mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-03-24 02:20:09 +08:00
Merge branch 'master' of github.com:LCTT/TranslateProject
This commit is contained in:
commit
081002151e
82
README.md
82
README.md
@ -1,16 +1,16 @@
|
||||
简介
|
||||
-------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
LCTT是“Linux中国”([https://linux.cn/](https://linux.cn/))的翻译组,负责从国外优秀媒体翻译Linux相关的技术、资讯、杂文等内容。
|
||||
LCTT 是“Linux中国”([https://linux.cn/](https://linux.cn/))的翻译组,负责从国外优秀媒体翻译 Linux 相关的技术、资讯、杂文等内容。
|
||||
|
||||
LCTT已经拥有几百名活跃成员,并欢迎更多的Linux志愿者加入我们的团队。
|
||||
LCTT 已经拥有几百名活跃成员,并欢迎更多的Linux志愿者加入我们的团队。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
LCTT的组成
|
||||
LCTT 的组成
|
||||
-------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
**选题**,负责选择合适的内容,并将原文转换为markdown格式,提交到LCTT的[TranslateProject](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 库中。
|
||||
**选题**,负责选择合适的内容,并将原文转换为 markdown 格式,提交到 LCTT 的 [TranslateProject](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 库中。
|
||||
|
||||
**译者**,负责从选题中选择内容进行翻译。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -21,38 +21,38 @@ LCTT的组成
|
||||
加入我们
|
||||
-------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
请首先加入翻译组的QQ群,群号是:198889102,加群时请说明是“志愿者”。加入后记得修改您的群名片为您的github的ID。
|
||||
请首先加入翻译组的 QQ 群,群号是:198889102,加群时请说明是“志愿者”。加入后记得修改您的群名片为您的 GitHub 的 ID。
|
||||
|
||||
加入的成员,请先阅读[WIKI 如何开始](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject/wiki/01-如何开始)。
|
||||
加入的成员,请先阅读 [WIKI 如何开始](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject/wiki/01-如何开始)。
|
||||
|
||||
如何开始
|
||||
-------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
请阅读[WIKI](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject/wiki)。
|
||||
请阅读 [WIKI](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject/wiki)。
|
||||
|
||||
历史
|
||||
-------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
* 2013/09/10 倡议并得到了大家的积极响应,成立翻译组。
|
||||
* 2013/09/11 采用github进行翻译协作,并开始进行选题翻译。
|
||||
* 2013/09/11 采用 GitHub 进行翻译协作,并开始进行选题翻译。
|
||||
* 2013/09/16 公开发布了翻译组成立消息后,又有新的成员申请加入了。并从此建立见习成员制度。
|
||||
* 2013/09/24 鉴于大家使用Github的水平不一,容易导致主仓库的一些错误,因此换成了常规的fork+PR的模式来进行翻译流程。
|
||||
* 2013/10/11 根据对LCTT的贡献,划分了Core Translators组,最先的加入成员是vito-L和tinyeyeser。
|
||||
* 2013/10/12 取消对LINUX.CN注册用户的依赖,在QQ群内、文章内都采用github的注册ID。
|
||||
* 2013/10/18 正式启动man翻译计划。
|
||||
* 2013/09/24 鉴于大家使用 GitHub 的水平不一,容易导致主仓库的一些错误,因此换成了常规的 fork+PR 的模式来进行翻译流程。
|
||||
* 2013/10/11 根据对 LCTT 的贡献,划分了 Core Translators 组,最先的加入成员是 vito-L 和 tinyeyeser。
|
||||
* 2013/10/12 取消对 LINUX.CN 注册用户的依赖,在 QQ 群内、文章内都采用 GitHub 的注册 ID。
|
||||
* 2013/10/18 正式启动 man 翻译计划。
|
||||
* 2013/11/10 举行第一次北京线下聚会。
|
||||
* 2014/01/02 增加了Core Translators 成员: geekpi。
|
||||
* 2014/05/04 更换了新的QQ群:198889102
|
||||
* 2014/05/16 增加了Core Translators 成员: will.qian、vizv。
|
||||
* 2014/06/18 由于GOLinux令人惊叹的翻译速度和不错的翻译质量,升级为Core Translators成员。
|
||||
* 2014/01/02 增加了 Core Translators 成员: geekpi。
|
||||
* 2014/05/04 更换了新的 QQ 群:198889102
|
||||
* 2014/05/16 增加了 Core Translators 成员: will.qian、vizv。
|
||||
* 2014/06/18 由于 GOLinux 令人惊叹的翻译速度和不错的翻译质量,升级为 Core Translators 成员。
|
||||
* 2014/09/09 LCTT 一周年,做一年[总结](http://linux.cn/article-3784-1.html)。并将曾任 CORE 的成员分组为 Senior,以表彰他们的贡献。
|
||||
* 2014/10/08 提升bazz2为Core Translators成员。
|
||||
* 2014/11/04 提升zpl1025为Core Translators成员。
|
||||
* 2014/12/25 提升runningwater为Core Translators成员。
|
||||
* 2014/10/08 提升 bazz2 为 Core Translators 成员。
|
||||
* 2014/11/04 提升 zpl1025 为 Core Translators 成员。
|
||||
* 2014/12/25 提升 runningwater 为 Core Translators 成员。
|
||||
* 2015/04/19 发起 LFS-BOOK-7.7-systemd 项目。
|
||||
* 2015/06/09 提升ictlyh和dongfengweixiao为Core Translators成员。
|
||||
* 2015/11/10 提升strugglingyouth、FSSlc、Vic020、alim0x为Core Translators成员。
|
||||
* 2016/05/09 提升PurlingNayuki为校对。
|
||||
* 2015/06/09 提升 ictlyh 和 dongfengweixiao 为 Core Translators 成员。
|
||||
* 2015/11/10 提升 strugglingyouth、FSSlc、Vic020、alim0x 为 Core Translators 成员。
|
||||
* 2016/05/09 提升 PurlingNayuki 为校对。
|
||||
|
||||
活跃成员
|
||||
-------------------------------
|
||||
