This tutorial will show you how to add a secondSamba4domain controller, provisioned onUbuntu 16.04server, to the existingSamba AD DCforest in order to provide a degree of load balancing/failover for some crucial AD DC services, especially for services such as DNS and AD DC LDAP schema with SAM database.
#### Requirements
1. [Create an Active Directory Infrastructure with Samba4 on Ubuntu – Part 1][1]
This article is aPart-5ofSamba4 AD DCseries as follows:
Part 2:[Manage Samba4 AD Infrastructure from Linux Command Line][2]Part 3:[Manage Samba4 Active Directory Infrastructure from Windows10 via RSAT][3]Part 4:[Manage Samba4 AD Domain Controller DNS and Group Policy from Windows][4]
### Step 1: Initial Configuration for Samba4 Setup
1.Before you start to actually perform domain joining for the second DC, you need to take care of few initial settings. First, make sure thehostnameof the system which will be integrated intoSamba4 AD DCcontains a descriptive name.
Assuming that thehostnameof the first provisioned realm is called`adc1`, you can name the second DC with`adc2`in order to provide a consistent naming scheme across your Domain Controllers.
To change the systemhostnameyou can issue the below command.
```
# hostnamectl set-hostname adc2
```
else you can manually edit/etc/hostnamefile and add a new line with the desired name.
```
# nano /etc/hostname
```
Here add the hostname.
```
adc2
```
2.Next, open local system resolution file and add an entry with the IP address witch points to the short name andFQDNof the main domain controller, as illustrated in the below screenshot.
Through this tutorial, the primary DC name is`adc1.tecmint.lan`and it resolves to192.168.1.254IP address.

][5]
Set Hostname for Samba4 AD DC
3.On the next step, open/etc/network/interfacesand assign a static IP address for your system as illustrated in the below screenshot.
Pay attention todns-nameserversanddns-searchvariables. These values should be configured to point back to the IP address of the primarySamba4 AD DCand realm in order for DNS resolution to work correctly.
Restart the network daemon in order to reflect changes. Verify/etc/resolv.conffile to assure that both DNS values from your network interface are updated to this file.
```
# nano /etc/network/interfaces
```
Edit and replace with your custom IP settings:
```
auto ens33
iface ens33 inet static
address 192.168.1.253
netmask 255.255.255.0
brodcast 192.168.1.1
gateway 192.168.1.1
dns-nameservers 192.168.1.254
dns-search tecmint.lan
```
Restart network service and confirm changes.
```
# systemctl restart networking.service
# cat /etc/resolv.conf
```
[

][6]
Configure DNS for Samba4 AD
Thedns-searchvalue will automatically append the domain name when you query a host by its short name (will form the FQDN).
4.In order to test if DNS resolution is working as expected, issue a series ofpingcommands against your domain short name, FQDN and realm as shown in the below screenshot.
In all these casesSamba4 AD DC DNSserver should reply with the IP address of your main DC.
[

][7]
Verify DNS Resolution for Samba4 AD
5.The final additional step that you need to take care off is time synchronization with your main Domain Controller. This can be accomplished by installingNTPclient utility on your system by issuing the below command:
```
# apt-get install ntpdate
```
6.Assuming that you want to manually force time synchronization withsamba4 AD DC, runntpdatecommand against the primary DC by issuing the following command.
```
# ntpdate adc1
```
[

][8]
Time Synchronize with Samba4 AD
### Step 2: Install Samba4 with Required Dependencies
7.In order to enrollUbuntu 16.04system into your domain, first installSamba4,Kerberosclient and a few other important packages for later use from Ubuntu official repositories by issuing the below command:
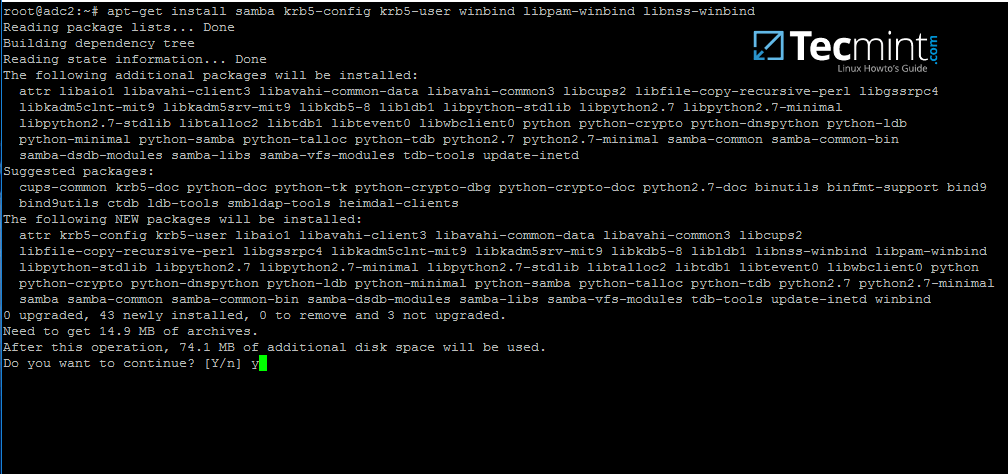
][9]
Install Samba4 in Ubuntu
8.During the installation you will need to provide Kerberos realm name. Write your domain name with upper cases and press[Enter]key to finish the installation process.
[

