2018-12-09 11:55:06 +08:00
|
|
|
|
9 个鲜为人知的 Python 数据科学库
|
2018-11-25 16:09:10 +08:00
|
|
|
|
======
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2018-12-09 11:55:06 +08:00
|
|
|
|
> 除了 pandas、scikit-learn 和 matplotlib,还要学习一些用 Python 进行数据科学的新技巧。
|
2018-11-25 16:09:10 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2018-12-09 11:55:06 +08:00
|
|
|
|
Python 是一种令人惊叹的语言。事实上,它是世界上增长最快的编程语言之一。它一次又一次地证明了它在各个行业的开发者和数据科学者中的作用。Python 及其库的整个生态系统使其成为全世界用户的恰当选择,无论是初学者还是高级用户。它成功和受欢迎的原因之一是它的一组强大的库,使它如此动态和快速。
|
2018-11-25 16:09:10 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
2018-12-09 11:55:06 +08:00
|
|
|
|
在本文中,我们将看到 Python 库中的一些数据科学工具,而不是那些常用的工具,如 pandas、scikit-learn 和 matplotlib。虽然像 pandas、scikit-learn 这样的库是机器学习中最常想到的,但是了解这个领域的其他 Python 库也是非常有帮助的。
|
2018-11-25 16:09:10 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
### Wget
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2018-12-09 11:55:06 +08:00
|
|
|
|
提取数据,尤其是从网络中提取数据,是数据科学家的重要任务之一。[Wget][1] 是一个免费的工具,用于从网络上非交互式下载文件。它支持 HTTP、HTTPS 和 FTP 协议,以及通过 HTTP 代理进行访问。因为它是非交互式的,所以即使用户没有登录,它也可以在后台工作。所以下次你想下载一个网站或者网页上的所有图片,wget 会提供帮助。
|
2018-11-25 16:09:10 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
2018-12-09 11:55:06 +08:00
|
|
|
|
安装:
|
2018-11-25 16:09:10 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ pip install wget
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2018-12-09 11:55:06 +08:00
|
|
|
|
例子:
|
2018-11-25 16:09:10 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
import wget
|
|
|
|
|
|
url = 'http://www.futurecrew.com/skaven/song_files/mp3/razorback.mp3'
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
filename = wget.download(url)
|
|
|
|
|
|
100% [................................................] 3841532 / 3841532
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
filename
|
|
|
|
|
|
'razorback.mp3'
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
### 钟摆
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2018-12-09 11:55:06 +08:00
|
|
|
|
对于在 Python 中处理日期时间感到沮丧的人来说, [Pendulum][2] 库是很有帮助的。这是一个 Python 包,可以简化日期时间操作。它是 Python 原生类的一个替代品。有关详细信息,请参阅其[文档][3]。
|
2018-11-25 16:09:10 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
2018-12-09 11:55:06 +08:00
|
|
|
|
安装:
|
2018-11-25 16:09:10 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ pip install pendulum
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2018-12-09 11:55:06 +08:00
|
|
|
|
例子:
|
2018-11-25 16:09:10 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
import pendulum
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
dt_toronto = pendulum.datetime(2012, 1, 1, tz='America/Toronto')
|
|
|
|
|
|
dt_vancouver = pendulum.datetime(2012, 1, 1, tz='America/Vancouver')
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
print(dt_vancouver.diff(dt_toronto).in_hours())
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
### 不平衡学习
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2018-12-09 11:55:06 +08:00
|
|
|
|
当每个类别中的样本数几乎相同(即平衡)时,大多数分类算法会工作得最好。但是现实生活中的案例中充满了不平衡的数据集,这可能会影响到机器学习算法的学习和后续预测。幸运的是,[imbalanced-learn][4] 库就是为了解决这个问题而创建的。它与 [scikit-learn][5] 兼容,并且是 [scikit-learn-contrib][6] 项目的一部分。下次遇到不平衡的数据集时,可以尝试一下。
|
2018-11-25 16:09:10 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
2018-12-09 11:55:06 +08:00
|
|
|
|
安装:
|
2018-11-25 16:09:10 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
pip install -U imbalanced-learn
|
|
|
|
|
|
# or
|
|
|
|
|
|
conda install -c conda-forge imbalanced-learn
