2018-11-05 09:49:53 +08:00
|
|
|
|
Python 机器学习的必备技巧
|
|
|
|
|
|
======
|
2018-11-08 09:58:12 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
2018-11-05 09:49:53 +08:00
|
|
|
|
> 尝试使用 Python 掌握机器学习、人工智能和深度学习。
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2018-11-08 09:58:12 +08:00
|
|
|
|
想要入门机器学习并不难。除了<ruby>大规模网络公开课<rt>Massive Open Online Courses</rt></ruby>(MOOC)之外,还有很多其它优秀的免费资源。下面我分享一些我觉得比较有用的方法。
|
2018-11-05 09:49:53 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
2018-11-08 09:58:12 +08:00
|
|
|
|
1. 从一些 YouTube 上的好视频开始,阅览一些关于这方面的文章或者书籍,例如 《[主算法:终极学习机器的探索将如何重塑我们的世界][29]》,而且我觉得你肯定会喜欢这些[关于机器学习的很酷的互动页面][30]。
|
|
|
|
|
|
2. 对于“<ruby>机器学习<rt>machine learning</rt></ruby>”、“<ruby>人工智能<rt>artificial intelligence</rt></ruby>”、“<ruby>深度学习<rt>deep learning</rt></ruby>”、“<ruby>数据科学<rt>data science</rt></ruby>”、“<ruby>计算机视觉<rt>computer vision</rt></ruby>”和“<ruby>机器人技术<rt>robotics</rt></ruby>”这一堆新名词,你需要知道它们之间的区别。你可以阅览或聆听这些领域的专家们的演讲,例如这位有影响力的[数据科学家 Brandon Rohrer 的精彩视频][1]。或者这个讲述了数据科学相关的[各种角色之间的区别][2]的视频。
|
|
|
|
|
|
3. 明确你自己的学习目标,并选择合适的 [Coursera 课程][3],或者参加高校的网络公开课,例如[华盛顿大学的课程][4]就很不错。
|
|
|
|
|
|
4. 关注优秀的博客:例如 [KDnuggets][32] 的博客、[Mark Meloon][33] 的博客、[Brandon Rohrer][34] 的博客、[Open AI][35] 的研究博客,这些都值得推荐。
|
|
|
|
|
|
5. 如果你热衷于在线课程,后文中会有如何[正确选择 MOOC 课程][31]的指导。
|
|
|
|
|
|
6. 最重要的是,培养自己对这些技术的兴趣。加入一些优秀的社交论坛,不要被那些耸人听闻的头条和新闻所吸引,专注于阅读和了解,将这些技术的背景知识和发展方向理解透彻,并积极思考在日常生活和工作中如何应用机器学习或数据科学的原理。例如建立一个简单的回归模型来预测下一次午餐的成本,又或者是从电力公司的网站上下载历史电费数据,在 Excel 中进行简单的时序分析以发现某种规律。在你对这些技术产生了浓厚兴趣之后,可以观看以下这个视频。
