In this part of the[Samba4 AD DC infrastructure series][8]we will talk on how join aWindows 10machine into aSamba4realm and how to administer the domain from aWindows 10workstation.
Once aWindows 10system has been joined toSamba4 AD DCwe can create, remove or disable domain users and groups, we can create newOrganizational Units, we can create, edit and manage domain policy or we can manage Samba4 domain DNS service.
All of the above functions and other complex tasks concerning domain administration can be achieved via any modern Windows platform with the help ofRSAT – Microsoft Remote Server Administration Tools.
#### Requirements
1. [Create an AD Infrastructure with Samba4 on Ubuntu 16.04 – Part 1][1]
2. [Manage Samba4 AD Infrastructure from Linux Command Line – Part 2][2]
3. [Manage Samba4 AD Domain Controller DNS and Group Policy from Windows – Part 4][3]
### Step 1: Configure Domain Time Synchronization
1.Before starting to administerSamba4 ADDCfromWindows 10with the help ofRSATtools, we need to know and take care of a crucial piece of service required for anActive Directoryand this service refers to[accurate time synchronization][9].
Time synchronization can be offered byNTPdaemon in most of the Linux distributions. The default maximum time period discrepancy an AD can support is about5minutes.
If the divergence time period is greater than5minutes you should start experience various errors, most important concerning AD users, joined machines or share access.
To installNetwork Time Protocoldaemon andNTPclient utility inUbuntu, execute the below command.
```
$ sudo apt-get install ntp ntpdate
```
[

][10]
Install NTP on Ubuntu
2.Next, open and edit NTP configuration file and replace the default NTP pool server list with a new list of NTP servers which are geographically located near your current physical equipment location.
The list of NTP servers can be obtained by visiting official NTP Pool Project webpage[http://www.pool.ntp.org/en/][11].
```
$ sudo nano /etc/ntp.conf
```
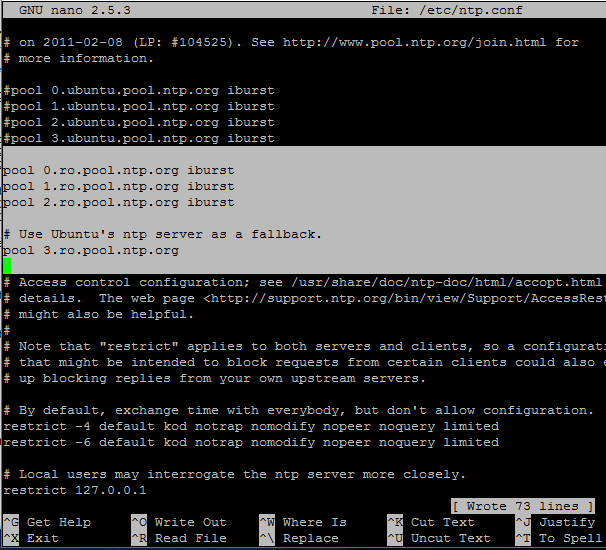
Comment the default server list by adding a`#`in front of each pool line and add the below pool lines with your proper NTP servers as illustrated on the below screenshot.
```
pool 0.ro.pool.ntp.org iburst
pool 1.ro.pool.ntp.org iburst
pool 2.ro.pool.ntp.org iburst
# Use Ubuntu's ntp server as a fallback.
pool 3.ro.pool.ntp.org
```
[
][12]
Configure NTP Server in Ubuntu
3.Now, don’t close the file yet. Move to the top at the file and add the below line after the driftfile statement. This setup allows the clients to query the server using AD signed NTP requests.
```
ntpsigndsocket /var/lib/samba/ntp_signd/
```
[

][13]
Sync AD with NTP
4.Finally, move to the bottom of the file and add the below line, as illustrated on the below screenshot, which will allow network clients only to query the time on the server.
```
restrict default kod nomodify notrap nopeer mssntp
```
[

