mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-02-03 23:40:14 +08:00
commit
04eae1a150
@ -0,0 +1,213 @@
|
||||
如何在 Ubuntu 15.04/CentOS 7 中安装 Lighttpd Web 服务器
|
||||
=================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
Lighttpd 是一款开源 Web 服务器软件。Lighttpd 安全快速,符合行业标准,适配性强并且针对高配置环境进行了优化。相对于其它的 Web 服务器而言,Lighttpd 占用内存更少;因其对 CPU 占用小和对处理速度的优化而在效率和速度方面从众多 Web 服务器中脱颖而出。而 Lighttpd 诸如 FastCGI、CGI、认证、输出压缩、URL 重写等高级功能更是那些面临性能压力的服务器的福音。
|
||||
|
||||
以下便是我们在运行 Ubuntu 15.04 或 CentOS 7 Linux 发行版的机器上安装 Lighttpd Web 服务器的简要流程。
|
||||
|
||||
### 安装Lighttpd
|
||||
|
||||
#### 使用包管理器安装
|
||||
|
||||
这里我们通过使用包管理器这种最简单的方法来安装 Lighttpd。只需以 sudo 模式在终端或控制台中输入下面的指令即可。
|
||||
|
||||
**CentOS 7**
|
||||
|
||||
由于 CentOS 7.0 官方仓库中并没有提供 Lighttpd,所以我们需要在系统中安装额外的软件源 epel 仓库。使用下面的 yum 指令来安装 epel。
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install epel-release
|
||||
|
||||
然后,我们需要更新系统及为 Lighttpd 的安装做前置准备。
|
||||
|
||||
# yum update
|
||||
# yum install lighttpd
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Ubuntu 15.04**
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu 15.04 官方仓库中包含了 Lighttpd,所以只需更新本地仓库索引并使用 apt-get 指令即可安装 Lighttpd。
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get update
|
||||
# apt-get install lighttpd
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### 从源代码安装 Lighttpd
|
||||
|
||||
如果想从 Lighttpd 源码安装最新版本(例如 1.4.39),我们需要在本地编译源码并进行安装。首先我们要安装编译源码所需的依赖包。
|
||||
|
||||
# cd /tmp/
|
||||
# wget http://download.lighttpd.net/lighttpd/releases-1.4.x/lighttpd-1.4.39.tar.gz
|
||||
|
||||
下载完成后,执行下面的指令解压缩。
|
||||
|
||||
# tar -zxvf lighttpd-1.4.39.tar.gz
|
||||
|
||||
然后使用下面的指令进行编译。
|
||||
|
||||
# cd lighttpd-1.4.39
|
||||
# ./configure
|
||||
# make
|
||||
|
||||
**注:**在这份教程中,我们安装的是默认配置的 Lighttpd。其他拓展功能,如对 SSL 的支持,mod_rewrite,mod_redirect 等,需自行配置。
|
||||
|
||||
当编译完成后,我们就可以把它安装到系统中了。
|
||||
|
||||
# make install
|
||||
|
||||
### 设置 Lighttpd
|
||||
|
||||
如果有更高的需求,我们可以通过修改默认设置文件,如`/etc/lighttpd/lighttpd.conf`,来对 Lighttpd 进行进一步设置。 而在这份教程中我们将使用默认设置,不对设置文件进行修改。如果你曾做过修改并想检查设置文件是否出错,可以执行下面的指令。
|
||||
|
||||
# lighttpd -t -f /etc/lighttpd/lighttpd.conf
|
||||
|
||||
#### 使用 CentOS 7
|
||||
|
||||
在 CentOS 7 中,我们需创建一个在 Lighttpd 默认配置文件中设置的 webroot 文件夹,例如`/src/www/htdocs`。
|
||||
|
||||
# mkdir -p /srv/www/htdocs/
|
||||
|
||||
而后将默认欢迎页面从`/var/www/lighttpd`复制至刚刚新建的目录中:
|
||||
|
||||
# cp -r /var/www/lighttpd/* /srv/www/htdocs/
|
||||
|
||||
### 开启服务
|
||||
|
||||
现在,通过执行 systemctl 指令来重启 Web 服务。
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl start lighttpd
|
||||
|
||||
然后我们将它设置为伴随系统启动自动运行。
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl enable lighttpd
|
||||
|
||||
### 设置防火墙
|
||||
|
||||
如要让我们运行在 Lighttpd 上的网页或网站能在 Internet 或同一个网络内被访问,我们需要在防火墙程序中设置打开 80 端口。由于 CentOS 7 和 Ubuntu15.04 都附带 Systemd 作为默认初始化系统,所以我们默认用的都是 firewalld。如果要打开 80 端口或 http 服务,我们只需执行下面的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=http
|
||||
success
|
||||
# firewall-cmd --reload
|
||||
success
|
||||
|
||||
### 连接至 Web 服务器
|
||||
|
||||
在将 80 端口设置为默认端口后,我们就可以直接访问 Lighttpd 的默认欢迎页了。我们需要根据运行 Lighttpd 的设备来设置浏览器的 IP 地址和域名。在本教程中,我们令浏览器访问 [http://lighttpd.linoxide.com/](http://lighttpd.linoxide.com/) ,同时将该子域名指向上述 IP 地址。如此一来,我们就可以在浏览器中看到如下的欢迎页面了。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
此外,我们可以将网站的文件添加到 webroot 目录下,并删除 Lighttpd 的默认索引文件,使我们的静态网站可以在互联网上访问。
|
||||
|
||||
如果想在 Lighttpd Web 服务器中运行 PHP 应用,请参考下面的步骤:
|
||||
|
||||
### 安装 PHP5 模块
|
||||
|
||||
在 Lighttpd 成功安装后,我们需要安装 PHP 及相关模块,以在 Lighttpd 中运行 PHP5 脚本。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 使用 Ubuntu 15.04
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get install php5 php5-cgi php5-fpm php5-mysql php5-curl php5-gd php5-intl php5-imagick php5-mcrypt php5-memcache php-pear
|
||||
|
||||
#### 使用 CentOS 7
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install php php-cgi php-fpm php-mysql php-curl php-gd php-intl php-pecl-imagick php-mcrypt php-memcache php-pear lighttpd-fastcgi
|
||||
|
||||
### 设置 Lighttpd 的 PHP 服务
|
||||
|
||||
如要让 PHP 与 Lighttpd 协同工作,我们只要根据所使用的发行版执行如下对应的指令即可。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 使用 CentOS 7
|
||||
|
||||
首先要做的便是使用文件编辑器编辑 php 设置文件(例如`/etc/php.ini`)并取消掉对**cgi.fix_pathinfo=1**这一行的注释。
|
||||
|
||||
# nano /etc/php.ini
|
||||
|
||||
完成上面的步骤之后,我们需要把 PHP-FPM 进程的所有权从 Apache 转移至 Lighttpd。要完成这些,首先用文件编辑器打开`/etc/php-fpm.d/www.conf`文件。
|
||||
|
||||
# nano /etc/php-fpm.d/www.conf
|
||||
|
||||
然后在文件中增加下面的语句:
|
||||
|
||||
user = lighttpd
|
||||
group = lighttpd
|
||||
|
||||
做完这些,我们保存并退出文本编辑器。然后从`/etc/lighttpd/modules.conf`设置文件中添加 FastCGI 模块。
|
||||
|
||||
# nano /etc/lighttpd/modules.conf
|
||||
|
||||
然后,去掉下面语句前面的`#`来取消对它的注释。
|
||||
|
||||
include "conf.d/fastcgi.conf"
|
||||
|
||||
最后我们还需在文本编辑器设置 FastCGI 的设置文件。
|
||||
|
||||
# nano /etc/lighttpd/conf.d/fastcgi.conf
|
||||
|
||||
在文件尾部添加以下代码:
|
||||
|
||||
fastcgi.server += ( ".php" =>
|
||||
((
|
||||
"host" => "127.0.0.1",
|
||||
"port" => "9000",
|
||||
"broken-scriptfilename" => "enable"
|
||||
))
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
在编辑完成后保存并退出文本编辑器即可。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 使用 Ubuntu 15.04
|
||||
|
||||
如需启用 Lighttpd 的 FastCGI,只需执行下列代码:
|
||||
|
||||
# lighttpd-enable-mod fastcgi
|
||||
|
||||
Enabling fastcgi: ok
|
||||
Run /etc/init.d/lighttpd force-reload to enable changes
|
||||
|
||||
# lighttpd-enable-mod fastcgi-php
|
||||
|
||||
Enabling fastcgi-php: ok
|
||||
Run `/etc/init.d/lighttpd` force-reload to enable changes
|
||||
|
||||
然后,执行下列命令来重启 Lighttpd。
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl force-reload lighttpd
|
||||
|
||||
### 检测 PHP 工作状态
|
||||
|
||||
如需检测 PHP 是否按预期工作,我们需在 Lighttpd 的 webroot 目录下新建一个 php 文件。本教程中,在 Ubuntu 下 /var/www/html 目录,CentOS 下 /src/www/htdocs 目录下使用文本编辑器创建并打开 info.php。
|
||||
|
||||
**使用 CentOS 7**
|
||||
|
||||
# nano /var/www/info.php
|
||||
|
||||
**使用 Ubuntu 15.04**
|
||||
|
||||
# nano /srv/www/htdocs/info.php
|
||||
|
||||
然后只需将下面的语句添加到文件里即可。
|
||||
|
||||
<?php phpinfo(); ?>
|
||||
|
||||
在编辑完成后保存并推出文本编辑器即可。
|
||||
|
||||
现在,我们需根据路径 [http://lighttpd.linoxide.com/info.php](http://lighttpd.linoxide.com/info.php) 下的 info.php 文件的 IP 地址或域名,来让我们的网页浏览器指向系统上运行的 Lighttpd。如果一切都按照以上说明进行,我们将看到如下图所示的 PHP 页面信息。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 总结
|
||||
|
||||
至此,我们已经在 CentOS 7 和 Ubuntu 15.04 Linux 发行版上成功安装了轻巧快捷并且安全的 Lighttpd Web 服务器。现在,我们已经可以上传网站文件到网站根目录、配置虚拟主机、启用 SSL、连接数据库,在我们的 Lighttpd Web 服务器上运行 Web 应用等功能了。 如果你有任何疑问,建议或反馈请在下面的评论区中写下来以让我们更好的改良 Lighttpd。谢谢!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/linux-how-to/setup-lighttpd-web-server-ubuntu-15-04-centos-7/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Arun Pyasi][a]
|
||||
译者:[HaohongWANG](https://github.com/HaohongWANG)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arunp/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,37 @@
|
||||
构建在开源之上的商业软件市场持续成长
|
||||
=====================================================================
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
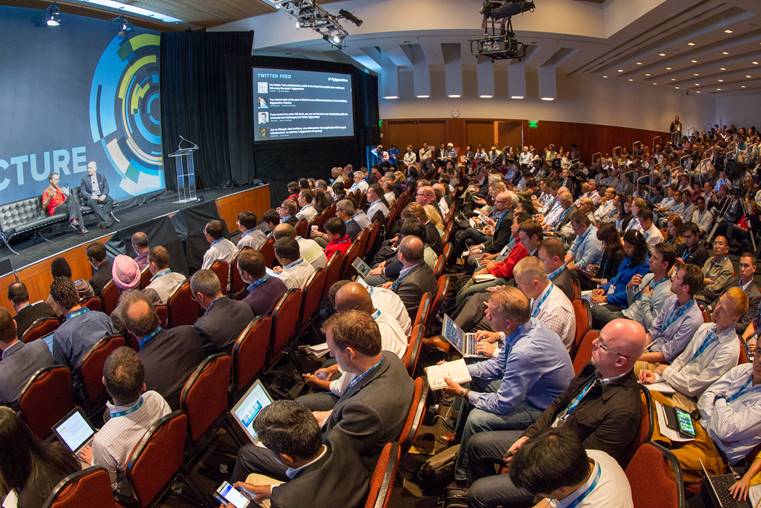
*与会者在 Structure 上听取演讲,Structure Data 2016 也将在 UCSF Mission Bay 会议中心举办。图片来源:Structure Events。*
|
||||
|
||||
如今真的很难低估开源项目对于企业软件市场的影响;开源软件的集成如此快速地形成了业界常态,我们没能捕捉到转折点也情有可原。
|
||||
|
||||
举个例子,Hadoop,改变的不止是数据分析界,它引领了新一代数据公司,它们围绕开源项目创造自己的软件,按需调整和支持那些代码,更像红帽在上世纪 90 年代和本世纪早期拥抱 Linux 那样。软件越来越多地通过公有云交付,而不是运行在购买者自己的服务器,拥有了令人惊奇的操作灵活性,但同时也带来了一些关于授权、支持以及价格之类的新问题。
|
||||
|
||||
我们多年来持续追踪这个趋势,这些话题充斥了我们的 Structure Data 会议,而今年的 Structure Data 2016 也不例外。三家围绕 Hadoop 最重要的大数据公司——Hortonworks、Cloudera 和 MapR ——的 CEO 们将会共同讨论它们是如何销售他们围绕开源项目的企业软件和服务,获利的同时回报社区项目。
|
||||
|
||||
以前在企业软件上获利是很容易的事情。一个客户购买了之后,企业供应商的一系列软件就变成了收银机,从维护合同和阶段性升级中获得近乎终生的收入,软件也越来越难以被替代,因为它已经成为了客户的业务核心。客户抱怨这种绑定,但如果它们想提高工作队伍的生产力也确实没有多少选择。
|
||||
|
||||
而现在的情况不再是这样了。尽管无数的公司还陷于在他们的基础设施上运行至关重要的巨型软件包,新的项目被部署到使用开源技术的云服务器上。这让升级功能不再需要去掉大量软件包再重新安装别的,同时也让公司按需付费,而不是为一堆永远用不到的特性买单。
|
||||
|
||||
有很多客户想要利用开源项目的优势,而又不想建立和支持一支工程师队伍来调整那些开源项目以满足自己的需求。这些客户愿意为开源项目和在这之上的专有特性之间的差异付费。
|
||||
|
||||
这对于基础设施相关的软件来说格外正确。当然,你的客户们可以自己对项目进行调整,比如 Hadoop,Spark 或 Node.js,但付费可以帮助他们自定义地打包部署如今这些重要的开源技术,而不用自己干这些活儿。只需看看 Structure Data 2016 的发言者就明白了,比如 Confluent(Kafka),Databricks(Spark),以及 Cloudera-Hortonworks-MapR(Hadoop)三人组。
|
||||
|
||||
当然还有一个值得提到的是在出错的时候有个供应商给你背锅。如果你的工程师弄糟了开源项目的实现,那你只能怪你自己了。但是如果你和一个愿意提供服务级品质、能确保性能和正常运行时间指标的公司签订了合同,你实际上就是为得到支持、指导,以及有人背锅而买单。
|
||||
|
||||
构建在开源之上的商业软件市场的持续成长是我们在 Structure Data 上追踪多年的内容,如果这个话题正合你意,我们鼓励你加入我们,在旧金山,3 月 9 日和 10 日。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://www.linux.com/news/enterprise/cloud-computing/889564-the-evolving-market-for-commercial-software-built-on-open-source-
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Tom Krazit][a]
|
||||
译者:[alim0x](https://github.com/alim0x)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: https://www.linux.com/community/forums/person/70513
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,86 @@
|
||||
Linux 下五个顶级的开源命令行 Shell
|
||||
===============================================
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
这个世界上有两种 Linux 用户:敢于冒险的和态度谨慎的。
|
||||
|
||||
其中一类用户总是本能的去尝试任何能够戳中其痛点的新选择。他们尝试过不计其数的窗口管理器、系统发行版和几乎所有能找到的桌面插件。
|
||||
|
||||
另一类用户找到他们喜欢的东西后,会一直使用下去。他们往往喜欢所使用的系统发行版的默认配置。最先熟练掌握的文本编辑器会成为他们最钟爱的那一个。
|
||||
|
||||
作为一个使用桌面版和服务器版十五年之久的 Linux 用户,比起第一类来,我无疑属于第二类用户。我更倾向于使用现成的东西,如此一来,很多时候我就可以通过文档和示例方便地找到我所需要的使用案例。如果我决定选择使用非费标准的东西,这个切换过程一定会基于细致的研究,并且前提是来自好基友的大力推荐。
|
||||
|
||||
但这并不意味着我不喜欢尝试新事物并且查漏补失。所以最近一段时间,在我不假思索的使用了 bash shell 多年之后,决定尝试一下另外四个 shell 工具:ksh、tcsh、zsh 和 fish。这四个 shell 都可以通过我所用的 Fedora 系统的默认库轻松安装,并且他们可能已经内置在你所使用的系统发行版当中了。
|
||||
|
||||
这里对它们每个选择都稍作介绍,并且阐述下它适合做为你的下一个 Linux 命令行解释器的原因所在。
|
||||
|
||||
### bash
|
||||
|
||||
首先,我们回顾一下最为熟悉的一个。 [GNU Bash][1],又名 Bourne Again Shell,它是我这些年使用过的众多 Linux 发行版的默认选择。它最初发布于 1989 年,并且轻松成长为 Linux 世界中使用最广泛的 shell,甚至常见于其他一些类 Unix 系统当中。
|
||||
|
||||
Bash 是一个广受赞誉的 shell,当你通过互联网寻找各种事情解决方法所需的文档时,总能够无一例外的发现这些文档都默认你使用的是 bash shell。但 bash 也有一些缺点存在,如果你写过 Bash 脚本就会发现我们写的代码总是得比真正所需要的多那么几行。这并不是说有什么事情是它做不到的,而是说它读写起来并不总是那么直观,至少是不够优雅。
|
||||
|
||||
如上所述,基于其巨大的安装量,并且考虑到各类专业和非专业系统管理员已经适应了它的使用方式和独特之处,至少在将来一段时间内,bash 或许会一直存在。
|
||||
|
||||
### ksh
|
||||
|
||||
[KornShell][4],或许你对这个名字并不熟悉,但是你一定知道它的调用命令 ksh。这个替代性的 shell 于 80 年代起源于贝尔实验室,由 David Korn 所写。虽然最初是一个专有软件,但是后期版本是在 [Eclipse Public 许可][5]下发布的。
|
||||
|
||||
ksh 的拥趸们列出了他们觉得其优越的诸多理由,包括更好的循环语法,清晰的管道退出代码,处理重复命令和关联数组的更简单的方式。它能够模拟 vi 和 emacs 的许多行为,所以如果你是一个重度文本编辑器患者,它值得你一试。最后,我发现它虽然在高级脚本方面拥有不同的体验,但在基本输入方面与 bash 如出一辙。
|
||||
|
||||
### tcsh
|
||||
|
||||
[tcsh][6] 衍生于 csh(Berkely Unix C shell),并且可以追溯到早期的 Unix 和计算机时代开始。
|
||||
|
||||
tcsh 最大的卖点在于它的脚本语言,对于熟悉 C 语言编程的人来说,看起来会非常亲切。tcsh 的脚本编写有人喜欢,有人憎恶。但是它也有其他的技术特色,包括可以为 aliases 添加参数,各种可能迎合你偏好的默认行为,包括 tab 自动完成和将 tab 完成的工作记录下来以备后查。
|
||||
|
||||
tcsh 以 [BSD 许可][7]发布。
|
||||
|
||||
### zsh
|
||||
|
||||
[zsh][8] 是另外一个与 bash 和 ksh 有着相似之处的 shell。诞生于 90 年代初,zsh 支持众多有用的新技术,包括拼写纠正、主题化、可命名的目录快捷键,在多个终端中共享同一个命令历史信息和各种相对于原来的 bash 的轻微调整。
|
||||
|
||||
虽然部分需要遵照 GPL 许可,但 zsh 的代码和二进制文件可以在一个类似 MIT 许可证的许可下进行分发; 你可以在 [actual license][9] 中查看细节。
|
||||
|
||||
### fish
|
||||
|
||||
之前我访问了 [fish][10] 的主页,当看到 “好了,这是一个为 90 后而生的命令行 shell” 这条略带调侃的介绍时(fish 完成于 2005 年),我就意识到我会爱上这个交互友好的 shell 的。
|
||||
|
||||
fish 的作者提供了若干切换过来的理由,这些理由有点小幽默并且能戳中笑点,不过还真是那么回事。这些特性包括自动建议(“注意, Netscape Navigator 4.0 来了”,LCTT 译注:NN4 是一个重要版本。),支持“惊人”的 256 色 VGA 调色,不过也有真正有用的特性,包括根据你机器上的 man 页面自动补全命令,清除脚本和基于 web 界面的配置方式。
|
||||
|
||||
fish 的许可主要基于 GPLv2,但有些部分是在其他许可下的。你可以查看资源库来了解[完整信息][11]。
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想要寻找关于每个选择确切不同之处的详尽纲要,[这个网站][12]应该可以帮到你。
|
||||
|
||||
我的立场到底是怎样的呢?好吧,最终我应该还是会重新投入 bash 的怀抱,因为对于大多数时间都在使用命令行交互的人来说,切换过程对于编写高级的脚本能带来的好处微乎其微,并且我已经习惯于使用 bash 了。
|
||||
|
||||
但是我很庆幸做出了敞开大门并且尝试新选择的决定。我知道门外还有许许多多其他的东西。你尝试过哪些 shell,更中意哪一个?请在评论里告诉我们。
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://opensource.com/business/16/3/top-linux-shells
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Jason Baker][a]
|
||||
译者:[mr-ping](https://github.com/mr-ping)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://opensource.com/users/jason-baker
|
||||
|
||||
[1]: https://www.gnu.org/software/bash/
|
||||
[2]: http://mywiki.wooledge.org/BashPitfalls
|
||||
[3]: http://www.gnu.org/licenses/gpl.html
|
||||
[4]: http://www.kornshell.org/
|
||||
[5]: https://www.eclipse.org/legal/epl-v10.html
|
||||
[6]: http://www.tcsh.org/Welcome
|
||||
[7]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/BSD_licenses
|
||||
[8]: http://www.zsh.org/
|
||||
[9]: https://sourceforge.net/p/zsh/code/ci/master/tree/LICENCE
|
||||
[10]: https://fishshell.com/
|
||||
[11]: https://github.com/fish-shell/fish-shell/blob/master/COPYING
|
||||
[12]: http://hyperpolyglot.org/unix-shells
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,14 +1,15 @@
|
||||
在 Ubuntu Linux 中使用 WEBP 图片
|
||||
在 Ubuntu Linux 中使用 WebP 图片
|
||||
=========================================
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>简介:这篇指南会向你展示如何在 Linux 下查看 WebP 图片以及将 WebP 图片转换为 JPEG 或 PNG 格式。
|
||||
|
||||
### 什么是 WEBP?
|
||||
> 简介:这篇指南会向你展示如何在 Linux 下查看 WebP 图片以及将 WebP 图片转换为 JPEG 或 PNG 格式。
|
||||
|
||||
Google 为图片推出 [WebP 文件格式][0]已经超过五年了。Google 说,WebP 提供有损和无损压缩,相比 JPEG 压缩,WebP 压缩文件大小能更小约 25%。
|
||||
### 什么是 WebP?
|
||||
|
||||
Google 的目标是让 WebP 成为 web 图片的新标准,但是我没能看到这一切发生。已经五年过去了,除了谷歌的生态系统以外它仍未被接受成为一个标准。但正如我们所知的,Google 对它的技术很有进取心。几个月前 Google 将 Google Plus 的所有图片改为了 WebP 格式。
|
||||
自从 Google 推出 [WebP 图片格式][0],已经过去五年了。Google 说,WebP 提供有损和无损压缩,相比 JPEG 压缩,WebP 压缩文件大小,能更小约 25%。
|
||||
|
||||
Google 的目标是让 WebP 成为 web 图片的新标准,但是并没有成为现实。已经五年过去了,除了谷歌的生态系统以外它仍未被接受成为一个标准。但正如我们所知的,Google 对它的技术很有进取心。几个月前 Google 将 Google Plus 的所有图片改为了 WebP 格式。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你用 Google Chrome 从 Google Plus 上下载那些图片,你会得到 WebP 图片,不论你之前上传的是 PNG 还是 JPEG。这都不是重点。真正的问题在于当你尝试着在 Ubuntu 中使用默认的 GNOME 图片查看器打开它时你会看到如下错误:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -17,7 +18,8 @@ Google 的目标是让 WebP 成为 web 图片的新标准,但是我没能看
|
||||
> **Unrecognized image file format(未识别文件格式)**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>GNOME 图片查看器不支持 WebP 图片
|
||||
|
||||
*GNOME 图片查看器不支持 WebP 图片*
|
||||
|
||||
在这个教程里,我们会看到
|
||||
|
||||
@ -41,7 +43,8 @@ sudo apt-get install gthumb
|
||||
一旦安装完成,你就可以简单地右键点击 WebP 图片,选择 gThumb 来打开它。你现在应该可以看到如下画面:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>gThumb 中显示的 WebP 图片
|
||||
|
||||
*gThumb 中显示的 WebP 图片*
|
||||
|
||||
### 让 gThumb 成为 Ubuntu 中 WebP 图片的默认应用
|
||||
|
||||
@ -50,28 +53,30 @@ sudo apt-get install gthumb
|
||||
#### 步骤 1:右键点击 WebP 文件选择属性。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>从右键菜单中选择属性
|
||||
|
||||
*从右键菜单中选择属性*
|
||||
|
||||
#### 步骤 2:转到打开方式标签,选择 gThumb 并点击设置为默认。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>让 gThumb 成为 Ubuntu 中 WebP 图片的默认应用
|
||||
|
||||
*让 gThumb 成为 Ubuntu 中 WebP 图片的默认应用*
|
||||
|
||||
### 让 gThumb 成为所有图片的默认应用
|
||||
|
||||
gThumb 的功能比图片查看器更多。举个例子,你可以做一些简单的编辑,给图片添加滤镜等。添加滤镜的效率没有 XnRetro(在[ Linux 下添加类似 Instagram 滤镜效果][5]的专用工具)那么高,但它还是有一些基础的滤镜可以用。
|
||||
gThumb 的功能比图片查看器更多。举个例子,你可以做一些简单的图片编辑,给图片添加滤镜等。添加滤镜的效率没有 XnRetro(在[ Linux 下添加类似 Instagram 滤镜效果][5]的专用工具)那么高,但它还是有一些基础的滤镜可以用。
|
||||
|
||||
我非常喜欢 gThumb 并且决定让它成为默认的图片查看器。如果你也想在 Ubuntu 中让 gThumb 成为所有图片的默认默认应用,遵照以下步骤操作:
|
||||
我非常喜欢 gThumb 并且决定让它成为默认的图片查看器。如果你也想在 Ubuntu 中让 gThumb 成为所有图片的默认应用,遵照以下步骤操作:
|
||||
|
||||
#### 步骤1:打开系统设置
|
||||
步骤1:打开系统设置
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### 步骤2:转到详情(Details)
|
||||
步骤2:转到详情(Details)
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### 步骤3:在这里将 gThumb 设置为图片的默认应用
|
||||
步骤3:在这里将 gThumb 设置为图片的默认应用
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@ -100,7 +105,7 @@ sudo apt-get install webp
|
||||
|
||||
##### 将 JPEG/PNG 转换为 WebP
|
||||
|
||||
我们将使用 cwebp 命令(它代表压缩为 WebP 吗?)来将 JPEG 或 PNG 文件转换为 WebP。命令格式是这样的:
|
||||
我们将使用 cwebp 命令(它代表转换为 WebP 的意思吗?)来将 JPEG 或 PNG 文件转换为 WebP。命令格式是这样的:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
cwebp -q [图片质量] [JPEG/PNG_文件名] -o [WebP_文件名]
|
||||
@ -132,7 +137,7 @@ dwebp example.webp -o example.png
|
||||
|
||||
[下载 XnConvert][1]
|
||||
|
||||
XnConvert 是个强大的工具,你可以用它来批量修改图片尺寸。但在这个教程里,我们只能看到如何将单个 WebP 图片转换为 PNG/JPEG。
|
||||
XnConvert 是个强大的工具,你可以用它来批量修改图片尺寸。但在这个教程里,我们只介绍如何将单个 WebP 图片转换为 PNG/JPEG。
|
||||
|
||||
打开 XnConvert 并选择输入文件:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -148,24 +153,24 @@ XnConvert 是个强大的工具,你可以用它来批量修改图片尺寸。
|
||||
|
||||
也许你一点都不喜欢 WebP 图片格式,也不想在 Linux 仅仅为了查看 WebP 图片而安装一个新软件。如果你不得不将 WebP 文件转换以备将来使用,这会是件更痛苦的事情。
|
||||
|
||||
一个解决这个问题更简单,不那么痛苦的途径是安装一个 Chrome 扩展 Save Image as PNG。有了这个插件,你可以右键点击 WebP 图片并直接存储为 PNG 格式。
|
||||
解决这个问题的一个更简单、不那么痛苦的途径是安装一个 Chrome 扩展 Save Image as PNG。有了这个插件,你可以右键点击 WebP 图片并直接存储为 PNG 格式。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>在 Google Chrome 中将 WebP 图片保存为 PNG 格式
|
||||
|
||||
[获取 Save Image as PNG 扩展][2]
|
||||
*在 Google Chrome 中将 WebP 图片保存为 PNG 格式*
|
||||
|
||||
- [获取 Save Image as PNG 扩展][2]
|
||||
|
||||
### 你的选择是?
|
||||
|
||||
我希望这个详细的教程能够帮你在 Linux 上获取 WebP 支持并帮你转换 WebP 图片。你在 Linux 怎么处理 WebP 图片?你使用哪个工具?以上描述的方法中,你最喜欢哪一个?
|
||||
|
||||
我希望这个详细的教程能够帮你在 Linux 上支持 WebP 并帮你转换 WebP 图片。你在 Linux 怎么处理 WebP 图片?你使用哪个工具?以上描述的方法中,你最喜欢哪一个?
|
||||
|
||||
----------------------
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/webp-ubuntu-linux/?utm_source=feedburner&utm_medium=feed&utm_campaign=Feed%3A+ItsFoss+%28Its+FOSS%21+An+Open+Source+Blog%29
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/webp-ubuntu-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek Prakash][a]
|
||||
译者:[alim0x](https://github.com/alim0x)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
63
published/20160531 Why Ubuntu-based Distros Are Leaders.md
Normal file
63
published/20160531 Why Ubuntu-based Distros Are Leaders.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,63 @@
|
||||
为什么 Ubuntu 家族会占据 Linux 发行版的主导地位?
|
||||
=========================================
|
||||
|
||||
在过去的数年中,我体验了一些优秀的 Linux 发行版。给我印象最深刻的是那些由强大的社区维护的发行版,而流行的发行版比强大的社区给我的印象更深。流行的 Linux 发行版往往能吸引新用户,这通常是由于其流行而使得使用该发行版会更加容易。并非绝对如此,但一般来说是这样的。
|
||||
|
||||
说到这里,首先映入我脑海的一个发行版是 [Ubuntu][1]。其基于健壮的 [Debian][2] 发行版构建,它不仅成为了一个非常受欢迎的 Linux 发行版,而且它也衍生出了不可计数的其他分支,比如 Linux Mint 就是一个例子。在本文中,我会探讨为何我认为 Ubuntu 会赢得 Linux 发行版之战的原因,以及它是怎样影响到了整个 Linux 桌面领域。
|
||||
|
||||
### Ubuntu 易于使用
|
||||
|
||||
在我几年前首次尝试使用 Ubuntu 前,我更喜欢使用 KED 桌面。在那个时期,我接触的大多是这种 KDE 桌面环境。主要原因还是 KDE 是大多数新手容易入手的 Linux 发行版中最受欢迎的。这些新手友好的发行版有 Knoppix、Simply Mepis、Xandros、Linspire 以及其它的发行版等等,这些发行版都推荐他们的用户去使用广受欢迎的 KDE。
|
||||
|
||||
现在 KDE 能满足我的需求,我也没有什么理由去折腾其他的桌面环境。有一天我的 Debian 安装失败了(由于我个人的操作不当),我决定尝试开发代号为 Dapper Drake 的 Ubuntu 版本(LCTT 译注:Ubuntu 6.06 - Dapper Drake,发布日期:2006 年 6 月 1 日),每个人都对它赞不绝口。那个时候,我对于它的印象仅限于屏幕截图,但是我想试试也挺有趣的。
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu Dapper Drake 给我的最大的印象是它让我很清楚地知道每个东西都在哪儿。记住,我是来自于 KDE 世界的用户,在 KDE 上要想改变菜单的设置就有 15 种方法 !而 Ubuntu 上的 GNOME 实现极具极简主义的。
|
||||
|
||||
时间来到 2016 年,最新的版本号是 16.04:我们有了好几种 Ubuntu 特色版本,也有一大堆基于 Ubuntu 的发行版。所有的 Ubuntu 特色版和衍生发行版的共同具有的核心都是为易用而设计。发行版想要增大用户基数时,这就是最重要的原因。
|
||||
|
||||
### Ubuntu LTS
|
||||
|
||||
过去,我几乎一直坚持使用 LTS(Long Term Support)发行版作为我的主要桌面系统。10月份的发行版很适合我测试硬盘驱动器,甚至把它用在一个老旧的手提电脑上。我这样做的原因很简单——我没有兴趣在一个正式使用的电脑上折腾短期发行版。我是个很忙的家伙,我觉得这样会浪费我的时间。
|
||||
|
||||
对于我来说,我认为 Ubuntu 提供 LTS 发行版是 Ubuntu 能够变得流行的最大的原因。这样说吧———给普罗大众提供一个桌面 Linux 发行版,这个发行版能够得到长期的有效支持就是它的优势。事实上,不只 Ubuntu 是这样,其他的分支在这一点上也做的很好。长期支持策略以及对新手的友好环境,我认为这就为 Ubuntu 的普及带来了莫大的好处。
|
||||
|
||||
### Ubuntu Snap 软件包
|
||||
|
||||
以前,用户会夸赞可以在他们的系统上使用 PPA(personal package archive 个人软件包档案)获得新的软件。不好的是,这种技术也有缺点。当它用在各种软件名称时, PPA 经常会找不到,这种情况很常见。
|
||||
|
||||
现在有了 [Snap 软件包][3] 。当然这不是一个全新的概念,过去已经进行了类似的尝试。用户可以在一个长期支持版本上运行最新的软件,而不必去使用最新的 Ubuntu 发行版。虽然我认为目前还处于 Snap 软件包的早期,但是我很期待可以在一个稳定的发行版上运行的崭新的软件。
|
||||
|
||||
最明显的问题是,如果你要运行很多软件,那么 Snap 包实际会占用很多硬盘空间。不仅如此,大多数 Ubuntu 软件仍然需要由官方从 deb 包进行转换。第一个问题可以通过使用更大的硬盘空间得到解决,而后一个问题的解决则需要等待。
|
||||
|
||||
### Ubuntu 社区
|
||||
|
||||
首先,我承认大多数主要的 Linux 发行版都有强大的社区。然而,我坚信 Ubuntu 社区的成员是最多样化的,他们来自各行各业。例如,我们的论坛包括从苹果硬件支持到游戏等不同分类。特别是这些专业的讨论话题还非常广泛。
|
||||
|
||||
除过论坛,Ubuntu 也提供了一个很正式的社区组织。这个组织包括一个理事会、技术委员会、[本地社区团队][4]和开发者成员委员会。还有很多,但是这些都是我知道的社区组织部分。
|
||||
|
||||
我们还有一个 [Ubuntu 问答][5]版块。我认为,这种功能可以代替人们从论坛寻求帮助的方式,我发现在这个网站你得到有用信息的可能性更大。不仅如此,那些提供的解决方案中被选出的最精准的答案也会被写入到官方文档中。
|
||||
|
||||
### Ubuntu 的未来
|
||||
|
||||
我认为 Ubuntu 的 Unity 界面(LCTT 译注:Unity 是 Canonical 公司为 Ubuntu 操作系统的 GNOME 桌面环境开发的图形化界面)在提升桌面占有率上少有作为。我能理解其中的缘由,现在它主要做一些诸如可以使开发团队的工作更轻松的事情。但是最终,我还是认为 Unity 为 Ubuntu MATE 和 Linux Mint 的普及铺平道路。
|
||||
|
||||
我最好奇的一点是 Ubuntu's IRC 和邮件列表的发展(LCTT 译注:可以在 Ubuntu LoCo Teams 的 IRC Chat 上提问关于地方团队和计划的事件的问题,也可以和一些不同团队的成员进行交流)。事实是,他们都不能像 Ubuntu 问答板块那样文档化。至于邮件列表,我一直认为这对于合作是一种很痛苦的过时方法,但这仅仅是我的个人看法——其他人可能有不同的看法,也可能会认为它很好。
|
||||
|
||||
你怎么看?你认为 Ubuntu 将来会占据主要的份额吗?也许你会认为 Arch 和 Linux Mint 或者其他的发行版会在普及度上打败 Ubuntu? 既然这样,那请大声说出你最喜爱的发行版。如果这个发行版是 Ubuntu 衍生版 ,说说你为什么更喜欢它而不是 Ubuntu 本身。如果不出意外,Ubuntu 会成为构建其他发行版的基础,我想很多人都是这样认为的。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.datamation.com/open-source/why-ubuntu-based-distros-are-leaders.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Matt Hartley][a]
|
||||
译者:[vim-kakali](https://github.com/vim-kakali)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: http://www.datamation.com/author/Matt-Hartley-3080.html
|
||||
[1]: http://www.ubuntu.com/
|
||||
[2]: https://www.debian.org/
|
||||
[3]: http://www.datamation.com/open-source/ubuntu-snap-packages-the-good-the-bad-the-ugly.html
|
||||
[4]: http://loco.ubuntu.com/
|
||||
[5]: http://askubuntu.com/
|
||||
@ -3,21 +3,21 @@
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**马克·理查德·沙特尔沃思(马克Richard Shuttleworth)** 是 Ubuntu 的创始人,也被称作 [Debian 背后的人][1]([之一][2])。他于 1973 年出生在南非的韦尔科姆(Welkom)。他不仅是个企业家,还是个太空游客——他是第一个前往太空旅行的非洲独立国家的公民。
|
||||
**马克·理查德·沙特尔沃思(Mark Richard Shuttleworth)** 是 Ubuntu 的创始人,也被称作 [Debian 背后的人][1]([之一][2])。他于 1973 年出生在南非的韦尔科姆(Welkom)。他不仅是个企业家,还是个太空游客——他是第一个前往太空旅行的非洲独立国家的公民。
|
||||
|
||||
马克曾在 1996 年成立了一家名为 **Thawte** 的互联网商务安全公司,那时他还在开普敦大学( University of Cape Town)的学习金融和信息技术。
|
||||
|
||||
2000 年,马克创立了 HBD(Here be Dragons (此处有龙/危险)的缩写,所以其吉祥物是一只龙),这是一家投资公司,同时他还创立了沙特尔沃思基金会(Shuttleworth Foundation),致力于给社会中有创新性的领袖以奖金和投资等形式提供资助。
|
||||
2000 年,马克创立了 HBD(Here be Dragons (此处有龙/危险)的缩写,所以其吉祥物是一只龙),这是一家投资公司,同时他还创立了沙特尔沃思基金会(Shuttleworth Foundation),致力于以奖金和投资等形式给社会中有创新性的领袖提供资助。
|
||||
|
||||
> "移动设备对于个人电脑行业的未来而言至关重要。比如就在这个月,相对于平板电脑的发展而言,传统 PC 行业很明显正在萎缩。所以如果我们想要涉足个人电脑产业,我们必须首先涉足移动行业。移动产业之所以有趣,是因为在这里没有盗版 Windows 操作系统的市场。所以如果你为你的操作系统赢得了一台设备的市场份额,这台设备会一直使用你的操作系统。在传统 PC 行业,我们时不时得和“免费”的 Windows 产生竞争,这是一种非常微妙的挑战。所以我们现在的重心是围绕 Ubuntu 和移动设备——手机和平板——以图与普通用户建立更深层次的联系。"
|
||||
> “移动设备对于个人电脑行业的未来而言至关重要。比如就在这个月,相对于平板电脑的发展而言,传统 PC 行业很明显正在萎缩。所以如果我们想要涉足个人电脑产业,我们必须首先涉足移动行业。移动产业之所以有趣,是因为在这里没有盗版 Windows 操作系统的市场。所以如果你为你的操作系统赢得了一台设备的市场份额,这台设备会一直使用你的操作系统。在传统 PC 行业,我们时不时得和“免费”的 Windows 产生竞争,这是一种非常微妙的挑战。所以我们现在的重心是围绕 Ubuntu 和移动设备——手机和平板——以图与普通用户建立更深层次的联系。”
|
||||
>
|
||||
> — 马克·沙特尔沃思
|
||||
|
||||
2002 年,他在俄罗斯的星城(Star City)接受了为期一年的训练,随后作为联盟号 TM-34 任务组的一员飞往了国际空间站。再后来,在面向有志于航空航天或者其相关学科的南非学生群体发起了推广科学、编程及数学的运动后,马克 创立了 **Canonical Ltd**。此后直至2013年,他一直在领导 Ubuntu 操作系统的开发。
|
||||
|
||||
现今,Shuttleworth 拥有英国与南非双重国籍并和 18 只可爱的鸭子住在英国的 Isle of Man 小岛上的一处花园,一同的还有他可爱的女友 Claire,两条黑色母狗以及时不时经过的羊群。
|
||||
现今,沙特尔沃思拥有英国与南非双重国籍并和 18 只可爱的鸭子住在英国的 Isle of Man 小岛上的一处花园,一同的还有他可爱的女友 Claire,两条黑色母狗以及时不时经过的羊群。
|
||||
|
||||
> "电脑不仅仅是一台电子设备了。它现在是你思维的延续,以及通向他人的大门。"
|
||||
> “电脑不仅仅是一台电子设备了。它现在是你思维的延续,以及通向他人的大门。”
|
||||
>
|
||||
> — 马克·沙特尔沃思
|
||||
|
||||
@ -41,7 +41,7 @@
|
||||
>
|
||||
> — 马克·沙特尔沃思
|
||||
|
||||
### Linux、免费开源软件与马克·沙特尔沃思 ###
|
||||
### Linux、自由开源软件与马克·沙特尔沃思 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在 90 年代后期,马克曾作为一名开发者参与 Debian 操作系统项目。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -49,7 +49,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
2004 年,马克通过出资开发基于 Debian 的 Ubuntu 操作系统返回了自由软件界,这一切也经由他的 Canonical 公司完成。
|
||||
|
||||
2005 年,马克出资建立了 Ubuntu 基金会并投入了一千万美元作为启动资金。在 Ubuntu 项目内,马克经常被一个朗朗上口的名字称呼——“**SABDFL :自封的生命之仁慈独裁者(Self-Appointed Benevolent Dictator for Life)**”。为了能够找到足够多的高手开发这个巨大的项目,马克花费了 6 个月的时间从 Debian 邮件列表里寻找,这一切都是在他乘坐在南极洲的一艘破冰船——赫列布尼科夫船长号(Kapitan Khlebnikov)——上完成的。同年,马克买下了 Impi Linux 65% 的股份。
|
||||
2005 年,马克出资建立了 Ubuntu 基金会并投入了一千万美元作为启动资金。在 Ubuntu 项目内,人们经常用一个朗朗上口的名字称呼他——“**SABDFL :自封的生命之仁慈独裁者(Self-Appointed Benevolent Dictator for Life)**”。为了能够找到足够多的高手开发这个巨大的项目,马克花费了 6 个月的时间从 Debian 邮件列表里寻找,这一切都是在他乘坐在南极洲的一艘破冰船——赫列布尼科夫船长号(Kapitan Khlebnikov)——上完成的。同年,马克买下了 Impi Linux 65% 的股份。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
> “我呼吁电信公司的掌权者们尽快开发出跨洲际的高效信息传输服务。”
|
||||
@ -78,7 +78,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在太空中,马克与纳尔逊·曼德拉(Nelson Mandela)和另一个 14 岁的南非女孩米歇尔·福斯特(Michelle Foster) (她问马克要不要娶她)通过无线电进行了交谈。马克礼貌地回避了这个结婚问题,在巧妙地改换话题之前他说他感到很荣幸。身患绝症的女孩福斯特通过梦想基金会( Dream foundation)的赞助获得了与马克和纳尔逊·曼德拉交谈的机会。
|
||||
在太空中,马克与纳尔逊·曼德拉(Nelson Mandela)和另一个 14 岁的南非女孩米歇尔·福斯特(Michelle Foster) (她问马克要不要娶她)通过无线电进行了交谈。马克礼貌地回避了这个结婚问题,但在巧妙地改换话题之前他说他感到很荣幸。身患绝症的女孩福斯特通过梦想基金会( Dream foundation)的赞助获得了与马克和纳尔逊·曼德拉交谈的机会。
|
||||
|
||||
归来后,马克在世界各地做了旅行,并和各地的学生就太空之旅发表了感言。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,106 @@
|
||||
与 Linux 一同驾车奔向未来
|
||||
===========================================
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
当我驾车的时候并没有这么想过,但是我肯定喜欢一个配有这样系统的车子,它可以让我按下几个按钮就能与我的妻子、母亲以及孩子们语音通话。这样的系统也可以让我选择是否从云端、卫星广播、以及更传统的 AM/FM 收音机收听音乐流媒体。我也会得到最新的天气情况,以及它可以引导我的车载 GPS 找到抵达下一个目的地的最快路线。[车载娱乐系统(In-vehicle infotainment)][1],业界常称作 IVI,它已经普及出现在最新的汽车上了。
|
||||
|
||||
前段时间,我乘坐飞机跨越了数百英里,然后租了一辆汽车。令人愉快的是,我发现我租赁的汽车上配置了类似我自己车上同样的 IVI 技术。毫不犹豫地,我就通过蓝牙连接把我的联系人上传到了系统当中,然后打电话回家给我的家人,让他们知道我已经安全抵达了,然后我的主机会让他们知道我正在去往他们家的路上。
|
||||
|
||||
在最近的[新闻综述][2]中,Scott Nesbitt 引述了一篇文章,说福特汽车公司因其开源的[智能设备连接(Smart Device Link)][3](SDL)从竞争对手汽车制造商中得到了足够多的回报,这个中间件框架可以用于支持移动电话。 SDL 是 [GENIVI 联盟][4]的一个项目,这个联盟是一个非营利性组织,致力于建设支持开源车载娱乐系统的中间件。据 GENIVI 的执行董事 [Steven Crumb][5] 称,他们的[成员][6]有很多,包括戴姆勒集团、现代、沃尔沃、日产、本田等等 170 个企业。
|
||||
|
||||
为了在同行业间保持竞争力,汽车生产企业需要一个中间设备系统,以支持现代消费者所使用的各种人机界面技术。无论您使用的是 Android、iOS 还是其他设备,汽车 OEM 厂商都希望自己的产品能够支持这些。此外,这些的 IVI 系统必须有足够适应能力以支持日益变化的移动技术。OEM 厂商希望提供有价值的服务,并可以在他们的 IVI 之上增加服务,以满足他们客户的各种需求。
|
||||
|
||||
### 步入 Linux 和开源软件
|
||||
|
||||
除了 GENIVI 在努力之外,[Linux 基金会][7]也赞助支持了[车载 Linux(Automotive Grade Linux)][8](AGL)工作组,这是一个致力于为汽车应用寻求开源解决方案的软件基金会。虽然 AGL 初期将侧重于 IVI 系统,但是未来他们希望发展到不同的方向,包括[远程信息处理(telematics)][9]、抬头显示器(HUD)及其他控制系统等等。 现在 AGL 已经有超过 50 名成员,包括捷豹、丰田、日产,并在其[最近发布的一篇公告][10]中宣称福特、马自达、三菱、和斯巴鲁也加入了。
|
||||
|
||||
为了了解更多信息,我们采访了这一新兴领域的两位领导人。具体来说,我们想知道 Linux 和开源软件是如何被使用的,并且它们是如何事实上改变了汽车行业的面貌。首先,我们将与 [Alison Chaiken][11] 谈谈,她是一位任职于 Peloton Technology 的软件工程师,也是一位在车载 Linux 、网络安全和信息透明化方面的专家。她曾任职于 [Alison Chaiken][11] 公司、诺基亚和斯坦福直线性加速器。然后我们和 [Steven Crumb][12] 进行了交谈,他是 GENIVI 执行董事,他之前从事于高性能计算环境(超级计算机和早期的云计算)的开源工作。他说,虽然他再不是一个程序员了,但是他乐于帮助企业解决在使用开源软件时的实际业务问题。
|
||||
|
||||
### 采访 Alison Chaiken (by [Deb Nicholson][13])
|
||||
|
||||
#### 你是如何开始对汽车软件领域感兴趣的?
|
||||
|
||||
我曾在诺基亚从事于手机上的 [MeeGo][14] 产品,2009 年该项目被取消了。我想,我下一步怎么办?其时,我的一位同事正在从事于 [MeeGo-IVI][15],这是一个早期的车载 Linux 发行版。 “Linux 在汽车方面将有很大发展,” 我想,所以我就朝着这个方向努力。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 你能告诉我们你在这些日子里工作在哪些方面吗?
