mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-02-28 01:01:09 +08:00
141 lines
4.5 KiB
Markdown
141 lines
4.5 KiB
Markdown
|
|
Linux and Unix nload App: Monitor Network Traffic and Bandwidth Usage In Real Time
|
|||
|
|
================================================================================
|
|||
|
|
If you want to monitor network throughput on the command line interface, use nload application. It is a console application which monitors network traffic and bandwidth usage in real time. It visualizes the in and outgoing traffic using two graphs and provides additional info like total amount of transferred data and min/max network usage.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
#### Install nload on a CentOS/RHEL/Red Hat/Fedora Linux ####
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
First, [turn on EPEL repo on a CentOS or RHEL][1] based system. Type the following [yum command][2] to install nload:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
# yum install nload
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
#### Install nload on a Debian or Ubuntu Linux ####
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Type the following [apt-get command][3]:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
$ sudo apt-get install nload
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
#### Install nload on a FreeBSD system ####
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
To install the nload via port, type:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
# cd /usr/ports/net/nload/ && make install clean
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Or add the package
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
# pkg install net/nload
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
#### Install nload on a OpenBSD system ####
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Type the following command:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
$ sudo pkg_add -i nload
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
#### Install nload using a source code on a Unix-like systems ####
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
First, grab the source code using either wget command or curl command:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
$ cd /tmp
|
|||
|
|
$ wget http://www.roland-riegel.de/nload/nload-0.7.4.tar.gz
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
To [untar a tar file called nload-0.7.4.tar.gz, use tar command][4], enter:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
$ tar xvf nload-0.7.4.tar.gz
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Cd to the directory containing the nloads's source code using cd command:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
$ cd nload*
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
And type ./configure to configure the package for your system:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
$ sh ./configure
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
OR
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
$ ./configure
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Running configure takes a while. Type make command to compile the nload:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
$ make
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Finally, type make install to install the nload programs and related files as root user:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
$ sudo make install
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
OR
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
# make install
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
How do I use nload to display the current network usage?
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
The basic syntax is:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
nload
|
|||
|
|
nload device
|
|||
|
|
nload [options] device1 device2
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Just type the following command:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
$ nload
|
|||
|
|
$ nload eth0
|
|||
|
|
$ nload em0 em2
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Sample outputs:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
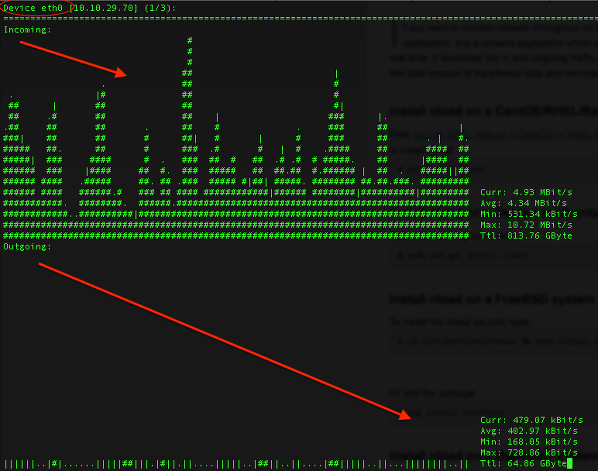
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Fig. 01: nload command in action
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
#### Controlling nload app ####
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Once nload command executed, it begins to monitor the network devices. You can control nload with the following key shortcuts:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
1. You can switch between the devices by pressing the left and right arrow keys or Enter/Tab key.
|
|||
|
|
1. Press F2 to show the option window
|
|||
|
|
1. Press F5 to save current settings to the user’s config file.
|
|||
|
|
1. Press F6 reload settings from the config files.
|
|||
|
|
1. Press q or hit Ctrl+C to quit nload.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
#### Setting the refresh interval of the display ####
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
The default value of interval is 100 milliseconds to refresh interval of the display. In this example, change to 500 milliseconds:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
$ nload -t {interval_number_in_millisec}
|
|||
|
|
$ nload -t 500
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Sample outputs:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|

|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Animated gif 01 - nload command in action
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
#### Setting the type of unit used for the display of traffic numbers ####
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
The syntax is:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
$ nload -u h|H|b|B|k|K|m|M|g|G
|
|||
|
|
$ nload -U h|H|b|B|k|K|m|M|g|G
|
|||
|
|
$ nload -u h
|
|||
|
|
$ nload -u G
|
|||
|
|
$ nload -U G
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Where,
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
- The lower case -u option: h means human readable (auto), b Bit/s, k kBit/s, m MBit/s and g GBit/s. The upper case letters mean the corresponding units in Bytes (instead of Bits). The default is k.
|
|||
|
|
- The upper case -U option is same as lower case -u option, but for an amount of data, e.g. Bit, kByte, GBit etc. (without "/s"). The default is M.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
### Conclusion ###
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
I found nload to be reliable and stable application. If you enjoyed nload, you might also like to try out vnstat and iftop tools on Linux/Unix-like systems.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
via: http://www.cyberciti.biz/networking/nload-linux-command-to-monitor-network-traffic-bandwidth-usage/
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
[1]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/fedora-sl-centos-redhat6-enable-epel-repo/
|
|||
|
|
[2]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/rhel-centos-fedora-linux-yum-command-howto/
|
|||
|
|
[3]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/linux-debian-package-management-cheat-sheet.html
|
|||
|
|
[4]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/tar-extract-linux/
|