mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2024-12-23 21:20:42 +08:00
354 lines
15 KiB
Markdown
354 lines
15 KiB
Markdown
|
|
在Linux中使用逻辑卷管理器构建灵活的磁盘存储——第一部分
|
|||
|
|
================================================================================
|
|||
|
|
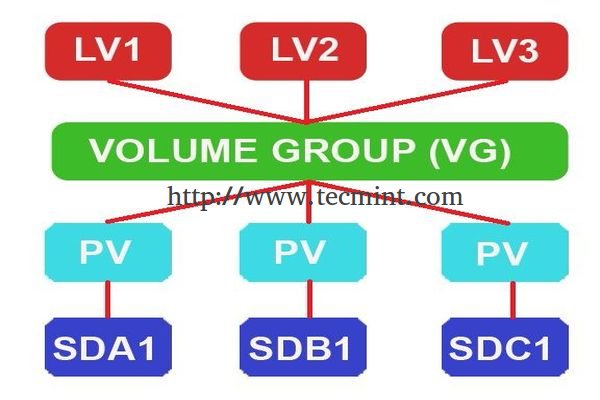
**逻辑卷管理器(LVM)**让磁盘空间管理更为便捷。如果一个文件系统需要更多的空间,它可以在它的卷组中将空闲空间添加到它的逻辑卷中,而文件系统可以根据你的意愿调整大小。如果某个磁盘启动失败,替换磁盘可以使用卷组注册成一个物理卷,而逻辑卷扩展可以将数据迁移到新磁盘而不会丢失数据。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
在Linux中创建LVM存储
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
在现代世界中,每台服务器空间都会因为我们的需求增长而不断扩展。逻辑卷可以用于RAID,SAN。单个物理卷将会被加入组以创建卷组,在卷组中,我们需要切割空间以创建逻辑卷。在使用逻辑卷时,我们可以使用某些命令来跨磁盘、跨逻辑卷扩展,或者减少逻辑卷大小,而不用重新格式化和重新对当前磁盘分区。卷可以跨磁盘抽取数据,这会增加I/O数据量。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
### LVM特性 ###
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
- 可以在任何时候灵活地扩展空间。
|
|||
|
|
- 可以安装和处理任何文件系统。
|
|||
|
|
- 可以通过迁移来恢复错误磁盘。
|
|||
|
|
- 可以使用快照功能恢复文件系统到先前的阶段。等等……
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
####我的服务器设置 - 需求 ####
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
- 操作系统 —— 安装有LVM的CentOS 6.5
|
|||
|
|
- 服务器IP地址 —— 192.168.0.200
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
### 在Linux中创建LVM磁盘存储 ###
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
**1.** 我们已经在虚拟磁盘(VDA)中使用了带LVM的CentOS 6.5操作系统。在此,我们可以使用下列命令查看到物理卷(PV),卷组(VG),逻辑卷(LV)。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
# pvs
|
|||
|
|
# vgs
|
|||
|
|
# lvs
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|

|
|||
|
|
检查物理卷
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
下面是上面截图中各个参数的说明。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
- 物理磁盘大小(PV Size)
|
|||
|
|
- 用作虚拟磁盘vda的磁盘
|
|||
|
|
- 卷组大小(VG Size)
|
|||
|
|
- 卷组名称(vg_tecmint)
|
|||
|
|
- 逻辑卷名称(LogVol00,LogVol01)
|
|||
|
|
- LogVol00分配给swap,大小1GB
|
|||
|
|
- LogVol01分配给/,大小16.5GB
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
从上面看,我们可以知道VDA磁盘中没有足够的空闲空间。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
**2.** 为了创建一个**新卷组**,我们需要在这台服务器上添加额外的**3个硬盘**。3个驱动器不是强制使用的,只要一个就足够用来创建新的**VG**,并在其中创建**LV**了。我在这里添加了更多的磁盘,目的只是用于演示和更多命令功能的说明。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
下面是我已经额外添加的磁盘。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
sda, sdb, sdc
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
----------
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
# fdisk -l
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|

|
|||
|
|
验证添加的磁盘
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
- 用于操作系统(CentOS 6.5)的默认磁盘。
|
|||
|
|
- 默认磁盘上定义的分区(vda1 = swap),(vda2 = /)。
|
|||
|
|
- 额外添加的磁盘Disk1,Disk2,Disk3。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
各个磁盘大小都是20GB,默认的卷组的PE大小为4MB,我们在该服务器上配置的卷组使用默认PE。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|