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2018-12-09 11:55:06 +08:00
|
|
|
|
例子:
|
2018-11-25 16:09:10 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
2018-12-09 11:55:06 +08:00
|
|
|
|
有关用法和示例,请参阅其[文档][7] 。
|
2018-11-25 16:09:10 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
2018-12-09 11:55:06 +08:00
|
|
|
|
### FlashText
|
2018-11-25 16:09:10 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
2018-12-09 11:55:06 +08:00
|
|
|
|
在自然语言处理(NLP)任务中清理文本数据通常需要替换句子中的关键词或从句子中提取关键词。通常,这种操作可以用正则表达式来完成,但是如果要搜索的术语数达到数千个,它们可能会变得很麻烦。
|
2018-11-25 16:09:10 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
2018-12-09 11:55:06 +08:00
|
|
|
|
Python 的 [FlashText][8] 模块,基于 [FlashText 算法][9],为这种情况提供了一个合适的替代方案。FlashText 的最佳部分是运行时间与搜索项的数量无关。你可以在其 [文档][10] 中读到更多关于它的信息。
|
2018-11-25 16:09:10 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
2018-12-09 11:55:06 +08:00
|
|
|
|
安装:
|
2018-11-25 16:09:10 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ pip install flashtext
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2018-12-09 11:55:06 +08:00
|
|
|
|
例子:
|
2018-11-25 16:09:10 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
2018-12-09 11:55:06 +08:00
|
|
|
|
提取关键词:
|
2018-11-25 16:09:10 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
from flashtext import KeywordProcessor
|
|
|
|
|
|
keyword_processor = KeywordProcessor()
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
# keyword_processor.add_keyword(<unclean name>, <standardised name>)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
keyword_processor.add_keyword('Big Apple', 'New York')
|
|
|
|
|
|
keyword_processor.add_keyword('Bay Area')
|
|
|
|
|
|
keywords_found = keyword_processor.extract_keywords('I love Big Apple and Bay Area.')
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
keywords_found
|
|
|
|
|
|
['New York', 'Bay Area']
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2018-12-09 11:55:06 +08:00
|
|
|
|
替代关键词:
|
2018-11-25 16:09:10 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
keyword_processor.add_keyword('New Delhi', 'NCR region')
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
new_sentence = keyword_processor.replace_keywords('I love Big Apple and new delhi.')
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
new_sentence
|
|
|
|
|
|
'I love New York and NCR region.'
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2018-12-09 11:55:06 +08:00
|
|
|
|
有关更多示例,请参阅文档中的 [用法][11] 一节。
|
2018-11-25 16:09:10 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
### 模糊处理
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2018-12-09 11:55:06 +08:00
|
|
|
|
这个名字听起来很奇怪,但是 [FuzzyWuzzy][12] 在字符串匹配方面是一个非常有用的库。它可以很容易地实现字符串匹配率、令牌匹配率等操作。对于匹配保存在不同数据库中的记录也很方便。
|
2018-11-25 16:09:10 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
2018-12-09 11:55:06 +08:00
|
|
|
|
安装:
|
2018-11-25 16:09:10 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ pip install fuzzywuzzy
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2018-12-09 11:55:06 +08:00
|
|
|
|
例子:
|
2018-11-25 16:09:10 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
from fuzzywuzzy import fuzz
|
|
|
|
|
|
from fuzzywuzzy import process
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
# 简单的匹配率
|
|
|
|
|
|
fuzz.ratio("this is a test", "this is a test!")
|
|
|
|
|
|
97
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
# 部分的匹配率
|
|
|
|
|
|
fuzz.partial_ratio("this is a test", "this is a test!")
