked but a major of these won’t run in other shell. Here we go into the amazing and mysterious uses of `'!'` symbol or operator in Linux commands.
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Run a command from history by command number. ###
|
||||
|
||||
You might not be aware of the fact that you can run a command from your history command (already/earlier executed commands). To get started first find the command number by running ‘history‘ command.
|
||||
|
||||
$ history
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Now run a command from history just by the number at which it appears, in the output of history. Say run a command that appears at number 1551 in the output of ‘history‘ command.
|
||||
|
||||
$ !1551
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
And, it runs the command ([top command][1] in the above case), that was listed at number 1551. This way to retrieving already executed command is very helpful specially in case of those commands which are long. You just need to call it using **![Number at which it appears in the output of history command]**.
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Run previously executed command as 2nd last command, 7th last command,etc. ###
|
||||
|
||||
You may run those commands which you have run previously by their running sequence being the last run command will be represented as -1, second last as -2, seventh last as -7,….
|
||||
|
||||
First run history command to get a list of last executed command. It is necessary to run history command, so that you can be sure that there is no command like `rm command > file` and others just to make sure you do not run any dangerous command accidentally. And then check Sixth last command, Eight last command and Tenth last command.
|
||||
|
||||
$ history
|
||||
$ !-6
|
||||
$ !-8
|
||||
$ !-10
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Run Last Executed Commands By Numbers
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. Pass arguments of last command that we run to the new command without retyping ###
|
||||
|
||||
I need to list the content of directory ‘/home/$USER/Binary/firefox‘ so I fired.
|
||||
|
||||
$ ls /home/$USER/Binary/firefox
|
||||
|
||||
Then I realized that I should have fired ‘ls -l‘ to see which file is executable there? So should I type the whole command again! No I don’t need. I just need to carry the last argument to this new command as:
|
||||
|
||||
$ ls -l !$
|
||||
|
||||
Here `!$` will carry arguments passed in last command to this new command.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Pass Arguments of Last Executed Command to New
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. How to handle two or more arguments using (!) ###
|
||||
|
||||
Let’s say I created a text file 1.txt on the Desktop.
|
||||
|
||||
$ touch /home/avi/Desktop/1.txt
|
||||
|
||||
and then copy it to ‘/home/avi/Downloads‘ using complete path on either side with cp command.
|
||||
|
||||
$ cp /home/avi/Desktop/1.txt /home/avi/downloads
|
||||
|
||||
Now we have passed two arguments with cp command. First is ‘/home/avi/Desktop/1.txt‘ and second is ‘/home/avi/Downloads‘, lets handle them differently, just execute `echo [arguments]` to print both arguments differently.
|
||||
|
||||
$ echo “1st Argument is : !^”
|
||||
$ echo “2nd Argument is : !cp:2”
|
||||
|
||||
Note 1st argument can be printed as `“!^”` and rest of the arguments can be printed by executing `“![Name_of_Command]:[Number_of_argument]”`.
|
||||
|
||||
In the above example the first command was ‘cp‘ and 2nd argument was needed to print. Hence `“!cp:2”`, if any command say xyz is run with 5 arguments and you need to get 4th argument, you may use `“!xyz:4”`, and use it as you like. All the arguments can be accessed by `“!*”`.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Handle Two or More Arguments
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. Execute last command on the basis of keywords ###
|
||||
|
||||
We can execute the last executed command on the basis of keywords. We can understand it as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
$ ls /home > /dev/null [Command 1]
|
||||
$ ls -l /home/avi/Desktop > /dev/null [Command 2]
|
||||
$ ls -la /home/avi/Downloads > /dev/null [Command 3]
|
||||
$ ls -lA /usr/bin > /dev/null [Command 4]
|
||||
|
||||
Here we have used same command (ls) but with different switches and for different folders. Moreover we have sent to output of each command to ‘/dev/null‘ as we are not going to deal with the output of the command also the console remains clean.
|
||||
|
||||
Now Execute last run command on the basis of keywords.
|
||||
|
||||
$ ! ls [Command 1]
|
||||
$ ! ls -l [Command 2]
|
||||
$ ! ls -la [Command 3]
|
||||
$ ! ls -lA [Command 4]
|
||||
|
||||
Check the output and you will be astonished that you are running already executed commands just by `ls` keywords.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Run Commands Based on Keywords
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. The power of !! Operator ###
|
||||
|
||||
You can run/alter your last run command using `(!!)`. It will call the last run command with alter/tweak in the current command. Lets show you the scenario
|
||||
|
||||
Last day I run a one-liner script to get my private IP so I run,
|
||||
|
||||
$ ip addr show | grep inet | grep -v 'inet6'| grep -v '127.0.0.1' | awk '{print $2}' | cut -f1 -d/
|
||||
|
||||
Then suddenly I figured out that I need to redirect the output of the above script to a file ip.txt, so what should I do? Should I retype the whole command again and redirect the output to a file? Well an easy solution is to use `UP` navigation key and add `'> ip.txt'` to redirect the output to a file as.
|
||||
|
||||
$ ip addr show | grep inet | grep -v 'inet6'| grep -v '127.0.0.1' | awk '{print $2}' | cut -f1 -d/ > ip.txt
|
||||
|
||||
Thanks to the life Savior `UP` navigation key here. Now consider the below condition, the next time I run below one-liner script.
|
||||
|
||||
$ ifconfig | grep "inet addr:" | awk '{print $2}' | grep -v '127.0.0.1' | cut -f2 -d:
|
||||
|
||||
As soon as I run script, the bash prompt returned an error with the message `“bash: ifconfig: command not found”`, It was not difficult for me to guess I run this command as user where it should be run as root.
|
||||
|
||||
So what’s the solution? It is difficult to login to root and then type the whole command again! Also (UP Navigation Key) in last example didn’t came to rescue here. So? We need to call `“!!”` without quotes, which will call the last command for that user.
|
||||
|
||||
$ su -c “!!” root
|
||||
|
||||
Here su is switch user which is root, `-c` is to run the specific command as the user and the most important part `!!` will be replaced by command and last run command will be substituted here. Yeah! You need to provide root password.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
The Power of !! Key
|
||||
|
||||
I make use of `!!` mostly in following scenarios,
|
||||
|
||||
1. When I run apt-get command as normal user, I usually get an error saying you don’t have permission to execute.
|
||||
|
||||
$ apt-get upgrade && apt-get dist-upgrade
|
||||
|
||||
Opps error…don’t worry execute below command to get it successful..
|
||||
|
||||
$ su -c !!
|
||||
|
||||
Same way I do for,
|
||||
|
||||
$ service apache2 start
|
||||
or
|
||||
$ /etc/init.d/apache2 start
|
||||
or
|
||||
$ systemctl start apache2
|
||||
|
||||
OOPS User not authorized to carry such task, so I run..
|
||||
|
||||
$ su -c 'service apache2 start'
|
||||
or
|
||||
$ su -c '/etc/init.d/apache2 start'
|
||||
or
|
||||
$ su -c 'systemctl start apache2'
|
||||
|
||||
### 7. Run a command that affects all the file except ![FILE_NAME] ###
|
||||
|
||||
The `!` (Logical NOT) can be used to run the command on all the files/extension except that is behind `'!'`.
|
||||
|
||||
A. Remove all the files from a directory except the one the name of which is 2.txt.
|
||||
|
||||
$ rm !(2.txt)
|
||||
|
||||
B. Remove all the file type from the folder except the one the extension of which is ‘pdf‘.
|
||||
|
||||
$ $ rm !(*.pdf)
|
||||
|
||||
### 8. Check if a directory (say /home/avi/Tecmint)exist or not? Printf if the said directory exist or not. ###
|
||||
|
||||
Here we will use `'! -d'` to validate if the directory exist or not followed by Logical AND Operator `(&&)` to print that directory does not exist and Logical OR Operator `(||)` to print the directory is present.
|
||||
|
||||
Logic is, when the output of `[ ! -d /home/avi/Tecmint ]` is 0, it will execute what lies beyond Logical AND else it will go to Logical OR `(||)` and execute what lies beyond Logical OR.
|
||||
|
||||
$ [ ! -d /home/avi/Tecmint ] && printf '\nno such /home/avi/Tecmint directory exist\n' || printf '\n/home/avi/Tecmint directory exist\n'
|
||||
|
||||
### 9. Check if a directory exist or not? If not exit the command. ###
|
||||
|
||||
Similar to the above condition, but here if the desired directory doesn’t exist it will exit the command.
|
||||
|
||||
$ [ ! -d /home/avi/Tecmint ] && exit
|
||||
|
||||
### 10. Create a directory (say test) in your home directory if it does not exist. ###
|
||||
|
||||
A general implementation in Scripting Language where if the desired directory does not exist, it will create one.
|
||||
|
||||
[ ! -d /home/avi/Tecmint ] && mkdir /home/avi/Tecmint
|
||||
|
||||
That’s all for now. If you know or come across any other use of `'!'` which is worth knowing, you may like to provide us with your suggestion in the feedback. Keep connected!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/mysterious-uses-of-symbol-or-operator-in-linux-commands/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Avishek Kumar][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/avishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/12-top-command-examples-in-linux/
|
||||
182
sources/tech/20150518 How to set up a Replica Set on MongoDB.md
Normal file
182
sources/tech/20150518 How to set up a Replica Set on MongoDB.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,182 @@
|
||||
How to set up a Replica Set on MongoDB
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
MongoDB has become the most famous NoSQL database on the market. MongoDB is document-oriented, and its scheme-free design makes it a really attractive solution for all kinds of web applications. One of the features that I like the most is Replica Set, where multiple copies of the same data set are maintained by a group of mongod nodes for redundancy and high availability.
|
||||
|
||||
This tutorial describes how to configure a Replica Set on MonoDB.
|
||||
|
||||
The most common configuration for a Replica Set involves one primary and multiple secondary nodes. The replication will then be initiated from the primary toward the secondaries. Replica Sets can not only provide database protection against unexpected hardware failure and service downtime, but also improve read throughput of database clients as they can be configured to read from different nodes.
|
||||
|
||||
### Set up the Environment ###
|
||||
|
||||
In this tutorial, we are going to set up a Replica Set with one primary and two secondary nodes.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
In order to implement this lab, we will use three virtual machines (VMs) running on VirtualBox. I am going to install Ubuntu 14.04 on the VMs, and install official packages for Mongodb.
|
||||
|
||||
I am going to set up a necessary environment on one VM instance, and then clone it to the other two VM instances. Thus pick one VM named master, and perform the following installations.
|
||||
|
||||
First, we need to add the MongoDB key for apt:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-key adv --keyserver hkp://keyserver.ubuntu.com:80 --recv 7F0CEB10
|
||||
|
||||
Then we need to add the official MongoDB repository to our source.list:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo su
|
||||
# echo "deb http://repo.mongodb.org/apt/ubuntu "$(lsb_release -sc)"/mongodb-org/3.0 multiverse" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/mongodb-org-3.0.list
|
||||
|
||||
Let's update repositories and install MongoDB.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get update
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install -y mongodb-org
|
||||
|
||||
Now let's make some changes in /etc/mongodb.conf.
|
||||
|
||||
auth = true
|
||||
dbpath=/var/lib/mongodb
|
||||
logpath=/var/log/mongodb/mongod.log
|
||||
logappend=true
|
||||
keyFile=/var/lib/mongodb/keyFile
|
||||
replSet=myReplica
|
||||
|
||||
The first line is to make sure that we are going to have authentication on our database. keyFile is to set up a keyfile that is going to be used by MongoDB to replicate between nodes. replSet sets up the name of our replica set.
|
||||
|
||||
Now we are going to create our keyfile, so that it can be in all our instances.
|
||||
|
||||
$ echo -n "MyRandomStringForReplicaSet" | md5sum > keyFile
|
||||
|
||||
This will create keyfile that contains a MD5 string, but it has some noise that we need to clean up before using it in MongoDB. Use the following command to clean it up:
|
||||
|
||||
$ echo -n "MyReplicaSetKey" | md5sum|grep -o "[0-9a-z]\+" > keyFile
|
||||
|
||||
What grep command does is to print MD5 string with no spaces or other characters that we don't want.
|
||||
|
||||
Now we are going to make the keyfile ready for use:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo cp keyFile /var/lib/mongodb
|
||||
$ sudo chown mongodb:nogroup keyFile
|
||||
$ sudo chmod 400 keyFile
|
||||
|
||||
Now we have our Ubuntu VM ready to be cloned. Power it off, and clone it to the other VMs.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
I name the cloned VMs secondary1 and secondary2. Make sure to reinitialize the MAC address of cloned VMs and clone full disks.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
All three VM instances should be on the same network to communicate with each other. For this, we are going to attach all three VMs to "Internet Network".
|
||||
|
||||
It is recommended that each VM instances be assigned a static IP address, as opposed to DHCP IP address, so that the VMs will not lose connectivity among themselves when a DHCP server assigns different IP addresses to them.