|
|||
|
|
卷组显示
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
- **VG Name** – 卷组名称。
|
|||
|
|
- **Format** – LVM架构使用LVM2。
|
|||
|
|
- **VG Access** – 卷组为读写模式,备好待用。
|
|||
|
|
- **VG Status** – 卷组可调整大小,如果我们需要添加更多空间,我们可以扩展更多。
|
|||
|
|
- **Cur LV** – 当前卷组中有2个逻辑卷。
|
|||
|
|
- **CurPV and Act PV** – 当前使用的物理磁盘是1(vda),已被激活,因此我们可以使用该卷组。
|
|||
|
|
- **PE Size** – 磁盘的物理扩展大小,可以定义使用PE,或者GB,LVM的默认PE大小是4MB。例如,如果我们需要创建5GB大小的逻辑卷,我们可以使用总计1280 PE,你们懂我的意思么?
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
这里解释一下 -> 1024MB = 1GB,这样的话,1024MB x 5 = 5120PE = 5GB,然后5120/4 = 1280,4是默认的PE大小。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
- Total PE – 该卷组具有的PE数量。
|
|||
|
|
- Alloc PE – 总的PE使用量,已经使用的全部PE,4482 x 4PE = 17928。
|
|||
|
|
- Free PE – 这里因为已经使用,所以没有空闲PE了。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
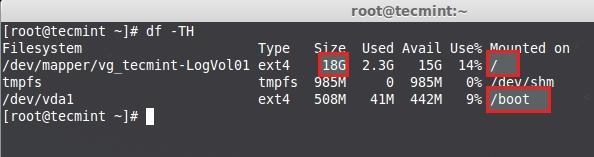
**3.** 只使用了vda,当前CentOS在使用lvm的vda物理磁盘中安装了**/boot,/,swap,**,该磁盘中没有空间剩余。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
# df -TH
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
检查磁盘空间
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
上面的图片中显示了用于根的挂载点已使用了**18GB**,因此没有空闲空间可用了。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
**4.** 那么,让我们创建新的物理卷(**pv**),以及名为**tecmint_add_vg**的卷组(**vg**),并在其中创建逻辑卷(**lv**)。这里,我们可以创建4个逻辑卷,分别名为 **tecmint_documents**,**tecmint_manager**以及**tecmint_add_vg**。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
我们可以扩展当前使用的卷组以获得更多空间。但在这里,我们将要做的是,创建新的卷组,然后在里面肆意妄为吧。过会儿,我们可以看到怎样来扩展使用中的卷组的文件系统。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
在使用新磁盘钱,我们需要使用fdisk来对磁盘分区。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
# fdisk -cu /dev/sda
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
- **c** – 关闭DOS兼容模式,推荐使用该选项。
|
|||
|
|
- **u** – 当列出分区表时,会以扇区而不是柱面显示。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|

|
|||
|
|
创建新的物理分区
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
接下来,请遵循以下步骤来创建新分区。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
- 选择**n**来创建新分区。
|
|||
|
|
- 选择**p**来创建主分区。
|
|||
|
|
- 选择我们需要创建的分区号。
|
|||
|
|
- 按**Enter**两次来使用整个磁盘空间。
|
|||
|
|
- 我们需要修改新创建的分区类型,输入**t**。
|
|||
|
|
- 选择需要修改的分区号,选择我们创建的分区号**1**。
|
|||
|
|
- 这里,我们需要修改类型。我们需要创建LVM,因此我们使用LVM的类型代码8e。如果不知道类型代码,按**L**来列出所有类型代码。
|
|||
|
|
- 打印我们创建的分区以确认。
|
|||
|
|
- 这里我们可以看到Linux LVM的ID 8e。
|
|||
|
|
- 写入修改并退出fdisk。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
重复以上步骤,为另外2个磁盘sdb和sdc创建新分区。然后重启机器,使用fdisk命令来验证分区表。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
# fdisk -l
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|

|
|||
|
|
验证分区表
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
### 创建物理卷 ###
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
**5.** 现在,该使用3个磁盘来创建物理卷了。这里,我已经使用pvs命令将物理磁盘列了出来,现在只有一个默认的**pvs**被列出来了。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
# pvs
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
然后,使用命令创建新的物理磁盘。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
# pvcreate /dev/sda1 /dev/sdb1 /dev/sdc1
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
再次列出磁盘来查看新创建物理磁盘。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
# pvs
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|

|
|||
|
|
创建物理卷
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
### 创建卷组 ###
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
**6.** 使用可用的空闲PV来创建名为**tecmint_add_vg**的卷组,PE大小为32。显示当前卷组,我们可以看到只有带有1个PV的一个卷组在使用。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
# vgs
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
这将使用上面创建的3个物理卷创建名为**tecmint_add_vg**的卷组,PE大小为32MB。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
# vgcreate -s 32M tecmint_add_vg /dev/sda1 /dev/sdb1 /dev/sdc1
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
接下来,再次运行vgs命令来验证卷组。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
# vgs
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|