|
|
|
|
|
|
100
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2018-12-09 11:55:06 +08:00
|
|
|
|
更多的例子可以在 FuzzyWuzy 的 [GitHub 仓库][12]得到。
|
2018-11-25 16:09:10 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
### PyFlux
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2018-12-09 11:55:06 +08:00
|
|
|
|
时间序列分析是机器学习中最常遇到的问题之一。[PyFlux][13] 是 Python 中的开源库,专门为处理时间序列问题而构建的。该库拥有一系列优秀的现代时间序列模型,包括但不限于 ARIMA、GARCH 以及 VAR 模型。简而言之,PyFlux 为时间序列建模提供了一种概率方法。这值得一试。
|
2018-11-25 16:09:10 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
2018-12-09 11:55:06 +08:00
|
|
|
|
安装:
|
2018-11-25 16:09:10 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
pip install pyflux
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2018-12-09 11:55:06 +08:00
|
|
|
|
例子:
|
2018-11-25 16:09:10 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
2018-12-09 11:55:06 +08:00
|
|
|
|
有关用法和示例,请参阅其 [文档][14]。
|
2018-11-25 16:09:10 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
### IPyvolume
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2018-12-09 11:55:06 +08:00
|
|
|
|
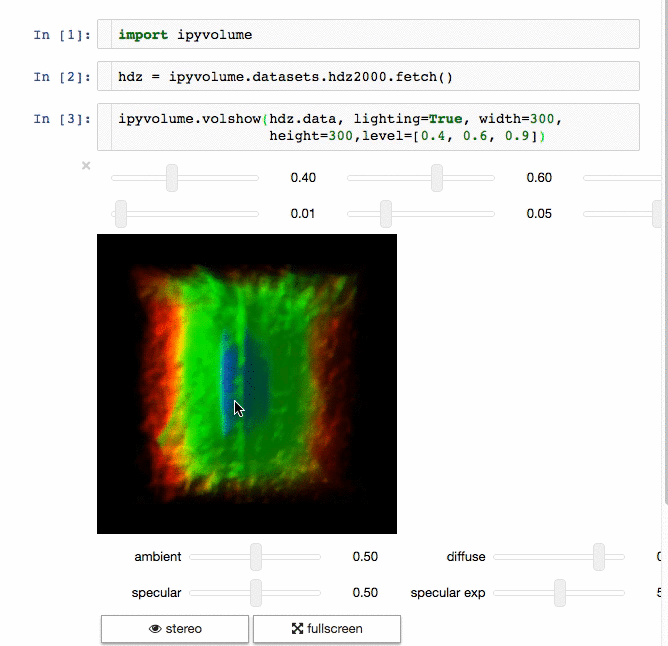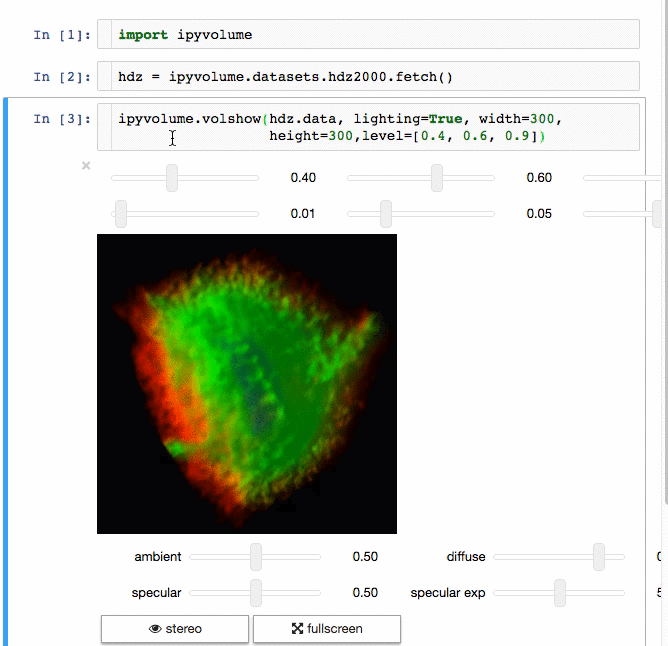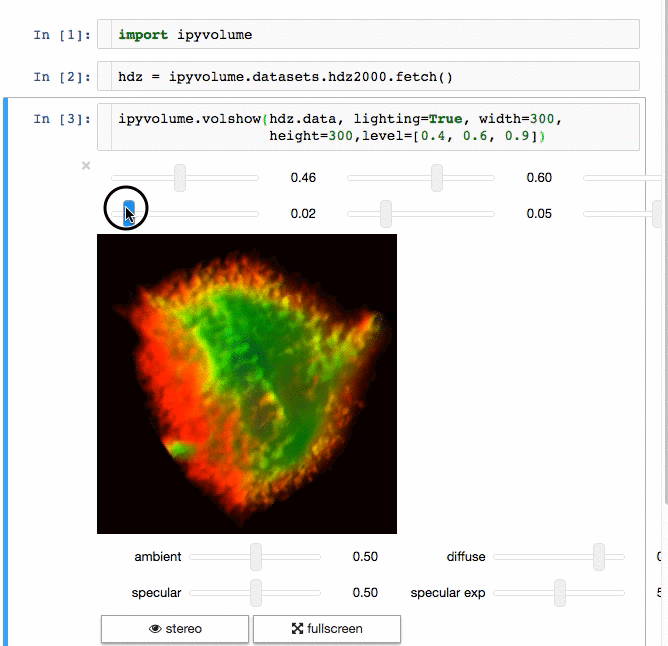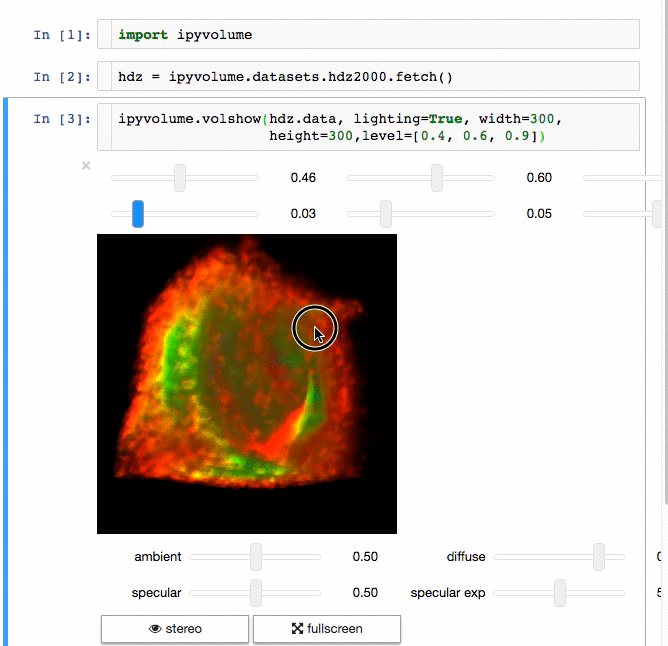