|
||||
|
||||
Let's edit /etc/networks/interfaces of each VM as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
On primary:
|
||||
|
||||
auto eth1
|
||||
iface eth1 inet static
|
||||
address 192.168.50.2
|
||||
netmask 255.255.255.0
|
||||
|
||||
On secondary1:
|
||||
|
||||
auto eth1
|
||||
iface eth1 inet static
|
||||
address 192.168.50.3
|
||||
netmask 255.255.255.0
|
||||
|
||||
On secondary2:
|
||||
|
||||
auto eth1
|
||||
iface eth1 inet static
|
||||
address 192.168.50.4
|
||||
netmask 255.255.255.0
|
||||
|
||||
Another file that needs to be set up is /etc/hosts, because we don't have DNS. We need to set the hostnames in /etc/hosts.
|
||||
|
||||
On primary:
|
||||
|
||||
127.0.0.1 localhost primary
|
||||
192.168.50.2 primary
|
||||
192.168.50.3 secondary1
|
||||
192.168.50.4 secondary2
|
||||
|
||||
On secondary1:
|
||||
|
||||
127.0.0.1 localhost secondary1
|
||||
192.168.50.2 primary
|
||||
192.168.50.3 secondary1
|
||||
192.168.50.4 secondary2
|
||||
|
||||
On secondary2:
|
||||
|
||||
127.0.0.1 localhost secondary2
|
||||
192.168.50.2 primary
|
||||
192.168.50.3 secondary1
|
||||
192.168.50.4 secondary2
|
||||
|
||||
Check connectivity among themselves by using ping command:
|
||||
|
||||
$ ping primary
|
||||
$ ping secondary1
|
||||
$ ping secondary2
|
||||
|
||||
### Set up a Replica Set ###
|
||||
|
||||
After verifying connectivity among VMs, we can go ahead and create the admin user so that we can start working on the Replica Set.
|
||||
|
||||
On primary node, open /etc/mongodb.conf, and comment out two lines that start with auth and replSet:
|
||||
|
||||
dbpath=/var/lib/mongodb
|
||||
logpath=/var/log/mongodb/mongod.log
|
||||
logappend=true
|
||||
#auth = true
|
||||
keyFile=/var/lib/mongodb/keyFile
|
||||
#replSet=myReplica
|
||||
|
||||
Restart mongod daemon.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo service mongod restart
|
||||
|
||||
Create an admin user after conencting to MongoDB:
|
||||
|
||||
> use admin
|
||||
> db.createUser({
|
||||
user:"admin",
|
||||
pwd:"
|
||||
})
|
||||
$ sudo service mongod restart
|
||||
|
||||
Connect to MongoDB and use these commands to add secondary1 and secondary2 to our Replicat Set.
|
||||
|
||||
> use admin
|
||||
> db.auth("admin","myreallyhardpassword")
|
||||
> rs.initiate()
|
||||
> rs.add ("secondary1:27017")
|
||||
> rs.add("secondary2:27017")
|
||||
|
||||
Now that we have our Replica Set, we can start working on our project. Consult the [official driver documentation][1] to see how to connect to a Replica Set. In case you want to query from shell, you have to connect to primary instance to insert or query the database. Secondary nodes will not let you do that. If you attempt to access the database on a secondary node, you will get this error message:
|
||||
|
||||
myReplica:SECONDARY>
|
||||
myReplica:SECONDARY> show databases
|
||||
2015-05-10T03:09:24.131+0000 E QUERY Error: listDatabases failed:{ "note" : "from execCommand", "ok" : 0, "errmsg" : "not master" }
|
||||
at Error ()
|
||||
at Mongo.getDBs (src/mongo/shell/mongo.js:47:15)
|
||||
at shellHelper.show (src/mongo/shell/utils.js:630:33)
|
||||
at shellHelper (src/mongo/shell/utils.js:524:36)
|
||||
at (shellhelp2):1:1 at src/mongo/shell/mongo.js:47
|
||||
|
||||
I hope you find this tutorial useful. You can use Vagrant to automate your local environments and help you code faster.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/setup-replica-set-mongodb.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Christopher Valerio][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/valerio
|
||||
[1]:http://docs.mongodb.org/ecosystem/drivers/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,115 @@
|
||||
Translating by GOLinux!
|
||||
Linux FAQs with Answers--How to block specific user agents on nginx web server
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **Question**: I notice that some robots often visit my nginx-powered website and scan it aggressively, ending up wasting a lot of my web server resources. I am trying to block those robots based on their user-agent string. How can I block specific user agent(s) on nginx web server?
|
||||
|
||||
The modern Internet is infested with various malicious robots and crawlers such as malware bots, spambots or content scrapers which are scanning your website in surreptitious ways, for example to detect potential website vulnerabilities, harvest email addresses, or just to steal content from your website. Many of these robots can be identified by their signature "user-agent" string.
|
||||
|
||||
As a first line of defense, you could try to block malicious bots from accessing your website by blacklisting their user-agents in robots.txt file. However, unfortunately this works only for "well-behaving" robots which are designed to obey robots.txt. Many malicious bots can simply ignore robots.txt and scan your website at will.
|
||||
|
||||
An alternative way to block particular robots is to configure your web server, such that it refuses to serve content to requests with certain user-agent strings. This post explains how to **block certain user-agent on nginx web server**.
|
||||
|
||||
### Blacklist Certain User-Agents in Nginx ###
|
||||
|
||||
To configure user-agent block list, open the nginx configuration file of your website, where the server section is defined. This file can be found in different places depending on your nginx setup or Linux distribution (e.g., /etc/nginx/nginx.conf, /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/<your-site>, /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf, /etc/nginx/conf.d/<your-site>).
|
||||
|
||||
server {
|
||||
listen 80 default_server;
|
||||
server_name xmodulo.com;
|
||||
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
|
||||
|
||||
....
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Once you open the config file with the server section, add the following if statement(s) somewhere inside the section.
|
||||
|
||||
server {
|
||||
listen 80 default_server;
|
||||
server_name xmodulo.com;
|
||||
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
|
||||
|
||||
# case sensitive matching
|
||||
if ($http_user_agent ~ (Antivirx|Arian) {
|
||||
return 403;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# case insensitive matching
|
||||
if ($http_user_agent ~* (netcrawl|npbot|malicious)) {
|
||||
return 403;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
....
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
As you can guess, these if statements match any bad user-string with regular expressions, and return 403 HTTP status code when a match is found. $http_user_agent is a variable that contains the user-agent string of an HTTP request. The '~' operator does case-sensitive matching against user-agent string, while the '~' operator does case-insensitive matching. The '|' operator is logical-OR, so you can put as many user-agent keywords in the if statements, and block them all.
|
||||
|
||||
After modifying the configuration file, you must reload nginx to activate the blocking:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo /path/to/nginx -s reload
|
||||
|
||||
You can test user-agent blocking by using wget with "--user-agent" option.
|
||||
|
||||
$ wget --user-agent "malicious bot" http://<nginx-ip-address>
|
||||
|
||||
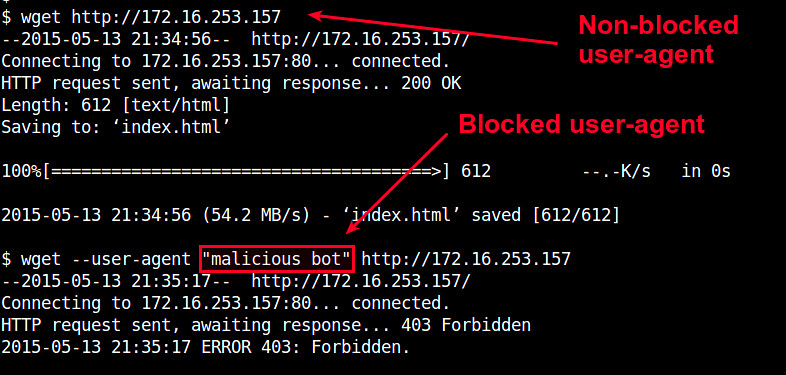
|
||||
|
||||
### Manage User-Agent Blacklist in Nginx ###
|
||||
|
||||
So far, I have shown how to block HTTP requests with a few user-agents in nginx. What if you have many different types of crawling bots to block?
|
||||
|
||||
Since the user-agent blacklist can grow very big, it is not a good idea to put them all inside your nginx's server section. Instead, you can create a separate file which lists all blocked user agents. For example, let's create /etc/nginx/useragent.rules, and define a map with all blocked user agents in the following format.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo vi /etc/nginx/useragent.rules
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
map $http_user_agent $badagent {
|
||||
default 0;
|
||||
~*malicious 1;
|
||||
~*backdoor 1;
|
||||
~*netcrawler 1;
|
||||
~Antivirx 1;
|
||||
~Arian 1;
|
||||
~webbandit 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Similar to the earlier setup, '~*' will match a keyword in case-insensitive manner, while '~' will match a keyword using a case-sensitive regular expression. The line that says "default 0" means that any other user-agent not listed in the file will be allowed.
|
||||
|
||||
Next, open an nginx configuration file of your website, which contains http section, and add the following line somewhere inside the http section.
|
||||
|
||||
http {
|
||||
.....
|
||||
include /etc/nginx/useragent.rules
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Note that this include statement must appear before the server section (this is why we add it inside http section).
|
||||
|
||||
Now open an nginx configuration where your server section is defined, and add the following if statement:
|
||||
|
||||
server {
|
||||
....
|
||||
|
||||
if ($badagent) {
|
||||
return 403;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
....
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, reload nginx.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo /path/to/nginx -s reload
|
||||
|
||||
Now any user-agent which contains a keyword listed in /etc/nginx/useragent.rules will be automatically banned by nginx.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/block-specific-user-agents-nginx-web-server.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/author/nanni
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
|
||||
Linux FAQs with Answers--How to fix “Encountered a section with no Package: header” error on Raspbian
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **Question**: I installed fresh Rasbian on Raspberry Pi. But when I tried to update APT package index by running sudo apt-get update, it throws the following error:
|
||||
|
||||
E: Encountered a section with no Package: header
|
||||
E: Problem with MergeList /var/lib/dpkg/status
|
||||
E: The package lists or status file could not be parsed or opened.
|
||||
|
||||
> I then cannot install any package on Raspbian. How can I solve this error?
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
The error saying "Problem with MergeList /var/lib/dpkg/status" indicates that the status file got corrupted for some reason, and so cannot be parsed. This status file contains information about installed deb packages, and thus needs to be carefully backed up.
|
||||
|
||||
In this case, since this is freshly installed Raspbian, you can safely remove the status file, and re-generate it as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo rm /var/lib/dpkg/status
|
||||
$ sudo touch /var/lib/dpkg/status
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get update
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/encountered-section-with-no-package-header-error.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/author/nanni
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
|
||||
Linux FAQs with Answers--How to fix “fatal error: security/pam_modules.h: No such file or directory”
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **Question**: I was trying to compile a program on [insert your Linux distro], but was getting the following compile error:
|
||||
>
|
||||
> "pam_otpw.c:27:34: fatal error: security/pam_modules.h: No such file or directory"
|
||||
>
|
||||
> How can I fix this error?
|
||||
|
||||
The missing header file 'security/pam_modules.h' is part of development files for libpam, a PAM (Pluggable Authentication Modules) library. Thus to fix this error, you need to install libpam development package, as described below.
|
||||
|
||||
On Debian, Ubuntu or Linux Mint:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install libpam0g-dev
|
||||
|
||||
On CentOS, Fedora or RHEL:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install gcc pam-devel
|
||||
|
||||
Now verify that the missing header file is installed under /usr/include/security.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/fatal-error-security-pam-modules.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/author/nanni
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,81 @@
|
||||
Linux FAQs with Answers--What is the Apache error log location on Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **Question**: I am trying to troubleshoot Apache web server errors on my Linux system. Where is the Apache error log file located on [insert your Linux distro]?
|
||||
|
||||
Error log and access log files are a useful piece of information for system admins, for example to troubleshoot their web server, [protect][1] it from various malicious activities, or just to run [various][2] [analytics][3] for HTTP server monitoring. Depending on your web server setup, its error/access logs may be found in different places on your system.
|
||||
|
||||
This post may help you **find Apache error log location on Linux**.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Apache Error Log Location on Debian, Ubuntu or Linux Mint ###
|
||||
|
||||
#### Default Error Log ####
|
||||
|
||||
On Debian-based Linux, the system-wide default location of Apache error log is **/var/log/apache2/error.log**. The default location can be customized by editing Apache configuration file.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Custom Error Log ####
|
||||
|
||||
To find a custom error log location, open /etc/apache2/apache2.conf with a text editor, and look for a line that starts with ErrorLog. This line specifies a custom location of Apache error log file. For example, the unmodified Apache configuration file has the following line:
|
||||
|
||||
ErrorLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/error.log
|
||||
|
||||
In this case, the location is configured using APACHE_LOG_DIR environment variable, which is defined in /etc/apache2/envvars.
|
||||
|
||||
export APACHE_LOG_DIR=/var/log/apache2$SUFFIX
|
||||
|
||||
In reality, ErrorLog may point to any arbitrary path on your Linux system.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Custom Error Log with VirtualHost ####
|
||||
|
||||
If VirtualHost is used in Apache web server, ErrorLog directive can be specified within VirtualHost container, in which case the system-wide error log location described above will be ignored.