@ -74,16 +74,16 @@ LCTT的组成
|
||||
- CORE @dongfengweixiao,
|
||||
- CORE @alim0x,
|
||||
- Senior @DeadFire,
|
||||
- Senior @reinoir,
|
||||
- Senior @reinoir222,
|
||||
- Senior @tinyeyeser,
|
||||
- Senior @vito-L,
|
||||
- Senior @jasminepeng,
|
||||
- Senior @willqian,
|
||||
- Senior @vizv,
|
||||
- ZTinoZ,
|
||||
- theo-l,
|
||||
- luoxcat,
|
||||
- martin2011qi,
|
||||
- theo-l,
|
||||
- Luoxcat,
|
||||
- wi-cuckoo,
|
||||
- disylee,
|
||||
- haimingfg,
|
||||
@ -91,8 +91,8 @@ LCTT的组成
|
||||
- wwy-hust,
|
||||
- felixonmars,
|
||||
- su-kaiyao,
|
||||
- ivo-wang,
|
||||
- GHLandy,
|
||||
- ivo-wang,
|
||||
- cvsher,
|
||||
- wyangsun,
|
||||
- DongShuaike,
|
||||
@ -119,6 +119,7 @@ LCTT的组成
|
||||
- blueabysm,
|
||||
- boredivan,
|
||||
- name1e5s,
|
||||
- StdioA,
|
||||
- yechunxiao19,
|
||||
- l3b2w1,
|
||||
- XLCYun,
|
||||
@ -134,8 +135,8 @@ LCTT的组成
|
||||
- 1w2b3l,
|
||||
- JonathanKang,
|
||||
- crowner,
|
||||
- mtunique,
|
||||
- dingdongnigetou,
|
||||
- mtunique,
|
||||
- CNprober,
|
||||
- hyaocuk,
|
||||
- szrlee,
|
||||
@ -146,37 +147,22 @@ LCTT的组成
|
||||
- xiaoyu33,
|
||||
- guodongxiaren,
|
||||
- ynmlml,
|
||||
- kylepeng93,
|
||||
- vim-kakali,
|
||||
- ggaaooppeenngg,
|
||||
- Ricky-Gong,
|
||||
- zky001,
|
||||
- Flowsnow,
|
||||
- lfzark,
|
||||
- 213edu,
|
||||
- Tanete,
|
||||
- liuaiping,
|
||||
- bestony,
|
||||
- mudongliang,
|
||||
- liuaiping,
|
||||
- Timeszoro,
|
||||
- rogetfan,
|
||||
- itsang,
|
||||
- JeffDing,
|
||||
- Yuking-net,
|
||||
- MikeCoder,
|
||||
- zhangboyue,
|
||||
- liaoishere,
|
||||
- yupmoon,
|
||||
- Medusar,
|
||||
- zzlyzq,
|
||||
- yujianxuechuan,
|
||||
- ailurus1991,
|
||||
- tomatoKiller,
|
||||
- stduolc,
|
||||
- shaohaolin,
|
||||
- FineFan,
|
||||
- kingname,
|
||||
- CHINAANSHE,
|
||||
|
||||
(按提交行数排名前百)
|
||||
|
||||
(按增加行数排名前百)
|
||||
|
||||
LFS 项目活跃成员有:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -188,7 +174,7 @@ LFS 项目活跃成员有:
|
||||
- @KevinSJ
|
||||
- @Yuking-net
|
||||
|
||||
(更新于2016/05/09)
|
||||
(更新于2016/06/20)
|
||||
|
||||
谢谢大家的支持!
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,39 +1,41 @@
|
||||
修补 Linux 系统 glibc 严重漏洞
|
||||
=================================================
|
||||
|
||||
**谷歌揭露的一个严重漏洞影响主流的 Linux 发行版。glibc 的漏洞可能导致远程代码执行。**
|
||||
**谷歌披露的一个严重漏洞影响到了主流的 Linux 发行版。glibc 的漏洞可能导致远程代码执行。**
|
||||
|
||||
Linux 用户今天都竞相给一个可以使系统暴露在远程代码执行风险中的核心 glibc 开放源码库的严重漏洞打补丁。glibc 的漏洞被确定为 CVE-2015-7547,题为“getaddrinfo 基于堆栈的缓冲区溢出”。
|
||||
编者按:这个消息并不是一个新闻,基于技术的原因,我们还是分享给大家。
|
||||
|
||||
Linux 用户都在竞相给一个可以使系统暴露在远程代码执行风险中的核心 glibc 开放源码库的严重漏洞打补丁。这个 glibc 的漏洞编号被确定为 CVE-2015-7547,题为“getaddrinfo 基于堆栈的缓冲区溢出”。
|
||||
|
||||
glibc,或 GNU C 库,是一个开放源码的 C 和 C++ 编程语言库的实现,是每一个主流 Linux 发行版的一部分。谷歌工程师们在他们试图连接到某个主机系统时发生了一个段错误导致连接崩溃,偶然发现了 CVE-2015-7547 问题。进一步的研究表明, glibc 有缺陷而且该崩溃可能实现任意远程代码执行的条件。
|
||||
|
||||
谷歌在一篇博客文章中写道, “当 getaddrinfo() 库函数被使用时,glibc 的 DNS 客户端解析器易受基于堆栈缓冲区溢出的攻击,使用该功能的软件可能被利用为攻击者控制的域名,攻击者控制的 DNS[域名系统] 服务器,或通过中间人攻击。”
|
||||
谷歌在一篇博客文章中写道, “当 getaddrinfo() 库函数被使用时,glibc 的 DNS 客户端解析器易受基于堆栈缓冲区溢出的攻击,使用该功能的软件可能通过攻击者控制的域名、攻击者控制的 DNS [域名系统] 服务器,或通过中间人攻击方式(MITM)进行破坏。”
|
||||
|
||||
其实利用 CVE-2015-7547 问题并不简单,但它是可能的。为了证明这个问题能被利用,谷歌发布了论证一个终端用户或系统是否易受攻击的概念验证(POC)代码到 GitHub 上。
|
||||
|
||||
GitHub 上的 POC 网页声明“服务器代码触发漏洞,因此会使客户端代码崩溃”。
|
||||
GitHub 上的 POC 网页说“服务器代码会触发漏洞,因此会使客户端代码崩溃”。
|
||||
|
||||
Duo Security 公司的高级安全研究员 Mark Loveless 解释说 CVE-2015-7547 的主要风险在于 Linux 上依赖于 DNS 响应的基于客户端的应用程序。
|
||||
Duo Security 公司的高级安全研究员 Mark Loveless 解释说 CVE-2015-7547 的主要风险在于依赖于 DNS 响应的基于 Linux 客户端的应用程序。
|
||||
|
||||
Loveless 告诉 eWEEK “需要一些特定的条件,所以不是每个应用程序都会受到影响,但似乎一些命令行工具,包括流行的 SSH[安全 Shell] 客户端都可能触发该漏洞,我们认为这是严重的,主要是因为对 Linux 系统存在的风险,但也因为潜在的其他问题。”
|
||||
|
||||
其他问题可能包括一种触发调用易受攻击的 glibc 库 getaddrinfo() 的基于电子邮件攻击的风险。另外值得注意的是,该漏洞被发现之前已存在于代码之中多年。
|
||||
其他问题可能包括一种通过电子邮件触发调用易受攻击的 glibc 库 getaddrinfo() 攻击的风险。另外值得注意的是,该漏洞被发现之前已存在于代码之中多年。
|
||||
|
||||
谷歌的工程师不是第一或唯一发现 glibc 中的安全风险的团体。这个问题于 2015 年 7 月 13 日首先被报告给了 glibc 的 bug[跟踪系统](https://sourceware.org/bugzilla/show_bug.cgi?id=1866)。该缺陷的根源可以更进一步追溯到在 2008 五月发布的 glibc 2.9 的代码提交时首次引入缺陷。