|
||||
|
||||
我目前正在启动一个高级巡航控制系统的项目,它用在大型卡车上,使用实时 Linux 以提升安全性和燃油经济性。我喜欢在这方面的工作,因为没有人会反对提升货运的能力。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 近几年有几则汽车被黑的消息。开源代码方案可以帮助解决这个问题吗?
|
||||
|
||||
我恰好针对这一话题准备了一次讲演,我会在南加州 Linux 2016 博览会上就 Linux 能否解决汽车上的安全问题做个讲演 ([讲演稿在此][16])。值得注意的是,GENIVI 和车载 Linux 项目已经公开了他们的代码,这两个项目可以通过 Git 提交补丁。(如果你有补丁的话),请给上游发送您的补丁!许多眼睛都盯着,bug 将无从遁形。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 执法机构和保险公司可以找到很多汽车上的数据的用途。他们获取这些信息很容易吗?
|
||||
|
||||
好问题。IEEE-1609 专用短程通信标准(Dedicated Short Range Communication Standard)就是为了让汽车的 WiFi 消息可以安全、匿名地传递。不过,如果你从你的车上发推,那可能就有人能够跟踪到你。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 开发人员和公民个人可以做些什么,以在汽车技术进步的同时确保公民自由得到保护?
|
||||
|
||||
电子前沿基金会( Electronic Frontier Foundation)(EFF)在关注汽车问题方面做了出色的工作,包括对哪些数据可以存储在汽车 “黑盒子”里通过官方渠道发表了看法,以及 DMCA 规定 1201 如何应用于汽车上。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在未来几年,你觉得在汽车方面会发生哪些令人激动的发展?
|
||||
|
||||
可以拯救生命的自适应巡航控制系统和防撞系统将取得长足发展。当它们大量进入汽车里面时,我相信这会使得(因车祸而导致的)死亡人数下降。如果这都不令人激动,我不知道还有什么会更令人激动。此外,像自动化停车辅助功能,将会使汽车更容易驾驶,减少汽车磕碰事故。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 我们需要做什么?人们怎样才能参与?
|
||||
|
||||
车载 Linux 开发是以开源的方式开发,它运行在每个人都能买得起的廉价硬件上(如树莓派 2 和中等价位的 Renesas Porter 主板)。 GENIVI 汽车 Linux 中间件联盟通过 Git 开源了很多软件。此外,还有很酷的 [OSVehicle 开源硬件][17]汽车平台。
|
||||
|
||||
只需要不太多的预算,人们就可以参与到 Linux 软件和开放硬件中。如果您感兴趣,请加入我们在 Freenode 上的IRC #automotive 吧。
|
||||
|
||||
### 采访 Steven Crumb (by Don Watkins)
|
||||
|
||||
#### GENIVI 在 IVI 方面做了哪些巨大贡献?
|
||||
|
||||
GENIVI 率先通过使用自由开源软件填补了汽车行业的巨大空白,这包括 Linux、非安全关键性汽车软件(如车载娱乐系统(IVI))等。作为消费者,他们很期望在车辆上有和智能手机一样的功能,对这种支持 IVI 功能的软件的需求量成倍地增长。不过不断提升的软件数量也增加了建设 IVI 系统的成本,从而延缓了其上市时间。
|
||||
|
||||
GENIVI 使用开源软件和社区开发的模式为汽车制造商及其软件提供商节省了大量资金,从而显著地缩短了产品面市时间。我为 GENIVI 而感到激动,我们有幸引导了一场革命,在缓慢进步的汽车行业中,从高度结构化和专有的解决方案转换为以社区为基础的开发方式。我们还没有完全达成目标,但是我们很荣幸在这个可以带来实实在在好处的转型中成为其中的一份子。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 你们的主要成员怎样推动了 GENIVI 的发展方向?
|
||||
|
||||
GENIVI 有很多成员和非成员致力于我们的工作。在许多开源项目中,任何公司都可以通过通过技术输出而发挥影响,包括简单地贡献代码、补丁、花点时间测试。前面说过,宝马、奔驰、现代汽车、捷豹路虎、标致雪铁龙、雷诺/日产和沃尔沃都是 GENIVI 积极的参与者和贡献者,其他的许多 OEM 厂商也在他们的汽车中采用了 IVI 解决方案,广泛地使用了 GENIVI 的软件。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 这些贡献的代码使用了什么许可证?
|
||||
|
||||
GENIVI 采用了一些许可证,包括从(L)GPLv2 到 MPLv2 和 Apache2.0。我们的一些工具使用的是 Eclipse 许可证。我们有一个[公开许可策略][18],详细地说明了我们的许可证偏好。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 个人或团体如何参与其中?社区的参与对于这个项目迈向成功有多重要?
|
||||
|
||||
GENIVI 的开发完全是开放的([projects.genivi.org][19]),因此,欢迎任何有兴趣在汽车中使用开源软件的人参加。也就是说,公司可以通过成员的方式[加入该联盟][20],联盟以开放的方式资助其不断进行开发。GENIVI 的成员可以享受各种各样的便利,在过去六年中,已经有多达 140 家公司参与到这个全球性的社区当中。
|
||||
|
||||
社区对于 GENIVI 是非常重要的,没有一个活跃的贡献者社区,我们不可能在这些年开发和维护了这么多有价值的软件。我们努力让参与到 GENIVI 更加简单,现在只要加入一个[邮件列表][21]就可以接触到各种软件项目中的人们。我们使用了许多开源项目采用的标准做法,并提供了高品质的工具和基础设施,以帮助开发人员宾至如归而富有成效。
|
||||
|
||||
无论你是否熟悉汽车软件,都欢迎你加入我们的社区。人们已经对汽车改装了许多年,所以对于许多人来说,在汽车上修修改改是自热而然的做法。对于汽车来说,软件是一个新的领域,GENIVI 希望能为对汽车和开源软件有兴趣的人打开这扇门。
|
||||
|
||||
-------------------------------
|
||||
via: https://opensource.com/business/16/5/interview-alison-chaiken-steven-crumb
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Don Watkins][a]
|
||||
译者:[erlinux](https://github.com/erlinux)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: https://opensource.com/users/don-watkins
|
||||
[1]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/In_car_entertainment
|
||||
[2]: https://opensource.com/life/16/1/weekly-news-jan-9
|
||||
[3]: http://projects.genivi.org/smartdevicelink/home
|
||||
[4]: http://www.genivi.org/
|
||||
[5]: https://www.linkedin.com/in/stevecrumb
|
||||
[6]: http://www.genivi.org/genivi-members
|
||||
[7]: http://www.linuxfoundation.org/
|
||||
[8]: https://www.automotivelinux.org/
|
||||
[9]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Telematics
|
||||
[10]: https://www.automotivelinux.org/news/announcement/2016/01/ford-mazda-mitsubishi-motors-and-subaru-join-linux-foundation-and
|
||||
[11]: https://www.linkedin.com/in/alison-chaiken-3ba456b3
|
||||
[12]: https://www.linkedin.com/in/stevecrumb
|
||||
[13]: https://opensource.com/users/eximious
|
||||
[14]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/MeeGo
|
||||
[15]: http://webinos.org/deliverable-d026-target-platform-requirements-and-ipr/automotive/
|
||||
[16]: http://she-devel.com/Chaiken_automotive_cybersecurity.pdf
|
||||
[17]: https://www.osvehicle.com/
|
||||
[18]: http://projects.genivi.org/how
|
||||
[19]: http://projects.genivi.org/
|
||||
[20]: http://genivi.org/join
|
||||
[21]: http://lists.genivi.org/mailman/listinfo/genivi-projects
|
||||
@ -1,9 +1,9 @@
|
||||
用 docker 创建 serverless 应用
|
||||
用 Docker 创建 serverless 应用
|
||||
======================================
|
||||
|
||||
当今世界会时不时地出现一波科技浪潮,将以前的技术拍死在海滩上。针对 serverless 应用的概念我们已经谈了很多,它是指将你的应用程序按功能来部署,这些功能在被用到时才会启动。你不用费心去管理服务器和程序规模,因为它们会在需要的时候在一个集群中启动并运行。
|
||||
当今世界会时不时地出现一波波科技浪潮,将以前的技术拍死在海滩上。针对 serverless 应用的概念我们已经谈了很多,它是指将你的应用程序按功能来部署,这些功能在被用到时才会启动。你不用费心去管理服务器和程序规模,因为它们会在需要的时候在一个集群中启动并运行。
|
||||
|
||||
但是 serverless 并不意味着没有 Docker 什么事儿,事实上 Docker 就是 serverless 的。你可以使用 Docker 来容器化这些功能,然后在 Swarm 中按需求来运行它们。Serverless 是一项构建分布式应用的技术,而 Docker 是它们完美的构建平台。
|
||||
但是 serverless 并不意味着没有 Docker 什么事儿,事实上 Docker 就是 serverless 的。你可以使用 Docker 来容器化这些功能,然后在 Swarm 中按需求来运行它们。serverless 是一项构建分布式应用的技术,而 Docker 是它们完美的构建平台。
|
||||
|
||||
### 从 servers 到 serverless
|
||||
|
||||
@ -28,13 +28,13 @@ client.run("bfirsh/serverless-record-vote-task", [voter_id, vote], detach=True)
|
||||
|
||||
这个投票处理进程和消息队列可以用运行在 Swarm 上的 Docker 容器来代替,并实现按需自动部署。
|
||||
|
||||
我们也可以用容器替换 web 前端,使用一个轻量级 HTTP 服务器来触发容器响应一个 HTTP 请求。Docker 容器代替长期运行的 HTTP 服务器来挑起响应请求的重担,这些容器可以自动扩容来支撑大访问量。
|
||||
我们也可以用容器替换 web 前端,使用一个轻量级 HTTP 服务器来触发容器响应一个 HTTP 请求。Docker 容器代替长期运行的 HTTP 服务器来挑起响应请求的重担,这些容器可以自动扩容来支撑更大访问量。
|
||||
|
||||
新的架构就像这样:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
红色框内是持续运行的服务,绿色框内是按需启动的容器。这个架构提供更少的长期运行服务让你管理,并且可以自动扩容(最大容量由你的 Swarm 决定)。
|
||||
红色框内是持续运行的服务,绿色框内是按需启动的容器。这个架构里需要你来管理的长期运行服务更少,并且可以自动扩容(最大容量由你的 Swarm 决定)。
|
||||
|
||||
### 我们可以做点什么?
|
||||
|
||||
@ -51,11 +51,11 @@ client.run("bfirsh/serverless-record-vote-task", [voter_id, vote], detach=True)
|
||||
|
||||
### 下一步怎么做
|
||||
|
||||
我们提供了这些前卫的工具和概念来构建应用,并没有深入发掘它们的功能。我们的架构里还是存在长期运行的服务,将来我们需要使用 Swarm 来把所有服务都用按需扩容的方式实现
|
||||
我们提供了这些前卫的工具和概念来构建应用,并没有深入发掘它们的功能。我们的架构里还是存在长期运行的服务,将来我们需要使用 Swarm 来把所有服务都用按需扩容的方式实现。
|
||||
|
||||
希望本文能在你搭建架构时给你一些启发,但我们还是需要你的帮助。我们提供了所有的基本工具,但它们还不是很完善,我们需要更多更好的工具、库、应用案例、文档以及其他资料。
|
||||
|
||||
[我们在这里发布了工具、库和文档][3]。如果想了解更多,请移步到那里,另外请贡献一些链接给我们,这样我们就能一直工作了。
|
||||
[我们在这里发布了工具、库和文档][3]。如果想了解更多,请贡献给我们一些你知道的资源,以便我们能够完善这篇文章。
|
||||
|
||||
玩得愉快。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -77,7 +77,7 @@ via: https://blog.docker.com/2016/06/building-serverless-apps-with-docker/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Ben Firshman][a]
|
||||
译者:[bazz2](https://github.com/bazz2)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
|
||||
ReactOS 新手指南
|
||||
====================================
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
ReactOS 是一个比较年轻的开源操作系统,它提供了一个和 Windows NT 类似的图形界面,并且它的目标也是提供一个与 NT 功能和应用程序兼容性差不多的系统。这个项目在没有使用任何 Unix 的情况下实现了一个类似 Wine 的用户模式。它的开发者们从头实现了 NT 的架构以及对于 FAT32 的兼容,因此它也不需要负任何法律责任。这也就是说,它不是又双叒叕一个 Linux 发行版,而是一个独特的类 Windows 系统,并且是开源世界的一部分。这份快速指南是给那些想要一个易于使用的 Windows 的开源替代品的人准备的。
|
||||
|
||||
ReactOS 是一个比较年轻的开源操作系统,它提供了一个和 Windows NT 类似的图形界面,并且它的目标也是提供一个与 NT 功能和应用程序兼容性差不多的系统。这个项目在没有使用任何 Unix 架构的情况下实现了一个类似 Wine 的用户模式。它的开发者们从头实现了 NT 的架构以及对于 FAT32 的兼容,因此它也不需要负任何法律责任。这也就是说,它不是又双叒叕一个 Linux 发行版,而是一个独特的类 Windows 系统,并且是开源世界的一部分。这份快速指南是给那些想要一个易于使用的 Windows 的开源替代品的人准备的。
|
||||
|
||||
### 安装系统
|
||||
|
||||
@ -31,7 +29,6 @@ ReactOS 是一个比较年轻的开源操作系统,它提供了一个和 Windo
|
||||
|
||||
下一步是选择分区的格式,不过现在我们只能选择 FAT32。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
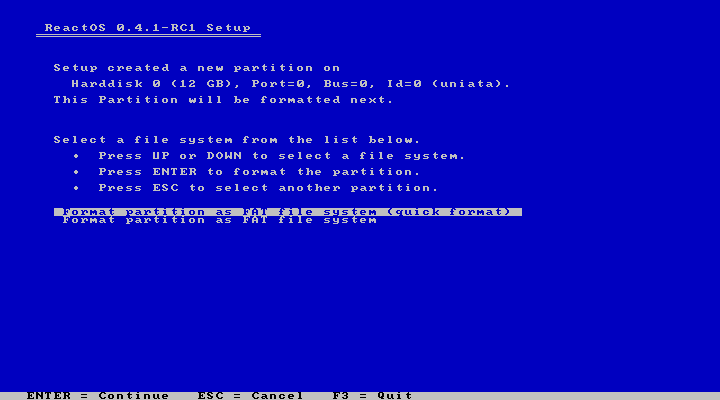
|
||||
|
||||
再下一步是选择安装文件夹。我就使用默认的“/ReactOS”了,应该没有问题。
|
||||
@ -96,7 +93,7 @@ ReactOS 是一个比较年轻的开源操作系统,它提供了一个和 Windo
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
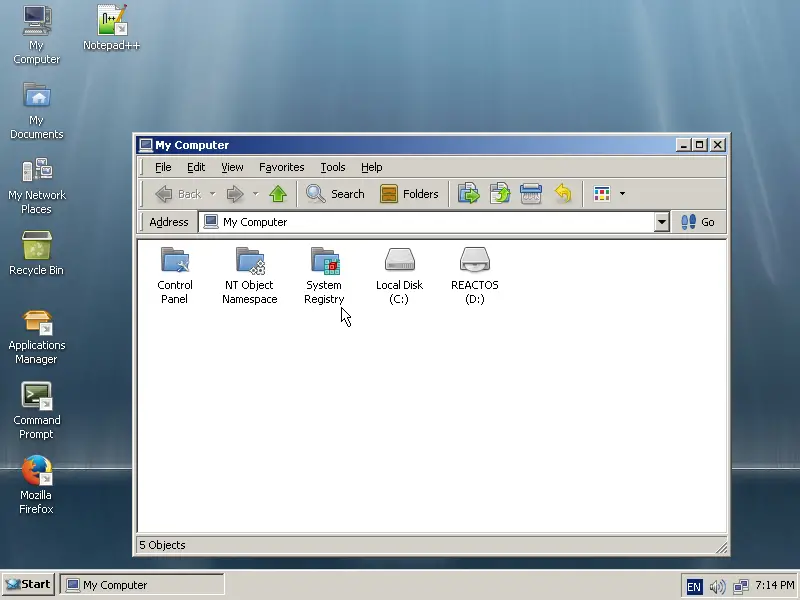
ReactOS 还有一个好啊,就是我们可以通过“我的电脑”来操作注册表。
|
||||
ReactOS 还有一个好的地方,就是我们可以通过“我的电脑”来操作注册表。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,141 @@
|
||||
Linux 新手必知必会的 10 条 Linux 基本命令
|
||||
=====================================================================
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Linux 对我们的生活产生了巨大的冲击。至少你的安卓手机使用的就是 Linux 核心。尽管如此,在第一次开始使用 Linux 时你还是会感到难以下手。因为在 Linux 中,通常需要使用终端命令来取代 Windows 系统中的点击启动图标操作。但是不必担心,这里我们会介绍 10 个 Linux 基本命令来帮助你开启 Linux 神秘之旅。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 帮助新手走出第一步的 10 个 Linux 基本命令
|
||||
|
||||
当我们谈论 Linux 命令时,实质上是在谈论 Linux 系统本身。这短短的 10 个 Linux 基本命令不会让你变成天才或者 Linux 专家,但是能帮助你轻松开始 Linux 之旅。使用这些基本命令会帮助新手们完成 Linux 的日常任务,由于它们的使用频率如此至高,所以我更乐意称他们为 Linux 命令之王!
|
||||
|
||||
让我们开始学习这 10 条 Linux 基本命令吧。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 1. sudo
|
||||
|
||||
这条命令的意思是“以超级用户的身份执行”,是 SuperUserDo 的简写,它是新手将要用到的最重要的一条 Linux 命令。当一条单行命令需要 root 权限的时候,`sudo`命令就派上用场了。你可以在每一条需要 root 权限的命令前都加上`sudo`。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo su
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2. ls (list)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
跟其他人一样,你肯定也经常想看看目录下都有些什么东西。使用列表命令,终端会把当前工作目录下所有的文件以及文件夹展示给你。比如说,我当前处在 /home 文件夹中,我想看看 /home 文件夹中都有哪些文件和目录。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/home$ ls
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
在 /home 中执行`ls`命令将会返回类似下面的内容:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
imad lost+found
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 3. cd
|
||||
|
||||
变更目录命令(cd)是终端中总会被用到的主要命令。它是最常用到的 Linux 基本命令之一。此命令使用非常简单,当你打算从当前目录跳转至某个文件夹时,只需要将文件夹键入此命令之后即可。如果你想跳转至上层目录,只需要在此命令之后键入两个点 (..) 就可以了。
|
||||
|
||||
举个例子,我现在处在 /home 目录中,我想移动到 /home 目录中的 usr 文件夹下,可以通过以下命令来完成操作。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/home $ cd usr
|
||||
|
||||
/home/usr $
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 4. mkdir
|
||||
|
||||
只是可以切换目录还是不够完美。有时候你会想要新建一个文件夹或子文件夹。此时可以使用 mkdir 命令来完成操作。使用方法很简单,只需要把新的文件夹名跟在 mkdir 命令之后就好了。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
~$ mkdir folderName
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 5. cp
|
||||
|
||||
拷贝-粘贴(copy-and-paste)是我们组织文件需要用到的重要命令。使用 `cp` 命令可以帮助你在终端当中完成拷贝-粘贴操作。首先确定你想要拷贝的文件,然后键入打算粘贴此文件的目标位置。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ cp src des
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
注意:如果目标目录对新建文件需要 root 权限时,你可以使用 `sudo` 命令来完成文件拷贝操作。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 6. rm
|
||||
|
||||
rm 命令可以帮助你移除文件甚至目录。如果不希望每删除一个文件都提示确认一次,可以用`-f`参数来强制执行。也可以使用 `-r` 参数来递归的移除文件夹。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ rm myfile.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 7. apt-get
|
||||
|
||||
这个命令会依据发行版的不同而有所区别。在基于 Debian 的发行版中,我们拥有 Advanced Packaging Tool(APT)包管理工具来安装、移除和升级包。apt-get 命令会帮助你安装需要在 Linux 系统中运行的软件。它是一个功能强大的命令行,可以用来帮助你对软件执行安装、升级和移除操作。
|
||||
|
||||
在其他发行版中,例如 Fedora、Centos,都各自不同的包管理工具。Fedora 之前使用的是 yum,不过现在 dnf 成了它默认的包管理工具。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get update
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo dnf update
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 8. grep
|
||||
|
||||
当你需要查找一个文件,但是又忘记了它具体的位置和路径时,`grep` 命令会帮助你解决这个难题。你可以提供文件的关键字,使用`grep`命令来查找到它。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ grep user /etc/passwd
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 9. cat
|
||||
|
||||
作为一个用户,你应该会经常需要浏览脚本内的文本或者代码。`cat`命令是 Linux 系统的基本命令之一,它的用途就是将文件的内容展示给你。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ cat CMakeLists.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 10. poweroff
|
||||
|
||||
最后一个命令是 `poweroff`。有时你需要直接在终端中执行关机操作。此命令可以完成这个任务。由于关机操作需要 root 权限,所以别忘了在此命令之前添加`sudo`。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo poweroff
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结
|
||||
|
||||
如我在文章开始所言,这 10 条命令并不会让你立即成为一个 Linux 大拿,但它们会让你在初期快速上手 Linux。以这些命令为基础,给自己设置一个目标,每天学习一到三条命令,这就是此文的目的所在。在下方评论区分享有趣并且有用的命令。别忘了跟你的朋友分享此文。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxandubuntu.com/home/10-basic-linux-commands-that-every-linux-newbies-should-remember
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Commenti][a]
|
||||
译者:[mr-ping](https://github.com/mr-ping)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: http://www.linuxandubuntu.com/home/10-basic-linux-commands-that-every-linux-newbies-should-remember#comments
|
||||
[1]: http://linuxandubuntu.com/home/category/linux
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,106 @@
|
||||
Android 4.4 移植到了 PowerPC 架构,支持大端架构
|
||||
===========================================================
|
||||
|
||||
eInfochips(一家软件厂商) 已将将 Android 4.4 系统移植到 PowerPC 架构,它将用于一家航空电子客户用来监视引擎的健康状况的人机界面(HMI:Human Machine Interface)。
|
||||
|
||||
eInfochips 已经开发了第一个面向 PowerPC 架构的 CPU 的 Android 移植版本,并支持大端(Big Endian)架构。此移植基于 Android 开源项目 [Android Open Source Project (AOSP)] 中 Android 4.4 (KitKat) 的代码,其功能内核的版本号为 3.12.19。
|
||||
|
||||
Android 开始兴起的时候,PowerPC 正在快速丢失和 ARM 架构共同角逐的市场。高端的网络客户和其它的企业级的嵌入式工具大多运行在诸如飞思卡尔(Freescale)的 PowerQUICC 和 QorIQ 这样的 PowerPC 处理器上,但是并不是 Linux 系统。不过,有几个 Android 的移植计划。在 2009 年,飞思卡尔和 Embedded Alley(一家软件厂商,当前是 Mentor Graphics 的 Linux 团队的一部分)[宣布了针对 PowerQUICC 和 QorIQ 芯片的移植版本][15],当前由 NXP 公司构建。另一个名为 [Android-PowerPC][16] 的项目也作出了相似的工作。
|
||||
|
||||
这些努力来的都并不容易,然而,当航空公司找到 eInfochips,希望能够为他们那些基于 PowerPC 的引擎监控系统添加 Android 应用程序以改善人机界面。该公司找出了这些早期的移植版本,然而,它们都相距甚远。所以,他们不得不从头开始新的移植。
|
||||
|
||||
最主要的问题是这些移植的 Android 版本实在是太老了,和现在的 Android 差别太大了。Embedded Alley 移植的版本为 Android 1.5 (Cupcake),它于 2009 年发布,Linux 内核版本为 2.6.28。而 Android-PowerPC 项目最后一版的移植是 Android 2.2 (Froyo),它于 2010 年发布,内核版本为 2.6.32。此外,航空公司还有一些额外的技术诉求,例如对大端架构(Big Endian)的支持,这种老式的内存访问方式仍旧应用于网络通信和电信行业。然而那些早期的移植版本仅能够支持小端(Little Endian)的内存访问。
|
||||
|
||||
### 来自 eInfochips 的全新 PowerPC 架构移植
|
||||
|
||||
eInfochips, 它最为出名的应该是那些基于 ARM/骁龙处理器的模块计算机板卡,例如 [Eragon 600][17]。 它已经完成了基于 QorIQ 的 Android 4.4 系统移植,且发布了白皮书介绍了该项目。采用该项目的航空电子设备客户仍旧不愿透露名称,目前仍旧不清楚什么时候会公开此该移植版本。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*图片来自 eInfochips 的博客日志*
|
||||
|
||||
全新的 PowerPC Android 项目包括:
|
||||
|
||||
- 基于 PowerPC [e5500][1] 仿生定制
|
||||
- 基于 Android KitKat 的大端支持
|
||||
- 使用 GCC 5.2 工具链开发
|
||||
- Android 4.4 框架的 PowerPC 支持
|
||||
- PowerPC e5500 的 Android 内核版本为 3.12.19
|
||||
|
||||
根据 eInfochips 的销售经理 Sooryanarayanan Balasubramanian 描述,该航空电子客户想要使用 Android 主要是因为熟悉的界面能够缩减培训的时间,并且让程序更新和增加新程序变得更加容易。他继续解释说:“这次成功的移植了 Android,使得今后的工作仅仅需要在应用层作出修修改改,而不再向以前一样需要在所有层面之间作相互的校验。”,“这是第一次在航空航天工业作出这些尝试,这需要在设计时尽量认真。”
|
||||
|
||||
通过白皮书,可以知道将 Android 移植到 PowerPC 上需要对框架、核心库、开发工具链、运行时链接器、对象链接器和开源编译工具作出大量的修改。在字节码生成阶段,移植团队决定使用便携模式(portable mode)而不是快速解释模式(fast interpreter mode)。这是因为还没有 PowerPC 可用的快速解释模式,而使用开源的 [libffi][18] 的便携模式能够支持 PowerPC。
|
||||
|
||||
同时,团队还面临着在 Android 运行时 (ART) 环境和 Dalvik 虚拟机 (DVM) 环境之间的选择。他们发现,ART 环境下的便携模式还未经测试且缺乏良好的文档支持,所以最终选择了 DVM 环境下的便携模式。
|
||||
|
||||
白皮书中还提及了其它的一些在移植过程中遇到的困难,包括重新开发工具链,重写脚本以解决 AOSP 对编译器标志“非标准”使用的问题。最终完成的移植版本提供了 37 个服务,以及提供了无界面的 Android 部署,在前端使用用户空间的模拟 UI。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 目标硬件
|
||||
|
||||
感谢来自 [eInfochips 博客日志][2] 的图片(如下图所示),让我们能够确认此 PowerPC 的 Android 移植项目的硬件平台。这个板卡为 [X-ES Xpedite 6101][3],它是一个加固级 XMC/PrPMC 夹层模组。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*X-ES Xpedite 6101 照片和框图*
|
||||
|
||||
X-ES Xpedite 6101 板卡拥有一个可选的 NXP 公司基于 QorIQ T 系列通信处理器(T2081、T1042 和 T1022),它们分别集成了 8 个、4 个和 2 个 e6500 核心,稍有不同的是,T2081 的处理器主频为 1.8GHz,T1042/22 的处理器主频为 1.4GHz。所有的核心都集成了 AltiVec SIMD 引擎,这也就意味着它能够提供 DSP 级别的浮点运算性能。所有以上 3 款 X-ES 板卡都能够支持最高 8GB 的 DDR3-1600 ECC SDRAM 内存。外加 512MB NOR 和 32GB 的 NAND 闪存。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*NXP T2081 框图*
|
||||
|
||||
板卡的 I/O 包括一个 x4 PCI Express Gen2 通道,以及双工的千兆级网卡、 RS232/422/485 串口和 SATA 3.0 接口。此外,它可选 3 款 QorIQ 处理器,Xpedite 6101 提供了三种 [X-ES 加固等级][19],分别是额定工作温度 0 ~ 55°C, -40 ~ 70°C, 或者是 -40 ~ 85°C,且包含 3 类冲击和抗振类别。
|
||||
|
||||
此外,我们已经介绍过的基于 X-ES QorIQ 的 XMC/PrPMC 板卡包括 [XPedite6401 和 XPedite6370][20],它们支持已有的板卡级 Linux 、风河的 VxWorks(一种实时操作系统) 和 Green Hills 的 Integrity(也是一种操作系统)。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 更多信息
|
||||
|
||||
eInfochips Android PowerPC 移植白皮书可以[在此][4]下载(需要先免费注册)。
|
||||
|
||||
### 相关资料
|
||||
|
||||
- [Commercial embedded Linux distro boosts virtualization][5]
|
||||
- [Freescale unveils first ARM-based QorIQ SoCs][6]
|
||||
- [High-end boards run Linux on 64-bit ARM QorIQ SoCs][7]
|
||||
- [Free, Open Enea Linux taps Yocto Project and Linaro code][8]
|
||||
- [LynuxWorks reverts to its LynxOS roots, changes name][9]
|
||||
- [First quad- and octa-core QorIQ SoCs unveiled][10]
|
||||
- [Free white paper shows how Linux won embedded][11]
|
||||
- [Quad-core Snapdragon COM offers three dev kit options][12]
|
||||
- [Tiny COM runs Linux on quad-core 64-bit Snapdragon 410][13]
|
||||
- [PowerPC based IoT gateway COM ships with Linux BSP][14]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://hackerboards.com/powerpc-gains-android-4-4-port-with-big-endian-support/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Eric Brown][a]
|
||||
译者:[dongfengweixiao](https://github.com/dongfengweixiao)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: http://hackerboards.com/powerpc-gains-android-4-4-port-with-big-endian-support/
|
||||
[1]: http://linuxdevices.linuxgizmos.com/low-cost-powerquicc-chips-offer-flexible-interconnect-options/
|
||||
[2]: https://www.einfochips.com/blog/k2-categories/aerospace/presenting-a-case-for-porting-android-on-powerpc-architecture.html
|
||||
[3]: http://www.xes-inc.com/products/processor-mezzanines/xpedite6101/
|
||||
[4]: http://biz.einfochips.com/portingandroidonpowerpc
|
||||
[5]: http://hackerboards.com/commercial-embedded-linux-distro-boosts-virtualization/
|
||||
[6]: http://hackerboards.com/freescale-unveils-first-arm-based-qoriq-socs/
|
||||
[7]: http://hackerboards.com/high-end-boards-run-linux-on-64-bit-arm-qoriq-socs/
|
||||
[8]: http://hackerboards.com/free-open-enea-linux-taps-yocto-and-linaro-code/
|
||||
[9]: http://hackerboards.com/lynuxworks-reverts-to-its-lynxos-roots-changes-name/
|
||||
[10]: http://hackerboards.com/first-quad-and-octa-core-qoriq-socs-unveiled/
|
||||
[11]: http://hackerboards.com/free-white-paper-shows-how-linux-won-embedded/
|
||||
[12]: http://hackerboards.com/quad-core-snapdragon-com-offers-three-dev-kit-options/
|
||||
[13]: http://hackerboards.com/tiny-com-runs-linux-and-android-on-quad-core-64-bit-snapdragon-410/
|
||||
[14]: http://hackerboards.com/powerpc-based-iot-gateway-com-ships-with-linux-bsp/
|
||||
[15]: http://linuxdevices.linuxgizmos.com/android-ported-to-powerpc/
|
||||
[16]: http://www.androidppc.com/
|
||||
[17]: http://hackerboards.com/quad-core-snapdragon-com-offers-three-dev-kit-options/
|
||||
[18]: https://sourceware.org/libffi/
|
||||
[19]: http://www.xes-inc.com/capabilities/ruggedization/
|
||||
[20]: http://hackerboards.com/high-end-boards-run-linux-on-64-bit-arm-qoriq-socs/
|
||||
@ -1,10 +1,10 @@
|
||||
LFCS 第十讲:学习简单的 Shell 脚本编程和文件系统故障排除
|
||||
LFCS 系列第十讲:学习简单的 Shell 脚本编程和文件系统故障排除
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Linux 基金会发起了 LFCS 认证 (Linux Foundation Certified Sysadmin, Linux 基金会认证系统管理员),这是一个全新的认证体系,主要目标是让全世界任何人都有机会考取认证。认证内容为 Linux 中间系统的管理,主要包括:系统运行和服务的维护、全面监控和分析的能力以及问题来临时何时想上游团队请求帮助的决策能力
|
||||
Linux 基金会发起了 LFCS 认证 (Linux Foundation Certified Sysadmin,Linux 基金会认证系统管理员),这是一个全新的认证体系,旨在让世界各地的人能够参与到中等水平的 Linux 系统的基本管理操作的认证考试中去,这项认证包括:维护正在运行的系统和服务的能力、全面监控和分析的能力以及何时向上游团队请求支持的决策能力。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
LFCS 系列第十讲
|
||||
*LFCS 系列第十讲*
|
||||
|
||||
请看以下视频,这里边介绍了 Linux 基金会认证程序。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -18,54 +18,53 @@ LFCS 系列第十讲
|
||||
首先要声明一些概念。
|
||||
|
||||
- Shell 是一个程序,它将命令传递给操作系统来执行。
|
||||
- Terminal 也是一个程序,作为最终用户,我们需要使用它与 Shell 来交互。比如,下边的图片是 GNOME Terminal。
|
||||
- Terminal 也是一个程序,允许最终用户使用它与 Shell 来交互。比如,下边的图片是 GNOME Terminal。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Gnome Terminal
|
||||
*Gnome Terminal*
|
||||
|
||||
启动 Shell 之后,会呈现一个命令提示符 (也称为命令行) 提示我们 Shell 已经做好了准备,接受标准输入设备输入的命令,这个标准输入设备通常是键盘。
|
||||
|
||||
你可以参考该系列文章的 [第一讲 使用命令创建、编辑和操作文件][1] 来温习一些常用的命令。
|
||||
你可以参考该系列文章的 [第一讲 如何在 Linux 上使用 GNU sed 等命令来创建、编辑和操作文件][1] 来温习一些常用的命令。
|
||||
|
||||
Linux 为提供了许多可以选用的 Shell,下面列出一些常用的:
|
||||
|
||||
**bash Shell**
|
||||
|
||||
Bash 代表 Bourne Again Shell,它是 GNU 项目默认的 Shell。它借鉴了 Korn shell (ksh) 和 C shell (csh) 中有用的特性,并同时对性能进行了提升。它同时也是 LFCS 认证中所涵盖的风发行版中默认 Shell,也是本系列教程将使用的 Shell。
|
||||
Bash 代表 Bourne Again Shell,它是 GNU 项目默认的 Shell。它借鉴了 Korn shell (ksh) 和 C shell (csh) 中有用的特性,并同时对性能进行了提升。它同时也是 LFCS 认证中所涵盖的各发行版中默认 Shell,也是本系列教程将使用的 Shell。
|
||||
|
||||
**sh Shell**
|
||||
|
||||
Bash Shell 是一个比较古老的 shell,一次多年来都是多数类 Unix 系统的默认 shell。
|
||||
Bourne SHell 是一个比较古老的 shell,多年来一直都是很多类 Unix 系统的默认 shell。
|
||||
|
||||
**ksh Shell**
|
||||
|
||||
Korn SHell (ksh shell) 也是一个 Unix shell,是贝尔实验室 (Bell Labs) 的 David Korn 在 19 世纪 80 年代初的时候开发的。它兼容 Bourne shell ,并同时包含了 C shell 中的多数特性。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
一个 shell 脚本仅仅只是一个可执行的文本文件,里边包含一条条可执行命令。
|
||||
|
||||
### 简单的 Shell 脚本编程 ###
|
||||
|
||||
如前所述,一个 shell 脚本就是一个纯文本文件,因此,可以使用自己喜欢的文本编辑器来创建和编辑。你可以考虑使用 vi/vim (参考本系列 [第二部分 - vi/vim 编辑器的使用][2]),它的语法高亮让我的编辑工作非常方便。
|
||||
如前所述,一个 shell 脚本就是一个纯文本文件,因此,可以使用自己喜欢的文本编辑器来创建和编辑。你可以考虑使用 vi/vim (参考本系列 [第二讲 如何安装和使用纯文本编辑器 vi/vim][2]),它的语法高亮让我的编辑工作非常方便。
|
||||
|
||||
输入如下命令来创建一个名为 myscript.sh 的脚本文件:
|
||||
|
||||
# vim myscript.sh
|
||||
|
||||
shell 脚本的第一行 (著名的 [shebang 符](http://smilejay.com/2012/03/linux_shebang/)) 必须如下:
|
||||
shell 脚本的第一行 (著名的 [释伴(shebang)行](https://linux.cn/article-3664-1.html)) 必须如下:
|
||||
|
||||
#!/bin/bash
|
||||
|
||||
这条语句“告诉”操作系统需要用那个解释器来运行这个脚本文件之后命令。
|
||||
这条语句“告诉”操作系统需要用哪个解释器来运行这个脚本文件之后命令。
|
||||
|
||||
现在可以添加需要执行的命令了。通过注释,我们可以声明每一条命令或者整个脚本的具体含义。注意,shell 会忽略掉以井号 (#) 开始的语句。
|
||||
现在可以添加需要执行的命令了。通过注释,我们可以声明每一条命令或者整个脚本的具体含义。注意,shell 会忽略掉以井号 (#) 开始的注释语句。
|
||||
|
||||
#!/bin/bash
|
||||
echo 这是关于 LFCS 认证系列的第十部分
|
||||
echo 今天是 $(date +%Y-%m-%d)
|
||||
|
||||
编写并保存脚本之后,通过以下命令来是脚本文件称为可执行文件:
|
||||
编写并保存脚本之后,通过以下命令来使脚本文件成为可执行文件:
|
||||
|
||||
# chmod 755 myscript.sh
|
||||
|
||||
@ -73,17 +72,17 @@ shell 脚本的第一行 (著名的 [shebang 符](http://smilejay.com/2012/03/li
|
||||
|
||||
echo $PATH
|
||||
|
||||
我们就会看到环境变量 ($PATH) 的具体内容:当输入命令是系统搜索可执行程序的目录,每一项之间使用冒号 (:) 隔开。称它为环境变量,是因为他本是就是 shell 环境的一部分 —— 当 shell 第每次启动时 shell 及其子进程可以获取的一系列信息。
|
||||
我们就会看到环境变量 ($PATH) 的具体内容:这是当输入命令时系统所搜索可执行程序的目录,每一项之间使用冒号 (:) 隔开。称它为环境变量,是因为它本是就是 shell 环境的一部分 —— 这是当 shell 每次启动时 shell 及其子进程可以获取的一系列信息。
|
||||
|
||||
当我们输入一个命令并按下回车时,shell 会搜索 $PATH 变量中列出的目录并执行第一个知道的实例。请看如下例子:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
环境变量
|
||||
*环境变量*
|
||||
|
||||
假如存在两个同名的可执行程序,一个在 /usr/local/bin,另一个在 /usr/bin,则会执行环境变量中最先列出的那个,并忽略另外一个。
|
||||
|
||||
如果我们自己编写的脚本没有在 $PATH 变量列出目录的其中一个,则需要输入 ./filename 来执行它。而如果存储在 $PATH 变量中的任意一个目录,我们就可以像运行其他命令一样来运行之前编写的脚本了。
|
||||
如果我们自己编写的脚本没有放在 $PATH 变量列出目录中的任何一个,则需要输入 ./filename 来执行它。而如果存储在 $PATH 变量中的任意一个目录,我们就可以像运行其他命令一样来运行之前编写的脚本了。
|
||||
|
||||
# pwd
|
||||
# ./myscript.sh
|
||||
@ -94,7 +93,7 @@ shell 脚本的第一行 (著名的 [shebang 符](http://smilejay.com/2012/03/li
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
执行脚本
|
||||
*执行脚本*
|
||||
|
||||
#### if 条件语句 ####
|
||||
|
||||
@ -106,22 +105,22 @@ shell 脚本的第一行 (著名的 [shebang 符](http://smilejay.com/2012/03/li
|
||||
OTHER-COMMANDS
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
其中,CONDITION 为如下情形的任意一项 (仅列出常用的),并且达到以下条件时返回 true:
|
||||
其中,CONDITION 可以是如下情形的任意一项 (仅列出常用的),并且达到以下条件时返回 true:
|
||||
|
||||
- [ -a file ] → 指定文件存在。
|
||||
- [ -d file ] → 指定文件存在,并且是一个目录。
|
||||
- [ -f file ] → 指定文件存在,并且是一个普通文件。
|
||||
- [ -u file ] → 指定文件存在,并设置了 SUID。
|
||||
- [ -g file ] → 指定文件存在,并设置了 SGID。
|
||||
- [ -u file ] → 指定文件存在,并设置了 SUID 权限位。
|
||||
- [ -g file ] → 指定文件存在,并设置了 SGID 权限位。
|
||||
- [ -k file ] → 指定文件存在,并设置了“黏连 (Sticky)”位。
|
||||
- [ -r file ] → 指定文件存在,并且文件可读。
|
||||
- [ -s file ] → 指定文件存在,并且文件为空。
|
||||
- [ -w file ] → 指定文件存在,并且文件可写入·
|
||||
- [ -s file ] → 指定文件存在,并且文件不为空。
|
||||
- [ -w file ] → 指定文件存在,并且文件可写入。
|
||||
- [ -x file ] → 指定文件存在,并且可执行。
|
||||
- [ string1 = string2 ] → 字符串相同。
|
||||
- [ string1 != string2 ] → 字符串不相同。
|
||||
|
||||
[ int1 op int2 ] 为前述列表中的一部分,紧跟着的项 (例如: -eq –> int1 与 int2 相同时返回 true) 则是 [ int1 op int2 ] 的一个子项, 其中 op 为以下比较操作符。
|
||||
[ int1 op int2 ] 为前述列表中的一部分 (例如: -eq –> int1 与 int2 相同时返回 true) ,其中比较项也可以是一个列表子项, 其中 op 为以下比较操作符。
|
||||
|
||||
- -eq –> int1 等于 int2 时返回 true。
|
||||
- -ne –> int1 不等于 int2 时返回 true。
|
||||
@ -142,13 +141,13 @@ shell 脚本的第一行 (著名的 [shebang 符](http://smilejay.com/2012/03/li
|
||||
|
||||
#### While 循环语句 ####
|
||||
|
||||
该循环结构会一直执行重复的命令,直到控制命令执行的退出状态值等于 0 时 (即执行成功) 停止。基本语法如下:
|
||||
该循环结构会一直执行重复的命令,直到控制命令(EVALUATION_COMMAND)执行的退出状态值等于 0 时 (即执行成功) 停止。基本语法如下:
|
||||
|
||||
while EVALUATION_COMMAND; do
|
||||
EXECUTE_COMMANDS;
|
||||
done
|
||||
|
||||
其中,EVALUATION_COMMAND 可以是任何能够返回成功 (0) 或失败 (0 以外的值) 的退出状态值的命令,EXECUTE_COMMANDS 则可以是任何的程序、脚本或者 shell 结构体,包括其他的嵌套循环。
|
||||
其中,EVALUATION\_COMMAND 可以是任何能够返回成功 (0) 或失败 (0 以外的值) 的退出状态值的命令,EXECUTE\_COMMANDS 则可以是任何的程序、脚本或者 shell 结构体,包括其他的嵌套循环。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 综合使用 ####
|
||||
|
||||
@ -168,7 +167,7 @@ shell 脚本的第一行 (著名的 [shebang 符](http://smilejay.com/2012/03/li
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
使用脚本监控 Linux 服务
|
||||
*使用脚本监控 Linux 服务*
|
||||
|
||||
我们编写的脚本看起来应该是这样的:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -188,7 +187,7 @@ shell 脚本的第一行 (著名的 [shebang 符](http://smilejay.com/2012/03/li
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Linux 服务监控脚本
|
||||
*Linux 服务监控脚本*
|
||||
|
||||
**我们来解释一下这个脚本的工作流程**
|
||||
|
||||
@ -196,21 +195,21 @@ Linux 服务监控脚本
|
||||
|
||||
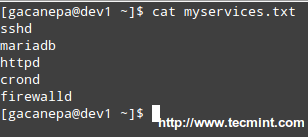
# cat myservices.txt
|
||||
|
||||
2). 以上命令由圆括号括着,并在前面添加美元符,表示它需要从 myservices.txt 的记录列表中取值作为变量传递给 for 循环。
|
||||
2). 以上命令由圆括号括着,并在前面添加美元符,表示它需要从 myservices.txt 的记录列表中取值并作为变量传递给 for 循环。
|
||||
|
||||
3). 对于记录列表中的每一项纪录 (即每一项纪录的服务变量),都会这行以下动作:
|
||||
3). 对于记录列表中的每一项纪录 (即每一项纪录的服务变量),都会执行以下动作:
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl status $service | grep --quiet "running"
|
||||
|
||||
此时,需要在每个通用变量名 (即每一项纪录的服务变量) 的前面添加美元符,以表明它是作为变量来传递的。其输出则通过管道符传给 grep。
|
||||
|
||||
其中,-quiet 选项用于阻止 grep 命令将出现 "running" 的行回显到屏幕。当 grep 捕获到 "running" 时,则会返回一个退出状态码 "0" (在 if 结构体表示为 $?),由此确认某个服务正在运行中。
|
||||
其中,-quiet 选项用于阻止 grep 命令将发现的 “running” 的行回显到屏幕。当 grep 捕获到 “running” 时,则会返回一个退出状态码 “0” (在 if 结构体表示为 $?),由此确认某个服务正在运行中。
|
||||
|
||||
如果退出状态码是非零值 (即 systemctl status $service 命令中的回显中没有出现 "running"),则表明某个服务为运行。
|
||||
如果退出状态码是非零值 (即 systemctl status $service 命令中的回显中没有出现 “running”),则表明某个服务为运行。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
服务监控脚本
|
||||
*服务监控脚本*
|
||||
|
||||
我们可以增加一步,在开始循环之前,先确认 myservices.txt 是否存在。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -236,7 +235,7 @@ Linux 服务监控脚本
|
||||
|
||||
你可能想把自己维护的主机写入一个文本文件,并使用脚本探测它们是否能够 ping 得通 (脚本中的 myhosts 可以随意替换为你想要的名称)。
|
||||
|
||||
内置的 read shell 命令将告诉 while 循环一行行的读取 myhosts,并将读取的每行内容传给 host 变量,随后 host 变量传递给 ping 命令。
|
||||
shell 的内置 read 命令将告诉 while 循环一行行的读取 myhosts,并将读取的每行内容传给 host 变量,随后 host 变量传递给 ping 命令。
|
||||
|
||||
#!/bin/bash
|
||||
|
||||
@ -248,18 +247,18 @@ Linux 服务监控脚本
|
||||
|
||||
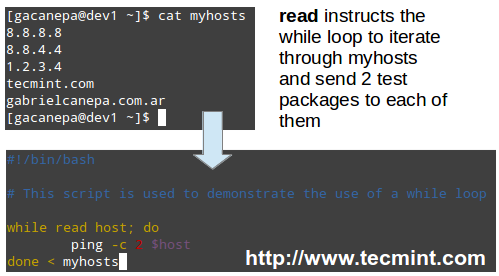
|
||||
|
||||
使用脚本 Ping 服务器
|
||||
*使用脚本 Ping 服务器*
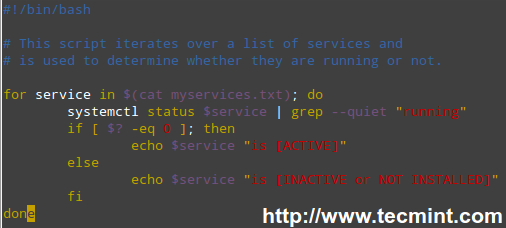
|
||||
|
||||
扩展阅读:
|
||||
|
||||
- [Learn Shell Scripting: A Guide from Newbies to System Administrator][3]
|
||||
- [5 Shell Scripts to Learn Shell Programming][4]
|
||||
|
||||
### 文件系统排除 ###
|
||||
### 文件系统排错 ###
|
||||
|
||||
尽管 Linux 是一个很稳定的操作系统,但仍然会因为某些原因出现崩溃 (比如以外断电等),正好你有一个 (或者更多个) 文件系统未能正确卸载,Linux 重启的时候就会自动检测其中可能发生的错误。
|
||||
尽管 Linux 是一个很稳定的操作系统,但仍然会因为某些原因出现崩溃时 (比如因为断电等),正好你有一个 (或者更多个) 文件系统未能正确卸载,Linux 重启的时候就会自动检测其中可能发生的错误。
|
||||
|
||||
此外,每次系统正常启动的时候,都会在文件系统挂载之前校验它们的完整度。而这些全部都依赖于 fsck 工具 ("文件系统校验")。
|
||||
此外,每次系统正常启动的时候,都会在文件系统挂载之前校验它们的完整度。而这些全部都依赖于 fsck 工具 (“file system check,文件系统校验”)。
|
||||
|
||||
如果对 fsck 进行设定,它除了校验文件系统的完整性之外,还可以尝试修复错误。fsck 能否成功修复错误,取决于文件系统的损伤程度;如果可以修复,被损坏部分的文件会恢复到位于每个文件系统根目录的 lost+found。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -279,13 +278,13 @@ fsck 的基本用如下:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
检查文件系统错误
|
||||
*检查文件系统错误*
|
||||
|
||||
除了 -y 选项,我们也可以使用 -a 选项来自动修复文件系统错误,而不必做出交互式应答,并在文件系统看起来 "干净" 的情况下强制校验。
|
||||
除了 -y 选项,我们也可以使用 -a 选项来自动修复文件系统错误,而不必做出交互式应答,并在文件系统看起来 “干净” 卸载的情况下强制校验。
|
||||
|
||||
# fsck -af /dev/sdg1
|
||||
|
||||
如果只是要找出什么地方发生了错误 (不用再检测到错误的时候修复),我们开使用 -n 选项,这样只会讲文集系统错误输出到标准输出设备。
|
||||
如果只是要找出什么地方发生了错误 (不用在检测到错误的时候修复),我们可以使用 -n 选项,这样只会将文件系统错误输出到标准输出设备上。
|
||||
|
||||
# fsck -n /dev/sdg1
|
||||
|
||||
@ -293,11 +292,11 @@ fsck 的基本用如下:
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结 ###
|
||||
|
||||
至此,系列教程的十讲就全部结束了,全系列教程涵盖了通过 LFCS 测试所需的基础内容。
|
||||
至此,系列教程的第十讲就全部结束了,全系列教程涵盖了通过 LFCS 测试所需的基础内容。
|
||||
|
||||
但显而易见的,本系列的十讲并不足以在单个主题方面做到全面描述,我们希望这一系列教程可以成为你学习的基础素材,并一直保持学习的热情。
|
||||
但显而易见的,本系列的十讲并不足以在单个主题方面做到全面描述,我们希望这一系列教程可以成为你学习的基础素材,并一直保持学习的热情(LCTT 译注:还有后继补充的几篇)。
|
||||
|
||||
我们欢迎你提出任何问题或者建议,所以你可以毫不犹豫的通过以下链接联系我们。
|
||||
我们欢迎你提出任何问题或者建议,所以你可以毫不犹豫的通过以下链接联系到我们: 成为一个 [Linux 认证系统工程师][5]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
@ -305,12 +304,13 @@ via: http://www.tecmint.com/linux-basic-shell-scripting-and-linux-filesystem-tro
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Gabriel Cánepa][a]
|
||||
译者:[GHLandy](https://github.com/GHLandy)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/gacanepa/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/sed-command-to-create-edit-and-manipulate-files-in-linux/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/vi-editor-usage/
|
||||
[1]:https://linux.cn/article-7161-1.html
|
||||
[2]:https://linux.cn/article-7165-1.html
|
||||
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/learning-shell-scripting-language-a-guide-from-newbies-to-system-administrator/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.tecmint.com/basic-shell-programming-part-ii/
|
||||
[5]:http://www.shareasale.com/r.cfm?b=768106&u=1260899&m=59485&urllink=&afftrack=
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
||||
chenxinlong translating
|
||||
IT runs on the cloud, and the cloud runs on Linux. Any questions?