|
||||
|
||||
With VirtualHost enabled, each VirtualHost can define its own custom error log location. To find out the error log location of a particular VirtualHost, you can open /etc/apache2/sites-enabled/<your-site>.conf, and look for ErrorLog directive, which will show a site-specific error log file.
|
||||
|
||||
### Apache Error Log Location on CentOS, Fedora or RHEL ###
|
||||
|
||||
#### Default Error Log ####
|
||||
|
||||
On Red Hat based Linux, a system-wide Apache error log file is by default placed in **/var/log/httpd/error_log**. This default location can be customized by editing Apache configuration file.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Custom Error Log ####
|
||||
|
||||
To find out the custom location of Apache error log, open /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf with a text editor, and look for ServerRoot, which shows the top of the Apache server directory tree, under which log files and configurations are located. For example:
|
||||
|
||||
ServerRoot "/etc/httpd"
|
||||
|
||||
Now look for a line that starts with ErrorLog, which indicates where Apache web server is writing its error logs. Note that the specified location is relative to the ServerRoot value. For example:
|
||||
|
||||
ErrorLog "log/error_log"
|
||||
|
||||
Combine the above two directives to obtain the full path of an error log, which is by default /etc/httpd/logs/error_log. This is a symlink to /var/log/httpd/error_log with freshly installed Apache.
|
||||
|
||||
In reality, ErrorLog may point to any arbitrary location on your Linux system.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Custom Error Log with VirtualHost ####
|
||||
|
||||
If you enabled VirtualHost, you can find the error log location of individual VirtualHosts by checking /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf (or any file where VirtualHost is defined). Look for ErrorLog inside individual VirtualHost sections. For example, in the following VirtualHost section, an error log is found in /var/www/xmodulo.com/logs/error_log.
|
||||
|
||||
<VirtualHost *:80>
|
||||
ServerAdmin webmaster@xmodulo.com
|
||||
DocumentRoot /var/www/xmodulo.com/public_html
|
||||
ServerName www.xmodulo.com
|
||||
ServerAlias xmodulo.com
|
||||
ErrorLog /var/www/xmodulo.com/logs/error_log
|
||||
CustomLog /var/www/xmodulo.com/logs/access_log
|
||||
<VirtualHost>
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/apache-error-log-location-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/author/nanni
|
||||
[1]:http://xmodulo.com/configure-fail2ban-apache-http-server.html
|
||||
[2]:http://xmodulo.com/interactive-apache-web-server-log-analyzer-linux.html
|
||||
[3]:http://xmodulo.com/sql-queries-apache-log-files-linux.html
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,115 @@
|
||||
Guake 0.7.0 已发布 - 一个用于Gnome桌面的下拉式终端
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Linux的命令行是最好、最强大的东西,它使新手着迷,并为老手和极客的提供极端强大的功能。那些在服务器和生产环境下工作的人早已认识到了这个事实。有趣的是,Linux终端是Linus Torvald在1991年写内核时实现的第一批功能之一。
|
||||
|
||||
终端是个强大的工具,由于它没有可移动的部分,所以十分可靠。终端介于控制台环境和GUI环境之间。终端自身作为一个GUI程序,运行在桌面环境下。有许多终端是适用于特定的桌面环境的,而其余是通用的。Terminator, Konsole, Gnome-Terminal, Terminology, XFCE terminal, xterm都是些常用的终端模拟器。
|
||||
|
||||
您可以从下面的链接中获得一份使用最广泛的终端模拟器的列表。
|
||||
|
||||
- [20 Useful Terminals for Linux][1]
|
||||
|
||||
前几日上网时,我偶遇了名为‘Guake’,它是用于gnome的终端模拟器。尽管这并不是我第一次听到Guake。实际上,我在大约一年前便知道了这个应用程序,但不知怎么搞的,我那时没有写写Guake,再后来我便渐渐忘掉了Guake,直到我再一次听到Guake。所以,最终,这篇文章诞生了。我将给你讲讲Guake的功能,在Debian、Ubuntu、Fedora上的安装过程以及一些测试。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 什么是Guake? ####
|
||||
|
||||
Guake是应用于Gnome环境的下拉式终端。主要由Python编写,使用了一些C,它以GPL2+证书发布,适用于Linux以及类似的系统。Guake的灵感来源于电脑游戏Quake(雷神之锤)的终端,Quake的终端能通过按下特定按键(默认为F12)从屏幕上滑下来,并在按下同样的键后滑上去。
|
||||
|
||||
值得注意的是,Guake并不是第一个这样的应用。Yakuake(Yet Another Kuake)是一个运行于KDE的终端模拟器,Tilda是一个用GTK+写成的终端模拟器。它们的灵感都来自于雷神之锤那上下滑动的终端。
|
||||
|
||||
#### Guake的功能 ####
|
||||
|
||||
- 轻量级
|
||||
- 简单而优雅
|
||||
- 众多功能
|
||||
- 强大的
|
||||
- 好看的
|
||||
- 平滑的集成于GUI
|
||||
- 在按下预定义的键后出现/消失
|
||||
- 支持热键、标签、透明化背景,这使得它适合所有Gnome用户
|
||||
- 极端地可配置
|
||||
- 包括许多颜色的调色板
|
||||
- 设定透明度的快捷方式
|
||||
- 通过Guake配置,可在启动时运行一个脚本
|
||||
- 可以在多个监视器上运行
|
||||
|
||||
Guake 0.7.0最近发布,它带来了一些修正以及上面提到的一些功能。完整的版本历史和源代码包可以在[这里][2]找到。
|
||||
|
||||
### 在Linux中安装Guake终端 ###
|
||||
|
||||
如果您对从源码编译Guake感兴趣,您可以从上面的链接处下载Guake,并在安装前进行编译。
|
||||
|
||||
然而Guake可以在许多的发行版中通过添加额外的仓库来安装。这里,我们将在Debian、Ubuntu、Linux Mint和Fedora下安装Guake。
|
||||
|
||||
首先从仓库获取最新的软件包列表,并从默认的仓库安装Guake,如下所示:
|
||||
|
||||
---------------- On Debian, Ubuntu and Linux Mint ----------------
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get update
|
||||
$ apt-get install guake
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
---------------- On Fedora 19 Onwards ----------------
|
||||
# yum update
|
||||
# yum install guake
|
||||
|
||||
安装后,可以从另一个终端中启动Guake:
|
||||
|
||||
$ guake
|
||||
|
||||
在启动它后,便可以在Gnome桌面中使用F12(默认配置)来下滑、上滑终端。
|
||||
|
||||
看起来非常漂亮,尤其是透明背景。滑下来...滑上去...滑下来...滑上去...执行命令,打开另一个标签,执行命令,滑上去...滑下来...(作者已沉迷其中)
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Guake实战
|
||||
|
||||
如果您的壁纸或活动窗口的颜色和Guake的颜色有些不搭。您可以改变您的壁纸,减少透明度或者改变Guake的颜色。
|
||||
|
||||
下一步便是进入Guake的配置,根据每个人的需求修改设置。可以通过应用菜单或者下面的命令来运行Guake的配置。
|
||||
|
||||
$ guake --preferences
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Guake终端配置
|
||||
|
||||
滚动配置
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Guake滚动配置
|
||||
|
||||
外观设置 - 在这里您可以修改文字颜色和背景色以及透明度。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
外观设置
|
||||
|
||||
键盘快捷键 - 在这里您可以修改Guake显示的开关快捷键。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
键盘快捷键
|
||||
|
||||
兼容性设置 - 基本上不必设置它。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
兼容性设置
|
||||
|
||||
### 结论 ###
|
||||
|
||||
这个项目即不是太年轻也不是太古老,因此它已经达到了一定的成熟度,足够可靠,可以开箱即用。像我这样需要在GUI和终端间频繁切换的人来说,Guake是一个福利。我不需要管理一个多余的窗口,频繁的打开和关闭,使用tab在大量打开的应用程序中寻找终端或切换到不同的工作区来管理终端,现在我需要的只有F12。
|
||||
|
||||
我认为对任何同时使用GUI和终端的Linux用户来说,Guake都是必须的工具。同样的,我会向任何想要在系统中结合使用GUI和终端的人推荐它,因为它既平滑又没有任何障碍。
|
||||
|
||||
上面就是我要说的全部了。如果在安装和使用时有任何问题,请告诉我,我们会帮助您。也请您告诉我您使用Guake的经验。在下面的评论区反馈您宝贵的经验。点赞和分享以帮助我们宣传。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/install-guake-terminal-ubuntu-mint-fedora/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Avishek Kumar][a]
|
||||
译者:[wwy-hust](https://github.com/wwy-hust)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/avishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/linux-terminal-emulators/
|
||||
[2]:https://github.com/Guake/guake/releases/tag/0.7.0
|
||||
@ -1,135 +0,0 @@
|
||||
什么是Linux上实用的命令行式网络监视工具
|
||||
===============================================================================
|
||||
对任何规模的业务来说,网络监视器都是一个重要的功能。网络监视的目标可能千差万别。比如,监视活动的目标可以是保证长期的网络供应、安全保护、对性能进行排查、网络使用统计等。由于它的目标不同,网络监视器使用很多不同的方式来完成任务。比如使用包层面的嗅探,使用流层面的统计数据,向网络中注入探测的流量,分析服务器日志等。
|
||||
|
||||
尽管有许多专用的网络监视系统可以365天24小时监视,但您依旧可以在特定的情况下使用命令行式的网络监视器,某些命令行式的网络监视器在某方面很有用。如果您是系统管理员,那您就应该有亲身使用一些知名的命令行式网络监视器的经历。这里有一份**Linux上流行且实用的网络监视器**列表。
|
||||
|
||||
### 包层面的嗅探器 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在这个类别下,监视工具在链路上捕捉独立的包,分析它们的内容,展示解码后的内容或者包层面的统计数据。这些工具在最底层对网络进行监视、管理,同样的也能进行最细粒度的监视,其代价是部分网络I/O和分析的过程。
|
||||
|
||||
1. **dhcpdump**:一个命令行式的DHCP流量嗅探工具,捕捉DHCP的请求/回复流量,并以用户友好的方式显示解码的DHCP协议消息。这是一款排查DHCP相关故障的实用工具。
|
||||
|
||||
2. **[dsniff][1]**:一个基于命令行的嗅探工具集合,拥有欺骗和劫持功能,被设计用于网络审查和渗透测试。它可以嗅探多种信息,比如密码、NSF流量、email消息、网络地址等。
|
||||
|
||||
3. **[httpry][2]**:一个HTTP报文嗅探器,用于捕获、解码HTTP请求和回复报文,并以用户友好的方式显示这些信息。
|
||||
|
||||
4. **IPTraf**:基于命令行的网络统计数据查看器。它实时显示包层面、连接层面、接口层面、协议层面的报文/字节数。抓包过程由协议过滤器控制,且操作过程全部是菜单驱动的。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
5. **[mysql-sniffer][3]**:一个用于抓取、解码MySQL请求相关的数据包的工具。它以可读的方式显示最频繁或全部的请求。
|
||||
|
||||
6. **[ngrep][4]**:在网络报文中执行grep。它能实时抓取报文,并用正则表达式或十六进制表达式的方式匹配报文。它是一个可以对异常流量进行检测、存储或者对实时流中特定模式报文进行抓取的实用工具。
|
||||
|
||||
7. **[p0f][5]**:一个被动的基于包嗅探的指纹采集工具,可以可靠地识别操作系统、NAT或者代理设置、网络链路类型以及许多其他与活动的TCP连接相关的属性。
|
||||
|
||||
8. **pktstat**:一个命令行式的工具,通过实时分析报文,显示连接带宽使用情况以及相关的协议(例如,HTTP GET/POST、FTP、X11)等描述信息。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
13. **[iftop][7]**:一个带宽使用监测工具,可以实时显示某个网络连接的带宽使用情况。它对所有带宽使用情况排序并通过ncurses的接口来进行可视化。他可以方便的监视哪个连接消耗了最多的带宽。
|
||||
|
||||
14. **nethogs**:一个进程监视工具,提供进程相关的实时的上行/下行带宽使用信息,并基于ncurses显示。它对检测占用大量带宽的进程很有用。
|
||||
|
||||
15. **netstat**:一个显示许多TCP/UDP的网络堆栈统计信息的工具。诸如网络接口发送/接收、路由表、协议/套接字的统计信息和属性。当您诊断与网络堆栈相关的性能、资源使用时它很有用。
|
||||
|
||||
16. **[speedometer][8]**:一个可视化某个接口发送/接收的带宽使用的历史趋势,并且基于ncurses的条状图进行显示的工具。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
17. **[sysdig][9]**:一个对Linux子系统拥有统一调试接口的系统级综合性debug工具。它的网络监视模块可以监视在线或离线、许多进程/主机相关的网络统计数据,例如带宽、连接/请求数等。
|
||||
|
||||
18. **tcptrack**:一个TCP连接监视工具,可以显示活动的TCP连接,包括源/目的IP地址/端口、TCP状态、带宽使用等。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
19. **vnStat**:一个维护了基于接口的历史接收/发送带宽视图(例如,当前、每日、每月)的流量监视器。作为一个后台守护进程,它收集并存储统计数据,包括接口带宽使用率和传输字节总数。
|
||||
|
||||
### 主动网络监视器 ###
|
||||
|
||||
不同于前面提到的被动的监听工具,这个类别的工具们在监听时会主动的“注入”探测内容到网络中,并且会收集相应的反应。监听目标包括路由路径、可供使用的带宽、丢包率、延时、抖动、系统设置或者缺陷等。
|
||||
|
||||
20. **[dnsyo][10]**:一个DNS检测工具,能够管理多达1500个不同网络的开放解析器集群的DNS查询。它在您检查DNS传播或排查DNS设置的时候很有用。
|
||||
|
||||
21. **[iperf][11]**:一个TCP/UDP带宽测量工具,能够测量两个结点间最大可用带宽。它通过在两个主机间单向或双向的输出TCP/UDP探测流量来测量可用的带宽。它在监测网络容量、调谐网络协议栈参数时很有用。一个叫做[netperf][12]的变种拥有更多的功能及更好的统计数据。
|
||||
|
||||
22. **[netcat][13]/socat**:通用的网络debug工具,可以对TCP/UDP套接字进行读、写或监听。它通常和其他的程序或脚本结合起来在后端对网络传输或端口进行监听。
|
||||
|
||||
23. **nmap**:一个命令行端口扫描和网络发现工具。它依赖于若干基于TCP/UDP的扫描技术来查找开放的端口、活动的主机或者在本地网络存在的操作系统。它在你审查本地主机漏洞或者建立主机映射时很有用。[zmap][14]是一个类似的替代品,是一个用于互联网范围的扫描工具。