|
||||
谷歌的工程师不是第一或唯一发现这个 glibc 安全风险的团体。这个问题于 2015 年 7 月 13 日首先被报告给了 glibc 的 bug[跟踪系统](https://sourceware.org/bugzilla/show_bug.cgi?id=1866)。该缺陷的根源可以更进一步追溯到在 2008 五月发布的 glibc 2.9 的代码提交时首次引入缺陷。
|
||||
|
||||
Linux 厂商红帽也独立找到了 glibc 中的这个 bug,而且在 2016 年 1 月 6 日,谷歌和红帽开发人员证实,他们作为最初与上游 glibc 的维护者私下讨论的部分人员,已经独立在为同一个漏洞工作。
|
||||
Linux 厂商红帽也独立找到了 glibc 中的这个 bug,而且是在 2016 年 1 月 6 日,谷歌和红帽开发人员证实,他们作为最初与上游 glibc 的维护者私下讨论的部分人员,已经独立在为同一个漏洞工作。
|
||||
|
||||
红帽产品安全首席软件工程师 Florian Weimer 告诉 eWEEK “一旦确认了两个团队都在为同一个漏洞工作,我们合作进行可能的修复,缓解措施和回归测试,我们还共同努力,使测试覆盖尽可能广,捕捉代码中的任何相关问题,以帮助避免今后更多问题。”
|
||||
红帽产品安全首席软件工程师 Florian Weimer 告诉 eWEEK “一旦确认了两个团队都在为同一个漏洞工作,我们会合作进行可能的修复,缓解措施和回归测试,我们还会共同努力,使测试覆盖尽可能广,捕捉代码中的任何相关问题,以帮助避免今后更多问题。”
|
||||
|
||||
由于缺陷不明显或不易立即显现,我们花了几年时间才发现 glibc 代码有一个安全问题。
|
||||
|
||||
Weimer 说“要诊断一个网络组件的漏洞,如 DNS 解析器,当遇到问题时通常要看被抓数据包的踪迹,在这种情况下这样的抓包不适用,所以需要一些实验来重现触发这个 bug 的确切场景。”
|
||||
Weimer 说“要诊断一个网络组件的漏洞,如 DNS 解析器,当遇到问题时通常要看抓到的数据包的踪迹,在这种情况下这样的抓包不适用,所以需要一些实验来重现触发这个 bug 的确切场景。”
|
||||
|
||||
Weimer 补充说,一旦可以抓取数据包,大量精力投入到验证修复程序中,最终导致回归测试套件一系列的改进,有助于上游 glibc 项目。
|
||||
Weimer 补充说,一旦可以抓取数据包,就会投入大量精力到验证修复程序中,最终完成回归测试套件一系列的改进,有助于上游 glibc 项目。
|
||||
|
||||
在许多情况下,安全增强式 Linux (SELinux) 的强制访问安全控制可以减少潜在漏洞风险,除了这个 glibc 的新问题。
|
||||
在许多情况下,安全增强式 Linux (SELinux) 的强制访问安全控制可以减少潜在漏洞风险,但是这个 glibc 的新问题例外。
|
||||
|
||||
Weimer 说“由于攻击者提供的任意代码的执行,风险是重要系统功能的一个妥协。一个合适的 SELinux 策略可以遏制一些攻击者可能会做的损害,并限制他们访问系统,但是 DNS 被许多应用程序和系统组件使用,所以 SELinux 策略只提供了针对此问题有限的遏制。”
|
||||
Weimer 说“由于攻击者提供的任意代码的执行,会对很多重要系统功能带来风险。一个合适的 SELinux 策略可以遏制一些攻击者可能会做的损害,并限制他们访问系统,但是 DNS 被许多应用程序和系统组件使用,所以 SELinux 策略只提供了针对此问题有限的遏制。”
|
||||
|
||||
在揭露漏洞的今天,现在有一个可用的补丁来减少 CVE-2015-7547 的潜在风险。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -43,7 +45,7 @@ via: http://www.eweek.com/security/linux-systems-patched-for-critical-glibc-flaw
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Michael Kerner][a]
|
||||
译者:[robot527](https://github.com/robot527)
|
||||
校对:[校对者 ID](https://github.com/校对者 ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux 中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
129
sources/tech/20160610 Getting started with ReactOS.md
Normal file
129
sources/tech/20160610 Getting started with ReactOS.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,129 @@
|
||||
Getting started with ReactOS
|
||||
==============================
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
ReactOS is a relatively new open source operating system that resembles the looks of Windows NT and aims to offer similar levels of functionality and application compatibility. Featuring a wine-based user mode, this system doesn't use any of the Unix architecture, but is a rewrite of the NT architecture from scratch, with its very own FAT32 implementation, and completely free of legal implications. That said, this is not yet another Linux distro, but a unique Windows-like system that is a part of the free software world. This quick guide aims at users who want an easy to use, open source replacement for their Windows system.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### System Installation
|
||||
|
||||
Before getting started with the installation process, I should point out that the minimum requirements of ReactOS are 500 MB of free disk space and only 96 MB of RAM. I will demonstrate the installation process on a 32-bit virtual machine.
|
||||
|
||||
Navigate with the arrow keys and select the desired language by pressing “Enter”.
|
||||
|
||||
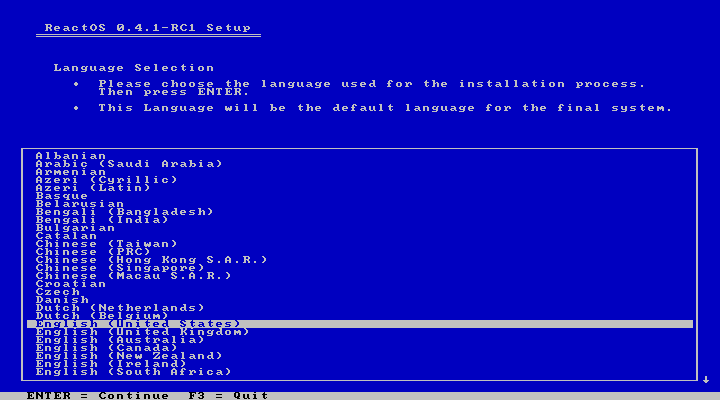
|
||||
|
||||
Next, hit “Enter” again to continue with the installation, or “R” to repair an existing install.
|
||||
|
||||
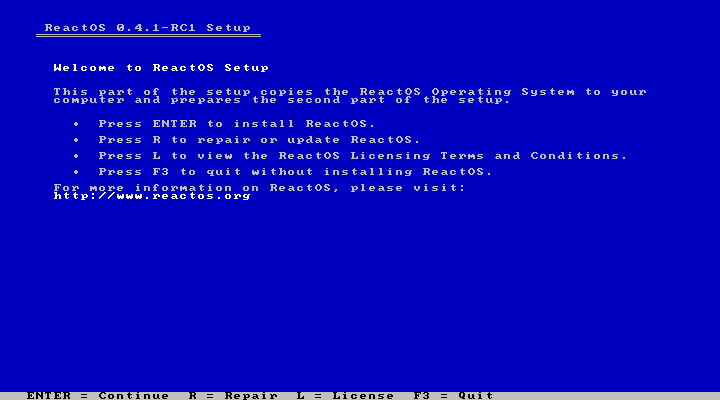
|
||||
|
||||
On the third screen, you'll get a warning about the current limitation that applies to this early development version of the OS. Continue with “Enter” again and you'll get a summary of the settings before the final user approval. If all is good, hit “Enter” once again.