|
||||
===================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
@ -37,7 +38,7 @@ So, just as the vast majority of Android phone and Chromebook users have no clue
|
||||
via: http://www.zdnet.com/article/it-runs-on-the-cloud-and-the-cloud-runs-on-linux-any-questions/#ftag=RSSbaffb68
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Steven J. Vaughan-Nichols][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
译者:[chenxinlong](https://github.com/chenxinlong)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,95 +0,0 @@
|
||||
translated by mudongliang
|
||||
|
||||
What do Linux developers think of Git and GitHub?
|
||||
=====================================================
|
||||
|
||||
**Also in today’s open source roundup: DistroWatch reviews XStream Desktop 153, and Street Fighter V is coming to Linux and SteamOS in the spring**
|
||||
|
||||
## What do Linux developers think of Git and GitHub?
|
||||
|
||||
The popularity of Git and GitHub among Linux developers is well established. But what do developers think of them? And should GitHub really be synonymous with Git itself? A Linux redditor recently asked about this and got some very interesting answers.
|
||||
|
||||
Dontwakemeup46 asked his question:
|
||||
|
||||
>I am learning Git and Github. What I am interested in is how these two are viewed by the community. That git and github are used extensively, is something I know. But are there serious issues with either Git or Github? Something that the community would love to change?
|
||||
|
||||
[More at Reddit](http://api.viglink.com/api/click?format=go&jsonp=vglnk_145580413015211&key=0a7039c08493c7c51b759e3d13019dbe&libId=iksc5hc8010113at000DL3yrsuvp7&loc=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.infoworld.com%2Farticle%2F3033059%2Flinux%2Fwhat-do-linux-developers-think-of-git-and-github.html&v=1&out=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.reddit.com%2Fr%2Flinux%2Fcomments%2F45jy59%2Fthe_popularity_of_git_and_github%2F&ref=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.linux.com%2Fnews%2Fsoftware%2Fapplications%2F886008-what-do-linux-developers-think-of-git-and-github&title=What%20do%20Linux%20developers%20think%20of%20Git%20and%20GitHub%3F%20%7C%20InfoWorld&txt=More%20at%20Reddit)
|
||||
|
||||
His fellow Linux redditors responded with their thoughts about Git and GitHub:
|
||||
|
||||
>Derenir: ”Github is not affliated with Git.
|
||||
|
||||
>Git is made by Linus Torvalds.
|
||||
|
||||
>Github hardly supports Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
>Github is a corporate bordelo that tries to make money from Git.
|
||||
|
||||
>[https://desktop.github.com/](http://api.viglink.com/api/click?format=go&jsonp=vglnk_145580415025712&key=0a7039c08493c7c51b759e3d13019dbe&libId=iksc5hc8010113at000DL3yrsuvp7&loc=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.infoworld.com%2Farticle%2F3033059%2Flinux%2Fwhat-do-linux-developers-think-of-git-and-github.html&v=1&type=U&out=https%3A%2F%2Fdesktop.github.com%2F&ref=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.linux.com%2Fnews%2Fsoftware%2Fapplications%2F886008-what-do-linux-developers-think-of-git-and-github&title=What%20do%20Linux%20developers%20think%20of%20Git%20and%20GitHub%3F%20%7C%20InfoWorld&txt=https%3A%2F%2Fdesktop.github.com%2F) see here no Linux Support.”
|
||||
|
||||
>**Bilog78**: ”A minor update: git hasn't been “made by Linus Torvalds” for a while. The maintainer is Junio C Hamano and the main contributors after him are Jeff King and Shawn O. Pearce.”
|
||||
|
||||
>**Fearthefuture**: ”I like git but can't understand why people even use github anymore. From my point of view the only thing it does better than bitbucket are user statistics and the larger userbase. Bitbucket has unlimited free private repos, much better UI and very good integration with other services such as Jenkins.”
|
||||
|
||||
>**Thunger**: ”Gitlab.com is also nice, especially since you can host your own instance on your own servers.”
|
||||
|
||||
>**Takluyver**: ”Lots of people are familiar with the UI of Github and associated services like Travis, and lots of people already have Github accounts, so it's a good place for projects to be. People also use their Github profile as a kind of portfolio, so they're motivated to put more projects on there. Github is a de facto standard for hosting open source projects.”
|
||||
|
||||
>**Tdammers**: ”Serious issue with git would be the UI, which is kind of counterintuitive, to the point that many users just stick with a handful of memorized incantations.
|
||||
|
||||
Github: most serious issue here is that it's a proprietary hosted solution; you buy convenience, and the price is that your code is on someone else's server and not under your control anymore. Another common criticism of github is that its workflow isn't in line with the spirit of git itself, particularly the way pull requests work. And finally, github is monopolizing the code hosting landscape, and that's bad for diversity, which in turn is crucial for a thriving free software community.”
|
||||
|
||||
>**Dies**: ”How is that the case? More importantly, if that is the case, then what's done is done and I guess we're stuck with Github since they control so many projects.”
|
||||
|
||||
>**Tdammers**: ”The code is hosted on someone else's server, "someone else" in this case being github. Which, for an open-source project, is not typically a huge problem, but still, you don't control it. If you have a private project on github, then the only assurance you have that it will remain private is github's word for it. If you decide to delete things, then you can never be sure whether it's been deleted, or just hidden.
|
||||
|
||||
Github doesn't control the projects themselves (you can always take your code and host it elsewhere, declaring the new location the "official" one), it just has deeper access to the code than the developers themselves.”
|
||||
|
||||
>**Drelos**: ”I have read a lot of praises and bad stuff about Github ([here's an example](http://api.viglink.com/api/click?format=go&jsonp=vglnk_145580428524613&key=0a7039c08493c7c51b759e3d13019dbe&libId=iksc5hc8010113at000DL3yrsuvp7&loc=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.infoworld.com%2Farticle%2F3033059%2Flinux%2Fwhat-do-linux-developers-think-of-git-and-github.html&v=1&out=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.wired.com%2F2015%2F06%2Fproblem-putting-worlds-code-github%2F&ref=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.linux.com%2Fnews%2Fsoftware%2Fapplications%2F886008-what-do-linux-developers-think-of-git-and-github&title=What%20do%20Linux%20developers%20think%20of%20Git%20and%20GitHub%3F%20%7C%20InfoWorld&txt=here%27s%20an%20example)) but my simple noob question is why aren't efforts towards a free and open "version" ?”
|
||||
|
||||
>**Twizmwazin**: ”GitLab is sorta pushing there.”
|
||||
|
||||
[More at Reddit](http://api.viglink.com/api/click?format=go&jsonp=vglnk_145580429720714&key=0a7039c08493c7c51b759e3d13019dbe&libId=iksc5hc8010113at000DL3yrsuvp7&loc=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.infoworld.com%2Farticle%2F3033059%2Flinux%2Fwhat-do-linux-developers-think-of-git-and-github.html&v=1&out=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.reddit.com%2Fr%2Flinux%2Fcomments%2F45jy59%2Fthe_popularity_of_git_and_github%2F&ref=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.linux.com%2Fnews%2Fsoftware%2Fapplications%2F886008-what-do-linux-developers-think-of-git-and-github&title=What%20do%20Linux%20developers%20think%20of%20Git%20and%20GitHub%3F%20%7C%20InfoWorld&txt=More%20at%20Reddit)
|
||||
|
||||
## DistroWatch reviews XStream Desktop 153
|
||||
|
||||
XStreamOS is a version of Solaris created by Sonicle. XStream Desktop brings the power of Solaris to desktop users, and distrohoppers might be interested in checking it out. DistroWatch did a full review of XStream Desktop 153 and found that it performed fairly well.
|
||||
|
||||
Jesse Smith reports for DistroWatch:
|
||||
|
||||
>I think XStream Desktop does a lot of things well. Admittedly, my trial got off to a rocky start when the operating system would not boot on my hardware and I could not get the desktop to use my display's full screen resolution when running in VirtualBox. However, after that, XStream performed fairly well. The installer works well, the operating system automatically sets up and uses boot environments, insuring we can recover the system if something goes wrong. The package management tools work well and XStream ships with a useful collection of software.
|
||||
|
||||
>I did run into a few problems playing media, specifically getting audio to work. I am not sure if that is another hardware compatibility issue or a problem with the media software that ships with the operating system. On the other hand, tools such as the web browser, e-mail, productivity suite and configuration tools all worked well.
|
||||
|
||||
>What I appreciate about XStream the most is that the operating system is a branch of the OpenSolaris family that is being kept up to date. Other derivatives of OpenSolaris tend to lag behind, at least with desktop software, but XStream is still shipping recent versions of Firefox and LibreOffice.
|
||||
|
||||
>For me personally, XStream is missing a few components, like a printer manager, multimedia support and drivers for my specific hardware. Other aspects of the operating system are quite attractive. I like the way the developers have set up LXDE, I like the default collection of software and I especially like the way file system snapshots and boot environments are enabled out of the box. Most Linux distributions, openSUSE aside, have not caught on to the usefulness of boot environments yet and I hope it is a technology that is picked up by more projects.
|
||||
|
||||
[More at DistroWatch](http://api.viglink.com/api/click?format=go&jsonp=vglnk_145580434172315&key=0a7039c08493c7c51b759e3d13019dbe&libId=iksc5hc8010113at000DL3yrsuvp7&loc=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.infoworld.com%2Farticle%2F3033059%2Flinux%2Fwhat-do-linux-developers-think-of-git-and-github.html&v=1&out=http%3A%2F%2Fdistrowatch.com%2Fweekly.php%3Fissue%3D20160215%23xstreamos&ref=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.linux.com%2Fnews%2Fsoftware%2Fapplications%2F886008-what-do-linux-developers-think-of-git-and-github&title=What%20do%20Linux%20developers%20think%20of%20Git%20and%20GitHub%3F%20%7C%20InfoWorld&txt=More%20at%20DistroWatch)
|
||||
|
||||
## Street Fighter V and SteamOS
|
||||
|
||||
Street Fighter is one of the most well known game franchises of all time, and now [Capcom has announced](http://api.viglink.com/api/click?format=go&jsonp=vglnk_145580435418216&key=0a7039c08493c7c51b759e3d13019dbe&libId=iksc5hc8010113at000DL3yrsuvp7&loc=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.infoworld.com%2Farticle%2F3033059%2Flinux%2Fwhat-do-linux-developers-think-of-git-and-github.html&v=1&out=http%3A%2F%2Fsteamcommunity.com%2Fgames%2F310950%2Fannouncements%2Fdetail%2F857177755595160250&ref=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.linux.com%2Fnews%2Fsoftware%2Fapplications%2F886008-what-do-linux-developers-think-of-git-and-github&title=What%20do%20Linux%20developers%20think%20of%20Git%20and%20GitHub%3F%20%7C%20InfoWorld&txt=Capcom%20has%20announced) that Street Fighter V will be coming to Linux and SteamOS in the spring. This is great news for Linux gamers.
|
||||
|
||||
Joe Parlock reports for Destructoid:
|
||||
|
||||
>Are you one of the less than one percent of Steam users who play on a Linux-based system? Are you part of the even smaller percentage of people who play on Linux and are excited for Street Fighter V? Well, I’ve got some good news for you.
|
||||
|
||||
>Capcom has announced via Steam that Street Fighter V will be coming to SteamOS and other Linux operating systems sometime this spring. It’ll come at no extra cost, so those who already own the PC build of the game will just be able to install it on Linux and be good to go.
|
||||
|
||||
[More at Destructoid](http://api.viglink.com/api/click?format=go&jsonp=vglnk_145580435418216&key=0a7039c08493c7c51b759e3d13019dbe&libId=iksc5hc8010113at000DL3yrsuvp7&loc=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.infoworld.com%2Farticle%2F3033059%2Flinux%2Fwhat-do-linux-developers-think-of-git-and-github.html&v=1&out=http%3A%2F%2Fsteamcommunity.com%2Fgames%2F310950%2Fannouncements%2Fdetail%2F857177755595160250&ref=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.linux.com%2Fnews%2Fsoftware%2Fapplications%2F886008-what-do-linux-developers-think-of-git-and-github&title=What%20do%20Linux%20developers%20think%20of%20Git%20and%20GitHub%3F%20%7C%20InfoWorld&txt=Capcom%20has%20announced)
|
||||
|
||||
Did you miss a roundup? Check the [Eye On Open home page](http://www.infoworld.com/blog/eye-on-open/) to get caught up with the latest news about open source and Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.infoworld.com/article/3033059/linux/what-do-linux-developers-think-of-git-and-github.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Jim Lynch][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.infoworld.com/author/Jim-Lynch/
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,281 @@
|
||||
Translating by Ping
|
||||
|
||||
Microservices with Python RabbitMQ and Nameko
|
||||
==============================================
|
||||
|
||||
>"Micro-services is the new black" - Splitting the project in to independently scalable services is the currently the best option to ensure the evolution of the code. In Python there is a Framework called "Nameko" which makes it very easy and powerful.
|
||||
|
||||
### Micro services
|
||||
|
||||
>The term "Microservice Architecture" has sprung up over the last few years to describe a particular way of designing software applications as suites of independently deployable services. - M. Fowler
|
||||
|
||||
I recommend reading the [Fowler's posts][1] to understand the theory behind it.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Ok I so what does it mean?
|
||||
|
||||
In brief a Micro Service Architecture exists when your system is divided in small (single context bound) responsibilities blocks, those blocks doesn't know each other, they only have a common point of communication, generally a message queue, and does know the communication protocol and interfaces.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Give me a real-life example
|
||||
|
||||
>The code is available on github: <http://github.com/rochacbruno/nameko-example> take a look at service and api folders for more info.
|
||||
|
||||
Consider you have an REST API, that API has an endpoint receiving some data and you need to perform some kind of computation with that data, instead of blocking the caller you can do it asynchronously, return an status "OK - Your request will be processed" to the caller and do it in a background task.
|
||||
|
||||
Also you want to send an email notification when the computation is finished without blocking the main computing process, so it is better to delegate the "email sending" to another service.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Scenario
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Show me the code!
|
||||
|
||||
Lets create the system to understand it in practice.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Environment
|
||||
|
||||
We need an environment with:
|
||||
|
||||
- A running RabbitMQ
|
||||
- Python VirtualEnv for services
|
||||
- Python VirtualEnv for API
|
||||
|
||||
#### Rabbit
|
||||
|
||||
The easiest way to have a RabbitMQ in development environment is running its official docker container, considering you have Docker installed run:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
docker run -d --hostname my-rabbit --name some-rabbit -p 15672:15672 -p 5672:5672 rabbitmq:3-management
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Go to the browser and access <http://localhost:15672> using credentials guest:guest if you can login to RabbitMQ dashboard it means you have it running locally for development.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### The Service environment
|
||||
|
||||
Now lets create the Micro Services to consume our tasks. We'll have a service for computing and another for mail, follow the steps.
|
||||
|
||||
In a shell create the root project directory
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ mkdir myproject
|
||||
$ cd myproject
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Create and activate a virtualenv (you can also use virtualenv-wrapper)
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ virtualenv service_env
|
||||
$ source service_env/bin/activate
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Install nameko framework and yagmail
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
(service_env)$ pip install nameko
|
||||
(service_env)$ pip install yagmail
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### The service code
|
||||
|
||||
Now having that virtualenv prepared (consider you can run service in a server and API in another) lets code the nameko RPC Services.
|
||||
|
||||
We are going to put both services in a single python module, but you can also split in separate modules and also run them in separate servers if needed.
|
||||
|
||||
In a file called `service.py`
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
import yagmail
|
||||
from nameko.rpc import rpc, RpcProxy
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Mail(object):
|
||||
name = "mail"
|
||||
|
||||
@rpc
|
||||
def send(self, to, subject, contents):
|
||||
yag = yagmail.SMTP('myname@gmail.com', 'mypassword')
|
||||
# read the above credentials from a safe place.
|
||||
# Tip: take a look at Dynaconf setting module
|
||||
yag.send(to=to.encode('utf-8),
|
||||
subject=subject.encode('utf-8),
|
||||
contents=[contents.encode('utf-8)])
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Compute(object):
|
||||
name = "compute"
|
||||
mail = RpcProxy('mail')
|
||||
|
||||
@rpc
|
||||
def compute(self, operation, value, other, email):
|
||||
operations = {'sum': lambda x, y: int(x) + int(y),
|
||||
'mul': lambda x, y: int(x) * int(y),
|
||||
'div': lambda x, y: int(x) / int(y),
|
||||
'sub': lambda x, y: int(x) - int(y)}
|
||||
try:
|
||||
result = operations[operation](value, other)
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
self.mail.send.async(email, "An error occurred", str(e))
|
||||
raise
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self.mail.send.async(
|
||||
email,
|
||||
"Your operation is complete!",
|
||||
"The result is: %s" % result
|
||||
)
|
||||
return result
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now with the above services definition we need to run it as a Nameko RPC service.
|
||||
|
||||
>NOTE: We are going to run it in a console and leave it running, but in production it is recommended to put the service to run using supervisord or an alternative.
|
||||
|
||||
Run the service and let it running in a shell
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
(service_env)$ nameko run service --broker amqp://guest:guest@localhost
|
||||
starting services: mail, compute
|
||||
Connected to amqp://guest:**@127.0.0.1:5672//
|
||||
Connected to amqp://guest:**@127.0.0.1:5672//
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Testing it
|
||||
|
||||
Go to another shell (with the same virtenv) and test it using nameko shell
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
(service_env)$ nameko shell --broker amqp://guest:guest@localhost
|
||||
Nameko Python 2.7.9 (default, Apr 2 2015, 15:33:21)
|
||||
[GCC 4.9.2] shell on linux2
|
||||
Broker: amqp://guest:guest@localhost
|
||||
>>>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You are now in the RPC client testing shell exposing the n.rpc object, play with it
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
>>> n.rpc.mail.send("name@email.com", "testing", "Just testing")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The above should sent an email and we can also call compute service to test it, note that it also spawns an async mail sending with result.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
>>> n.rpc.compute.compute('sum', 30, 10, "name@email.com")
|
||||
40
|
||||
>>> n.rpc.compute.compute('sub', 30, 10, "name@email.com")
|
||||
20
|
||||
>>> n.rpc.compute.compute('mul', 30, 10, "name@email.com")
|
||||
300
|
||||
>>> n.rpc.compute.compute('div', 30, 10, "name@email.com")
|
||||
3
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Calling the micro-service through the API
|
||||
|
||||
In a different shell (or even a different server) prepare the API environment
|
||||
|
||||
Create and activate a virtualenv (you can also use virtualenv-wrapper)
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ virtualenv api_env
|
||||
$ source api_env/bin/activate
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Install Nameko, Flask and Flasgger
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
(api_env)$ pip install nameko
|
||||
(api_env)$ pip install flask
|
||||
(api_env)$ pip install flasgger
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
>NOTE: In api you dont need the yagmail because it is service responsability
|
||||
|
||||
Lets say you have the following code in a file `api.py`
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
from flask import Flask, request
|
||||
from flasgger import Swagger
|
||||
from nameko.standalone.rpc import ClusterRpcProxy
|
||||
|
||||
app = Flask(__name__)
|
||||
Swagger(app)
|
||||
CONFIG = {'AMQP_URI': "amqp://guest:guest@localhost"}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@app.route('/compute', methods=['POST'])
|
||||
def compute():
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Micro Service Based Compute and Mail API
|
||||
This API is made with Flask, Flasgger and Nameko
|
||||
---
|
||||
parameters:
|
||||
- name: body
|
||||
in: body
|
||||
required: true
|
||||
schema:
|
||||
id: data
|
||||
properties:
|
||||
operation:
|
||||
type: string
|
||||
enum:
|
||||
- sum
|
||||
- mul
|
||||
- sub
|
||||
- div
|
||||
email:
|
||||
type: string
|
||||
value:
|
||||
type: integer
|
||||
other:
|
||||
type: integer
|
||||
responses:
|
||||
200:
|
||||
description: Please wait the calculation, you'll receive an email with results
|
||||
"""
|
||||
operation = request.json.get('operation')
|
||||
value = request.json.get('value')
|
||||
other = request.json.get('other')
|
||||
email = request.json.get('email')
|
||||
msg = "Please wait the calculation, you'll receive an email with results"
|
||||
subject = "API Notification"
|
||||
with ClusterRpcProxy(CONFIG) as rpc:
|
||||
# asynchronously spawning and email notification
|
||||
rpc.mail.send.async(email, subject, msg)
|
||||
# asynchronously spawning the compute task
|
||||
result = rpc.compute.compute.async(operation, value, other, email)
|
||||
return msg, 200
|
||||
|
||||
app.run(debug=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Put the above API to run in a different shell or server
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
(api_env) $ python api.py
|
||||
* Running on http://127.0.0.1:5000/ (Press CTRL+C to quit)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
and then access the url <http://localhost:5000/apidocs/index.html> you will see the Flasgger UI and you can interact with the api and start producing tasks on queue to the service to consume.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
>NOTE: You can see the shell where service is running for logging, prints and error messages. You can also access the RabbitMQ dashboard to see if there is some message in process there.
|
||||
|
||||
There is a lot of more advanced things you can do with Nameko framework you can find more information on <https://nameko.readthedocs.org/en/stable/>
|
||||
|
||||
Let's Micro Serve!
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://brunorocha.org/python/microservices-with-python-rabbitmq-and-nameko.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者: [Bruno Rocha][a]
|
||||
译者: [译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对: [校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://facebook.com/rochacbruno
|
||||
[1]:http://martinfowler.com/articles/microservices.html
|
||||
@ -1,88 +0,0 @@
|
||||
translating by kylepeng93
|
||||
A newcomer's guide to navigating OpenStack Infrastructure
|
||||
===========================================================
|
||||
|
||||
New contributors to OpenStack are welcome, but having a road map for navigating within this maturing, fast-paced open source community doesn't hurt. At OpenStack Summit in Austin, [Paul Belanger][1] (Red Hat, Inc.), [Elizabeth K. Joseph][2] (HPE), and [Christopher Aedo][3] (IBM) will lead a session on [OpenStack Infrastructure for Beginners][4]. In this interview, they offer tips and resources to help onboard new OpenStack contributors.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Your talk description says you'll be "diving into the heart of infrastructure and explain everything you need to know about the systems that keep OpenStack working." That's a tall order for a 40-minute time slot. What are the top things beginners should know about OpenStack infrastructure?**
|
||||
|
||||
**Elizabeth K. Joseph (EKJ)**: We don't use GitHub for OpenStack patches. This is something that trips up a lot of new contributors because we do maintain mirrors of all our repositories on GitHub for historical reasons. Instead we use a fully open source code review and continuous integration (CI) system maintained by the OpenStack Infrastructure team. Relatedly, since we run a CI system, every change proposed to OpenStack is tested before merging.
|
||||
|
||||
**Paul Belanger (PB)**: A lot of passionate people in the project, so don't get discouraged if your patch gets a -1.
|
||||
|
||||
**Christopher Aedo (CA)**: The community wants to help you succeed, don't be afraid to ask questions or ask for pointers to more information to improve your understanding.
|
||||
|
||||
### Which online resources would you recommend for beginners to fill in the holes for what you can't cover in your talk?
|
||||
|
||||
**PB**: Definitely our [OpenStack Project Infrastructure documentation][5]. At lot of effort has been taken to keep it up to date as much as possible. Every system used in running OpenStack as a project has a dedicated page, even the OpenStack cloud the Infrastructure teams is bringing online.
|
||||
|
||||
**EKJ**: I'll echo what Paul said about the Infrastructure documentation, and add that we love seeing patches from folks who are learning. We often don't realize what we're missing in terms of documentation until someone asks. So read, learn, and then help us fill in the gaps. You can ask questions on the [openstack-infra mailing list][6] or in our IRC channel at #openstack-infra on Freenode.
|
||||
|
||||
**CA**: I love [this detailed post][7] about building images, by Ian Wienand.
|
||||
|
||||
### Which "gotchas" should new OpenStack contributors look out for?
|
||||
|
||||
**EKJ**: Contributing is not just about submitting new code and new features; the OpenStack community places a very high value on doing code reviews. If you want people to look at a patch you submitted, consider reviewing some of the work of others and providing clear and constructive feedback. The more your fellow contributors know about your work and see you doing reviews, the more likely you'll get your code reviewed in a timely manner.
|
||||
|
||||
**CA**: I see a lot of newcomers getting tripped up with [Gerrit][8]. Read through the [developer workflow][9] in the Developers Guide, and then maybe read through it one more time. If you're not used to Gerrit, it can seem confusing and overwhelming at first, but walking through a few code reviews usually makes it all come together. Also, I'm a big fan of IRC. It can be a great place to get help, but it's best if you can maintain a persistent presence so people can answer your questions even if you're not "there" at that particular moment. (Read [IRC, the secret to success in open source][10].) You don't need to be "always on," but the ability to easily scroll back in a channel and catch up on a conversation can be invaluable.
|
||||
|
||||
**PB**: I agree with both Elizabeth and Chris—Gerrit is what to look out for. It is going to be the hub of your development effort. Not only will you be submitting code for people to review, but you'll also be reviewing other contributors' code. Watch out for the Gerrit UI; it can be confusing at times. I'd recommend trying out [Gertty][11], which is a console-based interface to the Gerrit Code Review system, which happens to be a project driven by OpenStack Infrastructure.
|
||||
|
||||
### What resources do you recommend for beginners to help them network with other OpenStack contributors?
|
||||
|
||||
**PB**: For me, it was using IRC and joining the #openstack-infra channel on Freenode ([IRC logs][12]). There is a lot of fantastic information and people in that channel. You get to see the day-to-day operations of the OpenStack project, and once you know how the project works, you'll have a better understanding on how to contribute to its future.
|
||||
|
||||
**CA**: I want to second that note for IRC; staying on IRC throughout the day made a huge difference for me in terms of feeling informed and connected. It's also such a great way to get help when you're stuck with someone on one of the projects—the ones with active IRC channels always have someone around willing to get your issues sorted out.
|
||||
|
||||
**EKJ**: The [openstack-dev mailing list][13] is quite important for staying up to date with news about projects you're working on inside of OpenStack, so I recommend subscribing to that. The mailing list uses subject tags to separate projects, so you can instruct your email client to use those and focus on threads that impact projects you care about. Beyond online resources, many OpenStack groups have popped up all over the world that serve the needs of both users and contributors to OpenStack, and many of them routinely have talks and events with key OpenStack contributors. You can search on Meetup.com in your area, or search on [groups.openstack.org][14] to see if there is an OpenStack group in your area. Finally, there are the [OpenStack Summits][15], which happen every six months, and where we'll be giving our Infrastructure talk. In their current format, the summits consist of both a user conference and a developer conference in one space to talk about everything related to OpenStack, past, present, and future.
|
||||
|
||||
### In which areas does OpenStack need to improve to become more beginner-friendly?
|
||||
|
||||
**PB**: I think our [account-setup][16] process could be made easier for new contributors, especially how many steps are needed to submit your first patch. There is a large cost to enroll into OpenStack development model, which maybe be too much for contributors; however, once enrolled, the model works fantastic for developers.
|
||||
|
||||
**CA**: We have a very pro-developer community, but the focus is on developing OpenStack itself, with less consideration given to the users of OpenStack clouds. We need to bring in application developers and encourage more people to develop things that run beautifully on OpenStack clouds, and encourage them to share those apps in the [Community App Catalog][17]. We can do this by continuing to improve our API standards and by ensuring different libraries (like libcloud, phpopencloud, and others) continue to work reliably for developers. Oh, also by sponsoring more OpenStack hackathons! All these things can ease entry for newcomers, which will lead to them sticking around.
|
||||
|
||||
**EKJ**: I've worked on open source software for many years, but for a large number of OpenStack developers, this is the first open source project they've every worked on. I've found that their proprietary software background doesn't prepare them for the open source ideals, methodologies, and collaboration techniques used in an open source project. I'd love to see us do a better job of welcoming people who have this proprietary software background and working with them so they can truly understand the value of what they're working on in the open source software community.
|
||||
|
||||
### I think 2016 is shaping up to be the Year of the Open Source Haiku. Explain OpenStack to beginners via Haiku.
|
||||
|
||||
**PB**: OpenStack runs clouds If you enjoy free software Submit your first patch
|
||||
|
||||
**CA**: In the near future OpenStack will rule the world Help make it happen!
|
||||
|
||||
**EKJ**: OpenStack is free Deploy on your own servers And run your own cloud!
|
||||
|
||||
*Paul, Elizabeth*, and Christopher will be [speaking at OpenStack Summit][18] in Austin on Monday, April 25, starting at 11:15am.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://opensource.com/business/16/4/interview-openstack-infrastructure-beginners
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[linux.com][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: http://rikkiendsley.com/
|
||||
[1]: https://twitter.com/pabelanger
|
||||
[2]: https://twitter.com/pleia2
|
||||
[3]: https://twitter.com/docaedo
|
||||
[4]: https://www.openstack.org/summit/austin-2016/summit-schedule/events/7337
|
||||
[5]: http://docs.openstack.org/infra/system-config/
|
||||
[6]: http://lists.openstack.org/cgi-bin/mailman/listinfo/openstack-infra
|
||||
[7]: https://www.technovelty.org/openstack/image-building-in-openstack-ci.html
|
||||
[8]: https://code.google.com/p/gerrit/
|
||||
[9]: http://docs.openstack.org/infra/manual/developers.html#development-workflow
|
||||
[10]: https://developer.ibm.com/opentech/2015/12/20/irc-the-secret-to-success-in-open-source/
|
||||
[11]: https://pypi.python.org/pypi/gertty
|
||||
[12]: http://eavesdrop.openstack.org/irclogs/%23openstack-infra/
|
||||
[13]: http://lists.openstack.org/cgi-bin/mailman/listinfo/openstack-dev
|
||||
[14]: https://groups.openstack.org/
|
||||
[15]: https://www.openstack.org/summit/
|
||||
[16]: http://docs.openstack.org/infra/manual/developers.html#account-setup
|
||||
[17]: https://apps.openstack.org/
|
||||
[18]: https://www.openstack.org/summit/austin-2016/summit-schedule/events/7337
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
||||
[Translating by cposture 2016.06.29]
|
||||
Data Structures in the Linux Kernel
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,302 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Install LEMP with MariaDB 10, PHP 7 and HTTP 2.0 Support for Nginx on Ubuntu 16.04
|
||||
=====================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
The LEMP stack is an acronym which represents is a group of packages (Linux OS, Nginx web server, MySQL\MariaDB database and PHP server-side dynamic programming language) which are used to deploy dynamic web applications and web pages.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>Install Nginx with MariaDB 10, PHP 7 and HTTP 2.0 Support on Ubuntu 16.04
|
||||
|
||||
This tutorial will guide you on how to install a LEMP stack (Nginx with MariaDB and PHP7) on Ubuntu 16.04 server.
|
||||
|
||||
Requirements
|
||||
|
||||
[Installation of Ubuntu 16.04 Server Edition][1]
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 1: Install the Nginx Web Server
|
||||
|
||||
#### 1. Nginx is a modern and resources efficient web server used to display web pages to visitors on the internet. We’ll start by installing Nginx web server from Ubuntu official repositories by using the [apt command line][2].
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install nginx
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
>Install Nginx on Ubuntu 16.04
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2. Next, issue the [netstat][3] and [systemctl][4] commands in order to confirm if Nginx is started and binds on port 80.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ netstat -tlpn
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
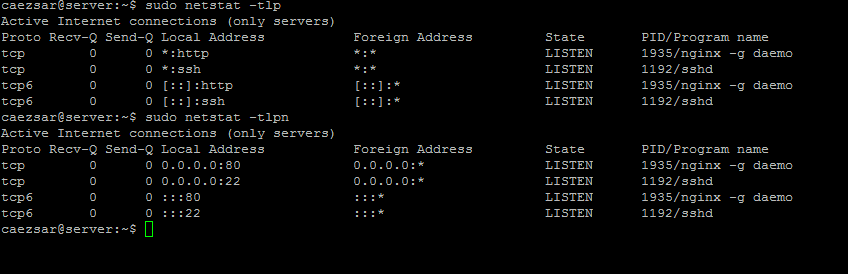
|
||||
>Check Nginx Network Port Connection
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo systemctl status nginx.service
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
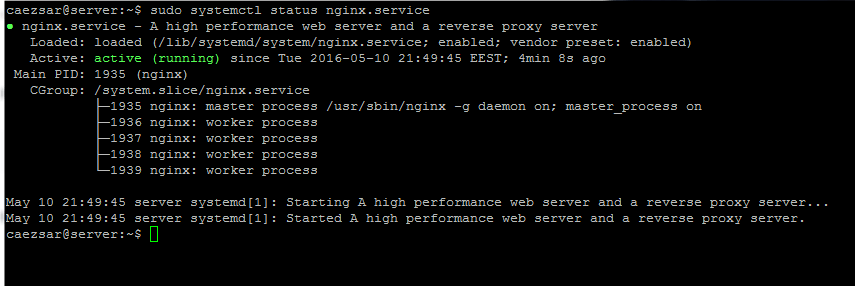
|
||||
>Check Nginx Service Status
|
||||
|
||||
Once you have the confirmation that the server is started you can open a browser and navigate to your server IP address or DNS record using HTTP protocol in order to visit Nginx default web page.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
http://IP-Address
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
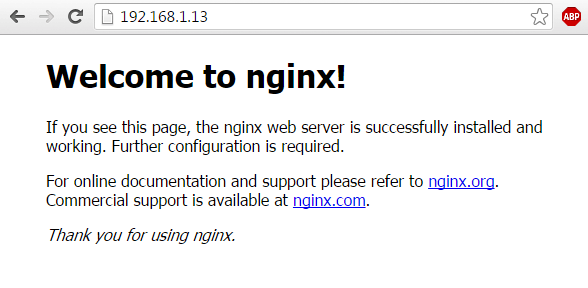
|
||||
>Verify Nginx Webpage
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 2: Enable Nginx HTTP/2.0 Protocol
|
||||
|
||||
#### 3. The HTTP/2.0 protocol which is build by default in the latest release of Nginx binaries on Ubuntu 16.04 works only in conjunction with SSL and promises a huge speed improvement in loading web SSL web pages.
|
||||
|
||||
To enable the protocol in Nginx on Ubuntu 16.04, first navigate to Nginx available sites configuration files and backup the default configuration file by issuing the below command.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ cd /etc/nginx/sites-available/
|
||||
$ sudo mv default default.backup
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
>Backup Nginx Sites Configuration File
|
||||
|
||||
#### 4. Then, using a text editor create a new default page with the below instructions:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
server {
|
||||
listen 443 ssl http2 default_server;
|
||||
listen [::]:443 ssl http2 default_server;
|
||||
|
||||
root /var/www/html;
|
||||
|
||||
index index.html index.htm index.php;
|
||||
|
||||
server_name 192.168.1.13;
|
||||
|
||||
location / {
|
||||
try_files $uri $uri/ =404;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
ssl_certificate /etc/nginx/ssl/nginx.crt;
|
||||
ssl_certificate_key /etc/nginx/ssl/nginx.key;
|
||||
|
||||
ssl_protocols TLSv1 TLSv1.1 TLSv1.2;
|
||||
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
|
||||
ssl_ciphers EECDH+CHACHA20:EECDH+AES128:RSA+AES128:EECDH+AES256:RSA+AES256:EECDH+3DES:RSA+3DES:!MD5;
|
||||
ssl_dhparam /etc/nginx/ssl/dhparam.pem;
|
||||
ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:20m;
|
||||
ssl_session_timeout 180m;
|
||||
resolver 8.8.8.8 8.8.4.4;
|
||||
add_header Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=31536000;
|
||||
#includeSubDomains" always;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
location ~ \.php$ {
|
||||
include snippets/fastcgi-php.conf;
|
||||
fastcgi_pass unix:/run/php/php7.0-fpm.sock;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
location ~ /\.ht {
|
||||
deny all;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
server {
|
||||
listen 80;
|
||||
listen [::]:80;
|
||||
server_name 192.168.1.13;
|
||||
return 301 https://$server_name$request_uri;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
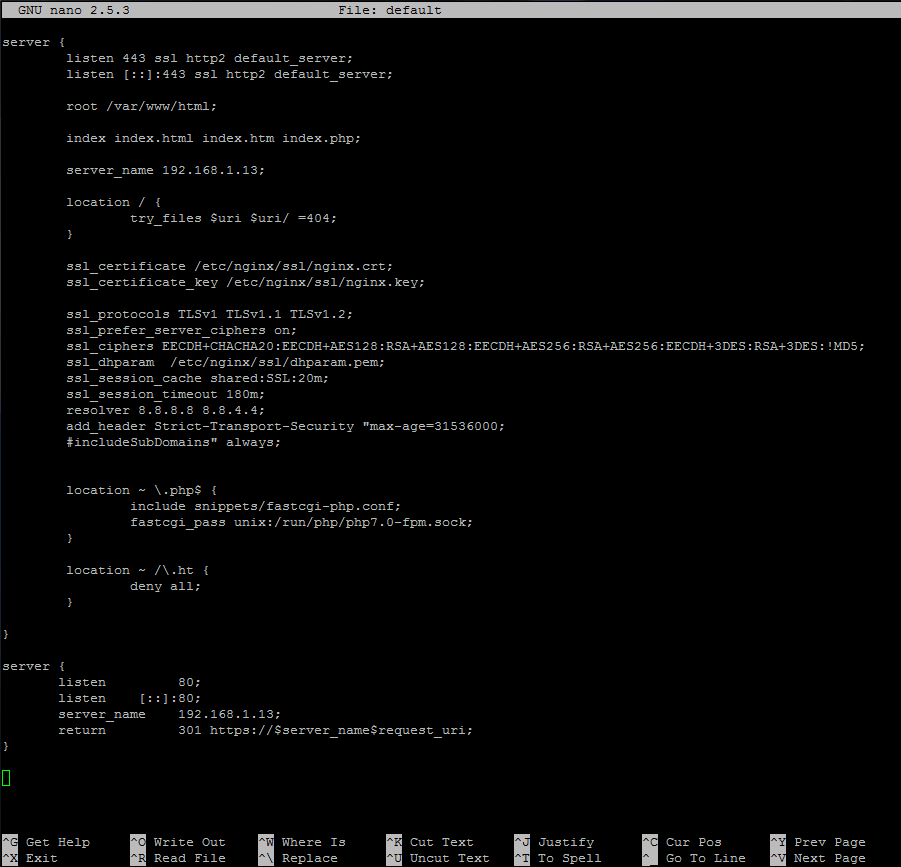
|
||||
>Enable Nginx HTTP 2 Protocol
|
||||
|
||||
The above configuration snippet enables the use of `HTTP/2.0` by adding the http2 parameter to all SSL listen directives.
|
||||
|
||||
Also, the last part of the excerpt enclosed in server directive is used to redirect all non-SSL traffic to SSL/TLS default host. Also, replace the `server_name` directive to match your own IP address or DNS record (FQDN preferably).
|
||||
|
||||
#### 5. Once you finished editing Nginx default configuration file with the above settings, generate and list the SSL certificate file and key by executing the below commands.
|
||||
|
||||
Fill the certificate with your own custom settings and pay attention to Common Name setting to match your DNS FQDN record or your server IP address that will be used to access the web page.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo mkdir /etc/nginx/ssl
|
||||
$ sudo openssl req -x509 -nodes -days 365 -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout /etc/nginx/ssl/nginx.key -out /etc/nginx/ssl/nginx.crt
|
||||
$ ls /etc/nginx/ssl/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
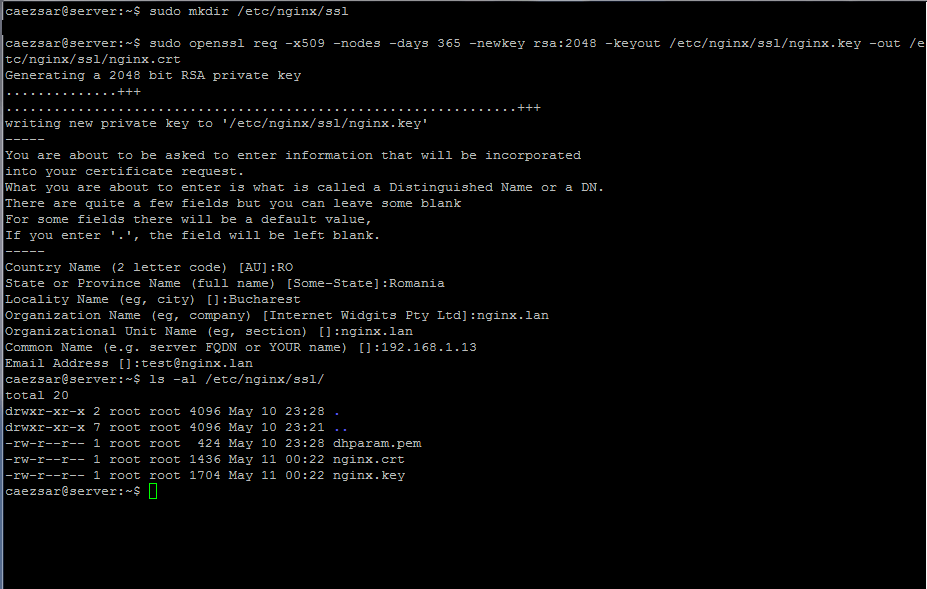
|
||||
>Generate SSL Certificate and Key for Nginx
|
||||
|
||||
#### 6. Also, create a strong DH cypher, which was changed on the above configuration file on `ssl_dhparam` instruction line, by issuing the below command:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo openssl dhparam -out /etc/nginx/ssl/dhparam.pem 2048
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
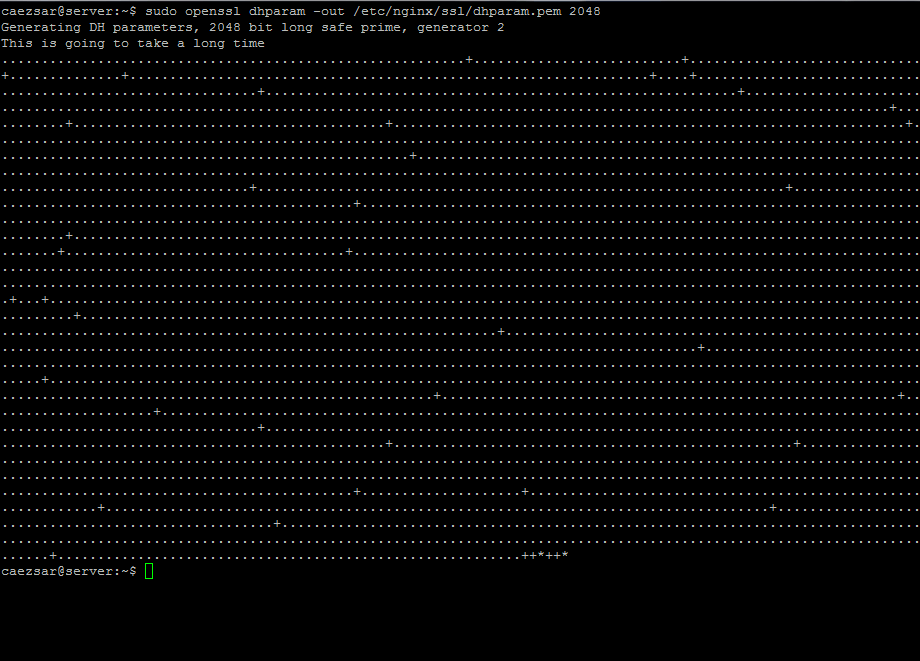
|
||||
>Create Diffie-Hellman Key
|
||||
|
||||
#### 7. Once the `Diffie-Hellman` key has been created, verify if Nginx configuration file is correctly written and can be applied by Nginx web server and restart the daemon to reflect changes by running the below commands.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo nginx -t
|
||||
$ sudo systemctl restart nginx.service
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
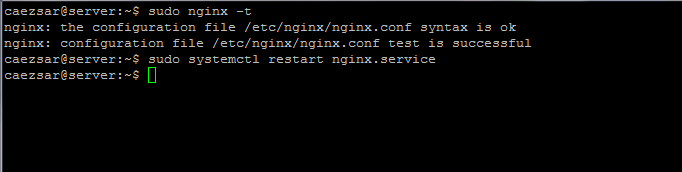
|
||||
>Check Nginx Configuration
|
||||
|
||||
#### 8. In order to test if Nginx uses HTTP/2.0 protocol issue the below command. The presence of `h2` advertised protocol confirms that Nginx has been successfully configured to use HTTP/2.0 protocol. All modern up-to-date browsers should support this protocol by default.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ openssl s_client -connect localhost:443 -nextprotoneg ''
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
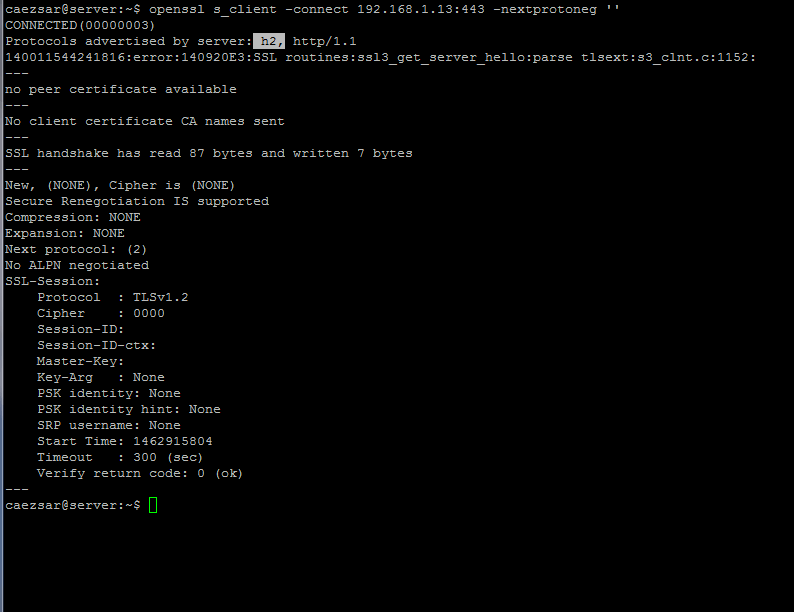
|
||||
>Test Nginx HTTP 2.0 Protocol
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 3: Install PHP 7 Interpreter
|
||||
|
||||
Nginx can be used with PHP dynamic processing language interpreter to generate dynamic web content with the help of FastCGI process manager obtained by installing the php-fpm binary package from Ubuntu official repositories.