|
2018-11-05 09:49:53 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
<https://www.youtube.com/embed/IpGxLWOIZy4>
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
### Python 是机器学习和人工智能方面的最佳语言吗?
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2018-11-08 09:58:12 +08:00
|
|
|
|
除非你是一名专业的研究一些复杂算法纯理论证明的研究人员,否则,对于一个机器学习的入门者来说,需要熟悉至少一种高级编程语言。因为大多数情况下都是需要考虑如何将现有的机器学习算法应用于解决实际问题,而这需要有一定的编程能力作为基础。
|
2018-11-05 09:49:53 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
2018-11-08 09:58:12 +08:00
|
|
|
|
哪一种语言是数据科学的最佳语言?这个讨论一直没有停息过。对于这方面,你可以提起精神来看一下 FreeCodeCamp 上这一篇关于[数据科学语言][6]的文章,又或者是 KDnuggets 关于 [Python 和 R 之争][7]的深入探讨。
|
2018-11-05 09:49:53 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
2018-11-08 09:58:12 +08:00
|
|
|
|
目前人们普遍认为 Python 在开发、部署、维护各方面的效率都是比较高的。与 Java、C 和 C++ 这些较为传统的语言相比,Python 的语法更为简单和高级。而且 Python 拥有活跃的社区群体、广泛的开源文化、数百个专用于机器学习的优质代码库,以及来自业界巨头(包括 Google、Dropbox、Airbnb 等)的强大技术支持。
|
2018-11-05 09:49:53 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
### 基础 Python 库
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
如果你打算使用 Python 实施机器学习,你必须掌握一些 Python 包和库的使用方法。
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#### NumPy
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
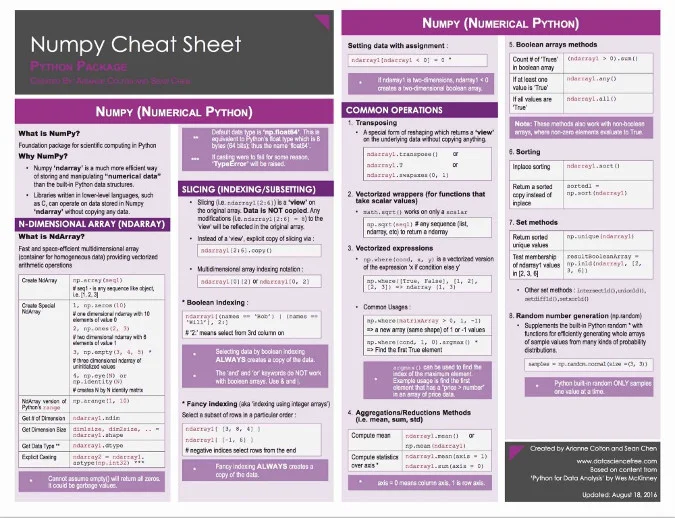
NumPy 的完整名称是 [Numerical Python][8],它是 Python 生态里高性能科学计算和数据分析都需要用到的基础包,几乎所有高级工具(例如 [Pandas][9] 和 [scikit-learn][10])都依赖于它。[TensorFlow][11] 使用了 NumPy 数组作为基础构建块以支持 Tensor 对象和深度学习的图形流。很多 NumPy 操作的速度都非常快,因为它们都是通过 C 实现的。高性能对于数据科学和现代机器学习来说是一个非常宝贵的优势。
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#### Pandas
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
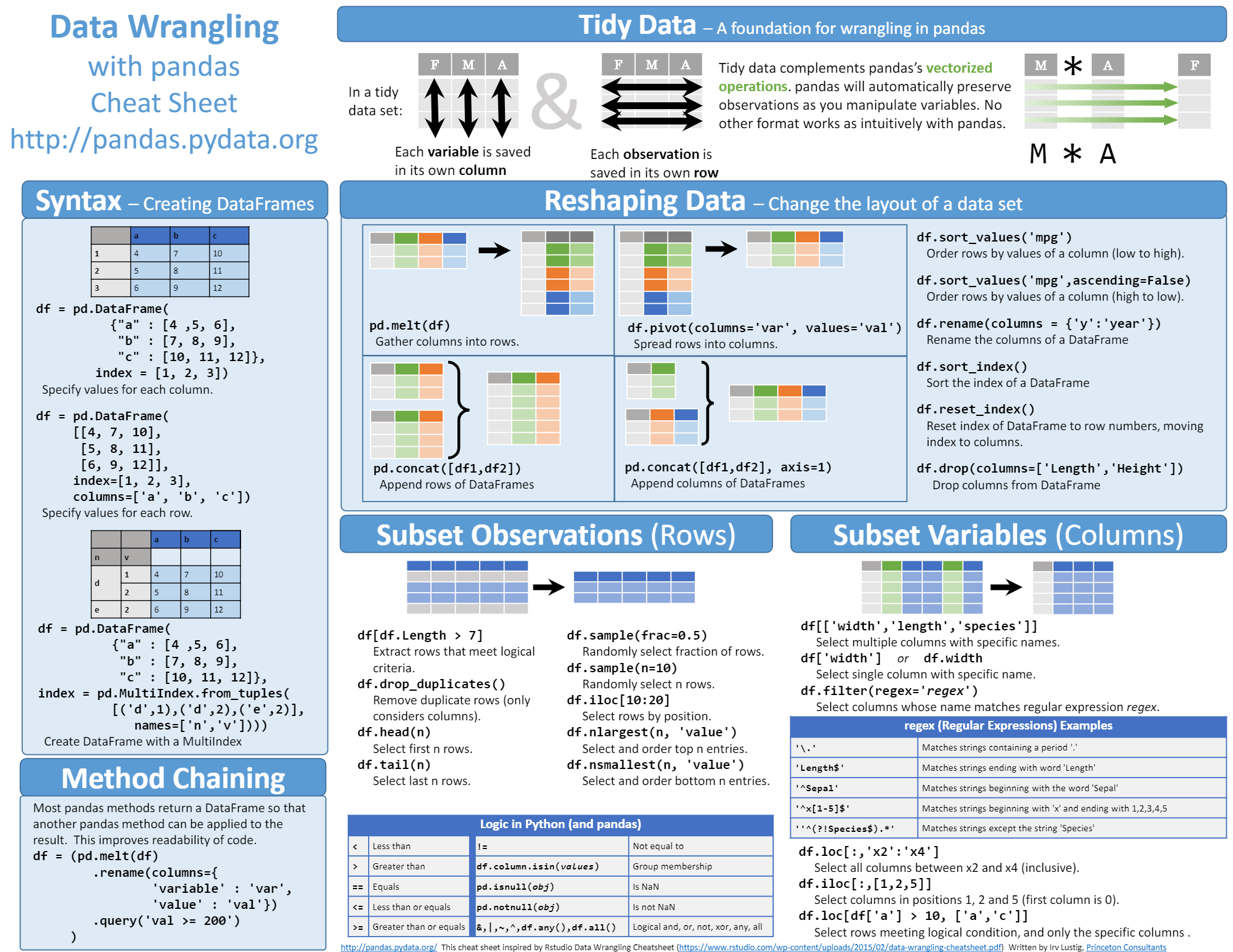