|
||||
|
||||
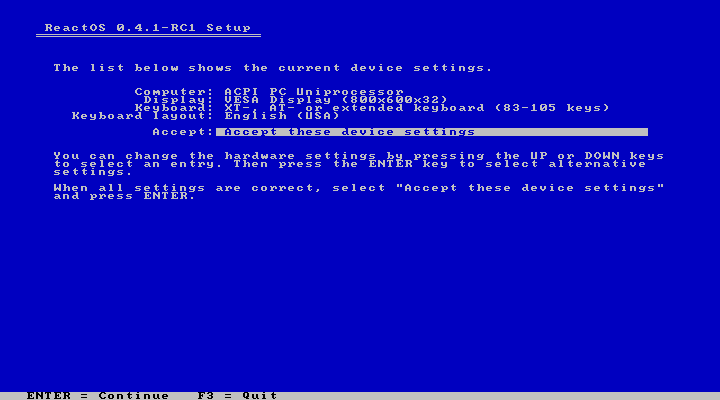
|
||||
|
||||
This will take you to the partitioning stage where you may delete the highlighted option by pressing “D”, and then add primary, extended, or logical partitions with “P”, “E”, and “L” respectively. If you choose to add a partition yourself, you will be given the option to set its size by entering a number of MBs and pressing “Enter” to confirm.
|
||||
|
||||
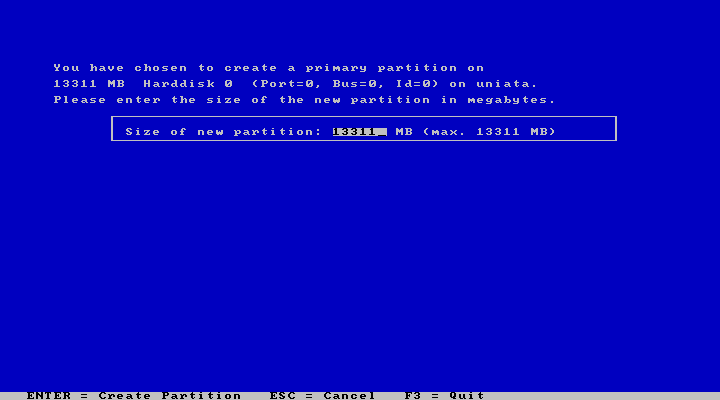
|
||||
|
||||
However, if you have already unused space available, hitting “Enter” once again during the partitioning stage will automatically install ReactOS in the selected partition.
|
||||
|
||||
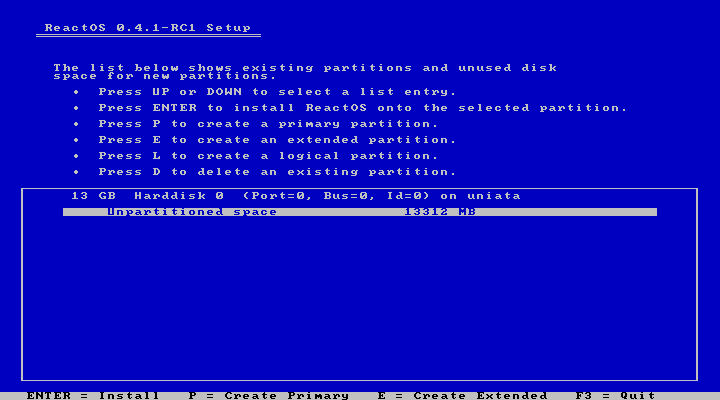
|
||||
|
||||
The next step is the selection of the filesystem type which for now is limited to FAT32 only.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
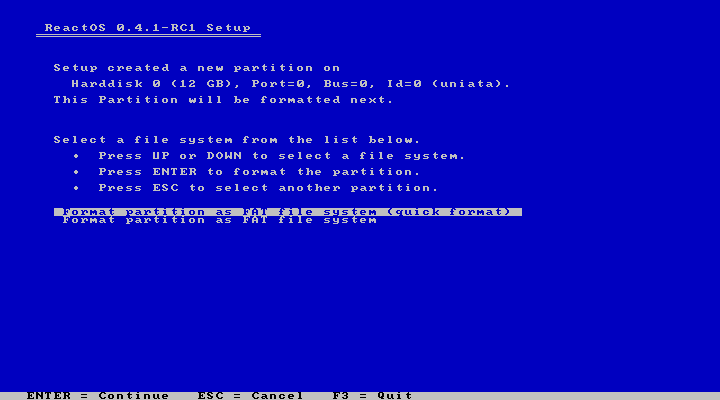
|
||||
|
||||
Next is the directory selection. I will leave this at the default “/ReactOS” and it should be fine.
|
||||
|
||||
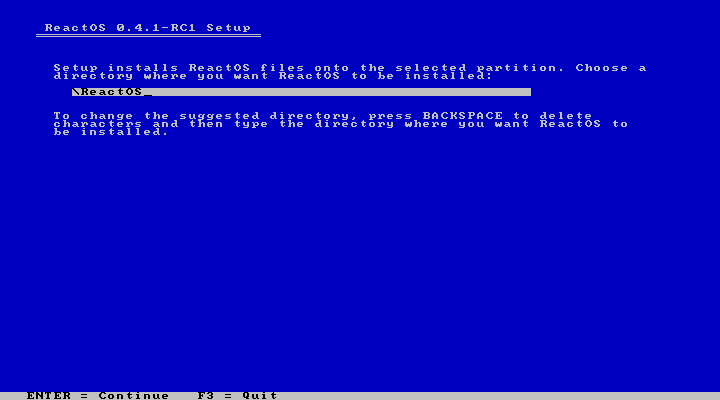
|
||||
|
||||
...and we're off
|
||||
|
||||
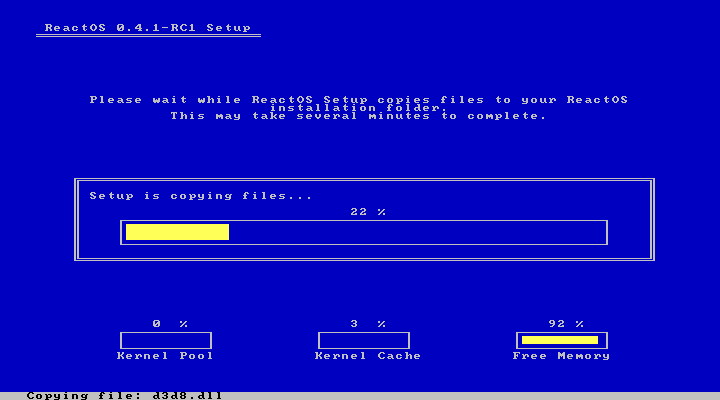
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, we're about the choose the location of the bootloader. The first option should be the safest if installing on a real disk.
