Sambais a free Open Source software which provides a standard interoperability betweenWindows OSandLinux/UnixOperating Systems.
Samba can operate as a standalone file and print server for Windows and Linux clients through theSMB/CIFSprotocol suite or can act as anActive Directory Domain Controlleror joined into aRealmas aDomain Member. The highestAD DCdomain and forest level that currentlySamba4can emulate isWindows 2008 R2.
The series will be titledSetting Up Samba4 Active Directory Domain Controller, which covers following topics forUbuntu,CentOS, andWindows:
Part 1:Install Active Directory Infrastructure with SAMBA4 on UbuntuPart 2:[Manage Samba4 AD Infrastructure from Linux Command Line][4]Part 3:Install RSAT on Windows 10 Client to Manage Samba4 AD InfrastructurePart 4:Joining Samba4 DC to Existing AD Infrastructure with Sysvol ReplicationPart 5:Add a Shared Volume from Linux DC and Map to AD via GPOPart 6:Integrate Ubuntu 16.04 to AD as a Domain MemberPart 7:Integrate CentOS 7 to AD as a Domain MemberPart 8:Create Apache Website with Kerberos Authentication on AD Intranet
This tutorial will start by explaining all the steps you need to take care off in order to install and configureSamba4as aDomain ControlleronUbuntu 16.04andUbuntu 14.04.
This configuration will provide a central management point for users, machines, volume shares, permissions and other resources in a mixed-up Windows – Linux infrastructure.
#### Requirements:
1. [Ubuntu 16.04 Server Installation][1].
2. [Ubuntu 14.04 Server Installation][2].
3. [A static IP Address configured][3]for yourAD DCserver.
### Step 1: Initial Configuration for Samba4
1.Before proceeding yourSamba4 AD DCinstallation first let’s run a few pre-required steps. First make sure the system is up to date with the last security features, kernels and packages by issuing the below command:
```
$ sudo apt-get update
$ sudo apt-get upgrade
$ sudo apt-get dist-upgrade
```
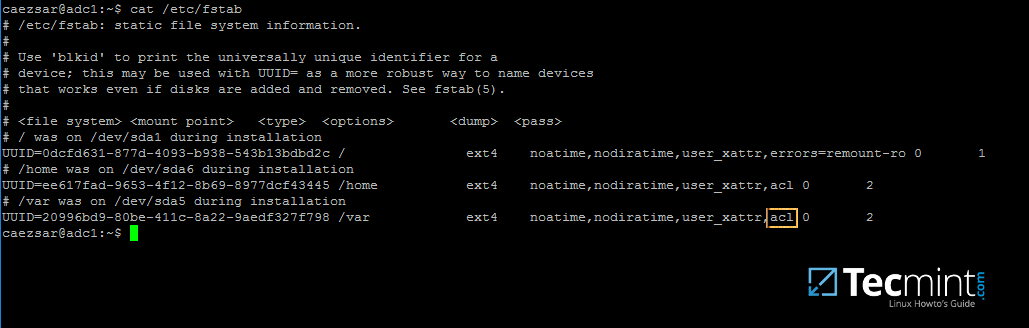
2.Next, open machine/etc/fstabfile and assure that your partitions file system hasACLsenabled as illustrated on the below screenshot.
Usually, common modern Linux file systems such asext3,ext4,xfsorbtrfssupport and have ACLs enabled by default. If that’s not the case with your file system just open/etc/fstabfile for editing and add`acl`string at the end of third column andrebootthe machine in order to apply changes.
[
][5]
Enable ACL’s on Linux Filesystem
3.Finally[setup your machine hostname][6]with a descriptive name, such as`adc1`used in this example, by editing/etc/hostnamefile or by issuing.
```
$ sudo hostnamectl set-hostname adc1
```
Arebootis necessary after you’ve changed your machine name in order to apply changes.
### Step 2: Install Required Packages for Samba4 AD DC
4.In order to transform your server into anActive Directory Domain Controller, installSambaand all the required packages on your machine by issuing the below command withrootprivileges in a console.