交流结果是数据科学的一个重要方面,可视化结果提供了显著优势。 [IPyvolume][15] 是一个 Python 库,用于在 Jupyter 笔记本中可视化 3D 体积和形状(例如 3D 散点图),配置和工作量极小。然而,它目前处于 1.0 之前的阶段。一个很好的类比是这样的: IPyVolumee volshow 是 3D 阵列,Matplotlib 的 imshow 是 2D 阵列。你可以在其 [文档][16] 中读到更多关于它的信息。
|
2018-11-25 16:09:10 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
2018-12-09 11:55:06 +08:00
|
|
|
|
安装:
|
2018-11-25 16:09:10 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
Using pip
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ pip install ipyvolume
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Conda/Anaconda
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ conda install -c conda-forge ipyvolume
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2018-12-09 11:55:06 +08:00
|
|
|
|
例子:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
动画:
|
2018-11-25 16:09:10 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
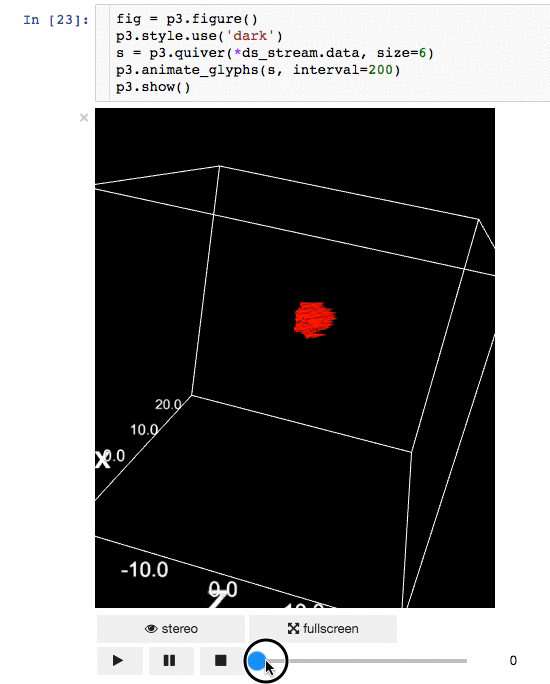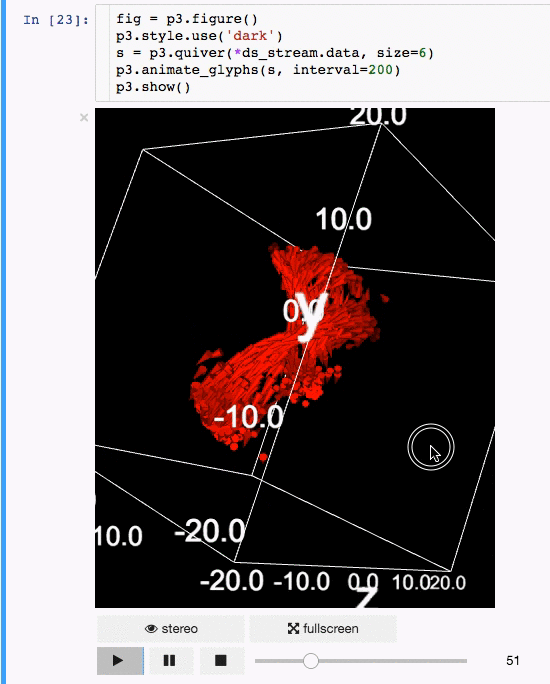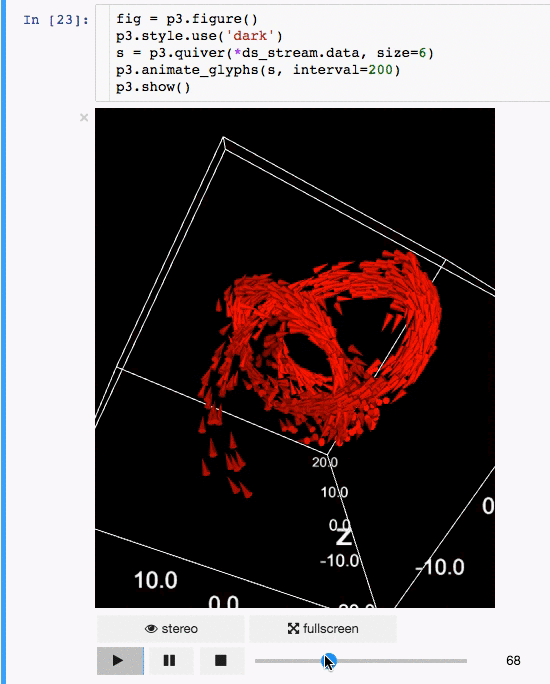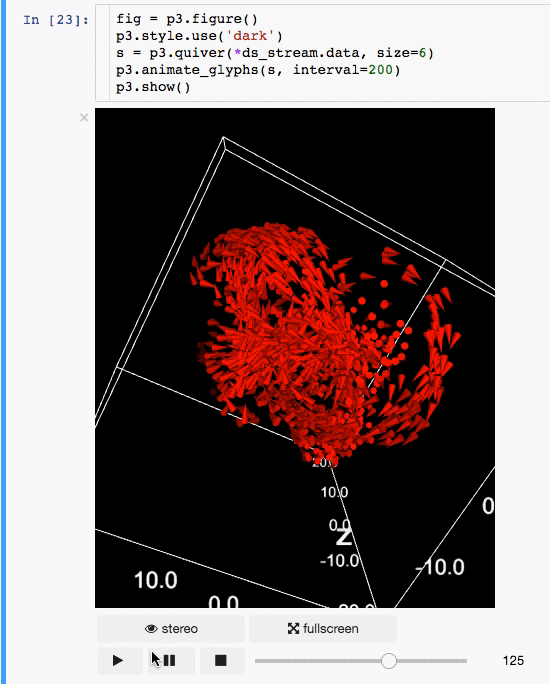
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2018-12-09 11:55:06 +08:00
|
|
|
|