|
||||
|
||||
#### 9. In order to grab PHP7.0 and the additional packages that will allow PHP to communicate with Nginx web server issue the below command on your server console:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo apt install php7.0 php7.0-fpm
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
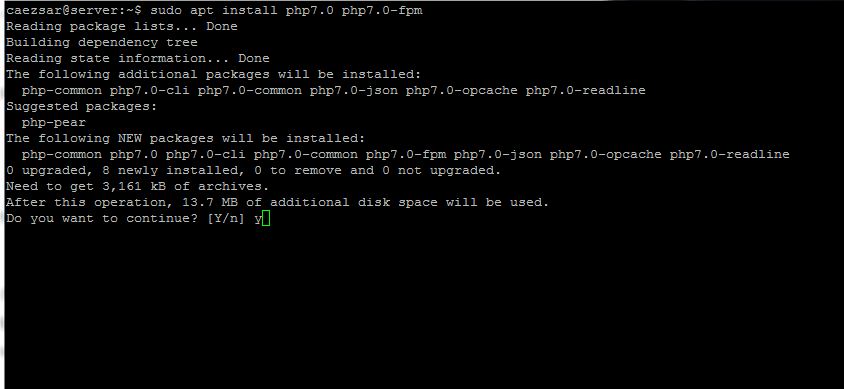
|
||||
>Install PHP 7 and PHP-FPM for Ngin
|
||||
|
||||
#### 10. Once the PHP7.0 interpreter has been successfully installed on your machine, start and check php7.0-fpm daemon by issuing the below command:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo systemctl start php7.0-fpm
|
||||
$ sudo systemctl status php7.0-fpm
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
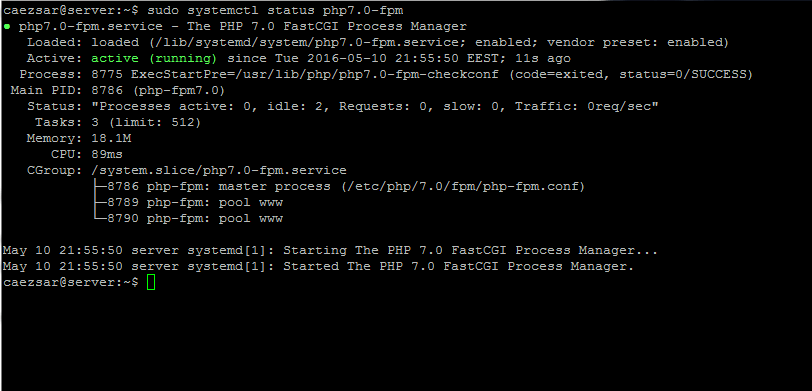
|
||||
>Start and Verify php-fpm Service
|
||||
|
||||
#### 11. The current configuration file of Nginx is already configured to use PHP FastCGI process manager in order to server dynamic content.
|
||||
|
||||
The server block that enables Nginx to use PHP interpreter is presented on the below excerpt, so no further modifications of default Nginx configuration file are required.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
location ~ \.php$ {
|
||||
include snippets/fastcgi-php.conf;
|
||||
fastcgi_pass unix:/run/php/php7.0-fpm.sock;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Below is a screenshot of what instructions you need to uncomment and modify is case of an original Nginx default configuration file.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
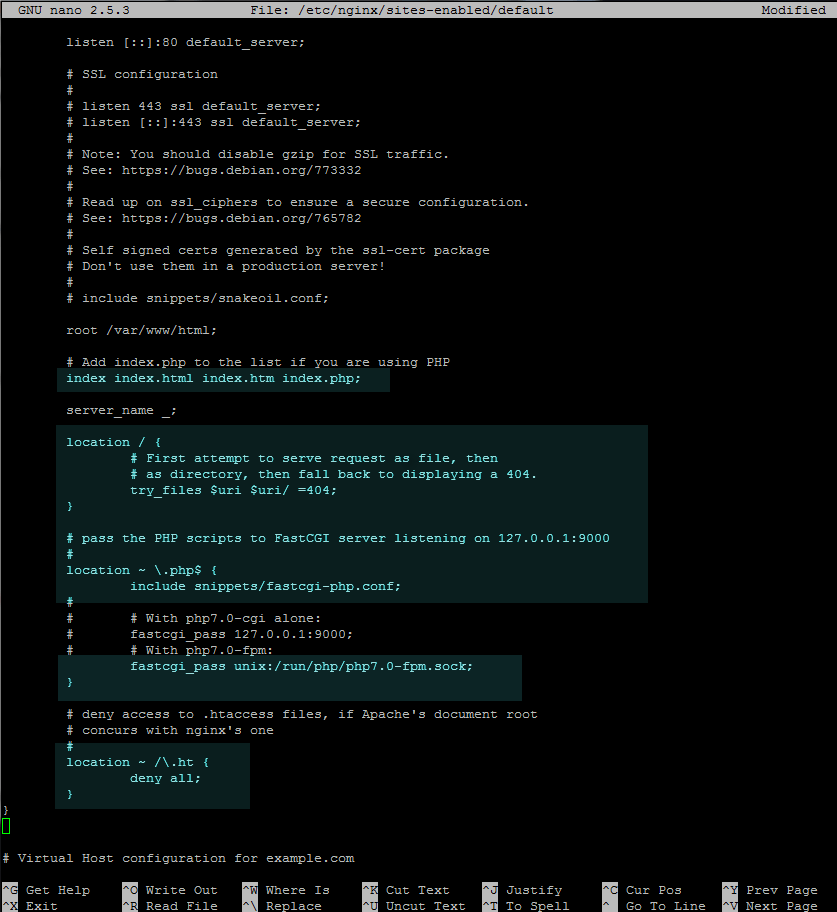
|
||||
>Enable PHP FastCGI for Nginx
|
||||
|
||||
#### 12. To test Nginx web server relation with PHP FastCGI process manager create a PHP `info.php` test configuration file by issuing the below command and verify the settings by visiting this configuration file using the below address: `http://IP_or domain/info.php`.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo su -c 'echo "<?php phpinfo(); ?>" |tee /var/www/html/info.php'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
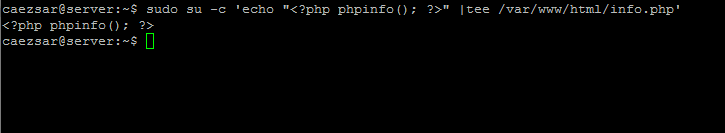
|
||||
>Create PHP Info File
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>Verify PHP FastCGI Info
|
||||
|
||||
Also check if HTTP/2.0 protocol is advertised by the server by locating the line `$_SERVER[‘SERVER_PROTOCOL’]` on PHP Variables block as illustrated on the below screenshot.
|
||||
|
||||
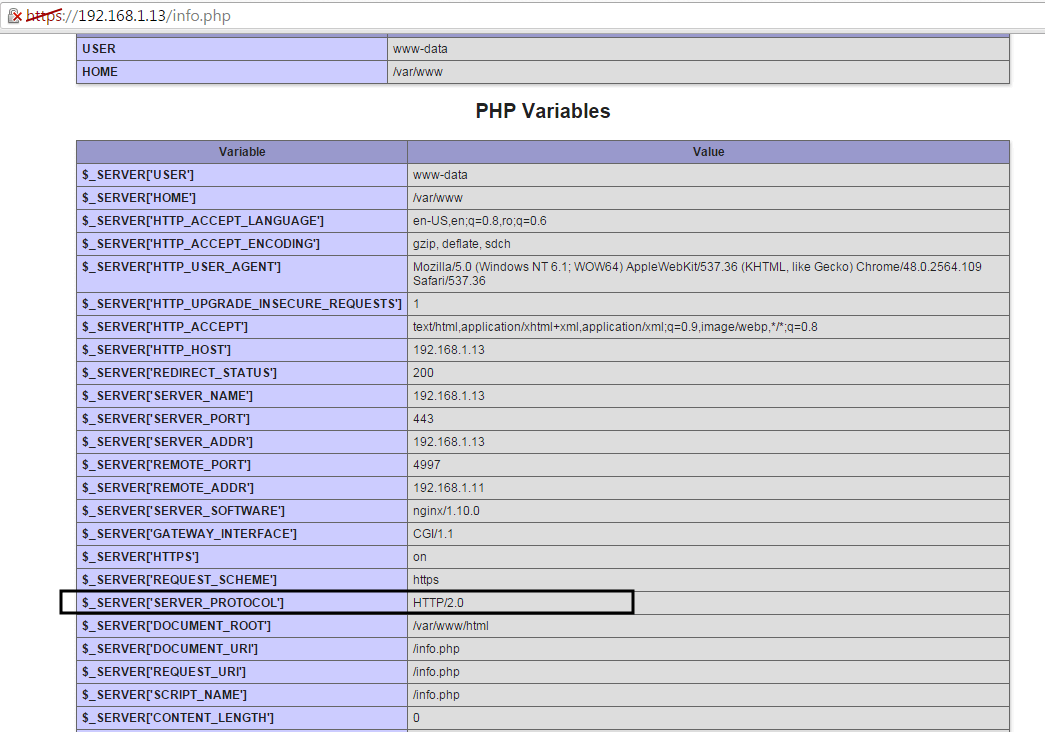
|
||||
>Check HTTP 2.0 Protocol Info
|
||||
|
||||
#### 13. In order to install extra PHP7.0 modules use the `apt search php7.0` command to find a PHP module and install it.
|
||||
|
||||
Also, try to install the following PHP modules which can come in handy in case you are planning to [install WordPress][5] or other CMS.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo apt install php7.0-mcrypt php7.0-mbstring
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
>Install PHP 7 Modules
|
||||
|
||||
#### 14. To register the PHP extra modules just restart PHP-FPM daemon by issuing the below command.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo systemctl restart php7.0-fpm.service
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 4: Install MariaDB Database
|
||||
|
||||
#### 15. Finally, in order to complete our LEMP stack we need the MariaDB database component to store and manage website data.
|
||||
|
||||
Install MariaDB database management system by running the below command and restart PHP-FPM service in order to use MySQL module to access the database.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo apt install mariadb-server mariadb-client php7.0-mysql
|
||||
$ sudo systemctl restart php7.0-fpm.service
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
>Install MariaDB for Nginx
|
||||
|
||||
#### 16. To secure the MariaDB installation, run the security script provided by the binary package from Ubuntu repositories which will ask you set a root password, remove anonymous users, disable root login remotely and remove test database.
|
||||
|
||||
Run the script by issuing the below command and answer all questions with yes. Use the below screenshot as a guide.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo mysql_secure_installation
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
>Secure MariaDB Installation for Nginx
|
||||
|
||||
#### 17. To configure MariaDB so that ordinary users can access the database without system sudo privileges, go to MySQL command line interface with root privileges and run the below commands on MySQL interpreter:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo mysql
|
||||
MariaDB> use mysql;
|
||||
MariaDB> update user set plugin=’‘ where User=’root’;
|
||||
MariaDB> flush privileges;
|
||||
MariaDB> exit
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
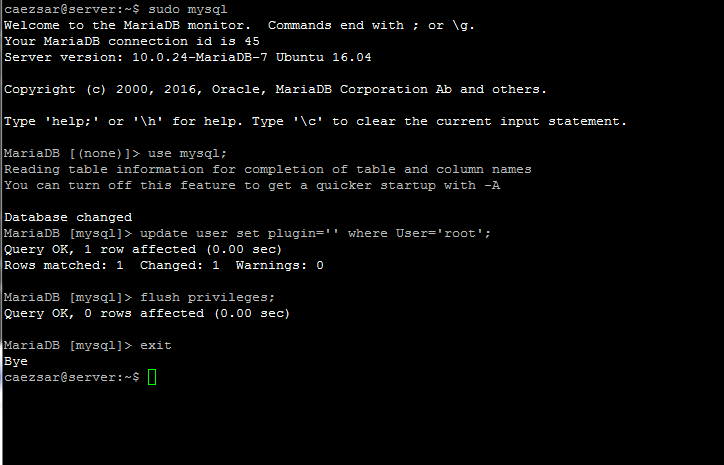
|
||||
>MariaDB User Permissions
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, login to MariaDB database and run an arbitrary command without root privileges by executing the below command:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ mysql -u root -p -e 'show databases'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
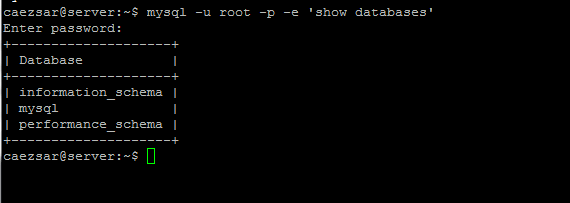
|
||||
>Check MariaDB Databases
|
||||
|
||||
That’ all! Now you have a **LEMP** stack configured on **Ubuntu 16.04** server that allows you to deploy complex dynamic web applications that can interact with databases.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/install-nginx-mariadb-php7-http2-on-ubuntu-16-04/?utm_source=feedburner&utm_medium=feed&utm_campaign=Feed%3A+tecmint+%28Tecmint%3A+Linux+Howto%27s+Guide%29
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Matei Cezar ][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: http://www.tecmint.com/author/cezarmatei/
|
||||
[1]: http://www.tecmint.com/installation-of-ubuntu-16-04-server-edition/
|
||||
[2]: http://www.tecmint.com/apt-advanced-package-command-examples-in-ubuntu/
|
||||
[3]: http://www.tecmint.com/20-netstat-commands-for-linux-network-management/
|
||||
[4]: http://www.tecmint.com/manage-services-using-systemd-and-systemctl-in-linux/
|
||||
[5]: http://www.tecmint.com/install-wordpress-using-lamp-or-lemp-on-rhel-centos-fedora/
|
||||
@ -1,285 +0,0 @@
|
||||
translating by wi-cuckoo
|
||||
Learn Python Control Flow and Loops to Write and Tune Shell Scripts – Part 2
|
||||
===============================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
In the previous article of this [Python series][1] we shared a brief introduction to Python, its command-line shell, and the IDLE. We also demonstrated how to perform arithmetic calculations, how to store values in variables, and how to print back those values to the screen. Finally, we explained the concepts of methods and properties in the context of Object Oriented Programming through a practical example.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>Write Linux Shell Scripts in Python Programming
|
||||
|
||||
In this guide we will discuss control flow (to choose different courses of action depending on information entered by a user, the result of a calculation, or the current value of a variable) and loops (to automate repetitive tasks) and then apply what we have learned so far to write a simple shell script that will display the operating system type, the hostname, the kernel release, version, and the machine hardware name.
|
||||
|
||||
This example, although basic, will help us illustrate how we can leverage Python OOP’s capabilities to write shell scripts easier than using regular bash tools.
|
||||
|
||||
In other words, we want to go from
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# uname -snrvm
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
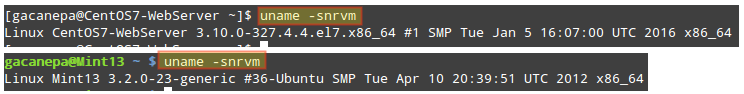
|
||||
>Check Hostname of Linux
|
||||
|
||||
to
|
||||
|
||||
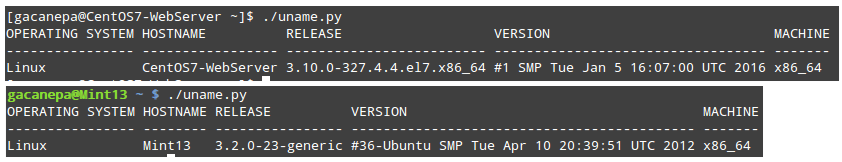
|
||||
>Check Linux Hostname Using Python Script
|
||||
|
||||
or
|
||||
|
||||
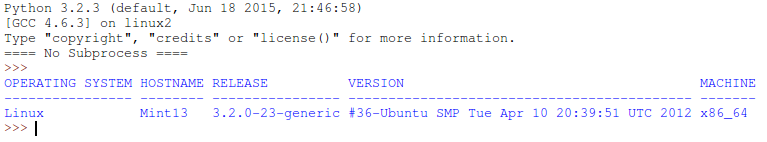
|
||||
>Script to Check Linux System Information
|
||||
|
||||
Looks pretty, doesn’t it? Let’s roll up our sleeves and make it happen.
|
||||
|
||||
### Control flow in Python
|
||||
|
||||
As we said earlier, control flow allows us to choose different outcomes depending on a given condition. Its most simple implementation in Python is an if / else clause.
|
||||
|
||||
The basic syntax is:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
if condition:
|
||||
# action 1
|
||||
else:
|
||||
# action 2
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
When condition evaluates to true, the code block below will be executed (represented by `# action 1`. Otherwise, the code under else will be run.
|
||||
A condition can be any statement that can evaluate to either true or false.
|
||||
|
||||
For example:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 1 < 3 # true
|
||||
|
||||
2. firstName == “Gabriel” # true for me, false for anyone not named Gabriel
|
||||
|
||||
- In the first example we compared two values to determine if one is greater than the other.
|
||||
- In the second example we compared firstName (a variable) to determine if, at the current execution point, its value is identical to “Gabriel”
|
||||
- The condition and the else statement must be followed by a colon (:)
|
||||
- Indentation is important in Python. Lines with identical indentation are considered to be in the same code block.
|
||||
|
||||
Please note that the if / else statement is only one of the many control flow tools available in Python. We reviewed it here since we will use it in our script later. You can learn more about the rest of the tools in the [official docs][2].
|
||||
|
||||
### Loops in Python
|
||||
|
||||
Simply put, a loop is a sequence of instructions or statements that are executed in order as long as a condition is true, or once per item in a list.
|
||||
|
||||
The most simple loop in Python is represented by the for loop iterates over the items of a given list or string beginning with the first item and ending with the last.
|
||||
|
||||
Basic syntax:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
for x in example:
|
||||
# do this
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Here example can be either a list or a string. If the former, the variable named x represents each item in the list; if the latter, x represents each character in the string:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
>>> rockBands = []
|
||||
>>> rockBands.append("Roxette")
|
||||
>>> rockBands.append("Guns N' Roses")
|
||||
>>> rockBands.append("U2")
|
||||
>>> for x in rockBands:
|
||||
print(x)
|
||||
or
|
||||
>>> firstName = "Gabriel"
|
||||
>>> for x in firstName:
|
||||
print(x)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The output of the above examples is shown in the following image:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>Learn Loops in Python
|
||||
|
||||
### Python Modules
|
||||
|
||||
For obvious reasons, there must be a way to save a sequence of Python instructions and statements in a file that can be invoked when it is needed.
|
||||
|
||||
That is precisely what a module is. Particularly, the os module provides an interface to the underlying operating system and allows us to perform many of the operations we usually do in a command-line prompt.
|
||||
|
||||
As such, it incorporates several methods and properties that can be called as we explained in the previous article. However, we need to import (or include) it in our environment using the import keyword:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
>>> import os
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Let’s print the current working directory:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
>>> os.getcwd()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
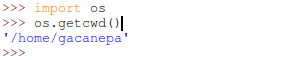
|
||||
>Learn Python Modules
|
||||
|
||||
Let’s now put all of this together (along with the concepts discussed in the previous article) to write the desired script.
|
||||
|
||||
### Python Script
|
||||
|
||||
It is considered good practice to start a script with a statement that indicates the purpose of the script, the license terms under which it is released, and a revision history listing the changes that have been made. Although this is more of a personal preference, it adds a professional touch to our work.
|
||||
|
||||
Here’s the script that produces the output we shown at the top of this article. It is heavily commented so that you can understand what’s happening.
|
||||
|
||||
Take a few minutes to go through it before proceeding. Note how we use an if / else structure to determine whether the length of each field caption is greater than the value of the field itself.
|
||||
|
||||
Based on the result, we use empty characters to fill in the space between a field caption and the next. Also, we use the right number of dashes as separator between the field caption and its value below.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/python3
|
||||
# Change the above line to #!/usr/bin/python if you don't have Python 3 installed
|
||||
|
||||
# Script name: uname.py
|
||||
# Purpose: Illustrate Python's OOP capabilities to write shell scripts more easily
|
||||
# License: GPL v3 (http://www.gnu.org/licenses/gpl.html)
|
||||
|
||||
# Copyright (C) 2016 Gabriel Alejandro Cánepa
|
||||
# Facebook / Skype / G+ / Twitter / Github: gacanepa
|
||||
# Email: gacanepa (at) gmail (dot) com
|
||||
|
||||
# This program is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
|
||||
# it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
|
||||
# the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
|
||||
# (at your option) any later version.
|
||||
|
||||
# This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
|
||||
# but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
|
||||
# MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
|
||||
# GNU General Public License for more details.
|
||||
|
||||
# You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
|
||||
# along with this program. If not, see .
|
||||
|
||||
# REVISION HISTORY
|
||||
# DATE VERSION AUTHOR CHANGE DESCRIPTION
|
||||
# ---------- ------- --------------
|
||||
# 2016-05-28 1.0 Gabriel Cánepa Initial version
|
||||
|
||||
# Import the os module
|
||||
import os
|
||||
|
||||
# Assign the output of os.uname() to the the systemInfo variable
|
||||
# os.uname() returns a 5-string tuple (sysname, nodename, release, version, machine)
|
||||
# Documentation: https://docs.python.org/3.2/library/os.html#module-os
|
||||
systemInfo = os.uname()
|
||||
|
||||
# This is a fixed array with the desired captions in the script output
|
||||
headers = ["Operating system","Hostname","Release","Version","Machine"]
|
||||
|
||||
# Initial value of the index variable. It is used to define the
|
||||
# index of both systemInfo and headers in each step of the iteration.
|
||||
index = 0
|
||||
|
||||
# Initial value of the caption variable.
|
||||
caption = ""
|
||||
|
||||
# Initial value of the values variable
|
||||
values = ""
|
||||
|
||||
# Initial value of the separators variable
|
||||
separators = ""
|
||||
|
||||
# Start of the loop
|
||||
for item in systemInfo:
|
||||
if len(item) < len(headers[index]):
|
||||
# A string containing dashes to the length of item[index] or headers[index]
|
||||
# To repeat a character(s), enclose it within quotes followed
|
||||
# by the star sign (*) and the desired number of times.
|
||||
separators = separators + "-" * len(headers[index]) + " "
|
||||
caption = caption + headers[index] + " "
|
||||
values = values + systemInfo[index] + " " * (len(headers[index]) - len(item)) + " "
|
||||
else:
|
||||
separators = separators + "-" * len(item) + " "
|
||||
caption = caption + headers[index] + " " * (len(item) - len(headers[index]) + 1)
|
||||
values = values + item + " "
|
||||
# Increment the value of index by 1
|
||||
index = index + 1
|
||||
# End of the loop
|
||||
|
||||
# Print the variable named caption converted to uppercase
|
||||
print(caption.upper())
|
||||
|
||||
# Print separators
|
||||
print(separators)
|
||||
|
||||
# Print values (items in systemInfo)
|
||||
print(values)
|
||||
|
||||
# INSTRUCTIONS:
|
||||
# 1) Save the script as uname.py (or another name of your choosing) and give it execute permissions:
|
||||
# chmod +x uname.py
|
||||
# 2) Execute it:
|
||||
# ./uname.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Once you have saved the above script to a file, give it execute permissions and run it as indicated at the bottom of the code:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# chmod +x uname.py
|
||||
# ./uname.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you get the following error while attempting to execute the script:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
-bash: ./uname.py: /usr/bin/python3: bad interpreter: No such file or directory
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
It means you don’t have Python 3 installed. If that is the case, you can either install the package or replace the interpreter line (pay special attention and be very careful if you followed the steps to update the symbolic links to the Python binaries as outlined in the previous article):
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/python3
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
with
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/python
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
which will cause the installed version of Python 2 to execute the script instead.
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**: This script has been tested successfully both in Python 2.x and 3.x.
|
||||
|
||||
Although somewhat rudimentary, you can think of this script as a Python module. This means that you can open it in the IDLE (File → Open… → Select file):
|
||||
|
||||
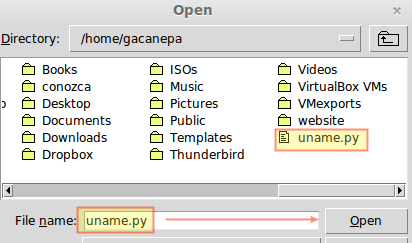
|
||||
>Open Python in IDLE
|
||||
|
||||
A new window will open with the contents of the file. Then go to Run → Run module (or just press F5). The output of the script will be shown in the original shell:
|
||||
|
||||
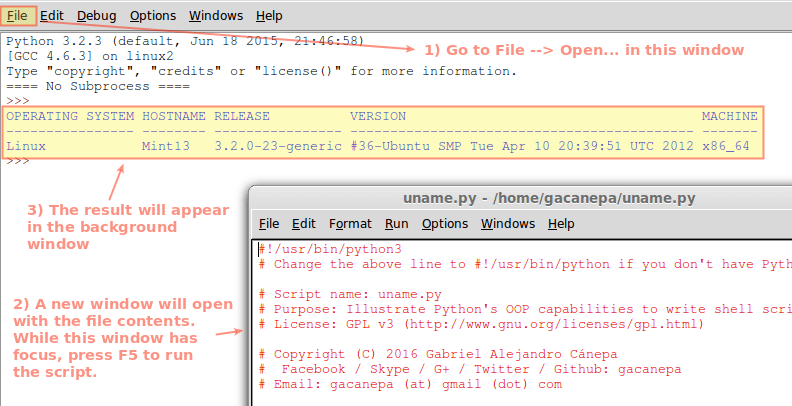
|
||||
>Run Python Script
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to obtain the same results with a script written purely in Bash, you would need to use a combination of [awk][3], [sed][4], and resort to complex methods to store and retrieve items in a list (not to mention the use of tr to convert lowercase letters to uppercase).
|
||||
|
||||
In addition, Python provides portability in that all Linux systems ship with at least one Python version (either 2.x or 3.x, sometimes both). Should you need to rely on a shell to accomplish the same goal, you would need to write different versions of the script based on the shell.
|
||||
|
||||
This goes to show that Object Oriented Programming features can become strong allies of system administrators.
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**: You can find [this python script][5] (and others) in one of my GitHub repositories.
|
||||
|
||||
### Summary
|
||||
|
||||
In this article we have reviewed the concepts of control flow, loops / iteration, and modules in Python. We have shown how to leverage OOP methods and properties in Python to simplify otherwise complex shell scripts.
|
||||
|
||||
Do you have any other ideas you would like to test? Go ahead and write your own Python scripts and let us know if you have any questions. Don’t hesitate to drop us a line using the comment form below, and we will get back to you as soon as we can.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/learn-python-programming-to-write-linux-shell-scripts/?utm_source=feedburner&utm_medium=feed&utm_campaign=Feed%3A+tecmint+%28Tecmint%3A+Linux+Howto%27s+Guide%29
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Gabriel Cánepa][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: http://www.tecmint.com/author/gacanepa/
|
||||
[1]: http://www.tecmint.com/learn-python-programming-and-scripting-in-linux/
|
||||
[2]: http://please%20note%20that%20the%20if%20/%20else%20statement%20is%20only%20one%20of%20the%20many%20control%20flow%20tools%20available%20in%20Python.%20We%20reviewed%20it%20here%20since%20we%20will%20use%20it%20in%20our%20script%20later.%20You%20can%20learn%20more%20about%20the%20rest%20of%20the%20tools%20in%20the%20official%20docs.
|
||||
[3]: http://www.tecmint.com/use-linux-awk-command-to-filter-text-string-in-files/
|
||||
[4]: http://www.tecmint.com/sed-command-to-create-edit-and-manipulate-files-in-linux/
|
||||
[5]: https://github.com/gacanepa/scripts/blob/master/python/uname.py
|
||||
231
sources/tech/20160620 Detecting cats in images with OpenCV.md
Normal file
231
sources/tech/20160620 Detecting cats in images with OpenCV.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,231 @@
|
||||
Detecting cats in images with OpenCV
|
||||
=======================================
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Did you know that OpenCV can detect cat faces in images…right out-of-the-box with no extras?
|
||||
|
||||
I didn’t either.
|
||||
|
||||
But after [Kendrick Tan broke the story][1], I had to check it out for myself…and do a little investigative work to see how this cat detector seemed to sneak its way into the OpenCV repository without me noticing (much like a cat sliding into an empty cereal box, just waiting to be discovered).
|
||||
|
||||
In the remainder of this blog post, I’ll demonstrate how to use OpenCV’s cat detector to detect cat faces in images. This same technique can be applied to video streams as well.
|
||||
|
||||
>Looking for the source code to this post? [Jump right to the downloads section][2].
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Detecting cats in images with OpenCV
|
||||
|
||||
If you take a look at the [OpenCV repository][3], specifically within the [haarcascades directory][4] (where OpenCV stores all its pre-trained Haar classifiers to detect various objects, body parts, etc.), you’ll notice two files:
|
||||
|
||||
- haarcascade_frontalcatface.xml
|
||||
- haarcascade_frontalcatface_extended.xml
|
||||
|
||||
Both of these Haar cascades can be used detecting “cat faces” in images. In fact, I used these very same cascades to generate the example image at the top of this blog post.
|
||||
|
||||
Doing a little investigative work, I found that the cascades were trained and contributed to the OpenCV repository by the legendary [Joseph Howse][5] who’s authored a good many tutorials, books, and talks on computer vision.
|
||||
|
||||
In the remainder of this blog post, I’ll show you how to utilize Howse’s Haar cascades to detect cats in images.
|
||||
|
||||
Cat detection code
|
||||
|
||||
Let’s get started detecting cats in images with OpenCV. Open up a new file, name it cat_detector.py , and insert the following code:
|
||||
|
||||
### Detecting cats in images with OpenCVPython
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# import the necessary packages
|
||||
import argparse
|
||||
import cv2
|
||||
|
||||
# construct the argument parse and parse the arguments
|
||||
ap = argparse.ArgumentParser()
|
||||
ap.add_argument("-i", "--image", required=True,
|
||||
help="path to the input image")
|
||||
ap.add_argument("-c", "--cascade",
|
||||
default="haarcascade_frontalcatface.xml",
|
||||
help="path to cat detector haar cascade")
|
||||
args = vars(ap.parse_args())
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Lines 2 and 3 import our necessary Python packages while Lines 6-12 parse our command line arguments. We only require a single argument here, the input `--image` that we want to detect cat faces in using OpenCV.
|
||||
|
||||
We can also (optionally) supply a path our Haar cascade via the `--cascade` switch. We’ll default this path to `haarcascade_frontalcatface.xml` and assume you have the `haarcascade_frontalcatface.xml` file in the same directory as your cat_detector.py script.
|
||||
|
||||
Note: I’ve conveniently included the code, cat detector Haar cascade, and example images used in this tutorial in the “Downloads” section of this blog post. If you’re new to working with Python + OpenCV (or Haar cascades), I would suggest downloading the provided .zip file to make it easier to follow along.
|
||||
|
||||
Next, let’s detect the cats in our input image:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# load the input image and convert it to grayscale
|
||||
image = cv2.imread(args["image"])
|
||||
gray = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
|
||||
|
||||
# load the cat detector Haar cascade, then detect cat faces
|
||||
# in the input image
|
||||
detector = cv2.CascadeClassifier(args["cascade"])
|
||||
rects = detector.detectMultiScale(gray, scaleFactor=1.3,
|
||||
minNeighbors=10, minSize=(75, 75))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
On Lines 15 and 16 we load our input image from disk and convert it to grayscale (a normal pre-processing step before passing the image to a Haar cascade classifier, although not strictly required).
|
||||
|
||||
Line 20 loads our Haar cascade from disk (in this case, the cat detector) and instantiates the cv2.CascadeClassifier object.
|
||||
|
||||
Detecting cat faces in images with OpenCV is accomplished on Lines 21 and 22 by calling the detectMultiScale method of the detector object. We pass four parameters to the detectMultiScale method, including:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Our image, gray , that we want to detect cat faces in.
|
||||
2.A scaleFactor of our [image pyramid][6] used when detecting cat faces. A larger scale factor will increase the speed of the detector, but could harm our true-positive detection accuracy. Conversely, a smaller scale will slow down the detection process, but increase true-positive detections. However, this smaller scale can also increase the false-positive detection rate as well. See the “A note on Haar cascades” section of this blog post for more information.
|
||||
3. The minNeighbors parameter controls the minimum number of detected bounding boxes in a given area for the region to be considered a “cat face”. This parameter is very helpful in pruning false-positive detections.
|
||||
4. Finally, the minSize parameter is pretty self-explanatory. This value ensures that each detected bounding box is at least width x height pixels (in this case, 75 x 75).
|
||||
|
||||
The detectMultiScale function returns rects , a list of 4-tuples. These tuples contain the (x, y)-coordinates and width and height of each detected cat face.
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, let’s draw a rectangle surround each cat face in the image:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# loop over the cat faces and draw a rectangle surrounding each
|
||||
for (i, (x, y, w, h)) in enumerate(rects):
|
||||
cv2.rectangle(image, (x, y), (x + w, y + h), (0, 0, 255), 2)
|
||||
cv2.putText(image, "Cat #{}".format(i + 1), (x, y - 10),
|
||||
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.55, (0, 0, 255), 2)
|
||||
|
||||
# show the detected cat faces
|
||||
cv2.imshow("Cat Faces", image)
|
||||
cv2.waitKey(0)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Given our bounding boxes (i.e., rects ), we loop over each of them individually on Line 25.
|
||||
|
||||
We then draw a rectangle surrounding each cat face on Line 26, while Lines 27 and 28 displays an integer, counting the number of cats in the image.
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, Lines 31 and 32 display the output image to our screen.
|
||||
|
||||
### Cat detection results
|
||||
|
||||
To test our OpenCV cat detector, be sure to download the source code to this tutorial using the “Downloads” section at the bottom of this post.
|
||||
|
||||
Then, after you have unzipped the archive, you should have the following three files/directories:
|
||||
|
||||
1. cat_detector.py : Our Python + OpenCV script used to detect cats in images.
|
||||
2. haarcascade_frontalcatface.xml : The cat detector Haar cascade.
|
||||
3. images : A directory of testing images that we’re going to apply the cat detector cascade to.
|
||||
|
||||
From there, execute the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
Detecting cats in images with OpenCVShell
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ python cat_detector.py --image images/cat_01.jpg
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
>Figure 1: Detecting a cat face in an image, even with parts of the cat occluded
|
||||
|
||||
Notice that we have been able to detect the cat face in the image, even though the rest of its body is obscured.
|
||||
|
||||
Let’s try another image:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
python cat_detector.py --image images/cat_02.jpg
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
>Figure 2: A second example of detecting a cat in an image with OpenCV, this time the cat face is slightly different
|
||||
|
||||
This cat’s face is clearly different from the other one, as it’s in the middle of a “meow”. In either case, the cat detector cascade is able to correctly find the cat face in the image.
|
||||
|
||||
The same is true for this image as well:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ python cat_detector.py --image images/cat_03.jpg
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
>Figure 3: Cat detection with OpenCV and Python
|
||||
|
||||
Our final example demonstrates detecting multiple cats in an image using OpenCV and Python:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ python cat_detector.py --image images/cat_04.jpg
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>Figure 4: Detecting multiple cats in the same image with OpenCV
|
||||
|
||||
Note that the Haar cascade can return bounding boxes in an order that you may not like. In this case, the middle cat is actually labeled as the third cat. You can resolve this “issue” by sorting the bounding boxes according to their (x, y)-coordinates for a consistent ordering.
|
||||
|
||||
#### A quick note on accuracy
|
||||
|
||||
It’s important to note that in the comments section of the .xml files, Joseph Howe details that the cat detector Haar cascades can report cat faces where there are actually human faces.
|
||||
|
||||
In this case, he recommends performing both face detection and cat detection, then discarding any cat bounding boxes that overlap with the face bounding boxes.
|
||||
|
||||
#### A note on Haar cascades
|
||||
|
||||
First published in 2001 by Paul Viola and Michael Jones, [Rapid Object Detection using a Boosted Cascade of Simple Features][7], this original work has become one of the most cited papers in computer vision.
|
||||
|
||||
This algorithm is capable of detecting objects in images, regardless of their location and scale. And perhaps most intriguing, the detector can run in real-time on modern hardware.
|
||||
|
||||
In their paper, Viola and Jones focused on training a face detector; however, the framework can also be used to train detectors for arbitrary “objects”, such as cars, bananas, road signs, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
#### The problem?
|
||||
|
||||
The biggest problem with Haar cascades is getting the detectMultiScale parameters right, specifically scaleFactor and minNeighbors . You can easily run into situations where you need to tune both of these parameters on an image-by-image basis, which is far from ideal when utilizing an object detector.
|
||||
|
||||
The scaleFactor variable controls your [image pyramid][8] used to detect objects at various scales of an image. If your scaleFactor is too large, then you’ll only evaluate a few layers of the image pyramid, potentially leading to you missing objects at scales that fall in between the pyramid layers.
|
||||
|
||||
On the other hand, if you set scaleFactor too low, then you evaluate many pyramid layers. This will help you detect more objects in your image, but it (1) makes the detection process slower and (2) substantially increases the false-positive detection rate, something that Haar cascades are known for.
|
||||
|
||||
To remember this, we often apply [Histogram of Oriented Gradients + Linear SVM detection][9] instead.
|
||||
|
||||
The HOG + Linear SVM framework parameters are normally much easier to tune — and best of all, HOG + Linear SVM enjoys a much smaller false-positive detection rate. The only downside is that it’s harder to get HOG + Linear SVM to run in real-time.
|
||||
|
||||
### Interested in learning more about object detection?
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>Figure 5: Learn how to build custom object detectors inside the PyImageSearch Gurus course.
|
||||
|
||||
If you’re interested in learning how to train your own custom object detectors, be sure to take a look at the PyImageSearch Gurus course.
|
||||
|
||||
Inside the course, I have 15 lessons covering 168 pages of tutorials dedicated to teaching you how to build custom object detectors from scratch. You’ll discover how to detect road signs, faces, cars (and nearly any other object) in images by applying the HOG + Linear SVM framework for object detection.
|
||||
|
||||
To learn more about the PyImageSearch Gurus course (and grab 10 FREE sample lessons), just click the button below:
|
||||
|
||||
### Summary
|
||||
|
||||
In this blog post, we learned how to detect cats in images using the default Haar cascades shipped with OpenCV. These Haar cascades were trained and contributed to the OpenCV project by [Joseph Howse][9], and were originally brought to my attention [in this post][10] by Kendrick Tan.
|
||||
|
||||
While Haar cascades are quite useful, we often use HOG + Linear SVM instead, as it’s a bit easier to tune the detector parameters, and more importantly, we can enjoy a much lower false-positive detection rate.
|
||||
|
||||
I detail how to build custom HOG + Linear SVM object detectors to recognize various objects in images, including cars, road signs, and much more [inside the PyImageSearch Gurus course][11].
|
||||
|
||||
Anyway, I hope you enjoyed this blog post!
|
||||
|
||||
Before you go, be sure to signup for the PyImageSearch Newsletter using the form below to be notified when new blog posts are published.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.pyimagesearch.com/2016/06/20/detecting-cats-in-images-with-opencv/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Adrian Rosebrock][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: http://www.pyimagesearch.com/author/adrian/
|
||||
[1]: http://kendricktan.github.io/find-cats-in-photos-using-computer-vision.html
|
||||
[2]: http://www.pyimagesearch.com/2016/06/20/detecting-cats-in-images-with-opencv/#
|
||||
[3]: https://github.com/Itseez/opencv
|
||||
[4]: https://github.com/Itseez/opencv/tree/master/data/haarcascades
|
||||
[5]: http://nummist.com/
|
||||
[6]: http://www.pyimagesearch.com/2015/03/16/image-pyramids-with-python-and-opencv/
|
||||
[7]: https://www.cs.cmu.edu/~efros/courses/LBMV07/Papers/viola-cvpr-01.pdf
|
||||
[8]: http://www.pyimagesearch.com/2015/03/16/image-pyramids-with-python-and-opencv/
|
||||
[9]: http://www.pyimagesearch.com/2014/11/10/histogram-oriented-gradients-object-detection/
|
||||
[10]: http://kendricktan.github.io/find-cats-in-photos-using-computer-vision.html
|
||||
[11]: https://www.pyimagesearch.com/pyimagesearch-gurus/
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
115
sources/tech/20160620 Monitor Linux With Netdata.md
Normal file
115
sources/tech/20160620 Monitor Linux With Netdata.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,115 @@
|
||||
Translating by GitFuture
|
||||
|
||||
Monitor Linux With Netdata
|
||||
===
|
||||
|
||||
Netdata is a real-time resource monitoring tool with a friendly web front-end developed and maintained by [FireHOL][1]. With this tool, you can read charts representing resource utilization of things like CPUs, RAM, disks, network, Apache, Postfix and more. It is similar to other monitoring software like Nagios; however, Netdata is only for real-time monitoring via a web interface.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Understanding Netdata
|
||||
|
||||
There’s currently no authentication, so if you’re concerned about someone getting information about the applications you’re running on your system, you should restrict who has access via a firewall policy. The UI is simplified in a way anyone could look at the graphs and understand what they’re seeing, or at least be impressed by your flashy setup.
|
||||
|
||||
The web front-end is very responsive and requires no Flash plugin. The UI doesn’t clutter things up with unneeded features, but sticks to what it does. At first glance, it may seem a bit much with the hundreds of charts you have access to, but luckily the most commonly needed charts (i.e. CPU, RAM, network, and disk) are at the top. If you wish to drill deeper into the graphical data, all you have to do is scroll down or click on the item in the menu to the right. Netdata even allows you to control the chart with play, reset, zoom and resize with the controls on the bottom right of each chart.
|
||||
|
||||
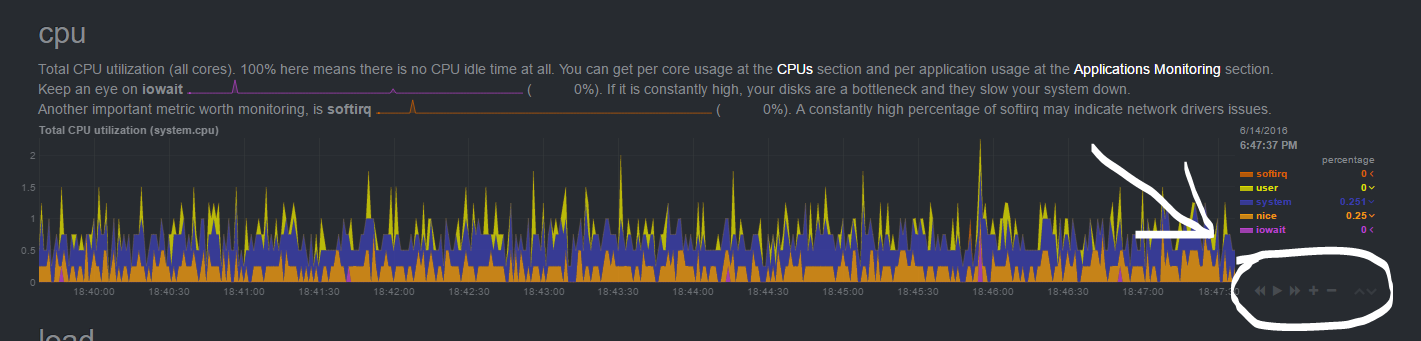
|
||||
>Netdata chart control
|
||||
|
||||
When it comes down to system resources, the software doesn’t need too much either. The creators choose to write the software in C. Netdata doesn’t use much more than ~40MB of RAM.
|
||||
|
||||
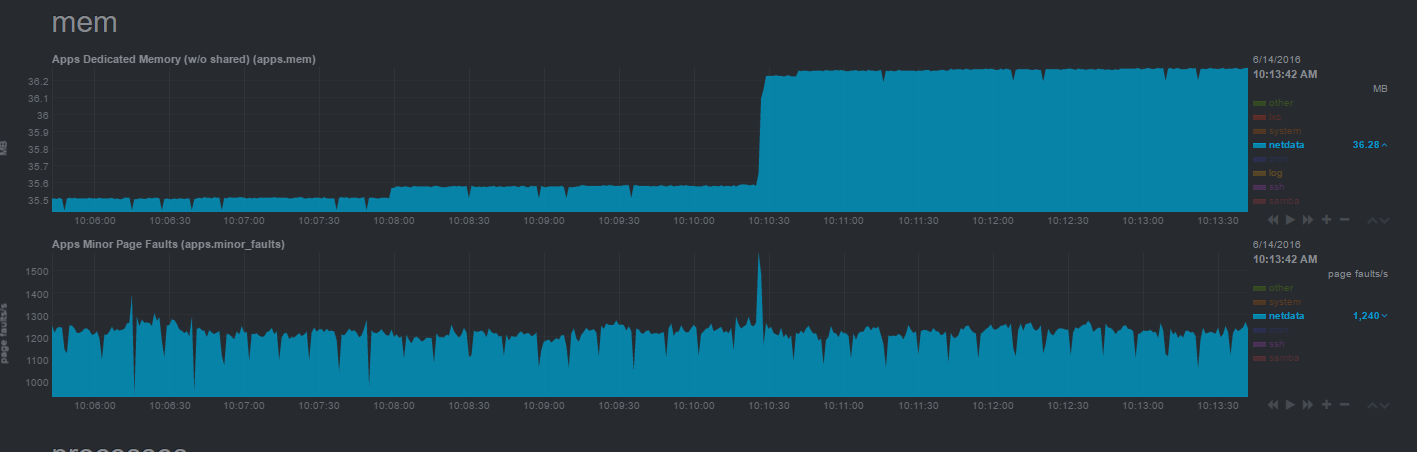
|
||||
>Netdata memory usage
|
||||
|
||||
### Download Netdata
|
||||
|
||||
To download this software, you can head over to [Netdata GitHub page][2]. Then click the “Clone or download” green button on the left of the page. You should then be presented with two options.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Via the ZIP file
|
||||
|
||||
One option is to download the ZIP file. This will include everything in the repository; however, if the repository is updated then you will need to download the ZIP file again. Once you download the ZIP file, you can use the `unzip` tool in the command line to extract the contents. Running the following command will extract the contents of the ZIP file into a “`netdata`” folder.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ cd ~/Downloads
|
||||
$ unzip netdata-master.zip
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
>Netdata unzipped
|
||||
|
||||
ou don’t need to add the `-d` option in unzip because their content is inside a folder at the root of the ZIP file. If they didn’t have that folder at the root, unzip would have extracted the contents in the current directory (which can be messy).
|
||||
|
||||
#### Via git
|
||||
|
||||
The next option is to download the repository via git. You will, of course, need git installed on your system. This is usually installed by default on Fedora. If not, you can install git from the command line with the following command.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo dnf install git
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
After installing git, you will need to “clone” the repository to your system. To do this, run the following command.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ git clone https://github.com/firehol/netdata.git
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This will then clone (or make a copy of) the repository in the current working directory.
|
||||
|
||||
### Install Netdata
|
||||
|
||||
There are some packages you will need to build Netdata successfully. Luckily, it’s a single line to install the things you need ([as stated in their installation guide][3]). Running the following command in the terminal will install all of the dependencies you need to use Netdata.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ dnf install zlib-devel libuuid-devel libmnl-devel gcc make git autoconf autogen automake pkgconfig
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Once the required packages are installed, you will need to cd into the netdata/ directory and run the netdata-installer.sh script.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo ./netdata-installer.sh
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You will then be prompted to press enter to build and install the program. If you wish to continue, press enter to be on your way!
