mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-01-07 22:11:09 +08:00
152 lines
5.4 KiB
Markdown
152 lines
5.4 KiB
Markdown
|
|
Linux Server See the Historical and Statistical Uptime of System With tuptime Utility
|
|||
|
|
================================================================================
|
|||
|
|
You can use the following tools to see how long system has been running on a Linux or Unix-like system:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
- uptime : Tell how long the server has been running.
|
|||
|
|
- lastt : Show the reboot and shutdown time.
|
|||
|
|
- tuptime : Report the historical and statistical running time of system, keeping it between restarts. Like uptime command but with more interesting output.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
#### Finding out the system last reboot time and date ####
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
You [can use the following commands to get the last reboot and shutdown time and date on a Linux][1] operating system (also works on OSX/Unix-like system):
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
## Just show system reboot and shutdown date and time ###
|
|||
|
|
who -b
|
|||
|
|
last reboot
|
|||
|
|
last shutdown
|
|||
|
|
## Uptime info ##
|
|||
|
|
uptime
|
|||
|
|
cat /proc/uptime
|
|||
|
|
awk '{ print "up " $1 /60 " minutes"}' /proc/uptime
|
|||
|
|
w
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
**Sample outputs:**
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
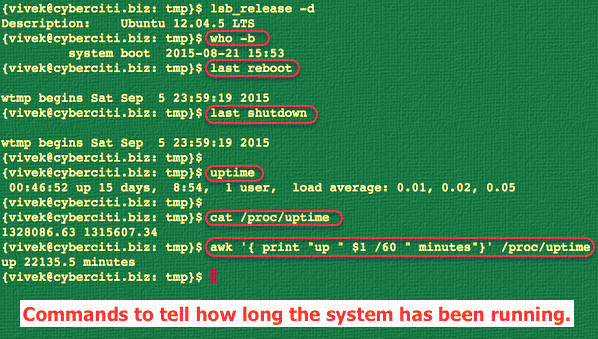
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Fig.01: Various Linux commands in action to find out the server uptime
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
**Say hello to tuptime**
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
The tuptime command line tool can report the following information on a Linux based system:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
1. Count system startups
|
|||
|
|
1. Register first boot time (a.k.a. installation time)
|
|||
|
|
1. Count nicely and accidentally shutdowns
|
|||
|
|
1. Average uptime and downtime
|
|||
|
|
1. Current uptime
|
|||
|
|
1. Uptime and downtime rate since first boot time
|
|||
|
|
1. Accumulated system uptime, downtime and total
|
|||
|
|
1. Report each startup, uptime, shutdown and downtime
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
#### Installation ####
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Type the [following command to clone a git repo on a Linux operating system][2]:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
$ cd /tmp
|
|||
|
|
$ git clone https://github.com/rfrail3/tuptime.git
|
|||
|
|
$ ls
|
|||
|
|
$ cd tuptime
|
|||
|
|
$ ls
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
**Sample outputs:**
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
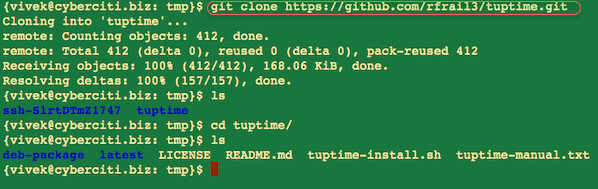
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Fig.02: Cloning a git repo
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Make sure you've Python v2.7 installed with sys, optparse, os, re, string, sqlite3, datetime, disutils, and locale modules.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
You can simply install it as follows:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
$ sudo tuptime-install.sh
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
OR do a manual installation (recommended method due to systemd or non-systemd based Linux system):
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
$ sudo cp /tmp/tuptime/latest/cron.d/tuptime /etc/cron.d/tuptime
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
If is a system with systemd, copy service file and enable it:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
$ sudo cp /tmp/tuptime/latest/systemd/tuptime.service /lib/systemd/system/
|
|||
|
|
$ sudo systemctl enable tuptime.service