|
|||
|
|
创建卷组
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|

|
|||
|
|
验证卷组
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
理解vgs命令输出:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
- 卷组名。
|
|||
|
|
- 本卷组中使用的物理卷。
|
|||
|
|
- 显示本卷组中的可用空闲空间。
|
|||
|
|
- 卷组总大小。
|
|||
|
|
- 本卷组中的逻辑卷,这里我们还没创建,所以是0。
|
|||
|
|
- SN = 卷组包含的快照数量。(后面,我们会创建一个快照。)
|
|||
|
|
- 卷组状态,如可写,可读,可调整大小,已导出,部分的和集群的。这里是wz——意为w = 可写,z = 可调整大小。
|
|||
|
|
- 卷组中使用的物理卷(PV)数量。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
**7.** 使用命令来显示更多卷组信息。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
# vgs -v
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|

|
|||
|
|
检查卷组信息
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
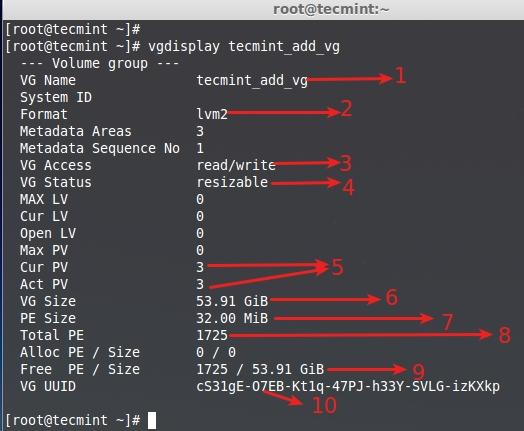
**8.** 要获取更多关于新创建的卷组信息,运行以下命令。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
# vgdisplay tecmint_add_vg
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
列出新卷组
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
- 卷组名称
|
|||
|
|
- 使用的LVM架构。
|
|||
|
|
- 可读写,备好待用。
|
|||
|
|
- 该卷组可以调整大小。
|
|||
|
|
- 使用和激活的物理磁盘数量。
|
|||
|
|
- 卷组总大小。
|
|||
|
|
- 这里单个PE大小为32。
|
|||
|
|
- 该卷组中可用的PE总数。
|
|||
|
|
- 当前还没有在卷组中创建任何LV,因此它是空闲的。
|
|||
|
|
- 该卷组的UUID。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
### 创建逻辑卷 ###
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
**9.** 现在,创建3个名为**tecmint_documents**,**tecmint_manager**和**tecmint_public**的逻辑卷。这里,我们可以看到如何分别以PE为单位和GB为单位来创建逻辑卷。首先,使用以下命令来列出当前逻辑卷。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
# lvs
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|

|
|||
|
|
列出当前卷组
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
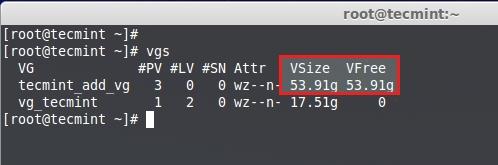
**10.** 这些逻辑卷处于**vg_tecmint**卷组中使用**pvs**命令来列出并查看有多少空闲空间可以创建逻辑卷。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
# pvs
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
检查空闲空间
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
**11.** 卷组大小为**54GB**,而且未被使用,所以我们可以在该组内创建LV。让我们将卷组平均划分大小来创建3个逻辑卷,就是说**54GB**/3 = **18GB**,创建出来的单个逻辑卷应该会是18GB。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
#### 方法1: 使用PE创建逻辑卷 ####
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
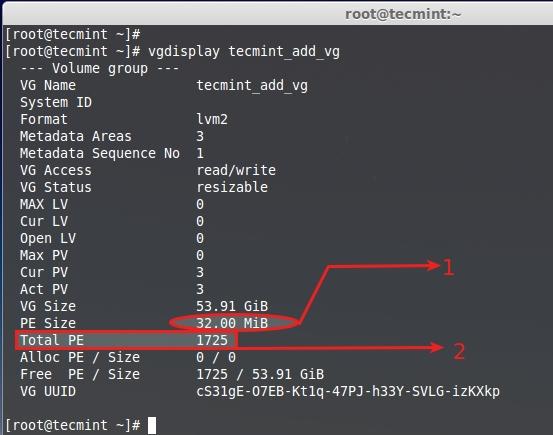
首先,让我们使用物理扩展(PE)为单位来创建逻辑卷。我们需要知道分配到该卷组的默认PE大小,以及总的可用PE大小来创建新的逻辑卷,运行下面的命令来获取使用中的卷组信息。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
# vgdisplay tecmint_add_vg
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
创建新逻辑卷
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
- 默认分配给该卷组的PE为32MB,这里单个的PE大小为32MB。
|
|||
|
|
- 总可用PE是1725。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
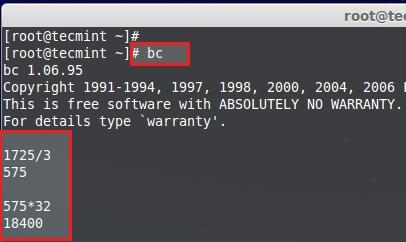
只要用bc命令做一点小小的计算来看看就知道了。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
# bc
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
----------
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
1725PE/3 = 575 PE.
|
|||
|
|
575 PE x 32MB = 18400 --> 18GB
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
计算磁盘空间
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
按**CRTL+D**退出**bc**。现在让我们使用575个PE来创建3个逻辑卷。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
# lvcreate -l (Extend size) -n (name_of_logical_volume) (volume_group)
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
# lvcreate -l 575 -n tecmint_documents tecmint_add_vg
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
# lvcreate -l 575 -n tecmint_manager tecmint_add_vg
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
# lvcreate -l 575 -n tecmint_public tecmint_add_vg
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
- -**l** – 使用扩展大小创建
|
|||
|
|
- -**n** – 给逻辑卷命名
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
使用lvs命令来列出创建的逻辑卷。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
# lvs
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|