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>Netdata install.
|
||||
|
||||
If all goes well, you will have Netdata built, installed, and running on your system. The installer will also add an uninstall script in the same folder as the installer called `netdata-uninstaller.sh`. If you change your mind later, running this script will remove it from your system.
|
||||
|
||||
You can see it running by checking its status via systemctl.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo systemctl status netdata
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Accessing Netdata
|
||||
|
||||
Now that we have Netdata installed and running, you can access the web interface via port 19999. I have it running on a test machine, as shown in the screenshot below.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>An overview of what Netdata running on your system looks like
|
||||
|
||||
Congratulations! You now have successfully installed and have access to beautiful displays, graphs, and advanced statistics on the performance of your machine. Whether it’s for a personal machine so you can show it off to your friends or for getting deeper insight into the performance of your server, Netdata delivers on performance reporting for any system you choose.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://fedoramagazine.org/monitor-linux-netdata/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Martino Jones][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: https://fedoramagazine.org/monitor-linux-netdata/
|
||||
[1]: https://firehol.org/
|
||||
[2]: https://github.com/firehol/netdata
|
||||
[3]: https://github.com/firehol/netdata/wiki/Installation
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,106 @@
|
||||
Container technologies in Fedora: systemd-nspawn
|
||||
===
|
||||
|
||||
Welcome to the “Container technologies in Fedora” series! This is the first article in a series of articles that will explain how you can use the various container technologies available in Fedora. This first article will deal with `systemd-nspawn`.
|
||||
|
||||
### What is a container?
|
||||
|
||||
A container is a user-space instance which can be used to run a program or an operating system in isolation from the system hosting the container (called the host system). The idea is very similar to a `chroot` or a [virtual machine][1]. The processes running in a container are managed by the same kernel as the host operating system, but they are isolated from the host file system, and from the other processes.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### What is systemd-nspawn?
|
||||
|
||||
The systemd project considers container technologies as something that should fundamentally be part of the desktop and that should integrate with the rest of the user’s systems. To this end, systemd provides `systemd-nspawn`, a tool which is able to create containers using various Linux technologies. It also provides some container management tools.
|
||||
|
||||
In many ways, `systemd-nspawn` is similar to `chroot`, but is much more powerful. It virtualizes the file system, process tree, and inter-process communication of the guest system. Much of its appeal lies in the fact that it provides a number of tools, such as `machinectl`, for managing containers. Containers run by `systemd-nspawn` will integrate with the systemd components running on the host system. As an example, journal entries can be logged from a container in the host system’s journal.
|
||||
|
||||
In Fedora 24, `systemd-nspawn` has been split out from the systemd package, so you’ll need to install the `systemd-container` package. As usual, you can do that with a `dnf install systemd-container`.
|
||||
|
||||
### Creating the container
|
||||
|
||||
Creating a container with `systemd-nspawn` is easy. Let’s say you have an application made for Debian, and it doesn’t run well anywhere else. That’s not a problem, we can make a container! To set up a container with the latest version of Debian (at this point in time, Jessie), you need to pick a directory to set up your system in. I’ll be using `~/DebianJessie` for now.
|
||||
|
||||
Once the directory has been created, you need to run `debootstrap`, which you can install from the Fedora repositories. For Debian Jessie, you run the following command to initialize a Debian file system.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ debootstrap --arch=amd64 stable ~/DebianJessie
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This assumes your architecture is x86_64. If it isn’t, you must change `amd64` to the name of your architecture. You can find your machine’s architecture with `uname -m`.
|
||||
|
||||
Once your root directory is set up, you will start your container with the following command.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ systemd-nspawn -bD ~/DebianJessie
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You’ll be up and running within seconds. You’ll notice something as soon as you try to log in: you can’t use any accounts on your system. This is because systemd-nspawn virtualizes users. The fix is simple: remove -b from the previous command. You’ll boot directly to the root shell in the container. From there, you can just use passwd to set a password for root, or you can use adduser to add a new user. As soon as you’re done with that, go ahead and put the -b flag back. You’ll boot to the familiar login console and you log in with the credentials you set.
|
||||
|
||||
All of this applies for any distribution you would want to run in the container, but you need to create the system using the correct package manager. For Fedora, you would use DNF instead of debootstrap. To set up a minimal Fedora system, you can run the following command, replacing the absolute path with wherever you want the container to be.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo dnf --releasever=24 --installroot=/absolute/path/ install systemd passwd dnf fedora-release
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Setting up the network
|
||||
|
||||
You’ll notice an issue if you attempt to start a service that binds to a port currently in use on your host system. Your container is using the same network interface. Luckily, `systemd-nspawn` provides several ways to achieve separate networking from the host machine.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Local networking
|
||||
|
||||
The first method uses the `--private-network` flag, which only creates a loopback device by default. This is ideal for environments where you don’t need networking, such as build systems and other continuous integration systems.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Multiple networking interfaces
|
||||
|
||||
If you have multiple network devices, you can give one to the container with the `--network-interface` flag. To give `eno1` to my container, I would add the flag `--network-interface=eno1`. While an interface is assigned to a container, the host can’t use it at the same time. When the container is completely shut down, it will be available to the host again.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Sharing network interfaces
|
||||
|
||||
For those of us who don’t have spare network devices, there are other options for providing access to the container. One of those is the `--port` flag. This forwards a port on the container to the host. The format is `protocol:host:container`, where protocol is either `tcp` or `udp`, `host` is a valid port number on the host, and `container` is a valid port on the container. You can omit the protocol and specify only `host:container`. I often use something similar to `--port=2222:22`.
|
||||
|
||||
You can enable complete, host-only networking with the `--network-veth` flag, which creates a virtual Ethernet interface between the host and the container. You can also bridge two connections with `--network-bridge`.
|
||||
|
||||
### Using systemd components
|
||||
|
||||
If the system in your container has D-Bus, you can use systemd’s provided utilities to control and monitor your container. Debian doesn’t include dbus in the base install. If you want to use it with Debian Jessie, you’ll want to run `apt install dbus`.
|
||||
|
||||
#### machinectl
|
||||
|
||||
To easily manage containers, systemd provides the machinectl utility. Using machinectl, you can log in to a container with machinectl login name, check the status with machinectl status name, reboot with machinectl reboot name, or power it off with machinectl poweroff name.
|
||||
|
||||
### Other systemd commands
|
||||
|
||||
Most systemd commands, such as journalctl, systemd-analyze, and systemctl, support containers with the `--machine` option. For example, if you want to see the journals of a container named “foobar”, you can use journalctl `--machine=foobar`. You can also see the status of a service running in this container with `systemctl --machine=foobar` status service.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Working with SELinux
|
||||
|
||||
If you’re running with SELinux enforcing (the default in Fedora), you’ll need to set the SELinux context for your container. To do that, you need to run the following two commands on the host system.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ semanage fcontext -a -t svirt_sandbox_file_t "/path/to/container(/.*)?"
|
||||
$ restorecon -R /path/to/container/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure you replace “/path/to/container” with the path to your container. For my container, “DebianJessie”, I would run the following:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ semanage fcontext -a -t svirt_sandbox_file_t "/home/johnmh/DebianJessie(/.*)?"
|
||||
$ restorecon -R /home/johnmh/DebianJessie/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/linux-how-to/set-nginx-reverse-proxy-centos-7-cpanel/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[John M. Harris, Jr.][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: http://linoxide.com/linux-how-to/set-nginx-reverse-proxy-centos-7-cpanel/
|
||||
[1]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Virtual_machine
|
||||
@ -1,5 +1,6 @@
|
||||
translated by pspkforever
|
||||
DOCKER DATACENTER IN AWS AND AZURE IN A FEW CLICKS
|
||||
====================================================
|
||||
===================================================
|
||||
|
||||
Introducing Docker Datacenter AWS Quickstart and Azure Marketplace Templates production-ready, high availability deployments in just a few clicks.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
|
||||
翻译中:by zky001
|
||||
Flatpak brings standalone apps to Linux
|
||||
===
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The development team behind [Flatpak][1] has [just announced the general availability][2] of the Flatpak desktop application framework. Flatpak (which was also known during development as xdg-app) provides the ability for an application — bundled as a Flatpak — to be installed and run easily and consistently on many different Linux distributions. Applications bundled as Flatpaks also have the ability to be sandboxed for security, isolating them from your operating system, and other applications. Check out the [Flatpak website][3], and the [press release][4] for more information on the tech that makes up the Flatpak framework.
|
||||
|
||||
### Installing Flatpak on Fedora
|
||||
|
||||
For users wanting to run applications bundled as Flatpaks, installation on Fedora is easy, with Flatpak already available in the official Fedora 23 and Fedora 24 repositories. The Flatpak website has [full details on installation on Fedora][5], as well as how to install on Arch, Debian, Mageia, and Ubuntu. [Many applications][6] have builds already bundled with Flatpak — including LibreOffice, and nightly builds of popular graphics applications Inkscape and GIMP.
|
||||
|
||||
### For Application Developers
|
||||
|
||||
If you are an application developer, the Flatpak website also contains some great resources on getting started [bundling and distributing your applications with Flatpak][7]. These resources contain information on using Flakpak SDKs to build standalone, sandboxed Flatpak applications.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://fedoramagazine.org/introducing-flatpak/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Ryan Lerch][a]
|
||||
译者:[zky001](https://github.com/zky001)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: https://fedoramagazine.org/introducing-flatpak/
|
||||
[1]: http://flatpak.org/
|
||||
[2]: http://flatpak.org/press/2016-06-21-flatpak-released.html
|
||||
[3]: http://flatpak.org/
|
||||
[4]: http://flatpak.org/press/2016-06-21-flatpak-released.html
|
||||
[5]: http://flatpak.org/getting.html
|
||||
[6]: http://flatpak.org/apps.html
|
||||
[7]: http://flatpak.org/developer.html
|
||||
124
sources/tech/20160623 Advanced Image Processing with Python.md
Normal file
124
sources/tech/20160623 Advanced Image Processing with Python.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,124 @@
|
||||
Johnny-Liao translating...
|
||||
|
||||
Advanced Image Processing with Python
|
||||
======================================
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Building an image processing search engine is no easy task. There are several concepts, tools, ideas and technologies that go into it. One of the major image-processing concepts is reverse image querying (RIQ) or reverse image search. Google, Cloudera, Sumo Logic and Birst are among the top organizations to use reverse image search. Great for analyzing images and making use of mined data, RIQ provides a very good insight into analytics.
|
||||
|
||||
### Top Companies and Reverse Image Search
|
||||
|
||||
There are many top tech companies that are using RIQ to best effect. For example, Pinterest first brought in visual search in 2014. It subsequently released a white paper in 2015, revealing the architecture. Reverse image search enabled Pinterest to obtain visual features from fashion objects and display similar product recommendations.
|
||||
|
||||
As is generally known, Google images uses reverse image search allowing users to upload an image and then search for connected images. The submitted image is analyzed and a mathematical model made out of it, by advanced algorithm use. The image is then compared with innumerable others in the Google databases before results are matched and similar results obtained.
|
||||
|
||||
**Here is a graph representation from the OpenCV 2.4.9 Features Comparison Report:**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Algorithms & Python Libraries
|
||||
|
||||
Before we get down to the workings of it, let us rush through the main elements that make building an image processing search engine with Python possible:
|
||||
|
||||
### Patented Algorithms
|
||||
|
||||
#### SIFT (Scale-Invariant Feature Transform) Algorithm
|
||||
|
||||
1. A patented technology with nonfree functionality that uses image identifiers in order to identify a similar image, even those clicked from different angles, sizes, depths and scale, that they are included in the search results. Check the detailed video on SIFT here.
|
||||
2. SIFT correctly matches the search criteria with a large database of features from many images.
|
||||
3. Matching same images with different viewpoints and matching invariant features to obtain search results is another SIFT feature. Read more about scale-invariant keypoints here.
|
||||
|
||||
#### SURF (Speeded Up Robust Features) Algorithm
|
||||
|
||||
1. [SURF][1] is also patented with nonfree functionality and a more ‘speeded’ up version of SIFT. Unlike SIFT, SURF approximates Laplacian of Gaussian (unlike SIFT) with Box Filter.
|
||||
|
||||
2. SURF relies on the determinant of Hessian Matrix for both its location and scale.
|
||||
|
||||
3. Rotation invariance is not a requisite in many applications. So not finding this orientation speeds up the process.
|
||||
|
||||
4. SURF includes several features that the speed improved in each step. Three times faster than SIFT, SURF is great with rotation and blurring. It is not as great in illumination and viewpoint change though.
|
||||
|
||||
5. Open CV, a programming function library provides SURF functionalities. SURF.compute() and SURF. Detect() can be used to find descriptors and keypoints. Read more about SURF [here][2].
|
||||
|
||||
### Open Source Algorithms
|
||||
|
||||
#### KAZE Algorithm
|
||||
|
||||
1.KAZE is a open source 2D multiscale and novel feature detection and description algorithm in nonlinear scale spaces. Efficient techniques in Additive Operator Splitting (AOS) and variable conductance diffusion is used to build the nonlinear scale space.
|
||||
|
||||
2. Multiscale image processing basics are simple – Creating an image’s scale space while filtering original image with right function over enhancing time or scale.
|
||||
|
||||
#### AKAZE (Accelerated-KAZE) Algorithm
|
||||
|
||||
1. As the name suggests, this is a faster mode to image search, finding matching keypoints between two images. AKAZE uses a binary descriptor and nonlinear scale space that balances accuracy and speed.
|
||||
|
||||
#### BRISK (Binary Robust Invariant Scalable Keypoints) Algorithm
|
||||
|
||||
1. BRISK is great for description, keypoint detection and matching.
|
||||
|
||||
2. An algorithm that is highly adaptive, scale-space FAST-based detector along with a bit-string descriptor, helps speed up the search significantly.
|
||||
|
||||
3. Scale-space keypoint detection and keypoint description helps optimize the performance with relation to the task at hand.
|
||||
|
||||
#### FREAK (Fast Retina Keypoint)
|
||||
|
||||
1. This is a novel keypoint descriptor inspired by the human eye.A binary strings cascade is efficiently computed by an image intensity comparison. The FREAK algorithm allows faster computing with lower memory load as compared to BRISK, SURF and SIFT.
|
||||
|
||||
#### ORB (Oriented FAST and Rotated BRIEF)
|
||||
|
||||
1.A fast binary descriptor, ORB is resistant to noise and rotation invariant. ORB builds on the FAST keypoint detector and the BRIEF descriptor, elements attributed to its low cost and good performance.
|
||||
|
||||
2. Apart from the fast and precise orientation component, efficiently computing the oriented BRIEF, analyzing variance and co-relation of oriented BRIEF features, is another ORB feature.
|
||||
|
||||
### Python Libraries
|
||||
|
||||
#### Open CV
|
||||
|
||||
1. OpenCV is available for both academic and commercial use. A open source machine learning and computer vision library, OpenCV makes it easy for organizations to utilize and modify code.
|
||||
|
||||
2. Over 2500 optimized algorithms, including state-of-the-art machine learning and computer vision algorithms serve various image search purposes – face detection, object identification, camera movement tracking, finding similar images from image database, following eye movements, scenery recognition, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
3. Top companies like Google, IBM, Yahoo, IBM, Sony, Honda, Microsoft and Intel make wide use of OpenCV.
|
||||
|
||||
4. OpenCV uses Python, Java, C, C++ and MATLAB interfaces while supporting Windows, Linux, Mac OS and Android.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Python Imaging Library (PIL)
|
||||
|
||||
1. The Python Imaging Library (PIL) supports several file formats while providing image processing and graphics solutions.The open source PIL adds image processing capabilities to your Python interpreter.
|
||||
2. The standard procedure for image manipulation include image enhancing, transparency and masking handling, image filtering, per-pixel manipulation, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
For detailed statistics and graphs, view the OpenCV 2.4.9 Features Comparison Report [here][3].
|
||||
|
||||
### Building an Image Search Engine
|
||||
|
||||
An image search engine helps pick similar images from a prepopulated set of image base. The most popular among these is Google’s well known image search engine. For starters, there are various approaches to build a system like this. To mention a few:
|
||||
|
||||
1.Using image extraction, image description extraction, meta data extraction and search result extraction to build an image search engine.
|
||||
2. Define your image descriptor, dataset indexing, define your similarity metric and then search and rank.
|
||||
3. Select image to be searched, select directory for carrying out search, search directory for all pictures, create picture feature index, evaluate same feature for search picture, match pictures in search and obtain matched pictures.
|
||||
|
||||
Our approach basically began with comparing grayscaled versions of the images, gradually moving on to complex feature matching algorithms like SIFT and SURF, and then finally settling down to am open source solution called BRISK. All these algorithms give efficient results with minor changes in performance and latency. An engine built on these algorithms have numerous applications like analyzing graphic data for popularity statistics, identification of objects in graphic contents, and many more.
|
||||
|
||||
**Example**: An image search engine needs to be build by an IT company for a client. So if a brand logo image is submitted in the search, all related brand image searches show up as results. The obtained results can also be used for analytics by the client, allowing them to estimate the brand popularity as per the geographic location. Its still early days though, RIQ or reverse image search has not been exploited to its full extent yet.
|
||||
|
||||
This concludes our article on building an image search engine using Python. Check our blog section out for the latest on technology and programming.
|
||||
|
||||
Statistics Source: OpenCV 2.4.9 Features Comparison Report (computer-vision-talks.com)
|
||||
|
||||
(Guidance and additional inputs by Ananthu Nair.)
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.cuelogic.com/blog/advanced-image-processing-with-python/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Snehith Kumbla][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: http://www.cuelogic.com/blog/author/snehith-kumbla/
|
||||
[1]: http://docs.opencv.org/3.0-beta/doc/py_tutorials/py_feature2d/py_surf_intro/py_surf_intro.html
|
||||
[2]: http://www.vision.ee.ethz.ch/~surf/eccv06.pdf
|
||||
[3]: https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/1gYJsy2ROtqvIVvOKretfxQG_0OsaiFvb7uFRDu5P8hw/edit#gid=10
|
||||
@ -1,127 +0,0 @@
|
||||
alim0x translating
|
||||
|
||||
How to permanently mount a Windows share on Linux
|
||||
==================================================
|
||||
|
||||
>If you get tired of having to remount Windows shares when you reboot your Linux box, read about an easy way to make those shares permanently mount.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>Image: Jack Wallen
|
||||
|
||||
It has never been easier for Linux to interact within a Windows network. And considering how many businesses are adopting Linux, those two platforms have to play well together. Fortunately, with the help of a few tools, you can easily map Windows network drives onto a Linux machine, and even ensure they are still there upon rebooting the Linux machine.
|
||||
|
||||
### Before we get started
|
||||
|
||||
For this to work, you will be using the command line. The process is pretty simple, but you will be editing the /etc/fstab file, so do use caution.
|
||||
Also, I assume you already have Samba working properly so you can manually mount shares from a Windows network to your Linux box, and that you know the IP address of the machine hosting the share.
|
||||
|
||||
Are you ready? Let's go.
|
||||
|
||||
### Create your mount point
|
||||
|
||||
The first thing we're going to do is create a folder that will serve as the mount point for the share. For the sake of simplicity, we'll name this folder share and we'll place it in /media. Open your terminal window and issue the command:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
sudo mkdir /media/share
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### A few installations
|
||||
|
||||
Now we have to install the system that allows for cross-platform file sharing; this system is cifs-utils. From the terminal window, issue the command:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
sudo apt-get install cifs-utils
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This command will also install all of the dependencies for cifs-utils.
|
||||
|
||||
Once this is installed, open up the file /etc/nsswitch.conf and look for the line:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
hosts: files mdns4_minimal [NOTFOUND=return] dns
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Edit that line so it looks like:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
hosts: files mdns4_minimal [NOTFOUND=return] wins dns
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now you must install windbind so that your Linux machine can resolve Windows computer names on a DHCP network. From the terminal, issue this command:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
sudo apt-get install libnss-windbind windbind
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Restart networking with the command:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
sudo service networking restart
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Mount the network drive
|
||||
|
||||
Now we're going to map the network drive. This is where we must edit the /etc/fstab file. Before you make that first edit, back up the file with this command:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
sudo cp /etc/fstab /etc/fstab.old
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you need to restore that file, issue the command:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
sudo mv /etc/fstab.old /etc/fstab
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Create a credentials file in your home directory called .smbcredentials. In that file, add your username and password, like so (USER is the actual username and password is the actual password):
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
username=USER
|
||||
|
||||
password=PASSWORD
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You now have to know the Group ID (GID) and User ID (UID) of the user that will be mounting the drive. Issue the command:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
id USER
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
USER is the actual username, and you should see something like:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
uid=1000(USER) gid=1000(GROUP)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
USER is the actual username, and GROUP is the group name. The numbers before (USER) and (GROUP) will be used in the /etc/fstab file.
|
||||
|
||||
It's time to edit the /etc/fstab file. Open that file in your editor and add the following line to the end (replace everything in ALL CAPS and the IP address of the remote machine):
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
//192.168.1.10/SHARE /media/share cifs credentials=/home/USER/.smbcredentials,iocharset=uft8,gid=GID,udi=UID,file_mode=0777,dir_mode=0777 0 0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**: The above should be on a single line.
|
||||
|
||||
Save and close that file. Issue the command sudo mount -a and the share will be mounted. Check in /media/share and you should see the files and folders on the network share.
|
||||
|
||||
### Sharing made easy
|
||||
|
||||
Thanks to cifs-utils and Samba, mapping network shares is incredibly easy on a Linux machine. And now, you won't have to manually remount those shares every time your machine boots.
|
||||
|
||||
For more networking tips and tricks, sign up for our Data Center newsletter.
|
||||
[SUBSCRIBE](https://secure.techrepublic.com/user/login/?regSource=newsletter-button&position=newsletter-button&appId=true&redirectUrl=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.techrepublic.com%2Farticle%2Fhow-to-permanently-mount-a-windows-share-on-linux%2F&)
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.techrepublic.com/article/how-to-permanently-mount-a-windows-share-on-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Jack Wallen][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: http://www.techrepublic.com/search/?a=jack+wallen
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,125 @@
|
||||
chunyang-wen translating
|
||||
How to Hide Linux Command Line History by Going Incognito
|
||||
================================================================
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
If you’re a Linux command line user, you’ll agree that there are times when you do not want certain commands you run to be recorded in the command line history. There could be many reasons for this. For example, you’re at a certain position in your company, and you have some privileges that you don’t want others to abuse. Or, there are some critical commands that you don’t want to run accidentally while you’re browsing the history list.
|
||||
|
||||
But is there a way to control what goes into the history list and what doesn’t? Or, in other words, can we turn on a web browser-like incognito mode in the Linux command line? The answer is yes, and there are many ways to achieve this, depending on what exactly you want. In this article we will discuss some of the popular solutions available.
|
||||
|
||||
Note: all the commands presented in this article have been tested on Ubuntu.
|
||||
|
||||
### Different ways available
|
||||
|
||||
The first two ways we’ll describe here have already been covered in [one of our previous articles][1]. If you are already aware of them, you can skip over these. However, if you aren’t aware, you’re advised to go through them carefully.
|
||||
|
||||
#### 1. Insert space before command
|
||||
|
||||
Yes, you read it correctly. Insert a space in the beginning of a command, and it will be ignored by the shell, meaning the command won’t be recorded in history. However, there’s a dependency – the said solution will only work if the HISTCONTROL environment variable is set to “ignorespace” or “ignoreboth,” which is by default in most cases.
|
||||
|
||||
So, a command like the following:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[space]echo "this is a top secret"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Won’t appear in the history if you’ve already done this command:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
export HISTCONTROL = ignorespace
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The below screenshot is an example of this behavior.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The fourth “echo” command was not recorded in the history as it was run with a space in the beginning.
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2. Disable the entire history for the current session
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to disable the entire history for a session, you can easily do that by unsetting the HISTSIZE environment variable before you start with your command line work. To unset the variable run the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
export HISTFILE=0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
HISTFILE is the number of lines (or commands) that can be stored in the history list for an ongoing bash session. By default, this variable has a set value – for example, 1000 in my case.
|
||||
|
||||
So, the command mentioned above will set the environment variable’s value to zero, and consequently nothing will be stored in the history list until you close the terminal. Keep in mind that you’ll also not be able to see the previously run commands by pressing the up arrow key or running the history command.
|
||||
|
||||
#### 3. Erase the entire history after you’re done
|
||||
|
||||
This can be seen as an alternative to the solution mentioned in the previous section. The only difference is that in this case you run a command AFTER you’re done with all your work. Thh following is the command in question:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
history -cw
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
As already mentioned, this will have the same effect as the HISTFILE solution mentioned above.
|
||||
|
||||
#### 4. Turn off history only for the work you do
|
||||
|
||||
While the solutions (2 and 3) described above do the trick, they erase the entire history, something which might be undesired in many situations. There might be cases in which you want to retain the history list up until the point you start your command line work. For situations like these you need to run the following command before starting with your work:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[space]set +o history
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Note: [space] represents a blank space.
|
||||
|
||||
The above command will disable the history temporarily, meaning whatever you do after running this command will not be recorded in history, although all the stuff executed prior to the above command will be there as it is in the history list.
|
||||
|
||||
To re-enable the history, run the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[Space]set -o history
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This brings things back to normal again, meaning any command line work done after the above command will show up in the history.
|
||||
|
||||
#### 5. Delete specific commands from history
|
||||
|
||||
Now suppose the history list already contains some commands that you didn’t want to be recorded. What can be done in this case? It’s simple. You can go ahead and remove them. The following is how to accomplish this:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[space]history | grep "part of command you want to remove"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The above command will output a list of matching commands (that are there in the history list) with a number [num] preceding each of them.
|
||||
|
||||
Once you’ve identified the command you want to remove, just run the following command to remove that particular entry from the history list:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
history -d [num]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The following screenshot is an example of this.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The second ‘echo’ command was removed successfully.
|
||||
|
||||
Alternatively, you can just press the up arrow key to take a walk back through the history list, and once the command of your interest appears on the terminal, just press “Ctrl + U” to totally blank the line, effectively removing it from the list.
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion
|
||||
|
||||
There are multiple ways in which you can manipulate the Linux command line history to suit your needs. Keep in mind, however, that it’s usually not a good practice to hide or remove a command from history, although it’s also not wrong, per se, but you should be aware of what you’re doing and what effects it might have.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://www.maketecheasier.com/linux-command-line-history-incognito/?utm_medium=feed&utm_source=feedpress.me&utm_campaign=Feed%3A+maketecheasier
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Himanshu Arora][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: https://www.maketecheasier.com/author/himanshu/
|
||||
[1]: https://www.maketecheasier.com/command-line-history-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,53 @@
|
||||
xinglianfly translate
|
||||
USE TASK MANAGER EQUIVALENT IN LINUX
|
||||
====================================
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
These are some of the most frequently asked questions by Linux beginners, “**is there a task manager for Linux**“, “how do you open task manager in Linux” ?
|
||||
|
||||
People who are coming from Windows know how useful is the task manager. You press the Ctrl+Alt+Del to get to task manager in Windows. This task manager shows you all the running processes and their memory consumption. You can choose to end a process from this task manager application.
|
||||
|
||||
When you have just begun with Linux, you look for a **task manager equivalent in Linux** as well. An expert Linux user prefers the command line way to find processes and memory consumption etc but you don’t have to go that way, at least not when you are just starting with Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
All major Linux distributions have a task manager equivalent. Mostly, **it is called System Monitor** but it actually depends on your Linux distribution and the [desktop environment][1] it uses.
|
||||
|
||||
In this article, we’ll see how to find and use the task manager in Linux with GNOME as the [desktop environment][2].
|
||||
|
||||
### TASK MANAGER EQUIVALENT IN LINUX WITH GNOME DESKTOP
|
||||
|
||||
While using GNOME, press super key (Windows Key) and look for System Monitor:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
When you start the System Monitor, it shows you all the running processes and the memory consumption by them.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
You can select a process and click on End process to kill it.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
You can also see some statistics about your system in the Resources tab such as CPU consumption per core basis, memory usage, network usage etc.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
This was the graphical way. If you want to go command line way, just run the command ‘top’ in terminal and you can see all the running processes and their memory consumption. You can easily [kill processes in Linux][3] command line.
|
||||
|
||||
This all you need to know about task manager equivalent in Fedora Linux. I hope you find this quick tutorial helpful. If you have questions or suggestions, feel free to ask.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://itsfoss.com/task-manager-linux/?utm_source=feedburner&utm_medium=feed&utm_campaign=Feed%3A+ItsFoss+%28Its+FOSS%21+An+Open+Source+Blog%29
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek Prakash][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: https://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/
|
||||
[1]: https://wiki.archlinux.org/index.php/desktop_environment
|
||||
[2]: https://itsfoss.com/best-linux-desktop-environments/
|
||||
[3]: https://itsfoss.com/how-to-find-the-process-id-of-a-program-and-kill-it-quick-tip/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
|
||||
(翻译中 by runningwater)
|
||||
CANONICAL CONSIDERING TO DROP 32 BIT SUPPORT IN UBUNTU
|
||||
========================================================
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Yesterday, developer [Dimitri John Ledkov][1] wrote a message on the [Ubuntu Mailing list][2] calling for the end of i386 support by Ubuntu 18.10. Ledkov argues that more software is being developed with 64-bit support. He is also concerned that it will be difficult to provide security support for the aging i386 architecture.
|
||||
|
||||
Ledkov also argues that building i386 images is not free, but takes quite a bit of Canonical’s resources.
|
||||
|
||||
>Building i386 images is not “for free”, it comes at the cost of utilizing our build farm, QA and validation time. Whilst we have scalable build-farms, i386 still requires all packages, autopackage tests, and ISOs to be revalidated across our infrastructure. As well as take up mirror space & bandwidth.
|
||||
|
||||
Ledkov offers a plan where the 16.10, 17.04, and 17.10 versions of Ubuntu will continue to have i386 kernels, netboot installers, and cloud images, but drop i386 ISO for desktop and server. The 18.04 LTS would then drop support for i386 kernels, netboot installers, and cloud images, but still provide the ability for i386 programs to run on 64-bit architecture. Then, 18.10 would end the i386 port and limit legacy 32-bit applications to snaps, containers, and virtual machines.
|
||||
|
||||
Ledkov’s plan had not been accepted yet, but it shows a definite push toward eliminating 32-bit support.
|
||||
|
||||
### GOOD NEWS
|
||||
|
||||
Don’t despair yet. this will not affect the distros used to resurrect your old system. [Martin Wimpress][3], the creator of [Ubuntu MATE][4], revealed during a discussion on Googl+ that these changes will only affect mainline Ubuntu.
|
||||
|
||||
>The i386 archive will continue to exist into 18.04 and flavours can continue to elect to build i386 isos. There is however a security concern, in that some larger applications (Firefox, Chromium, LibreOffice) are already presenting challenges in terms of applying some security patches to older LTS releases. So flavours are being asked to be mindful of the support period they can reasonably be expected to support i386 versions for.
|
||||
|
||||
### THOUGHTS
|
||||
|
||||
I understand why they need to make this move from a security standpoint, but it’s going to make people move away from mainline Ubuntu to either one of the flavors or a different architecture. Thankfully, we have alternative [lightweight Linux distributions][5].
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://itsfoss.com/ubuntu-32-bit-support-drop/?utm_source=feedburner&utm_medium=feed&utm_campaign=Feed%3A+ItsFoss+%28Its+FOSS%21+An+Open+Source+Blog%29
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[John Paul][a]
|
||||
译者:[runningwater](https://github.com/runningwater)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: https://itsfoss.com/author/john/
|
||||
[1]: https://plus.google.com/+DimitriJohnLedkov
|
||||
[2]: https://lists.ubuntu.com/archives/ubuntu-devel-discuss/2016-June/016661.html
|
||||
[3]: https://twitter.com/m_wimpress
|
||||
[4]: http://ubuntu-mate.org/
|
||||
[5]: https://itsfoss.com/lightweight-linux-beginners/
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,5 @@
|
||||
martin
|
||||
|
||||
Part 11 - How to Manage and Create LVM Using vgcreate, lvcreate and lvextend Commands
|
||||
============================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,85 +0,0 @@
|
||||
FSSlc translating
|
||||
|
||||
How to Use Awk to Filter Text or Strings Using Pattern Specific Actions
|
||||
=========================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
In the third part of the Awk command series, we shall take a look at filtering text or strings based on specific patterns that a user can define.
|
||||
|
||||
Sometimes, when filtering text, you want to indicate certain lines from an input file or lines of strings based on a given condition or using a specific pattern that can be matched. Doing this with Awk is very easy, it is one of the great features of Awk that you will find helpful.
|
||||
|
||||
Let us take a look at an example below, say you have a shopping list for food items that you want to buy, called food_prices.list. It has the following list of food items and their prices.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ cat food_prices.list
|
||||
No Item_Name Quantity Price
|
||||
1 Mangoes 10 $2.45
|
||||
2 Apples 20 $1.50
|
||||
3 Bananas 5 $0.90
|
||||
4 Pineapples 10 $3.46
|
||||
5 Oranges 10 $0.78
|
||||
6 Tomatoes 5 $0.55
|
||||
7 Onions 5 $0.45
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
And then, you want to indicate a `(*)` sign on food items whose price is greater than $2, this can be done by running the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ awk '/ *\$[2-9]\.[0-9][0-9] */ { print $1, $2, $3, $4, "*" ; } / *\$[0-1]\.[0-9][0-9] */ { print ; }' food_prices.list
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
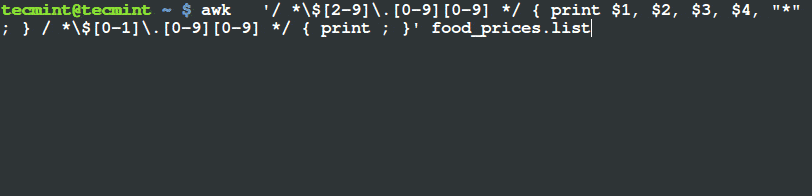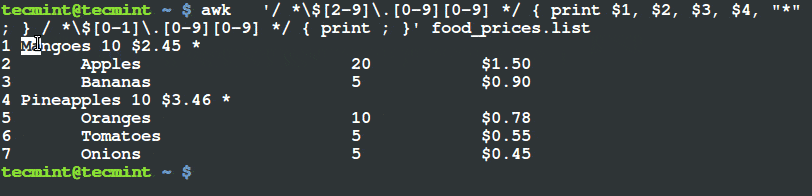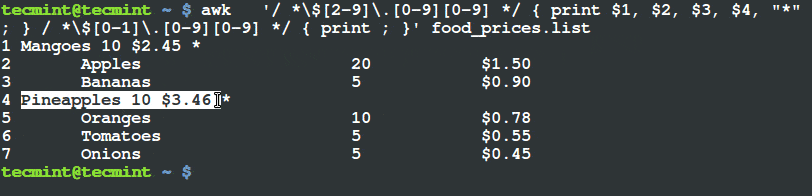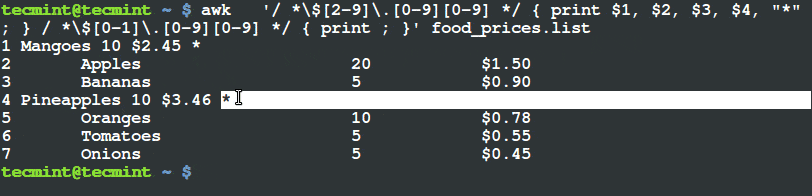
|
||||
>Print Items Whose Price is Greater Than $2
|
||||
|
||||
From the output above, you can see that the there is a `(*)` sign at the end of the lines having food items, mangoes and pineapples. If you check their prices, they are above $2.
|
||||
|
||||
In this example, we have used used two patterns:
|
||||
|
||||
- the first: `/ *\$[2-9]\.[0-9][0-9] */` gets the lines that have food item price greater than $2 and
|
||||
- the second: `/*\$[0-1]\.[0-9][0-9] */` looks for lines with food item price less than $2.
|
||||
|
||||
This is what happens, there are four fields in the file, when pattern one encounters a line with food item price greater than $2, it prints all the four fields and a `(*)` sign at the end of the line as a flag.
|
||||
|
||||
The second pattern simply prints the other lines with food price less than $2 as they appear in the input file, food_prices.list.
|
||||
|
||||
This way you can use pattern specific actions to filter out food items that are priced above $2, though there is a problem with the output, the lines that have the `(*)` sign are not formatted out like the rest of the lines making the output not clear enough.
|
||||
|
||||
We saw the same problem in Part 2 of the awk series, but we can solve it in two ways:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Using printf command which is a long and boring way using the command below:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ awk '/ *\$[2-9]\.[0-9][0-9] */ { printf "%-10s %-10s %-10s %-10s\n", $1, $2, $3, $4 "*" ; } / *\$[0-1]\.[0-9][0-9] */ { printf "%-10s %-10s %-10s %-10s\n", $1, $2, $3, $4; }' food_prices.list
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
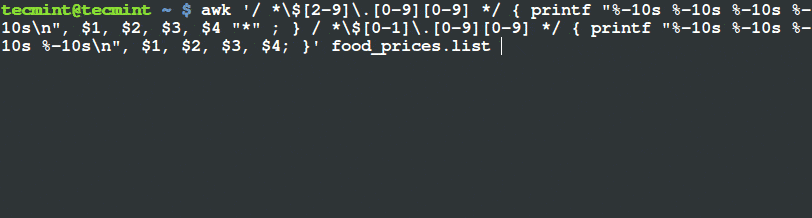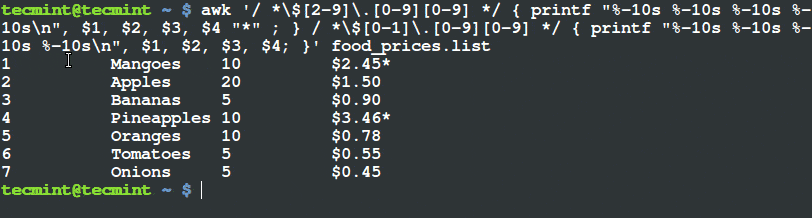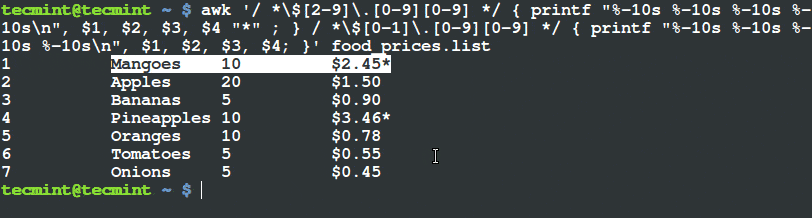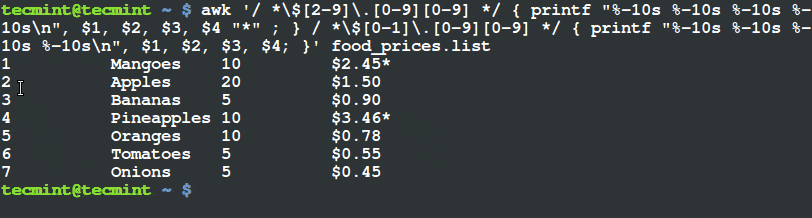
|
||||
>Filter and Print Items Using Awk and Printf
|
||||
|
||||
2. Using $0 field. Awk uses the variable 0 to store the whole input line. This is handy for solving the problem above and it is simple and fast as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ awk '/ *\$[2-9]\.[0-9][0-9] */ { print $0 "*" ; } / *\$[0-1]\.[0-9][0-9] */ { print ; }' food_prices.list
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
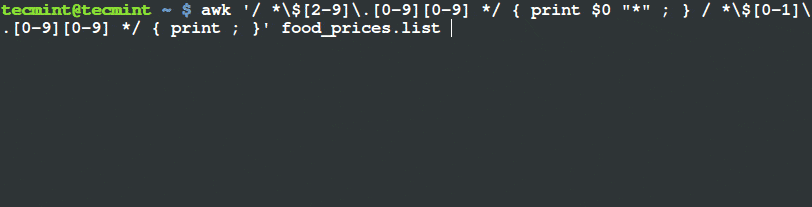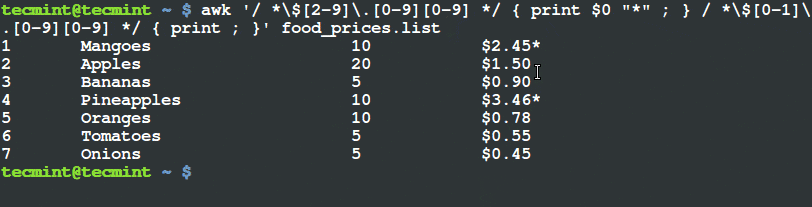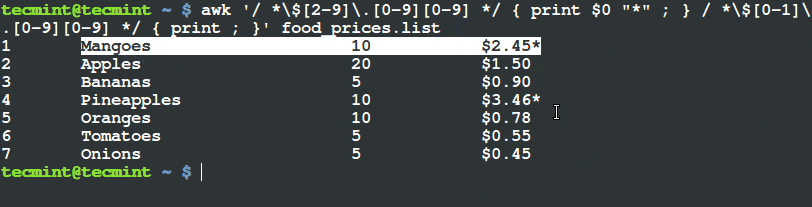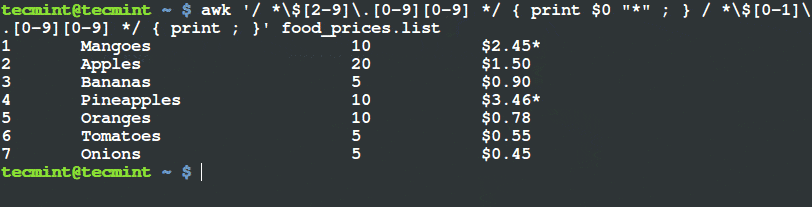
|
||||
>Filter and Print Items Using Awk and Variable
|
||||
|
||||
Conclusion
|
||||
That’s it for now and these are simple ways of filtering text using pattern specific action that can help in flagging lines of text or strings in a file using Awk command.
|
||||
|
||||
Hope you find this article helpful and remember to read the next part of the series which will focus on using comparison operators using awk tool.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/awk-filter-text-or-string-using-patterns/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Aaron Kili][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,97 +0,0 @@
|
||||
chunyang-wen translating
|
||||
|
||||
How to Use Comparison Operators with Awk in Linux
|
||||
===================================================
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
When dealing with numerical or string values in a line of text, filtering text or strings using comparison operators comes in handy for Awk command users.
|
||||
|
||||
In this part of the Awk series, we shall take a look at how you can filter text or strings using comparison operators. If you are a programmer then you must already be familiar with comparison operators but those who are not, let me explain in the section below.
|
||||
|
||||
### What are Comparison operators in Awk?
|
||||
|
||||
Comparison operators in Awk are used to compare the value of numbers or strings and they include the following:
|
||||
|
||||
- `>` – greater than
|
||||
- `<` – less than
|
||||
- `>=` – greater than or equal to
|
||||
- `<=` – less than or equal to
|
||||
- `==` – equal to
|
||||
- `!=` – not equal to
|
||||
- `some_value ~ / pattern/` – true if some_value matches pattern
|
||||
- `some_value !~ / pattern/` – true if some_value does not match pattern
|
||||
|
||||
Now that we have looked at the various comparison operators in Awk, let us understand them better using an example.
|
||||
|
||||
In this example, we have a file named food_list.txt which is a shopping list for different food items and I would like to flag food items whose quantity is less than or equal 20 by adding `(**)` at the end of each line.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
File – food_list.txt
|
||||
No Item_Name Quantity Price
|
||||
1 Mangoes 45 $3.45
|
||||
2 Apples 25 $2.45
|
||||
3 Pineapples 5 $4.45
|
||||
4 Tomatoes 25 $3.45
|
||||
5 Onions 15 $1.45
|
||||
6 Bananas 30 $3.45
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The general syntax for using comparison operators in Awk is:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# expression { actions; }
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To achieve the above goal, I will have to run the command below:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# awk '$3 <= 30 { printf "%s\t%s\n", $0,"**" ; } $3 > 30 { print $0 ;}' food_list.txt
|
||||
|
||||
No Item_Name` Quantity Price
|
||||
1 Mangoes 45 $3.45
|
||||
2 Apples 25 $2.45 **
|
||||
3 Pineapples 5 $4.45 **
|
||||
4 Tomatoes 25 $3.45 **
|
||||
5 Onions 15 $1.45 **
|
||||
6 Bananas 30 $3.45 **
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
In the above example, there are two important things that happen:
|
||||
|
||||
- The first expression `{ action ; }` combination, `$3 <= 30 { printf “%s\t%s\n”, $0,”**” ; }` prints out lines with quantity less than or equal to 30 and adds a `(**)` at the end of each line. The value of quantity is accessed using `$3` field variable.
|
||||
- The second expression `{ action ; }` combination, `$3 > 30 { print $0 ;}` prints out lines unchanged since their quantity is greater then `30`.
|
||||
|
||||
One more example:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# awk '$3 <= 20 { printf "%s\t%s\n", $0,"TRUE" ; } $3 > 20 { print $0 ;} ' food_list.txt
|
||||
|
||||
No Item_Name Quantity Price
|
||||
1 Mangoes 45 $3.45
|
||||
2 Apples 25 $2.45
|
||||
3 Pineapples 5 $4.45 TRUE
|
||||
4 Tomatoes 25 $3.45
|
||||
5 Onions 15 $1.45 TRUE
|
||||
6 Bananas 30 $3.45
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
In this example, we want to indicate lines with quantity less or equal to 20 with the word (TRUE) at the end.
|
||||
|
||||
### Summary
|
||||
|
||||
This is an introductory tutorial to comparison operators in Awk, therefore you need to try out many other options and discover more.
|
||||
|
||||
In case of any problems you face or any additions that you have in mind, then drop a comment in the comment section below. Remember to read the next part of the Awk series where I will take you through compound expressions.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/comparison-operators-in-awk/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Aaron Kili][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/
|
||||
@ -1,81 +0,0 @@
|
||||
martin
|
||||
|
||||
How to Use Compound Expressions with Awk in Linux
|
||||
====================================================
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
All along, we have been looking at simple expressions when checking whether a condition has been meet or not. What if you want to use more then one expression to check for a particular condition in?
|
||||
|
||||
In this article, we shall take a look at the how you can combine multiple expressions referred to as compound expressions to check for a condition when filtering text or strings.
|
||||
|
||||
In Awk, compound expressions are built using the `&&` referred to as `(and)` and the `||` referred to as `(or)` compound operators.
|
||||
|
||||
The general syntax for compound expressions is:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
( first_expression ) && ( second_expression )
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Here, `first_expression` and `second_expression` must be true to make the whole expression true.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
( first_expression ) || ( second_expression)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Here, one of the expressions either `first_expression` or `second_expression` must be true for the whole expression to be true.
|
||||
|
||||
**Caution**: Remember to always include the parenthesis.
|
||||
|
||||
The expressions can be built using the comparison operators that we looked at in Part 4 of the awk series.
|
||||
|
||||
Let us now get a clear understanding using an example below:
|
||||
|
||||
In this example, a have a text file named `tecmint_deals.txt`, which contains a list of some amazing random Tecmint deals, it includes the name of the deal, the price and type.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
TecMint Deal List
|
||||
No Name Price Type
|
||||
1 Mac_OS_X_Cleanup_Suite $9.99 Software
|
||||
2 Basics_Notebook $14.99 Lifestyle
|
||||
3 Tactical_Pen $25.99 Lifestyle
|
||||
4 Scapple $19.00 Unknown
|
||||
5 Nano_Tool_Pack $11.99 Unknown
|
||||
6 Ditto_Bluetooth_Altering_Device $33.00 Tech
|
||||
7 Nano_Prowler_Mini_Drone $36.99 Tech
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Say that we want only print and flag deals that are above $20 and of type “Tech” using the (**) sign at the end of each line.
|
||||
|
||||
We shall need to run the command below.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# awk '($3 ~ /^\$[2-9][0-9]*\.[0-9][0-9]$/) && ($4=="Tech") { printf "%s\t%s\n",$0,"*"; } ' tecmint_deals.txt
|
||||
|
||||
6 Ditto_Bluetooth_Altering_Device $33.00 Tech *
|
||||
7 Nano_Prowler_Mini_Drone $36.99 Tech *
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
In this example, we have used two expressions in a compound expression:
|
||||
|
||||
- First expression, `($3 ~ /^\$[2-9][0-9]*\.[0-9][0-9]$/)` ; checks the for lines with deals with price above `$20`, and it is only true if the value of $3 which is the price matches the pattern `/^\$[2-9][0-9]*\.[0-9][0-9]$/`
|
||||
- And the second expression, `($4 == “Tech”)` ; checks whether the deal is of type “`Tech`” and it is only true if the value of `$4` equals to “`Tech`”.
|
||||
Remember, a line will only be flagged with the `(**)`, if first expression and second expression are true as states the principle of the `&&` operator.
|
||||
|
||||
### Summary
|
||||
|
||||
Some conditions always require building compound expressions for you to match exactly what you want. When you understand the use of comparison and compound expression operators then, filtering text or strings based on some difficult conditions will become easy.