|
||||
|
||||
24. ping:一个常用的网络测试工具。通过对ICMP的echo和reply报文进行增强来实现其功能。它在测量路由的RTT、丢包率以及检测远端系统防火墙规则时很有用。ping的变种有更漂亮的界面(例如,[noping][15])、多协议支持(例如,[hping][16])或者并行探测能力(例如,[fping][17])。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
25. **[sprobe][18]**:一个启发式推断本地主机和任意远端IP地址的网络带宽瓶颈的命令行工具。它使用TCP三次握手机制来评估带宽的瓶颈。它在检测大范围网络性能和路由相关的问题时很有用。
|
||||
|
||||
26. **traceroute**:一个能发现从本地到远端主机的第三层路由/转发路径的网络发现工具。它发送有限TTL的探测报文,收集中间路由的ICMP反馈信息。它在排查低速网络连接或者路由相关的问题时很有用。traceroute的变种有更好的RTT统计功能(例如,[mtr][19])。
|
||||
|
||||
### 应用日志解析器 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在这个类别下,网络监测器把特定的服务器应用程序作为目标(例如,web服务器或者数据库服务器)。由服务器程序产生或消耗的网络流量通过它的日志被分析和监测。不像前面提到的网络层的监视器,这个类别的工具能够在应用层面分析和监控网络流量。
|
||||
|
||||
27. **[GoAccess][20]**:一个针对Apache和Nginx服务器流量的交互式查看器。基于对获取到的日志的分析,它能展示包括日访问量、最多请求、客户端操作系统、客户端位置、客户端浏览器等在内的多个实时的统计信息,并以滚动方式显示。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
28. **[mtop][21]**:一个面向MySQL/MariaDB服务器的命令行监视器,它可以将当前数据库服务器负载中代价最大的查询以可视化的方式进行显示。它在您优化MySQL服务器性能、调谐服务器参数时很有用。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
29. **[ngxtop][22]**:一个面向Nginx和Apache服务器的流量监测工具,能够以类似top指令的方式可视化的显示Web服务器的流量。它解析web服务器的查询日志文件并收集某个目的地或请求的流量统计信息。
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
在这篇文章中,我展示了许多的命令行式监测工具,从最底层的包层面的监视器到最高层应用程序层面的网络监视器。知道那个工具的作用是一回事,选择哪个工具使用又是另外一回事。单一的一个工具不能作为您每天使用的通用的解决方案。一个好的系统管理员应该能决定哪个工具更适合当前的环境。希望这个列表对此有所帮助。
|
||||
|
||||
欢迎您通过回复来改进这个列表的内容!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/useful-command-line-network-monitors-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
|
||||
译者:[wwy-hust](https://github.com/wwy-hust)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/nanni
|
||||
[1]:http://www.monkey.org/~dugsong/dsniff/
|
||||
[2]:http://xmodulo.com/monitor-http-traffic-command-line-linux.html
|
||||
[3]:https://github.com/zorkian/mysql-sniffer
|
||||
[4]:http://ngrep.sourceforge.net/
|
||||
[5]:http://lcamtuf.coredump.cx/p0f3/
|
||||
[6]:http://xmodulo.com/recommend/firewallbook
|
||||
[7]:http://xmodulo.com/how-to-install-iftop-on-linux.html
|
||||
[8]:https://excess.org/speedometer/
|
||||
[9]:http://xmodulo.com/monitor-troubleshoot-linux-server-sysdig.html
|
||||
[10]:http://xmodulo.com/check-dns-propagation-linux.html
|
||||
[11]:https://iperf.fr/
|
||||
[12]:http://www.netperf.org/netperf/
|
||||
[13]:http://xmodulo.com/useful-netcat-examples-linux.html
|
||||
[14]:https://zmap.io/
|
||||
[15]:http://noping.cc/
|
||||
[16]:http://www.hping.org/
|
||||
[17]:http://fping.org/
|
||||
[18]:http://sprobe.cs.washington.edu/
|
||||
[19]:http://xmodulo.com/better-alternatives-basic-command-line-utilities.html#mtr_link
|
||||
[20]:http://goaccess.io/
|
||||
[21]:http://mtop.sourceforge.net/
|
||||
[22]:http://xmodulo.com/monitor-nginx-web-server-command-line-real-time.html
|
||||
@ -1,171 +1,172 @@
|
||||
Inxi: Find System And Hardware Information On Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
We already have shown different [applications][1] and ways to find the system and hardware information on Linux. In that series, today we will see how to find such details using **inxi**. It can be used for forum technical support, as a debugging tool, to quickly ascertain user system configuration and hardware.
|
||||
|
||||
**Inxi** is a command line tool that can be used to find the complete system and hardware details such as;
|
||||
|
||||
- Hardware,
|
||||
- CPU,
|
||||
- Drivers,
|
||||
- Xorg,
|
||||
- Desktop,
|
||||
- Kernel,
|
||||
- GCC version,
|
||||
- Processes,
|
||||
- RAM usage,
|
||||
- and other useful information.
|
||||
|
||||
### Installation ###
|
||||
|
||||
Inxi is available in the default repositories of most modern GNU/Linux operating systems. So, we can simply install it by running the following commands.
|
||||
|
||||
**On Debian based system:**
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install inxi
|
||||
|
||||
**On Fedora:**
|
||||
|
||||
sudo yum install inxi
|
||||
|
||||
**On RHEL based systems:**
|
||||
|
||||
Install EPEL repository:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo yum install epel-release
|
||||
|
||||
Then, install inxi using command:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo yum install inxi
|
||||
|
||||
### Usage ###
|
||||
|
||||
To find the quick view of the system information, run the following command from Terminal.
|
||||
|
||||
inxi
|
||||
|
||||
**Sample output:**
|
||||
|
||||
CPU~Dual core Intel Core i3-2350M CPU (-HT-MCP-) clocked at Min:800.000Mhz Max:1200.000Mhz Kernel~3.13.0-45-generic x86_64 Up~6:41 Mem~1537.7/3861.3MB HDD~500.1GB(52.5% used) Procs~183 Client~Shell inxi~1.9.17
|
||||
|
||||
Ofcourse, we can retrieve a particular hardware details. For example to retrieve the **Audio/Sound hardware details**, run the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
inxi -A
|
||||
|
||||
**Sample output:**
|
||||
|
||||
Audio: Card: Intel 6 Series/C200 Series Family High Definition Audio Controller driver: snd_hda_intel
|
||||
Sound: Advanced Linux Sound Architecture ver: k3.13.0-45-generic
|
||||
|
||||
Cool, isn’t it?
|
||||
|
||||
Likewise, you can retrieve the details of **Graphic card** information.
|
||||
|
||||
inxi -G
|
||||
|
||||
**Sample output:**
|
||||
|
||||
Graphics: Card: Intel 2nd Generation Core Processor Family Integrated Graphics Controller
|
||||
X.Org: 1.15.1 drivers: intel (unloaded: fbdev,vesa) Resolution: 1366x768@60.0hz
|
||||
GLX Renderer: Mesa DRI Intel Sandybridge Mobile GLX Version: 3.0 Mesa 10.3.0
|
||||
|
||||
What about harddisk information? That’s also possible. To view the full **harddisk** information, run the following command.
|
||||
|
||||
inxi -D
|
||||
|
||||
**Sample Output:**
|
||||
|
||||
Drives: HDD Total Size: 500.1GB (52.5% used) 1: id: /dev/sda model: ST9601325BD size: 500.1GB
|
||||
|
||||
To display the Bios and Motherboard details:
|
||||
|
||||
inxi -M
|
||||
|
||||
**Sample output:**
|
||||
|
||||
Machine: System: Dell (portable) product: Inspiron N5050
|
||||
Mobo: Dell model: 01HXXJ version: A05 Bios: Dell version: A05 date: 08/03/2012
|
||||
|
||||
Not only hardware details, it can also displays the **list of available repositories** in our system.
|
||||
|
||||
inxi -r
|
||||
|
||||
**Sample output:**
|
||||
|
||||
Repos: Active apt sources in file: /etc/apt/sources.list
|
||||
deb http://ubuntu.excellmedia.net/archive/ trusty main restricted
|
||||
deb-src http://ubuntu.excellmedia.net/archive/ trusty main restricted
|
||||
deb http://ubuntu.excellmedia.net/archive/ trusty-updates main restricted
|
||||
deb-src http://ubuntu.excellmedia.net/archive/ trusty-updates main restricted
|
||||
deb http://ubuntu.excellmedia.net/archive/ trusty universe
|
||||
.
|
||||
.
|
||||
Active apt sources in file: /etc/apt/sources.list.d/intellinuxgraphics.list
|
||||
deb https://download.01.org/gfx/ubuntu/14.04/main trusty main #Intel Graphics drivers
|
||||
Active apt sources in file: /etc/apt/sources.list.d/linrunner-tlp-trusty.list
|
||||
Active apt sources in file: /etc/apt/sources.list.d/wseverin-ppa-trusty.list
|
||||
deb http://ppa.launchpad.net/wseverin/ppa/ubuntu trusty main
|
||||
|
||||
Inxi will also display the Weather details of your location. Surprised? Yes, It should.
|
||||
|
||||
inxi -W Erode,Tamilnadu
|
||||
|
||||
Here **Erode** is the District and **Tamilnadu** is a state in India.
|
||||
|
||||
Sample output:
|
||||
|
||||
Weather: Conditions: 79 F (26 C) - Clear Time: February 4, 6:00 PM IST
|
||||
|
||||
### Viewing Complete Hardware details ###
|
||||
|
||||
Tired of finding each hardware details? Well, you can list all details at once using command:
|
||||
|
||||
inxi -F
|
||||
|
||||
**Sample output:**
|
||||
|
||||
System: Host: sk Kernel: 3.13.0-45-generic x86_64 (64 bit) Desktop: LXDE (Openbox 3.5.2) Distro: Ubuntu 14.04 trusty
|
||||
Machine: System: Dell (portable) product: Inspiron N5050
|
||||
Mobo: Dell model: 01HXXJ version: A05 Bios: Dell version: A05 date: 08/03/2012
|
||||
CPU: Dual core Intel Core i3-2350M CPU (-HT-MCP-) cache: 3072 KB flags: (lm nx sse sse2 sse3 sse4_1 sse4_2 ssse3 vmx)
|
||||
Clock Speeds: 1: 800.00 MHz 2: 1000.00 MHz 3: 800.00 MHz 4: 800.00 MHz
|
||||
Graphics: Card: Intel 2nd Generation Core Processor Family Integrated Graphics Controller
|
||||
X.Org: 1.15.1 drivers: intel (unloaded: fbdev,vesa) Resolution: 1366x768@60.0hz
|
||||
GLX Renderer: Mesa DRI Intel Sandybridge Mobile GLX Version: 3.0 Mesa 10.3.0
|
||||
Audio: Card: Intel 6 Series/C200 Series Family High Definition Audio Controller driver: snd_hda_intel
|
||||
Sound: Advanced Linux Sound Architecture ver: k3.13.0-45-generic
|
||||
Network: Card-1: Qualcomm Atheros AR9285 Wireless Network Adapter (PCI-Express) driver: ath9k
|
||||
IF: wlan0 state: up mac:
|
||||
Card-2: Realtek RTL8101E/RTL8102E PCI Express Fast Ethernet controller driver: r8169
|
||||
IF: eth0 state: down mac:
|
||||
Drives: HDD Total Size: 500.1GB (52.5% used) 1: id: /dev/sda model: ST9500325AS size: 500.1GB
|
||||
Partition: ID: / size: 455G used: 245G (57%) fs: ext4 ID: /boot size: 236M used: 159M (72%) fs: ext2
|
||||
ID: swap-1 size: 4.19GB used: 0.00GB (0%) fs: swap
|
||||
RAID: No RAID devices detected - /proc/mdstat and md_mod kernel raid module present
|
||||
Sensors: System Temperatures: cpu: 64.5C mobo: N/A
|
||||
Fan Speeds (in rpm): cpu: N/A
|
||||
Info: Processes: 186 Uptime: 6:52 Memory: 1547.2/3861.3MB Client: Shell (bash) inxi: 1.9.17
|
||||
|
||||
As you see in the above, inxi displays the complete hardware details.