][10]
Configure Kerberos Authentication for Samba4
9.After the packages installation finishes, verify the settings by requesting a Kerberos ticket for a domain administrator usingkinitcommand. Useklistcommand to list granted Kerberos ticket.
```
# kinit domain-admin-user@YOUR_DOMAIN.TLD
# klist
```
[
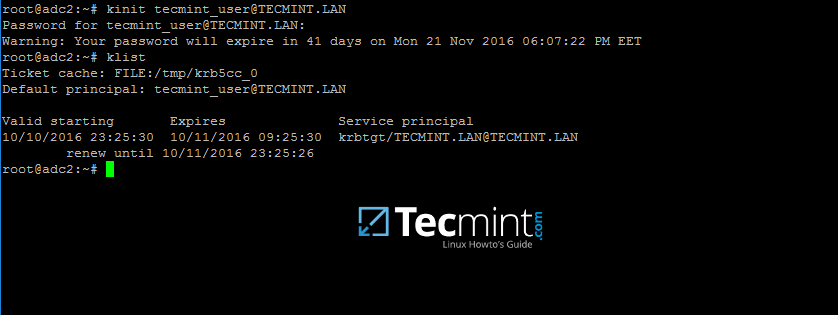
][11]
Verify Kerberos on Samba4 Domain
### Step 3: Join to Samba4 AD DC as a Domain Controller
10.Before integrating your machine intoSamba4 DC, first make sure all Samba4 daemons running on your system are stopped and, also, rename the default Samba configuration file in order to start clean. While provisioning the domain controller, samba will create a new configuration file from scratch.
11.In order to start the domain joining process, first start onlysamba-ad-dcdaemon, after which you will runsamba-toolcommand to join the realm using an account with administrative privileges on your domain.
Sending DsReplicaUpdateRefs for all the replicated partitions
Setting isSynchronized and dsServiceName
Setting up secrets database
Joined domain TECMINT (SID S-1-5-21-715537322-3397311598-55032968) as a DC
```
[

][12]
Join Domain to Samba4 AD DC
12.After the Ubuntu with samba4 software has been integrated into the domain, open samba main configuration file and add the following lines:
```
# nano /etc/samba/smb.conf
```
Add following excerpt to smb.conf file.
```
dns forwarder = 192.168.1.1
idmap_ldb:use rfc2307 = yes
template shell = /bin/bash
winbind use default domain = true
winbind offline logon = false
winbind nss info = rfc2307
winbind enum users = yes
winbind enum groups = yes
```
Replacedns forwarder IPaddress with your own DNS forwarder IP. Samba will forward all DNS resolution queries that are outside your domain authoritative zone to this IP address.
13.Finally, restart samba daemon to reflect changes and check active directory replication by executing the following commands.
14.Additionally, rename initial Kerberos configuration file from/etcpath and replace it with the newkrb5.confconfiguration file generated by samba while provisioning the domain.
The file is located in/var/lib/samba/privatedirectory. Use Linux symlink to link this file to/etcdirectory.
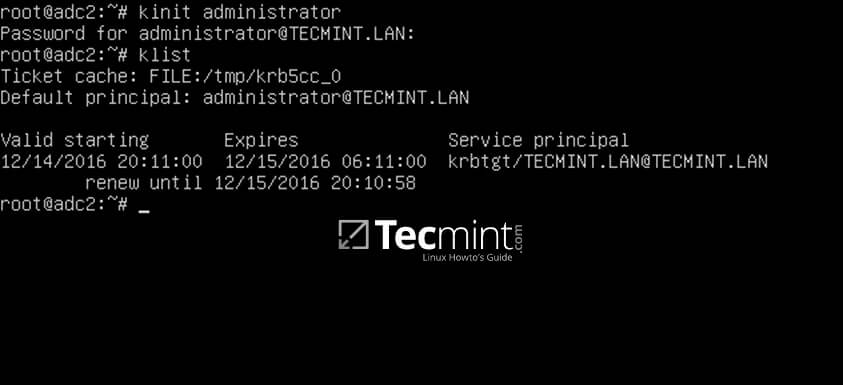
15.Also, verify Kerberos authentication with sambakrb5.conffile. Request a ticket for an administrator user and list the cached ticket by issuing the below commands.
```
# kinit administrator
# klist
```
[
16.The first test you need to perform isSamba4 DC DNSresolution. To validate your domain DNS resolution, query the domain name usinghostcommand against a few crucial AD DNS records as presented on the below screenshot.
The DNS server should replay by now with a pair of two IP addresses for each query.
```