|
||||
|
||||
Hope you find this guide useful and for any questions or additions, always remember to leave a comment and your concern will be solved accordingly.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/combine-multiple-expressions-in-awk/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Aaron Kili][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/
|
||||
@ -1,73 +0,0 @@
|
||||
vim-kakali translating
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
How to Read Awk Input from STDIN in Linux
|
||||
============================================
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
In the previous parts of the Awk tool series, we looked at reading input mostly from a file(s), but what if you want to read input from STDIN.
|
||||
In this Part 7 of Awk series, we shall look at few examples where you can filter the output of other commands instead of reading input from a file.
|
||||
|
||||
We shall start with the [dir utility][1] that works similar to [ls command][2], in the first example below, we use the output of `dir -l` command as input for Awk to print owner’s username, groupname and the files he/she owns in the current directory:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# dir -l | awk '{print $3, $4, $9;}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
>List Files Owned By User in Directory
|
||||
|
||||
Take a look at another example where we [employ awk expressions][3], here, we want to print files owned by the root user by using an expression to filter strings as in the awk command below:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# dir -l | awk '$3=="root" {print $1,$3,$4, $9;} '
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
>List Files Owned by Root User
|
||||
|
||||
The command above includes the `(==)` comparison operator to help us filter out files in the current directory which are owned by the root user. This is achieved using the expression `$3==”root”`.
|
||||
|
||||
Let us look at another example of where we use a [awk comparison operator][4] to match a certain string.
|
||||
|
||||
Here, we have used the [cat utility][5] to view the contents of a file named tecmint_deals.txt and we want to view the deals of type Tech only, so we shall run the following commands:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# cat tecmint_deals.txt
|
||||
# cat tecmint_deals.txt | awk '$4 ~ /tech/{print}'
|
||||
# cat tecmint_deals.txt | awk '$4 ~ /Tech/{print}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
>Use Awk Comparison Operator to Match String
|
||||
|
||||
In the example above, we have used the value `~ /pattern/` comparison operator, but there are two commands to try and bring out something very important.
|
||||
|
||||
When you run the command with pattern tech nothing is printed out because there is no deal of that type, but with Tech, you get deals of type Tech.
|
||||
|
||||
So always be careful when using this comparison operator, it is case sensitive as we have seen above.
|
||||
|
||||
You can always use the output of another command instead as input for awk instead of reading input from a file, this is very simple as we have looked at in the examples above.
|
||||
|
||||
Hope the examples were clear enough for you to understand, if you have any concerns, you can express them through the comment section below and remember to check the next part of the series where we shall look at awk features such as variables, numeric expressions and assignment operators.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/read-awk-input-from-stdin-in-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Aaron Kili][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/
|
||||
[1]: http://www.tecmint.com/linux-dir-command-usage-with-examples/
|
||||
[2]: http://www.tecmint.com/15-basic-ls-command-examples-in-linux/
|
||||
[3]: http://www.tecmint.com/combine-multiple-expressions-in-awk
|
||||
[4]: http://www.tecmint.com/comparison-operators-in-awk
|
||||
[5]: http://www.tecmint.com/13-basic-cat-command-examples-in-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,108 +0,0 @@
|
||||
|
||||
驾车通往未来Linux
|
||||
===========================================
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
当我开车的时候不认为和 Linux 有多大联系,但是我肯定我是喜欢一个配备有系统的车子,让我按几个按钮语音就可以传给我的妻子母亲以及孩子。同样,这样的系统可以让我选择是否从云端流媒体收听音乐,卫星广播,以及传统的 AM/FM 收音机。我也会得到天气更新以及可以给我的车载信息娱乐 GPS 找到最快的下一个目的地[In-vehicle infotainment][1],以及 IVI 作为行业知名产业,已经普及到最新的汽车生产商。
|
||||
|
||||
前段时间,我不得坐飞机飞跃数百英里,租一辆车。令人愉快的是,我发现我的租凭车配置了 IVI 技术。任何时候,我只要通过蓝牙连接,上传联系人到系统中,打电话回家给我的家人,让他们知道我已经安全到家了。然后“主人“会知道我再途中还是已经到他们家了。
|
||||
|
||||
在最近的 [news roundup][2],Scott Nesbitt 引用一篇文章,说福特汽车公司是由它的开源 [Smart Device Link][3](SDL)中间设备框架,对手汽车制造商,支持那个移动手机获得大量的支持。 SDL 是 [GENIVI Alliance][4] 的项目,一个非营利性的致力于建设中间件支持开源的车载信息娱乐系统。根据文献 [[Steven Crumb][5],GENIVI 执行董事,他们 [membership][6] 很广,包括 Daimler 集团,现代,沃尔沃,日产,本田等等 170 个。
|
||||
|
||||
为了在同行业中保持竞争力,汽车企业需要一个中间设备系统,可以支持当今消费者提供的各种人机界面技术。无论您拥有 Android,iOS 或其他设备,汽车 OEM 厂商希望自己的系统单位能够支持这些。此外,这些的 IVI 系统必须有足够适应能力以支持移动技术的不断下降,半衰期。 OEM 厂商要提供价值服务,并在他们的 IVI 堆栈支持各种为他们的客户添加选择。进入 Linux 和开源软件。
|
||||
|
||||
除了 GENIVI 的努力下,[Linux Foundation][7] 赞助 [Automotive Grade Linux][8](AGL)工作组,一个软件基金会,致力于寻找针对汽车应用的开源解决方案。虽然 AGL 初期将侧重于 IVI 系统,他们展望不同的分歧,包括 [telematics][9],小心显示器和其他控制系统。 AGL 有超过 50 名成员在这个时候,包括捷豹,丰田,日产,并在 [recent press release][10] 宣布福特、马自达、三菱、和斯巴鲁加入。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
为了了解更多信息,我们在这一新鲜兴领域采访了两位领导人。明确地来说,我们想知道是如何被使用的 Linux 和开源软件,如果它们实际上是改变汽车行业的面貌。首先,我们谈谈 [Alison Chaiken][11],在大集团技术的软件工程师和汽车 Linux 专家,网络安全和透明度。她曾任职于 [Alison Chaiken][11] 公司,诺基亚和斯坦福直线性加速器。然后我们用 [Steven Crumb][12],GENIVI 执行董事,谁得到了在开源环境高性能计算(超级计算机和早期的云计算)开始聊天。他说,虽然他再不是一个程序员了,但是他喜欢帮助企业解决开源软件的实际业务问题。
|
||||
|
||||
### 采访 Alison Chaiken (by [Deb Nicholson][13])
|
||||
|
||||
#### 你是如何开始对汽车软件空间感兴趣的?
|
||||
|
||||
我是在诺基亚手机产品时, 2009 年该项目被取消。我想,下一步是什么?一位同事正在对 [MeeGo-IVI][15],早期的汽车 Linux 发行版。 “Linux 在汽车是大了,” 我想,所以我在朝着这个方向努力。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 你能告诉我们你这些日子工作在哪些方面?
|
||||
|
||||
我目前正在启动为使用 Linux 系统增加大货车钻机的安全性和燃油经济性的先进巡航控制。我喜欢在这方面的工作,因为没有人会反对卡车得以提升。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 目前关于汽车已在近年来砍死几个人故事。开源代码方案可以帮助解决这个问题吗?
|
||||
|
||||
I presented a talk on precisely this topic, on how Linux can (and cannot) contribute to security solutions in automotive at Southern California Linux Expo 2016 ([Slides][16]). Notably, GENIVI and Automotive Grade Linux have published their code and both projects take patches via Git. Please send your fixes upstream! Many eyes make all bugs shallow.
|
||||
我提出的谈话正是这一主题,就如何 Linux 可以(或不可以)在南加州 2016 年世博会作出贡献的安全解决方案的 Linux汽车([Slides][16])。值得注意的是,GENIVI 和汽车级 Linux 已经公布了他们的代码,这两个项目的 Git 通过采取补丁。请上游发送您的修复!许多眼睛都盯着肤浅的bugs。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 执法机构和保险公司可以找到很多有关数据用途的驱动程序。它将如何容易成为他们获取这些信息?
|
||||
|
||||
好问题。该专用短程通信标准(IEEE-1609),以保持匿名的 Wi-Fi 安全消息驱动程序。不过,如果你从你的车张贴到 Twitter,有人能够跟踪你。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 有什么可以开发人员和公民个人一起完成,以确保公民自由受到保护作为汽车技术发展的?
|
||||
|
||||
电子前沿基金会(EFF)一样对汽车保持的问题上,通过什么样的数据可以存储在汽车 “黑盒子”,并在 DMCA 的规定 1201 如何应用于汽车官方渠道评论已经出色的工作了。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在未来几年令人兴奋的事情上,那些是你看到的驱动因素?
|
||||
|
||||
自适应巡航控制和防撞系统有足够的预付款来挽救生命。当他们通过运输车队的推出,我真的相信死亡人数会下降。如果这还不是令人兴奋的,我不知道是什么。此外,像自动化停车辅助功能,将会使汽车更容易驾驶,减少汽车相撞事故。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 有什么是需要人参与以及如何建造?
|
||||
|
||||
汽车 Linux 级开发是开放源代码的,运行在廉价硬件(如树莓派 Pi 2 和中等价位的 Renesas Porter board),任何人都可以购买。 GENIVI 汽车 Linux 的中间设备联盟有很多软件通过 Git 的公开。此外,还有很酷的 [OSVehicle open hardware][17] 汽车平台。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 这里是 Linux 软件和开放硬件,许多方面具有中等人数预算的参与。如果您有任何疑问,加入我们在 Freenode 上 IRC#automotive。
|
||||
|
||||
### 采访 Steven Crumb (by Don Watkins)
|
||||
|
||||
#### 关于GENIVI's 对 IVI 为什么那么大 ?
|
||||
|
||||
GENIVI 率先通过使用自由和开源软件,包括 Linux,像车载信息娱乐(IVI)系统的非安全关键汽车软件填补了汽车行业的巨大差距。作为消费者来到期望在他们的车辆相同的功能在智能手机上的软件,以支持 IVI 功能所需的量成倍增长。软件增加量也增加了建设 IVI 系统的成本,从而延缓了上市时间。
|
||||
|
||||
GENIVI 的使用开源软件和社区发展模式节省了汽车制造商和他们的软件提供商显著大量的资金,而显著减少了产品上市时间。我很兴奋,因为 GENIVI 我们很幸运慢慢从高度结构化和专有的方法来社区为基础的方法不断发展的组织领导排序在汽车行业的一场革命。我们还没有完成,但它一直是一个荣幸参加正在产生实实在在的好处的转换。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 你的庞大会员怎么才可以驱动 GENIVI 方向?
|
||||
|
||||
GENIVI 有很多会员和非会员促进我们的工作。与许多开源项目,任何公司都可以通过简单地贡献代码,修补程序和时间来检验影响的技术输出。随着中说,宝马,奔驰,现代汽车,捷豹路虎,标致雪铁龙,雷诺 / 日产和沃尔沃是所有积极采用者和贡献者 GENIVI 和其他许多 OEM 厂商已经在他们的汽车 IVI 解决方案,广泛使用 GENIVI 的软件。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 贡献的代码使用了什么许可证?
|
||||
|
||||
GENIVI 采用数量的许可证从(L)GPLv2 许可,以 MPLv2 到 Apache2.0。我们的一些工具使用 Eclipse 许可证。我们有一个[public licensing policy][18],详细说明我们的许可偏好。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 一个人或一群人如何参与其中?重要的是如何对项目的持续成功的社区贡献?
|
||||
|
||||
GENIVI 完全做它开放发展的在([projects.genivi.org][19]),因此,有兴趣的人在汽车使用开源软件,欢迎参加。这就是说,该联盟能够通过公司 [joining GENIVI][20] 作为成员不断发展的开放基金。 GENIVI 会员享受各种各样的福利,而不是其中最重要的是在已经发展了近六年来 140 家公司全球社区参与。
|
||||
|
||||
社区是 GENIVI 非常重要的,我们不可能生产和维护我们发展了很多年没有贡献者一个活跃的社区有价值的软件。我们努力做出贡献 GENIVI 简单,只要加入一个 [邮件列表] [21] 并连接到人们在不同的软件项目。我们使用许多开源项目采用的标准做法,并提供高质量的工具和基础设施,以帮助开发人员有宾至如归的感觉,并富有成效。
|
||||
|
||||
无论在汽车软件某人的熟悉,欢迎他们加入我们的社区。人们已经改装车多年,所以对于许多人来说,是一种天然的抽奖,任何汽车。软件是汽车的新域,GENIVI 希望成为敞开的门有兴趣的人与汽车,开源软件的工作。
|
||||
|
||||
-------------------------------
|
||||
via: https://opensource.com/business/16/5/interview-alison-chaiken-steven-crumb
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Don Watkins][a]
|
||||
译者:[erlinux](https://github.com/erlinux)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: https://opensource.com/users/don-watkins
|
||||
[1]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/In_car_entertainment
|
||||
[2]: https://opensource.com/life/16/1/weekly-news-jan-9
|
||||
[3]: http://projects.genivi.org/smartdevicelink/home
|
||||
[4]: http://www.genivi.org/
|
||||
[5]: https://www.linkedin.com/in/stevecrumb
|
||||
[6]: http://www.genivi.org/genivi-members
|
||||
[7]: http://www.linuxfoundation.org/
|
||||
[8]: https://www.automotivelinux.org/
|
||||
[9]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Telematics
|
||||
[10]: https://www.automotivelinux.org/news/announcement/2016/01/ford-mazda-mitsubishi-motors-and-subaru-join-linux-foundation-and
|
||||
[11]: https://www.linkedin.com/in/alison-chaiken-3ba456b3
|
||||
[12]: https://www.linkedin.com/in/stevecrumb
|
||||
[13]: https://opensource.com/users/eximious
|
||||
[14]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/MeeGo
|
||||
[15]: http://webinos.org/deliverable-d026-target-platform-requirements-and-ipr/automotive/
|
||||
[16]: http://she-devel.com/Chaiken_automotive_cybersecurity.pdf
|
||||
[17]: https://www.osvehicle.com/
|
||||
[18]: http://projects.genivi.org/how
|
||||
[19]: http://projects.genivi.org/
|
||||
[20]: http://genivi.org/join
|
||||
[21]: http://lists.genivi.org/mailman/listinfo/genivi-projects
|
||||
@ -1,85 +0,0 @@
|
||||
为什么 Ubuntu 家族会占据 Linux 发行版的主导地位?
|
||||
=========================================
|
||||
|
||||
在过去的数年中,我已经尝试了大量的优秀 Linux 发行版。我印象最深刻的是那些被强大的社区维护的发行版。但是这样的发行版却比他们s所属的社区更受人欢迎。流行的 Linux 发行版吸引着更多的人,通常由于这样的特点使得使用该发行版更加容易。这很明显毫无关系,但一般认为这种说法是正确的。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
我想到的一个发行版 [Ubuntu][1]。它属于健壮的 [Debian][2]分支,Ubuntu 不可思议的成为了受欢迎的 Linux 发行版,而且它也衍生出了其他的版本,比如 Linux Mint。在本文中,我会探讨我坚信 Ubuntu 会赢得 Linux 发行版战争的原因,以及它在整个 Linux 桌面领域有着怎样的影响力。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Ubuntu容易使用
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
多年前我第一次尝试使用Ubuntu,在这之前我更喜欢使用 KED 桌面。在那个时期,我接触的大多是这种 KDE 桌面环境。主要原因还是 KDE 是大多数新手友好的 Linux 发行版中最受欢迎的。新手友好的发行版有 Knoppix,Simply Mepis, Xandros, Linspire等,另外一些发行版和这些发行版都指出他们的用户趋向于使用 KDE。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
现在KDE能满足我的需求,也没有什么理由去折腾其他的桌面环境了。有一天我的 Debian 安装失败了(由于我个人的操作不当),我决定尝试开发代号为「整洁的公鸭(Ubuntu Dapper Drake)」的 Ubuntu 版本【译者注:ubuntu 6.06 - Dapper Drake(整洁的公鸭),发布日期:2006年6月1日】。那个时候,我对于它的印象比一个屏幕截图还要少,但是我认为它很有趣并且毫无顾忌的使用它。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu Dapper Drake 给我的最大的印象是它的操作很简单。记住,我是来自于 KDE 世界的用户,在 KDE 上要想改变菜单的设置就有15钟方法。Ubuntu 图形界面的安装启动极具极简主义。
|
||||
|
||||
时间来到2016年,最新的版本号是16.04:我们有多种可用的 Ubuntu 衍生版本,许多的都是基于 Ubuntu 的。所有的 Ubuntu 风格和公用发行版的核心都被设计的容易使用。并且发行版想要增大用户基数的时候,这就是最重要的原因。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Ubuntu LTS
|
||||
|
||||
过去,我几乎一直坚持使用 LTS(Long Term Support)发行版作为我的主要桌面系统。10月份的发行版很适合我测试硬盘驱动器,甚至把它用在一个老旧的手提电脑上。我这样做的原因很简单——我没有兴趣在一个作为实验品的电脑上折腾短期发行版。我是个很忙的家伙,我觉得这样会浪费我的时间。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
对于我来说,我认为 Ubuntu 提供 LTS 发行版是 Ubuntu 能够变得流行的原因。这样说吧———提供一个大众的桌面 Linux 发行版,这个发行版能够得到长期的充分支持就是它的优势。事实上,Ubuntu 的优势不只这一点,其他的分支在这一点上也做的很好。长期支持版带有一个对新手的友好环境的策略,我认为这就为 Ubuntu 的普及带来了莫大的好处。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Ubuntu Snap 包
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
以前,用户在他们的系统上使用很多 PPA(personal package archive个人软件包档案),他们总会抱怨它获得新的软件名称的能力。不好的是,这种技术也有缺点。它工作的时候带有任意的软件名称,而 PPA 却没有发现,这种情况很常见。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
现在有了[Snap 包][3] 。当然这不是一个全新的概念,过去已经进行了类似的尝试。用户不必要在最新的 Ubuntu 发行版上运行最新的软件,我认为这才是 Snap 将要长期提供给 Ubuntu 用户的东西。然而我仍然认为我们将会看到 Snap 淘汰的的那一天,我很期待看到一个在稳定的发行版上运行的优秀软件。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
如果你要运行很多软件,那么 Snap 包实际使用的硬盘空间很明显存在问题。不仅如此,大多数 Ubuntu 软件也是通过由官方开发的 deb 包进行管理的。当后者需要花费一些时间的时候,这个问题可以通过 Snap 使用更大的硬盘驱动器空间得到解决。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Ubuntu 社区
|
||||
|
||||
首先,我承认大多数主要的 Linux 发行版都有强大的社区。然而,我坚信 Ubuntu 社区的成员是最多样化的,他们来自各行各业。例如,我们有一个论坛来分类不同的苹果硬件对于游戏的支持程度。这些大量的专业讨论特别广泛。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
除过论坛,Ubuntu 也提供了一个很正式的社区组织。这个组织包括一个委员会,技术板块,[各地的团队LoCo teams][4](Ubuntu Local Community Teams)和开发人员板块。还有很多,但是这些都是我知道的社区组织部分。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
我们还有一个[Ubuntu 问答][5]板块。我认为,这种特色可以代替人们从论坛寻求帮助的方式,我发现在这个网站你得到有用信息的可能行更大。不仅如此,那些提供的解决方案中被选出的最精准的答案也会被写入到官方文档中。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Ubuntu 的未来
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
我认为 Ubuntu 的 Unity 接口【译者注:Unity 是 Canonical 公司为 Ubuntu 操作系统的 GNOME 桌面环境开发的图形化 shell】在增加桌面舒适性上少有作为。我能理解其中的缘由,现在它主要做一些诸如可以使开发团队的工作更轻松的事情。但是最终,我还是希望 Unity 可以为 Ubuntu MATE 和 Linux Mint 的普及铺平道路。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
我最好奇的一点是 Ubuntu's IRC(Internet Relay Chat) 和邮件列表的发展【译者注:可以在 Ubuntu LoCo Teams IRC Chat上提问关于地方团队和计划的事件的问题,也可以和一些不同团队的成员进行交流】。事实是,他们都不能像 Ubuntu 问答板块那样为它们自己增添一些好的文档。至于邮件列表,我一直认为这对于合作是一种很痛苦的过时方法,但这仅仅是我的个人看法——其他人可能有不同的看法,也可能会认为它很好。
|
||||
|
||||
你说什么?你认为 Ubuntu 将来会剩下一点主要的使用者?也许你相信 Arch 和 Linux Mint 或者其他的发行版会在普及度上打败 Ubuntu 。 既然这样,那请大声说出你最喜爱的发行版。如果这个发行版是 Ubuntu 衍生版 ,说说你为什么更喜欢它而不是 Ubuntu 本身。如果不出意外,Ubuntu 会成为构建其他发行版的基础,我想很多人都是这样认为的。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.datamation.com/open-source/why-ubuntu-based-distros-are-leaders.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Matt Hartley][a]
|
||||
译者:[vim-kakali](https://github.com/vim-kakali)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: http://www.datamation.com/author/Matt-Hartley-3080.html
|
||||
[1]: http://www.ubuntu.com/
|
||||
[2]: https://www.debian.org/
|
||||
[3]: http://www.datamation.com/open-source/ubuntu-snap-packages-the-good-the-bad-the-ugly.html
|
||||
[4]: http://loco.ubuntu.com/
|
||||
[5]: http://askubuntu.com/
|
||||
@ -1,54 +1,53 @@
|
||||
(翻译中 by runningwater)
|
||||
Explanation of “Everything is a File” and Types of Files in Linux
|
||||
诠释 Linux 中“一切都是文件”概念和相应的文件类型
|
||||
====================================================================
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>Everything is a File and Types of Files in Linux
|
||||
>Linux 系统中一切都是文件并有相应的文件类型
|
||||
|
||||
That is in fact true although it is just a generalization concept, in Unix and its derivatives such as Linux, everything is considered as a file. If something is not a file, then it must be running as a process on the system.
|
||||
在 Unix 和它衍生的比如 Linux 系统中,一切都可以看做文件。虽然它仅仅只是一个泛泛的概念,但这是事实。如果有不是文件的,那它一定是正运行的进程。
|
||||
|
||||
To understand this, take for example the amount of space on your root (/) directory is always consumed by different types of Linux files. When you create a file or transfer a file to your system, it occupies some space on the physical disk and it is considered to be in a specific format (file type).
|
||||
要理解这点,可以举个例子,您的根目录(/) 的空间是由不同类型的 Linux 文件所占据的。当您创建一个文件或向系统传一个文件时,它在物理磁盘上占据的一些空间,可以认为是一个特定的格式(文件类型)。
|
||||
|
||||
And also the Linux system does not differentiate between files and directories, but directories do one important job, that is store other files in groups in a hierarchy for easy location. All your hardware components are represented as files and the system communicates with them using these files.
|
||||
虽然 Linux 系统中文件和目录没有什么不同,但目录还有一个重要的功能,那就是有结构性的分组存储其它文件,以方便查找访问。所有的硬件部件都表示为文件,系统使用这些文件来与硬件通信。
|
||||
|
||||
The idea is an important description of a great property of Linux, where input/output resources such as your documents, directories (folders in Mac OS X and Windows), keyboard, monitor, hard-drives, removable media, printers, modems, virtual terminals and also inter-process and network communication are streams of bytes defined by file system space.
|
||||
这些思想是对伟大的 Linux 财产的重要阐述,因此像文档、目录(Mac OS X 和 Windows 系统下是文件夹)、键盘、监视器、硬盘、可移动媒体设备、打印机、调制解调器、虚拟终端,还有进程间通信(IPC)和网络通信等输入/输出资源都在定义在文件系统空间下的字节流。
|
||||
|
||||
A notable advantage of everything being a file is that the same set of Linux tools, utilities and APIs can be used on the above input/output resources.
|
||||
一切都可看作是文件,其最显著的好处是对于上面所列出的输入/输出资源,只需要相同的一套 Linux 工具、实用程序和 API。
|
||||
|
||||
Although everything in Linux is a file, there are certain special files that are more than just a file for example [sockets and named pipes][1].
|
||||
虽然在 Linux 中一切都可看作是文件,但也有一些特殊的文件,比如[套接字和命令管道][1]。
|
||||
|
||||
### What are the different types of files in Linux?
|
||||
### Linux 文件类型的不同之处?
|
||||
|
||||
In Linux there are basically three types of files:
|
||||
Linux 系统中有三种基本的文件类型:
|
||||
|
||||
- Ordinary/Regular files
|
||||
- Special files
|
||||
- Directories
|
||||
- 普通/常规文件
|
||||
- 特殊文件
|
||||
- 目录文件
|
||||
|
||||
#### Ordinary/Regular Files
|
||||
#### 普通/常规文件
|
||||
|
||||
These are files data contain text, data or program instructions and they are the most common type of files you can expect to find on a Linux system and they include:
|
||||
它们是包含文本、数据、程序指令等数据的文件,其在 Linux 系统中是最常见的一种。包括如下:
|
||||
|
||||
- Readable files
|
||||
- Binary files
|
||||
- Image files
|
||||
- Compressed files and so on.
|
||||
- 只读文件
|
||||
- 二进制文件
|
||||
- 图像文件
|
||||
- 压缩文件等等
|
||||
|
||||
#### Special Files
|
||||
#### 特殊文件
|
||||
|
||||
Special files include the following:
|
||||
特殊文件包括以下几种:
|
||||
|
||||
Block files : These are device files that provide buffered access to system hardware components. They provide a method of communication with device drivers through the file system.
|
||||
块文件:设备文件,对访问系统硬件部件提供了缓存接口。他们提供了一种使用文件系统与设备驱动通信的方法。
|
||||
|
||||
One important aspect about block files is that they can transfer a large block of data and information at a given time.
|
||||
有关于块文件一个重要的性能就是它们能在指定时间内传输大块的数据和信息。
|
||||
|
||||
Listing block files sockets in a directory:
|
||||
列出某目录下的块文件:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# ls -l /dev | grep "^b"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Sample Output
|
||||
输出例子
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
brw-rw---- 1 root disk 7, 0 May 18 10:26 loop0
|
||||
@ -74,15 +73,15 @@ brw-rw---- 1 root disk 1, 5 May 18 10:26 ram5
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Character files : These are also device files that provide unbuffered serial access to system hardware components. They work by providing a way of communication with devices by transferring data one character at a time.
|
||||
字符文件: 也是设备文件,对访问系统硬件组件提供了非缓冲串行接口。它们与设备的通信工作方式是一次只传输一个字符的数据。
|
||||
|
||||
Listing character files sockets in a directory:
|
||||
列出某目录下的字符文件:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# ls -l /dev | grep "^c"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Sample Output
|
||||
输出例子
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
crw------- 1 root root 10, 235 May 18 15:54 autofs
|
||||
@ -114,15 +113,15 @@ crw-rw-rw- 1 root tty 5, 2 May 18 17:40 ptmx
|
||||
crw-rw-rw- 1 root root 1, 8 May 18 10:26 random
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Symbolic link files : A symbolic link is a reference to another file on the system. Therefore, symbolic link files are files that point to other files, and they can either be directories or regular files.
|
||||
符号链接文件 : 符号链接是指向系统上其他文件的引用。因此,符号链接文件是指向其它文件的文件,也可以是目录或常规文件。
|
||||
|
||||
Listing symbolic link sockets in a directory:
|
||||
列出某目录下的符号链接文件:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# ls -l /dev/ | grep "^l"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Sample Output
|
||||
输出例子
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 3 May 18 10:26 cdrom -> sr0
|
||||
@ -135,27 +134,27 @@ lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 15 May 18 15:54 stdin -> /proc/self/fd/0
|
||||
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 15 May 18 15:54 stdout -> /proc/self/fd/1
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can make symbolic links using the `ln` utility in Linux as in the example below.
|
||||
Linux 中使用 `ln` 工具就可以创建一个符号链接文件,如下所示:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# touch file1.txt
|
||||
# ln -s file1.txt /home/tecmint/file1.txt [create symbolic link]
|
||||
# ls -l /home/tecmint/ | grep "^l" [List symbolic links]
|
||||
# ln -s file1.txt /home/tecmint/file1.txt [创建符号链接文件]
|
||||
# ls -l /home/tecmint/ | grep "^l" [列出符号链接文件]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
In the above example, I created a file called `file1.txt` in `/tmp` directory, then created the symbolic link, `/home/tecmint/file1.txt` to point to `/tmp/file1.txt`.
|
||||
在上面的例子中,首先我们在 `/tmp` 目录创建了一个名叫 `file1.txt` 的文件,然后创建符号链接文件,所以 `/home/tecmint/file1.txt` 指向 `/tmp/file1.txt` 文件。
|
||||
|
||||
Pipes or Named pipes : These are files that allow inter-process communication by connecting the output of one process to the input of another.
|
||||
套接字和命令管道 : 连接一个进行的输出和另一个进程的输入,允许进程间通信的文件。
|
||||
|
||||
A named pipe is actually a file that is used by two process to communicate with each and it acts as a Linux pipe.
|
||||
命名管道实际上是一个文件,用来使两个进程彼此通信,就像一个 Linux pipe(管道) 命令一样。
|
||||
|
||||
Listing pipes sockets in a directory:
|
||||
列出某目录下的管道文件:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# ls -l | grep "^p"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Sample Output
|
||||
输出例子
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
prw-rw-r-- 1 tecmint tecmint 0 May 18 17:47 pipe1
|
||||
@ -165,62 +164,64 @@ prw-rw-r-- 1 tecmint tecmint 0 May 18 17:47 pipe4
|
||||
prw-rw-r-- 1 tecmint tecmint 0 May 18 17:47 pipe5
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can use the mkfifo utility to create a named pipe in Linux as follows.
|
||||
在 Linux 中可以使用 `mkfifo` 工具来创建一个命名管道,如下所示:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# mkfifo pipe1
|
||||
# echo "This is named pipe1" > pipe1
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
In the above example, I created a named pipe called pipe1, then I passed some data to it using the [echo command][2], after that the shell became un-interactive while processing the input.
|
||||
在上的例子中,我们创建了一个名叫 `pipe1` 的命名管道,然后使用 [echo 命令][2] 加入一些数据,在这操作后,要使用这些输入数据就要用非交互的 shell 了。
|
||||
|
||||
Then I opened another shell and run the another command to print out what was passed to pipe.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
然后,我们打开另外的 shell 终端,运行另外的命令来打印出刚加入管道的数据。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# while read line ;do echo "This was passed-'$line' "; done<pipe1
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Socket files : These are files that provide a means of inter-process communication, but they can transfer data and information between process running on different environments.
|
||||
套接字文件 : 提供进程间通信方法的文件,它们能为运行在不同环境中的进程之间的数据和信息提供传输的能力。
|
||||
|
||||
This means that sockets provide data and information transfer between process running on different machines on a network.
|
||||
这就是说,套接字 (sockets) 可以对运行网络上不同机器中的进行之间的数据和信息进行传输。
|
||||
|
||||
An example to show the work of sockets would be a web browser making a connection to a web server.
|
||||
一个 socket 运行的例子就是网页浏览器连接到网站服务器的过程。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# ls -l /dev/ | grep "^s"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Sample Output
|
||||
输出例子
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
srw-rw-rw- 1 root root 0 May 18 10:26 log
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This is an example of a socket create in C by using the `socket()` system call.
|
||||
下面是使用 C 语言编写的调用 `socket()` 函数的例子。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
int socket_desc= socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0 );
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
In the above:
|
||||
上例中:
|
||||
|
||||
- `AF_INET` is the address family(IPv4)
|
||||
- `SOCK_STREAM` is the type (connection is TCP protocol oriented)
|
||||
- `0` is the protocol(IP Protocol)
|
||||
- `AF_INET` 指的是地址域(IPv4)
|
||||
- `SOCK_STREAM` 指的是类型 (默认使用 TCP 协议连接)
|
||||
- `0` 指协议(IP 协议)
|
||||
|
||||
To refer to the socket file, use the `socket_desc`, which is the same as the file descriptor, and use `read()` and `write()` system calls to read and write from the socket respectively.
|
||||
使用 `socket_desc` 来引用管道文件,它跟文件描述符是一样的,然后再使用系统函数 `read()` 和 `write()` 来分别从这个管道文件读写数据。
|
||||
|
||||
### Directories
|
||||
### 目录文件
|
||||
|
||||
These are special files that store both ordinary and other special files and they are organized on the Linux file system in a hierarchy starting from the root (/) directory.
|
||||
是一些特殊的文件,既可以包含普通文件又可包含特殊文件,它们在 Linux 文件系统中是以根(/)目录为起点分层组织存在的。
|
||||
|
||||
Listing sockets in a directory:
|
||||
列出某目录下的目录文件:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# ls -l / | grep "^d"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Sample Output
|
||||
输出例子
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 May 5 15:49 bin
|
||||
@ -246,7 +247,7 @@ drwxr-xr-x 11 root root 4096 Mar 31 16:00 usr
|
||||
drwxr-xr-x 12 root root 4096 Nov 12 2015 var
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can make a directory using the mkdir command.
|
||||
您可以使用 mkdir 命令来创建一个目录。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# mkdir -m 1666 tecmint.com
|
||||
@ -254,11 +255,11 @@ You can make a directory using the mkdir command.
|
||||
# mkdir -m 1775 linuxsay.com
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Summary
|
||||
### 结论
|
||||
|
||||
You should now be having a clear understanding of why everything in Linux is a file and the different types of files that can exit on your Linux system.
|
||||
现在应该有一个清楚的认识为什么 Linux 系统中一切都是文件以及 Linux 系统中可以存在哪些类型的文件了。
|
||||
|
||||
You can add more to this by reading more about the individual file types and they are created. I hope this find this guide helpful and for any questions and additional information that you would love to share, please leave a comment and we shall discuss more.
|
||||
您可以通过阅读更多有关各个文件类型的文章和对应的创建过程等来增加更多知识。我希望这篇教程对您有所帮助。有任何疑问或有补充的知识,请留下评论,一起来讨论。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,93 @@
|
||||
Linux 开发者如何看待 Git 和 Github?
|
||||
=====================================================
|
||||
|
||||
**同样在今日的开源摘要: DistroWatch 评估 XStream 桌面 153 版本,街头霸王 V 即将在这个春天进入 Linux 和 SteamOS**
|
||||
|
||||
## Linux 开发者如何看待 Git 和 Github?
|
||||
|
||||
Git 和 Github 在 Linux 开发者中有很高的知名度。但是开发者如何看待它们呢?另外,Github 是不是真的和 Git 是一个意思?一个 Linux reddit 用户最近问到了这个问题,并且得到了很有意思的答案。
|
||||
|
||||
Dontwakemeup46 提问:
|
||||
|
||||
> 我正在学习 Git 和 Github。我感兴趣的是社区如何看待两者?据我所知,Git 和 Github 应用十分广泛。但是 Git 或 Github 有没有严重的,社区喜欢去修改的问题呢?
|
||||
|
||||
[更多见 Reddit](http://api.viglink.com/api/click?format=go&jsonp=vglnk_145580413015211&key=0a7039c08493c7c51b759e3d13019dbe&libId=iksc5hc8010113at000DL3yrsuvp7&loc=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.infoworld.com%2Farticle%2F3033059%2Flinux%2Fwhat-do-linux-developers-think-of-git-and-github.html&v=1&out=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.reddit.com%2Fr%2Flinux%2Fcomments%2F45jy59%2Fthe_popularity_of_git_and_github%2F&ref=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.linux.com%2Fnews%2Fsoftware%2Fapplications%2F886008-what-do-linux-developers-think-of-git-and-github&title=What%20do%20Linux%20developers%20think%20of%20Git%20and%20GitHub%3F%20%7C%20InfoWorld&txt=More%20at%20Reddit)
|
||||
|
||||
与他志同道合的 Linux reddit 用户回答了他们对于 Git 和 Github的想法:
|
||||
|
||||
>Derenir: “Github 并不隶属于 Git。
|
||||
|
||||
>Git 是由 Linus Torvalds 开发的。
|
||||
|
||||
>Github 几乎不支持 Linux。
|
||||
|
||||
>Github 是一家唯利是图的,企图借助 Git 赚钱的公司。
|
||||
|
||||
>[https://desktop.github.com/](http://api.viglink.com/api/click?format=go&jsonp=vglnk_145580415025712&key=0a7039c08493c7c51b759e3d13019dbe&libId=iksc5hc8010113at000DL3yrsuvp7&loc=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.infoworld.com%2Farticle%2F3033059%2Flinux%2Fwhat-do-linux-developers-think-of-git-and-github.html&v=1&type=U&out=https%3A%2F%2Fdesktop.github.com%2F&ref=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.linux.com%2Fnews%2Fsoftware%2Fapplications%2F886008-what-do-linux-developers-think-of-git-and-github&title=What%20do%20Linux%20developers%20think%20of%20Git%20and%20GitHub%3F%20%7C%20InfoWorld&txt=https%3A%2F%2Fdesktop.github.com%2F) 并没有支持 Linux。”
|
||||
|
||||
>**Bilog78**: “一个简单的更新: Linus Torvalds 已经不再维护 Git了。维护者是 Junio C Hamano,以及 Linus 之后的主要贡献者是Jeff King 和 Shawn O. Pearce。”
|
||||
|
||||
>**Fearthefuture**: “我喜欢 Git,但是不明白人们为什么还要使用 Github。从我的角度,Github 比 Bitbucket 好的一点是用户统计和更大的用户基础。Bitbucket 有无限的免费私有库,更好的 UI,以及更好地继承其他服务,比如说 Jenkins。”
|
||||
|
||||
>**Thunger**: “Gitlab.com 也很不错,特别是你可以在自己的服务器上架设自己的实例。”
|
||||
|
||||
>**Takluyver**: “很多人熟悉 Github 的 UI 以及相关联的服务,像 Travis 。并且很多人都有 Github 账号,所以它是一个很好地存储项目的地方。人们也使用他们的 Github 简况作为一种求职用的作品选辑,所以他们很积极地将更多的项目放在这里。Github 是一个事实上的,存放开源项目的标准。”
|
||||
|
||||
>**Tdammers**: “Git 严重问题在于 UI,它有些违反直觉,到很多用户只使用一些容易记住的咒语程度。”
|
||||
|
||||
Github:最严重的问题在于它是私人拥有的解决方案;你买了方便,但是代价是你的代码在别人的服务器上面,已经不在你的掌控范围之内了。另一个对于 Github 的普遍批判是它的工作流和 Git 本身的精神不符,特别是 pull requests 工作的方式。最后, Github 垄断代码的托管环境,同时对于多样性是很不好的,这反过来对于旺盛的免费软件社区很重要。”
|
||||
|
||||
>**Dies**: “更重要的是,如果一旦是这样,做过的都做过了,并且我猜我们会被 Github 所困,因为它们控制如此多的项目。”
|
||||
|
||||
>**Tdammers**: “代码托管在别人的服务器上,别人指的是 Github。这对于开源项目来说,并不是什么太大的问题,但是仍然,你无法控制它。如果你在 Github 上有私有项目,唯一的保险在于它将保持私有是 Github 的承诺。如果你决定删除东西,你不能确定东西是否被删除了,或者只是隐藏了。
|
||||
|
||||
Github 并不自己控制这些项目(你总是可以拿走你的代码,然后托管到别的地方,声明新位置是“官方”的),它只是有比开发者本身有更深的使用权。”
|
||||
|
||||
>**Drelos**: “我已经读了大量的关于 Github 的赞美与批评。(这里有一个[例子](http://api.viglink.com/api/click?format=go&jsonp=vglnk_145580428524613&key=0a7039c08493c7c51b759e3d13019dbe&libId=iksc5hc8010113at000DL3yrsuvp7&loc=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.infoworld.com%2Farticle%2F3033059%2Flinux%2Fwhat-do-linux-developers-think-of-git-and-github.html&v=1&out=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.wired.com%2F2015%2F06%2Fproblem-putting-worlds-code-github%2F&ref=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.linux.com%2Fnews%2Fsoftware%2Fapplications%2F886008-what-do-linux-developers-think-of-git-and-github&title=What%20do%20Linux%20developers%20think%20of%20Git%20and%20GitHub%3F%20%7C%20InfoWorld&txt=here%27s%20an%20example)),但是我的新手问题是为什么不向一个免费开源的版本努力呢?”