|
||||
|
||||
For more details, refer the man pages.
|
||||
|
||||
man inxi
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
Are you searching for a simple tool which displays your complete system and hardware details? Then, don’t look anywhere, inxi will give you what actually want. And, it is light weight tool available in your default repositories. What else you want more? Give it a try, you won’t be disappointed.
|
||||
|
||||
Cheers!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.unixmen.com/inxi-find-system-hardware-information-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[SK][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.unixmen.com/author/sk/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.unixmen.com/screenfetch-bash-screenshot-information-tool/
|
||||
Inxi——获取Linux的系统和硬件信息
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
我们已经展示了一些不同的[应用程序][1]和方法来获取Linux的系统和硬件信息。在这一系列,我们将看到如何使用**inxi**来获取这些详情信息。在论坛技术支持中,它可以作为调试工具,迅速确定用户的系统配置和硬件信息。
|
||||
|
||||
**Inxi**是一个可以获取完整的系统和硬件详情信息的命令行工具,内容包括:
|
||||
|
||||
- 硬件
|
||||
- CPU
|
||||
- 磁盘驱动器
|
||||
- Xorg
|
||||
- 桌面环境
|
||||
- 内核
|
||||
- GCC版本
|
||||
- 进程
|
||||
- 内存占用
|
||||
- 和其他有用的信息
|
||||
|
||||
### 安装方法 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Inxi在多数现代GNU/Linux操作系统的默认软件仓库中。所以我们可以简单地运行下列命令安装。
|
||||
|
||||
**在基于Debian的发行版:**
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install inxi
|
||||
|
||||
**在Fedora:**
|
||||
|
||||
sudo yum install inxi
|
||||
|
||||
**在基于RHEL的发行版:**
|
||||
|
||||
安装EPEL软件仓库:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo yum install epel-release
|
||||
|
||||
然后使用如下命令安装inxi:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo yum install inxi
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用方法 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在终端运行如下命令可以获取系统的概况信息。
|
||||
|
||||
inxi
|
||||
|
||||
**示例输出:**
|
||||
|
||||
CPU~Dual core Intel Core i3-2350M CPU (-HT-MCP-) clocked at Min:800.000Mhz Max:1200.000Mhz Kernel~3.13.0-45-generic x86_64 Up~6:41 Mem~1537.7/3861.3MB HDD~500.1GB(52.5% used) Procs~183 Client~Shell inxi~1.9.17
|
||||
|
||||
当然,我们可以获取一个特定硬件的详情信息。比如获取**声音/音频硬件详情信息**,可以运行如下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
inxi -A
|
||||
|
||||
**示例输出:**
|
||||
|
||||
Audio: Card: Intel 6 Series/C200 Series Family High Definition Audio Controller driver: snd_hda_intel
|
||||
Sound: Advanced Linux Sound Architecture ver: k3.13.0-45-generic
|
||||
|
||||
很酷是吧?
|
||||
|
||||
同样的,你可以获取**显卡**的详情信息。
|
||||
|
||||
inxi -G
|
||||
|
||||
**示例输出:**
|
||||
|
||||
Graphics: Card: Intel 2nd Generation Core Processor Family Integrated Graphics Controller
|
||||
X.Org: 1.15.1 drivers: intel (unloaded: fbdev,vesa) Resolution: 1366x768@60.0hz
|
||||
GLX Renderer: Mesa DRI Intel Sandybridge Mobile GLX Version: 3.0 Mesa 10.3.0
|
||||
|
||||
硬盘信息呢?也是可以的。运行如下命令来获取完整的**硬盘**信息。
|
||||
|
||||
inxi -D
|
||||
|
||||
**示例输出:**
|
||||
|
||||
Drives: HDD Total Size: 500.1GB (52.5% used) 1: id: /dev/sda model: ST9601325BD size: 500.1GB
|
||||
|
||||
显示Bios和主板详情信息:
|
||||
|
||||
inxi -M
|
||||
|
||||
**示例输出:**
|
||||
|
||||
Machine: System: Dell (portable) product: Inspiron N5050
|
||||
Mobo: Dell model: 01HXXJ version: A05 Bios: Dell version: A05 date: 08/03/2012
|
||||
|
||||
不只有硬性详情信息,它也可以显示我们系统中的**可用软件仓库列表**。
|
||||
|
||||
inxi -r
|
||||
|
||||
**示例输出:**
|
||||
|
||||
Repos: Active apt sources in file: /etc/apt/sources.list
|
||||
deb http://ubuntu.excellmedia.net/archive/ trusty main restricted
|
||||
deb-src http://ubuntu.excellmedia.net/archive/ trusty main restricted
|
||||
deb http://ubuntu.excellmedia.net/archive/ trusty-updates main restricted
|
||||
deb-src http://ubuntu.excellmedia.net/archive/ trusty-updates main restricted
|
||||
deb http://ubuntu.excellmedia.net/archive/ trusty universe
|
||||
.
|
||||
.
|
||||
Active apt sources in file: /etc/apt/sources.list.d/intellinuxgraphics.list
|
||||
deb https://download.01.org/gfx/ubuntu/14.04/main trusty main #Intel Graphics drivers
|
||||
Active apt sources in file: /etc/apt/sources.list.d/linrunner-tlp-trusty.list
|
||||
Active apt sources in file: /etc/apt/sources.list.d/wseverin-ppa-trusty.list
|
||||
deb http://ppa.launchpad.net/wseverin/ppa/ubuntu trusty main
|
||||
|
||||
Inxi还可以显示你所在位置的天气信息。感到意外吗?是的,它可以。
|
||||
|
||||
inxi -W Erode,Tamilnadu
|
||||
|
||||
这里**Erode**是区,**Tamilnadu**是印度的一个邦。
|
||||
|
||||
示例输出:
|
||||
|
||||
Weather: Conditions: 79 F (26 C) - Clear Time: February 4, 6:00 PM IST
|
||||
|
||||
### 查看完整的硬件详情信息 ###
|
||||
|
||||
厌倦了获取每种硬件的信息?你可以使用如下命令将所有信息一次列出:
|
||||
|
||||
inxi -F
|
||||
|
||||
**示例输出:**
|
||||
|
||||
System: Host: sk Kernel: 3.13.0-45-generic x86_64 (64 bit) Desktop: LXDE (Openbox 3.5.2) Distro: Ubuntu 14.04 trusty
|
||||
Machine: System: Dell (portable) product: Inspiron N5050
|
||||
Mobo: Dell model: 01HXXJ version: A05 Bios: Dell version: A05 date: 08/03/2012
|
||||
CPU: Dual core Intel Core i3-2350M CPU (-HT-MCP-) cache: 3072 KB flags: (lm nx sse sse2 sse3 sse4_1 sse4_2 ssse3 vmx)
|
||||
Clock Speeds: 1: 800.00 MHz 2: 1000.00 MHz 3: 800.00 MHz 4: 800.00 MHz
|
||||
Graphics: Card: Intel 2nd Generation Core Processor Family Integrated Graphics Controller
|
||||
X.Org: 1.15.1 drivers: intel (unloaded: fbdev,vesa) Resolution: 1366x768@60.0hz
|
||||
GLX Renderer: Mesa DRI Intel Sandybridge Mobile GLX Version: 3.0 Mesa 10.3.0
|
||||
Audio: Card: Intel 6 Series/C200 Series Family High Definition Audio Controller driver: snd_hda_intel
|
||||
Sound: Advanced Linux Sound Architecture ver: k3.13.0-45-generic
|
||||
Network: Card-1: Qualcomm Atheros AR9285 Wireless Network Adapter (PCI-Express) driver: ath9k
|
||||
IF: wlan0 state: up mac:
|
||||
Card-2: Realtek RTL8101E/RTL8102E PCI Express Fast Ethernet controller driver: r8169
|
||||
IF: eth0 state: down mac:
|
||||
Drives: HDD Total Size: 500.1GB (52.5% used) 1: id: /dev/sda model: ST9500325AS size: 500.1GB
|
||||
Partition: ID: / size: 455G used: 245G (57%) fs: ext4 ID: /boot size: 236M used: 159M (72%) fs: ext2
|
||||
ID: swap-1 size: 4.19GB used: 0.00GB (0%) fs: swap
|
||||
RAID: No RAID devices detected - /proc/mdstat and md_mod kernel raid module present
|
||||
Sensors: System Temperatures: cpu: 64.5C mobo: N/A
|
||||
Fan Speeds (in rpm): cpu: N/A
|
||||
Info: Processes: 186 Uptime: 6:52 Memory: 1547.2/3861.3MB Client: Shell (bash) inxi: 1.9.17
|
||||
|
||||
就像上面你看到的那样,inxi显示出了完整的硬件详情信息。
|
||||
|
||||
更多的细节可以参考man手册。
|
||||
|
||||
man inxi
|
||||
|
||||
### 结论 ###
|
||||
|
||||
你在寻找一个可以显示完整的系统和硬件详情信息的简单工具吗?那么不用再找了,inxi会提供你所需要的。并且,它还是在你系统默认的软件仓库中的轻量级工具。你还想要更多东西吗?试一试它,你不会失望。
|
||||
|
||||
欢呼吧!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.unixmen.com/inxi-find-system-hardware-information-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[SK][a]
|
||||
译者:[goreliu](https://github.com/goreliu)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.unixmen.com/author/sk/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.unixmen.com/screenfetch-bash-screenshot-information-tool/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,63 @@
|
||||
zBackup——一个通用的重复数据备份工具
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
zbackup是一个基于rsync思想的全局重复数据备份工具。给它传入一个大的tar文件后,它会存储该文件的重复区域(仅进行一次),然后对结果进行压缩,并根据参数确定是否对其加密。传入另一个tar文件后,它会从之前的已备份文件中复用重复的数据。只有新的改动会被保存,并且只要文件变动不是很大,需要的存储空间非常少。任何时候之前的已备份文件都可以被完整地读出来。
|
||||
|
||||
### zBackup特性 ###
|
||||
|
||||
- 使用并行的LZMA或者LZO压缩算法压缩已备份数据
|
||||
- 使用内置的AES加密算法加密已备份数据
|
||||
- 可以删除旧的已备份数据
|
||||
- 使用一个64位滚动哈希,保持软碰撞数量为0
|
||||
- 已备份数据由不可更改的文件组成。任何现有文件都没有被更改过
|
||||
- 使用C++语言编写,并且只有适量的依赖库
|
||||
- 可以在生产环境安全使用
|
||||
- 可以在不同备份库中交换数据而无需重新压缩
|
||||
|
||||
### 在ubuntu中安装zBackup ###
|
||||
|
||||
打开终端并运行如下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install zbackup
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用zBackup ###
|
||||
|
||||
`zbackup init`命令会初始化一个备份库,用来存放待备份的数据。
|
||||
|
||||
zbackup init [--non-encrypted] [--password-file ~/.my_backup_password ] /my/backup/repo
|
||||
|
||||
`zbackup backup`命令备份一个由`tar c`创建的tar文件到刚才使用`zbackup init`初始化的备份库。(译注:实际使用时类似这样,tar c files | zbackup ...)