][14]
Query Clients to NTP Server
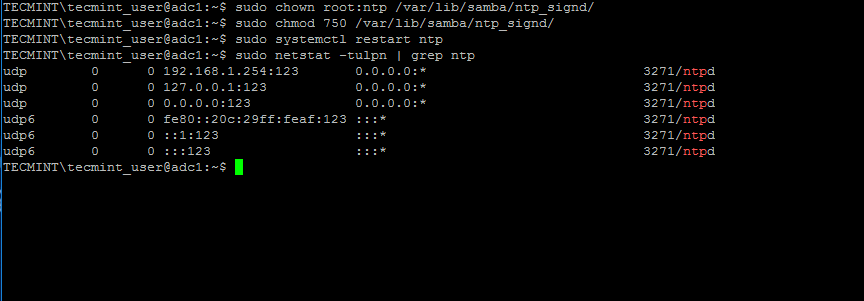
5.When finished, save and close the NTP configuration file and grant NTP service with the proper permissions in order to read the ntp_signed directory.
This is the system path whereSamba NTPsocket is located. Afterwards, restart NTP daemon to apply changes and verify if NTP has open sockets in your system network table using[netstat command][15]combined with[grep filter][16].
```
$ sudo chown root:ntp /var/lib/samba/ntp_signd/
$ sudo chmod 750 /var/lib/samba/ntp_signd/
$ sudo systemctl restart ntp
$ sudo netstat –tulpn | grep ntp
```
[
][17]
Grant Permission to NTP
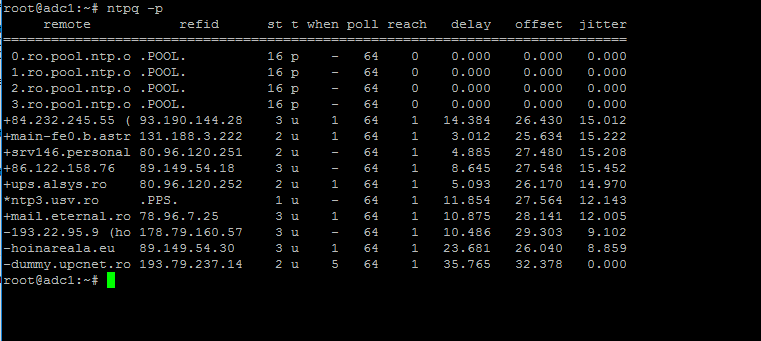
Use thentpqcommand line utility to monitor NTP daemon along with the`-p`flag in order to print a summary of peers state.
```
$ ntpq -p
```
[
][18]
Monitor NTP Server Pool
### Step 2: Troubleshoot NTP Time Issues
6.Sometimes the NTP daemon gets stuck in calculations while trying to synchronize time with an upstream ntp server peer, resulting the following error messages when manually trying to force time synchronization by runningntpdateutility on a client side:
```
# ntpdate -qu adc1
ntpdate[4472]: no server suitable for synchronization found
```
[

][19]
NTP Time Synchronization Error
when usingntpdatecommand with`-d`flag.
```
# ntpdate -d adc1.tecmint.lan
Server dropped: Leap not in sync
```
[