|
||||
|
||||
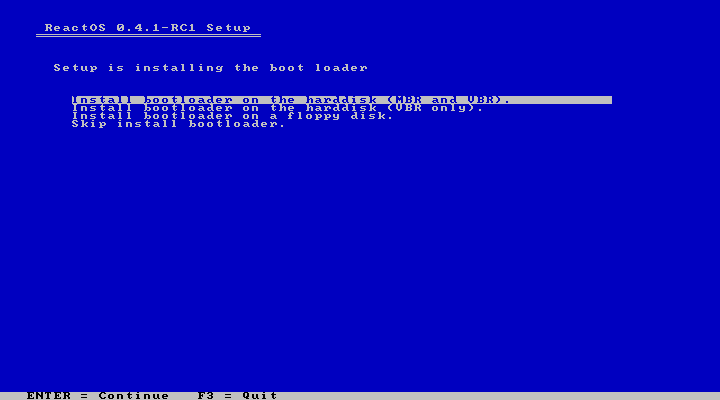
|
||||
|
||||
In general, I could say that the installation of ReactOS is pretty straight forward. The interface may not look friendly or modern at all, but hitting “Enter” in every step will work just fine in most cases. That said, the development version of ReactOS it's fairly simple and easy to install.
|
||||
|
||||
### Setting Up ReactOS
|
||||
|
||||
Once we reboot and get into our new system, we're offered the help of the “Setup Wizard”. This wizard is basically allowing us to set up the language and keyboard layout settings.
|
||||
|
||||
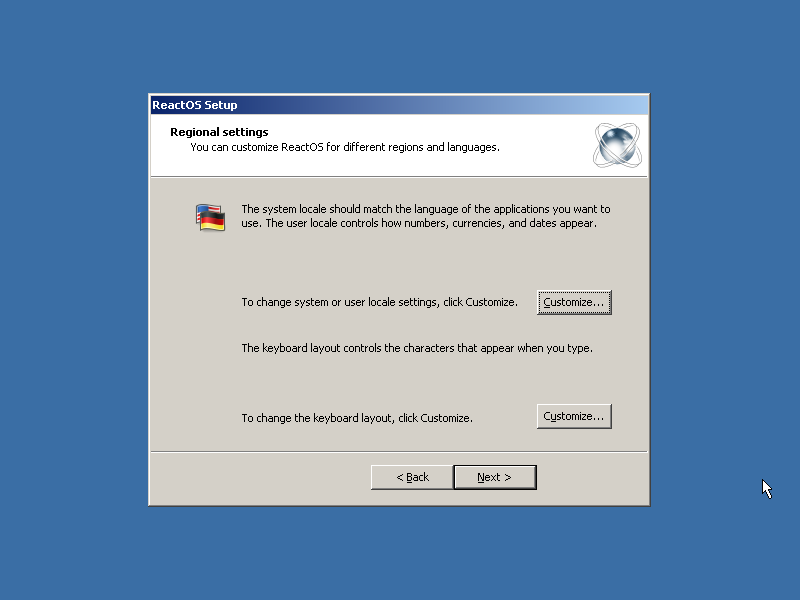
|
||||
|
||||
I used this step to add a second keyboard layout.
|
||||
|
||||
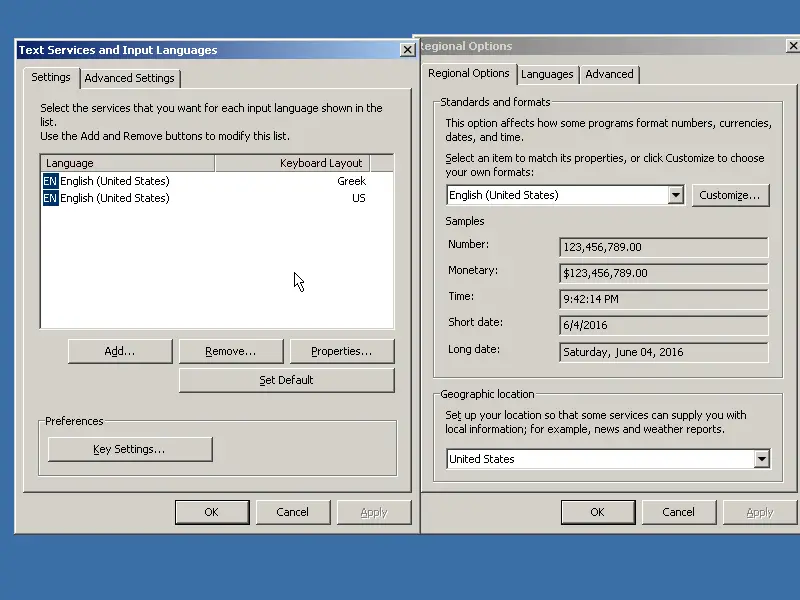
|
||||
|
||||
I can even set a different key combination for changing the layout.
|
||||
|
||||
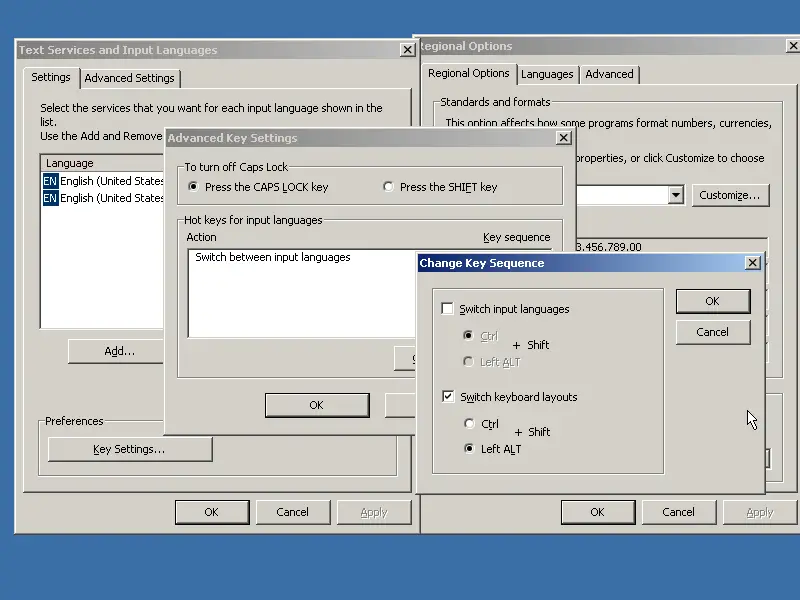
|
||||
|
||||
Then I add the username...