|
||||
|
||||
zbackup [--password-file ~/.my_backup_password ] [--threads number_of_threads ] backup /my/backup/repo/backups/backup-`date ‘+%Y-%m-%d'`
|
||||
|
||||
`zbackup restore`命令从备份库中恢复一个已备份文件到tar文件中。
|
||||
|
||||
zbackup [--password-file ~/.my_backup_password ] [--cache-size cache_size_in_mb ] restore /my/backup/repo/backups/backup-`date ‘+%Y-%m-%d'` > /my/precious/backup-restored.tar
|
||||
|
||||
### 可用选项 ###
|
||||
|
||||
- -non-encrypted -- 不加密备份库。
|
||||
- --password-file ~/.my_backup_password -- 使用位于~/.my_backup_password的口令文件来加密备份库和待备份文件,以及解密已备份文件。
|
||||
- --threads number_of_threads -- 限制并行LZMA压缩的线程数到number_of_threads。建议在32位的系统平台使用。
|
||||
- --cache-size cache_size_in_mb -- 使用cache_size_in_mb中的缓存大小来加速恢复文件的过程。
|
||||
|
||||
### zBackup相关文件 ###
|
||||
|
||||
~/.my_backup_password 用来加密备份库和待备份文件,以及解密已备份文件。更多细节见zbackup。
|
||||
|
||||
/my/backup/repo 存放备份库的目录。
|
||||
|
||||
/my/precious/restored-tar 用来恢复已备份文件的tar文件。
|
||||
|
||||
/my/backup/repo/backups/backup-`date ‘+%Y-%m-%d'` 指定的之前已备份文件的文件名。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.ubuntugeek.com/zbackup-a-versatile-deduplicating-backup-tool.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[ruchi][a]
|
||||
译者:[goreliu](https://github.com/goreliu)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.ubuntugeek.com/author/ubuntufix
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,113 @@
|
||||
使用ARChon环境在Ubuntu上运行Android应用
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
在此之前,我们尝试过在多款安卓应用模拟器工具上运行安卓应用,比如Genymotion、VirtualBox和Android SDK等。但是,有了这套全新的Chrome安卓运行环境,就可以在Chrome浏览器中运行安卓应用了。所以,下面是一些步骤来指导如何使用ARChon运行环境在Ubuntu上安装安卓应用。
|
||||
|
||||
谷歌已经公布了[首批支持原生运行在Chrome OS的安卓应用][1],而使用一个全新的“**安卓运行环境**”扩展程序使其成为可能。如今,一位名为Vlad Filippov的开发者已经找到了一种把安卓应用移植到桌面端Chrome浏览器的方法。他把chromeos-apk脚本和ARChon安卓运行环境扩展程序两者紧密结合在一起,使得安卓应用可以运行在Windows、Max和Linux系统的桌面端Chrome浏览器中。
|
||||
|
||||
应用借助这种运行环境时的性能并不是很好。同样,由于它是官方运行环境的非官方二次开发包,而且运行在Google的Chrome OS之外,因此一些如webcam和speaker等系统集成工具可能需要通过打补丁获得或者根本就没有。
|
||||
|
||||
### 安装Chrome ###
|
||||
|
||||
首先,需要在机器上安装Chrome,版本要求是Chrome 37或者更高。可以从[Chrome浏览器的下载页面][2]下载。
|
||||
|
||||
如果打算安装Dev Channel版本,按照如下操作。
|
||||
|
||||
首先,使用这个命令为Google Chrome添加软件源列表:
|
||||
|
||||
$ wget -q -O - https://dl-ssl.google.com/linux/linux_signing_key.pub | sudo apt-key add -
|
||||
$ sudo sh -c 'echo "deb http://dl.google.com/linux/chrome/deb/ stable main" >> /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome.list'
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
添加完软件源列表后,使用下列命令更新本地的软件库索引。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get update
|
||||
|
||||
现在,就可以安装非稳定版的google chrome,即开发版。
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install google-chrome-unstable
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 安装Archon运行时环境 ###
|
||||
|
||||
接下来,需要下载定制版的运行环境安装包,因为官方版本不被Google或Vlad Filippov创建的Chromium安卓运行环境认可。它在很多方面有别于官方版本,主要区别是它可以用于Google浏览器的各个桌面端。下面是需要下载的运行环境安装包,请根据所安装的Ubuntu系统位数选择下列的一种。
|
||||
|
||||
**32位** Ubntu发行版:
|
||||
|
||||
- [Download Archron for 32-bit Ubuntu][3]
|
||||
|
||||
**64位** Ubntu发行版:
|
||||
|
||||
- [Download Archron for 64-bit Ubuntu][4]
|
||||
|
||||
下载好运行环境安装包后,从.zip文件中解压,并将解压得到的目录移动到Home目录。操作命令如下:
|
||||
|
||||
$ wget https://github.com/vladikoff/chromeos-apk/releases/download/v3.0.0/ARChon-v1.1-x86_32.zip
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
$ unzip ARChon-v1.1-x86_32.zip ~/
|
||||
|
||||
接下来是安装运行时环境,首先打开Google Chrome浏览器,在地址栏键入**chrome://extensions**。然后,选中“**开发者模式**”。最后,点击“**载入未打包扩展程序**”,选择刚才放置在**~/Home**下面的文件夹。
|
||||
|
||||
### 安装 ChromeOS-APK ###
|
||||
|
||||
如果要用到上面提到的应用,那么手动转换这些APKs无需复杂的操作——只需要安装“[chromeos-apk][5]”命令行JavaScript工具。可以在Node Package Modules(npm)管理器中安装它。为了安装npm和chromeos-apk,在shell或终端中运行下面命令:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install npm nodejs nodejs-legacy
|
||||
|
||||
如果**操作系统是64位**,需要安装下面这个库,命令如下:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install lib32stdc++6
|
||||
|
||||
然后,运行这条命令来安装最新的chromeos-apk:
|
||||
|
||||
$ npm install -g chromeos-apk@latest
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
取决于系统配置,可能需要以sudo权限运行后一条命令。
|
||||
|
||||
现在,我们将找一个应用程序的APK来在Google浏览器上试一试,但务必牢记**并非所有的安卓应用都可以**,有一些可能不稳定或者缺少某些特性。大部分安装即用的通讯类应用都不适用这个环境。
|
||||
|
||||
### 转换APK ###
|
||||
|
||||
将**安卓APK放到~/Home**下,然后在**终端**执行下列命令进行转换:
|
||||
|
||||
$ chromeos-apk myapp.apk --archon
|
||||
|
||||
如果想以全屏模式运行应用,请替换成这条命令:
|
||||
|
||||
$ chromeos-apk myapp.apk --archon --tablet
|
||||
|
||||
注意:请将myapp.apk替换成待转换的安卓APK应用的文件名。
|
||||
|
||||
为了方便,也可以使用[Twerk][6]来进行转换,这样可以跳过这一步。
|
||||
|
||||
### 运行安卓Apk ###
|
||||
|
||||
最后,打开chrome浏览器,然后进入chrome://extensions页面,勾选开发者模式。点击“载入未打包扩展程序”按钮,选择文件夹载入刚创建的脚本。
|
||||
|
||||
至此,就可以打开Chrome应用启动器运行安卓应用了。
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结 ###
|
||||
|
||||
万岁!我们已经成功在Chrome浏览器中安装好安卓Apk应用程序了。这篇文章是关于一款由Vlad Filippov开发的、名为Archon的、时下流行的Chrome安卓运行环境。这个运行环境使用户在Chrome浏览器中运行转换过的Apk文件。目前它还不支持通讯类应用,诸如Whatsapp。因此,如果你有任何问题、建议和反馈,请在下面的评论框中写出来。非常感谢!去拥抱Archon吧!:-)
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/ubuntu-how-to/android-apps-ubuntu-archon-runtime/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Arun Pyasi][a]
|
||||
译者:[KayGuoWhu](https://github.com/KayGuoWhu)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arunp/
|
||||
[1]:http://chrome.blogspot.com/2014/09/first-set-of-android-apps-coming-to.html
|
||||
[2]:https://www.google.com/chrome/browser
|
||||
[3]:https://github.com/vladikoff/chromeos-apk/releases/download/v3.0.0/ARChon-v1.1-x86_32.zip
|
||||
[4]:https://github.com/vladikoff/chromeos-apk/releases/download/v3.0.0/ARChon-v1.1-x86_64.zip
|
||||
[5]:https://github.com/vladikoff/chromeos-apk/blob/master/README.md
|
||||
[6]:https://chrome.google.com/webstore/detail/twerk/jhdnjmjhmfihbfjdgmnappnoaehnhiaf
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,85 @@
|
||||
|
||||
KDE Plasma 5.3已发布,Kubuntu 15.04升级攻略
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**KDE[已经宣布][1]Plasma 5.3的稳定版已经准备就绪,它包含了一个新的电源管理方面的稳定特性。**
|
||||
|
||||
[先前四月份的beta版][2]已经让我们印象深刻,甚至跃跃欲试了,Plasma 5桌面环境的稳定版更新的最新更新已经稳定,并且可以下载了。
|
||||
|
||||
Plasma 5.3继续改善和细化了全新的KDE桌面,它添加了大量的特性供桌面用户体验。同时也修复了**多达400个错误**,这对性能和稳定性方面也进行了大量改善。
|
||||
|
||||
### Plasma 5.3中的新东西 ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Plasma 5.3中更好的蓝牙管理
|
||||
|
||||
而[在早期关于Plasma 5.3的文章][3]中,我们触及了大量**新特性**,这其中很多都值得反复说道说道。
|
||||
|
||||
**加强的电源管理**特性和配置选项,包括**新的电源小程序、能源使用监控**和**动态屏幕亮度变化**,将有助于让KDE在移动设备上加强续航能力。
|
||||
|
||||
在连接了外部监视器的时候合上笔记本盖子时,不会再触发‘挂起’操作。这个新的行为被称之为‘**影院模式**’,并且默认开启。但是,可以通功过电源管理设置中的相关选项禁用。
|
||||
|
||||
**蓝牙功能被改善**,带来了一个全新的面板小程序,使得在连接到并配置配对的蓝牙设备,如只能手机、键盘和扬声器时,比以往更为便捷。
|
||||
|
||||
同样,对于Plasma 5.3,**KDE中的轨迹板配置更为方便**,这多亏了新的安装和设置模块。
|
||||

|
||||
轨迹板、触控板。Tomato, Tomayto。
|
||||
|
||||
对于Plasma小部件狂热者,带来了一个**按住并锁定**手势。当启用该功能,会隐藏移动鼠标时出现的设置处理。取而代之的是,它只会在长点击小部件时发生该行为。
|
||||
|
||||
谈到widget-y这类事情时,该发布版中**再次引入了几个旧的Plasmoid最受欢迎的东西**,包括一个有用的系统监视器、便利的硬盘驱动器统计和一个漫画阅读器。
|
||||
|
||||
### 了解更多&尝试 ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
一张全部内容的完整列表——我说全部内容——是指Plasma 5.3中[在官方修改日志中][4]列出的新的和改进的内容。
|
||||
|
||||
你可以从KDE社区获取Live镜像,试用Kubuntu上的Plasma 5.3,**而不会影响到你自己的系统**:
|
||||
|
||||
- [下载KDE Plasma Live镜像][5]
|
||||
|
||||
如果你需要超级稳定的系统,你可以使用这些镜像来尝试新特性,但是你可以继续使用你的主要计算机上与你的版本对应的KDE版本。
|
||||
|
||||
但是,如果你对实验版满意——请阅:能够处理任何包冲突,或者由尝试升级桌面环境而导致的系统问题——那么你可以安装。
|
||||
|
||||
### 安装Plasma 5.3到Kubuntu 15.04 ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
要**安装Plasma 5.3到Kubuntu 15.04**中,你需要添加KDE 移植PPA,运行软件更新器工具并安装任何可用的更新。
|
||||
|
||||
Kubuntu移植PPA可能也会升级除了安装在你系统上的Plasma外的其它KDE平台组件,包括KDE应用程序、框架和Kubuntu特定配置文件。
|
||||
|
||||
目前为止,使用命令行来升级Kubuntu中的到Plasma 5.3是最快速的方法:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:kubuntu-ppa/backports
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get dist-upgrade
|
||||
|
||||
在升级过程完成后,如果一切顺利,你应该重启计算机。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你正在使用一个备用桌面环境,比如LXDE、Unity或者GNOME,则你需要在运行完上面的两个命令后安装Kubuntu桌面包(你可以在Ubuntu软件中心找到)。
|
||||
To downgrade to the stock version of Plasma in 15.04 you can use the PPA-Purge tool:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install ppa-purge
|
||||
|
||||
sudo ppa-purge ppa:kubuntu-ppa/backports
|
||||
|
||||
请在下面的评论中留言,让我们知道你怎么升级/测试过程是怎样的,别忘了告诉我们你在下一个Plasma 5桌面中要看到的特性。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2015/04/kde-plasma-5-3-released-heres-how-to-upgrade-in-kubuntu-15-04
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Joey-Elijah Sneddon][a]
|
||||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://plus.google.com/117485690627814051450/?rel=author
|
||||
[1]:https://www.kde.org/announcements/plasma-5.3.0.php
|
||||
[2]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2015/04/beta-plasma-5-3-features
|
||||
[3]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2015/04/beta-plasma-5-3-features
|
||||
[4]:https://www.kde.org/announcements/plasma-5.2.2-5.3.0-changelog.php
|
||||
[5]:https://community.kde.org/Plasma/Live_Images
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,134 @@
|
||||
在 Debian, Ubuntu, Linux Mint 及 Fedora 中安装 uGet 下载管理器 2.0
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
在经历了一段漫长的开发期后,期间发布了超过 11 个开发版本,最终 uGet 项目小组高兴地宣布 uGet 的最新稳定版本 uGet 2.0 已经可以下载使用了。最新版本包含许多吸引人的特点,例如一个新的设定对话框,改进了 aria2 插件对 BitTorrent 和 Metalink 协议的支持,同时对位于横栏中的 uGet RSS 信息提供了更好的支持,其他特点包括:
|
||||
|
||||
- 一个新的 “检查更新” 按钮,提醒您有关新的发行版本的信息;
|
||||
- 增添新的语言支持并升级了现有的语言;
|
||||
- 增加了一个新的 “信息横栏” ,允许开发者轻松地向所有的用户提供有关 uGet 的信息;
|
||||
- 通过对文档、提交反馈和错误报告等内容的链接,增强了帮助菜单;
|
||||
- 将 uGet 下载管理器集成到了 Linux 平台下的两个主要的浏览器 Firefox 和 Google Chrome 中;
|
||||
- 改进了对 Firefox 插件 ‘FlashGot’ 的支持;
|
||||
|
||||
### 何为 uGet ###
|
||||
|
||||
uGet (先前名为 UrlGfe) 是一个开源,免费,且极其强大的基于 GTK 的多平台下载管理器应用程序,它用 C 语言写就,在 GPL 协议下发布。它提供了一大类的功能,如恢复先前的下载任务,支持多重下载,使用一个独立的配置来支持分类,剪贴板监视,下载队列,从 HTML 文件中导出 URL 地址,集成在 Firefox 中的 Flashgot 插件中,使用集成在 uGet 中的 aria2(一个命令行下载管理器) 来下载 torrent 和 metalink 文件。
|
||||
|
||||
我已经在下面罗列出了 uGet 下载管理器的所有关键特点,并附带了详细的解释。
|
||||
|
||||
#### uGet 下载管理器的关键特点 ####
|
||||
|
||||
- 下载队列: 可以将你的下载任务放入一个队列中。当某些下载任务完成后,将会自动开始下载队列中余下的文件;
|
||||
- 恢复下载: 假如在某些情况下,你的网络中断了,不要担心,你可以从先前停止的地方继续下载或重新开始;
|
||||
- 下载分类: 支持多种分类来管理下载;
|
||||
- 剪贴板监视: 将要下载的文件类型复制到剪贴板中,便会自动弹出下载提示框以下载刚才复制的文件;
|
||||
- 批量下载: 允许你轻松地一次性下载多个文件;
|
||||
- 支持多种协议: 允许你轻松地使用 aria2 命令行插件通过 HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, BitTorrent 及 Metalink 等协议下载文件;
|
||||
- 多连接: 使用 aria2 插件,每个下载同时支持多达 20 个连接;
|
||||
- 支持 FTP 登录或匿名 FTP 登录: 同时支持使用用户名和密码来登录 FTP 或匿名 FTP ;
|
||||
- 队列下载: 新增队列下载,现在你可以对你的所有下载进行安排调度;
|
||||
- 通过 FlashGot 与 FireFox 集成: 与作为一个独立支持的 Firefox 插件的 FlashGot 集成,从而可以处理单个或大量的下载任务;
|
||||
- CLI 界面或虚拟终端支持: 提供命令行或虚拟终端选项来下载文件;
|
||||
- 自动创建目录: 假如你提供了一个先前并不存在的保存路径,uGet 将会自动创建这个目录;
|
||||
- 下载历史管理: 跟踪记录已下载和已删除的下载任务的条目,每个列表支持 9999 个条目,比当前默认支持条目数目更早的条目将会被自动删除;
|
||||
- 多语言支持: uGet 默认使用英语,但它可支持多达 23 种语言;
|
||||
- Aria2 插件: uGet 集成了 Aria2 插件,来为 aria2 提供更友好的 GUI 界面;
|
||||
|
||||
如若你想了解更加完整的特点描述,请访问 uGet 官方的 [特点页面][1].