体绘制:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2018-11-25 16:09:10 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
### Dash
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2018-12-09 11:55:06 +08:00
|
|
|
|
[Dash][17] 是一个用于构建 Web 应用程序的高效 Python 框架。它构建于 Flask、Plotty.js 和 Response.js 之上,将下拉菜单、滑块和图形等流行 UI 元素与你的 Python 分析代码联系起来,而不需要JavaScript。Dash 非常适合构建可在 Web 浏览器中呈现的数据可视化应用程序。有关详细信息,请参阅其 [用户指南][18] 。
|
2018-11-25 16:09:10 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
2018-12-09 11:55:06 +08:00
|
|
|
|
安装:
|
2018-11-25 16:09:10 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
pip install dash==0.29.0 # The core dash backend
|
|
|
|
|
|
pip install dash-html-components==0.13.2 # HTML components
|
|
|
|
|
|
pip install dash-core-components==0.36.0 # Supercharged components
|
|
|
|
|
|
pip install dash-table==3.1.3 # Interactive DataTable component (new!)
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2018-12-09 11:55:06 +08:00
|
|
|
|
例子:
|
2018-11-25 16:09:10 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
2018-12-09 11:55:06 +08:00
|
|
|
|
下面的示例显示了一个具有下拉功能的高度交互的图表。当用户在下拉列表中选择一个值时,应用程序代码将数据从 Google Finance 动态导出到 Pandas 数据框架中。
|
2018-11-25 16:09:10 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