|
||||
|
||||
>**Twizmwazin**: “Gitlab 的源码就存在这里”
|
||||
|
||||
[更多见 Reddit](http://api.viglink.com/api/click?format=go&jsonp=vglnk_145580429720714&key=0a7039c08493c7c51b759e3d13019dbe&libId=iksc5hc8010113at000DL3yrsuvp7&loc=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.infoworld.com%2Farticle%2F3033059%2Flinux%2Fwhat-do-linux-developers-think-of-git-and-github.html&v=1&out=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.reddit.com%2Fr%2Flinux%2Fcomments%2F45jy59%2Fthe_popularity_of_git_and_github%2F&ref=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.linux.com%2Fnews%2Fsoftware%2Fapplications%2F886008-what-do-linux-developers-think-of-git-and-github&title=What%20do%20Linux%20developers%20think%20of%20Git%20and%20GitHub%3F%20%7C%20InfoWorld&txt=More%20at%20Reddit)
|
||||
|
||||
## DistroWatch 评估 XStream 桌面 153 版本
|
||||
|
||||
XStreamOS 是一个由 Sonicle 创建的 Solaris 的一个版本。XStream 桌面将 Solaris 的强大带给了桌面用户,同时新手用户很可能有兴趣体验一下。DistroWatch 对于 XStream 桌面 153 版本做了一个很全面的评估,并且发现它运行相当好。
|
||||
|
||||
Jesse Smith 为 DistroWatch 报道:
|
||||
|
||||
> 我认为 XStream 桌面做好了很多事情。无可否认地,我的实验陷入了头晕目眩的状态当操作系统无法在我的硬件上启动。同时,当运行在 VirtualBox 中我无法使得桌面使用我显示器的完整分辨率。
|
||||
|
||||
> 我确实在播放多媒体文件时遇见一些问题,特别是使声卡工作。我不确定是不是另外一个硬件兼容问题,或者一个关于操作系统自带的多媒体软件的问题。另一方面,像 Web 浏览器,电子邮件,生产工具套件以及配置工具这样的工作都工作的很好。
|
||||
|
||||
> 我最欣赏 XStream 的地方是这个操作系统是 OpenSolaris 家族的一个使用保持最新的分支。OpenSolaris 的其他衍生系统有落后的倾向,至少在桌面软件上,但是 XStream 仍然搭载最新版本的火狐和 LibreOffice。
|
||||
|
||||
>对我个人来说,XStream 缺少一些组件,比如打印机管理器,多媒体支持和我特定硬件的驱动。这个操作系统的其他方面也是相当吸引人的。我喜欢开发者搭建 LXDE 的方式,软件的默认组合,以及我最喜欢文件系统快照和启动环境开箱即用的方式。大多数的 Linux 发行版,openSUSE 除外,并没有使得启动环境的有用性流行起来。我希望它是一个被更多项目采用的技术。
|
||||
|
||||
[更多见 DistroWatch](http://api.viglink.com/api/click?format=go&jsonp=vglnk_145580434172315&key=0a7039c08493c7c51b759e3d13019dbe&libId=iksc5hc8010113at000DL3yrsuvp7&loc=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.infoworld.com%2Farticle%2F3033059%2Flinux%2Fwhat-do-linux-developers-think-of-git-and-github.html&v=1&out=http%3A%2F%2Fdistrowatch.com%2Fweekly.php%3Fissue%3D20160215%23xstreamos&ref=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.linux.com%2Fnews%2Fsoftware%2Fapplications%2F886008-what-do-linux-developers-think-of-git-and-github&title=What%20do%20Linux%20developers%20think%20of%20Git%20and%20GitHub%3F%20%7C%20InfoWorld&txt=More%20at%20DistroWatch)
|
||||
|
||||
## 街头霸王 V 和 SteamOS
|
||||
|
||||
街头霸王是最出名的游戏之一,并且 [Capcom 已经宣布](http://api.viglink.com/api/click?format=go&jsonp=vglnk_145580435418216&key=0a7039c08493c7c51b759e3d13019dbe&libId=iksc5hc8010113at000DL3yrsuvp7&loc=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.infoworld.com%2Farticle%2F3033059%2Flinux%2Fwhat-do-linux-developers-think-of-git-and-github.html&v=1&out=http%3A%2F%2Fsteamcommunity.com%2Fgames%2F310950%2Fannouncements%2Fdetail%2F857177755595160250&ref=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.linux.com%2Fnews%2Fsoftware%2Fapplications%2F886008-what-do-linux-developers-think-of-git-and-github&title=What%20do%20Linux%20developers%20think%20of%20Git%20and%20GitHub%3F%20%7C%20InfoWorld&txt=Capcom%20has%20announced) 街头霸王 V 将会在这个春天进入 Linux 和 StreamOS。这对于 Linux 游戏者是非常好的消息。
|
||||
|
||||
Joe Parlock 为 Destructoid 报道:
|
||||
|
||||
>你是少于 1% 的,在 Linux 系统上玩游戏的 Stream 用户吗?你是更少百分比的,在 Linux 平台上玩游戏,同时很喜欢街头霸王 V 的人之一吗?是的话,我有一些好消息要告诉你。
|
||||
|
||||
>Capcom 已经宣布,这个春天街头霸王 V 通过 Stream 进入 StreamOS 以及其他 Linux 发行版。它无需任何额外的成本,所以那些已经个人电脑建立的游戏的人可以很容易在 Linux 上安装它,并且运行良好。
|
||||
|
||||
[更多 Destructoid](http://api.viglink.com/api/click?format=go&jsonp=vglnk_145580435418216&key=0a7039c08493c7c51b759e3d13019dbe&libId=iksc5hc8010113at000DL3yrsuvp7&loc=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.infoworld.com%2Farticle%2F3033059%2Flinux%2Fwhat-do-linux-developers-think-of-git-and-github.html&v=1&out=http%3A%2F%2Fsteamcommunity.com%2Fgames%2F310950%2Fannouncements%2Fdetail%2F857177755595160250&ref=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.linux.com%2Fnews%2Fsoftware%2Fapplications%2F886008-what-do-linux-developers-think-of-git-and-github&title=What%20do%20Linux%20developers%20think%20of%20Git%20and%20GitHub%3F%20%7C%20InfoWorld&txt=Capcom%20has%20announced)
|
||||
|
||||
你是否错过了摘要?检查 [Eye On Open home page](http://www.infoworld.com/blog/eye-on-open/) 来获得关于 Linux 和开源的最新的新闻。
|
||||
|
||||
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.infoworld.com/article/3033059/linux/what-do-linux-developers-think-of-git-and-github.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Jim Lynch][a]
|
||||
译者:[mudongliang](https://github.com/mudongliang)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.infoworld.com/author/Jim-Lynch/
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,210 +0,0 @@
|
||||
[Translated] Haohong Wang
|
||||
如何在Ubuntu 15.04/CentOS 7中安装Lighttpd Web server
|
||||
=================================================================================
|
||||
Lighttpd 是一款开源Web服务器软件。Lighttpd 安全快速,符合行业标准,适配性强并且针对高配置环境进行了优化。Lighttpd因其CPU、内存占用小,针对小型CPU加载的快速适配以及出色的效率和速度而从众多Web服务器中脱颖而出。 而Lighttpd诸如FastCGI,CGI,Auth,Out-Compression,URL-Rewriting等高级功能更是那些低配置的服务器的福音。
|
||||
|
||||
以下便是在我们运行Ubuntu 15.04 或CentOS 7 Linux发行版的机器上安装Lighttpd Web服务器的简要流程。
|
||||
|
||||
### 安装Lighttpd
|
||||
|
||||
#### 使用包管理器安装
|
||||
|
||||
这里我们通过使用包管理器这种最简单的方法来安装Lighttpd。只需以sudo模式在终端或控制台中输入下面的指令即可。
|
||||
|
||||
**CentOS 7**
|
||||
|
||||
由于CentOS 7.0官方repo中并没有提供Lighttpd,所以我们需要在系统中安装额外的软件源epel repo。使用下面的yum指令来安装epel。
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install epel-release
|
||||
|
||||
然后,我们需要更新系统及进程为Lighttpd的安装做准备。
|
||||
|
||||
# yum update
|
||||
# yum install lighttpd
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Ubuntu 15.04**
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu 15.04官方repo中包含了Lighttpd,所以只需更新本地repo并使用apt-get指令即可安装Lighttpd。
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get update
|
||||
# apt-get install lighttpd
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### 从源代码安装Lighttpd
|
||||
|
||||
如果想从Lighttpd源码安装最新版本(例如1.4.39),我们需要在本地编译源码并进行安装。首先我们要安装编译源码所需的依赖包。
|
||||
|
||||
# cd /tmp/
|
||||
# wget http://download.lighttpd.net/lighttpd/releases-1.4.x/lighttpd-1.4.39.tar.gz
|
||||
|
||||
下载完成后,执行下面的指令解压缩。
|
||||
|
||||
# tar -zxvf lighttpd-1.4.39.tar.gz
|
||||
|
||||
然后使用下面的指令进行编译。
|
||||
|
||||
# cd lighttpd-1.4.39
|
||||
# ./configure
|
||||
# make
|
||||
|
||||
**注:**在这份教程中,我们安装的是默认配置的Lighttpd。其他诸如高级功能或拓展功能,如对SSL的支持,mod_rewrite,mod_redirect等,需自行配置。
|
||||
|
||||
当编译完成后,我们就可以把它安装到系统中了。
|
||||
|
||||
# make install
|
||||
|
||||
### 设置Lighttpd
|
||||
|
||||
如果有更高的需求,我们可以通过修改默认设置文件,如`/etc/lighttpd/lighttpd.conf`,来对Lighttpd进行进一步设置。 而在这份教程中我们将使用默认设置,不对设置文件进行修改。如果你曾做过修改并想检查设置文件是否出错,可以执行下面的指令。
|
||||
|
||||
# lighttpd -t -f /etc/lighttpd/lighttpd.conf
|
||||
|
||||
#### 使用 CentOS 7
|
||||
|
||||
在CentOS 7中,我们需在Lighttpd默认设置中创设一个例如`/src/www/htdocs`的webroot文件夹。
|
||||
|
||||
# mkdir -p /srv/www/htdocs/
|
||||
|
||||
而后将默认欢迎页面从`/var/www/lighttpd`复制至刚刚新建的目录中:
|
||||
|
||||
# cp -r /var/www/lighttpd/* /srv/www/htdocs/
|
||||
|
||||
### 开启服务
|
||||
|
||||
现在,通过执行systemctl指令来重启数据库服务。
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl start lighttpd
|
||||
|
||||
然后我们将它设置为伴随系统启动自动运行。
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl enable lighttpd
|
||||
|
||||
### 设置防火墙
|
||||
|
||||
如要让我们运行在Lighttpd上的网页和网站能在Internet或相似的网络上被访问,我们需要在防火墙程序中设置打开80端口。由于CentOS 7和Ubuntu15.04都附带Systemd作为默认初始化系统,所以我们安装firewalld作为解决方案。如果要打开80端口或http服务,我们只需执行下面的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=http
|
||||
success
|
||||
# firewall-cmd --reload
|
||||
success
|
||||
|
||||
### 连接至Web Server
|
||||
在将80端口设置为默认端口后,我们就可以默认直接访问Lighttpd的欢迎页了。我们需要根据运行Lighttpd的设备来设置浏览器的IP地址和域名。在本教程中,我们令浏览器指向 [http://lighttpd.linoxide.com/](http://lighttpd.linoxide.com/) 同时将子域名指向它的IP地址。如此一来,我们就可以在浏览器中看到如下的欢迎页面了。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
此外,我们可以将网站的文件添加到webroot目录下,并删除lighttpd的默认索引文件,使我们的静态网站链接至互联网上。
|
||||
|
||||
如果想在Lighttpd Web Server中运行PHP应用,请参考下面的步骤:
|
||||
|
||||
### 安装PHP5模块
|
||||
在Lighttpd成功安装后,我们需要安装PHP及相关模块以在Lighttpd中运行PHP5脚本。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 使用 Ubuntu 15.04
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get install php5 php5-cgi php5-fpm php5-mysql php5-curl php5-gd php5-intl php5-imagick php5-mcrypt php5-memcache php-pear
|
||||
|
||||
#### 使用 CentOS 7
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install php php-cgi php-fpm php-mysql php-curl php-gd php-intl php-pecl-imagick php-mcrypt php-memcache php-pear lighttpd-fastcgi
|
||||
|
||||
### 设置Lighttpd的PHP服务
|
||||
|
||||
如要让PHP与Lighttpd协同工作,我们只要根据所使用的发行版执行如下对应的指令即可。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 使用 CentOS 7
|
||||
|
||||
首先要做的便是使用文件编辑器编辑php设置文件(例如`/etc/php.ini`)并取消掉对**cgi.fix_pathinfo=1**的注释。
|
||||
|
||||
# nano /etc/php.ini
|
||||
|
||||
完成上面的步骤之后,我们需要把PHP-FPM进程的所有权从Apache转移至Lighttpd。要完成这些,首先用文件编辑器打开`/etc/php-fpm.d/www.conf`文件。
|
||||
|
||||
# nano /etc/php-fpm.d/www.conf
|
||||
|
||||
然后在文件中增加下面的语句:
|
||||
|
||||
user = lighttpd
|
||||
group = lighttpd
|
||||
|
||||
做完这些,我们保存并退出文本编辑器。然后从`/etc/lighttpd/modules.conf`设置文件中添加FastCGI模块。
|
||||
|
||||
# nano /etc/lighttpd/modules.conf
|
||||
|
||||
然后,去掉下面语句前面的`#`来取消对它的注释。
|
||||
|
||||
include "conf.d/fastcgi.conf"
|
||||
|
||||
最后我们还需在文本编辑器设置FastCGI的设置文件。
|
||||
|
||||
# nano /etc/lighttpd/conf.d/fastcgi.conf
|
||||
|
||||
在文件尾部添加以下代码:
|
||||
|
||||
fastcgi.server += ( ".php" =>
|
||||
((
|
||||
"host" => "127.0.0.1",
|
||||
"port" => "9000",
|
||||
"broken-scriptfilename" => "enable"
|
||||
))
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
在编辑完成后保存并退出文本编辑器即可。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 使用 Ubuntu 15.04
|
||||
|
||||
如需启用Lighttpd的FastCGI,只需执行下列代码:
|
||||
|
||||
# lighttpd-enable-mod fastcgi
|
||||
|
||||
Enabling fastcgi: ok
|
||||
Run /etc/init.d/lighttpd force-reload to enable changes
|
||||
|
||||
# lighttpd-enable-mod fastcgi-php
|
||||
|
||||
Enabling fastcgi-php: ok
|
||||
Run `/etc/init.d/lighttpd` force-reload to enable changes
|
||||
|
||||
然后,执行下列命令来重启Lighttpd。
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl force-reload lighttpd
|
||||
|
||||
### 检测PHP工作状态
|
||||
|
||||
如需检测PHP是否按预期工作,我们需在Lighttpd的webroot目录下新建一个php文件。本教程中,在Ubuntu下/var/www/html 目录,CentOS下/src/www/htdocs目录下使用文本编辑器创建并打开info.php。
|
||||
|
||||
**使用 CentOS 7**
|
||||
|
||||
# nano /var/www/info.php
|
||||
|
||||
**使用 Ubuntu 15.04**
|
||||
|
||||
# nano /srv/www/htdocs/info.php
|
||||
|
||||
然后只需将下面的语句添加到文件里即可。
|
||||
|
||||
<?php phpinfo(); ?>
|
||||
|
||||
在编辑完成后保存并推出文本编辑器即可。
|
||||
|
||||
现在,我们需根据路径 [http://lighttpd.linoxide.com/info.php](http://lighttpd.linoxide.com/info.php) 下的info.php文件的IP地址或域名,来让我们的网页浏览器指向系统上运行的Lighttpd。如果一切都按照以上说明进行,我们将看到如下图所示的PHP页面信息。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 总结
|
||||
|
||||
至此,我们已经在CentOS 7和Ubuntu 15.04 Linux 发行版上成功安装了轻巧快捷并且安全的Lighttpd Web服务器。现在,我们已经可以利用Lighttpd Web服务器来实现上传网站文件到网站根目录,配置虚拟主机,启用SSL,连接数据库,运行Web应用等功能了。 如果你有任何疑问,建议或反馈请在下面的评论区中写下来以让我们更好的改良Lighttpd。谢谢!(译注:评论网址 http://linoxide.com/linux-how-to/setup-lighttpd-web-server-ubuntu-15-04-centos-7/ )
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/linux-how-to/setup-lighttpd-web-server-ubuntu-15-04-centos-7/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Arun Pyasi][a]
|
||||
译者:[HaohongWANG](https://github.com/HaohongWANG)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arunp/
|
||||
@ -1,36 +0,0 @@
|
||||
构建在开源之上的商业软件市场持续成长
|
||||
=====================================================================
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
> 与会者在 Structure 上听取演讲,Structure Data 2016 也将在 UCSF Mission Bay 会议中心举办。图片来源:Structure Events。
|
||||
|
||||
如今真的很难低估开源项目对于企业软件市场的影响;开源集成如此快速地形成了规范,我们没能捕捉到转折点也情有可原。
|
||||
|
||||
举个例子,Hadoop,改变的不止是数据分析的世界。它引领了新一代数据公司,它们围绕开源项目创造自己的软件,按需调整和支持那些代码,更像红帽在 90 年代和 21 世纪早期拥抱 Linux 那样。软件越来越多地通过公有云交付,而不是购买者自己的服务器,拥有了令人惊奇的操作灵活性,但同时也带来了一些关于授权,支持以及价格之类的新问题。
|
||||
|
||||
我们多年来持续追踪这个趋势,它们组成了我们的 Structure Data 会议,而 Structure Data 2016 也不例外。三家围绕 Hadoop 最重要的大数据公司——Hortonworks,Cloudera 和 MapR——的 CEO 将会共同讨论它们是如何销售他们围绕开源项目的企业软件和服务,获利的同时回报那个社区项目。
|
||||
|
||||
以前在企业软件上获利是很容易的事情。一个客户购买了之后,企业供应商的一系列大型软件就变成了它自己的收银机,从维护合同和阶段性升级中获得近乎终生的收入,软件也越来越难以被替代,因为它已经成为了客户的业务核心。客户抱怨这种绑定,但如果它们想提高工作队伍的生产力也确实没有多少选择。
|
||||
|
||||
而现在的情况不再是这样了。尽管无数的公司还陷于在他们的基础设施上运行至关重要的巨大软件包,新的项目被使用开源技术部署到云服务器上。这让升级功能不再需要去掉大量软件包再重新安装别的,同时也让公司按需付费,而不是为一堆永远用不到的特性买单。
|
||||
|
||||
有很多客户想要利用开源项目的优势,而又不想建立和支持一支工程师队伍来调整开源项目以满足自己的需求。这些客户愿意为开源项目和在这之上的专有特性之间的差异付费。
|
||||
|
||||
这对于基础设施相关的软件来说格外正确。当然,你的客户们可以安装他们自己对项目的调整,比如 Hadoop,Spark 或 Node.js,但付费可以帮助他们自定义包部署如今重要的开源技术而不用自己干这些活儿。只需看看 Structure Data 2016 的发言者就明白了,比如 Confluent(Kafka),Databricks(Spark),以及 Cloudera-Hortonworks-MapR(Hadoop)三人组。
|
||||
|
||||
当然还有一个值得提到的是在出错的时候有个供应商给你指责。如果你的工程师弄糟了开源项目的实现,那你只能怪你自己了。但是如果你和一个愿意保证在服务级别的特定性能和正常运行时间指标的公司签订了合同,你就是愿意为支持,指导,以及在突然出现不可避免的问题时朝你公司外的人发火的机会买单。
|
||||
|
||||
构建在开源之上的商业软件市场的持续成长是我们在 Structure Data 上追踪多年的内容,如果这个话题正合你意,我们鼓励你加入我们,在旧金山,3 月 9 日和 10 日。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://www.linux.com/news/enterprise/cloud-computing/889564-the-evolving-market-for-commercial-software-built-on-open-source-
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Tom Krazit ][a]
|
||||
译者:[alim0x](https://github.com/alim0x)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: https://www.linux.com/community/forums/person/70513
|
||||
@ -1,86 +0,0 @@
|
||||
最牛的五个Linux开源command shell
|
||||
===============================================
|
||||
|
||||
关键字: shell , Linux , bash , zsh , fish , ksh , tcsh , license
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
这个世界上有两种Linux用户:敢于冒险的和态度谨慎的。
|
||||
|
||||
其中一类用户总是本能的去尝试任何能够戳中其痛点的新选择。他们尝试过不计其数的窗口管理器、系统发行版和几乎所有能找到的桌面插件。
|
||||
|
||||
另一类用户找到他们喜欢的东西后,会一直使用下去。他们往往喜欢所使用的系统发行版的默认选项。最先熟练掌握的文本编辑器会成为他们最钟爱的那一个。
|
||||
|
||||
作为一个使用桌面版和服务器版十五年之久的Linux用户,比起第一类来,我无疑属于第二类用户。我更倾向于使用现成的东西,如此一来,很多时候我就可以通过文档和示例方便地找到我所需要的使用案例。如果我决定选择使用非费标准的东西,这个切换过程一定会基于细致的研究,并且前提是来自挚友的大力推荐。
|
||||
|
||||
但这并不意味着我不喜欢尝试新事物并且查漏补失。所以最近一段时间,在我不假思索的使用了bash shell多年之后,决定尝试一下另外四个shell工具:ksh, tcsh, zsh, 和 fish. 这四个shell都可以通过我所以用的Fedora系统的默认库轻松安装,并且他们可能已经内置在你所使用的系统发行版当中了。
|
||||
|
||||
这里对每个选择都稍作介绍,并且阐述下它适合做为你的下一个Linux命令行解释器的原因所在。
|
||||
|
||||
### bash
|
||||
|
||||
首先,我们回顾一下最为熟悉的一个。 [GNU Bash][1],又名 Bourne Again Shell,它是我这些年使用过的众多Linux发行版的默认选择。它最初发布于1989年,并且轻松成长为Linux世界中使用最广泛的shell,甚至常见于其他一些类Unix系统当中。
|
||||
|
||||
Bash是一个广受赞誉的shell,当你通过互联网寻找各种事情解决方法所需的文档时,总能够无一例外的发现这些文档都默认你使用的是bash shell。但Bash也有一些缺点存在,如果你写过Bash脚本就会发现我们写的代码总是得比真正所需要的多那么几行。这并不是说有什么事情是它做不到的,而是说它读写起来并不总是那么直观,至少是不够优雅。
|
||||
|
||||
如上所述,基于其巨大的安装量,并且考虑到各类专业和非专业系统管理员已经适应了它的使用方式和独特之处,至少在将来一段时间内,bash或许会一直存在。
|
||||
|
||||
### ksh
|
||||
|
||||
[KornShell][4],或许你对这个名字并不熟悉,但是你一定知道它的调用命令 ksh。这个替代性的shell于80年代起源于贝尔实验室,由David Korn所写。虽然最初是一个专有软件,但是后期版本是在[Eclipse Public 许可][5]下发布的。
|
||||
|
||||
ksh的拥趸们列出了他们觉得其优越的诸多理由,包括更好的循环语法,清晰的管道退出代码,更简单的方式来处理重复命令和关联数组。它能够模拟vi和emacs的许多行为,所以如果你是一个重度文本编辑器患者,它值得你一试。最后,我发现它虽然在高级脚本方面拥有不同的体验,但在基本输入方面与bash如出一辙。
|
||||
|
||||
### tcsh
|
||||
|
||||
[Tcsh][6]衍生于csh(Berkely Unix C shell),并且可以追溯到早期的Unix和计算本身。
|
||||
|
||||
Tcsh最大的卖点在于它的脚本语言,对于熟悉C语言编程的人来说,看起来会非常亲切。Tcsh的脚本编写有人喜欢,有人憎恶。但是它也有其他的技术特色,包括可以为aliases添加参数,各种可能迎合你偏好的默认行为,包括tab自动完成和将tab完成的工作记录下来以备后查。
|
||||
|
||||
你可以在[BSD 许可][7]下找到tcsh。
|
||||
|
||||
### zsh
|
||||
|
||||
[Zsh][8]是另外一个与bash和ksh有着相似之处的shell。产生于90年代初,zsh支持众多有用的新技术,包括拼写纠正,主题化,可命名的目录快捷键,在多个终端中分享命令历史信息和各种相对于original Bourne shell的轻微调整。
|
||||
|
||||
虽然部分需要遵照GPL许可,但zsh的代码和二进制文件可以在MIT-like许可下进行分发; 你可以在 [actual license][9] 中查看细节。
|
||||
|
||||
### fish
|
||||
|
||||
之前我访问了[fish][10]的主页,当看到 “好了,这是一个为90年代而生的命令行shell” 这条略带调侃的介绍时(fish完成于2005年),我就意识到我会爱上这个交互友好的shell的。
|
||||
|
||||
Fish的作者提供了若干切换过来的理由,shell中所有的不太实用的调用都有点小幽默并且能戳中笑点。这些特性包括自动建议("Watch out, Netscape Navigator 4.0"),支持“惊人”的256色VGA调色,不过也有真正有用的特性,包括根据机器的man页面自动补全命令,清除脚本和基于web的配置。
|
||||
|
||||
Fish的许可主要基于第二版GPL,但有些部分是在其他许可下的。你可以查看资源库来了解[完整信息][11]
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想要寻找关于每个选择确切不同之处的详尽纲要,[这个网站][12]应该可以帮到你。
|
||||
|
||||
我的立场到底是怎样的呢?好吧,最终我应该还是会重新投入bash的怀抱,因为对于大多数时间都在使用命令行交互的人来说,切换过程对于高级脚本能带来的好处微乎其微,并且我已经习惯于使用bash了。
|
||||
|
||||
但是我很庆幸做出了敞开大门并且尝试新选择的决定。我知道门外还有许许多多其他的东西。你尝试过哪些shell,更中意哪一个?请在评论里告诉我们。
|
||||
|
||||
本文来源: https://opensource.com/business/16/3/top-linux-shells
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Jason Baker][a]
|
||||
译者:[mr-ping](https://github.com/mr-ping)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://opensource.com/users/jason-baker
|
||||
|
||||
[1]: https://www.gnu.org/software/bash/
|
||||
[2]: http://mywiki.wooledge.org/BashPitfalls
|
||||
[3]: http://www.gnu.org/licenses/gpl.html
|
||||
[4]: http://www.kornshell.org/
|
||||
[5]: https://www.eclipse.org/legal/epl-v10.html
|
||||
[6]: http://www.tcsh.org/Welcome
|
||||
[7]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/BSD_licenses
|
||||
[8]: http://www.zsh.org/
|
||||
[9]: https://sourceforge.net/p/zsh/code/ci/master/tree/LICENCE
|
||||
[10]: https://fishshell.com/
|
||||
[11]: https://github.com/fish-shell/fish-shell/blob/master/COPYING
|
||||
[12]: http://hyperpolyglot.org/unix-shells
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,21 +1,20 @@
|
||||
ictlyh Translating
|
||||
How to Use Awk to Print Fields and Columns in File
|
||||
如何使用 Awk 打印文件中的字段和列
|
||||
===================================================
|
||||
|
||||
In this part of our [Linux Awk command series][1], we shall have a look at one of the most important features of Awk, which is field editing.
|
||||
在 [Linux Awk 命令系列介绍][1] 的这部分,我们来看一下 awk 最重要的功能之一,字段编辑。
|
||||
|
||||
It is good to know that Awk automatically divides input lines provided to it into fields, and a field can be defined as a set of characters that are separated from other fields by an internal field separator.
|
||||
首先我们要知道 Awk 会自动把输入的行切分为字段,字段可以定义为是一些字符集,这些字符集和其它字段被内部字段分隔符分离。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>Awk Print Fields and Columns
|
||||
>Awk 输出字段和列
|
||||
|
||||
If you are familiar with the Unix/Linux or do [bash shell programming][2], then you should know what internal field separator (IFS) variable is. The default IFS in Awk are tab and space.
|
||||
如果你熟悉 Unix/Linux 或者懂得 [bash shell 编程][2],那么你也应该知道内部字段分隔符(IFS)变量。Awk 默认的 IFS 是 tab 和空格。
|
||||
|
||||
This is how the idea of field separation works in Awk: when it encounters an input line, according to the IFS defined, the first set of characters is field one, which is accessed using $1, the second set of characters is field two, which is accessed using $2, the third set of characters is field three, which is accessed using $3 and so forth till the last set of character(s).
|
||||
Awk 字段切分的工作原理如下:当获得一行输入时,根据定义的 IFS,第一个字符集是字段一,用 $1 表示,第二个字符集是字段二,用 $2 表示,第三个字符集是字段三,用 $3 表示,以此类推直到最后一个字符集。
|
||||
|
||||
To understand this Awk field editing better, let us take a look at the examples below:
|
||||
为了更好的理解 Awk 的字段编辑,让我们来看看下面的例子:
|
||||
|
||||
**Example 1**: I have created a text file called tecmintinfo.txt.
|
||||
**事例 1:**: 我创建了一个名为 tecmintinfo.txt 的文件。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# vi tecmintinfo.txt
|
||||
@ -23,24 +22,23 @@ To understand this Awk field editing better, let us take a look at the examples
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>Create File in Linux
|
||||
>在 Linux 中创建文件
|
||||
|
||||
Then from the command line, I try to print the first, second and third fields from the file tecmintinfo.txt using the command below:
|
||||
然后在命令行中使用以下命令打印 tecmintinfo.txt 文件中的第一、第二和第三个字段。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ awk '//{print $1 $2 $3 }' tecmintinfo.txt
|
||||
TecMint.comisthe
|
||||
```
|
||||
从上面的输出中你可以看到,三个字段中的第一个是按照定义的 IFS,也就是空格,打印的。
|
||||
|
||||
From the output above, you can see that the characters from the first three fields are printed based on the IFS defined which is space:
|
||||
- 字段一 “TecMint.com” 使用 $1 访问。
|
||||
- 字段二 “is” 通过 $2 访问。
|
||||
- 字段三 “the” 通过 $3 访问。
|
||||
|
||||
- Field one which is “TecMint.com” is accessed using $1.
|
||||
- Field two which is “is” is accessed using $2.
|
||||
- Field three which is “the” is accessed using $3.
|
||||
如果你注意打印的输出,可以看到字段值之间并没有分隔开,这是 print 默认的方式。
|
||||
|
||||
If you have noticed in the printed output, the field values are not separated and this is how print behaves by default.
|
||||
|
||||
To view the output clearly with space between the field values, you need to add (,) operator as follows:
|
||||
为了在字段值之间加入空格,你需要像下面这样添加(,)分隔符:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ awk '//{print $1, $2, $3; }' tecmintinfo.txt
|
||||
@ -48,11 +46,11 @@ $ awk '//{print $1, $2, $3; }' tecmintinfo.txt
|
||||
TecMint.com is the
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
One important thing to note and always remember is that the use of ($) in Awk is different from its use in shell scripting.
|
||||
很重要而且必须牢记的一点是,Awk 中 ($) 的使用和在 shell 脚本中不一样。
|
||||
|
||||
Under shell scripting ($) is used to access the value of variables while in Awk ($) it is used only when accessing the contents of a field but not for accessing the value of variables.
|
||||
在 shell 脚本中 ($) 用于获取变量的值,而在 Awk 中 ($) 只用于获取一个字段的内容,而不能用于获取变量的值。
|
||||
|
||||
**Example 2**: Let us take a look at one other example using a file which contains multiple lines called my_shoping.list.
|
||||
**事例2**: 让我们再看一个使用多行文件 my_shoping.list 的例子。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
No Item_Name Unit_Price Quantity Price
|
||||
@ -62,7 +60,7 @@ No Item_Name Unit_Price Quantity Price
|
||||
4 Ethernet_Cables #30,000 4 #120,000
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Say you wanted to only print Unit_Price of each item on the shopping list, you will need to run the command below:
|
||||
假设你只想打印购物清单中每个物品的 Unit_Price,你需要允许下面的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ awk '//{print $2, $3 }' my_shopping.txt
|
||||
@ -74,9 +72,9 @@ RAM_Chips #150,000
|
||||
Ethernet_Cables #30,000
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Awk also has a printf command that helps you to format your output is a nice way as you can see the above output is not clear enough.
|
||||
Awk 也有一个 printf 命令,它能帮助你用更好的方式格式化输出,正如你可以看到上面的输出并不清晰。
|
||||
|
||||
Using printf to format output of the Item_Name and Unit_Price:
|
||||
使用 printf 格式化输出 Item_Name 和 Unit_Price:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ awk '//{printf "%-10s %s\n",$2, $3 }' my_shopping.txt
|
||||
@ -88,18 +86,18 @@ RAM_Chips #150,000
|
||||
Ethernet_Cables #30,000
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Summary
|
||||
### 总结
|
||||
|
||||
Field editing is very important when using Awk to filter text or strings, it helps you get particular data in columns in a list. And always remember that the use of ($) operator in Awk is different from that in shell scripting.
|
||||
使用 Awk 进行文本和字符串过滤时字段编辑功能非常重要,它能帮助你从列表中获取列的特定数据。同时需要记住 Awk 中 ($) 操作符和 shell 脚本中不一样。
|
||||
|
||||
I hope the article was helpful to you and for any additional information required or questions, you can post a comment in the comment section.
|
||||
我希望这篇文章能对你有所帮助,如果你需要获取其它信息或者有任何疑问,都可以在下面的评论框中告诉我们。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/awk-print-fields-columns-with-space-separator/?utm_source=feedburner&utm_medium=feed&utm_campaign=Feed%3A+tecmint+%28Tecmint%3A+Linux+Howto%27s+Guide%29
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Aaron Kili][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
译者:[ictlyh](https://github.com/ictlyh)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,302 @@
|
||||
在 Ubuntu 16.04 为 Nginx 服务器安装 LEMP 环境(MariaDB, PHP 7 并且支持 HTTP 2.0)
|
||||
=====================
|
||||
|
||||
LEMP 是字首组合词,代表一组软件包(Linux OS,Nginx 网络服务器,MySQL\MariaDB 数据库和 PHP 服务端动态编程语言),它被用来搭建动态的网络应用和网页。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>在 Ubuntu 16.04 安装 Nginx 以及 MariaDB,PHP7 并且支持 HTTP 2.0
|
||||
|
||||
这篇教程会教你怎么在 Ubuntu 16.04 的服务器上安装 LEMP (Nginx 和 MariaDB 以及 PHP7)。
|
||||
|
||||
准备
|
||||
|
||||
[安装 Ubuntu 16.04 服务器版本][1]
|
||||
|
||||
### 步骤 1:安装 Nginx 服务器
|
||||
|
||||
#### 1. Nginx 是一个先进的、资源优化的网络服务器程序,用来向因特网上的访客展示网页。我们从 Nginx 服务器的安装开始介绍,使用 [apt 命令][2] 从 Ubuntu 的官方软件仓库中获取 Nginx 程序。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install nginx
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>在 Ubuntu 16.04 安装 Nginx
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2. 然后输入 [netstat][3] 和 [systemctl][4] 命令,确认 Nginx 进程已经启动并且绑定在 80 端口。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ netstat -tlpn
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>检查 Nginx 网络端口连接
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo systemctl status nginx.service
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>检查 Nginx 服务状态
|
||||
|
||||
当你确认服务进程已经启动了,你可以打开一个浏览器,使用 HTTP 协议访问你的服务器 IP 地址或者域名,浏览 Nginx 的默认网页。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
http://IP-Address
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>验证 Nginx 网页
|
||||
|
||||
### 步骤 2:启用 Nginx HTTP/2.0 协议
|
||||
|
||||
#### 3. HTTP/2.0 协议默认包含在 Ubuntu 16.04 最新发行版的 Nginx 二进制文件中,它只能通过 SSL 连接并且保证加载网页的速度有巨大提升。
|
||||
|
||||
要启用Nginx 的这个协议,首先找到 Nginx 提供的网站配置文件,输入下面这个命令备份配置文件。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ cd /etc/nginx/sites-available/
|
||||
$ sudo mv default default.backup
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>备份 Nginx 的网站配置文件
|
||||
|
||||
#### 4. 然后,用文本编辑器新建一个默认文件,输入以下内容:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
server {
|
||||
listen 443 ssl http2 default_server;
|
||||
listen [::]:443 ssl http2 default_server;
|
||||
|
||||
root /var/www/html;
|
||||
|
||||
index index.html index.htm index.php;
|
||||
|
||||
server_name 192.168.1.13;
|
||||
|
||||
location / {
|
||||
try_files $uri $uri/ =404;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
ssl_certificate /etc/nginx/ssl/nginx.crt;
|
||||
ssl_certificate_key /etc/nginx/ssl/nginx.key;
|
||||
|
||||
ssl_protocols TLSv1 TLSv1.1 TLSv1.2;
|
||||
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
|
||||
ssl_ciphers EECDH+CHACHA20:EECDH+AES128:RSA+AES128:EECDH+AES256:RSA+AES256:EECDH+3DES:RSA+3DES:!MD5;
|
||||
ssl_dhparam /etc/nginx/ssl/dhparam.pem;
|
||||
ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:20m;
|
||||
ssl_session_timeout 180m;
|
||||
resolver 8.8.8.8 8.8.4.4;
|
||||
add_header Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=31536000;
|
||||
#includeSubDomains" always;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
location ~ \.php$ {
|
||||
include snippets/fastcgi-php.conf;
|
||||
fastcgi_pass unix:/run/php/php7.0-fpm.sock;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
location ~ /\.ht {
|
||||
deny all;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
server {
|
||||
listen 80;
|
||||
listen [::]:80;
|
||||
server_name 192.168.1.13;
|
||||
return 301 https://$server_name$request_uri;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>启用 Nginx HTTP 2 协议
|
||||
|
||||
上面的配置片段向所有的 SSL 监听指令中添加 http2 参数来启用 `HTTP/2.0`。
|
||||
|
||||
添加到服务器配置的最后一段,是用来将所有非 SSL 的流量重定向到 SSL/TLS 默认主机。然后用你主机的 IP 地址或者 DNS 记录(优先 FQDN)替换掉 `server_name` 选项。 (directive 的翻译是指令,但我觉得翻译成选项更好)
|
||||
|
||||
#### 5. 当你按照以上步骤编辑完 Nginx 的默认配置文件之后,用下面这些命令来生成、查看 SSL 证书和密钥。
|
||||
|
||||
用你自定义的设置完成证书的制作,注意常用名设置成和你的 DNS FQDN 记录或者服务器 IP 地址相匹配,DNS 记录或者 IP 地址是用来访问网页的。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo mkdir /etc/nginx/ssl
|
||||
$ sudo openssl req -x509 -nodes -days 365 -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout /etc/nginx/ssl/nginx.key -out /etc/nginx/ssl/nginx.crt
|
||||
$ ls /etc/nginx/ssl/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>生成 Nginx 的 SSL 证书和密钥
|
||||
|
||||
#### 6. 通过输入以下命令使用一个强 DH 加密算法,在之前的配置文件 `ssl_dhparam` 这一行中进行修改。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo openssl dhparam -out /etc/nginx/ssl/dhparam.pem 2048
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>创建 Diffie-Hellman 密钥
|
||||
|
||||
#### 7. 当 `Diffie-Hellman` 密钥生成之后,验证 Nginx 的配置文件是否正确、能否被 Nginx 网络服务程序应用。然后运行以下命令重启守护进程来观察有什么变化。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo nginx -t
|
||||
$ sudo systemctl restart nginx.service
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>检查 Nginx 的配置
|
||||
|
||||
#### 8. 键入下面的命令来测试 Nginx 使用的是 HTTP/2.0 协议。看到协议中有 `h2` 的话,表明 Nginx 已经成功配置使用 HTTP/2.0 协议。所有最新的浏览器默认都能够支持这个协议。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ openssl s_client -connect localhost:443 -nextprotoneg ''
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>测试 Nginx HTTP 2.0 协议
|
||||
|
||||
### 第 3 步:安装 PHP 7 解释器
|
||||
|
||||
通过 FastCGI 进程管理程序的协助,Nginx 能够使用 PHP 动态语言解释器生成动态网络内容。FastCGI 能够从 Ubuntu 官方仓库中安装 php-fpm 二进制包来获取。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 9. 在你的服务器控制台里输入下面的命令来获取 PHP7.0 和扩展包,这能够让 PHP 与 Nginx 网络服务进程通信,
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo apt install php7.0 php7.0-fpm
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>安装 PHP 7 以及 PHP-FPM
|
||||
|
||||
#### 10. 当 PHP7.0 解释器安装成功后,输入以下命令启动或者检查 php7.0-fpm 守护进程:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo systemctl start php7.0-fpm
|
||||
$ sudo systemctl status php7.0-fpm
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>开启、验证 php-fpm 服务
|
||||
|
||||
#### 11. 当前的 Nginx 配置文件已经配置了使用 PHP FPM 来提供动态内容。
|
||||
|
||||
下面给出的这部分服务器配置让 Nginx 能够使用 PHP 解释器,所以不需要对 Nginx 配置文件作别的修改。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
location ~ \.php$ {
|
||||
include snippets/fastcgi-php.conf;
|
||||
fastcgi_pass unix:/run/php/php7.0-fpm.sock;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
下面是的截图是 Nginx 默认配置文件的内容。你可能需要对其中的代码进行修改或者取消注释。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>启用 PHP FastCGI
|
||||
|
||||
#### 12. 要测试启用了 PHP-FPM 的 Nginx 服务器,用下面的命令创建一个 PHP 测试配置文件 `info.php`。接着用 `http://IP_or domain/info.php` 这个网址来查看配置。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo su -c 'echo "<?php phpinfo(); ?>" |tee /var/www/html/info.php'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>创建 PHP Info 文件
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>检查 PHP FastCGI 的信息
|
||||
|
||||
检查服务器是否应用 HTTP/2.0 协议,定位到 PHP 变量区域中的 `$_SERVER[‘SERVER_PROTOCOL’]` 就像下面这张截图一样。(advertised by server 翻译不清楚,这里翻译成服务器应用了 HTTP/2.0 协议)
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>检查 HTTP2.0 协议信息
|
||||
|
||||
#### 13. 为了安装其它的 PHP7.0 模块,使用 `apt search php7.0` 命令查找 php 的模块然后安装。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想要 [安装 WordPress][5] 或者别的 CMS,需要安装以下的 PHP 模块,这些模块迟早有用。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo apt install php7.0-mcrypt php7.0-mbstring
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>安装 PHP 7 模块
|
||||
|
||||
#### 14. 注册 PHP 额外的模块,输入下面的命令重启 PHP-FPM 守护进程。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo systemctl restart php7.0-fpm.service
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 第 4 步:安装 MariaDB 数据库
|
||||
|
||||
#### 15. 最后,我们需要 MariaDB 数据库来存储、管理网站数据来完成搭建 LEMP
|
||||
|
||||
运行下面的命令安装 MariaDB 数据库管理系统,重启 PHP-FPM 服务使用 MySQL 模块与数据库通信。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo apt install mariadb-server mariadb-client php7.0-mysql
|
||||
$ sudo systemctl restart php7.0-fpm.service
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>安装 MariaDB
|
||||
|
||||
#### 16. 为了保证 MariaDB 的安装,运行来自 Ubuntu 软件仓库中的二进制包提供的安全脚本,这会询问你设置一个根用户密码,移除匿名用户,禁用根用户远程登陆,移除测试数据库。
|
||||
|
||||
输入下面的命令运行脚本,并且确认所有的选择。参照下面的截图。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo mysql_secure_installation
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>MariaDB 的安全安装
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 17. 配置 MariaDB 以便普通用户能够不使用 系统的 sudo 权限来访问数据库。用根用户权限打开 MySQL 命令行界面,运行下面的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo mysql
|
||||
MariaDB> use mysql;
|
||||
MariaDB> update user set plugin=’‘ where User=’root’;
|
||||
MariaDB> flush privileges;
|
||||
MariaDB> exit
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>MariaDB 的用户权限
|
||||
|
||||
最后登陆到 MariaDB 数据库,通过以下命令不使用 root 权限执行任意一个命令:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ mysql -u root -p -e 'show databases'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>查看 MariaDB 数据库
|
||||
|
||||
好了!现在你拥有了配置在 **Ubuntu 16.04** 服务器上的 **LEMP** 环境,你能够部署能够与数据库交互的复杂动态网络应用。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/install-nginx-mariadb-php7-http2-on-ubuntu-16-04/?utm_source=feedburner&utm_medium=feed&utm_campaign=Feed%3A+tecmint+%28Tecmint%3A+Linux+Howto%27s+Guide%29
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Matei Cezar ][a]
|
||||
译者:[GitFuture](https://github.com/GitFuture)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: http://www.tecmint.com/author/cezarmatei/
|
||||
[1]: http://www.tecmint.com/installation-of-ubuntu-16-04-server-edition/
|
||||
[2]: http://www.tecmint.com/apt-advanced-package-command-examples-in-ubuntu/
|
||||
[3]: http://www.tecmint.com/20-netstat-commands-for-linux-network-management/
|
||||
[4]: http://www.tecmint.com/manage-services-using-systemd-and-systemctl-in-linux/
|
||||
[5]: http://www.tecmint.com/install-wordpress-using-lamp-or-lemp-on-rhel-centos-fedora/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,285 @@
|
||||
学习使用 python 控制流和循环来编写和执行 Shell 脚本 —— Part 2
|
||||
======================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
在[Python series][1]之前的文章里,我们分享了 Python的一个简介,它的命令行 shell 和 IDLE(译者注:python 自带的一个IDE)。我们也演示了如何进行数值运算,如何用变量存储值,还有如何打印那些值到屏幕上。最后,我们通过一个练习示例讲解了面向对象编程中方法和属性概念。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>在 Python 编程中写 Linux Shell 脚本
|
||||
|
||||
本篇中,我嫩会讨论控制流(根据用户输入的信息,计算的结果,或者一个变量的当前值选择不同的动作行为)和循环(自动重复执行任务),接着应用到我们目前所学东西中,编写一个简单的 shell 脚本,这个脚本会显示操作系统类型,主机名,内核发行版,版本号和机器硬件名字。
|
||||
|
||||
这个例子尽管很基础,但是会帮助我们证明,比起使用一些 bash 工具写 shell 脚本,我们可以使得用 Python OOP 的兼容特性来编写 shell 脚本会更简单些。
|
||||
|
||||
换句话说,我们想从这里出发
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# uname -snrvm
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
> 检查 Linux 的主机号
|
||||
|
||||
到
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
> 用 Python 脚本来检查 Linux 的主机号
|
||||
|
||||
或者
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
> 用脚本检查 Linux 系统信息
|
||||
|
||||
看着不错,不是吗?那我们就挽起袖子,开干吧。
|
||||
|
||||
### Python 中的控制流
|
||||
|
||||
如我们刚说那样,控制流允许我们根据一个给定的条件,选择不同的输出结果。在 Python 中最简单的实现就是一个 if/else 语句。
|
||||
|
||||
基本语法是这样的:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
if condition:
|
||||
# action 1
|
||||
else:
|
||||
# action 2
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
当 condition 求值为真(true),下面的代码块就会被执行(`# action 1`代表的部分)。否则,else 下面的代码就会运行。
|
||||
condition 可以是任何表达式,只要可以求得值为真或者假。
|
||||
|
||||
举个例子:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 1 < 3 # 真
|
||||
|
||||
2. firstName == "Gabriel" # 对 firstName 为 Gabriel 的人是真,对其他不叫 Gabriel 的人为假
|
||||
|
||||
- 在第一个例子中,我们比较了两个值,判断 1 是否小于 3。
|
||||
- 在第二个例子中,我们比较了 firstName(一个变量)与字符串 “Gabriel”,看在当前执行的位置,firstName 的值是否等于该字符串。
|
||||
- 条件和 else 表达式都必须带着一个冒号(:)。
|
||||
- 缩进在 Python 非常重要。同样缩进下的行被认为是相同的代码块。
|
||||
|
||||
请注意,if/else 表达式只是 Python 中许多控制流工具的一个而已。我们先在这里了解以下,后面会用在我们的脚本中。你可以在[官方文档][2]中学到更多工具。
|
||||
|
||||
### Python 中的循环
|
||||
|
||||
简单来说,一个循环就是一组指令或者表达式序列,可以按顺序一直执行,只要一个条件为真,或者在一个列表里一次执行一个条目。
|
||||
|
||||
Python 中最简单的循环,就是 for 循环迭代一个给定列表的元素,或者一个字符串从第一个字符开始到最后一个字符结束。
|
||||
|
||||
基本语句:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
for x in example:
|
||||
# do this
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
这里的 example 可以是一个列表或者一个字符串。如果是列表,变量 x 就代表列表中每个元素;如果是字符串,x 就代表字符串中每个字符。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
>>> rockBands = []
|
||||
>>> rockBands.append("Roxette")
|
||||
>>> rockBands.append("Guns N' Roses")
|
||||
>>> rockBands.append("U2")
|
||||
>>> for x in rockBands:
|
||||
print(x)
|
||||
or
|
||||
>>> firstName = "Gabriel"
|
||||
>>> for x in firstName:
|
||||
print(x)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
上面例子的输出如下图所示:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>学习 Python 中的循环
|
||||
|
||||
### Python 模块
|
||||
|
||||
很明显,必须有个途径可以保存一系列的 Python 指令和表达式到文件里,然后需要的时候再取出来。
|
||||
|
||||
准确来说模块就是这样的。特别地,os 模块提供了一个接口到操作系统的底层,允许我们做许多通常在命令行下的操作。
|
||||
|
||||
没错,os 模块包含了许多方法和属性,可以用来调用,就如我们之前文章里讲解的那样。尽管如此,我们需要使用 import 关键词导入(或者叫包含)模块到开发环境里来:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
>>> import os
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
我们来打印出当前的工作目录:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
>>> os.getcwd()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
>学习 Python 模块
|
||||
|
||||
现在,让我们把所有结合在一起(包括之前文章里讨论的概念),编写需要的脚本。
|
||||
|
||||
### Python 脚本
|
||||
|
||||
以一个声明开始一个脚本是个不错的想法,表明脚本的目的,发行所依据的证书,和一个修订历史列出所做的修改。尽管这主要是个人喜好,但这会让我们的工作看起来比较专业。
|
||||
|
||||
这里有个脚本,可以输出这篇文章最前面展示的那样。脚本做了大量的注释,为了让大家可以理解发生了什么。
|
||||
|
||||
在进行下一步之前,花点时间来理解它。注意,我们是如何使用一个 if/else 结构,判断每个字段标题的长度是否比字段本身的值还大。
|
||||
|
||||
基于这个结果,我们用空字符去填充一个字段标题和下一个之间的空格。同时,我们使用一定数量的短线作为字段标题与其值之间的分割符。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/python3
|
||||
# Change the above line to #!/usr/bin/python if you don't have Python 3 installed
|
||||
|
||||
# Script name: uname.py
|
||||
# Purpose: Illustrate Python's OOP capabilities to write shell scripts more easily
|
||||
# License: GPL v3 (http://www.gnu.org/licenses/gpl.html)
|
||||
|
||||
# Copyright (C) 2016 Gabriel Alejandro Cánepa
|
||||
# Facebook / Skype / G+ / Twitter / Github: gacanepa
|
||||
# Email: gacanepa (at) gmail (dot) com
|
||||
|
||||
# This program is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
|
||||
# it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
|
||||
# the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
|
||||
# (at your option) any later version.
|
||||
|
||||
# This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
|
||||
# but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
|
||||
# MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
|
||||
# GNU General Public License for more details.
|
||||
|
||||
# You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
|
||||
# along with this program. If not, see .
|
||||
|
||||
# REVISION HISTORY
|
||||
# DATE VERSION AUTHOR CHANGE DESCRIPTION
|
||||
# ---------- ------- --------------
|
||||
# 2016-05-28 1.0 Gabriel Cánepa Initial version
|
||||
|
||||
# Import the os module
|
||||
import os
|
||||
|
||||
# Assign the output of os.uname() to the the systemInfo variable
|
||||
# os.uname() returns a 5-string tuple (sysname, nodename, release, version, machine)
|
||||
# Documentation: https://docs.python.org/3.2/library/os.html#module-os
|
||||
systemInfo = os.uname()
|
||||
|
||||
# This is a fixed array with the desired captions in the script output
|
||||
headers = ["Operating system","Hostname","Release","Version","Machine"]
|
||||
|
||||
# Initial value of the index variable. It is used to define the
|
||||
# index of both systemInfo and headers in each step of the iteration.
|
||||
index = 0
|
||||
|
||||
# Initial value of the caption variable.
|
||||
caption = ""
|
||||
|
||||
# Initial value of the values variable
|
||||
values = ""
|
||||
|
||||
# Initial value of the separators variable
|
||||
separators = ""
|
||||
|
||||
# Start of the loop
|
||||
for item in systemInfo:
|
||||
if len(item) < len(headers[index]):
|
||||
# A string containing dashes to the length of item[index] or headers[index]
|
||||
# To repeat a character(s), enclose it within quotes followed
|
||||
# by the star sign (*) and the desired number of times.
|
||||
separators = separators + "-" * len(headers[index]) + " "
|
||||
caption = caption + headers[index] + " "
|
||||
values = values + systemInfo[index] + " " * (len(headers[index]) - len(item)) + " "
|
||||
else:
|
||||
separators = separators + "-" * len(item) + " "
|
||||
caption = caption + headers[index] + " " * (len(item) - len(headers[index]) + 1)
|
||||
values = values + item + " "
|
||||
# Increment the value of index by 1
|
||||
index = index + 1
|
||||
# End of the loop
|
||||
|
||||
# Print the variable named caption converted to uppercase
|
||||
print(caption.upper())
|
||||
|
||||
# Print separators
|
||||
print(separators)
|
||||
|
||||
# Print values (items in systemInfo)
|
||||
print(values)
|
||||
|
||||
# INSTRUCTIONS:
|
||||
# 1) Save the script as uname.py (or another name of your choosing) and give it execute permissions:
|
||||
# chmod +x uname.py
|
||||
# 2) Execute it:
|
||||
# ./uname.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果你已经保存上面的脚本到一个文件里,给文件执行权限,并且运行它,像代码底部描述的那样:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# chmod +x uname.py
|
||||
# ./uname.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果试图运行脚本时,你得到了如下的错误:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
-bash: ./uname.py: /usr/bin/python3: bad interpreter: No such file or directory
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
这意味着你没有安装 Python3。如果那样的话,你要么安装 Python3 的包,要么替换解释器那行(如果你跟着下面的步骤去更新 Python 执行文件的软连接,如之前文章里概述的那样,要特别注意并且非常小心):
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/python3
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
为
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/python
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
这样会导致使用安装好的 Python 2 版本去执行该脚本。
|
||||
|
||||
**注意**: 该脚本在 Python 2.x 与 Pyton 3.x 上都测试成功过了。
|
||||
|
||||
尽管比较粗糙,你可以认为该脚本就是一个 Python 模块。这意味着你可以在 IDLE 中打开它(File → Open… → Select file):
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>在 IDLE 中打开 Python
|
||||
|
||||
一个包含有文件内容的新窗口就会打开。然后执行 Run → Run module(或者按 F5)。脚本的输出就会在原 Shell 里显示出来:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>执行 Python 脚本
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想纯粹用 bash 写一个脚本,也获得同样的结果,你可能需要结合使用 [awk][3],[sed][4],并且借助复杂的方法来存储与获得列表中的元素(忘了提醒使用 tr 命令将小写字母转为大写)
|
||||
|
||||
另外,Python 在所有的 Linux 系统版本中集成了至少一个 Python 版本(2.x 或者 3.x,或者两者都有)。你还需要依赖 shell 去完成同样的目标吗,那样你可能会为不同的 shell 编写不同的版本。
|
||||
|
||||
这里演示了面向对象编程的特性,会成为一个系统管理员得力的助手。
|
||||
|
||||
**注意**:你可以在我的 Github 仓库里获得 [这个 python 脚本][5](或者其他的)。
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结
|
||||
|
||||
这篇文章里,我们讲解了 Python 中控制流,循环/迭代,和模块的概念。我们也演示了如何利用 Python 中 OOP 的方法和属性,来简化复杂的 shell 脚本。
|
||||
|
||||
你有任何其他希望去验证的想法吗?开始吧,写出自己的 Python 脚本,如果有任何问题可以咨询我们。不必犹豫,在分割线下面留下评论,我们会尽快回复你。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/learn-python-programming-to-write-linux-shell-scripts/?utm_source=feedburner&utm_medium=feed&utm_campaign=Feed%3A+tecmint+%28Tecmint%3A+Linux+Howto%27s+Guide%29
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Gabriel Cánepa][a]
|
||||
译者:[wi-cuckoo](https://github.com/wi-cuckoo)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: http://www.tecmint.com/author/gacanepa/
|
||||
[1]: http://www.tecmint.com/learn-python-programming-and-scripting-in-linux/
|
||||
[2]: http://please%20note%20that%20the%20if%20/%20else%20statement%20is%20only%20one%20of%20the%20many%20control%20flow%20tools%20available%20in%20Python.%20We%20reviewed%20it%20here%20since%20we%20will%20use%20it%20in%20our%20script%20later.%20You%20can%20learn%20more%20about%20the%20rest%20of%20the%20tools%20in%20the%20official%20docs.
