mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-01-16 22:42:21 +08:00
170 lines
7.7 KiB
Markdown
170 lines
7.7 KiB
Markdown
|
|
How to protect SSH server from brute force attacks using fail2ban
|
||
|
|
================
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
One common attack on SSH service is brute force attacks where a remote attacker indefinitely attempts to log in with different passwords. Of course there are arguments against password authentication for SSH, and alternative authentication mechanisms such as [public key authentication][1] or [two-factor authentication][2] exist to obsolete such attacks. Putting aside pros and cons of different authentication methods, let's consider the situation where password authentication is required. How would you protect your SSH server against brute-force attacks?
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
[fail2ban][3] is a well-known open-source intrusion prevention framework on Linux that monitors various system log files (e.g., /var/log/auth.log or /var/log/secure) and automatically triggers various defensive actions upon detecting any suspicious activities. In fact, fail2ban can be quite useful to defend against brute force password guessing attacks on an SSH server.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
In this guide, I will demonstrate **how to install and configure fail2ban to protect an SSH server against brute force attacks from a remote IP address**.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
### Install Fail2ban on Linux
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
To install fail2ban on CentOS or RHEL, first [set up EPEL repository][4], and then run the following command.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
$ sudo yum install fail2ban
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
To install fail2ban on Fedora, simply run:
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
$ sudo yum install fail2ban
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
To install fail2ban on Ubuntu, Debian or Linux Mint:
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
$ sudo apt-get install fail2ban
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
### Configure Fail2ban for SSH Server
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Now you are ready to configure fail2ban to harden your SSH server. You need to edit the configuration file at /etc/fail2ban/jail.conf. The configuration file contains "DEFAULT" section where you define default parameters for all monitored services, and service-specific sections where you define any service-specific jails (e.g., SSH, Apache, etc) to overwrite default parameters.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
In the service-specific jail sections (somewhere after [DEFAULT] section), you need to define [ssh-iptables] section, where you define SSH-specific jail configurations. Actual IP address banning is done by iptables.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
The following is an example of /etc/fail2ban/jail.conf which contains "ssh-iptables" jail configuration. Of course there could be other application-specific jails depending on your needs.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
$ sudo vi /etc/fail2ban/jail.local
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
[DEFAULT]
|
||
|
|
# a space delimited list of IP addresses, CIDR prefixes, or DNS hostnames
|
||
|
|
# to bypass fail2ban protection
|
||
|
|
ignoreip = 127.0.0.1 172.31.0.0/24 10.10.0.0/24 192.168.0.0/24
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
# number of seconds during which a client host is blocked
|
||
|
|
bantime = 86400
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
# number of failures before a client host is blocked
|
||
|
|
maxretry = 5
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
# number of seconds within which "maxentry" failures result in banning
|
||
|
|
findtime = 600
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
mta = sendmail
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
[ssh-iptables]
|
||
|
|
enabled = true
|
||
|
|
filter = sshd
|
||
|
|
action = iptables[name=SSH, port=ssh, protocol=tcp]
|
||
|
|
sendmail-whois[name=SSH, dest=your@email.com, sender=fail2ban@email.com]
|
||
|
|
# for Debian-based distros
|
||
|
|
logpath = /var/log/auth.log
|
||
|
|
# for Red Hat-based distros
|
||
|
|
logpath = /var/log/secure
|
||
|
|
# ssh-specific max-retry threshold
|
||
|
|
maxretry = 3
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
According to the above configuration, fail2ban will automatically ban any remote IP address from which there have been at least 3 failed login attempts within the last 10 minutes. Once banned, the offending IP address will remain blocked for 24 hours. Such an event will be notified by sendemail to a recipient email address.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Once the configuration file is ready, restart fail2ban service as follows.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
On Debian, Ubuntu or CentOS/RHEL 6:
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
$ sudo service fail2ban restart
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
On Fedora or CentOS/RHEL 7:
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
$ sudo systemctl restart fail2ban
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
To verify fail2ban is running successfully, run fail2ban-client command with "ping" argument. If fail2ban service is running okay, you should see "pong" as a response.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