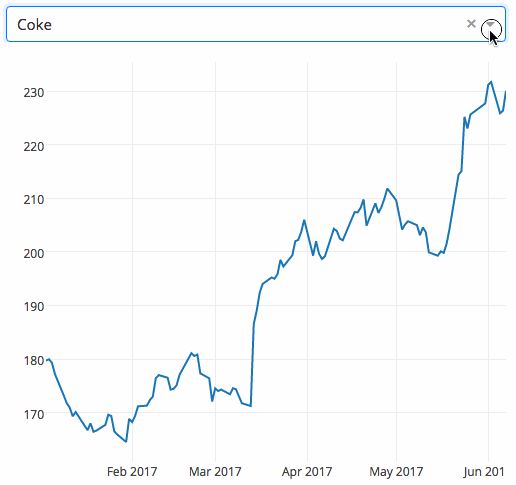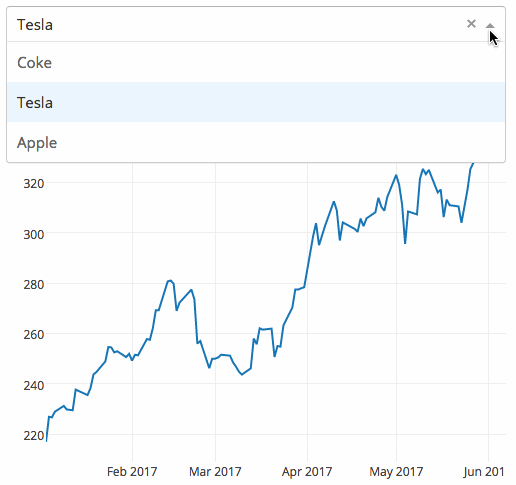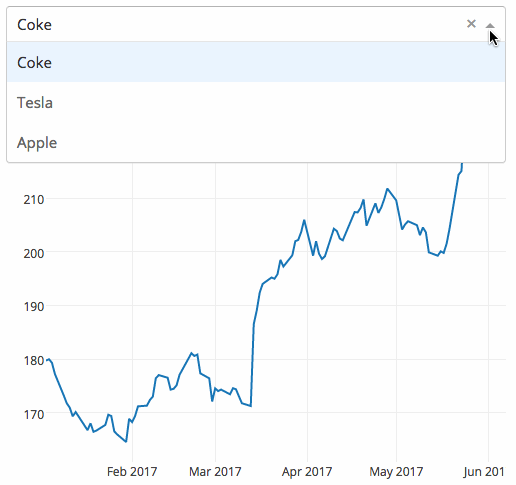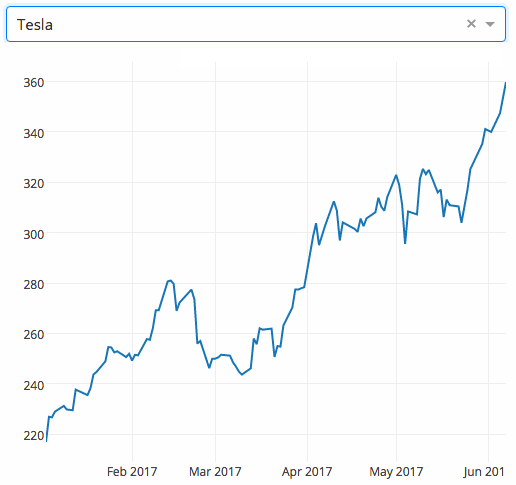
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
### Gym
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2018-12-09 11:55:06 +08:00
|
|
|
|
从 [OpenAI][20] 而来的 [Gym][19] 是开发和比较强化学习算法的工具包。它与任何数值计算库兼容,如 TensorFlow 或 Theano。Gym 是一个测试问题的集合,也称为“环境”,你可以用它来制定你的强化学习算法。这些环境有一个共享的接口,允许您编写通用算法。
|
2018-11-25 16:09:10 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
2018-12-09 11:55:06 +08:00
|
|
|
|
安装:
|
2018-11-25 16:09:10 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
pip install gym
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2018-12-09 11:55:06 +08:00
|
|
|
|
例子:
|
2018-11-25 16:09:10 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
2018-12-09 11:55:06 +08:00
|
|
|
|
以下示例将在 [CartPole-v0][21] 环境中,运行 1000 次,在每一步渲染环境。
|
2018-11-25 16:09:10 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
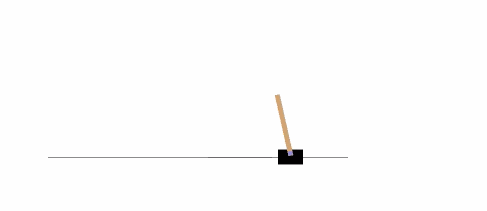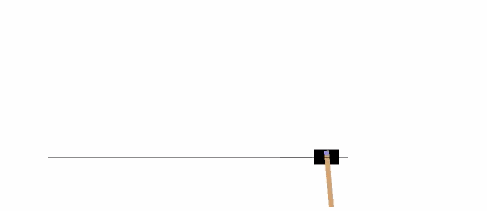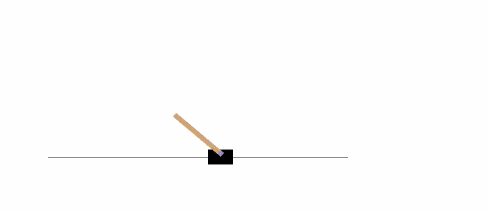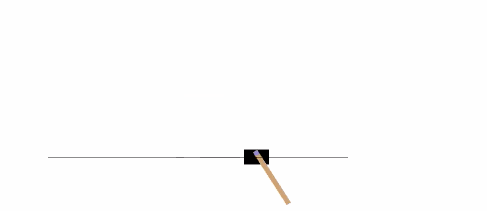
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2018-12-09 11:55:06 +08:00
