mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-02-28 01:01:09 +08:00
215 lines
9.0 KiB
Markdown
215 lines
9.0 KiB
Markdown
|
|
RHCSA 系列:安全 SSH,设定主机名及开启网络服务 – Part 8
|
|||
|
|
================================================================================
|
|||
|
|
作为一名系统管理员,你将经常使用一个终端模拟器来登陆到一个远程的系统中,执行一系列的管理任务。你将很少有机会坐在一个真实的(物理)终端前,所以你需要设定好一种方法来使得你可以登陆到你被要求去管理的那台远程主机上。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
事实上,当你必须坐在一台物理终端前的时候,就可能是你登陆到该主机的最后一种方法。基于安全原因,使用 Telnet 来达到以上目的并不是一个好主意,因为穿行在线缆上的流量并没有被加密,它们以文本方式在传送。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
另外,在这篇文章中,我们也将复习如何配置网络服务来使得它在开机时被自动开启,并学习如何设置网络和静态或动态地解析主机名。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|

|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
RHCSA: 安全 SSH 和开启网络服务 – Part 8
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
### 安装并确保 SSH 通信安全 ###
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
对于你来说,要能够使用 SSH 远程登陆到一个 RHEL 7 机子,你必须安装 `openssh`,`openssh-clients` 和 `openssh-servers` 软件包。下面的命令不仅将安装远程登陆程序,也会安装安全的文件传输工具以及远程文件复制程序:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
# yum update && yum install openssh openssh-clients openssh-servers
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
注意,安装上服务器所需的相应软件包是一个不错的主意,因为或许在某个时刻,你想使用同一个机子来作为客户端和服务器。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
在安装完成后,如若你想安全地访问你的 SSH 服务器,你还需要考虑一些基本的事情。下面的设定应该在文件 `/etc/ssh/sshd_config` 中得以呈现。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
1. 更改 sshd 守护进程的监听端口,从 22(默认的端口值)改为一个更高的端口值(2000 或更大),但首先要确保所选的端口没有被占用。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
例如,让我们假设你选择了端口 2500 。使用 [netstat][1] 来检查所选的端口是否被占用:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
# netstat -npltu | grep 2500
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
假如 netstat 没有返回任何信息,则你可以安全地为 sshd 使用端口 2500,并且你应该在上面的配置文件中更改端口的设定,具体如下:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Port 2500
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
2. 只允许协议 2:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Protocol 2
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
3. 配置验证超时的时间为 2 分钟,不允许以 root 身份登陆,并将允许通过 ssh 登陆的人数限制到最小:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
LoginGraceTime 2m
|
|||
|
|
PermitRootLogin no
|
|||
|
|
AllowUsers gacanepa
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
4. 假如可能,使用基于公钥的验证方式而不是使用密码:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
PasswordAuthentication no
|
|||
|
|
RSAAuthentication yes
|
|||
|
|
PubkeyAuthentication yes
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
这假设了你已经在你的客户端机子上创建了带有你的用户名的一个密钥对,并将公钥复制到了你的服务器上。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
- [开启 SSH 无密码登陆][2]
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
### 配置网络和名称的解析 ###
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
1. 每个系统管理员应该对下面这个系统配置文件非常熟悉:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
- /etc/hosts 被用来在小型网络中解析名称 <---> IP 地址。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
文件 `/etc/hosts` 中的每一行拥有如下的结构:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
IP address - Hostname - FQDN
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
例如,
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
192.168.0.10 laptop laptop.gabrielcanepa.com.ar
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
2. `/etc/resolv.conf` 特别指定 DNS 服务器的 IP 地址和搜索域,它被用来在没有提供域名后缀时,将一个给定的查询名称对应为一个全称域名。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
在正常情况下,你不必编辑这个文件,因为它是由系统管理的。然而,若你非要改变 DNS 服务器的 IP 地址,建议你在该文件的每一行中,都应该遵循下面的结构:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
nameserver - IP address
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
例如,
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
nameserver 8.8.8.8
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
3. `/etc/host.conf` 特别指定在一个网络中主机名被解析的方法和顺序。换句话说,告诉名称解析器使用哪个服务,并以什么顺序来使用。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
尽管这个文件由几个选项,但最为常见和基本的设置包含如下的一行:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
order bind,hosts
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
它意味着解析器应该首先查看 `resolv.conf` 中特别指定的域名服务器,然后到 `/etc/hosts` 文件中查找解析的名称。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
4. `/etc/sysconfig/network` 包含了所有网络接口的路由和全局主机信息。下面的值可能会被使用:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
NETWORKING=yes|no
|
|||
|
|
HOSTNAME=value
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
其中的 value 应该是全称域名(FQDN)。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
GATEWAY=XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
其中的 XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX 是网关的 IP 地址。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
GATEWAYDEV=value
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
在一个带有多个网卡的机器中, value 为网关设备名,例如 enp0s3。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
5. 位于 `/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts` 中的文件(网络适配器配置文件)。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
在上面提到的目录中,你将找到几个被命名为如下格式的文本文件。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
ifcfg-name
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
其中 name 为网卡的名称,由 `ip link show` 返回:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|

