When you delete a file accidentally or intentionally on your system using ‘shift + delete‘ or delete option or empty Trash, the file content is not destroyed from the hard disk (or any storage media).
It is simply removed from the the directory structure and you cannot see the file in the directory where you deleted it, but it still remains somewhere in your hard drive.
If you have the appropriate tools and knowledge, you can[recover lost files from your computer][1]. However, as you store more files on your hard disk, the deleted files are overwritten, you may only recover recently deleted files.
In this tutorial, we will explain how to recover lost or deleted files on a hard disk in Linux usingTestdisk, is a remarkable recovery tool ships in with a free tool calledPhotoRec.
PhotoRecis used to recover lost files from storage media such as hard drives, digital camera and cdrom.
### Install Testdisk (PhotoRec) in Linux Systems
To installTestdiskby running the relevant command below for your distribution:
```
------- On Debian/Ubuntu/Linux Mint -------
$ sudo apt-get install testdisk
------- On CentOS/RHEL/Fedora -------
$ sudo yum install testdisk
------- On Fedora 22+ -------
$ sudo dnf install testdisk
------- On Arch Linux -------
$ pacman -S testdisk
------- On Gentoo -------
$ emerge testdisk
```
In case it is not available on your Linux distribution’s repositories, download it from[here][2]and run it on a Live CD.
It can also be found in rescue CD such asGparted LiveCD,Parted Magic,Ubuntu Boot CD,Ubuntu-Rescue-Remixand many more.
Once the installation is complete, startPhotoRecin a text window as follows with root privileges and specify the partition from which the files where deleted:
```
$ sudo photorec /dev/sda3
```
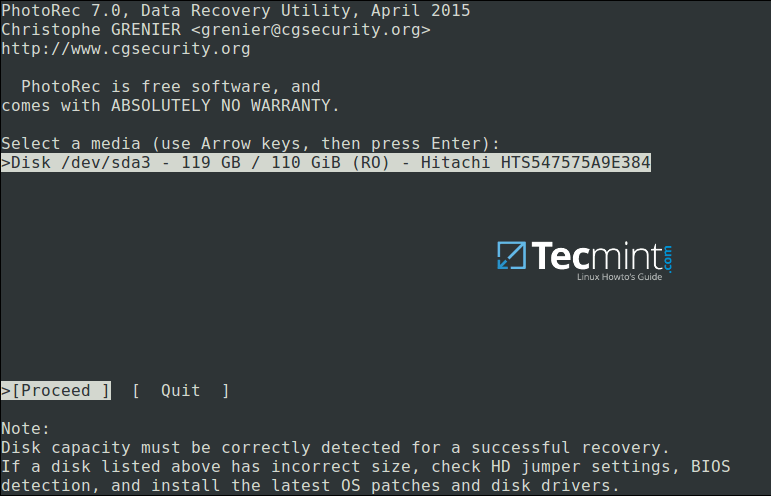
You’ll see the interface below:
[
][3]
PhotoRec Data Recovery Tool for Linux
Use the`right`and`left`arrow keys to select a menu item, and pressEnter. To continue with the recovery operation, select`[Proceed]`and hitEnter.
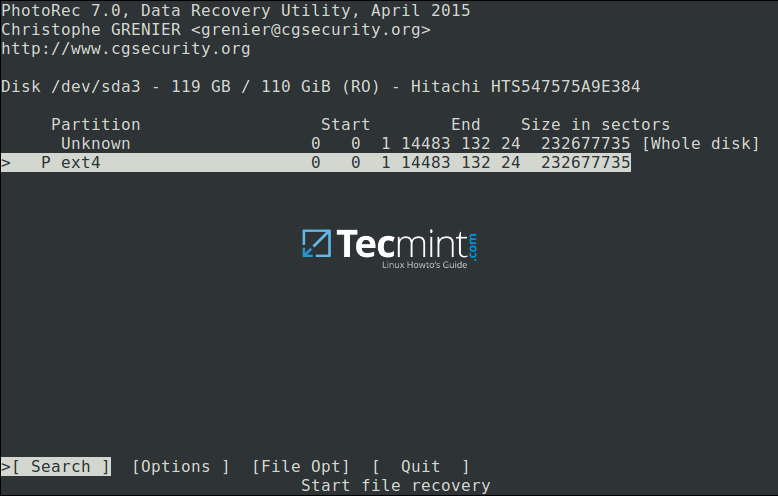
You will be at the following interface:
[
][4]
Select Partition to Proceed File Recovery
Select`[Options]`to view available recovery operation options as in the interface below:
Press`Q`to move back, at the interface below, you can specify the file extensions you want to search and recover. Therefore, select`[File Opt]`and pressEnter.
Press`s`to disable/enable all file extensions, and in case you have disabled all file extensions, only choose types of files you want to recover by selecting them using`right`arrow keys (or`left`arrow key to deselect).
For instance, I want to recover all`.mov`files that I lost on my system.
Then press`b`to save the setting, you should see the message below after pressing it. Move back by hittingEnter(or simply press`Q`button), then press`Q`again to go back to the main menu.
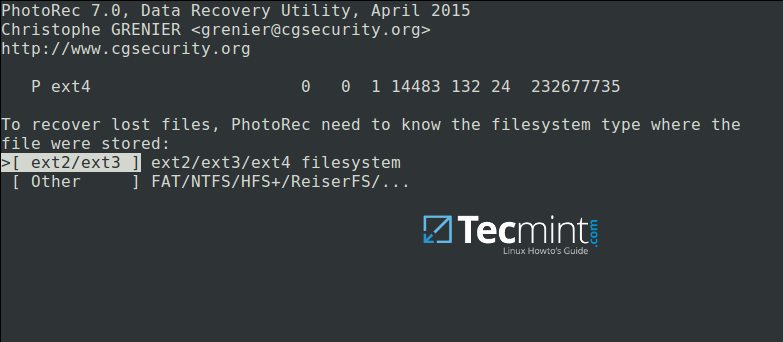
Now select`[Search]`to start the recovery process. In the interface below, choose the filesystem type where the file(s) were stored and hitEnter.