Pandas 是 Python 生态中用于进行通用数据分析的最受欢迎的库。Pandas 基于 NumPy 数组构建,在保证了可观的执行速度的同时,还提供了许多数据工程方面的功能,包括:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* 对多种不同数据格式的读写操作
|
|
|
|
|
|
* 选择数据子集
|
|
|
|
|
|
* 跨行列计算
|
|
|
|
|
|
* 查找并补充缺失的数据
|
2018-11-08 09:58:12 +08:00
|
|
|
|
* 将操作应用于数据中的独立分组
|
2018-11-05 09:49:53 +08:00
|
|
|
|
* 按照多种格式转换数据
|
|
|
|
|
|
* 组合多个数据集
|
|
|
|
|
|
* 高级时间序列功能
|
|
|
|
|
|
* 通过 Matplotlib 和 Seaborn 进行可视化
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#### Matplotlib 和 Seaborn
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
数据可视化和数据分析是数据科学家的必备技能,毕竟仅凭一堆枯燥的数据是无法有效地将背后蕴含的信息向受众传达的。这两项技能对于机器学习来说同样重要,因为首先要对数据集进行一个探索性分析,才能更准确地选择合适的机器学习算法。
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
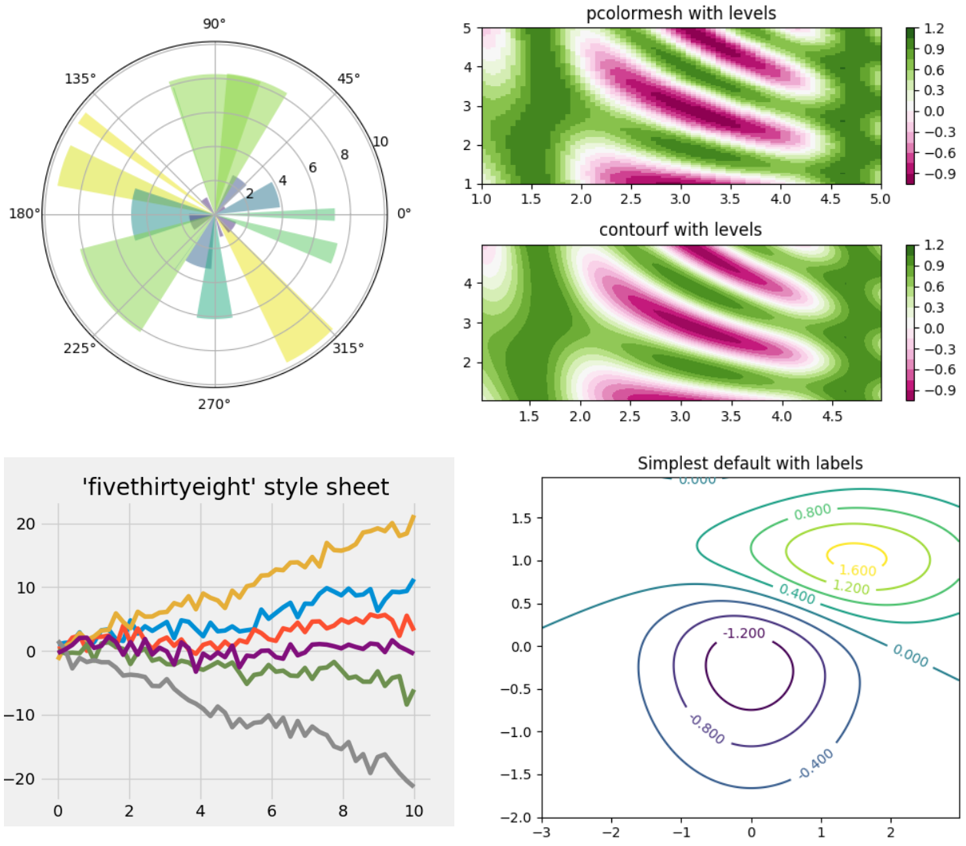
[Matplotlib][12] 是应用最广泛的 2D Python 可视化库。它包含海量的命令和接口,可以让你根据数据生成高质量的图表。要学习使用 Matplotlib,可以参考这篇详尽的[文章][13]。
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
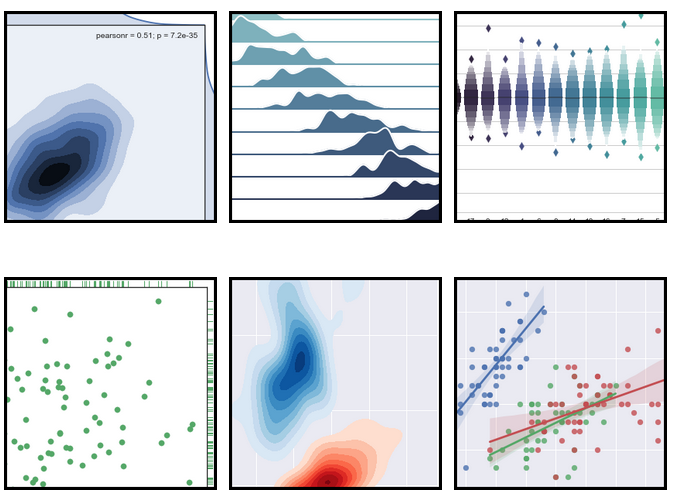
[Seaborn][14] 也是一个强大的用于统计和绘图的可视化库。它在 Matplotlib 的基础上提供样式灵活的 API、用于统计和绘图的常见高级函数,还可以和 Pandas 提供的功能相结合。要学习使用 Seaborn,可以参考这篇优秀的[教程][15]。
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#### Scikit-learn
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2018-11-08 09:58:12 +08:00
|
|
|
|
Scikit-learn 是机器学习方面通用的重要 Python 包。它实现了多种[分类][16]、[回归][17]和[聚类][18]算法,包括[支持向量机][19]、[随机森林][20]、[梯度增强][21]、[k-means 算法][22]和 [DBSCAN 算法][23],可以与 Python 的数值库 NumPy 和科学计算库 [SciPy][24] 结合使用。它通过兼容的接口提供了有监督和无监督的学习算法。Scikit-learn 的强壮性让它可以稳定运行在生产环境中,同时它在易用性、代码质量、团队协作、文档和性能等各个方面都有良好的表现。可以参考[这篇基于 Scikit-learn 的机器学习入门][25],或者[这篇基于 Scikit-learn 的简单机器学习用例演示][26]。
|
2018-11-05 09:49:53 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