|
||||
|
||||
### 在 Debian, Ubuntu, Linux Mint 及 Fedora 中安装 uGet ###
|
||||
|
||||
uGet 开发者在 Linux 平台下的各种软件仓库中添加了 uGet 的最新版本,所以你可以在你使用的 Linux 发行版本下使用受支持的软件仓库来安装或升级 uGet 。
|
||||
|
||||
当前,一些 Linux 发行版本下的 uGet 可能不是最新的,但你可以到 [uGet 下载页面][2] 去了解你所用发行版本的支持状态,在那里选择你喜爱的发行版本来了解更多的信息。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在 Debian 下 ####
|
||||
|
||||
在 Debian 的测试版本 (Jessie) 和不稳定版本 (Sid) 中,你可以在一个可信赖的基础上,使用官方的软件仓库轻易地安装和升级 uGet 。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get update
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install uget
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在 Ubuntu 和 Linux Mint 下 ####
|
||||
|
||||
在 Ubuntu 和 Linux Mint 下,你可以使用官方的 PPA `ppa:plushuang-tw/uget-stable` 安装和升级 uGet ,通过使用这个 PPA,你可以自动地与最新版本保持同步。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:plushuang-tw/uget-stable
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get update
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install uget
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在 Fedora 下 ####
|
||||
|
||||
在 Fedora 20 – 21 下,最新版本的 uGet(2.0) 可以从官方软件仓库中获得,从这些软件仓库中安装是非常值得信赖的。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install uget
|
||||
|
||||
**注**: 在旧版本的 Debian, Ubuntu, Linux Mint 和 Fedora 下,用户也可以安装 uGet , 但可获取的版本为 1.10.4 。假如你期待使用升级版本(例如 2.0 版本),你需要升级你的系统并添加 uGet 的 PPA 以此来获取最新的稳定版本。
|
||||
|
||||
### 安装 aria2 插件 ###
|
||||
|
||||
[aria2][3] 是一个卓越的命令行下载管理应用,在 uGet 中它作为一个 aria2 插件,为 uGet 增添了更为强大的功能,如下载 toorent,metalinks 文件,支持多种协议和多来源下载等功能。
|
||||
|
||||
默认情况下,uGet 在当今大多数的 Linux 系统中使用 `curl` 来作为后端,但 aria2 插件将 curl 替换为 aria2 来作为 uGet 的后端。
|
||||
|
||||
aria2 是一个单独的软件包,需要独立安装。你可以在你的 Linux 发行版本下,使用受支持的软件仓库来轻易地安装 aria2 的最新版本,或根据 [下载 aria2 页面][4] 来安装它,该页面详细解释了在各个发行版本中如何安装 aria2 。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在 Debian, Ubuntu 和 Linux Mint 下 ####
|
||||
|
||||
利用下面的命令,使用 aria2 的个人软件仓库来安装最新版本的 aria2 :
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:t-tujikawa/ppa
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get update
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install aria2
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在 Fedora 下 ####
|
||||
|
||||
Fedora 的官方软件仓库中已经添加了 aria2 软件包,所以你可以轻易地使用下面的 yum 命令来安装它:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install aria2
|
||||
|
||||
#### 开启 uGet ####
|
||||
|
||||
为了启动 uGet,从桌面菜单的搜索栏中键入 "uGet"。可参考如下的截图:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
开启 uGet 下载管理器
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
uGet 版本: 2.0
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在 uGet 中激活 aria2 插件 ####
|
||||
|
||||
为了激活 aria2 插件, 从 uGet 菜单接着到 `编辑 –> 设置 –> 插件` , 从下拉菜单中选择 "aria2"。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
为 uGet 启用 Aria2 插件
|
||||
|
||||
### uGet 2.0 截图赏析 ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
使用 Aria2 下载文件
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
使用 uGet 下载 Torrent 文件
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
使用 uGet 进行批量下载
|
||||
|
||||
针对其他 Linux 发行版本和 Windows 平台的 RPM 包和 uGet 的源文件都可以在 uGet 的[下载页面][5] 下找到。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/install-uget-download-manager-in-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Ravi Saive][a]
|
||||
译者:[FSSlc](https://github.com/FSSlc)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/admin/
|
||||
[1]:http://uget.visuex.com/features
|
||||
[2]:http://ugetdm.com/downloads
|
||||
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/install-aria2-a-multi-protocol-command-line-download-manager-in-rhel-centos-fedora/
|
||||
[4]:http://ugetdm.com/downloads-aria2
|
||||
[5]:http://ugetdm.com/downloads
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,399 @@
|
||||
70 个可能的 Shell 脚本面试问题及解答
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
我们为你的面试准备选择了 70 个可能的 shell 脚面问题及解答。了解脚本或至少知道基础知识对系统管理员来说至关重要,它也有助于你在工作环境中自动完成很多任务。在过去的几年里,我们注意到所有的 linux 工作职位都要求脚本技能。
|
||||
|
||||
### 1) 如何向脚本传递参数 ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
./script argument
|
||||
|
||||
**例子** : 显示文件名称脚本
|
||||
|
||||
./show.sh file1.txt
|
||||
|
||||
cat show.sh
|
||||
#!/bin/bash
|
||||
cat $1
|
||||
|
||||
### 2) 如何在脚本中使用参数 ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
第一个参数: $1,
|
||||
第二个参数 : $2
|
||||
|
||||
例子 : 脚本会复制文件(arg1) 到目标地址(arg2)
|
||||
|
||||
./copy.sh file1.txt /tmp/
|
||||
|
||||
cat copy.sh
|
||||
#!/bin/bash
|
||||
cp $1 $2
|
||||
|
||||
### 3) 如何计算传递进来的参数 ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
$#
|
||||
|
||||
### 4) 如何在脚本中获取脚本名称 ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
$0
|
||||
|
||||
### 5) 如何检查之前的命令是否运行成功 ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
$?
|
||||
|
||||
### 6) 如何获取文件的最后一行 ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
tail -1
|
||||
|
||||
### 7) 如何获取文件的第一行 ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
head -1
|
||||
|
||||
### 8) 如何获取一个文件每一行的第三个元素 ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
awk '{print $3}'
|
||||
|
||||
### 9) 假如第一个等于 FIND,如何获取文件中每行的第二个元素 ###
|
||||
|
||||
awk '{ if ($1 == "FIND") print $2}'
|
||||
|
||||
### 10) 如何调试 bash 脚本 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Add -xv to #!/bin/bash
|
||||
|
||||
例子
|
||||
|
||||
#!/bin/bash –xv
|
||||
|
||||
### 11) 举例如何写一个函数 ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
function example {
|
||||
echo "Hello world!"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
### 12) 如何向 string 添加 string ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
V1="Hello"
|
||||
V2="World"
|
||||
V3=$V1+$V2
|
||||
echo $V3
|
||||
|
||||
Output
|
||||
|
||||
Hello+World
|
||||
|
||||
### 13) 如何进行两个整数相加 ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
V1=1
|
||||
V2=2
|
||||
V3=$V1+$V2
|
||||
echo $V3
|
||||
|
||||
Output
|
||||
3
|
||||
|
||||
### 14) 如何检查文件系统中是否存在某个文件 ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
if [ -f /var/log/messages ]
|
||||
then
|
||||
echo "File exists"
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
### 15) 写出 shell 脚本中所有循环语法 ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
#### for loop : ####
|
||||
|
||||
for i in $( ls ); do
|
||||
echo item: $i
|
||||
done
|
||||
|
||||
#### while loop : ####
|
||||
|
||||
#!/bin/bash
|
||||
COUNTER=0
|
||||
while [ $COUNTER -lt 10 ]; do
|
||||
echo The counter is $COUNTER
|
||||
let COUNTER=COUNTER+1
|
||||
done
|
||||
|
||||
#### untill oop : ####
|
||||
|
||||
#!/bin/bash
|
||||
COUNTER=20
|
||||
until [ $COUNTER -lt 10 ]; do
|
||||
echo COUNTER $COUNTER
|
||||
let COUNTER-=1
|
||||
done
|
||||
|
||||
### 16) 每个脚本开始的 #!/bin/sh 或 #!/bin/bash 表示什么意思 ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
这一行说明要使用的 shell。#!/bin/bash 表示脚本使用 /bin/bash。对于 python 脚本,就是 #!/usr/bin/python
|
||||
|
||||
### 17) 如何获取文本文件的第 10 行 ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
head -10 file|tail -1
|
||||
|
||||
### 18) bash 脚本文件的第一个符号是什么 ###
|
||||
|
||||
#
|
||||
|
||||
### 19) 命令:[ -z "" ] && echo 0 || echo 1 的输出是什么 ###
|
||||
|
||||
0
|
||||
|
||||
### 20) 命令 “export” 有什么用 ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
使变量在子 shell 中公有
|
||||
|
||||
### 21) 如何在后台运行脚本 ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
在脚本后面添加 “&”
|
||||
|
||||
### 22) "chmod 500 script" 做什么 ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
使脚本所有者拥有可执行权限
|
||||
|
||||
### 23) ">" 做什么 ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
重定向输出流到文件或另一个流。
|
||||
|
||||
### 24) & 和 && 有什么区别 ###
|
||||
|
||||
& - 希望脚本在后台运行的时候使用它
|
||||
&& - 当第一个脚本成功完成才执行命令/脚本的时候使用它
|
||||
|
||||
### 25) 什么时候要在 [ condition ] 之前使用 “if” ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
当条件满足时需要运行多条命令的时候。
|
||||
|
||||
### 26) 命令: name=John && echo 'My name is $name' 的输出是什么 ###
|
||||
|
||||
My name is $name
|
||||
|
||||
### 27) bash shell 脚本中哪个符号用于注释 ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
#
|
||||
|
||||
### 28) 命令: echo ${new:-variable} 的输出是什么 ###
|
||||
|
||||
variable
|
||||
|
||||
### 29) ' 和 " 引号有什么区别 ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
' - 当我们不希望把变量转换为值的时候使用它。
|
||||
" - 会计算所有变量的值并用值代替。
|
||||
|
||||
### 30) 如何在脚本文件中重定向标准输入输出流到 log.txt 文件 ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
在脚本文件中添加 "exec >log.txt 2>&1" 命令
|
||||
|
||||
### 31) 如何只用 echo 命令获取 string 变量的一部分 ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
echo ${variable:x:y}
|
||||
x - 起始位置
|
||||
y - 长度
|
||||
例子:
|
||||
variable="My name is Petras, and I am developer."