# host your_domain.tld
# host -t SRV _kerberos._udp.your_domain.tld # UDP Kerberos SRV record
# host -t SRV _ldap._tcp.your_domain.tld # TCP LDAP SRV record
```
[

][16]
Verify Samba4 DC DNS
17.These DNS records should also be visible from an enrolled[Windows machine with RSAT tools installed][17]. Open DNS Manager and expand to your domain tcp records as shown in the below image.
[

][18]
Verify DNS Records on Windows RSAT Tool
18.The next test should indicate if domain LDAP replication works as expected. Usingsamba-tool, create an account on the second domain controller and verify if the account is automatically replicated on the first Samba4 AD DC.
##### On adc2:
```
# samba-tool user add test_user
```
##### On adc1:
```
# samba-tool user list | grep test_user
```
[

][19]
Create User Account on Samba4 AD
[
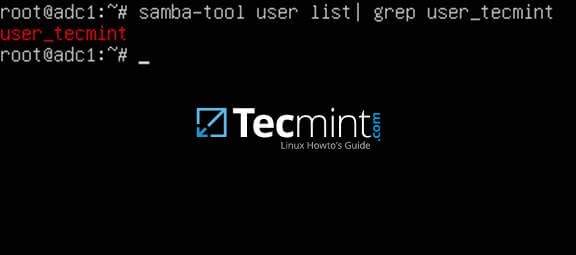
][20]
Verify Replication on Samba4 AD
19.You can also create an account from aMicrosoft AD UCconsole and verify if the account appears on both domain controllers.
By default, the account should be automatically created on both samba domain controllers. Query the account name from`adc1`usingwbinfocommand.
[

][21]
Create Account from Microsoft AD UC
[

][22]
Verify Account Replication On Samba4 AD
20.As a fact, openAD UCconsole from Windows, expand to Domain Controllers and you should see both enrolled DC machines.
21.In order to enable samba4 AD DC services system-wide, first disable some old and unused Samba daemons and enable onlysamba-ad-dcservice by running the below commands:
```
# systemctl disable smbd nmbd winbind
# systemctl enable samba-ad-dc
```
[

][24]
Enable Samba4 AD DC Services
22.If you remotely administer Samba4 domain controller from a Microsoft client or you have other Linux or Windows clients integrated into your domain, make sure you mention the IP address of the`adc2`machine to their network interface DNS server IP settings in order to gain a level of redundancy.
The below screenshots illustrates the configurations required for a Windows or a Debian/Ubuntu client.
[

][25]
Configure Client to Administer Samba4 DC
[

][26]
Configure Linux Client to Administer Samba4 DC
Assuming that the firstDCwith192.168.1.254goes offline, reverse the order of the DNS server IP addresses in the configuration file so it won’t try to query first an unavailable DNS server.
Finally, in case you want to perform local authentication on a Linux system with a Samba4 Active Directory account or grant root privileges for AD LDAP accounts in Linux, read the steps 2 and 3 from the tutorial[Manage Samba4 AD Infrastructure from Linux Command Line][27].
I am Ravi Saive, creator of TecMint. A Computer Geek and Linux Guru who loves to share tricks and tips on Internet. Most Of My Servers runs on Open Source Platform called Linux. Follow Me: Twitter, Facebook and Google+