][20]
NTP Server Dropped Leap Not in Sync
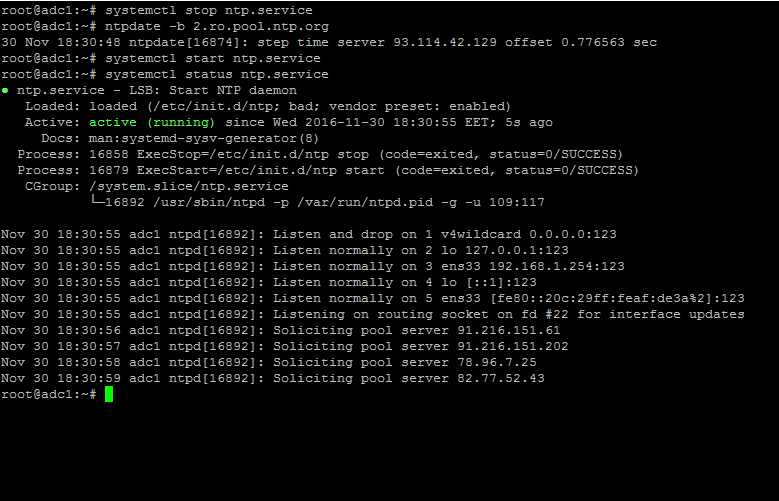
7.To circumvent this issue, use the following trick to solve the problem: On the server, stop the NTP service and use thentpdateclient utility to manually force time synchronization with an external peer using the`-b`flag as shown below:
```
# systemctl stop ntp.service
# ntpdate -b 2.ro.pool.ntp.org [your_ntp_peer]
# systemctl start ntp.service
# systemctl status ntp.service
```
[
][21]
Force NTP Time Synchronization
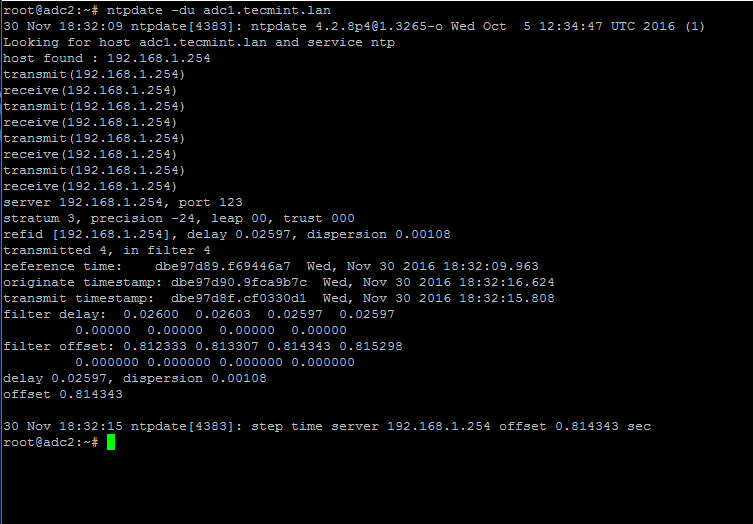
8.After the time has been accurately synchronized, start the NTP daemon on the server and verify from the client side if the service is ready to serve time for local clients by issuing the following command:
```
# ntpdate -du adc1.tecmint.lan [your_adc_server]
```
[
][22]
Verify NTP Time Synchronization
By now, NTP server should work as expected.
### Step 3: Join Windows 10 into Realm
9.As we saw in our previous tutorial,[Samba4 Active Directory can be managed from command line using samba-tool][23]utility interface which can be accessed directly from server’s VTY console or remotely connected through SSH.
Other, more intuitively and flexible alternative, would be to manage ourSamba4 AD Domain ControllerviaMicrosoft Remote Server Administration Tools (RSAT)from a Windows workstation integrated into the domain. These tools are available in almost all modern Windows systems.
The process of joiningWindows 10or older versions ofMicrosoft OS into Samba4 AD DCis very simple. First, make sure that your Windows 10 workstation has the correctSamba4 DNS IPaddress configured in order to query the proper realm resolver.
OpenControl panel->Network and Internet->Network and Sharing Center->Ethernet card->Properties->IPv4->Properties-> Use the following DNS server addresses and manually place Samba4 AD IP Address to the network interface as illustrated in the below screenshots.
[

][24]
join Windows to Samba4 AD
[

][25]
Add DNS and Samba4 AD IP Address
Here,192.168.1.254is the IP Address ofSamba4 AD Domain Controllerresponsible for DNS resolution. Replace the IP Address accordingly.
10.Next, apply the network settings by hitting onOKbutton, open aCommand Promptand issue apingagainst the generic domain name and Samba4 host FQDN in order to test if the realm is reachable through DNS resolution.
```
ping tecmint.lan
ping adc1.tecmint.lan
```
[