|
||||
echo ${variable:11:6} # 会显示 Petras
|
||||
|
||||
### 32) 如果给定字符串 variable="User:123:321:/home/dir" 如何只用 echo 命令获取 home_dir ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
echo ${variable#*:*:*:}
|
||||
或
|
||||
echo ${variable##*:}
|
||||
|
||||
### 33) 如何从上面的字符串中获取 “User” ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
echo ${variable%:*:*:*}
|
||||
或
|
||||
echo ${variable%%:*}
|
||||
|
||||
### 34) 如何使用 awk 列出 UID 小于 100 的用户 ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
awk -F: '$3<100' /etc/passwd
|
||||
|
||||
### 35) 写程序为用户计算主组数目并显示次数和组名 ###
|
||||
|
||||
cat /etc/passwd|cut -d: -f4|sort|uniq -c|while read c g
|
||||
do
|
||||
{ echo $c; grep :$g: /etc/group|cut -d: -f1;}|xargs -n 2
|
||||
done
|
||||
|
||||
### 36) 如何在 bash shell 中更改标注域分隔符为 ":" ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
IFS=":"
|
||||
|
||||
### 37) 如何获取变量长度 ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
${#variable}
|
||||
|
||||
### 38) 如何打印变量的最后 5 个字符 ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
echo ${variable: -5}
|
||||
|
||||
### 39) ${variable:-10} 和 ${variable: -10} 有什么区别? ###
|
||||
|
||||
${variable:-10} - 如果之前没有给 variable 赋值则输出 10
|
||||
${variable: -10} - 输出 variable 的最后 10 个字符
|
||||
|
||||
### 40) 如何只用 echo 命令替换字符串的一部分 ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
echo ${variable//pattern/replacement}
|
||||
|
||||
### 41) 哪个命令将命令替换为大写 ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
tr '[:lower:]' '[:upper:]'
|
||||
|
||||
### 42) 如何计算本地用户数目 ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
wc -l /etc/passwd|cut -d" " -f1
|
||||
或者
|
||||
cat /etc/passwd|wc -l
|
||||
|
||||
### 43) 不用 wc 命令如何计算字符串中的单词数目 ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
set ${string}
|
||||
echo $#
|
||||
|
||||
### 44) "export $variable" 或 "export variable" 哪个正确 ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
export variable
|
||||
|
||||
### 45) 如何列出第二个字母是 a 或 b 的文件 ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
ls -d ?[ab]*
|
||||
|
||||
### 46) 如何将整数 a 加到 b 并赋值给 c ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
c=$((a+b))
|
||||
或
|
||||
c=`expr $a + $b`
|
||||
或
|
||||
c=`echo "$a+$b"|bc`
|
||||
|
||||
### 47) 如何去除字符串中的所有空格 ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
echo $string|tr -d " "
|
||||
|
||||
### 48) 重写命令输出变量转换为复数的句子: item="car"; echo "I like $item" ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
item="car"; echo "I like ${item}s"
|
||||
|
||||
### 49) 写出输出数字 0 到 100 中 3 的倍数(0 3 6 9 …)的命令 ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
for i in {0..100..3}; do echo $i; done
|
||||
或
|
||||
for (( i=0; i<=100; i=i+3 )); do echo "Welcome $i times"; done
|
||||
|
||||
### 50) 如何打印传递给脚本的所有参数 ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
echo $*
|
||||
或
|
||||
echo $@
|
||||
|
||||
### 51) [ $a == $b ] 和 [ $a -eq $b ] 有什么区别 ###
|
||||
|
||||
[ $a == $b ] - 用于字符串比较
|
||||
[ $a -eq $b ] - 用于数字比较
|
||||
|
||||
### 52) = 和 == 有什么区别 ###
|
||||
|
||||
= - 用于为变量复制
|
||||
== - 用于字符串比较
|
||||
|
||||
### 53) 写出测试 $a 是否大于 12 的命令 ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
[ $a -gt 12 ]
|
||||
|
||||
### 54) 写出测试 $b 是否小于等于 12 的命令 ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
[ $b -le 12 ]
|
||||
|
||||
### 55) 如何检查字符串是否以字母 "abc" 开头 ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
[[ $string == abc* ]]
|
||||
|
||||
### 56) [[ $string == abc* ]] 和 [[ $string == "abc*" ]] 有什么区别 ###
|
||||
|
||||
[[ $string == abc* ]] - 检查字符串是否以字母 abc 开头
|
||||
[[ $string == "abc* " ]] - 检查字符串是否完全等于 abc*
|
||||
|
||||
### 57) 如何列出以 ab 或 xy 开头的用户名 ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
egrep "^ab|^xy" /etc/passwd|cut -d: -f1
|
||||
|
||||
### 58) bash 中 $! 表示什么意思 ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
后台最近命令的 PID
|
||||
|
||||
### 59) $? 表示什么意思 ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
前台最近命令的结束状态
|
||||
|
||||
### 60) 如何输出当前 shell 的 PID ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
echo $$
|
||||
|
||||
### 61) 如何获取传递给脚本的参数数目 ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
echo $#
|
||||
|
||||
### 62) $* 和 $@ 有什么区别 ###
|
||||
|
||||
$* - 以一个字符串形式输出所有传递到脚本的参数
|
||||
$@ - 以 $IFS 为分隔符列出所有传递到脚本中的参数
|
||||
|
||||
### 63) 如何在 bash 中定义数组 ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
array=("Hi" "my" "name" "is")
|
||||
|
||||
### 64) 如何打印数组的第一个元素 ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
echo ${array[0]}
|
||||
|
||||
### 65) 如何打印数组的所有元素 ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
echo ${array[@]}
|
||||
|
||||
### 66) 如何输出所有数组索引 ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
echo ${!array[@]}
|
||||
|
||||
### 67) 如何移除数组中索引为 2 的元素 ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
unset array[2]
|
||||
|
||||
### 68) 如何在数组中添加 id 为 333 的元素 ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
array[333]="New_element"
|
||||
|
||||
### 69) shell 脚本如何获取输入的值 ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
a) 通过参数
|
||||
|
||||
./script param1 param2
|
||||
|
||||
b) 通过 read 命令
|
||||
|
||||
read -p "Destination backup Server : " desthost
|
||||
|
||||
### 70) 在脚本中如何使用 "expect" ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
/usr/bin/expect << EOD
|
||||
spawn rsync -ar ${line} ${desthost}:${destpath}
|
||||
expect "*?assword:*"
|
||||
send "${password}\r"
|
||||
expect eof
|
||||
EOD
|
||||
|
||||
好运 !! 如果你有任何疑问或者问题需要解答都可以在下面的评论框中写下来。让我们知道这对你的面试有所帮助:-)
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/linux-shell-script/shell-scripting-interview-questions-answers/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Petras Liumparas][a]
|
||||
译者:[ictlyh](https://github.com/ictlyh)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/petrasl/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,45 @@
|
||||
Linux有问必答——在旧的Ubuntu上如何修复“apt-get update”的“404 Not Found”错误
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **问题**: 我的PC上安装了旧版的Ubuntu 13.04(急切的浣熊)。当我在上面运行“sudo apt-get update”时,它丢给了我一大堆“404 Not Found”错误,结果是我不能使用apt-get或aptitude来安装或更新任何软件包了。由于该错误的原因,我甚至不能将它升级到更新的版本。我怎样才能修复这个问题啊?
|
||||
>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
每个Ubuntu版本都有生命结束周期(EOL)时间;常规的Ubuntu发行版提供18个月的支持,而LTS(长期支持)版本则长达3年(服务器版本)和5年(桌面版本)。当某个Ubuntu版本达到生命结束周期时,其仓库就不能再访问了,你也不能再从Canonical获取任何维护更新和安全补丁。在撰写本文时,Ubuntu 13.04(急切的浣熊)已经达到了它的生命结束周期。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你所使用的Ubuntu系统已经被结束生命周期,你就会从apt-get或aptitude得到以下404错误,因为它的仓库已经被遗弃了。
|
||||
|
||||
W: Failed to fetch http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/dists/raring-backports/multiverse/binary-i386/Packages 404 Not Found [IP: 91.189.91.13 80]
|
||||
|
||||
W: Failed to fetch http://extras.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/dists/raring/main/binary-amd64/Packages 404 Not Found
|
||||
|
||||
W: Failed to fetch http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/dists/raring-security/universe/binary-i386/Packages 404 Not Found [IP: 91.189.88.149 80]
|
||||
|
||||
E: Some index files failed to download. They have been ignored, or old ones used instead
|
||||
|
||||
对于那些还在使用旧版本Ubuntu的用户,Canonical维护了一个old-releases.ubuntu.com的网站,这里包含了结束生命周期的仓库归档。因此,当Canonical对你安装的Ubuntu版本结束支持时,你需要将仓库切换到old-releases.ubuntu.com(除非你在结束生命周期之前想要升级)。
|
||||
|
||||
这里,通过切换到旧版本仓库提供了一个快速修复“404 Not Found”错误的便捷方式。
|
||||
|
||||
首先,使用旧版本仓库替换main/security仓库,就像下面这样。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo sed -i -r 's/([a-z]{2}\.)?archive.ubuntu.com/old-releases.ubuntu.com/g' /etc/apt/sources.list
|
||||
$ sudo sed -i -r 's/security.ubuntu.com/old-releases.ubuntu.com/g' /etc/apt/sources.list
|
||||
|
||||
然后,使用文本编辑器打开/etc/apt/sources.list,并查找extras.ubuntu.com。该仓库也不再支持Ubuntu 13.04了,所以你需要使用“#”号将extras.ubuntu.com注释掉。
|
||||
|
||||
#deb http://extras.ubuntu.com/ubuntu raring main
|
||||
#deb-src http://extras.ubuntu.com/ubuntu raring main
|
||||
|
||||
现在,你应该可以在旧版不受支持的Ubuntu上安装或更新软件包了。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/404-not-found-error-apt-get-update-ubuntu.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
|
||||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/author/nanni
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,57 @@
|
||||
Linux有问必答——Linux上如何查看某个进程的线程
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **问题**: 我的程序创建并在它里头执行了多个线程,我怎样才能在该程序创建线程后监控其中单个线程?我想要看到带有它们名称的单个线程详细情况(如,CPU/内存使用率)。
|
||||
|
||||
线程是现代操作系统上进行并行执行的一个流行的编程方面的抽象概念。当一个程序内有多个线程被叉分出用以执行多个流时,这些线程就会在它们之间共享特定的资源(如,内存地址空间、打开的文件),以使叉分开销最小化,并避免大量花销IPC(进程间通信)频道。这些功能让线程在并发执行时成为一个高效的机制。
|
||||
|
||||
在Linux中,程序中创建的线程(也称为轻量级进程,LWP)会具有和程序的PID相同的“线程组ID”。然后,各个线程会获得其自身的线程ID(TID)。对于Linux内核调度器而言,线程不过是恰好共享特定资源的标准的进程。经典的命令行工具,如ps或top,都可以用来显示线程级别的信息,默认情况下它们会显示进程级别的信息。
|
||||
|
||||
这里提供了**在Linux上显示某个进程的线程**的几种方式。
|
||||
|
||||
### 方法一:PS ###
|
||||
|
||||
在ps命令中,“-T”选项可以开启线程查看。下面的命令列出了由进程号为<pid>的进程创建的所有线程。
|
||||
|
||||
$ ps -T -p <pid>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
“SID”栏表示线程ID,而“CMD”栏则显示了线程名称。
|
||||
|
||||
### 方法二: Top ###
|
||||
|
||||
top命令可以实时显示各个线程情况。要在top输出中开启线程查看,请调用top命令的“-H”选项,该选项会列出所有Linux线程。在top运行时,你也可以通过按“H”键将线程查看模式切换为开或关。
|
||||
|
||||
$ top -H
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
要让top输出某个特定进程<pid>并检查该进程内运行的线程状况:
|
||||
|
||||
$ top -H -p <pid>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 方法三: Htop ###
|
||||
|
||||
一个对用户更加友好的方式是,通过htop查看单个进程的线程,它是一个基于ncurses的交互进程查看器。该程序允许你在树状视图中监控单个独立线程。
|
||||
|
||||
要在htop中启用线程查看,请开启htop,然后按<F2>来进入htop的设置菜单。选择“设置”栏下面的“显示选项”,然后开启“树状视图”和“显示自定义线程名”选项。按<F10>退出设置。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
现在,你就会看到下面这样单个进程的线程视图。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/view-threads-process-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
|
||||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/author/nanni
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user