mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-01-13 22:30:37 +08:00
103 lines
6.5 KiB
Markdown
103 lines
6.5 KiB
Markdown
|
|
[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
|
||
|
|
[#]: translator: ( )
|
||
|
|
[#]: reviewer: ( )
|
||
|
|
[#]: publisher: ( )
|
||
|
|
[#]: url: ( )
|
||
|
|
[#]: subject: (Automatic continuous development and delivery of a hybrid mobile app)
|
||
|
|
[#]: via: (https://opensource.com/article/18/12/hybrid-mobile-app-development)
|
||
|
|
[#]: author: (Angelo Manganiello https://opensource.com/users/amanganiello90)
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Automatic continuous development and delivery of a hybrid mobile app
|
||
|
|
======
|
||
|
|
Hybrid apps are a good middle ground between native and web apps.
|
||
|
|

|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Offering a mobile app is essentially a business requirement for organizations today. One of the first steps in developing an app is to understand the different types—native, hybrid (or cross-platform), and web—so you can decide which one will best meet your needs.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
### Native is better, right?
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
**Native apps** represent the vast majority of applications that people download every day. Native applications are developed specifically for an operating system. Thus, a native iOS application will not work on an Android system and vice versa. To develop a native app, you need to know two things:
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
1. How to develop in a specific programming language (e.g., Swift for Apple devices; Java for Android)
|
||
|
|
2. The app will not work for other platforms
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Even though native apps will work only on the platform they're developed for, they have several notable advantages over hybrid and web apps:
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
* Increased speed, reliability, and responsiveness and higher resolution, all of which provide a better user experience
|
||
|
|
* May work offline/without internet service
|
||
|
|
* Easier access to all phone features (e.g., accelerometer, camera, microphone)
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
### But my business is still linked to the web…
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Most companies have focused their resources on web development and now want to enter the mobile market. But many don't have the right technical resources to develop a native app for each platform. For these companies, **hybrid** development is the right choice. In this model, developers can use their existing frontend skills to develop a single, cross-platform mobile app.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
![Hybrid mobile apps][2]
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Hybrid apps are a good middle ground: they're faster and less expensive to develop than native apps, and they offer more possibilities than web apps. The tradeoffs are they don't perform as well as native apps and developers can't maintain their existing tight focus on web development (as they could with web apps).
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
If you already are a fan of the [Angular][3] cross-platform development framework, I recommend trying the [Ionic][4] framework, which "lets web developers build, test, and deploy cross-platform hybrid mobile apps." I see Ionic as an extension of the [Apache Cordova][5] framework, which enables a normal web app (JS, HTML, or CSS) to run as a mobile app in a container. Ionic uses the base Cordova features that support the Angular development for its user interface.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
The advantage of this approach is simple: the Angular paradigm is maintained, so developers can continue writing [TypeScript][6] files but target a build for Android, iOS, and Windows by properly configuring the development environment. It also provides two important tools:
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
* An appealing design and widget that are very similar to a native app's, so your hybrid app will look less "web"
|
||
|
|
* Cordova Plugins allow the app to communicate with all phone features
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
### What about the Node.js backend?
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
The programming world likes to standardize, which is why hybrid apps are so popular. Frontend developers' common skills are useful in the mobile world. But if we have a technology stack for the user interface, why not focus on a single backend with the same programming paradigm?
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
This makes [Node.js][7] an appealing option. Node.js is a JavaScript runtime built on the Chrome V8 JavaScript engine. It can make the API development backend very fast and easy, and it integrates fully with web technologies. You can develop a Cordova plugin, using your Node.js backend, internally in your hybrid app, as I did with the [nodejs-cordova-plugin][8]. This plugin, following the Cordova guidelines, integrates a mobile-compatible version of the Node.js platform to provide a full-stack mobile app.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
If you need a simple CRUD Node.js backend, you can use my [API][9] [node generator][9] that generates an app using a [MongoDB][10] embedded database.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
![Cordova Full Stack application][12]
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
### Deploying your app
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Open source offers everything you need to deploy your app in the best way. You just need a GitHub repository and a good continuous integration tool. I recommend [Travis-ci][13], an excellent tool that allows you to build and deploy your product for every commit.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Travis-ci is a fork of the better known [Jenkins][14]. Like with Jenkins, you have to configure your pipeline through a configuration file (in this case a **.travis.yml** file) in your GitHub repo. See the [.travis.yml file][15] in my repository as an example.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
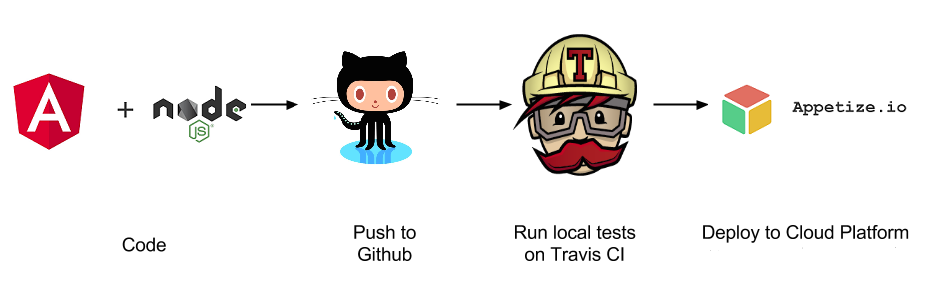
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
In addition, this pipeline automatically delivers and installs your app on [Appetize.io][16], a web-based iOS simulator and Android emulator, for testing.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
You can learn more in the [Cordova Android][17] section of my GitHub repository.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
via: https://opensource.com/article/18/12/hybrid-mobile-app-development
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
作者:[Angelo Manganiello][a]
|
||
|
|
选题:[lujun9972][b]
|
||
|
|
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||
|
|
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
[a]: https://opensource.com/users/amanganiello90
|
||
|
|
[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
|
||
|
|
[1]: /file/416441
|
||
|
|
[2]: https://opensource.com/sites/default/files/uploads/1-title.png (Hybrid mobile apps)
|
||
|
|
[3]: https://angular.io/
|
||
|
|
[4]: https://ionicframework.com/
|
||
|
|
[5]: https://cordova.apache.org/
|
||
|
|
[6]: https://www.typescriptlang.org/
|
||
|
|
[7]: https://nodejs.org/
|
||
|
|
[8]: https://github.com/fullStackApp/nodejs-cordova-plugin
|
||
|
|
[9]: https://github.com/fullStackApp/generator-full-stack-api
|
||
|
|
[10]: https://www.mongodb.com/
|
||
|
|
[11]: /file/416351
|
||
|
|
[12]: https://opensource.com/sites/default/files/uploads/2-cordova-full-stack-app.png (Cordova Full Stack application)
|
||
|
|
[13]: https://travis-ci.org/
|
||
|
|
[14]: https://jenkins.io/
|
||
|
|
[15]: https://github.com/amanganiello90/java-angular-web-app/blob/master/.travis.yml
|
||
|
|
[16]: https://appetize.io/
|
||
|
|
[17]: https://github.com/amanganiello90/java-angular-web-app#cordova-android
|