mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-02-28 01:01:09 +08:00
365 lines
8.7 KiB
Markdown
365 lines
8.7 KiB
Markdown
|
|
Server Monitoring with Shinken on Ubuntu 16.04
|
||
|
|
=====
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Shinken is an open source computer and network monitoring framework written in python and compatible with Nagios. Shinken can be used on all operating systems that can run python applications like Linux, Unix, and Windows. Shinken was written by Jean Gabes as proof of concept for a new Nagios architecture, but it was turned down by the Nagios author and became an independent network and system monitoring tool that stays compatible with Nagios.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
In this tutorial, I will show you how to install Shinken from source and add a Linux host to the monitoring system. I will use Ubuntu 16.04 Xenial Xerus as the operating system for the Shinken server and monitored host.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
### Step 1 - Install Shinken Server
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Shinken is a python framework, we can install it with pip or install it from source. In this step, we will install Shinken from source.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
There are some tasks that have to be completed before we start installing Shinken.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Install some new python packages and create Linux user with the name "shinken":
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
sudo apt-get install python-setuptools python-pip python-pycurl
|
||
|
|
useradd -m -s /bin/bash shinken
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Download the Shinken source from GitHub repository:
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
git clone https://github.com/naparuba/shinken.git
|
||
|
|
cd shinken/
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Then install Shinken with the command below:
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
git checkout 2.4.3
|
||
|
|
python setup.py install
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Next, for better results, we need to install 'python-cherrypy3' from the ubuntu repository:
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
sudo apt-get install python-cherrypy3
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Now Shinken is installed, next we add Shinken to start at boot time and start it:
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
update-rc.d shinken defaults
|
||
|
|
systemctl start shinken
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
### Step 2 - Install Shinken Webui2
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Webui2 is the Shinken web interface available from shinken.io. The easiest way to install Sshinken webui2 is by using the shinken CLI command (which has to be executed as shinken user).
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Login to the shinken user:
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
su - shinken
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Initialize the shinken configuration file - The command will create a new configuration .shinken.ini:
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
shinken --init
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
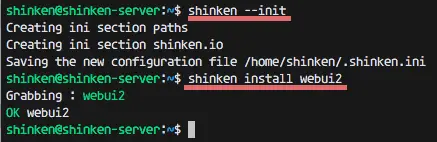
And install webui2 with this shinken CLI command:
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
shinken install webui2
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Webui2 is installed, but we need to install MongoDB and another python package with pip. Run command below as root:
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
sudo apt-get install mongodb
|
||
|
|
pip install pymongo>=3.0.3 requests arrow bottle==0.12.8
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Next, go to the shinken directory and add the new webui2 module by editing the 'broker-master.cfg' file:
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
cd /etc/shinken/brokers/
|
||
|
|
vim broker-master.cfg
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Add a new option inside module on line 40:
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
modules webui2
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Save the file and exit the editor.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Now go to the contacts directory and edit the file 'admin.cfg' for the admin configuration.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
cd /etc/shinken/contacts/
|
||
|
|
vim admin.cfg
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Change the values shown below:
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
contact_name admin # Username 'admin'
|
||
|
|
password yourpass # Pass 'mypass'
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Save and exit.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
### Step 3 - Install Nagios-plugins and Shinken Packages
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
In this step, we will install Nagios-plugins and some Perl module. Then install additional shinken packages from shinken.io to perform the monitoring.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Install Nagios-plugins and cpanminus which is required for building and installing the Perl modules:
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
sudo apt-get install nagios-plugins* cpanminus
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Install these Perl modules with the cpanm command:
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
cpanm Net::SNMP
|
||
|
|
cpanm Time::HiRes
|
||
|
|
cpanm DBI
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Now create new link for utils.pm file to shinken the directory and create a new directory for Log_File_Health:
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
chmod u+s /usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_icmp
|
||
|
|
ln -s /usr/lib/nagios/plugins/utils.pm /var/lib/shinken/libexec/
|
||
|
|
mkdir -p /var/log/rhosts/
|
||
|
|
touch /var/log/rhosts/remote-hosts.log
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Next, install the shinken packages ssh and linux-snmp for monitoring SSH and SNMP sources from shinken.io:
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
su - shinken
|
||
|
|
shinken install ssh
|
||
|
|
shinken install linux-snmp
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
### Step 4 - Add a New Linux Host/host-one
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
We will add a new Linux host that shall be monitored by using an Ubuntu 16.04 server with IP address 192.168.1.121 and hostname 'host-one'.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Connect to the Linux host-one:
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
ssh host1@192.168.1.121
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Install the snmp and snmpd packages from the Ubuntu repository:
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
sudo apt-get install snmp snmpd
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Next, edit the configuration file 'snmpd.conf' with vim:
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
vim /etc/snmp/snmpd.conf
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Comment line 15 and uncomment line 17:
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
#agentAddress udp:127.0.0.1:161
|
||
|
|
agentAddress udp:161,udp6:[::1]:161
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Comment line 51 and 53, then add new line configuration below:
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
#rocommunity mypass default -V systemonly
|
||
|
|
#rocommunity6 mypass default -V systemonly
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
rocommunity mypass
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Save and exit.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Now start the snmpd service with the systemctl command:
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
systemctl start snmpd
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Go to the shinken server and define the new host by creating a new file in the 'hosts' directory.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
cd /etc/shinken/hosts/
|
||
|
|
vim host-one.cfg
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Paste configuration below:
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
define host{
|
||
|
|
use generic-host,linux-snmp,ssh
|
||
|
|
contact_groups admins
|
||
|
|
host_name host-one
|
||
|
|
address 192.168.1.121
|
||
|
|
_SNMPCOMMUNITY mypass # SNMP Pass Config on snmpd.conf
|
||
|
|
}
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Save and exit.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Edit the SNMP configuration on the Shinken server:
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
vim /etc/shinken/resource.d/snmp.cfg
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Change 'public' to 'mypass' - must be the same password that you used in the snmpd configuration file on the client host-one.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
$SNMPCOMMUNITYREAD$=mypass
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Save and exit.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Now reboot both servers - Shinken server and the monitored Linux host:
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
reboot
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
The new Linux host has been added successfully to the Shinken server.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
### Step 5 - Access Shinken Webui2
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Visit the Shinken webui2 on port 7677 (replace the IP in the URL with your IP):
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
http://192.168.1.120:7767
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
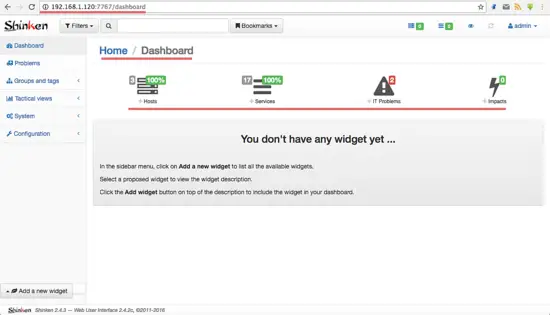
Log in with user admin and your password (the one that you have set in the admin.cfg configuration file).
