mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-01-04 22:00:34 +08:00
206 lines
8.1 KiB
Markdown
206 lines
8.1 KiB
Markdown
|
|
How to Install a DHCP Server in CentOS, RHEL and Fedora
|
|||
|
|
============================================================
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) is a network protocol that enables a server to automatically assign an IP address and provide other related network configuration parameters to a client on a network, from a pre-defined IP pool.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
This means that each time a client (connected to the network) boots up, it gets a “dynamic” IP address, as opposed to “static” IP address that never changes. The IP address assigned by a DHCP server to DHCP client is on a “lease”, the lease time can vary depending on how long a client is likely to require the connection or DHCP configuration.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
In this tutorial, we will cover how to install and configure a DHCP server in CentOS/RHEL and Fedora distributions.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
#### Testing Environment Setup
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
We are going to use following testing environment for this setup.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
DHCP Server - CentOS 7
|
|||
|
|
DHCP Clients - Fedora 25 and Ubuntu 16.04
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
#### How Does DHCP Work?
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Before we move any further, let’s briefly explain how DHCP works:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
* When a client computer (configured to use DHCP) and connected to a network is powered on, it forwards a DHCPDISCOVER message to the DHCP server.
|
|||
|
|
* And after the DHCP server receives the DHCPDISCOVER request message, it replies with a DHCPOFFER message.
|
|||
|
|
* Then the client receives the DHCPOFFER message, and it sends a DHCPREQUEST message to the server indicating, it is prepared to get the network configuration offered in the DHCPOFFERmessage.
|
|||
|
|
* Last but not least, the DHCP server receives the DHCPREQUEST message from the client, and sends the DHCPACK message showing that the client is now permitted to use the IP address assigned to it.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
### Step 1: Installing DHCP Server in CentOS
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
1. Installing DCHP is quite straight forward, simply run the command below.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
# yum -y install dhcp
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Important: Assuming there is more than one network interface attached to the system, but you want the DHCP server to only be started on one of the interfaces, set the DHCP server to start only on that interface as follows.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
2. Open the file /etc/sysconfig/dhcpd, add the name of the specific interface to the list of DHCPDARGS, for example if the interface is `eth0`, then add:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
DHCPDARGS=eth0
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Save the file and exit.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
### Step 2: Configuring DHCP Server in CentOS
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
3. For starters, to setup a DHCP server, the first step is to create the `dhcpd.conf` configuration file, and the main DHCP configuration file is normally /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf (which is empty by default), it keeps all network information sent to clients.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
However, there is a sample configuration file /usr/share/doc/dhcp*/dhcpd.conf.sample, which is a good starting point for configuring a DHCP server.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
And, there are two types of statements defined in the DHCP configuration file, these are:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
* parameters – state how to carry out a task, whether to perform a task, or what network configuration options to send to the DHCP client.
|
|||
|
|
* declarations – specify the network topology, define the clients, offer addresses for the clients, or apply a group of parameters to a group of declarations.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Therefore, start by copying the sample configuration file as the main configuration file like so:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
# cp /usr/share/doc/dhcp-4.2.5/dhcpd.conf.example /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
4. Now, open the main configuration file and define your DHCP server options:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
# vi /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Start by setting the following global parameters which will apply to all the subnetworks (do specify values that apply to your scenario) at the top of the file:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
option domain-name "tecmint.lan";
|
|||
|
|
option domain-name-servers ns1.tecmint.lan, ns2.tecmint.lan;
|
|||
|
|
default-lease-time 3600;
|
|||
|
|
max-lease-time 7200;
|
|||
|
|
authoritative;
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
5. Now, define a subnetwork; in this example, we will configure DHCP for 192.168.56.0/24 LAN network (remember to use parameters that apply to your scenario):
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
subnet 192.168.56.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 {
|
|||
|
|
option routers 192.168.56.1;
|
|||
|
|