$ sudo fail2ban-client ping
|
||
|
|
Server replied: pong
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
### Test Protection against SSH Brute-Force Attacks with Fail2ban
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
To test whether fail2ban works, try to SSH to the server using incorrect passwords to simulate a brute-force attack. In the mean time, monitor /var/log/fail2ban.log, which is logging any interesting events that are happening in fail2ban.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
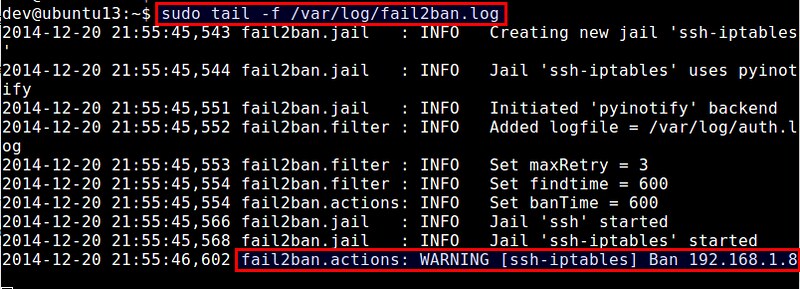
$ sudo tail -f /var/log/fail2ban.log
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
According to the log file above, fail2ban has banned an IP address 192.168.1.8, upon detecting multiple failed SSH login attempts from the IP address.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
### Check Fail2ban Status and Unban Blocked IP Addresses
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
As fail2ban's "ssh-iptables" jail uses iptables to block offending IP addresses, you can easily verify the ban by checking current iptables rules as follows.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
$ sudo iptables --list -n
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT)
|
||
|
|
target prot opt source destination
|
||
|
|
fail2ban-SSH tcp -- 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 tcp dpt:22
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT)
|
||
|
|
target prot opt source destination
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT)
|
||
|
|
target prot opt source destination
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Chain fail2ban-SSH (1 references)
|
||
|
|
target prot opt source destination
|
||
|
|
DROP all -- 192.168.1.8 0.0.0.0/0
|
||
|
|
RETURN all -- 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
If you want to unblock the IP address from fail2ban, you can also use iptables command:
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
$ sudo iptables -D fail2ban-SSH -s 192.168.1.8 -j DROP
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
While you can check and manage fail2ban's IP blocklist manually with iptables command like above, a proper way is in fact to use fail2ban-client command-line tool. This tool allows you to manage not only "ssh-iptables" jail, but also any other types of fail2ban jails in a unified command-line interface.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
To check fail2ban status (which will show a list of currently active jails):
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
$ sudo fail2ban-client status
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
To check the status of a particular jail (e.g., ssh-iptables):
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
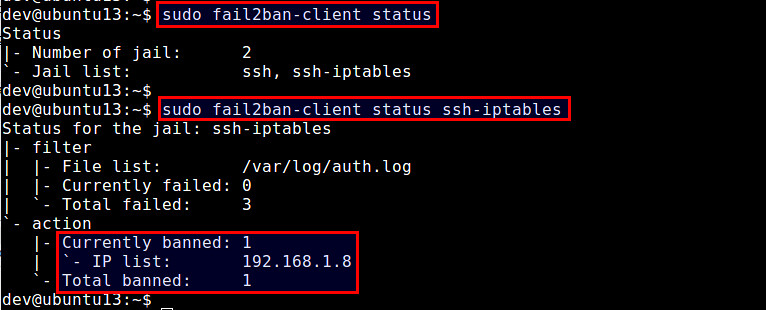
$ sudo fail2ban-client status ssh-iptables
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
The above command will show a list of banned IP addresses.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
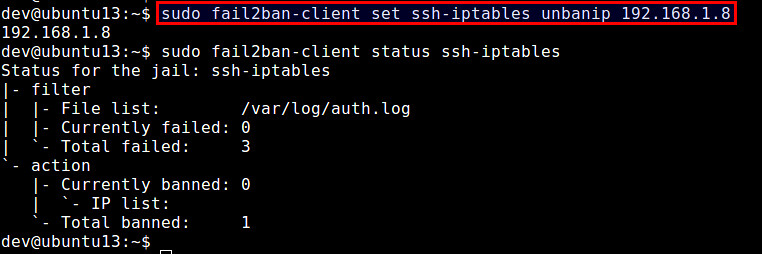
To unban a particular IP address:
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
$ sudo fail2ban-client set ssh-iptables unbanip 192.168.1.8
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Note that if you stop fail2ban, all blocked IP addresses will be unblocked. When you restart fail2ban, it will find a list of offending IP addresses from /var/log/secure (or /var/log/auth.log), and re-ban those IP addresses if the elapsed time of the offenses are still within ban time.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
### Set Fail2ban to Auto-start on Boot
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Once you haved tested fail2ban successfully, the last step is to enable fail2ban to launch automatically upon powering on your server. On Debian-based distributions, fail2ban auto-start is enabled by default. On Red Hat-based distributions, enable auto-start as follows.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
On CentOS/RHEL 6:
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
$ sudo chkconfig fail2ban on
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
On Fedora or CentOS/RHEL 7:
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
$ sudo systemctl enable fail2ban
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
### Summary
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
In this tutorial, I demonstrated how to install and configure fail2ban to protect an SSH server. While fail2ban can mitigate brute-force password guessing attacks, please note that it cannot protect SSH servers against sophisticated distributed brute-force campaigns, where an attacker bypasses fail2ban by using many thousands of bot-controlled IP addresses.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
-----------
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
via: http://linoxide.com/tools/linux-compress-decompress-tools/
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
|
||
|
|
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||
|
|
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/nanni
|
||
|
|
[1]:http://xmodulo.com/how-to-force-ssh-login-via-public-key-authentication.html
|
||
|
|
[2]:http://xmodulo.com/two-factor-authentication-ssh-login-linux.html
|
||
|
|
[3]:http://www.fail2ban.org/
|
||
|
|
[4]:http://xmodulo.com/2013/03/how-to-set-up-epel-repository-on-centos.html
|