本文使用 [CC BY-SA 4.0][28] 许可,在 [Heartbeat][27] 上首发。
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
via: https://opensource.com/article/18/10/machine-learning-python-essential-hacks-and-tricks
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
作者:[Tirthajyoti Sarkar][a]
|
|
|
|
|
|
选题:[lujun9972][b]
|
|
|
|
|
|
译者:[HankChow](https://github.com/HankChow)
|
2018-11-08 09:58:12 +08:00
|
|
|
|
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
2018-11-05 09:49:53 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
[a]: https://opensource.com/users/tirthajyoti
|
|
|
|
|
|
[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
|
|
|
|
|
|
[1]: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tKa0zDDDaQk
|
|
|
|
|
|
[2]: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ura_ioOcpQI
|
|
|
|
|
|
[3]: https://www.coursera.org/learn/machine-learning
|
|
|
|
|
|
[4]: https://www.coursera.org/specializations/machine-learning
|
|
|
|
|
|
[5]: https://towardsdatascience.com/how-to-choose-effective-moocs-for-machine-learning-and-data-science-8681700ed83f
|
|
|
|
|
|
[6]: https://medium.freecodecamp.org/which-languages-should-you-learn-for-data-science-e806ba55a81f
|
|
|
|
|
|
[7]: https://www.kdnuggets.com/2017/09/python-vs-r-data-science-machine-learning.html
|
|
|
|
|
|
[8]: http://numpy.org/
|
|
|
|
|
|
[9]: https://pandas.pydata.org/
|
|
|
|
|
|
[10]: http://scikit-learn.org/
|
|
|
|
|
|
[11]: https://www.tensorflow.org/
|
|
|
|
|
|
[12]: https://matplotlib.org/
|
|
|
|
|
|
[13]: https://realpython.com/python-matplotlib-guide/
|
|
|
|
|
|
[14]: https://seaborn.pydata.org/
|
|
|
|
|
|
[15]: https://www.datacamp.com/community/tutorials/seaborn-python-tutorial