][7]
Install Samba on Ubuntu
5.While the installation is running a series of questions will be asked by the installer in order to configure the domain controller.
On the first screen you will need to add a name forKerberosdefault`REALM`in uppercase. Enter the name you will be using for your domain in uppercase and hitEnterto continue..
9.Next, rename or remove samba original configuration. This step is absolutely required before provisioningSamba ADbecause at the provision timeSambawill create a new configuration file from scratch and will throw up some errors in case it finds an old`smb.conf`file.
10.Now, start the domain provisioning interactively by issuing the below command with root privileges and accept the default options that Samba provides you.
Also, make sure you supply the IP address for a DNS forwarder at your premises (or external) and choose a strong password for Administrator account. If you choose a week password for Administrator account the domain provision will fail.
11.Finally, rename or remove Kerberos main configuration file from/etcdirectory and replace it using a symlink with Samba newly generated Kerberos file located in/var/lib/samba/privatepath by issuing the below commands:
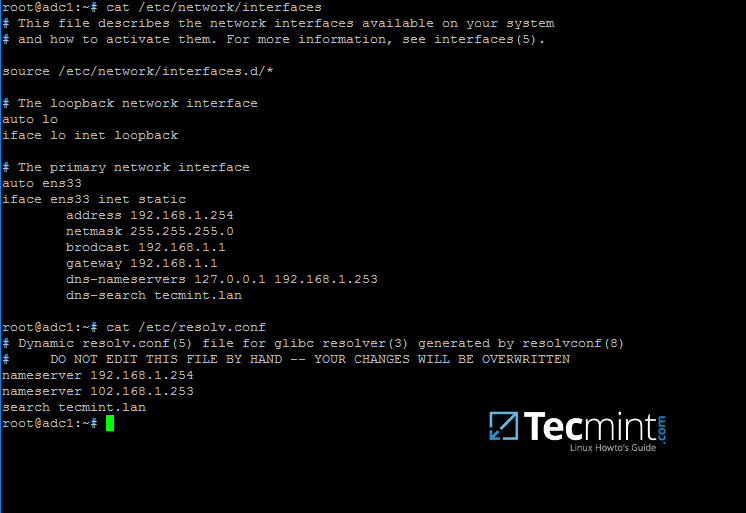
15.In order forDNSresolution to work locally, you need to open end edit network interface settings and point the DNS resolution by modifyingdns-nameserversstatement to the IP Address of yourDomain Controller(use127.0.0.1for local DNS resolution) anddns-searchstatement to point to yourrealm.
```
$ sudo cat /etc/network/interfaces
$ sudo cat /etc/resolv.conf
```
[
][17]
Configure DNS for Samba AD
When finished,rebootyour server and take a look at your resolver file to make sure it points back to the right DNS name servers.
16.Finally, test the DNS resolver by issuing queries and pings against someAD DCcrucial records, as in the below excerpt. Replace the domain name accordingly.
```
$ ping –c3 tecmint.lan #Domain Name
$ ping –c3 adc1.tecmint.lan #FQDN
$ ping –c3 adc1 #Host
```
[

][18]
Check Samba AD DNS Records
Run following few queries against Samba Active Directory Domain Controller..
```
$ host –t A tecmint.lan
$ host –t A adc1.tecmint.lan
$ host –t SRV _kerberos._udp.tecmint.lan # UDP Kerberos SRV record
$ host -t SRV _ldap._tcp.tecmint.lan # TCP LDAP SRV record
```
17.Also, verifyKerberosauthentication by requesting a ticket for the domain administrator account and list the cached ticket. Write the domain name portion with uppercase.
```
$ kinit administrator@TECMINT.LAN
$ klist
```
[

][19]
Check Kerberos Authentication on Domain
That’s all! Now you have a fully operationalAD Domain Controllerinstalled in your network and you can start integrateWindowsorLinuxmachines intoSamba AD.
On the next series we’ll cover otherSamba ADtopics, such as how to manage you’re the domain controller from Samba command line, how to integrate Windows 10 into the domain name and manage Samba AD remotely using RSAT and other important topics.