|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
检查网络连接状态
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
例如:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
网络文件
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
除了环回接口,你还可以为你的网卡进行一个相似的配置。注意,假如设定了某些变量,它们将为这个特别的接口,覆盖掉 `/etc/sysconfig/network` 中定义的值。在这篇文章中,为了能够解释清楚,每行都被加上了注释,但在实际的文件中,你应该避免加上注释:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
HWADDR=08:00:27:4E:59:37 # The MAC address of the NIC
|
|||
|
|
TYPE=Ethernet # Type of connection
|
|||
|
|
BOOTPROTO=static # This indicates that this NIC has been assigned a static IP. If this variable was set to dhcp, the NIC will be assigned an IP address by a DHCP server and thus the next two lines should not be present in that case.
|
|||
|
|
IPADDR=192.168.0.18
|
|||
|
|
NETMASK=255.255.255.0
|
|||
|
|
GATEWAY=192.168.0.1
|
|||
|
|
NM_CONTROLLED=no # Should be added to the Ethernet interface to prevent NetworkManager from changing the file.
|
|||
|
|
NAME=enp0s3
|
|||
|
|
UUID=14033805-98ef-4049-bc7b-d4bea76ed2eb
|
|||
|
|
ONBOOT=yes # The operating system should bring up this NIC during boot
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
### 设定主机名 ###
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
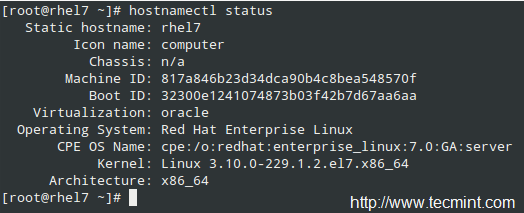
在 RHEL 7 中, `hostnamectl` 命令被同时用来查询和设定系统的主机名。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
要展示当前的主机名,输入:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
# hostnamectl status
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
检查系统的主机名
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
要更改主机名,使用
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
# hostnamectl set-hostname [new hostname]
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
例如,
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
# hostnamectl set-hostname cinderella
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
要想使得更改生效,你需要重启 hostnamed 守护进程(这样你就不必因为要应用更改而登出系统并再登陆系统):
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
# systemctl restart systemd-hostnamed
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|

|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
设定系统主机名
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
另外, RHEL 7 还包含 `nmcli` 工具,它可被用来达到相同的目的。要展示主机名,运行:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
# nmcli general hostname
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
且要改变主机名,则运行:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
# nmcli general hostname [new hostname]
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
例如,
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
# nmcli general hostname rhel7
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|

|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
使用 nmcli 命令来设定主机名
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
### 在开机时开启网络服务 ###
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
作为本文的最后部分,就让我们看看如何确保网络服务在开机时被自动开启。简单来说,这个可通过创建符号链接到某些由服务的配置文件中的 [Install] 小节中指定的文件来实现。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
以 firewalld(/usr/lib/systemd/system/firewalld.service) 为例:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
[Install]
|
|||
|
|
WantedBy=basic.target
|
|||
|
|
Alias=dbus-org.fedoraproject.FirewallD1.service
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
要开启该服务,运行:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
# systemctl enable firewalld
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
另一方面,要禁用 firewalld,则需要移除符号链接:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
# systemctl disable firewalld
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|

|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
在开机时开启服务
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
### 总结 ###
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
在这篇文章中,我们总结了如何安装 SSH 及使用它安全地连接到一个 RHEL 服务器,如何改变主机名,并在最后如何确保在系统启动时开启服务。假如你注意到某个服务启动失败,你可以使用 `systemctl status -l [service]` 和 `journalctl -xn` 来进行排错。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
请随意使用下面的评论框来让我们知晓你对本文的看法。提问也同样欢迎。我们期待着你的反馈!
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
via: http://www.tecmint.com/rhcsa-series-secure-ssh-set-hostname-enable-network-services-in-rhel-7/
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
作者:[Gabriel Cánepa][a]
|
|||
|
|
译者:[FSSlc](https://github.com/FSSlc)
|
|||
|
|
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/gacanepa/
|
|||
|
|
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/20-netstat-commands-for-linux-network-management/
|
|||
|
|
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/ssh-passwordless-login-using-ssh-keygen-in-5-easy-steps/
|