|
||||
[3]: http://www.tecmint.com/use-linux-awk-command-to-filter-text-string-in-files/
|
||||
[4]: http://www.tecmint.com/sed-command-to-create-edit-and-manipulate-files-in-linux/
|
||||
[5]: https://github.com/gacanepa/scripts/blob/master/python/uname.py
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,62 @@
|
||||
在 Ubuntu Mate 16.04("Xenial Xerus") 上通过 PPA 安装 Mate 1.14
|
||||
=================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
Mate 桌面环境 1.14 现在可以在 Ubuntu Mate 16.04("Xenial Xerus") 上使用了。根据这个[发布版本][1]的描述, 为了全面测试 Mate 1.14,所以在 PPA 上发布 Mate 桌面环境 1.14大概了用2个月的时间。因此,你不太可能遇到安装的问题。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**现在 PPA 提供 Mate 1.14.1 包含如下改变(Ubuntu Mate 16.04 默认安装的是 Mate 1.12.x):**
|
||||
|
||||
- 客户端的装饰应用现在可以正确的在所有主题中渲染;
|
||||
- 触摸板配置现在支持边缘操作和双指的滚动;
|
||||
- 在 Caja 中的 Python 扩展可以被单独管理;
|
||||
- 所有三个窗口焦点模式都是是可选的;
|
||||
- Mate Panel 中的所有菜单栏图标和菜单图标可以改变大小;
|
||||
- 音量和亮度 OSD 目前可以启用和禁用;
|
||||
- 更多的改进和 bug 修改;
|
||||
|
||||
Mate 1.14 同时改进了整个桌面环境中对 GTK+3 的支持,包括各种各项的 GTK+3 小应用。但是,Ubuntu MATE 的博客中提到:PPA 的发行包使用 GTK+2编译"为了确保对 Ubuntu MATE 16.05还有各种各样的第三方 MATE 应用,插件,扩展的支持"。
|
||||
|
||||
MATE 1.14 的完成修改列表[点击此处][2]阅读。
|
||||
|
||||
### 在 Ubuntu MATE 16.04 中升级 MATE 1.14.x
|
||||
|
||||
在 Ubuntu MATE 16.04 中打开终端,并且输入如下命令,来从官方的 Xenial MATE PPA 中升级最新的 MATE 桌面环境:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
sudo apt-add-repository ppa:ubuntu-mate-dev/xenial-mate
|
||||
sudo apt update
|
||||
sudo apt dist-upgrade
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**注意**: mate-netspeed 应用将会在升级中删除。因为该应用现在已经是 mate-applets 应用报的一部分,所以他依旧是可以获得的。
|
||||
|
||||
一旦升级完成,请重启你的系统,享受全新的 MATE!
|
||||
|
||||
### 如何回滚这次升级
|
||||
|
||||
如果你并不满意 MATE 1.14, 比如你遭遇了一些 bug 。或者你想回到 MATE 的官方源版本,你可以使用如下的命令清除 PPA,并且下载降级包。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
sudo apt install ppa-purge
|
||||
sudo ppa-purge ppa:ubuntu-mate-dev/xenial-mate
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在所有的 MATE 包降级之后,重启系统。
|
||||
|
||||
via [Ubuntu MATE blog][3]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.webupd8.org/2016/06/install-mate-114-in-ubuntu-mate-1604.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Andrew][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/MikeCoder)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: http://www.webupd8.org/p/about.html
|
||||
[1]: https://ubuntu-mate.org/blog/mate-desktop-114-for-xenial-xerus/
|
||||
[2]: http://mate-desktop.com/blog/2016-04-08-mate-1-14-released/
|
||||
[3]: https://ubuntu-mate.org/blog/mate-desktop-114-for-xenial-xerus/
|
||||
@ -1,141 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Linux新手必知必会的10条Linux基本命令
|
||||
=====================================================================
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
[Linux][1]对我们的生活产生了巨大的冲击。至少你的安卓手机使用的就是Linux核心。尽管如此,在第一次开始使用Linux时你还是会感到难以下手。因为在Linux中,通常需要使用终端命令来取代Windows系统中的点击启动图标操作。但是不必担心,这里我们会介绍10个Linux基本命令来帮助你开启Linux神秘之旅。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 帮助新手走出第一步的10个Linux基本命令
|
||||
|
||||
当我们谈论Linux命令时,实质上是在谈论Linux系统本身。这短短的10个Linux基本命令不会让你变成天才或者Linux专家,但是能帮助你轻松开始Linux之旅。使用这些基本命令会帮助新手们完成Linux的日常任务,由于它们的使用频率如此至高,所以我更乐意称他们为Linux命令之王!
|
||||
|
||||
让我们开始学习这10条Linux基本命令吧。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 1. sudo
|
||||
|
||||
这条命令的意思是“以超级用户的身份执行”,是 SuperUserDo 的简写,它是新手将要用到的最重要的一条Linux命令。当一条单行命令需要root权限的时候,`sudo`命令就派上用场了。你可以在每一条需要root权限的命令前都加上`sudo`。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo su
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2. ls (list)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
跟其他人一样,你肯定也经常想看看目录下都有些什么东西。使用列表命令,终端会把当前工作目录下所有的文件以及文件夹展示给你。比如说,我当前处在 /home 文件夹中,我想看看 /home文件夹中都有哪些文件和目录。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/home$ ls
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
在/home中执行`ls`命令将会返回以下内容
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
imad lost+found
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 3. cd
|
||||
|
||||
变更目录命令(cd)是终端中总会被用到的主要命令。他是最常用到的Linux基本命令之一。此命令使用非常简单,当你打算从当前目录跳转至某个文件夹时,只需要将文件夹键入此命令之后即可。如果你想跳转至上层目录,只需要在此命令之后键入两个点(..)就可以了。
|
||||
|
||||
举个例子,我现在处在/home目录中,我想移动到/home目录中的usr文件夹下,可以通过以下命令来完成操作。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/home $ cd usr
|
||||
|
||||
/home/usr $
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 4. mkdir
|
||||
|
||||
只是可以切换目录还是不够完美。有时候你会想要新建一个文件夹或子文件夹。此时可以使用mkdir命令来完成操作。使用方法很简单,只需要把新的文件夹名跟在mkdir命令之后就好了。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
~$ mkdir folderName
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 5. cp
|
||||
|
||||
拷贝-粘贴(copy-and-paste)是我们组织文件需要用到的重要命令。使用 `cp` 命令可以帮助你在终端当中完成拷贝-粘贴操作。首先确定你想要拷贝的文件,然后键入打算粘贴此文件的目标位置。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ cp src des
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
注意:如果目标目录对新建文件需要root权限时,你可以使用`sudo`命令来完成文件拷贝操作。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 6. rm
|
||||
|
||||
rm命令可以帮助你移除文件甚至目录。如果文件需要root权限才能移除,可以用`-f`参数来强制执行。也可以使用`-r`参数来递归的移除文件夹。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ rm myfile.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 7. apt-get
|
||||
|
||||
这个命令会依据发行版的不同而有所区别。在基于Debian的发行版中,我们拥有Advanced Packaging Tool(APT)包管理工具来安装、移除和升级包。apt-get命令会帮助你安装需要在Linux系统中运行的软件。它是一个功能强大的命令行,可以用来帮助你对软件执行安装、升级和移除操作。
|
||||
|
||||
在其他发行版中,例如Fedora、Centos,都各自不同的包管理工具。Fedora之前使用的是yum,不过现在dnf成了它默认的包管理工具。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get update
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo dnf update
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 8. grep
|
||||
|
||||
当你需要查找一个文件,但是又忘记了它具体的位置和路径时,`grep`命令会帮助你解决这个难题。你可以提供文件的关键字,使用`grep`命令来查找到它。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ grep user /etc/passwd
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 9. cat
|
||||
|
||||
作为一个用户,你应该会经常需要浏览脚本内的文本或者代码。`cat`命令是Linux系统的基本命令之一,它的用途就是将文件的内容展示给你。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ cat CMakeLists.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 10. poweroff
|
||||
|
||||
最后一个命令是 `poweroff`。有时你需要直接在终端中执行关机操作。此命令可以完成这个任务。由于关机操作需要root权限,所以别忘了在此命令之前添加`sudo`。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo poweroff
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结
|
||||
|
||||
如我在文章开始所言,这10条命令并不会让你立即成为一个Linux大拿。它们会让你在初期快速上手Linux。以这些命令为基础,给自己设置一个目标,每天学习一到三条命令,这就是此文的目的所在。在下方评论区分享有趣并且有用的命令。别忘了跟你的朋友分享此文。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxandubuntu.com/home/10-basic-linux-commands-that-every-linux-newbies-should-remember
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Commenti][a]
|
||||
译者:[mr-ping](https://github.com/mr-ping)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: http://www.linuxandubuntu.com/home/10-basic-linux-commands-that-every-linux-newbies-should-remember#comments
|
||||
[1]: http://linuxandubuntu.com/home/category/linux
|
||||
@ -1,103 +0,0 @@
|
||||
PowerPC 获得大端 Android 4.4 系统的移植
|
||||
===========================================================
|
||||
|
||||
eInfochips(一家软件厂商) 已将将 Android 4.4 系统移植到 PowerPC 架构,它将作为一家航空电子客户的人机界面(HMI:Human Machine Interface)用来监视引擎的建康状况。
|
||||
|
||||
eInfochips 已经开发了第一个面向 PowerPC 架构的 CPU 的 Android 移植版本,它使用较新的大端 Android 系统。此移植基于 Android 开源项目[Android Open Source Project (AOSP)] 中 Android 4.4 (KitKat) 的代码,其功能内核的版本号为 3.12.19。
|
||||
|
||||
Android 开始兴起的时候,PowerPC正在快速失去和 ARM 架构共通角逐的市场。高端的网络客户和以市场为导向的嵌入式工具大多运行在诸如飞思卡尔(Freescale)的 PowerQUICC 和 QorIQ 上,而不取决于 Linux 系统。一些 Android 的移植计划最终失败,然而在 2009 年,飞思卡尔和 Embedded Alley(一家软件厂商,当前是 Mentor Graphics 的 Linux 团队的一部分)[宣布了针对 PowerQUICC 和 QorIQ 芯片的移植版本][15],当前由 NXP 公司构建。另一个名为[Android-PowerPC][16] 的项目也作出了相似的工作。
|
||||
|
||||
这些努力来的都并不容易,然而,当航空公司找到 eInfochips,希望能够为他们那些基于 PowerPC 的引擎监控系统添加 Android 应用程序以改善人机界面。此公司找出了这些早期的移植版本,然而,他们都很难达到标准。所以,他们不得不从头开始新的移植。
|
||||
|
||||
最主要的问题是这些移植的 Android 版本实在是太老了,且 very different。Embedded Alley 移植的版本为 Android 1.5 (Cupcake),它于 2009 年发布,Linux 内核版本为 2.6.28。最后一版的移植为 Android-PowerPC 项目的 Android 2.2 (Froyo)它于 2010 年发布,内核版本为 2.6.32。此外,航空公司还有一些额外的技术诉求,例如对大端的支持. 现有的存储器接入方案仍旧应用于网络通信和电信行业。然而那些早期的移植版本仅能够支持小端的存储器访问。
|
||||
|
||||
### 来自 eInfochips 的全新 PowerPC 架构移植
|
||||
|
||||
eInfochips, 它最为出名的应该是那些基于 ARM/骁龙处理器的模块计算机板卡,例如 [Eragon 600][17]。 它已经完成了基于 QorIQ 的 Android 4.4 系统移植,且发布了白皮书描述了此项目。采用该项目的航空电子设备客户仍旧不愿透露姓名,目前仍旧不清楚什么时候会公开此该移植版本。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>图片来自 eInfochips 的博客日志
|
||||
|
||||
- 全新的 PowerPC Android 项目包括:
|
||||
- 基于 PowerPC [e5500][1] 深度定制(bionic 定制不知道什么鬼,校对的时候也可以想想怎么处理)
|
||||
- 基于 Android KitKat 的大端序支持
|
||||
- 开发工具链为 Gcc 5.2
|
||||
- Android 4.4 框架的 PowerPC 支持
|
||||
- PowerPC e5500 的 Android 内核版本为 3.12.19
|
||||
|
||||
根据 eInfochips 的销售经理 Sooryanarayanan Balasubramanian 描述,航空电子客户想要使用 Android 主要是因为熟悉的界面能够缩减培训的时间,并且让程序更新和提供新的程序变得更加容易。他继续解释说:“这次成功的移植了 Android,使得今后的工作仅仅需要在应用层作出修修改改,而不再向以前一样需要在所有层之间作相互的校验。”“这是第一次在航空航天工业作出这些尝试,这需要在设计时作出尽职的调查。”
|
||||
|
||||
通过白皮书,可以知道将 Android 移植到 PowerPC 上需要对框架,核心库,开发工具链,运行时链接器,对象链接器和开源编译工具作出大量的修改。在字节码生成阶段,移植团队决定使用便携模式而不是快速的解释模式。这是因为,还没有 PowerPC 可用的快速解释模式,而使用 [libffi][18] 的便携模式能够支持 PowerPC。
|
||||
|
||||
同时,团队还面临在 Android 运行时 (ART) 环境和 Dalvik 虚拟机 (DVM) 环境之间的选择。他们发现,ART 环境下的便携模式还未经测试且缺乏良好的文档支持,所以最终选择了 DVM 环境下的便携模式。
|
||||
|
||||
白皮书中还提及了其它的一些在移植过程中遇到的困难,包括重新开发工具链,重写脚本以解决 AOSP “非标准”的使用编译器标志的问题。最终,移植提供了 37 个服务,and features a headless Android deployment along with an emulated UI in user space.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 目标硬件
|
||||
|
||||
感谢来自 [eInfochips 博客日志][2] 的图片(如下图所示),我们能够确认此 PowerPC 的 Android 移植项目的硬件平台。这个板卡为 [X-ES Xpedite 6101][3],它是固实的 XMC/PrPMC 夹层模组。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>X-ES Xpedite 6101 照片和框图
|
||||
|
||||
X-ES Xpedite 6101 板卡拥有可选择的 NXP 公司基于 QorIQ T系列通信处理器 T2081, T1042, 和 T1022,他们分别拥有 8 个,4 个和 2 个 e6500 核心,稍有不同的是,T2081 的处理器主频为 1.8GHz,T1042/22 的处理器主频为 1.4GHz。所有的核心都集成了 AltiVec SIMD 引擎,这也就意味着它能够提供 DSP 级别的浮点运算性能。所有以上 3 款 X-ES 板卡都能够支持最高 8GB 的 DDR3-1600 ECC SDRAM 内存。外加 512MB NOR 和 32GB 的 NAND 闪存。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>NXP T2081 框图
|
||||
|
||||
板卡的 I/O 包括一个 x4 PCI Express Gen2 通到,along with dual helpings of Gigabit Ethernet, RS232/422/485 串口和 SATA 3.0 接口。此外,它可选 3 款 QorIQ 处理器,Xpedite 6101 提供了三种[X-ES 加固等级][19],分别是额定工作温度 0 ~ 55°C, -40 ~ 70°C, 或者是 -40 ~ 85°C,且包含 3 类冲击和抗振类别。
|
||||
|
||||
此外,我们已经介绍过的基于 X-ES QorIQ 的 XMC/PrPMC 板卡包括[XPedite6401 和 XPedite6370][20],它们支持已有的板卡级 Linux Linux,Wind River VxWorks(一种实时操作系统) 和 Green Hills Integrity(也是一种操作系统)。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 更多信息
|
||||
|
||||
eInfochips Android PowerPC 移植白皮书可以[在此[4]下载(需要先免费注册)。
|
||||
|
||||
### Related posts:
|
||||
|
||||
- [Commercial embedded Linux distro boosts virtualization][5]
|
||||
- [Freescale unveils first ARM-based QorIQ SoCs][6]
|
||||
- [High-end boards run Linux on 64-bit ARM QorIQ SoCs][7]
|
||||
- [Free, Open Enea Linux taps Yocto Project and Linaro code][8]
|
||||
- [LynuxWorks reverts to its LynxOS roots, changes name][9]
|
||||
- [First quad- and octa-core QorIQ SoCs unveiled][10]
|
||||
- [Free white paper shows how Linux won embedded][11]
|
||||
- [Quad-core Snapdragon COM offers three dev kit options][12]
|
||||
- [Tiny COM runs Linux on quad-core 64-bit Snapdragon 410][13]
|
||||
- [PowerPC based IoT gateway COM ships with Linux BSP][14]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://hackerboards.com/powerpc-gains-android-4-4-port-with-big-endian-support/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Eric Brown][a]
|
||||
译者:[dongfengweixiao](https://github.com/dongfengweixiao)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: http://hackerboards.com/powerpc-gains-android-4-4-port-with-big-endian-support/
|
||||
[1]: http://linuxdevices.linuxgizmos.com/low-cost-powerquicc-chips-offer-flexible-interconnect-options/
|
||||
[2]: https://www.einfochips.com/blog/k2-categories/aerospace/presenting-a-case-for-porting-android-on-powerpc-architecture.html
|
||||
[3]: http://www.xes-inc.com/products/processor-mezzanines/xpedite6101/
|
||||
[4]: http://biz.einfochips.com/portingandroidonpowerpc
|
||||
[5]: http://hackerboards.com/commercial-embedded-linux-distro-boosts-virtualization/
|
||||
[6]: http://hackerboards.com/freescale-unveils-first-arm-based-qoriq-socs/
|
||||
[7]: http://hackerboards.com/high-end-boards-run-linux-on-64-bit-arm-qoriq-socs/
|
||||
[8]: http://hackerboards.com/free-open-enea-linux-taps-yocto-and-linaro-code/
|
||||
[9]: http://hackerboards.com/lynuxworks-reverts-to-its-lynxos-roots-changes-name/
|
||||
[10]: http://hackerboards.com/first-quad-and-octa-core-qoriq-socs-unveiled/
|
||||
[11]: http://hackerboards.com/free-white-paper-shows-how-linux-won-embedded/
|
||||
[12]: http://hackerboards.com/quad-core-snapdragon-com-offers-three-dev-kit-options/
|
||||
[13]: http://hackerboards.com/tiny-com-runs-linux-and-android-on-quad-core-64-bit-snapdragon-410/
|
||||
[14]: http://hackerboards.com/powerpc-based-iot-gateway-com-ships-with-linux-bsp/
|
||||
[15]: http://linuxdevices.linuxgizmos.com/android-ported-to-powerpc/
|
||||
[16]: http://www.androidppc.com/
|
||||
[17]: http://hackerboards.com/quad-core-snapdragon-com-offers-three-dev-kit-options/
|
||||
[18]: https://sourceware.org/libffi/
|
||||
[19]: http://www.xes-inc.com/capabilities/ruggedization/
|
||||
[20]: http://hackerboards.com/high-end-boards-run-linux-on-64-bit-arm-qoriq-socs/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,122 @@
|
||||
如何在 Linux 上永久挂载一个 Windows 共享
|
||||
==================================================
|
||||
|
||||
> 如果你已经厌倦了每次重启 Linux 就得重新挂载 Windows 共享,读读这个让共享永久挂载的简单方法。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>图片: Jack Wallen
|
||||
|
||||
在 Linux 上和一个 Windows 网络进行交互从来就不是件轻松的事情。想想多少企业正在采用 Linux,这两个平台不得不一起好好协作。幸运的是,有了一些工具的帮助,你可以轻松地将 Windows 网络驱动器映射到一台 Linux 机器上,甚至可以确保在重启 Linux 机器之后共享还在。
|
||||
|
||||
### 在我们开始之前
|
||||
|
||||
要实现这个,你需要用到命令行。过程十分简单,但你需要编辑 /etc/fstab 文件,所以小心操作。还有,我假设你已经有正常工作的 Samba 了,可以手动从 Windows 网络挂载共享到你的 Linux 机器,还知道这个共享的主机 IP 地址。
|
||||
|
||||
准备好了吗?那就开始吧。
|
||||
|
||||
### 创建你的挂载点
|
||||
|
||||
我们要做的第一件事是创建一个文件夹,他将作为共享的挂载点。为了简单起见,我们将这个文件夹命名为 share,放在 /media 之下。打开你的终端执行以下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
sudo mkdir /media/share
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 一些安装
|
||||
|
||||
现在我们得安装允许跨平台文件共享的系统;这个系统是 cifs-utils。在终端窗口输入:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
sudo apt-get install cifs-utils
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
这个命令同时还会安装 cifs-utils 所有的依赖。
|
||||
|
||||
安装完成之后,打开文件 /etc/nsswitch.conf 并找到这一行:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
hosts: files mdns4_minimal [NOTFOUND=return] dns
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
编辑这一行,让它看起来像这样:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
hosts: files mdns4_minimal [NOTFOUND=return] wins dns
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
现在你必须安装 windbind 让你的 Linux 机器可以在 DHCP 网络中解析 Windows 机器名。在终端里执行:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
sudo apt-get install libnss-windbind windbind
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
用这个命令重启网络服务:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
sudo service networking restart
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 挂载网络驱动器
|
||||
|
||||
现在我们要映射网络驱动器。这里我们必须编辑 /etc/fstab 文件。在你做第一次编辑之前,用这个命令备份以下这个文件:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
sudo cp /etc/fstab /etc/fstab.old
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果你需要恢复这个文件,执行以下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
sudo mv /etc/fstab.old /etc/fstab
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在你的主目录创建一个认证信息文件 .smbcredentials。在这个文件里添加你的用户名和密码,就像这样(USER 和 PASSWORD 是实际的用户名和密码):
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
username=USER
|
||||
|
||||
password=PASSWORD
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
你需要知道挂载这个驱动器的用户的组 ID(GID)和用户 ID(UID)。执行命令:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
id USER
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
USER 是实际的用户名,你应该会看到类似这样的信息:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
uid=1000(USER) gid=1000(GROUP)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
USER 是实际的用户名,GROUP 是组名。在(USER)和(GROUP)之前的数字将会被用在 /etc/fstab 文件之中。
|
||||
|
||||
是时候编辑 /etc/fstab 文件了。在你的编辑器中打开那个文件并添加下面这行到文件末尾(替换以下全大写字段以及远程机器的 IP 地址):
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
//192.168.1.10/SHARE /media/share cifs credentials=/home/USER/.smbcredentials,iocharset=uft8,gid=GID,udi=UID,file_mode=0777,dir_mode=0777 0 0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**注意**:上面这些内容应该在同一行上。
|
||||
|
||||
保存并关闭那个文件。执行 sudo mount -a 命令,共享将被挂载。检查一下 /media/share,你应该能看到那个网络共享上的文件和文件夹了。
|
||||
|
||||
### 共享很简单
|
||||
|
||||
有了 cifs-utils 和 Samba,映射网络共享在一台 Linux 机器上简单得让人难以置信。现在,你再也不用在每次机器启动的时候手动重新挂载那些共享了。
|
||||
|
||||
更多网络提示和技巧,订阅我们的 Data Center 消息吧。
|
||||
[订阅](https://secure.techrepublic.com/user/login/?regSource=newsletter-button&position=newsletter-button&appId=true&redirectUrl=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.techrepublic.com%2Farticle%2Fhow-to-permanently-mount-a-windows-share-on-linux%2F&)
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.techrepublic.com/article/how-to-permanently-mount-a-windows-share-on-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Jack Wallen][a]
|
||||
译者:[alim0x](https://github.com/alim0x)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: http://www.techrepublic.com/search/?a=jack+wallen
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,65 @@
|
||||
translating by kylepeng93
|
||||
给学习OpenStack基础设施的新手的入门指南
|
||||
===========================================================
|
||||
|
||||
任何一个为OpenStack贡献源码的人会受到社区的欢迎,但是,对于一个发展趋近成熟并且快速迭代的开源社区而言,能够拥有一个新手指南并不是
|
||||
件坏事。在奥斯汀举办的OpenStack峰会上,[Paul Belanger][1] (红帽公司), [Elizabeth K. Joseph][2] (HPE公司),和[Christopher Aedo][3] (IBM公司)将会就针对新人的OpenStack基础设施作一场专门的会谈。在这次采访中,他们将会提供一些建议和资源来帮助新人成为OpenStack贡献者中的一员。
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**你在谈话中表示你将“投入全部身心于基础设施并解释你需要知道的有关于维持OpenStack正常工作的系统的每一件事情”。这是一个持续了40分钟的的艰巨任务。那么,对于学习OpenStack基础设施的新手来说最需要知道那些事情呢?**
|
||||
**Elizabeth K. Joseph (EKJ)**: 我们没有为OpenStack使用GitHub这种提交补丁的方式,这是因为这样做会对新手造成巨大的困扰,尽管由于历史原因我们还是保留了所有原先就在GitHub上的所有库的镜像。相反,我们使用了一种完全开源的复查形式,并通过OpenStack基础设施团队来持续的维持系统集成(CI)。相关的,自从我们使用了CI系统,每一个提交给OpenStack的改变都会在被合并之前进行测试。
|
||||
**Paul Belanger (PB)**: 这个项目中的大多数都是富有激情的人,因此当你提交的补丁被某个人否定时不要感到沮丧。
|
||||
**Christopher Aedo (CA)**:社区很想帮助你取得成功,因此不要害怕提问或者寻求更多的那些能够促进你理解某些事物的引导者。
|
||||
|
||||
### 在你的讲话中,对于一些你无法涉及到的方面,你会向新手推荐哪些在线资源来让他们更加容易入门?
|
||||
**PB**:当然是我们的[OpenStack项目基础设施文档][5]。我们已经花了足够大的努力来尽可能让这些文档能够随时保持最新状态。我们对每个运行OpenStack项目并投入使用的系统都有制作专门的页面来进行说明。甚至于连OpenStack云基础设施团队也即将上线。
|
||||
|
||||
**EKJ**:我对于将基础设施文档作为新手入门教程这件事上的观点和Paul是一致的,另外,我们十分乐意看到来自那些folk了我们项目的学习者提交上来的补丁。我们通常不会意识到我们忽略了文档中的某些内容,除非它们恰好被人问起。因此,阅读,学习,然后帮助我们修补这些知识上的漏洞。你可以在[OpenStack基础设施邮件清单]提出你的问题,或者在我们位于FreeNode上的#OpenStack-infra的IRC专栏发起你的提问。
|
||||
**CA**:我喜欢[这个详细的发布][7],它是由Ian Wienand写的一篇关于构建图片的文章。
|
||||
### "gotchas" 会是OpenStack新的代码贡献者苦苦寻找的吗?
|
||||
**EKJ**:向项目作出贡献并不仅仅是提交新的代码和新的特性;OpenStack社区高度重视代码复查。如果你想要别人查看你的补丁,那你最好先看看其他人是如何做的,然后参考他们的风格,最后一步布做到你也能够向其他人一样提交清晰且结构分明的代码补丁。你越是能让你的同伴了解你的工作并知道你正在做的复查,那他们也就更有可能形成及时复查你的代码的风格。
|
||||
**CA**:我看到过大量的新手在面对Gerrit时受挫,阅读开发者引导中的[开发者工作步骤][9]时,可能只是将他通读了一遍。如果你没有经常使用Gerrit,那你最初对它的感觉可能是困惑和无力的。但是,如果你随后做了一些代码复查的工作,那么你马上就能轻松应对它。同样,我是IRC的忠实粉丝。它可能是一个获得帮助的好地方,但是,你最好保持一个长期保留的状态,这样,尽管你在某个时候没有出现,人们也可以回答你的问题。(阅读[IRC,开源界的成功秘诀][10]。)你不必总是在线,但是你最好能够轻松的在一个通道中进行回滚操作,以此来跟上最新的动态,这种能力非常重要。
|
||||
**PB**:我同意Elizabeth和Chris—Gerrit关于寻求何种方式来学习的观点。每个开发人员所作出的努力都将让社区变得更加美好。你不仅仅要提交代码给别人去复查,同时,你也要能够复查其他人的代码。留意Gerrit的用户接口,你可能一时会变的很疑惑。我推荐新手去尝试[Gertty][11],它是一个基于控制台的终端接口,用于Gerrit代码复查系统,而它恰好也是OpenStack基础设施所驱动的一个项目。
|
||||
### 你对于OpenStack新手如何通过网络与其他贡献者交流方面有什么好的建议?
|
||||
**PB**:对我来说,是通过IRC以及在Freenode上参加#OpenStack-infra专栏([IRC logs][12]).这专栏上面有很多对新手来说很有价值的资源。你可以看到OpenStack项目日复一日的运作情况,同时,一旦你知道了OpenStack项目的工作原理,你将更好的知道如何为OpenStack的未来发展作出贡献。
|
||||
**CA**:我想要为IRC再次说明一点,在IRC上保持一整天的在线记录对我来说有非常重大的意义,因为我会感觉到被重视并且时刻保持连接。这也是一种非常好的获得帮助的方式,特别是当你卡在了项目中出现的某一个难题的时候,而在专栏中,总会有一些人很乐意为你解决问题。
|
||||
**EKJ**:[OpenStack开发邮件列表][13]对于能够时刻查看到你所致力于的OpenStack项目的最新情况是非常重要的。因此,我推荐一定要订阅它。邮件列表使用课题标签来区分项目,因此你可以设置你的邮件客户端来使用它,并且集中精力于你所关心的项目。除了在线资源之外,全世界范围内也成立了一些OpenStack小组,他们被用来为OpenStack的用户和贡献者提供服务。这些小组可能会定期举行座谈和针对OpenStack主要贡献者的一些活动。你可以在MeetUp.com上搜素你所在地域的贡献者活动聚会,或者在[groups.openstack.org]上查看你所在的地域是否存在OpenStack小组。最后,还有一个每六个月举办一次的OpenStack峰会,这个峰会上会作一些关于基础设施的演说。当前状态下,这个峰会包含了用户会议和开发者会议,会议内容都是和OpenStack相关的东西,包括它的过去,现在和未来。
|
||||
### OpenStack需要在那些方面得到提升来让新手更加容易学会并掌握?
|
||||
**PB**: 我认为我们的[account-setup][16]过程对于新的贡献者已经做的比较容易了,特别是教他们如何提交他们的第一个补丁。真正参与到OpenStack开发者模式的过程是需要花费很大的努力的,可能对于开发者来说已经显得非常多了;然而,一旦融入进去了,这个模式将会运转的十分高效和令人满意。
|
||||
**CA**: 我们拥有一个由专业开发者组成的社区,而且我们的关注点都是发展OpenStack本身,同时,我们致力于让用户付出更小的代价去使用OpenStack云基础设施平台。我们需要发掘更多的应用开发者,并且鼓励更多的人去开发能在OpenStack云上完美运行的云应用程序,我们还鼓励他们在[社区App目录]上去贡献那些由他们开发的app。我们可以通过提升我们的API标准和保证我们不同的库(比如libcloud,phpopencloud已经其他一些库),并让他们持续的为开发者提供可信赖的支持来实现这一目标。还有一点就是通过倡导更多的OpenStack黑客加入进来。所有的这些事情都可以降低新人的学习门槛,这样也能引导他们与这个社区之间的关系更加紧密。y.
|
||||
**EKJ**: 我已经致力于开源软件很多年了。但是,对于大量的OpenStack开发者而言,这是一个他们每个人都在从事的第一个开源项目。我发现他们之前使用私有软件的背景并没有为他们塑造开源的观念和方法论,还有在开源项目中需要具备的合作技巧。我乐于看到我们能够让那些曾经一直在使用私有软件工作的人能够真正的明白他们在开源如软件社区所从事的事情的巨大价值。
|
||||
### 我认为2016年对于开源Haiku的进一步增长是具有重大意义的一年。通过Haiku来向新手解释OpenStack。
|
||||
**PB**: 如果你喜欢自由软件,你可以向OpenStack提交你的第一个补丁。
|
||||
**CA**: 在不久的未来,OpenStack将以统治世界的姿态让这个世界变得更好。
|
||||
**EKJ**: OpenStack是一个可以免费部署在你的服务器上面并且运行你自己的云的一个软件。
|
||||
*Paul,Elizabeth和Christopher将会在4月25号星期一上午11:15于奥斯汀举办的OpenStack峰会上进行演说。
|
||||
|
||||
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://opensource.com/business/16/4/interview-openstack-infrastructure-beginners
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[linux.com][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: http://rikkiendsley.com/
|
||||
[1]: https://twitter.com/pabelanger
|
||||
[2]: https://twitter.com/pleia2
|
||||
[3]: https://twitter.com/docaedo
|
||||
[4]: https://www.openstack.org/summit/austin-2016/summit-schedule/events/7337
|
||||
[5]: http://docs.openstack.org/infra/system-config/
|
||||
[6]: http://lists.openstack.org/cgi-bin/mailman/listinfo/openstack-infra
|
||||
[7]: https://www.technovelty.org/openstack/image-building-in-openstack-ci.html
|
||||
[8]: https://code.google.com/p/gerrit/
|
||||
[9]: http://docs.openstack.org/infra/manual/developers.html#development-workflow
|
||||
[10]: https://developer.ibm.com/opentech/2015/12/20/irc-the-secret-to-success-in-open-source/
|
||||
[11]: https://pypi.python.org/pypi/gertty
|
||||
[12]: http://eavesdrop.openstack.org/irclogs/%23openstack-infra/
|
||||
[13]: http://lists.openstack.org/cgi-bin/mailman/listinfo/openstack-dev
|
||||
[14]: https://groups.openstack.org/
|
||||
[15]: https://www.openstack.org/summit/
|
||||
[16]: http://docs.openstack.org/infra/manual/developers.html#account-setup
|
||||
[17]: https://apps.openstack.org/
|
||||
[18]: https://www.openstack.org/summit/austin-2016/summit-schedule/events/7337
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,82 @@
|
||||
如何使用 Awk 来筛选文本或字符串
|
||||
=========================================================================
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
作为 Awk 命令系列的第三部分,这次我们将看一看如何基于用户定义的特定模式来筛选文本或字符串。
|
||||
|
||||
在筛选文本时,有时你可能想根据某个给定的条件或使用一个特定的可被匹配的模式,去标记某个文件或数行字符串中的某几行。使用 Awk 来完成这个任务是非常容易的,这也正是 Awk 中可能对你有所帮助的几个特色之一。
|
||||
|
||||
让我们看一看下面这个例子,比方说你有一个写有你想要购买的食物的购物清单,其名称为 food_prices.list,它所含有的食物名称及相应的价格如下所示:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ cat food_prices.list
|
||||
No Item_Name Quantity Price
|
||||
1 Mangoes 10 $2.45
|
||||
2 Apples 20 $1.50
|
||||
3 Bananas 5 $0.90
|
||||
4 Pineapples 10 $3.46
|
||||
5 Oranges 10 $0.78
|
||||
6 Tomatoes 5 $0.55
|
||||
7 Onions 5 $0.45
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
然后,你想使用一个 `(*)` 符号去标记那些单价大于 $2 的食物,那么你可以通过运行下面的命令来达到此目的:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ awk '/ *\$[2-9]\.[0-9][0-9] */ { print $1, $2, $3, $4, "*" ; } / *\$[0-1]\.[0-9][0-9] */ { print ; }' food_prices.list
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>打印出单价大于 $2 的项目
|
||||
|
||||
从上面的输出你可以看到在含有 芒果(mangoes) 和 菠萝(pineapples) 的那行末尾都已经有了一个 `(*)` 标记。假如你检查它们的单价,你可以看到它们的单价的确超过了 $2 。
|
||||
|
||||
在这个例子中,我们已经使用了两个模式:
|
||||
|
||||
- 第一个模式: `/ *\$[2-9]\.[0-9][0-9] */` 将会得到那些含有食物单价大于 $2 的行,
|
||||
- 第二个模式: `/*\$[0-1]\.[0-9][0-9] */` 将查找那些食物单价小于 $2 的那些行。
|
||||
|
||||
上面的命令具体做了什么呢?这个文件有四个字段,当模式一匹配到含有食物单价大于 $2 的行时,它便会输出所有的四个字段并在该行末尾加上一个 `(*)` 符号来作为标记。
|
||||
|
||||
第二个模式只是简单地输出其他含有食物单价小于 $2 的行,因为它们出现在输入文件 food_prices.list 中。
|
||||
|
||||
这样你就可以使用模式来筛选出那些价格超过 $2 的食物项目,尽管上面的输出还有些问题,带有 `(*)` 符号的那些行并没有像其他行那样被格式化输出,这使得输出显得不够清晰。
|
||||
|
||||
我们在 Awk 系列的第二部分中也看到了同样的问题,但我们可以使用下面的两种方式来解决:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 可以像下面这样使用 printf 命令,但这样使用又长又无聊:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ awk '/ *\$[2-9]\.[0-9][0-9] */ { printf "%-10s %-10s %-10s %-10s\n", $1, $2, $3, $4 "*" ; } / *\$[0-1]\.[0-9][0-9] */ { printf "%-10s %-10s %-10s %-10s\n", $1, $2, $3, $4; }' food_prices.list
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>使用 Awk 和 Printf 来筛选和输出项目
|
||||
|
||||
2. 使用 `$0` 字段。Awk 使用变量 **0** 来存储整个输入行。对于上面的问题,这种方式非常方便,并且它还简单、快速:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ awk '/ *\$[2-9]\.[0-9][0-9] */ { print $0 "*" ; } / *\$[0-1]\.[0-9][0-9] */ { print ; }' food_prices.list
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>使用 Awk 和变量来筛选和输出项目
|
||||
|
||||
### 结论
|
||||
|
||||
这就是全部内容了,使用 Awk 命令你便可以通过几种简单的方法去利用模式匹配来筛选文本,帮助你在一个文件中对文本或字符串的某些行做标记。
|
||||
|
||||
希望这篇文章对你有所帮助。记得阅读这个系列的下一部分,我们将关注在 awk 工具中使用比较运算符。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/awk-filter-text-or-string-using-patterns/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Aaron Kili][a]
|
||||
译者:[FSSlc](https://github.com/FSSlc)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,95 @@
|
||||
在 Linux 下如何使用 Awk 比较操作符
|
||||
===================================================
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
对于 Awk 命令的用户来说,处理一行文本中的数字或者字符串时,使用比较运算符来过滤文本和字符串是十分方便的。
|
||||
|
||||
在 Awk 系列的此部分中,我们将探讨一下如何使用比较运算符来过滤文本或者字符串。如果你是程序员,那么你应该已经熟悉比较运算符;对于其它人,下面的部分将介绍比较运算符。
|
||||
|
||||
### Awk 中的比较运算符是什么?
|
||||
|
||||
Awk 中的比较运算符用于比较字符串和或者数值,包括以下类型:
|
||||
|
||||
- `>` – 大于
|
||||
- `<` – 小于
|
||||
- `>=` – 大于等于
|
||||
- `<=` – 小于等于
|
||||
- `==` – 等于
|
||||
- `!=` – 不等于
|
||||
- `some_value ~ / pattern/` – 如果some_value匹配模式pattern,则返回true
|
||||
- `some_value !~ / pattern/` – 如果some_value不匹配模式pattern,则返回true
|
||||
|
||||
现在我们通过例子来熟悉 Awk 中各种不同的比较运算符。
|
||||
|
||||
在这个例子中,我们有一个文件名为 food_list.txt 的文件,里面包括不同食物的购买列表。我想给食物数量小于或等于30的物品所在行的后面加上`(**)`
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
File – food_list.txt
|
||||
No Item_Name Quantity Price
|
||||
1 Mangoes 45 $3.45
|
||||
2 Apples 25 $2.45
|
||||
3 Pineapples 5 $4.45
|
||||
4 Tomatoes 25 $3.45
|
||||
5 Onions 15 $1.45
|
||||
6 Bananas 30 $3.45
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Awk 中使用比较运算符的通用语法如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# expression { actions; }
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
为了实现刚才的目的,执行下面的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# awk '$3 <= 30 { printf "%s\t%s\n", $0,"**" ; } $3 > 30 { print $0 ;}' food_list.txt
|
||||
|
||||
No Item_Name` Quantity Price
|
||||
1 Mangoes 45 $3.45
|
||||
2 Apples 25 $2.45 **
|
||||
3 Pineapples 5 $4.45 **
|
||||
4 Tomatoes 25 $3.45 **
|
||||
5 Onions 15 $1.45 **
|
||||
6 Bananas 30 $3.45 **
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在刚才的例子中,发生如下两件重要的事情:
|
||||
|
||||
- 第一个表达式 `{ action ; }` 组合, `$3 <= 30 { printf “%s\t%s\n”, $0,”**” ; }` 打印出数量小于等于30的行,并且在后面增加`(**)`。物品的数量是通过 `$3`这个域变量获得的。
|
||||
- 第二个表达式 `{ action ; }` 组合, `$3 > 30 { print $0 ;}` 原样输出数量小于等于 `30` 的行。
|
||||
|
||||
再举一个例子:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# awk '$3 <= 20 { printf "%s\t%s\n", $0,"TRUE" ; } $3 > 20 { print $0 ;} ' food_list.txt
|
||||
|
||||
No Item_Name Quantity Price
|
||||
1 Mangoes 45 $3.45
|
||||
2 Apples 25 $2.45
|
||||
3 Pineapples 5 $4.45 TRUE
|
||||
4 Tomatoes 25 $3.45
|
||||
5 Onions 15 $1.45 TRUE
|
||||
6 Bananas 30 $3.45
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在这个例子中,我们想通过在行的末尾增加 (TRUE) 来标记数量小于等于20的行。
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结
|
||||
|
||||
这是一篇对 Awk 中的比较运算符介绍性的指引,因此你需要尝试其他选项,发现更多使用方法。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你遇到或者想到任何问题,请在下面评论区留下评论。请记得阅读 Awk 系列下一部分的文章,那里我将介绍组合表达式。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/comparison-operators-in-awk/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Aaron Kili][a]
|
||||
译者:[chunyang-wen](https://github.com/chunyang-wen)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,79 @@
|
||||
如何使用 Awk 复合表达式
|
||||
====================================================
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
一直以来在查对条件是否匹配时,我们寻求的都是简单的表达式。那如果你想用超过一个表达式,来查对特定的条件呢?
|
||||
|
||||
本文,我们将看看如何在过滤文本和字符串时,结合多个表达式,即复合表达式,用以查对条件。
|
||||
|
||||
Awk 的复合表达式可由表示`与`的组合操作符 `&&` 和表示`或`的 `||` 构成。
|
||||
|
||||
复合表达式的常规写法如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
( first_expression ) && ( second_expression )
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
为了保证整个表达式的正确,在这里必须确保 `first_expression` 和 `second_expression` 是正确的。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
( first_expression ) || ( second_expression)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
为了保证整个表达式的正确,在这里必须确保 `first_expression` 或 `second_expression` 是正确的。
|
||||
|
||||
**注意**:切记要加括号。
|
||||
|
||||
表达式可以由比较操作符构成,具体可查看 awk 系列的第四部分。
|
||||
|
||||
现在让我们通过一个例子来加深理解:
|
||||
|
||||
此例中,有一个文本文件 `tecmint_deals.txt`,文本中包含着一张随机的 Tecmint 交易清单,其中包含了名称、价格和种类。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
TecMint Deal List
|
||||
No Name Price Type
|
||||
1 Mac_OS_X_Cleanup_Suite $9.99 Software
|
||||
2 Basics_Notebook $14.99 Lifestyle
|
||||
3 Tactical_Pen $25.99 Lifestyle
|
||||
4 Scapple $19.00 Unknown
|
||||
5 Nano_Tool_Pack $11.99 Unknown
|
||||
6 Ditto_Bluetooth_Altering_Device $33.00 Tech
|
||||
7 Nano_Prowler_Mini_Drone $36.99 Tech
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
我们只想打印出价格超过 $20 的物品,并在其中种类为 “Tech” 的物品的行末用 (**) 打上标记。
|
||||
|
||||
我们将要执行以下命令。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# awk '($3 ~ /^\$[2-9][0-9]*\.[0-9][0-9]$/) && ($4=="Tech") { printf "%s\t%s\n",$0,"*"; } ' tecmint_deals.txt
|
||||
|
||||
6 Ditto_Bluetooth_Altering_Device $33.00 Tech *
|
||||
7 Nano_Prowler_Mini_Drone $36.99 Tech *
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
此例,在复合表达式中我们使用了两个表达式:
|
||||
|
||||
- 表达式 1:`($3 ~ /^\$[2-9][0-9]*\.[0-9][0-9]$/)` ;查找交易价格超过 `$20` 的行,即只有当 `$3` 也就是价格满足 `/^\$[2-9][0-9]*\.[0-9][0-9]$/` 时值才为 true。
|
||||
- 表达式 2:`($4 == “Tech”)` ;查找是否有种类为 “`Tech`”的交易,即只有当 `$4` 等于 “`Tech`” 时值才为 true。
|
||||
切记,只有当 `&&` 操作符的两端状态,也就是两个表达式都是 true 的情况下,这一行才会被打上 `(**)` 标志。
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结
|
||||
|
||||
有些时候为了匹配你的真实想法,就不得不用到复合表达式。当你掌握了比较和复合表达式操作符的用法之后,在难的文本或字符串过滤条件也能轻松解决。
|
||||
|
||||
希望本向导对你有所帮助,如果你有任何问题或者补充,可以在下方发表评论,你的问题将会得到相应的解释。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/combine-multiple-expressions-in-awk/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Aaron Kili][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,76 @@
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
在 Linux 上怎么读取标准输入(STDIN)作为 Awk 的输入
|
||||
============================================
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
在 Awk 工具系列的前几节,我们看到大多数操作都是从一个文件或多个文件读取输入,或者你想要把标准输入作为 Awk 的输入.
|
||||
在 Awk 系列的第7节中,我们将会看到几个例子,这些例子都是关于你可以筛选其他命令的输出代替从一个文件读取输入作为 awk 的输入.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
我们开始使用 [dir utility][1] , dir 命令和 [ls 命令][2] 相似,在第一个例子下面,我们使用 'dir -l' 命令的输出作为 Awk 命令的输入,这样就可以打印出文件拥有者的用户名,所属组组名以及在当前路径下他/她拥有的文件.
|
||||
```
|
||||
# dir -l | awk '{print $3, $4, $9;}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>列出当前路径下的用户文件
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
看另一个例子,我们 [使用 awk 表达式][3] ,在这里,我们想要在 awk 命令里使用一个表达式筛选出字符串,通过这样来打印出 root 用户的文件.命令如下:
|
||||
```
|
||||
# dir -l | awk '$3=="root" {print $1,$3,$4, $9;} '
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
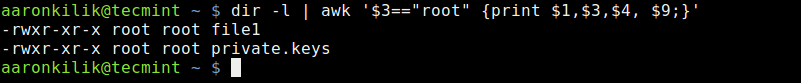
|
||||
>列出 root 用户的文件
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
上面的命令包含了 '(==)' 来进行比较操作,这帮助我们在当前路径下筛选出 root 用户的文件.这种方法的实现是通过使用 '$3=="root"' 表达式.
|
||||
|
||||
让我们再看另一个例子,我们使用一个 [awk 比较运算符][4] 来匹配一个确定的字符串.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
现在,我们已经用了 [cat utility][5] 来浏览文件名为 tecmint_deals.txt 的文件内容,并且我们想要仅仅查看有字符串 Tech 的部分,所以我们会运行下列命令:
|
||||
```
|
||||
# cat tecmint_deals.txt
|
||||
# cat tecmint_deals.txt | awk '$4 ~ /tech/{print}'
|
||||
# cat tecmint_deals.txt | awk '$4 ~ /Tech/{print}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>用 Awk 比较运算符匹配字符串
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
在上面的例子中,我们已经用了参数为 `~ /匹配字符/` 的比较操作,但是上面的两个命令给我们展示了一些很重要的问题.
|
||||
|
||||
当你运行带有 tech 字符串的命令时终端没有输出,因为在文件中没有 tech 这种字符串,但是运行带有 Tech 字符串的命令,你却会得到包含 Tech 的输出.
|
||||
|
||||
所以你应该在进行这种比较操作的时候时刻注意这种问题,正如我们在上面看到的那样, awk 对大小写很敏感.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
你可以一直使用另一个命令的输出作为 awk 命令的输入来代替从一个文件中读取输入,这就像我们在上面看到的那样简单.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
希望这些例子足够简单可以使你理解 awk 的用法,如果你有任何问题,你可以在下面的评论区提问,记得查看 awk 系列接下来的章节内容,我们将关注 awk 的一些功能,比如变量,数字表达式以及赋值运算符.
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/read-awk-input-from-stdin-in-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Aaron Kili][a]
|
||||
译者:[vim-kakali](https://github.com/vim-kakali)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/
|
||||
[1]: http://www.tecmint.com/linux-dir-command-usage-with-examples/
|
||||
[2]: http://www.tecmint.com/15-basic-ls-command-examples-in-linux/
|
||||
[3]: http://www.tecmint.com/combine-multiple-expressions-in-awk
|
||||
[4]: http://www.tecmint.com/comparison-operators-in-awk
|
||||
[5]: http://www.tecmint.com/13-basic-cat-command-examples-in-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user