|
|
|
|
你可以在 Gym 网站上读到 [其它的环境][22] 。
|
2018-11-25 16:09:10 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
### 结论
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
这些是我挑选的有用但鲜为人知的数据科学 Python 库。如果你知道另一个要添加到这个列表中,请在下面的评论中提及。
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2018-12-09 11:55:06 +08:00
|
|
|
|
本文最初发表在 [Analytics Vidhya][23] 的媒体频道上,并经许可转载。
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
------
|
2018-11-25 16:09:10 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
via: https://opensource.com/article/18/11/python-libraries-data-science
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
作者:[Parul Pandey][a]
|
|
|
|
|
|
选题:[lujun9972][b]
|
|
|
|
|
|
译者:[heguangzhi](https://github.com/heguangzhi)
|
2018-12-09 11:55:06 +08:00
|
|
|
|
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
2018-11-25 16:09:10 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
[a]: https://opensource.com/users/parul-pandey
|
|
|
|
|
|
[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
|
|
|
|
|
|
[1]: https://pypi.org/project/wget/
|
|
|
|
|
|
[2]: https://github.com/sdispater/pendulum
|
|
|
|
|
|
[3]: https://pendulum.eustace.io/docs/#installation
|
|
|
|
|
|
[4]: https://github.com/scikit-learn-contrib/imbalanced-learn
|
|
|
|
|
|
[5]: http://scikit-learn.org/stable/
|
|
|
|
|
|
[6]: https://github.com/scikit-learn-contrib
|
|
|
|
|
|
[7]: http://imbalanced-learn.org/en/stable/api.html
|
|
|
|
|
|
[8]: https://github.com/vi3k6i5/flashtext
|
|
|
|
|
|
[9]: https://arxiv.org/abs/1711.00046
|
|
|
|
|
|
[10]: https://flashtext.readthedocs.io/en/latest/
|
|
|
|
|
|
[11]: https://flashtext.readthedocs.io/en/latest/#usage
|
|
|
|
|
|
[12]: https://github.com/seatgeek/fuzzywuzzy
|
|
|
|
|
|
[13]: https://github.com/RJT1990/pyflux
|
|
|
|
|
|
[14]: https://pyflux.readthedocs.io/en/latest/index.html
|
|
|
|
|
|
[15]: https://github.com/maartenbreddels/ipyvolume
|
|
|
|
|
|
[16]: https://ipyvolume.readthedocs.io/en/latest/?badge=latest
|
|
|
|
|
|
[17]: https://github.com/plotly/dash
|
|
|
|
|
|
[18]: https://dash.plot.ly/
|
|
|
|
|
|
[19]: https://github.com/openai/gym
|
|
|
|
|
|
[20]: https://openai.com/
|
|
|
|
|
|
[21]: https://gym.openai.com/envs/CartPole-v0
|
|
|
|
|
|
[22]: https://gym.openai.com/
|
|
|
|
|
|
[23]: https://medium.com/analytics-vidhya/python-libraries-for-data-science-other-than-pandas-and-numpy-95da30568fad
|