|
||||
|
||||
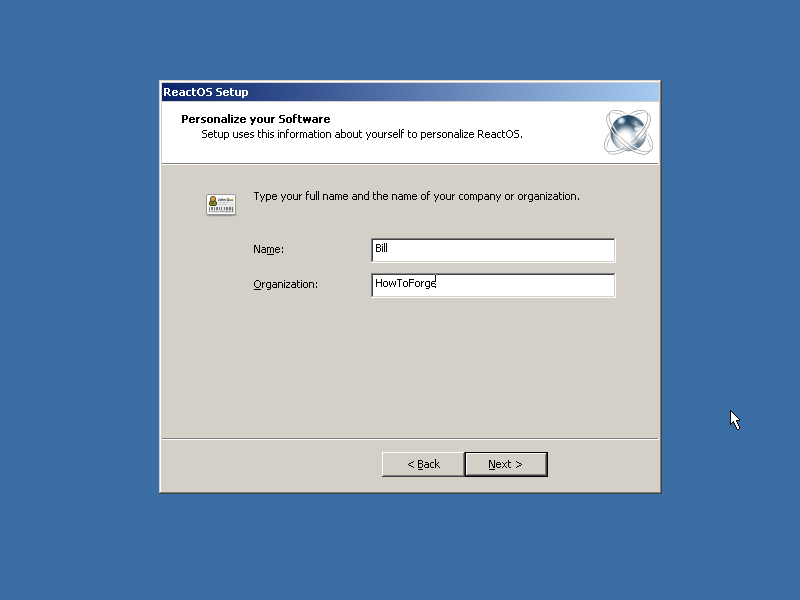
|
||||
|
||||
...and an admin pass...
|
||||
|
||||
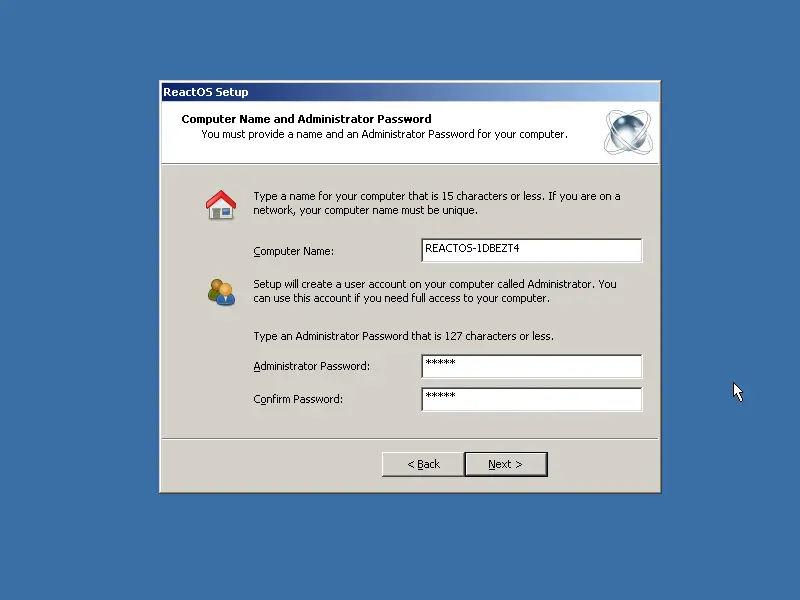
|
||||
|
||||
After the time settings are also set, ReactOS finalizes its configuration.
|
||||
|
||||
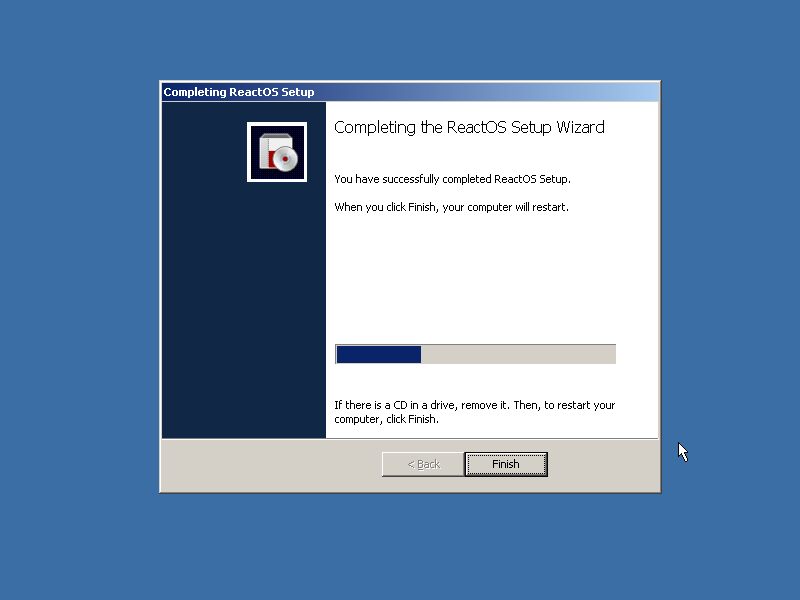
|
||||
|
||||
### Inside ReactOS
|
||||
|
||||
When we finally enter ReactOS for the first time, new hardware is detected and we're offered to install the available drivers automatically.
|
||||
|
||||
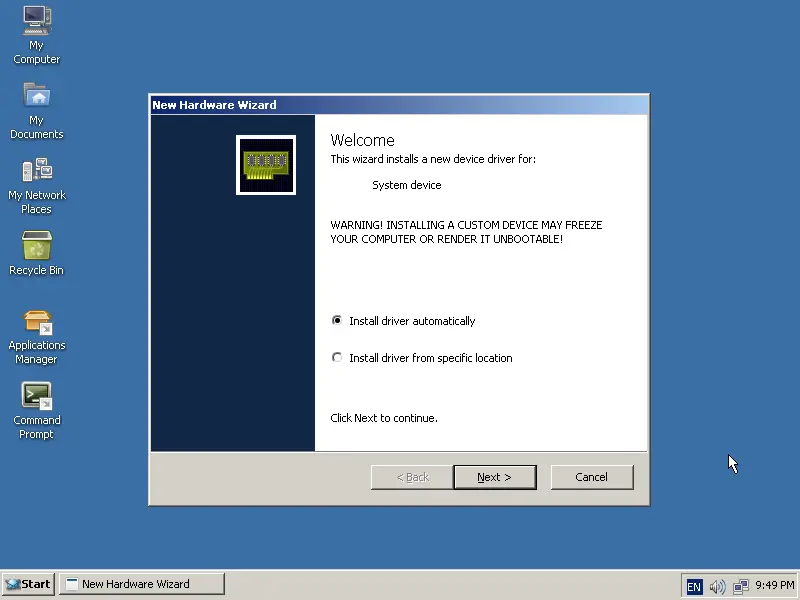
|
||||
|
||||
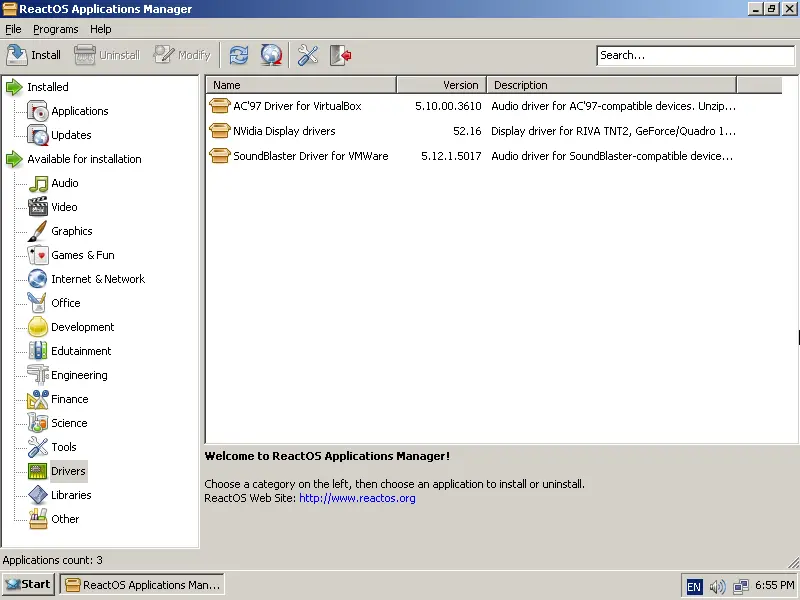
These are the three devices that were automatically detected by ReactOS in my case:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
What you're looking at in the above screenshot is ReactOS's “applications manager” which is of course to the standards of Linux systems. You won't find anything Linux-related here, though. Only open source applications that are known to work well with the particular system are offered. That said, some categories are well populated, while others are completely empty.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