[
][8]
Select Filesystem to Recover Deleted Files
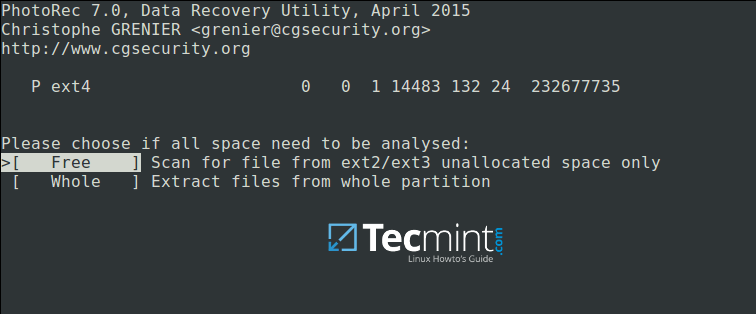
Next, choose if only free space or the whole partition needs to be analyzed as below. Note that choosing whole partition will make the operation slower and longer. Once you have selected the appropriate option, pressEnterto proceed.
[
][9]
Choose Filesystem to Analyze
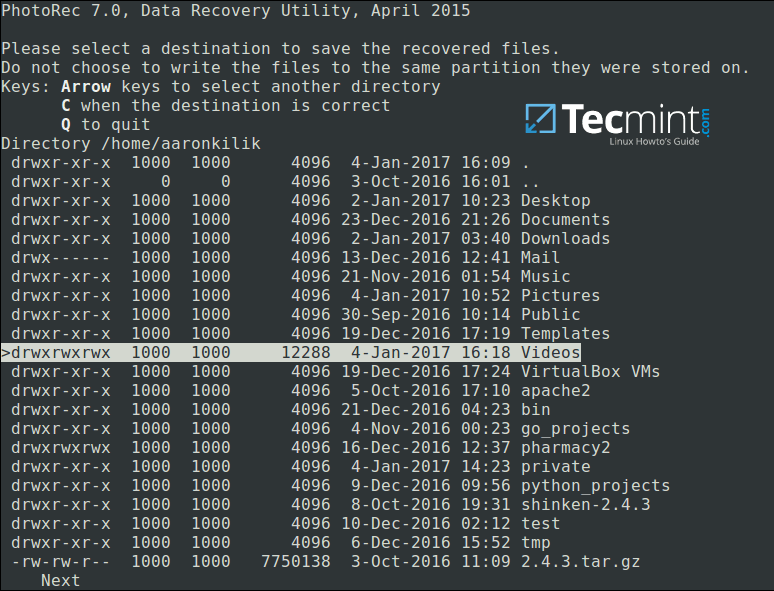
Closely select a directory where recovered files will be stored, if the destination is correct, press`C`button to continue. Choose a directory on a different partition to avoid deleted files being overwritten when more data is stored on the partition.
To move back until the root partition, use the`left`arrow key.
[
][10]
Select Directory to Save Recovered Files
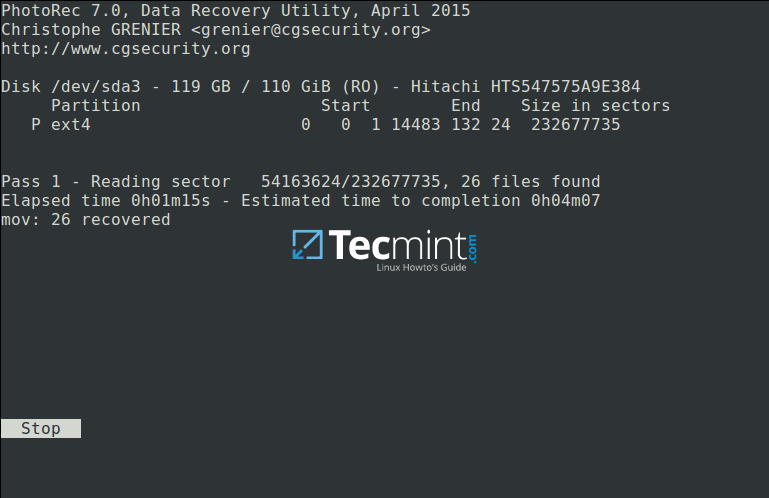
The screenshot below shows deleted files of the specified type being recovered. You can stop the operation by pressingEnter.
Note: Your system may become slow, and possibly freeze at certain moments, so you need to be patient until when the process is complete.
[
][11]
Recovering Deleted Files in Linux
At the end of the operation,Photorecwill show you the number and the location of files recovered.
The recovered files will be stored with root privileges by default, therefore open your file manager with elevated privileges to access the files.
Use the command below (specify your file manager):
```
$ gksudo nemo
or
$ gksudo nautilus
```
For more information, visit PhotoRec homepage:[http://www.cgsecurity.org/wiki/PhotoRec][13].
That’s all! In this tutorial, we explained the necessary steps to recover deleted or lost files from hard disk using PhotoRec. This is so far the most reliable and effective recovery tool I have ever used, if you know any other similar tool, do share with us in the comments.
Aaron Kili is a Linux and F.O.S.S enthusiast, an upcoming Linux SysAdmin, web developer, and currently a content creator for TecMint who loves working with computers and strongly believes in sharing knowledge.