|
|||
|
|
列出创建的逻辑卷
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
#### 方法2: 使用GB大小创建逻辑卷 ####
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
在使用GB大小创建逻辑卷时,我们不能获得精确的大小。因此,最好的办法是用扩展。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
# lvcreate -L 18G -n tecmint_documents tecmint_add_vg
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
# lvcreate -L 18G -n tecmint_manager tecmint_add_vg
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
# lvcreate -L 18G -n tecmint_public tecmint_add_vg
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
# lvcreate -L 17.8G -n tecmint_public tecmint_add_vg
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
使用lvs命令来列出创建的逻辑卷。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
# lvs
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|

|
|||
|
|
验证创建的逻辑卷
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
这里,我们可以看到,当创建第三个LV的时候,我们不能收集到18GB空间。这是因为尺寸有小小的改变,但在使用或者尺寸来创建LV时,这个问题会被忽略。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
### 创建文件系统 ###
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
**12.** 要使用逻辑卷,我们需要格式化。这里我使用ext4文件系统来创建卷,并打算挂载到**/mnt**。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
# mkfs.ext4 /dev/tecmint_add_vg/tecmint_documents
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
# mkfs.ext4 /dev/tecmint_add_vg/tecmint_public
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
# mkfs.ext4 /dev/tecmint_add_vg/tecmint_manager
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|

|
|||
|
|
创建Ext4文件系统
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
**13.** 让我们在**/mnt**下创建目录,并将已创建好文件系统的逻辑卷挂载上去。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
# mount /dev/tecmint_add_vg/tecmint_documents /mnt/tecmint_documents/
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
# mount /dev/tecmint_add_vg/tecmint_public /mnt/tecmint_public/
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
# mount /dev/tecmint_add_vg/tecmint_manager /mnt/tecmint_manager/
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
使用下面的命令来列出并确认挂载点。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
# df -h
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|

|
|||
|
|
挂载逻辑卷
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
#### 永久挂载 ####
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
现在,这些逻辑卷是临时挂载上去的,要永久挂载,我们需要添加条目到fstab中。要达到这个目的,让我们使用下面的命令来获取挂载条目
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
# cat /etc/mtab
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
在输入来自mtab中的挂载条目内容时,我们需要在fstab中做些小小的改变,修改rw为默认。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
# vim /etc/fstab
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
我们的fstab条目应该和下面的类似,使用wq!保存并退出fstab。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
/dev/mapper/tecmint_add_vg-tecmint_documents /mnt/tecmint_documents ext4 defaults 0 0
|
|||
|
|
/dev/mapper/tecmint_add_vg-tecmint_public /mnt/tecmint_public ext4 defaults 0 0
|
|||
|
|
/dev/mapper/tecmint_add_vg-tecmint_manager /mnt/tecmint_manager ext4 defaults 0 0
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|

|
|||
|
|
获取mtab挂载条目
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
打开fstab文件
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|

|
|||
|
|
添加自动挂载条目
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
重启前,执行mount -a命令来检查fstab条目。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
# mount -av
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|

|
|||
|
|
验证fstab条目
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
这里,我们已经了解了怎样来使用逻辑卷构建灵活的存储,从使用物理磁盘到物理卷,物理卷到卷组,卷组再到逻辑卷。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
在我即将奉献的文章中,我将介绍如何扩展卷组、逻辑卷,减少逻辑卷,拍快照以及从快照中恢复。到那时,保持TecMint更新到这些精彩文章中的内容。
|
|||
|
|
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
via: http://www.tecmint.com/create-lvm-storage-in-linux/
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
作者:[Babin Lonston][a]
|
|||
|
|
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
|
|||
|
|
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/babinlonston/
|