mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-01-07 22:11:09 +08:00
147 lines
5.7 KiB
Markdown
147 lines
5.7 KiB
Markdown
|
|
# How to Convert Files to UTF-8 Encoding in Linux
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
In this guide, we will describe what character encoding and cover a few examples of converting files from one character encoding to another using a command line tool. Then finally, we will look at how to convert several files from any character set (charset) to UTF-8 encoding in Linux.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
As you may probably have in mind already, a computer does not understand or store letters, numbers or anything else that we as humans can perceive except bits. A bit has only two possible values, that is either a `0` or `1`, `true` or `false`, `yes` or `no`. Every other thing such as letters, numbers, images must be represented in bits for a computer to process.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
In simple terms, character encoding is a way of informing a computer how to interpret raw zeroes and ones into actual characters, where a character is represented by set of numbers. When we type text in a file, the words and sentences we form are cooked-up from different characters, and characters are organized into a charset.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
There are various encoding schemes out there such as ASCII, ANSI, Unicode among others. Below is an example of ASCII encoding.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
Character bits
|
|||
|
|
A 01000001
|
|||
|
|
B 01000010
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
In Linux, the iconv command line tool is used to convert text from one form of encoding to another.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
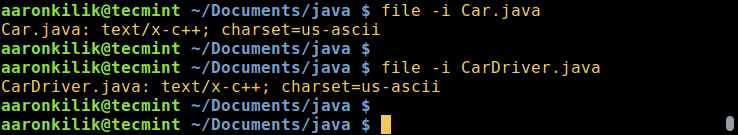
You can check the encoding of a file using the file command, by using the `-i` or `--mime` flag which enables printing of mime type string as in the examples below:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
$ file -i Car.java
|
|||
|
|
$ file -i CarDriver.java
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
[
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
][3]
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Check File Encoding in Linux
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
The syntax for using iconv is as follows:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
$ iconv option
|
|||
|
|
$ iconv options -f from-encoding -t to-encoding inputfile(s) -o outputfile
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Where `-f` or `--from-code` means input encoding and `-t` or `--to-encoding` specifies output encoding.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
To list all known coded character sets, run the command below:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
$ iconv -l
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
[
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
][2]
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
List Coded Charsets in Linux
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
### Convert Files from UTF-8 to ASCII Encoding
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
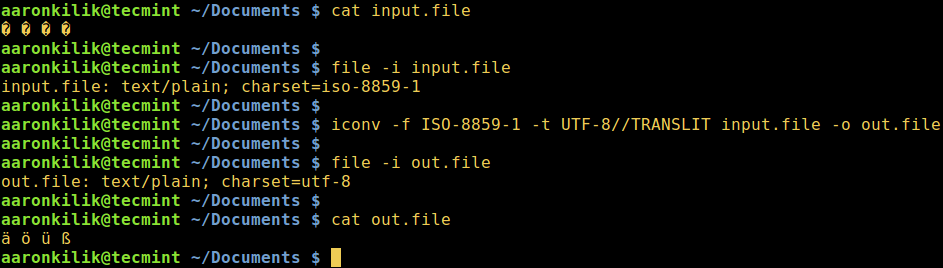
Next, we will learn how to convert from one encoding scheme to another. The command below converts from ISO-8859-1 to UTF-8 encoding.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Consider a file named `input.file` which contains the characters:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
<EFBFBD> <20> <20> <20>
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Let us start by checking the encoding of the characters in the file and then view the file contents. Closely, we can convert all the characters to ASCII encoding.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
After running the iconv command, we then check the contents of the output file and the new encoding of the characters as below.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
$ file -i input.file
|
|||
|
|
$ cat input.file
|
|||
|
|
$ iconv -f ISO-8859-1 -t UTF-8//TRANSLIT input.file -o out.file
|
|||
|
|
$ cat out.file
|
|||
|
|
$ file -i out.file
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
[
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
][1]
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Convert UTF-8 to ASCII in Linux
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Note: In case the string `//IGNORE` is added to to-encoding, characters that can’t be converted and an error is displayed after conversion.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Again, supposing the string `//TRANSLIT` is added to to-encoding as in the example above (ASCII//TRANSLIT), characters being converted are transliterated as needed and if possible. Which implies in the event that a character can’t be represented in the target character set, it can be approximated through one or more similar looking characters.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Consequently, any character that can’t be transliterated and is not in target character set is replaced with a question mark `(?)` in the output.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
### Convert Multiple Files to UTF-8 Encoding
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Coming back to our main topic, to convert multiple or all files in a directory to UTF-8 encoding, you can write a small shell script called encoding.sh as follows:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
#!/bin/bash
|
|||
|
|
#enter input encoding here
|
|||
|
|
FROM_ENCODING="value_here"
|
|||
|
|
#output encoding(UTF-8)
|
|||
|
|
TO_ENCODING="UTF-8"
|
|||
|
|
#convert
|
|||
|
|
CONVERT=" iconv -f $FROM_ENCODING -t $TO_ENCODING"
|
|||
|
|
#loop to convert multiple files
|
|||
|
|
for file in *.txt; do
|
|||
|
|
$CONVERT "$file" -o "${file%.txt}.utf8.converted"
|
|||
|
|
done
|
|||
|
|
exit 0
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Save the file, then make the script executable. Run it from the directory where your files (`*.txt`) are located.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
$ chmod +x encoding.sh
|
|||
|
|
$ ./encoding.sh
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Important: You can as well use this script for general conversion of multiple files from one given encoding to another, simply play around with the values of the `FROM_ENCODING` and `TO_ENCODING`variable, not forgetting the output file name `"${file%.txt}.utf8.converted"`.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
For more information, look through the iconv man page.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
$ man iconv
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
To sum up this guide, understanding encoding and how to convert from one character encoding scheme to another is necessary knowledge for every computer user more so for programmers when it comes to dealing with text.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Lastly, you can get in touch with us by using the comment section below for any questions or feedback.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
via: http://www.tecmint.com/convert-files-to-utf-8-encoding-in-linux/#
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
作者:[Aaron Kili][a]
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/
|
|||
|
|
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/Converts-UTF8-to-ASCII-in-Linux.png
|
|||
|
|
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/List-Coded-Charsets-in-Linux.png
|
|||
|
|
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/Check-File-Encoding-in-Linux.png
|