mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-02-28 01:01:09 +08:00
translated wi-cuckoo
This commit is contained in:
parent
23ae12c584
commit
0041c53ea2
@ -1,97 +0,0 @@
|
||||
translating wi-cuckoo
|
||||
Linux FAQs with Answers--How to configure a Linux bridge with Network Manager on Ubuntu
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **Question**: I need to set up a Linux bridge on my Ubuntu box to share a NIC with several other virtual machines or containers created on the box. I am currently using Network Manager on my Ubuntu, so preferrably I would like to configure a bridge using Network Manager. How can I do that?
|
||||
|
||||
Network bridge is a hardware equipment used to interconnect two or more Layer-2 network segments, so that network devices on different segments can talk to each other. A similar bridging concept is needed within a Linux host, when you want to interconnect multiple VMs or Ethernet interfaces within a host. That is one use case of a software Linux bridge.
|
||||
|
||||
There are several different ways to configure a Linux bridge. For example, in a headless server environment, you can use [brctl][1] to manually configure a bridge. In desktop environment, bridge support is available in Network Manager. Let's examine how to configure a bridge with Network Manager.
|
||||
|
||||
### Requirement ###
|
||||
|
||||
To avoid [any issue][2], it is recommended that you have Network Manager 0.9.9 and higher, which is the case for Ubuntu 15.04 and later.
|
||||
|
||||
$ apt-cache show network-manager | grep Version
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
Version: 0.9.10.0-4ubuntu15.1
|
||||
Version: 0.9.10.0-4ubuntu15
|
||||
|
||||
### Create a Bridge ###
|
||||
|
||||
The easiest way to create a bridge with Network Manager is via nm-connection-editor. This GUI tool allows you to configure a bridge in easy-to-follow steps.
|
||||
|
||||
To start, invoke nm-connection-editor.
|
||||
|
||||
$ nm-connection-editor
|
||||
|
||||
The editor window will show you a list of currently configured network connections. Click on "Add" button in the top right to create a bridge.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Next, choose "Bridge" as a connection type.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Now it's time to configure a bridge, including its name and bridged connection(s). With no other bridges created, the default bridge interface will be named bridge0.
|
||||
|
||||
Recall that the goal of creating a bridge is to share your Ethernet interface via the bridge. So you need to add the Ethernet interface to the bridge. This is achieved by adding a new "bridged connection" in the GUI. Click on "Add" button.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Choose "Ethernet" as a connection type.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
In "Device MAC address" field, choose the interface that you want to enslave into the bridge. In this example, assume that this interface is eth0.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
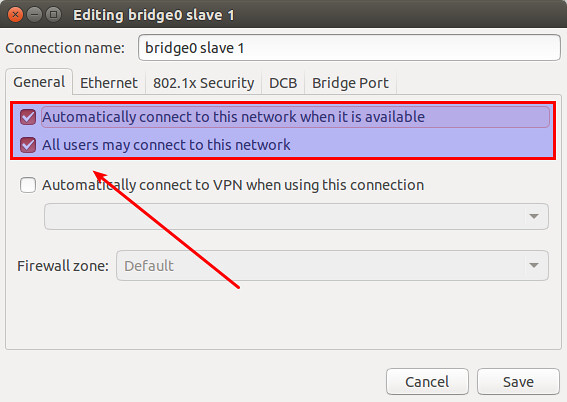
Click on "General" tab, and enable both checkboxes that say "Automatically connect to this network when it is available" and "All users may connect to this network".
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Save the change.