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
If the systemd don't have systemd, copy init file:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
$ sudo cp /tmp/tuptime/latest/init.d/tuptime.init.d-debian7 /etc/init.d/tuptime
|
|||
|
|
$ sudo update-rc.d tuptime defaults
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
**Run it**
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Simply type the following command:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
$ sudo tuptime
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
**Sample outputs:**
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
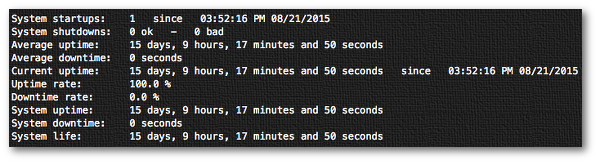
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Fig.03: tuptime in action
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
After kernel upgrade I rebooted the box and typed the same command again:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
$ sudo tuptime
|
|||
|
|
System startups: 2 since 03:52:16 PM 08/21/2015
|
|||
|
|
System shutdowns: 1 ok - 0 bad
|
|||
|
|
Average uptime: 7 days, 16 hours, 48 minutes and 3 seconds
|
|||
|
|
Average downtime: 2 hours, 30 minutes and 5 seconds
|
|||
|
|
Current uptime: 5 minutes and 28 seconds since 06:23:06 AM 09/06/2015
|
|||
|
|
Uptime rate: 98.66 %
|
|||
|
|
Downtime rate: 1.34 %
|
|||
|
|
System uptime: 15 days, 9 hours, 36 minutes and 7 seconds
|
|||
|
|
System downtime: 5 hours, 0 minutes and 11 seconds
|
|||
|
|
System life: 15 days, 14 hours, 36 minutes and 18 seconds
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
You can change date and time format as follows:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
$ sudo tuptime -d '%H:%M:%S %m-%d-%Y'
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
**Sample outputs:**
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
System startups: 1 since 15:52:16 08-21-2015
|
|||
|
|
System shutdowns: 0 ok - 0 bad
|
|||
|
|
Average uptime: 15 days, 9 hours, 21 minutes and 19 seconds
|
|||
|
|
Average downtime: 0 seconds
|
|||
|
|
Current uptime: 15 days, 9 hours, 21 minutes and 19 seconds since 15:52:16 08-21-2015
|
|||
|
|
Uptime rate: 100.0 %
|
|||
|
|
Downtime rate: 0.0 %
|
|||
|
|
System uptime: 15 days, 9 hours, 21 minutes and 19 seconds
|
|||
|
|
System downtime: 0 seconds
|
|||
|
|
System life: 15 days, 9 hours, 21 minutes and 19 seconds
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Enumerate each startup, uptime, shutdown and downtime:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
$ sudo tuptime -e
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
**Sample outputs:**
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Startup: 1 at 03:52:16 PM 08/21/2015
|
|||
|
|
Uptime: 15 days, 9 hours, 22 minutes and 33 seconds
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
System startups: 1 since 03:52:16 PM 08/21/2015
|
|||
|
|
System shutdowns: 0 ok - 0 bad
|
|||
|
|
Average uptime: 15 days, 9 hours, 22 minutes and 33 seconds
|
|||
|
|
Average downtime: 0 seconds
|
|||
|
|
Current uptime: 15 days, 9 hours, 22 minutes and 33 seconds since 03:52:16 PM 08/21/2015
|
|||
|
|
Uptime rate: 100.0 %
|
|||
|
|
Downtime rate: 0.0 %
|
|||
|
|
System uptime: 15 days, 9 hours, 22 minutes and 33 seconds
|
|||
|
|
System downtime: 0 seconds
|
|||
|
|
System life: 15 days, 9 hours, 22 minutes and 33 seconds
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
via: http://www.cyberciti.biz/hardware/howto-see-historical-statistical-uptime-on-linux-server/
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
作者:Vivek Gite
|
|||
|
|
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
|||
|
|
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
[1]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/hardware/howto-see-historical-statistical-uptime-on-linux-server/
|
|||
|
|
[2]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/debian-ubunut-linux-download-a-git-repository/
|