][26]
Check Network Connectivity Between Windows and Samba4 AD
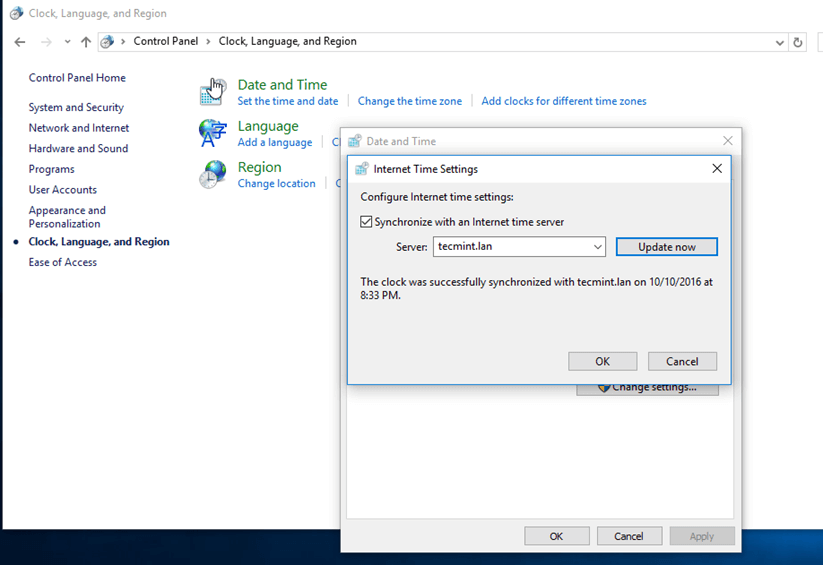
11.If the resolver correctly responds to Windows client DNS queries, then, you need to assure that the time is accurately synchronized with the realm.
OpenControl Panel->Clock,LanguageandRegion->Set Time and Date->Internet Time tab->Change Settingsand write your domain name on Synchronize with and Internet time server field.
Hit onUpdate Nowbutton to force time synchronization with the realm and hitOKto close the window.
[
][27]
Synchronize Time with Internet Server
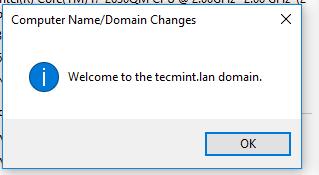
12.Finally, join the domain by openingSystem Properties->Change->Member of Domain, write your domain name, hitOK, enter your domain administrative account credentials and hitOKagain.
A new pop-up window should open informing you’re a member of the domain. HitOKto close the pop-up window andrebootthe machine in order to apply domain changes.
The below screenshot will illustrate these steps.
[

][30]
Domain Joined to Samba4 AD Confirmation
[

][31]
Restart Windows Server for Changes
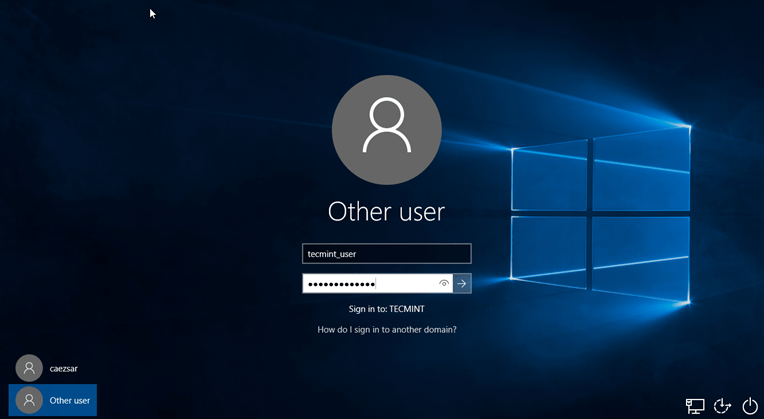
13.After restart, hit onOtheruser and logon to Windows with a Samba4 domain account with administrative privileges and you should be ready to move to the next step.
[
][32]
Login to Windows Using Samba4 AD Account
#### Step 4: Administer Samba4 AD DC with RSAT
14.Microsoft Remote Server Administration Tools (RSAT), which will be further used to administerSamba4 Active Directory, can be downloaded from the following links, depending on your Windows version:
1. Windows 10:[https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=45520][4]
2. Windows 8.1:[http://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=39296][5]
3. Windows 8:[http://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=28972][6]
4. Windows 7:[http://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=7887][7]
Once the update standalone installer package forWindows 10has been downloaded on your system, run the installer, wait for the installation to finish and restart the machine to apply all updates.
Afterreboot, openControl Panel->Programs(Uninstall a Program) ->Turn Windows features on or offand check allRemote Server Administration Tools.
ClickOKto start the installation and after the installation process finishes, restart the system.
[
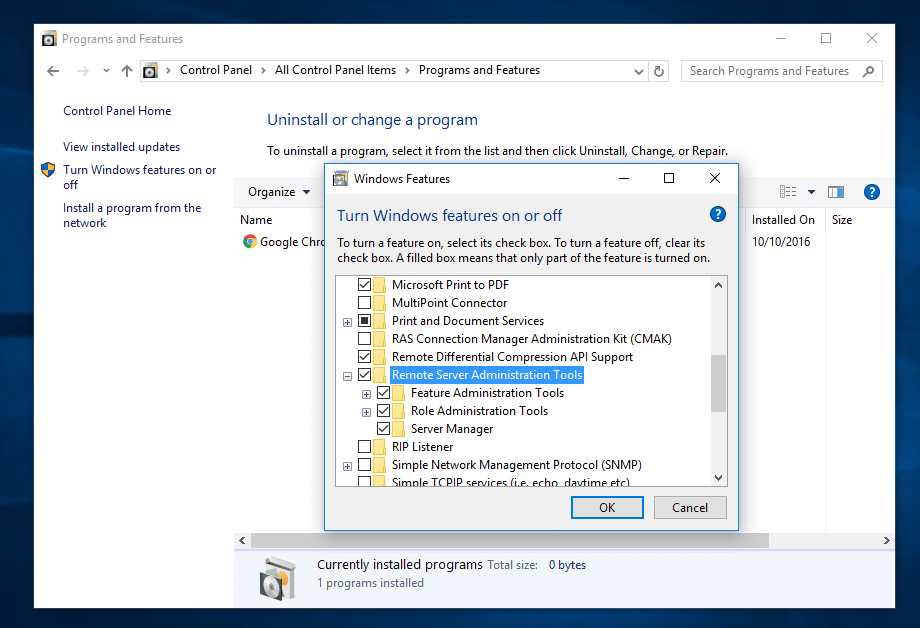
][33]
Administer Samba4 AD from Windows
15.To accessRSATtools go toControl Panel->System and Security->Administrative Tools.
The tools can also be found in theAdministrativetools menu from start menu. Alternatively, you can openWindows MMCand add Snap-ins using theFile->Add/RemoveSnap-in menu.
[