option subnet-mask 255.255.255.0;
|
|||
|
|
option domain-search "tecmint.lan";
|
|||
|
|
option domain-name-servers 192.168.56.1;
|
|||
|
|
range 192.168.56.10 192.168.56.100;
|
|||
|
|
range 192.168.56.120 192.168.56.200;
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
### Step 3: Assign Static IP to DHCP Client
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
You can assign a static IP address to a specific client computer on the network, simply define the section below in /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf file, where you must explicitly specify it’s MAC addresses and the fixed IP to be assigned:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
host ubuntu-node {
|
|||
|
|
hardware ethernet 00:f0:m4:6y:89:0g;
|
|||
|
|
fixed-address 192.168.56.105;
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
host fedora-node {
|
|||
|
|
hardware ethernet 00:4g:8h:13:8h:3a;
|
|||
|
|
fixed-address 192.168.56.110;
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Save the file and close it.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Note: You can find out or display the Linux MAC address using following command.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
# ifconfig -a eth0 | grep HWaddr
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
6. Now start the DHCP service for the mean time and enable it to start automatically from the next system boot, using following commands:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
---------- On CentOS/RHEL 7 ----------
|
|||
|
|
# systemctl start dhcpd
|
|||
|
|
# systemctl enable dhcpd
|
|||
|
|
---------- On CentOS/RHEL 6 ----------
|
|||
|
|
# service dhcpd start
|
|||
|
|
# chkconfig dhcpd on
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
7. Next, do not forget to permit DHCP service (DHCPD daemon listens on port 67/UDP) as below:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
---------- On CentOS/RHEL 7 ----------
|
|||
|
|
# firewall-cmd --add-service=dhcp --permanent
|
|||
|
|
# firewall-cmd --reload
|
|||
|
|
---------- On CentOS/RHEL 6 ----------
|
|||
|
|
# iptables -A INPUT -p tcp -m state --state NEW --dport 67 -j ACCEPT
|
|||
|
|
# service iptables save
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
### Step 4: Configuring DHCP Clients
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
8. Now, you can configure your clients on the network to automatically receive IP addresses from the DHCP server. Login to the client machine and modify the Ethernet interface configuration file as follows (take not of the interface name/number):
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
# vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Add the options below:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
DEVICE=eth0
|
|||
|
|
BOOTPROTO=dhcp
|
|||
|
|
TYPE=Ethernet
|
|||
|
|
ONBOOT=yes
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Save the file and exit.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
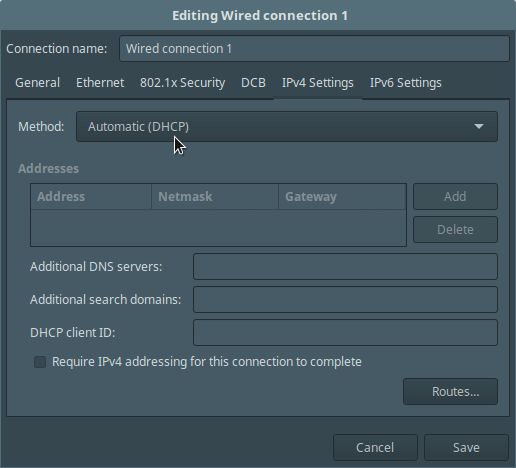
9. You can also perform the settings using the GUI on a desktop computer, set the Method to Automatic (DHCP) as shown in the screenshot below (Ubuntu 16.04 desktop).
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
[
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
][3]
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Set DHCP in Client Network
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
10. Then restart network services as follows (you can possibly reboot the system):
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
---------- On CentOS/RHEL 7 ----------
|
|||
|
|
# systemctl restart network
|
|||
|
|
---------- On CentOS/RHEL 6 ----------
|
|||
|
|
# service network restart
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
At this point, if all settings were correct, your clients should be receiving IP addresses automatically from the DHCP server.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
You may also read:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
1. [How to Install and Configure Multihomed ISC DHCP Server on Debian Linux][1]
|
|||
|
|
2. [10 Useful “IP” Commands to Configure Network Interfaces][2]
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
In this tutorial, we showed you how to setup a DHCP server in RHEL/CentOS. Use the comment form below to write back top us. In an upcoming article, we will show you how to setup a DHCP server in Debian/Ubuntu. Until then, always stay connected to TecMint.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
作者简介:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Aaron Kili is a Linux and F.O.S.S enthusiast, an upcoming Linux SysAdmin, web developer, and currently a content creator for TecMint who loves working with computers and strongly believes in sharing knowledge.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
via: http://www.tecmint.com/install-dhcp-server-in-centos-rhel-fedora/
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
作者:[Aaron Kili][a]
|
|||
|
|
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
|||
|
|
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/
|
|||
|
|
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/install-and-configure-multihomed-isc-dhcp-server-on-debian-linux/
|
|||
|
|
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/ip-command-examples/
|
|||
|
|
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/Set-DHCP-in-Client-Network.png
|
|||
|
|
[4]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/
|
|||
|
|
[5]:http://www.tecmint.com/10-useful-free-linux-ebooks-for-newbies-and-administrators/
|
|||
|
|
[6]:http://www.tecmint.com/free-linux-shell-scripting-books/
|