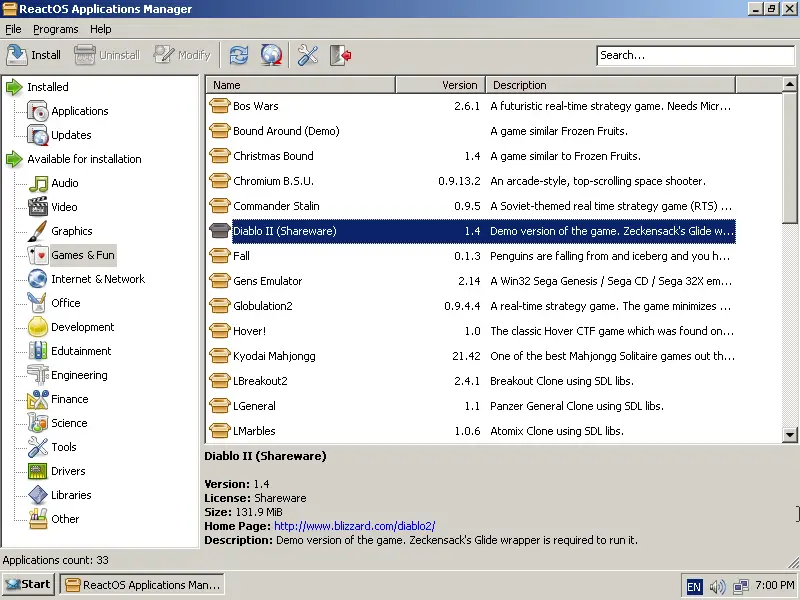
I took the liberty to install Firefox through the software center, and Notepad++ by downloading the .exe file and installing it by simply double-clicking the executable. Both worked perfectly well, their desktop icons were created, menu entries added, and Notepad++ was added in the applications manager and in the right category as well.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
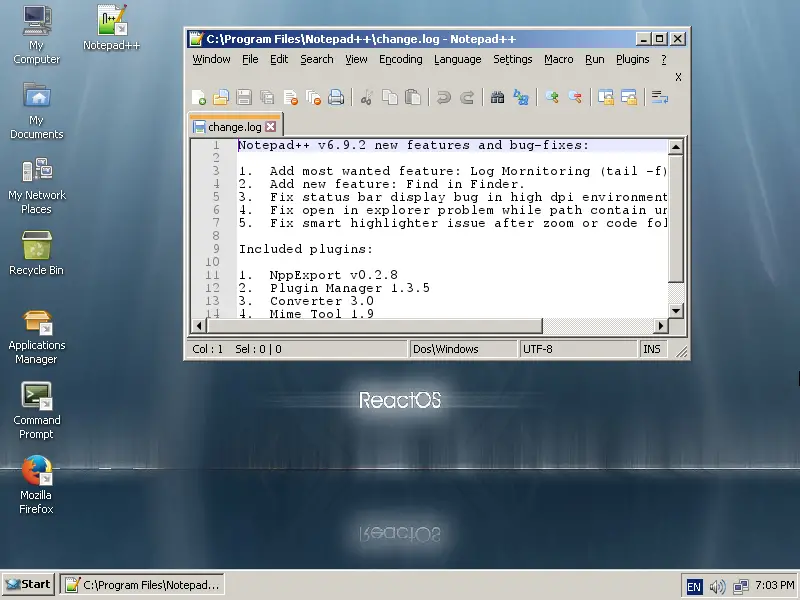
I wouldn't try running any modern Windows games, but if you want to setup the Direct 3D settings you can go to “My Computer/Control Panel/WineD3D Options”. There you will find multiple options about the Direct3D which is presumably resembling dx version 8.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
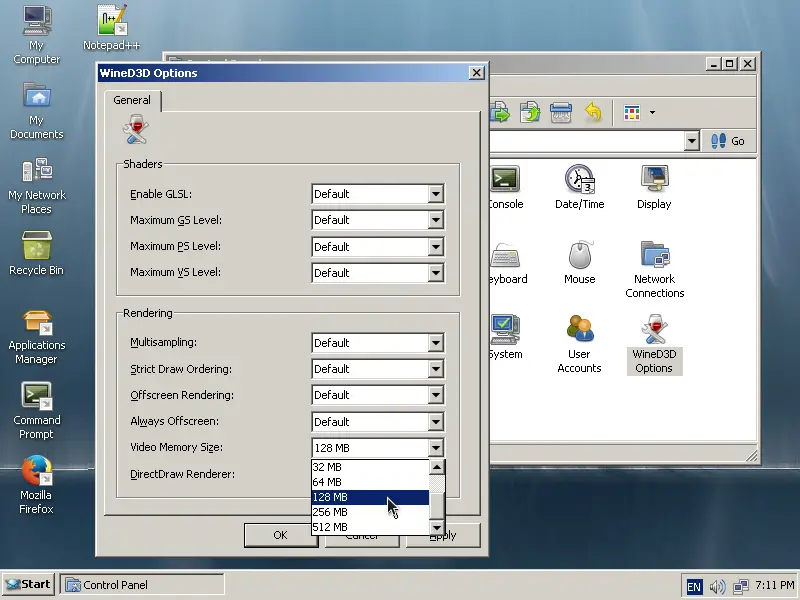
Another good thing with ReactOS is the fact that the Registry entries can be accessed and set as needed through “My Computer” again.