][34]
Access Remote Server Administration Tools
The most used tools, such asAD UC,DNSandGroup Policy Managementcan be launched directly from Desktop by creating shortcuts using Send to feature from menu.
16.You can verifyRSATfunctionality by openingAD UCand list domain Computers (newly joined windows machine should appear in the list), create a newOrganizational Unitor a new user or group.
Verify if the users or groups had been properly created by issuingwbinfocommand from Samba4 server side.
[

][35]
Active Directory Users and Computers
[
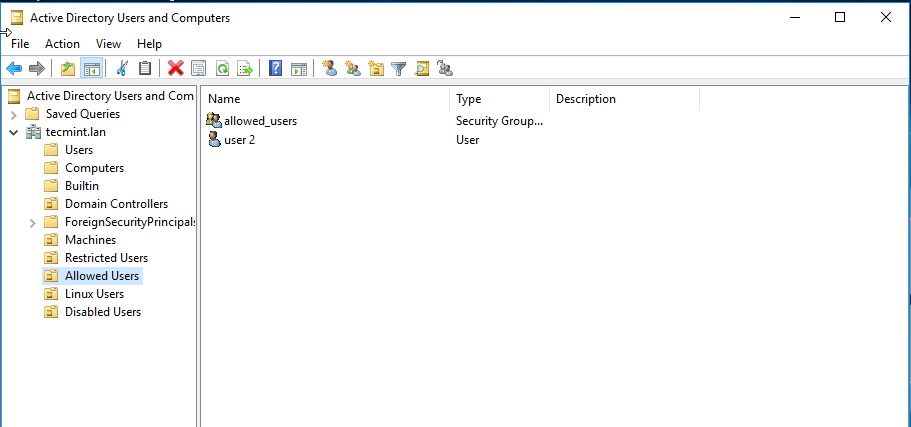
][36]
Create Organizational Units and New Users
[
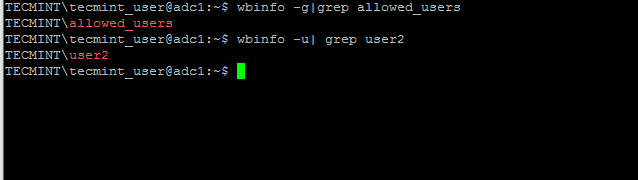
][37]
Confirm Samba4 AD Users
That’s it! On the next part of this topic we will cover other important aspects of aSamba4 Active Directorywhich can be administered viaRSAT, such as, how to manage DNS server, add DNS records and create a reverse DNS lookup zone, how to manage and apply domain policy and how to create an interactive logon banner for your domain users.
------
作者简介:I'am a computer addicted guy, a fan of open source and linux based system software, have about 4 years experience with Linux distributions desktop, servers and bash scripting.