|
||||
|
||||
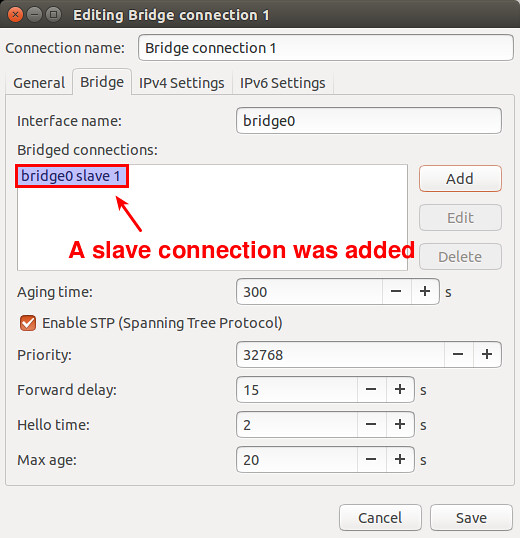
Now you will see a new slave connection created in the bridge.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
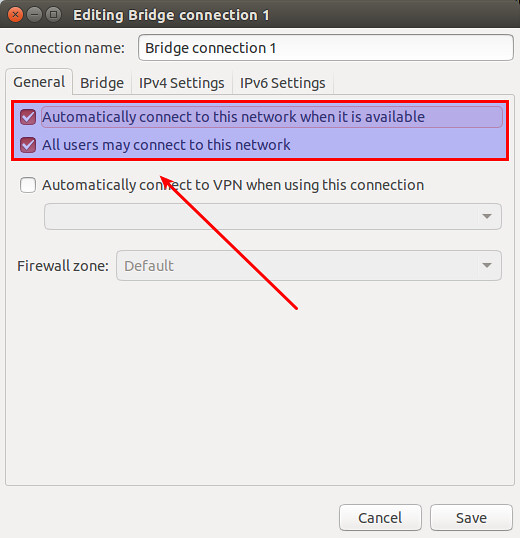
Click on "General" tab of the bridge, and make sure that top-most two checkboxes are enabled.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
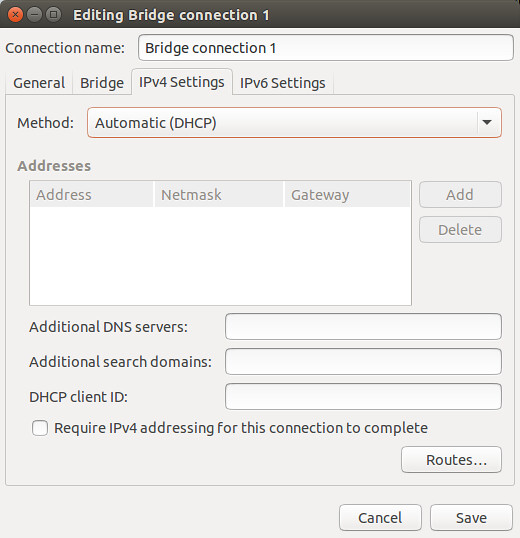
Go to "IPv4 Settings" tab, and configure either DHCP or static IP address for the bridge. Note that you should use the same IPv4 settings as the enslaved Ethernet interface eth0. In this example, we assume that eth0 is configured via DHCP. Thus choose "Automatic (DHCP)" here. If eth0 is assigned a static IP address, you should assign the same IP address to the bridge.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, save the bridge settings.
|
||||
|
||||
Now you will see an additional bridge connection created in "Network Connections" window. You no longer need a previously-configured wired connection for the enslaved interface eth0. So go ahead and delete the original wired connection.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
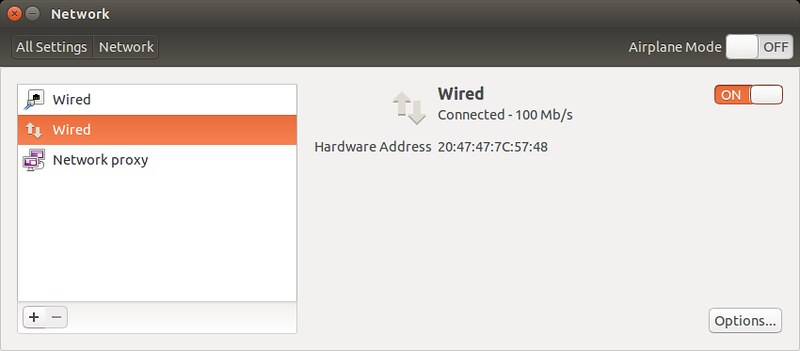
At this point, the bridge connection will automatically be activated. You will momentarily lose a connection, since the IP address assigned to eth0 is taken over by the bridge. Once an IP address is assigned to the bridge, you will be connected back to your Ethernet interface via the bridge. You can confirm that by checking "Network" settings.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
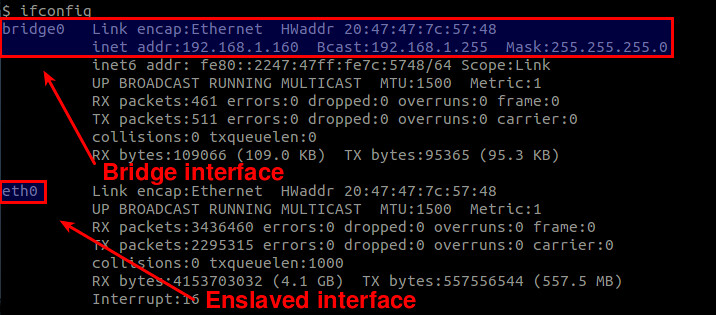
Also, check the list of available interfaces. As mentioned, the bridge interface must have taken over whatever IP address was possessed by your Ethernet interface.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
That's it, and now the bridge is ready to use!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/configure-linux-bridge-network-manager-ubuntu.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/author/nanni
|
||||
[1]:http://xmodulo.com/how-to-configure-linux-bridge-interface.html
|
||||
[2]:https://bugs.launchpad.net/ubuntu/+source/network-manager/+bug/1273201
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,98 @@
|
||||
nux常见问题解答--如何在Ubuntu上使用网络管理配置一个Linux网桥
|
||||
===============================================================================
|
||||
> **Question**: 我需要在我的Ubuntu主机上建立一个Linux网桥,共享一个NIC给其他一些虚拟主机或者主机上创建的容器。我目前正在Ubunut上使用网络管理,所以最好>能使用网络管理来配置一个网桥。我该怎么做?
