mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-01-07 22:11:09 +08:00
80 lines
3.5 KiB
Markdown
80 lines
3.5 KiB
Markdown
|
|
How To Assign Output of a Linux Command to a Variable
|
|||
|
|
============================================================
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
When you run a command, it produces some kind of output: either the result of a program is suppose to produce or status/error messages of the program execution details. Sometimes, you may want to store the output of a command in a variable to be used in a later operation.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
In this post, we will review the different ways of assigning the output of a shell command to a variable, specifically useful for shell scripting purpose.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
To store the output of a command in a variable, you can use the shell command substitution feature in the forms below:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
variable_name=$(command)
|
|||
|
|
variable_name=$(command [option ...] arg1 arg2 ...)
|
|||
|
|
OR
|
|||
|
|
variable_name='command'
|
|||
|
|
variable_name='command [option ...] arg1 arg2 ...'
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Below are a few examples of using command substitution.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
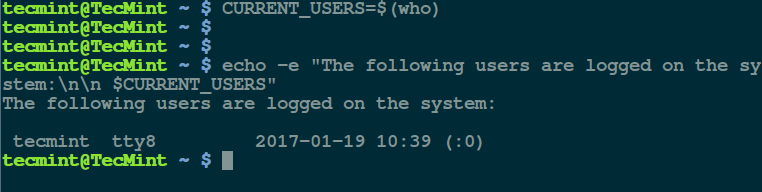
In this first example, we will store the value of `who` (which shows who is logged on the system) command in the variable `CURRENT_USERS` user:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
$ CURRENT_USERS=$(who)
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Then we can use the variable in a sentence displayed using the [echo command][1] like so:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
$ echo -e "The following users are logged on the system:\n\n $CURRENT_USERS"
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
In the command above: the flag `-e` means interpret any escape sequences ( such as `\n` for newline) used. To avoid wasting time as well as memory, simply perform the command substitution within the [echo command][2] as follows:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
$ echo -e "The following users are logged on the system:\n\n $(who)"
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
[
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
][3]
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Shows Current Logged Users in Linux
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
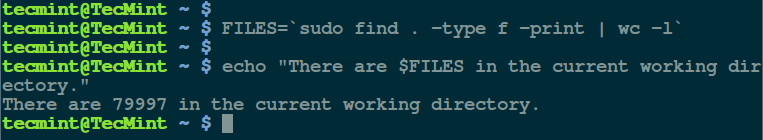
Next, to demonstrate the concept using the second form; we can store the total number of files in the current working directory in a variable called `FILES` and echo it later as follows:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
$ FILES=`sudo find . -type f -print | wc -l`
|
|||
|
|
$ echo "There are $FILES in the current working directory."
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
[
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
][4]
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Show Number of Files in Directory
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
That’s it for now, in this article, we explained the methods of assigning the output of a shell command to a variable. You can add your thoughts to this post via the feedback section below.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
作者简介:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|

|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Aaron Kili is a Linux and F.O.S.S enthusiast, an upcoming Linux SysAdmin, web developer, and currently a content creator for TecMint who loves working with computers and strongly believes in sharing knowledge.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
via: http://www.tecmint.com/assign-linux-command-output-to-variable/
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
作者:[Aaron Kili][a]
|
|||
|
|
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
|||
|
|
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/
|
|||
|
|
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/echo-command-in-linux/
|
|||
|
|
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/echo-command-in-linux/
|
|||
|
|
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/01/Shows-Current-Logged-Users-in-Linux.png
|
|||
|
|
[4]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/01/Show-Number-of-Files-in-Directory.png
|