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|

|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Shinken Dashboard in Webui2.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
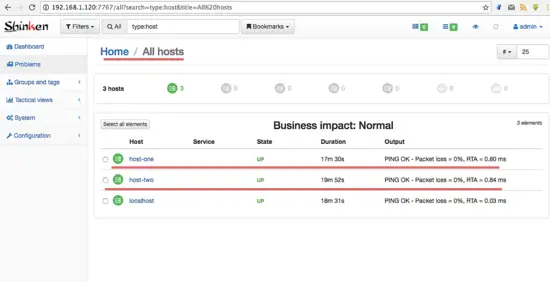
Our 2 servers are monitored with Shinken.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
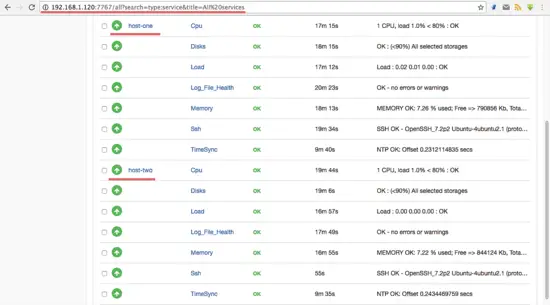
List all services that are monitored with linux-snmp.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
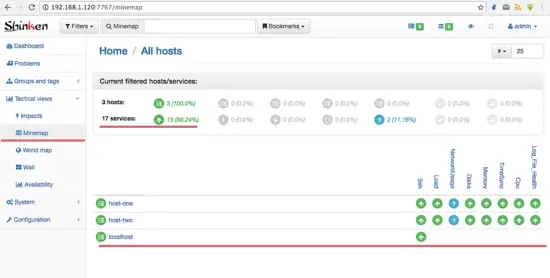
Status of all hosts and services.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
### Step 6 - Common Problems with Shinken
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
- Problems with the NTP server
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
When you get this error with NTP.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
TimeSync - CRITICAL ( NTP CRITICAL: No response from the NTP server)
|
||
|
|
TimeSync - CRITICAL ( NTP CRITICAL: Offset unknown )
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
To solve this problem, install ntp on all Linux hosts.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
sudo apt-get install ntp ntpdate
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Edit the ntp configuration:
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
vim /etc/ntp.conf
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Comment all the pools and replace it with:
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
#pool 0.ubuntu.pool.ntp.org iburst
|
||
|
|
#pool 1.ubuntu.pool.ntp.org iburst
|
||
|
|
#pool 2.ubuntu.pool.ntp.org iburst
|
||
|
|
#pool 3.ubuntu.pool.ntp.org iburst
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
pool 0.id.pool.ntp.org
|
||
|
|
pool 1.asia.pool.ntp.org
|
||
|
|
pool 0.asia.pool.ntp.org
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Next, add a new line inside restrict:
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
# Local users may interrogate the ntp server more closely.
|
||
|
|
restrict 127.0.0.1
|
||
|
|
restrict 192.168.1.120 #shinken server IP address
|
||
|
|
restrict ::1
|
||
|
|
NOTE: 192.168.1.120 is the Shinken server IP address.
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Save and exit.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Start ntp and check the Shinken dashboard:
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
ntpd
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
- Problem check_netint.pl Not Found
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Download the source from the github repository to the shinken lib directory:
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
cd /var/lib/shinken/libexec/
|
||
|
|
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Sysnove/shinken-plugins/master/check_netint.pl
|
||
|
|
chmod +x check_netint.pl
|
||
|
|
chown shinken:shinken check_netint.pl
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
- Problem with NetworkUsage
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
There is error message:
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
ERROR : Unknown interface eth\d+
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Check your network interface and edit the linux-snmp template.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
On my Ubuntu server, the network interface is 'enp0s8', not eth0, so I got this error.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Edit the linux-snmp template packs with vim:
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
vim /etc/shinken/packs/linux-snmp/templates.cfg
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Add the network interface to line 24:
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
_NET_IFACES eth\d+|em\d+|enp0s8
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
via: https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/server-monitoring-with-shinken-on-ubuntu-16-04/
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
作者:[Muhammad Arul][a]
|
||
|
|
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||
|
|
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
[a]: https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/server-monitoring-with-shinken-on-ubuntu-16-04/
|
||
|
|
Save and exit.
|