|
|
|
|
|
|
[16]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Statistical_classification
|
|
|
|
|
|
[17]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Regression_analysis
|
|
|
|
|
|
[18]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cluster_analysis
|
|
|
|
|
|
[19]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Support_vector_machine
|
|
|
|
|
|
[20]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Random_forests
|
|
|
|
|
|
[21]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gradient_boosting
|
|
|
|
|
|
[22]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/K-means_clustering
|
|
|
|
|
|
[23]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/DBSCAN
|
|
|
|
|
|
[24]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/SciPy
|
|
|
|
|
|
[25]: http://scikit-learn.org/stable/tutorial/basic/tutorial.html
|
|
|
|
|
|
[26]: https://towardsdatascience.com/machine-learning-with-python-easy-and-robust-method-to-fit-nonlinear-data-19e8a1ddbd49
|
|
|
|
|
|
[27]: https://heartbeat.fritz.ai/some-essential-hacks-and-tricks-for-machine-learning-with-python-5478bc6593f2
|
|
|
|
|
|
[28]: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/
|
|
|
|
|
|
[29]: https://www.goodreads.com/book/show/24612233-the-master-algorithm
|
|
|
|
|
|
[30]: http://www.r2d3.us/visual-intro-to-machine-learning-part-1/
|
|
|
|
|
|
[31]: https://towardsdatascience.com/how-to-choose-effective-moocs-for-machine-learning-and-data-science-8681700ed83f
|
|
|
|
|
|
[32]: https://www.kdnuggets.com/
|
|
|
|
|
|
[33]: http://www.markmeloon.com/
|
|
|
|
|
|
[34]: https://brohrer.github.io/blog.html
|
|
|
|
|
|
[35]: https://blog.openai.com/
|
|
|
|
|
|
|