|
||||
|
||||
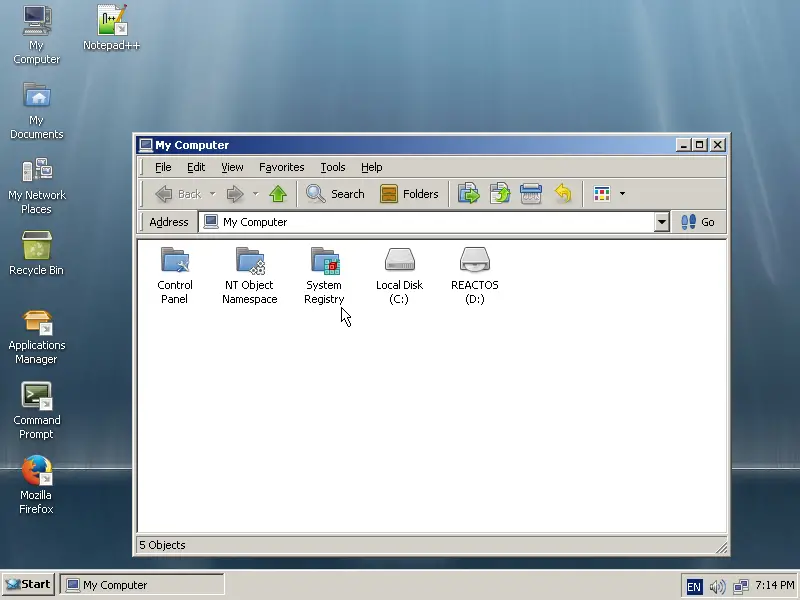
|
||||
|
||||
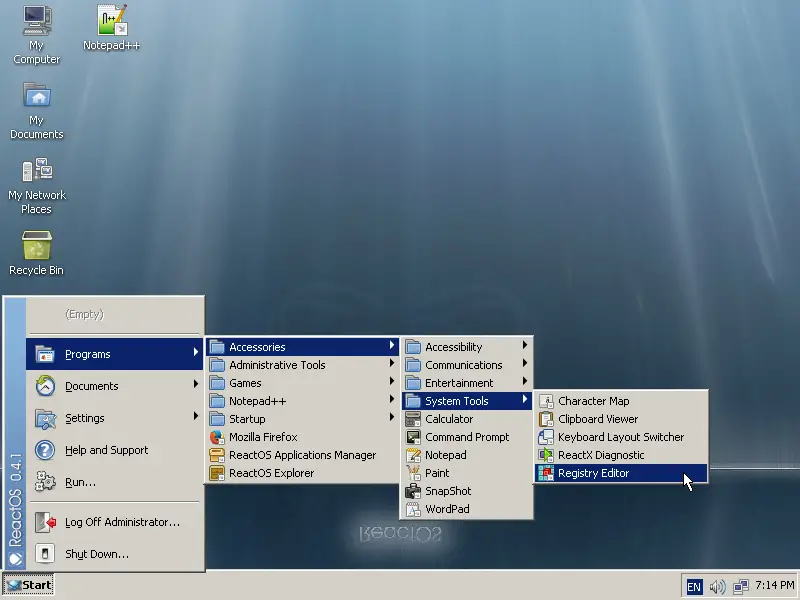
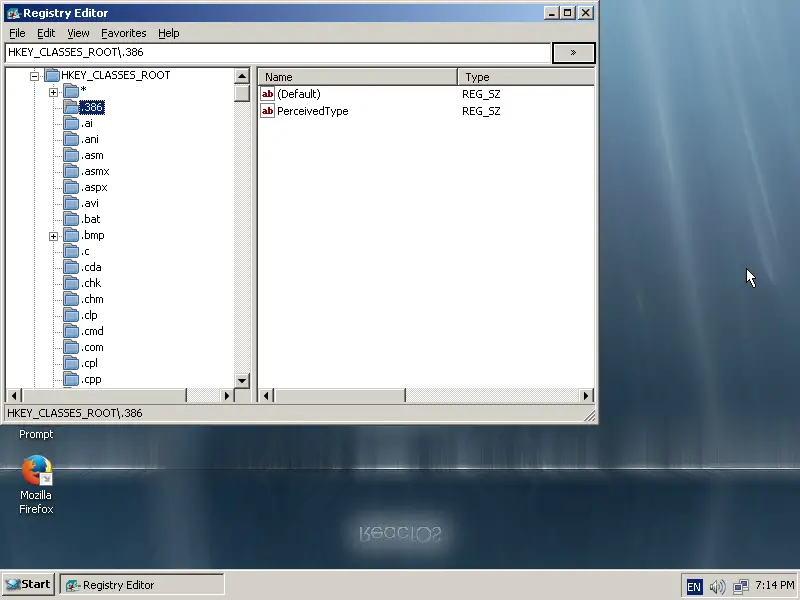
If you need something handier though, you may find a Registry Editor utility from the applications menu.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
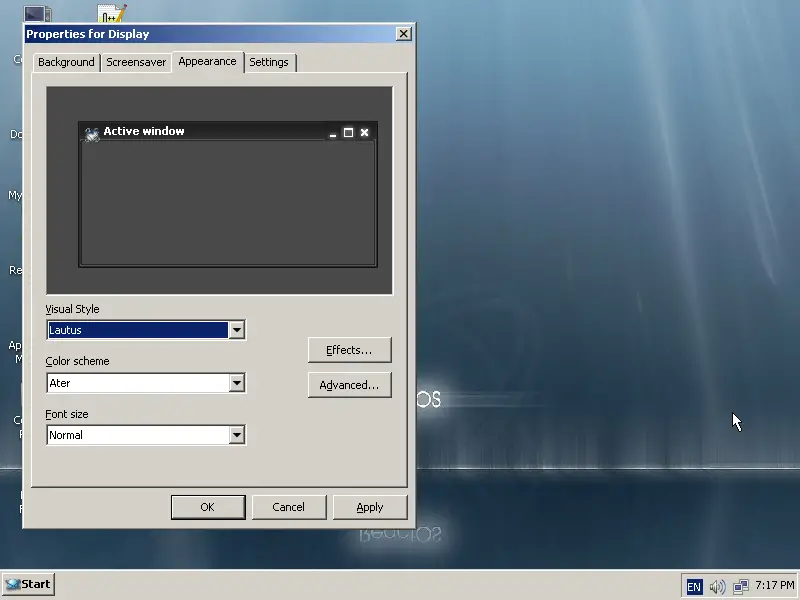
Finally, if the looks of ReactOS look somewhat outdated to you, right click on the desktop and select “Properties”. Then choose the “Appearance” tab and set the theme and color that you prefer.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion
|
||||
|
||||
Honestly, I was impressed by the way ReactOS works. It's quite solid, coherent, speedy, and really user-friendly. Leaving aside the negatives that stem from the Windows design (deprecated applications menu, irrational directory structure), ReactOS is almost perfect on what it does. It may not be very rich in terms of application selection, and it may not be very powerful in terms of features yet, but I am sure it's going to flourish. The numbers show great popularity, and I'm sure the community that's going to build up around it will soon be large enough to lead the project to success. Right now, version 0.4.1 looks promising to say the least. If you care about running Windows applications and doing so in an open way, give it a try!
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/getting-started-with-reactos/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Bill Toulas][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/getting-started-with-reactos/
|
||||
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user