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
网桥是一个硬件装备,用来内部连接两个或多个数据链路层(OSI七层模型中第二层),所以使得不同段上的网络设备可以互相访问。当你想要内连多个虚拟机器或者一个>主机里的以太接口时,就需要在Linux主机里有一个类似桥接的概念。
|
||||
|
||||
有很多的方法来配置一个Linux网桥。举个例子,在一个无中心的服务器环境里,你可以使用[brct][1]手动地配置一个网桥。在桌面环境下,在网络管理里有建立网桥支持
|
||||
。那就让我们测试一下如何用网络管理配置一个网桥吧。
|
||||
|
||||
### 要求 ###
|
||||
|
||||
为了避免[任何问题][2],建议你的网络管理版本为0.9.9或者更高,这主要为了配合Ubuntu15.05或者更新的版本。
|
||||
|
||||
$ apt-cache show network-manager | grep Version
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
Version: 0.9.10.0-4ubuntu15.1
|
||||
Version: 0.9.10.0-4ubuntu15
|
||||
|
||||
### 创建一个网桥 ###
|
||||
|
||||
使用网络管理创建网桥最简单的方式就是通过nm-connection-editor。这款GUI(图形用户界面)的工具允许你傻瓜式地配置一个网桥。
|
||||
|
||||
首先,启动nm-connection-editor。
|
||||
|
||||
$ nm-connection-editor
|
||||
|
||||
该编辑器的窗口会显示给你一个列表,关于目前配置好的网络连接。点击右上角的“Click”按钮,创建一个网桥。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
接下来,选择“Bridge”作为连接类型。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
现在,开始配置网桥,包括它的名字和桥接。如果没有其他网桥被创建,那么默认的网桥接口会被命名为bridge0。
|
||||
|
||||
回顾一下,创建网桥的目的是为了通过网桥共享你的以太网卡接口。所以你需要添加以太网卡接口到网桥。在图形界面添加一个新的“bridged connection”可以实现上述目的。点击“Add”按钮。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
选择“Ethernet”作为连接类型。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在“Device MAC address”区域,选择你想要控制的接口到bridge里。本例中,假设接口是eth0。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
点击“General”标签,并且选中两个复选框,分别是“Automatically connect to this network when it is available”和“All users may connect to this network”。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
保存更改。
|
||||
|
||||
现在,你会在网桥里看见一个新的从属连接被建立。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
点击网桥的“General”标签,并且确保最上面的两个复选框被选中了。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
切换到“IPv4 Setting”标签,为网桥配置DHCP或者是静态IP地址。注意,你应该使用相同的IPv4设定作为从属的以太网卡接口eth0。本例中,我们假设eth0是用过DHCP配置的。因此,此处选择“Automatic(DHCP)”。如果eth0被指定了一个静态IP地址,那么你应该指定相同的IP地址给网桥。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
最后,保存网桥的设置。
|
||||
|
||||
现在,你会看见一个额外的网桥连接被创建在“Network Connection”窗口里。你不再需要一个预先配置的有线连接,为着从属的eth0接口。所以去删除原来的有线连接吧。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
这时候,网桥连接会被自动激活。你将会暂时失去一个连接,从指定给eth0的IP地址被网桥接管。一旦IP地址指定给了网桥,你将会连接回你的以太网卡接口,通过网桥。你可以通过“Network”设置确认一下。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
同时,检查可用的接口。提醒一下,网桥接口必须已经取代了任何通过你的以太网卡接口的IP地址。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
就这么多了,现在,网桥已经可以用了。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/configure-linux-bridge-network-manager-ubuntu.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
|
||||
译者:[wi-cuckoo](https://github.com/wi-cuckoo)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/author/nanni
|
||||
[1]:http://xmodulo.com/how-to-configure-linux-bridge-interface.html
|
||||
[2]:https://bugs.launchpad.net/ubuntu/+source/network-manager/+bug/1273201
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user